Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about How to "Refractive index difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
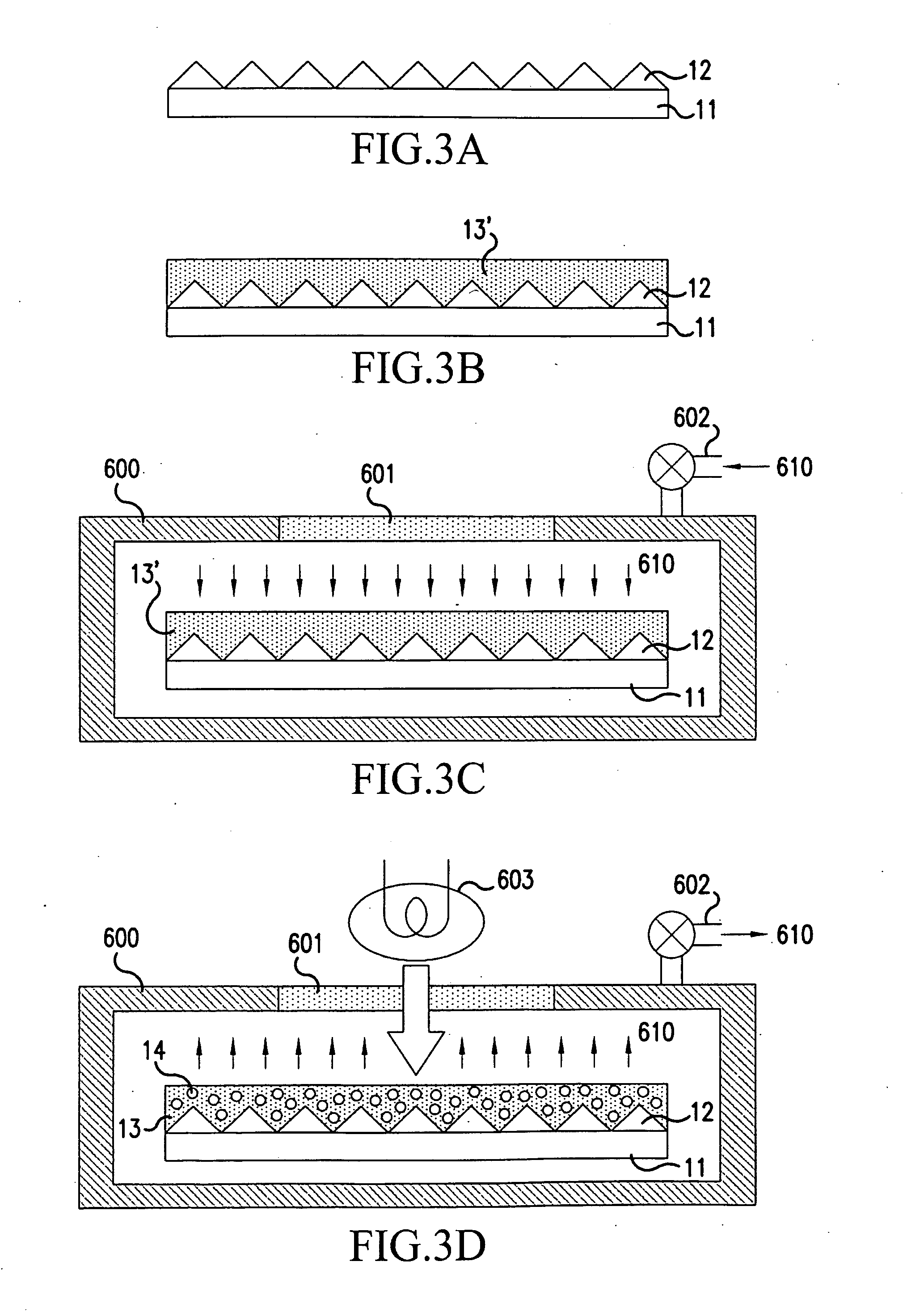
Diffuse reflective articles
InactiveUS20030118805A1Required thicknessImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusVehicle headlampsLiquid-crystal displayDiluent
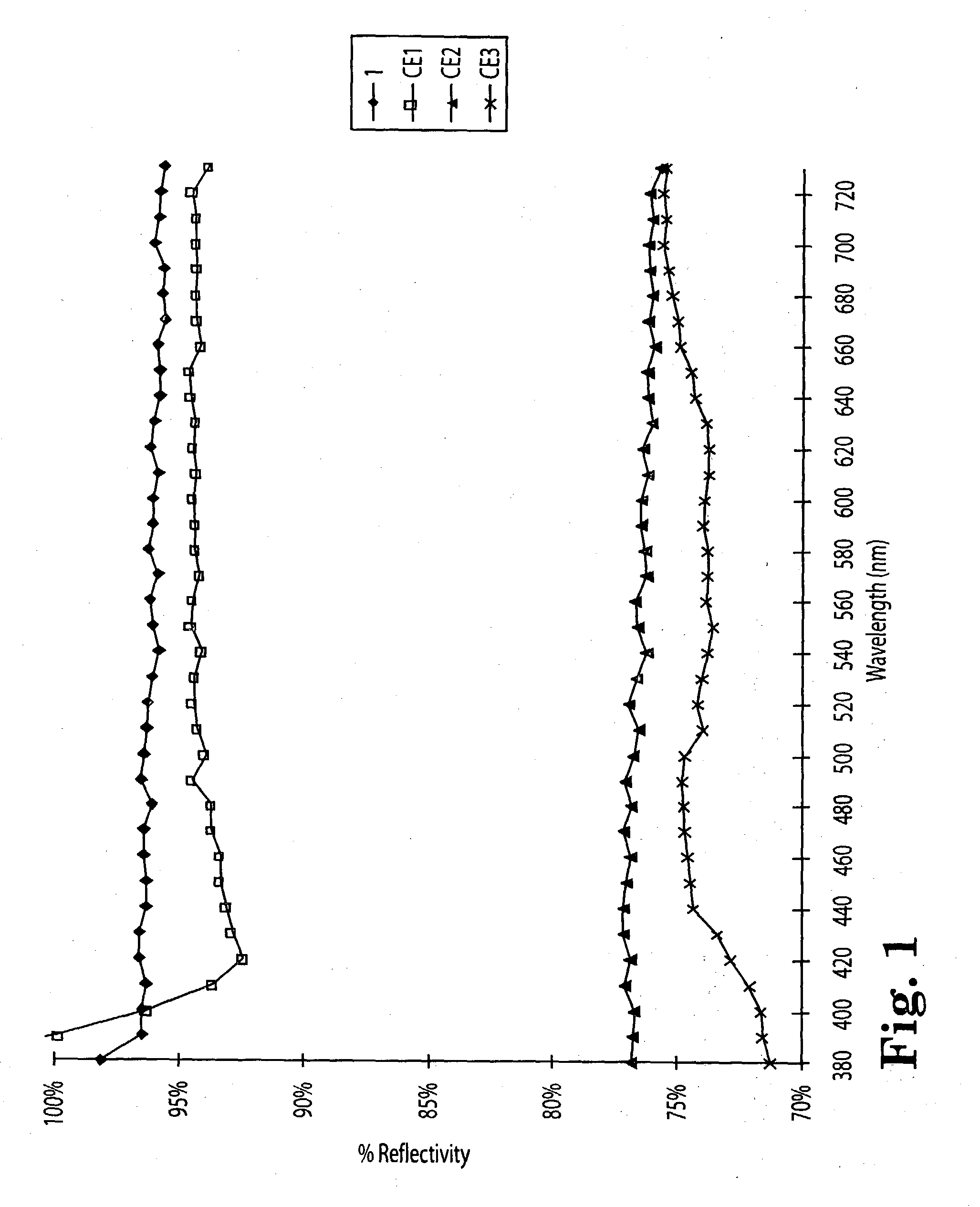
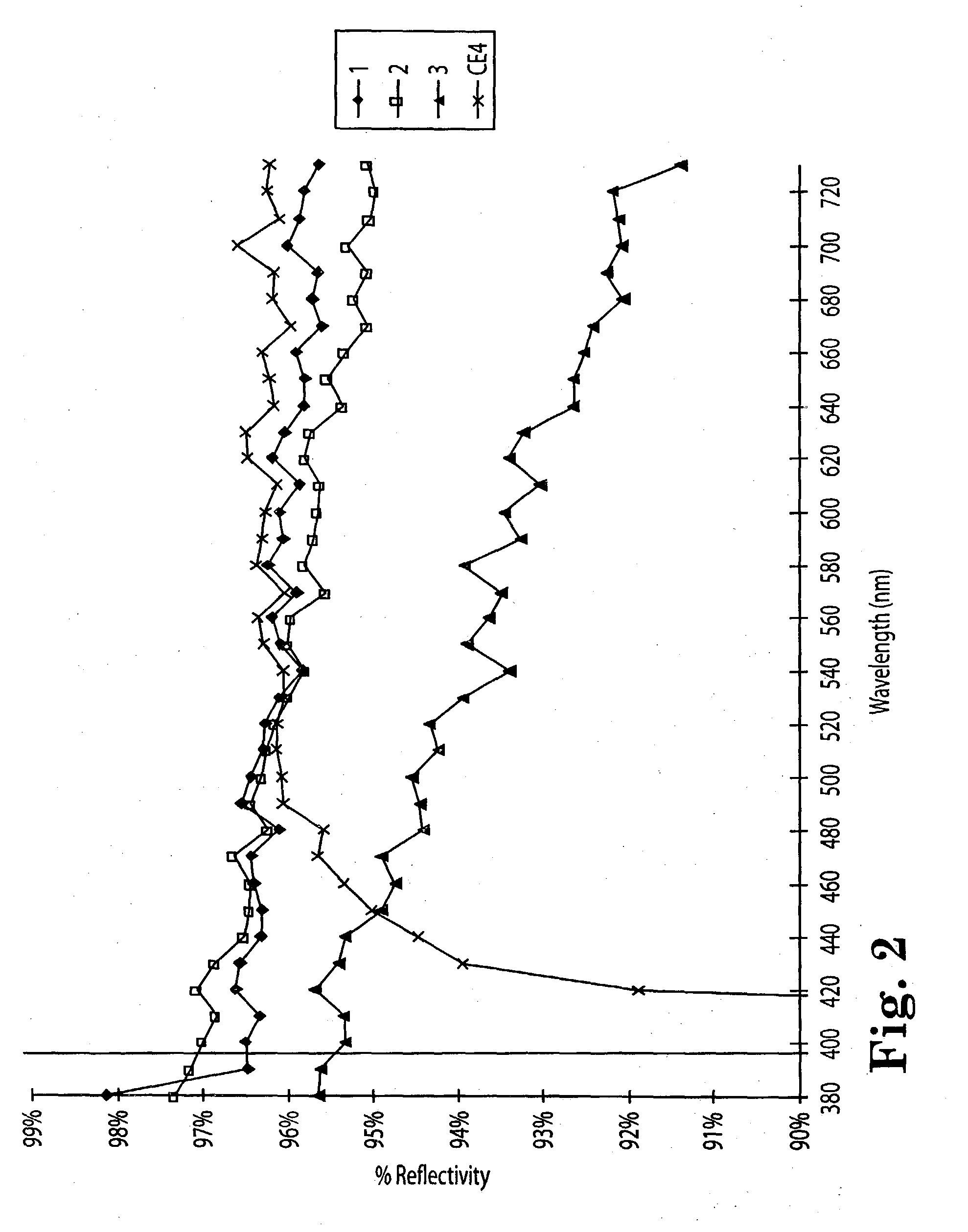
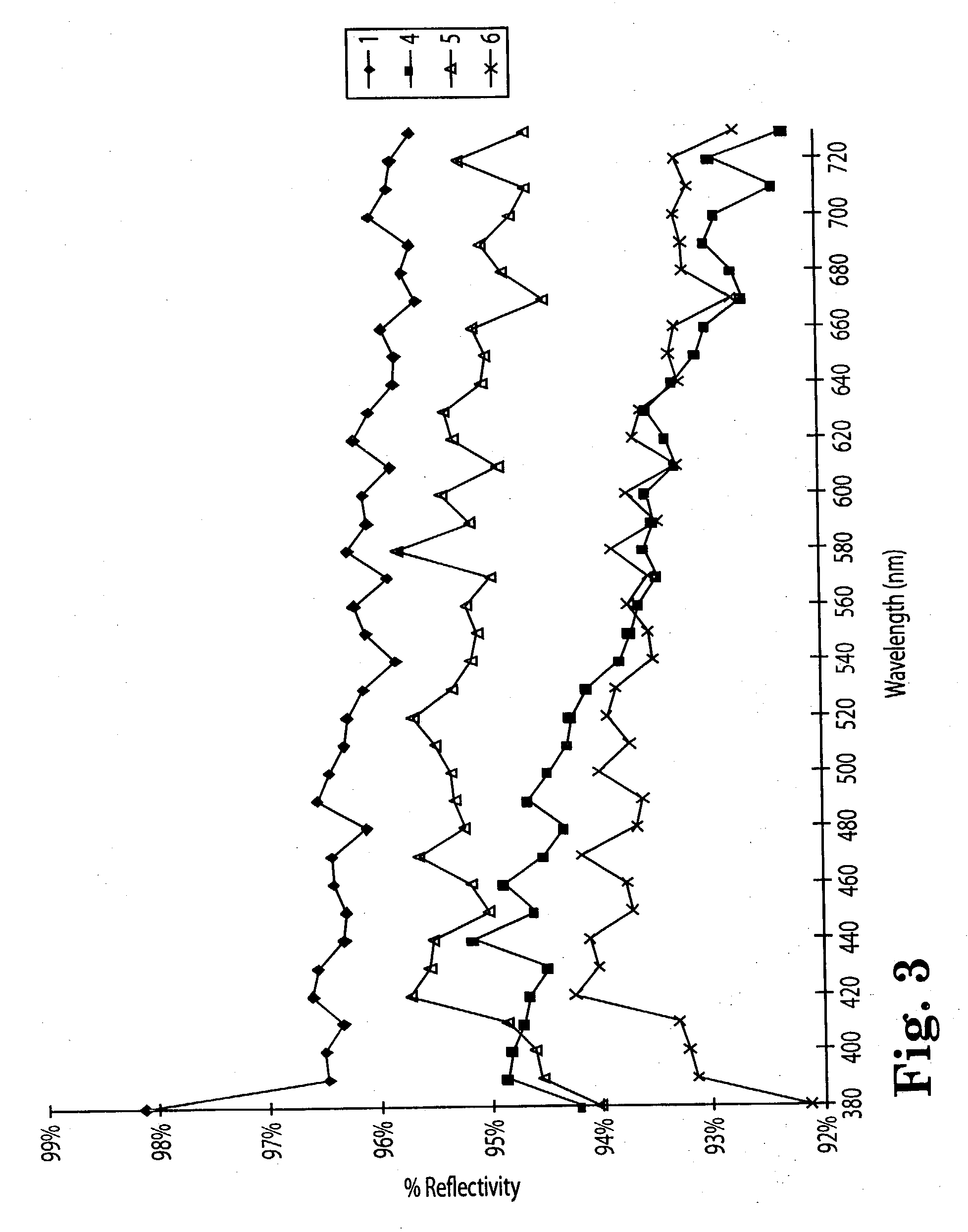
Diffuse reflective materials proximate to a structure formed by thermally induced phase separation of a thermoplastic polymer and a diluent providing enhanced flexibility and reflectivity especially in the visible wavelengths of 380-730 nanometers are described. Such materials find a wide variety of application among combinations with other reflective layers. The diffuse reflective articles are useful in backlight units of liquid crystal displays, lights, copy machines, projection system displays, facsimile apparatus, electronic blackboards, diffuse white standards, photographic lights and the like.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Optical adjusting member, and illumination device and liquid crystal display device including the same
InactiveUS20080303777A1Suppressing damages at the top edgeConvenient lightingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical transparencyLiquid-crystal display
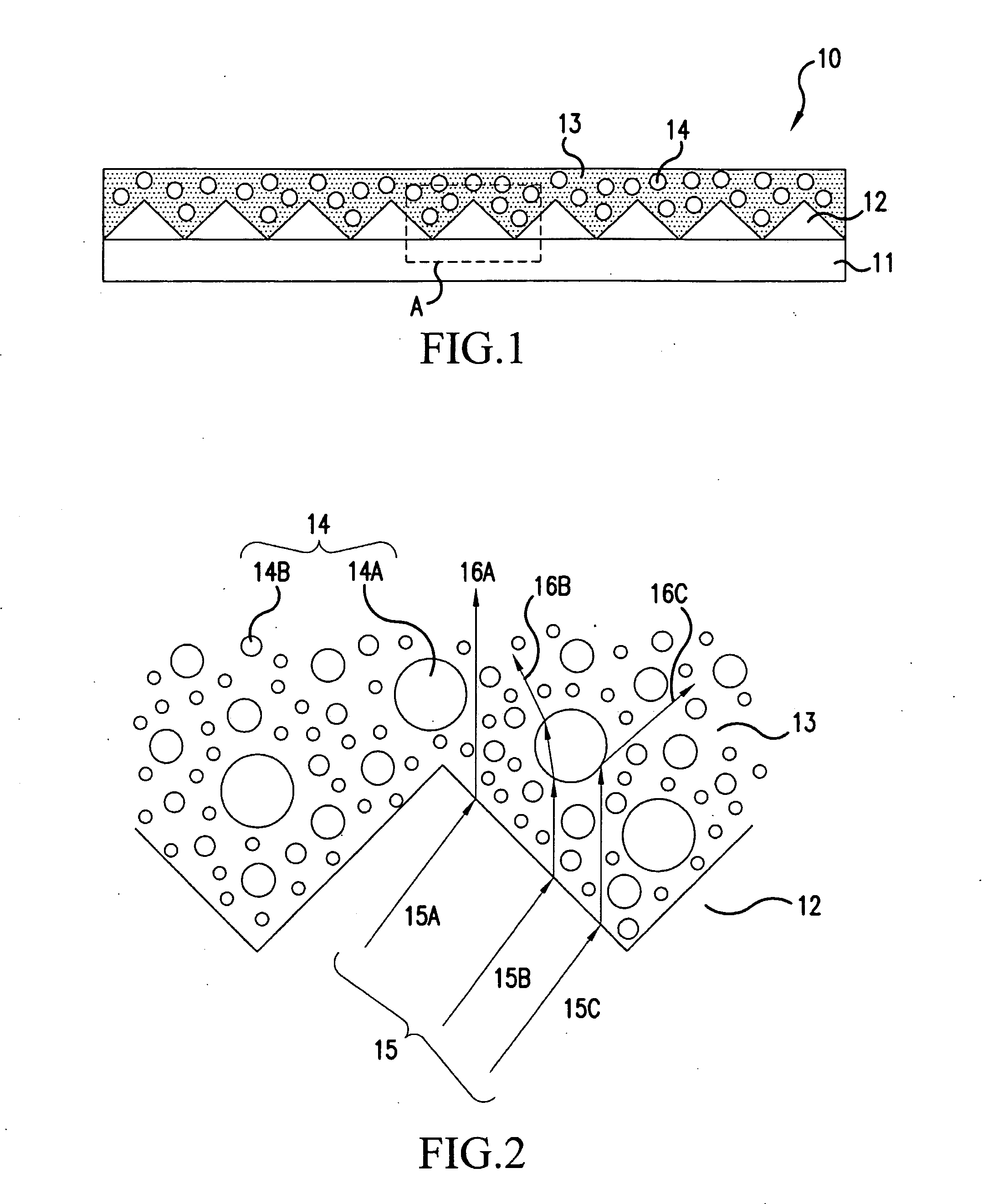
