Latch circuit and flip-flop circuit
A technology of latch circuit and trigger circuit, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, electric pulse generation, pulse generation, etc., can solve the problems that soft errors cannot be suppressed, can not suppress soft errors, etc., and achieve the goal of suppressing soft errors and reducing the soft error rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
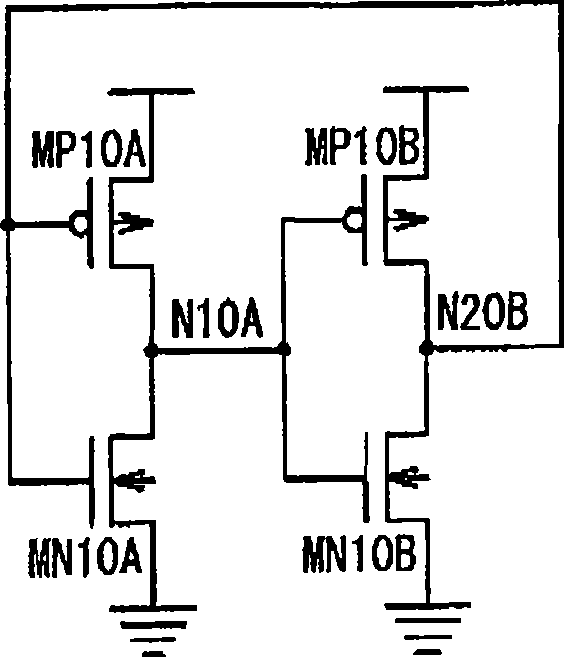
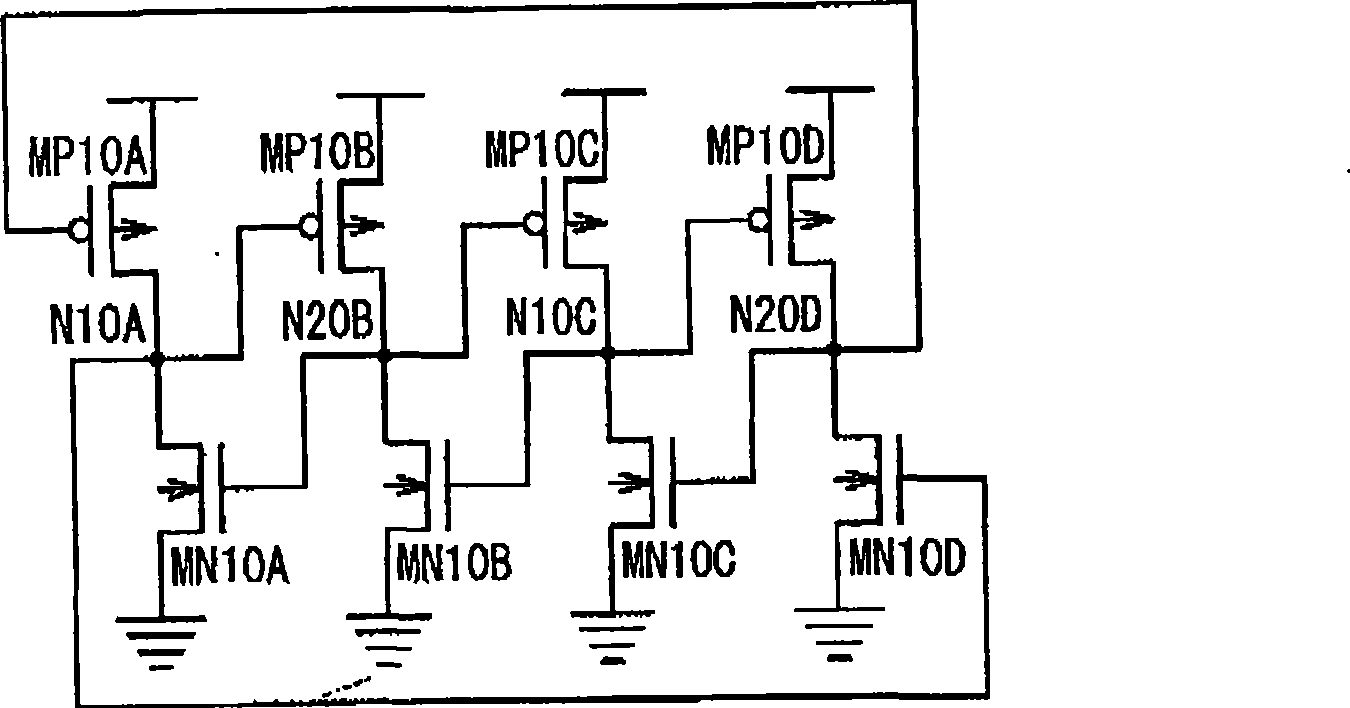
[0030] FIG. 4 is a circuit diagram showing the configuration of the latch circuit 10 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The latch circuit 10 in the first embodiment is provided with: three or more nodes N1A, N1C, N1E, and N1G as the first node in which the voltage of the first signal level is set; Three or more nodes N2B, N2D, N2F, and N2H in which the voltage of the second signal level obtained by inverting the first signal level is set. For example, when data "1" is set in nodes N1A, N1C, N1E, and N1G, data "0" obtained by inverting the data "1" is set in nodes N2B, N2D, N2F, and N2H. Here, transmission gates (not shown) are connected to nodes N1A, N1C, N1E, and N1G as first nodes, and receive data latched by the latch circuit through the nodes N1A, N1C, N1E, and N1G. In addition, transmission gates may be connected between the nodes N1A, N1C, N1E, and N1G as the first node and the nodes N2B, N2D, N2F, and N2H as the second node. Hereinafter, the p...
no. 2 example
[0069] The latch circuit 10 shown in FIG. 4 may be changed within a part of its configuration. For example, any one of the P-channel type MOS transistor MP1A to the N-channel type MOS transistor MN2H for suppressing the voltage value of the data holding node may be eliminated from the latch circuit 10 shown in FIG. 4 . FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram showing a latch circuit 10 according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In the latch circuit 10 shown in FIG. 6, the P-channel type MOS transistors MP2B, MP2D, MP2F, and MP2H and the N-channel type MOS transistor MN2B are removed from the configuration of the latch circuit 10 shown in FIG. , MN2D, MN2F, and MN2H.
