Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Leaching achieved" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
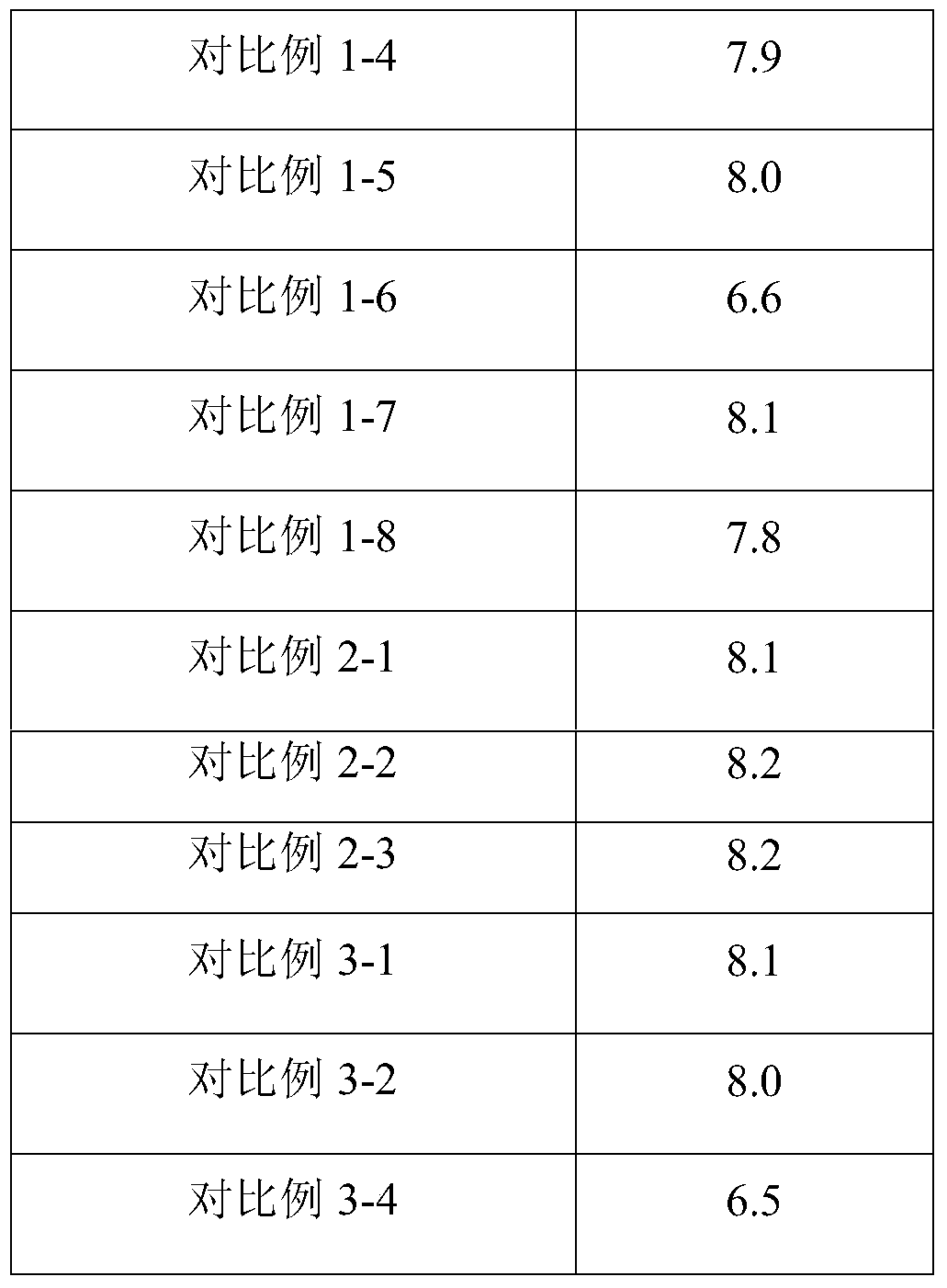
Method for recycling platinum group metal from ineffective automobile catalysts
ActiveCN106011477AHigh reactivityFully dispersedProcess efficiency improvementWater immersionBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for recycling platinum group metal from ineffective automobile catalysts. The method includes the steps of (1) mechanical activation, (2) high-temperature roasting, (3) ball-milling water immersion, (4) diluted acid leaching and (5) platinum group metal refining. Platinum group metal enriched products obtained in the step (4) are processed according to existing refining processes, so that platinum group metal products are obtained. The ineffective automobile catalysts are processed through the method of combining mechanical activation, sodium salt roasting, water immersion and acid leaching, the reaction activity of materials is improved through mechanical activation, phase transformation of catalyst carrier components occurs due to sodium salt roasting, insoluble residues are enriched with the platinum group metal after water immersion and acid leaching, and separation between carriers and the platinum group metal is achieved. Equipment needed for the method is conventional metallurgical equipment, the technological process is simple, industrial implementation is easy, and the total recovery rate of the platinum group metal is larger than 98%.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Leaching method for associated copper, molybdenum and nickel in coal mine containing scherbinaite
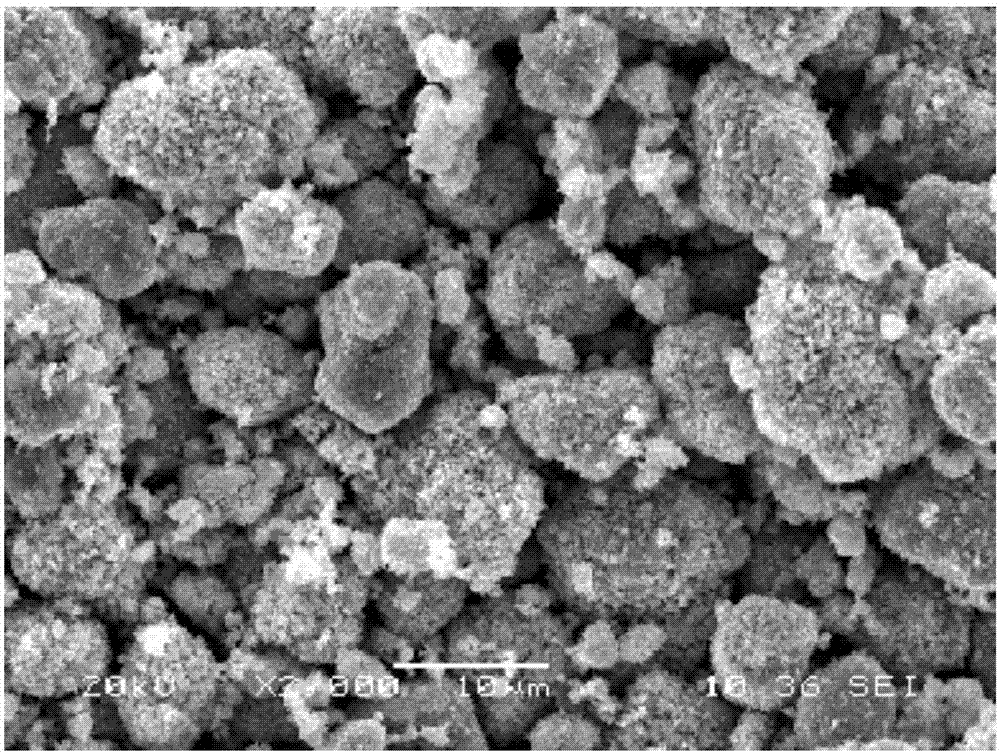
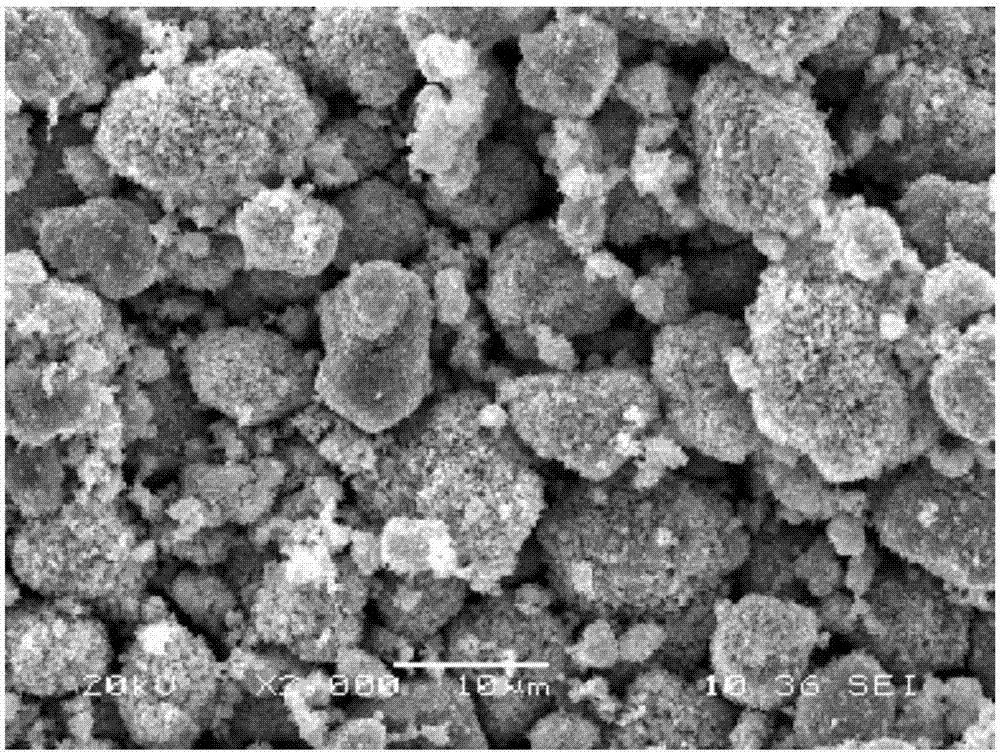
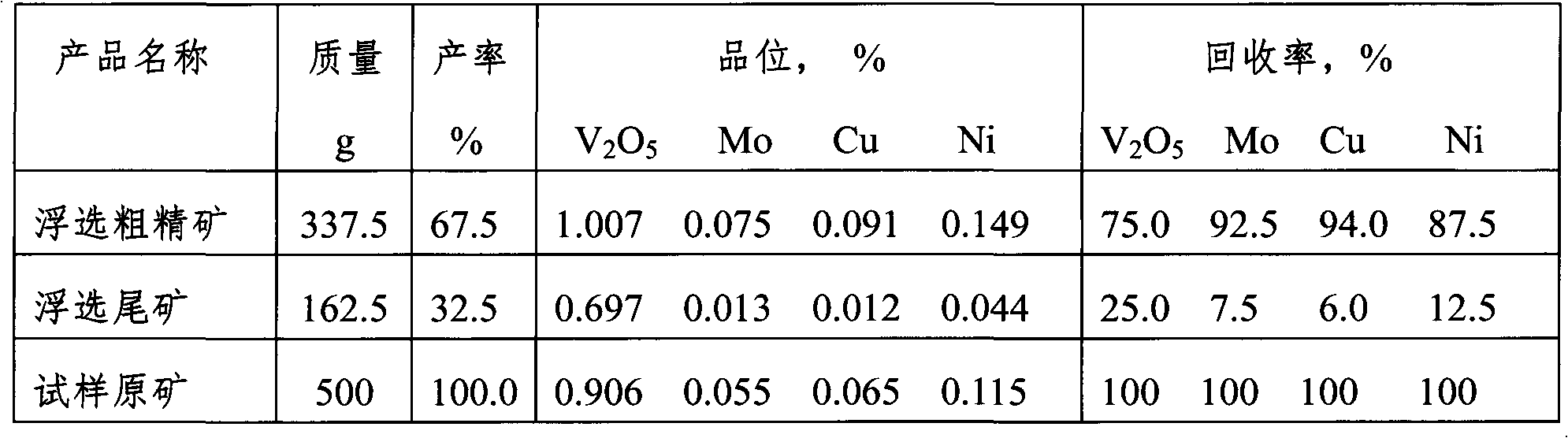
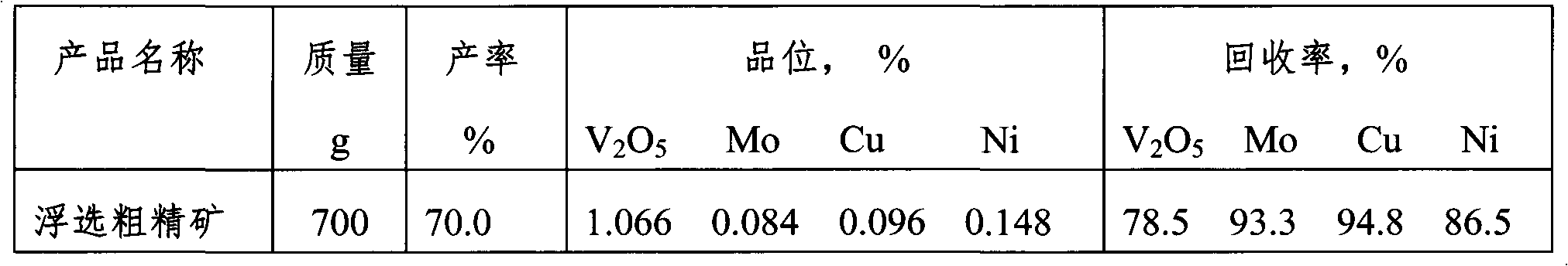
InactiveCN102634658ALeaching achievedImprove leaching rateFlotationProcess efficiency improvementSlurryCoal
The invention discloses a leaching method for associated copper, molybdenum and nickel in a coal mine containing scherbinaite. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of crushing the coal mine containing scherbinaite, grinding the coal mine to the required granularity in a wet way, adjusting the mine slurry concentration, then putting the mine slurry into a floatation tank, adding industrial sodium sulfide and ammonium aerofloat butyl into the floatation tank to be stirred, carrying out the floatation to obtain rough floatation concentrate, adding industrial sulphuric acid and sodium chlorate into the rough floatation concentrate, leaching the rough floatation concentrate added with the industrial sulphuric acid and the sodium chlorate at the temperature of 80 DEG C to 95 DEG C for 18-24 hours, carrying out the solid and liquid separation and the washing on the mine slurry after the leaching to obtain a leaching agent containing the copper, the molybdenum and the nickel. The leaching method disclosed by the invention has the following beneficial effects that: (1) the gross of the materials in the leaching process is reduced by utilizing the floatation method to enrich the copper, the molybdenum and the nickel in the coal mine containing scherbinaite; (2) in the wet acid leaching process, the leaching of the copper, the molybdenum and the nickel can be realized at the same time, and the high leaching rates of the copper, the molybdenum and the nickel can be ensured by adding a small amount of oxidant; and the leaching rates of the coal mine containing scherbinaite can respectively reach 60%-70%, 75%-85% and 75%-85%; and (3) the leaching method can favorably realize the comprehensive recycle and utilization of the copper, the molybdenum and the nickel in the coal mine containing scherbinaite.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method for extracting metal copper using microbe and its use
