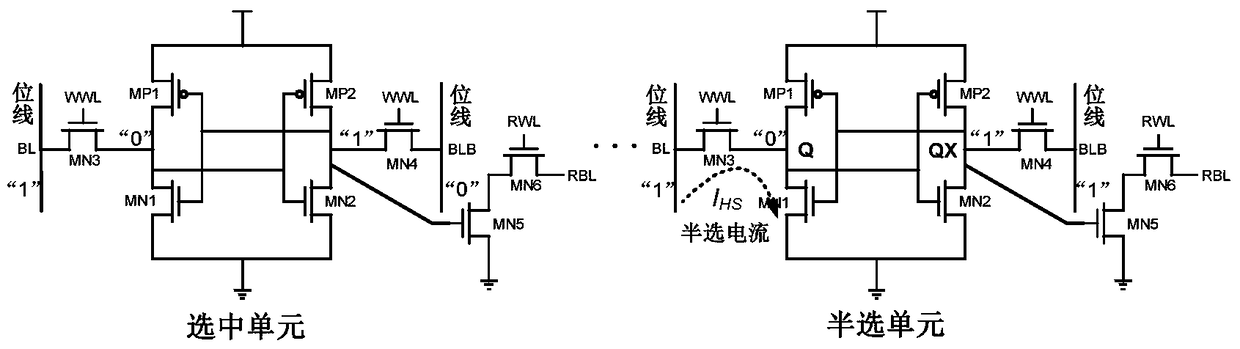
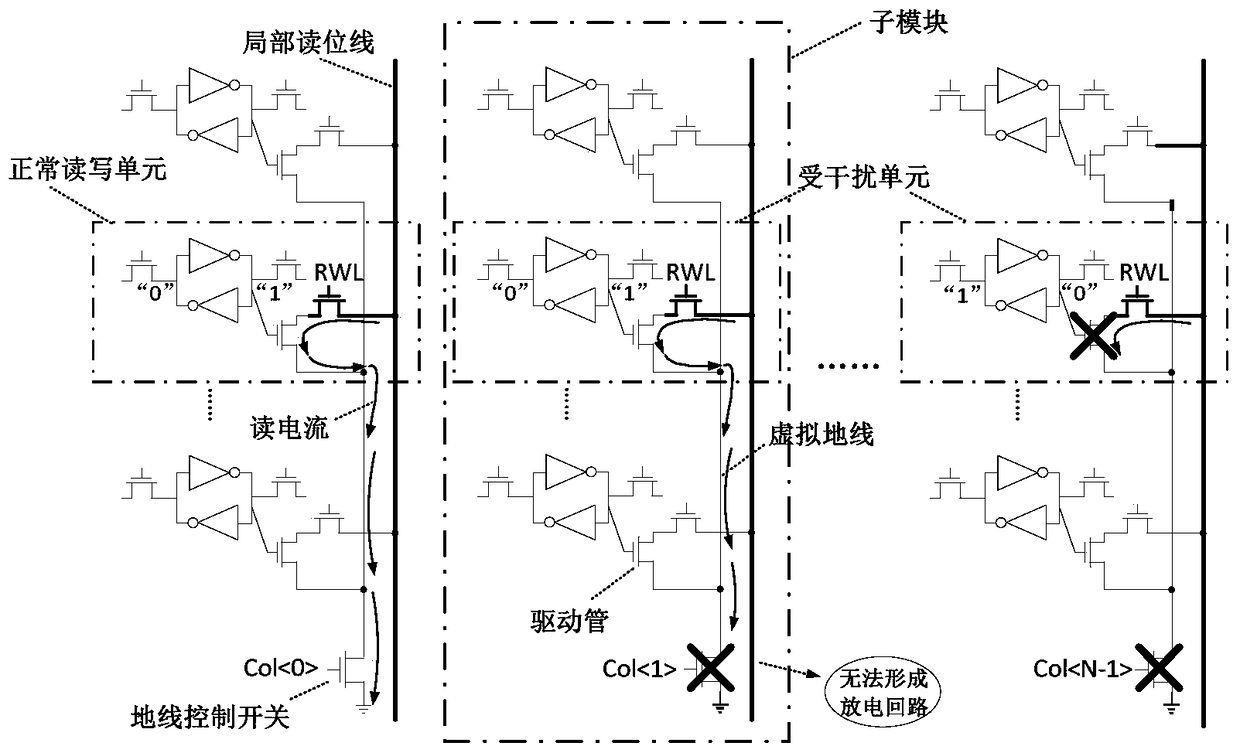
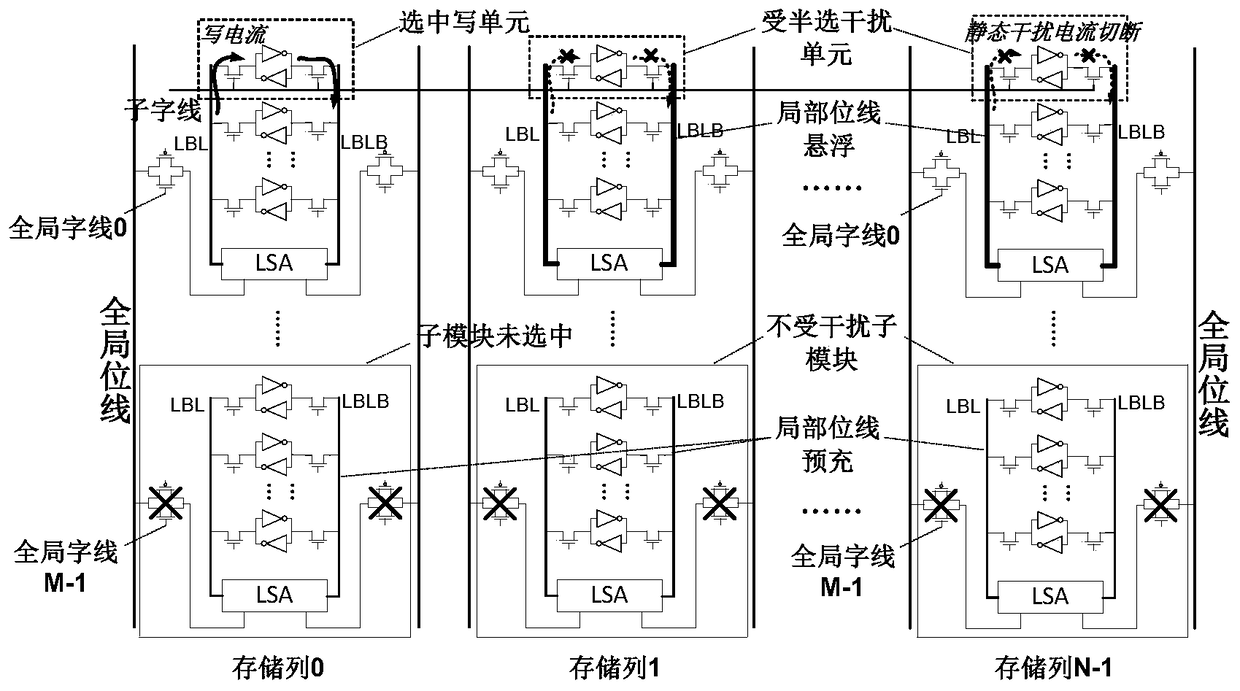
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Reduce soft error rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
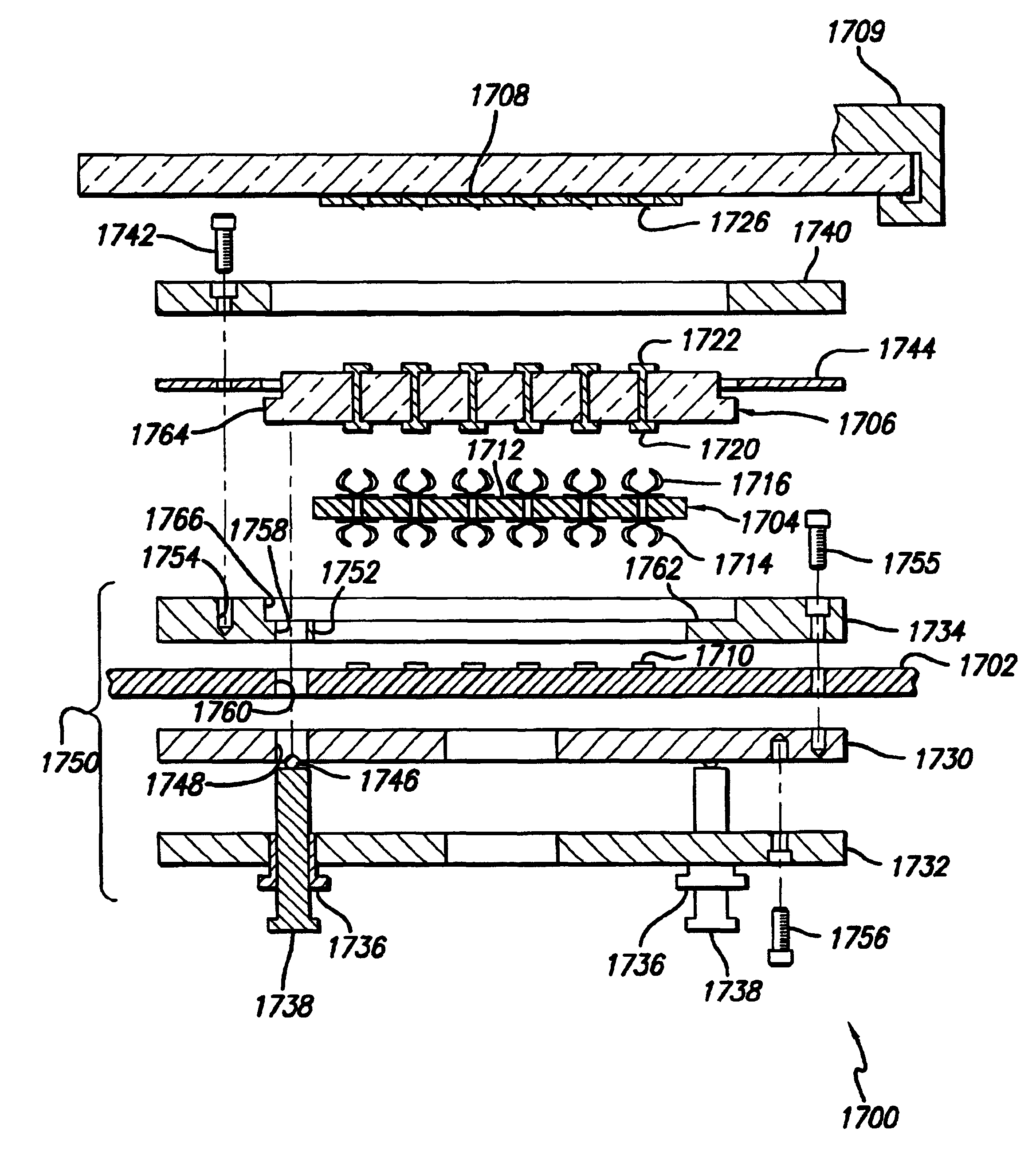
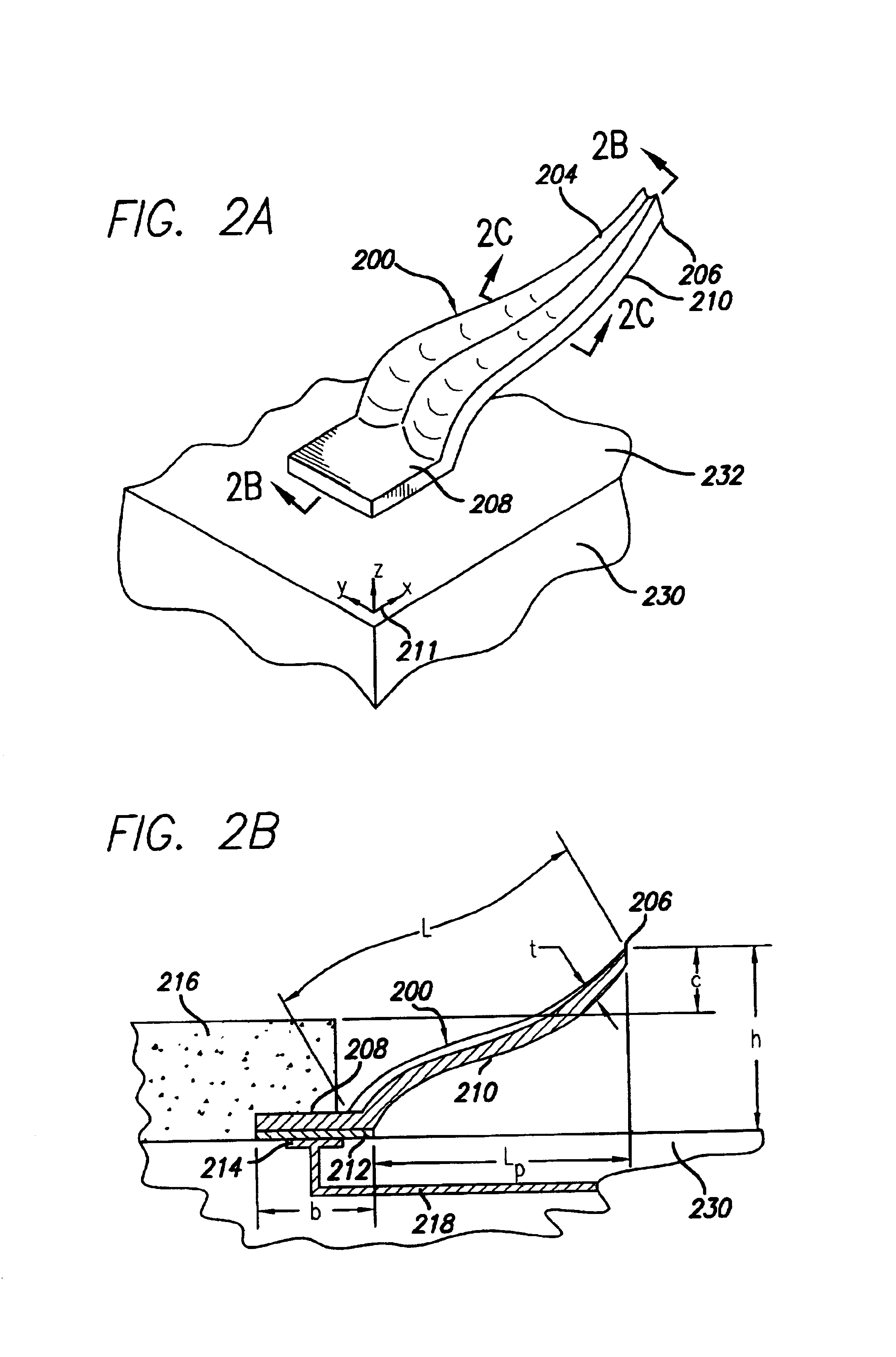
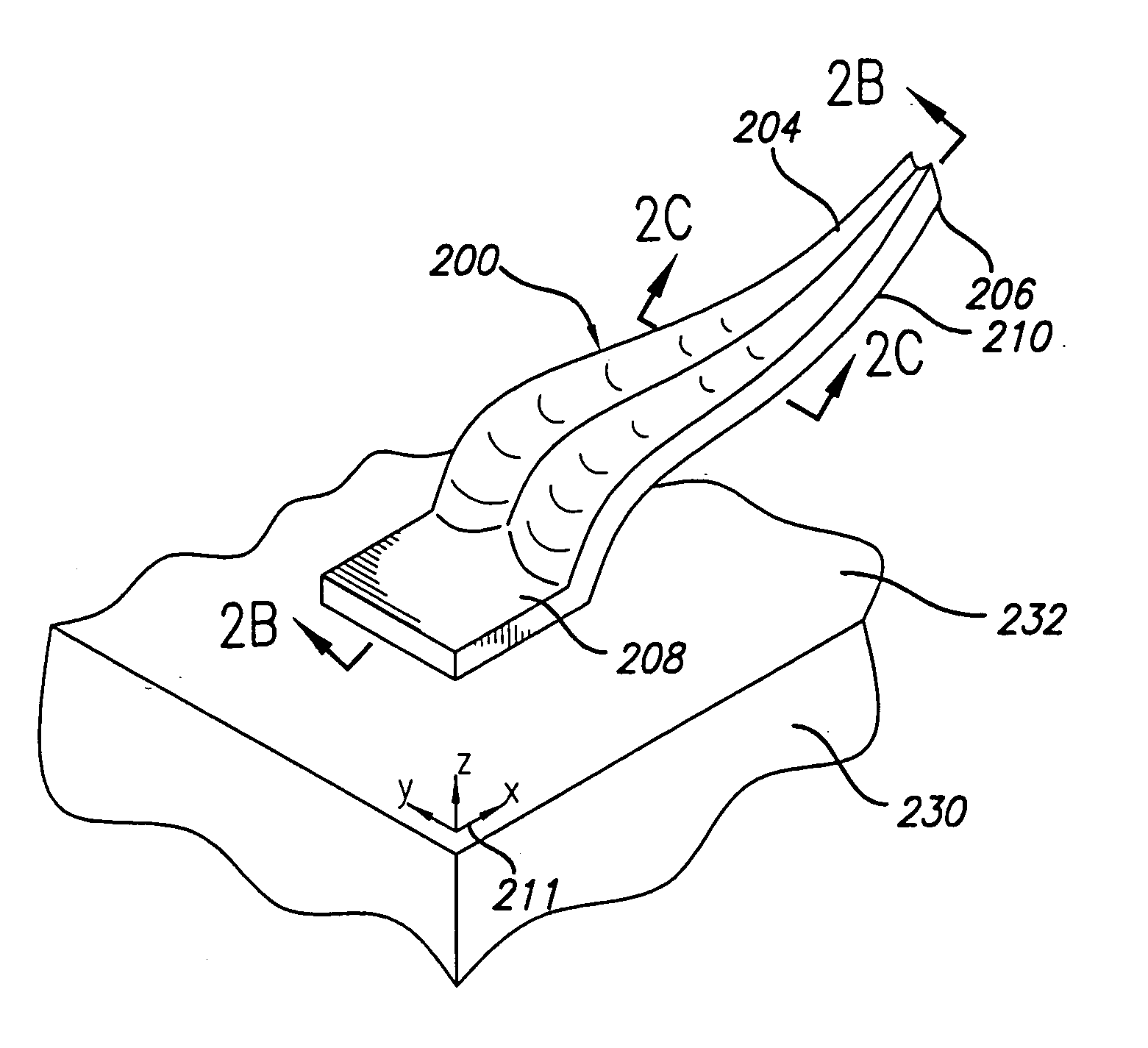
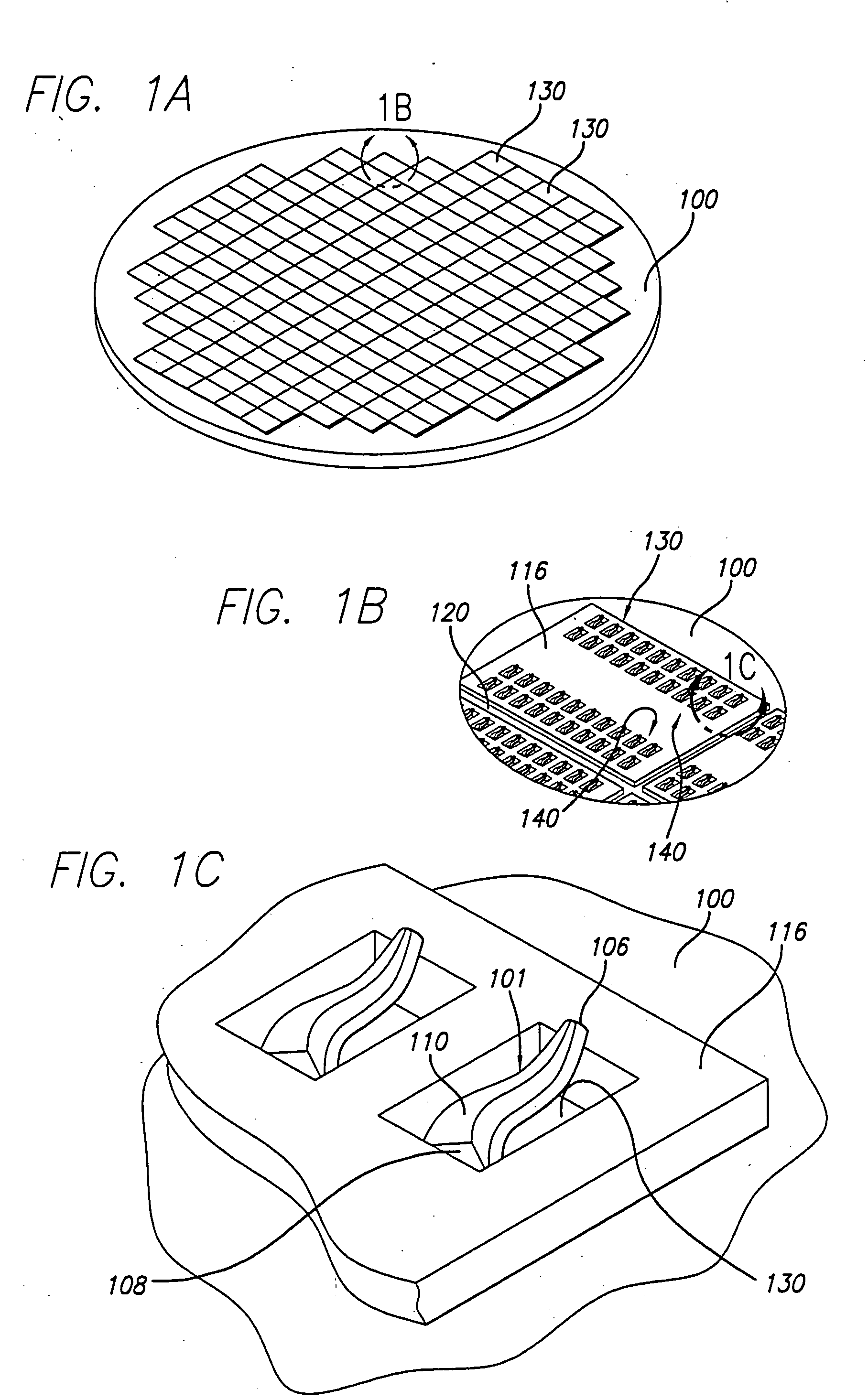
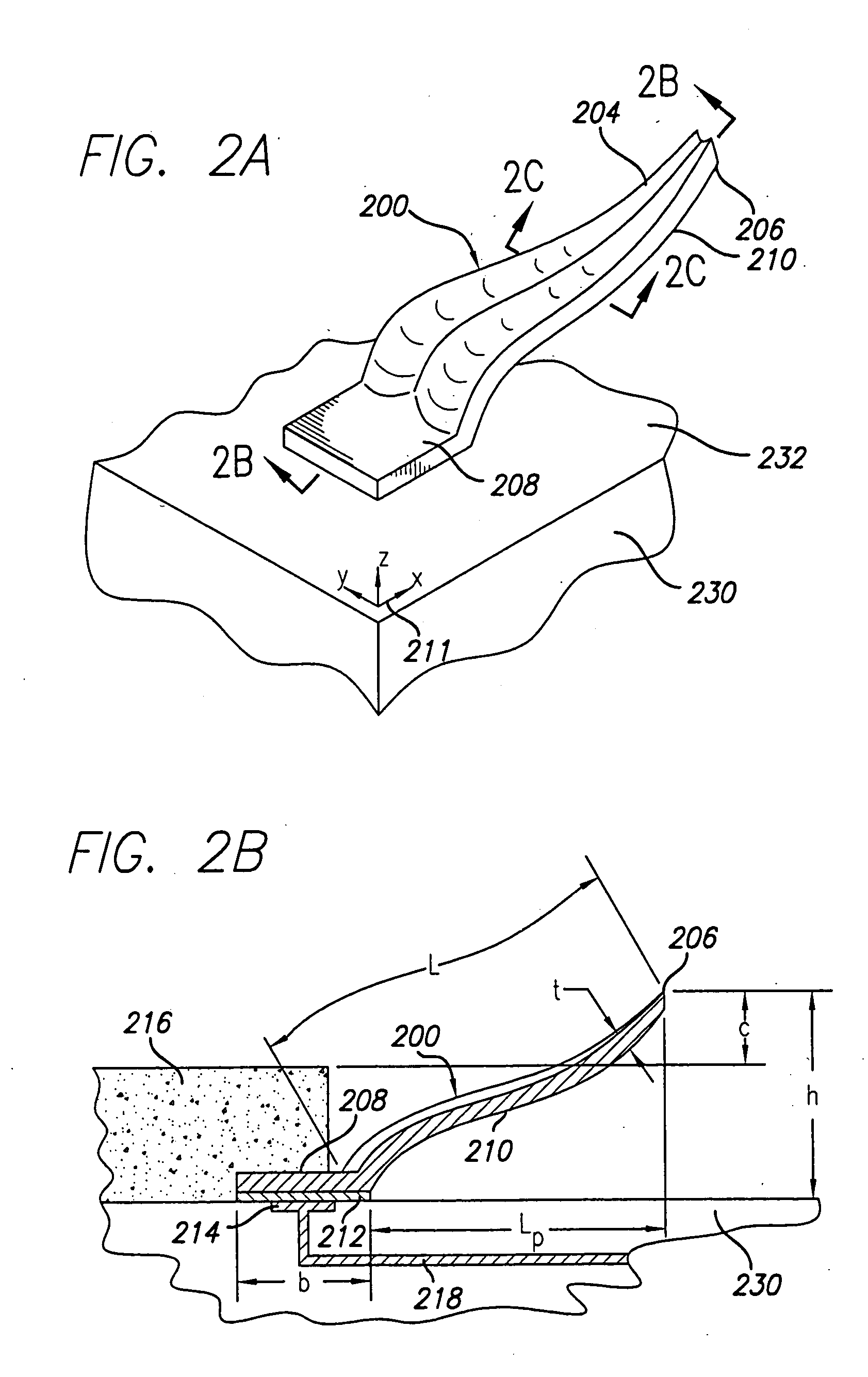
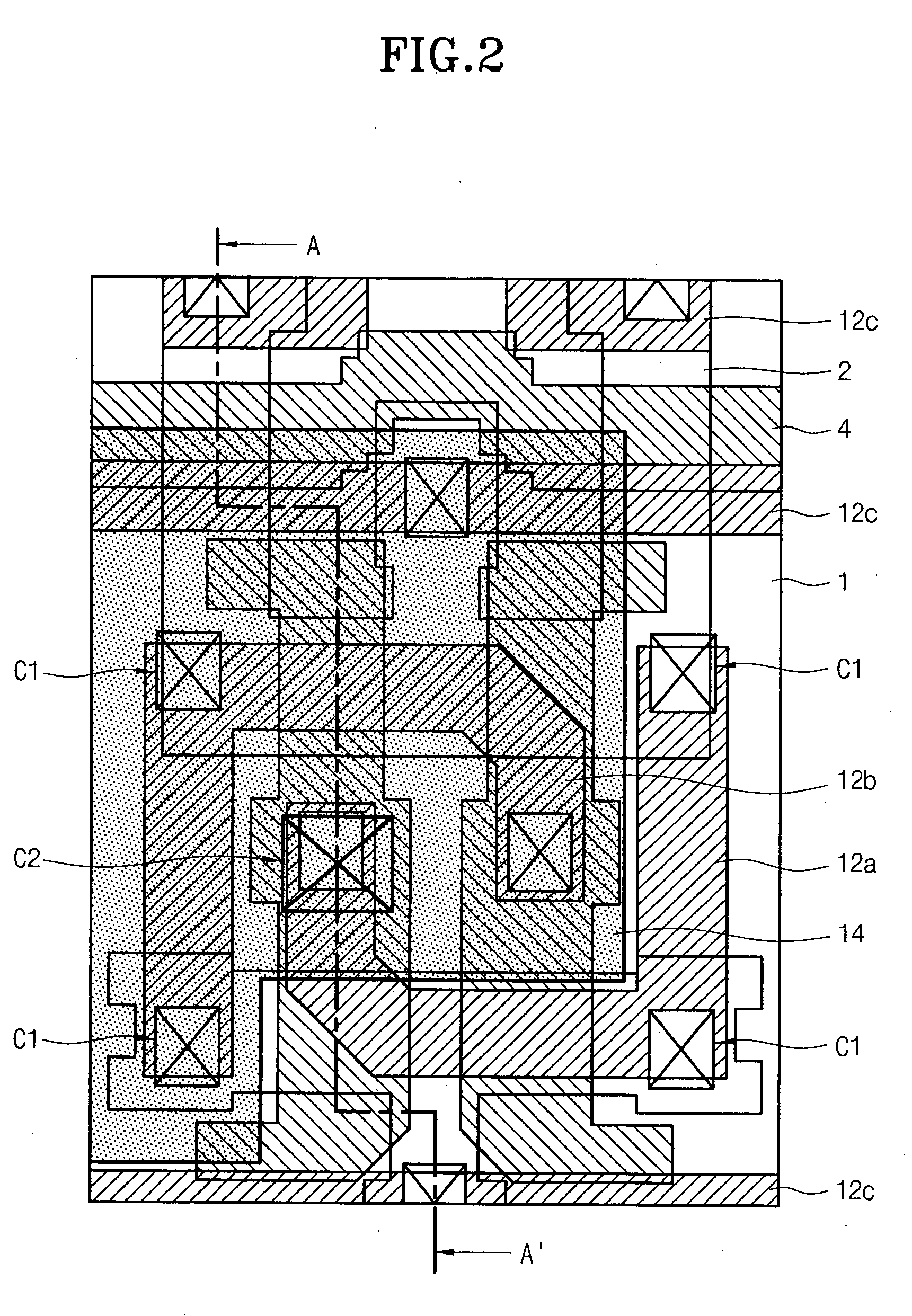
Test head assembly for electronic components with plurality of contoured microelectronic spring contacts
InactiveUS6888362B2Reduce soft error rateKeep distanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTip positionEngineering
An electronic component is disclosed, having a plurality of microelectronic spring contacts mounted to a planar face of the component. Each of the microelectronic spring contacts has a contoured beam, which may be formed of an integral layer of resilient material deposited over a contoured sacrificial substrate, and comprises a base mounted to the planar face of the component, a beam connected to the base at a first end of the beam, and a tip positioned at a free end of the beam opposite to the base. The beam has an unsupported span between its free end and its base. The microelectronic spring contacts are advantageously formed by depositing a resilient material over a molded, sacrificial substrate. The spring contacts may be provided with various innovative contoured shapes. In various embodiments of the invention, the electronic component comprises a semiconductor die, a semiconductor wafer, a LGA socket, an interposer, or a test head assembly.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Ultra high-speed si/sige modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin soi/sgoi substrate
InactiveUS20050045905A1Improve RF performanceUltra-high speed performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow noiseUltra high speed
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
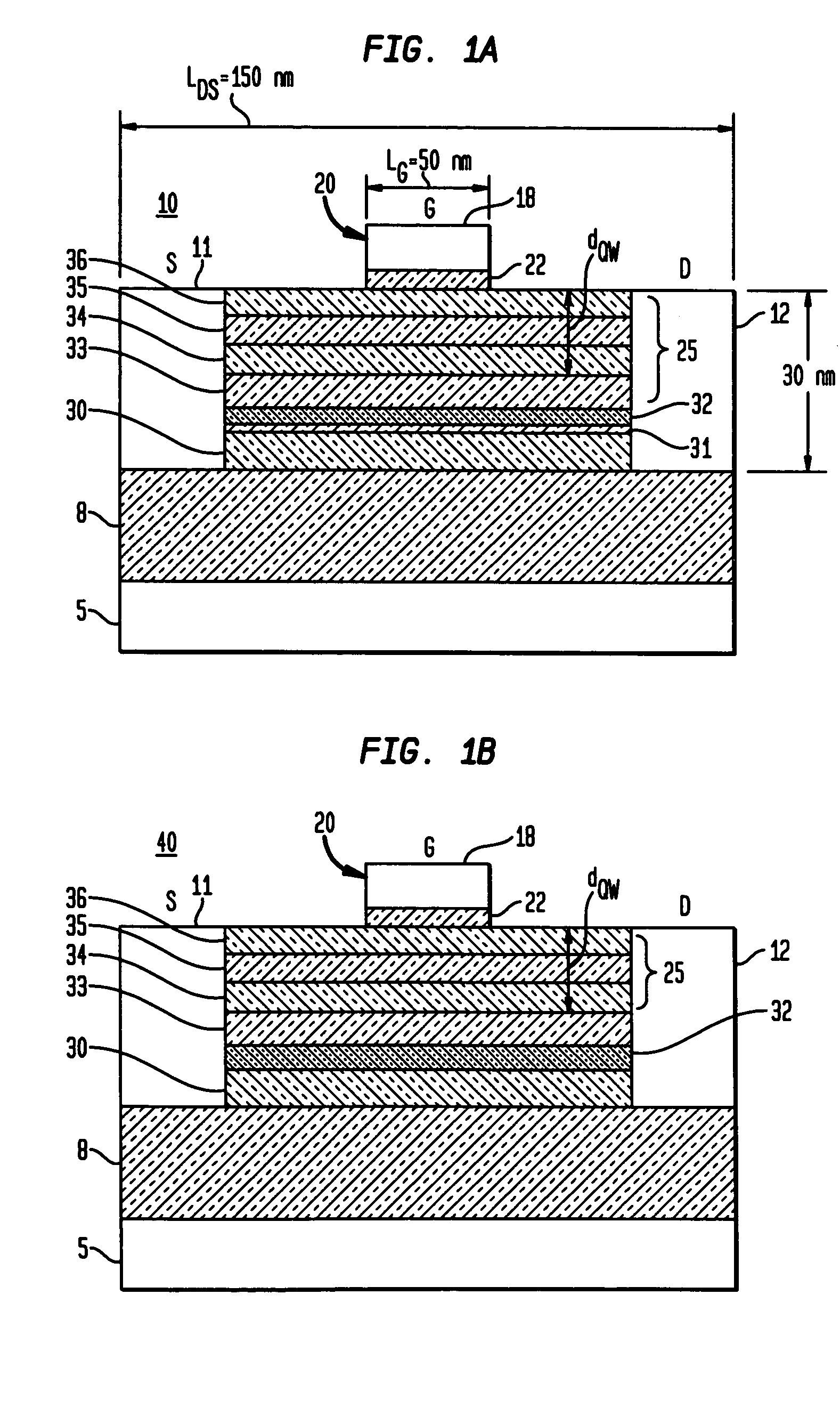
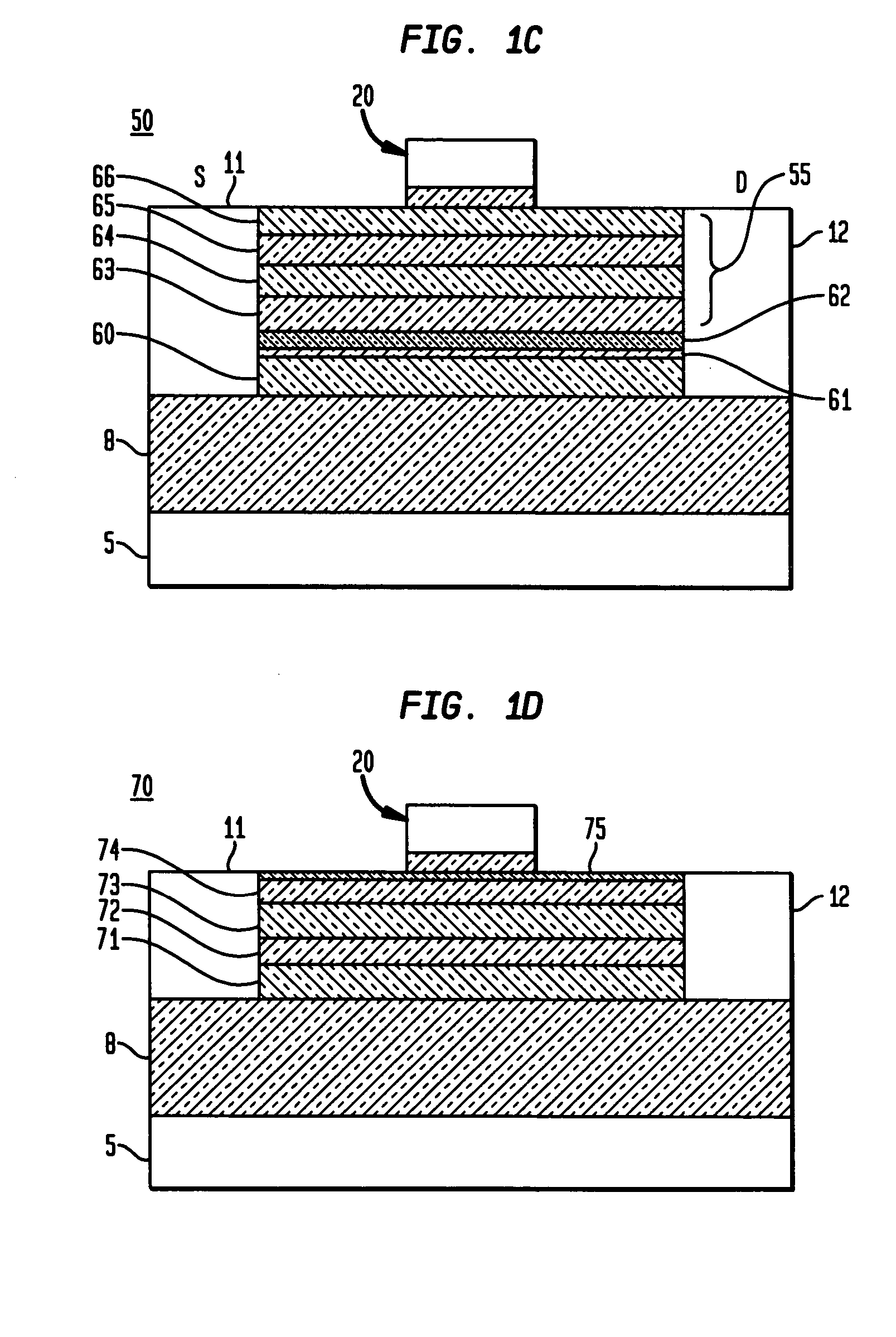
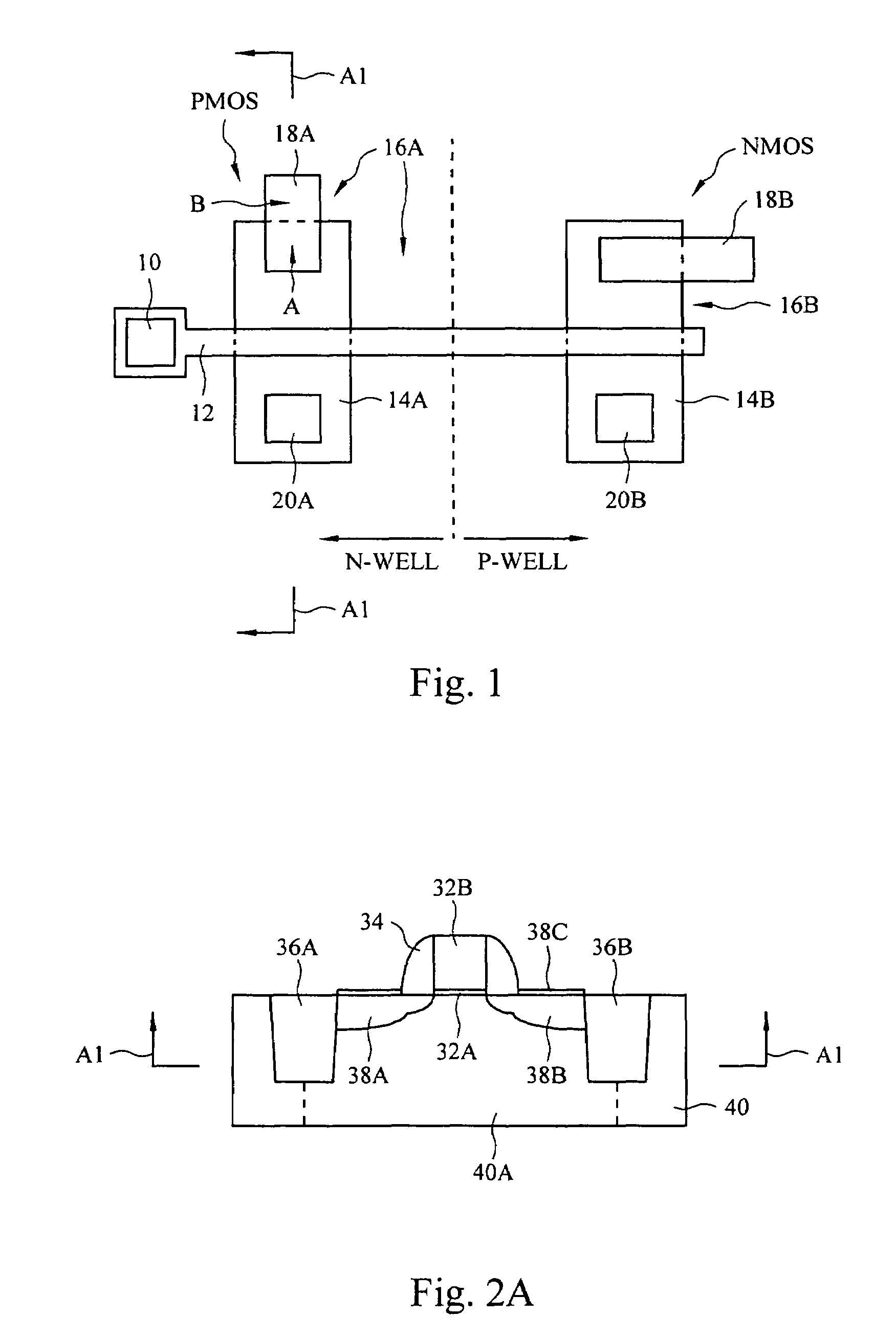
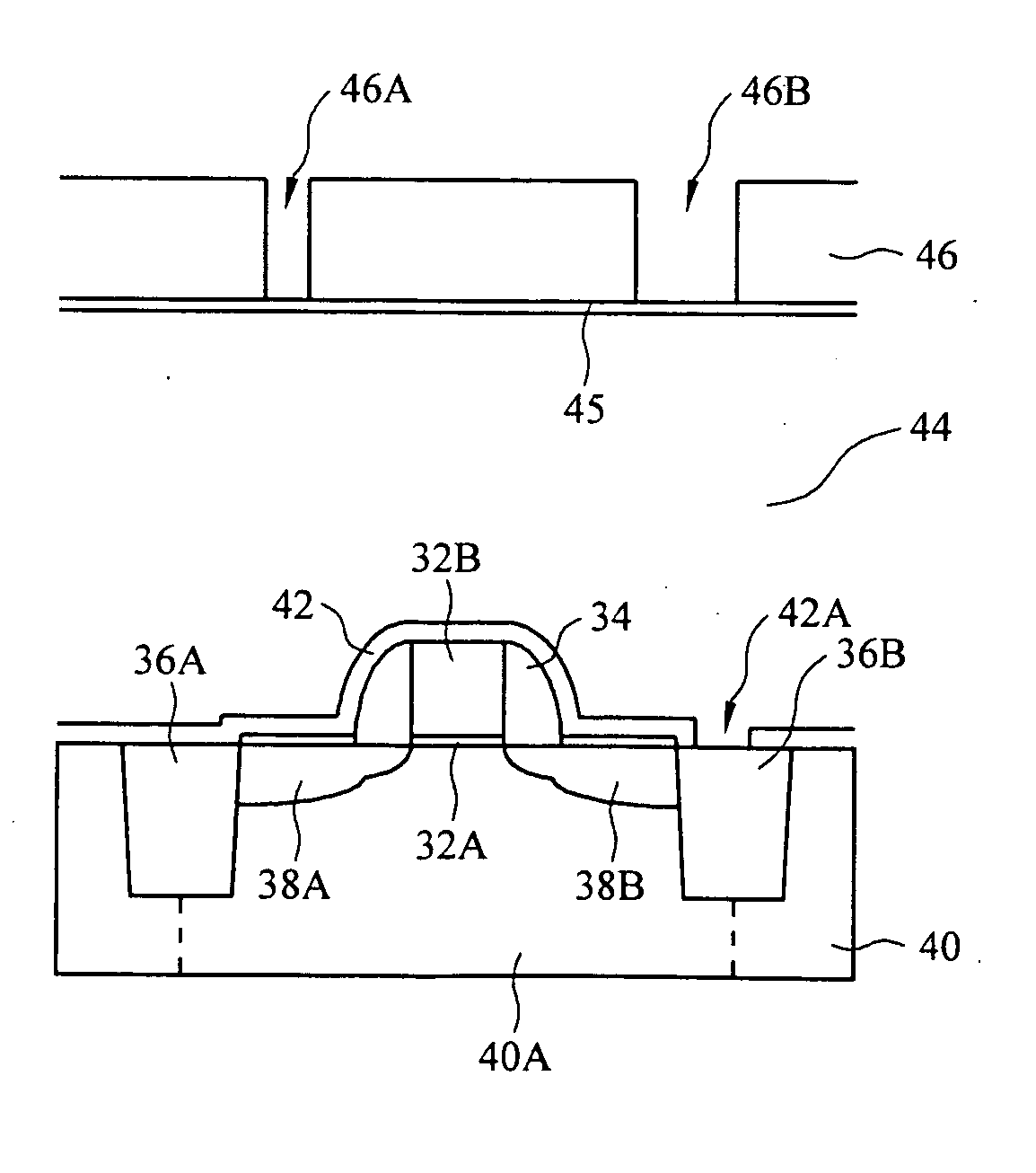
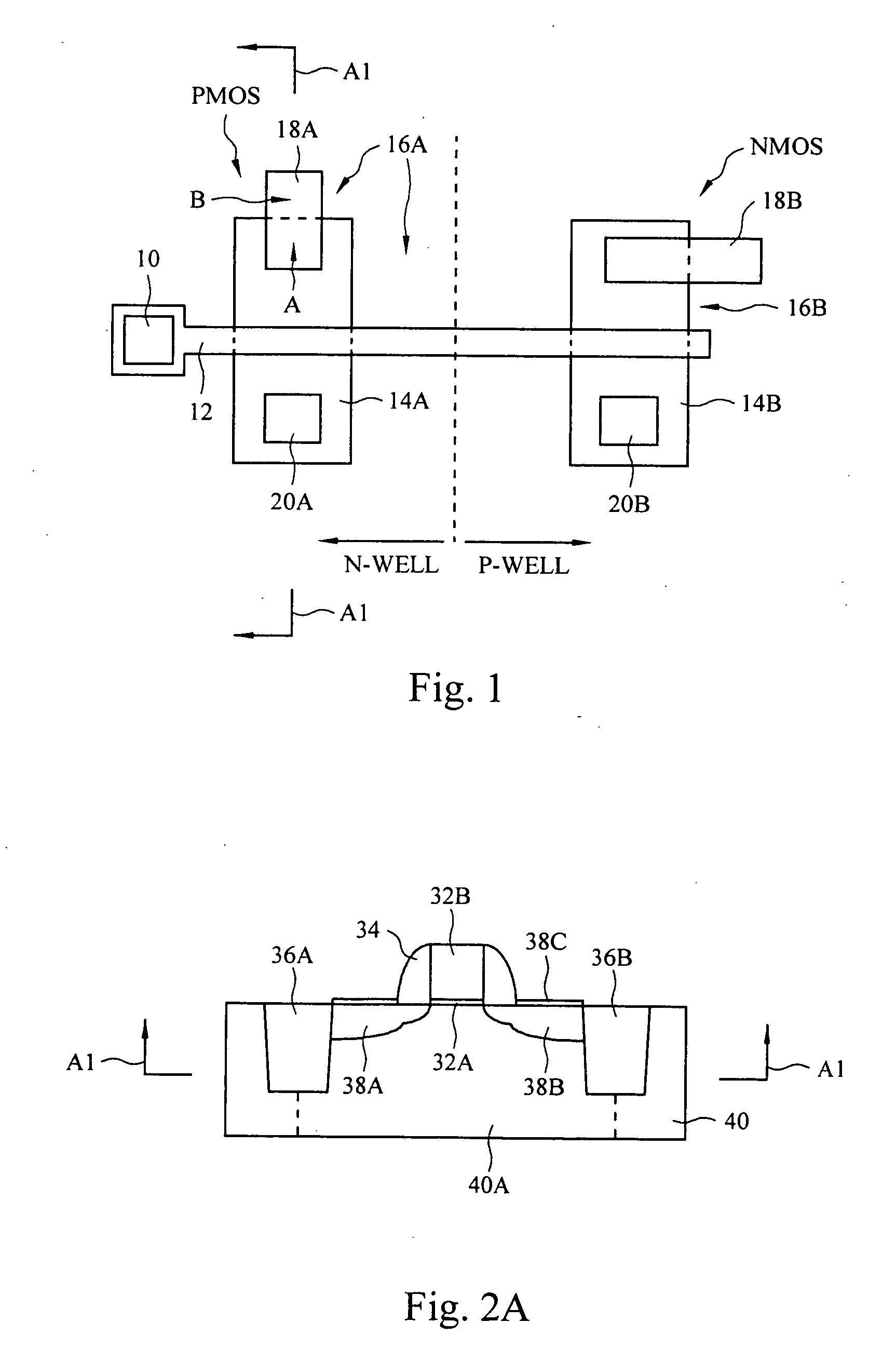
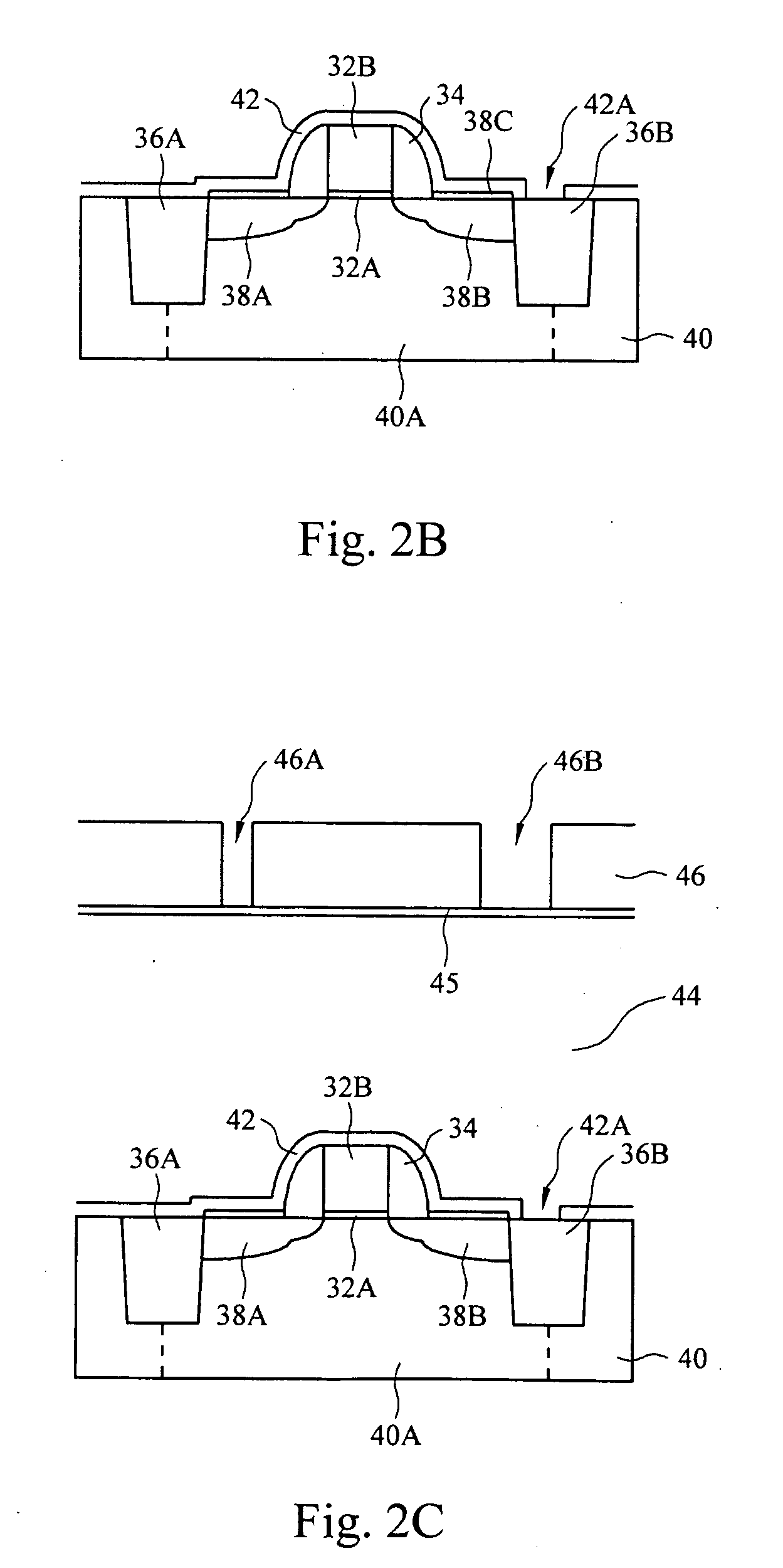
Butted source contact and well strap
ActiveUS7586147B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETSemiconductor
A butted contact structure forming a source contact electrically connecting a voltage node and a well region and method for forming the same, the butted contact structure including an active region having a well region disposed adjacent an electrical isolation region on a semiconductor substrate; a MOSFET device including a source and drain region on the active region; and, a conductive contact having a first portion formed to the source region and a second portion formed through the electrical isolation region to the doped well region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Ultra high-speed Si/SiGe modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin SOI/SGOI substrate
ActiveUS6855963B1Improve RF performanceUltra-high speed performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow noiseUltra high speed
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Butted source contact and well strap
ActiveUS20070243671A1Improve performanceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETElectrical isolation
A butted contact structure forming a source contact electrically connecting a voltage node and a well region and method for forming the same, the butted contact structure including an active region having a well region disposed adjacent an electrical isolation region on a semiconductor substrate; a MOSFET device including a source and drain region on the active region; and, a conductive contact having a first portion formed to the source region and a second portion formed through the electrical isolation region to the doped well region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
