Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
118results about How to "Reduce the number of updates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-performance reliable solid-state disk realizing method
ActiveCN103488583AImprove performanceImprove reliabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDData error
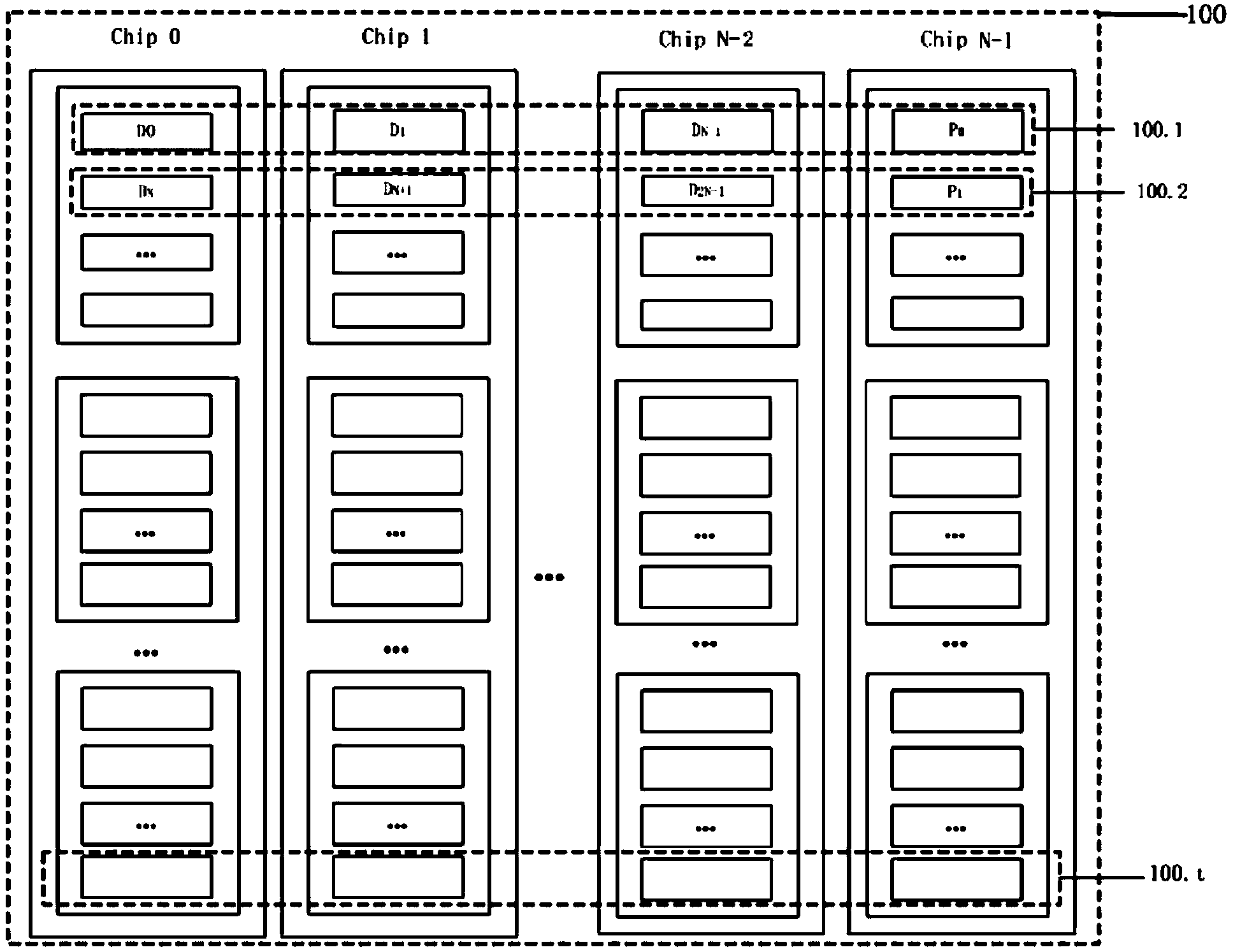
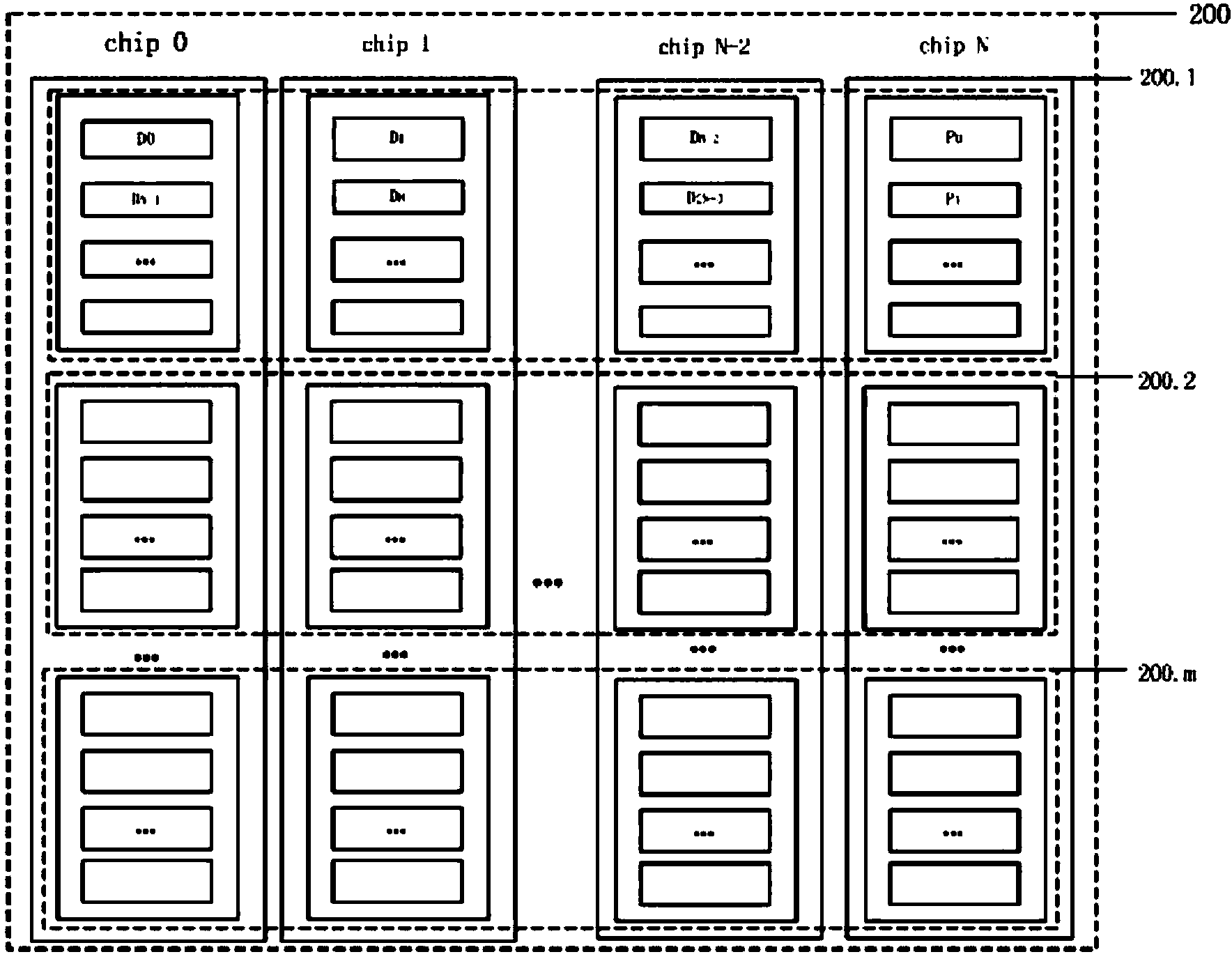
The invention provides a high-performance reliable solid-state disk realizing method. The method includes: (1), dividing all flash memory chips in a solid-state disk into groups and forming an RAID (redundant array of independent disks) 4-level flash array in each group by N successive flash chips; (2), receiving and storing data through a cache; (3), judging whether the cache is filled up or not, if yes, entering the step (4), and if not, returning to the step (2); (4), extracting N-1 data blocks from the cache and computing check values of the N-1 data blocks; making up the N-1 data blocks and the check values into filled stripe data and writing back the flash array; returning to the step (2). The flash chips in the solid-state disk are used for establishing the RAID4-level physical array to assure data reliability. Faults at different levels including page level, block level, or even chip level can be processed. Besides, writing-in performance is improved by writing of filled stripes and sequence, and spatial and performance loss resulted from data errors can be reduced to the utmost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
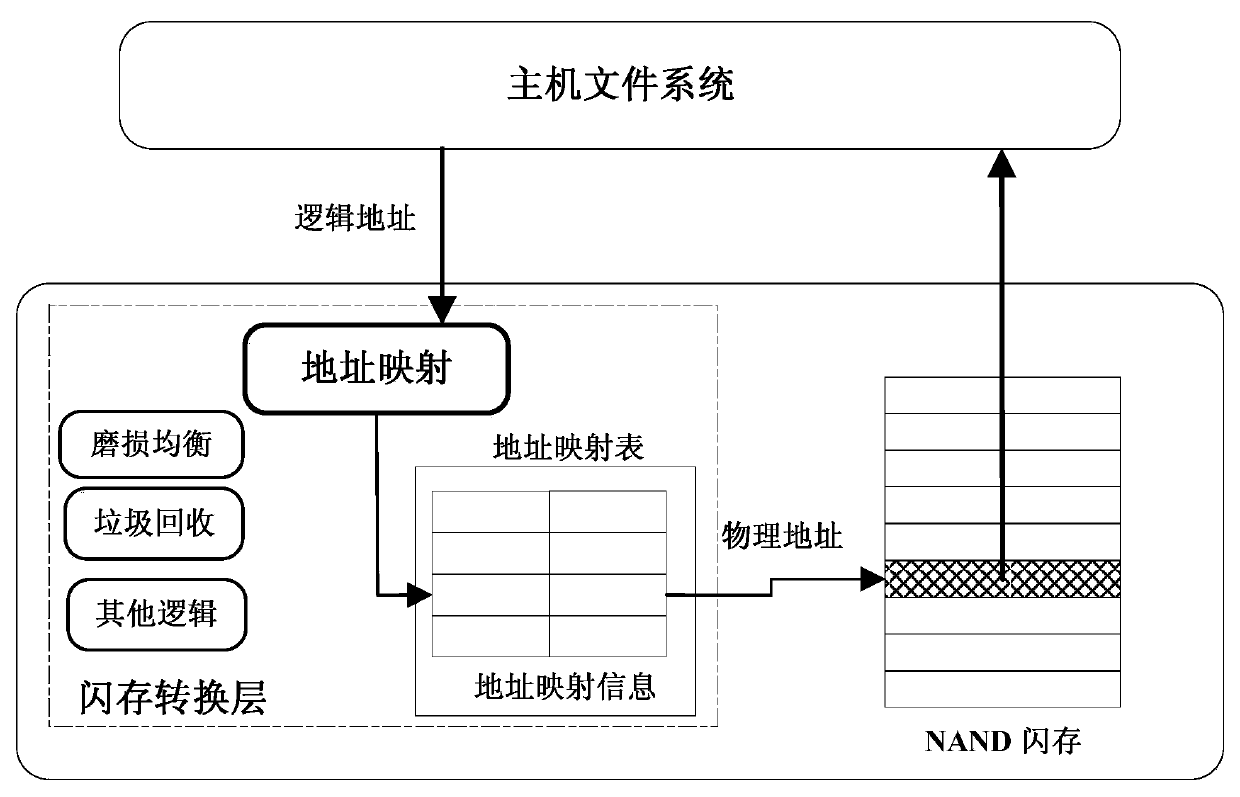
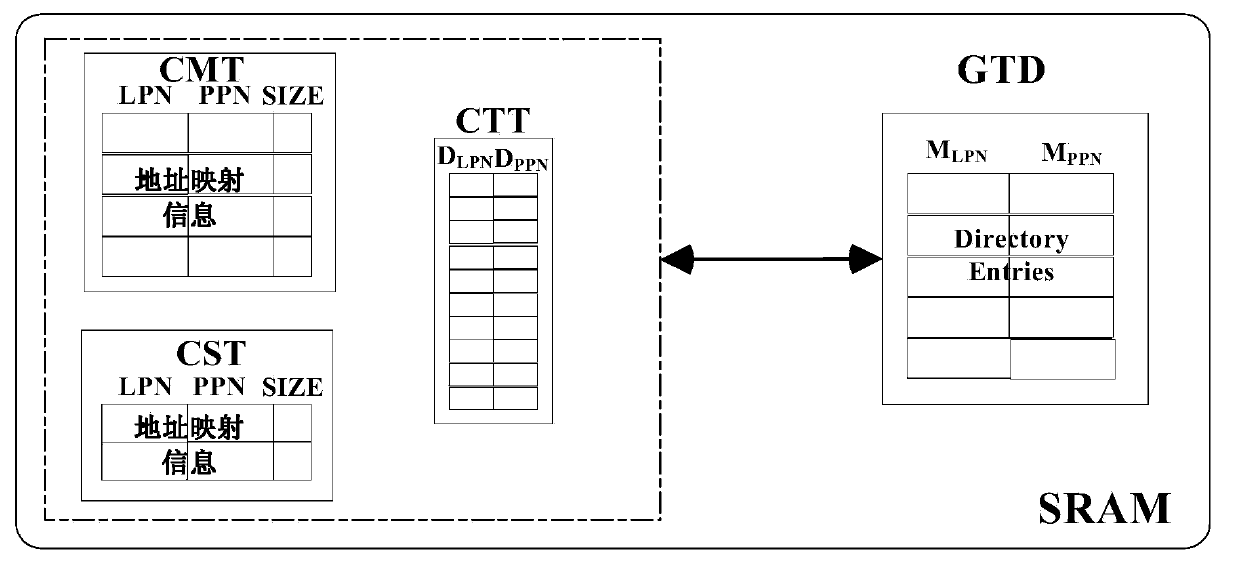
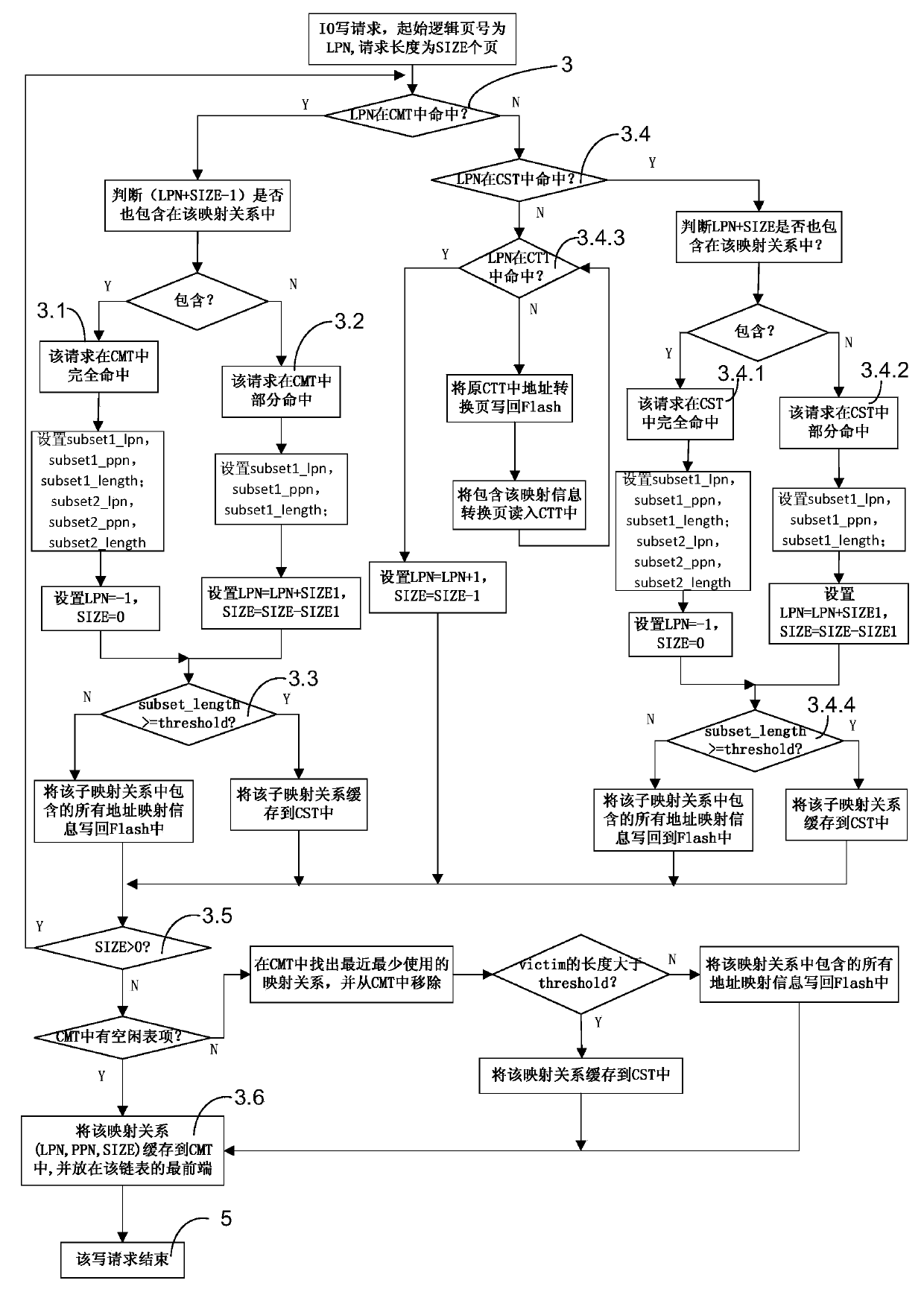
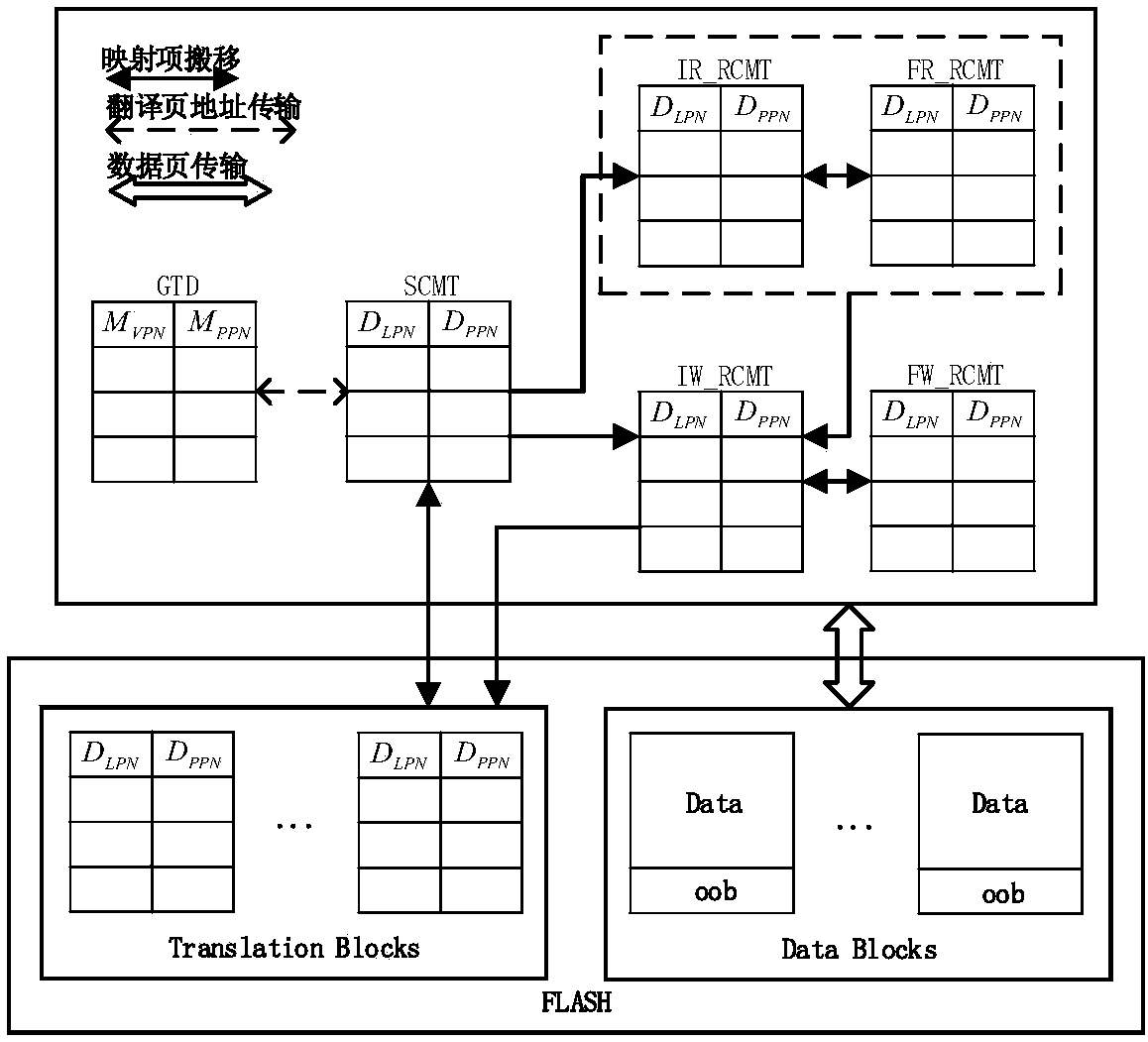
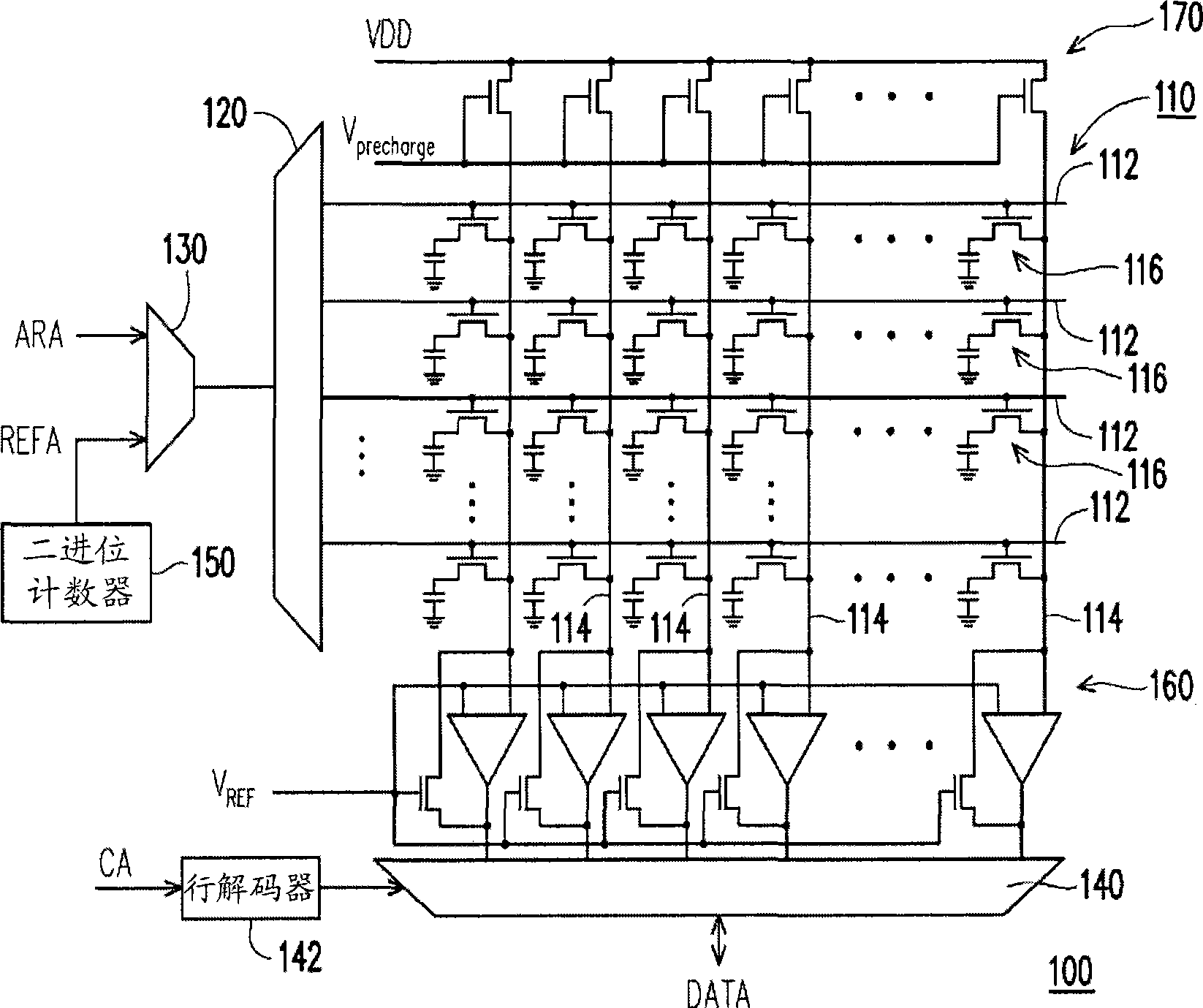
Address mapping method for flash translation layer of solid state drive
ActiveCN103425600AImprove random write performanceImprove hit rateMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic random-access memorySolid-state drive
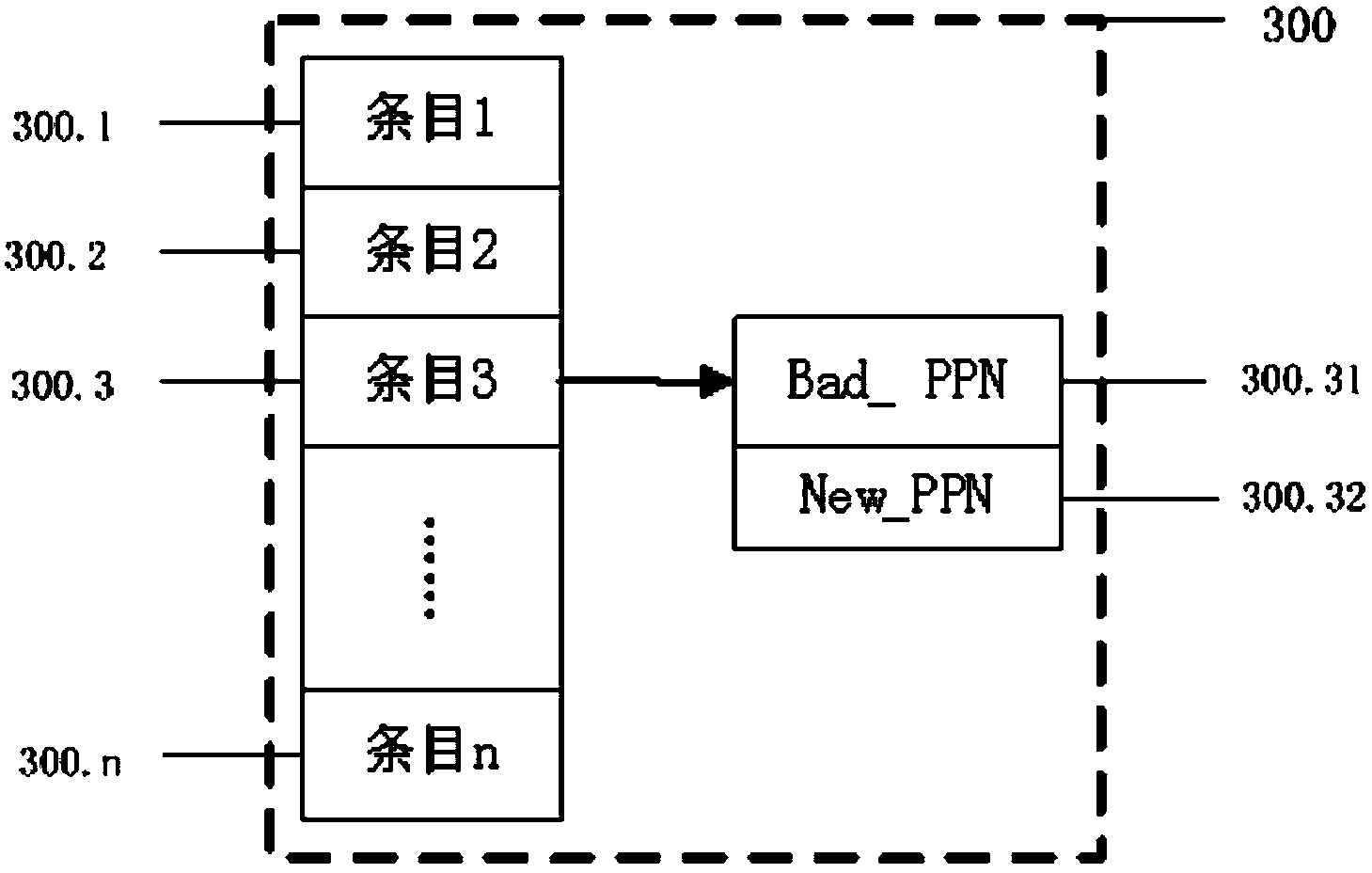
The invention discloses an address mapping method for a flash translation layer of a solid state drive. The method comprises the following steps of (1) establishing a cached mapping table, a cached split table, a cached translation table and a global translation directory in an SRAM (static random access memory) in advance; (2) receiving an IO (input / output) request, turning to a step (3) if the IO request is a write request, otherwise turning to a step (4); (3) preferentially and sequentially searching the tables in the SRAM for the hit condition of the current IO request, finishing write operation according to hit mapping information, and caching the mapping information according to a hit type and a threshold value; (4) preferentially searching the tables in the SRAM for the hit condition of the current IO request, and finishing read operation according to the hit mapping information in the SRAM. The method has the advantages that the random write performance of the solid state drive can be improved, the service life of the solid state drive can be prolonged, the efficiency of the flash translation layer is high, the hit ratio of address mapping information in the SRAM is high, and less additional read-write operation between the SRAM and the solid state drive Flash is realized.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
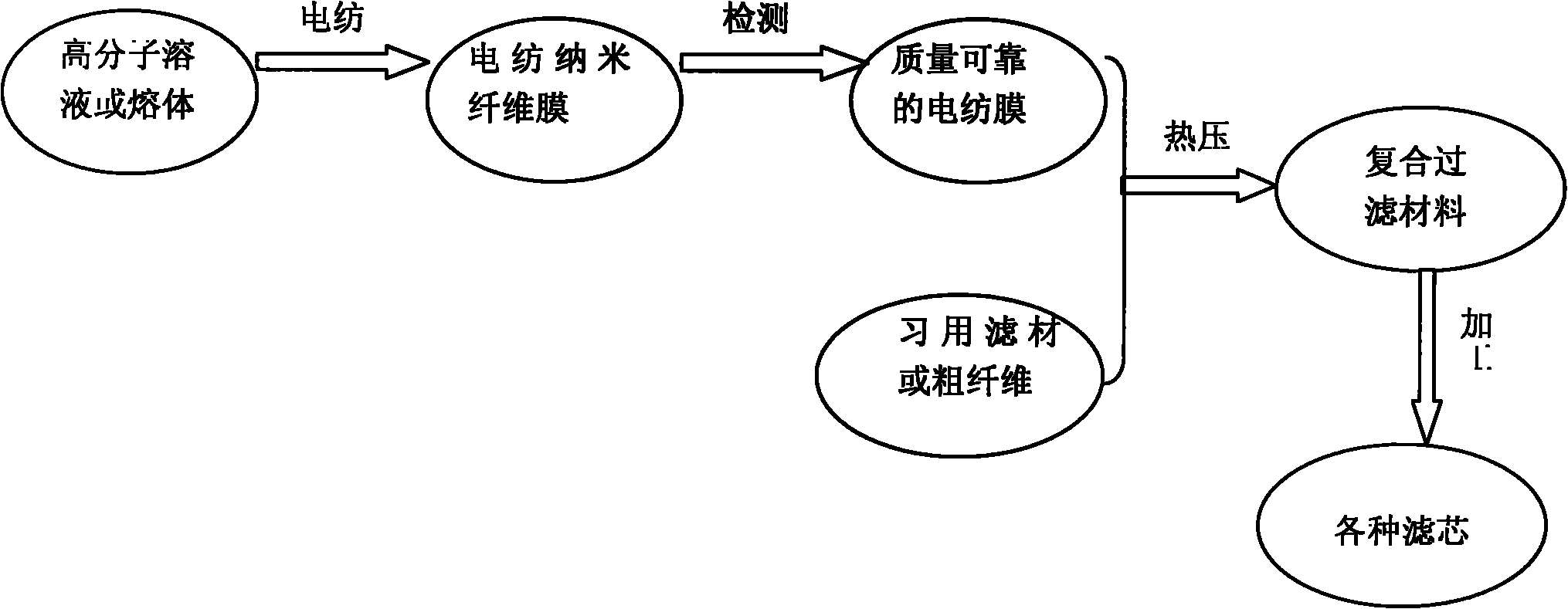
Preparation method of electric spinning-based composite nano fiber material for filters
InactiveCN101829454AExtended service lifeReduce wearLayered productsFiltration separationFiberComposite nanofibers