InactiveCN1858276AHigh recovery rateAddressing effective recyclingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementEconomic benefitsCopper
The present invention discloses microbe extracting method of metal copper and its application. The method includes crushing copper connecting material into powder; soaking the powder in culture liquid containing microbe to leach out for 15-60 days; solid-liquid separating to obtain leach solution and extracting with copper extractant; reverse extracting copper from the copper extracting liquid with reverse extractant; and final electrolyzing the copper containing reverse extracting liquid to obtain metal copper. The said method may be used in extracting metal copper from printed circuit board. The method has high economic benefit and environment benefit.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Technology for extracting vanadium from scherbinaite-containing coal mine by slurry electrolysis method
ActiveCN104017988AImprove resource utilizationImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementResource utilizationHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a technology for extracting vanadium from scherbinaite-containing coal mine by a slurry electrolysis method, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy of vanadium. The technology comprises the following steps: adding water-soluble chlorine salt into slurry in an electrolytic cell by taking alkaline scherbinaite-containing coal slurry as a raw material according to the mole ratio of Cl<-1> to V<3+>= (2-3) to 1, stirring and electrolyzing under the condition of introducing oxygen-containing gas; and controlling the cell voltage to be 4.5-6V and the current density to be 10-40A / dm<2> in electrolysis. In electrolysis by introducing the gas, chlorine generated in an anode region acts as an oxidizing agent for leaching vanadium; air is ceaselessly introduced into a cathode region; oxygen in air in the cathode region reacts to generate OH<-1> ions so as to provide an alkaline environment for leaching vanadium; meanwhile, the explosion generated by the hydrogen evolution reaction in the cathode region and chlorine generated in the anode region can be prevented. According to the technology disclosed by the invention, the leaching rate of vanadium is greater than or equal to 90%, and the electrolytic current efficiency is greater than or equal to 95%. The technology provided by the invention has the advantages of short flow, high efficiency, low cost, high resource utilization ratio, environmental friendliness, safety and the like, and is convenient for industrial application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for aluminum electrolysis cell waste cathode stripping treatment and fluoride recovery
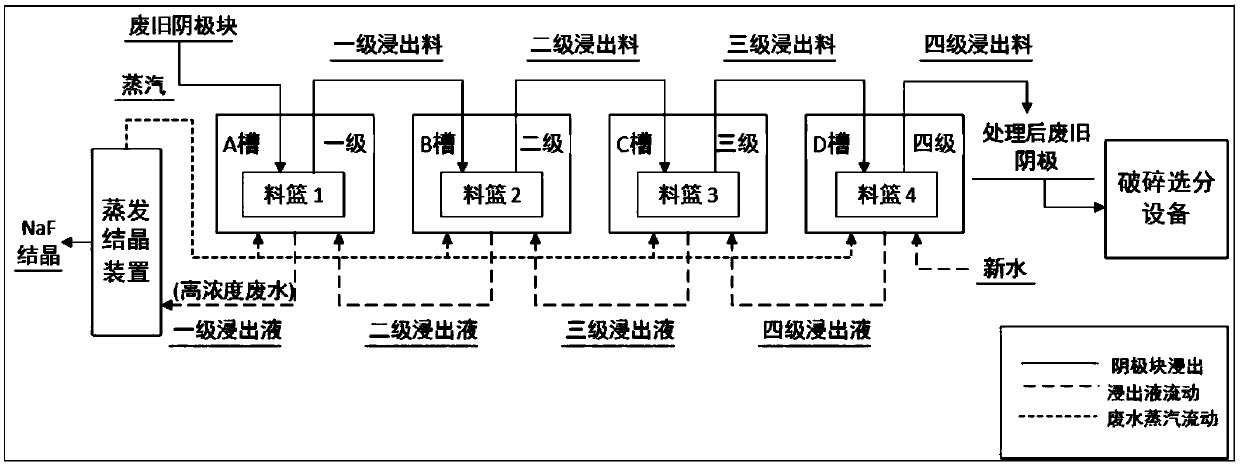
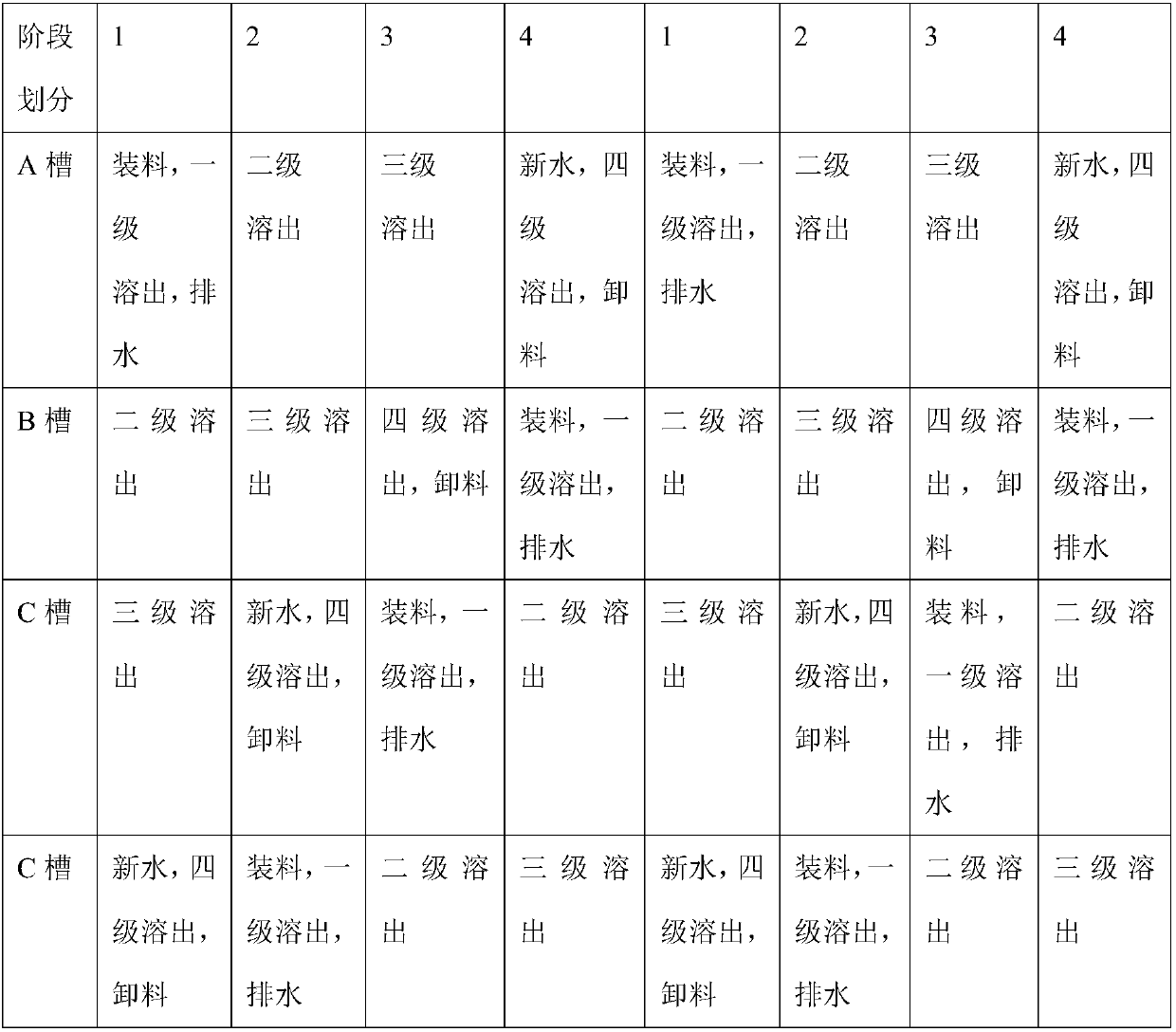