An optical adjusting member according to the invention includes a base member, a plurality of lenses, and a light diffusion layer. The base member has optical transparency. The plurality of lenses are formed on the base member. The light diffusion layer is formed on the plurality of lenses, and at least top edge parts of the lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer. In the optical adjusting member according to the invention, at least the top edge parts of the plurality of lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer and therefore the lenses are less susceptible to damages. The optical adjusting member according to the invention has a light collecting function by the lenses and a diffusion function by the light diffusion layer.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
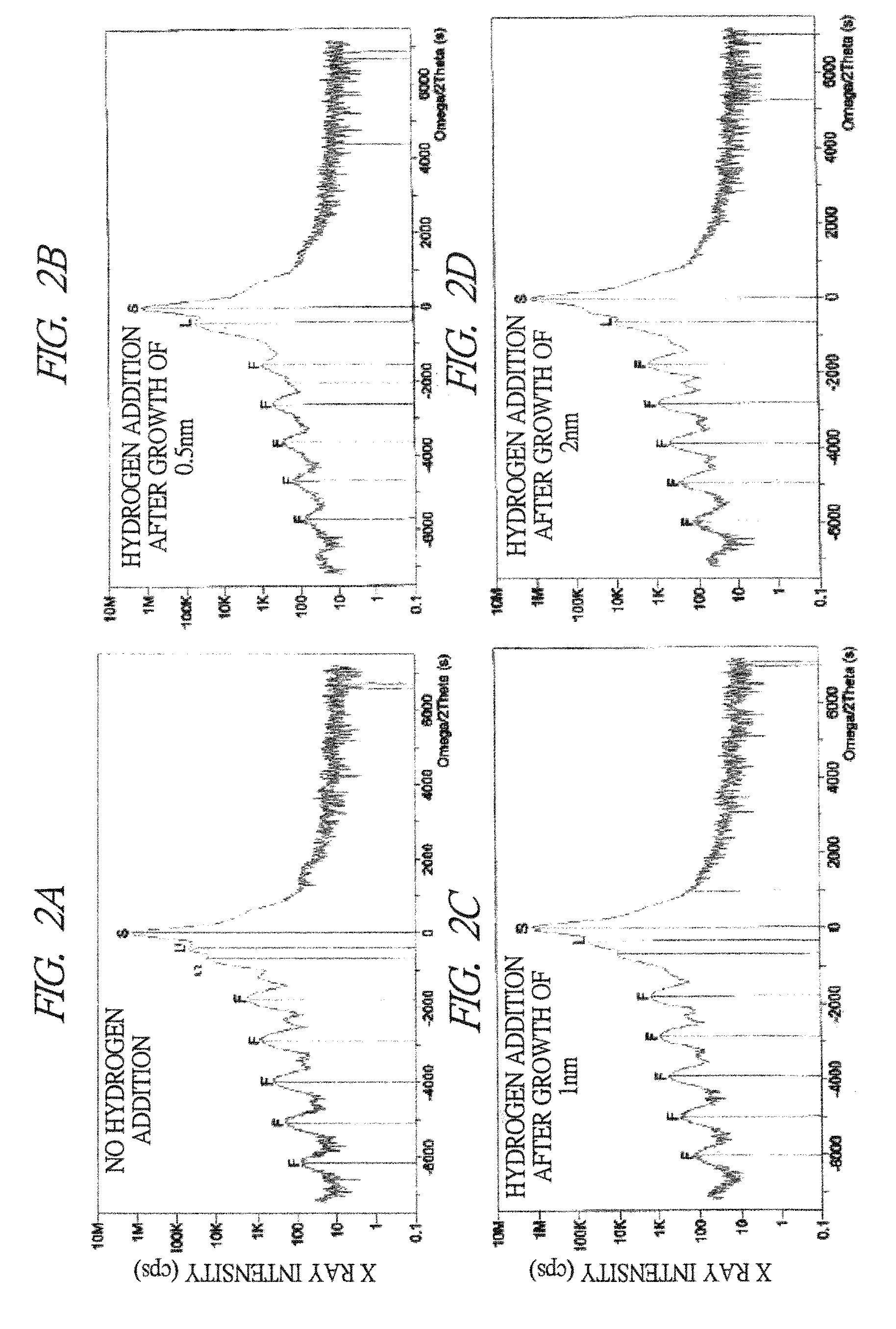
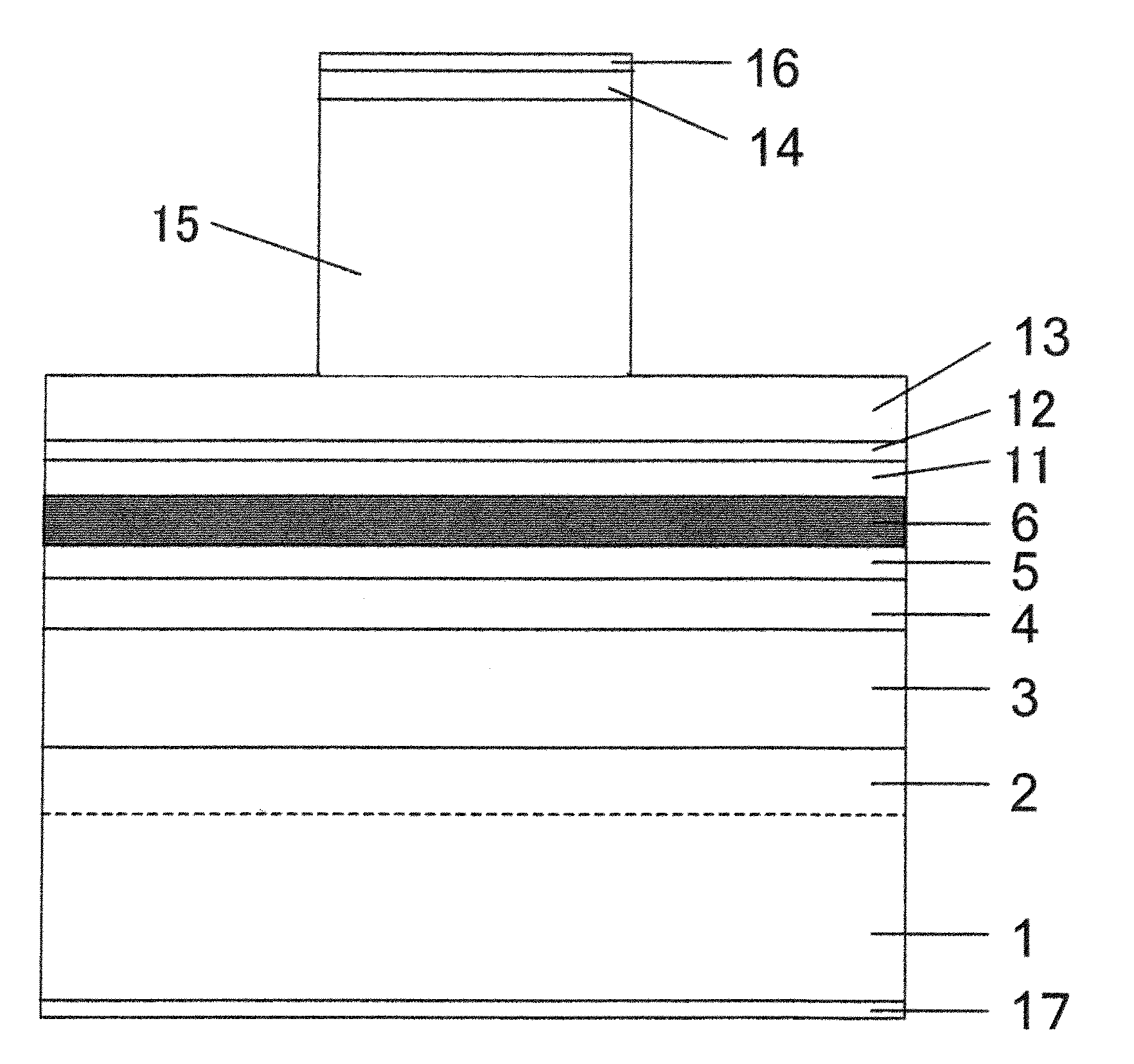
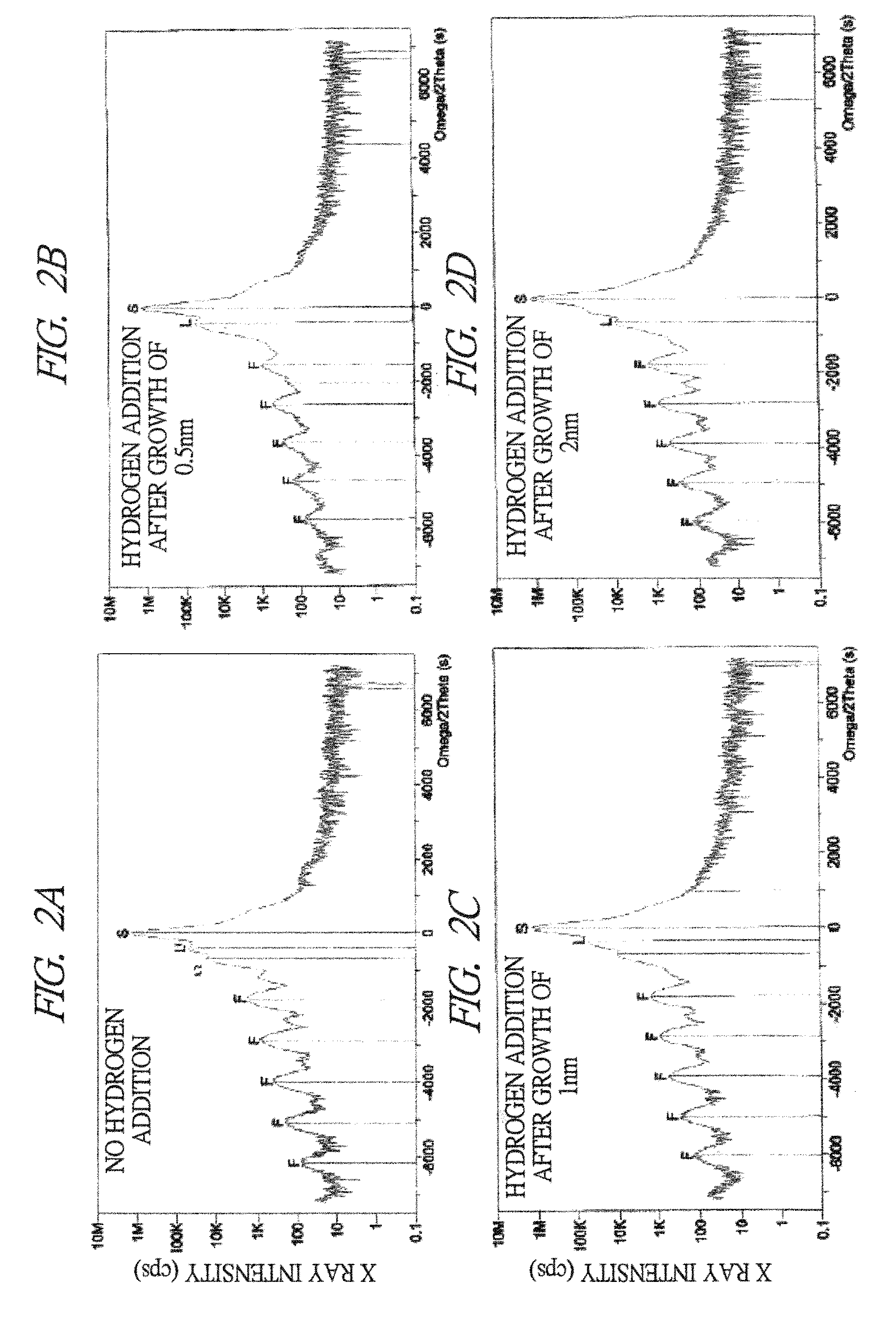
Nitride semiconductor optical element and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100150194A1High crystallinityEliminate segregationLaser detailsLaser active region structureIndiumHydrogen
In an InGaN-based nitride semiconductor optical device having a long wavelength (440 nm or more) equal to or more than that of blue, the increase of a wavelength is realized while suppressing In (Indium) segregation and deterioration of crystallinity. In the manufacture of an InGaN-based nitride semiconductor optical device having an InGaN-based quantum well active layer including an InGaN well layer and an InGaN barrier layer, a step of growing the InGaN barrier layer includes: a first step of adding hydrogen at 1% or more to a gas atmosphere composed of nitrogen and ammonia and growing a GaN layer in the gas atmosphere; and a second step of growing the InGaN barrier layer in a gas atmosphere composed of nitrogen and ammonia.
