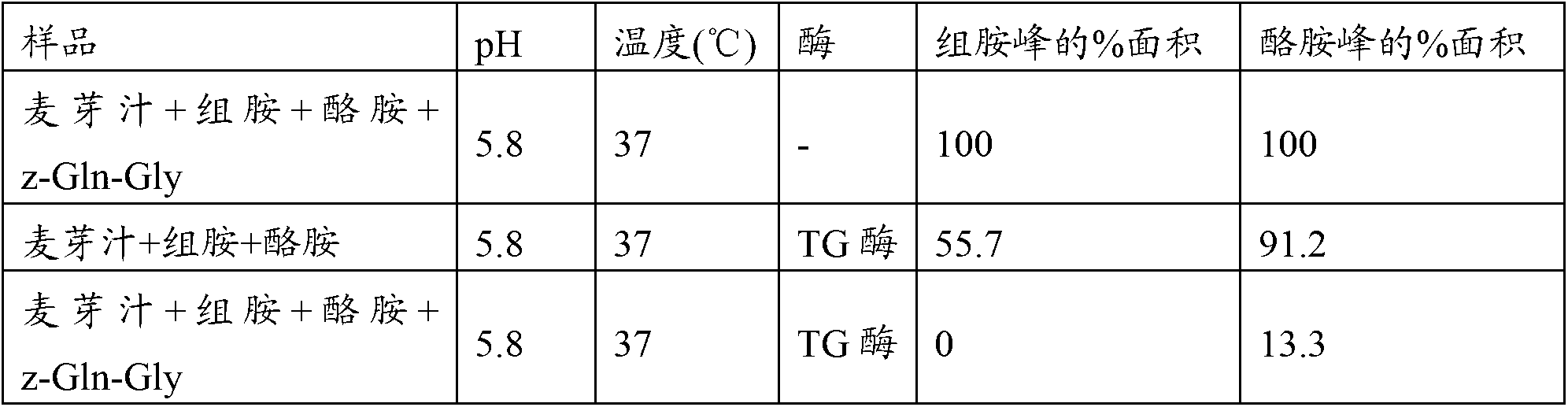
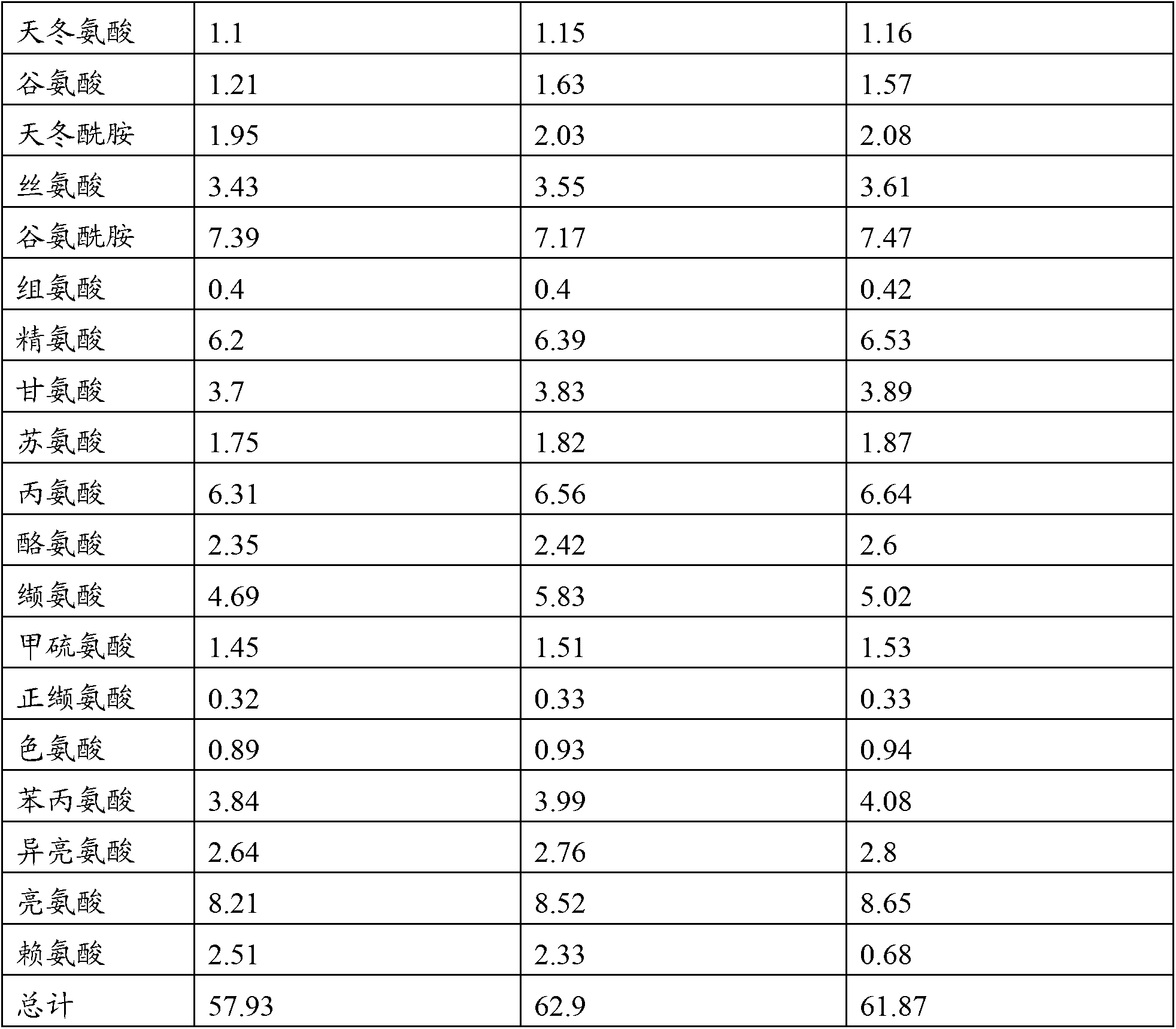
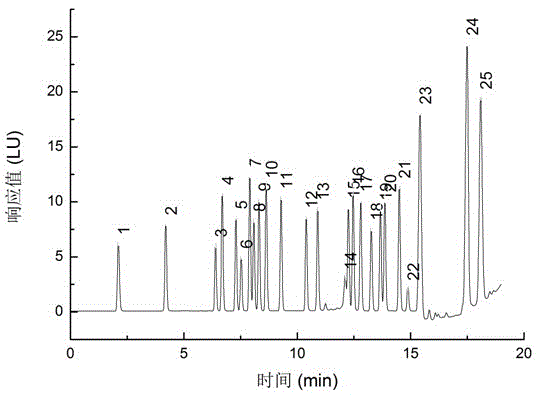
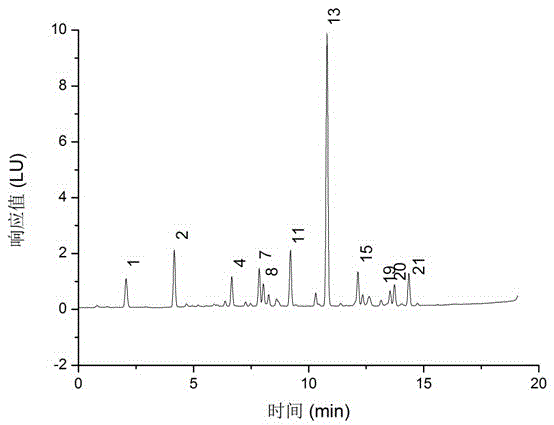
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
318 results about "Biogenic amine formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A biogenic amine is a biogenic substance with one or more amine groups. They are basic nitrogenous compounds formed mainly by decarboxylation of amino acids or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones.
Sensor for monitoring an analyte
InactiveUS7319038B2Easily detectable indicationEasy to mergeAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalyteColor changes
A food spoilage sensor of the general formulawherein M is a transition metal ion; D1, D2, D3 and D4 can be the same or different and can be N or P; R1 and R2, R3 and R4, R5 and R6, and R7 and R8 can be the same or different and from, taken together with the adjacent carbon atoms to which they are bonded and joined together, an aromatic or a cyclic group with at least one of the aromatic or cyclic groups possessing one or more polymerizable moieties. The complex selectively binds biogenic amines which are released by food spoilage microorganisms and undergo a detectable color change upon exposure thereto.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
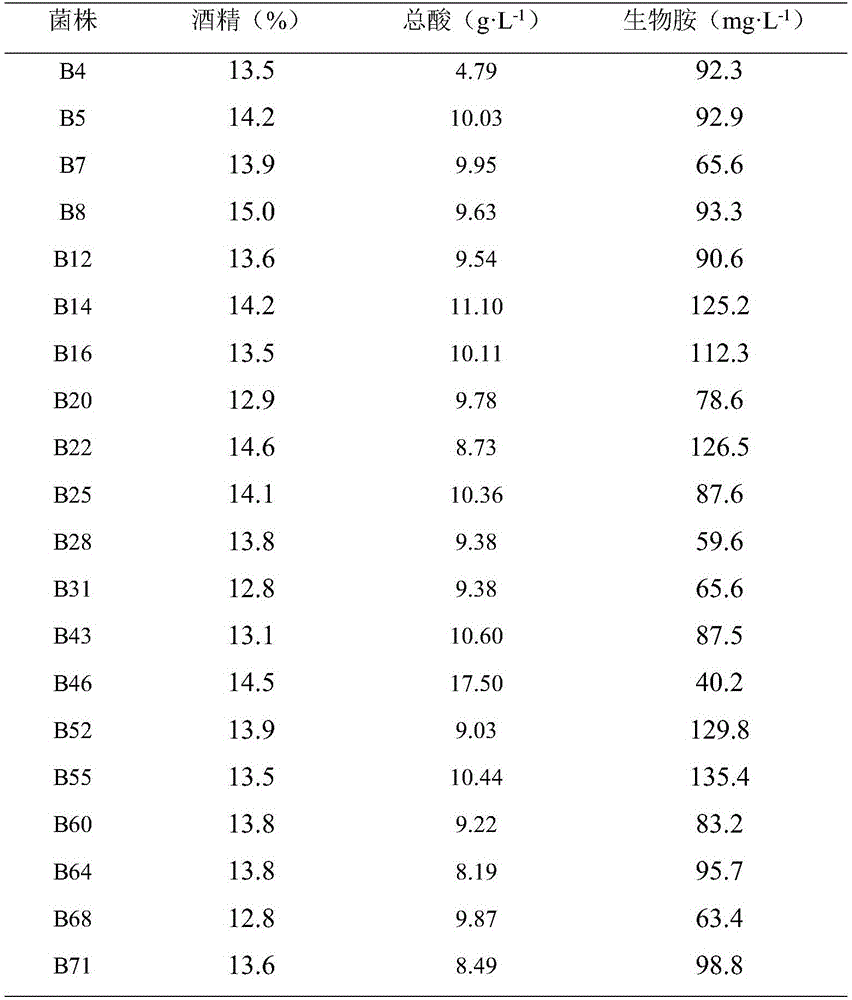
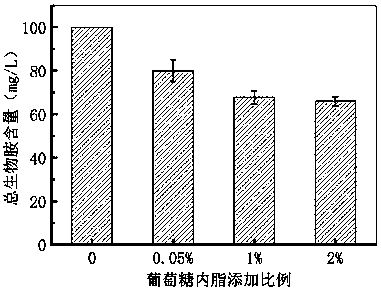
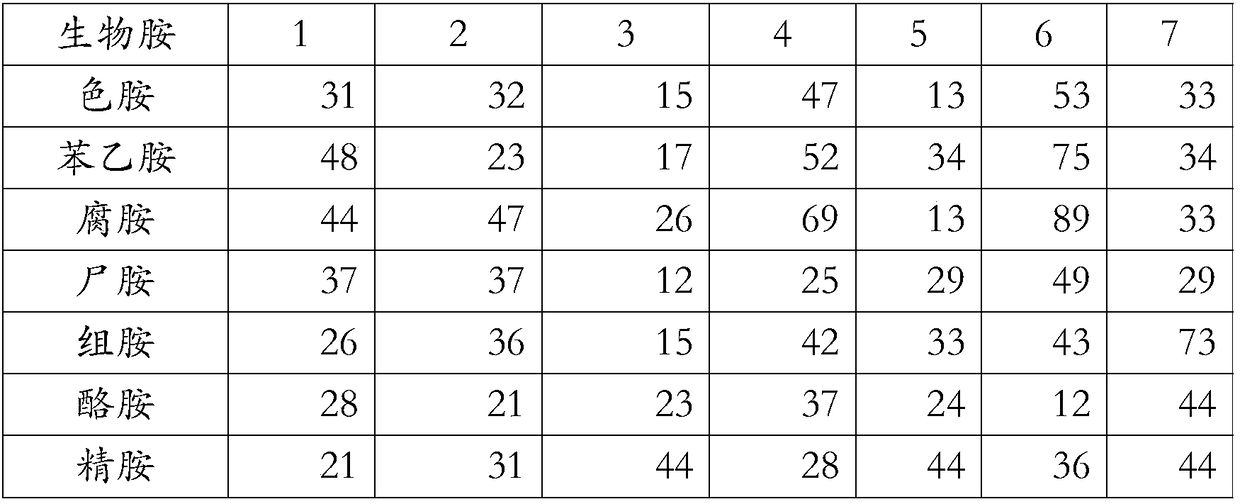
Lactobacillus plantarum with function of reducing contents of biogenic amines in foods and application of lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN105132308AAcid resistantHas the ability to clearBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and discloses lactobacillus plantarum with a function of reducing contents of biogenic amines in foods and application of the lactobacillus plantarum. The lactobacillus plantarum is resistant to acids and capable of strongly removing eight types of biogenic amines (including tryptamine, phenethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine, spermidine and spermine) in vitro. After 1*1010CFU / ml of the lactobacillus plantarum and the eight types of biogenic amines are co-cultured for 24h, wherein the concentration of each type of the biogenic amines is 100mg / L, and the total amine concentration is 800mg / L, the total amine content is reduced by 70% approximately, the content of each type of the biogenic amines is reduced by 30%-100%, and the removal rate of histamine highest in toxicity is up to 96.69%. Further, the lactobacillus plantarum is capable of lowering pH to 4 in eight hours owing to quickness in acid generation, thereby having favorable fermentation potential. The lactobacillus plantarum is used for degradation of the biogenic amines in foods, especially in fermented foods and extensive in application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