The invention relates to a preparation method of an electric spinning-based composite nano fiber material for filters, comprising the following steps of: preparing an electric spinning nano fiber film with reliable quality by adopting a polymer solution or a fusant through an electrostatic spinning device, and combining the electric spinning nano fiber film with a conventional filtering material to form a sandwich composite nano filtering material. Compared with the prior art, the nano fiber film with reliable quality in the invention can filter particles of 1 micrometer, and the filtering efficiency is 100%; the conventional filtering material and coarse fibers not only are used as supporting materials, but also can filter larger particles in advance, and the preparation method reduces the abrasion of the nano fiber film, prolongs the service life of the composite nano filtering material, reduces the updating time of the composite nano filtering material, and lowers filtering expenses.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF CLOTHING TECHNOLOGY
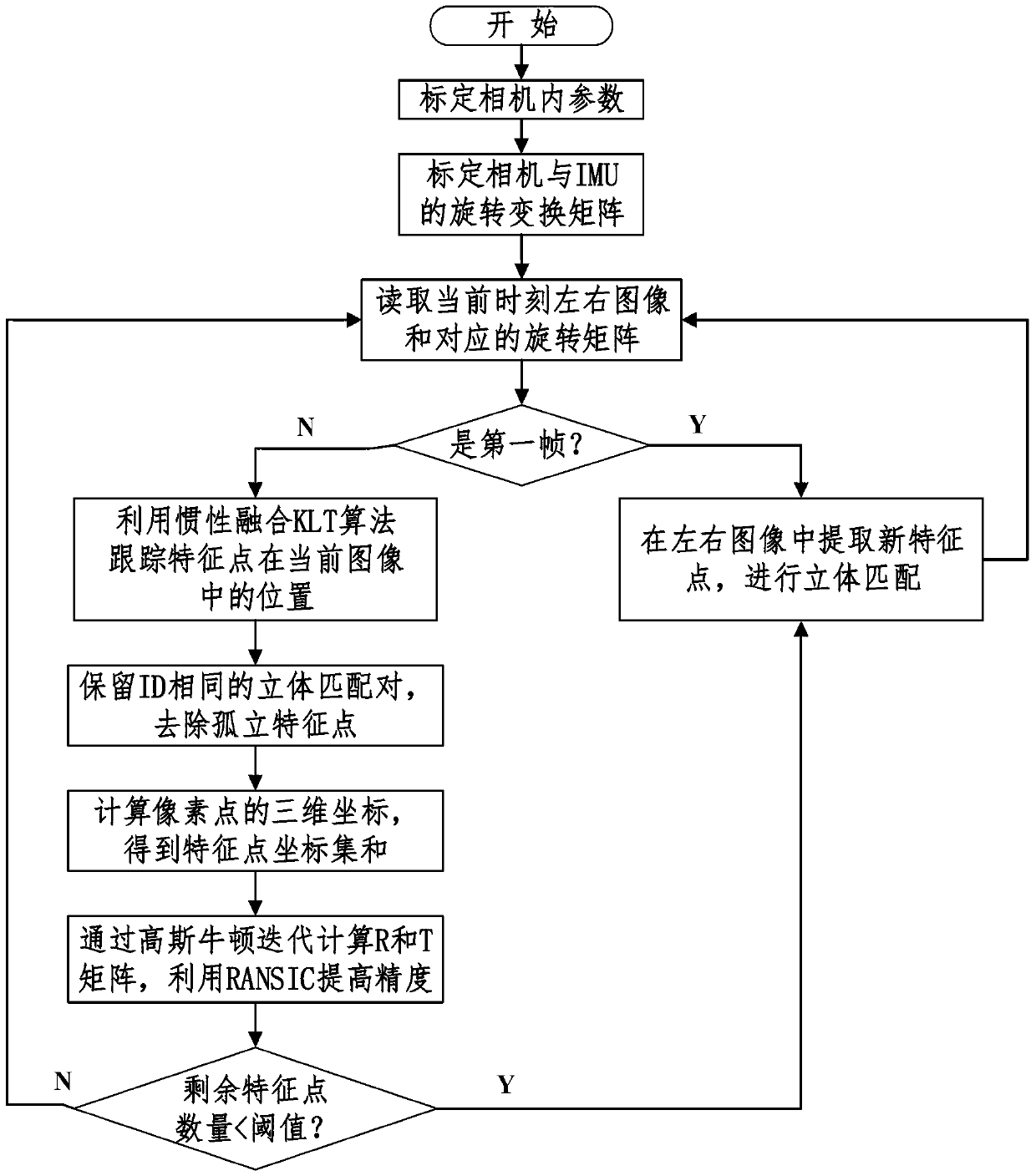
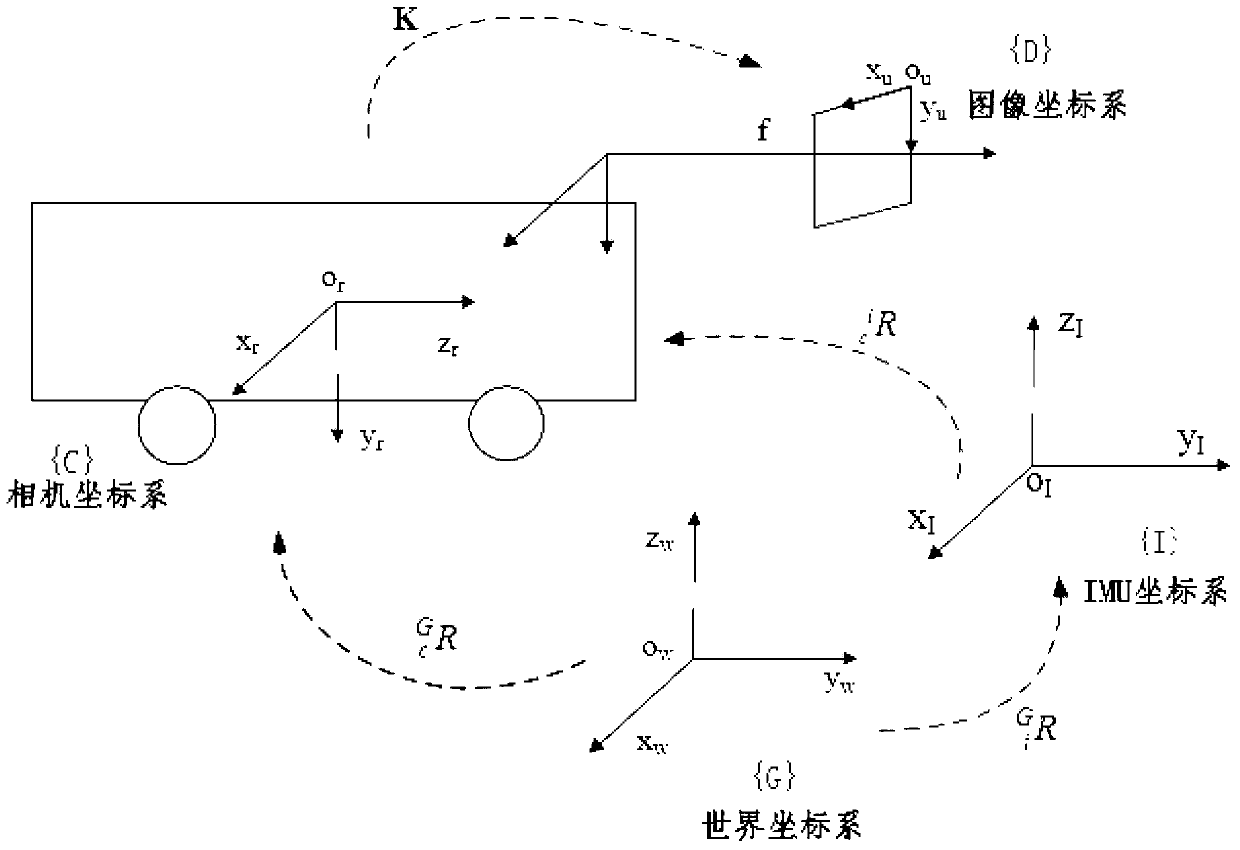
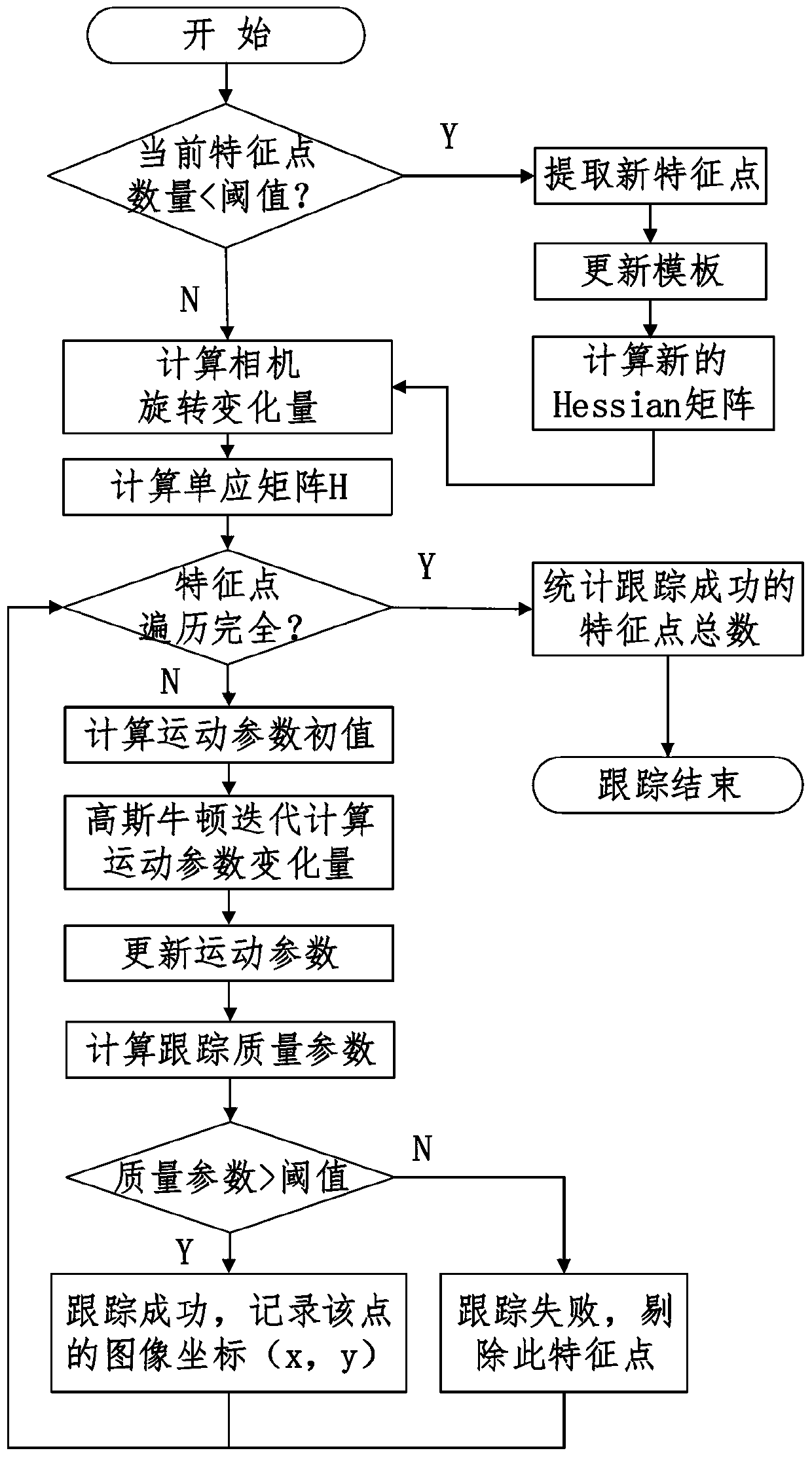
Visual positioning method based on robust feature tracking
InactiveCN103345751AImprove convergence rateImprove feature tracking performanceImage analysisFeature extraction algorithmVisual positioning
The method discloses a robust feature tracking and stereoscopic vision positioning technology based on image processing and machine vision. The technology can integrate inertial information and visual information and achieve reliable stereoscopic vision positioning under camera waggling conditions and outdoor light conditions. Images are collected through a binocular video camera in real time, and rotation information of the camera is collected with an inertial measurement unit. Feature points in the images are extracted with a feature extraction algorithm, and the feature points of the left image and the feature points of the right images are matched stereoscopically. The inertial information is combined and the inertia and the KLT algorithm are integrated to track the feature points, so that the reliability of the feature tracking is promoted. Three-dimensional information of the feature points is restored according to the double vision geometric principle. Motion parameters of the camera are obtained through position information of the feature points with the Gaussian and Newton iteration method. The accuracy of visual positioning is further promoted with the RANSIC algorithm. The whole process is iterated continuously, and thus real-time calculation of the posture and the position of the camera is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
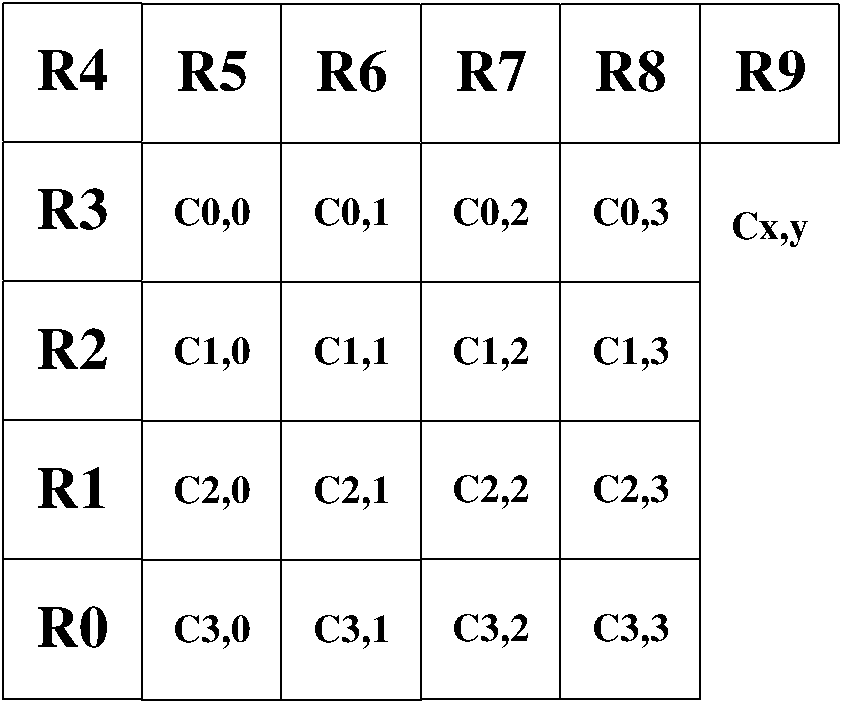
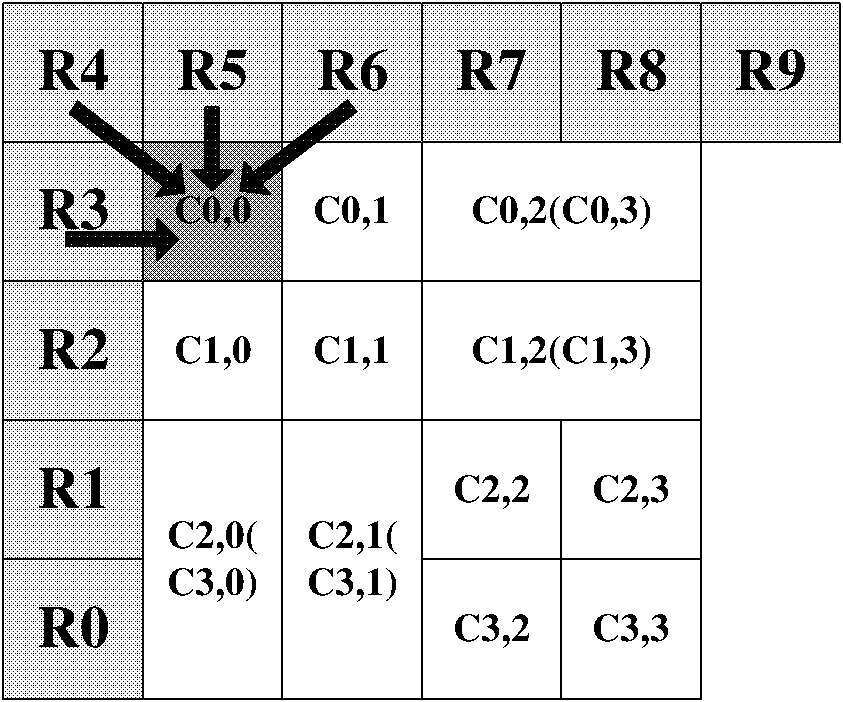
Method for processing adjacent block information in video decoding macro-block prediction and boundary filtering
InactiveCN101924938AEasy to implementSave storage spaceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationAlgorithmProcessor register
The invention relates to a method for processing adjacent block information in video decoding macro-block prediction and boundary filtering, which belongs to the technical field of video decoding. The method comprises the following steps of: storing adjacent block information by ten registers; performing subscript mapping processing on a 4*4 segmented block at an upper left corner and performing offset calculation to obtain the numbers of the registers of a left block, an upper block, a right block and an upper left block; after processing is finished by the prior art, updating the subscript mapping until an entire macro-block is processed; and updating the macro-block of the register to obtain new line buffer content and the information of an adjacent register so as to process a next macro-block. The method is suitable for predicting the macro-block and calculating the intensity of boundary filtering in H.264 and AVS decoding, can effectively reduce the storage spaces of adjacent block registers, multiplexes and simplifies hardware design and improves video decoding efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