InactiveCN107892312ALeaching achievedEfficient separationWaste processingSolid waste disposalHigh concentrationElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for aluminum electrolysis cell waste cathode stripping treatment and fluoride recovery. The method comprises the steps that treatment is performed by adopting a large-particle waste cathode and multi-basin countercurrent leaching way for 10-14 hours; heating is performed by utilizing evaporated crystallized steam, leaching water is stirred, heat is recovered, andcondensation is performed; high-concentration fluorine-containing waste with the fluorine concentration of 16000-18000 ppm is obtained after dissolution, villiaumite is obtained through crystallization and evaporation, the evaporated water steam is used for heating, and water for leaching is stirred. The leaching efficiency of a system is remarkably improved, the water consumption and energy consumption are obviously reduced, and the problem of fluorine-containing and salt-containing wastewater discharge of the system can be thoroughly solved.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
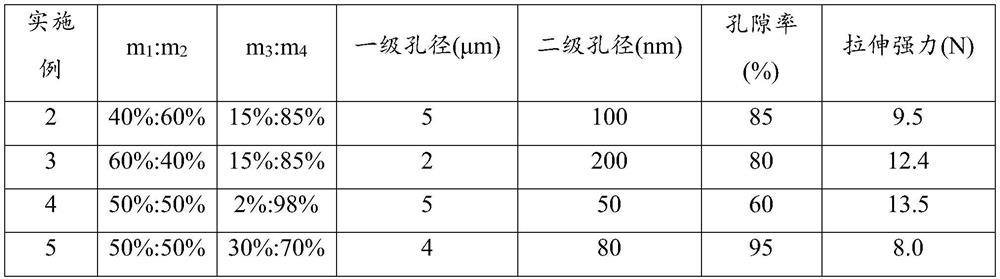
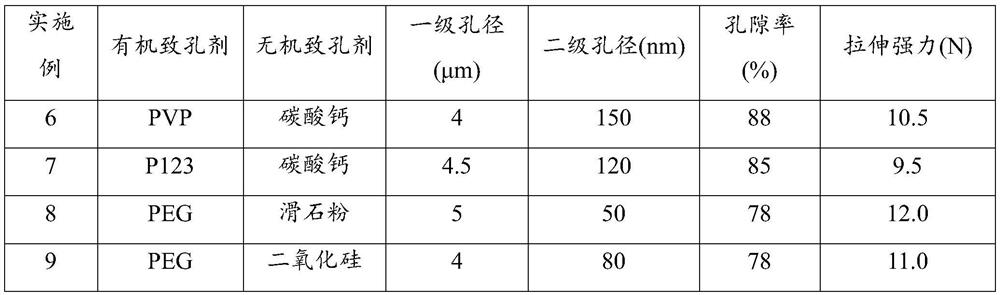
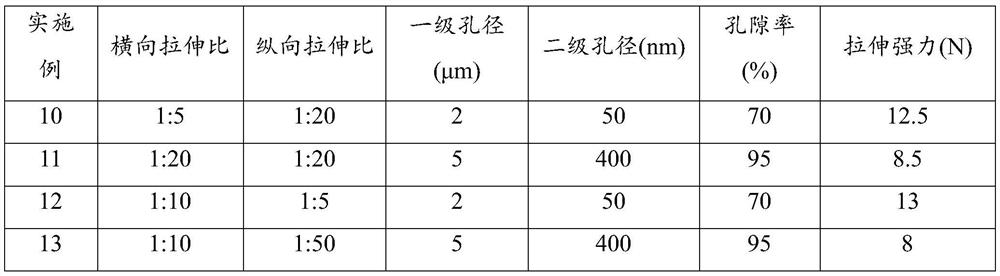
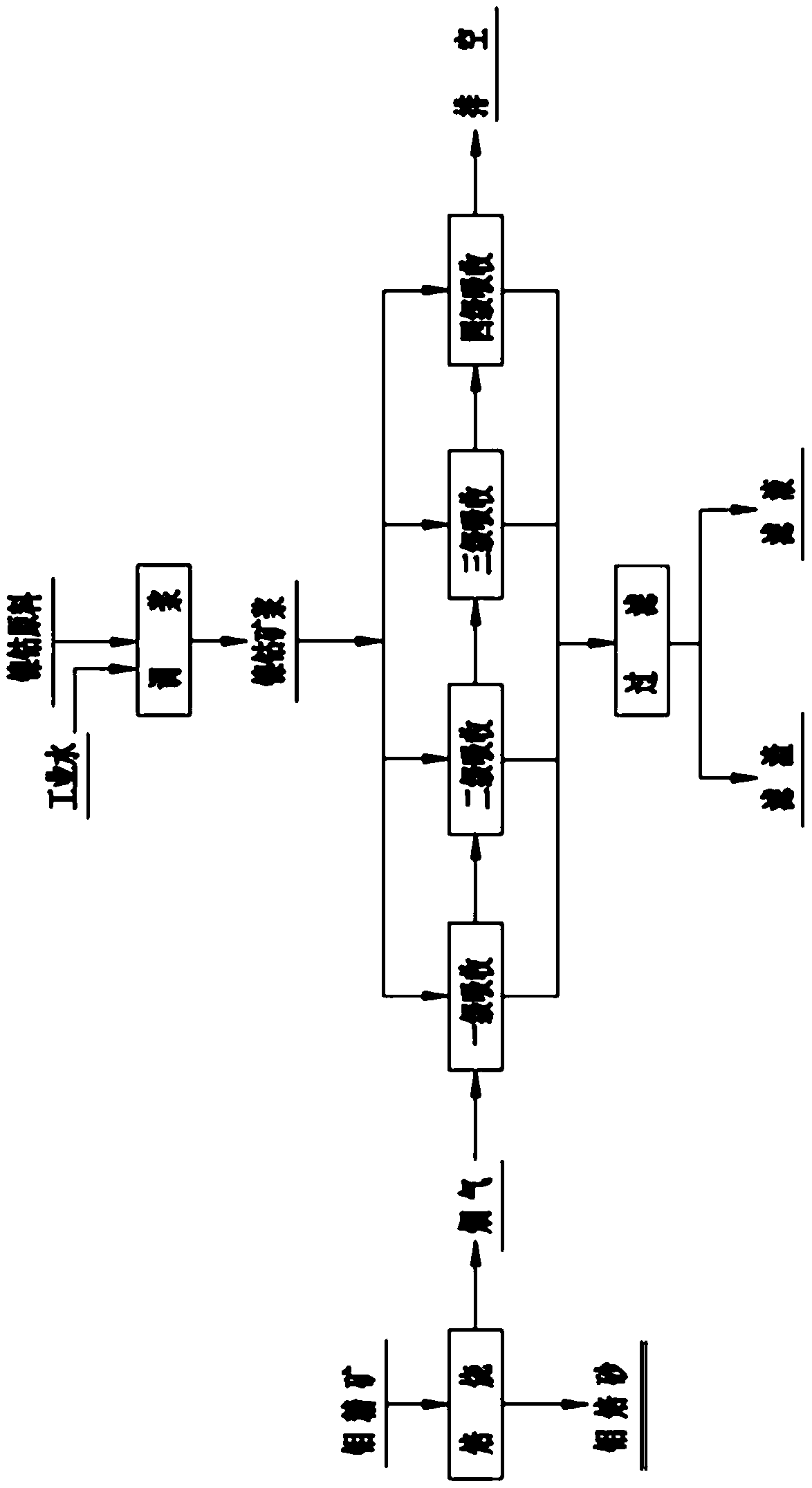
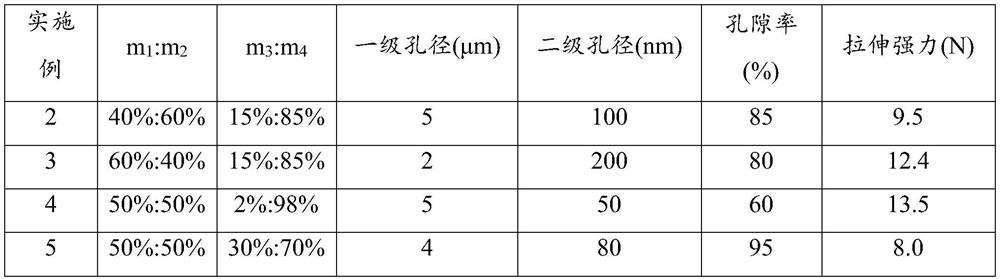
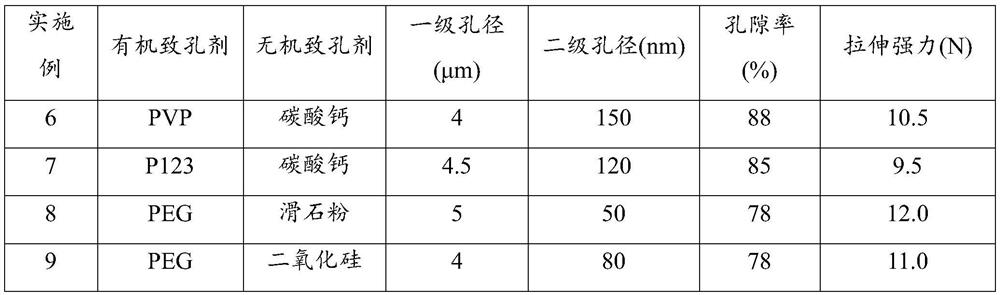
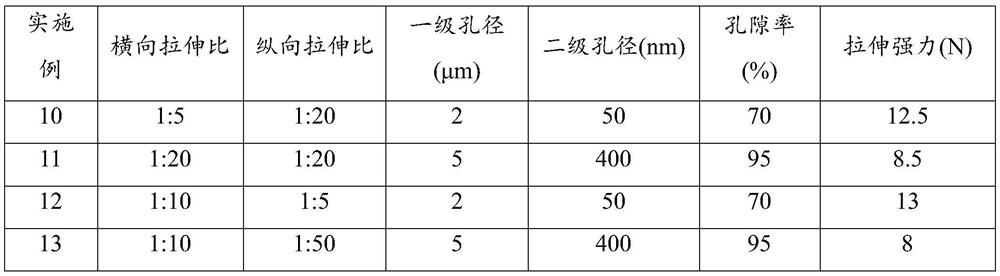
Porous polyolefin film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112812340AImprove performance uniformityImprove dispersion uniformityCell component detailsMicro nanoPolyolefin
The invention provides a hierarchical pore structure polyolefin film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, uniformly mixing a water-soluble organic pore-foaming agent and an inorganic pore-foaming agent to prepare a multi-stage composite pore-foaming material; melting, blending and extruding polyolefin, and molding the material to obtain a composite polyolefin sheet; and carrying out water bath dipping and two-way stretching treatment, and removing the pore-foaming agent in the stretching process to obtain the porous polyolefin film. Herein, a polyolefin material is used as a base material, and a polyolefin film material with a micro-nano hierarchical pore structure on the surface is obtained through a multi-phase pore-forming process. By means of water bath dipping bidirectional stretching treatment, the bidirectional stretching treatment is performed in the dipping extraction process in water, such that the leaching of the water-soluble organic pore-foaming agent and the inorganic pore-foaming agent is easily achieved, the multi-phase pore forming is achieved, and the hierarchical pore structure polyolefin film material is obtained. The preparation method has the characteristics of simple preparation process, high adjustability of the porous structure and suitability for industrialization, and can be widely applied to the fields of medical protection and energy battery diaphragms.
Owner:湖北拓盈新材料有限公司 +1
Coal dearsenification method and additive thereof
ActiveCN107118820APromote leachingLow toxicityGas treatmentDispersed particle separationSulfateCoal slurry
The invention discloses a coal dearsenification method and an additive thereof, and belongs to the technical field of coal and smoke gas purification. The additive is a composite additive prepared from at least one of aluminum chloride, ferric chloride, sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, ferric sulfate and aluminum sulfate or prepared according to a certain proportion. The additive is added into coal slurry, and is used for washing smoke gas containing sulfur dioxide; inorganic arsenium in the coal is leached out by the sulfur dioxide; meanwhile, the smoke gas desulfurization is realized. The used additive can promote the leaching of the inorganic arsenium in the coal and / or can accelerate the oxidization of trivalent arsenic in the leaching liquid into pentavalent arsenic, so that the toxicity of the arsenium is reduced; the subsequent treatment of the leached arsenium is facilitated.