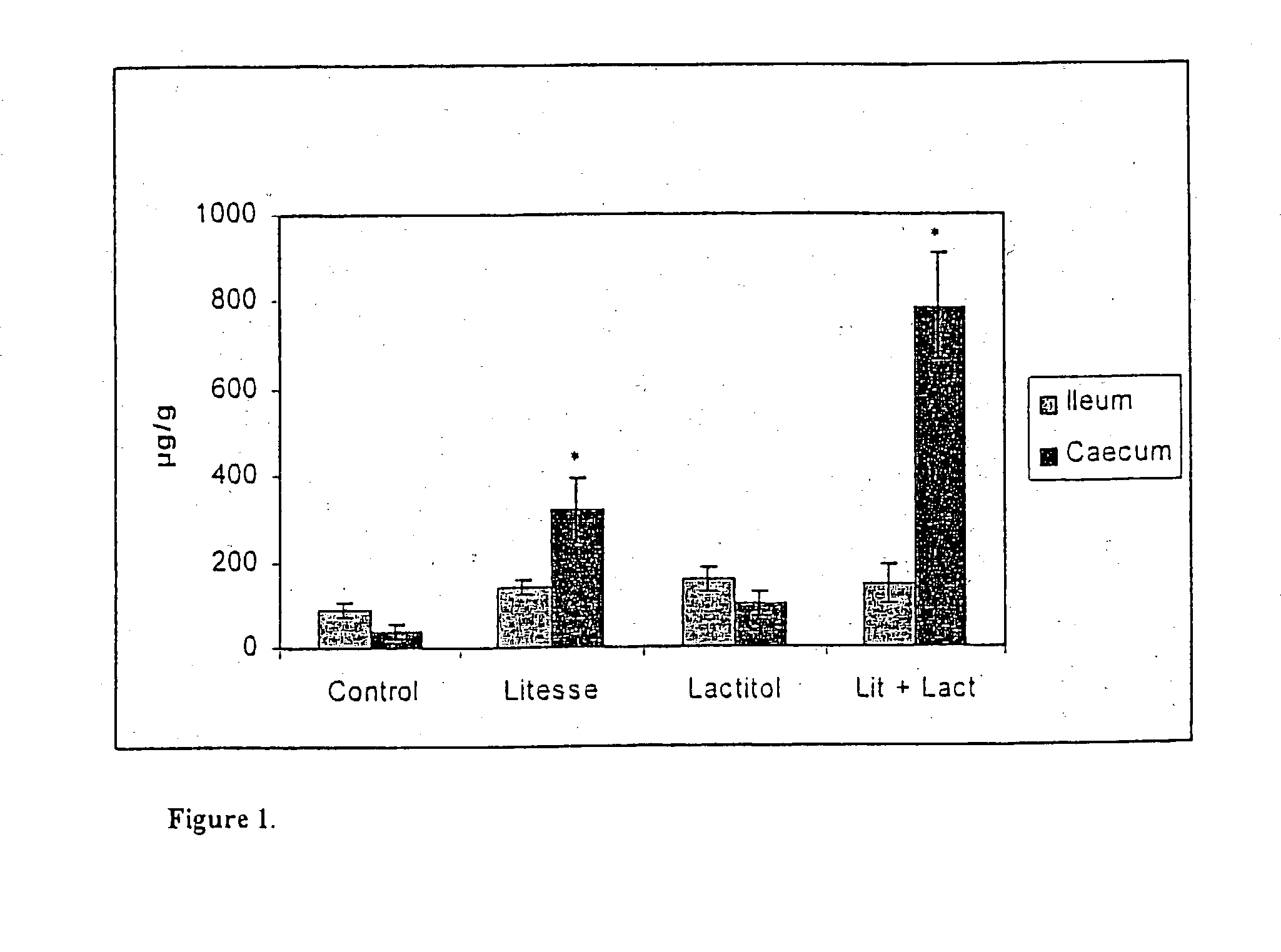
Stimulation of the immune system with polydextrose
InactiveUS20030157146A1Strengthening and improving health conditionImprove concentrationPowder deliveryBiocideImmunoglobulin APolyol
The invention relates to the use of polydextrose for stimulating the immune response (IgA) in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammal. Furthermore, the invention provides a method to potentiate the immunostimulative effect of polydextrose by mixing at least one polyol with polydextrose, said polyol being effective to synergistically increase the immunoglobulin A (IgA) concentration in the gut of a mammal. On the other hand, the invention provides also compositions containing polydextrose and polyols in which the laxative effects of polyols are reduced and which are effective to reduce the amount of biogenic amines in the gut of a mammal.
Owner:AS DE DANSKE SUKKERFABRIKKER
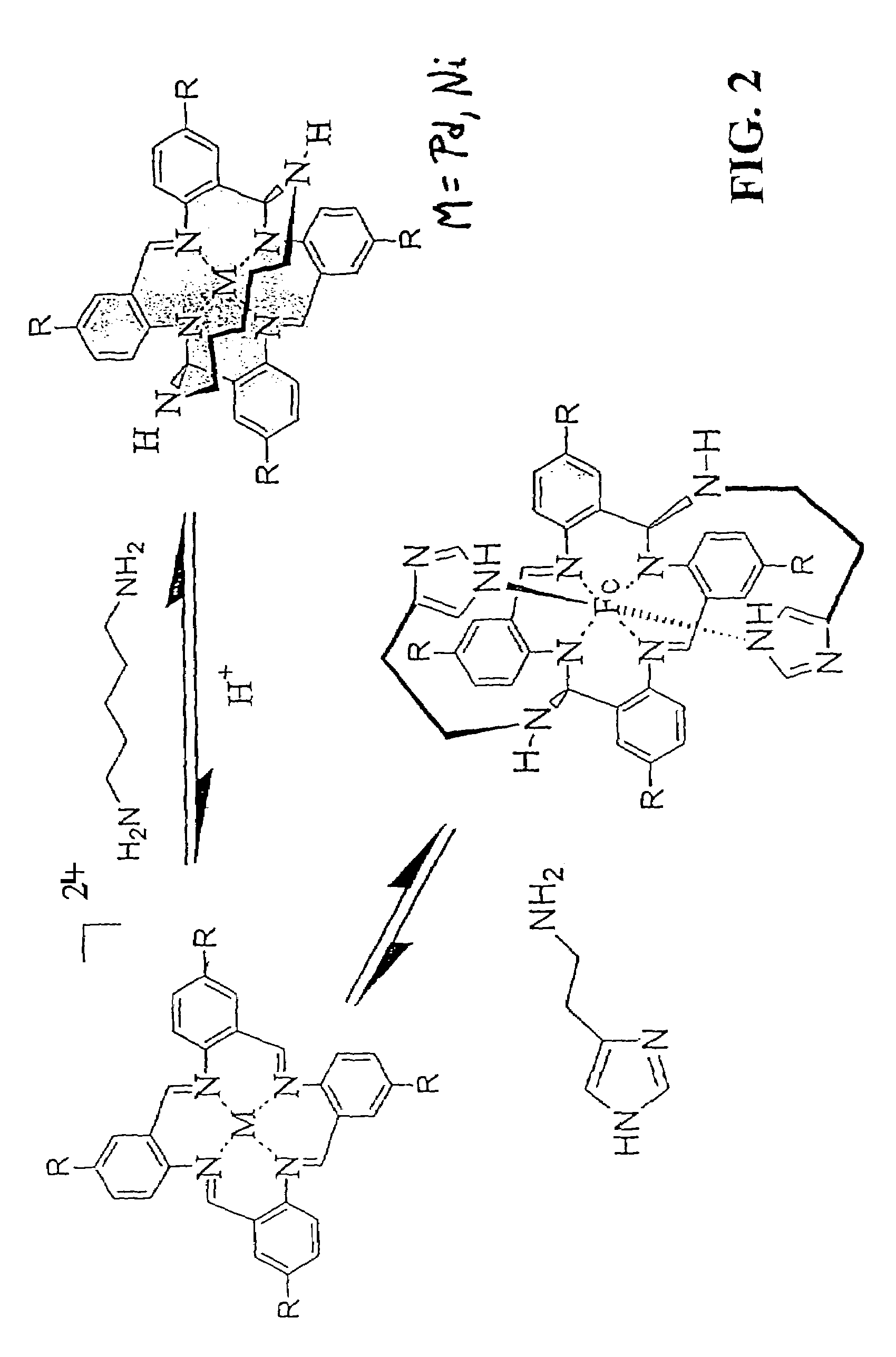
Methods and compositions for production, formulation and use of 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes
The invention provides novel 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes that are active for modulating biogenic amine transport, along with compositions and methods for using these compounds to treat central nervous system disorders. Certain 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes are provided that have at least one substituent on the aryl ring. In other embodiments 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes are provided that have a substitution on the nitrogen at the ‘3’ position. In additional embodiments 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes are provided which have one substitution on the aryl ring, as well as a substitution on the nitrogen at the ‘3’ position. The invention also provides novel methods of making aryl- and aza-substituted 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes, including synthetic methods that form novel intermediate compounds of the invention for producing aryl- and aza-substituted 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes.
Owner:DOV PHARMA
New biomarkers for assessing kidney diseases
The present invention relates to a metabolic biomarker set for assessing kidney disease comprising at least two amino acids, at least two acylcarnitines and at least two biogenic amines. Moreover, the present invention relates to a method for assessing kidney disease in a mammalian subject which comprises obtaining a biological sample, preferably blood and / or urine, from the subject and measuring in the biological sample the amount of at least two amino acids, of at least two acylcarnitines and of at least two biogenic amines, as well as to a kit adapted to carry out the method. By employing the specific biomarkers and the method according to the present invention it becomes possible to more properly and reliably assess kidney disease.