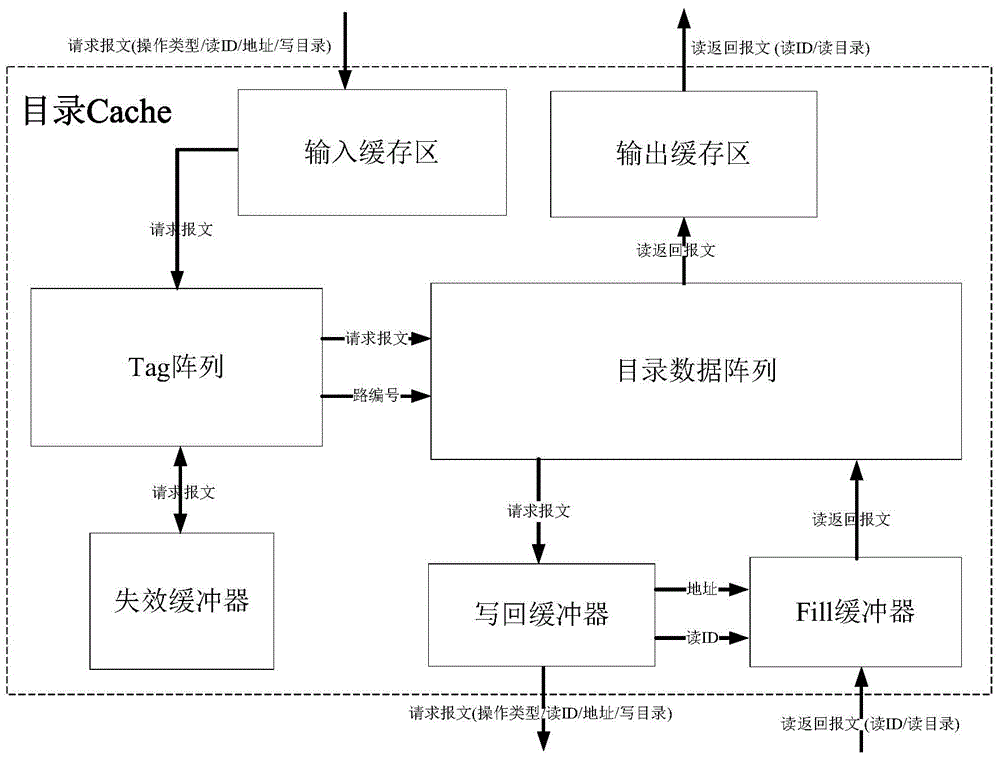
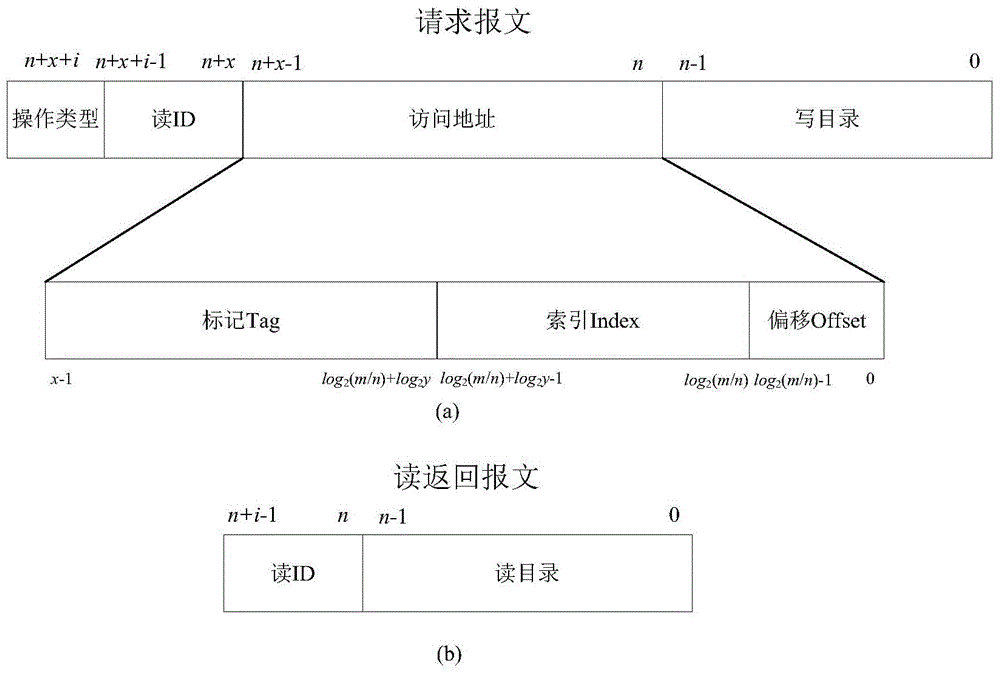
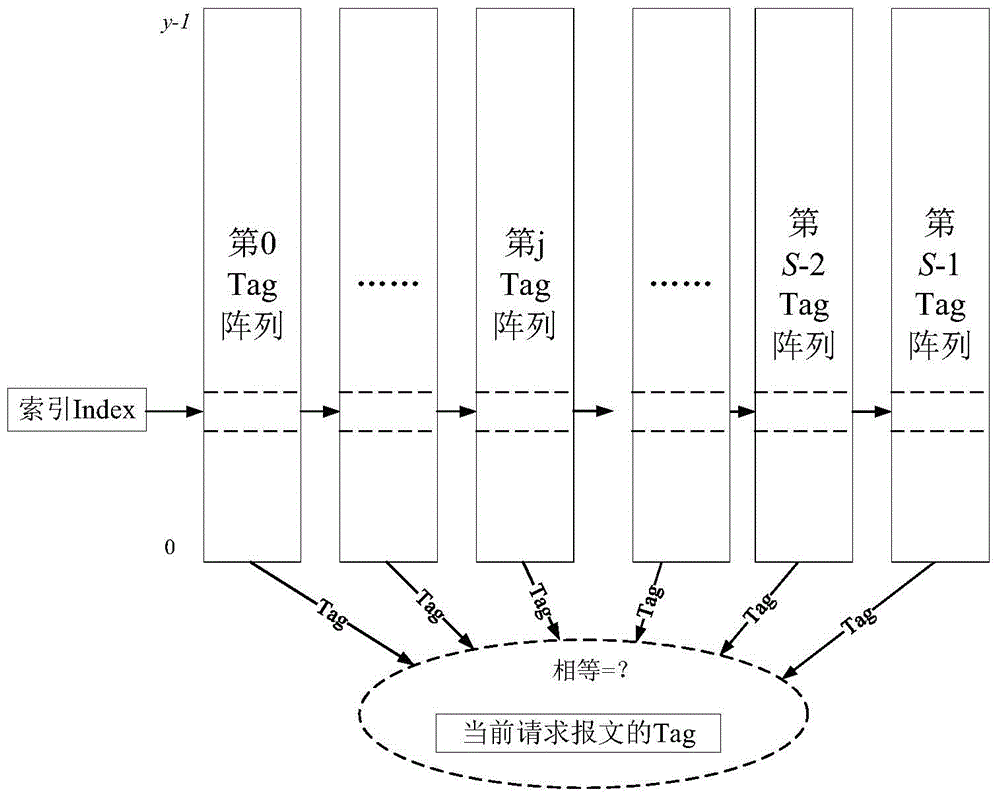
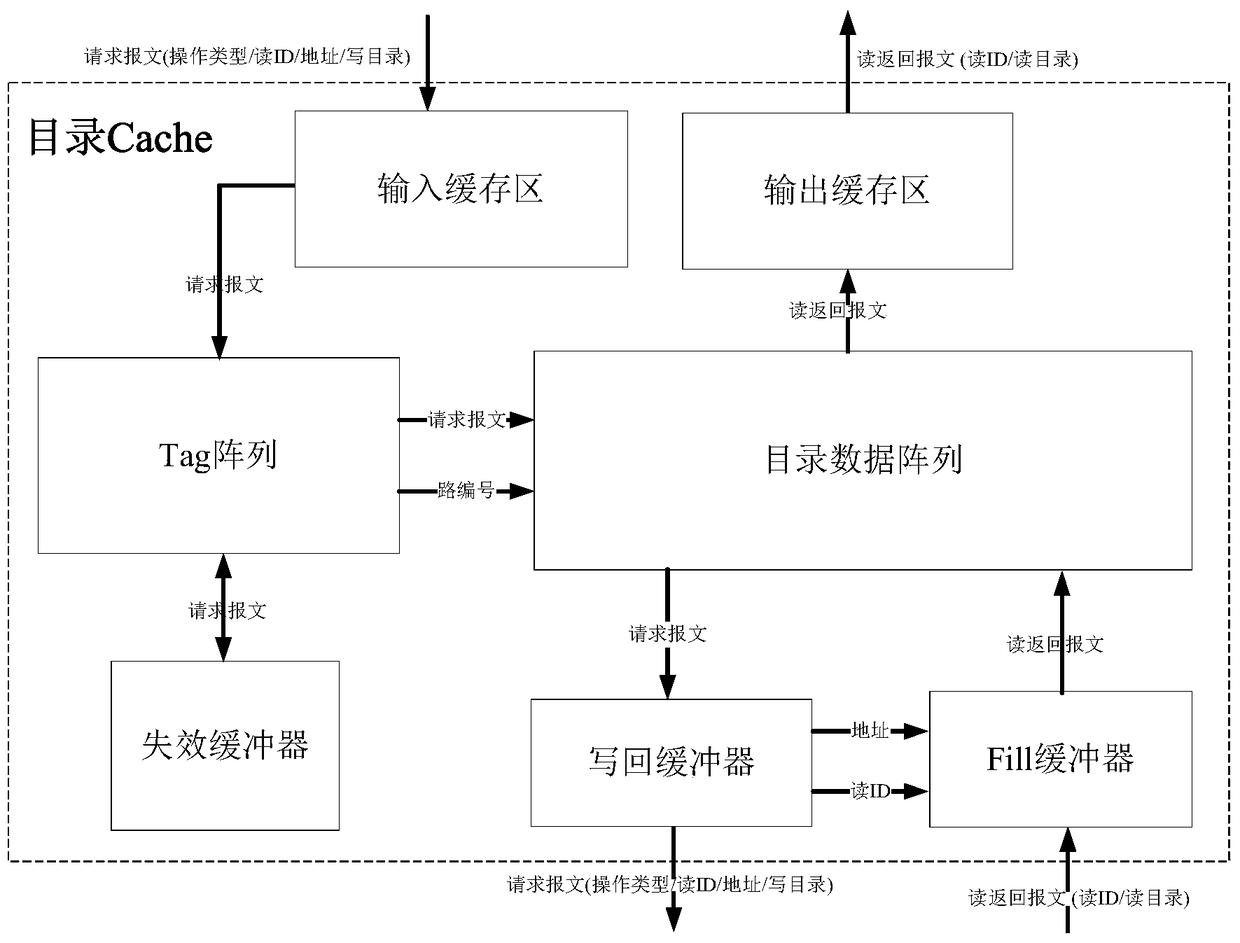
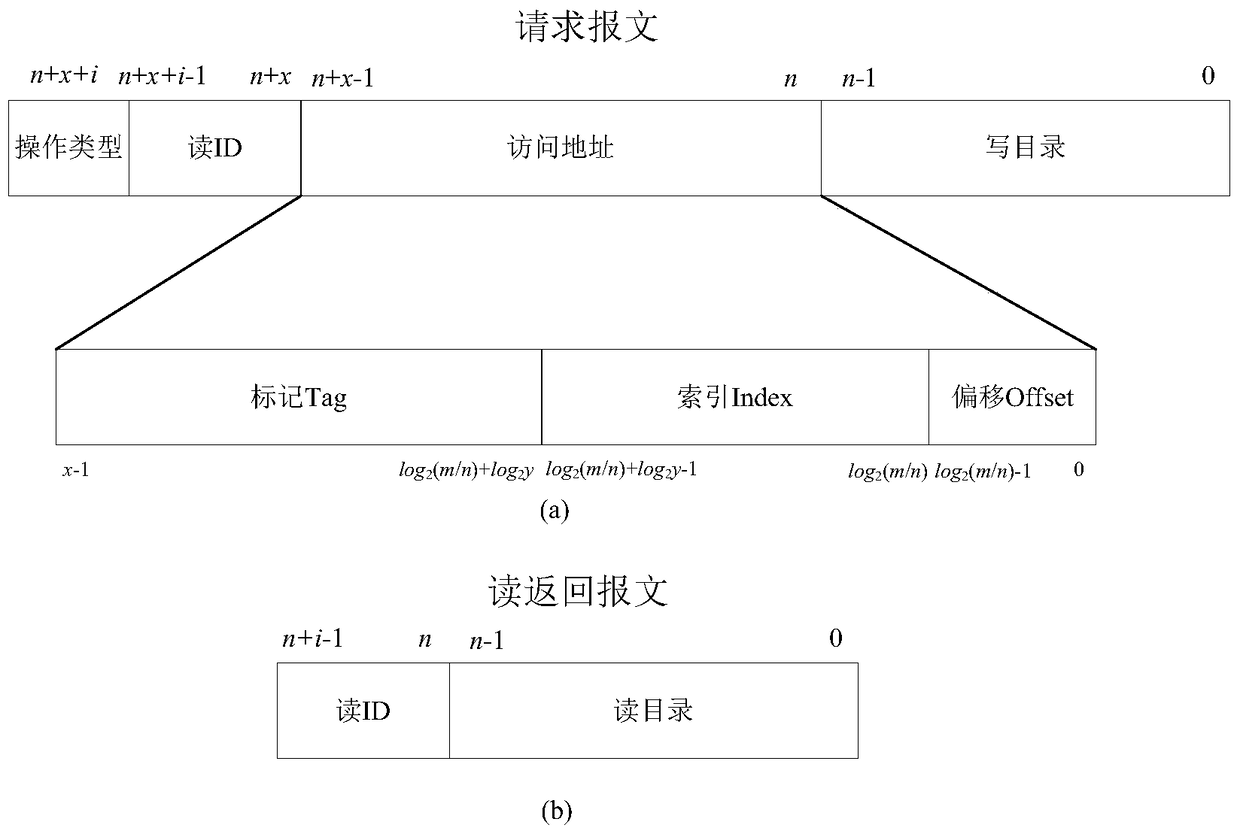
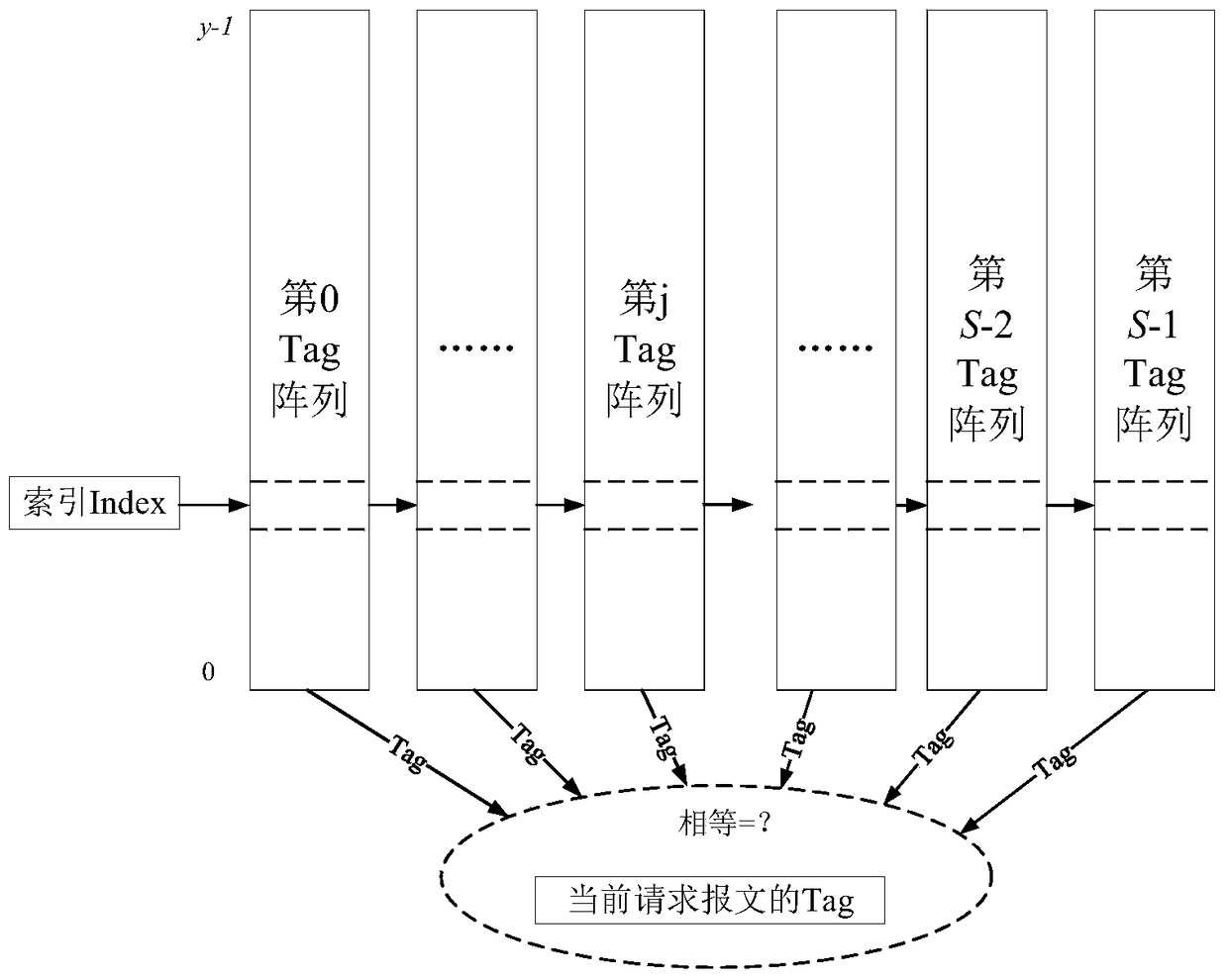
Fault-tolerant directory cache controller
ActiveCN105740168AAvoid failurePerformance priorityMemory systemsSystem structureElectromagnetic environment
The invention discloses a fault-tolerant directory cache controller for the problem that a conventional directory cache is poor in fault tolerance and low in reliability, and cannot meet the requirements of a spatial environment or a complicated electromagnetic environment. The fault-tolerant directory cache controller comprises four identical directory cache bodies, a directory access bypass, a directory access crossbar switch, an access crossbar switch and a configuration register. By designing the four directory cache bodies, the configuration register, the full interconnected access crossbar switch and the directory access crossbar switch, two working modes can be flexibly configured, so that both the performance and the fault tolerance are preferred. By designing a directory access bypass module, the complete failure of a directory Cache function in a bad condition such as a space high-radiation environment is prevented, so that the reliability is enhanced. Compared with the conventional directory Cache, the fault-tolerant directory cache controller has the advantages that a multilevel fault-tolerant technology from a system structure level to a circuit design level is adopted, so that on the premise of no performance loss, the fault tolerance and reliability of the directory Cache are remarkably improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
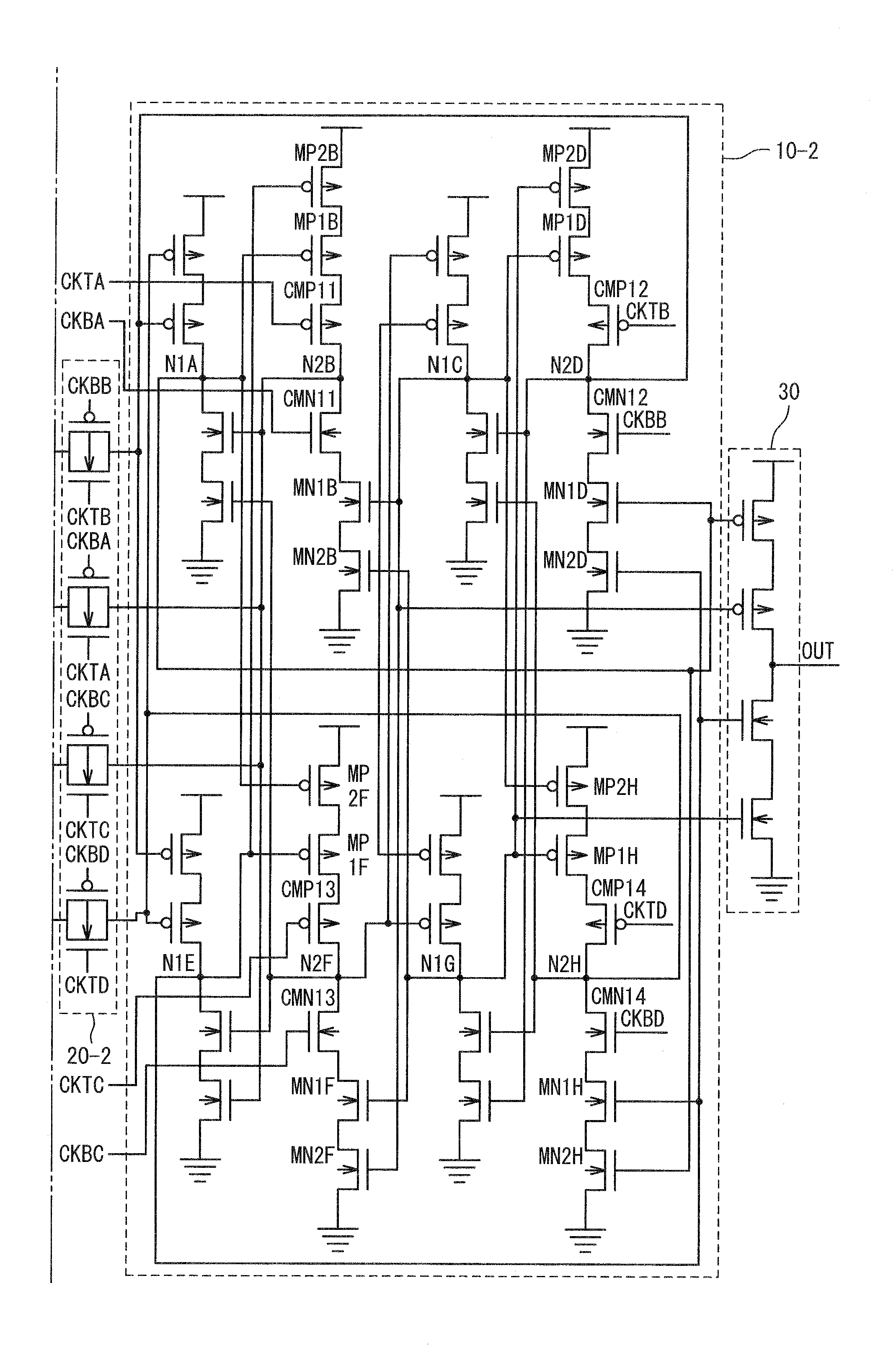
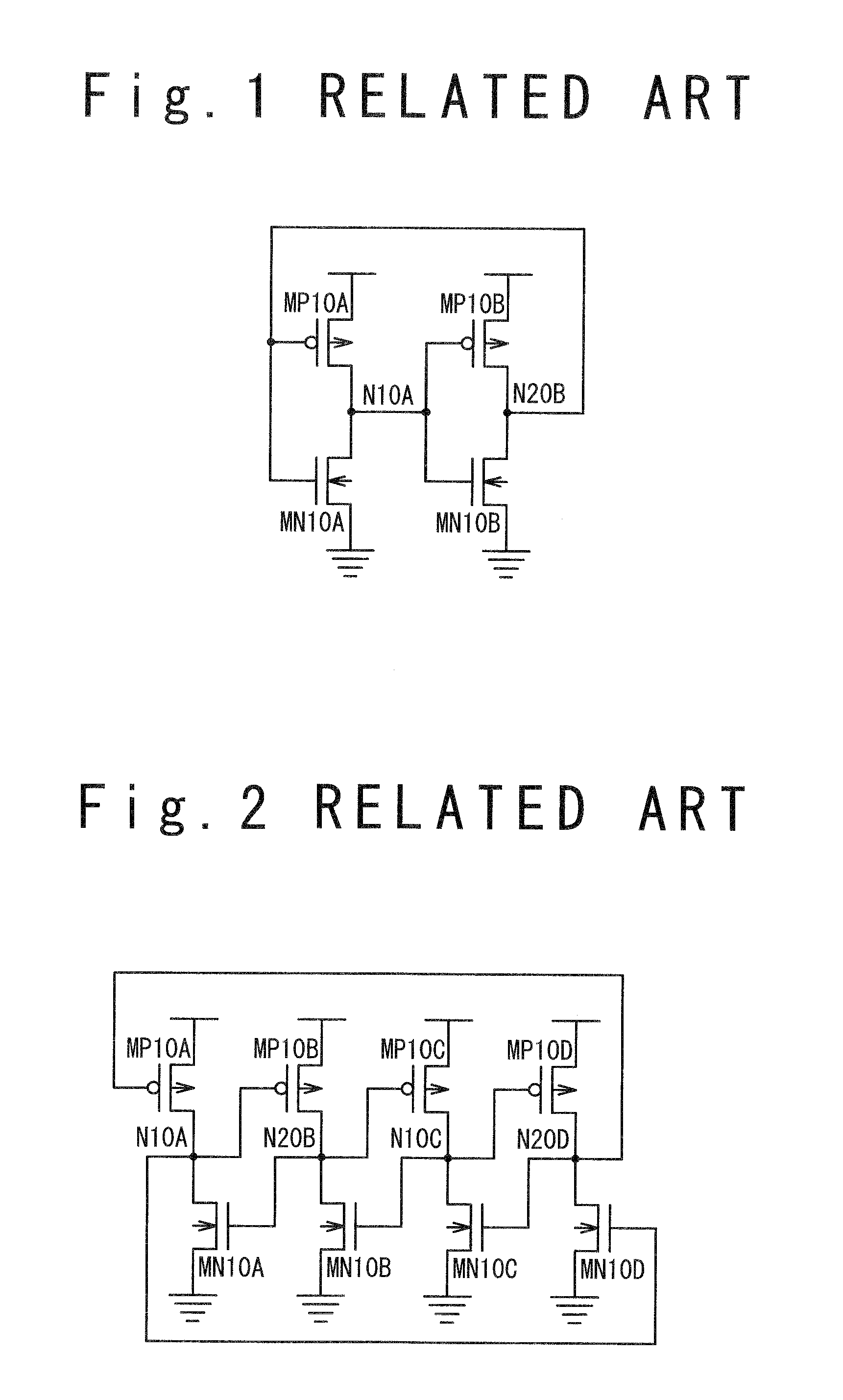
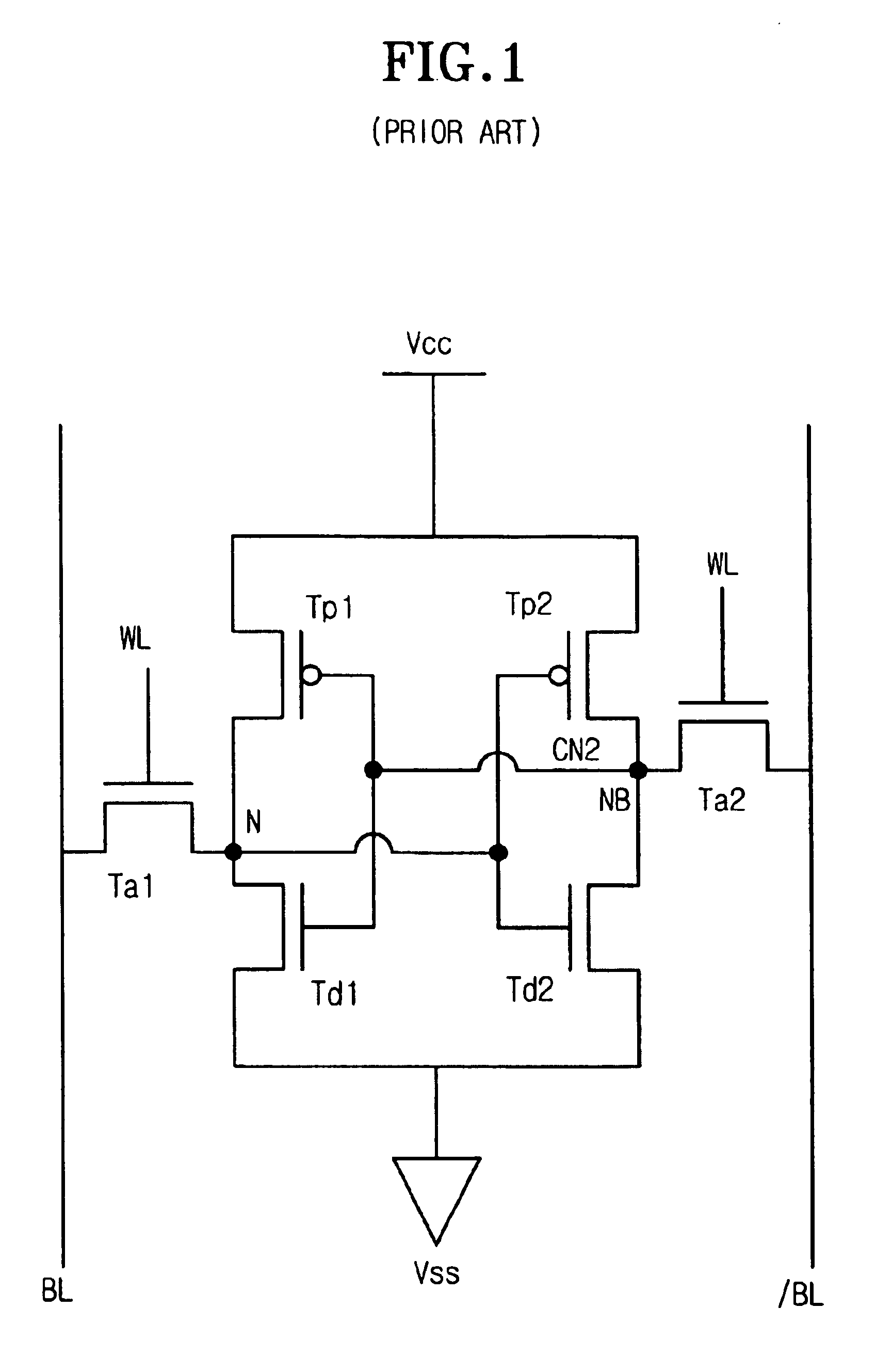
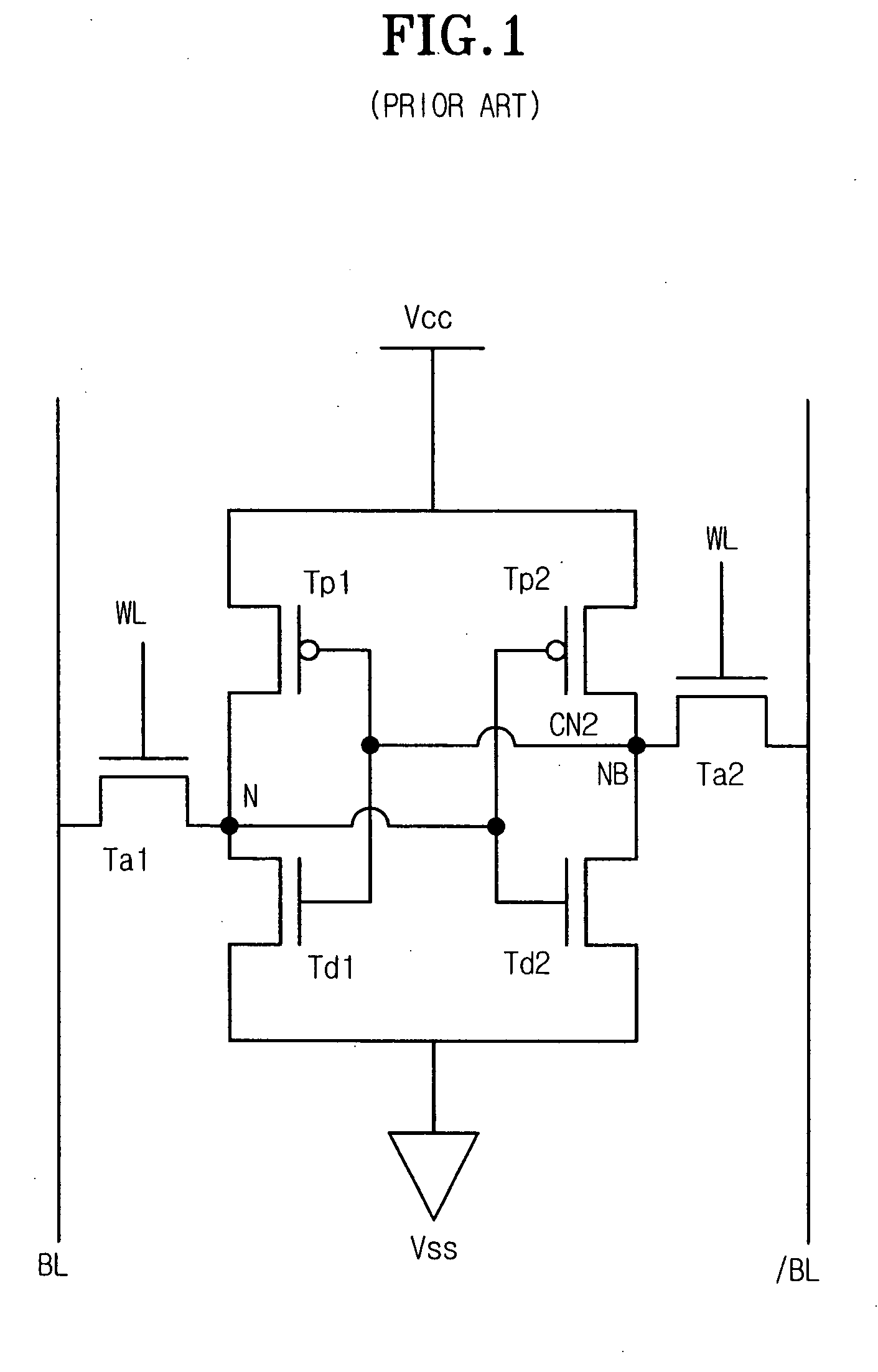
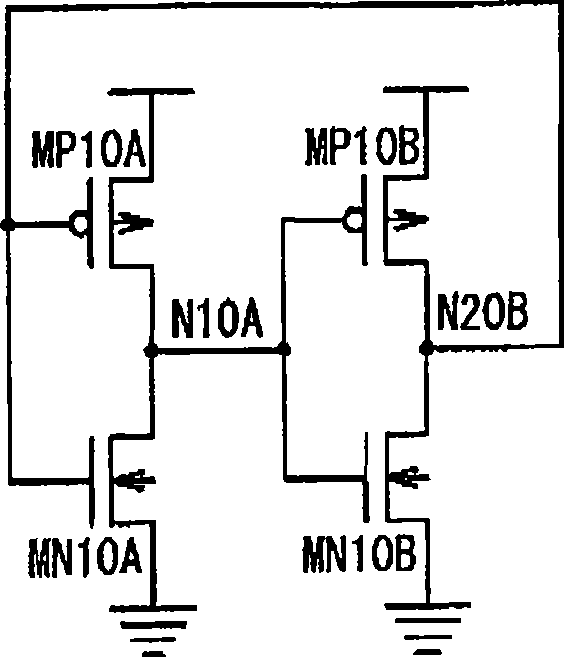
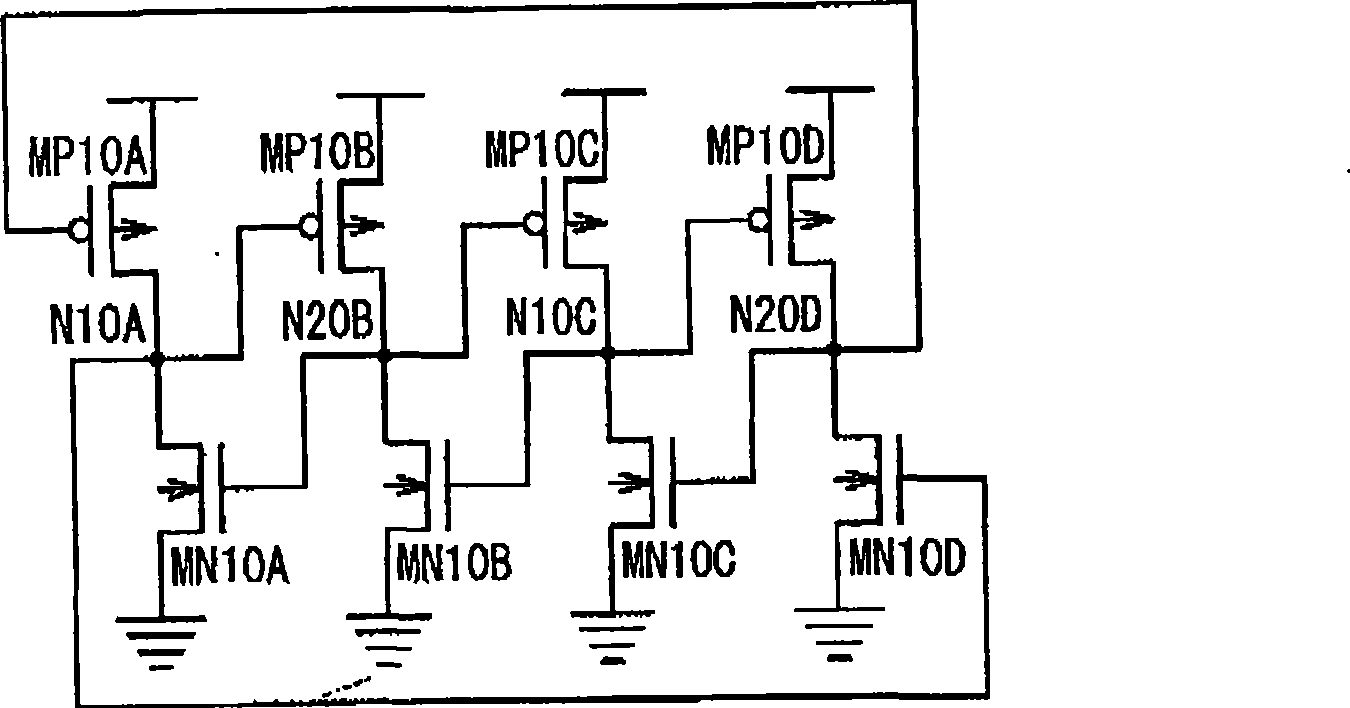
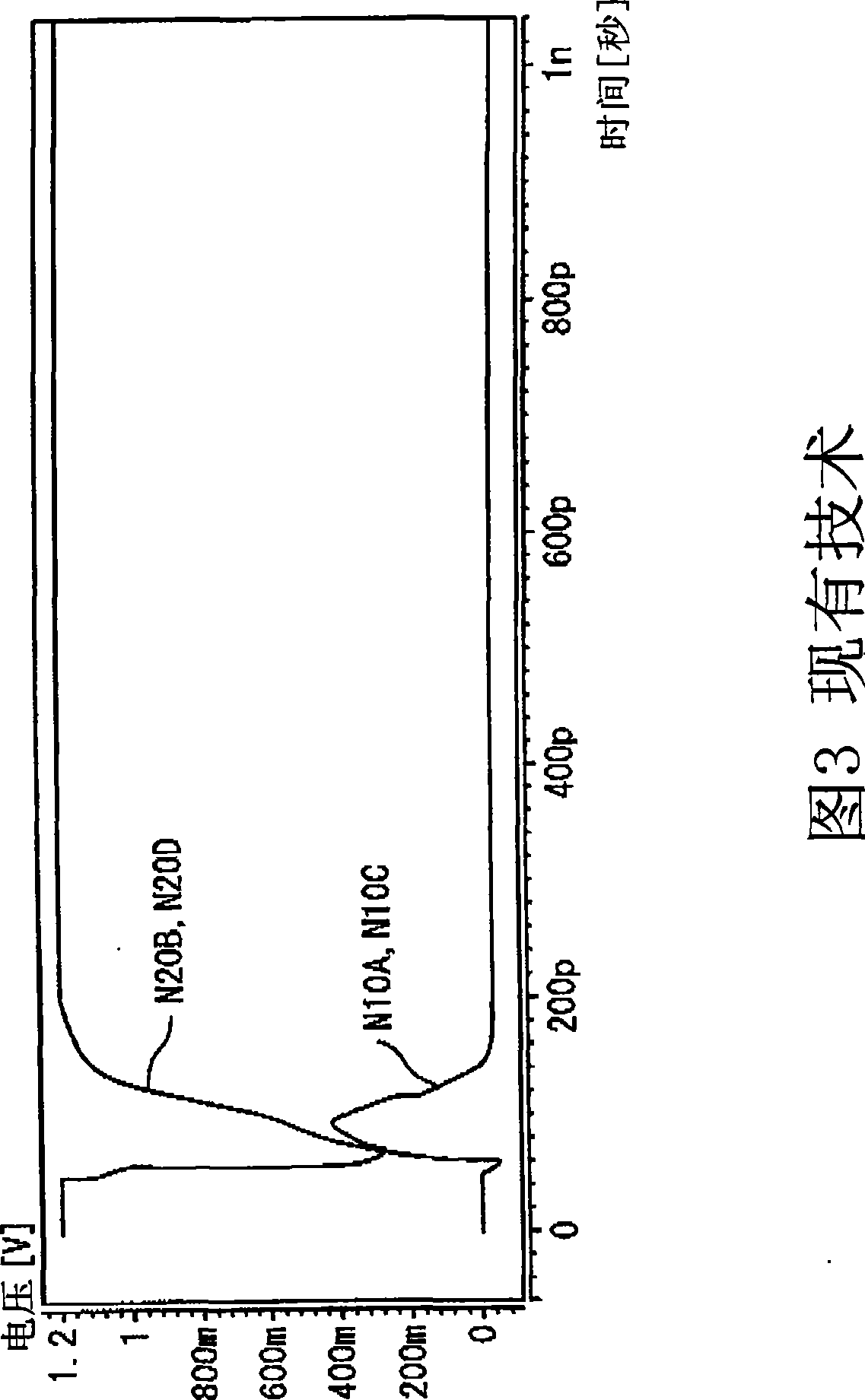
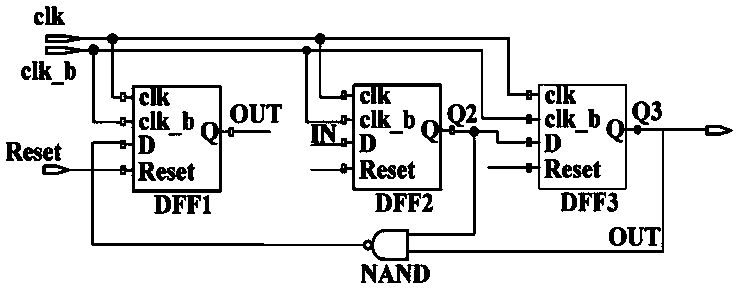
Latch circuit and flip-flop circuit
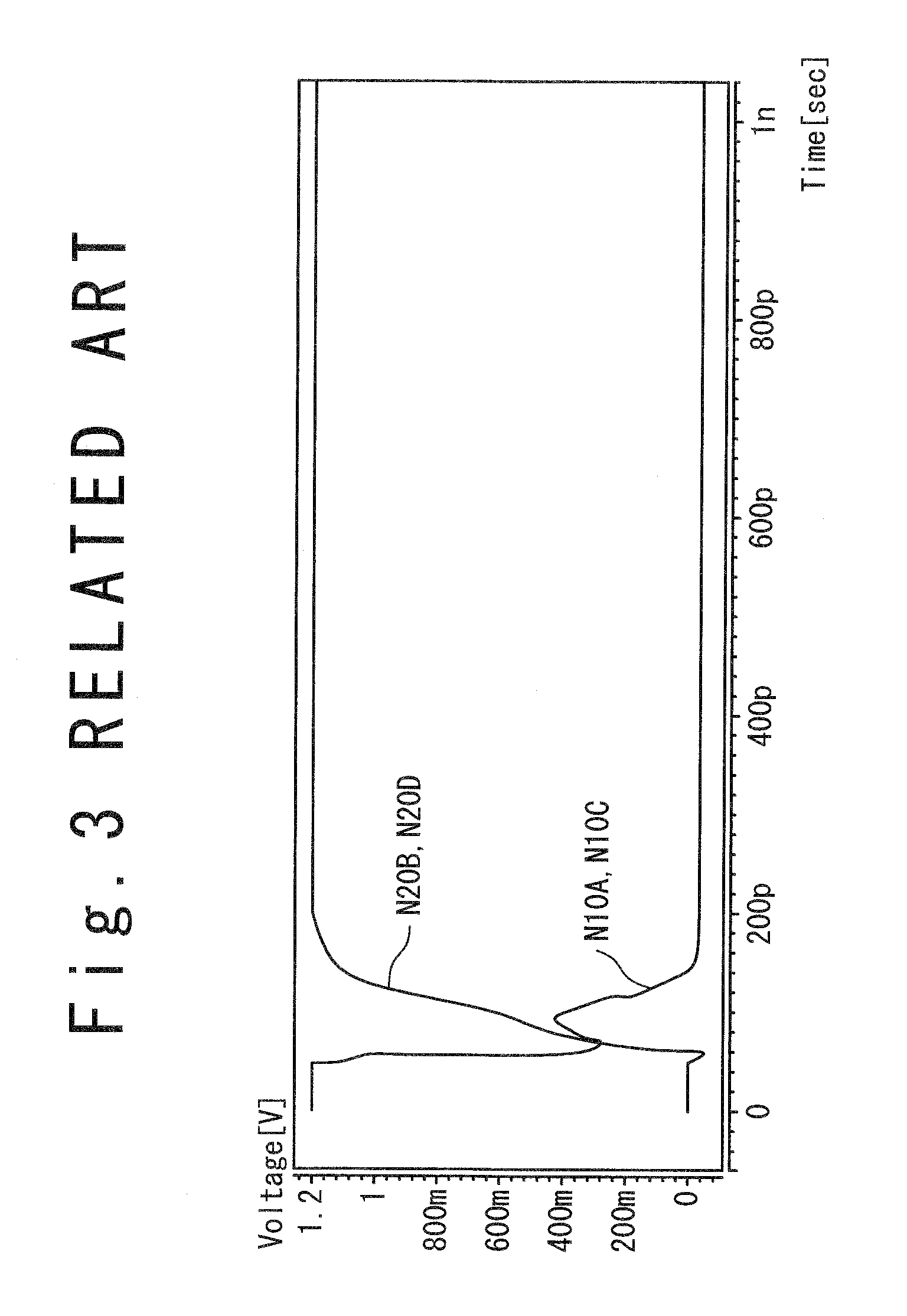
InactiveUS20090121765A1Reduce soft error rateInhibitionElectric pulse generatorEngineeringVoltage control
A latch circuit includes: first nodes which are three or more and to which a voltage in a first signal level is set; second nodes which are three or more and to which a voltage in a second signal level obtained by inverting the first signal level is set; and first node voltage control circuits having the first nodes; and second node voltage control circuits having the second nodes. Each of the first node voltage control circuits is connected with at least two of the three or more second nodes, and controls the voltage of the first node based on the voltages of the at least two second modes. Each of the second node voltage control circuits is connected with at least two of the three or more first nodes and controls the voltage of the second node based on the voltages of the at least two first nodes.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
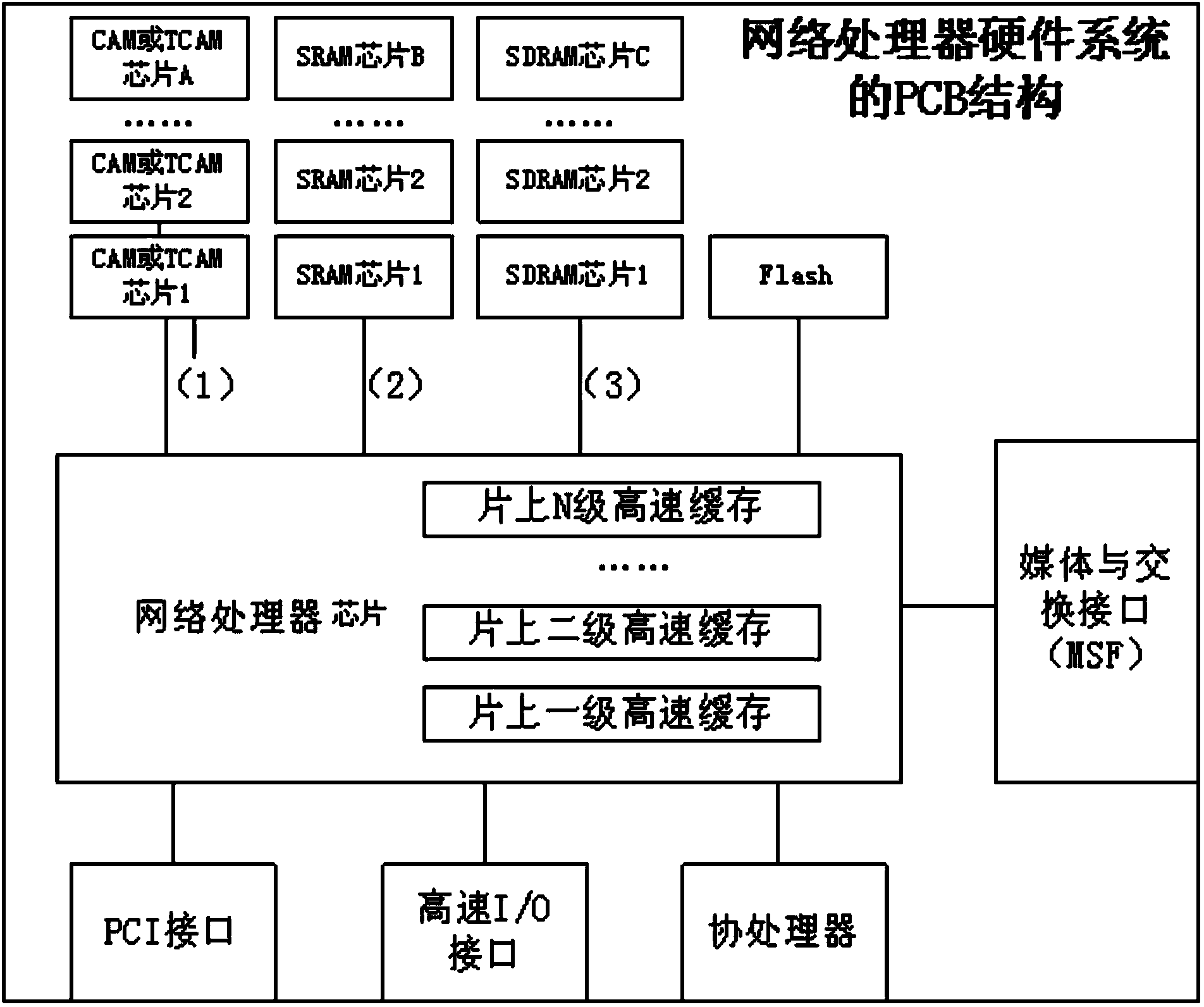
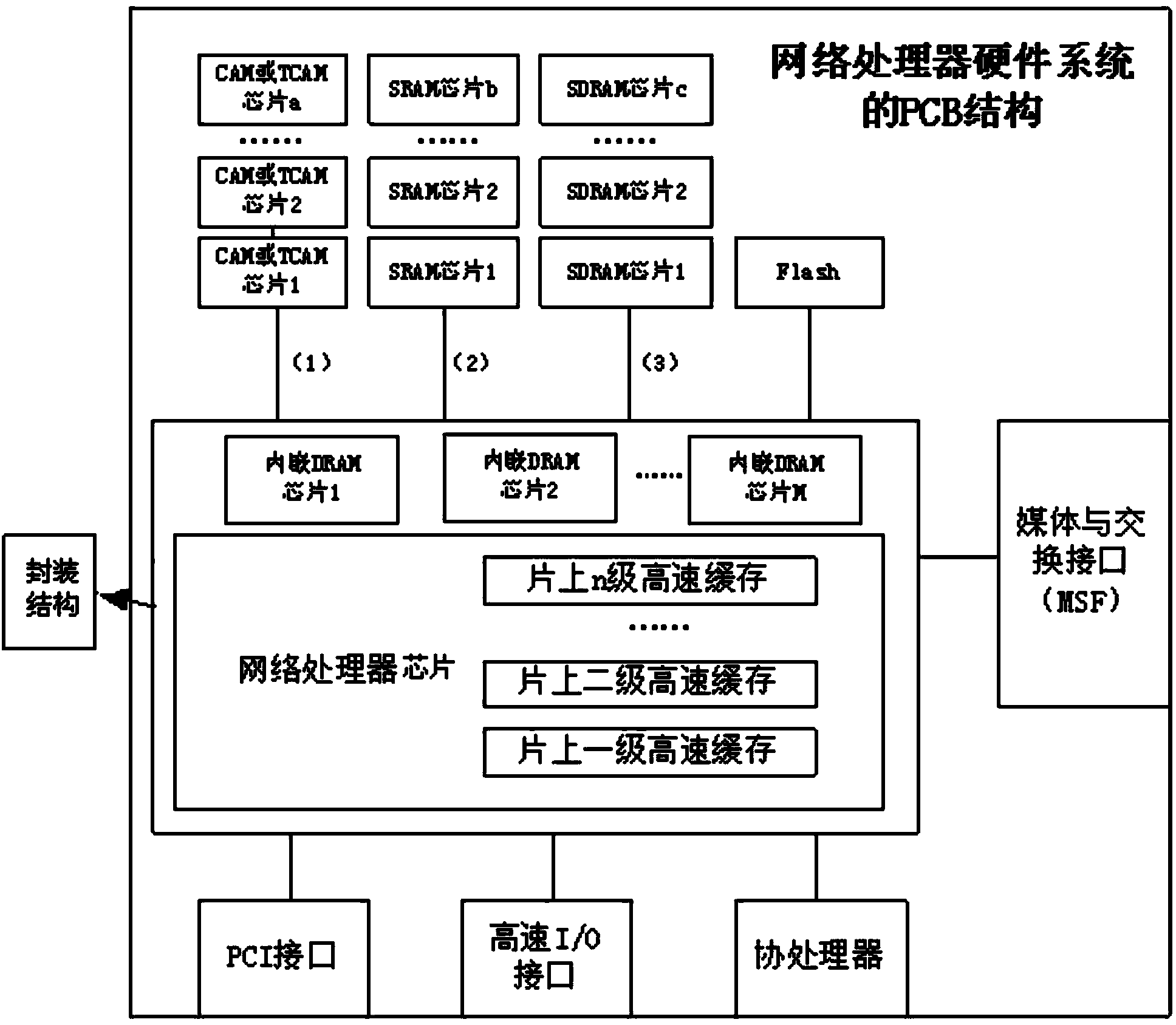
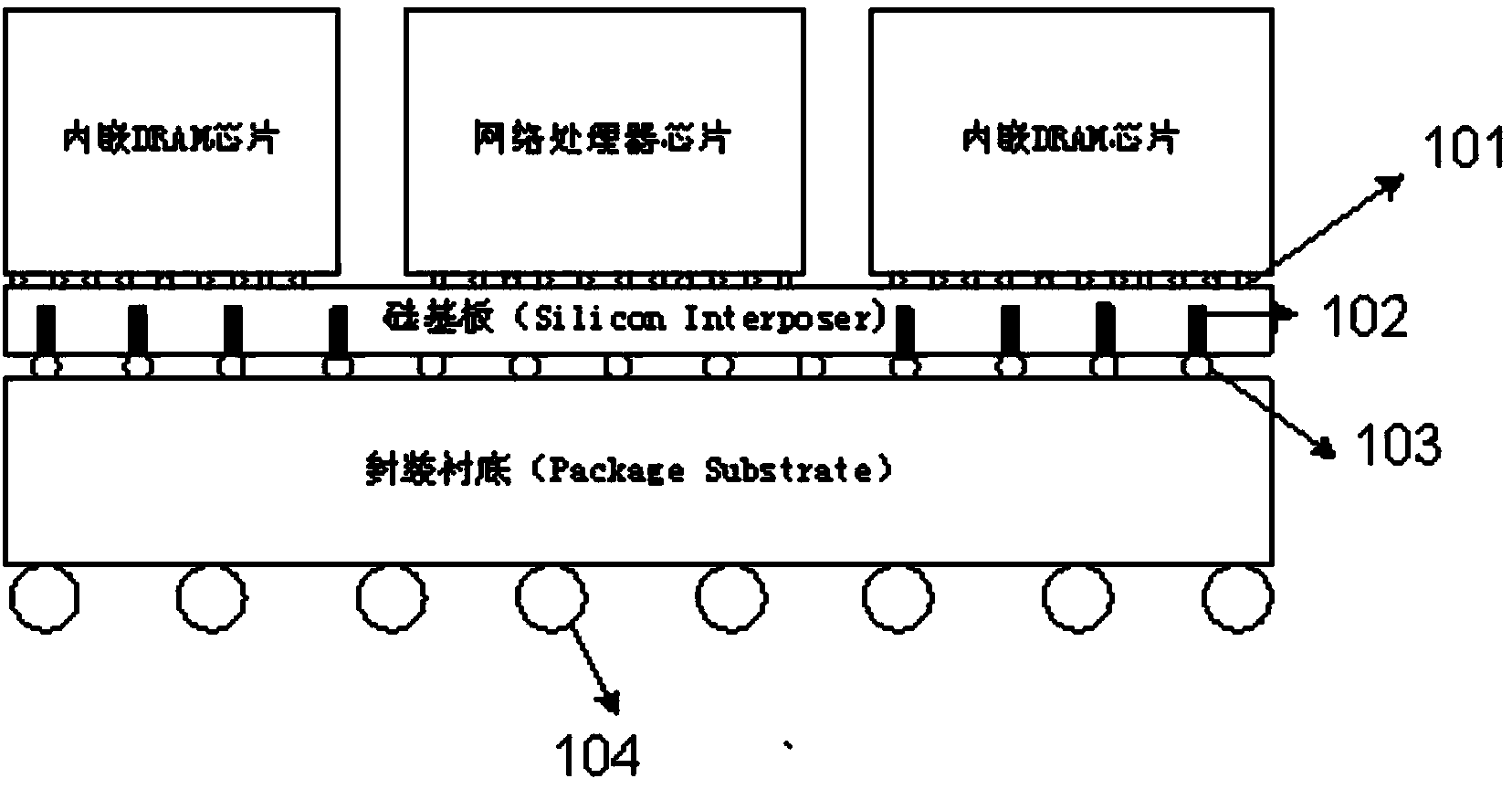
Network processor
ActiveCN104038416ADistinctive featuresObvious shapeData switching networksNetwork processorDram chip
The invention discloses a network processor. Part or all of off-chip CAM (or TCAM) chips and off-chip SRAM chips, the last few on-chip CACHES of a traditional network processor and part of SDRAM chips of a network processor system are replaced by embedded DRAM chips. Both the cost and soft error occurrence probability are greatly lowered; the speed and the data throughout are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINCHU INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
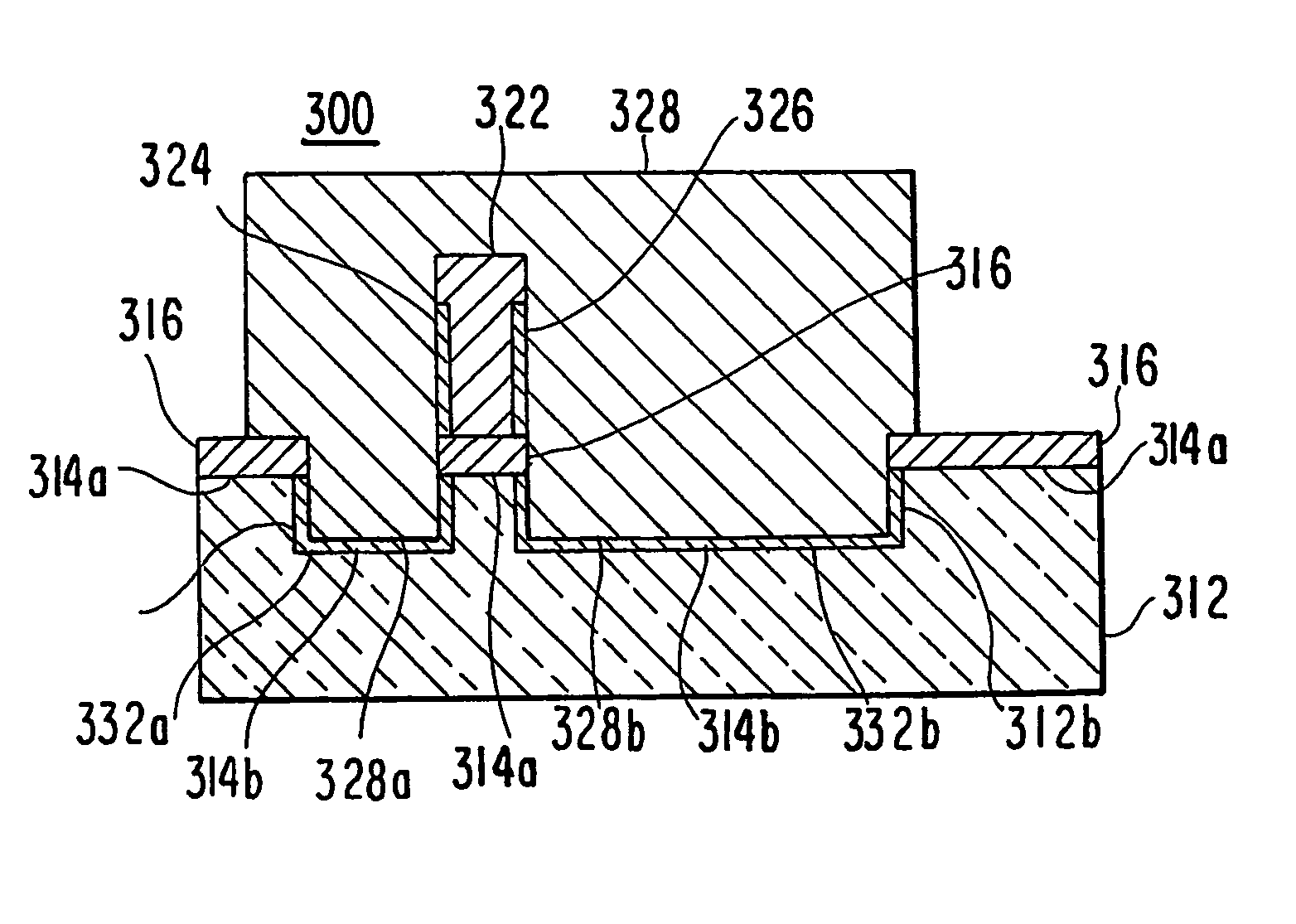