Owner:USHIO OPTO SEMICON
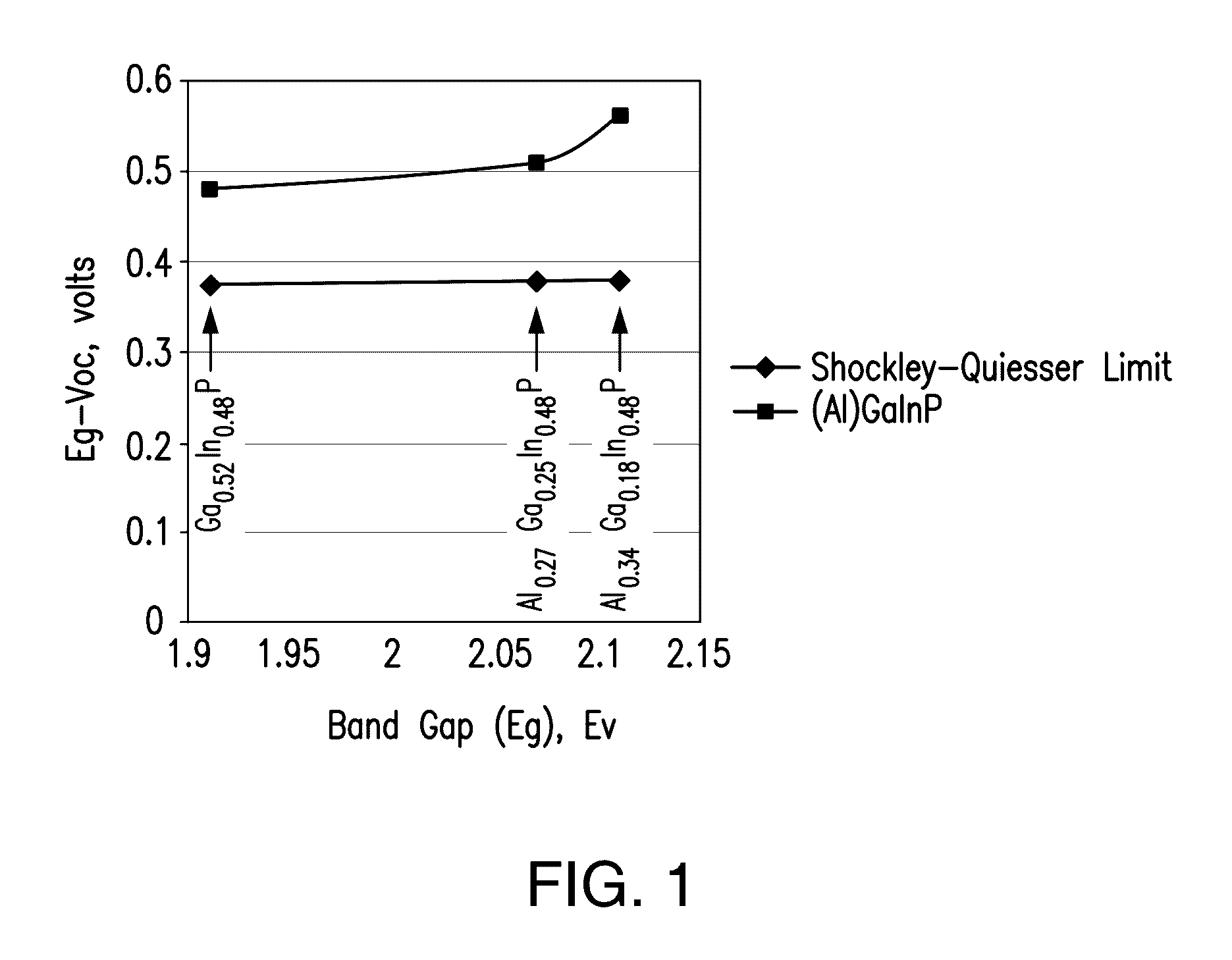
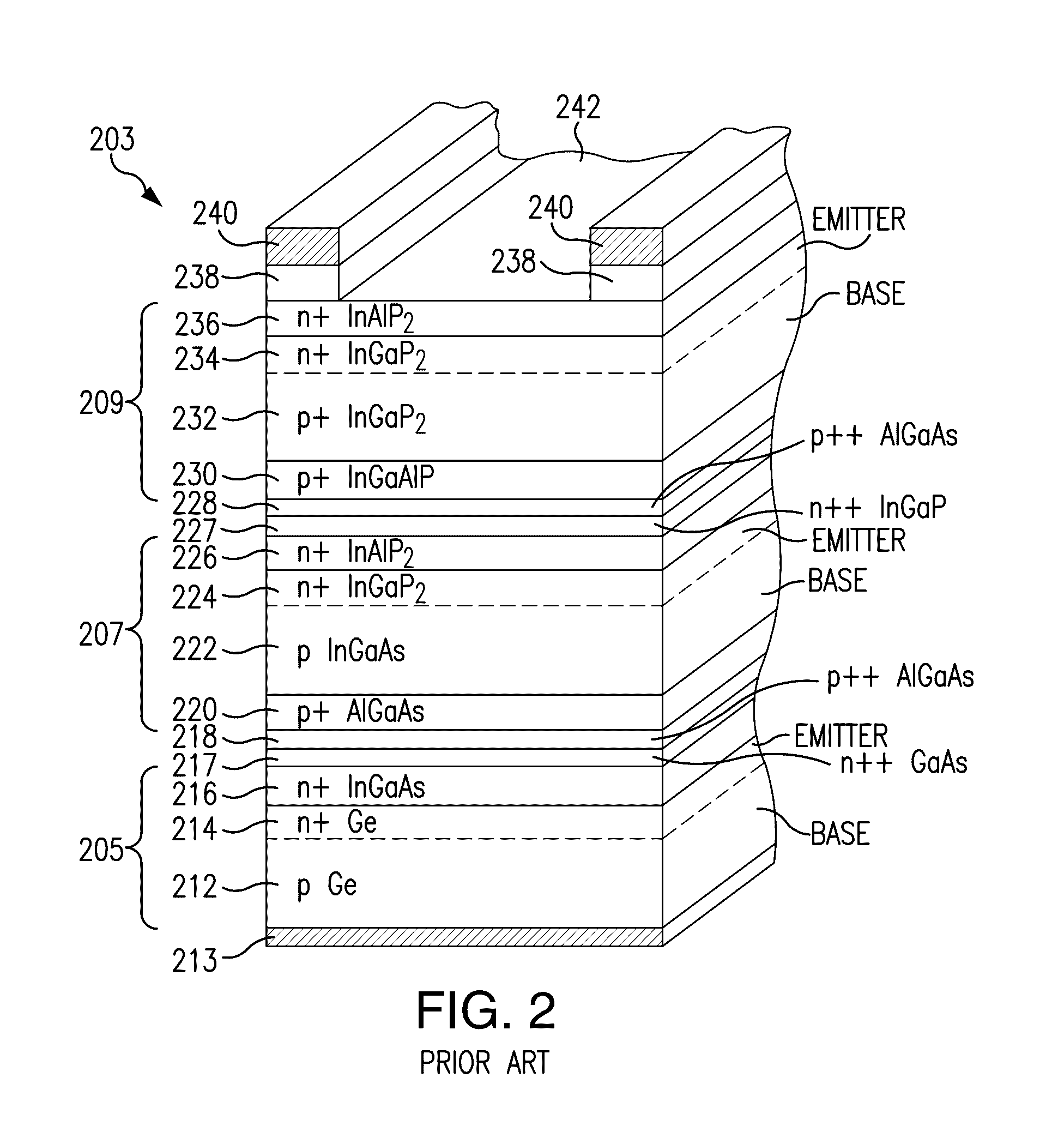
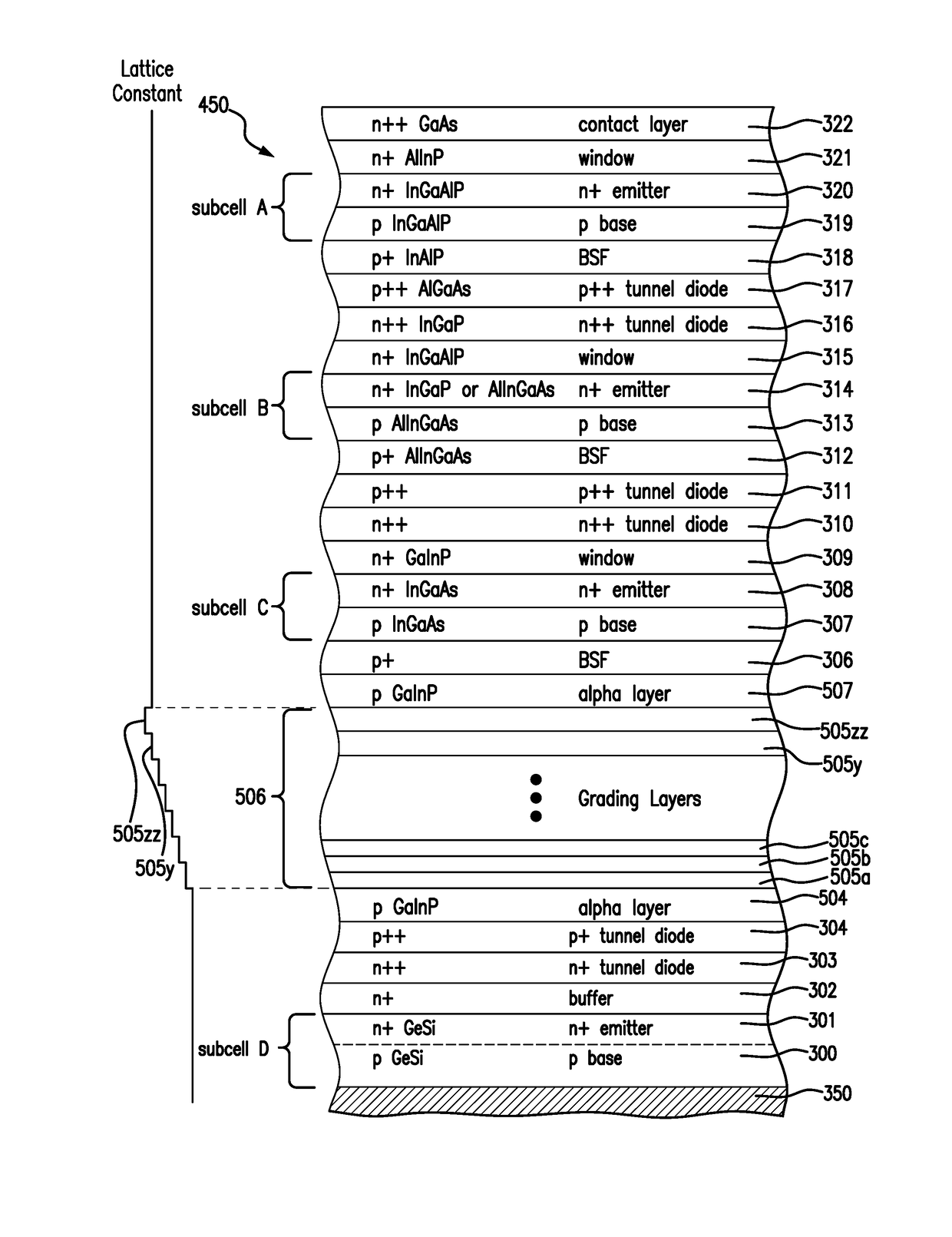
Four junction solar cell for space applications
InactiveUS20170054048A1Photo-conversion efficiency can be improvedMaximize efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationBand gapSolar cell
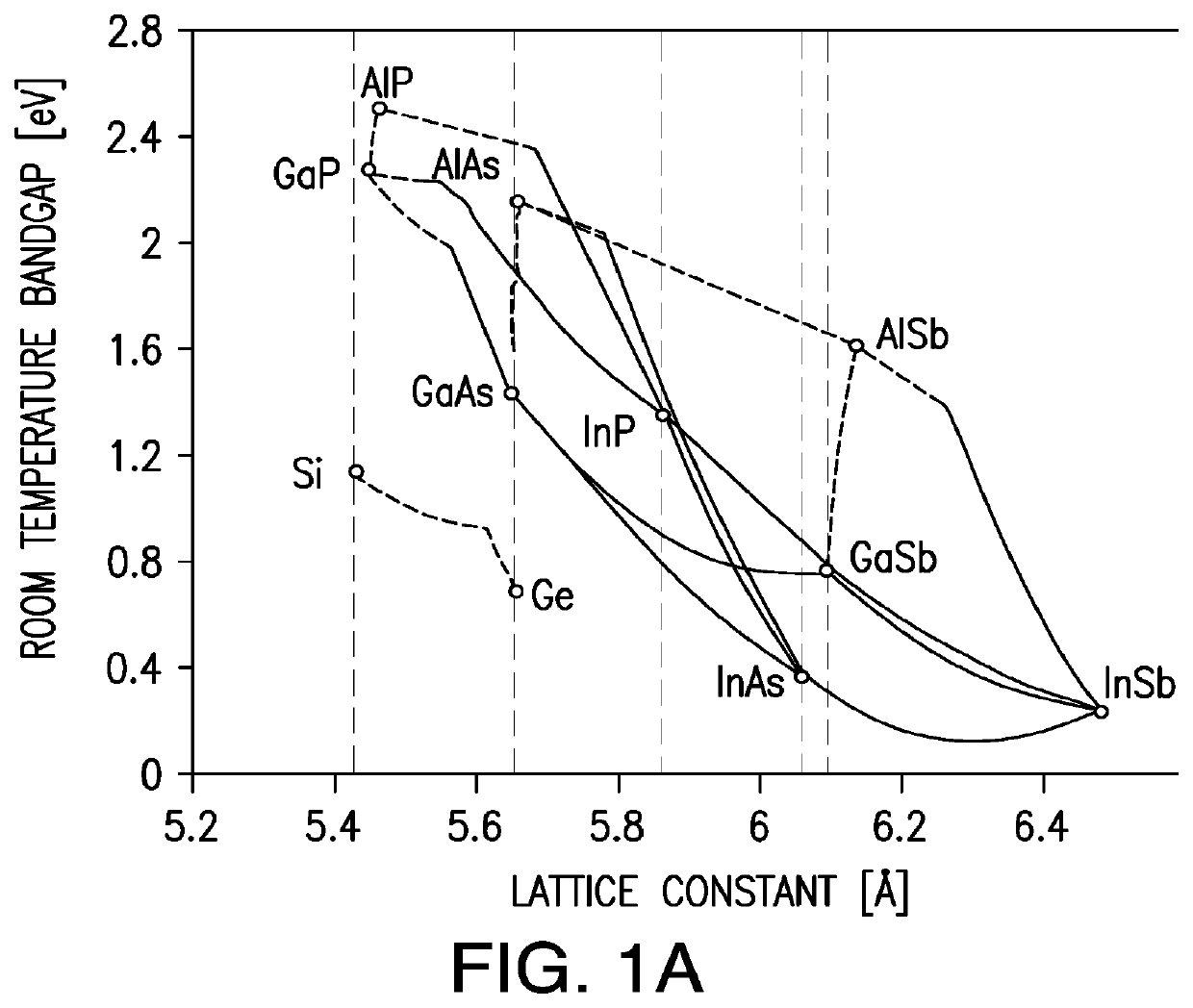
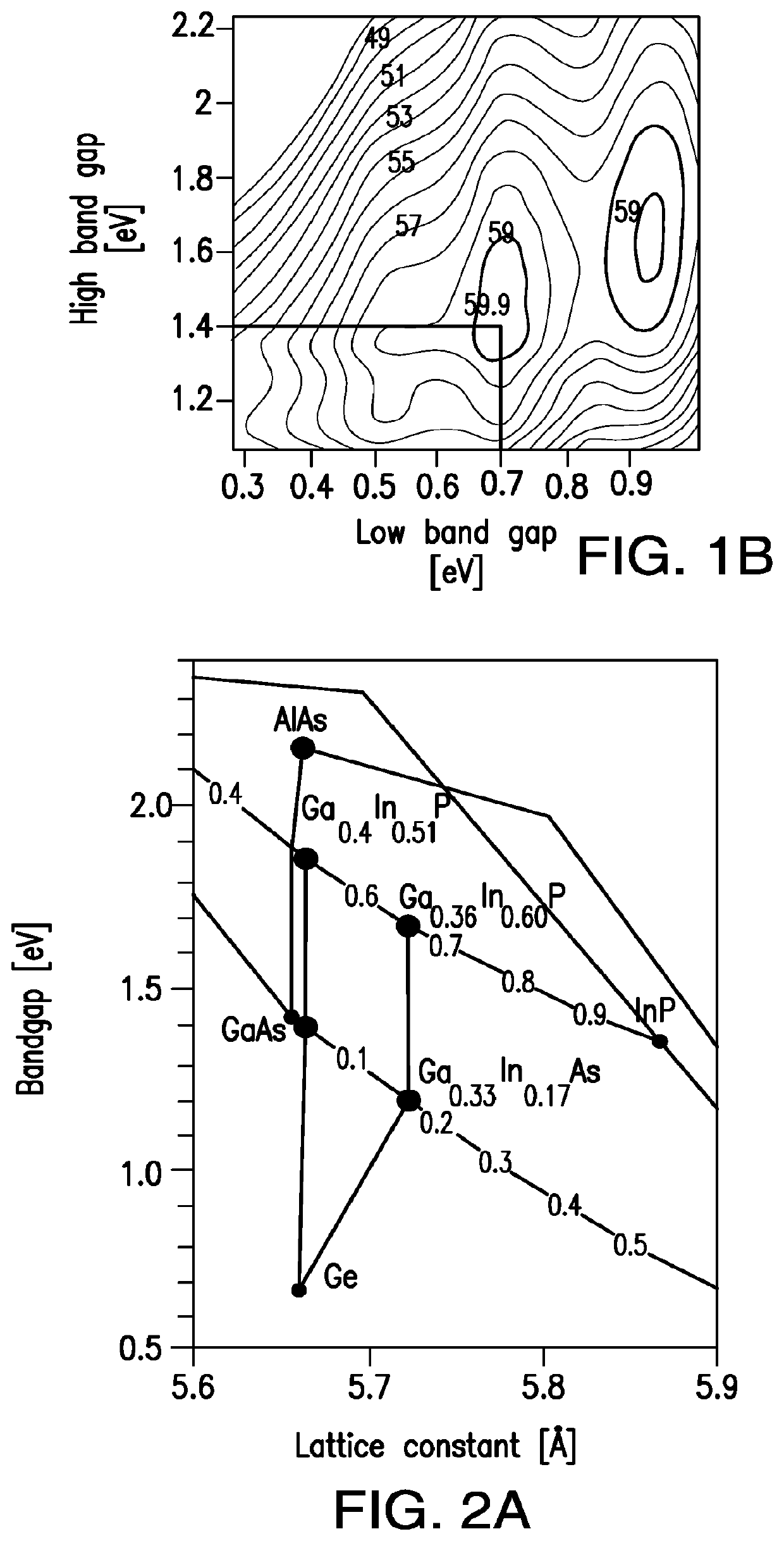
A four junction solar cell having an upper first solar subcell composed of a semiconductor material having a first band gap; a second solar subcell adjacent to said first solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a second band gap smaller than the first band gap and being lattice matched with the upper first solar subcell; a third solar subcell adjacent to said second solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a third band gap smaller than the second band gap and being lattice matched with the second solar subcell; and a fourth solar subcell adjacent to said third solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a fourth band gap smaller than the third band gap; wherein the fourth subcell has a direct bandgap of greater than 0.75 eV.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Display device
InactiveUS20120314144A1Refractive index differenceGood light scatteringSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayRefractive index
A display device, having: a display panel; and a liquid crystal lens panel for switching a 2D display and a 3D display with each other, and for forming a parallax barrier by controlling the refractive index as in a cylindrical lens, wherein the liquid crystal lens panel has: a pair of transparent substrates; comb-shaped electrodes, which are formed on the liquid crystal layer side of one of the transparent substrates, run in the X direction and are aligned in the Y direction; flat common electrodes; and post spacers having light transmitting properties for holding the pair of transparent substrates at a predetermined distance, wherein the post spacers are fixed to one of the pair of transparent substrates on the liquid crystal side and are placed in regions away from the comb-shaped electrodes in a plane of the transparent substrate.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Light diffusing element, polarizing plate with light diffusing element, liquid crystal display apparatus using both, and manufacturing method for light diffusing element
ActiveUS20110317099A1High haze valueImprove diffusivityDiffusing elementsProjectorsProduction rateLiquid-crystal display
There is provided a light diffusing element, which has a high haze value and strong diffusibility, has backscattering suppressed, and is low in cost and excellent in productivity.A light diffusing element of the present invention includes: a matrix containing a resin component and an ultrafine particle component; and light diffusing fine particles dispersed in the matrix, wherein: refractive indices of the resin component, the ultrafine particle component, and the light diffusing fine particles satisfy the below-indicated expression (1); and the light diffusing element comprises a concentration adjusted area, which is formed in an outer portion of a vicinity of a surface of each of the light diffusing fine particles, and in which a weight concentration of the resin component decreases and a weight concentration of the ultrafine particle component increases with increasing distance from the light diffusing fine particles:|nP−nA|<|nP−nB| (1)where nA represents the refractive index of the resin component of the matrix, nB represents the refractive index of the ultrafine particle component of the matrix, and nP represents the refractive index of the light diffusing fine particles.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070279560A1Reduce thicknessReduce weightStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLight reflectionRefractive index