Owner:BIOCRATES LIFE SCIENCES AG
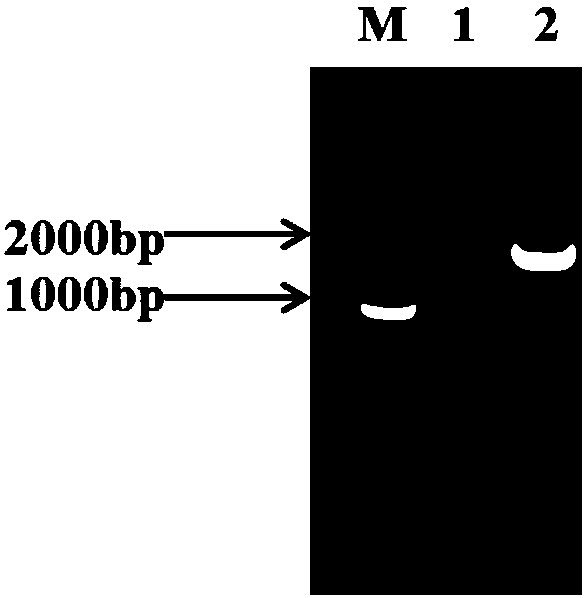
Separation and liquid chromatography column pre-column derivatization method of biogenic amine in soybean paste
InactiveCN101793642AReduce consumptionReduce distractionsComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationChromatography columnChemistry
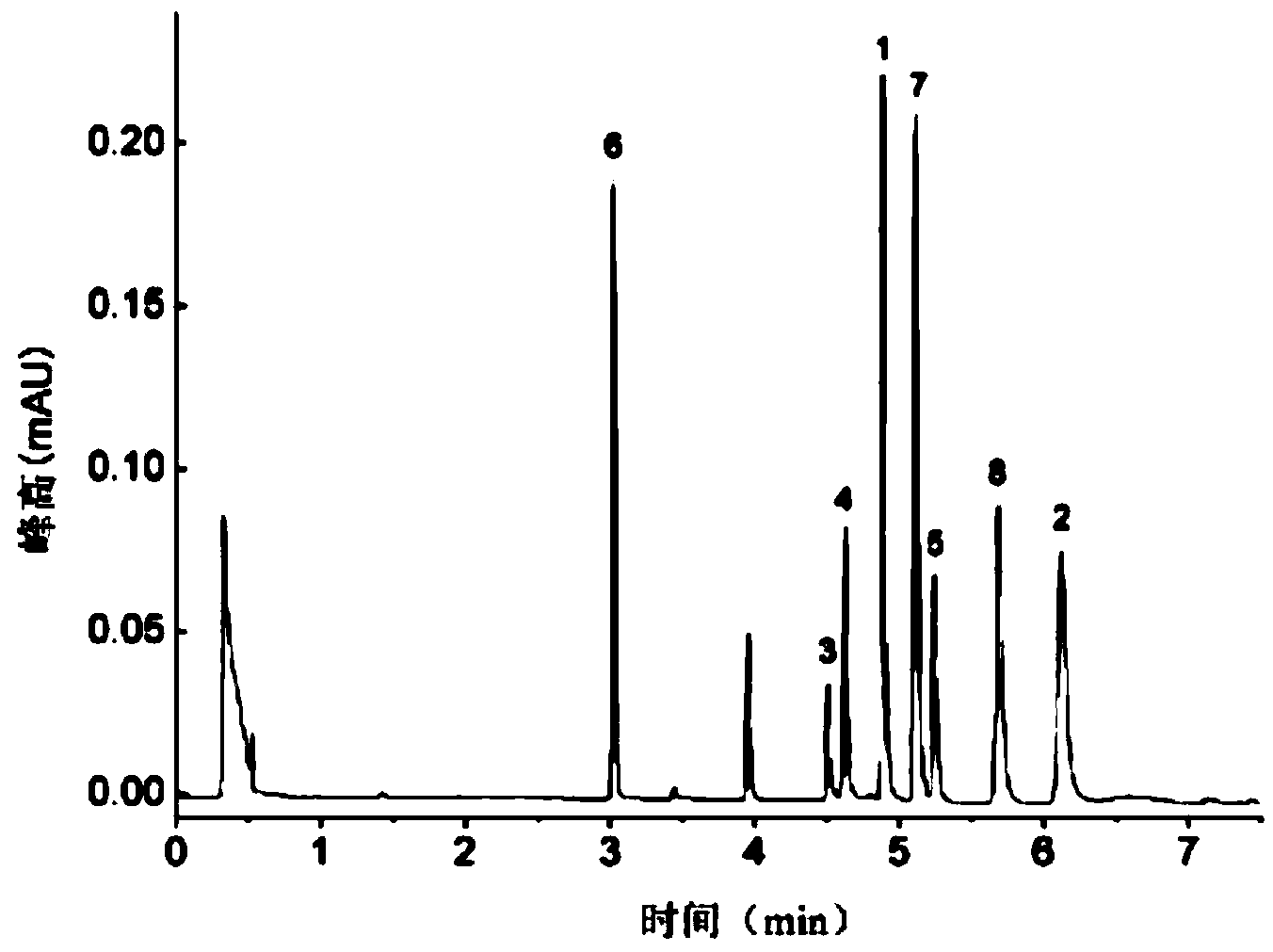
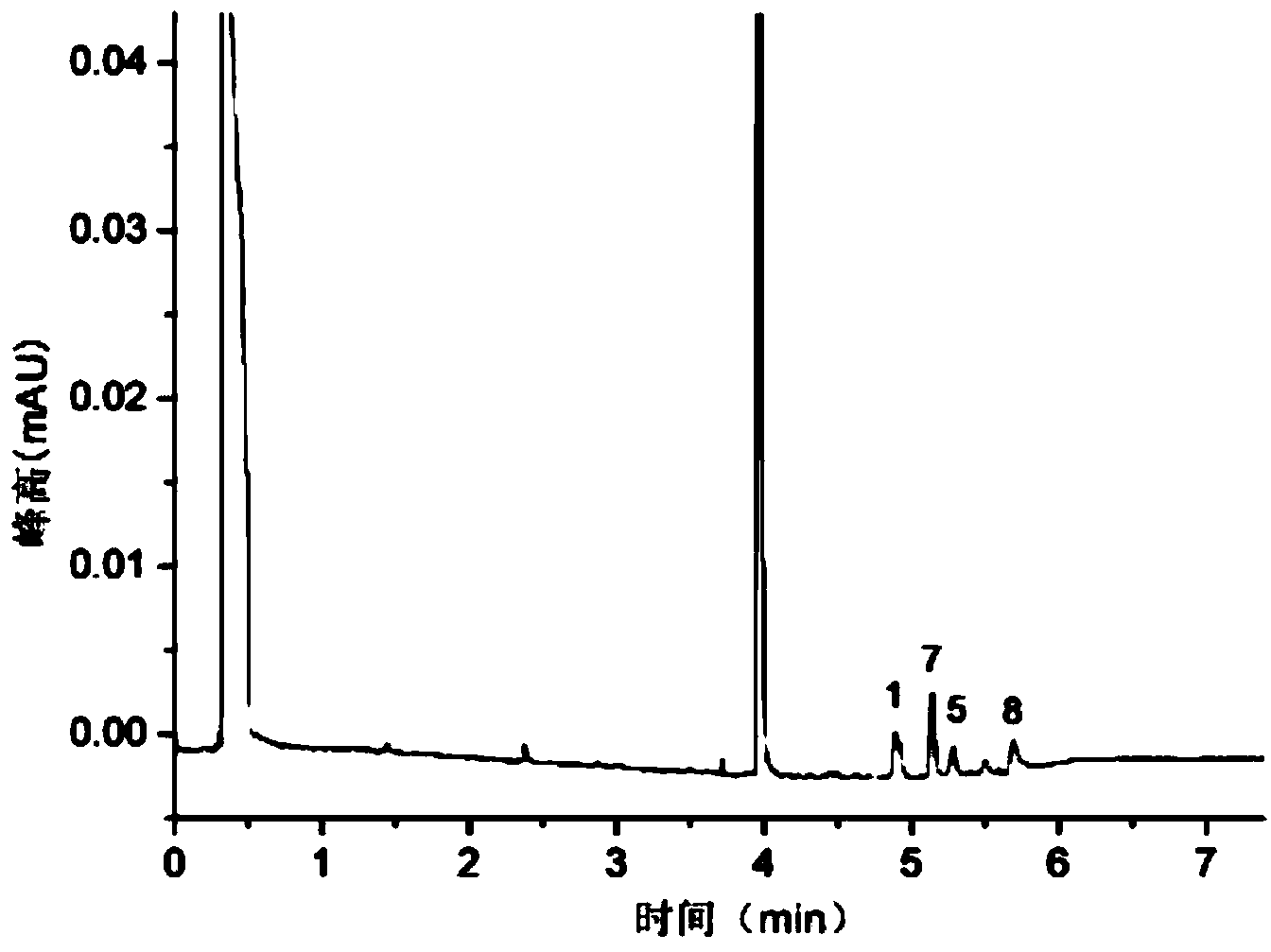
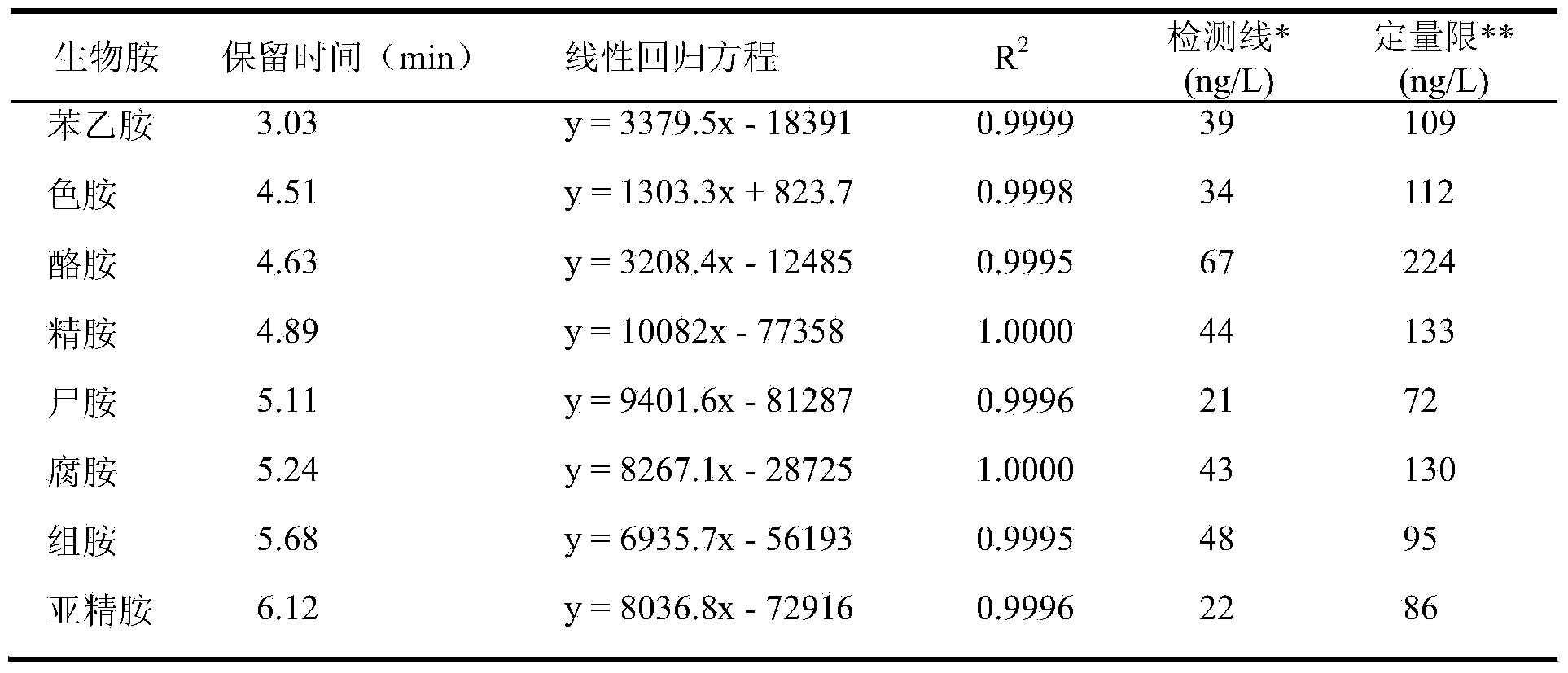
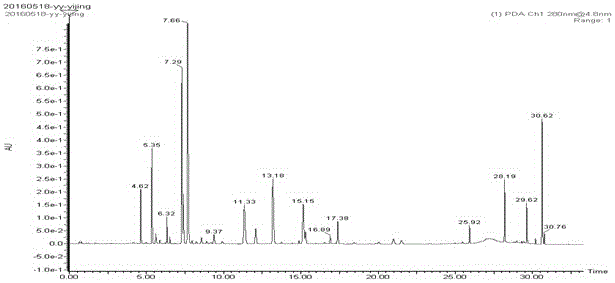
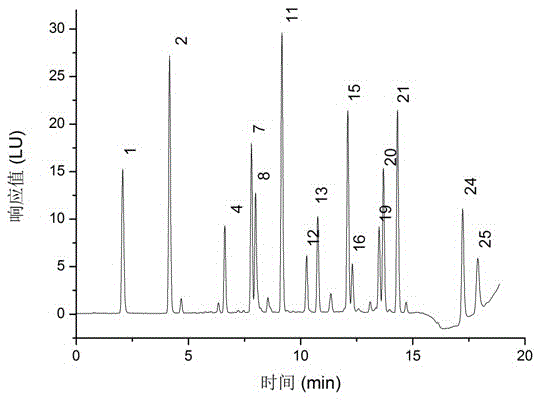
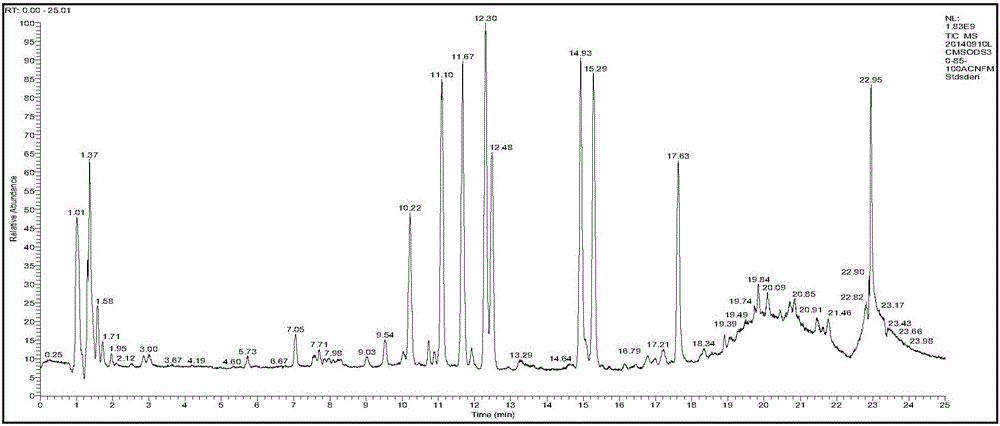
The invention discloses a separation and liquid chromatography column pre-column derivatization method of biogenic amine in a soybean paste, comprising the following steps of: (1) adding a trichloroacetic acid solution to the soybean paste, homogenizing, centrifuging and collecting a supernate; (2) adding normal hexane to the supernate, vibrating and taking out a lower layer trichloroacetic acid phase for later use after static layering; (3) adding an NaOH solution to the trichloroacetic acid phase, then adding an NaHCO3 solution for buffering, and mixing in a dansyl chloride acetone solution to carry out derivatization; and (4) removing dansyl chloride to terminate the reaction to obtain a derivative solution and filtering. The separation method has simple treatment process and low reagent consumption and avoids analyte loss caused by transfer. The soybean paste can reach detection demands after being separated and purified; undesired peak disturbance of a spectrogram is less and the determinand loss is low, and the recovery rate of the biogenic amine can reach more than 80 percent. The method determines the optimum condition for deriving the biogenic amine; dansyl chloride derivative products are stable and the detection sensitivity is high.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
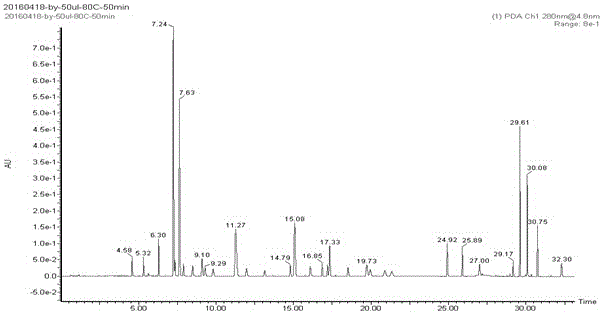
Method for determining content of biogenic amines in foods by adopting ultra-efficient bonded phase chromatography
The invention relates to the field of detection of harmful components in foods and particularly relates to a method for determining the content of biogenic amines in foods by adopting an ultra-efficient bonded phase chromatography. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out biogenic amines extraction treatment on foods to be detected with the mass of m by using an HClO4 solution to obtain liquid supernatant with the volume of V; adding an n-hexane solution with the equal volume into the liquid supernatant, extracting, and repeating for 1-2 times; removing an upper-layer organic phase part to obtain a purified extracting solution; carrying out pre-column derivatization on the purified extracting solution to obtain a derivatized extracting solution; and detecting the content of the biogenic amines in the derivatized extracting solution by using an ultra-efficient bonded phase chromatographic instrument to obtain the mass concentration of the biogenic amines in the extracting solution. According to the method, the content of the biogenic amines in the foods can be determined by adopting the ultra-efficient bonded phase chromatography and a mixed system of supercritical carbon dioxide and n-hexane / isopropanol / an ammonia water solution is used as a flowing phase; the viscosity is low, the mass transfer performance is good, the analyzing time is rapid, the solvent loading amount is samll and the environmental pollution is small.