Owner:青岛赛诺威尔工业水处理有限公司
Step leaching method for multi-element waste containing lithium
The invention discloses a step leaching method for multi-element waste containing lithium. The method is different from the traditional recovering route that one-time leaching and multi-process separation are conducted. According to the step leaching method for the multi-element waste containing the lithium, aiming at the characteristics that the multi-element waste containing the lithium is single and relatively intact in crystal structure, and the valence states and activity differences of all constituent elements are large, acid of different characteristics and different characteristics is adopted to sequentially leach the lithium element, the nickel and / or cobalt and the manganese element in a directional mode, and the specific elements are dissolved to cause lattice imperfection, so that the microcrystalline structure of a raw material is transitioned from a stable state to a meta-stable state, even an instable state, and leaching and separating of the subsequent elements is promoted accordingly. The leaching method for the multi-element waste containing the lithium is easy to operate, mild in condition and low in cost, sufficient recovering of the multiple constituent elements in the waste can be achieved, and industrialization is easy to achieve.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Technique for leaching molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ores by pulp electrolysis
ActiveCN104032127AImprove leaching rateLow priceElectrolysis componentsProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisResource utilization
The invention relates to a technique for leaching molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ores by a wet process, belonging to the technical field of wet-process smelting of molybdenum. The technique comprises the following steps: by using nickel-molybdenum ore pulp as the raw material, adding water-soluble chlorine salt into the pulp in a Cl<->:Mo mole ratio of (2-3):1, stirring, and carrying out electrolysis under the condition of introducing oxygen-containing gas, wherein the bath voltage in the electrolysis process is 5-7.5V, the current density is 20-50 A / dm<2>, and the electrolysis temperature is 40-60 DEG C. By using the pulp electrolysis technique to leach the molybdenum, the molybdenum leaching rate is greater than or equal to 95%, and the electrolysis current efficiency is greater than or equal to 90%; and the technique can effectively and comprehensively recover molybdenum in the nickel-molybdenum ores and enhance the molybdenum resource utilization ratio. The technique has the advantages of low reaction temperature, high reaction speed, low energy consumption, high economy, environmental protection, high safety and high molybdenum leaching rate, and is convenient for implementing industrial application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
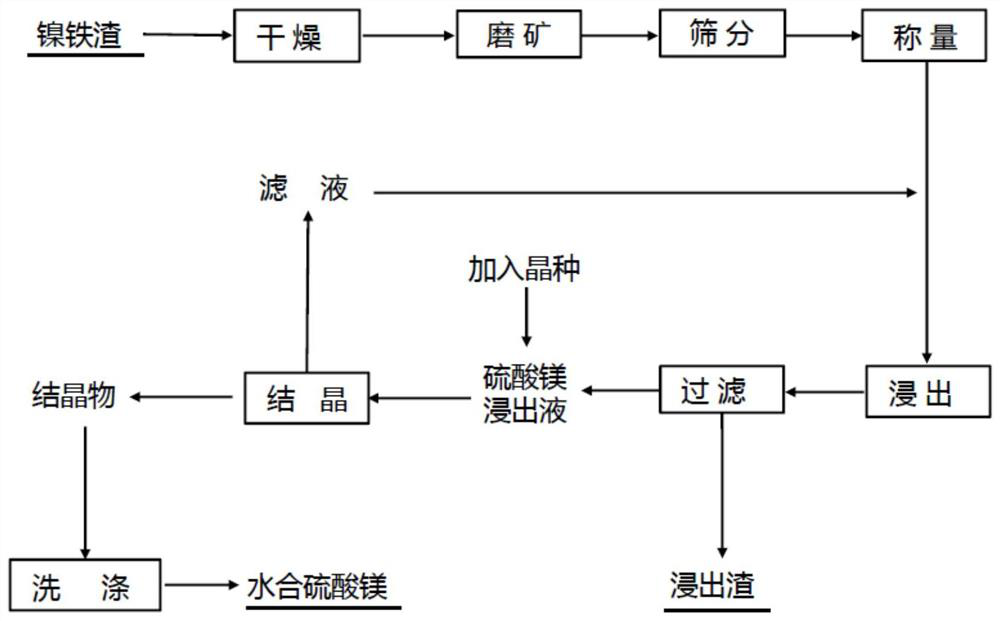
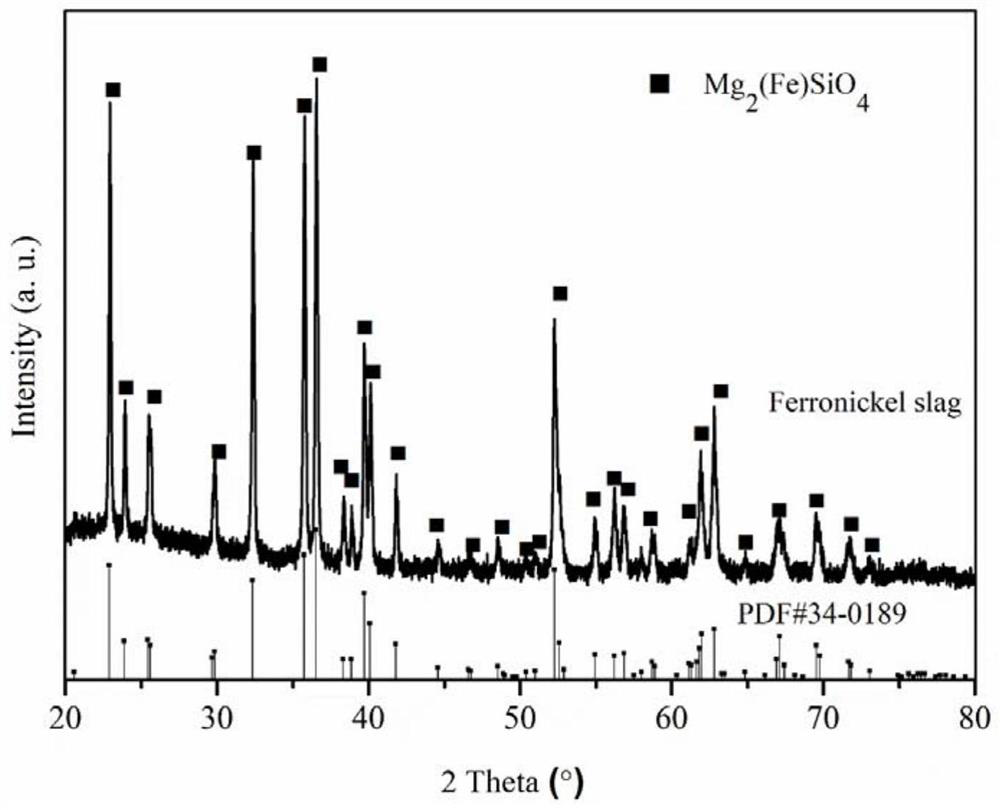
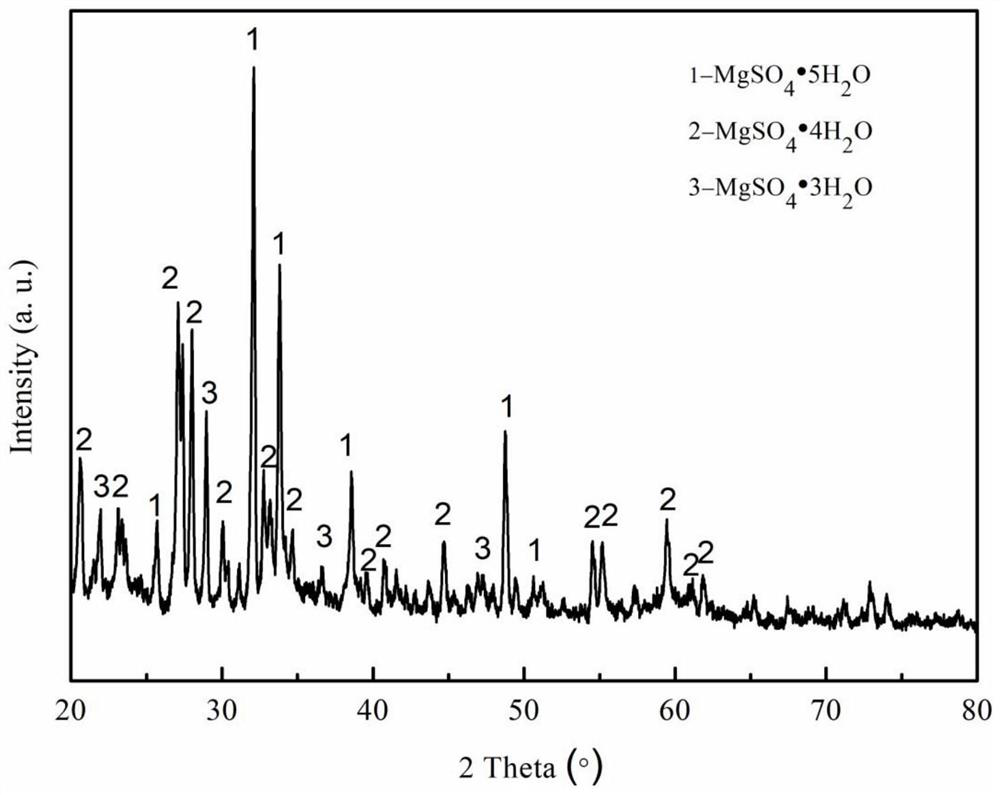
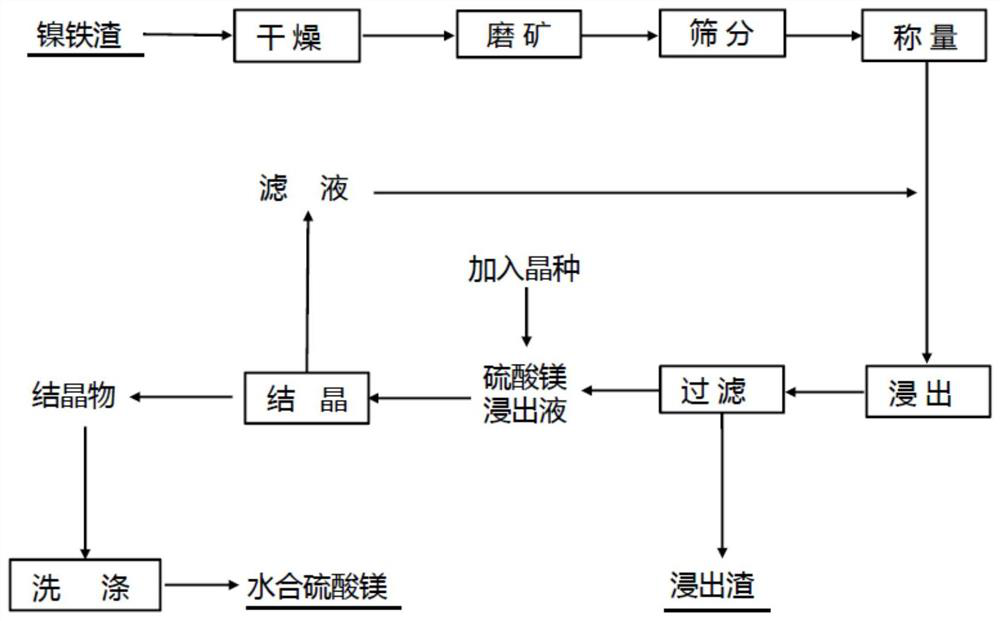
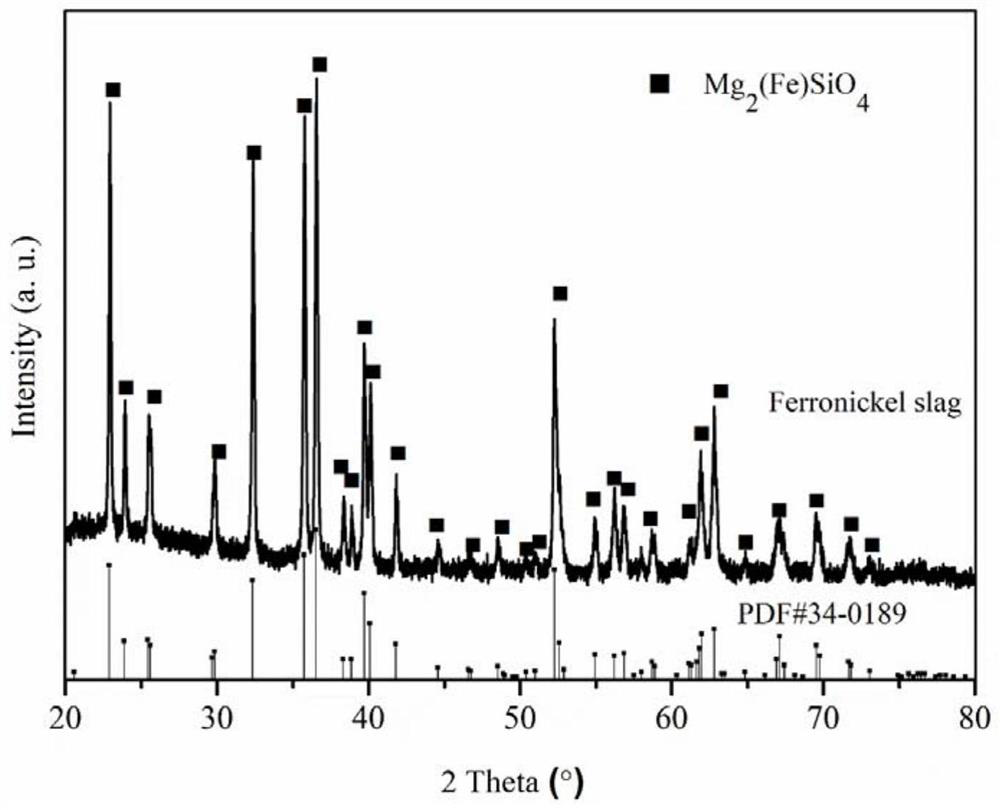
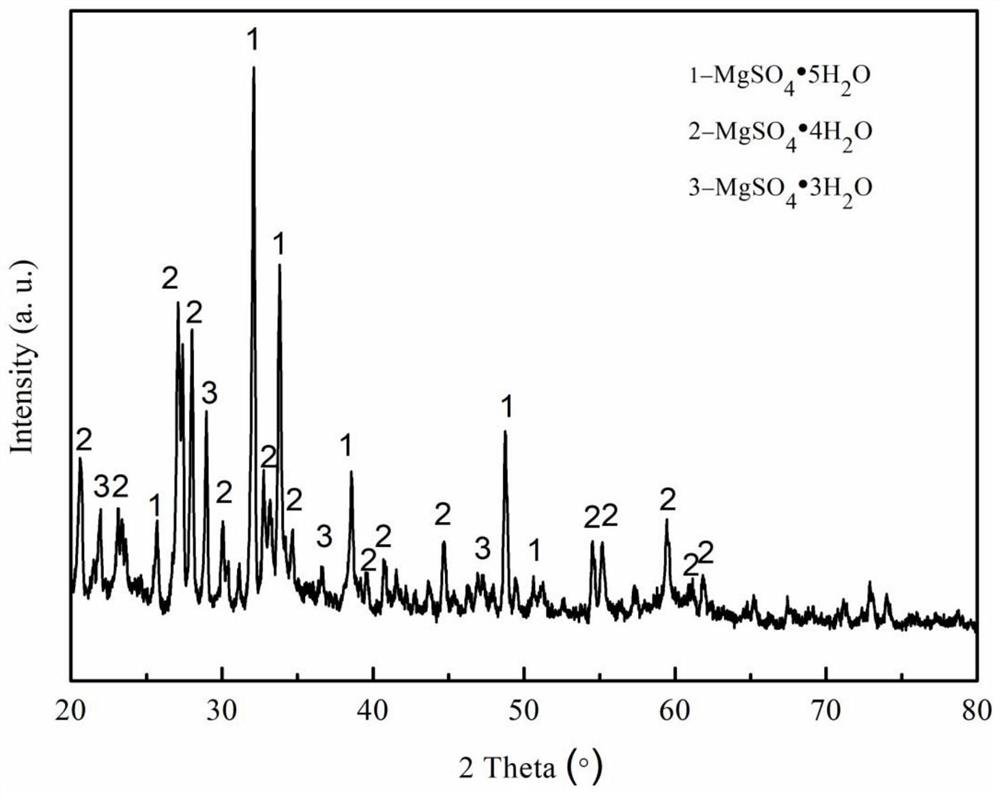
Method for recovering magnesium from ferronickel slag
ActiveCN111926193ASimple processEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsChemical industrySeed crystal
The invention relates to the field of chemical industry, in particular to a method for recovering magnesium from ferronickel slag. The method comprises the following steps of impregnating the ferronickel slag in concentrated sulfuric acid at normal pressure, adding a seed crystal, and crystallizing to precipitate magnesium sulfate. The magnesium in the ferronickel slag is converted into magnesiumsulfate for magnesium recovery through a full-wet process, the process is simple, operation is easy, the requirement for equipment is low, the magnesium recovery rate is high, the application range ofmagnesium sulfate is wide, the added value of products is high, and the comprehensive utilization rate of the ferronickel slag can be increased.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for leaching nickel-cobalt raw material by roasting SO2-containing tail gas by using molybdenum concentrate
The invention discloses a method for leaching a nickel-cobalt raw material by roasting SO2-containing tail gas by using molybdenum concentrate. The method comprises the following steps that water is added into the nickel-cobalt raw material to be mixed, stirred and sizing mixing is carried out for later use, the SO2 tail gas generated by the roasting is guided into an absorption tank, and the SO2emission standard is reached after the SO2 tail gas is continuously absorbed for 3-4 stages; and in the absorption process, the nickel-cobalt is combined with S to form sulfate while the nickel-cobaltis leached, a nickel-cobalt leachate enters a subsequent impurity removal process. According to the method, the SO2 tail gas with low concentration can be discharged after being purified and absorbed, meanwhile, the leaching of the nickel-cobalt raw material is realized, and finally, the nickel-cobalt containing of final leached slag is lower than 0.5%.
