Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53results about How to "Small refractive index" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
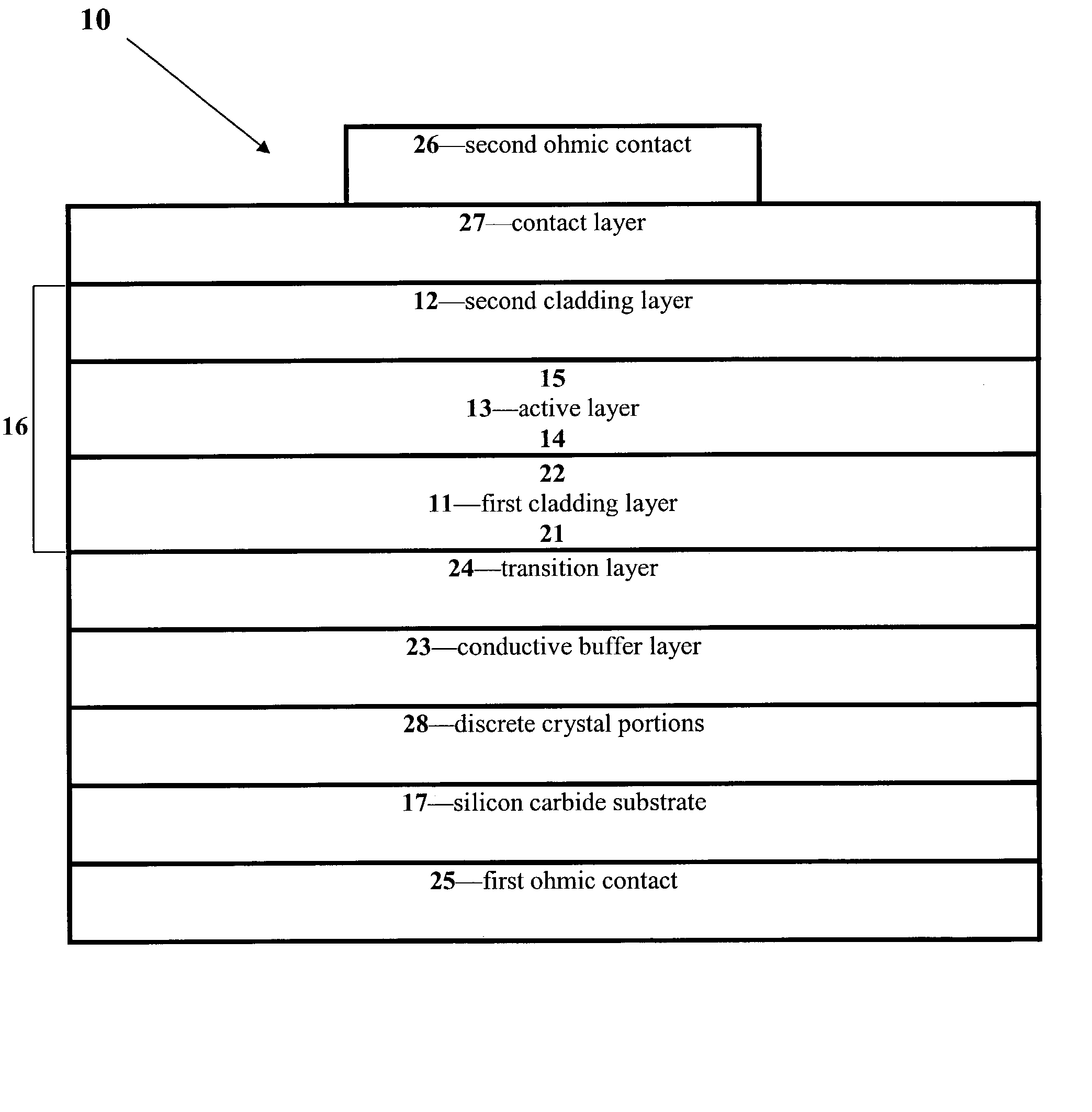
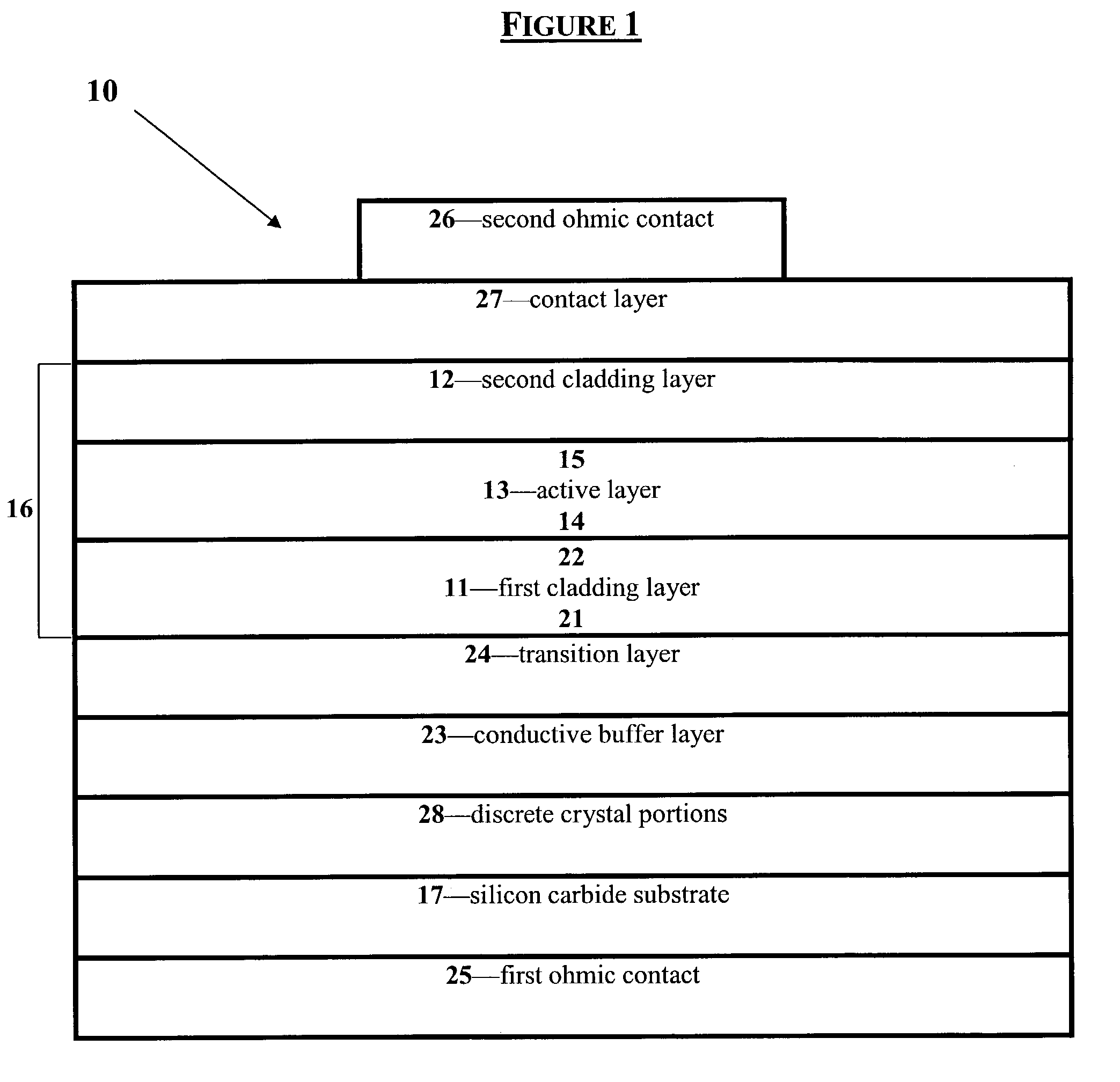
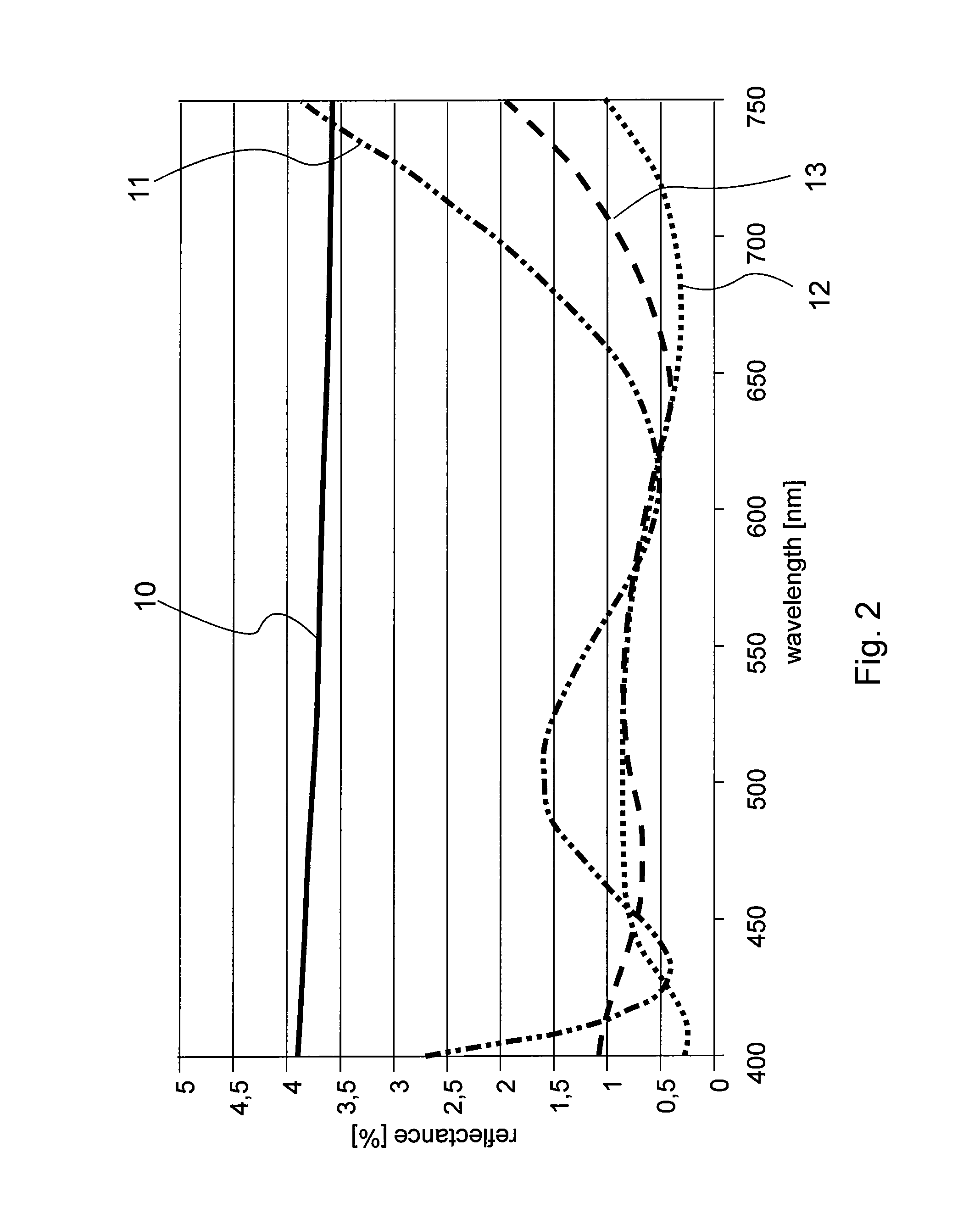
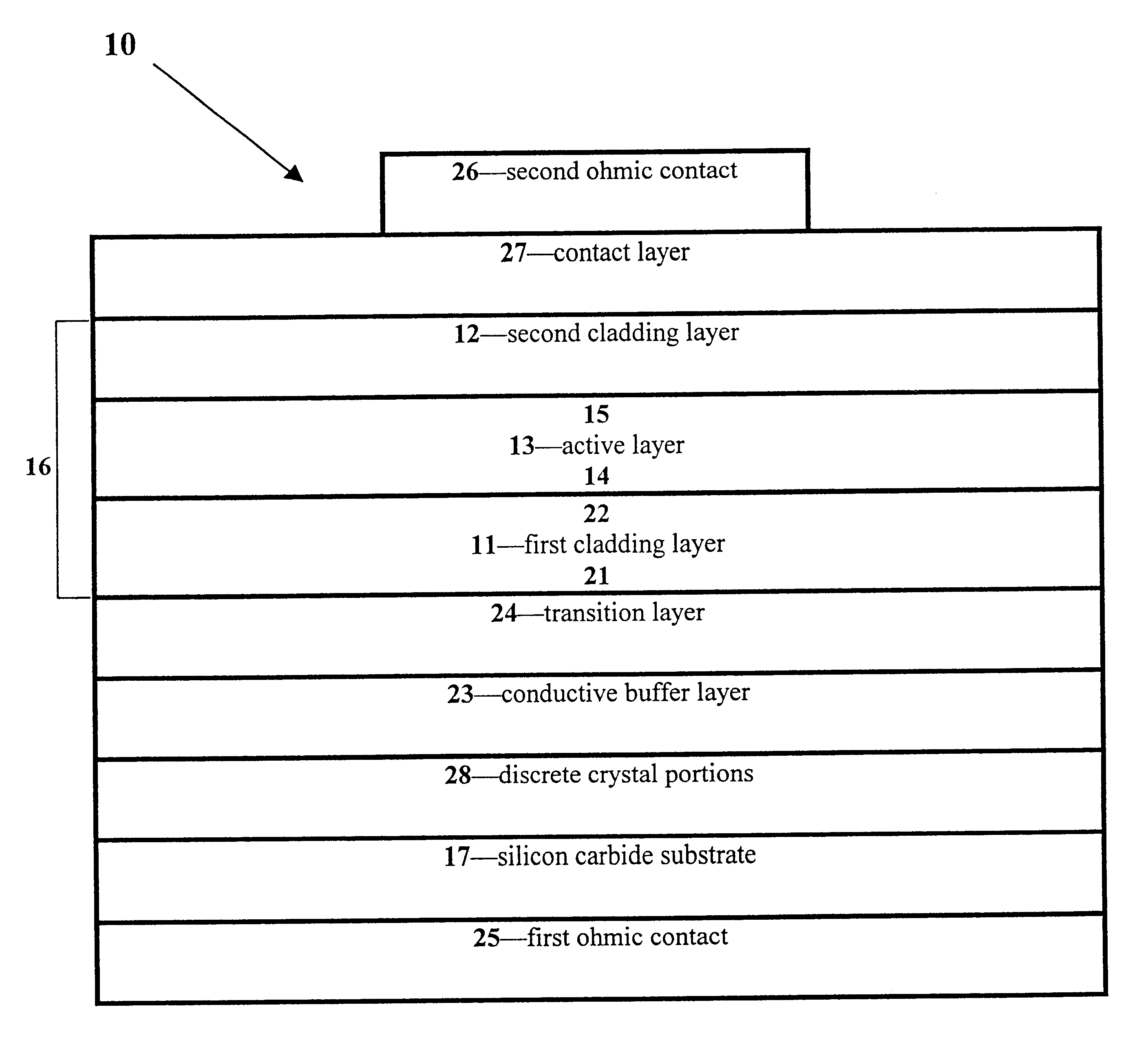
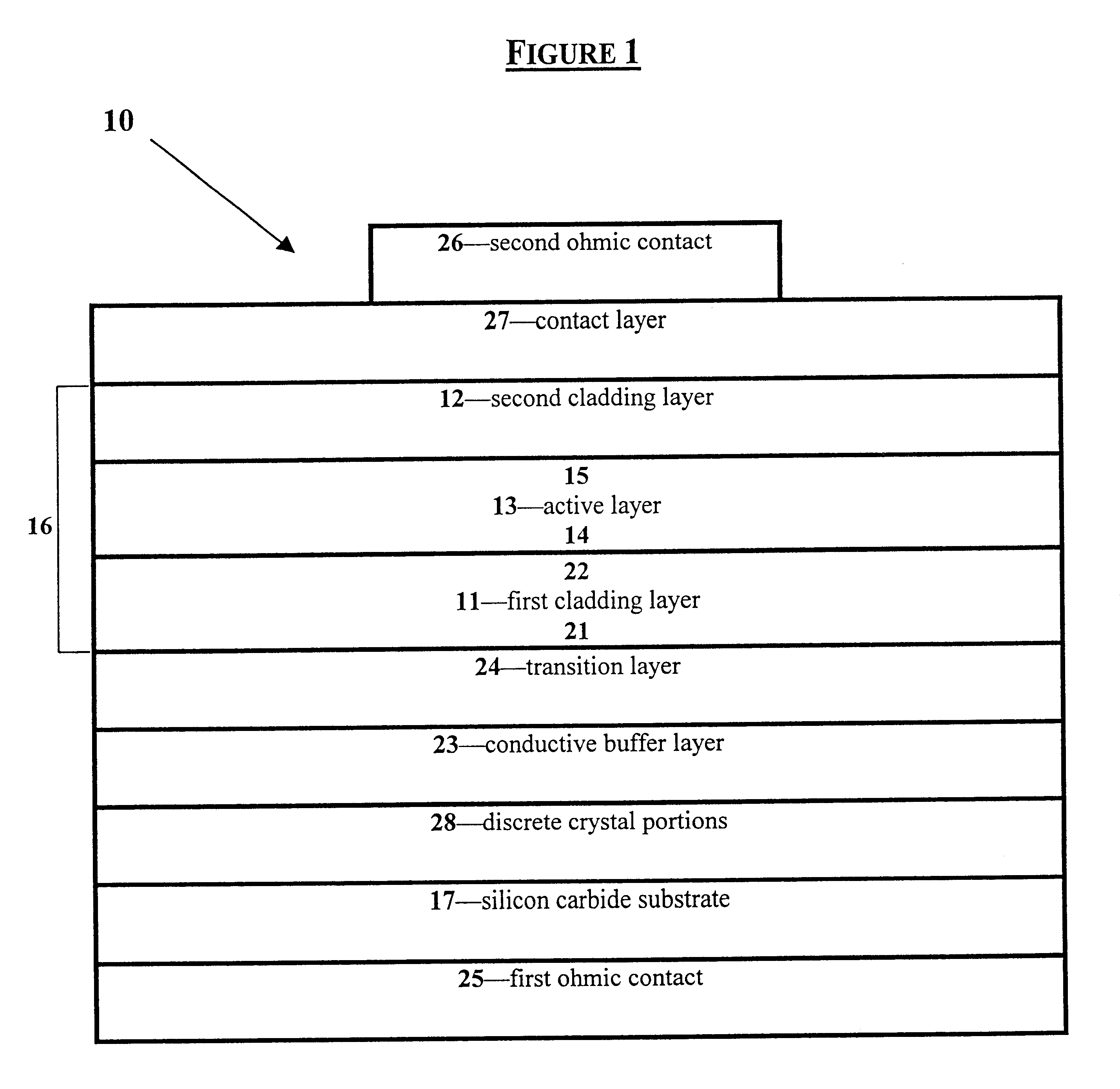
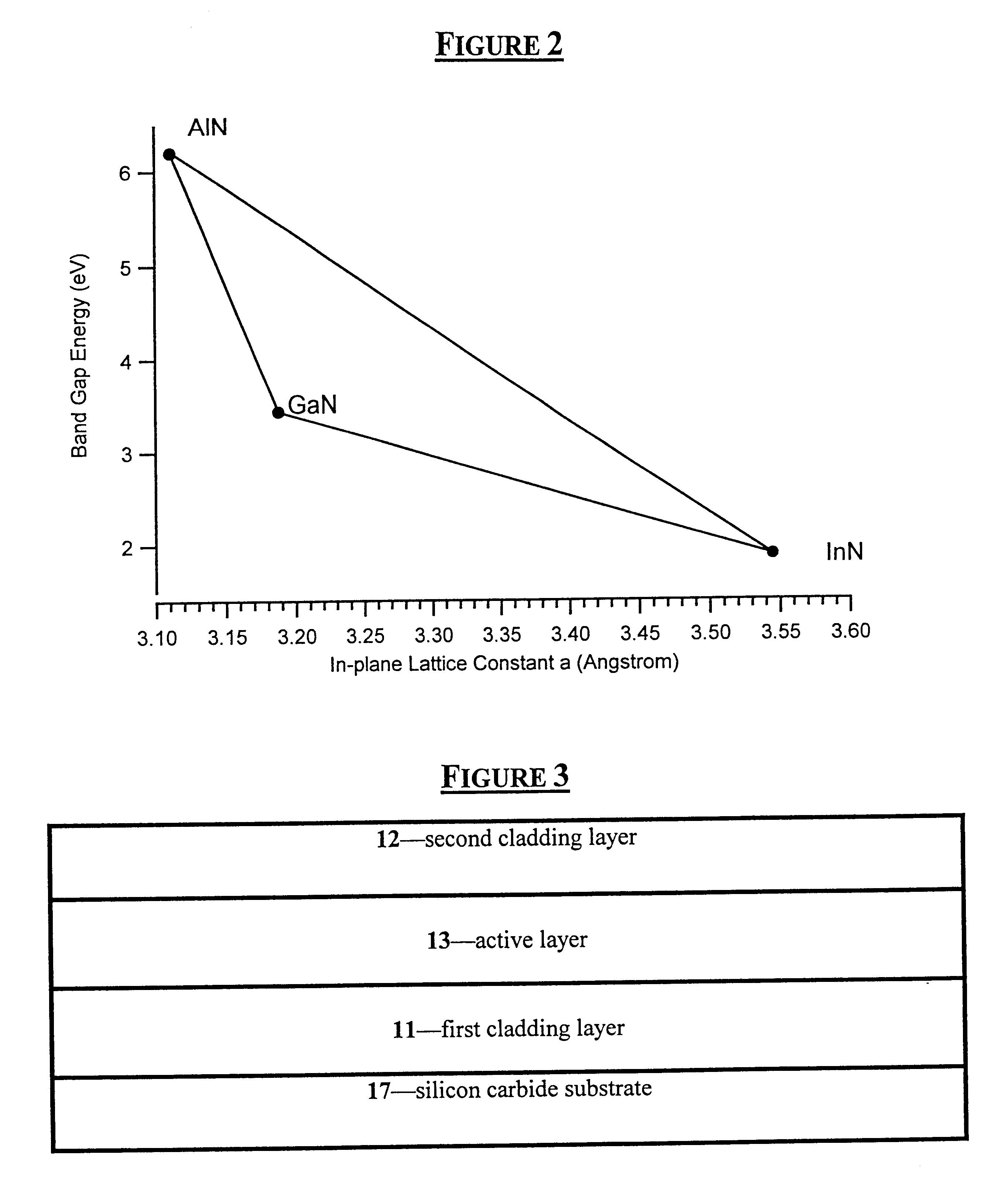
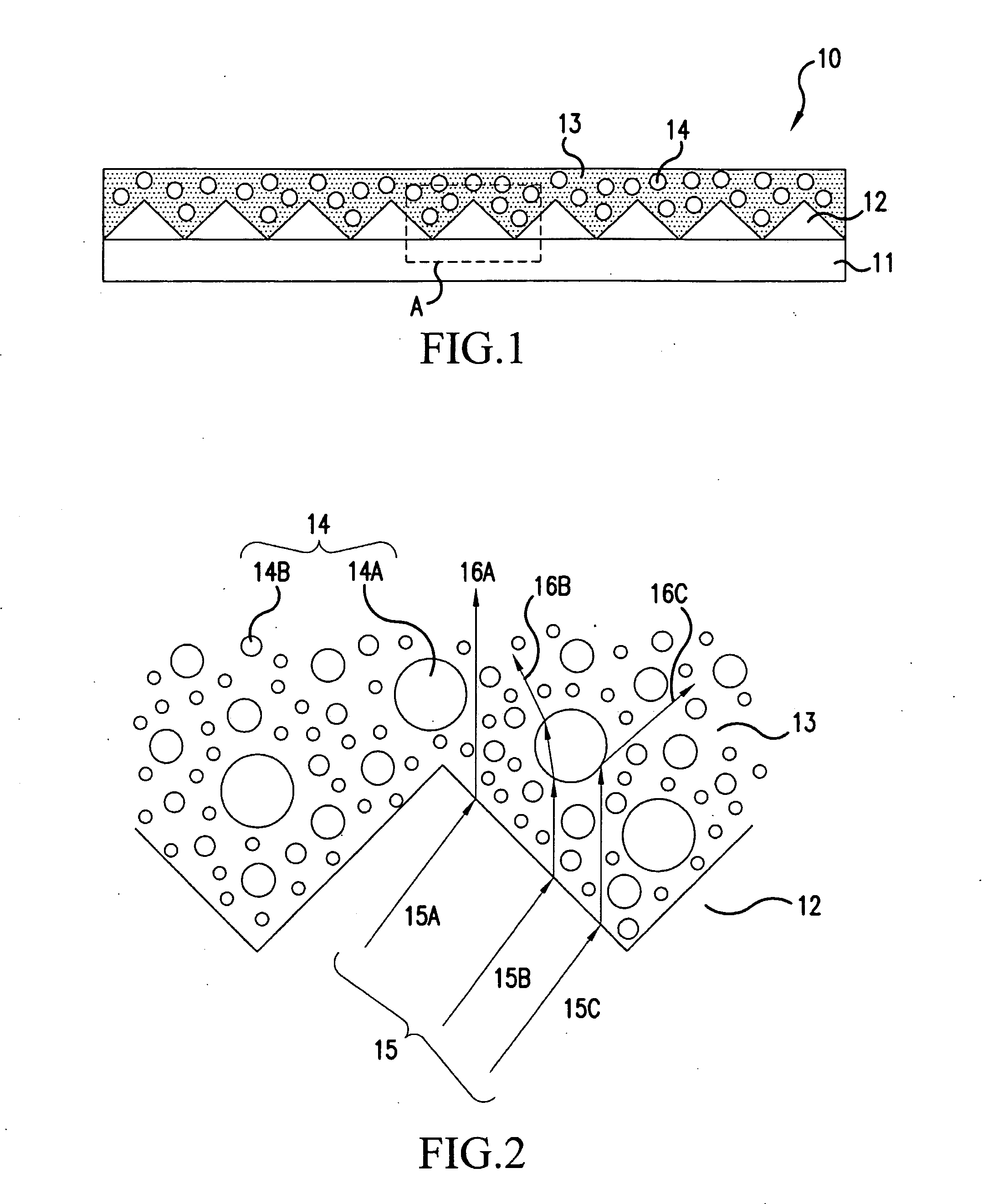