Owner:广东广垦农产品质量安全检测中心有限公司
Analysis method for simultaneous detection of amino acids and biogenic amines in foods
ActiveCN105866316AEasy to separateHigh detection sensitivityComponent separationDerivatizationUltrasound assisted
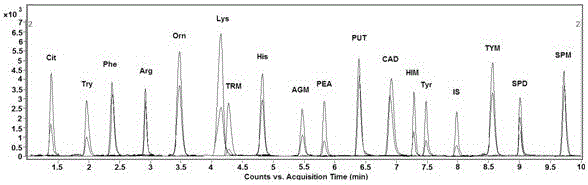
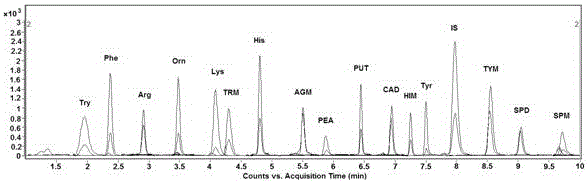
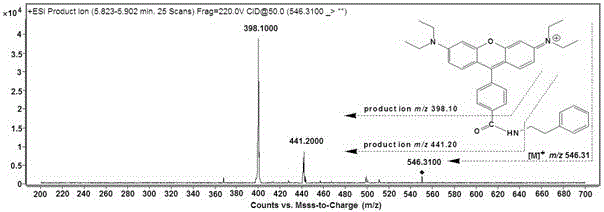
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and particularly relates to an analysis method for simultaneous detection of amino acids and biogenic amines in foods. The method is characterized in that for the first time, 4'-carbonyl chloride-rhodamine is used as a derivatization reagent to realize simultaneous derivatization of the amino acids and the biogenic amines in the food by means of ultrasonic assistance, in-situ derivation and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction, and qualitative and quantitative detection and analysis are performed by means of ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry in multi-reaction monitoring mode. The method can be used for simultaneous analysis and detection of eight amino acids and nine biogenic amines; by adoption of 1,7-diamino heptane as an internal standard substance, contents of the amino acids and the biogenic amines in different foods can be obtained accurately according to an internal standard method for quantification. The method has advantages of simplicity, quickness, high sensitivity, high selectivity and the like, and high recovery rate is achieved. In addition, by the analysis method, accurate and reliable technical means can be provided for food quality assessment and supervision.
Owner:食药环检验研究院(山东)集团有限公司
Method and detecting tube for visually detecting meat freshness based on gold nanoparticle material
ActiveCN105203538ARich color variationThe measurement result is accurateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiotechnologyNanoparticle
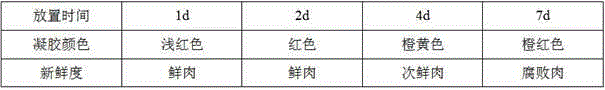
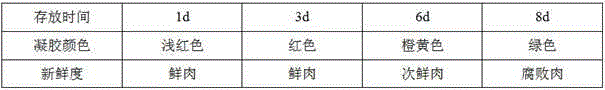
The invention discloses a method for visually detecting meat freshness based on a gold nanoparticle material. According to the method, different biogenic amines released by the meat in different freshness can hydrolyze a reducing agent precursor and generate different reducible matters, so that the visible detection for the meat freshness can be realized by inducing the chromogenic reaction between the reducible matters and the gold nanoparticle material under the condition of the existence of silver ion. Besides, the invention also provides a detecting tube for visually detecting the meat freshness. The detecting tube comprises a transparent tube body and a transparent tube cover connected with the transparent tube body; a gel is arranged in the transparent tube cover; the gold nanoparticle material, the reducing agent precursor and the silver nitrate are contained in the gel. The detecting tube can be used for performing the conventional quick test on the meat freshness or real-time indicating the freshness of the meat within the shelf life. The method and the detecting tube provided by the invention can be used for realizing the quick, accurate and real-time detection for the meat freshness; the detection cost is low; the operation is simple and convenient; the detecting tube can be conveniently carried and stored.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for promptly detecting biogenic amine in food
InactiveCN103149317ARaise the level of monitoringKeep healthyComponent separationSolventAnalysis method
The invention relates to a method for promptly detecting biogenic amine in food and belongs to the food analysis and security technical field. The method for promptly detecting the biogenic amine in food comprises the following steps: (1) extracting the biogenic amine from food samples; (2) purifying biogenic amine extracting solution; (3) derivatizing the biogenic amine extracting solution; and (4) optimizing developing solvent and analyzing thin layer chromatography. The method for promptly detecting the biogenic amine in food can be used for promptly detecting biogenic amine content in products of fish, meat, cheese, wine, vinegar and the like. Compared with the other analysis methods, the method for promptly detecting biogenic amine in food has the advantages of being free of expensive analytical instruments, low in cost, easy to operate, fast, and capable of effectively lowering monitoring cost in food production and circulation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparation of Sichuan sausages by fermentation
ActiveCN108587983AAdd flavorImprove securityBacteriaClimate change adaptationFood flavorFermentation starter
The invention relates to fermentation of microorganisms and meat food and specifically discloses lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparation of Sichuan sausages by fermentation. Theprovided lactobacillus plantarum 1-1 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation number is CGMCC NO. 15467, and the preservation date is March 20th, 2018. The strain is isolated from traditional sausages of Qingcheng Mountain in Dujiangyan City, Sichuan Province, grows well on an MRS agar culture medium, meets the requirements of meat fermenting agents due to main fermentation characteristics and is suitable for meat fermentation. The lactobacillus plantarum has the capability of degrading sarcoplasmic protein and biogenic amines in an in vitro simulation system, is used in production of the Sichuan sausages, can promote degradation of sarcoplasmic protein of the Sichuan sausages and significantly reduce the content of biogenic amines in the Sichuan sausages and have the potential to be used in actual production of the Sichuan sausages, so that it is ensured that the flavor, taste and safety of the Sichuan sausages are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Lactobacillus plantarum and its application in the high-acid yellow wine production for acid modulation
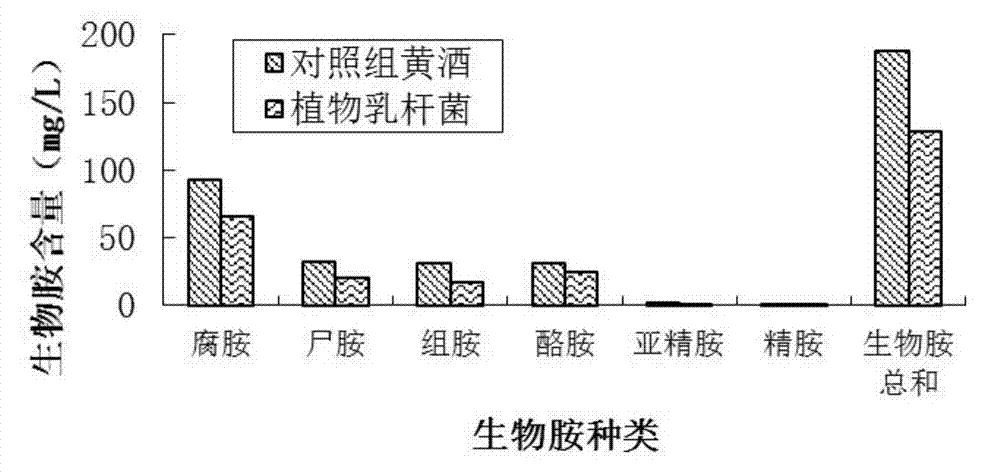
ActiveCN106350465AReduces biogenic amine levelsLittle difference in production processBacteriaAlcoholic beverage preparationPutrescineChemistry
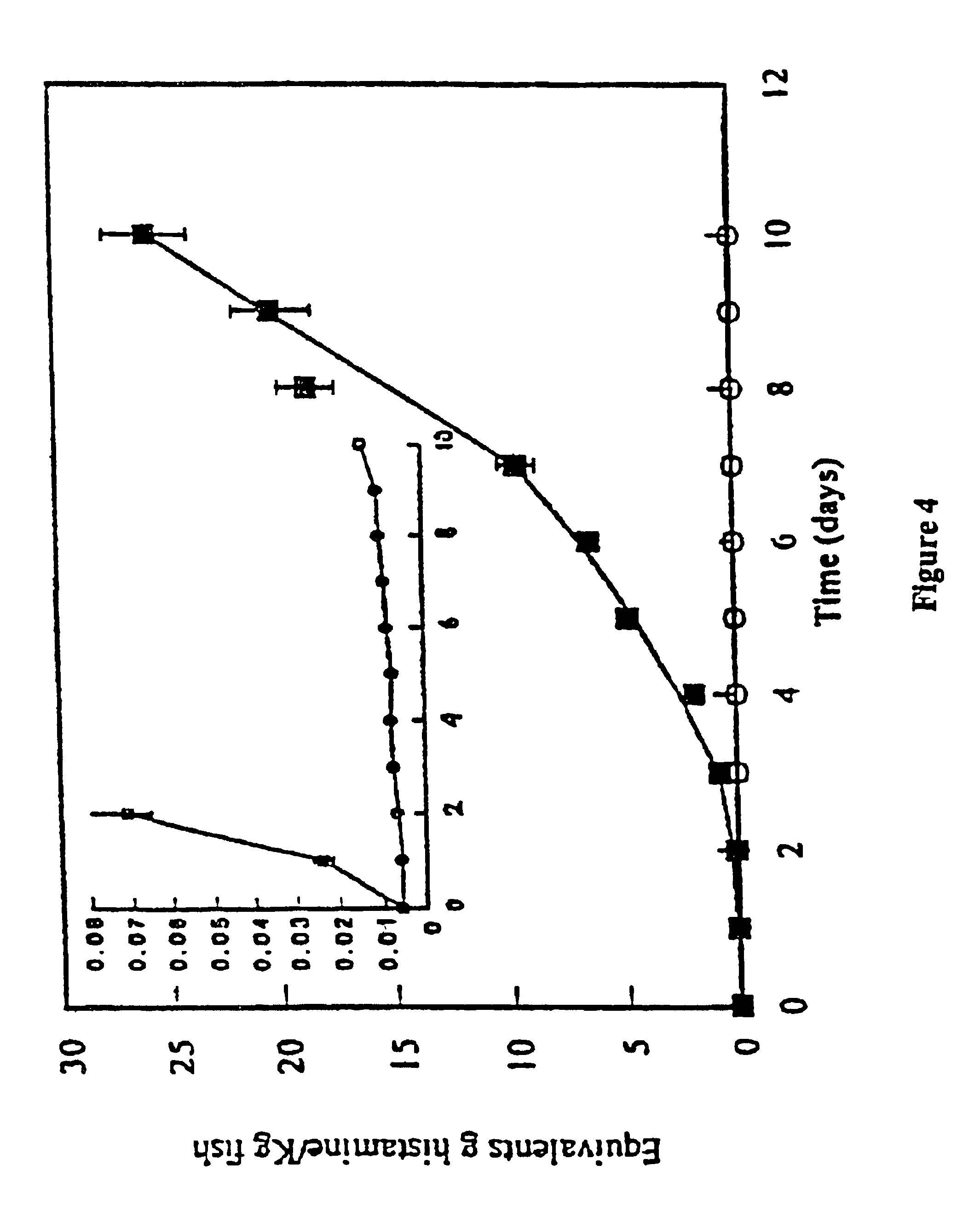
The invention discloses a lactobacillus plantarum and its application in the high-acid yellow wine production for acid modulation, belonging to the field of rice wine brewing technology. The lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No.12757, isolated from rice wine fermented mash. The lactobacillus plantarum comprises of total acid of rice wine produced of more than 17.5g / L (in lactic acid), lactic acid content of 70% or more accounting for the total organic acid, 14% (v / v) or more of alcohol content, 52mg / L biogenic amine content (the total amount of putrescine, histamine and tyramine), far lower than the rancid rice wine in the storage process, which can produce high-acid rice wine for acid modulation, greatly facilitating the production of low-grade rice wine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
New biomarkers for assessing kidney diseases
The present invention relates to a metabolic biomarker set for assessing kidney disease comprising at least two amino acids, at least two acylcarnitines and at least two biogenic amines. Moreover, the present invention relates to a method for assessing kidney disease in a mammalian subject which comprises obtaining a biological sample, preferably blood and / or urine, from the subject and measuring in the biological sample the amount of at least two amino acids, of at least two acylcarnitines and of at least two biogenic amines, as well as to a kit adapted to carry out the method. By employing the specific biomarkers and the method according to the present invention it becomes possible to more properly and reliably assess kidney disease.