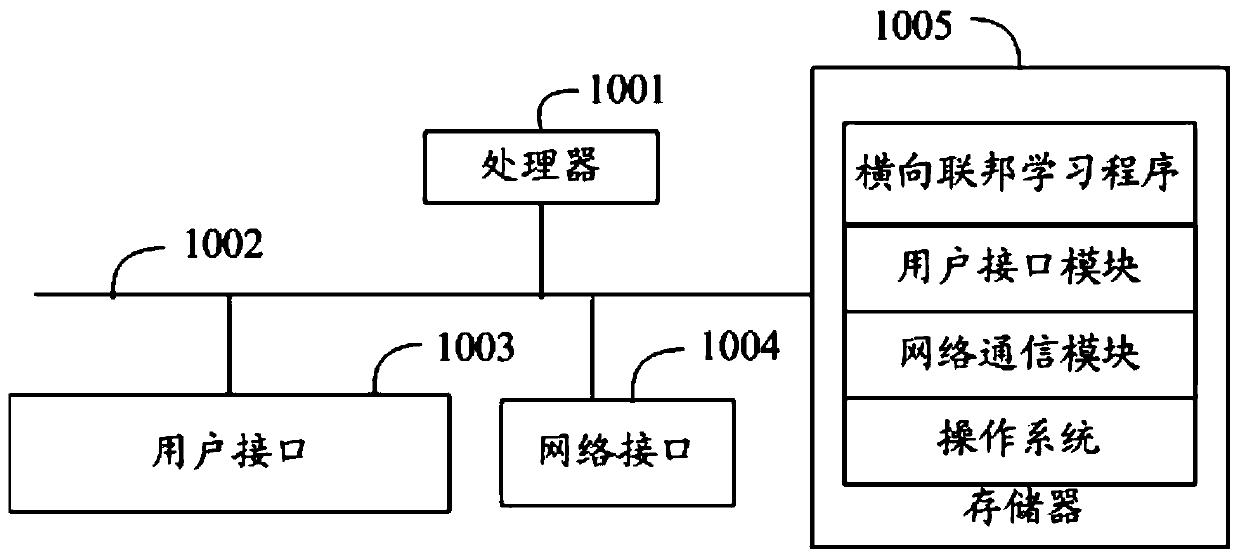
Transverse federated learning method, device and equipment and computer storage medium
PendingCN110263936AReduce the number of updatesReduce overheadFinanceMachine learningFederated learningGlobal model
The invention relates to the technical field of Fintech, and discloses a transverse federated learning method. The method comprises the following steps: a community coordinator acquiring global model parameters sent by a central coordinator and sending the global model parameters to each participant; obtaining model parameter update which is sent by each participant and is obtained by performing model training based on the global model parameters, fusing the model parameter update to obtain community model parameter update, and determining whether the community model parameter update needs to be sent to the central coordinator or not; and if yes, sending the community model parameter update to the central coordinator, obtaining global model parameter update returned by the central coordinator, and sending the global model parameter update to each participant, thereby enabling each participant to carry out model training based on the global model parameter update. The invention further discloses a transverse federated learning device and equipment and a computer storage medium. According to the invention, the learning efficiency of transverse federal learning is improved.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
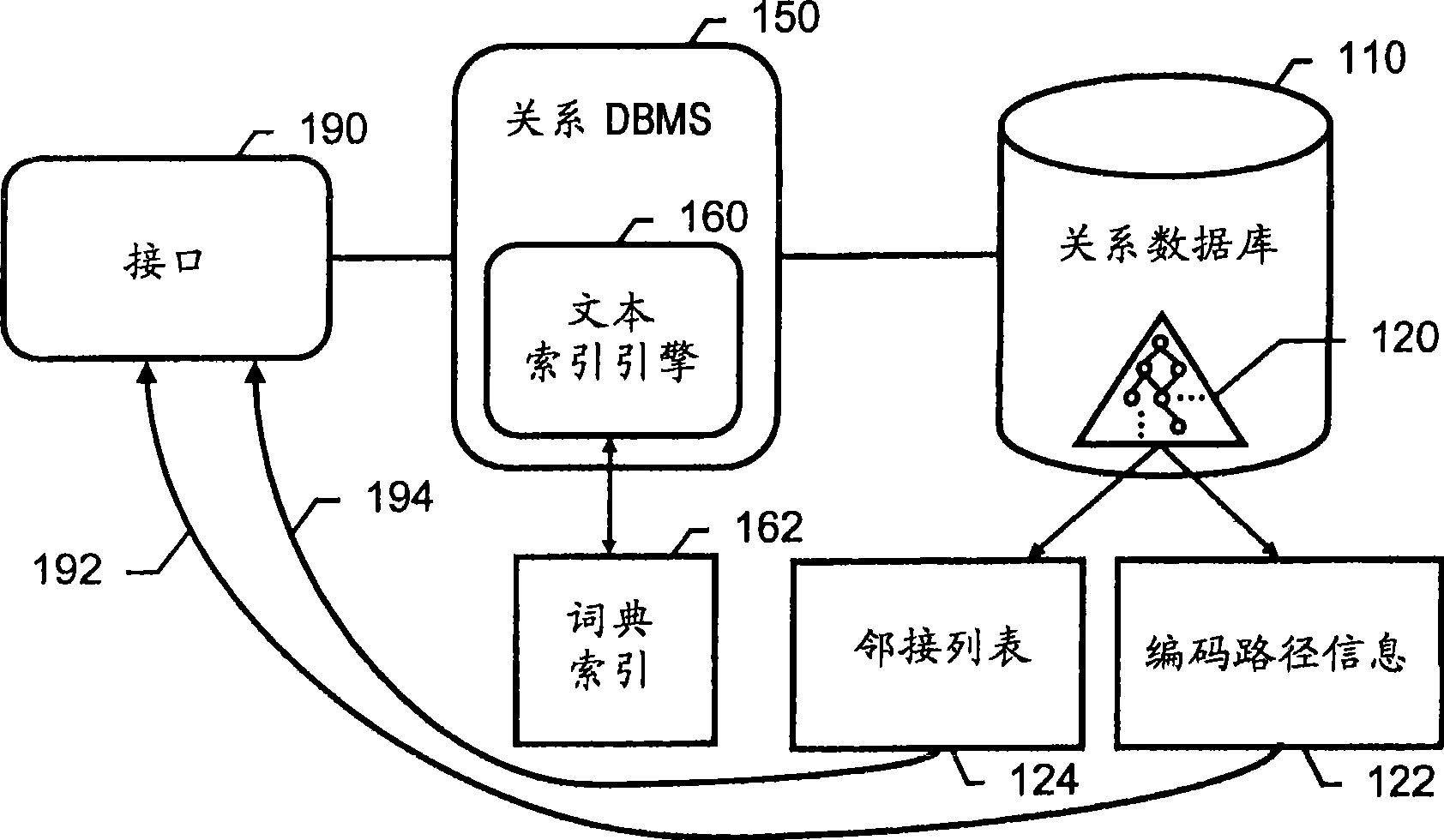
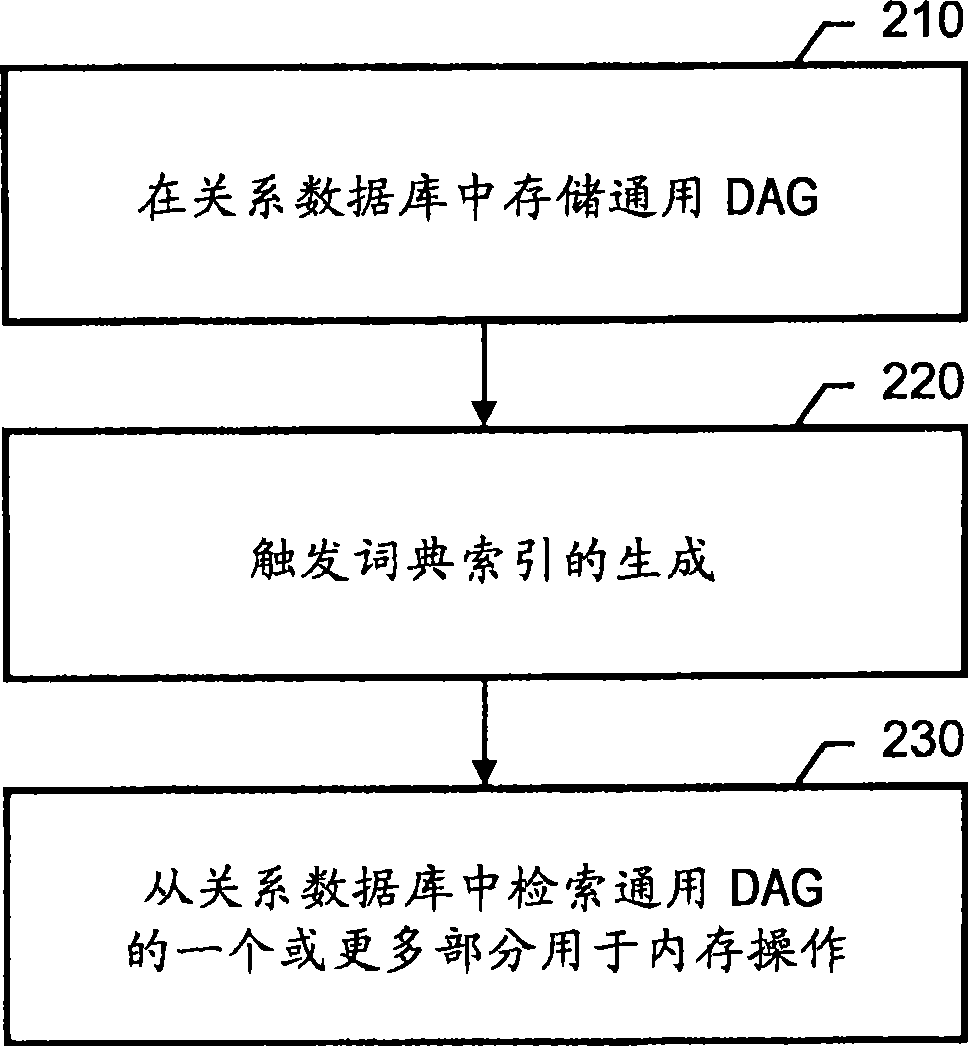
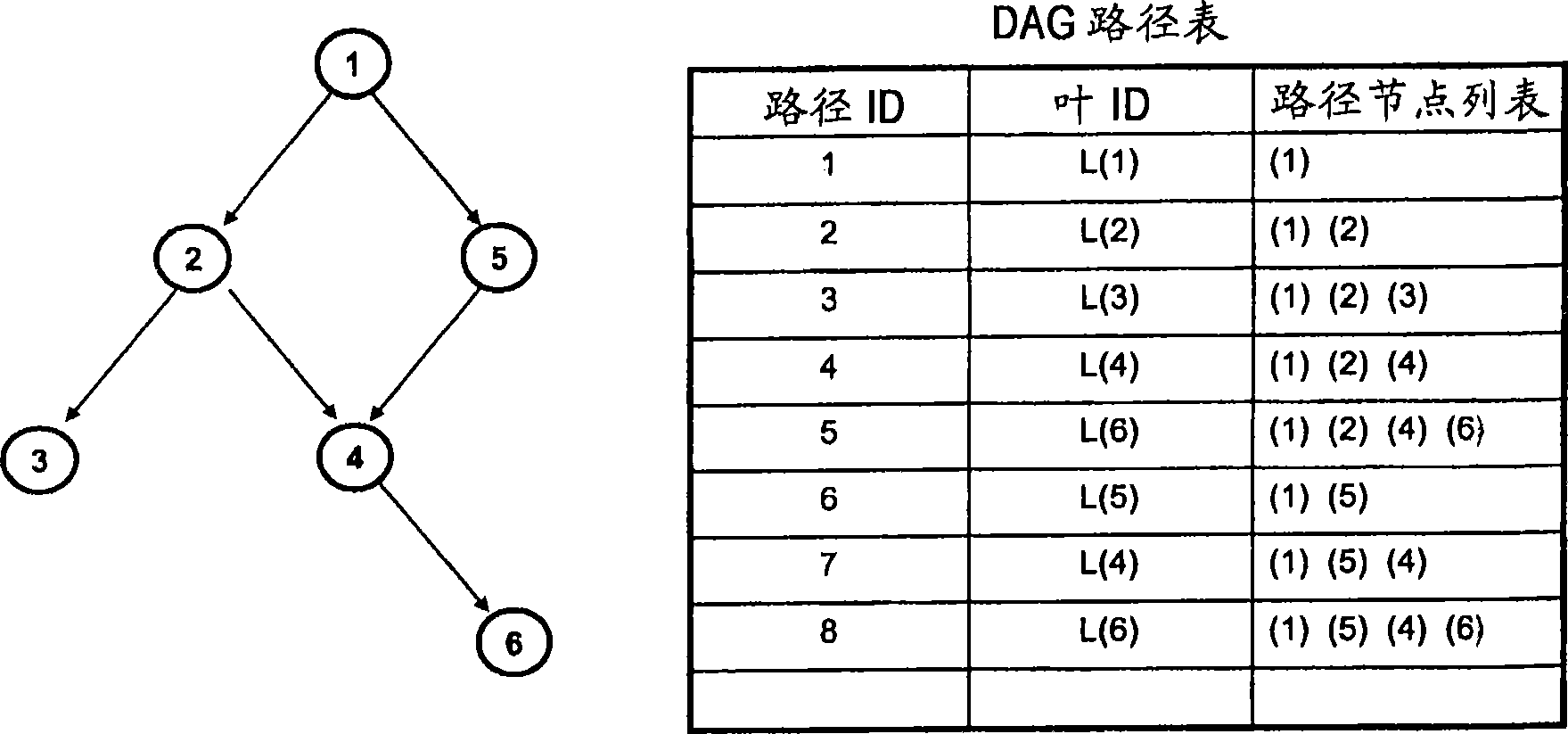
System and method of efficiently representing and searching directed acyclic graph structures in databases
InactiveCN101421729AEfficient retrievalFast reasoningSpecial data processing applicationsData miningText string
The present disclosure includes systems and techniques relating to representation and retrieval of data structures in databases. In general, embodiments of the invention feature a computer program product and a method including storing a generalized directed acyclic graph (DAG) in a database, wherein the storing includes encoding path information of the generalized DAG in entries of a path table in the database, the encoding includes converting the path information into text strings, and the entries of the path table correspond to paths in the generalized DAG from nodes of the generalized DAG to a root node of the generalized DAG; triggering generation of a lexical index of the path table using the text strings, wherein the lexical index separately lists tokens included in the entries; and retrieving one or more portions of the generalized DAG from the database for in-memory operations.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Method and device for processing dynamic system message block
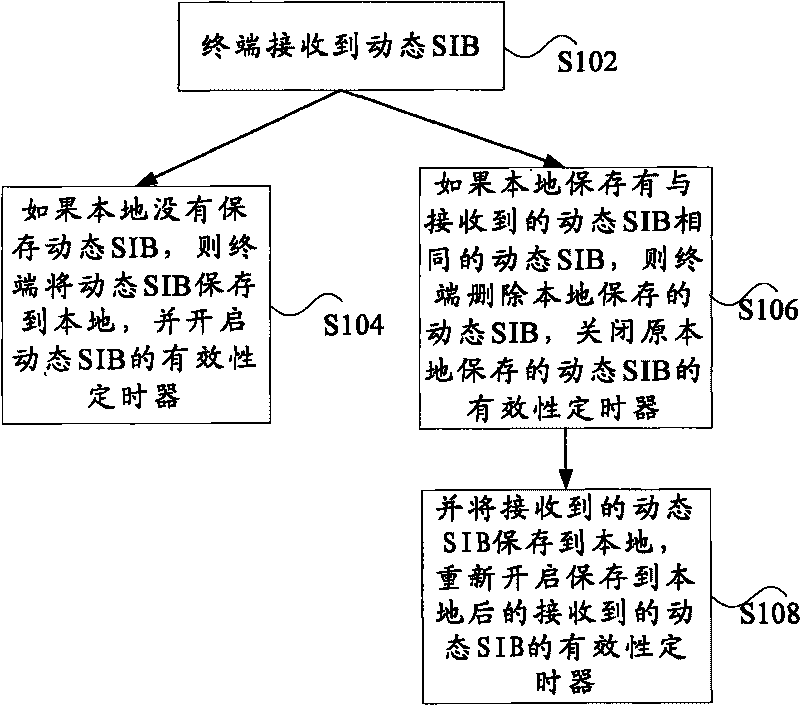
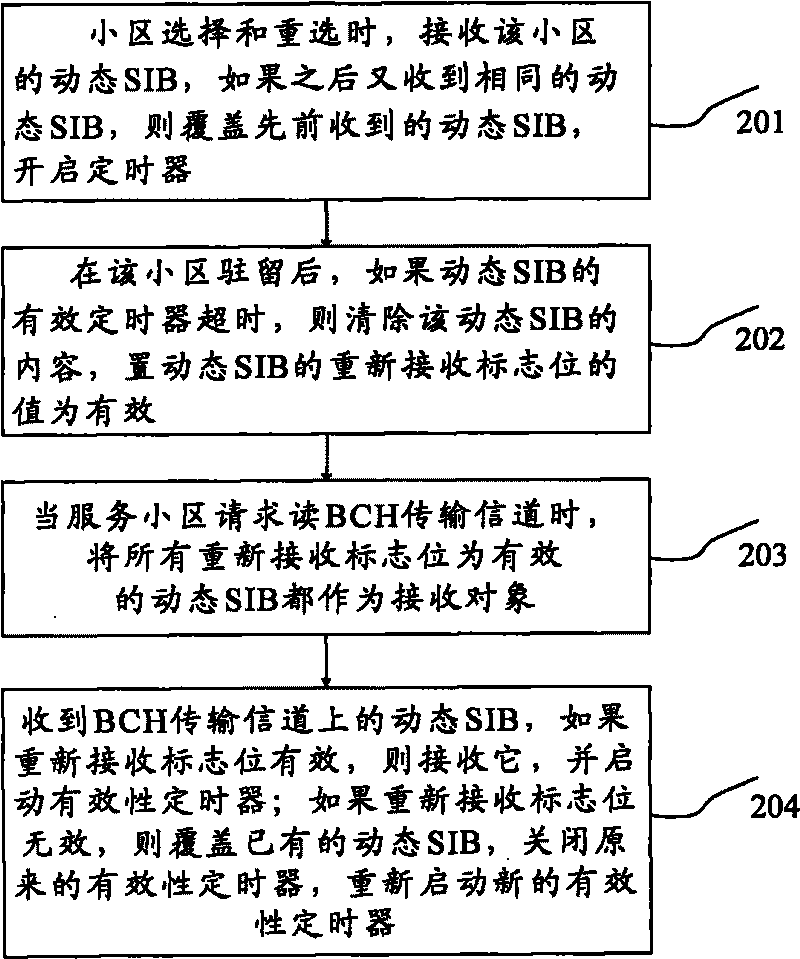
ActiveCN101697614AReduce the number of updatesReduce overheadEnergy efficient ICTAssess restrictionProcess dynamicsTransmission channel
The invention discloses method and device for processing a dynamic system message block. The method comprises the following steps: after a terminal receives dynamic SIB, if the local does not store the dynamic SIB, storing the dynamic SIB to the local by the terminal and starting a validity timer of the dynamic SIB; if the local stores dynamic SIB same with the received dynamic SIB, deleting the local-storing dynamic SIB by the terminal, closing the validity timer of the original local-storing dynamic SIB, storing the received dynamic SIB to the local, and opening the validity timer of the received dynamic SIB after being stored in the local. The updating frequencies of the dynamic SIB are reduced and the expenses for UE to frequently read a BCH transmission channel are decreased, further reducing the power consumption of UE.