Electronic components with plurality of contoured microelectronic spring contacts
InactiveUS20050189956A1Manufacturing cost to minimumKeep distanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTip positionInterposer
An electronic component is disclosed, having a plurality of microelectronic spring contacts mounted to a planar face of the component. Each of the microelectronic spring contacts has a contoured beam, which may be formed of an integral layer of resilient material deposited over a contoured sacrificial substrate, and comprises a base mounted to the planar face of the component, a beam connected to the base at a first end of the beam, and a tip positioned at a free end of the beam opposite to the base. The beam has an unsupported span between its free end and its base. The microelectronic spring contacts are advantageously formed by depositing a resilient material over a molded, sacrificial substrate. The spring contacts may be provided with various innovative contoured shapes. In various embodiments of the invention, the electronic component comprises a semiconductor die, a semiconductor wafer, a LGA socket, an interposer, or a test head assembly.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
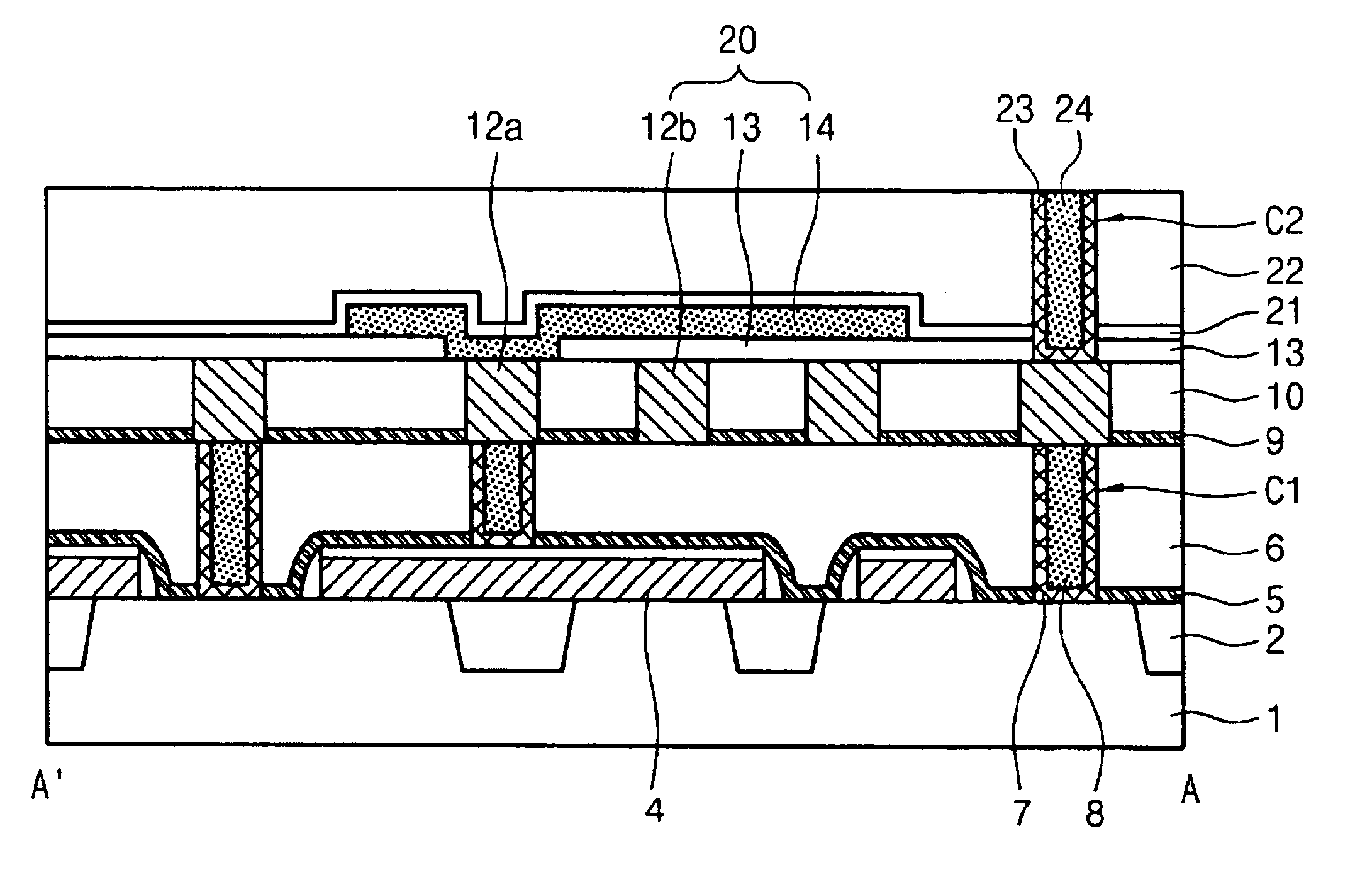
SRAM cell and method of manufacturing the same
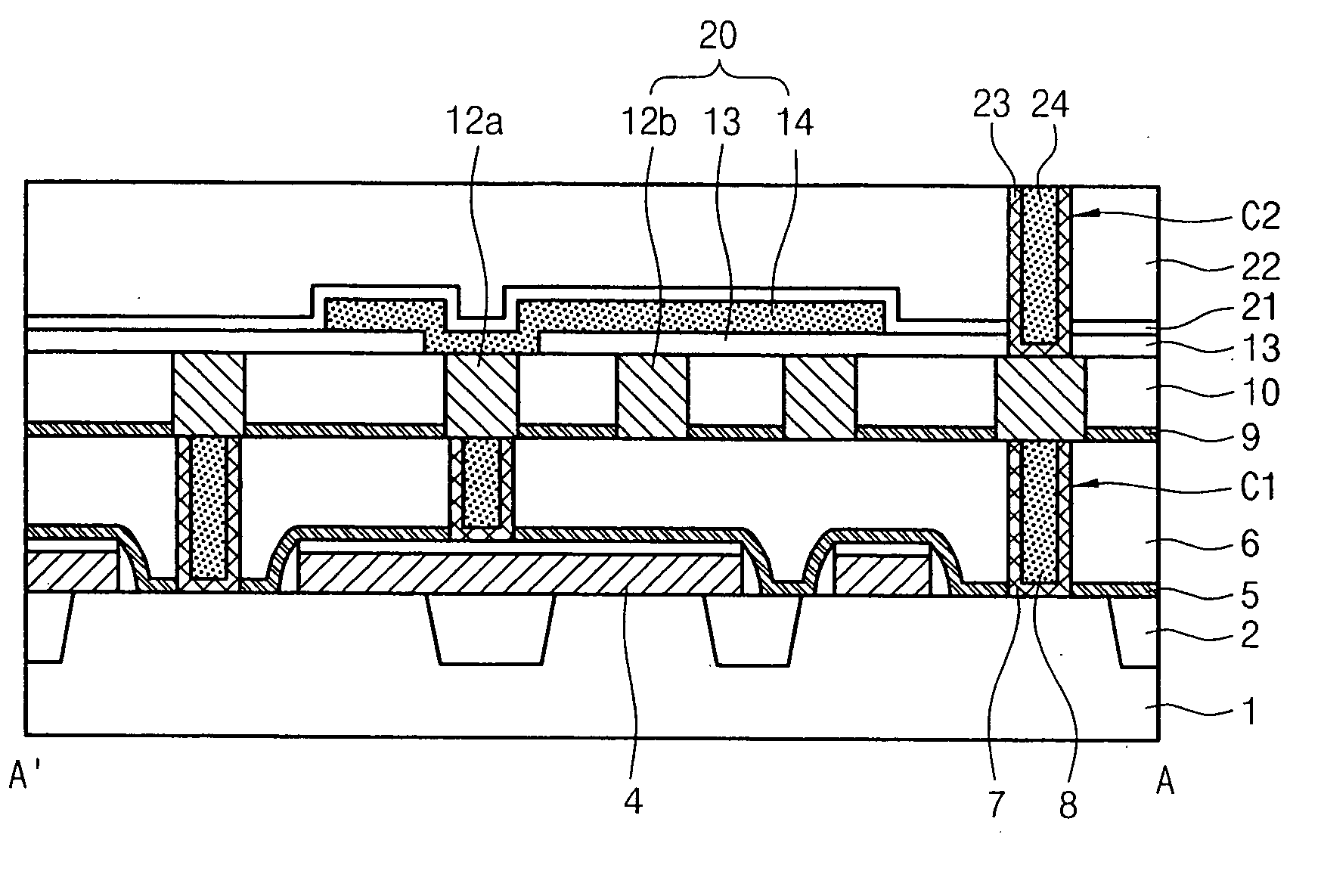
ActiveUS6902963B2Increase battery capacityReduce errorsTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceInterconnection
Disclosed is a SRAM cell and a method of manufacturing the same. The SRAM cell comprises: a pair of access devices; a pair of pull-up devices; a pair of pull-down devices; and at least one metal plate formed on metal interconnection lines in contact with a substrate, having a dielectric film interposed between the metal plate and the metal interconnection lines, so as to increase a cell capacitance, thereby reducing a soft error rate. Herein, one metal plate may be included in each cell. In this case, the metal plate overlaps with a first one of metal interconnection lines of a node side and a node bar side, while being in contact with a second one of the metal interconnection lines of the node side and the node bar side. Also, two metal plates may be included in each cell. In this case, the metal plates overlap, respectively, with one metal interconnection line of metal interconnection lines of a node side and a node bar side, while being in contact with another metal interconnection line of the node side or the node bar side, respectively. Therefore, capacitance is additionally formed to increase cell capacitance, so that variation of the electric potentials of cell nodes, which is caused by generated electrons, is prevented, and thereby soft error can be efficiently reduced.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
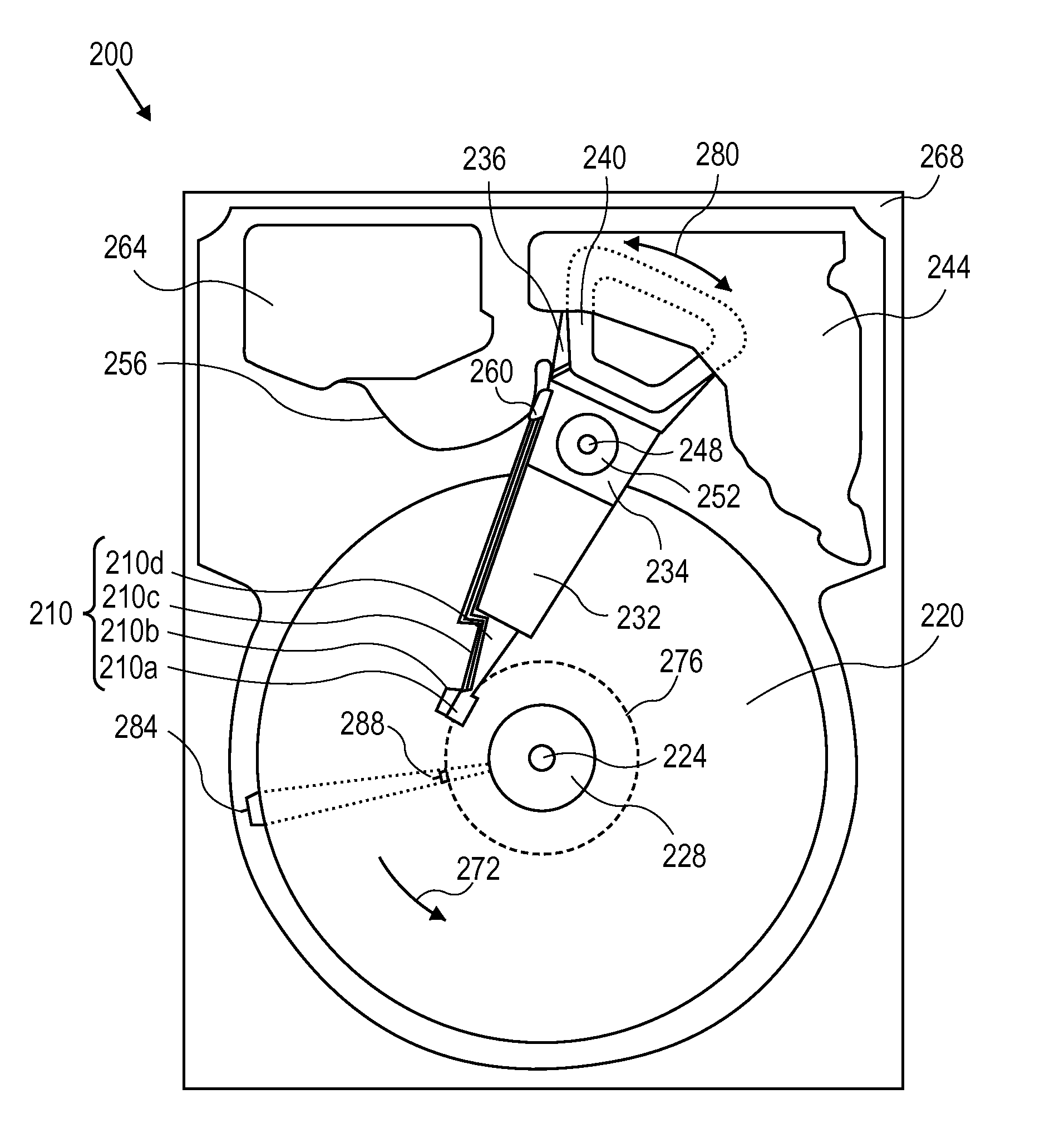
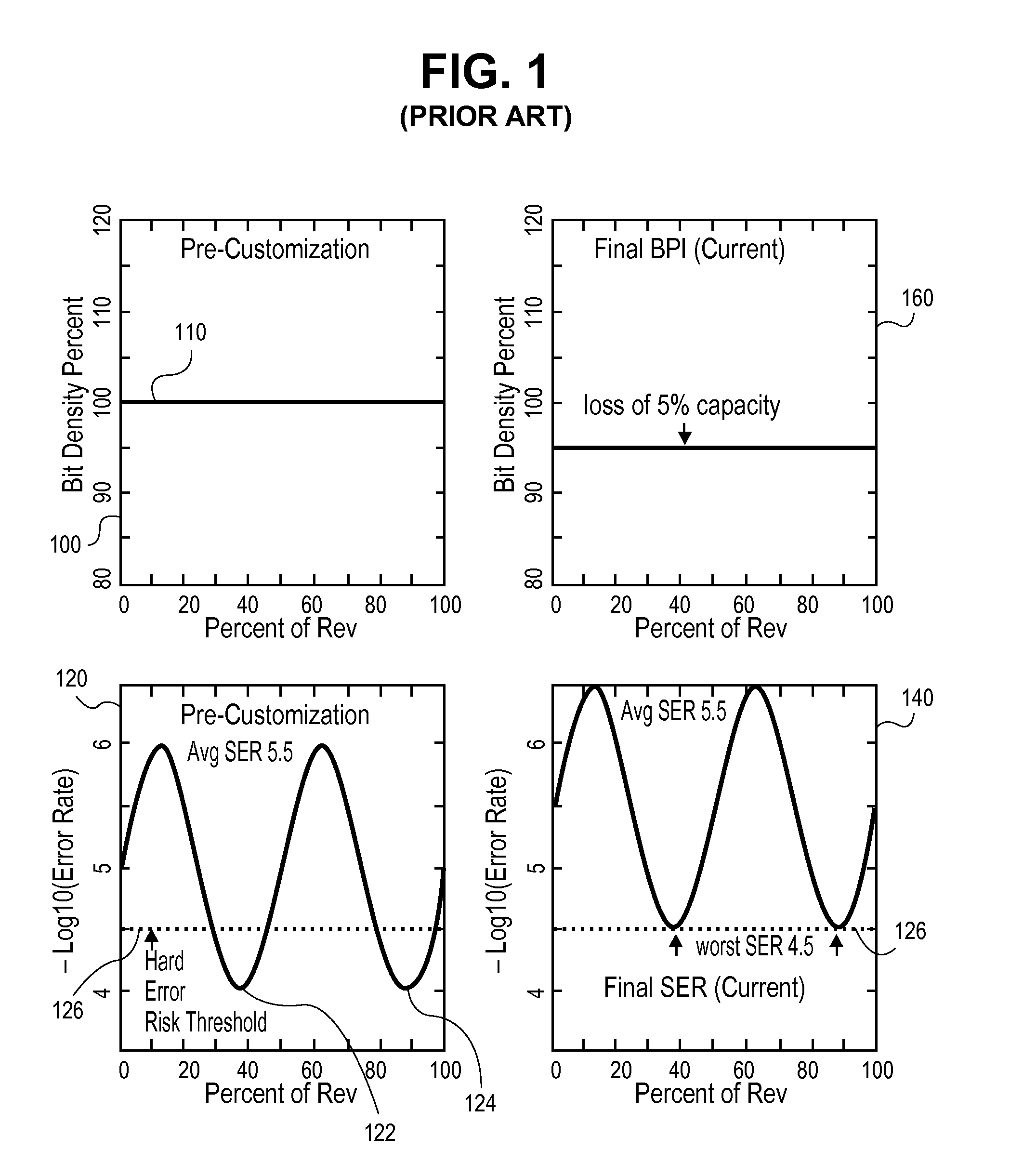
Adjusting Recording Density in a Circumferential Direction
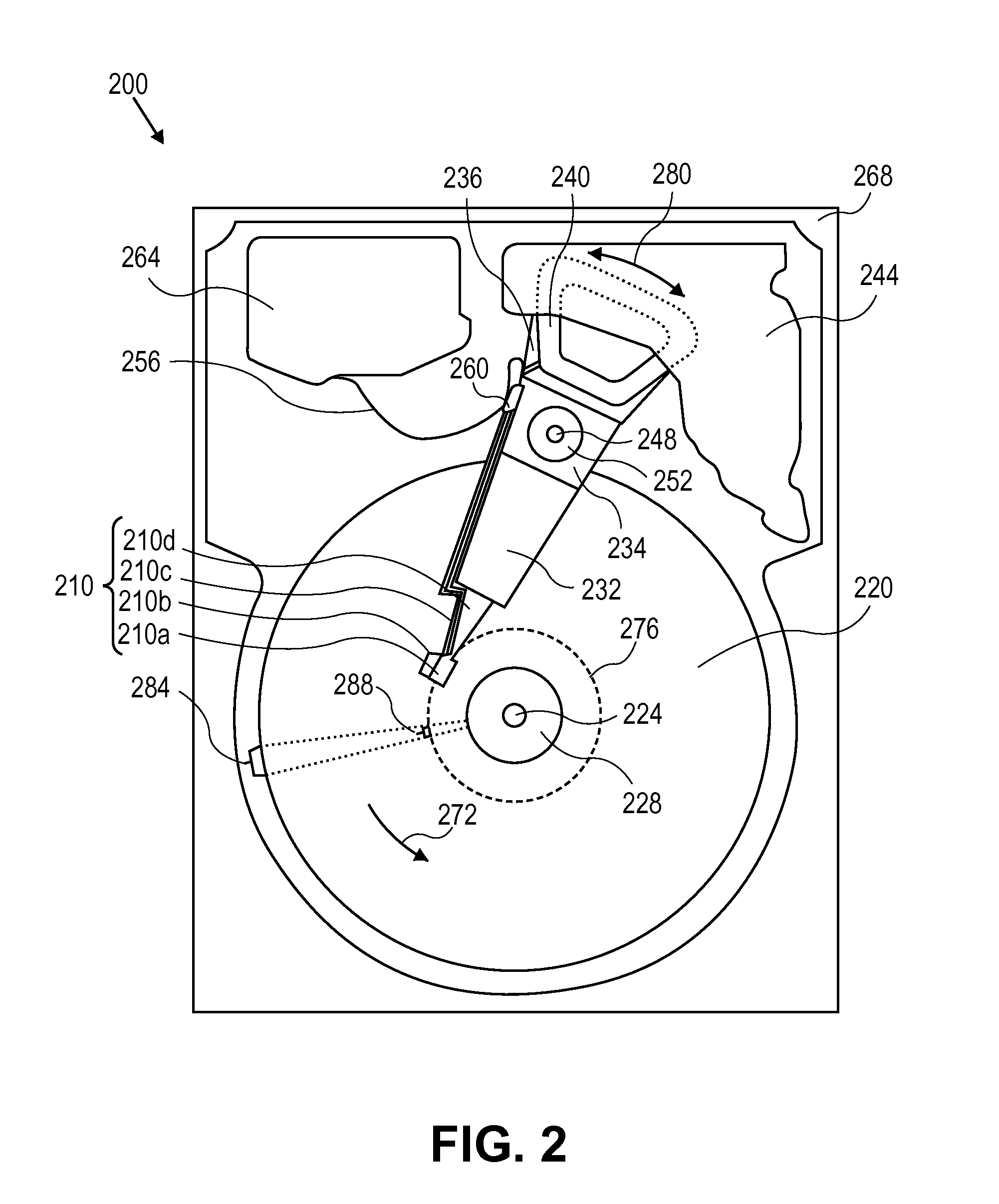
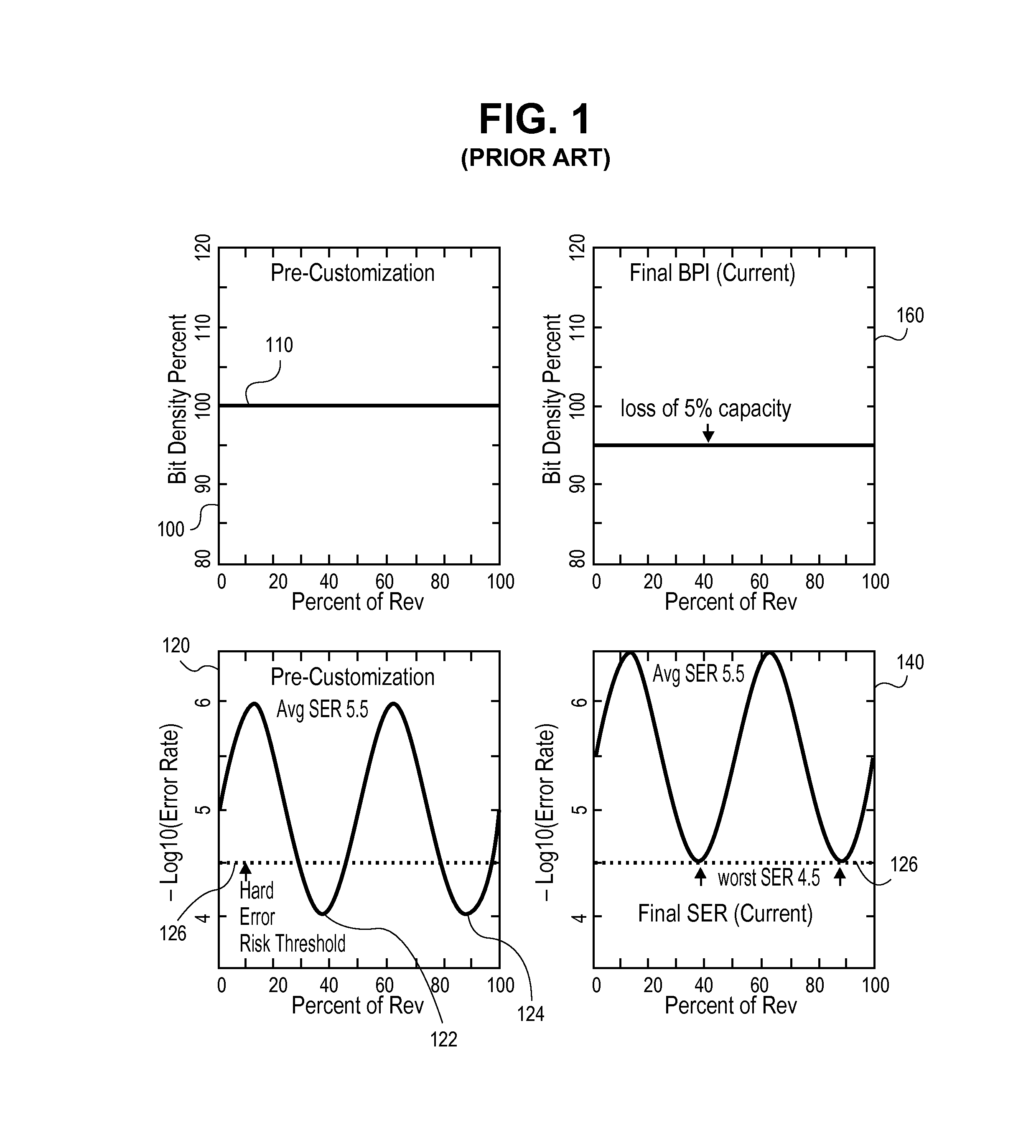
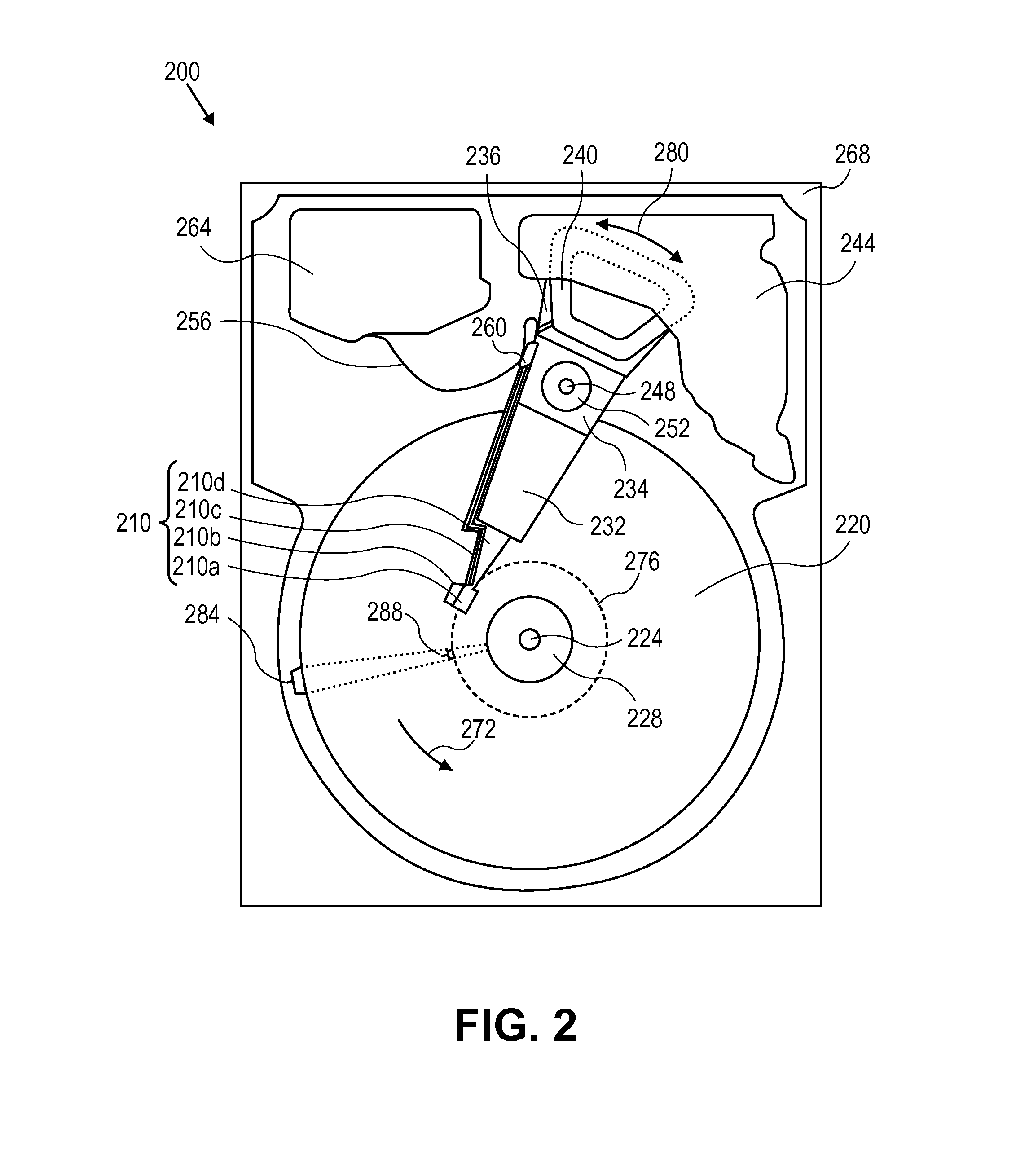
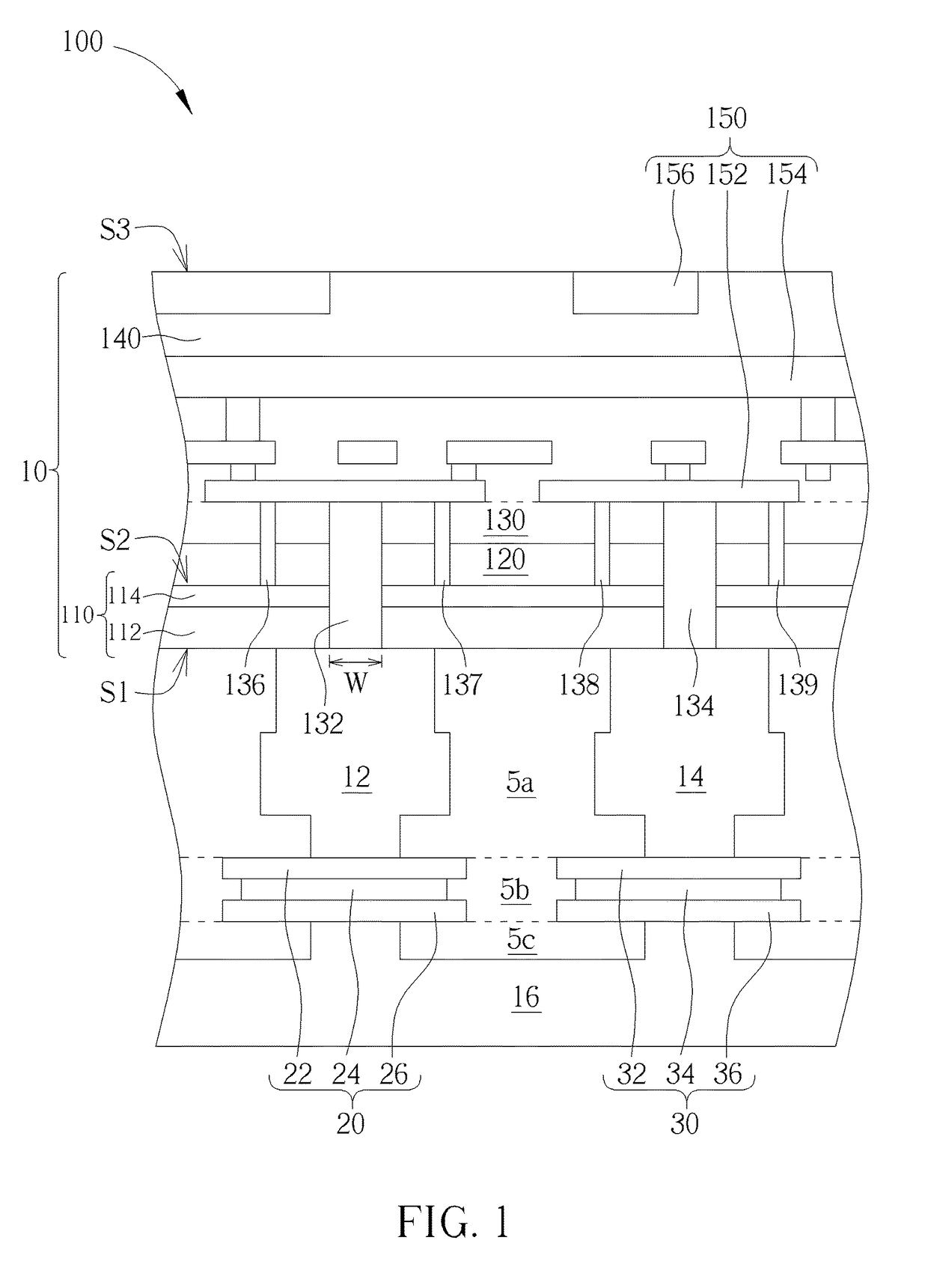
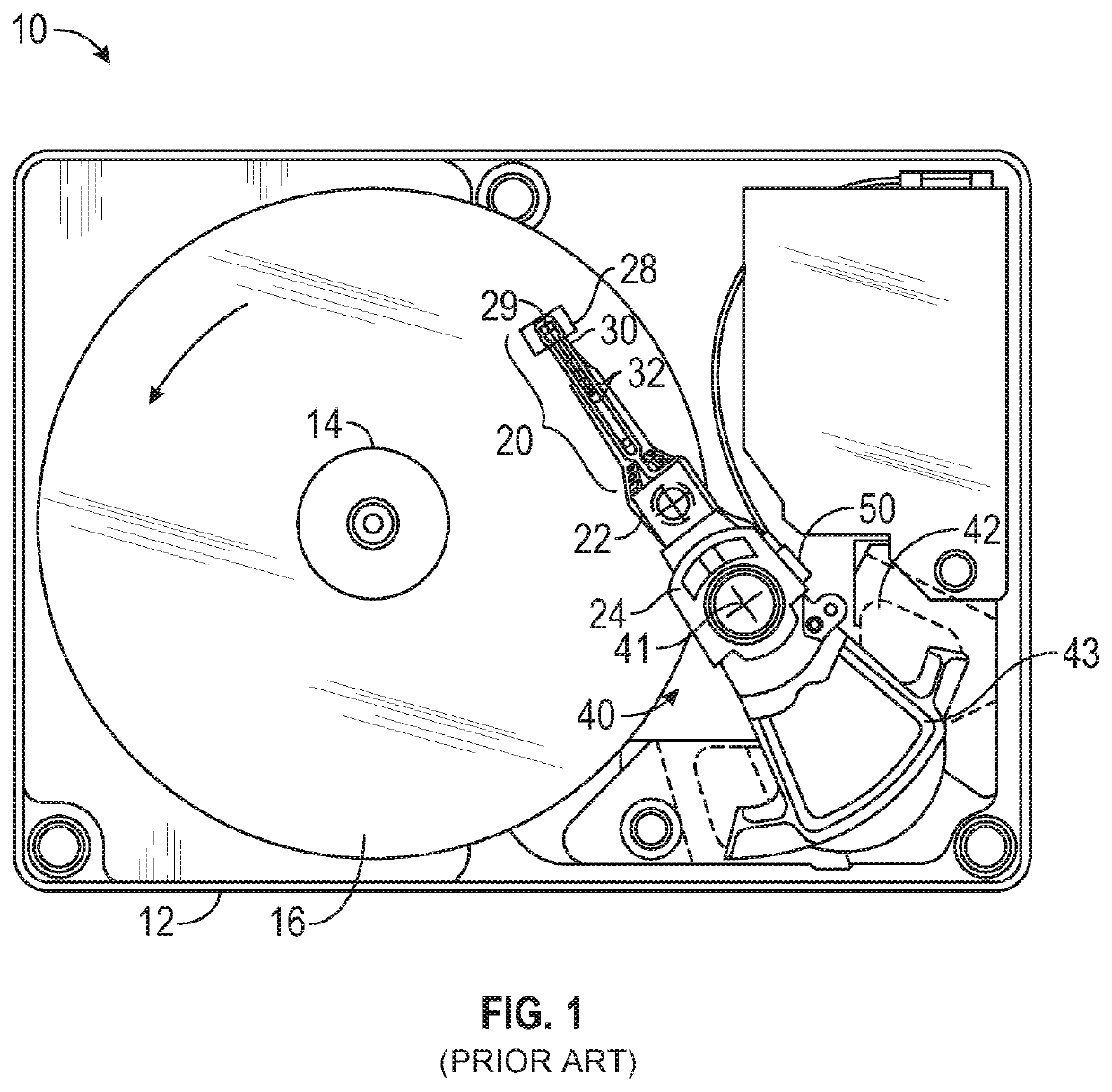
ActiveUS20110116186A1High rateReduce soft error rateDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveElectronic component
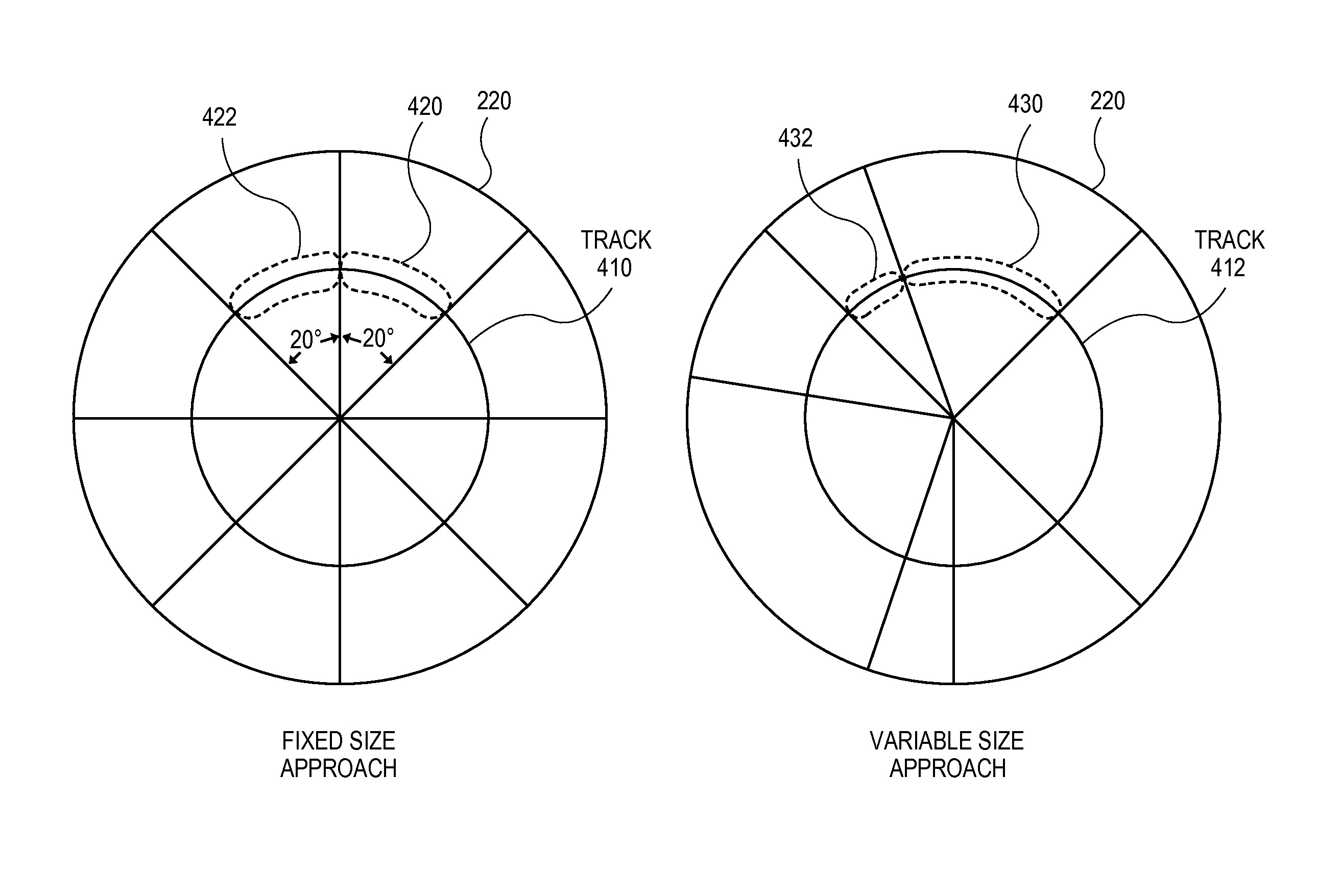
Approaches for adjusting the recording density of a recording medium in a circumferential direction are disclosed. A hard-disk drive includes one or more electronic components configured to divide a track, of a plurality of concentric tracks on a magnetic-recording disk, into a plurality of portions, and write data to each of the plurality of portions at a recording density that is independent of the recording density used for any of the other portions. Data may be written to a first portion of a track at a different frequency than to a second portion of the same track. The frequency at which data is written may be adjusted for different portions of the same track to allow the frequency to be reduced at certain portions shown to have relatively higher soft error rate while increasing the frequency for other portions to achieve a desired average error rate for the track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