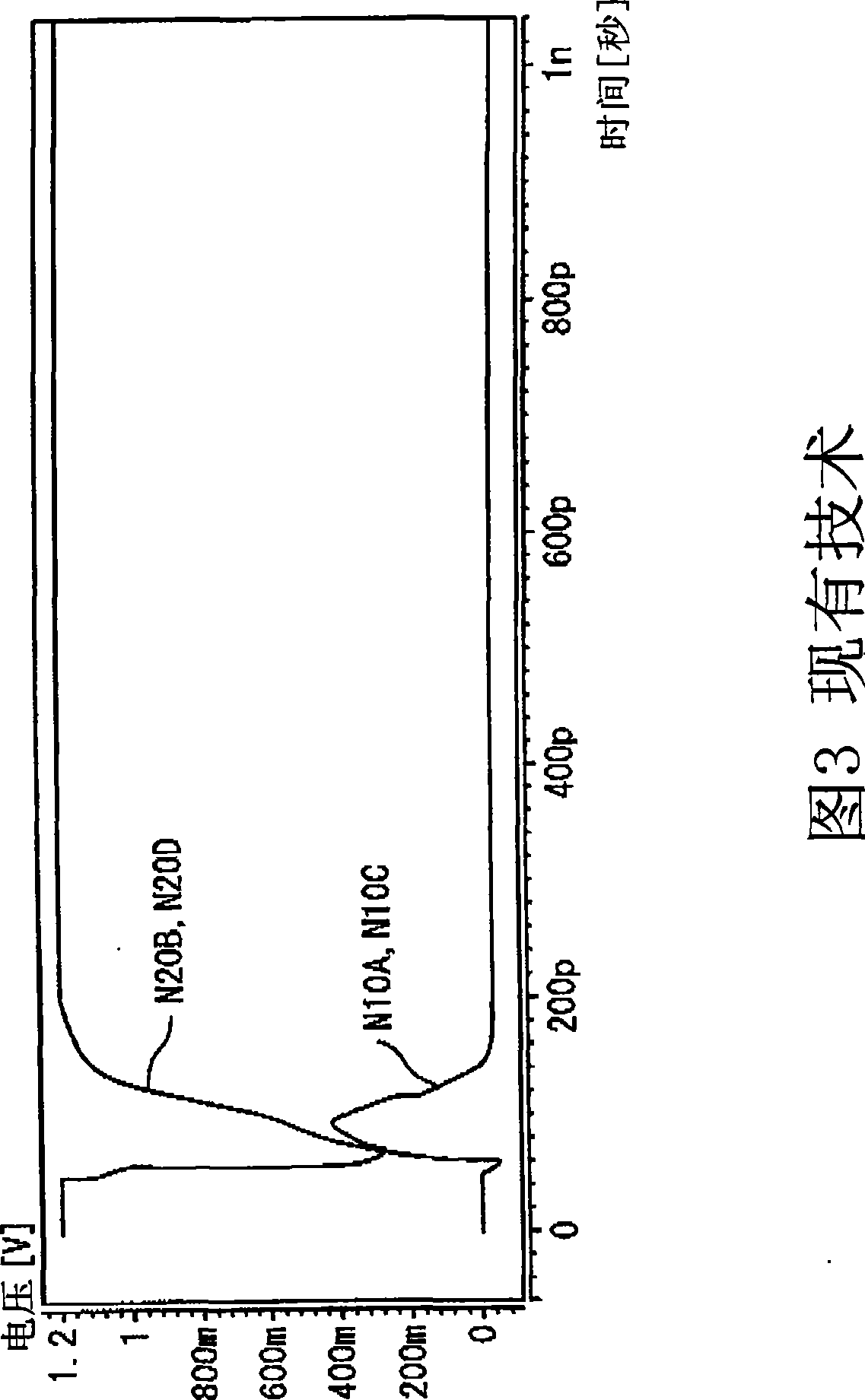
[0070] Since transistors having less influence of noise signals are removed in the latch circuit 10 shown in FIG. 6, although the latch circuit 10 has a higher soft error generation rate than the circuit shown in FIG. It also has the effect of reducing the circuit area. It is effective to use the circuit sh...
no. 3 example
[0072] Furthermore, any one of the node voltage control circuits 1A to 1H can be reduced from the flip-flop circuit 10 shown in FIG. 4 . FIG. 7 is a circuit diagram showing the configuration of a latch circuit 10 according to a third embodiment of the present invention. In the flip-flop circuit 10 shown in FIG. 7 , the node voltage control circuits 1G and 1H are removed from the latch circuit 10 shown in FIG. 4 . The gates of the P-channel type MOS transistor MP2D and the gates of the N-channel type MOS transistors MN2B and MN1F are connected to the node N1E, and the gates of the P-channel type MOS transistors MP2A and MP1E and the gates of the N-channel type MOS transistor MN2C The gate is connected to node N2C.
[0073] Since in the latch circuit 10 shown in FIG. 7, transistors causing less noise influence are removed and nodes whose voltage variations are small are removed, the generation rate of soft errors increases compared with the circuit shown in FIG. 4, but has It ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com