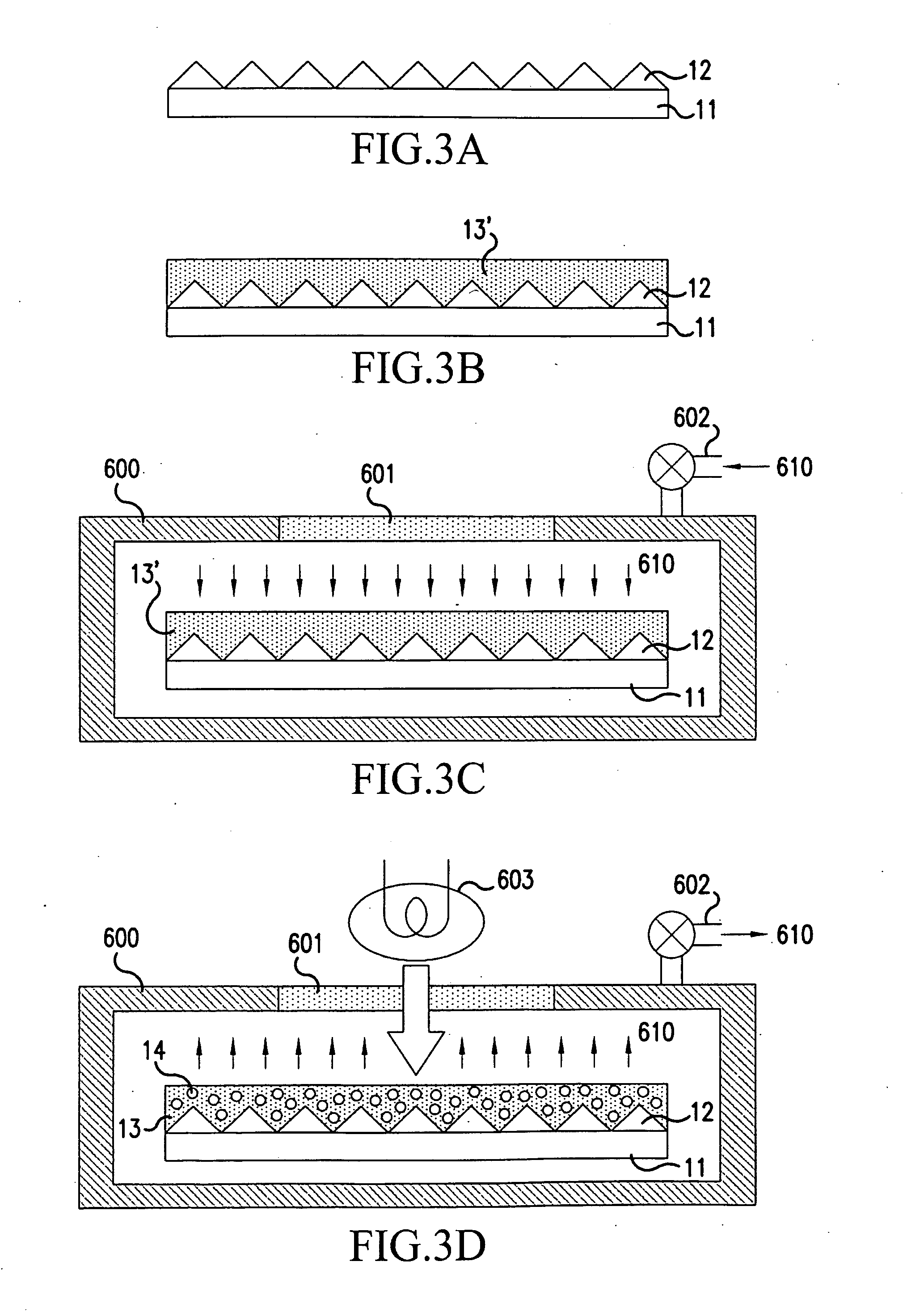
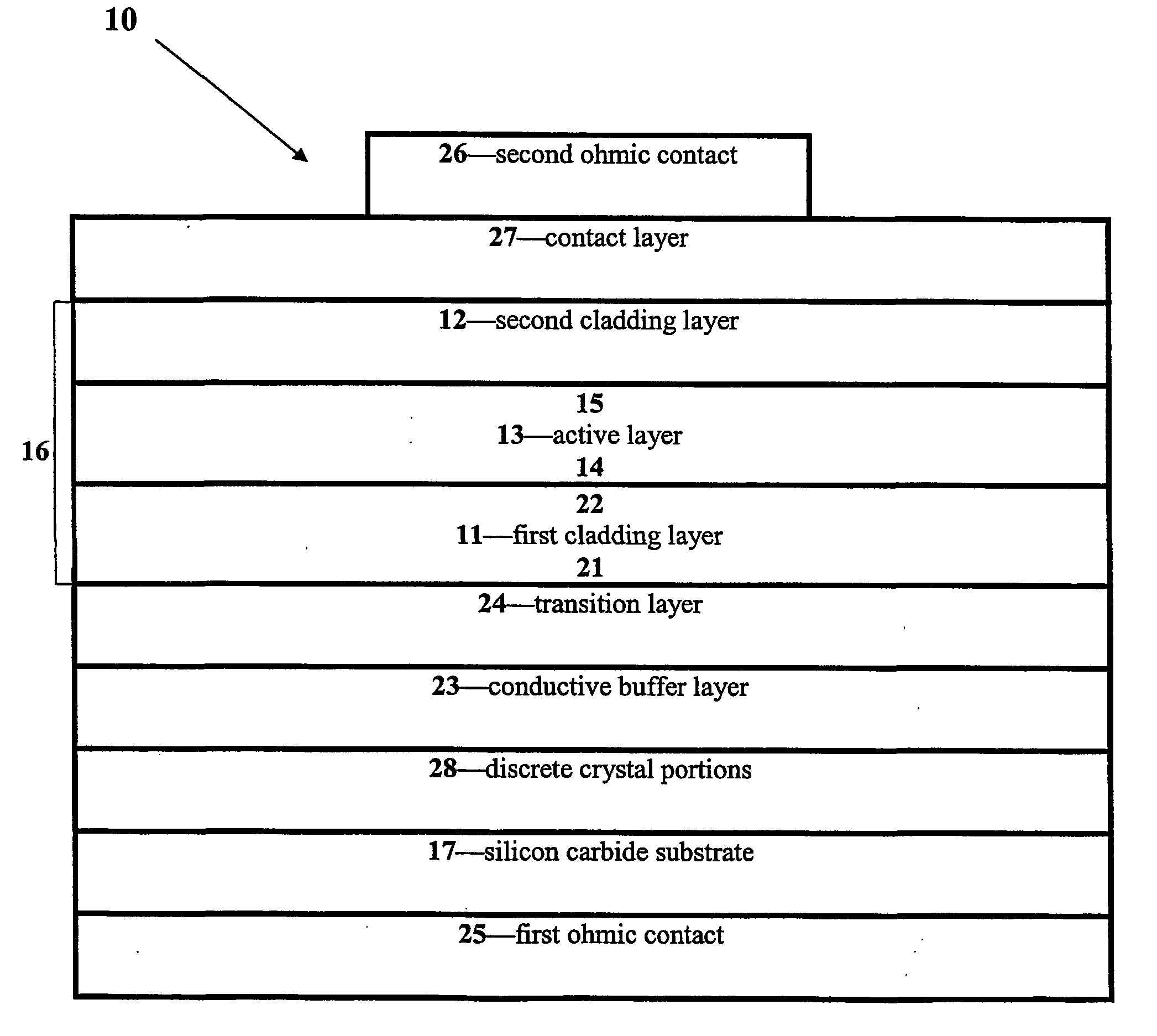
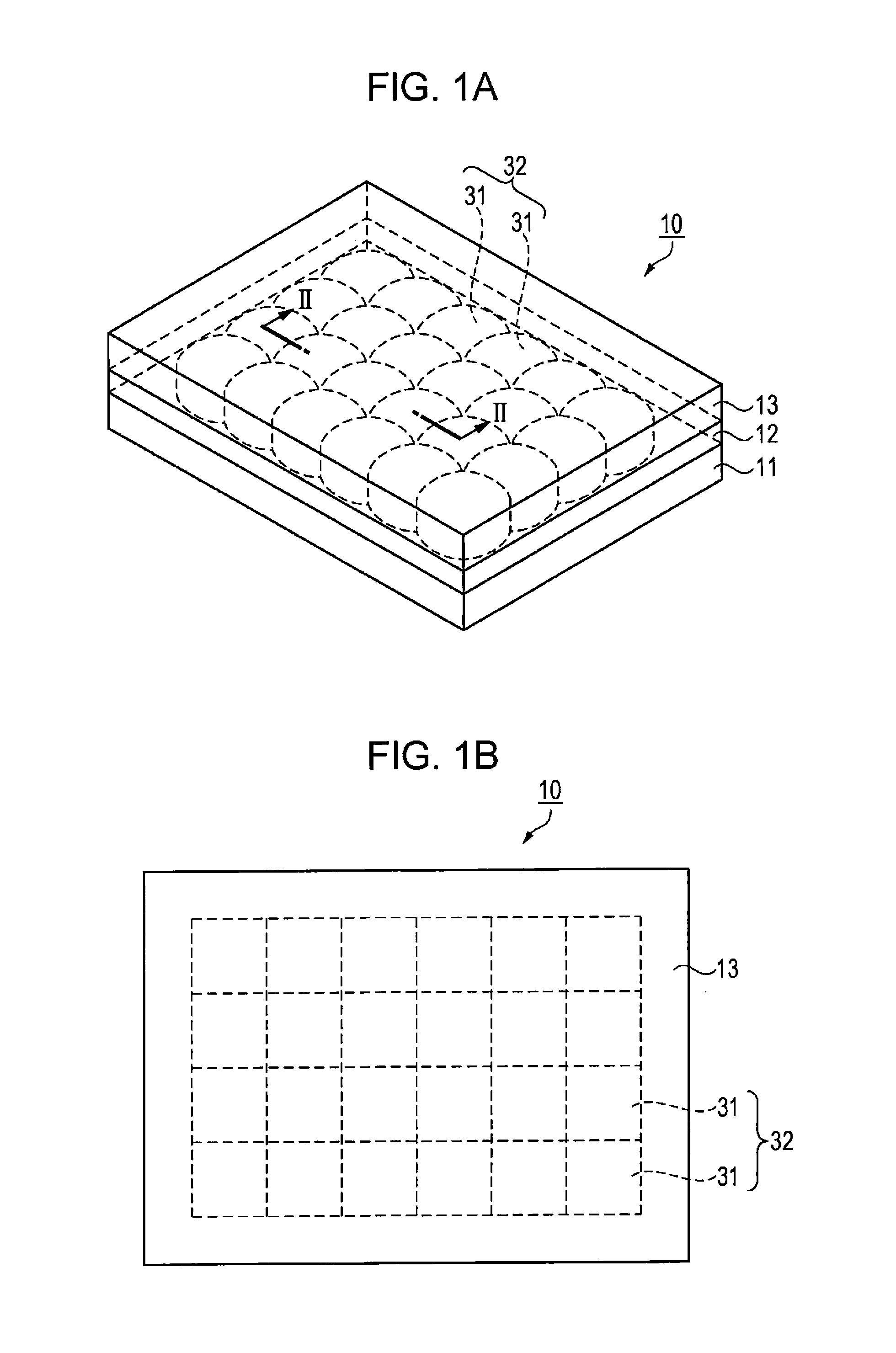
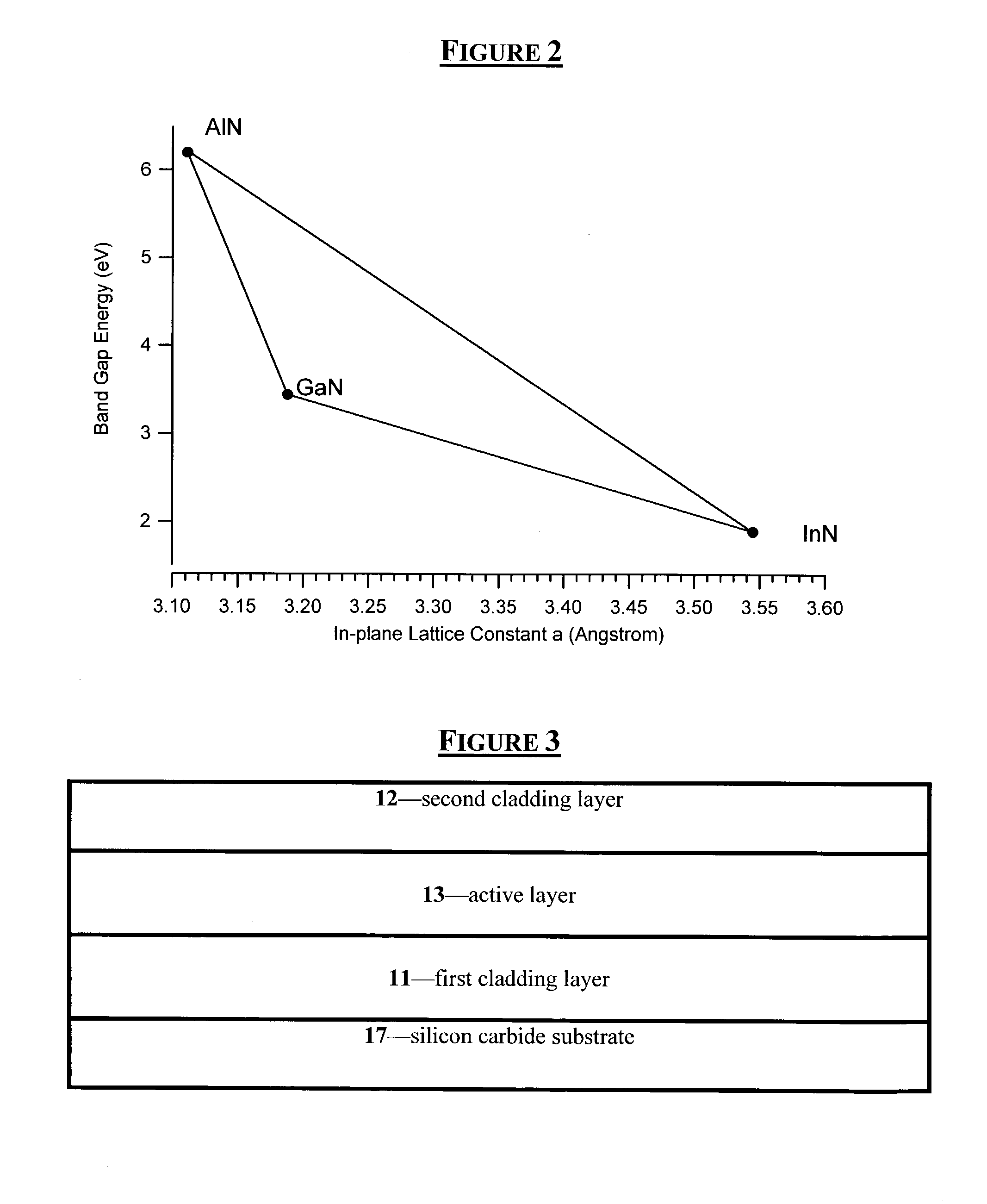
Group III nitride light emitting devices with progressively graded layers
InactiveUS20030164507A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce non-radiative recombinationLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The semiconductor structure includes a first cladding layer of a Group III nitride, a second cladding layer of a Group III nitride, and an active layer of a Group III nitride that is positioned between the first and second cladding layers, and whose bandgap is smaller than the respective bandgaps of the first and second cladding layers. The semiconductor structure is characterized by the absence of gallium in one or more of these structural layers.