External light is reflected due to a difference in refractive indices of a black matrix and a glass substrate. When the black matrix is a black resin, there is a difference in refractive indices of the black resin and a first substrate. Also, there is a difference in refractive indices of the colored layer and the first substrate. Therefore, external light is slightly reflected. There is a problem in that the reflected light reduces contrast. A structure in which one polarizing element having dichroism is interposed between a pair of substrates is employed, and a light interference layer is provided between a color filter and a glass substrate, whereby a difference in refractive indices is moderated to reduce light reflection.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Optical element, method for manufacturing optical element and semiconductor laser device using the optical element
InactiveUS20080031297A1Increase the refractive index differenceReliable acquisitionLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonic crystalRefractive index
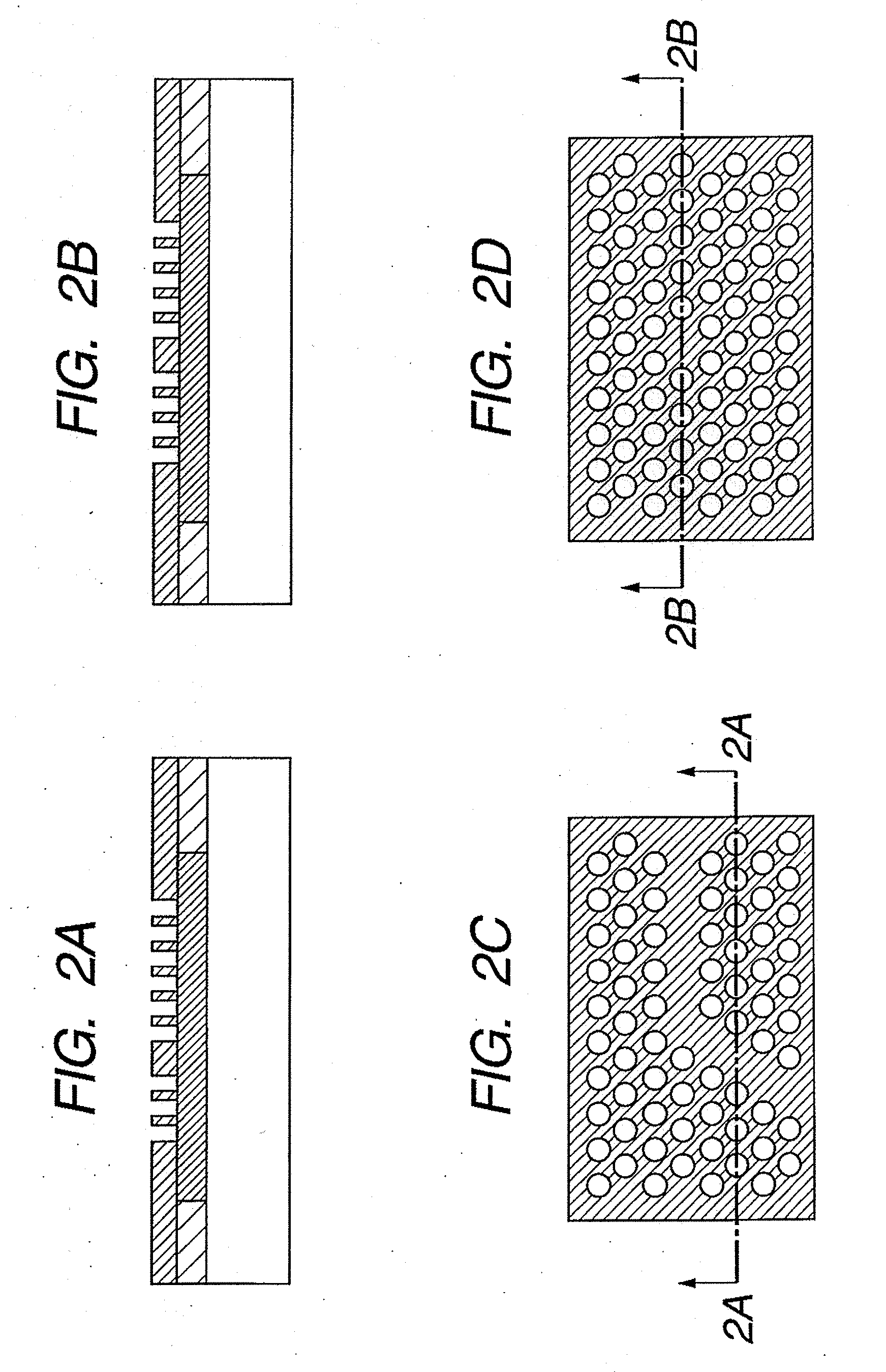
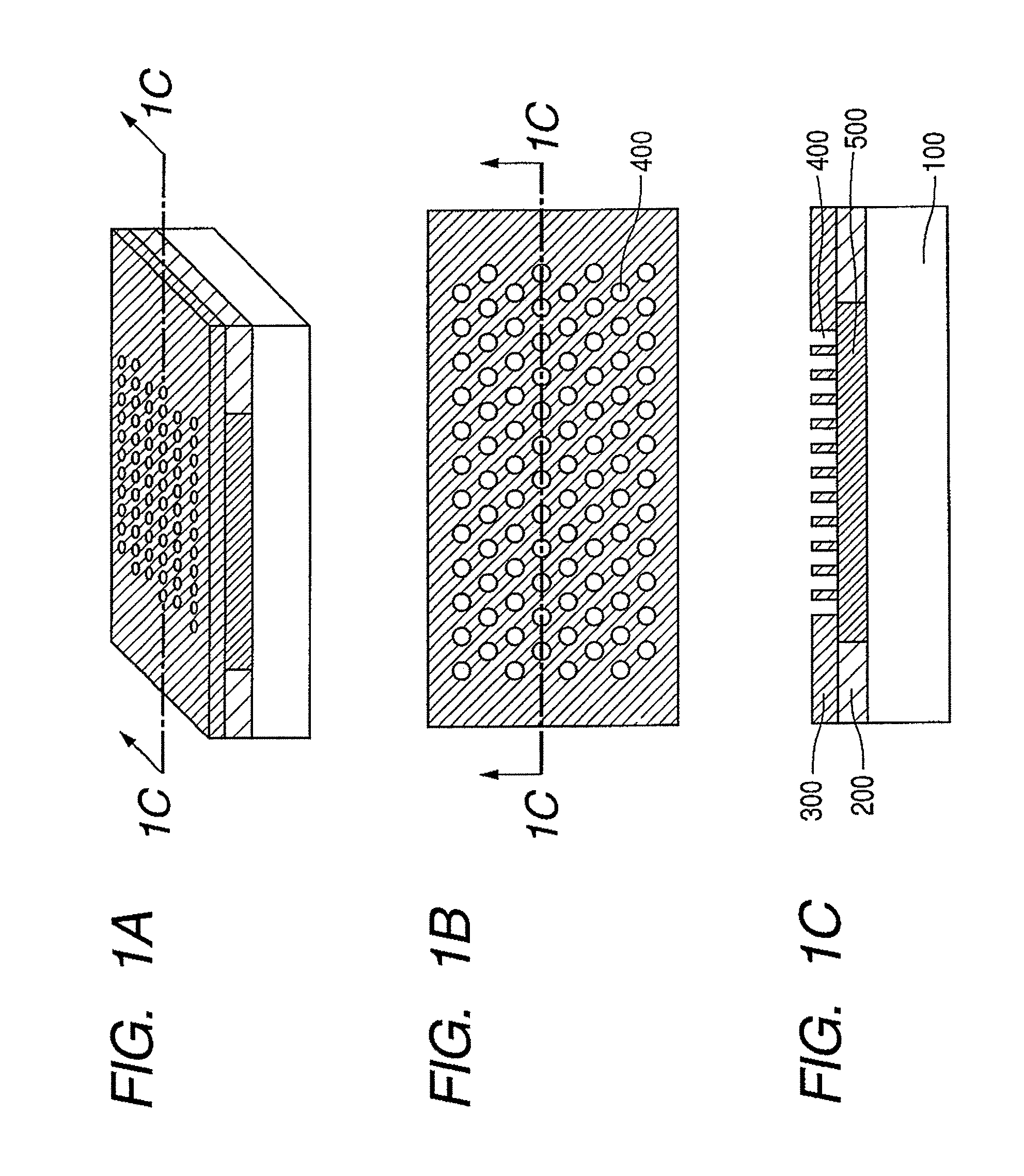
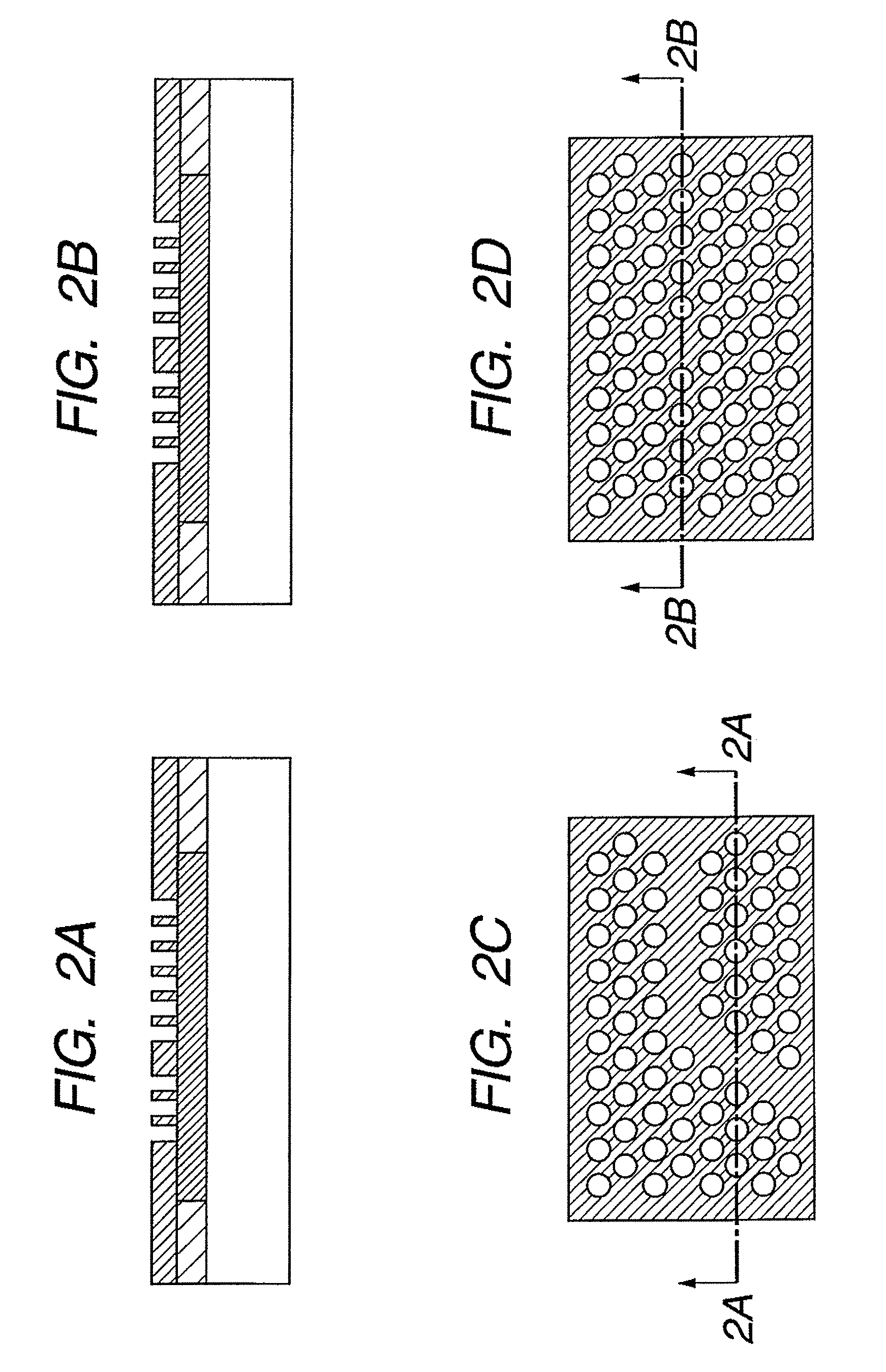
The present invention provides an optical element which can reliably acquire a difference of refractive indices between a member under a photonic crystal layer and the crystal layer without using such a stacking technique as in conventional processes; a method for manufacturing the optical element; and a semiconductor laser device with the use of the optical element. The optical element has the first layer 500 and the second layer 400 formed on a substrate 100, wherein the second layer includes pores and has a refractive-index periodically changing structure in which a refractive index periodically changes in an in-plane direction; and the first layer has an oxidized region with a lower refractive index than the refractive index of the second layer, in a lower side of the pores of the second layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical element, method for manufacturing optical element and semiconductor laser device using the optical element
InactiveUS7539226B2Increase the refractive index differenceReliable acquisitionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsIn planePhotonic crystal
The present invention provides an optical element which can reliably acquire a difference of refractive indices between a member under a photonic crystal layer and the crystal layer without using such a stacking technique as in conventional processes; a method for manufacturing the optical element; and a semiconductor laser device with the use of the optical element. The optical element has the first layer 500 and the second layer 400 formed on a substrate 100, wherein the second layer includes pores and has a refractive-index periodically changing structure in which a refractive index periodically changes in an in-plane direction; and the first layer has an oxidized region with a lower refractive index than the refractive index of the second layer, in a lower side of the pores of the second layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Multi-layer stretched film
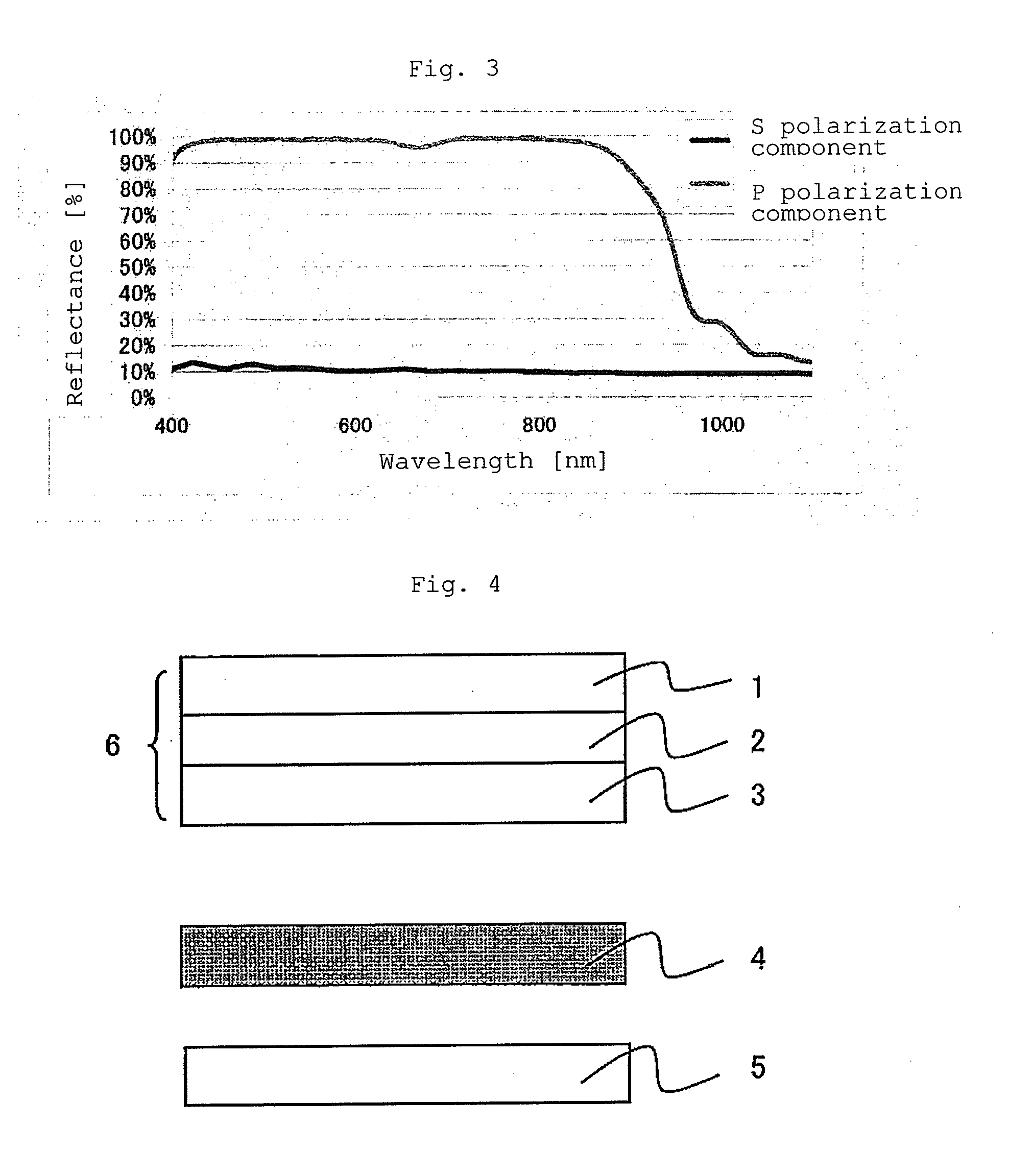
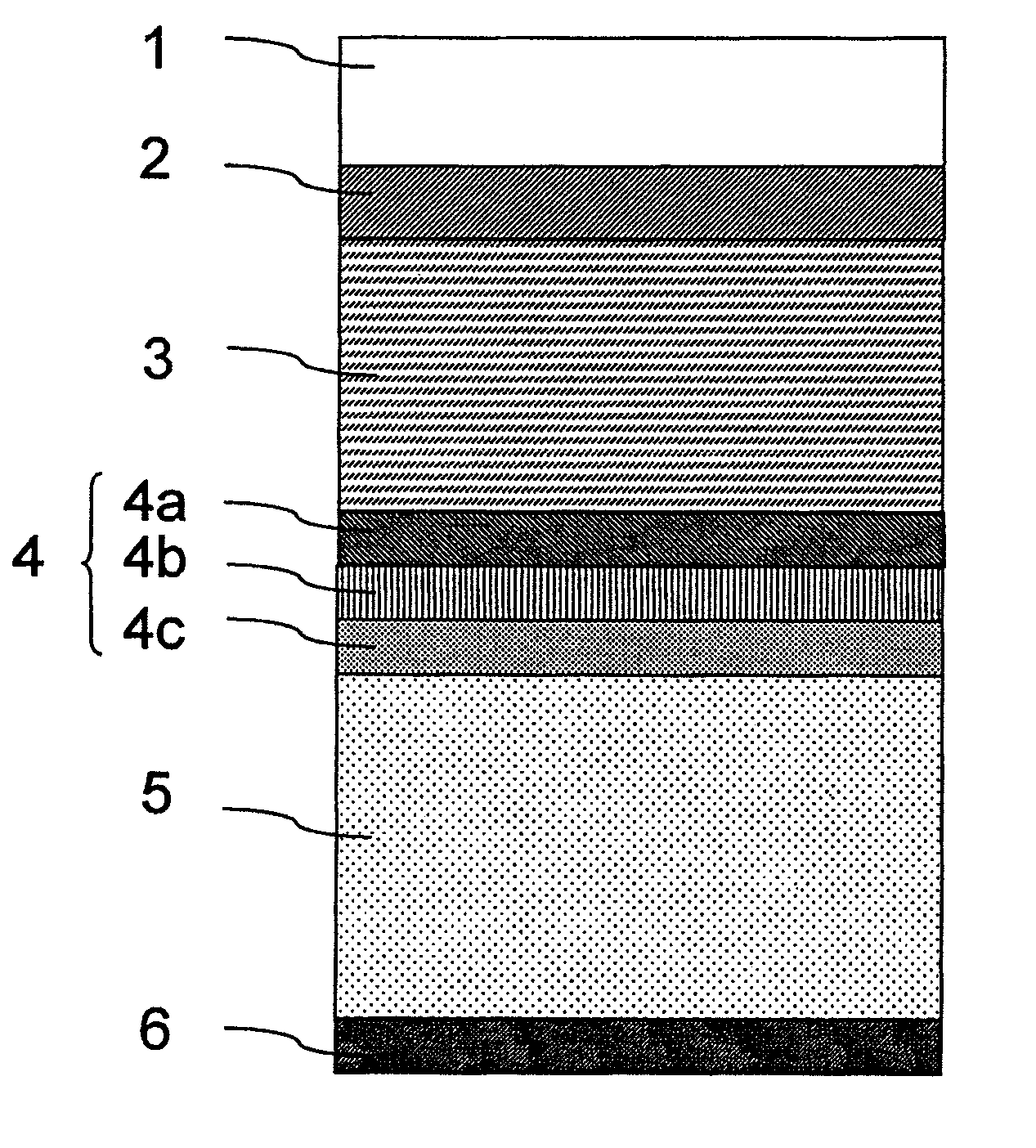
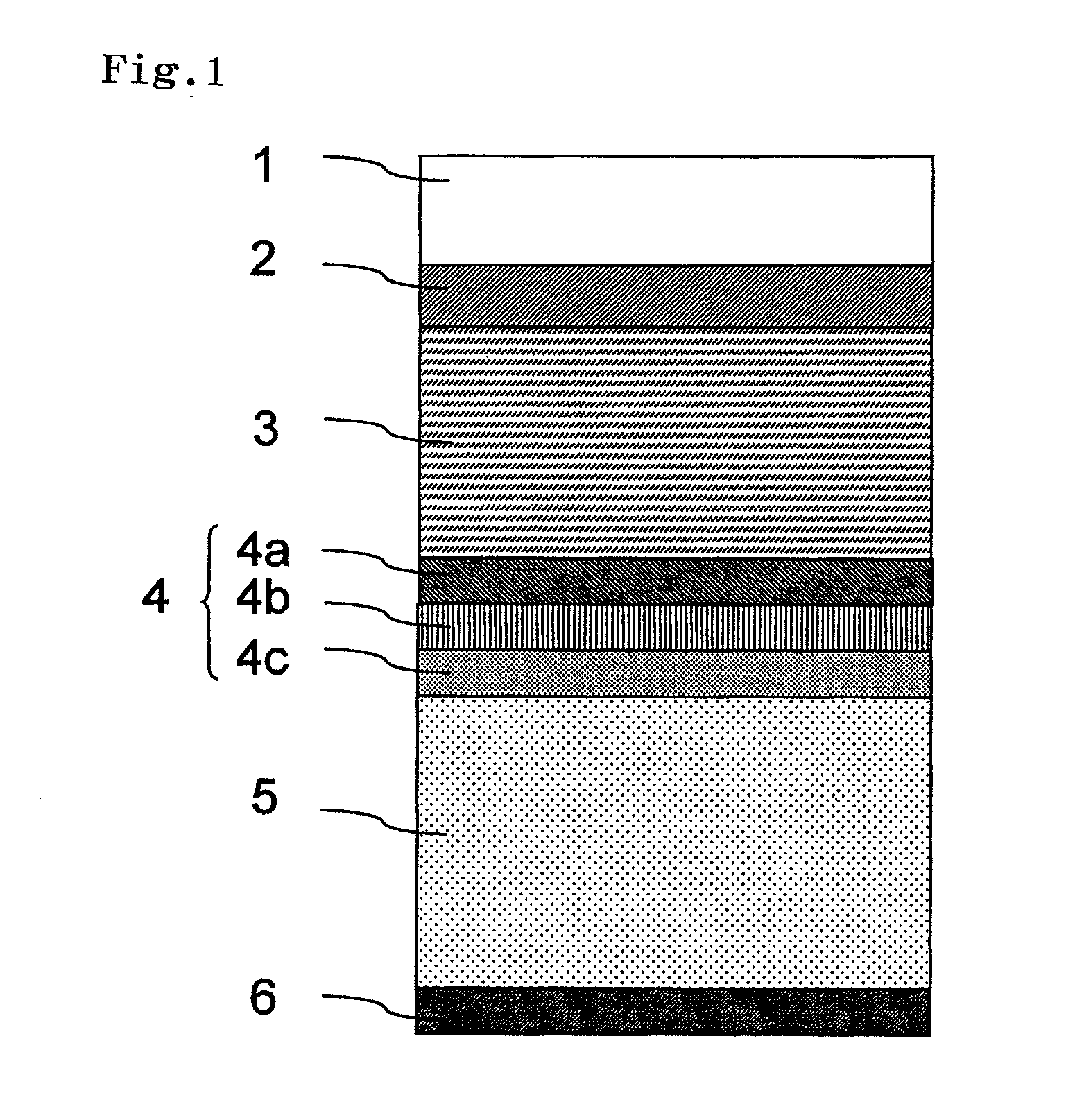
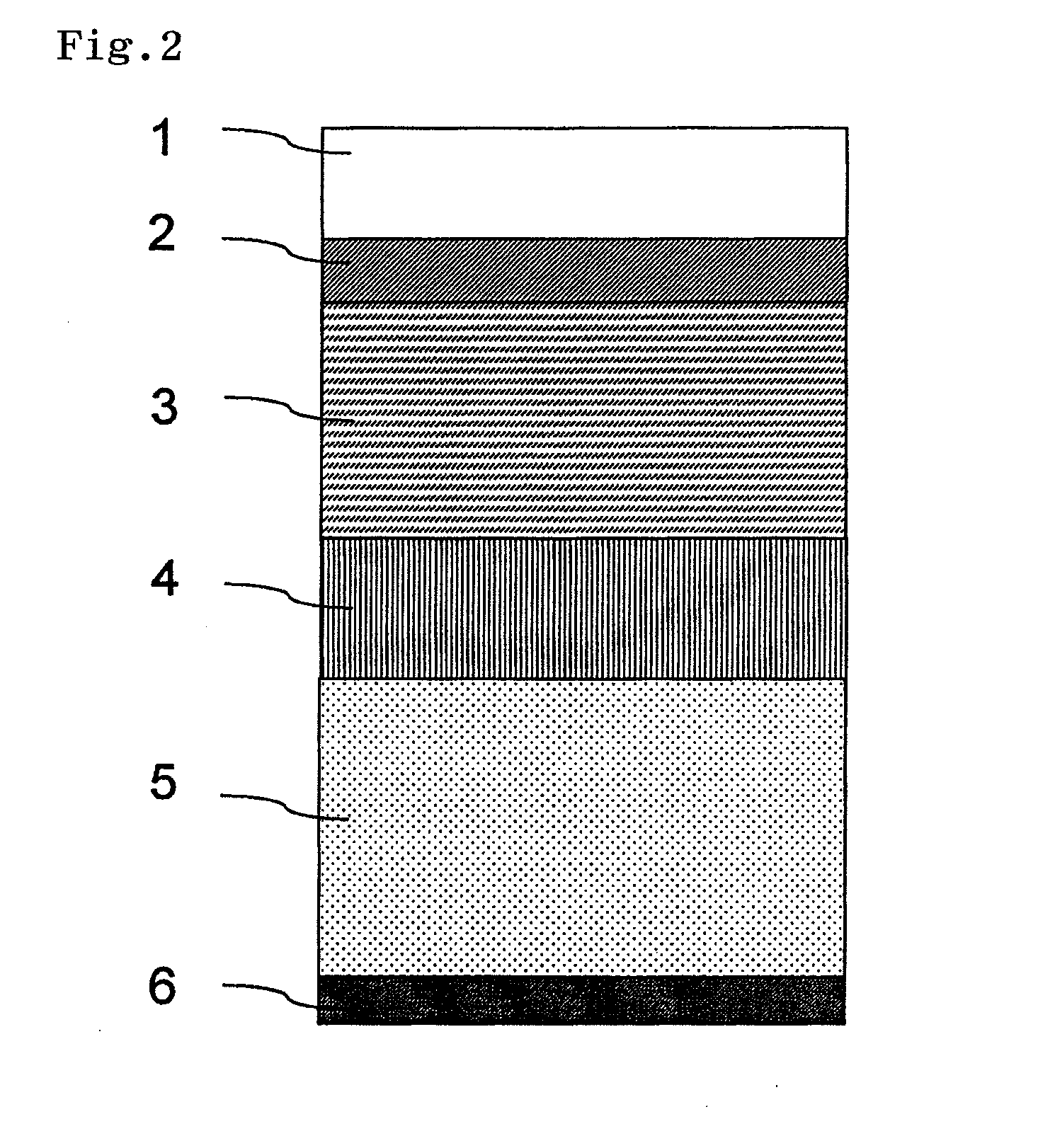
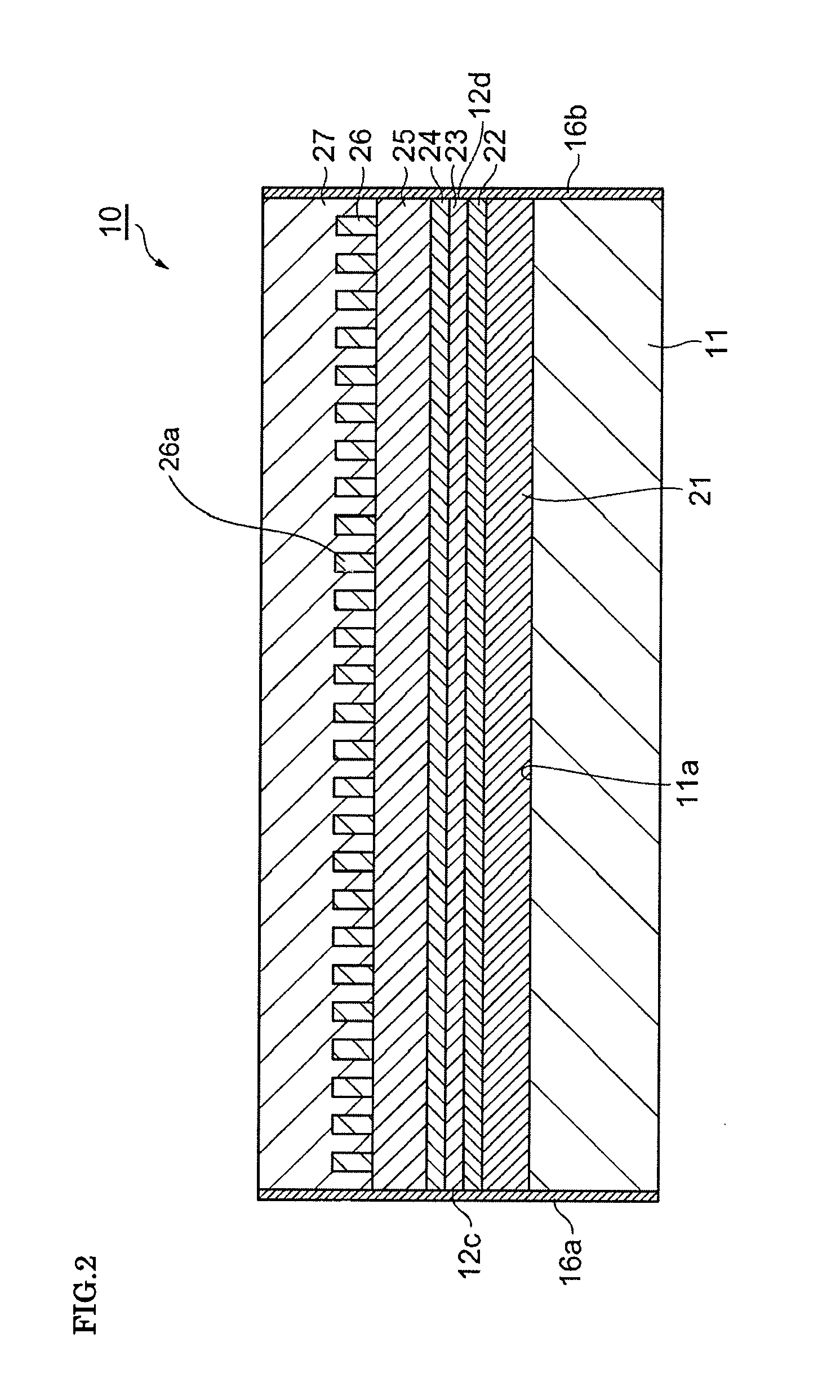
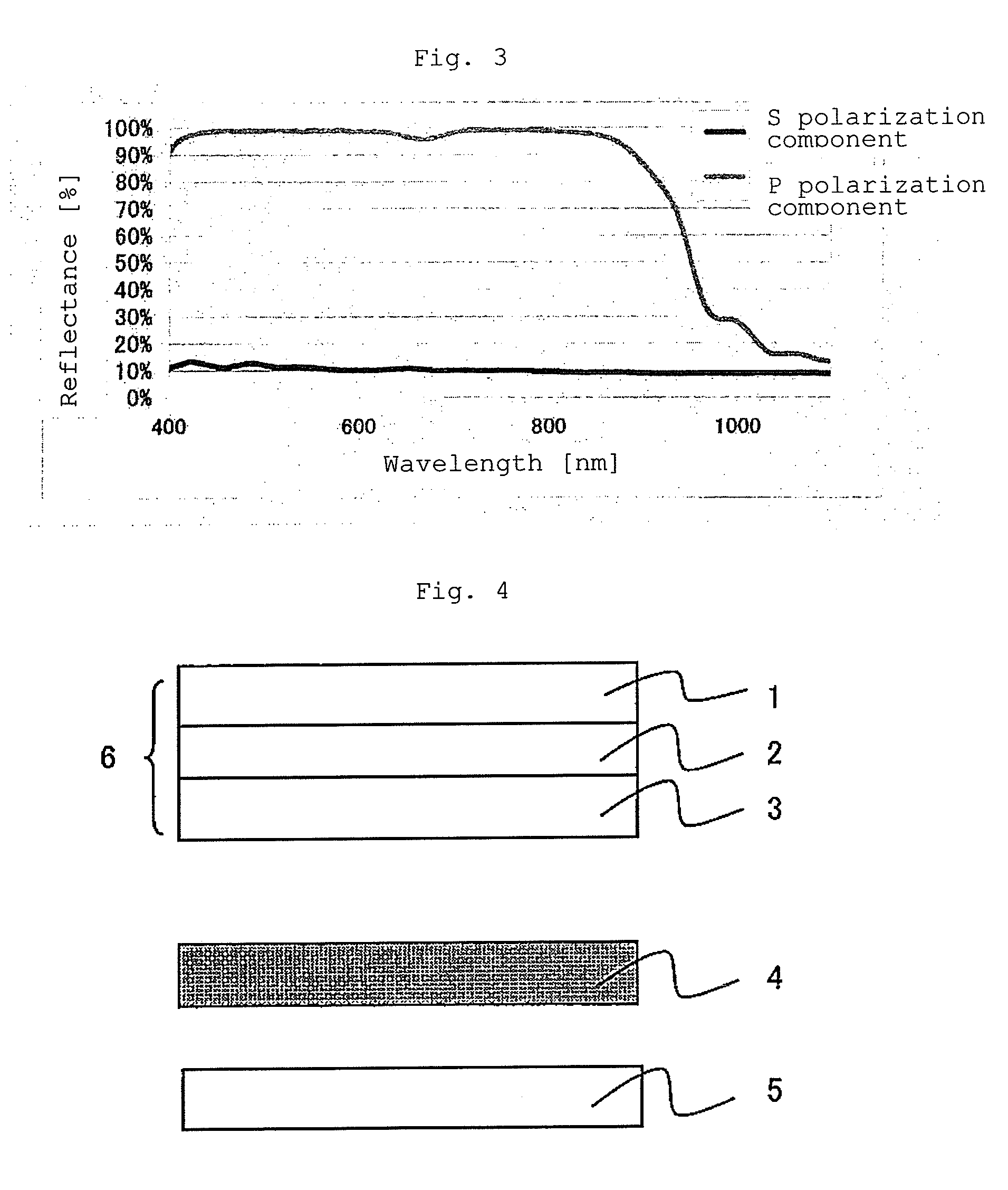
ActiveUS20120249935A1Improve polarization performanceRefractive index differenceSynthetic resin layered productsPolarising elementsPolyesterPolymer science
A multi-layer stretched film has 251 or more alternating layers which consist of first layers and second layers, wherein the first layers are made of a polyester which contains (i) 5 to 50 mol % of a naphthoic acid component as a dicarboxylic acid component and (ii) a diol having an alkylene group with 2 to 10 carbon atoms as a diol component; and the second layers are made of a thermoplastic resin having an average refractive index of 1.50 to 1.60 and differences in refractive index among a uniaxial stretching direction, a direction orthogonal to the uniaxial stretching direction and a film thickness direction of 0.05 or less before and after stretching, and the film has specific reflectance characteristics for a P polarization component and an S polarization component.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Thin-film photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20100243058A1Interface bonding is goodImprove propertiesPV power plantsFinal product manufactureCarbon layerElectrical resistance and conductance