Owner:成都虹波钼业有限责任公司
Combined leaching process of cobalt-sulfur concentrate and cobalt hydroxide ore
ActiveCN113789441AHigh recovery rateAchieve removalProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a combined leaching process of cobalt-sulfur concentrate and cobalt hydroxide ore. The process comprises the following steps that after the cobalt-sulfur concentrate and the cobalt hydroxide ore are pulped to obtain pulped liquid; reaction is carried out on on the pulped liquid under the pressure of 0.6 MPa to 1.25 MPa and the temperature of 150 DEG C to 180 DEG C, and solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain a solid phase and a liquid phase; and the liquid phase is the leachate. According to the process, the cobalt-sulfur concentrate and the cobalt hydroxide ore are subjected to high-pressure combined leaching, high-valence cobalt is reduced into low-valence cobalt by the cobalt-sulfur concentrate, and in the high-pressure oxidation leaching process, sulfur ions are oxidized into sulfate radicals, and ferrous ions are oxidized into iron ions; meanwhile, in the environment, the iron ions are hydrolyzed to finally form ferric oxide (Fe<2>O<3>) and hydrogen ions, cobalt hydroxide is leached out by utilizing the generated hydrogen ions, and meanwhile cobalt, copper and nickel in the cobalt-sulfur concentrate are leached into the solution; and the process for utilizing the cobalt-sulfur concentrate is simplified, and the leaching efficiency is improved.
Owner:湖南德景源科技有限公司
A process for leaching molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ore by slurry electrolysis
ActiveCN104032127BLeaching achievedImprove solubilityElectrolysis componentsProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a technique for leaching molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ores by a wet process, belonging to the technical field of wet-process smelting of molybdenum. The technique comprises the following steps: by using nickel-molybdenum ore pulp as the raw material, adding water-soluble chlorine salt into the pulp in a Cl<->:Mo mole ratio of (2-3):1, stirring, and carrying out electrolysis under the condition of introducing oxygen-containing gas, wherein the bath voltage in the electrolysis process is 5-7.5V, the current density is 20-50 A / dm<2>, and the electrolysis temperature is 40-60 DEG C. By using the pulp electrolysis technique to leach the molybdenum, the molybdenum leaching rate is greater than or equal to 95%, and the electrolysis current efficiency is greater than or equal to 90%; and the technique can effectively and comprehensively recover molybdenum in the nickel-molybdenum ores and enhance the molybdenum resource utilization ratio. The technique has the advantages of low reaction temperature, high reaction speed, low energy consumption, high economy, environmental protection, high safety and high molybdenum leaching rate, and is convenient for implementing industrial application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for intensifying coal arsenic leaching by using organic additive
ActiveCN113832347AImprove leaching rateLow toxicityProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATESulfate radicals
The invention belongs to the technical field of coal and flue gas purification, and relates to a method for intensifying coal arsenic leaching by using an organic additive, which is characterized by comprising the following specific steps: adding water into pulverized coal with the particle size of 200-450 microns to prepare coal slurry, adding a carboxyl-containing additive into the coal slurry, and then carrying out contact mass transfer reaction with flue gas containing sulfur dioxide, leaching soluble arsenic in the coal into a solution, and oxidizing the sulfur dioxide in the flue gas into sulfate radicals; the pH value of the coal slurry is 1.4-2.8, and the temperature is 35-75 DEG C; and the additive is at least one of oxalic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid and ferric citrate. The inventor finds for the first time that the carboxyl-containing organic additive can promote leaching of coal arsenic, increase the arsenic leaching rate and increase the removal rate of sulfur dioxide; and the method is scientific, simple to operate, high in arsenic removal effect and wide in market application prospect.
Owner:青岛赛诺威尔工业水处理有限公司
Porous polyolefin film and its preparation method
ActiveCN112812340BImprove performance uniformityImprove dispersion uniformityCell component detailsMicro nanoPolymer science
The invention provides a polyolefin film with a multi-level porous structure and a preparation method thereof. First, the water-soluble organic porogen and the inorganic porogen are mixed uniformly to prepare a multi-level composite porogen material; then the polyolefin is melt-blended and extruded to form a composite polyolefin sheet; the biaxial stretching treatment is carried out in a water bath, and the The porogen is removed during stretching to obtain the porous polyolefin film. The invention uses the polyolefin material as the base material, and obtains the polyolefin membrane material with the micro-nano hierarchical pore structure on the surface through a multi-phase pore-inducing process. Water-bath immersion biaxial stretching treatment, in the process of water immersion extraction, biaxial stretching treatment is more conducive to the leaching of water-soluble organic porogens and inorganic porogens, realizing multi-phase pore formation and obtaining hierarchical pores Structural polyolefin membrane material. The preparation process is simple, the porous structure is highly adjustable, and it is suitable for industrialization, and can be widely used in the fields of medical protection and energy battery separators.
Owner:湖北拓盈新材料有限公司 +1
Method for acid-free leaching of cobalt intermediate product from sulfate
ActiveCN113151677AEfficient leachingEliminate environmental pollutionProcess efficiency improvementAmmoniacal nitrogenPregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a method for acid-free leaching of a cobalt intermediate product from sulfate, and aims to solve the technical problems that inorganic acid and a reducing agent need to be added in the leaching process of the cobalt intermediate product, gas pollution is easy to generate, acid leaching liquid needs to be neutralized subsequently to adjust the pH value, the acid and alkali consumption is large, pollutants of ammonia nitrogen or sodium are generated, meanwhile, filtration is difficult, operation efficiency is low, production cost is high, and auxiliary material consumption in the iron removal process of the cobalt leaching solution containing ferrous sulfate is large. According to the method, a solution containing ferrous sulfate is used for leaching the cobalt intermediate product, then solid-liquid separation is carried out, valuable elements such as cobalt and copper are left in filtrate, and impurity elements such as iron and silicon are left in filter residues. According to the method, the cobalt intermediate product can be leached without using inorganic acid such as sulfuric acid and a reducing agent, so that the situation that sulfur dioxide pollutes the environment is thoroughly eliminated, and meanwhile, the cobalt leaching liquid containing ferrous sulfate is used for leaching, so that consumption of alkali is avoided, leaching of the cobalt intermediate product is achieved, and two purposes are achieved.
Owner:赣州逸豪优美科实业有限公司
A method for removing arsenic from coal
ActiveCN107118820BPromote leachingLow toxicityGas treatmentDispersed particle separationIron sulfateAluminium chloride
The invention discloses a coal dearsenification method and an additive thereof, and belongs to the technical field of coal and smoke gas purification. The additive is a composite additive prepared from at least one of aluminum chloride, ferric chloride, sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, ferric sulfate and aluminum sulfate or prepared according to a certain proportion. The additive is added into coal slurry, and is used for washing smoke gas containing sulfur dioxide; inorganic arsenium in the coal is leached out by the sulfur dioxide; meanwhile, the smoke gas desulfurization is realized. The used additive can promote the leaching of the inorganic arsenium in the coal and / or can accelerate the oxidization of trivalent arsenic in the leaching liquid into pentavalent arsenic, so that the toxicity of the arsenium is reduced; the subsequent treatment of the leached arsenium is facilitated.