Owner:BIOCRATES LIFE SCIENCES AG
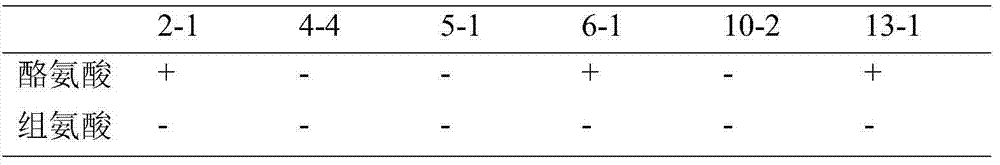
Lactic acid bacteria not generating amino acid decarboxylase high-yield urease and application of lactic acid bacteria
ActiveCN104762238AReduce contentReduce biogenic amine concentrationBacteriaAlcoholic beverage preparationReference sampleAmino acid
The invention discloses lactic acid bacteria not generating amino acid decarboxylase high-yield urease and application of the lactic acid bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of biological fermentation. The lactobacillus plantarum L10-2 provided by the invention is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 15, 2015 and has a preservation number of CCTCC No.M2015118, and the preservation address is the China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuchang Luojiashan Wuhan University in Wuhan City of Hubei Province. At the beginning of the brewing of a rice wine, the lactobacillus plantarum, a raw material (rice), a seeding yeast and a wheat koji are added into a fermentation tank together to perform rice wine brewing, and a physical and chemical index evaluation is performed by taking a control group, namely the rice wine as a reference sample. The result shows that by adding the lactobacillus plantarum, the contents of biogenic amine and ethyl carbamate in the rice wine can be effectively reduced, and the safety of the rice wine is greatly improved.
Owner:广东至善智造科技有限公司
Application of lactobacillus plantarum in degradation of biogenic amines in wine making
ActiveCN104388329AGood winemaking adaptabilityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGrape wine
Belonging to the field of biotechnology and fermentation, the invention discloses a method for degradation of biogenic amines in wine making by lactobacillus plantarum. The strain is obtained by screening the surfaces of wine grapes, not only can effectively reduce the content of biogenic amines in an MRS medium added with putrescine, histamine and tyramine, but also can be directly applied in the wine making process. With good high acid and high alcohol content and high SO2 tolerance, and very high malic acid-lactic acid conversion rate, the strain can effectively decrease the content of biogenic amines in the wine making process.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
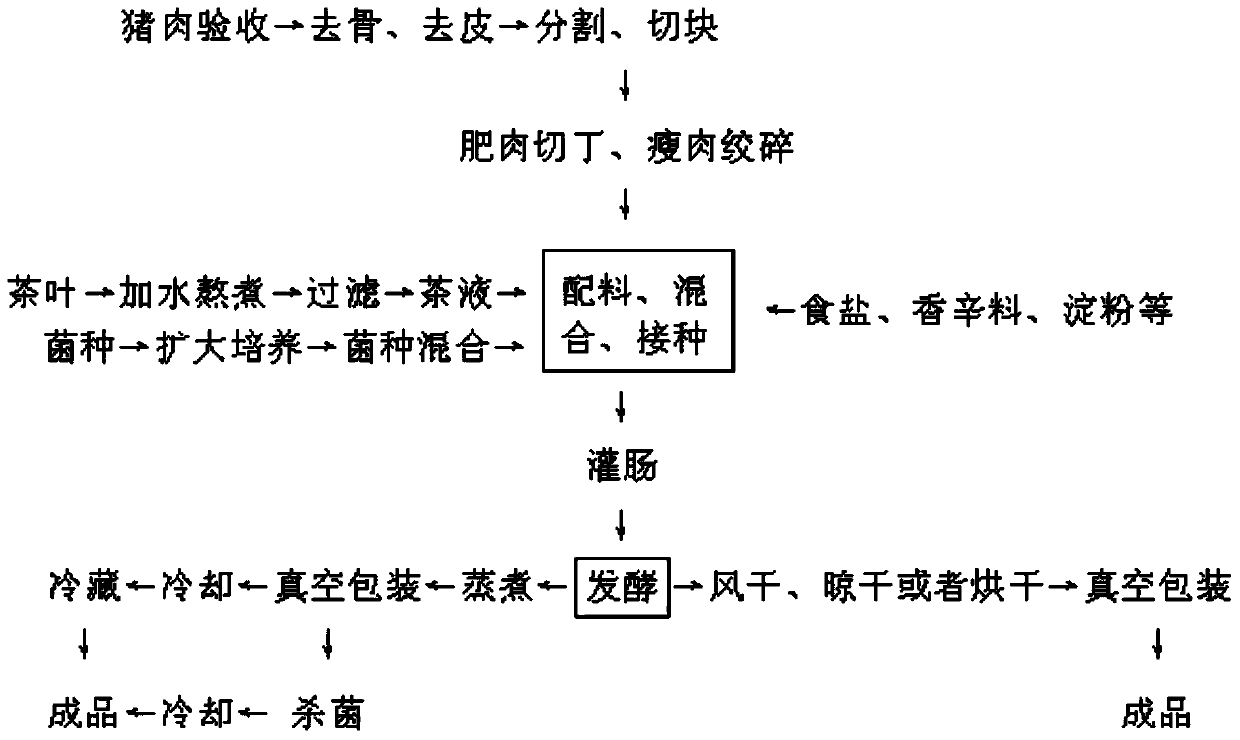
Fermented tea sausage and processing method thereof
ActiveCN103798831ADeliciousHigh nutritional valueFood freezingMeat/fish preservation by heatingNutritive valuesFood flavor
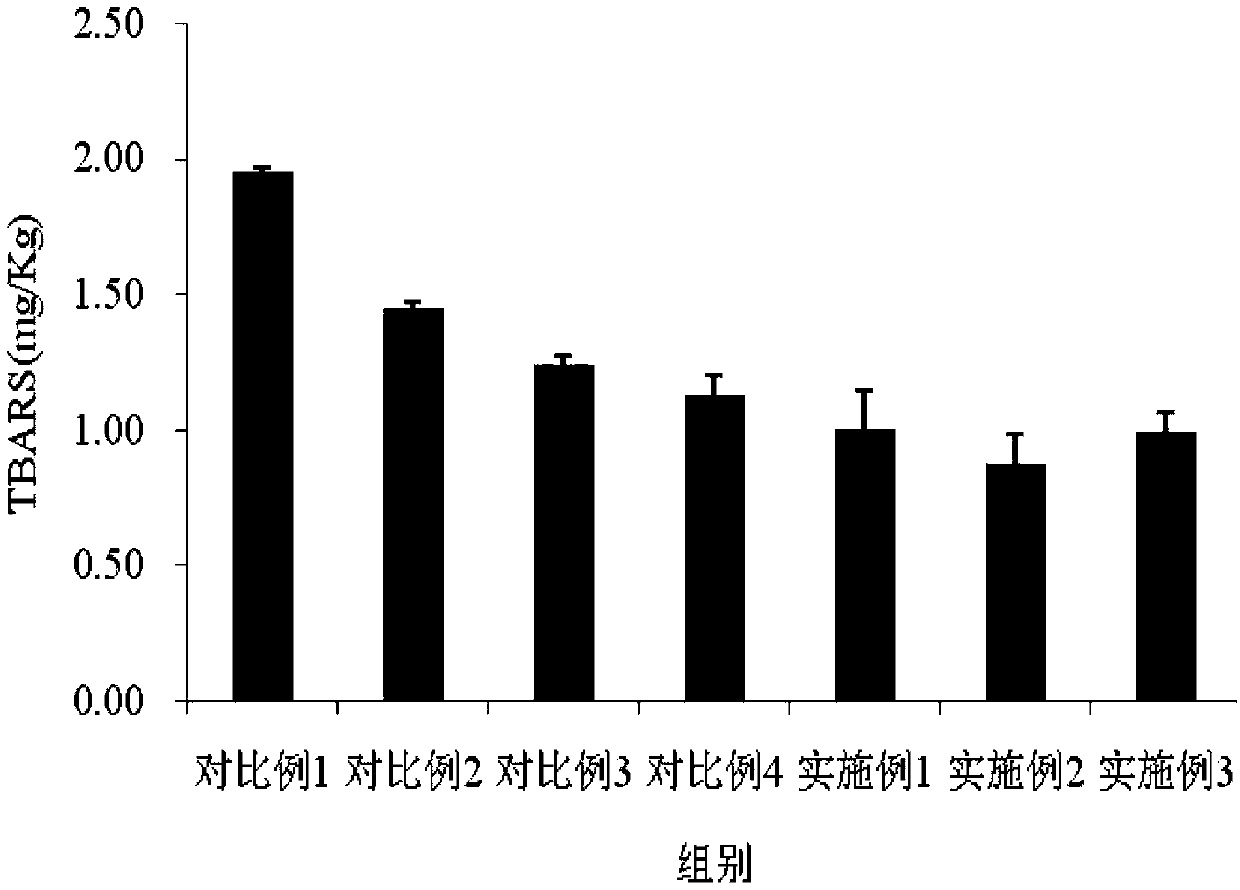
The invention discloses fermented tea sausage and processing methods thereof. The fermented tea sausage is produced by adopting tea liquid and pork as main raw materials to be fermented by a mixed strain consisting of lactobacillus, saccharomycetes and micrococcus. According to different product preservation methods, the invention provides the processing methods of three products such as dry-type fermented tea sausage, cold-stored cooked fermented tea sausage and normal-temperature-stored cooked fermented tea sausage. By adding the tea liquid and the mixed strain which is prepared from the purely-cultured lactobacillus, saccharomycetes and micrococcus into the processing flow of the sausage, the growth and propagation of inoculated microorganisms, such as the lactobacillus, which are beneficial to processing and cooking of the sausage can be effectively promoted, the production and accumulation of nitrite and biogenic amine in the sausage processing process can be suppressed by adequately utilizing tea polyphenol in the tea liquid; meanwhile, the sausage is unique in flavor, and the grease of the sausage can be reduced; the fermented tea sausage is delicious in taste, high in nutritional value, low inn nitrite and biogenic amine content, free from benzopyrene and high in food safety.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Methods For Inhibiting Native And Promiscuous Uptake Of Monoamine Neurotransmitters
InactiveUS20140228421A1Great extracellular levelGood treatment effectBiocideOrganic chemistryReuptake inhibitorMonoamine neurotransmitter
The present invention relates to methods of inhibiting native and promiscuous uptake of biogenic amine neurotransmitters with triple reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of conditions affected by monoamine neurotransmitters.