This invention intends to develop a technique for forming an interlayer with excellent optical characteristics and to provide a photoelectric conversion device having high conversion efficiency. To realize this purpose, a series connection through an intermediate layer is formed in the thin-film photoelectric conversion device of the invention, and the interlayer is a transparent oxide layer in its front surface and n pairs of layers stacked therebehind (n is an integer of 1 or more), wherein each of the pair of layers is a carbon layer and a transparent oxide layer stacked in this order. Film thicknesses of each layer are optimized to improve wavelength selectivity and stress resistance while keeping the series resistance.An embodiment of the photoelectric conversion device is characterized in that; a transparent insulating substrate is located on the light incidence side, and a transparent conductive layer, at least one photoelectric conversion unit, a transparent electrode layer having electrical conductivity as typified by zinc oxide, a hard carbon layer having electrical conductivity as typified by diamond-like carbon, and a high reflecting electrode layer are stacked in this order on an opposite surface from a light incidence side of the transparent insulating substrate.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
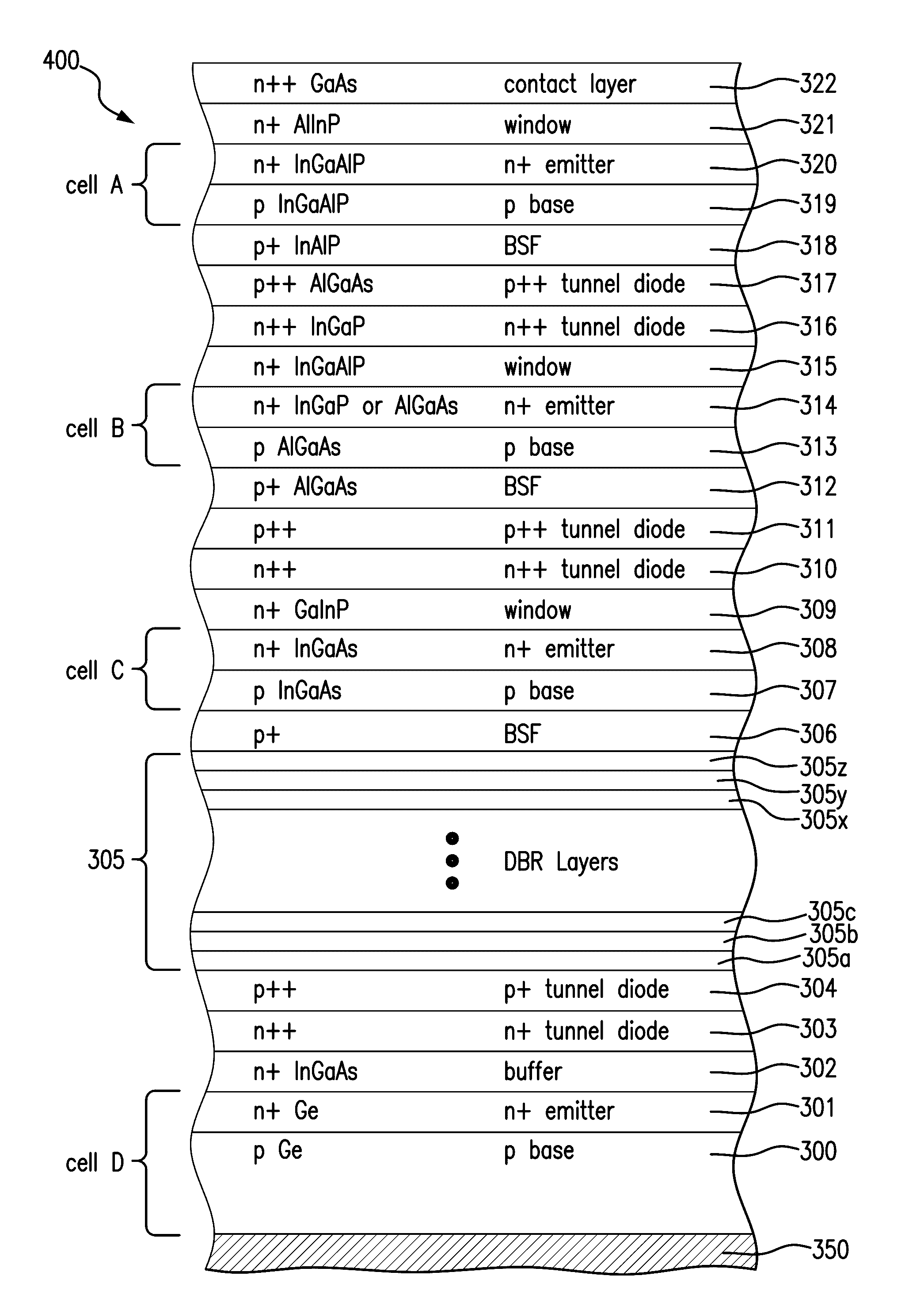
Distributed bragg reflector structures in multijunction solar cells
InactiveUS20200251603A1Photo-conversion efficiency can be improvedRefractive index differenceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsDistributed Bragg reflector
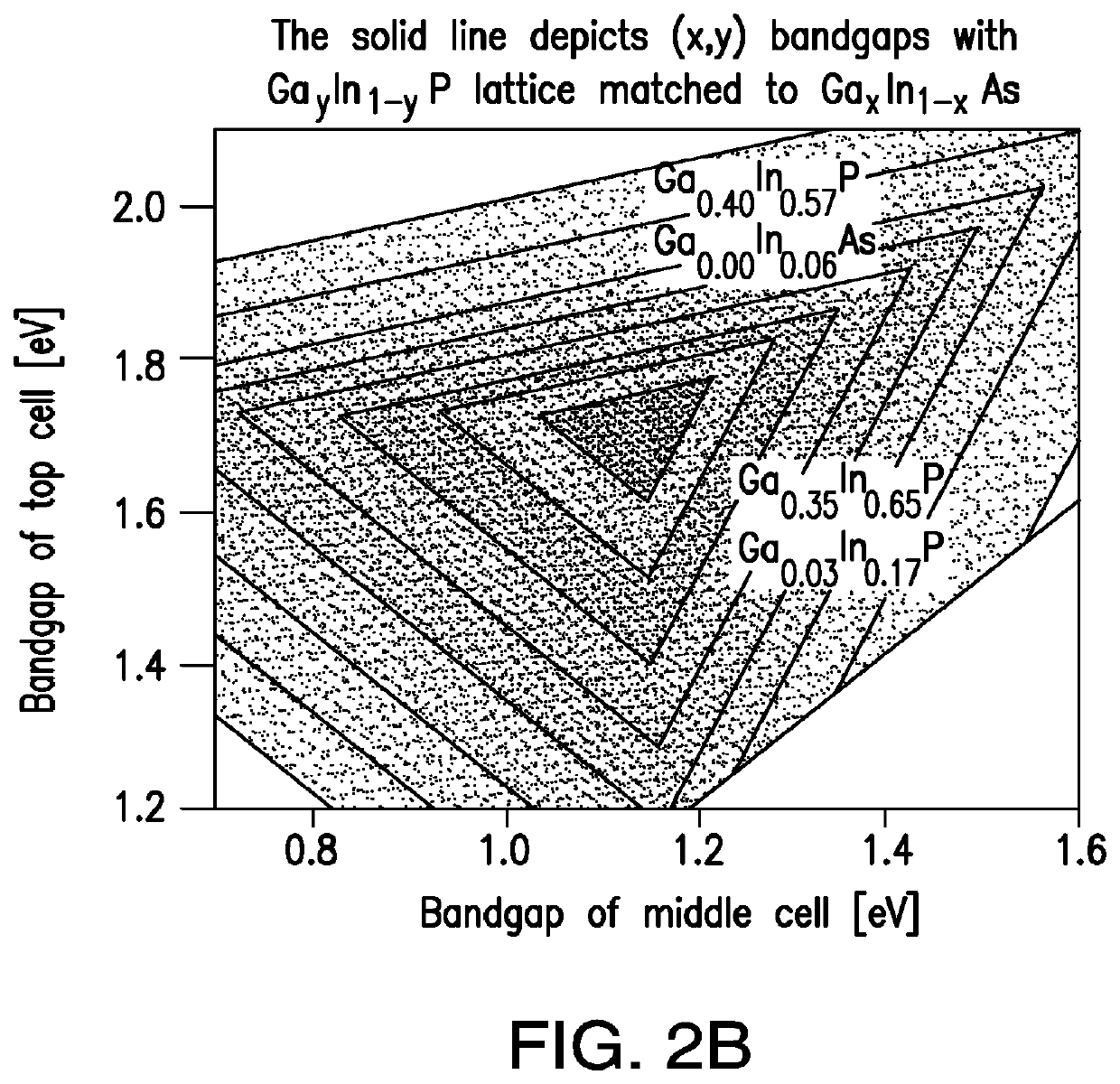
A multijunction solar cell and its method of fabrication, having an upper first solar subcell composed of a semiconductor material including aluminum and having a first band gap; a second solar subcell adjacent to said first solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a second band gap smaller than the first band gap and being lattice matched with the upper first solar subcell; a third solar subcell adjacent to said second solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a third band gap smaller than the second band gap and being lattice matched with the second solar subcell; a first and second DBR structure adjacent to the third solar subcell; and a fourth solar subcell adjacent to the DBR structures and lattice matched with said third solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a fourth band gap smaller than the third band gap; wherein the fourth subcell has a direct bandgap of greater than 0.75 eV.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Lens array substrate, electro-optical apparatus and electronic equipment
InactiveUS20160018568A1Avoid reflectionsEasy to controlMountingsNon-linear opticsRefractive indexElectron
When it comes to configuring the lens array substrate on which a multistage lens array is formed, a first concavity which is formed of the concave surface is formed on a first surface which is formed of a substrate surface of one of several translucent substrates. In addition, on the substrate surface of one of the translucent substrates, a first lens layer, a first translucent layer, a second lens layer, a second translucent layer, a translucent protective layer, and a common electrode are stacked in order. The first translucent layer has the same refractive index as that of the first lens layer and the second lens layer. In addition, a refractive index of the protective layer is within a range between the refractive index of the second translucent layer and the refractive index of the common electrode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
MULTIJUNCTION SOLAR CELLS ON BULK GeSi SUBSTRATE
ActiveUS20180226528A1Improve energy conversion efficiencyIncrease the open circuit voltageFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSolar cellGermanium
A solar cell comprising a bulk germanium silicon growth substrate; a diffused photoactive junction in the germanium silicon substrate; and a sequence of subcells grown over the substrate, with the first grown subcell either being lattice matched or lattice mis-matched to the growth substrate.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Light diffusing element, polarizing plate with light diffusing element, liquid crystal display apparatus using both, and manufacturing method for light diffusing element