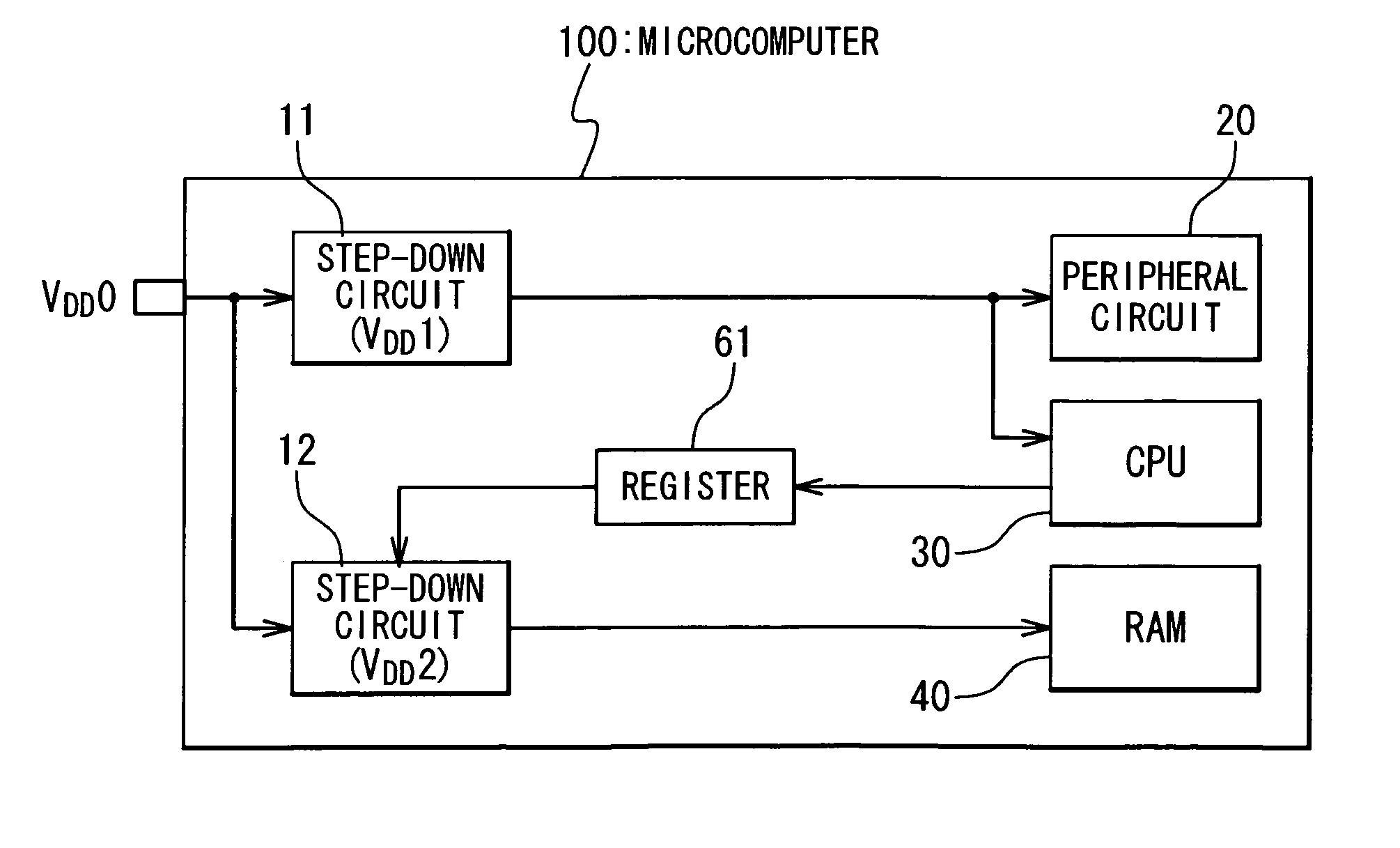
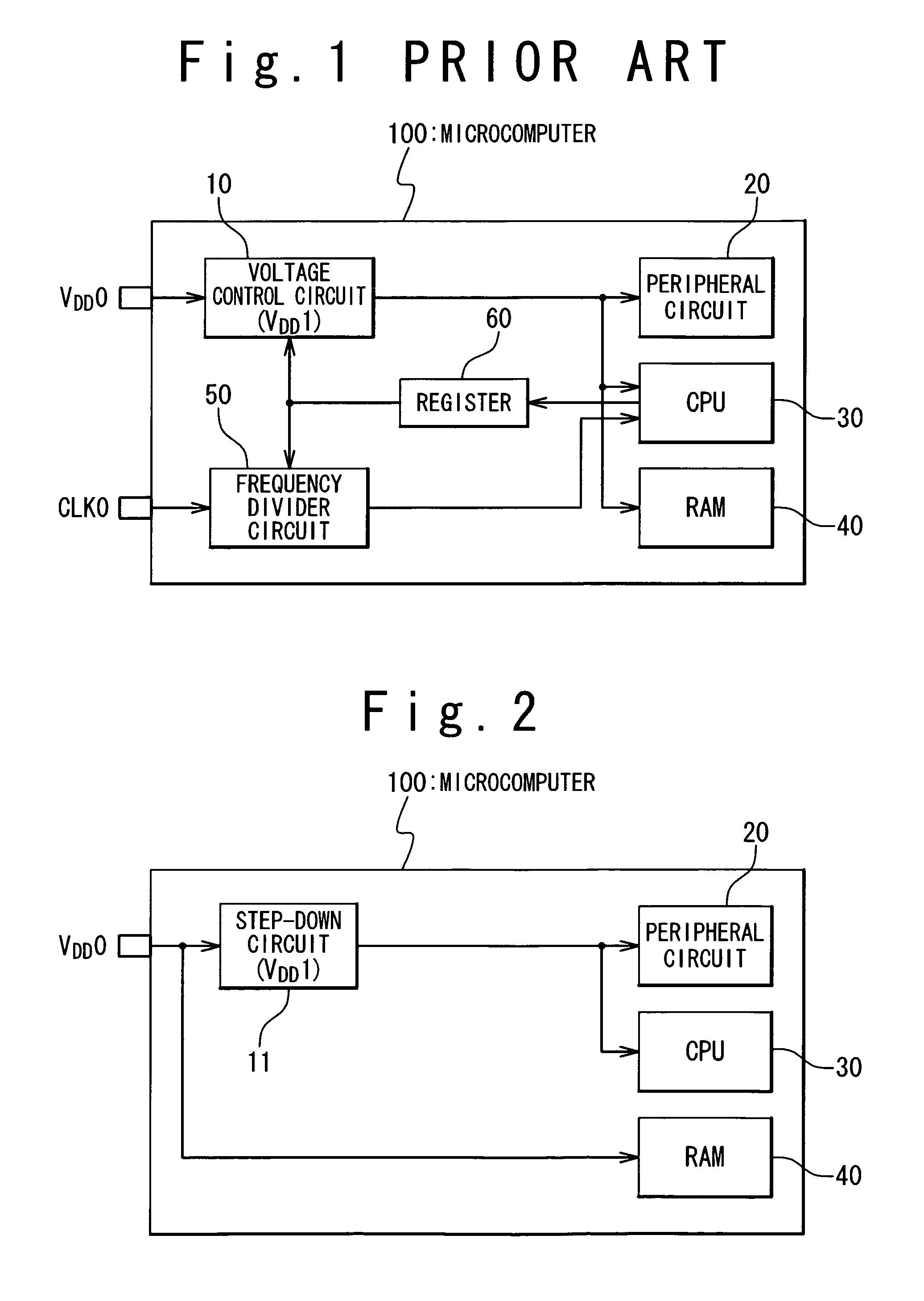
Semiconductor device for reducing soft error rate with reduced power consumption
ActiveUS7652944B2Reduce soft error rateReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device is composed of a first circuit receiving a first power supply voltage; and a second circuit receiving a second power supply voltage. The second power supply voltage is higher than the first power supply voltage. Such device arrangement is effective for reducing the soft error rate, when the second circuit is more susceptive to a soft error than the first circuit, especially when the second circuit is a memory device.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Soft error resistant memory cell and method of manufacture
ActiveUS7355880B1Simple processIncrease resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesStorage cellEngineering
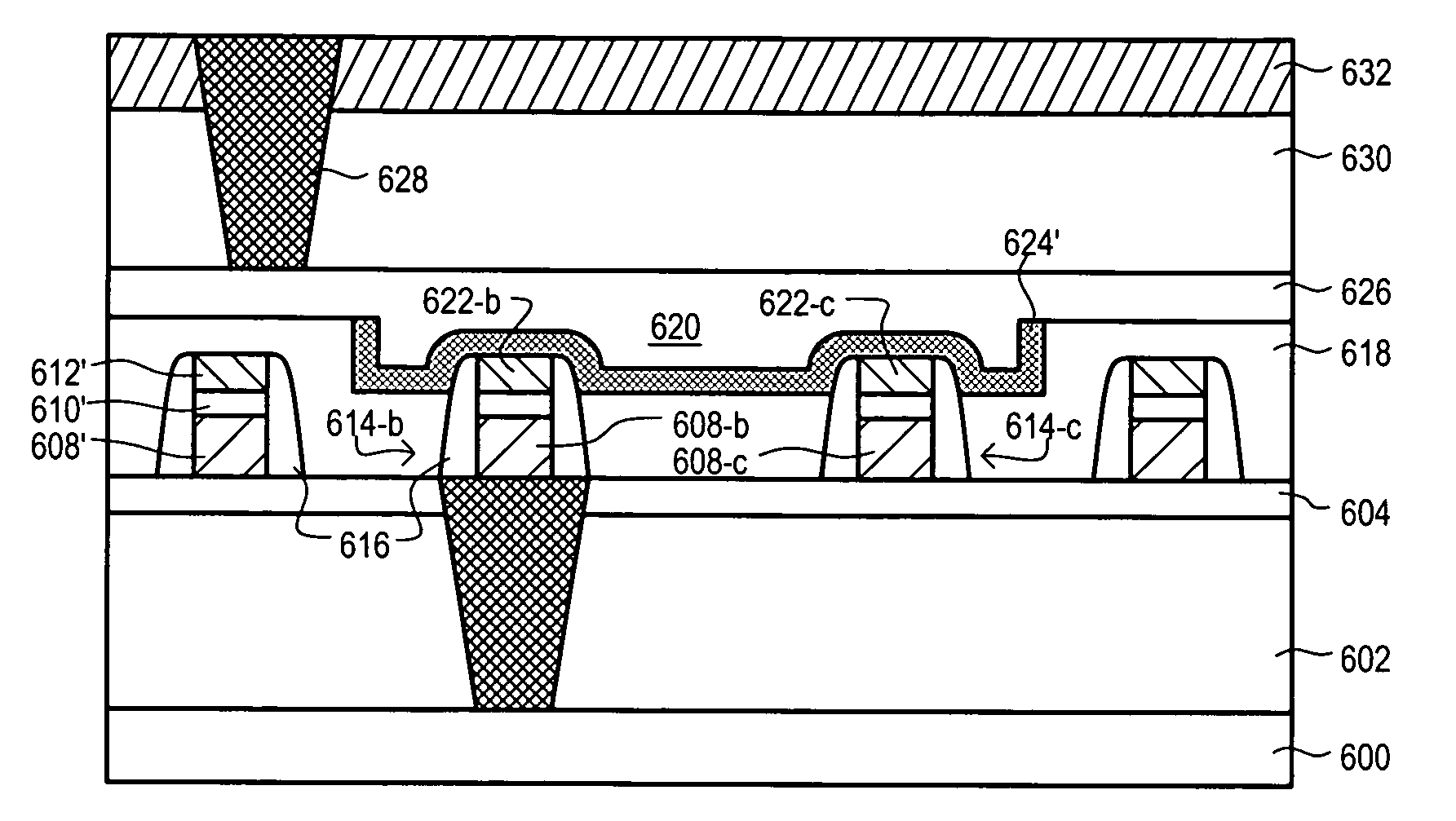
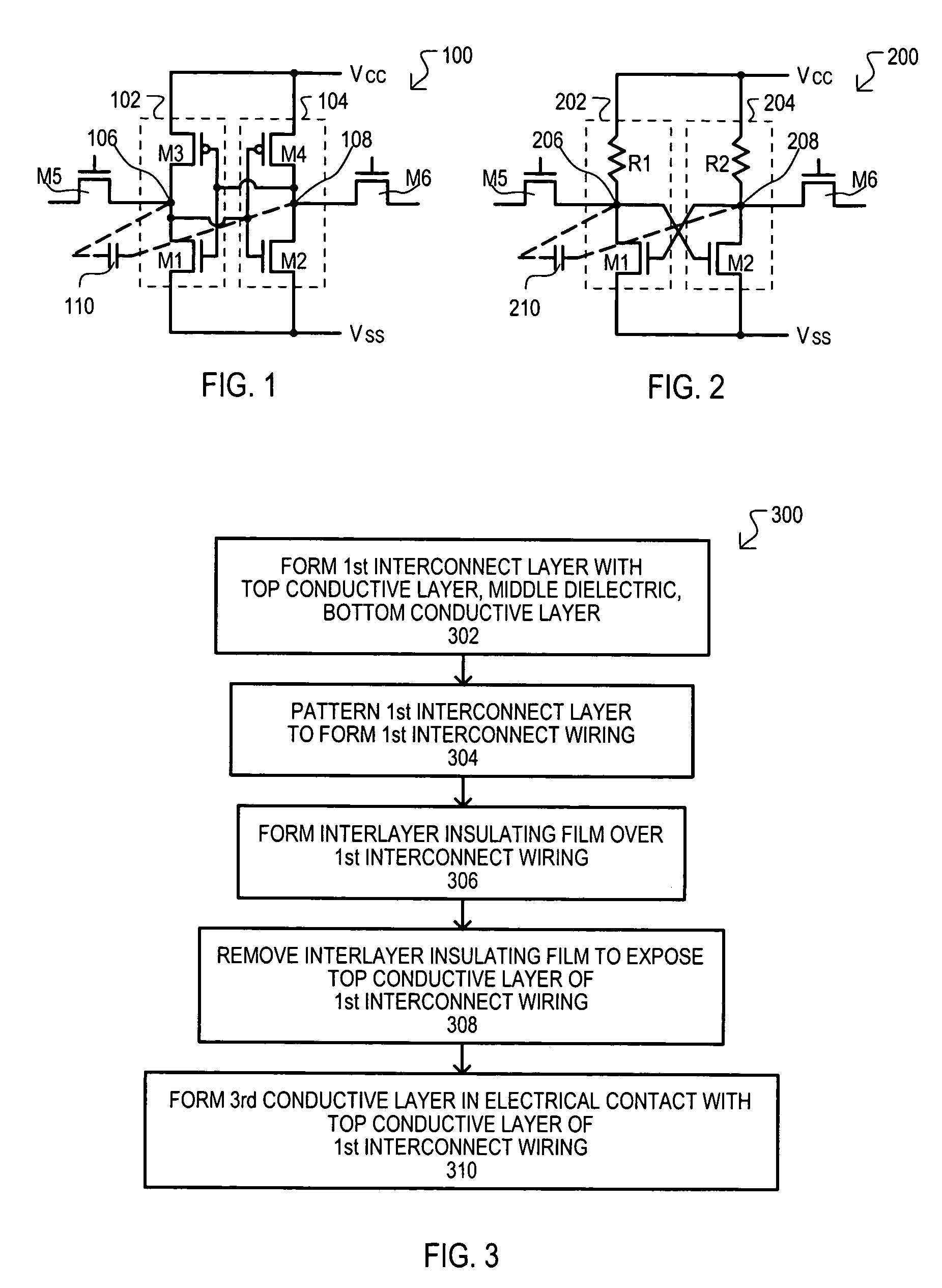
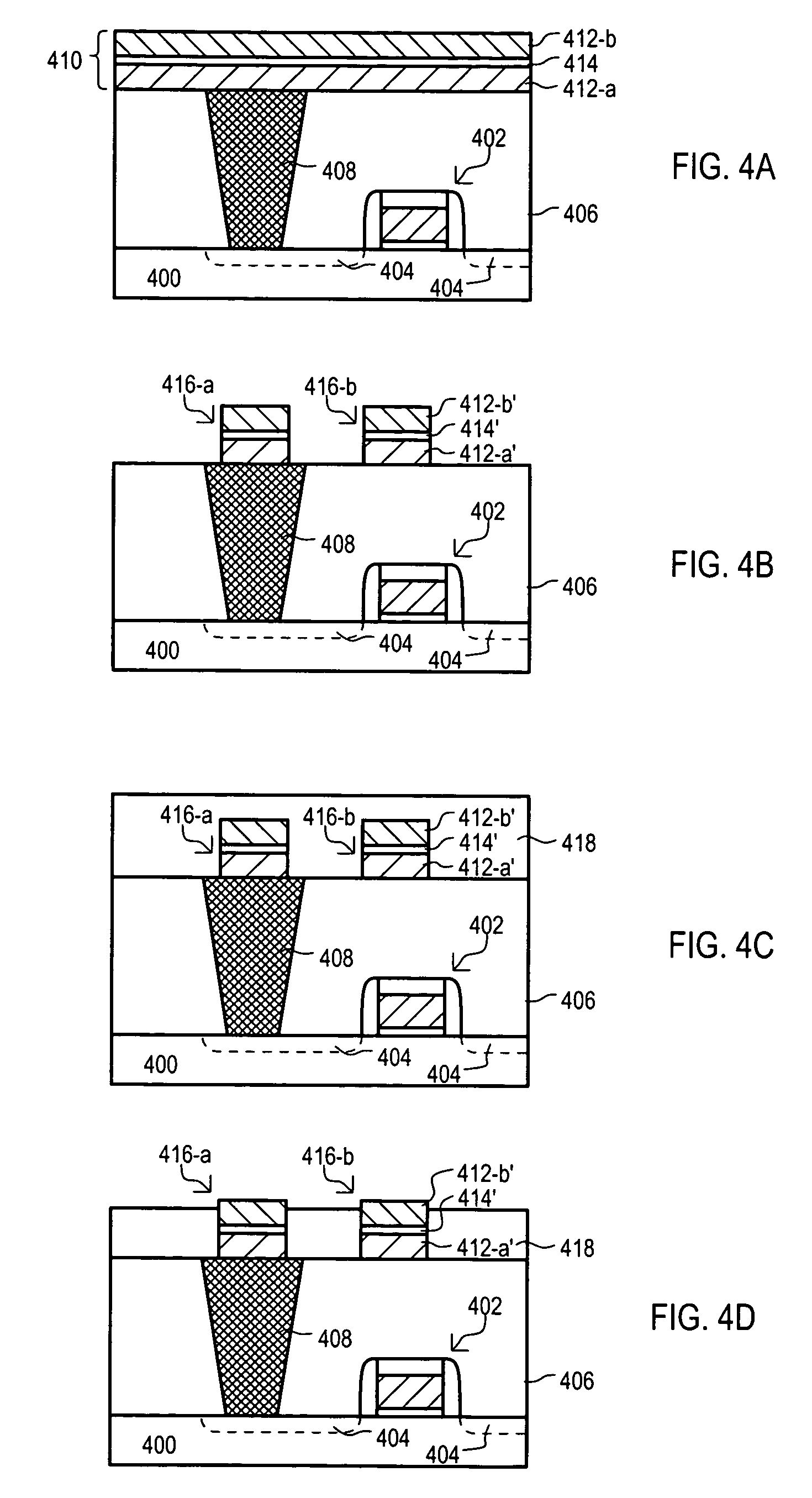
A semiconductor device memory cell (100) can include a built-in capacitor for reducing a soft-error rate (SER). A memory cell (100) can include a first inverter (102) and second inverter (104) arranged in a cross-coupled configuration. A capacitor (110) can be coupled between a first storage node (106) and second storage node (108). A capacitor (110) can be a “built-in” capacitor formed with interconnect wirings utilized to connect memory cell circuit components.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
Adjusting recording density in a circumferential direction
ActiveUS9047921B2High rateReduce soft error rateDriving/moving recording headsFilamentary/web record carriersHard disc driveElectronic component
Approaches for adjusting the recording density of a recording medium in a circumferential direction are disclosed. A hard-disk drive includes one or more electronic components configured to divide a track, of a plurality of concentric tracks on a magnetic-recording disk, into a plurality of portions, and write data to each of the plurality of portions at a recording density that is independent of the recording density used for any of the other portions. Data may be written to a first portion of a track at a different frequency than to a second portion of the same track. The frequency at which data is written may be adjusted for different portions of the same track to allow the frequency to be reduced at certain portions shown to have relatively higher soft error rate while increasing the frequency for other portions to achieve a desired average error rate for the track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
SRAM cell and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050179094A1Reduce soft error rateImprove featuresTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
Disclosed is a SRAM cell and a method of manufacturing the same. The SRAM cell comprises: a pair of access devices; a pair of pull-up devices; a pair of pull-down devices; and at least one metal plate formed on metal interconnection lines in contact with a substrate, having a dielectric film interposed between the metal plate and the metal interconnection lines, so as to increase a cell capacitance, thereby reducing a soft error rate. Herein, one metal plate may be included in each cell. In this case, the metal plate overlaps with a first one of metal interconnection lines of a node side and a node bar side, while being in contact with a second one of the metal interconnection lines of the node side and the node bar side. Also, two metal plates may be included in each cell. In this case, the metal plates overlap, respectively, with one metal interconnection line of metal interconnection lines of a node side and a node bar side, while being in contact with another metal interconnection line of the node side or the node bar side, respectively. Therefore, capacitance is additionally formed to increase cell capacitance, so that variation of the electric potentials of cell nodes, which is caused by generated electrons, is prevented, and thereby soft error can be efficiently reduced.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