Owner:ETHISMOS RES INC
Enzyme for degrading biogenic amine in soy sauce
The invention discloses enzyme for degrading biogenic amine in soy sauce, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation. A sequence of multi-copper oxidase crude enzyme provided by the inventionis as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The enzyme disclosed by the invention has different degrees of degradation functions on biogenic amine of tryptamine, phenylethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine and spermidine in the soy sauce, wherein the concentration of the tyramine of which the content in the soy sauce is the most is 540.71 mg / L. After adding the multi-copper oxidase crude enzymeprovided by the invention, the content of the biogenic amines is reduced by 100 mg / L within 24 hours; compared with an existing technology for reducing the content of the biogenic amine by 58.57 mg / Lby adding pure enzyme in a biogenic amine mixed solution for 24 hours, the degradation time is short, and the effect is good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
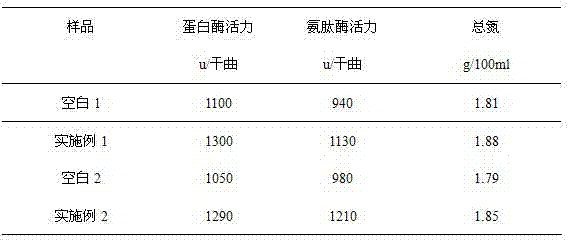
Preparation method of low-biogenic amine soy sauce
The invention provides a preparation method of low-biogenic amine soy sauce. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding glycine and citric acid in starter propagation process, fermenting for 60-90 days by adopting a high-salt diluted-state fermented soy sauce brewing method, then squeezing and filtering, thereby being capable of obviously reducing the number of microorganisms in the yeast of the soy sauce. With the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the total content of biogenic amine in the crude soy sauce can be reduced by more than 60%, the activity of neutral protease and acid protease in the yeast of the soy sauce can be increased by more than 10%, the aminopeptidase activity can be increased by more than 20%, and the recovery rate of the protein can be increased by more than 3%.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Chromatographic detection method for simultaneously analyzing ammonium ions, amino acids and biogenic amine in tobacco leaves
ActiveCN106053674ALow priceHigh detection sensitivity and stabilityComponent separationDiethyl ethoxymethylenemalonateDerivatization
The invention discloses a chromatographic detection method for simultaneously analyzing ammonium ions, amino acids and biogenic amine in tobacco leaves. Thechromatographic detection method comprises the following steps of A, extracting the ammonium ions, amino acids and biogenic amines in the tobacco leaves; B, deriving the ammonium ions, amino acids and biogenic amines in the tobacco leaves; C, performing the chromatographic analysis on the derived products of ammonium ions, amino acids and biogenic amines in the tobacco leaves; D, quantitatively analyzing the ammonium ions, amino acids and biogenic amines in the tobacco leaves. The chromatographic detection method has the advantagesthattheammonium ions, 25 types of amino acids and 8 types of biogenic amines in tobacco leaves can be simultaneously measured by microwave-assisted extraction, ethoxy methylene malonic diethyl esterderiving, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and ultraviolet detectors; the simplicity and rapidityare realized, the sensitivity is high, thestability is good, and the like; the detection flux and data accuracy of the sample can be improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Fermenting agent for reducing biogenic amine in meat products by compound-bacteria temperature shift fermentation and fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN103907940ANo biogenic aminesNo amine productionSugar food ingredientsFood preparationFlavorD-Glucose
The invention relates to a fermenting agent for reducing biogenic amine in meat products by compound-bacteria temperature-shift fermentation and a fermentation method thereof, belongs to the technical field of biological fermentation of meat food, and particularly relates to a method of reducing biogenic amine in meat products by compound-bacteria temperature-shift fermentation. The method includes: adding compound bacteria into a meat product to be fermented all at once, performing low-temperature lactobacillus pentosus fermentation at 20-30 DEG C, immediately raising the fermentation temperature after the low-temperature fermentation is finished and performing medium-temperature fermentation at 35-45 DEG C with lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus coryniformis, namely, the meat product is fermented by a two-step method that is low temperature firstly and medium temperature secondly by utilization of the compound bacteria. The fermenting agent comprises 8.0-12.0 g of glucose, 2.0-3.0 g of pentose and 2.0-3.0 g of fructosan. The fermenting agent and the fermentation method are advantageous in that, by two fermentation steps at different temperatures and with different bacteria or bacterium compositions, the content of the biogenic amine in the meat product is obviously lower than that of a meat product only subjected low-temperature fermentation or only subjected to medium-temperature fermentation; and the flavor of the meat product subjected to the low-temperature fermentation firstly and medium-temperature fermentation secondly is significantly improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES +1
Biosensor
InactiveUS6897035B1Rapid and accurate and simple and handyRapid, accurate, simple and handy analytical instrumental toolMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPeroxidaseEnzyme system
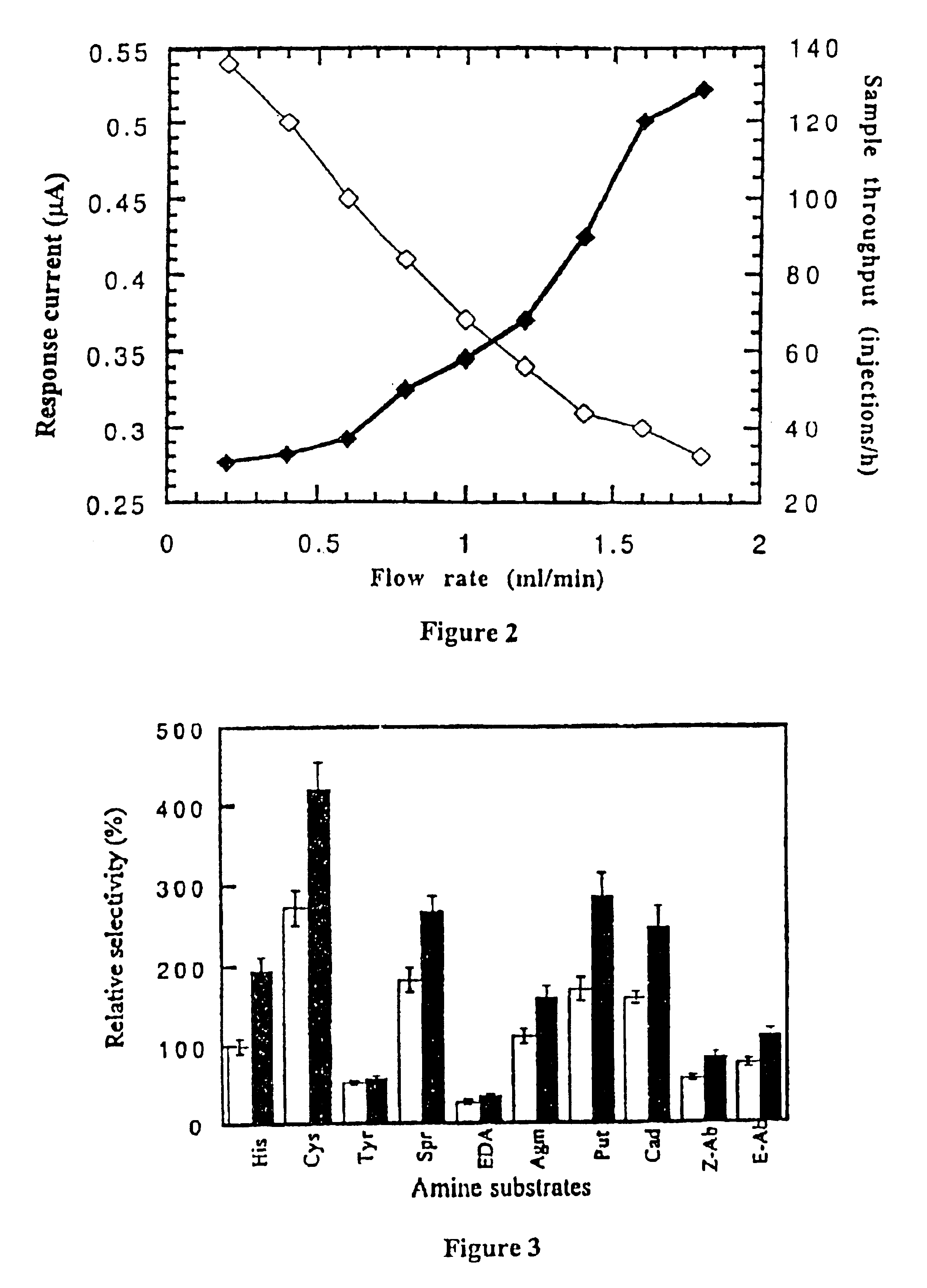
The present invention relates to a biosensor for the detection and / or the determination of freshness biomarkers, such as biogenic amines (preferably histamine) in food and beverage, comprising an electrode and a mono-enzyme system, such as an amine oxidase, or a bi-enzyme system of an amine oxidase and a peroxidase. The enzymes are optionally crosslinked into an osmium based redox polymer.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Multicopper oxidase recombinase capable of degrading biogenic amine
ActiveCN108165515AStrong performance in degrading biogenic aminesBroad degradation spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliTryptamine
The invention discloses a multicopper oxidase recombinase capable of degrading biogenic amine, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation. According to a degradation method, an appropriate amount of the multicopper oxidase recombinase is added into soy sauce, biogenic amine is degraded by the multicopper oxidase recombinase into aldehydes and ammonias, and degradation of biogenic amine isrealized, wherein the multicopper oxidase recombinase is obtained via heterologous expression of multicopper oxidase recombinase genes from Lactobacillus paracasei in Escherichia coli. The multicopperoxidase recombinase possesses relatively excellent biogenic amine degradation capacity, is capable of degrading tryptamine, phenylethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine, spermine, and spermidine in 24h, and the highest degradation efficiency is 75%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method capable of reducing biogenic amine of conventional pickled vegetables
ActiveCN108142890AReduce biogenic aminesPromote degradationSugar food ingredientsBacteriaGlycineD-Glucose
The invention relates to the technical field of processing of pickled vegetables, in particular to a preparation method capable of reducing biogenic amine of conventional pickled vegetables. The method comprises the following steps of (1) screening bacterial strains capable of degrading biogenic amine; (2) re-screening bacterial strains good in flavor; (3) preparing obtained lactobacillus pentosusand obtained lactococcus lactis which are high in capacity of degrading the biogenic amine and good in flavor into bacterium paste; (4) performing radiation treatment on raw materials of the pickledvegetables; (5) preparing the pickled vegetables; and (7) adding glucose, aged water for making pickled vegetables, glycine, gluconolactone and the like. The conventional Sichuan pickled vegetables obtained by the method disclosed by the invention are low in the content of the biogenic amine, appropriate in acidity and good in flavor.