ActiveUS8405794B2Increase valueImprove diffusivityDiffusing elementsProjectorsLiquid-crystal displayRefractive index
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
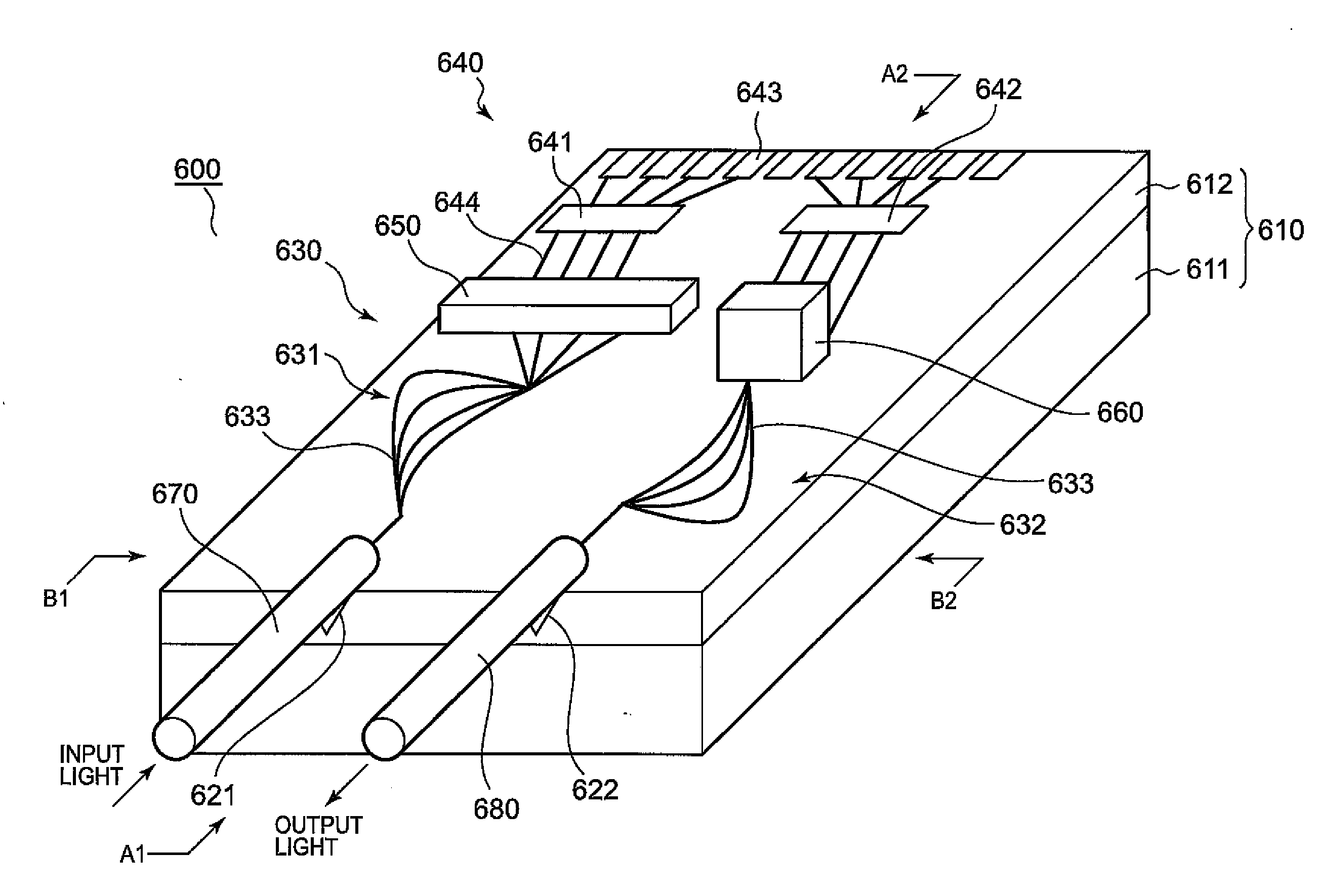
Manufacturing method for an optical waveguide and optical waveguide body used therefor
InactiveUS20120195562A1Improve cutting accuracyIncrease awarenessOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesVisibilityElectrical conductor
Provided is a manufacturing method for an optical waveguide in which, when the optical waveguide is cut and a contour thereof is processed, accuracy of a cut position is improved by improving visibility of an alignment mark. An undercladding layer, cores, and alignment marks are formed on a front surface of a substrate. Then, an overcladding layer is formed using a photomask so as to cover the cores with the alignment marks being exposed. After the substrate is separated to manufacture an optical waveguide body, a cut position is located with reference to the alignment marks from a rear surface side of the undercladding layer, and the undercladding layer and the overcladding layer are cut to manufacture the optical waveguide.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Organic light emitting display devices and methods of manufacturing organic light emitting display devices
ActiveUS9620613B2Sufficient capacitanceIncrease the areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120228661A1Wide viewing angleImprove the display effectSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsPower semiconductor deviceRefractive index
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20120020377A1Reduce variationWavelength chirping can be suppressedOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical couplingWaveguide
A semiconductor laser device includes a lower cladding layer; an active layer disposed on the lower cladding layer; all upper cladding layer disposed on the active layer; a diffraction-grating layer disposed on the upper cladding layer, the diffraction-grating layer including periodic projections and recesses; and a buried layer disposed on the periodic projections and recesses in the diffraction-grating layer. In addition, the diffraction-grating layer and the buried layer constitute a diffraction grating. The lower cladding layer, the active layer, and the upper cladding layer constitute a first optical waveguide, the active layer constituting a first core region in the first optical waveguide. The upper cladding layer, the diffraction-grating layer, and the buried layer constitute a second optical waveguide, the diffraction-grating layer constituting a second core region in the second optical waveguide. Furthermore, the first optical waveguide and the second optical waveguide are optically coupled through the upper cladding layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Multi-layer stretched film
ActiveUS8703252B2Elimination of shiftImprove performanceLiquid crystal compositionsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterPolymer science
A multi-layer stretched film has 251 or more alternating layers which consist of first layers and second layers, wherein the first layers are made of a polyester which contains (i) 5 to 50 mol % of a naphthoic acid component as a dicarboxylic acid component and (ii) a diol having an alkylene group with 2 to 10 carbon atoms as a diol component; and the second layers are made of a thermoplastic resin having an average refractive index of 1.50 to 1.60 and differences in refractive index among a uniaxial stretching direction, a direction orthogonal to the uniaxial stretching direction and a film thickness direction of 0.05 or less before and after stretching, and the film has specific reflectance characteristics for a P polarization component and an S polarization component.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Structure and Manufacturing Method of the Same
InactiveUS20090122407A1Refractive index differenceHigh refractive indexEnvelopes/bags making machineryPrismsRefractive indexPulsed laser beam
The present invention may provide a structure capable of obtaining a higher difference in refractive indices between that of a transparent material and that of a cavity, than in the past, and a manufacturing method thereof, and the present invention provides a structure having a transparent material and an internal cavity which is formed by irradiating said transparent material with a pulse laser beam having a pulse width of 10×10−12 seconds or less, and wherein refractive index of said transparent material at d line is nd≧1.3