Owner:青岛赛诺威尔工业水处理有限公司
A kind of method of recovering magnesium from nickel iron slag
ActiveCN111926193BIncrease profitHigh recovery ratePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsChemical industrySlag
The invention relates to the field of chemical industry, in particular to a method for recovering magnesium from ferronickel slag, which comprises the steps of immersing the ferronickel slag in concentrated sulfuric acid at atmospheric pressure, adding crystal seeds, and crystallizing out magnesium sulfate. The magnesium in the ferronickel slag is converted into magnesium sulfate for recovery of magnesium by adopting the all-wet process. The process is simple, easy to operate, requires low equipment, and has a high recovery rate of magnesium. Magnesium sulfate has a wide range of applications and high added value. It can improve the comprehensive utilization rate of nickel-iron slag.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
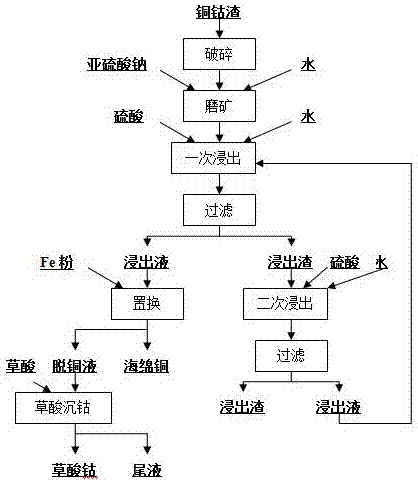
A kind of hydrometallurgical recovery copper and cobalt method of copper cobalt slag
ActiveCN106222430BLeaching achievedImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementOxalatePregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a hydrometallurgy method for recovering copper and cobalt from copper and cobalt slag. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, reducing ground ores by adopting a reducing agent; secondly, performing acid leaching until leachate containing copper and cobalt is obtained; and thirdly, displacing with iron powder to obtain sponge copper, and precipitating with oxalic acid to obtain cobalt oxalate. According to the method provided by the invention, leaching rates of the copper and the cobalt in the copper and cobalt slag are higher; the copper and the cobalt are better separated from other impurities; the required cost of equipment is low; and the method is small in environmental pollution and simple in process.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
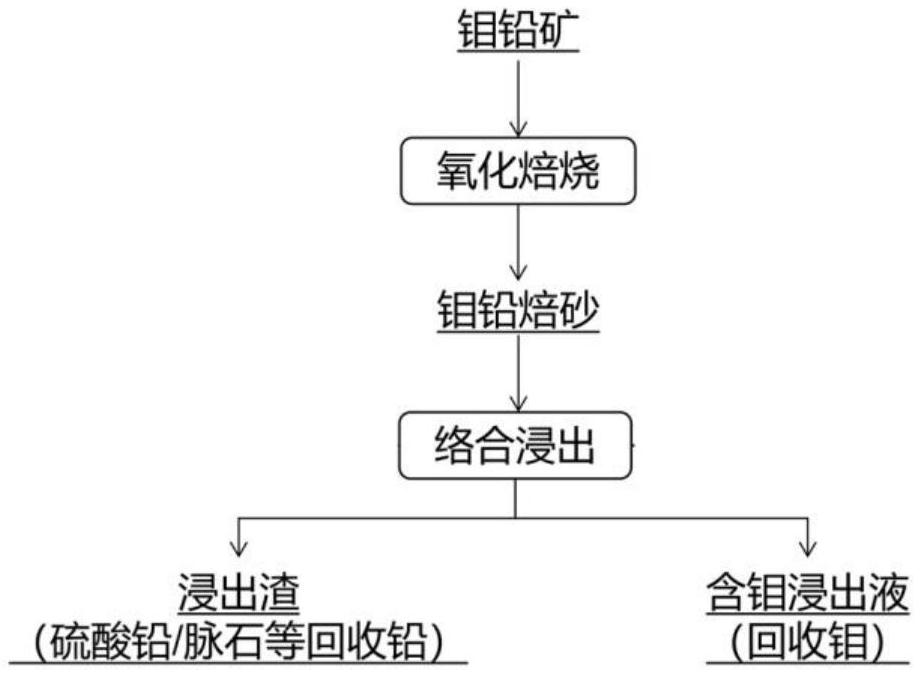
Method for recovering molybdenum and lead from wulfenite
The invention relates to a method for recovering molybdenum and lead from molybdenum lead ore, belongs to the technical field of metal smelting, and solves the problems that in the prior art, strong base is adopted for leaching the molybdenum lead ore, the lead content in an obtained molybdenum product exceeds the standard, and thorough separation of the molybdenum and the lead cannot be achieved; sodium sulfide is used for leaching, temperature is high, and energy consumption is large; the use amount of sodium sulfide is difficult to control in the sodium sulfide leaching process; and hydrogen sulfide gas is generated by acidification in the process of recovering molybdenum after precipitating lead after leaching by a sodium sulfide method. The method for recovering the molybdenum and the lead from the wulfenite, provided by the invention, comprises the following steps: roasting the wulfenite to obtain roasted lead molybdate; adding a leaching agent and an auxiliary leaching agent to digest and leach the roasted lead molybdate, separating to obtain a leaching solution containing molybdenum and leaching residues enriched with lead sulfate, and directly using the leaching residues for further purification of lead; and extracting molybdenum from the leachate by using an extracting agent to obtain raffinate and molybdenum-containing extract liquor. And clean extraction of the wulfenite is realized.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
A kind of cascade leaching method of lithium-containing multi-element waste
ActiveCN106947868BLeaching achievedPromote leachingProcess efficiency improvementStable stateLithium
The invention discloses a step leaching method for multi-element waste containing lithium. The method is different from the traditional recovering route that one-time leaching and multi-process separation are conducted. According to the step leaching method for the multi-element waste containing the lithium, aiming at the characteristics that the multi-element waste containing the lithium is single and relatively intact in crystal structure, and the valence states and activity differences of all constituent elements are large, acid of different characteristics and different characteristics is adopted to sequentially leach the lithium element, the nickel and / or cobalt and the manganese element in a directional mode, and the specific elements are dissolved to cause lattice imperfection, so that the microcrystalline structure of a raw material is transitioned from a stable state to a meta-stable state, even an instable state, and leaching and separating of the subsequent elements is promoted accordingly. The leaching method for the multi-element waste containing the lithium is easy to operate, mild in condition and low in cost, sufficient recovering of the multiple constituent elements in the waste can be achieved, and industrialization is easy to achieve.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
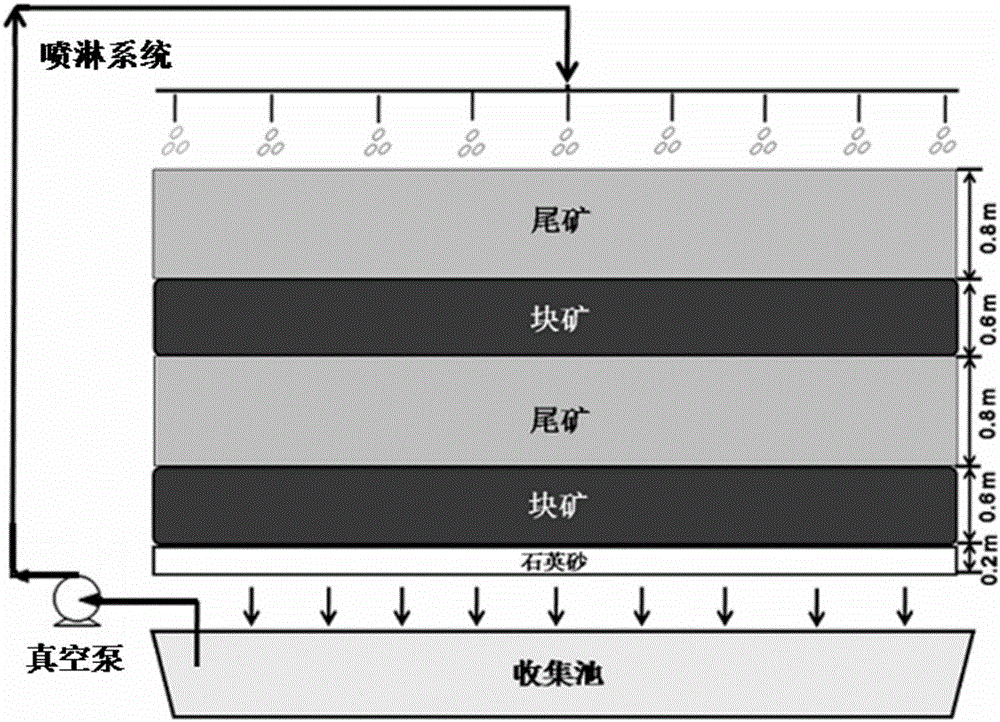
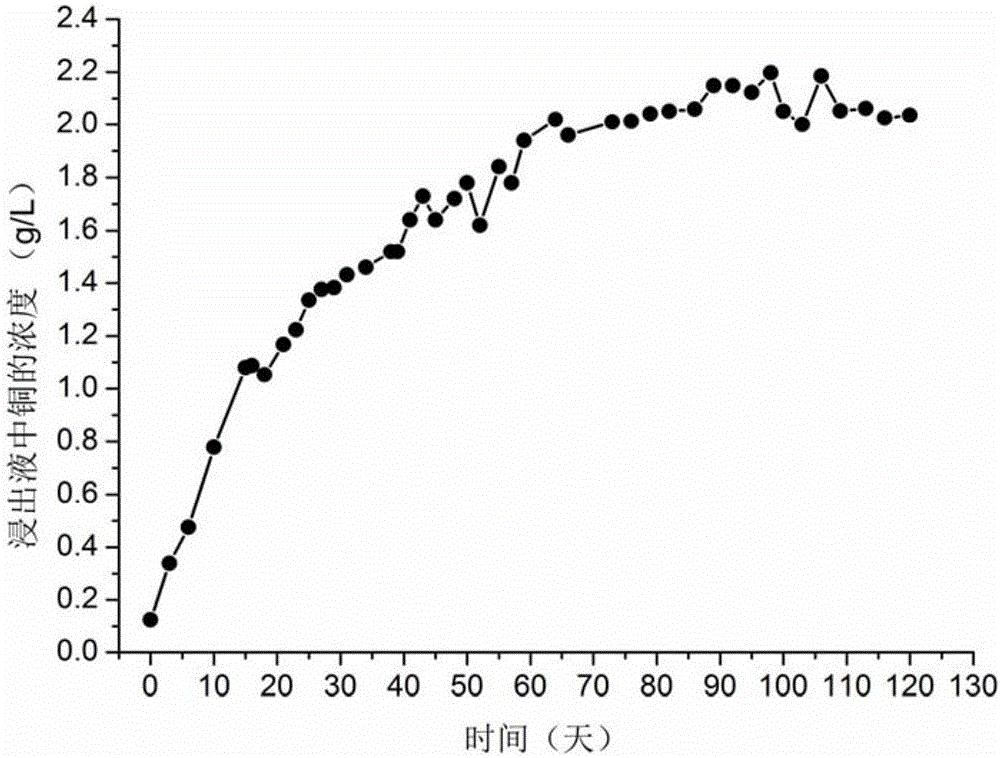
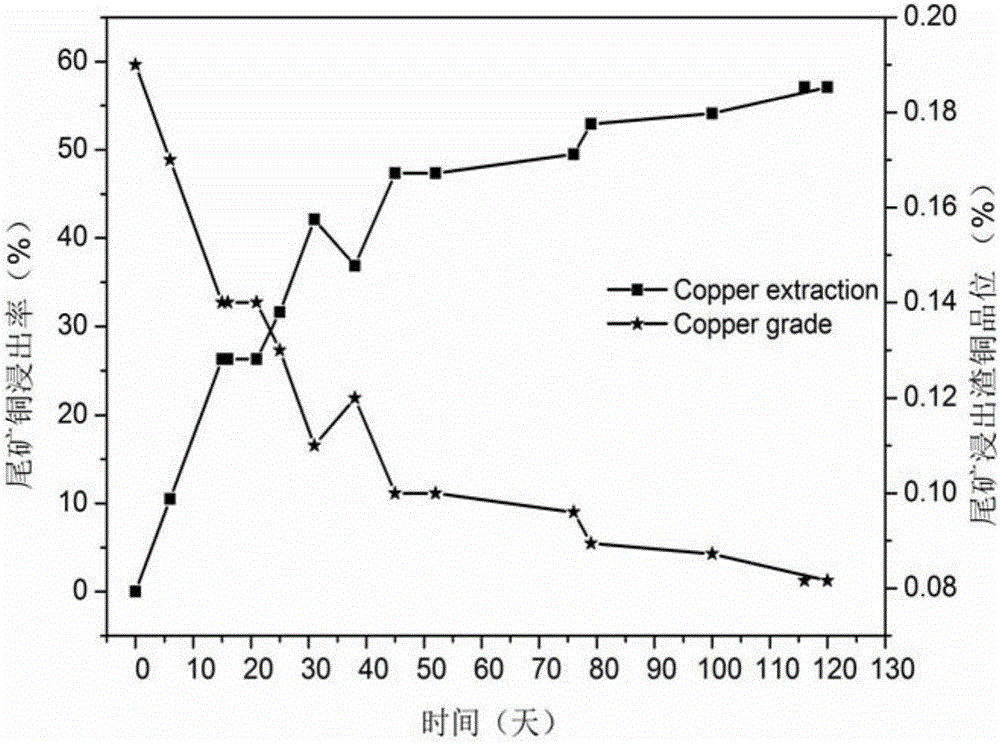
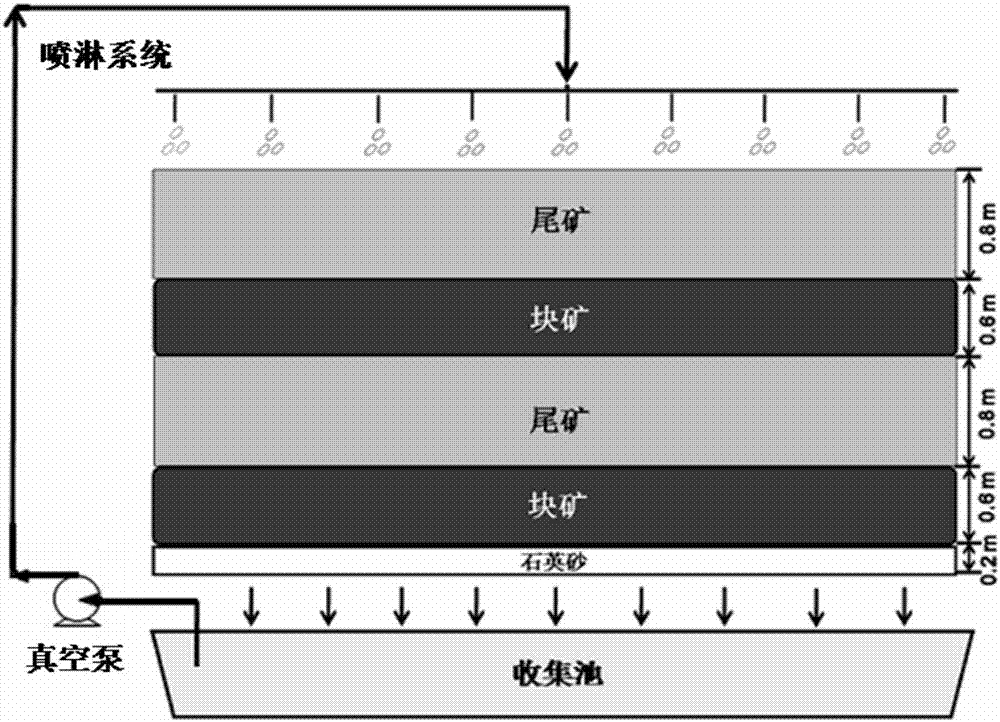
Method for disposing fine-grain-containing tailings on basis of biological lamina heap construction
ActiveCN105821210AImprove bioleaching efficiencyUniform seepageProcess efficiency improvementFloraLower grade