Owner:ZTE CORP
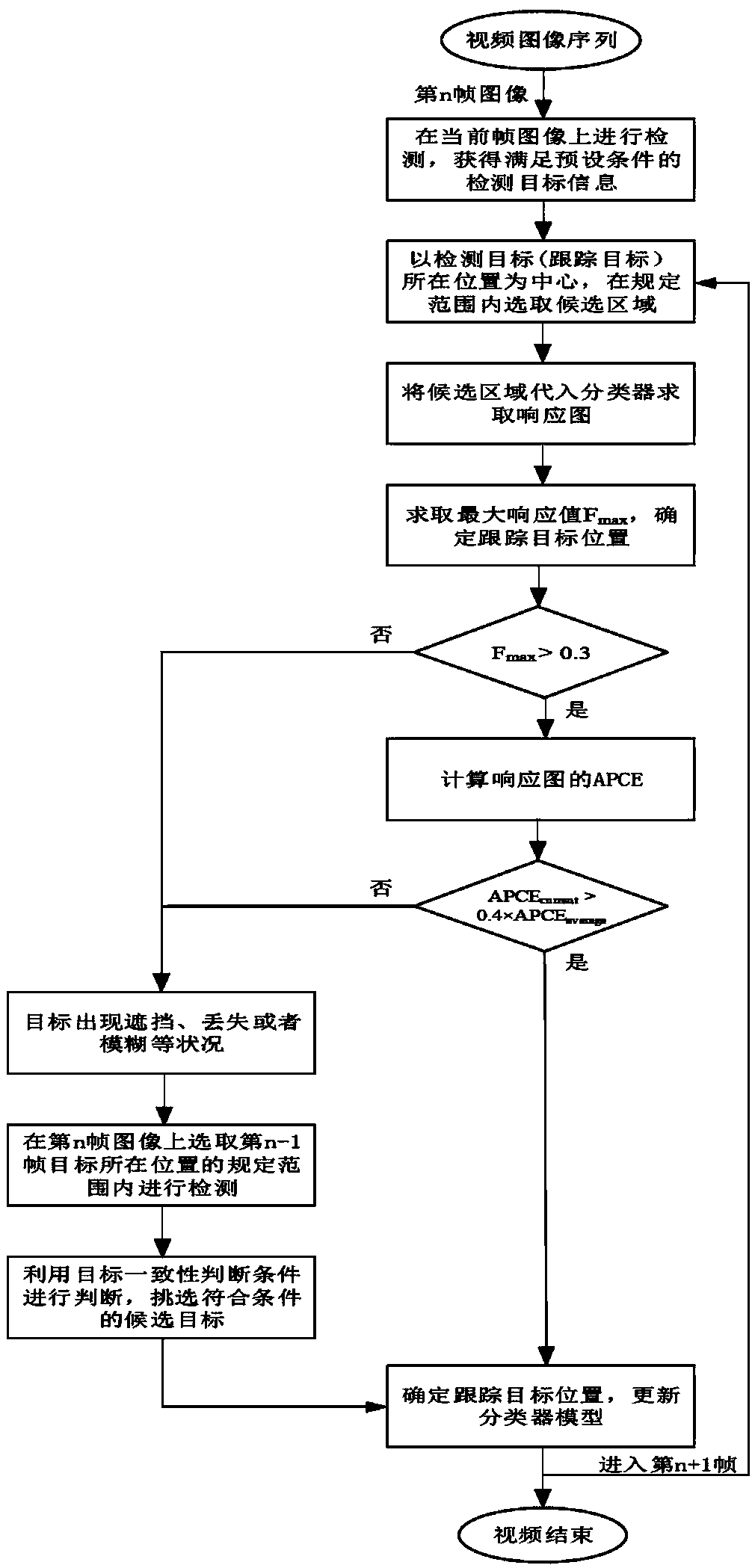
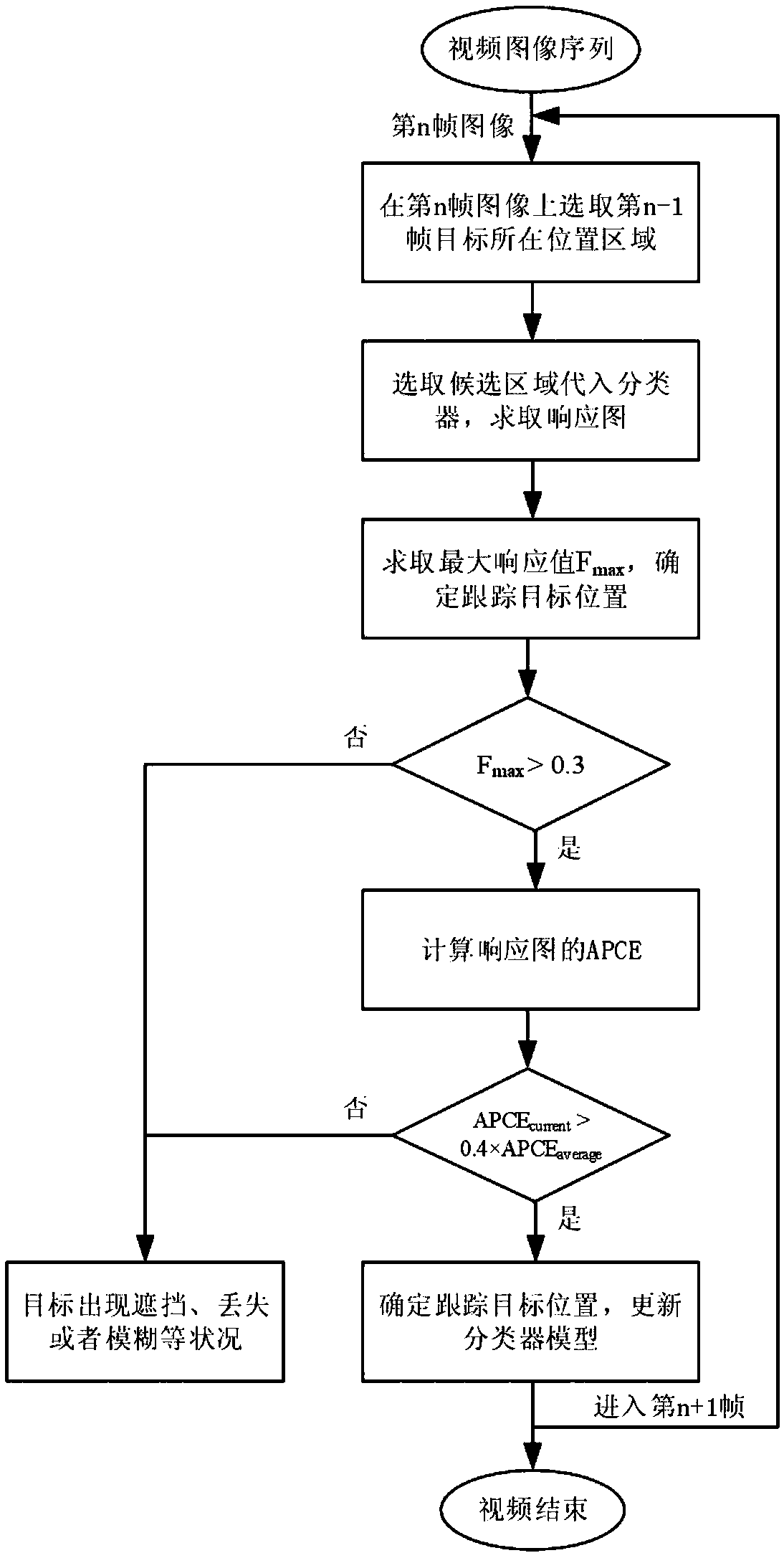
Method for detecting and tracking moving object under complex background
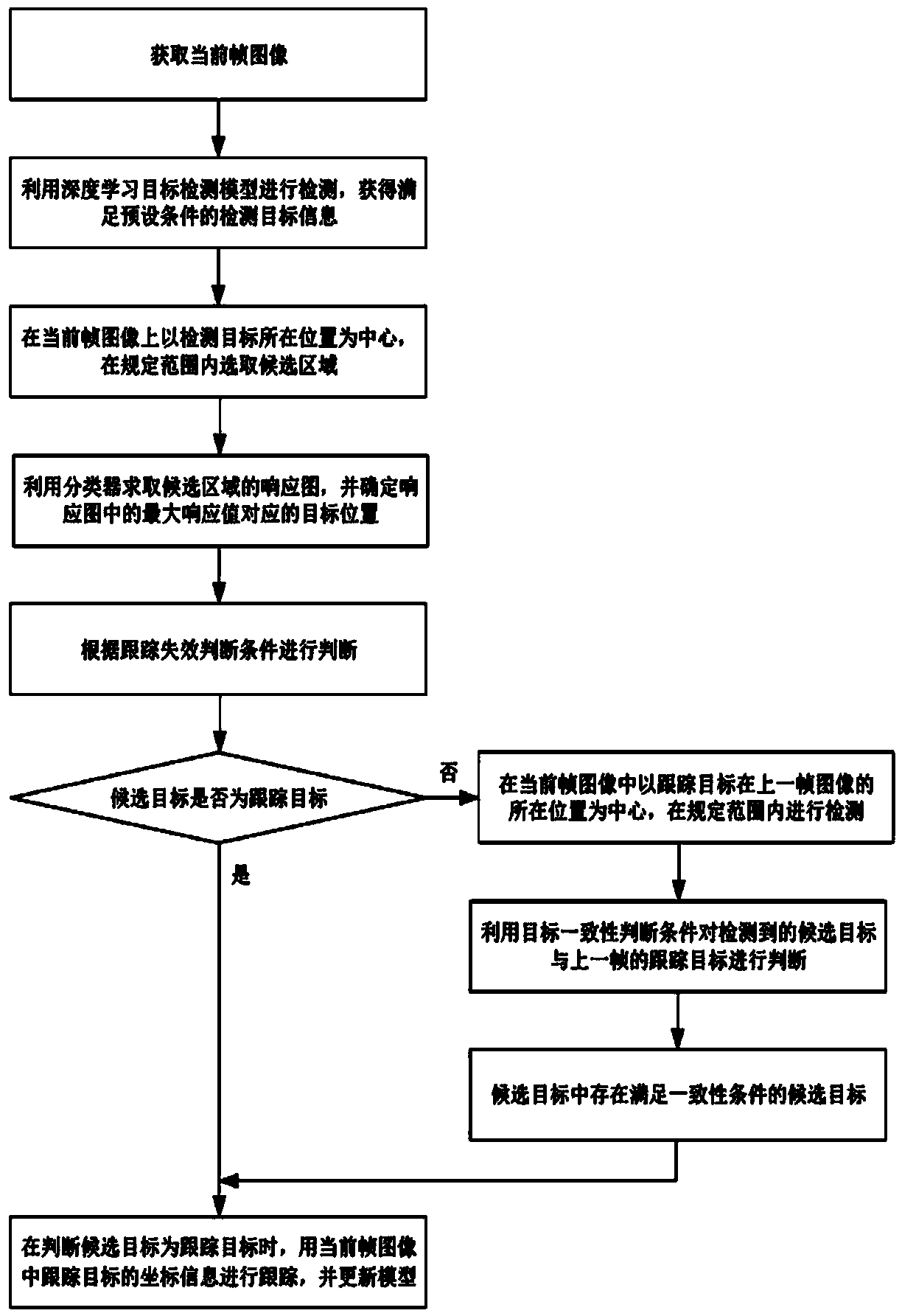
InactiveCN108765452AChoose accuratelyReduce driftImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMedicine
A method for detecting and tracking a moving object under a complex background belongs to the field of object tracking, and a method of stably tracking the object under the complex background is involved particularly. The method comprises the following steps: detecting the acquired current frame image to obtain detection object information satisfying preset conditions; at the current frame image,selecting a candidate region by taking the position of a tracking object as the center; and obtaining the object position corresponding to a candidate object in the candidate region by using a classifier model. The method of the invention sets the tracking loss judgment condition by the response diagram oscillation between a candidate sample and a classifier, so as to accurately judge whether theobject meets the conditions such as occlusion, loss or blur or not. At the same time, the historical value of a response value in a response diagram is used to judge the model update, which reduces the model drift and the number of model update. In a complex scene, the tracking object can be accurately selected from the candidate sample, and the fast and stable tracking of the object can be achieved.
Owner:XIAN TIANHE DEFENCE TECH
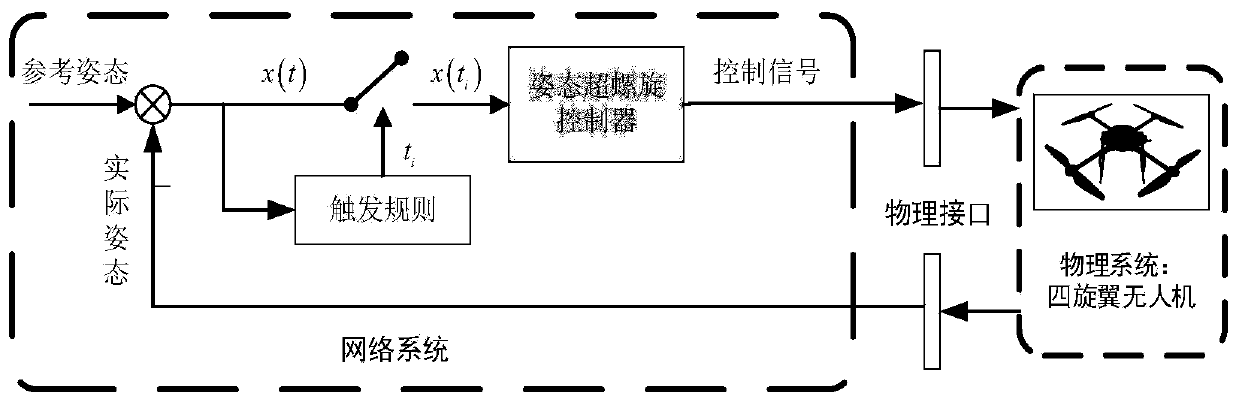
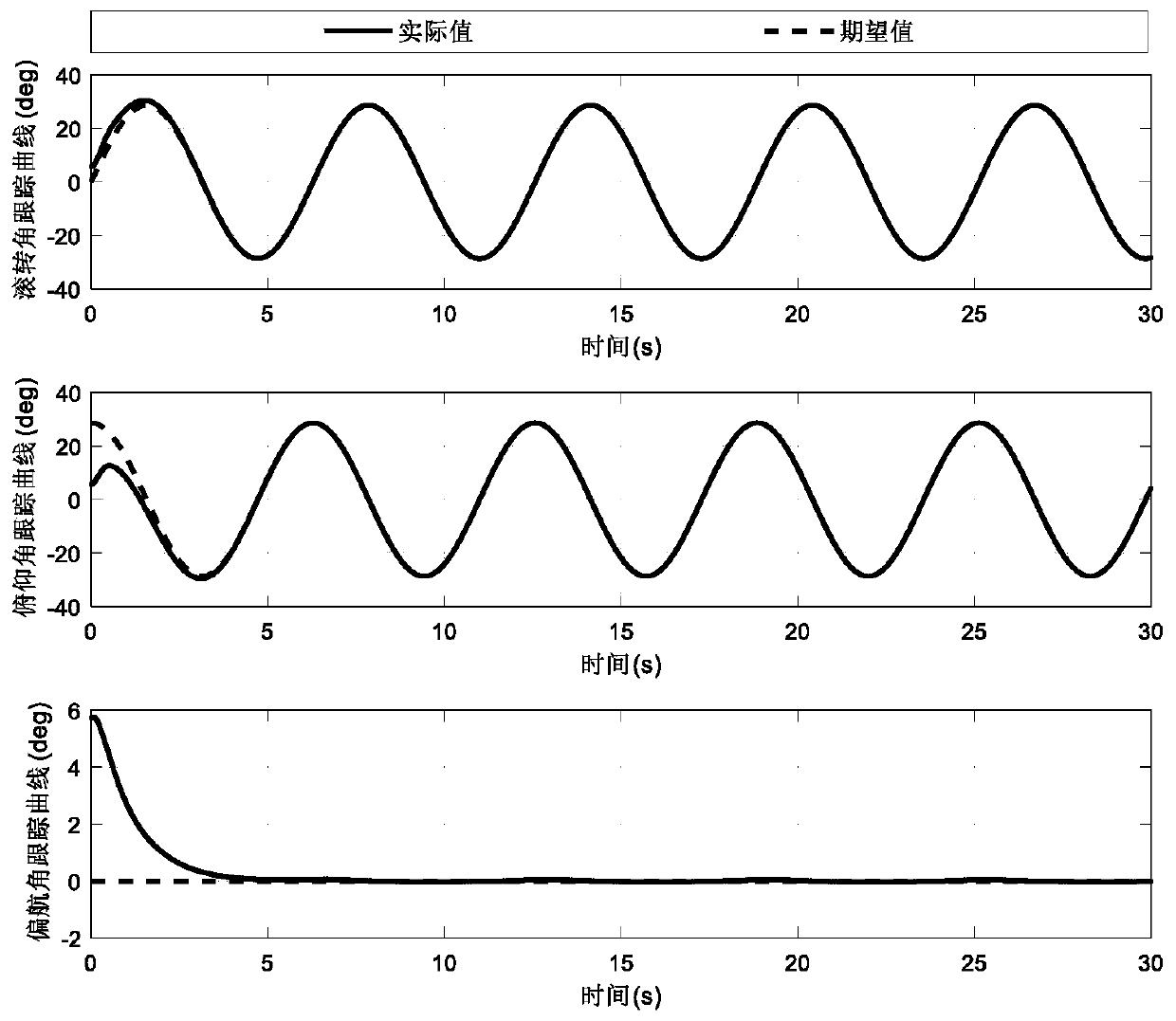
Event-triggered quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle attitude control method
ActiveCN109976361AHigh precisionStable trackingAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsLyapunov stabilityMathematical model
The invention relates to the unmanned aerial vehicle control technology field. A high-precision rapid attitude tracking control problem of a quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle under comprehensive effects of uncertain model parameters, unmodeled dynamics, an external disturbance and the like is solved. And purposes of saving network and calculating resources and increasing system endurance under the condition of ensuring control performance of the quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle are achieved. An event-triggered quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle attitude control method comprises the following steps of a first portion, a quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle attitude mathematical model; a second portion, an attitude superhelical controller design under an event trigger mechanism; and a thirdportion, an event trigger rule design: according to Lyapunov stability analysis, designing an event trigger rule and ensuring that internal event time is greater than a positive constant through analysis. The method is mainly applied to the aircraft automatic obstacle avoidance control occasion.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
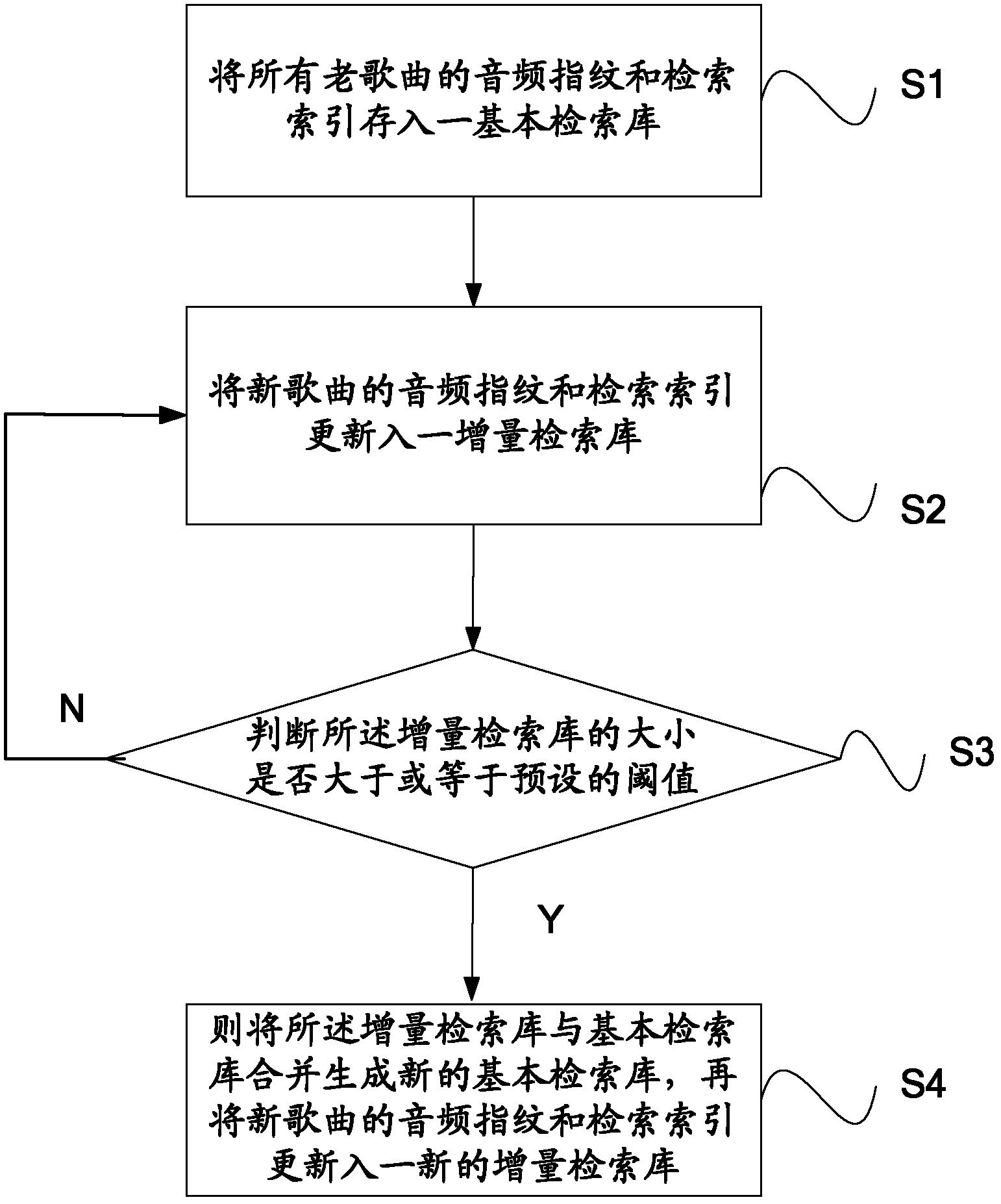
Method and system for updating audio fingerprint retrieval database
InactiveCN102289518AQuick updateShorten update timeSpecial data processing applicationsLibrary scienceFingerprint retrieval
The invention relates to a method and system for updating an audio fingerprint search library. The method comprises the following steps of: storing audio fingerprints and retrieval indexes of all old songs in a basic search library; updating audio fingerprints and retrieval indexes of new songs in an incremental search library; judging whether the volume of the incremental search library is more than or equal to a preset threshold, if so, combining the incremental search library with the basic search library and generating a new basic search library, and updating the audio fingerprints and the retrieval indexes of the new songs in a new incremental search library; and, if not, updating the audio fingerprints and the retrieval indexes of the new songs in the incremental search library. According to the method and system disclosed by the invention, aiming at the condition that new songs are frequently added, when the incremental search library is very small and the cost for updating theincremental search library is very low, the incremental search library is only updated at each time, therefore, the time for updating the audio fingerprint search library is saved; and the audio fingerprint search library can be updated rapidly.
