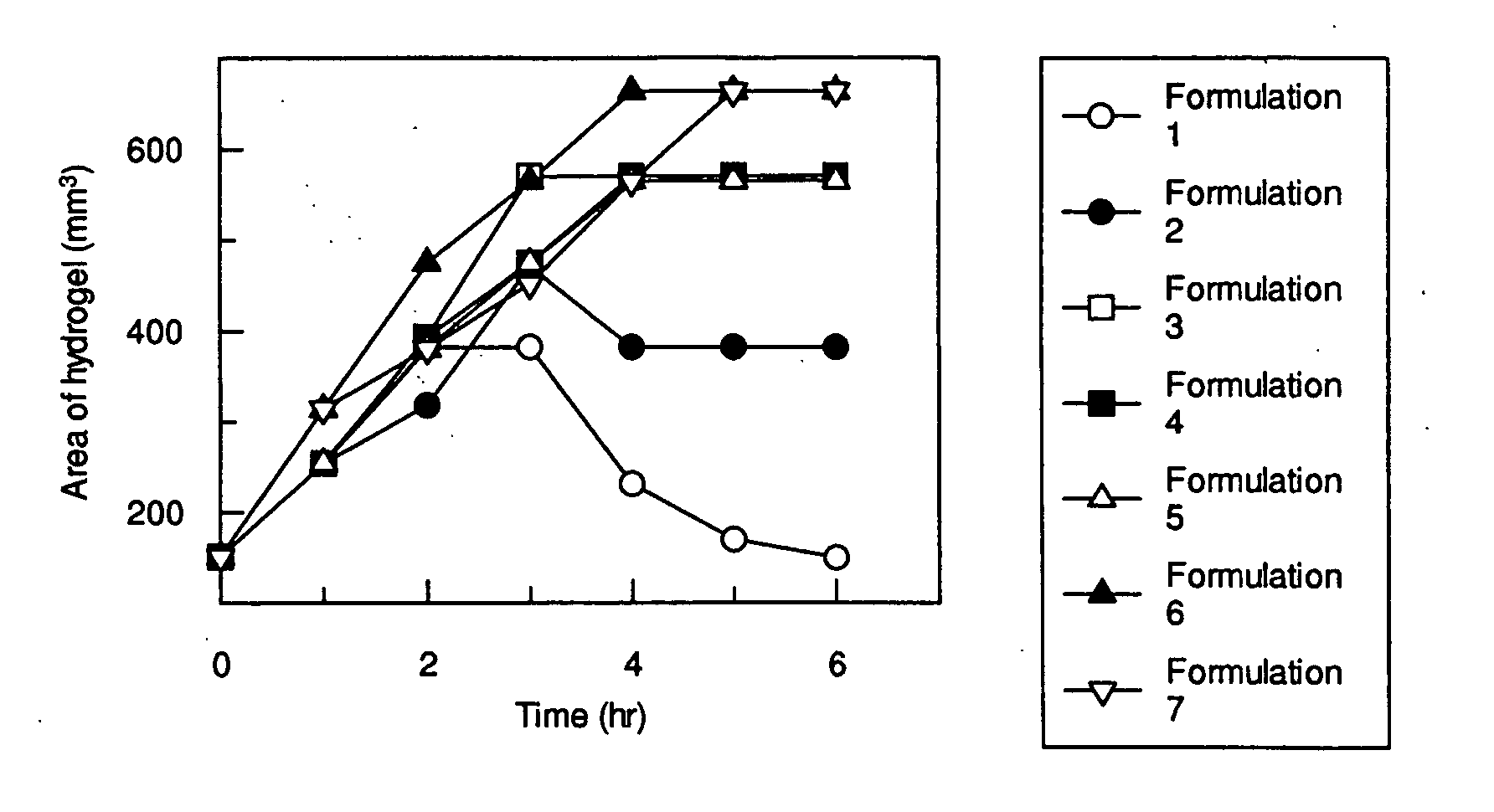
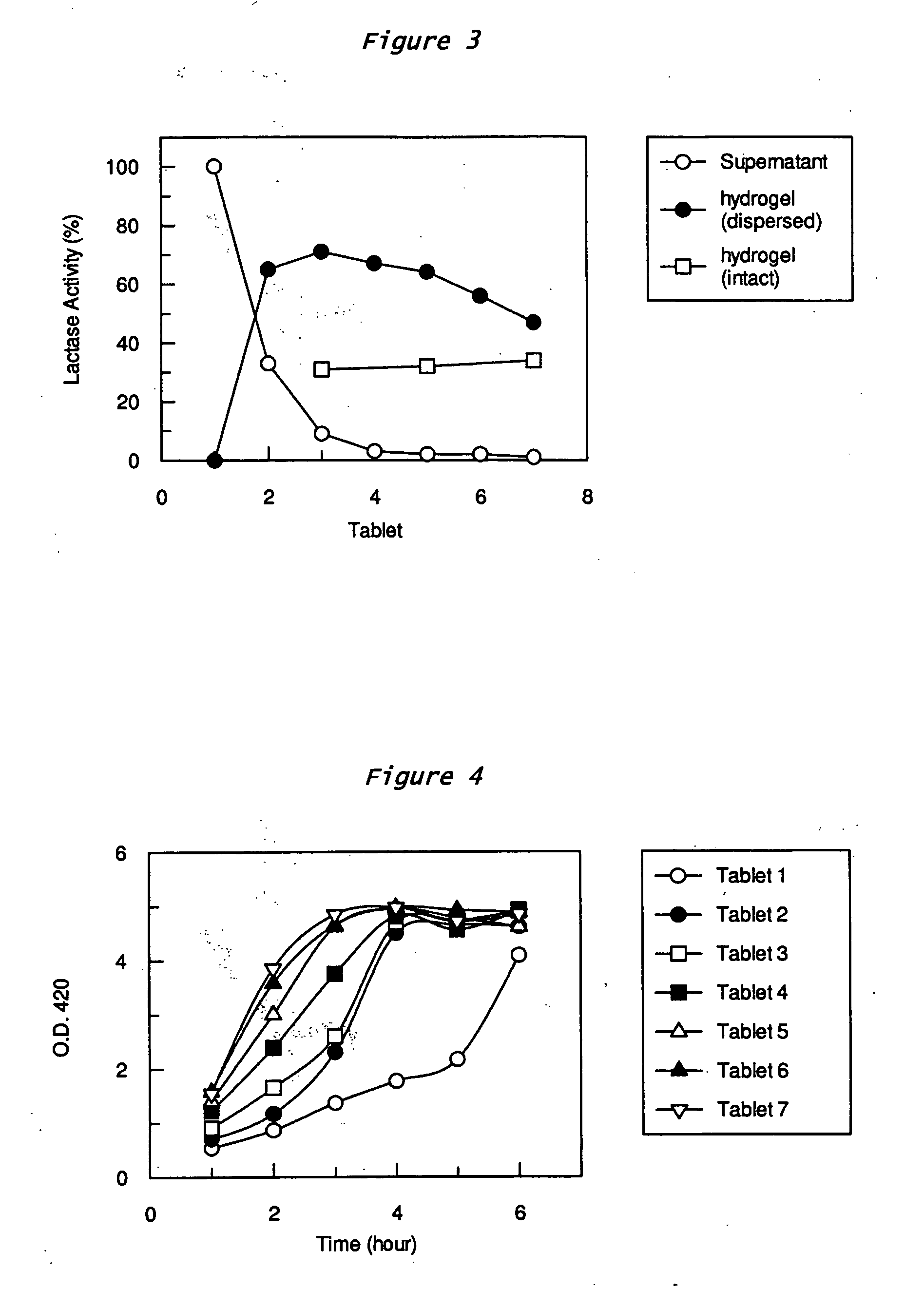
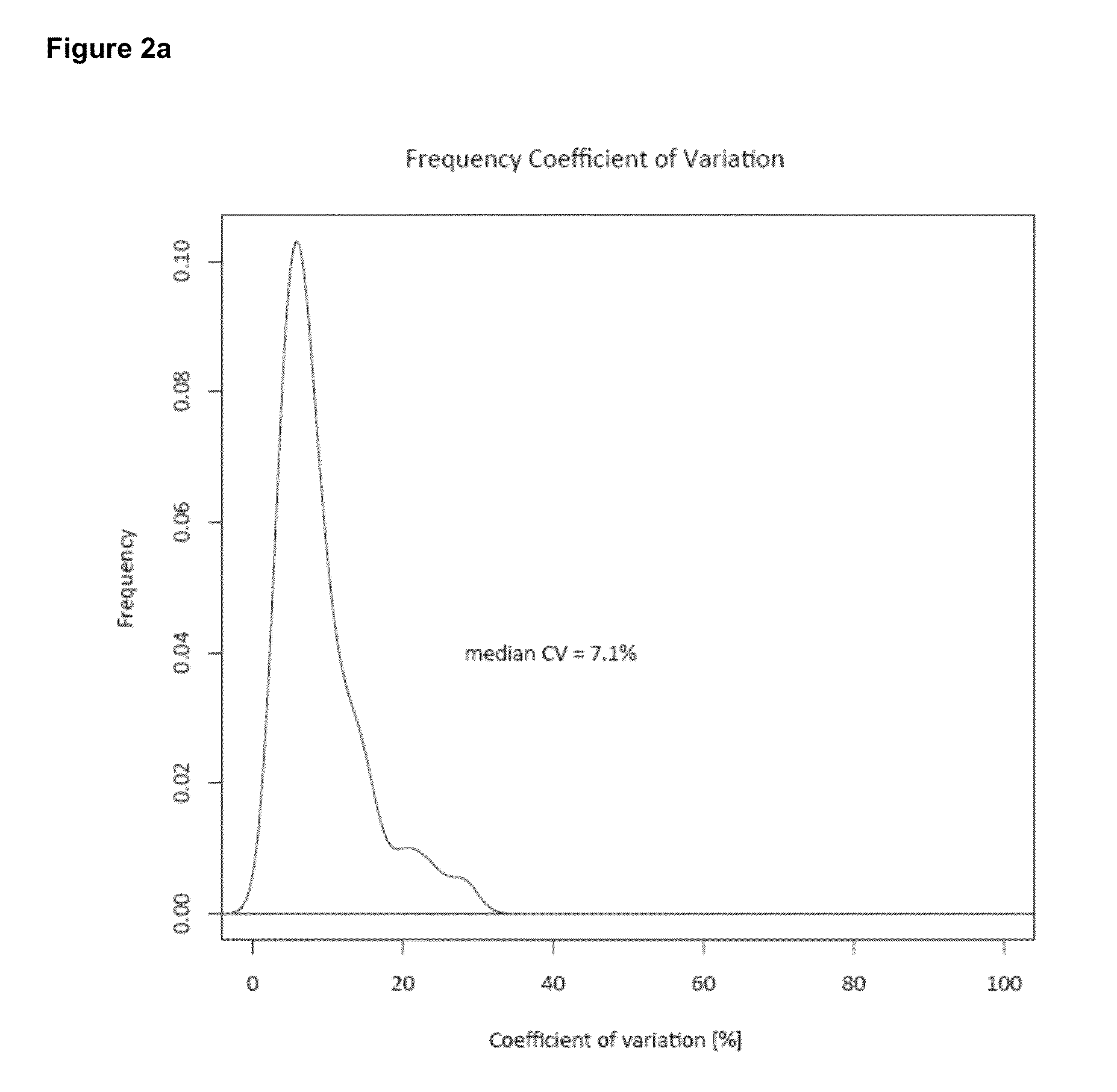
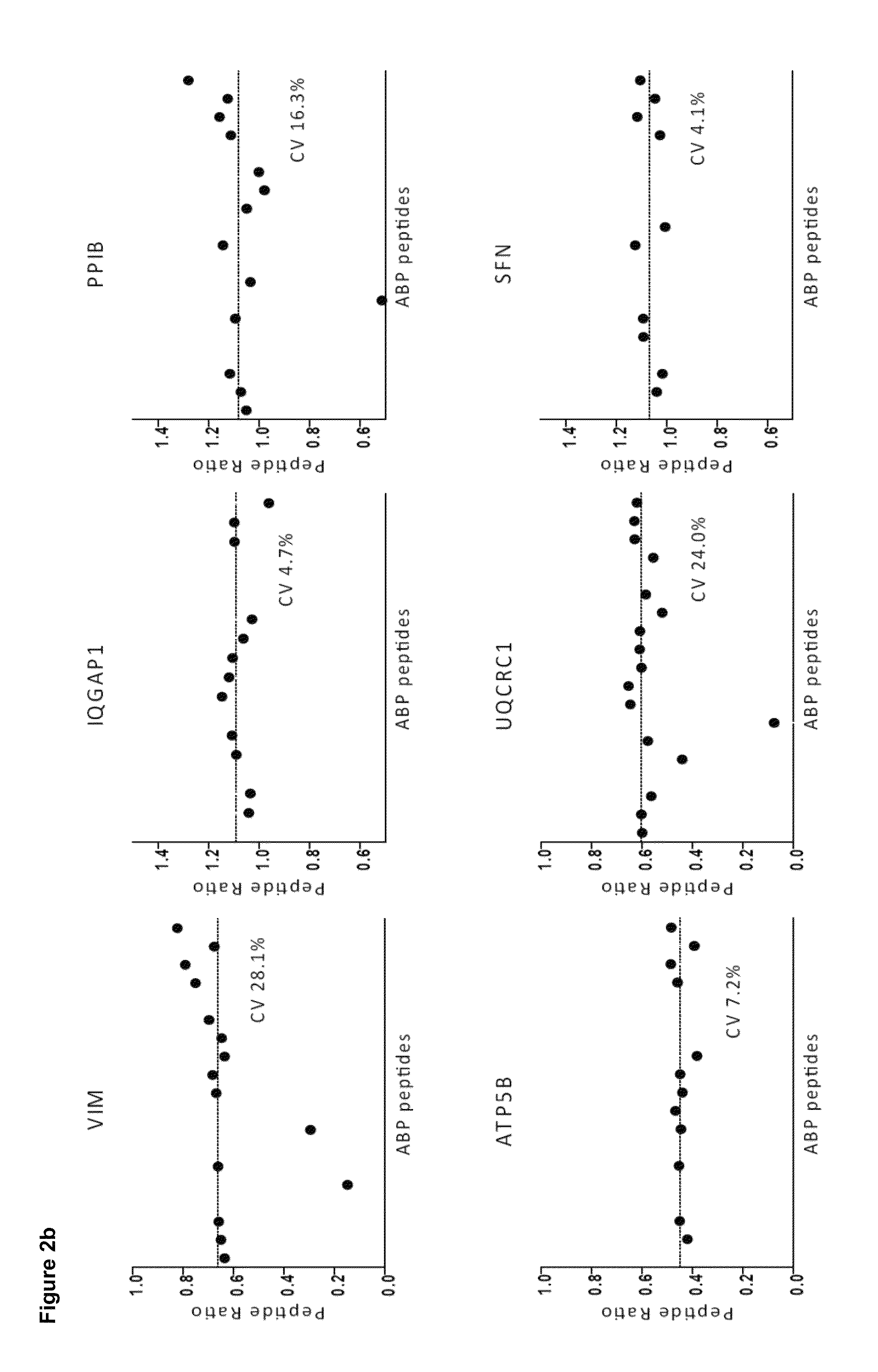
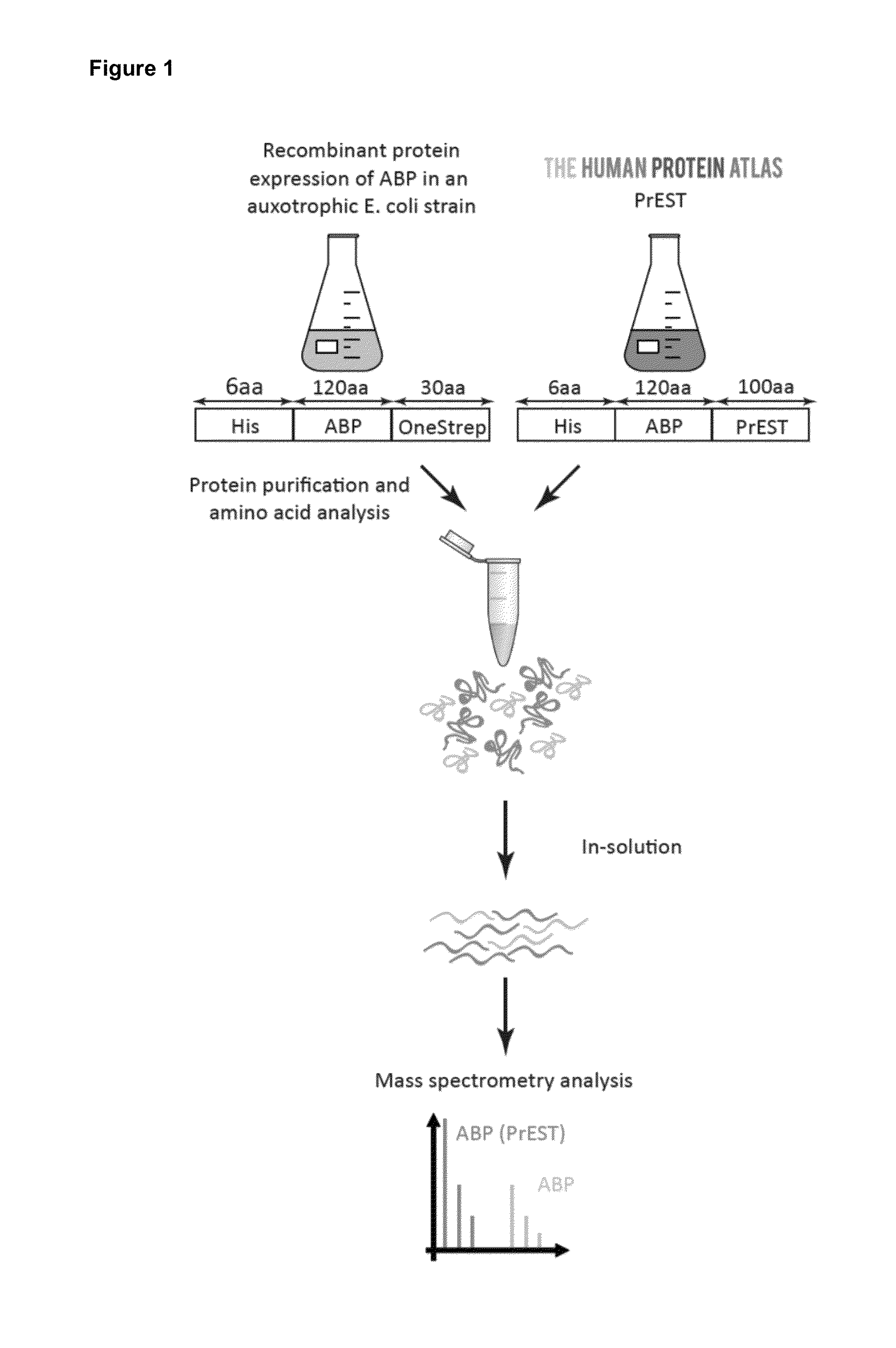
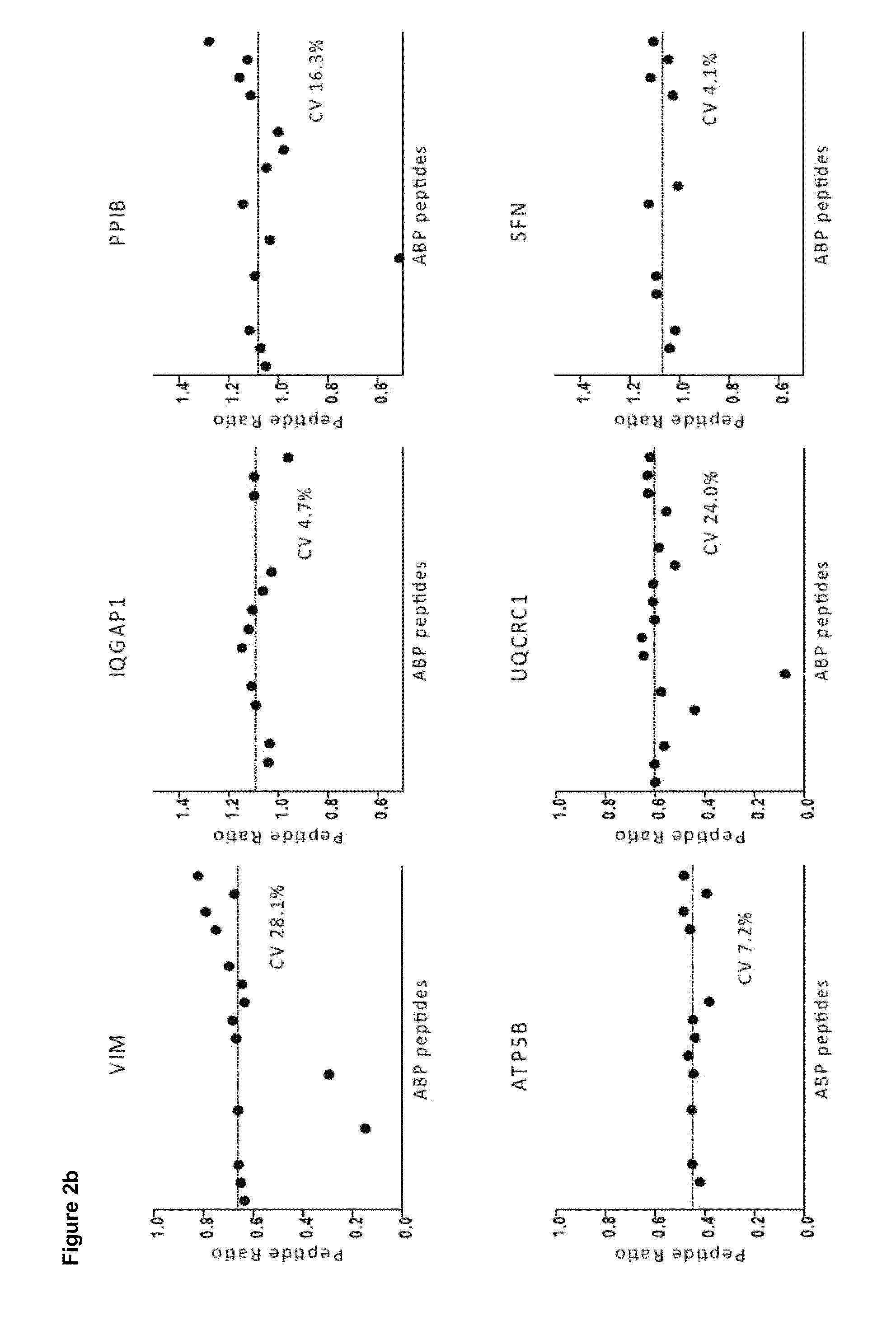
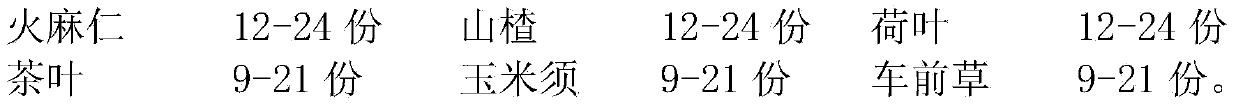Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57results about How to "Inhibit digestion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
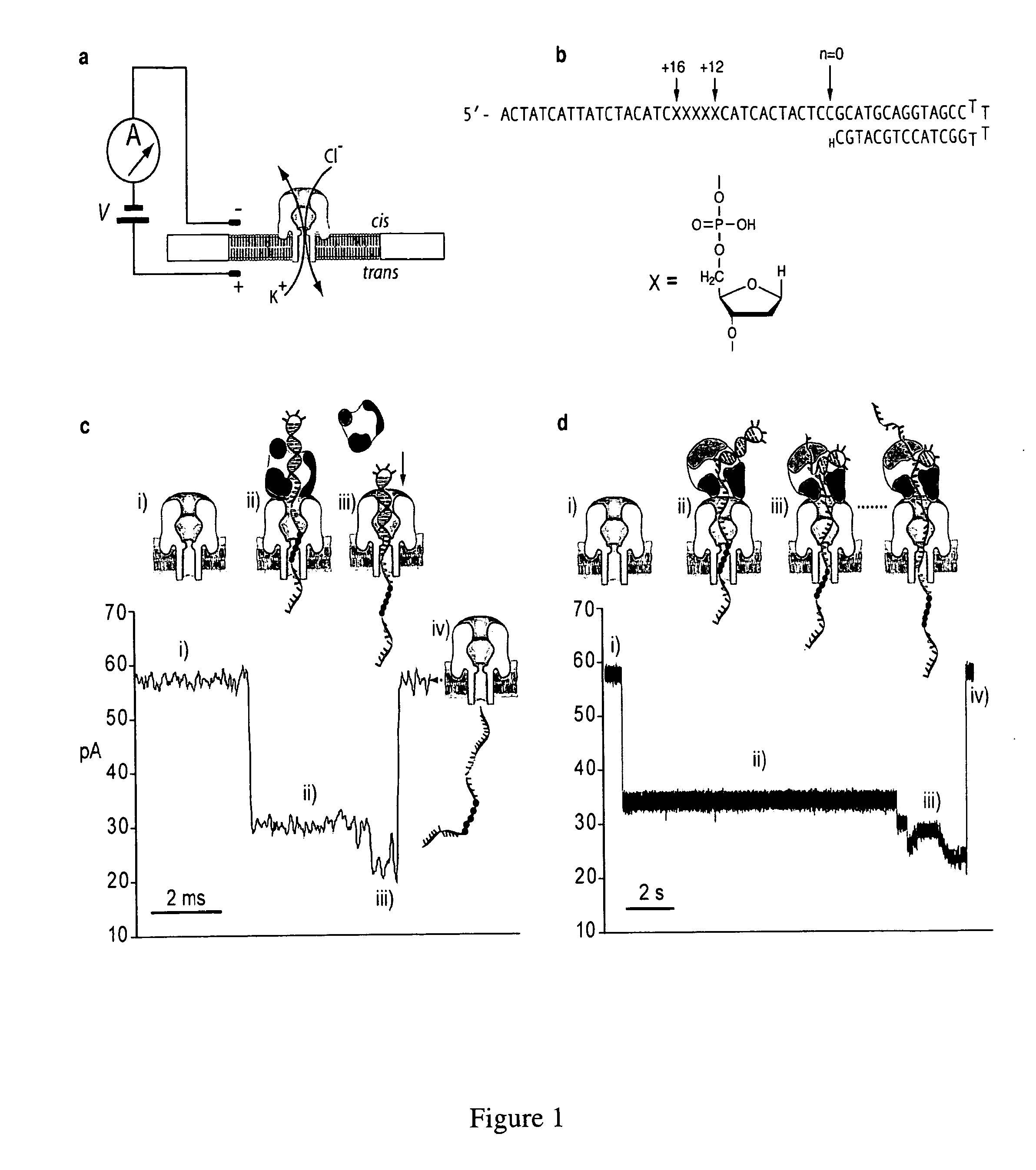
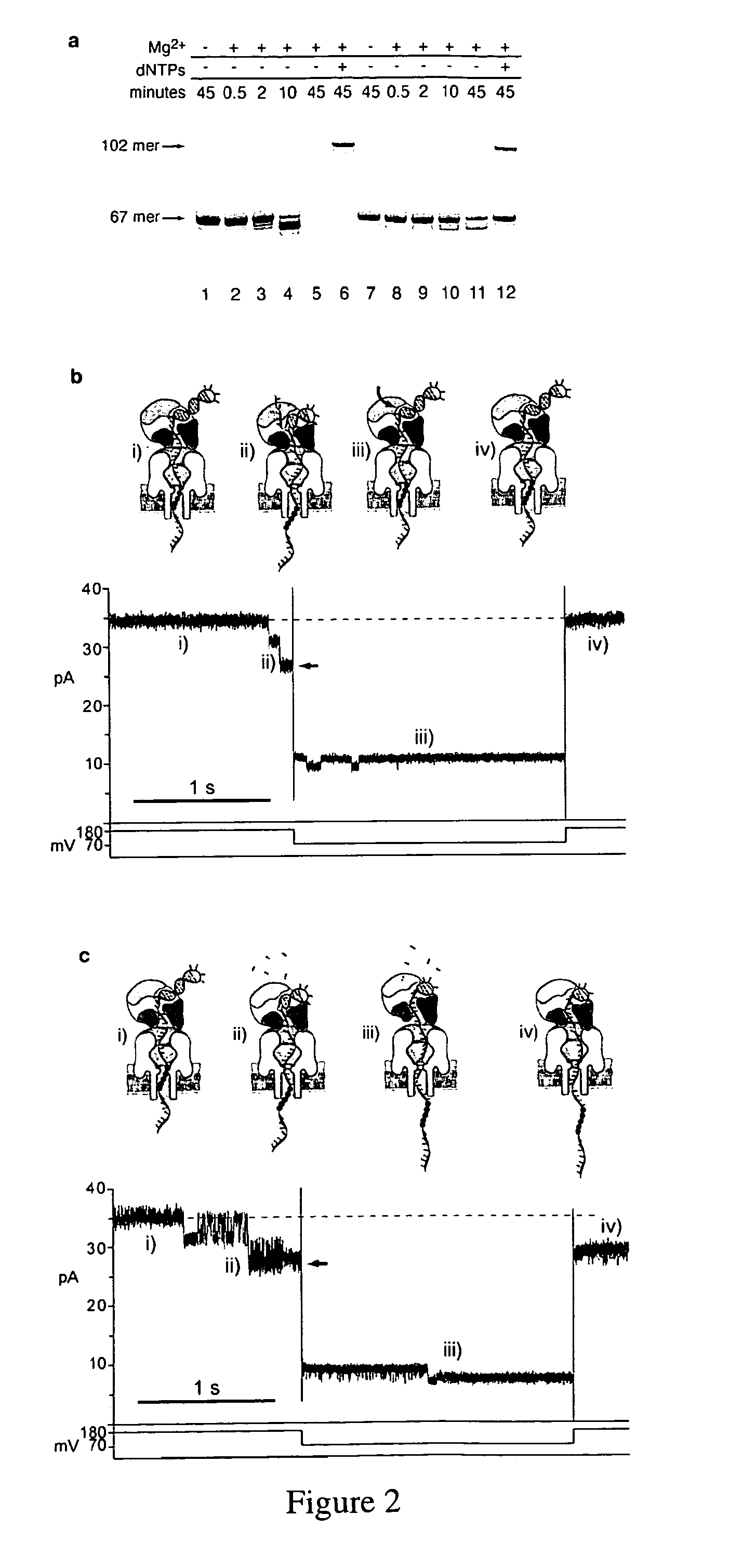