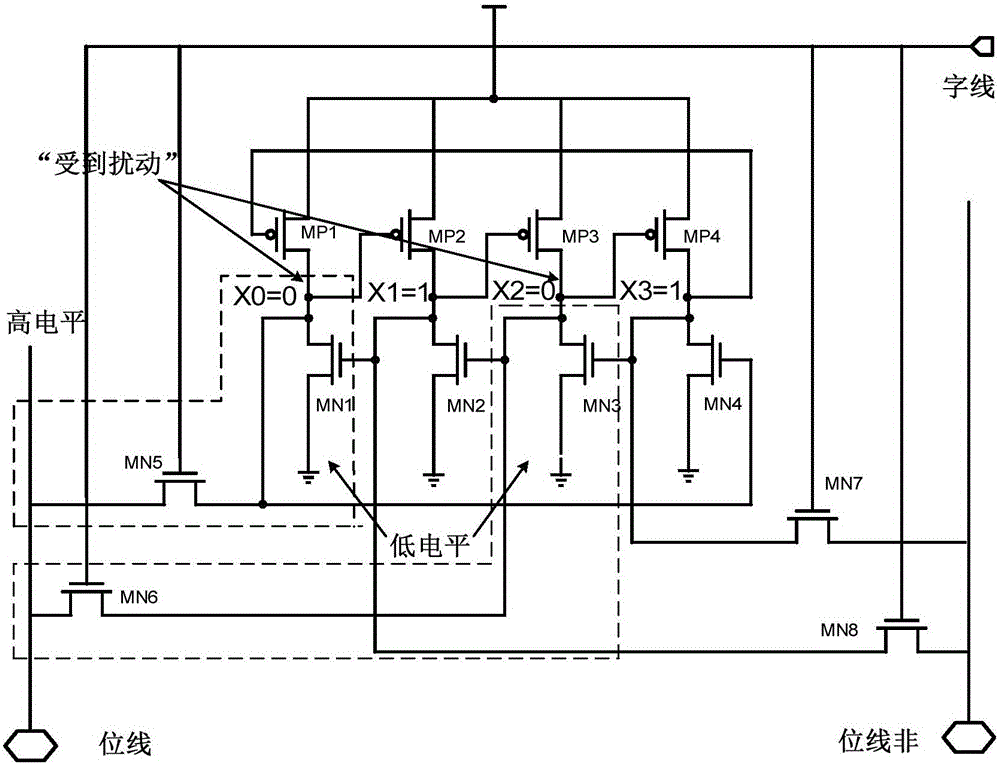
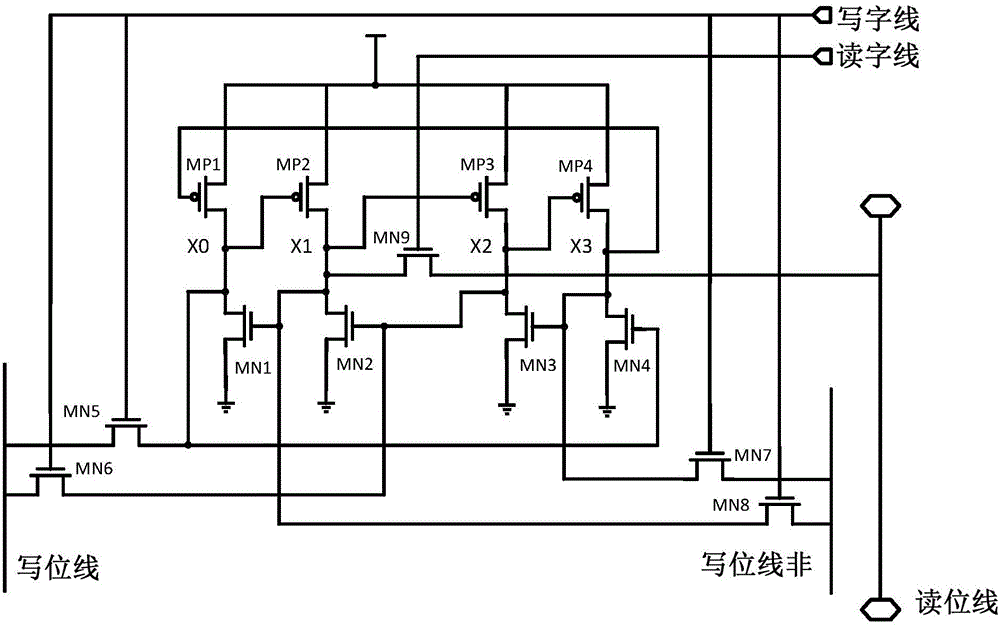
Radiation-proof DICE memory cell applied to DVS system
ActiveCN105869668ASolve the "read corruption" problemImprove stabilityDigital storageComputer architectureAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a radiation-proof DICE memory cell applied to a DVS system. An original DICE cell is provided with a read tube MN9, a read word line for controlling MN9 conduction, and a read bit line connected with a sensitive amplifier; above modification makes one and only one memory node be disturbed by a bit line partial pressure when the read word line starts; and disturbance to a single node automatically recovers after a disturbance source disappears by using the "binode feedback" structural characteristic of the DICE cell, and data stored in the memory cell is not affected, so the "read destroy" phenomenon is eliminated. The structure of the DICE cell becomes connection of the read bit line with one memory node from connection of the read bit line with two in-phase nodes, solves the problem of simultaneous overturning of the two in-phase nodes, induced by the bit line partial pressure when the word line starts, guarantees normal read of data, and improves the robustness of the memory cell in the subthreshold working process.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Latch circuit and flip-flop circuit
InactiveCN101431321AReduce soft error rateSoft error suppressionElectric pulse generatorEngineeringControl circuit
A latch circuit includes: first nodes which are three or more and to which a voltage in a first signal level is set; second nodes which are three or more and to which a voltage in a second signal level obtained by inverting the first signal level is set; and first node voltage control circuits having the first nodes; and second node voltage control circuits having the second nodes. Each of the first node voltage control circuits is connected with at least two of the three or more second nodes, and controls the voltage of the first node based on the voltages of the at least two second modes. Each of the second node voltage control circuits is connected with at least two of the three or more first nodes and controls the voltage of the second node based on the voltages of the at least two first nodes.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
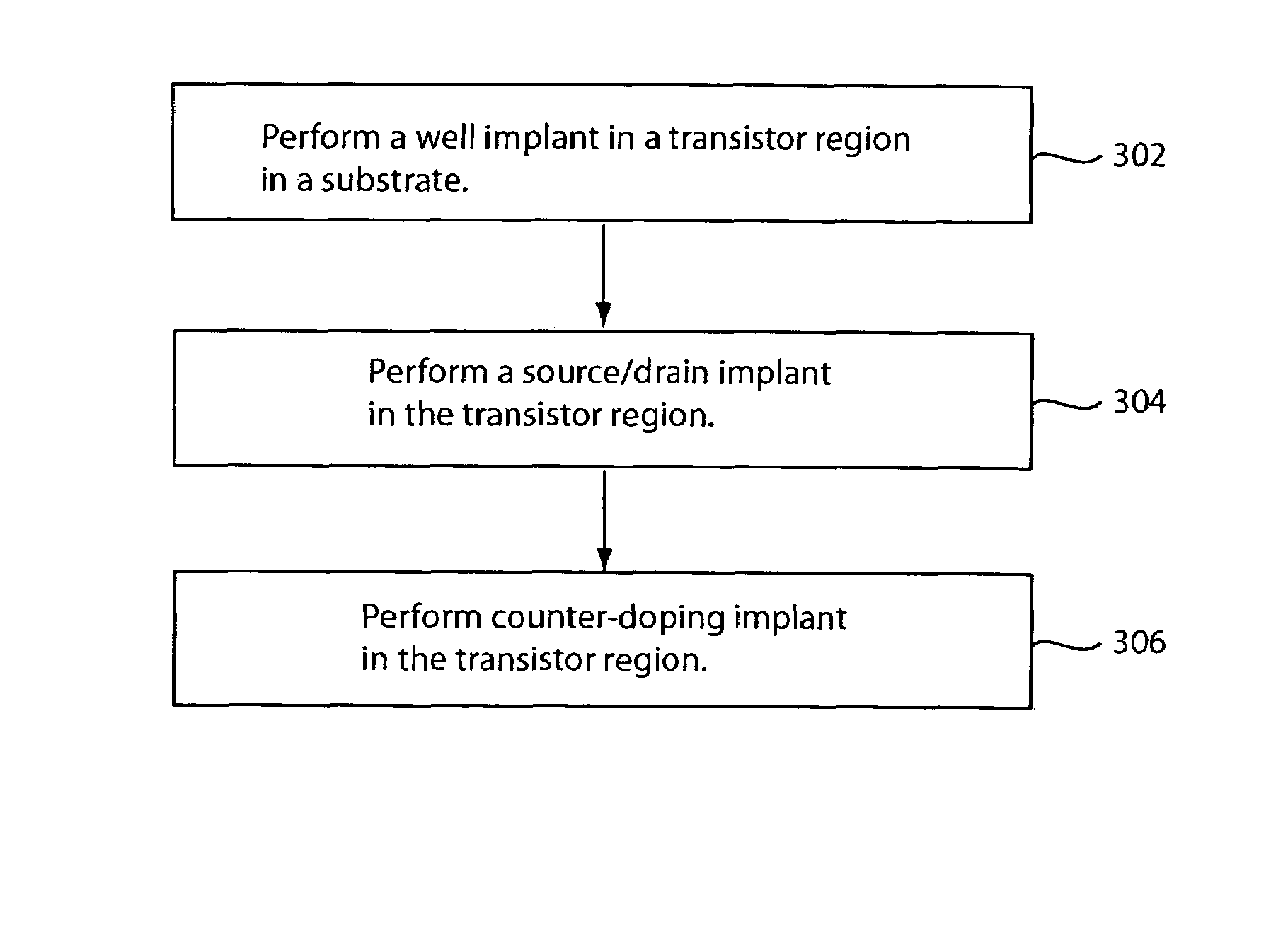
Method for reducing soft error rates of memory cells
ActiveUS7268052B1Increase the doping concentrationReduce soft error rateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDopantMedicine
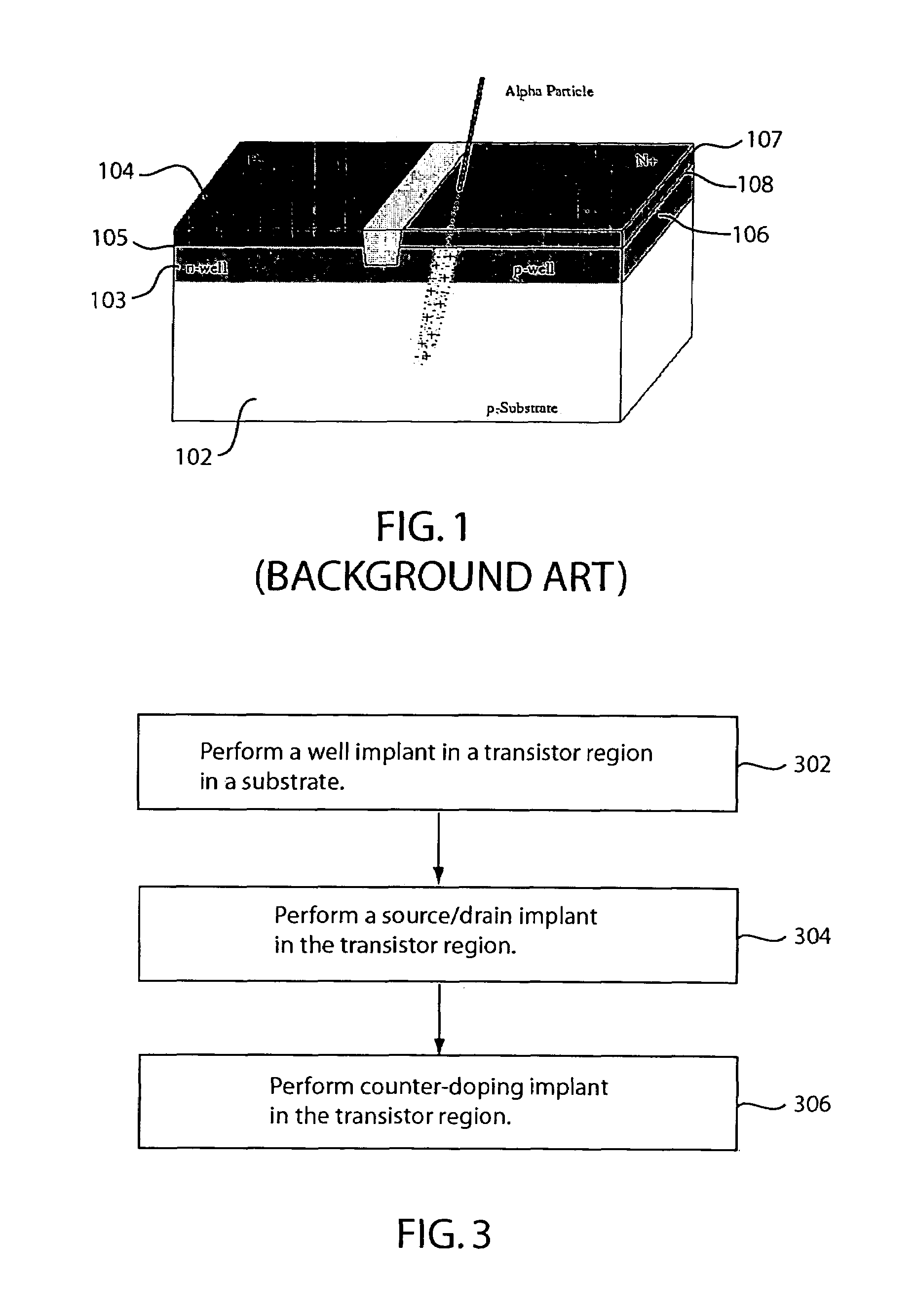
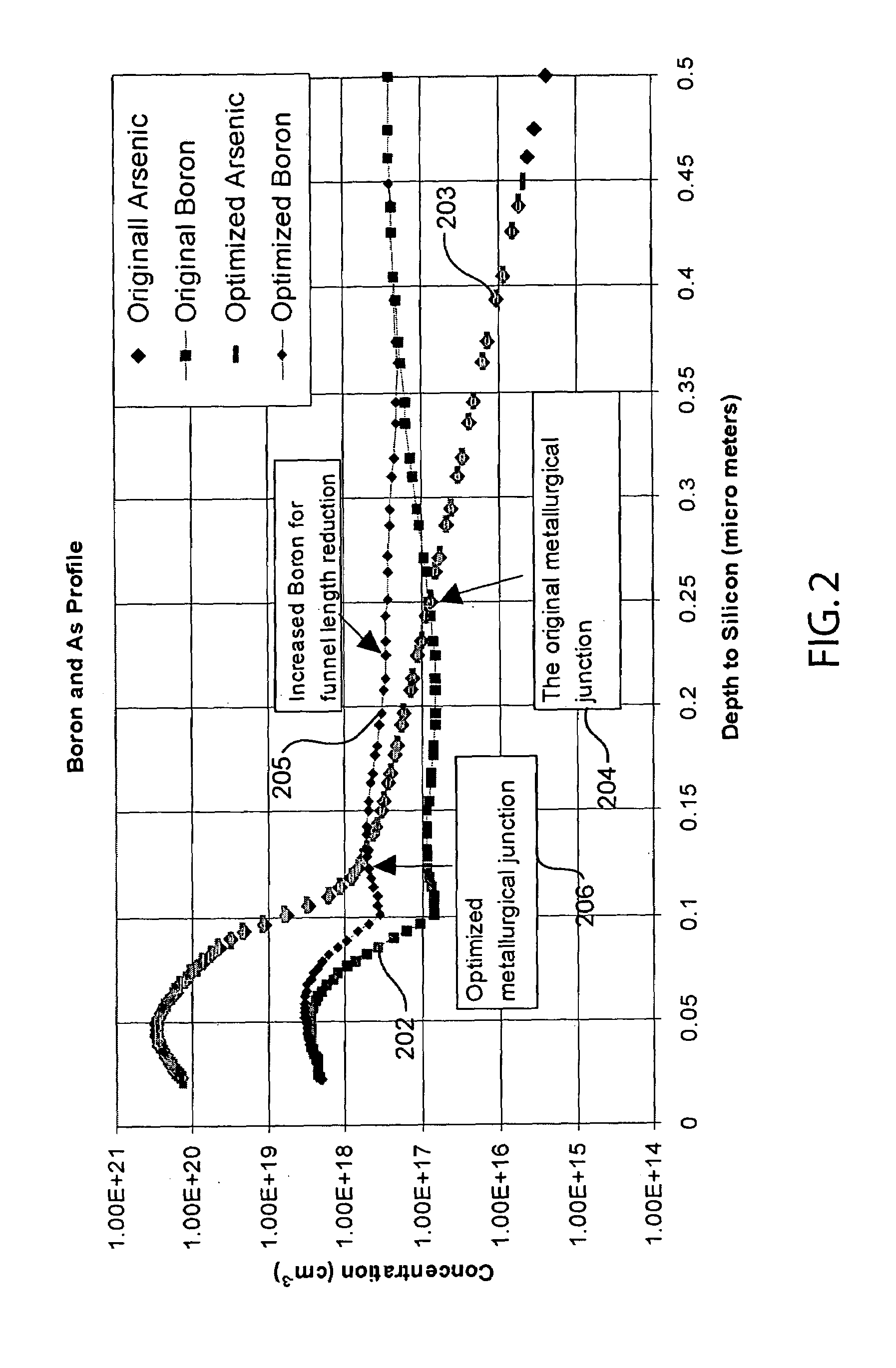
In one embodiment, a method of fabricating a transistor for a memory cell includes the steps of performing a counter doping implant before or after a source / drain implant. The counter doping implant may comprise one or more implant steps that move a metallurgical junction formed by a well and a highly doped region closer to a surface of the substrate. The counter doping implant may also increase the concentration of the dopant of the well. The counter doping implant and the source / drain implant may be performed using the same mask. Transistors fabricated using embodiments of the present invention may be employed in memory cells to reduce soft error rates.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Current-assisted magnetic recording write head with wide conductive element in the write gap