The invention discloses a method for disposing fine-grain-containing tailings on the basis of biological lamina heap construction. The method comprises the following steps: by taking a quartz sand layer as a substrate, sequentially paving low-grade copper lump ores and copper tailings cured by a sulfuric acid solution on the substrate to construct multiple tailings-lump ore mixed ore lamellae, so as to form a tailings-lump ore mixed ore stack; spraying the sulfuric acid solution to the top of the mixed ore stack to perform mixed ore pre-oxidation; and then adding mixed acidophilus ore leaching microbial flora to the top of the mixed ore stack to perform bioleaching on copper ore. The tailings-lump ore mixed ore stack is uniform in gas-liquid seepage, thus being beneficial for microbial growth and improving the bioleaching efficiency, and after the leaching period of 120 days, the leaching efficiency of copper in the tailings reaches 57.10%, and the leaching efficiency of copper in the lump ore reaches 65.52%; and the heap construction manner of the ore stack is simple, the cost is low, and the method has wide application prospect in the field of metallurgy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
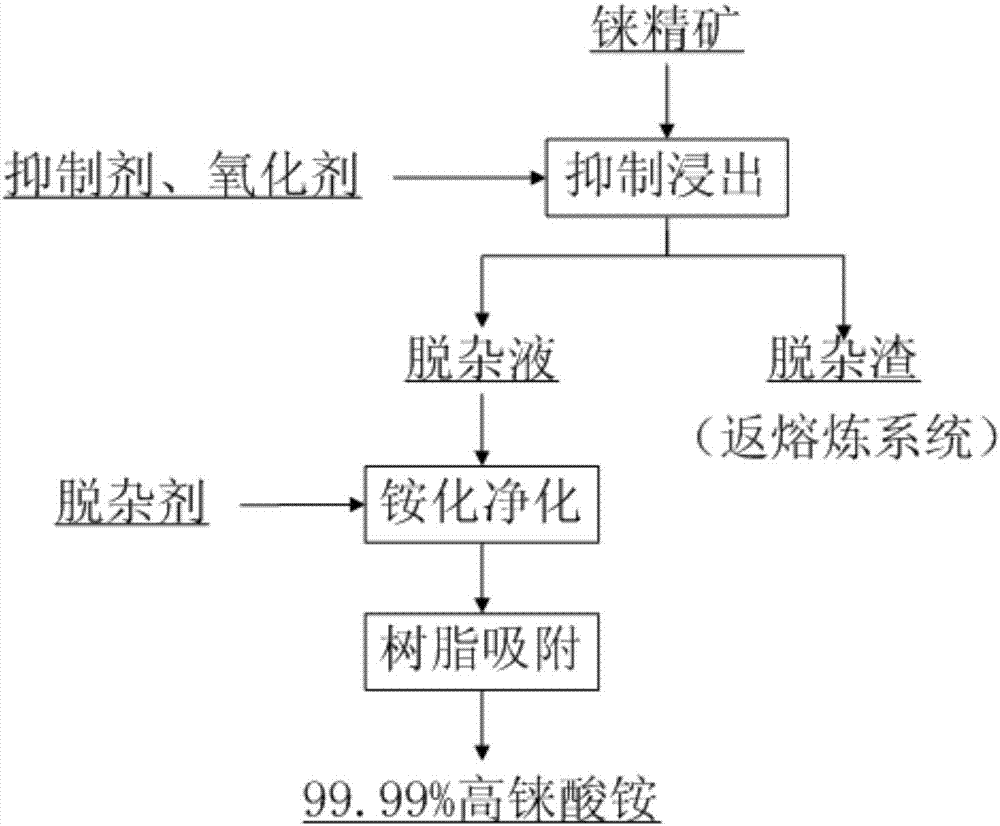
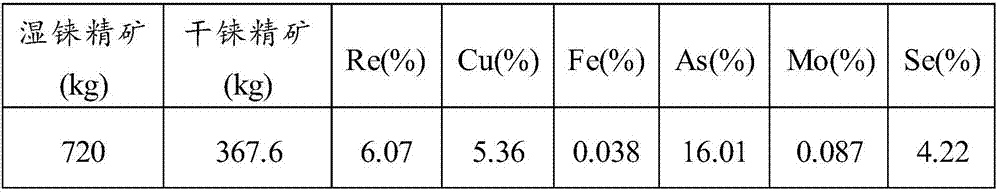
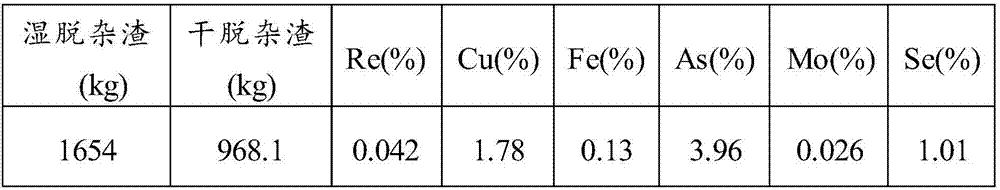
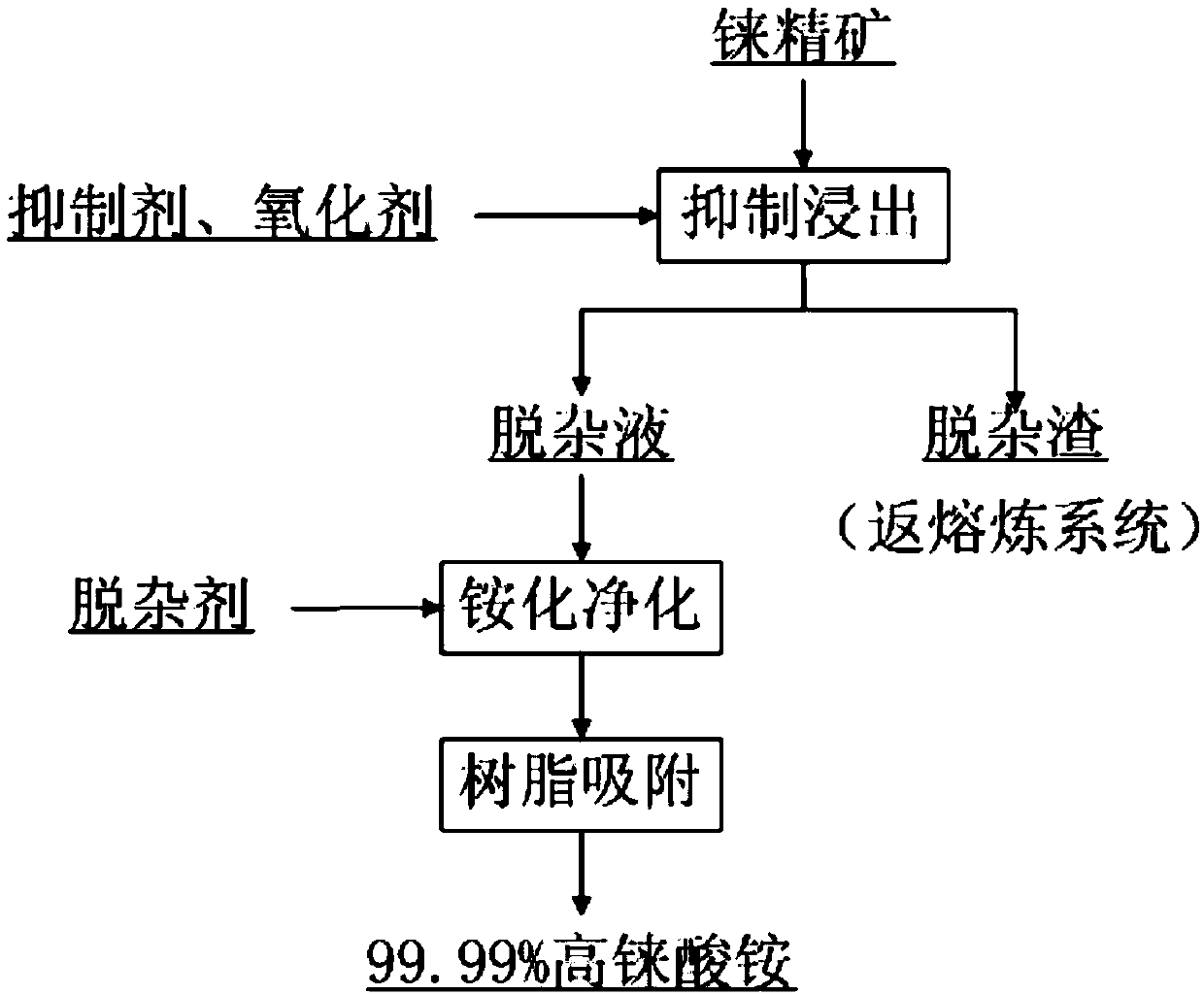
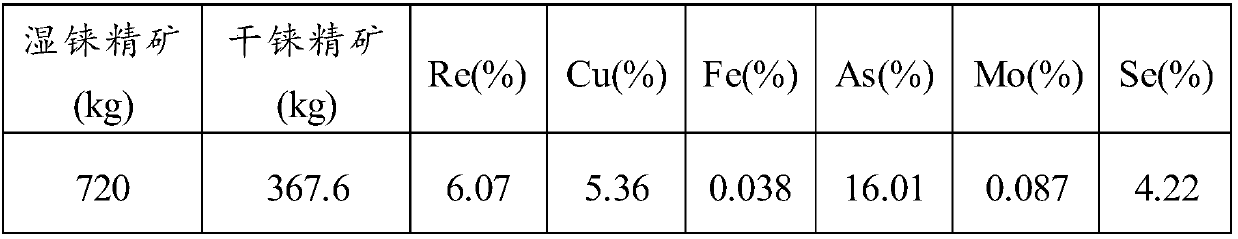
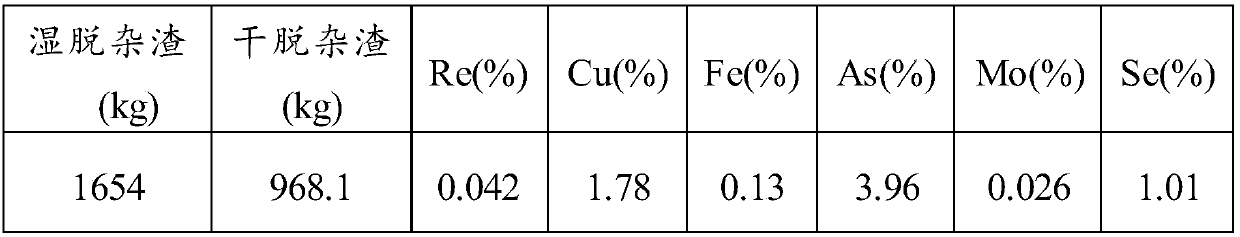
Method for recovering rhenium from rhenium concentrate
ActiveCN107058768AEffective separationHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementChemistryArsenic
The invention provides a method for recovering rhenium from rhenium concentrate. The method for recovering rhenium from rhenium concentrate comprises the following steps that (A) a copper-arsenic inhibitor and an oxidizing agent are added for selective leaching after rhenium concentrate is pulpified, and thus leached pulp is obtained; (B) ammonifying purification is conducted on the leached pulp, so that liquid before adsorption is obtained; and (C) concentrating-crystallization is conducted after the liquid before adsorption is adsorbed, so that ammonium rhenate is obtained. According to the method for recovering rhenium from rhenium concentrate, by adding the copper-arsenic inhibitor and the oxidizing agent in the leaching stage, leaching, oxidization and purification are combined, and selective leaching of arsenic is achieved; and then through subsequent purification, adsorption and concentrating-crystallization, the recovery rate of rhenium is increased.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
A method for treating tailings with high content of fine particles based on bio-thin layer heaping
ActiveCN105821210BImprove bioleaching efficiencyUniform seepageProcess efficiency improvementLower gradeLow graded
The invention discloses a method for disposing fine-grain-containing tailings on the basis of biological lamina heap construction. The method comprises the following steps: by taking a quartz sand layer as a substrate, sequentially paving low-grade copper lump ores and copper tailings cured by a sulfuric acid solution on the substrate to construct multiple tailings-lump ore mixed ore lamellae, so as to form a tailings-lump ore mixed ore stack; spraying the sulfuric acid solution to the top of the mixed ore stack to perform mixed ore pre-oxidation; and then adding mixed acidophilus ore leaching microbial flora to the top of the mixed ore stack to perform bioleaching on copper ore. The tailings-lump ore mixed ore stack is uniform in gas-liquid seepage, thus being beneficial for microbial growth and improving the bioleaching efficiency, and after the leaching period of 120 days, the leaching efficiency of copper in the tailings reaches 57.10%, and the leaching efficiency of copper in the lump ore reaches 65.52%; and the heap construction manner of the ore stack is simple, the cost is low, and the method has wide application prospect in the field of metallurgy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting metal copper using microbe and its use
InactiveCN100404705CLeaching achievedAchieve recyclingPhotography auxillary processesRecovering materialsPregnant leach solutionElectrolysis
The present invention discloses microbe extracting method of metal copper and its application. The method includes crushing copper connecting material into powder; soaking the powder in culture liquid containing microbe to leach out for 15-60 days; solid-liquid separating to obtain leach solution and extracting with copper extractant; reverse extracting copper from the copper extracting liquid with reverse extractant; and final electrolyzing the copper containing reverse extracting liquid to obtain metal copper. The said method may be used in extracting metal copper from printed circuit board. The method has high economic benefit and environment benefit.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
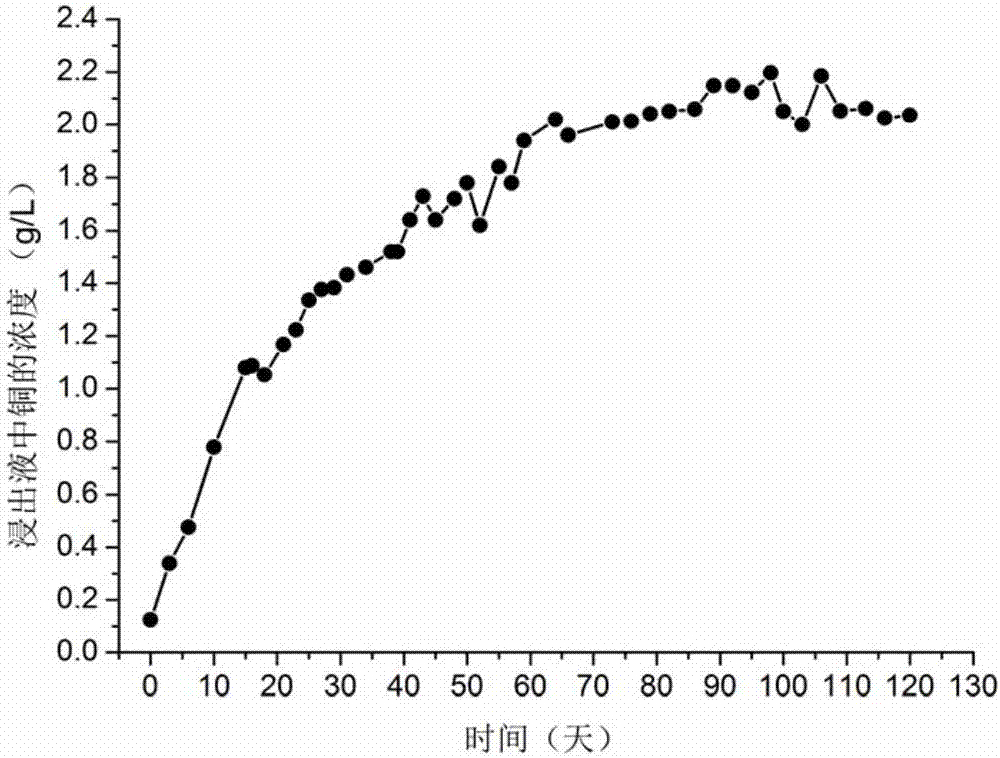
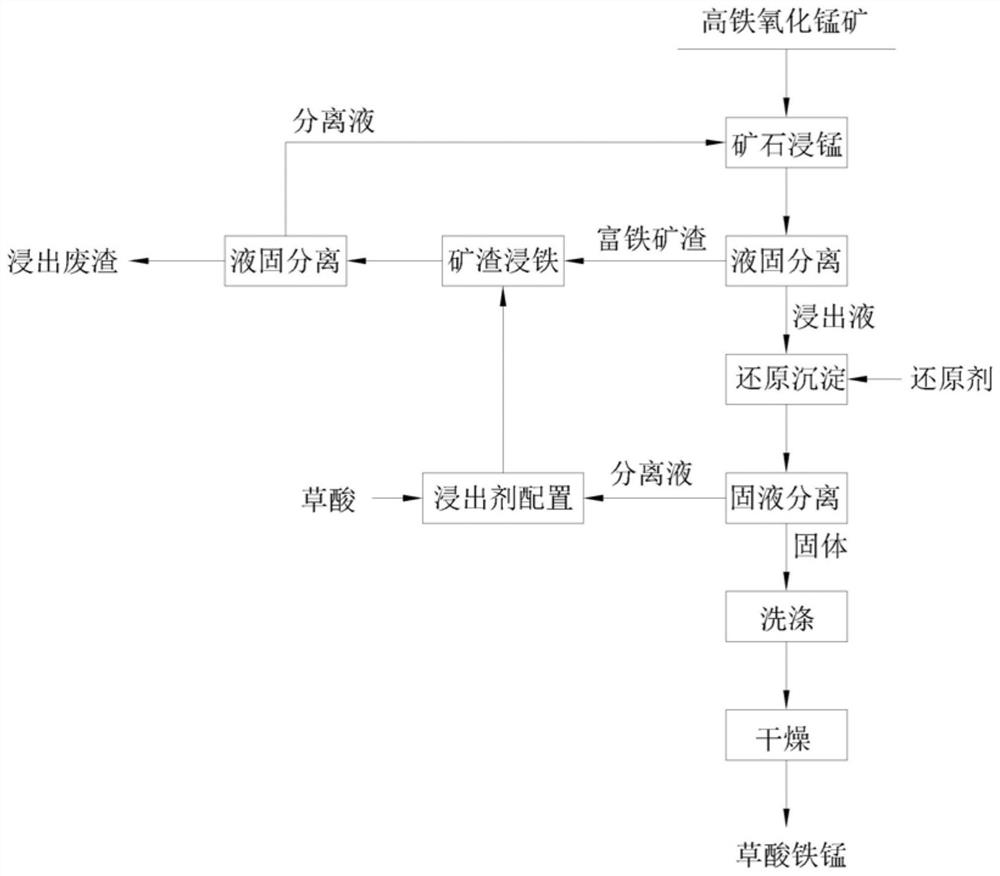
Method for preparing ferric manganese oxalate from high-iron manganese oxide ore
ActiveCN114621080AImprove leaching efficiencyImprove recycling efficiencyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid salt preparationFerric oxalateOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATE