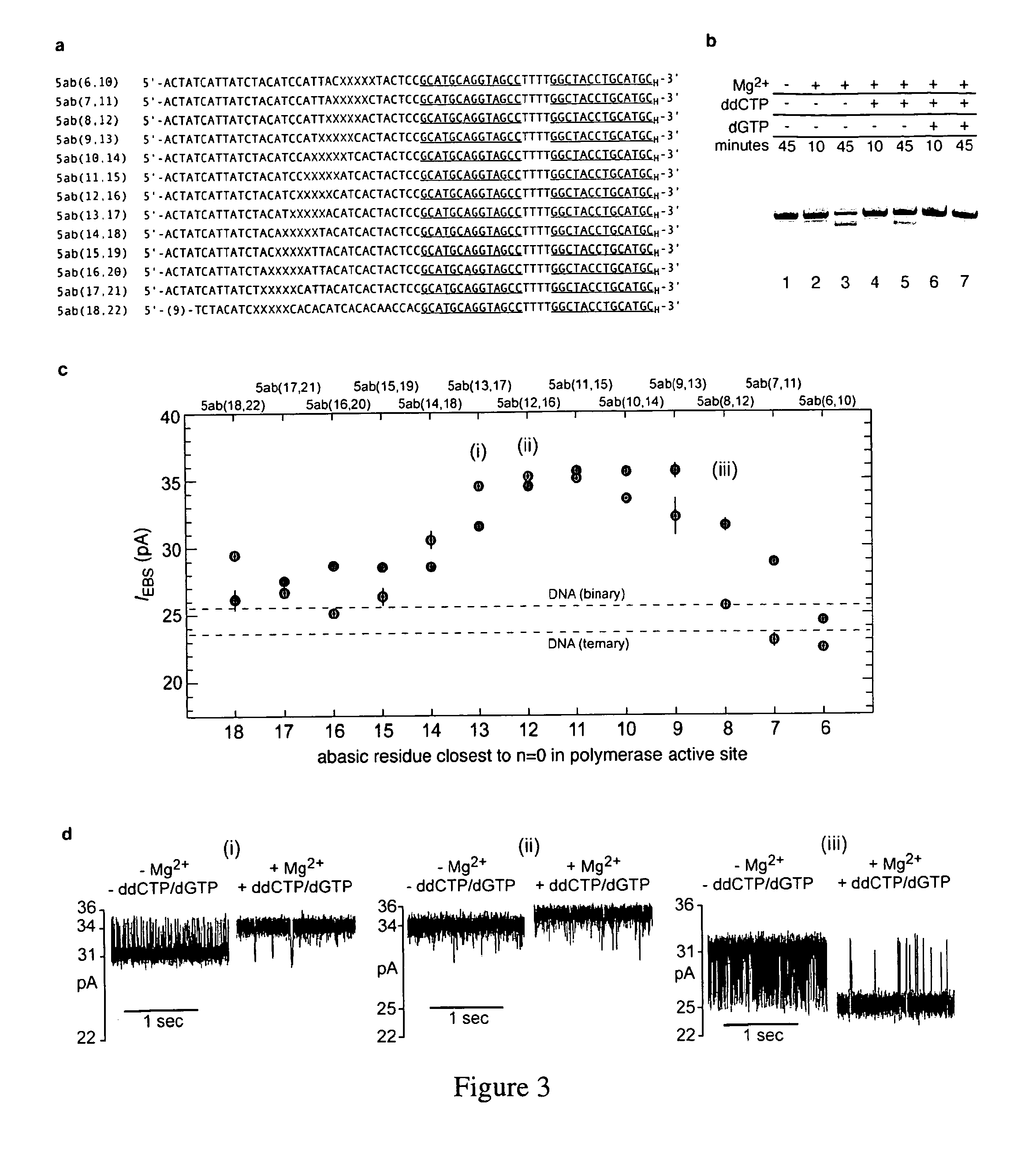
Control of DNA movement in a nanopore at one nucleotide precision by a processive enzyme
InactiveUS20140051068A1Improve the activity rateReduce decreaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore. Of particular note is the stability of the system in a saline medium and to detect individual nucleotide bases in a polynucleotide in real time and which may be used to sequence DNA for many hours without change of reagents. The invention is