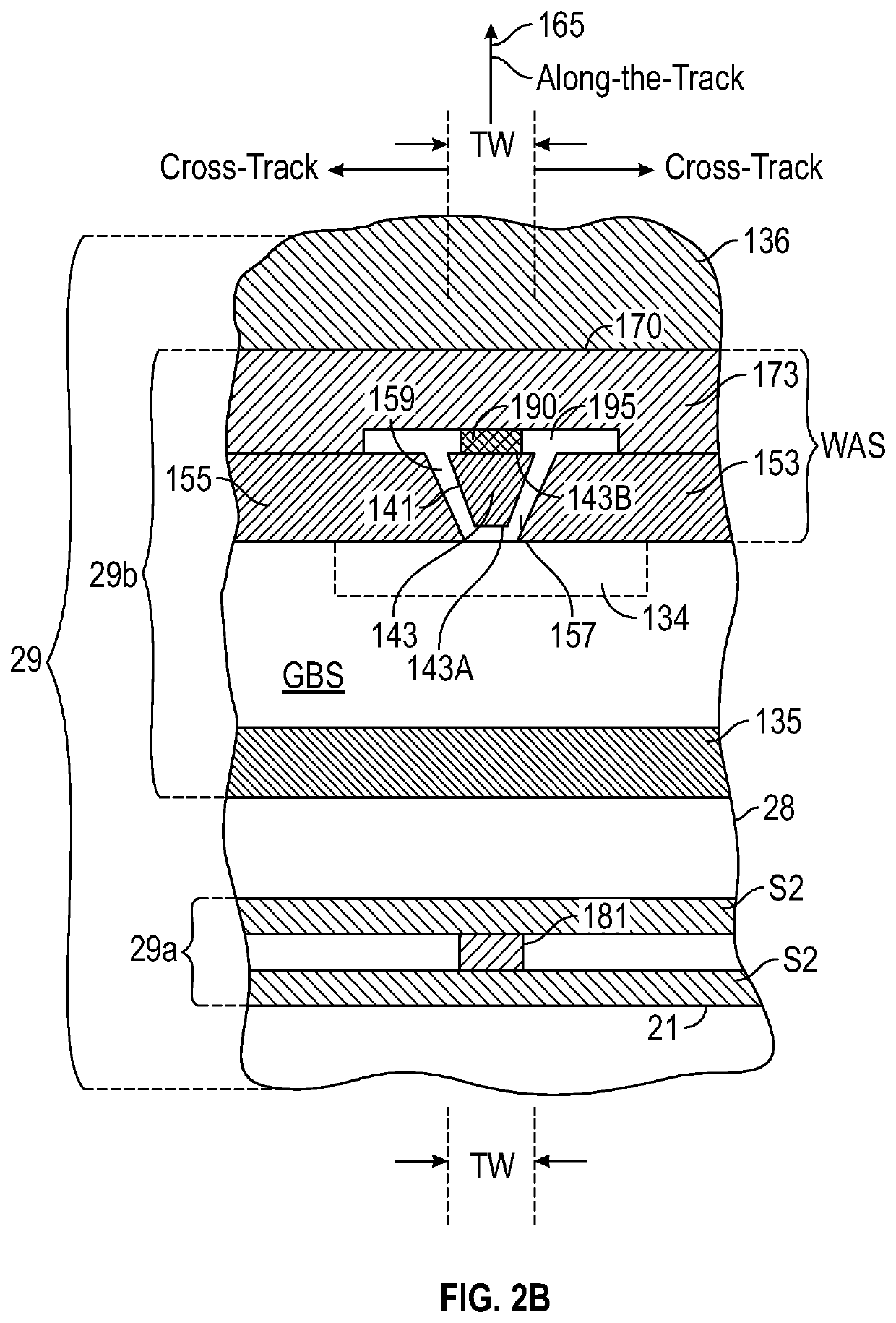
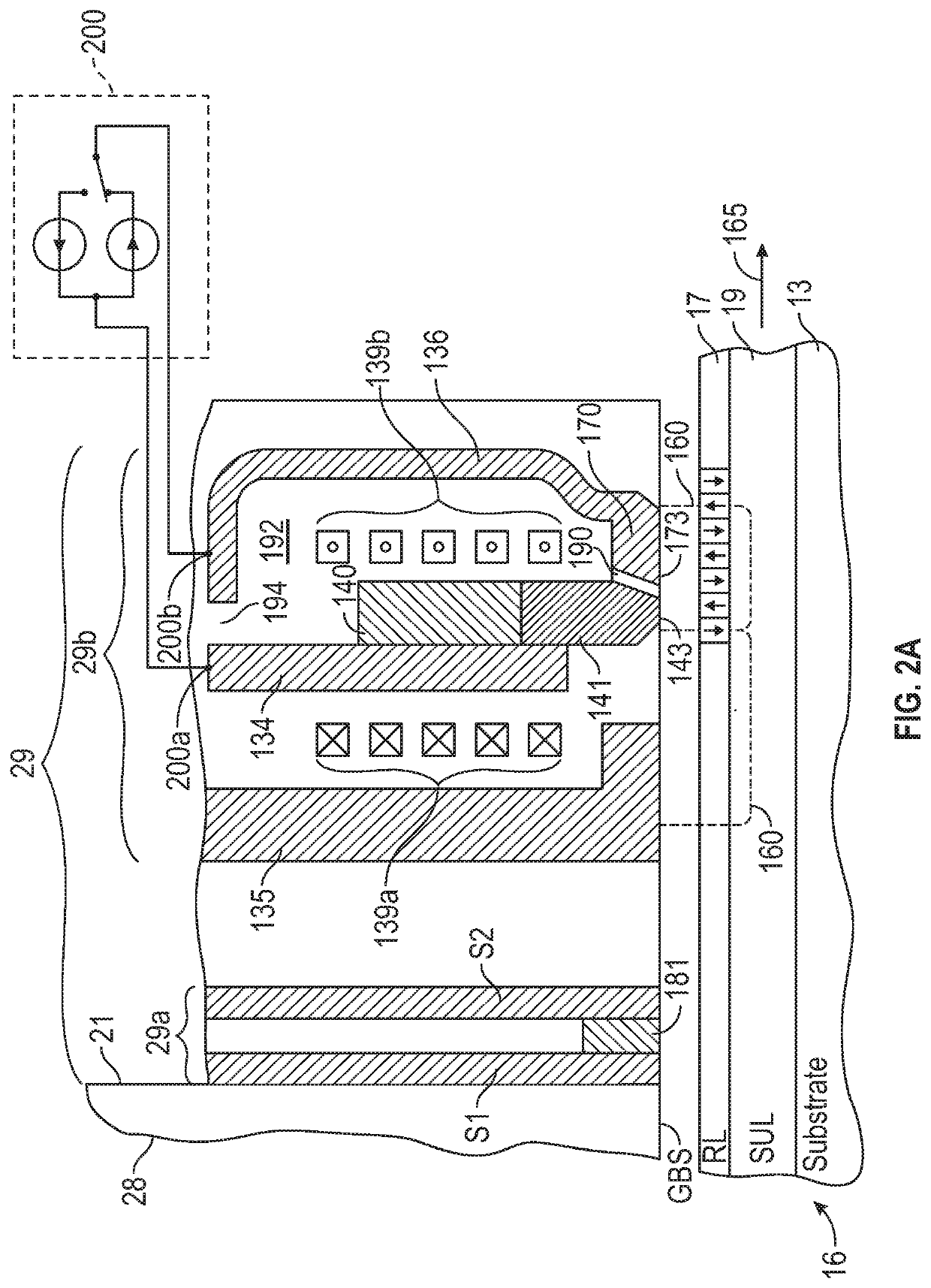
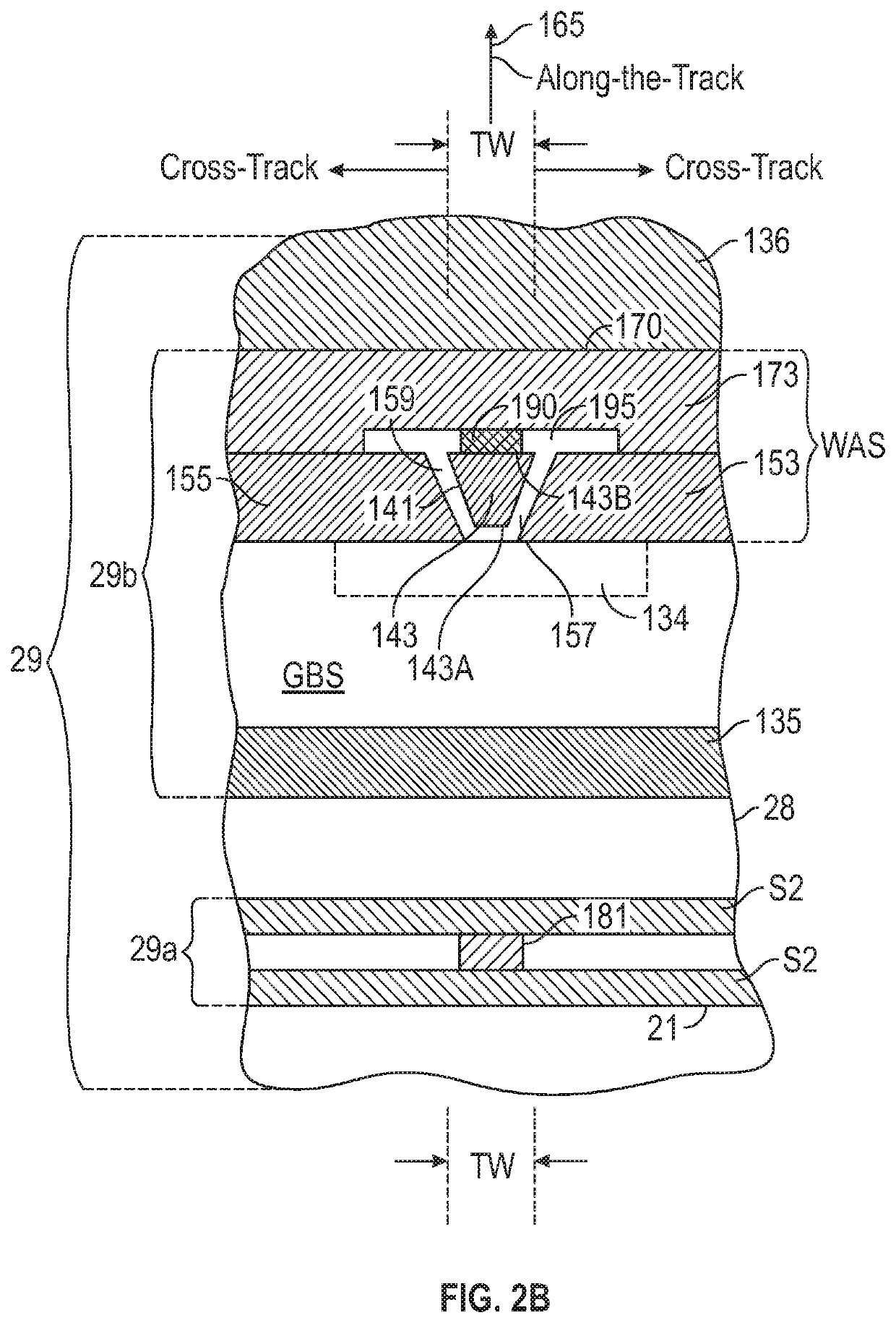
ActiveUS10839844B1Improve write pole magnetization switchingReduce soft error rateFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageElectrically conductiveHemt circuits
A current-assisted magnetic recording write head has an electrically conductive layer in the write gap between the write pole and the trailing shield. Electrical circuitry directs current between the write pole and the trailing shield, through the conductive layer in the write gap. The current through the conductive layer generates an Ampere field substantially orthogonal to the magnetization in the write pole to assist magnetization switching of the write pole. The conductive layer is wider in the cross-track direction than the trailing edge of the write pole and may extend beyond the write pole side gaps so as to be in contact with both the side shields and the trailing shield. The conductive layer may have substantially the same along-the-track thickness across its width or it may have a thicker central region at the write pole trailing edge and thinner side regions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
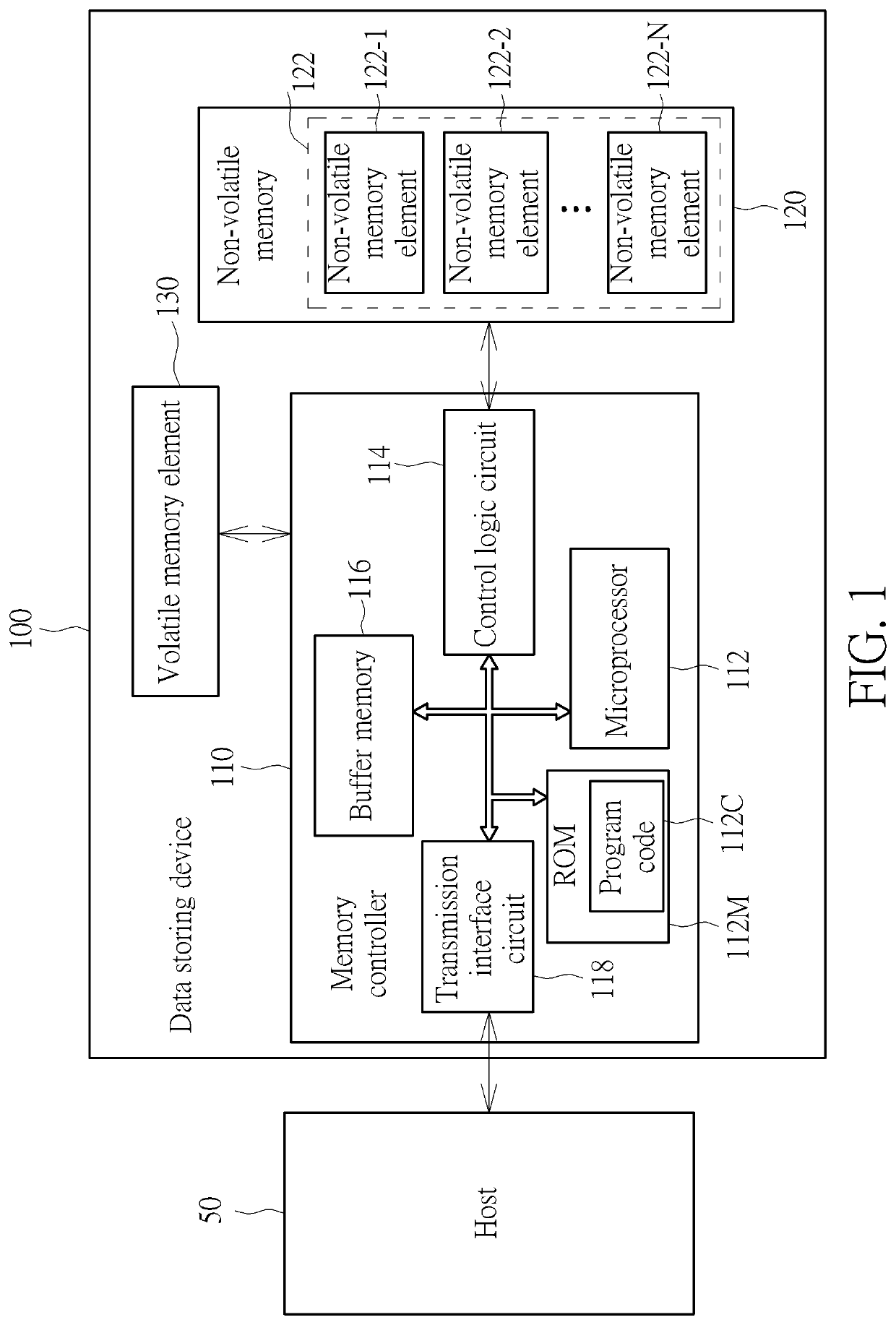
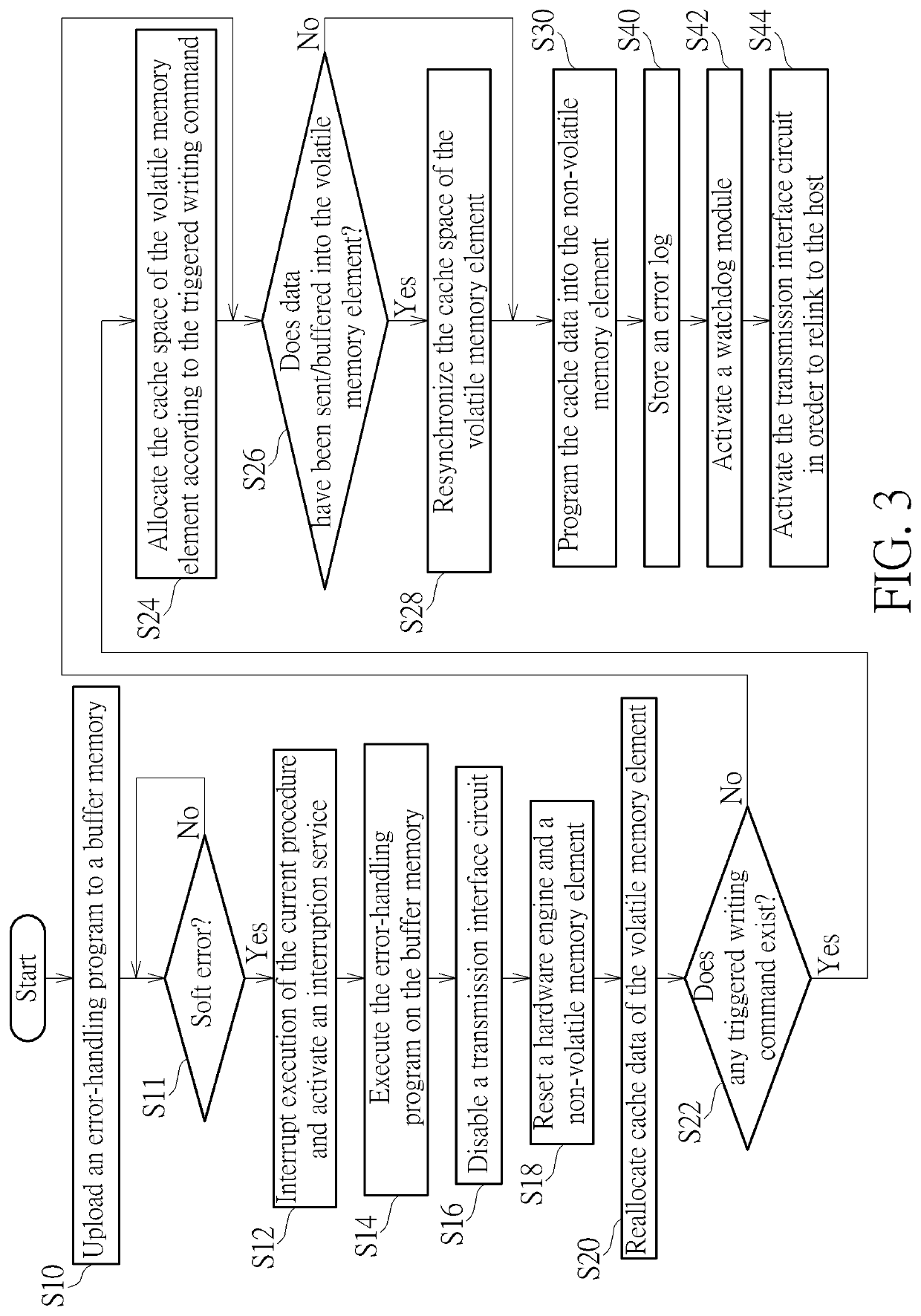
Error-handling method, associated data storage device and controller thereof
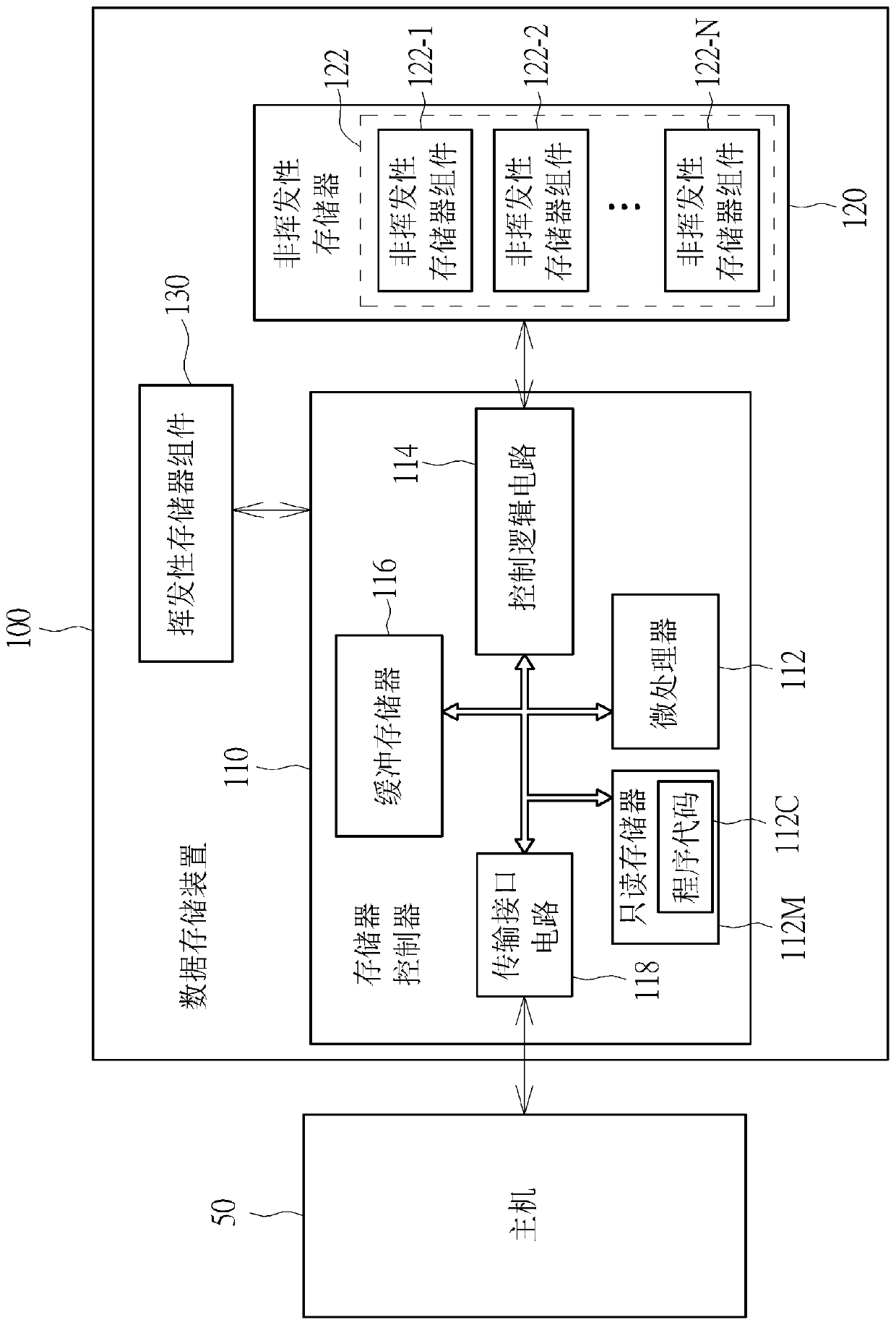
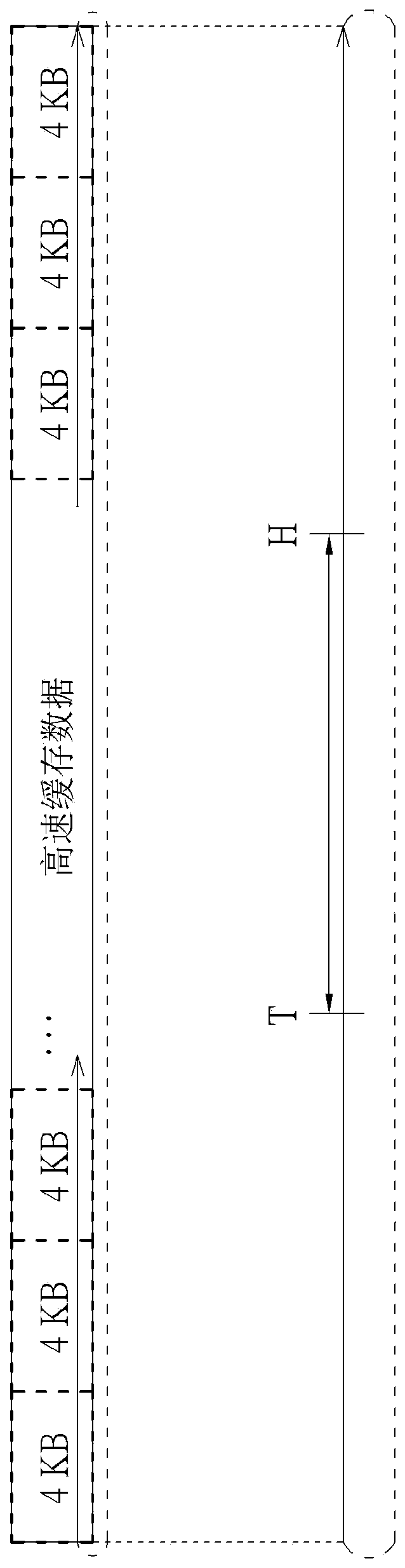
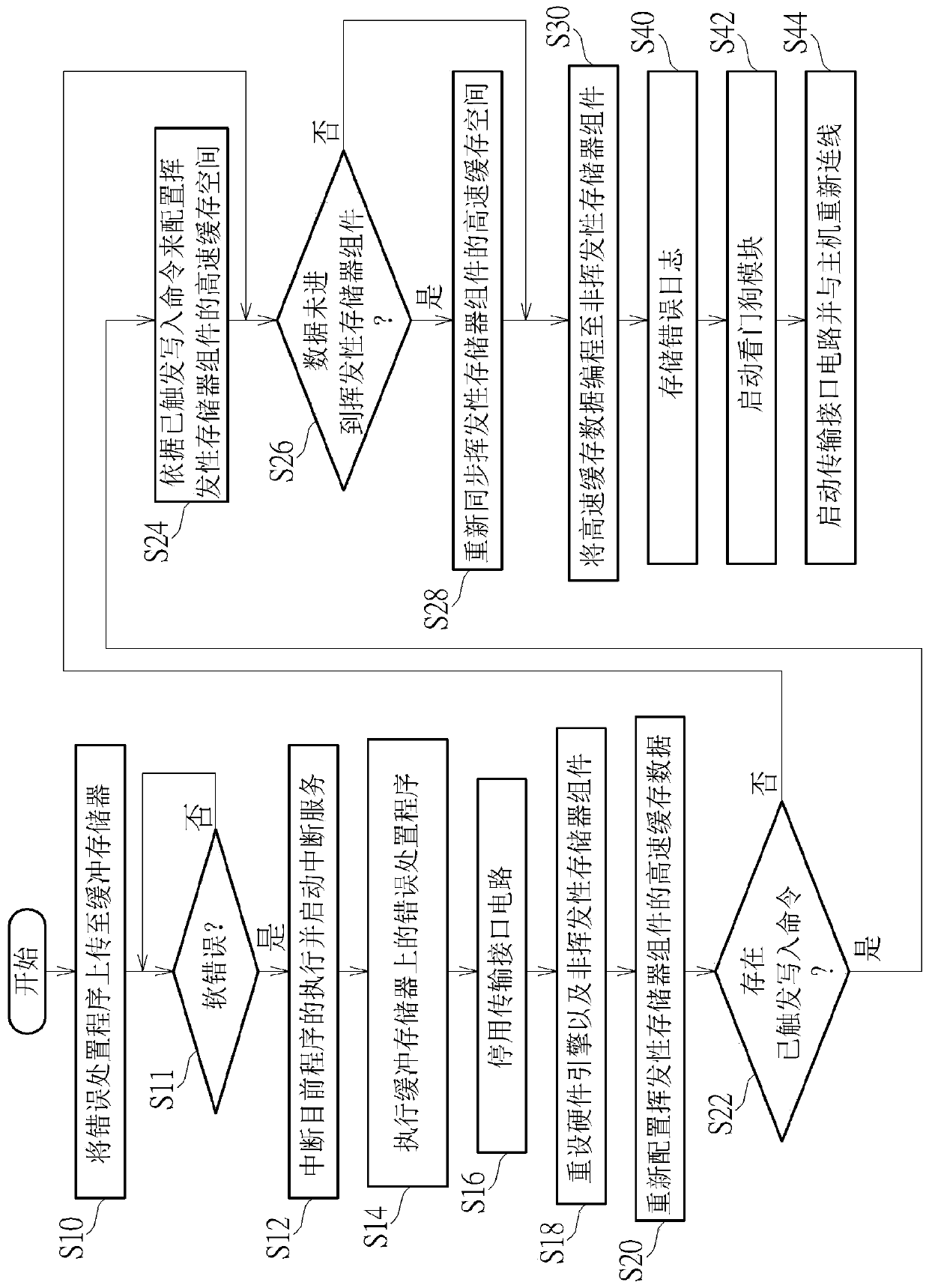
ActiveUS20200110662A1Reduce soft error rateIncrease costNon-redundant fault processingRedundant data error correctionEngineeringData store
An error-handling method, an associated data storage device and the controller thereof are provided. The error-handling method may include: uploading an error-handling program to a buffer memory equipped with error correction code (ECC) protection capability; in response to at least one error, interrupting execution of a current procedure and activating an interruption service; executing the error-handling program on the buffer memory; disabling a transmission interface circuit; resetting at least one hardware engine and at least one NV memory element; performing cache rearrangement regarding a data cache within the data storage device, and programming rearranged cache data into the NV memory element, to perform data recovery; and through activating a watchdog module and the transmission interface circuit and relinking with a host device, completing soft reset to make the data storage device operate normally again.
Owner:SILICON MOTION INC (TW)
Semiconductor memory device with increased node capacitance
ActiveUS7352025B2Increased node capacitanceReduce soft error rateTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
An integrated circuit semiconductor memory device having the BOX layer removed from under the gate of a storage transistor to increase the gate-to-substrate capacitance and reduce the soft error rate. The increased node capacitance thus obtained is achieved without requiring a corresponding increase in area.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
Static random access memory device and forming method thereof
ActiveUS9871049B1Reduce leakageReduce distractionsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityStatic random-access memory
A static random access memory device includes two body contacts and two resistive-switching devices. The body contacts are disposed in a wafer and are exposed from a back side of the wafer, wherein the body contacts electrically connect a static random access memory cell through a metal interconnect in the wafer. The resistive-switching devices connect the two body contacts respectively from the back side of the wafer. A method of forming a static random access memory device is also provided in the following. A wafer having two body contacts exposed from a back side of the wafer and a metal interconnect electrically connecting a static random access memory cell to the body contacts is provided. Two resistive-switching devices are formed to connect the two body contacts respectively from the back side of the wafer.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Current-assisted magnetic recording write head with wide conductive element in the write gap