The invention discloses a method for preparing ferric manganese oxalate by using high-iron manganese oxide ore, which comprises the following steps: leaching manganese from ore: preparing slurry from an oxalic acid / ferric oxalate mixed solution as a leaching agent and high-iron manganese oxide, and carrying out solid-liquid separation after leaching to obtain iron-containing slag and a separation solution I; reducing and precipitating iron and manganese: reducing the separation liquid I, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain iron and manganese oxalate precipitate and a separation liquid II; recycling ferric manganese oxalate: washing and drying the ferric manganese oxalate precipitate to obtain pure ferric manganese oxalate; and preparing a leaching agent: supplementing oxalic acid into the separation liquid II to obtain a mixed solution, then performing slurry preparation on the mixed solution and iron-containing slag, performing solid-liquid separation after leaching to obtain leached waste residues and a mixed solution containing oxalic acid / ferric oxalate, and returning the mixed solution containing oxalic acid / ferric oxalate for reuse to form a circulating process. The preparation method can effectively solve the problems of high cost and large pollutant discharge amount in the existing method, and can realize resource utilization of the high-iron manganese oxide ore.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Green kumquat natural flavor and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a natural green kumquat flavor, which comprises the following components, by weight percentage: 50-70% of a green kumquat extracted liquid, 10-20% of a sweet orange flavoring base, 10-20% of a lemon flavoring base, and 10-20% of a lemon-citrus-limetta flavoring base. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the natural green kumquat flavor. According to the method, high-quality green kumquats are taken as a raw material and are subjected to pulverization; low-temperature enzymolysis and low-temperature supersonic extraction are combined, and modern membrane separation technology is adopted to concentrate, enrich, and purify flavor substances to obtain a pure natural green kumquat flavoring base, which is a green kumquat extracted liquid and has strong fragrance, freshness, and fruit juice taste; and the green kumquat flavor is finally prepared.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GREEN CRYSTAL FLAVOR
A method for recovering platinum group metals from spent auto catalysts
ActiveCN106011477BHigh reactivityFully dispersedProcess efficiency improvementWater immersionBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for recycling platinum group metal from ineffective automobile catalysts. The method includes the steps of (1) mechanical activation, (2) high-temperature roasting, (3) ball-milling water immersion, (4) diluted acid leaching and (5) platinum group metal refining. Platinum group metal enriched products obtained in the step (4) are processed according to existing refining processes, so that platinum group metal products are obtained. The ineffective automobile catalysts are processed through the method of combining mechanical activation, sodium salt roasting, water immersion and acid leaching, the reaction activity of materials is improved through mechanical activation, phase transformation of catalyst carrier components occurs due to sodium salt roasting, insoluble residues are enriched with the platinum group metal after water immersion and acid leaching, and separation between carriers and the platinum group metal is achieved. Equipment needed for the method is conventional metallurgical equipment, the technological process is simple, industrial implementation is easy, and the total recovery rate of the platinum group metal is larger than 98%.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
A recovery system and recovery method for waste resin powder
ActiveCN108070528BHigh degree of harmlessnessShorten the cycle of immersion copperBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRecovery methodRecovery stage
The invention discloses a recovery system for a waste resin powder. The recovery system comprises a microbial culture device, a leaching device, a settlement device, a copper recovery device, a brining device, a lead settling device, a washing device, a drying device and a solid liquid separating machine. The invention further discloses a recovery method for the waste resin powder. The recovery method comprises the microbial culture stage, the leaching stage, the settling stage, the copper recovery stage, the brining stage, the lead settling stage, the washing stage, and the drying stage. Thebiological copper leaching cycle of the waste resin powder is shortened, the production efficiency is improved, the sodium chloride is used in brining, the lead in the waste resin powder is effectively removed, the lead is separately recovered, the harmless degree of the leaching residue is high, and in addition, the recycling utilization of the resource is realized, the resource is saved, the useratio of the resource is also improved, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
A kind of method for reclaiming rhenium in rhenium concentrate
ActiveCN107058768BHigh recovery rateAvoid leachingProcess efficiency improvementRheniumSelective leaching
The invention provides a method for recovering rhenium from rhenium concentrate. The method for recovering rhenium from rhenium concentrate comprises the following steps that (A) a copper-arsenic inhibitor and an oxidizing agent are added for selective leaching after rhenium concentrate is pulpified, and thus leached pulp is obtained; (B) ammonifying purification is conducted on the leached pulp, so that liquid before adsorption is obtained; and (C) concentrating-crystallization is conducted after the liquid before adsorption is adsorbed, so that ammonium rhenate is obtained. According to the method for recovering rhenium from rhenium concentrate, by adding the copper-arsenic inhibitor and the oxidizing agent in the leaching stage, leaching, oxidization and purification are combined, and selective leaching of arsenic is achieved; and then through subsequent purification, adsorption and concentrating-crystallization, the recovery rate of rhenium is increased.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com