Owner:CREE INC
Substrate with antireflection coating and method for producing same
ActiveUS20120212826A1Decrease of antireflection effectHigh refractive indexElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingRefractive indexSilicon oxide
A substrate is provided with an abrasion resistance antireflection coating. The coated substrate includes a multilayer antireflection coating on at least one side. The coating has layers with different refractive indices, wherein higher refractive index layers alternate with lower refractive index layers. The layers having a lower refractive index are formed of silicon oxide with a proportion of aluminum, with a ratio of the amounts of aluminum to silicon is greater than 0.05, preferably greater than 0.08, but with the amount of silicon predominant relative to the amount of aluminum. The layers having a higher refractive index include a silicide, an oxide, or a nitride.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Group III nitride light emitting devices with gallium-free layers
InactiveUS6534797B1Maintain good propertiesImprove emission efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The semiconductor structure includes a first cladding layer of a Group III nitride, a second cladding layer of a Group III nitride, and an active layer of a Group III nitride that is positioned between the first and second cladding layers, and whose bandgap is smaller than the respective bandgaps of the first and second cladding layers. The semiconductor structure is characterized by the absence of gallium in one or more of these structural layers.
Owner:CREE INC
Optical adjusting member, and illumination device and liquid crystal display device including the same
InactiveUS20080303777A1Suppressing damages at the top edgeConvenient lightingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical transparencyLiquid-crystal display
An optical adjusting member according to the invention includes a base member, a plurality of lenses, and a light diffusion layer. The base member has optical transparency. The plurality of lenses are formed on the base member. The light diffusion layer is formed on the plurality of lenses, and at least top edge parts of the lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer. In the optical adjusting member according to the invention, at least the top edge parts of the plurality of lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer and therefore the lenses are less susceptible to damages. The optical adjusting member according to the invention has a light collecting function by the lenses and a diffusion function by the light diffusion layer.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Group lll nitride emitting devices with gallium-free layers
InactiveUS20040051108A1Maintain good propertiesImprove emission efficiencyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The semiconductor structure includes a first cladding layer of a Group III nitride, a second cladding layer of a Group III nitride, and an active layer of a Group III nitride that is positioned between the first and second cladding layers, and whose bandgap is smaller than the respective bandgaps of the first and second cladding layers. The semiconductor structure is characterized by the absence of gallium in one or more of these structural layers.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Substrate with antireflection coating and method for producing same
ActiveUS9296648B2Reduce wearSmall refractive indexElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingRefractive indexSilicon oxide
A substrate is provided with an abrasion resistance antireflection coating. The coated substrate includes a multilayer antireflection coating on at least one side. The coating has layers with different refractive indices, wherein higher refractive index layers alternate with lower refractive index layers. The layers having a lower refractive index are formed of silicon oxide with a proportion of aluminum, with a ratio of the amounts of aluminum to silicon is greater than 0.05, preferably greater than 0.08, but with the amount of silicon predominant relative to the amount of aluminum. The layers having a higher refractive index include a silicide, an oxide, or a nitride.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
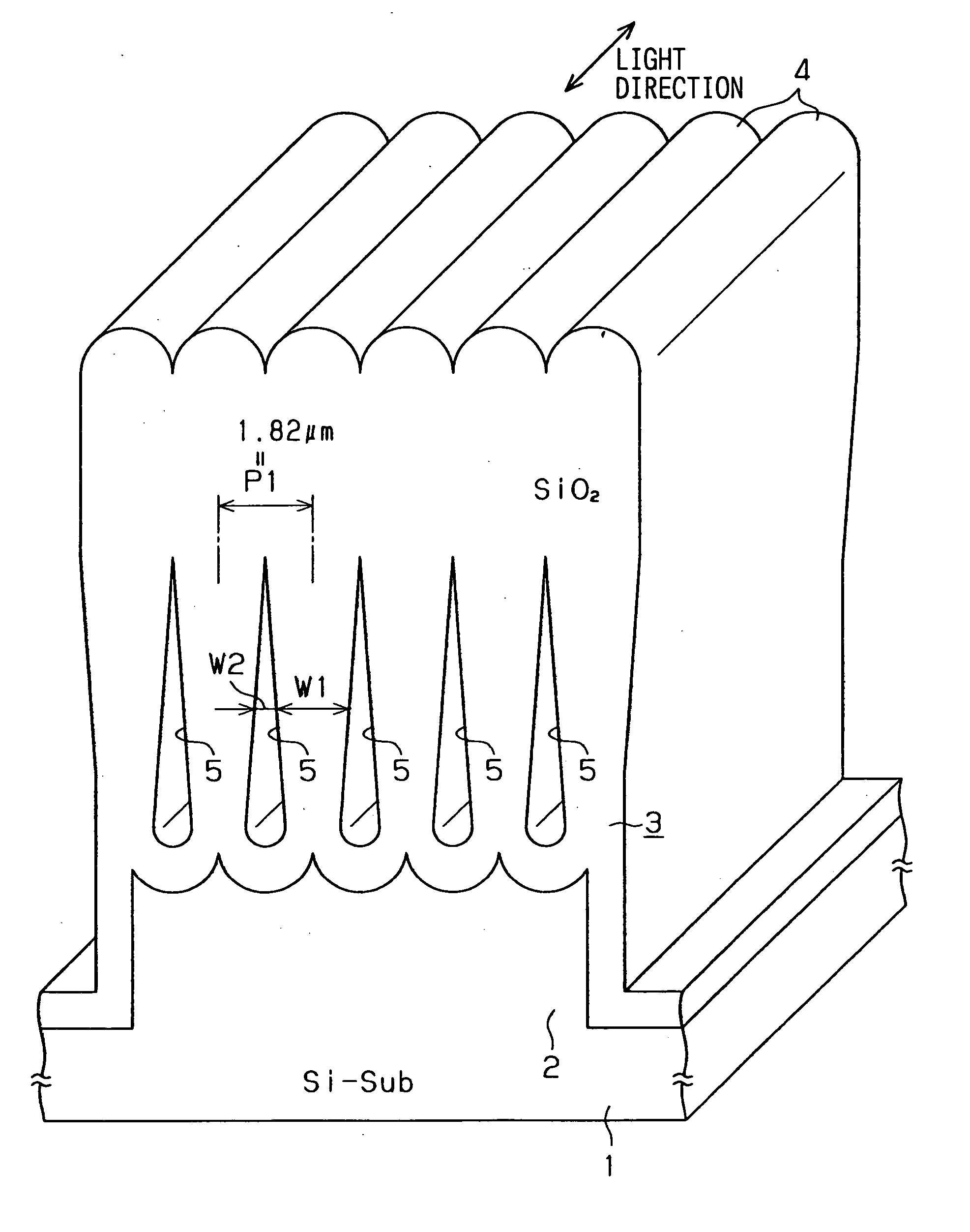
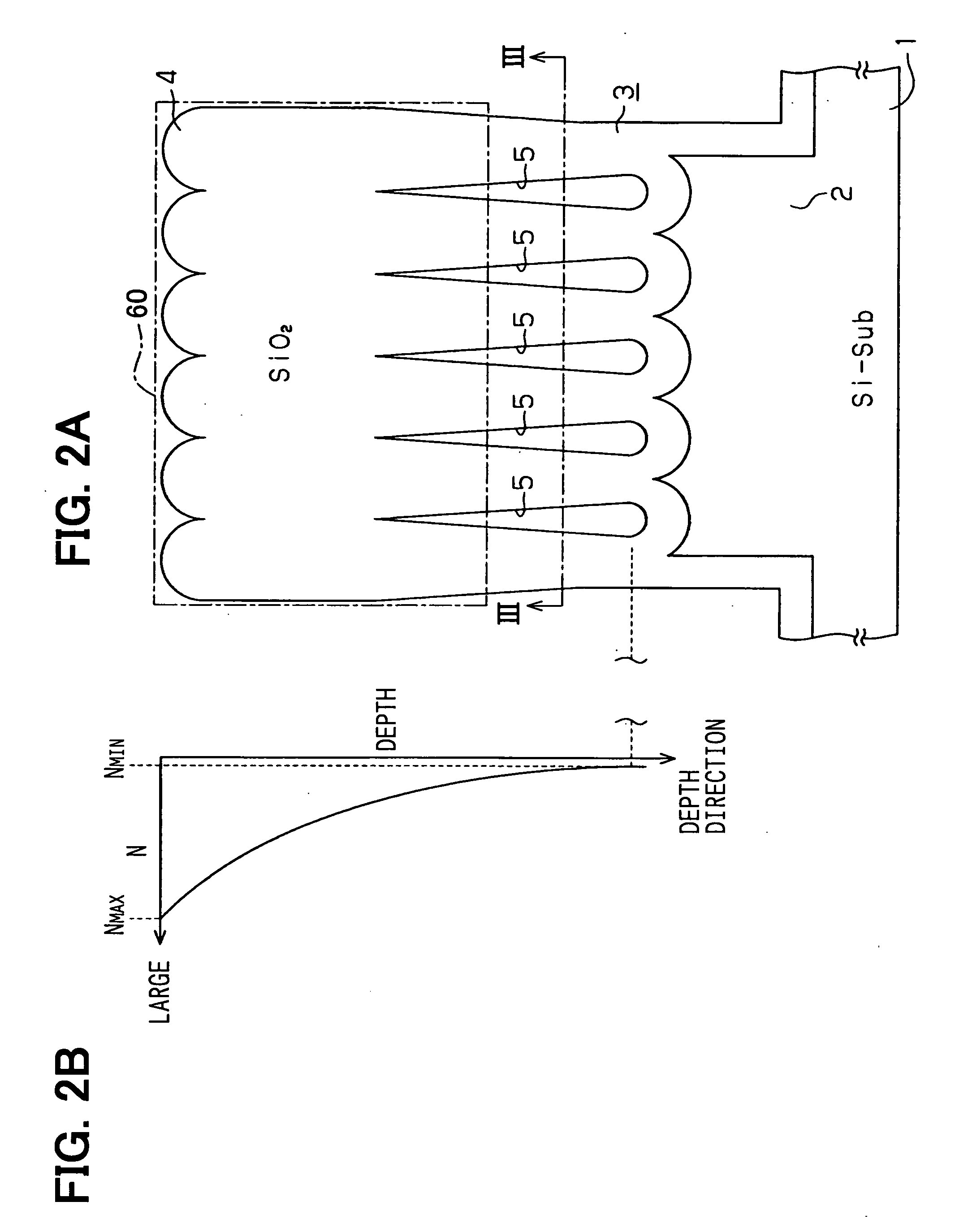
High light extraction efficiency nitride based light emitting diode by surface roughening
ActiveUS8114698B2Light extraction efficiency can be improvedImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEtchingNitride
A III-nitride light emitting diode (LED) and method of fabricating the same, wherein at least one surface of a semipolar or nonpolar plane of a III-nitride layer of the LED is textured, thereby forming a textured surface in order to increase light extraction. The texturing may be performed by plasma assisted chemical etching, photolithography followed by etching, or nano-imprinting followed by etching.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
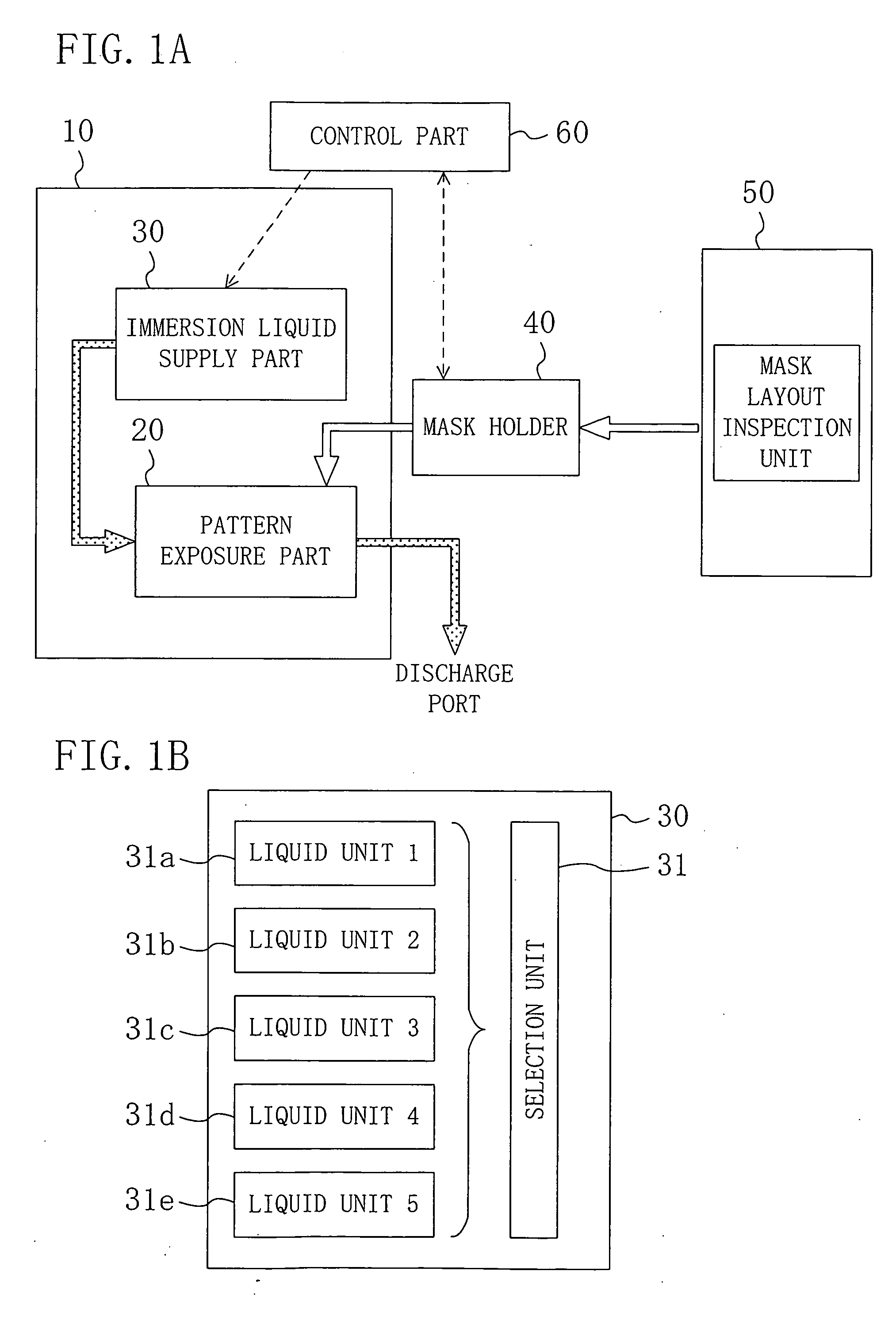
Exposure system, exposure method and method for fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060019204A1High resolutionIncrease valuePhotoprinting processesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistDevice material