Owner:SICHUAN DONGPO CHINESE PAOCAI IND TECH RES INST
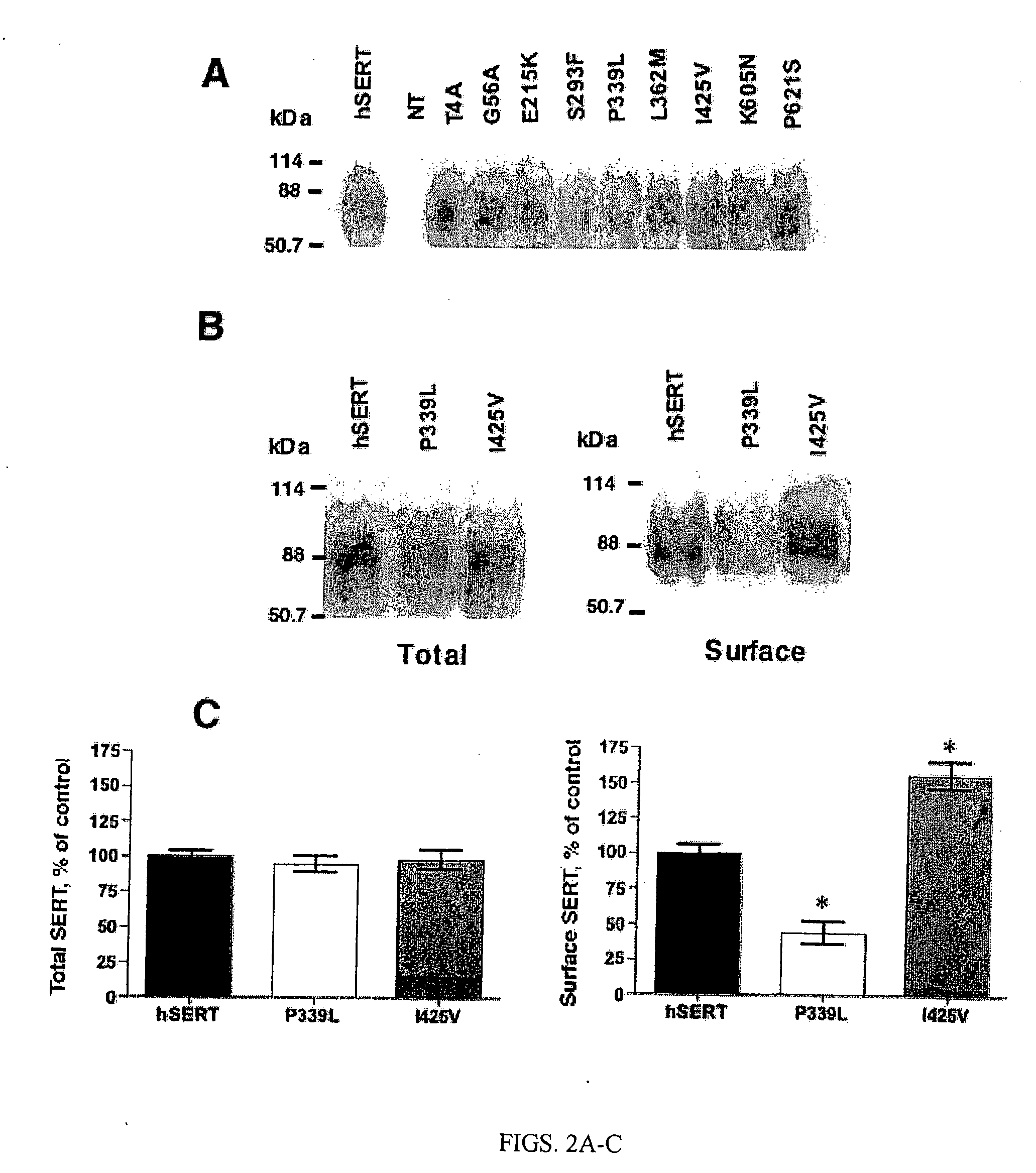
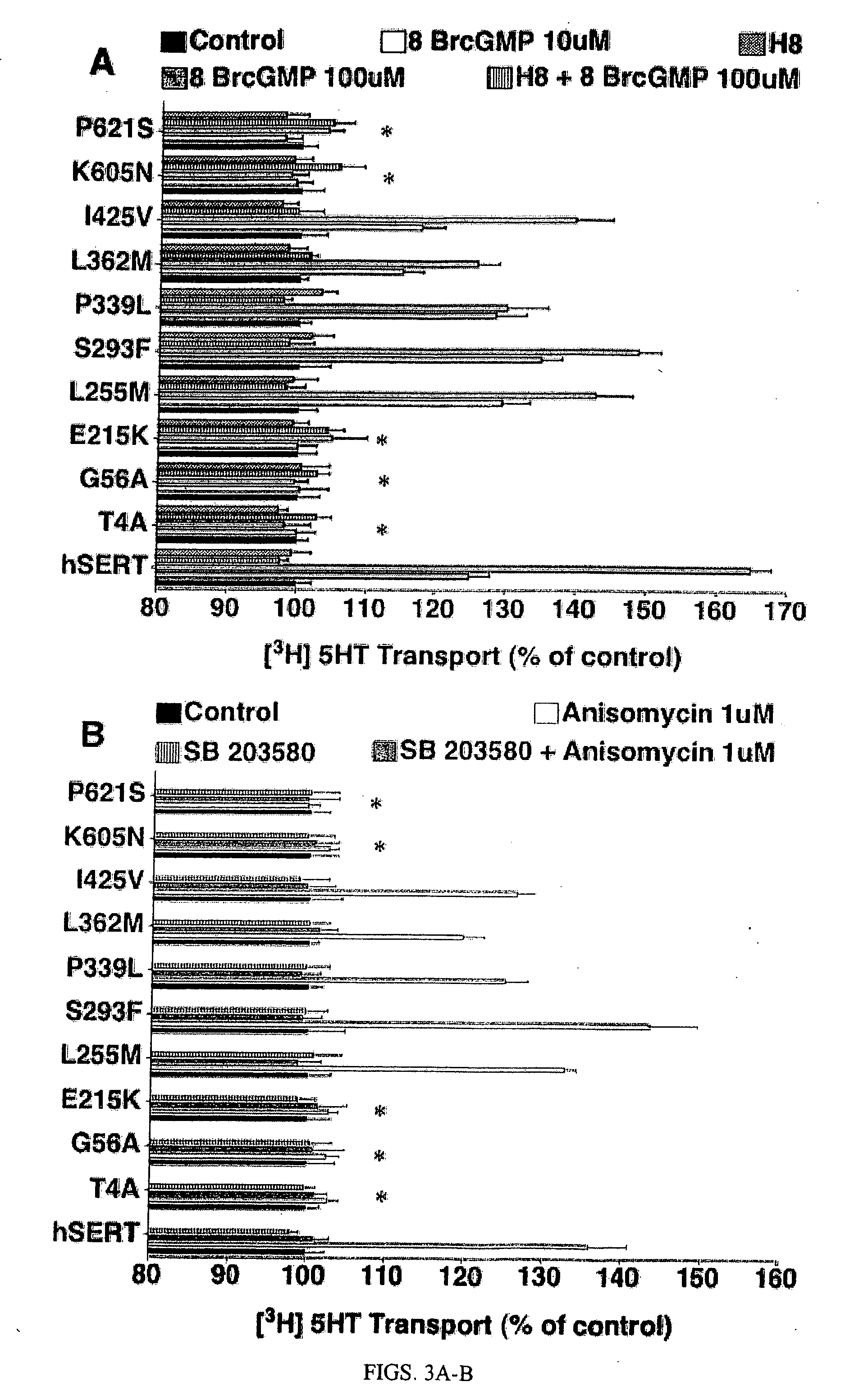
Genetic and pharmacological regulation of antidepressant-sensitive biogenic amine transporters through PKG/p38 map kinase
The invention relates to the observation that the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is an important regulator of biogenic amine transporter (BAT) function. By using modulator of p38 MAPK, one can alter BAT function in a specific manner. This recognition of the pathway and its interaction with the serotonin transporter (SERT) and the norepinephrine transporter (NET), along with the PPA, PKG and PDE pathways, also provides the opportunity to identify polymorphisms that will impact the efficacy of drugs that act though on these enzymes or their pathways.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
A method to reduce biogenic amine content in food
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for detecting free amino acid in biogas slurry
InactiveCN105548449AAvoid the disadvantages of non-selective adsorptionOvercoming selectivityComponent separationHigh concentrationFiltration membrane
The invention relates to a method which comprises the following steps: removing high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and volatile biogenic amine in a way of rotary evaporation after biogas slurry is regulated to be alkaline; removing macromolecular disruptors by applying a 3K Millipore ultra-filtration membrane; performing pre-column derivatization on amino acids by using OPA and FMOC derivatization reagents, so that the amino acid has fluorescence emission characteristics to improve the detection sensitivity and the separation and selection characteristics; then performing qualitative and quantitative analysis on 24 kinds of amino acids through a reverse-high-performance liquid chromatography. Compared with a conventional method, the method avoids the selectivity of an SCX-SPE (Strong Cation-Exchange Solid-Phase Extraction Column) for the amino acids caused by different isoelectric points of the amino acids and overcomes the defects of low recovery rate and poor reproducibility during sample determination. The method provided by the invention is simple in step and strong in operability and provides a technical basis for the study on a protein degradation mechanism in the process of anaerobic digestion and a scientific basis for biogas slurry and biogas residue agricultural resource development and utilization.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Saccharopolyspora for decreasing biogenic amine and application of saccharopolyspora
ActiveCN111961615ADoes not affect normal fermentationHigh in amino acidsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNutritive values
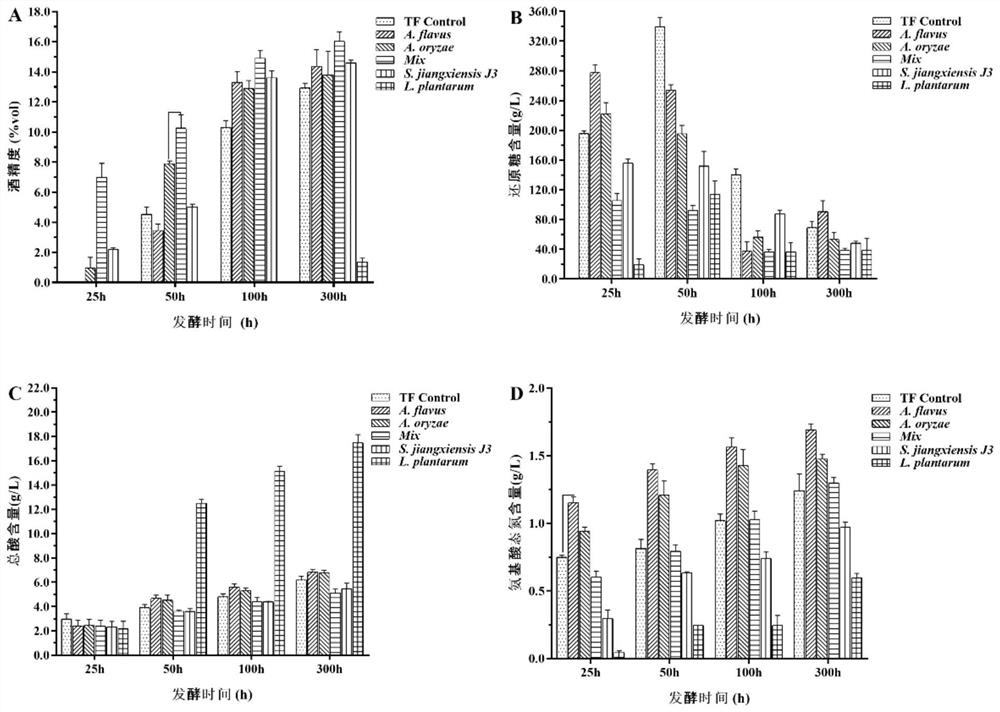
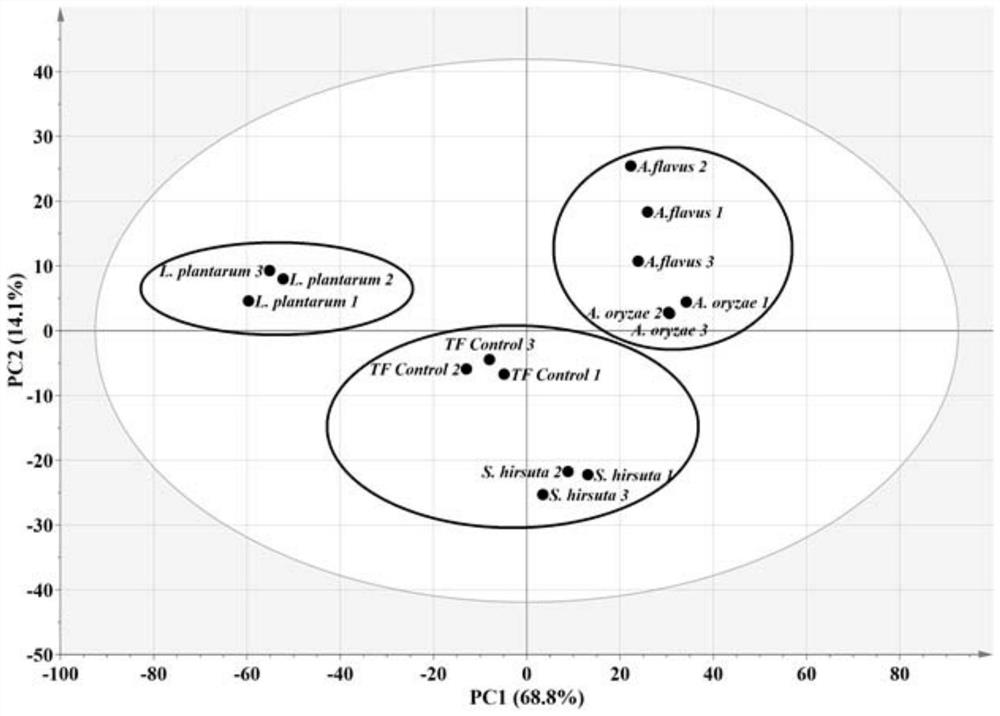
The invention discloses saccharopolyspora for decreasing biogenic amine and application of the saccharopolyspora, and belongs to the technical field of food fermentation. Saccharopolyspora hirsute J2capable of decreasing the content of the biogenic amine is screened from wheat koji and is applied to a brewing process of liquors (white spirits and yellow rice wine), fermented sausages or soy sauce, so that the content of the biogenic amine can be decreased, meanwhile, the content of amino acids can be increased, the nutrition value of a fermented product can be increased, and therefore, the saccharopolyspora is capable of improving the quality and safety of fermented foods and has wide application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Lactobacillus plantarum and method for mixed fermentation of sour plesiopidae