Owner:SHENGLE INFORMATION TECH SHANGHAI
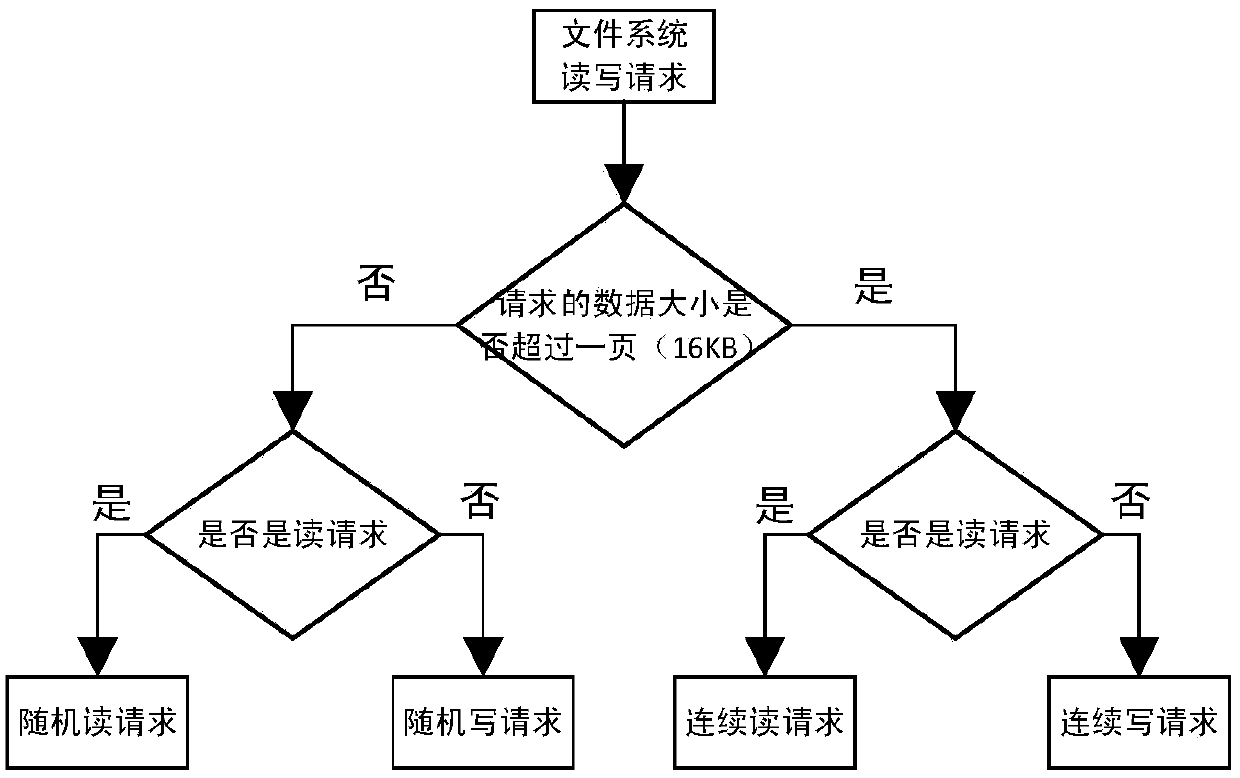
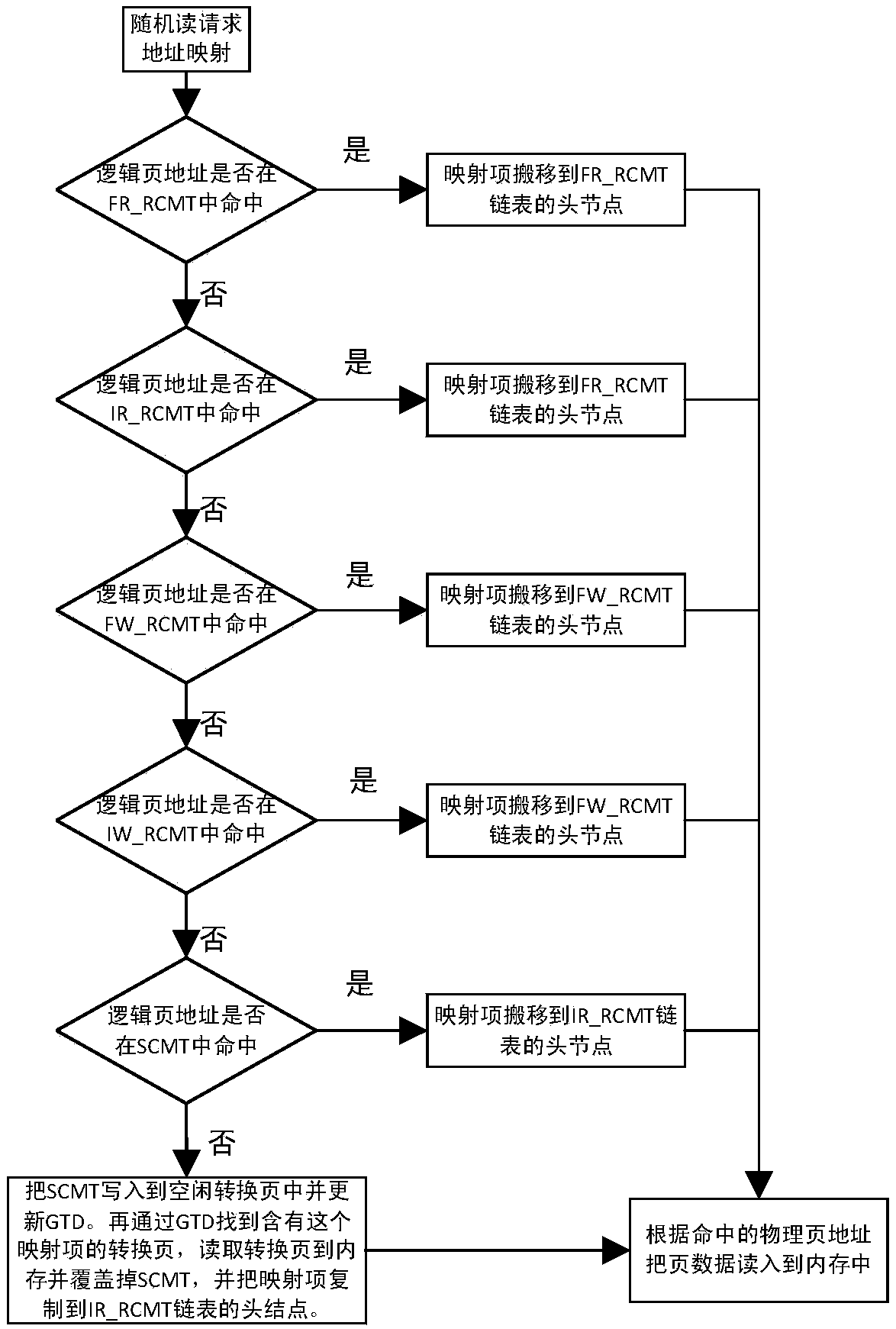
Flash conversion layer control method based on request classification
ActiveCN107943719AQuick hitQuick sortingMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsMemory addressFile system
The present invention discloses a flash conversion layer control method based on request classification. The method comprises the following steps: Step S1: setting a plurality of address mapping cachetables in a memory according to an operation request of the file system and an address request frequency; Step S2: obtaining the operation request of the file system in the flash conversion layer andparsing the operation request to determine the operation request type; Step S3: searching the logical page address of the operation request in multiple address mapping cache tables in different priority orders according to the operation request type until hitting the corresponding address mapping entry; and Step S4: updating the memory address mapping cache tables according to the operation request result. Compared with the prior art, according to the method disclosed by the present invention, the request is divided in a more fine-grained manner, quickly hitting the mapping entry is facilitated, and when removing the mapping entry, the classified removal can be carried out to accelerate the removal speed, the mapping entries that must be updated can be quickly sorted, and the update of the mapping entries that does not require to be updated is avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Learning target tracking algorithm based on twin network
PendingCN111126132ASolve driftReduce overfittingCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesCorrelation filterSearch graph
The invention discloses a learning target tracking algorithm based on a twin network. The method comprises the following steps: 1, setting a function f to compare the feature map similarity of a template image x and a candidate image y, the maximum response value corresponding to a target position, the x being generally an image with a target as the center in a first frame, and the y being an image searched by taking an (n-1) th frame of image target as the center in an nth frame; substituting the two inputs into a convolutional neural network, learning a network parameter rho by using a convolution processing function, generating two cross-correlation mappings, and performing exhaustive search on x at y to respond to the position of a target corresponding to the maximum value; wherein animproved discriminant correlation filter layer is added between input x and cross-correlation operation in the twin network, 3, performing tracking by measuring the similarity between a template imagex and a search image y, and online fine adjustment is carried out by means of a discriminant correlation filter module during online tracking so as to ensure the tracking accuracy.
Owner:浙江必创科技集团有限公司
Stable tracking method for target under complex background
InactiveCN108694723AReduce driftReduce the number of updatesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVideo image
The invention discloses a stable tracking method for target under a complex background, and relates to the field of target tracking. The method comprises the following steps that: obtaining the current frame of image of a video image; selecting a candidate area on the current frame of image; obtaining a target position corresponding to a candidate target by a classifier model; carrying out tracking failure judgment on the candidate target; and when the candidate target is the tracking target, carrying out tracking by the coordinate information of the tracking target in the current frame of image, and updating the classifier model to finish the stable tracking of the target in the video image. Through a response diagram oscillation situation between a candidate sample and a classifier model, a tracking losing judgment condition is set, and therefore, whether the target is under the situations including blocking, losing or blurring and the like can be accurately judged. Meanwhile, the historical value of the response value in the response diagram can be used for judging model update, a model drifting situation and a model update frequency are reduced, the tracking target can be accurately selected from the candidate samples from the complex scene, and the target can be quickly and stably tracked.
Owner:XIAN TIANHE DEFENCE TECH
3D graphics rending method and system
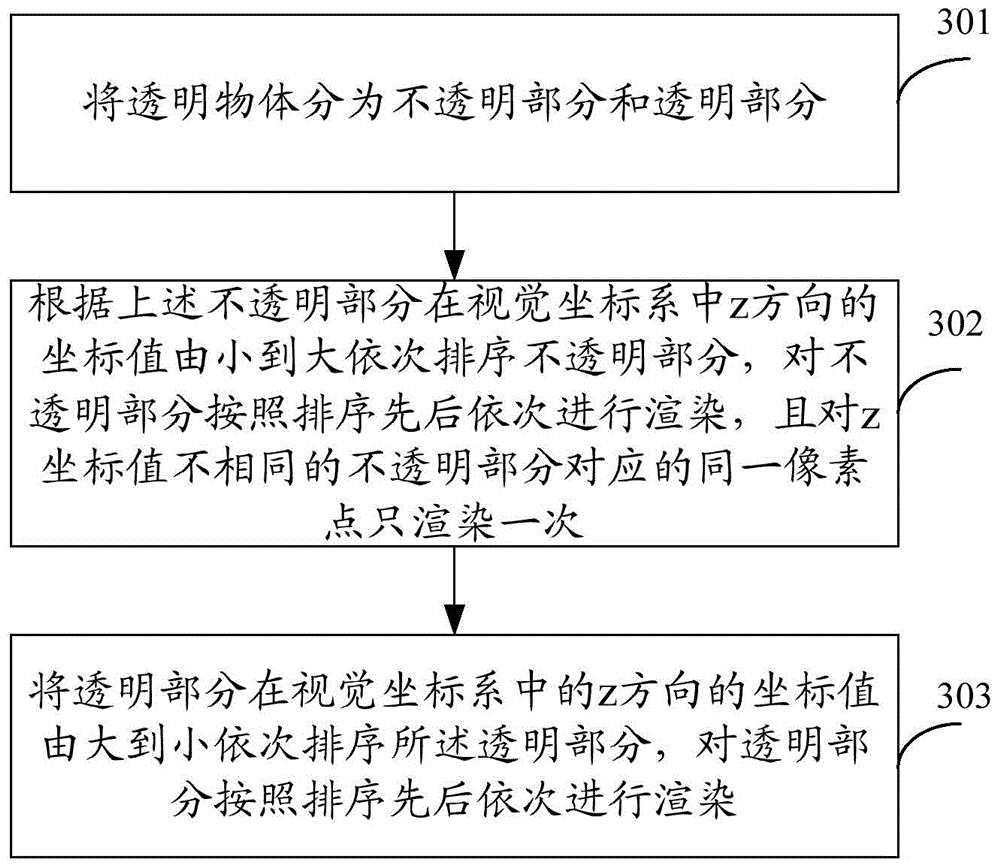
InactiveCN103955957AReduce the number of updatesImprove efficiency3D-image renderingGraphicsZ-Coordinate
The invention is applicable to the field of 3D technology and provides a 3D graphics rending method and system. According to the 3D graphics rending method, objects to be rendered are divided into opaque objects and transparent objects, the opaque objects are ranked according to coordinate values of the opaque objects in a z direction in a visual coordinate system from small to large in sequence, rending is performed on the opaque objects according to the rank in sequence, and rending is performed on the same pixel point corresponding to the opaque objects with different z-coordinate values for one time only. Therefore, rending in different depths is performed on the same position for one time only, updating frequency of pixels at the same position is reduced, and rending efficiency is increased.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
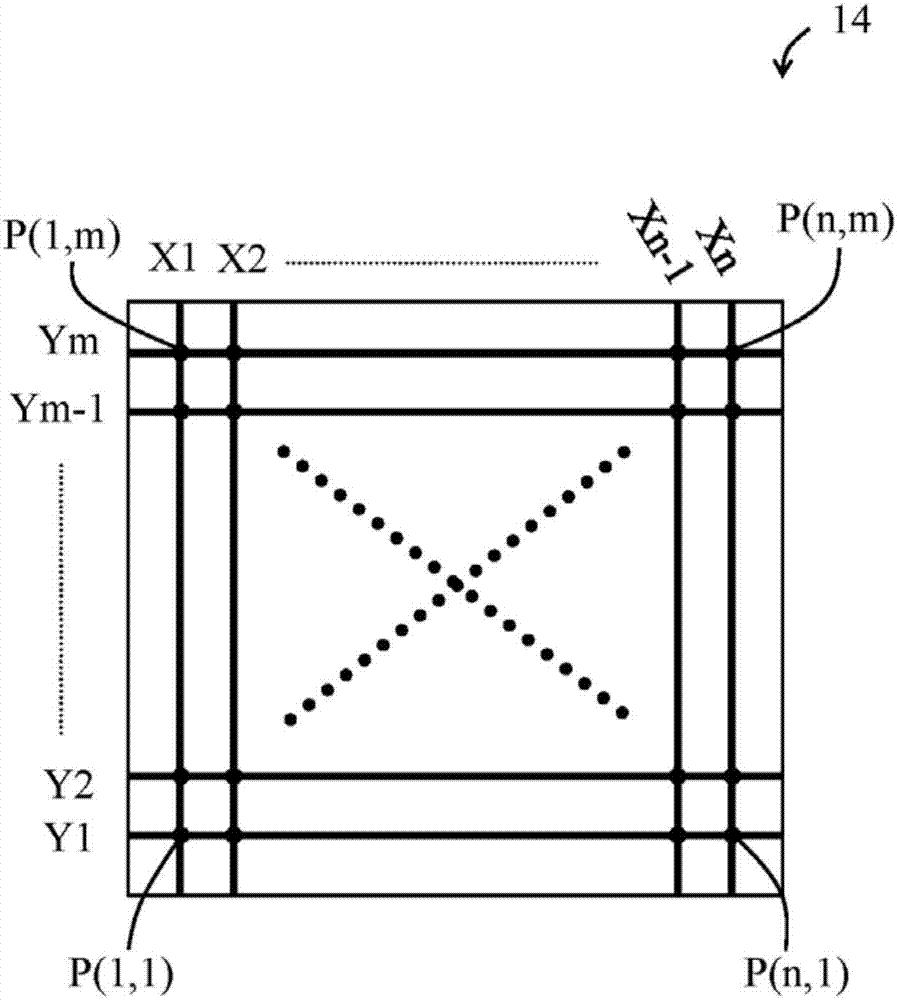
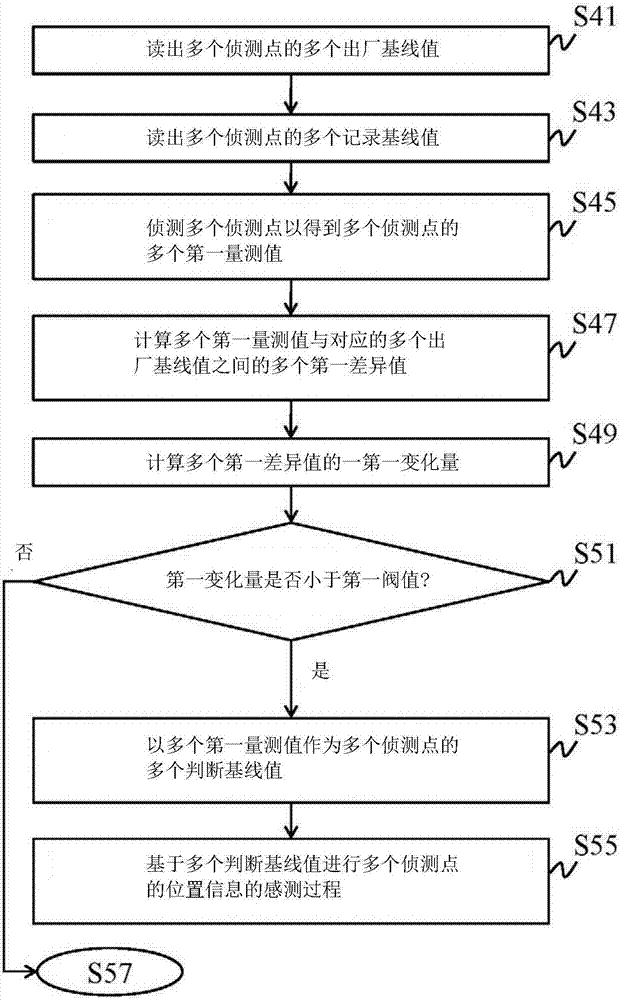
Refreshing method of sensing baseline values for capacitive sensor device and capacitive sensor device
ActiveCN107102785AReduce the number of updatesAvoid misjudgmentInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringBaselining
A refreshing method of sensing baseline values for a capacitive sensor device and the capacitive sensor device are applied to confirm whether the differences between the current measured values and the factory or record baseline values are approximately equal, to determine whether to use current measured values as the sensing baseline values used in the following sensing procedure. When the differences are approximately equal, the current measured values are used as the sensing baseline values. When the differences are not approximately equal, the factory baseline values are used as the sensing baseline values, and the correcting procedure of the sensing baseline values of the sensing points is executed. In the correcting procedure, the signal characteristic of the measured value of each sensing point is detected to be high frequency or low frequency, to determine whether to refresh and when to refresh the corresponding sensing baseline values by the current measured values. Thus, the updating times of the sensing base line values can be reduced and resources can be saved.
Owner:SALT INT CORP +1
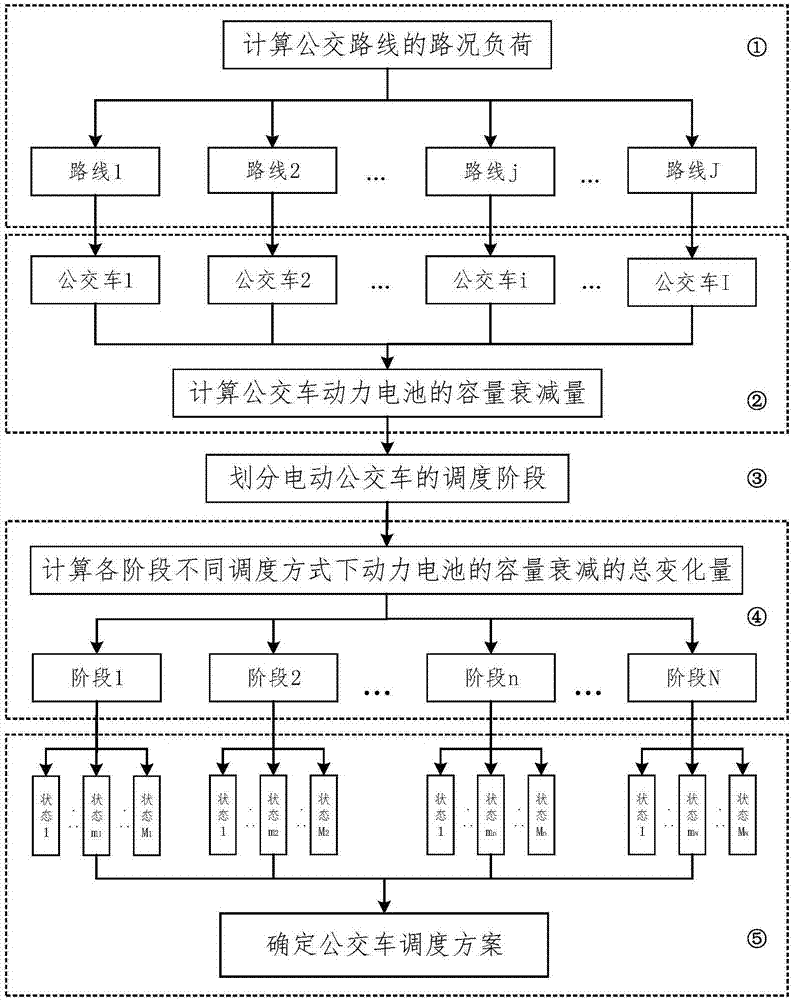
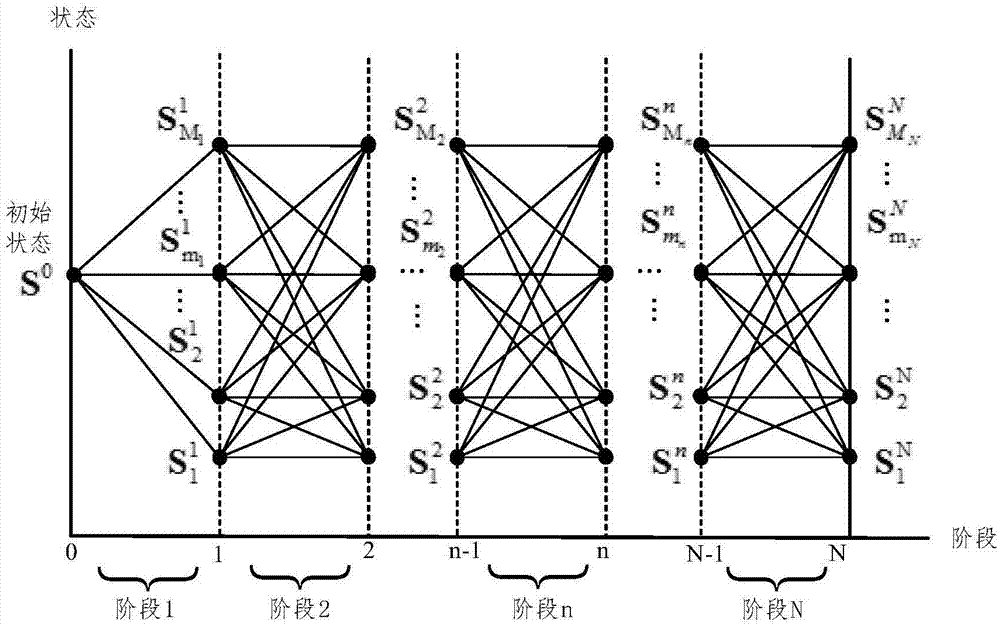
Pure electric bus dynamic route planning method capable of prolonging service life of power cell
ActiveCN107220730AReduce operating expensesExtended service lifeRoad vehicles traffic controlForecastingDynamic planningOptimal scheduling
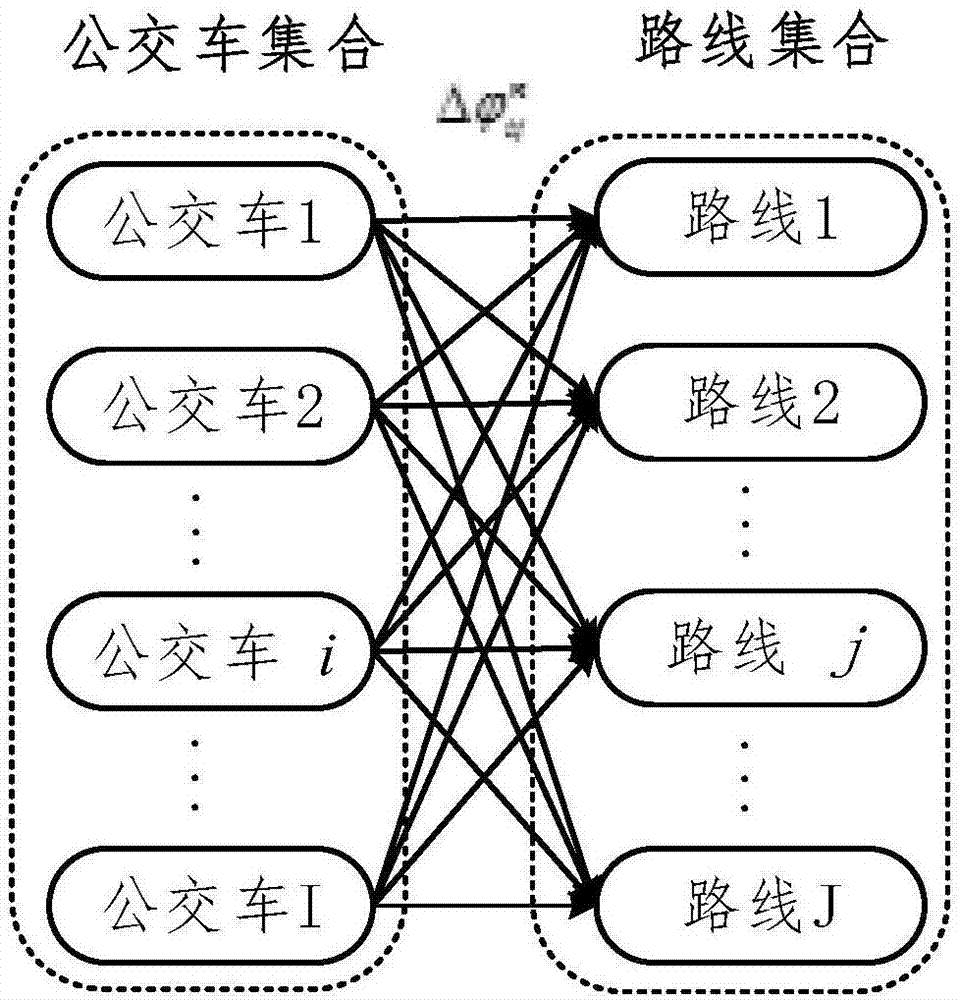
The invention relates to a pure electric bus dynamic route planning method capable of prolonging service life of power cells. On the basis of comprehensively considering the pure electric bus operation characteristic, the power cell capacity degradation characteristic and the bus route road condition characteristic and mutual influence of the three characteristics, possible scheduling schemes of pure electric buses at each stage and routes can be acquired through constructing a bigraph model, through calculating total change amount of capacity degradation of all the power cells in different scheduling states, a dynamic planning recursion algorithm is utilized to accomplish optimization of a scheduling period and the scheduling schemes of the full process. The method is advantaged in that service life of the power cells of the electric buses can be prolonged to a maximum degree through the acquired optimal scheduling scheme under the power cell technology level in the prior art, frequency of power cell update in the integral vehicle service life period can be reduced to a maximum degree, and operation cost of the pure electric buses can be effectively reduced.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Storage and indexing method and system based on traffic consumption model event