of particular use in the fields of forensic biology, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Integrated microfluidic device (ea)
InactiveUS20050277195A1Improve accuracyLow costChemical analysis using catalysisLaboratory glasswaresChemistryMicro cavities
A method for characterizing n components An of n catalytic systems. The method is characterized in comprising the steps of: I) providing a microfluidic device which comprises a plurality of identical microchannel structures, each microchannel structures comprising in the downstream direction (a) an inlet arrangement IA with at least one inlet port; (b) a catalytic microcavity MC1, which comprises an immobilized component Cim of the catalytic system CS used in the microchannel structure, and (c) a detection zone (DZ); ii) distributing to MC1 of each microchannel structure the remaining components of the CS used in the structure by a) dispensing to the inlet arrangement IA of each microchannel structure said remaining components; and b) transporting corresponding components for the microchannel structures in parallel to load MC1 in each microchannel structure; iii) performing the catalytic reaction in MC1 of each microchannel structure; iv) transporting in parallel the product formed in step (iii) from MC1 to DZ of each microchannel structure, if DZ and MC1 do not coincide; v) characterizing for each microchannel structure the result of the catalytic reaction performed in MC1 in DZ; and vi) characterizing An for each microchannel structure.
Owner:GYROS
Regulation of substrate activity
InactiveUS20060052310A1Improve bioavailabilityPositive therapeutic effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedical disorderAngiogenesis growth factor
A method for regulating substrate activity in vivo is useful for the treatment of medical disorders such as inflammation, arteriolosclerosis and angiogenesis. The method involves the administration of an effective amount of a DPP-IV inhibitor to a patient in need of such treatment.