InactiveCN109619457AShorten the fermentation cyclePrevent fat oxidationBacteriaLactobacillusBiotechnologyGram
The invention discloses a strain of lactobacillus plantarum 24. A method achieving mixed fermentation of sour plesiopidae based on the strain comprises the following steps that scales and internal organs of a raw material fish are removed, and the raw material fish is cut into fish blocks; the fish blocks, rice flour, salt, 106-108 CFU / mL of a lactobacillus plantarum 24 liquid and 10000-20000U / mLof a papain liquid are mixed uniformly and contained in a container, the uppermost layer is covered with the rice flour, fermentation is performed for 20-30 days at 20-30 DEG C, and the sour plesiopidae is obtained; the ratio of the fish blocks to the rice flour to the salt is (90-115):(50-70):(2-4); the addition amount of the lactobacillus plantarum 24 liquid is 0.0006-0.06mL for each gram of thefish blocks; the addition amount of the papain liquid is 0.005-0.025 mL for each gram of the fish blocks. The method shortens the fermentation cycle of the sour plesiopidae and reduces the biogenic amine, and the similarity of the flavor of the sour plesiopidae to the sour plesiopidae prepared by a traditional method is more than 85%.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
High temperature yeast for brewing msalais, preparation method thereof and brewed msalais
ActiveCN103243037AExcellent fermentation performanceImprove toleranceFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAlcohol content
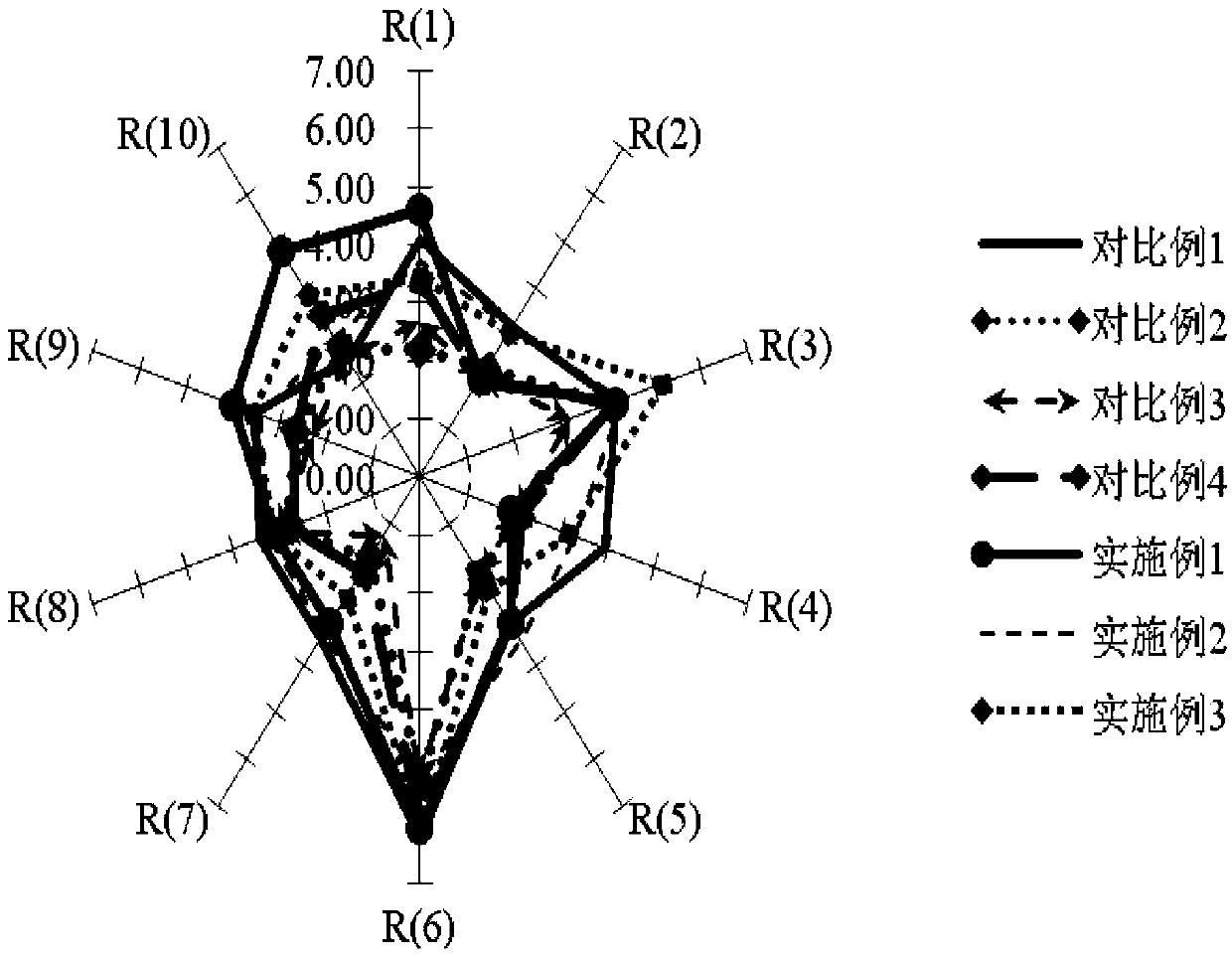
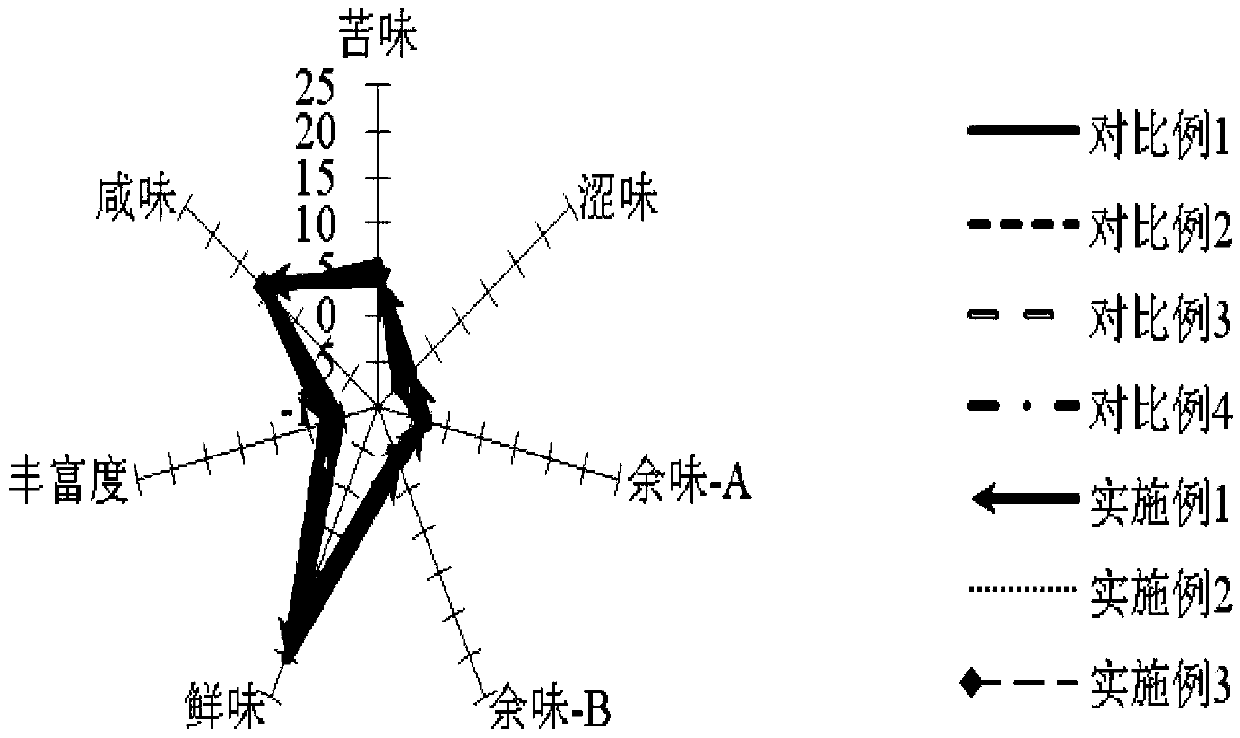
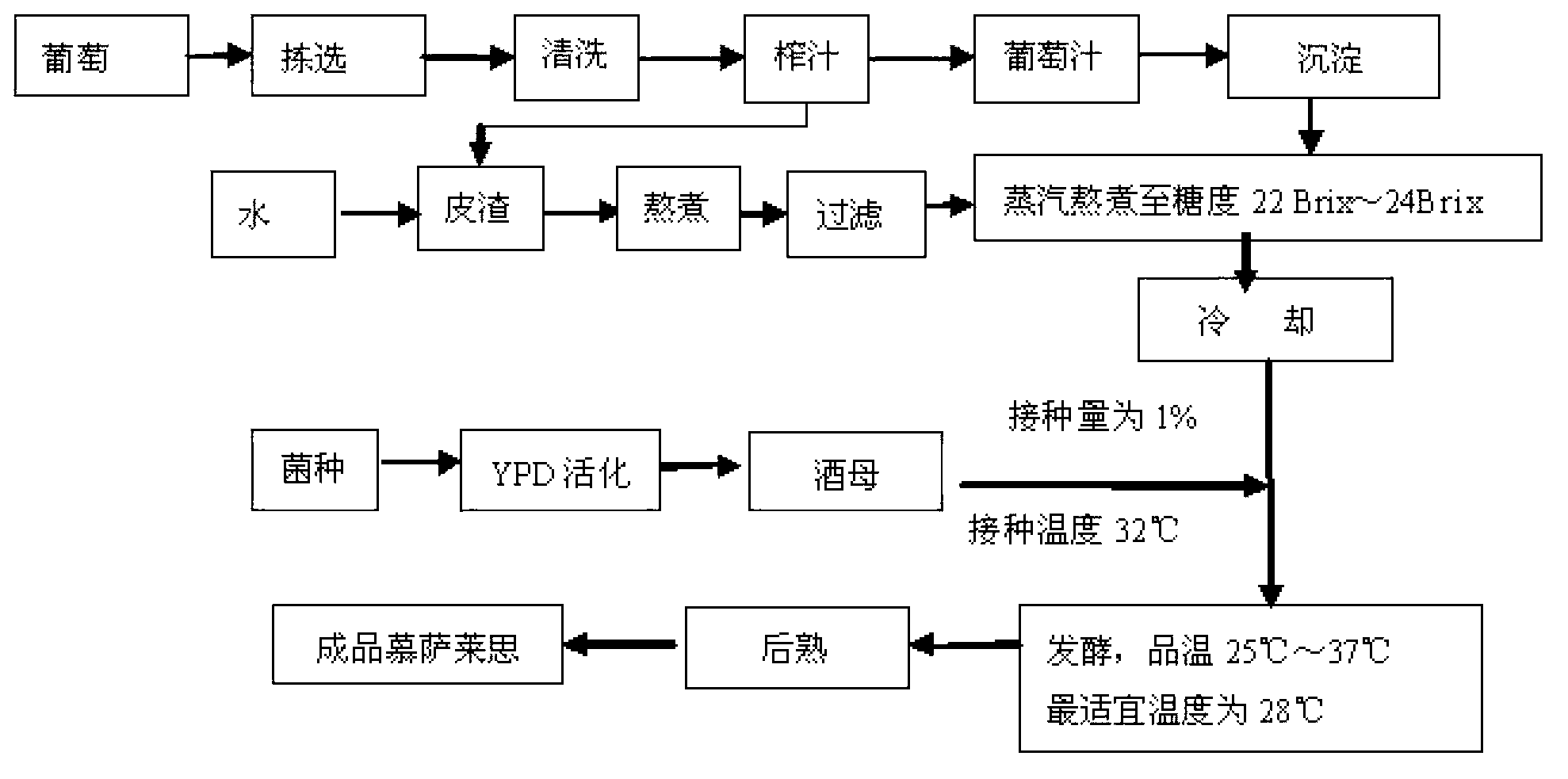
The invention discloses a high temperature yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) CGMCC No.7513 for producing msalais through fermentation and msalais obtained by a preparation method through fermentation by utilizing the strain. By virtue of analysis at different temperatures, sugar degrees, alcohol contents and low nitrogen tolerances, metabolism property determination, detection of wine production capacity, flocculability, autolysis, H2S production capacity and biogenic amine production characteristic, determination of pectinase activity and determination test on activity of beta-glucosaccharase, the high temperature msalais yeast strain with excellent brewing performance is screened, and the high temperature msalais yeast strain is widely applied to the fields of light industry production and the like.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![Methods and compositions for production, formulation and use of 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes Methods and compositions for production, formulation and use of 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f2ff27aa-cc53-46bd-b847-83ff08c2e684/US20060223875A1-20061005-C00001.png)
![Methods and compositions for production, formulation and use of 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes Methods and compositions for production, formulation and use of 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f2ff27aa-cc53-46bd-b847-83ff08c2e684/US20060223875A1-20061005-C00002.png)
![Methods and compositions for production, formulation and use of 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes Methods and compositions for production, formulation and use of 1-aryl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f2ff27aa-cc53-46bd-b847-83ff08c2e684/US20060223875A1-20061005-C00003.png)