ActiveCN104598475AReduce the number of updatesEvenly distributedMulti-dimensional databasesSpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataThe Internet
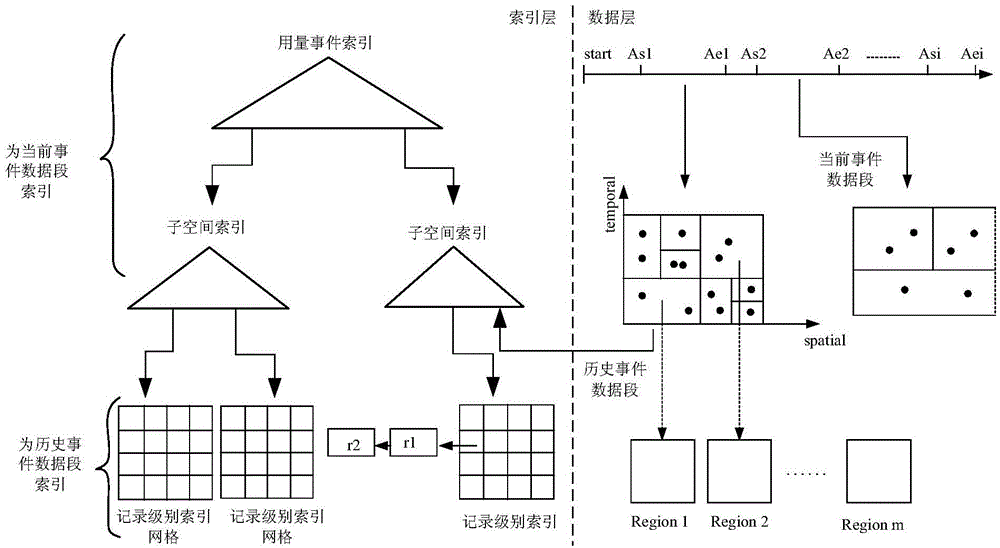
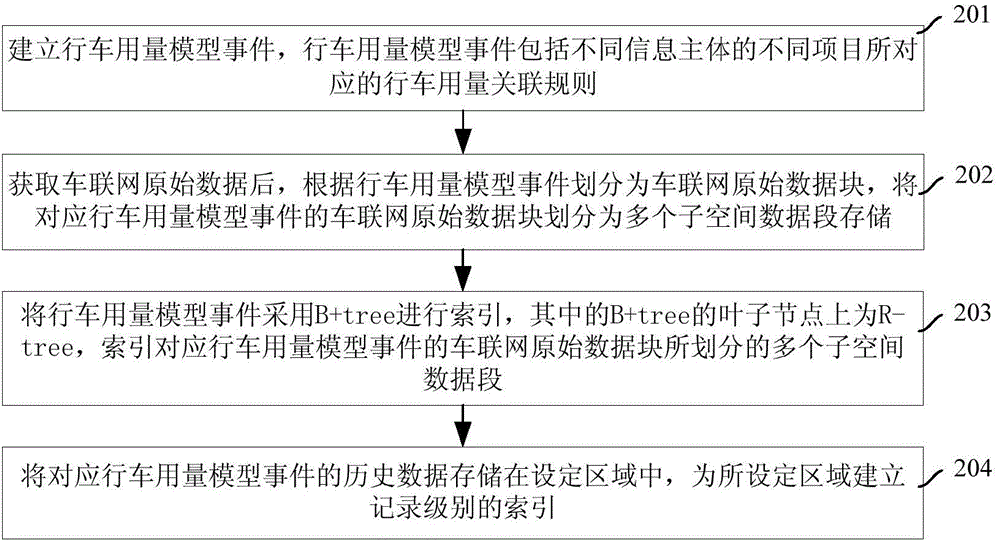
Disclosed are driving amount model event-based storage and index methods and a system. A driving amount model event is set and the amount model event comprises driving amount associated rules corresponding to different projects of different information main bodies. Data for Internet of vehicles comprises raw data and historical data provided by each information main body for the Internet of vehicles, wherein the driving amount model event and a coarse-grained-level index of a sub-space under the driving amount model event are used for the raw data for the Internet of vehicles, and a fine-grained-level index at a record level is set for the historical data in the driving amount model event. Therefore, the methods and the system provided by the present invention reduces a number of index update times and makes the data for the Internet of vehicles distributed evenly when storing and indexing the data for the Internet of vehicles.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
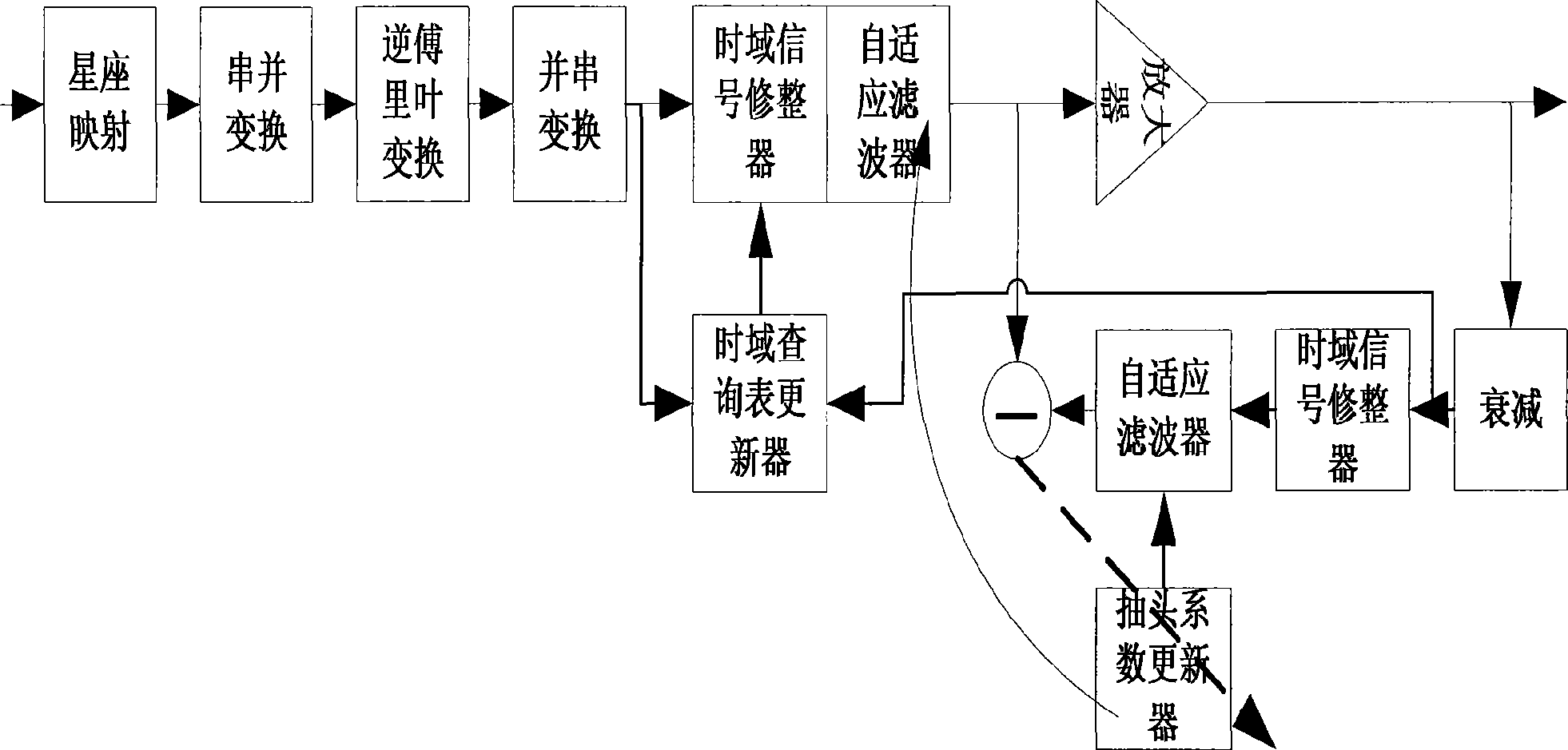
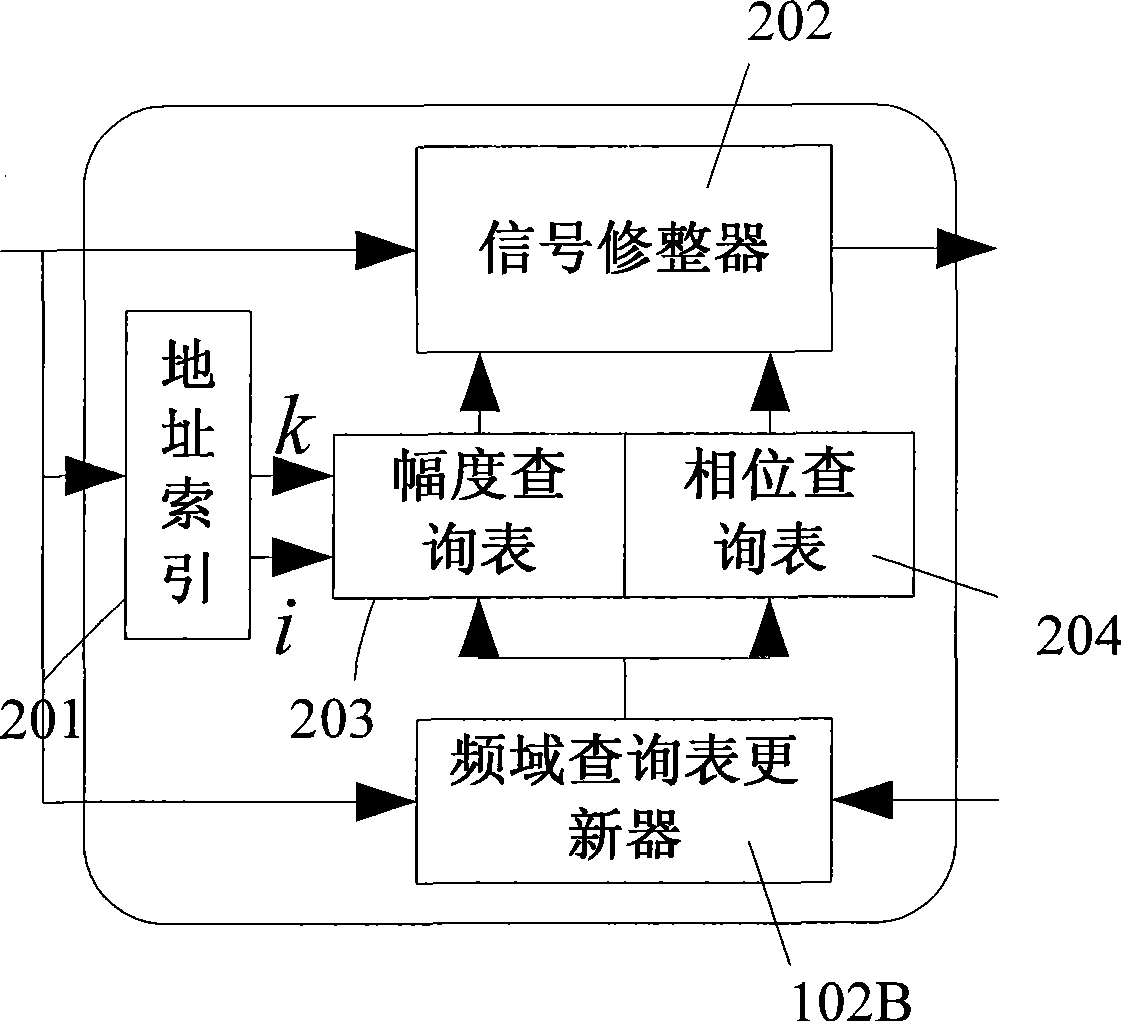
Linearization device and linearization method in broad-band communication system
ActiveCN101547178AEliminate memory nonlinear distortionImproved speed of distortion removalMulti-frequency code systemsSynchronous/start-stop systemsTime domainAdaptive filter
The invention discloses a linearization device with a memory nonlinear amplifier and a linearization method in a broad-band communication system. The linearization procedure is as follows: using a frequency domain dresser, a time domain dresser and a self-adaptive filter to respectively carry out frequency domain dressing, time domain dressing and filtering processing for transmitting signals and amplifying the dressed signals: attenuating the amplified signals to the electrical level before amplification and feeding back the signals and using feedback signals and input signals to respectively update filter tap coefficient, a time domain checking table and a frequency domain checking table; repeating the above steps to continually update the frequency domain checking table, the time domain checking table and the filter tap coefficient and then carrying out frequency domain dressing, time domain dressing and filtering processing for generated transmission signals by utilizing the updating value of the filter tap coefiicient, the dressing value of the time domain dresser and the dressing value of the frequency domain signal dresser; repeating the operation again and again till realizing the linearization function of an amplifier in a broad-band OFDM system. The invention has the advantages of high convergence speed, high convergence precision and high degree of linearization.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
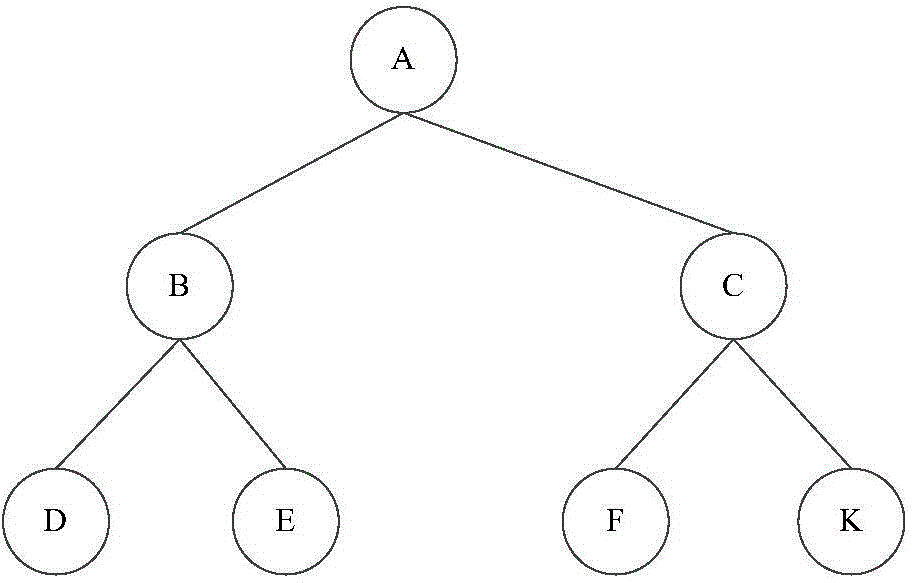
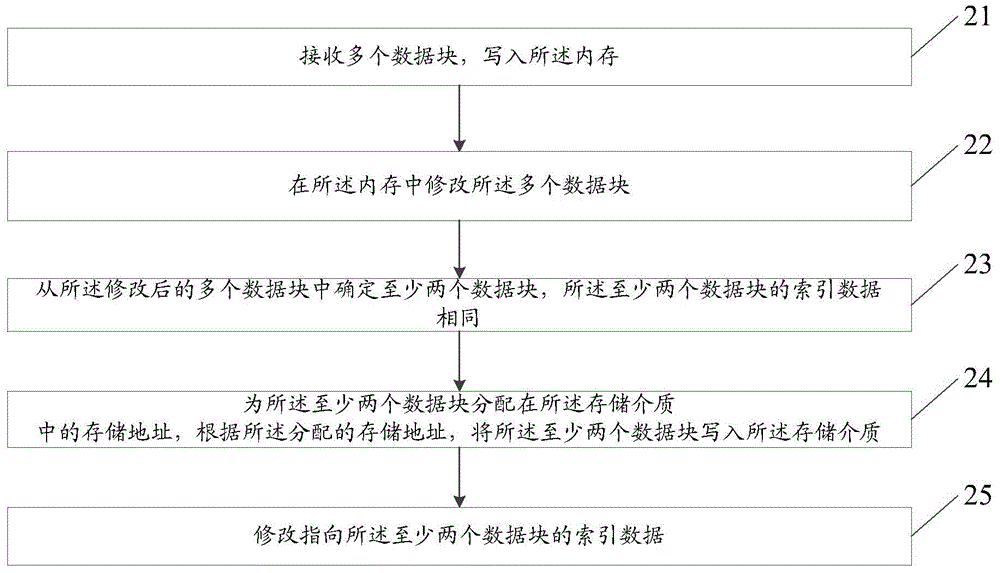
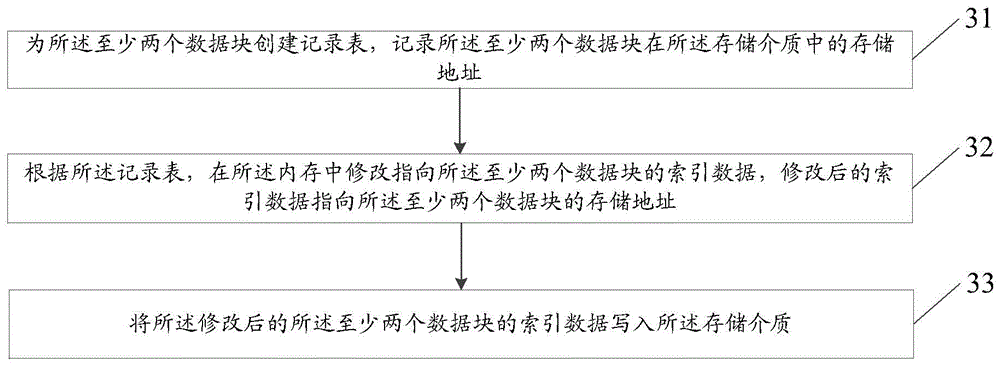
Data write-in method and storage device
ActiveCN104461384AReduce the number of updatesReduce write overheadInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRelationship - FatherStructure of Management Information
The invention provides a data write-in method and a storage device. The method is applied to the storage device. The storage device comprises a processor, an internal storage and storage media. Data blocks in the storage media are organized to be of a tree structure. Leaf nodes of the tree are used for storing the data blocks. Father nodes and root nodes of the tree are used for storing index data. The index data are used for indexing the data blocks. The method is executed by the processor and includes the steps that a plurality of data blocks are received, and the data blocks are written in the internal storage; the data blocks are modified in the internal storage; at least two data blocks are determined from the multiple modified data blocks, and the index data of the at least two data blocks are the same; storage addresses in the storage media are distributed to the at least two data blocks, the at least two data blocks are written in the storage media according to the distributed storage addresses; the index data pointing to the at least two data blocks are modified.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
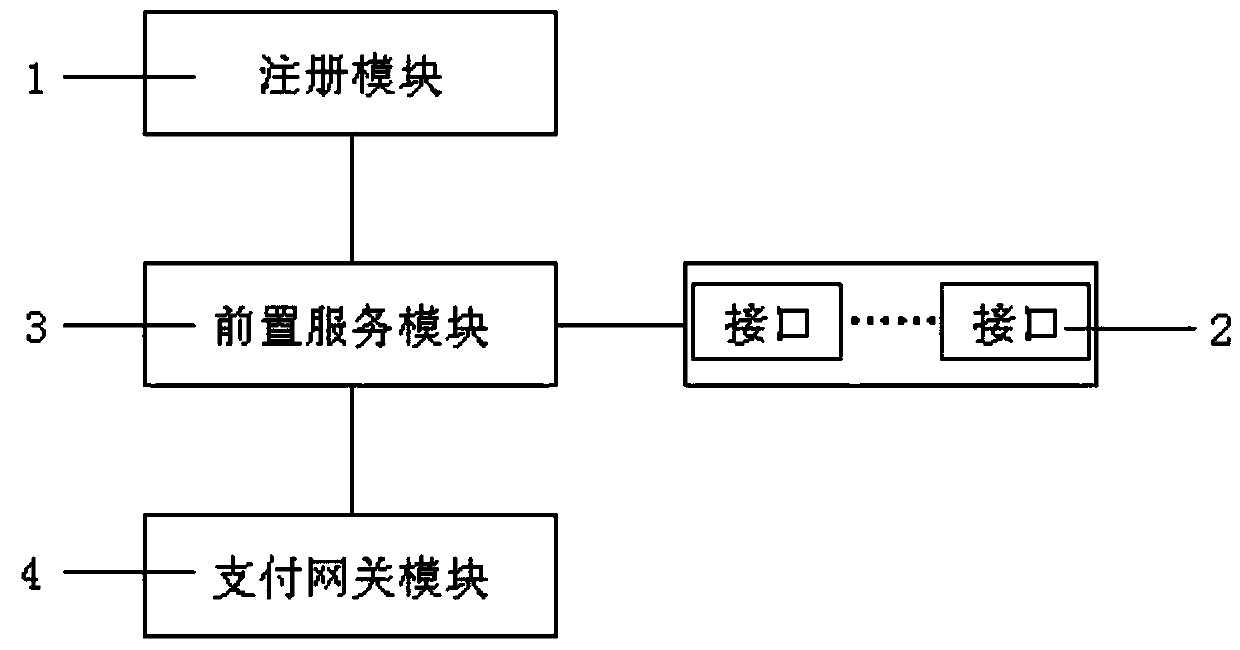
Compatible system of payment channel
ActiveCN110111092AReduce the number of updatesClear boundariesPayment architectureElectric digital data processingComputer moduleComputer science
The invention provides a compatible system of a payment channel. The compatible system comprises a plurality of interfaces, and the interfaces are used for accessing different payment systems into thecompatible system. The compatible system further comprises a registration module which is used for registering the payment system accessed into the compatible system so as to form corresponding payment channels according to payment system parameters provided by the payment system; a payment gateway module used for acquiring a payment request input by a user and preprocessing the payment request to obtain a processing result associated with the payment request; and a front-end service module connected with the interface, the payment gateway module and the registration module, and the front-endservice module forwarding the processing result to a payment system corresponding to the payment channel according to the payment channel corresponding to the processing result, so that the payment system processes the processing result. The system has the beneficial effects that the large-area updating frequency of the system is reduced, so that the cost is reduced, and the decoupling complexityof the system is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANDPAL INFORMATION TECH SERVICE
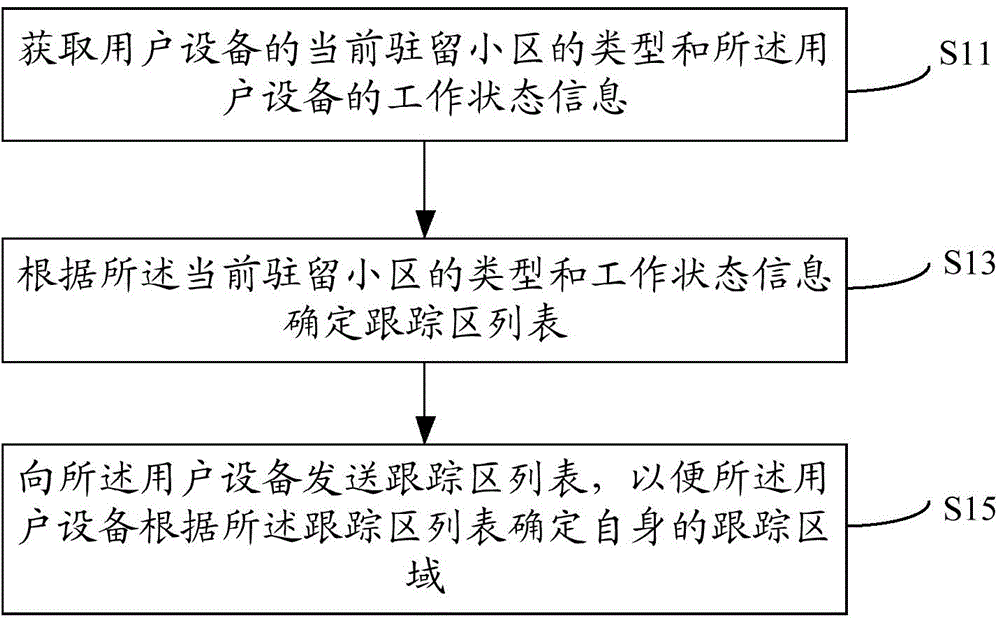
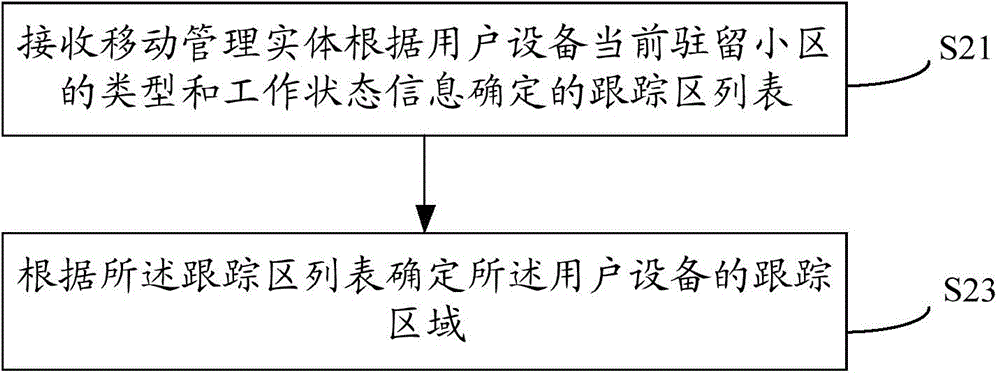
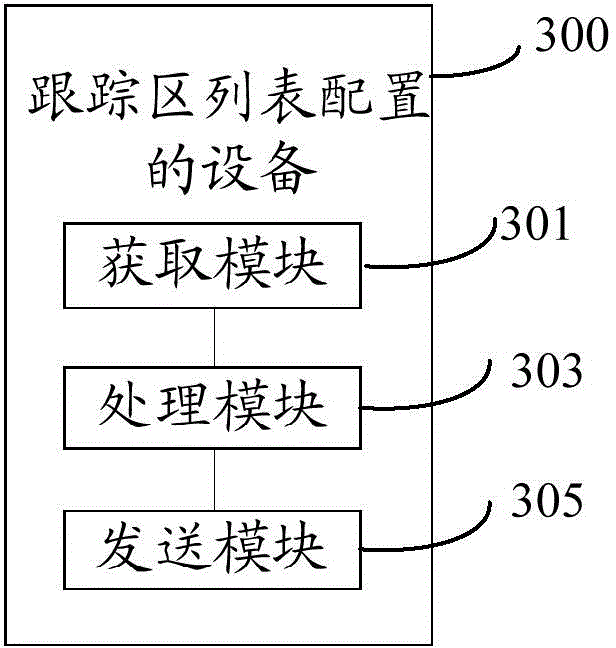
Tracking area list configuration method, device and system
ActiveCN106034297AReduce the number of updatesLittle impact on performanceNetwork data managementPagingMicrocell
The invention provides a tracking area list configuration method, device and system. The tracking area list configuration method comprises steps of obtaining a type of a cell where a user device currently resides, determining a tracking area list according to the type and a working state of the current residing cell, transmitting a tracking area list to the user device in order to make the user device determine the tracking area of the user device according to the tracking cell list. The tracking area list configuration method, device and system can dynamically configure the tracking area list for the user device by targeting the user device residing cell which can be a macrocell, a microcell or a picocell and user device working state information, reduce updating times of the tracking area when the user device moves among the macrocell and the microcell or the picocell under a condition that the tracking areas of the macro cell and the microcell or the picocell in the adjacent areas are different, and dramatically reduce a load of a paging amount of the microcell or the picocell.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Gray rubber quartz plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102617943AImprove wear resistanceGood acid and alkali resistanceRubber layered productsRough surfacePolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of rubber quartz plates, and particularly discloses a gray rubber quartz plate and a preparation method of the gray rubber quartz plate. The gray rubber quartz plate has the technical scheme that the quartz plate comprises a plate body and a rough surface layer, and is characterized in that the plate body comprises the following materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of rubber, 5.9-29 parts of quartz powder, 10-52 parts of white carbon black, 4-18 parts of activating agent, 0.8-5.5 parts of accelerating agent, 0.9-8.5 parts of vulcanizing agent, 2-50 parts of softener, 0.8-1.1 parts of coloring agent, 0.8-2 parts of bonding agent, 1-5 parts of anti-aging agent and 1.8-4.0 parts of solubilizer. The wear-resistant performance as well as the acid-resistant and alkaline-resistant properties of the rubber quartz plate can be improved, the heat absorption and the high light reflection can be reduced, and the service life is greatly prolonged.