An exposure system includes an exposure part for irradiating a resist film formed on a substrate with exposing light through a mask with a liquid provided on the resist film; and a liquid supply part for supplying the liquid to the exposure part. The liquid supplying part includes a plurality of liquid units respectively containing a plurality of liquids having different refractive indexes, and a selection unit for selecting one liquid unit from the plural liquid units and supplying a liquid contained in the selected liquid unit to the exposure part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Color filter with retardation layer and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20070159581A1Effectively restraining light leakageHigh contrast high quality displayNon-linear opticsLiquid crystallineOptical axis
The main object of the present invention is to provide a colour filter with a retardation layer, capable of minimising light leakage even in the case the visual angle is large in the black display state, for a liquid crystal display. The present invention achieves the object by providing a colour filter with a retardation layer comprising a substrate, a colour layer formed on the substrate, being arranged in a plurality of rows having different thicknesses according to each colour, a first retardation layer formed on the colour layer, made of a liquid crystalline polymer, having its optic axis perpendicular to a plane of the substrate so as to function as a C plate, and a second retardation layer the colour layer, wherein the optic axis of the second retardation layer is arranged parallel to the plane of the substrate so as to function as a positive Aplate with positive refractive index anisotropy, and the refractive index anisotropy of the second retardation layer in the visible light range decreases at shorter wavelenghts inverse dispersion characteristics.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Subwavelength Photonic Crystal Waveguide in Optical Systems
ActiveUS20170146738A1Reduce bend lossIncrease lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideElliptic cylinderPrism
An optical system is disclosed. The optical system comprising: a substrate; and a subwavelength photonic crystal waveguide atop the substrate, wherein the subwavelength photonic crystal waveguide comprises a periodic one or two-dimensional array of two or more interleaved dielectric pillars; wherein the periodicity of the one or two-dimensional array is constant, a combination of two or more periods, or random; wherein the one or two-dimensional array is substantially linear or curved; wherein each of the pillars of the one or two-dimensional array is at least one of a triangular prism, a trapezoidal prism, an elliptic cylinder, a cylinder, a tube, a frustum, a pyramid, a trapezoidal prism, and an asymmetric frustum; and wherein each of the pillars of the one or two-dimensional array comprises a solid, liquid, and / or gas. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Light-Receiving Device
InactiveUS20090008682A1Reduce ratioSmall refractive indexSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCyclic OlefinsEngineering
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Image sensor
ActiveUS10014338B2Improve accuracyEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesIsolation layerElectron
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Resin Material for Optical Use and Optical Device
InactiveUS20110262750A1High light transparencyThermal dependency be smallSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolymer chemistryOxide
Disclosed is a resin material for optical use, which has refractive index and transparency suitable for optical devices, while having extremely small change in refractive index dependent on temperature. In addition, the resin material for optical use is excellent in forming suitability and heat resistance after a reflow process. Also disclosed is an optical device using a resin material for optical use. Specifically disclosed is a transparent resin material for optical use which is composed of a curable resin containing inorganic fine particles whose surfaces are modified with an organic compound. This transparent resin material for optical use is characterized in that the inorganic fine particles are composed of an amorphous silica containing a metal oxide crystal, and have an average particle diameter of not less than 1 nm but more than 50 nm.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Composite laser gain medium
ActiveUS20150236470A1Small refractive indexLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialDopantRare-earth element
A composite laser gain medium is comprised of a first rare-earth element doped core; and a second rare-earth element doped cladding, at least partially, adjacent to the core. A portion of the lasing by the cladding at one wavelength within the composite laser gain medium is absorbed by the core so as to cause lasing of the core at a different wavelength. At least two distinct rare earth element pairs may be used in embodiments: (1) thulium (Tm) as a cladding rare-earth dopant and holmium (Ho) as the core rare-earth dopant; and (2) ytterbium (Yb) as a cladding rare-earth dopant and erbium (Er) as the core rare-earth dopant. Other rare earth element pairs are also believed possible. The laser composite gain medium may be configured to have a slab, or a cylindrical geometry.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Optical device having optical waveguide and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050265662A1Reduce connection lossLarge refractive indexSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesSilicon oxideWaveguide