Owner:OHARA +1
Optical waveguide
ActiveUS20190025504A1Improve reliabilityAvoid light decayCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesWaveguide
The present disclosure provides an optical waveguide capable of enhancing the suppression of crosstalk. This optical waveguide includes: under claddings; cores for light propagation arranged in side-by-side relation on surfaces of the respective under claddings; over claddings covering the cores; and a light absorbing part provided between adjacent ones of the cores and adjacent to light exit member connecting portions for connection to light exit members, the light exit member connecting portions being disposed in first end portions of the adjacent cores, the light absorbing part being in non-contacting relationship with the cores. The light absorbing part contains a light absorbing agent having an ability to absorb light exiting the light exit members. The optical waveguide is produced on a surface of a substrate.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Conductive anti-reflection film
InactiveUS6157125AQuality improvementLow costCathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersTransmittanceElectric field
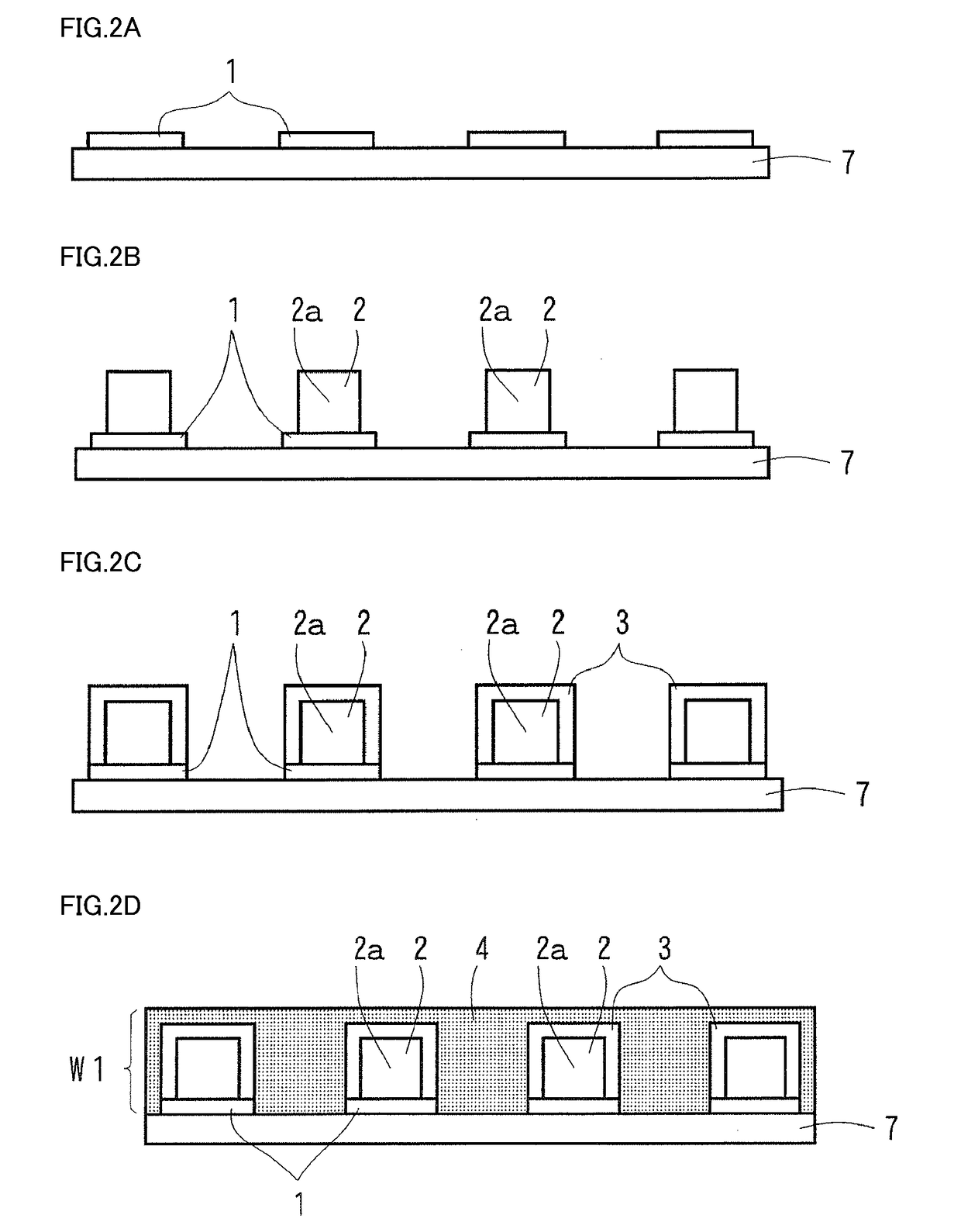
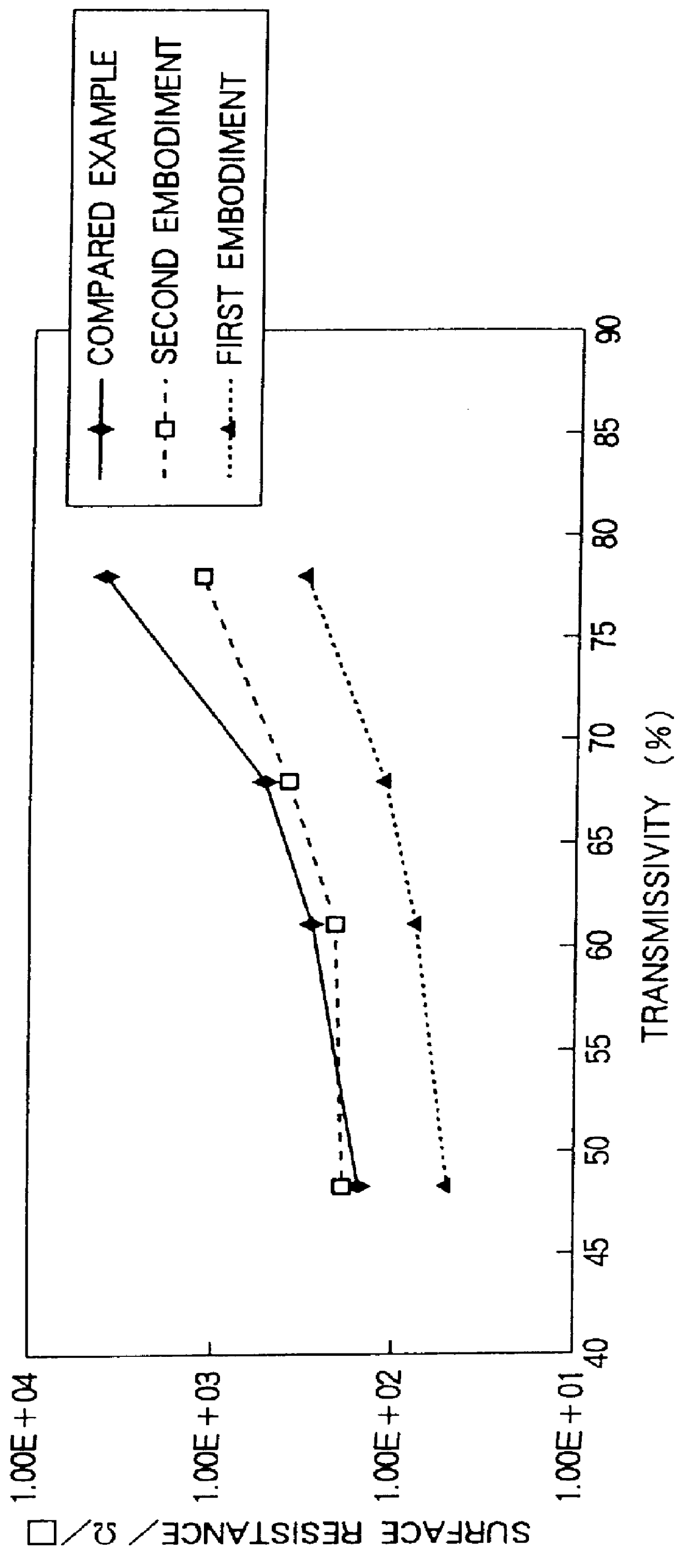
A second film that contains a substance that secures the conductivity of conductive particles is formed on a first film that contains the conductive particles. The first film and the second film are sintered at the same time. Thus, a conductive anti-reflection film having a sufficiently low surface resistance with a sufficient transmissivity for a high transparency can be obtained with high cost performance. When the conductive anti-reflection film is used for a cathode ray tube, it can almost prevent the AEF (Alternating Electric Field), display a picture in high quality, and be excellent in cost performance.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Manufacturing method of photonic crystal
InactiveUS20090169735A1Superior photonic bandgapImproved photonic crystal propertyNanoopticsSpecial surfacesPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
A manufacturing method of a photonic crystal is provided. In the method, a high-refractive-index material is conformally deposited on an exposed portion of a periodic template composed of a low-refractive-index material by an atomic layer deposition process so that a difference in refractive indices or dielectric constants between the template and adjacent air becomes greater, which makes it possible to form a three-dimensional photonic crystal having a superior photonic bandgap. Herein, the three-dimensional structure may be prepared by a layer-by-layer method.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Nitride semiconductor optical element and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8124432B2Composition variation regions in both interfaces of the well layer are reducedSimple interfaceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIndiumHydrogen
In an InGaN-based nitride semiconductor optical device having a long wavelength (440 nm or more) equal to or more than that of blue, the increase of a wavelength is realized while suppressing In (Indium) segregation and deterioration of crystallinity. In the manufacture of an InGaN-based nitride semiconductor optical device having an InGaN-based quantum well active layer including an InGaN well layer and an InGaN barrier layer, a step of growing the InGaN barrier layer includes: a first step of adding hydrogen at 1% or more to a gas atmosphere composed of nitrogen and ammonia and growing a GaN layer in the gas atmosphere; and a second step of growing the InGaN barrier layer in a gas atmosphere composed of nitrogen and ammonia.
Owner:USHIO OPTO SEMICON
Metamorphic solar cells
ActiveUS20200259039A1Current to decreaseLow power outputFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLattice mismatchBand gap