Owner:李彦峰
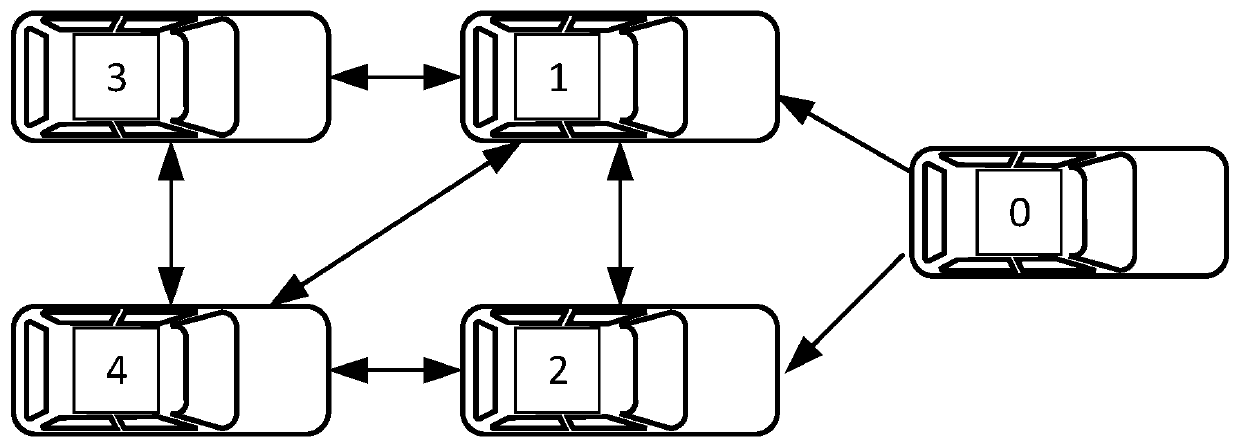
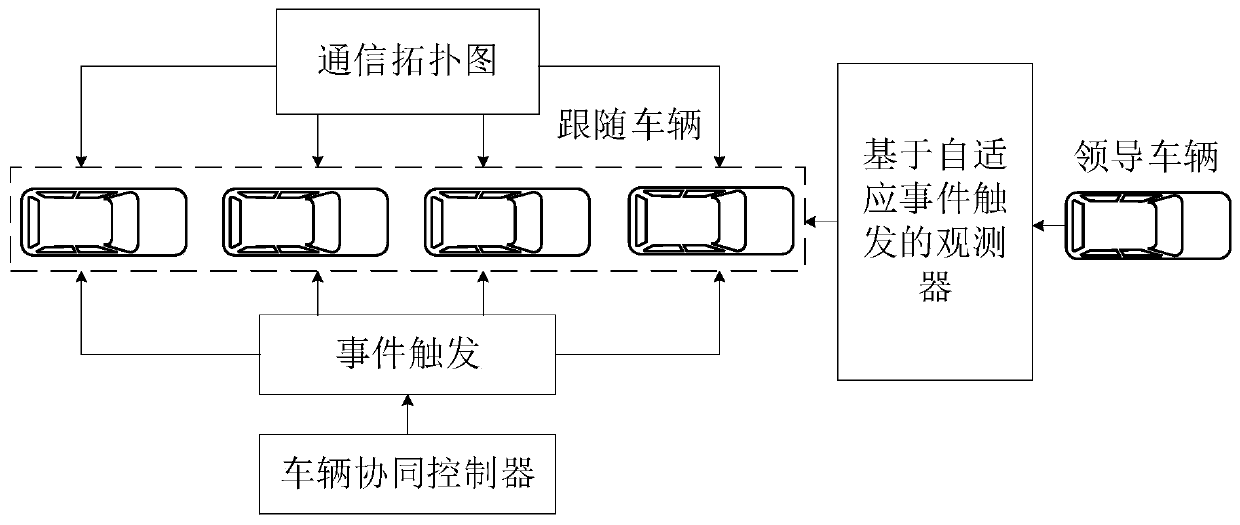
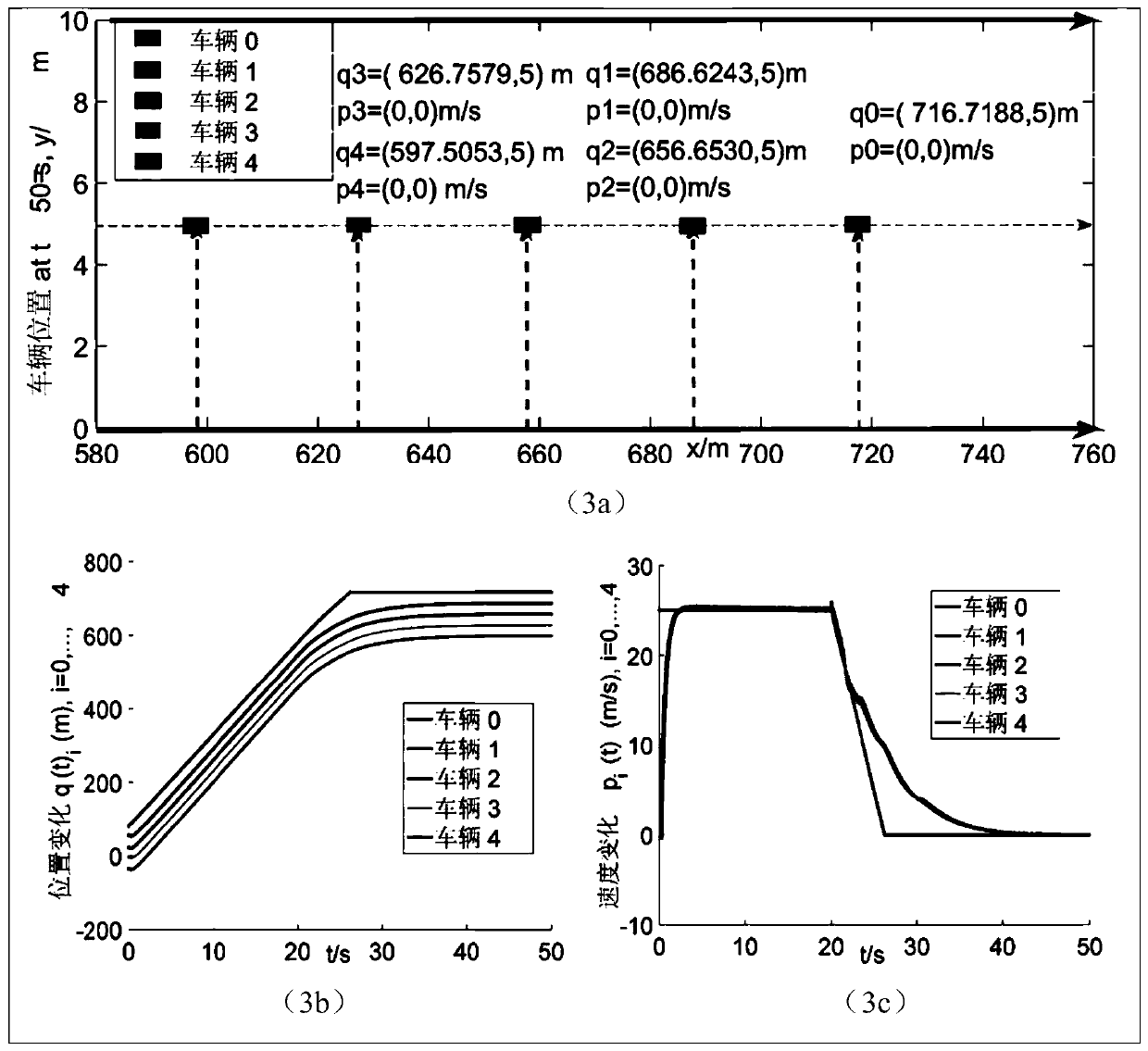
Traffic flow distributed cooperative formation control method based on adaptive event triggering
ActiveCN110782650AReduce communication loadReduce the number of updatesPlatooningTransmissionObstacle avoidanceSelf adaptive
The invention relates to a traffic flow distributed cooperative formation control method based on adaptive event triggering. The method comprises the steps: performing an obstacle avoidance control step; to be specific, building an unmanned vehicle linear kinetic model, and carrying out obstacle avoidance controlling with a neighbor vehicle based on global coordinate position information of an unmanned vehicle and a neighbor unmanned vehicle; performing a leader vehicle observation step; to be specific, acquiring state information of the leader vehicle by using a distributed observer based onadaptive event triggering; and performing a path following step; to be specific, adjusting the state information of the unmanned vehicle according to the state information of the leader vehicle by using a vehicle cooperative controller triggered based on an adaptive event. Compared with the prior art, the traffic flow distributed cooperative formation control method has the following advantages: with introduction of an event triggering mechanism, the communication load between vehicles is reduced and cooperative formation control over traffic flow is realized.
Owner:TONGJI ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE RES INST SUZHOU CO LTD
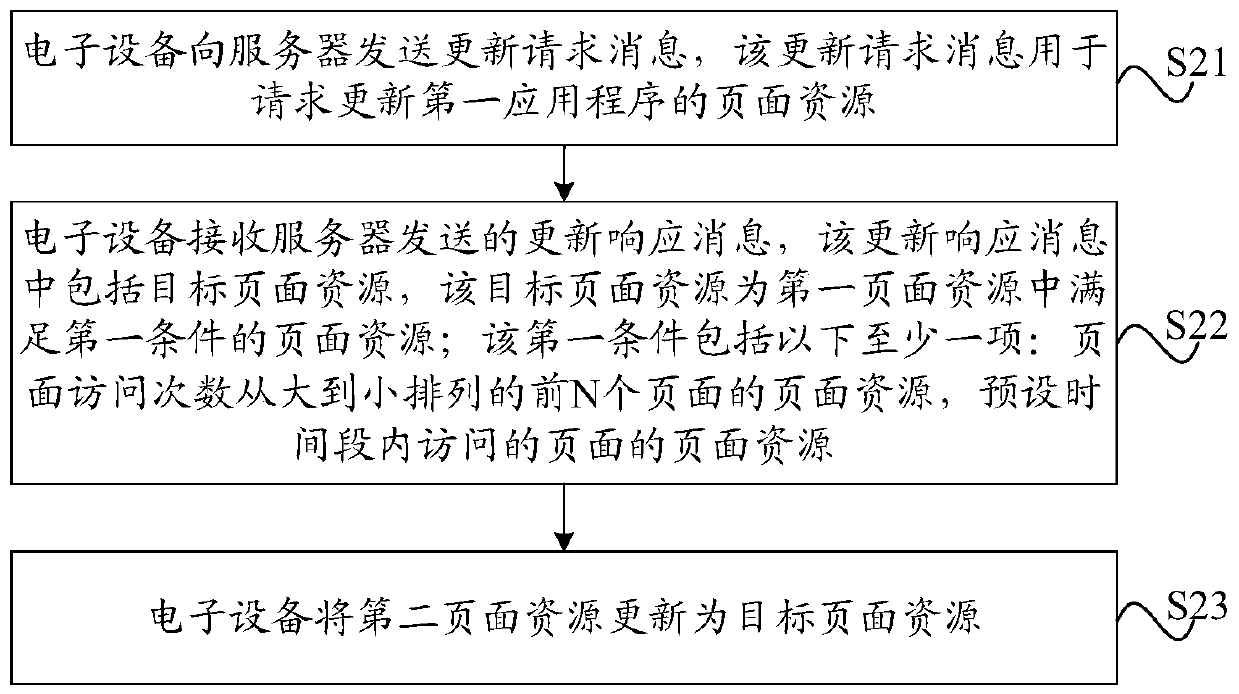
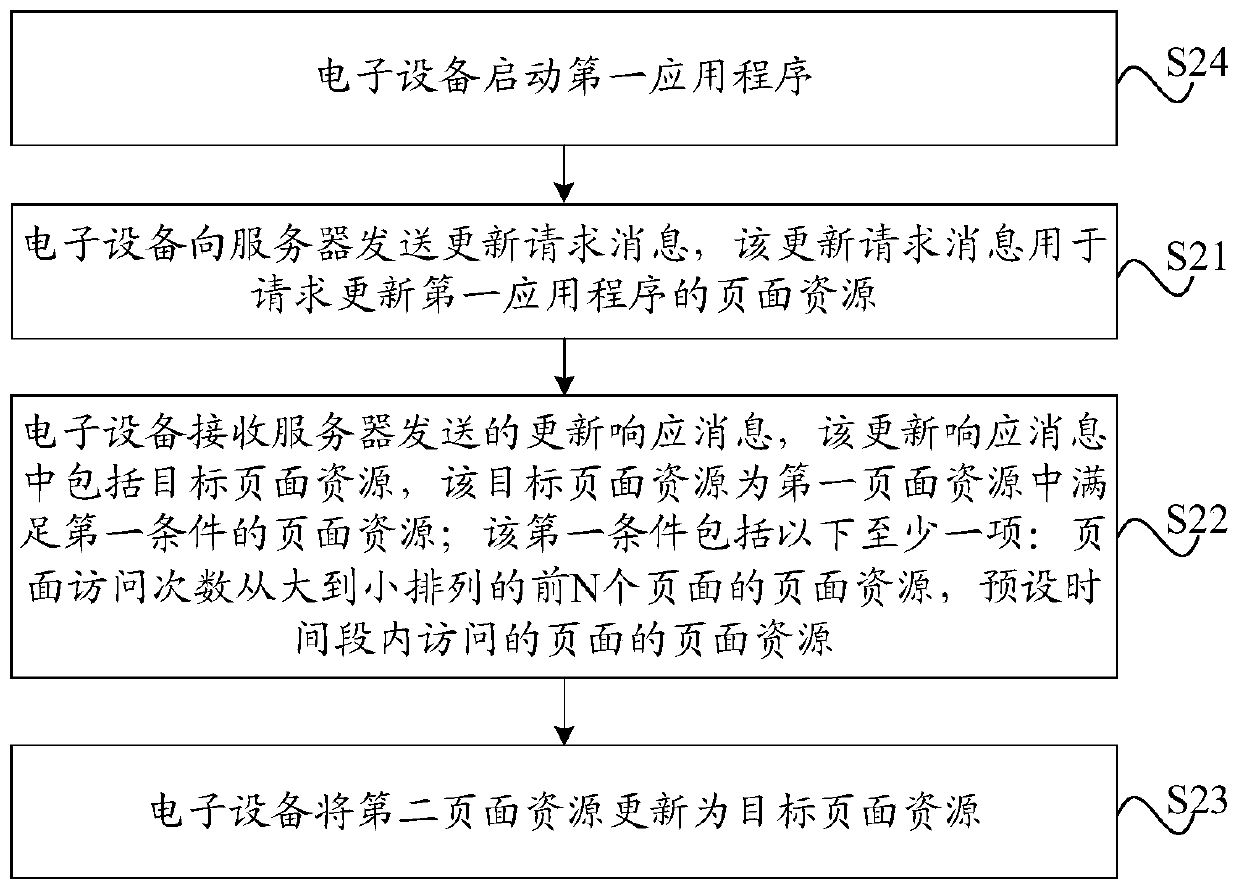
Page resource updating method and device, electronic equipment, server and storage medium
PendingCN111427648AReduce data trafficReduce the number of updatesExecution for user interfacesSpecial data processing applicationsAccess timeEngineering
The invention provides a page resource updating method and device, electronic equipment, a server and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: sending an update request message to aserver, wherein the update request message is used for requesting to update page resources of a first application program; receiving an update response message sent by the server, the update responsemessage comprising a target page resource, the target page resource being a page resource satisfying a first condition in a first page resource, and the first page resource being a page resource of afirst application stored by the server; wherein the first condition comprises at least one of the following items: page resources of first N pages of which the page access times are arranged from large to small, and page resources of pages accessed in a preset time period, and N is a positive integer; and updating a second page resource as a target page resource, the second page resource being apage resource of the first application stored in the electronic device, and the second page resource and the first page resource being page resources of different versions.