An optical device includes: a silicon substrate; a plurality of silicon oxide columns having a rectangular plan shape; and a cavity disposed between the columns. Each column has a lower portion disposed on the substrate. Each column has a width defined as W1. The cavity has a width defined as W2. A ratio of W1 / W2 becomes smaller as it goes to the lower portion of the column. A core layer provided by the columns and the cavity can have the thickness equal to or larger than a few dozen μm easily. Therefore, connection loss between a light source and the device is reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Optical unit and pojection type image display unit using it
InactiveUS20060126020A1Improve performanceLowering and reducing contrastProjectorsOptical elementsRefractive indexPolarizer
An optical unit, comprising: a light source; a color separation means for separating a light emitted from the light source into plural pieces of color lights; reflection-type image display elements, upon each being incident the corresponding color of the lights from the color separation means, and for forming an optical image for each of the color lights, depending upon an image signal, with using polarization characteristics which the reflection-type image display elements have; and a color synthesizing means for synthesizing the optical images of the respective color lights, to be projected through a projection lens, enlargedly, and further comprising: a reflection-type polarization plate functioning as a polarization plate due to diffraction, being provided on an optical path extending from the color separation means to the reflection-type image display elements, to be a polarizer and an analyzer to the reflection-type image display elements; and an optical chassis for holding the reflection-type polarization plate and the reflection-type image display elements thereon, and having a translucent window on an incident light side of the reflection-type polarization plate while an exiting light side of the reflection-type polarization plate is sealed with an incident surface of the color synthesizing means, wherein a hermetically sealed space is defined by the optical chassis, the reflection-type image display elements and the incident surface of the color synthesizing means, and within the hermetically sealed space is disposed a translucent liquid having refraction index from 1.2 to 1.9.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Microlens array substrate, electrooptical device including microlens array substrate, projection type display apparatus, and manufacturing method of microlens array substrate
ActiveUS20160097883A1Lengthening distanceInhibit deteriorationLaminationLamination apparatusRefractive indexConvex side
A microlens array substrate includes: a light transmitting substrate in which a first lens surface formed of a concave surface is formed on a substrate surface on one side; a first lens layer which covers the substrate surface on one side and has a refractive index which is different from that of the light transmitting substrate; a light transmitting layer which covers the first lens layer on the opposite side to the light transmitting substrate; and a second lens layer which covers the light transmitting layer on the opposite side to the light transmitting substrate and in which a second lens surface formed of a convex surface is formed on the opposite side to the light transmitting substrate, in which the light transmitting layer has smaller refractive index and coefficient of thermal expansion than those of the first lens layer and the second lens layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
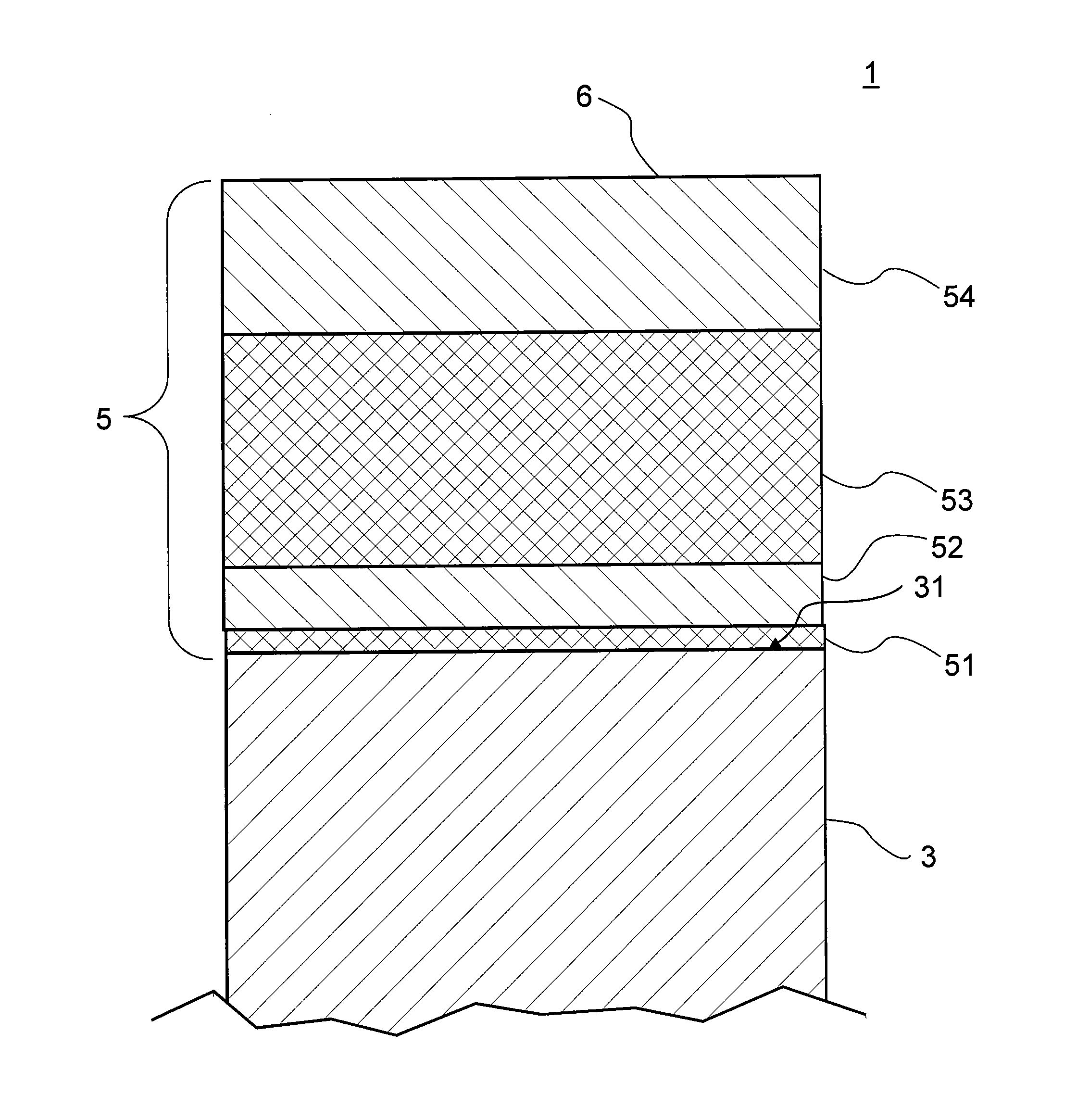
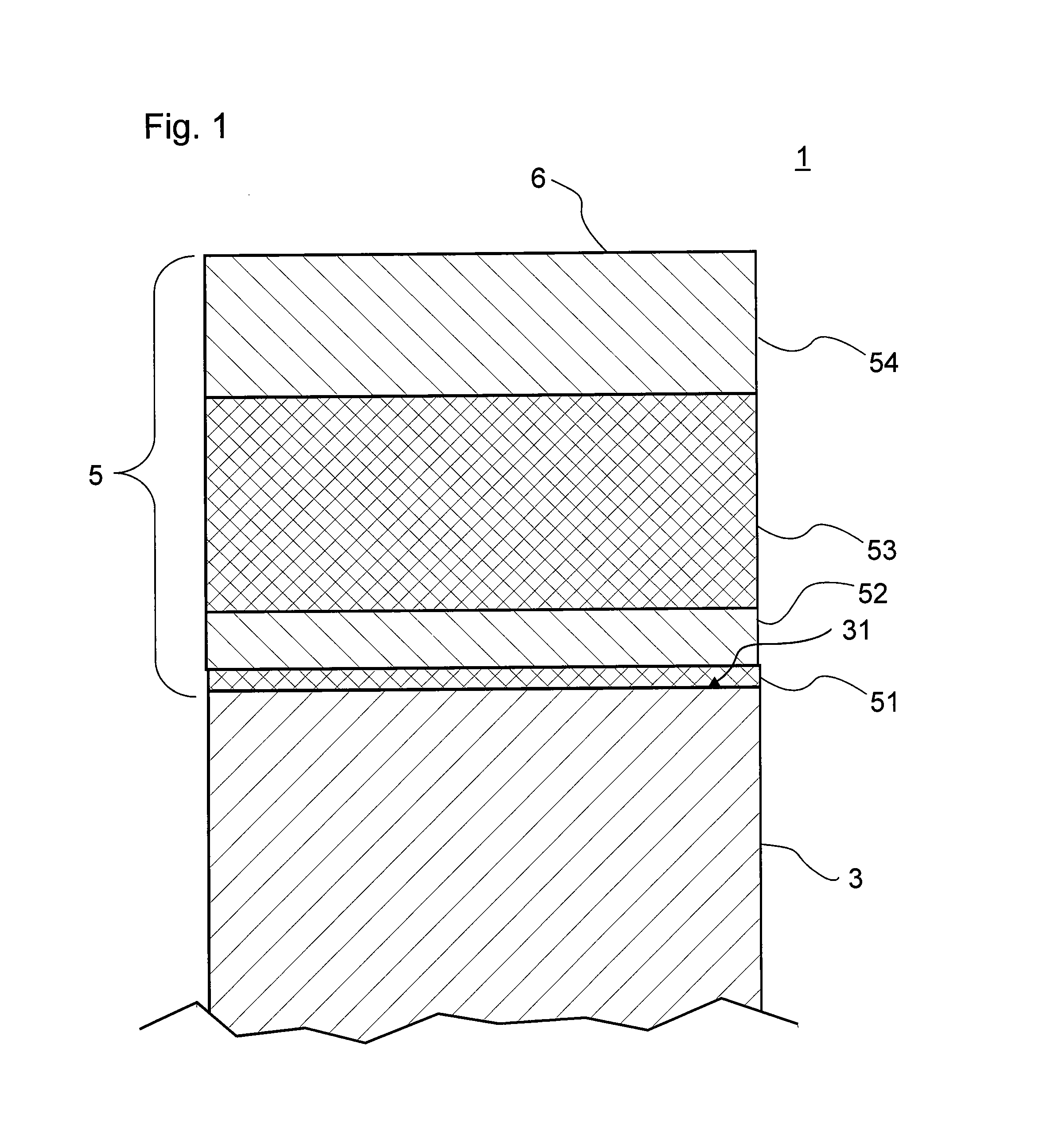
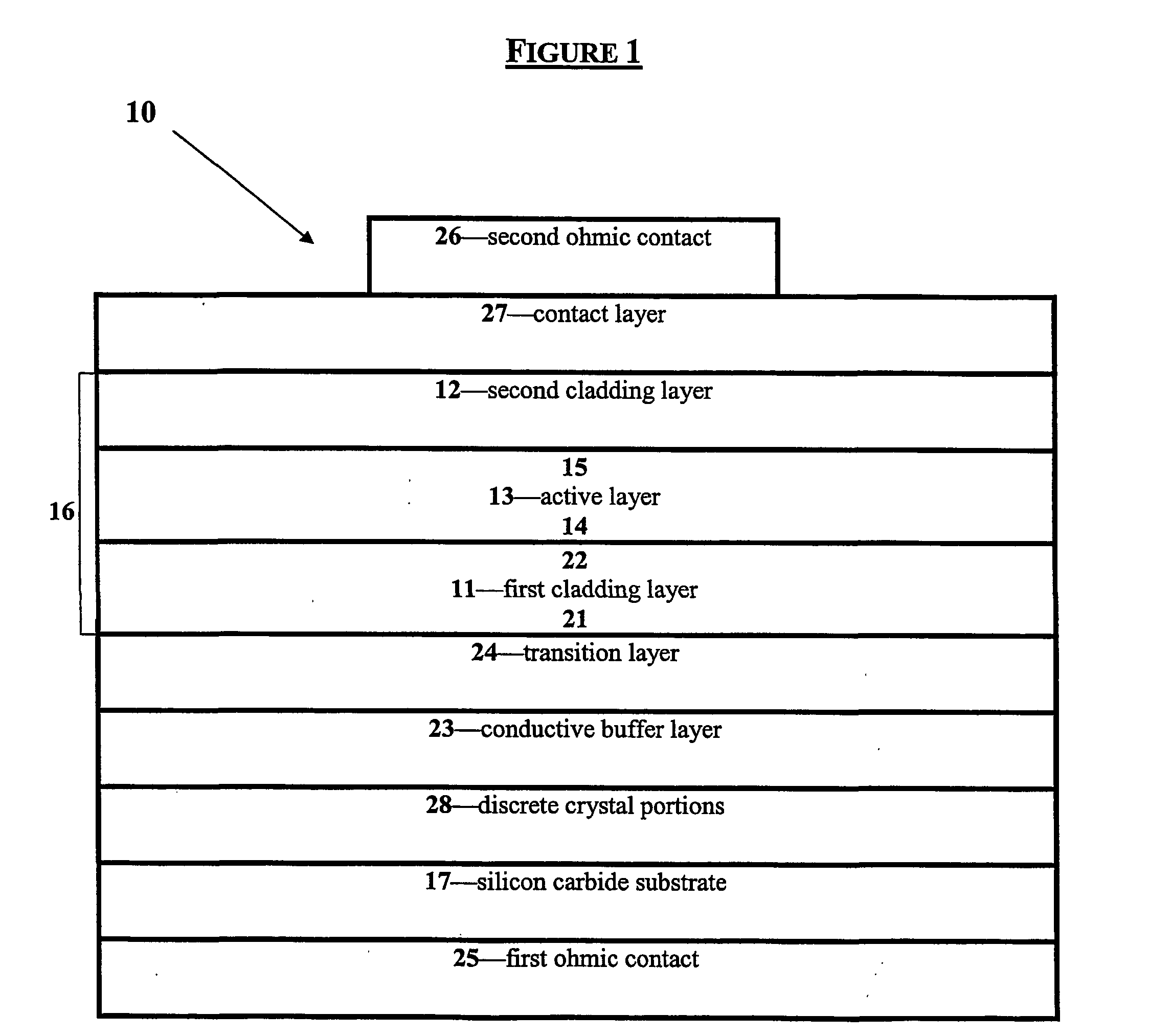
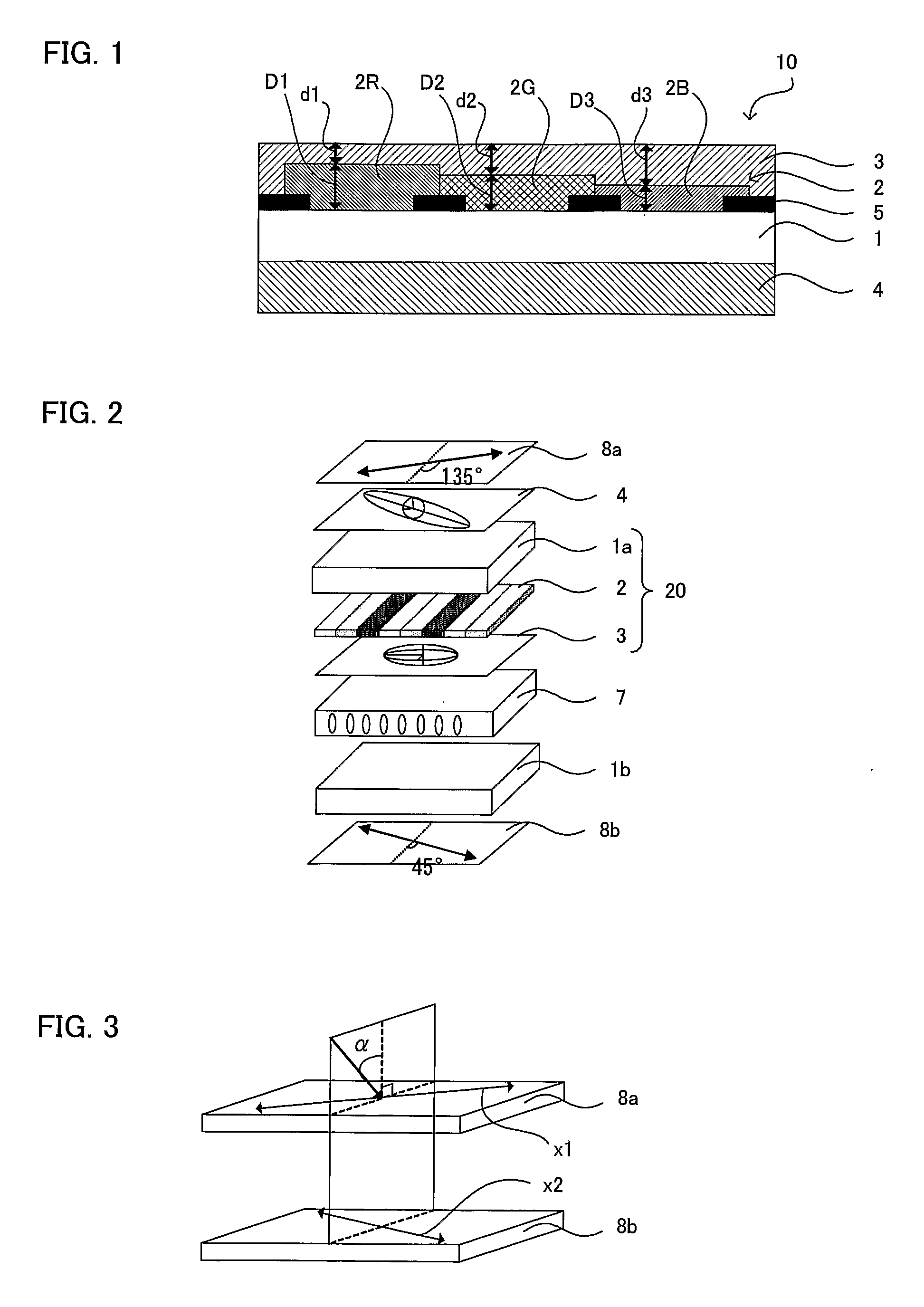
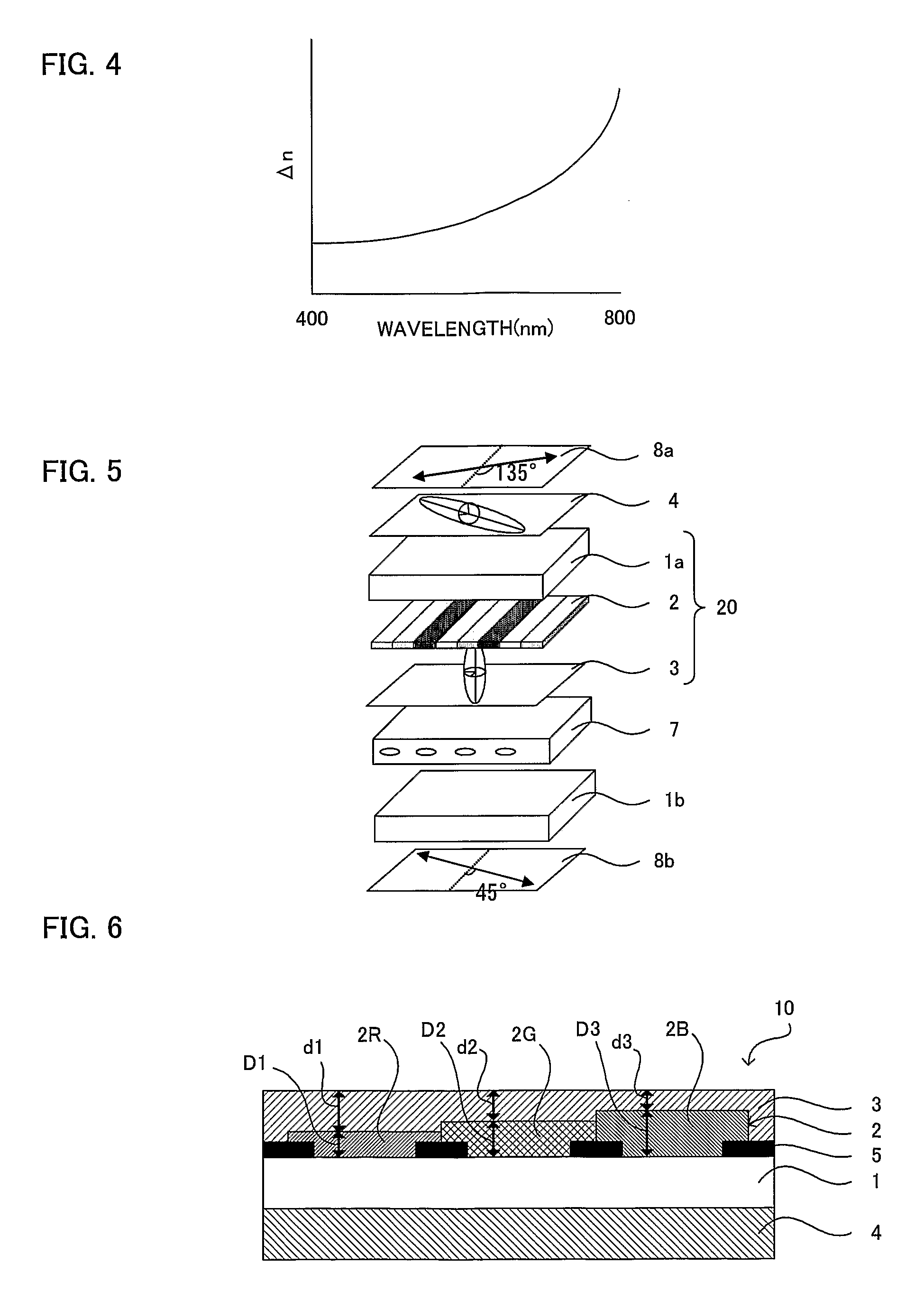
Photosemiconductor device
InactiveUS20050286582A1Improve device characteristicsLarge refractive index changeOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsComputational physicsRefractive index
In a TTG-DFB-LD including a MQW wavelength control layer 16 whose refractive index varies by the current injection, the effective forbidden bandwidth of the MQW wavelength control layer 16 is larger by a value in the range of above 40 meV including 40 meV and below 60 meV excluding 60 meV than an energy of light generated in the MQW active layer 20.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Light emitting devices with group III nitride contact layer and superlattice
InactiveUS20030164506A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce non-radiative recombinationLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
Owner:CREE INC
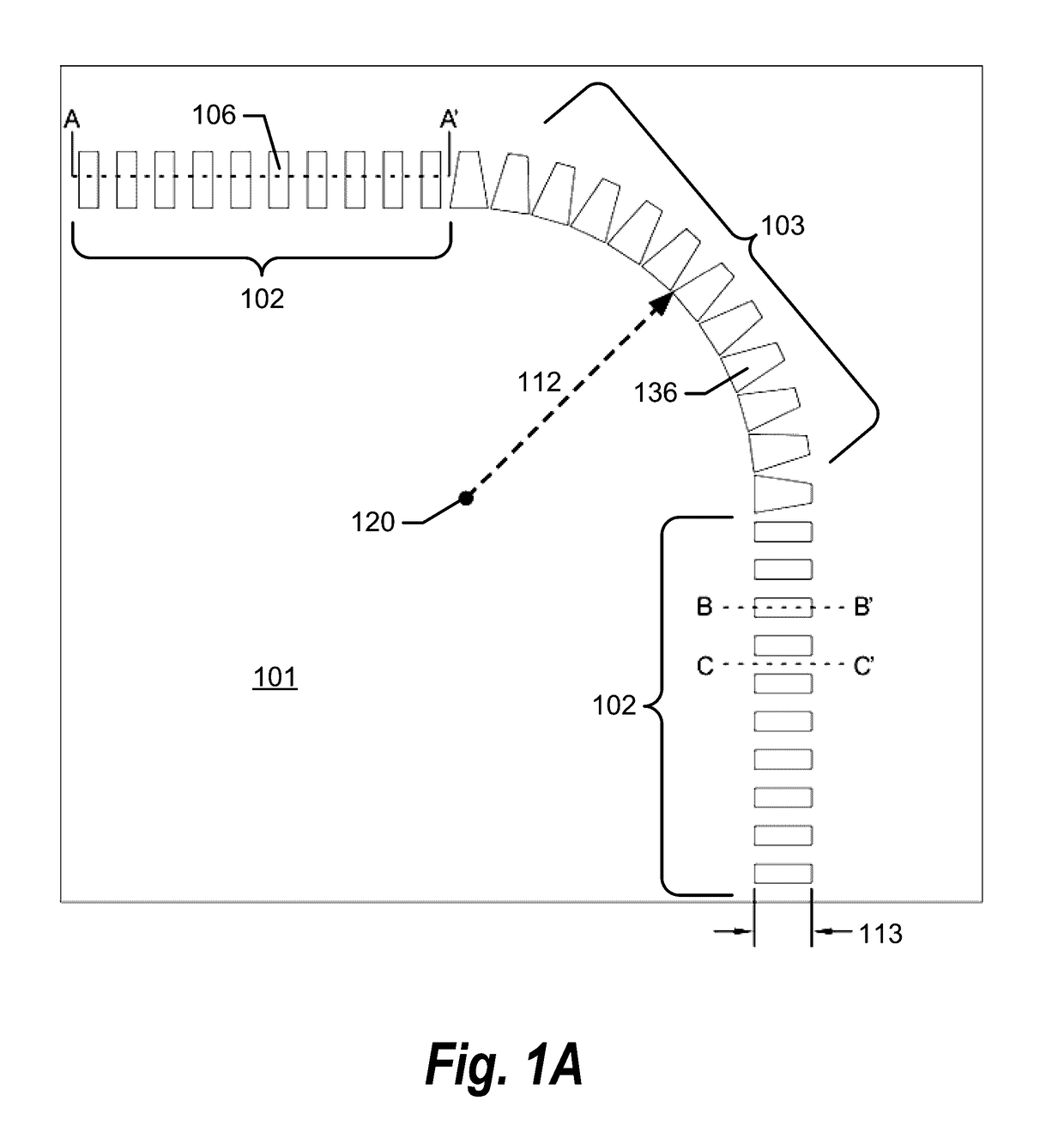
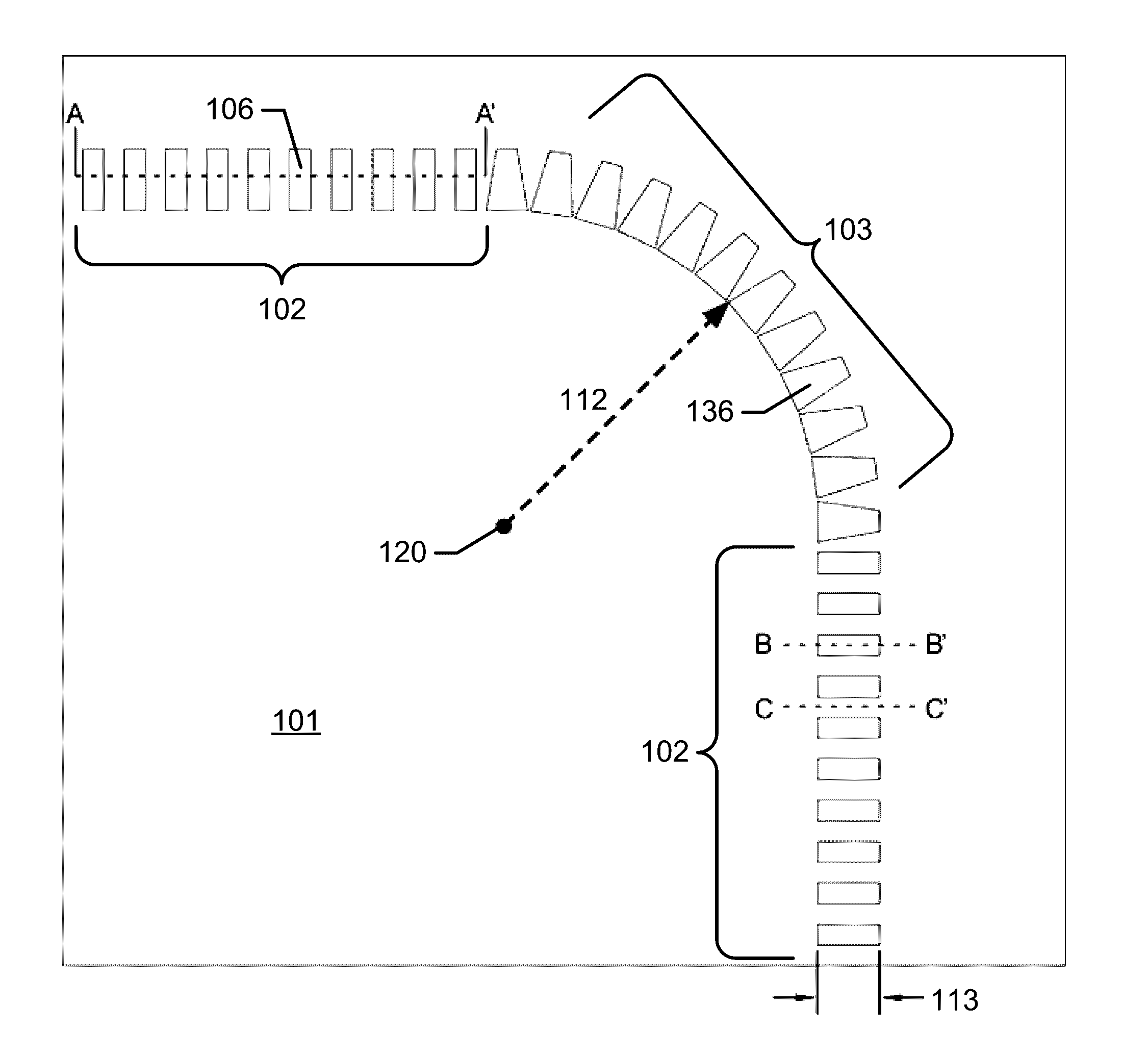
Subwavelength photonic crystal waveguide with trapezoidal shaped dielectric pillars in optical systems
ActiveUS9563016B1Reduce bend lossIncrease lossMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCoupling light guidesWavelengthBend radius
A method for reducing loss in a subwavelength photonic crystal waveguide bend is disclosed. The method comprising: forming the subwavelength photonic crystal waveguide bend with a series of trapezoidal shaped dielectric pillars centered about a bend radius; wherein each of the trapezoidal shaped dielectric pillars comprise a top width, a bottom width, and a trapezoid height; wherein the length of the bottom width is greater than the length of the top width; and wherein the bottom width is closer to the center of the bend radius of the subwavelength photonic crystal waveguide bend than the top width. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