A multijunction solar cell including a metamorphic layer, and particularly the design and specification of the composition, lattice constant, and band gaps of various layers above the metamorphic layer in order to achieve reduction in “bowing” of the semiconductor wafer caused by the lattice mismatch of layers associated with the metamorphic layer.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Distributed bragg reflector structures in multijunction solar cells
InactiveUS20200251604A1Photo-conversion efficiency can be improvedRefractive index differenceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsDistributed Bragg reflector
A multijunction solar cell and its method of fabrication, having an upper first solar subcell composed of a semiconductor material including aluminum and having a first band gap; a second solar subcell adjacent to said first solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a second band gap smaller than the first band gap and being lattice matched with the upper first solar subcell; a third solar subcell adjacent to said second solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a third band gap smaller than the second band gap and being lattice matched with the second solar subcell; a first and second DBR structure adjacent to the third solar subcell; and a fourth solar subcell adjacent to the DBR structures and lattice matched with said third solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a fourth band gap smaller than the third band gap; wherein the fourth subcell has a direct bandgap of greater than 0.75 eV.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Optical Integrated Circuit, Opto-Electronic Integrated Circuit and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20090196546A1Refractive index differenceShorten timeOptical waveguide light guideOpto electronicLight wave
In the opto-electronic integrated circuit, an optical waveguide in which a sapphire substrate for an SOS substrate is formed as a lower clad and a silicon film is formed as a core, an electronic integrated circuit formed in the silicon film, and grooves for fixing optical fibers are formed monolithically. Further, a photodiode array and a laser diode array are mounted on a hybrid basis. Since the lower clad of the optical waveguide is used as the sapphire substrate and the core is used as the silicon film, a difference in refractive index can be made large sufficiently, thus resulting in thinning of the silicon film. It is therefore possible to shorten the time required to process the core and the like. Further, since the electronic integrated circuit is formed on the sapphire substrate, the high-frequency characteristics are enhanced.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS SEMICON GK
Distributed BRAGG reflector structures in multijunction solar cells
ActiveUS10636926B1Photo-conversion efficiency can be improvedRefractive index differenceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsDistributed Bragg reflector
A multijunction solar cell and its method of fabrication, having an upper first solar subcell composed of a semiconductor material including aluminum and having a first band gap; a second solar subcell adjacent to said first solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a second band gap smaller than the first band gap and being lattice matched with the upper first solar subcell; a third solar subcell adjacent to said second solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a third band gap smaller than the second band gap and being lattice matched with the second solar subcell; a first and second DBR structure adjacent to the third solar subcell; and a fourth solar subcell adjacent to the DBR structures and lattice matched with said third solar subcell and composed of a semiconductor material having a fourth band gap smaller than the third band gap; wherein the fourth subcell has a direct bandgap of greater than 0.75 eV.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Metamorphic solar cells
ActiveUS20210408320A1Wafer “bow” has been minimizedReduce warpageFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingLattice mismatch
A multijunction solar cell including a metamorphic layer, and particularly the design and specification of the composition, lattice constant, and band gaps of various layers above the metamorphic layer in order to achieve reduction in “bowing” of the semiconductor wafer caused by the lattice mismatch of layers associated with the metamorphic layer.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com