Owner:BEIJING DAJIA INTERNET INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Application update prompt method and apparatus
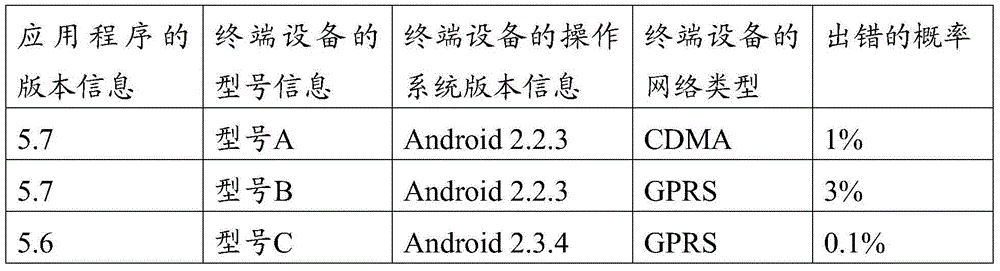
ActiveCN105224343AImprove stabilityReduce the number of updatesHardware monitoringError avoidanceTerminal equipmentApplication procedure
Embodiments of the application provide an application update method and apparatus. The method comprises: when a specified application has updateable content, making statistics on an error probability of the application running in one or more specified conditions, wherein one or more specified conditions involve attributes and / or an operating environment of the application; and when the error probability meets a set condition, pushing an application update prompt to a terminal device meeting one or more specified conditions. According to the application update method and apparatus provided by the embodiments of the application, the pushing number and frequency of other unnecessary update prompts are reduced, the system resource consumption of a server is reduced, the response number and frequency of the terminal device to the update prompts are reduced, and the system resource consumption of the terminal device is also reduced; in addition, the update prompt number and frequency are reduced, so that the user experience can be greatly improved; and furthermore, the update prompts are reduced, so that the application update number is also reduced and the network bandwidth occupation is greatly reduced.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
WSN pair key management method suitable for unicast communication
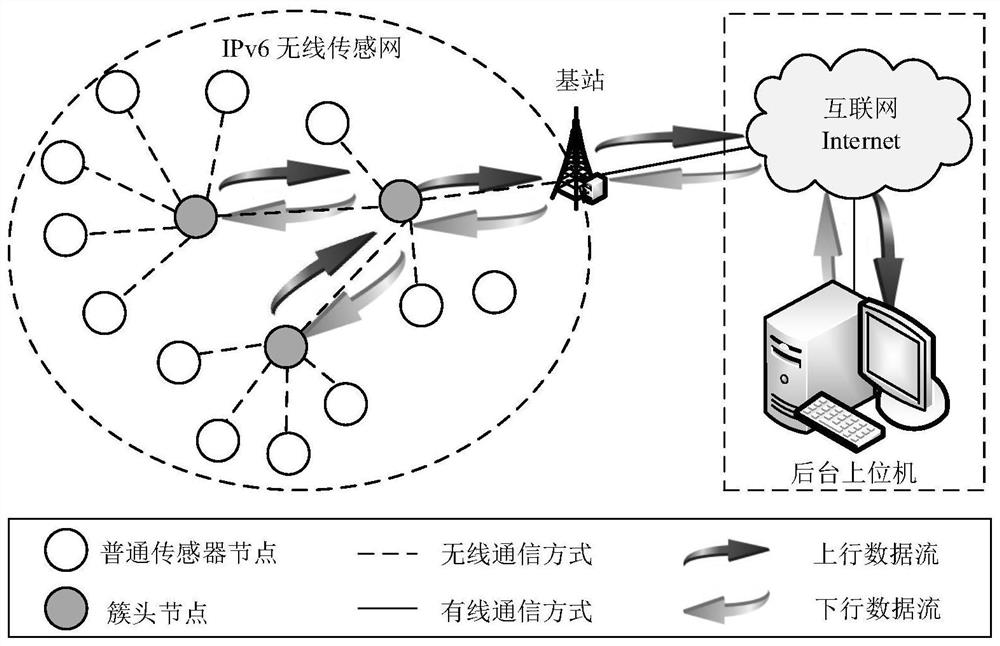
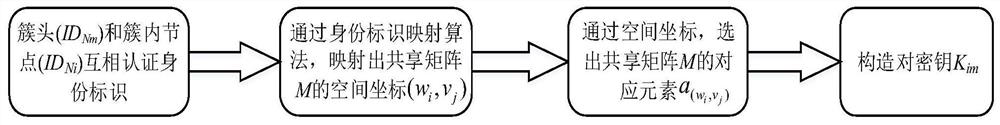
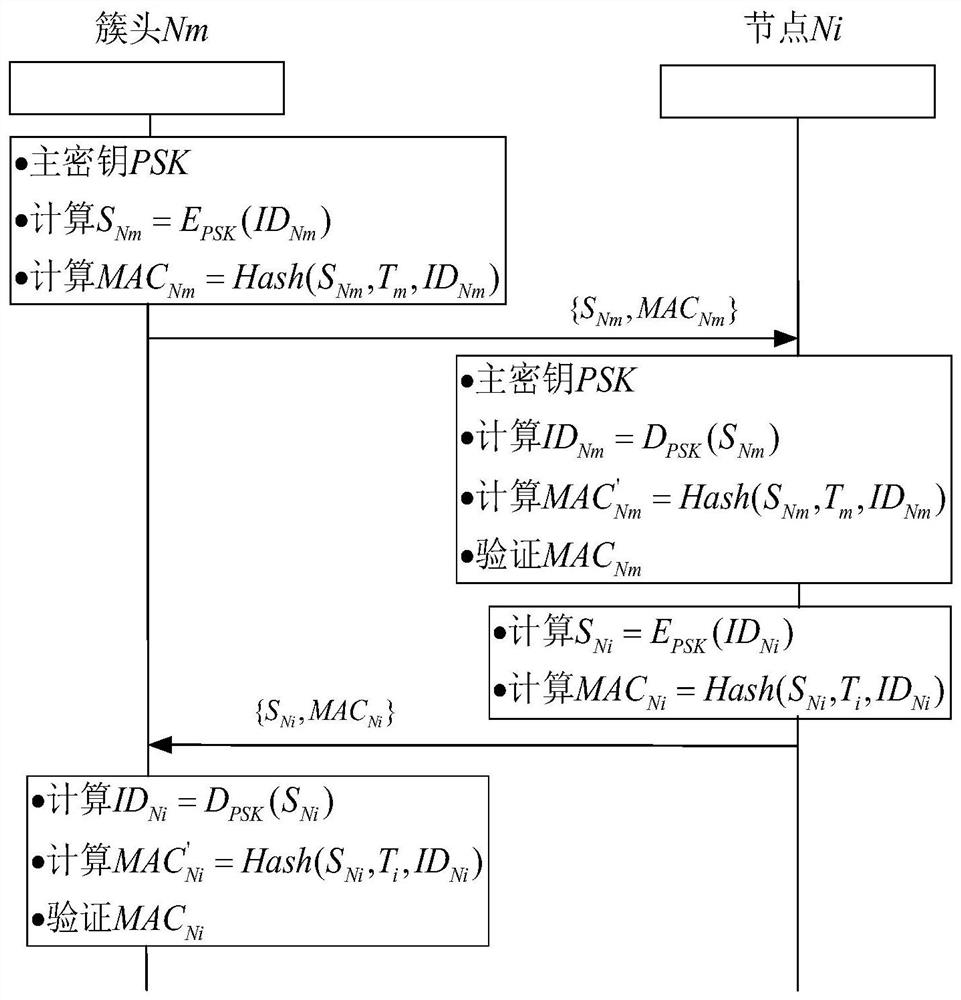
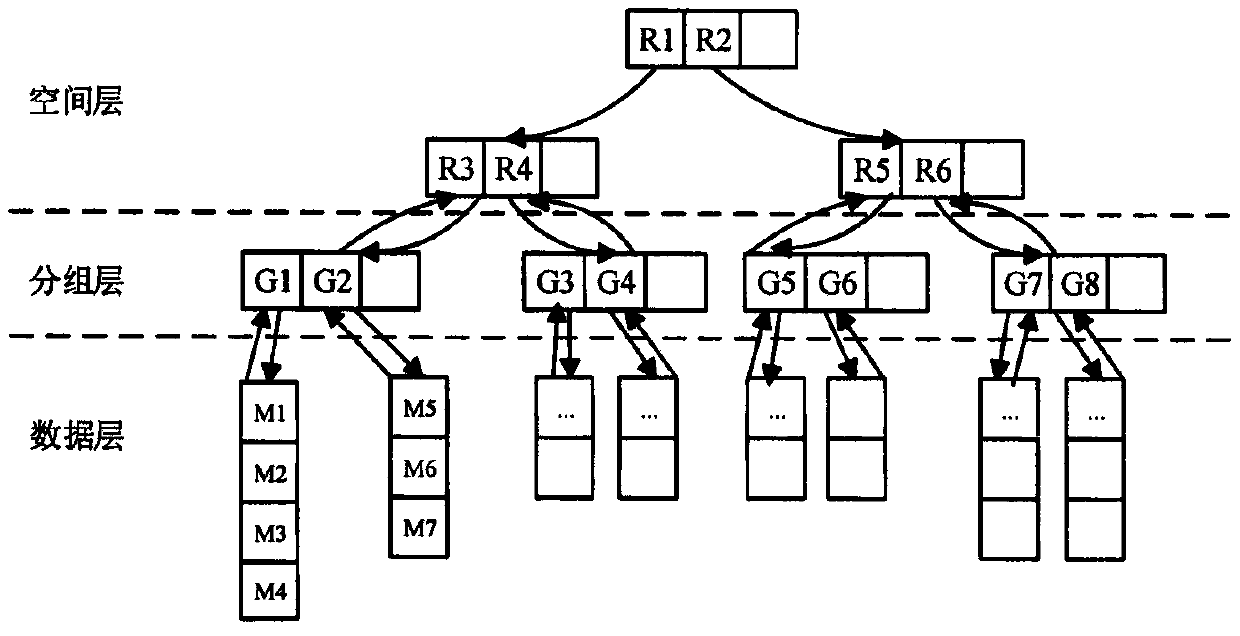
ActiveCN112383916AOvercoming Safety Threshold IssuesEnsure safetySecurity arrangementAttackEngineering
The invention relates to a WSN pair key management method suitable for unicast communication, and belongs to the field of network security and communication, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, initializing system parameters; S2, enabling two communication parties to mutually authenticate identities; S3, constructing space coordinates of the shared matrix M; s4, enabling the two communication parties to establish a pair key; s5: updating the key. According to the method, on the basis of reducing the storage overhead of each node, the establishment of the pair key and the updatingof the pair key are completed, the dynamic distribution of the pair key management scheme coefficient based on the symmetric polynomial is realized, the security threshold problem of the symmetric polynomial pair key management scheme is overcome, meanwhile, the forward security and the backward security in the whole network operation process are ensured, the key connectivity is relatively high,the network expansion performance is good, and the capability of resisting malicious attacks is very strong.
Owner:刘中亚
Method for indexing uncertain moving objects on basis of group division
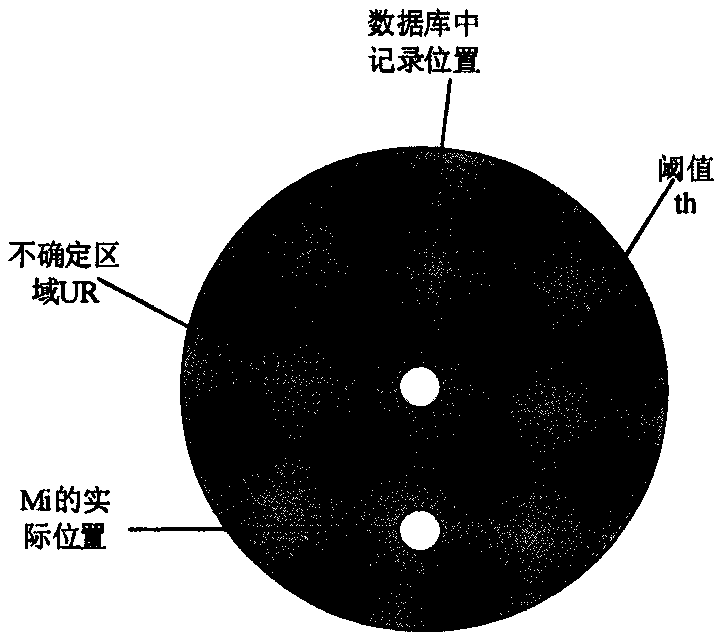
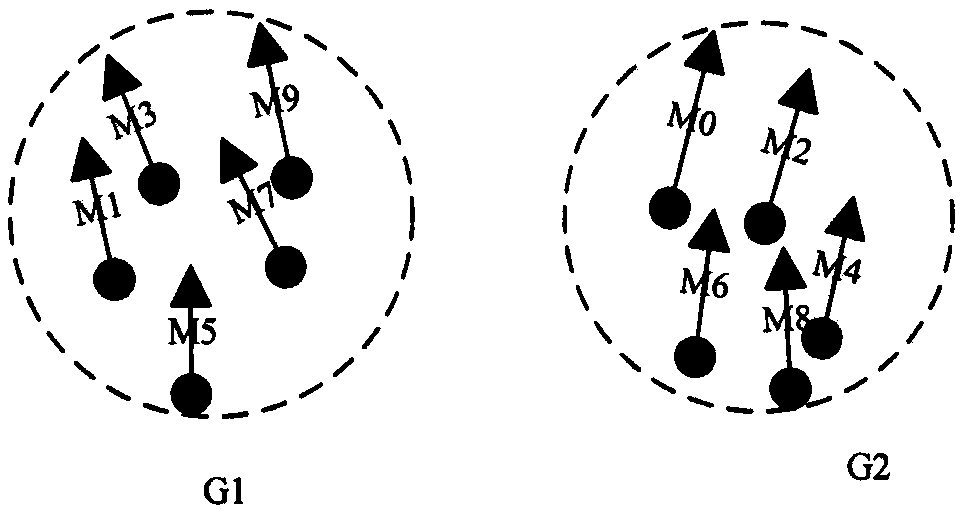
ActiveCN105512317AReduce the number of updatesReduce update costSpecial data processing applicationsComputer visionSpatial database
The invention relates to a method for indexing uncertain moving objects on basis of group division and belongs to the technical field of moving object management in a computer spatial database. According to the method, on the basis of a conventional uncertain indexing structure, a group division strategy is added to solve the problem of updating cost increase caused by updating of frequency positions. Some moving objects in a set of a large quantity of moving objects are found having similar moving tracks; if the tracks are similar, the moving objects are divided into one group, as for members in the same group, all that is required is to update the position of one moving object during position updating because of similarity of position information of the moving objects, and the position information of each moving object is not required to be displayed or updated in real time. A single moving object is taken as a moving object with the similar moving tracks in the representative group, the number of times for updating of the moving objects is reduced on the basis of the updating strategy, and the position updating cost of the moving objects is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
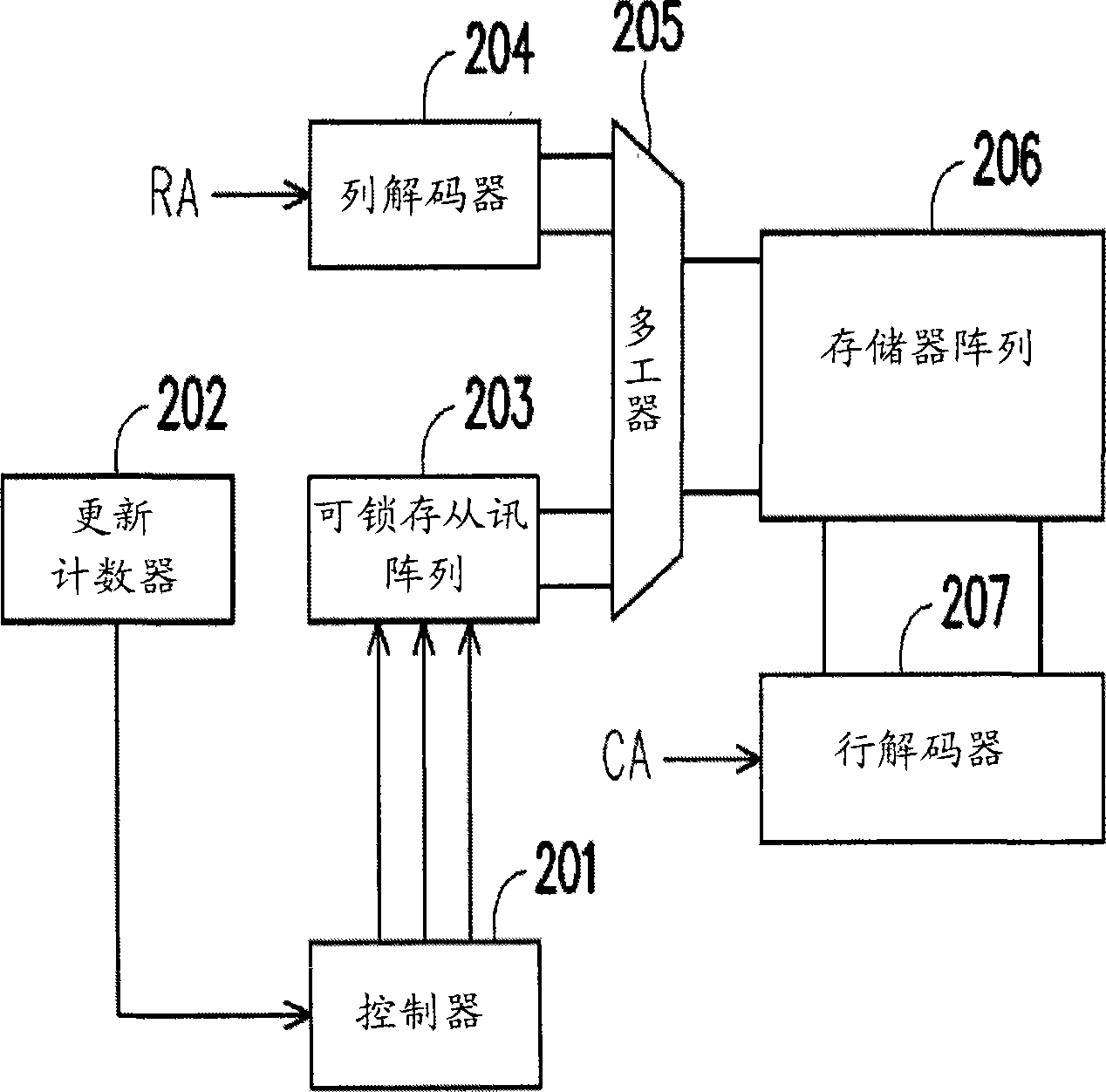
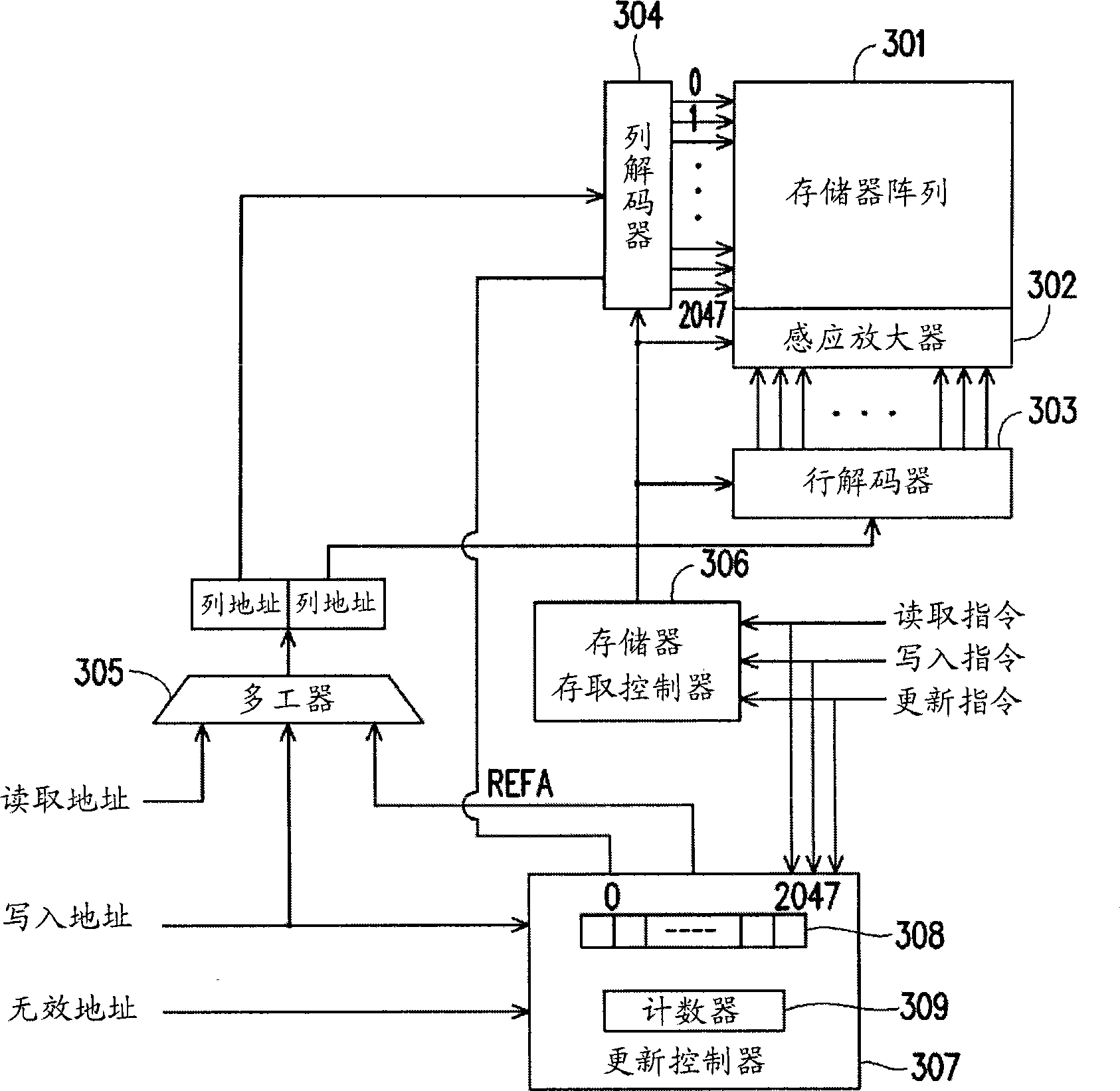
Memory device and its updating method
The invention relates to a storage device and an update method, wherein the storage device includes a storage array, which contains a plurality of storage rows. When a receiving array refreshes the impulse, the storage device can be indicated whether to be updated according to the storage rows used by a plurality of label sign setting systems and by resetting the corresponding status of the storage rows. When the receiving rows refresh the impulse, whether the storage rows shall be updated depend on the parameters like the counter value of the rows to refresh, the counter value of the remaining refresh deadline and the acceptable value of the queue. When the storage row is to be refreshed, a preferred storage row is selected to refresh according to the label and the status, also the corresponding status can be set.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
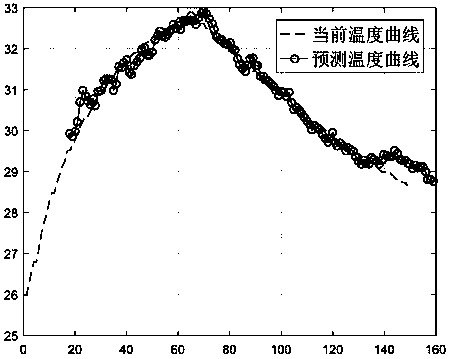
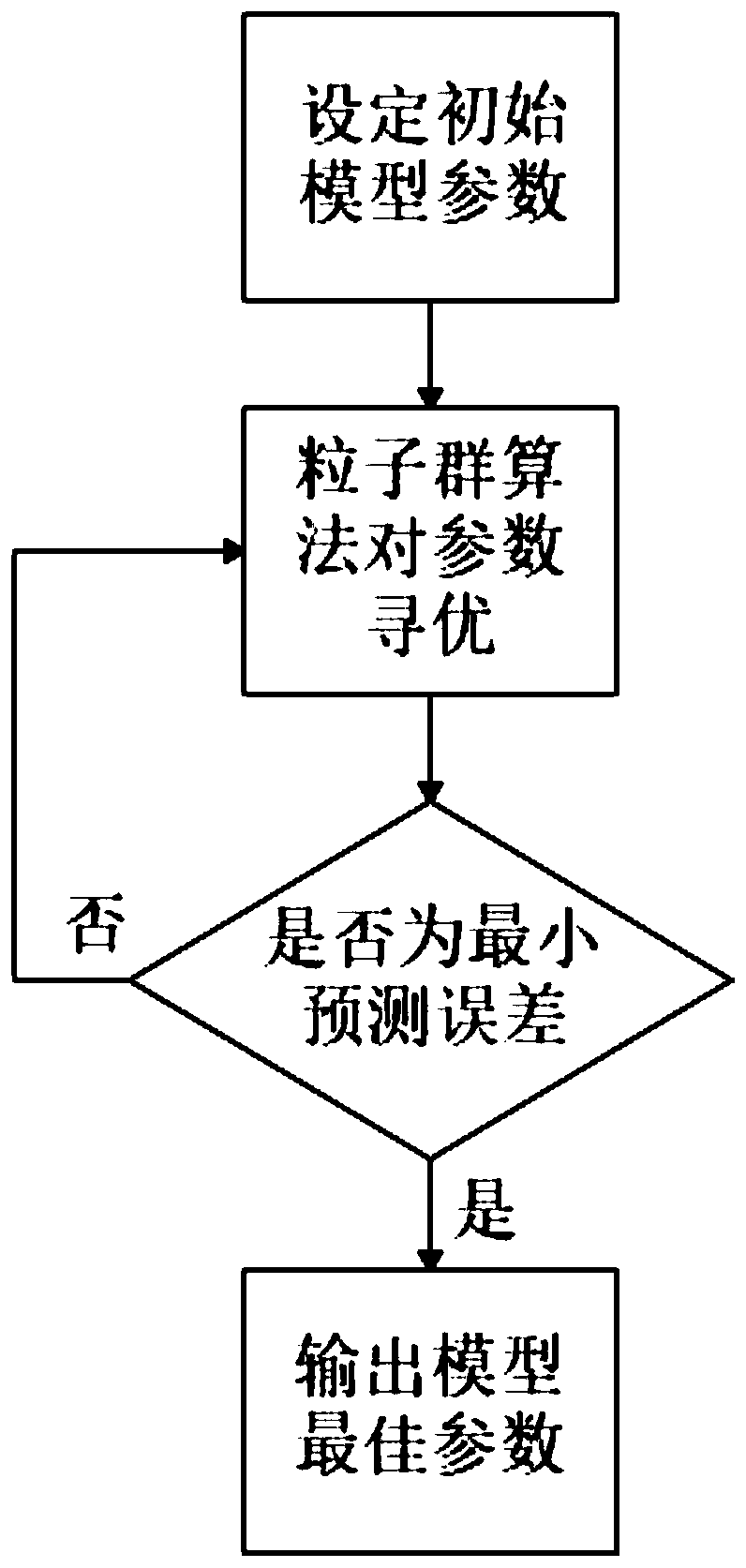
Power equipment temperature prediction method based on PSO-LSSVM online learning
PendingCN111523710AReduce the number of updatesAccurate removalForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionPredictive methodsElectric power equipment
The invention discloses a power equipment temperature prediction method based on PSO-LSSVM online learning, and the method carries out the online evaluation and screening of a training sample: firstlytransmitting the collected real-time temperature data of power equipment to a background system, and carrying out the preprocessing of the sampling data; then judging whether incremental learning iscarried out on newly added samples or not according to KKT conditions of an LSSVM model, Meanwhile, rejecting the samples with the maximum characteristic difference in the current training sample setthrough an adjusdesk cosine similarity method; and then, predicting the temperature of the power equipment after the moment t by using an online trained PSO-LSSVM model, and carrying out different levels of high-temperature early warning on the power equipment which may exceed a temperature threshold. According to the method, the contribution of the newly added samples is more emphasized, and thetraining sample set capable of best reflecting the current state is obtained, so that the generalization ability of the model is improved, the prediction operation efficiency is improved, the temperature at the next moment can be effectively predicted, and the safety of using electrical equipment is improved.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com