1,4-bis(4-amino-benzene oxymethylene) cyclohexyl and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101081819AReduce light lossHigh transparencyOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationChemical structureNitrobenzene
The present invention relates to 1, 4-bis(4-aminophenoxylmethylene)cyclohexane, which is white or light red crystal and has smelting point of 150-152 deg.c and chemical structure as shown. Its preparation process includes the reaction of 1, 4-cyclohexane dimethanol and p-halo nitrobenzene to obtain 1, 4-bis(4-nitrophenoxylmethylene)cyclohexane, and the further reaction with active carbon, ferric trichloride hexahydrate, anhydrous alcohol and hydrazine hydrate to obtain 1, 4-bis(4-aminophenoxylmethylene)cyclohexane. The compound 1, 4-bis(4-aminophenoxylmethylene)cyclohexane may be polymerized to form polyimide material with alicyclic ring structure, and the polyimide material may find its wide application in liquid crystal display, optical fiber communication and other hi-tech fields.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Resin composition for sealing optical device, cured product thereof, and method of sealing semiconductor element
ActiveUS7550204B2Improve adhesionImprove the level ofLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOptical transparencyPolystyrene
The present invention provides a composition for sealing an optical device comprising (i) a silylated organopolysiloxane with a polystyrene equivalent weight average molecular weight of 5×104 or greater, represented by an average composition formula:R1a(OX)bSiO(4−a−b) / 2 (wherein, R1 represents an alkyl group, alkenyl group, or aryl group; X represents a combination of a group represented by a formula —SiR2R3R4 (wherein, RE to R4 are monovalent hydrocarbon groups), and an alkyl group, alkenyl group, alkoxyalkyl group or acyl group; a represents a number within a range from 1.00 to 1.5; b represents a number that satisfies 0 b 2, and a+b satisfies 1.00 a+b 2), and (ii) a condensation catalyst, as well as a transparent cured product obtained by curing the composition, and a method of sealing a semiconductor element that comprises a step of applying the composition to a semiconductor element, and a step of curing the composition that has been applied to the semiconductor element. The composition can form a coating film that exhibits excellent levels of heat resistance, ultraviolet light resistance, optical transparency, toughness and adhesion.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Surface emitting semiconductor laser
A surface emitting semiconductor laser includes: a substrate; a first semiconductor multilayer reflector of a first conduction type that is formed on the substrate and is composed of stacked pairs of relatively high refractive index layers and relatively low refractive index layers; a cavity region that is formed on the first semiconductor multilayer reflector and includes an active region; and a second semiconductor multilayer reflector of a second conduction type that is formed on the cavity region and is composed of stacked pairs of relatively high refractive index layers and relatively low refractive index layers. A cavity length of a cavity that includes the cavity region and the active region between the first semiconductor multilayer reflector and the second semiconductor multilayer reflector is greater than an oscillation wavelength.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Epoxy resin composition for optical use, optical component using the same, and optical semiconductor device obtained using the same
InactiveUS20110298003A1Temperature stabilityExtensive and intensive investigationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhotovoltaic energy generationChemistryRefractive index
The present invention relates to an epoxy resin composition for optical use including the following ingredients (A) to (C): (A) an epoxy resin; (B) a curing agent; and (C) an inorganic filler including (c1) an inorganic filler having a refractive index larger than a refractive index of a cured product obtained from the ingredients of the epoxy resin composition excluding the (C) inorganic filler and (c2) an inorganic filler having a refractive index smaller than the refractive index of the cured product obtained from the ingredients of the epoxy resin composition excluding the (C) inorganic filler.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Light emitting apparatus and light emitting method
ActiveUS7635948B2Improve efficiencyEffective radiationLaser detailsIncadescent screens/filtersLength waveLight emitting device
A light emitting apparatus of the present invention includes: an EL emitting unit including at least a light emitting layer which generates an EL light; and a pair of light blocking layers arranged such that they sandwich the light emitting layer so that the layers block the EL light generated in the light emitting layer and that the EL light is radiated only from the end of the light emitting layer; and a light emitting unit which optically guides the EL light radiated from the end of the light emitting layer and emits a light having a wavelength equal to or different from that of the EL light. The EL light is emitted only from the end of the light emitting layer since the EL light generated in the light emitting layer is blocked by the pair of light blocking layers. This emitted EL light is optically guided by the light emitting unit and emitted as it is or a light having a different wavelength from the EL light.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Light-emitting device and production method therefor