ActiveUS20200402532A1Reduce soft error rateImprove the write pole magnetization switchingRecord information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsHemt circuitsEngineering physics
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Error-handling method, data storage device and controller thereof
ActiveCN110990175AAchieve optimal performanceReduce the risk of lossNon-redundant fault processingRedundant data error correctionData storeInterface circuits
An error-handling method, a data storage device and controller thereof are provided. The error-handling method may include: uploading an error-handling program to a buffer memory equipped with error correction code (ECC) protection capability; in response to at least one error, interrupting execution of a current procedure and activating an interruption service; executing the error-handling program on the buffer memory (116); disabling a transmission interface circuit; resetting at least one hardware engine and at least one NV memory element; performing cache rearrangement regarding a data cache within the data storage device, and programming rearranged cache data into the NV memory element, to perform data recovery; and through activating a watchdog module and the transmission interface circuit and relinking with a host device, completing soft reset to make the data storage device operate normally again. According to the invention, the data storage device can be self-repaired when a soft error occurs, so that the soft error rate is reduced.
Owner:SILICON MOTION INC
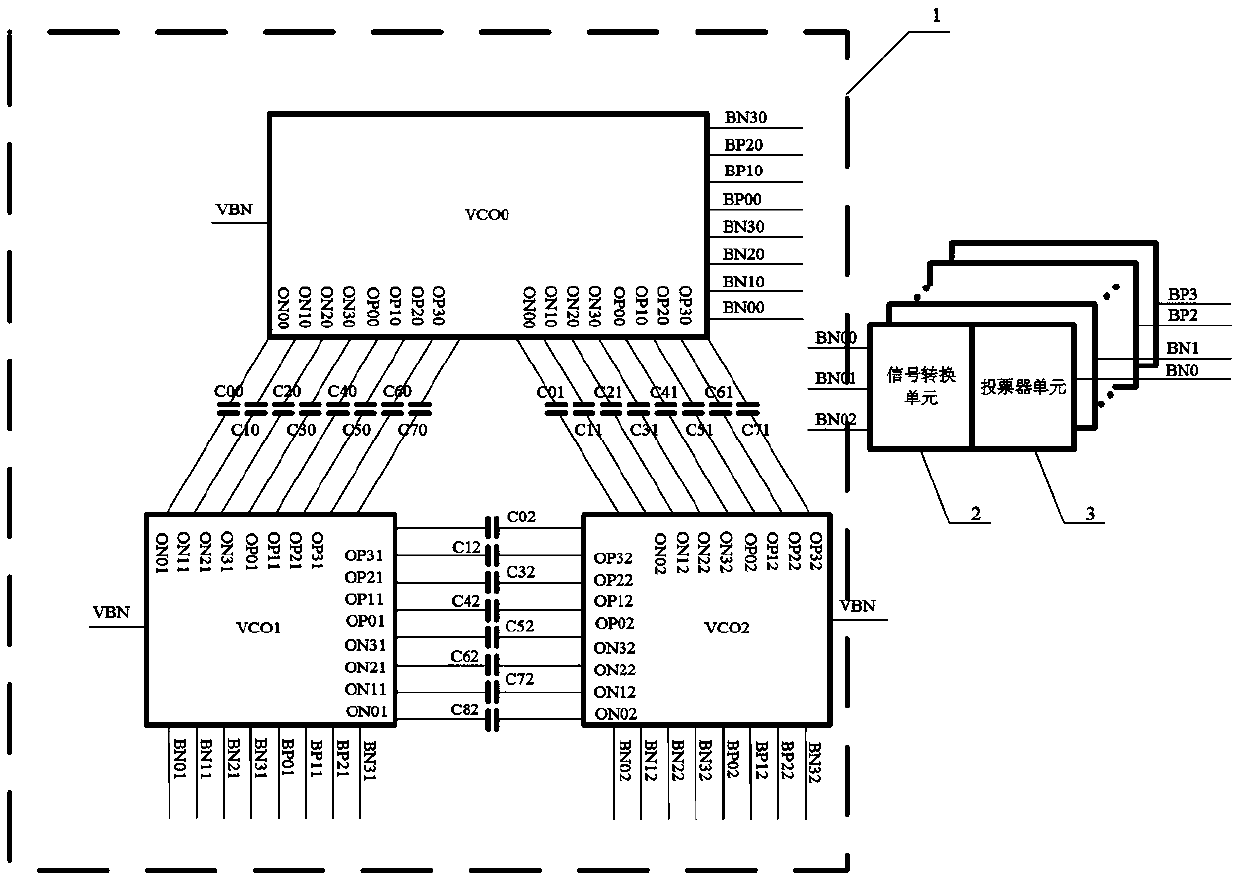
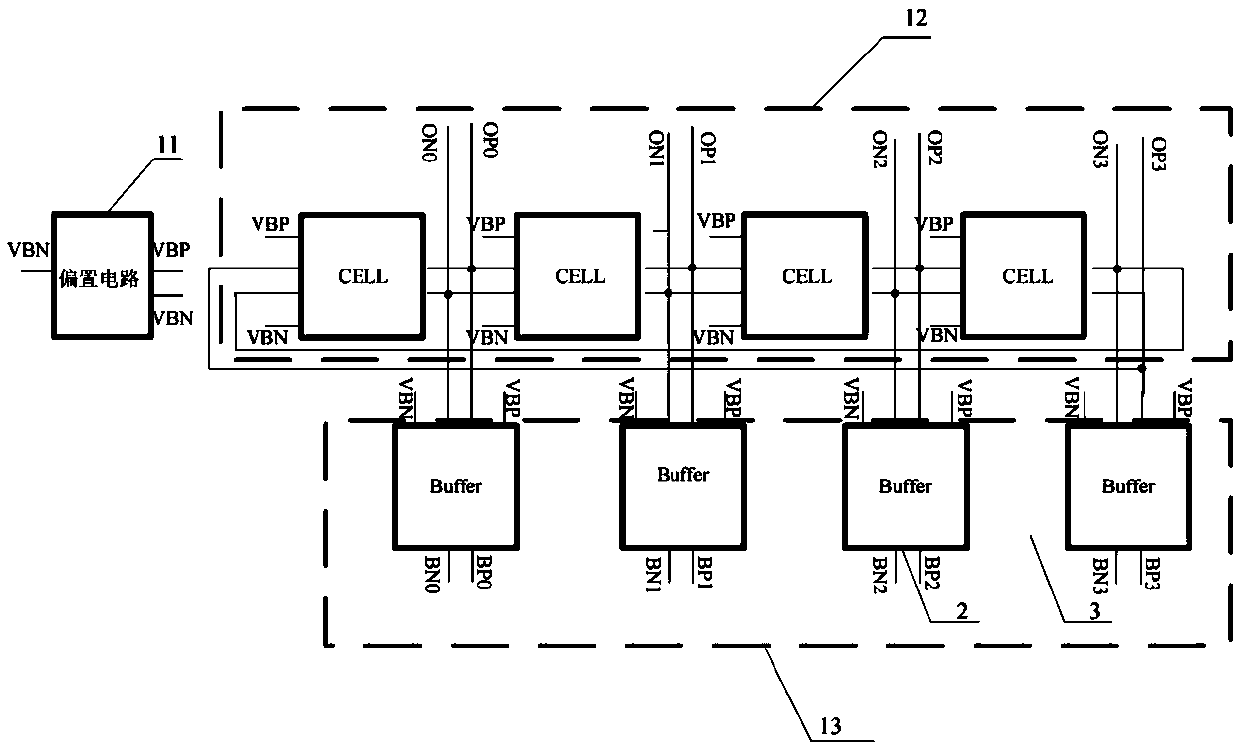
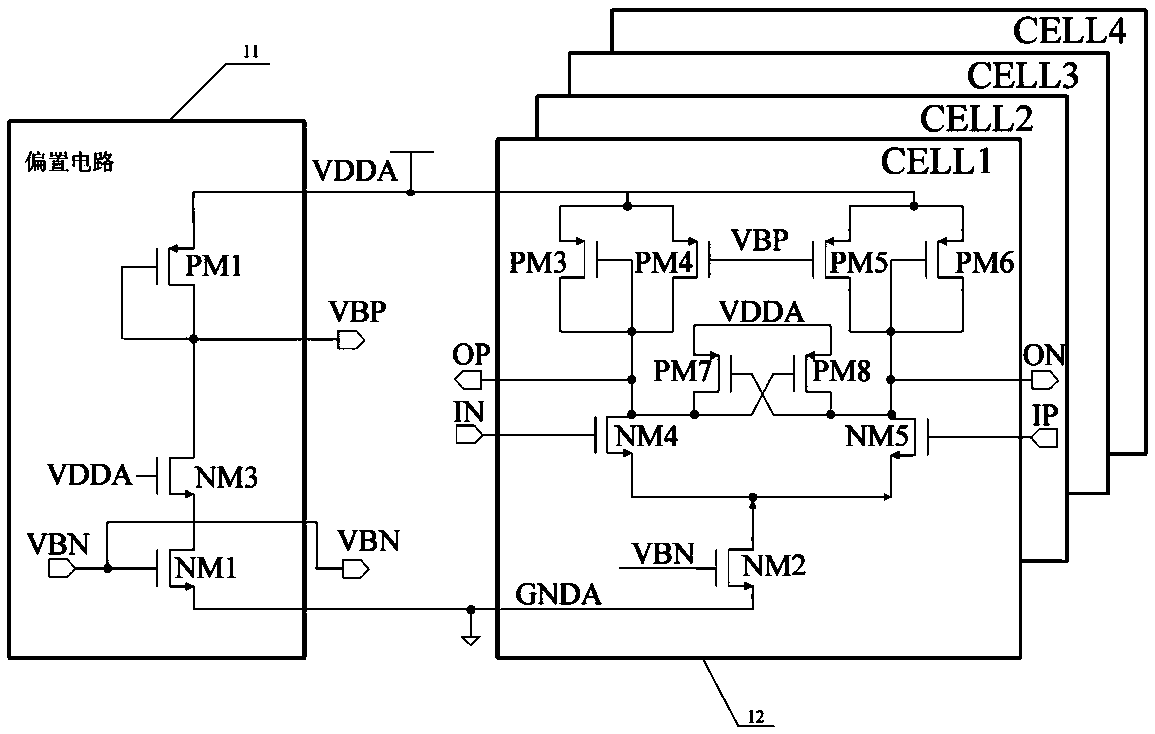
Cross-coupling voltage-controlled oscillator with anti-irradiation function
ActiveCN109560813AWith anti-irradiation functionSingle event suppressionPulse automatic controlCouplingIrradiation
The invention discloses a cross-coupling voltage-controlled oscillator with an anti-irradiation function. The cross-coupling voltage-controlled oscillator comprises a VCO unit, a signal conversion unit and a voting device unit which are sequentially connected. The VCO unit comprises three or more VCO circuits, and each VCO circuit outputs a path of current output signal of the same phase to the signal conversion unit. The signal conversion unit receives the three paths of current output signals and converts them into voltage signals. The three paths of voltage output signals obtained through conversion are supplied to the voting device unit, and the voting device unit selects and outputs the final voltage output signal. The cross-coupling voltage-controlled oscillator has the advantages ofsimple structure, low cost, anti-irradiation function, low soft error rate and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method of fabricating a semiconductor device having a photo-sensitive polyimide layer and a device fabricated in accordance with the method
InactiveUS20050029631A1Avoid developmentCracking of the PSPL layer is mitigated or eliminatedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
In a semiconductor device fabrication method and in a product formed according to the method, a photosensitive polyimide layer (PSPL) layer is applied to a semiconductor device in a manner which overcomes the limitations of the conventional approaches. The beneficial qualities of an added photoresist layer are utilized to avoid unwanted development of the underlying PSPL layer. In this manner, cracking of the PSPL layer is mitigated or eliminated, reducing the device soft error rate (SER) and increasing device yield. This is accomplished in a reliable and low-cost approach that employs standard device fabrication techniques.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