The light-emitting device of the present technique includes a substrate, a Group III nitride semiconductor layer disposed on the substrate, a current-blocking layer disposed on the Group III nitride semiconductor layer, a transparent conductive oxide film disposed on the Group III nitride semiconductor layer and the current-blocking layer, a dielectric film covering the Group III nitride semiconductor layer and at least a part of the transparent conductive oxide film, and a phosphor-containing resin coating disposed on the dielectric film. The Group III nitride semiconductor layer has a refractive index greater than that of the transparent conductive oxide film. The transparent conductive oxide film has a refractive index greater than that of the dielectric film. The dielectric film has a refractive index greater than that of the phosphor-containing resin coating. The current-blocking layer has a refractive index smaller than that of the phosphor-containing resin coating.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Color filter with retardation layer and liquid crystal display
The main object of the present invention is to provide a colour filter with a retardation layer, capable of minimizing light leakage even in the case the visual angle is large in the black display state, for a liquid crystal display. The present invention achieves the object by providing a colour filter with a retardation layer comprising a substrate, a colour layer formed on the substrate, being arranged in a plurality of rows having different thicknesses according to each colour, a first retardation layer formed on the colour layer, made of a liquid crystalline polymer, having its optic axis perpendicular to a plane of the substrate so as to function as a C plate, and a second retardation layer the colour layer, wherein the optic axis of the second retardation layer is arranged parallel to the plane of the substrate so as to function as a positive Aplate with positive refractive index anisotropy, and the refractive index anisotropy of the second retardation layer in the visible light range decreases at shorter wavelengths inverse dispersion characteristics.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Thin display device
InactiveUS20130222737A1Light reflection efficiencyLuminance non-uniformity is increasedOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLight guideDisplay device
A display device that economically improves light entry efficiency and non-uniformity of luminance of a light guide plate includes a plurality of light sources arranged at specified intervals so as to face a plane of incidence of the light guide plate to illuminate a liquid crystal module from the rear such that the light guide plate is illuminated with light from the light sources passing through the plane of incidence of the light guide plate. An optically anisotropic member is disposed on the plane of incidence and is configured such that a refractive index along a vertical direction with respect to the plane of incidence of the light guide plate is relatively small and a refractive index along a parallel direction with respect to the plane of incidence is large compared to the relatively small refractive index.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20120020377A1Reduce variationWavelength chirping can be suppressedOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical couplingWaveguide
A semiconductor laser device includes a lower cladding layer; an active layer disposed on the lower cladding layer; all upper cladding layer disposed on the active layer; a diffraction-grating layer disposed on the upper cladding layer, the diffraction-grating layer including periodic projections and recesses; and a buried layer disposed on the periodic projections and recesses in the diffraction-grating layer. In addition, the diffraction-grating layer and the buried layer constitute a diffraction grating. The lower cladding layer, the active layer, and the upper cladding layer constitute a first optical waveguide, the active layer constituting a first core region in the first optical waveguide. The upper cladding layer, the diffraction-grating layer, and the buried layer constitute a second optical waveguide, the diffraction-grating layer constituting a second core region in the second optical waveguide. Furthermore, the first optical waveguide and the second optical waveguide are optically coupled through the upper cladding layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Ink level detecting apparatus having optical fiber to detect the ink level in inkjet printer
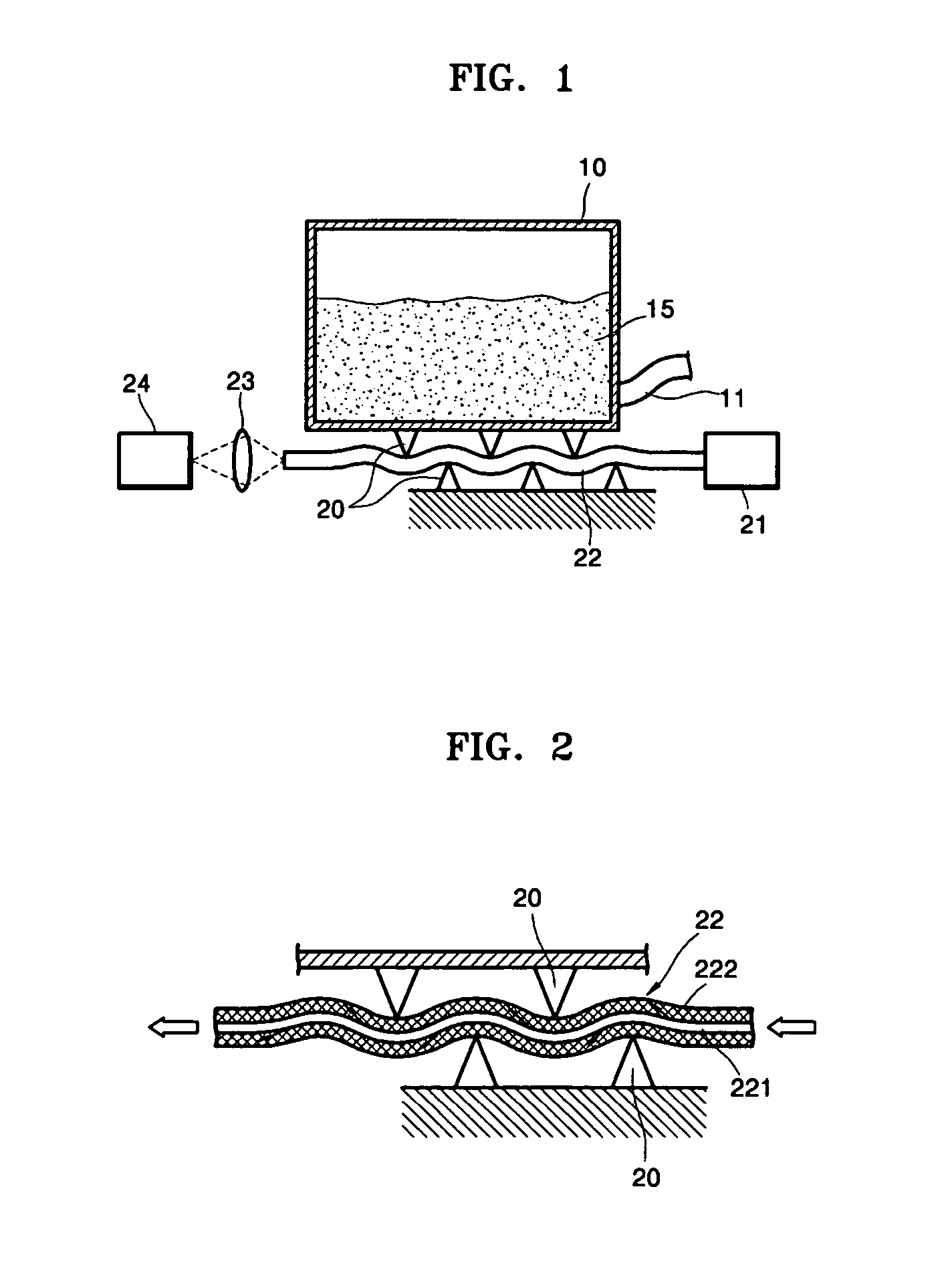
InactiveUS20070013727A1High refractive indexSmall refractive indexOther printing apparatusEngineeringLight source
An ink level detecting apparatus usable with an inkjet printer, which uses an optical fiber to detect the ink level. The ink level detecting apparatus includes: an ink tank having an ink outlet; an optical fiber disposed near the ink tank; a light source which is disposed at a front end of the optical fiber and emits light; a light receiving sensor which is disposed at a rear end of the optical fiber and senses light propagating through the optical fiber; and a pressuring unit which presses the optical fiber so as to bend the optical fiber according to the weight of the ink tank.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com