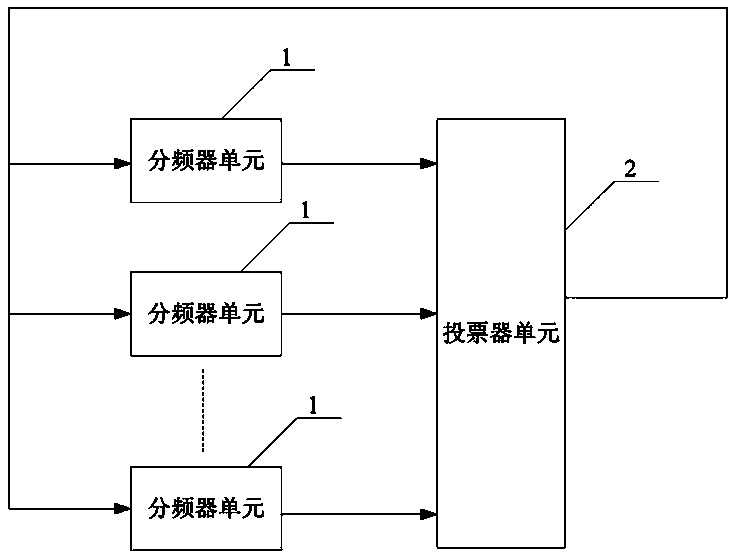
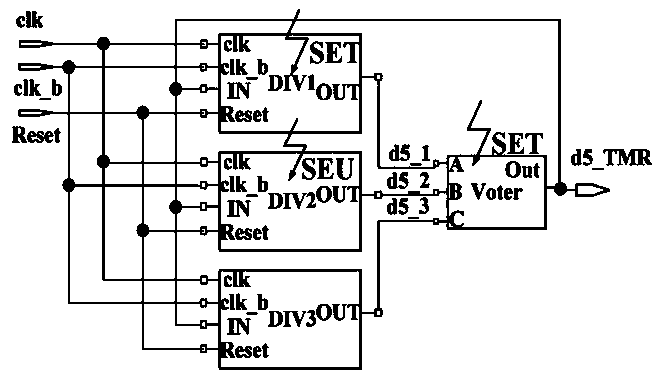
Frequency divider circuit with anti-irradiation function
ActiveCN109525243AWith anti-irradiation functionSuppression of single event effectsCounting chain pulse counters using semiconductor devicesEngineeringIrradiation
The invention discloses a frequency divider circuit with anti-irradiation function, comprising more than three frequency divider units and a voting unit, wherein the output ends of each frequency divider unit are respectively connected to the input end of the voting unit, and the output end of the voting unit is in feedback connection to the input ends of each frequency divider unit. The frequencydivider circuit has the advantages such as simple structure, low cost, anti-irradiation function and low soft error rate.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
A Fault Tolerant Directory Cache Controller
The invention discloses a fault-tolerant directory cache controller for the problem that a conventional directory cache is poor in fault tolerance and low in reliability, and cannot meet the requirements of a spatial environment or a complicated electromagnetic environment. The fault-tolerant directory cache controller comprises four identical directory cache bodies, a directory access bypass, a directory access crossbar switch, an access crossbar switch and a configuration register. By designing the four directory cache bodies, the configuration register, the full interconnected access crossbar switch and the directory access crossbar switch, two working modes can be flexibly configured, so that both the performance and the fault tolerance are preferred. By designing a directory access bypass module, the complete failure of a directory Cache function in a bad condition such as a space high-radiation environment is prevented, so that the reliability is enhanced. Compared with the conventional directory Cache, the fault-tolerant directory cache controller has the advantages that a multilevel fault-tolerant technology from a system structure level to a circuit design level is adopted, so that on the premise of no performance loss, the fault tolerance and reliability of the directory Cache are remarkably improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Semiconductor device and method of forming the same
ActiveCN105097711BAdjust Threshold VoltageImprove electrical performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceElectrical conductor
A semiconductor device and a method for forming the same, wherein the method for forming the semiconductor device includes: providing a substrate, the substrate including a first semiconductor layer, an insulating layer positioned on the surface of the first semiconductor layer, and a second semiconductor layer positioned on the surface of the insulating layer, The substrate has a first region, a second region and a third region, the second region is adjacent to the first region and the third region, wherein the thickness of the insulating layer in the first region and the third region is greater than that of the insulating layer in the second region The bottom surface of the insulating layer in the first region, the second region and the third region is flush; the gate structure is formed on the surface of the second semiconductor layer in the second region; the first region and the third region on both sides of the gate structure A doped region is formed in the second semiconductor layer. The thickness of the insulating layer under the gate structure of the present invention is smaller than the thickness of the insulating layer under the doped region. Since the effective resistance of the insulating layer under the gate structure is small, the threshold voltage of the semiconductor device can be effectively improved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com