Owner:DARA BIOSCI
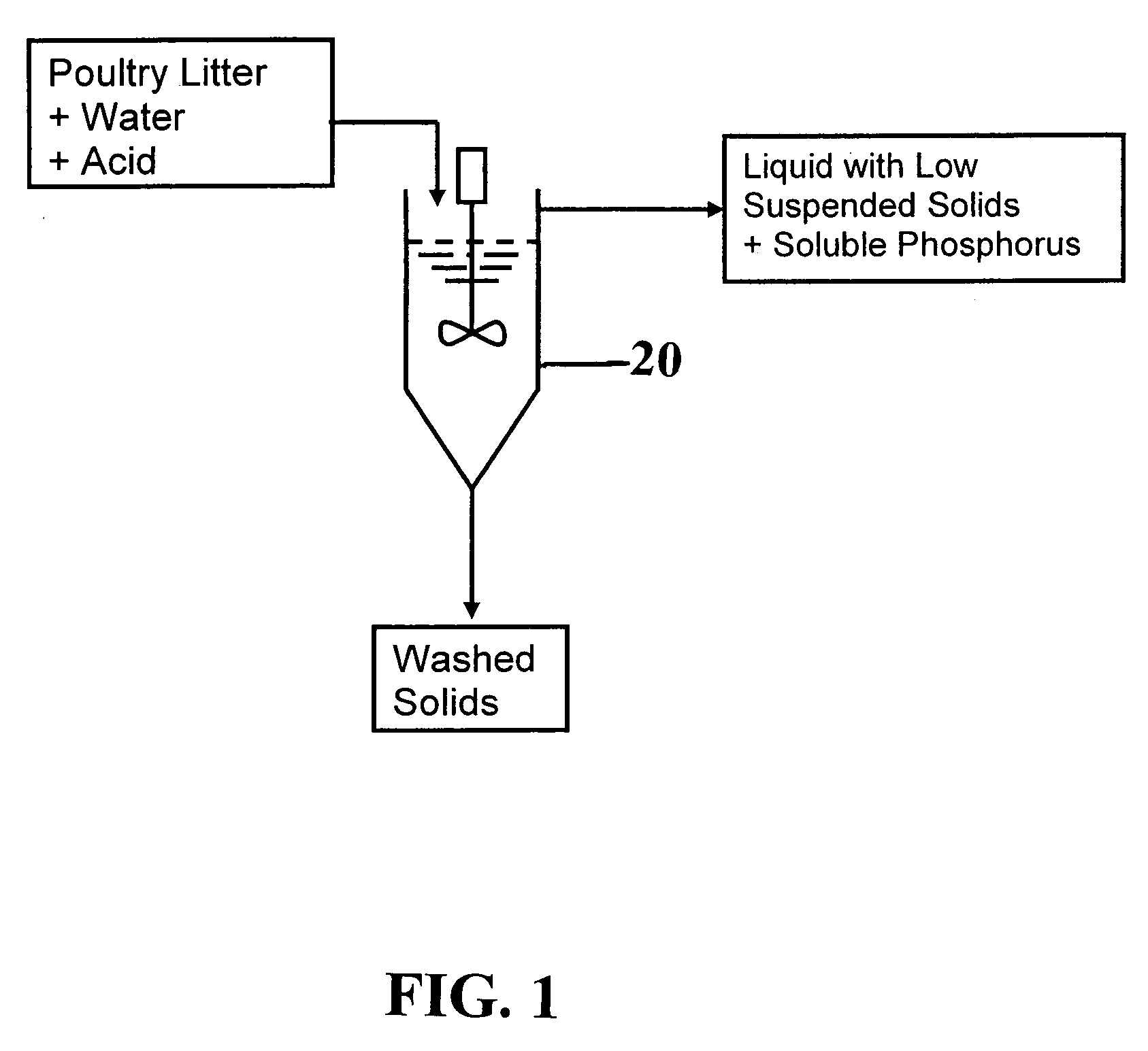
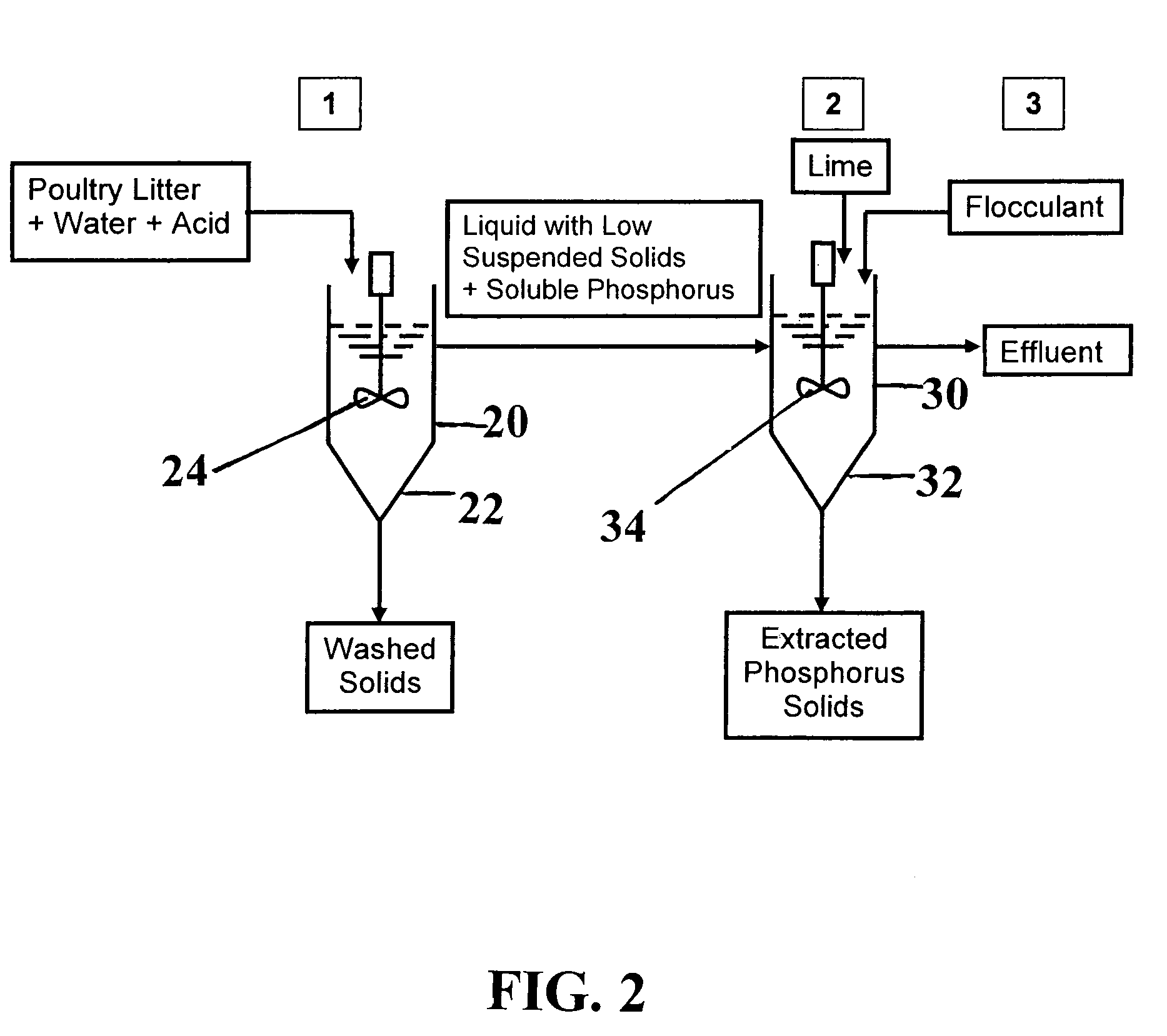
Process for Removing and Recovering Phosphorus from Animal Waste
InactiveUS20090193863A1Environment safetyInhibit digestionBio-organic fraction processingProductsAnimal wastePoultry litter
A process for extraction and recovery of phosphorus from solid animal wastes such as for example, poultry litter waste, includes the steps of phosphorus extraction, phosphorus recovery, and phosphorus recovery enhancement. The process can be performed in batch or continuous mode.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Diagnostic test for borrelia infection
InactiveUS6617441B1Inhibit digestionSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseLone star ticks
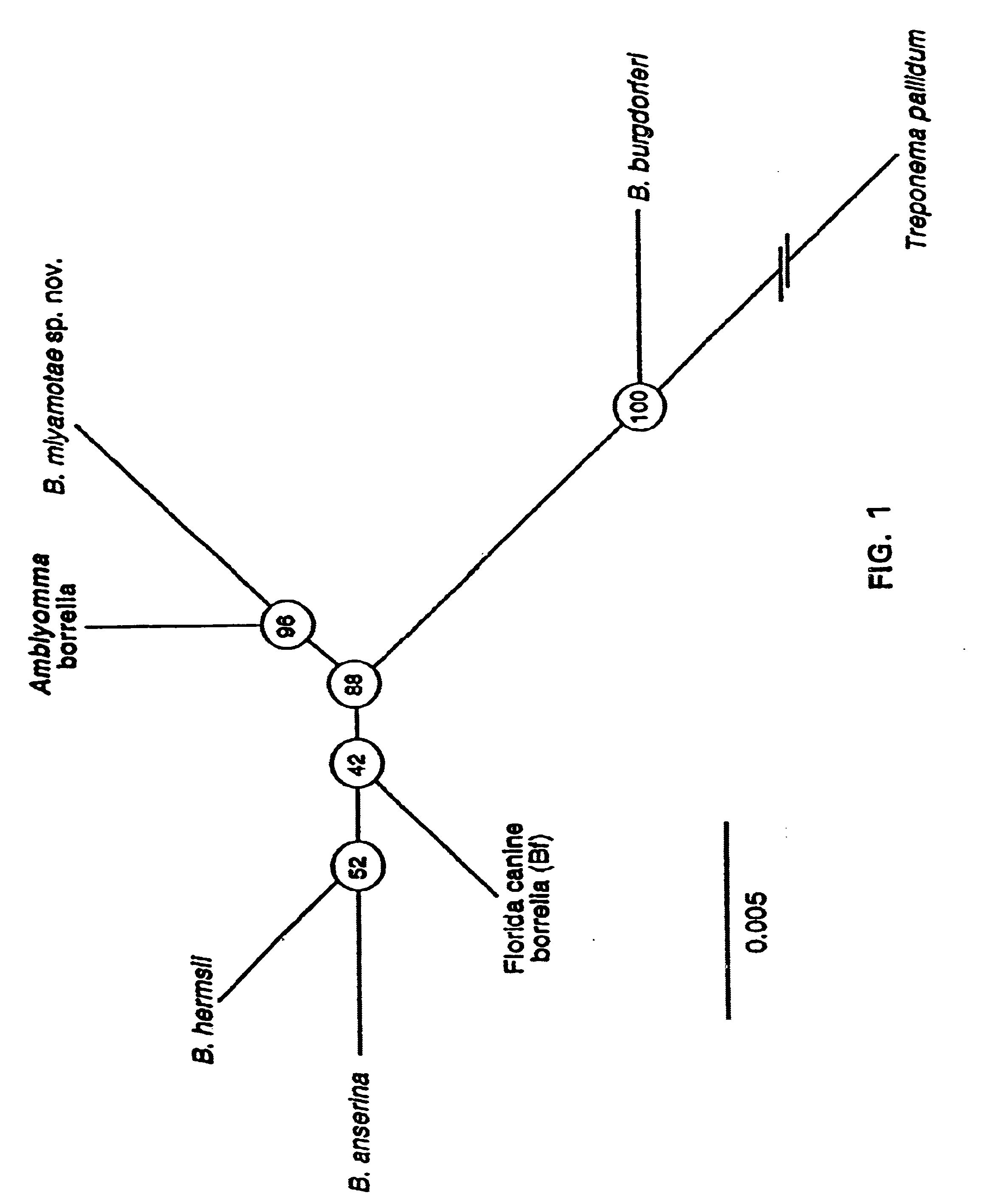
Bites from Amblyomma americanum, a hard tick, have been associated with a Lyme disease-like illness in the southeastern and south-central United States. Present in 2% of ticks collected in four states were uncultivable spirochetes. Through use of the polymerase chain reaction, partial sequences of the flagellin and 16s rRNA genes of microorganisms from Texas and New Jersey were obtained. The sequences showed that the spirochete was a Borrelia sp. but distinct from other known members of this genus, including B. burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease. Species-specific differences in the sequences of the flagellin protein, the flagellin gene and the 16s rRNA gene between the new Borrelia species and previously known species provide compositions and methods for assay for determining the presence of this new spirochete, or for providing evidence of past or present infection by this spirochete in animal reservoirs and humans.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compositions and methods for improving sample identification in indexed nucleic acid libraries
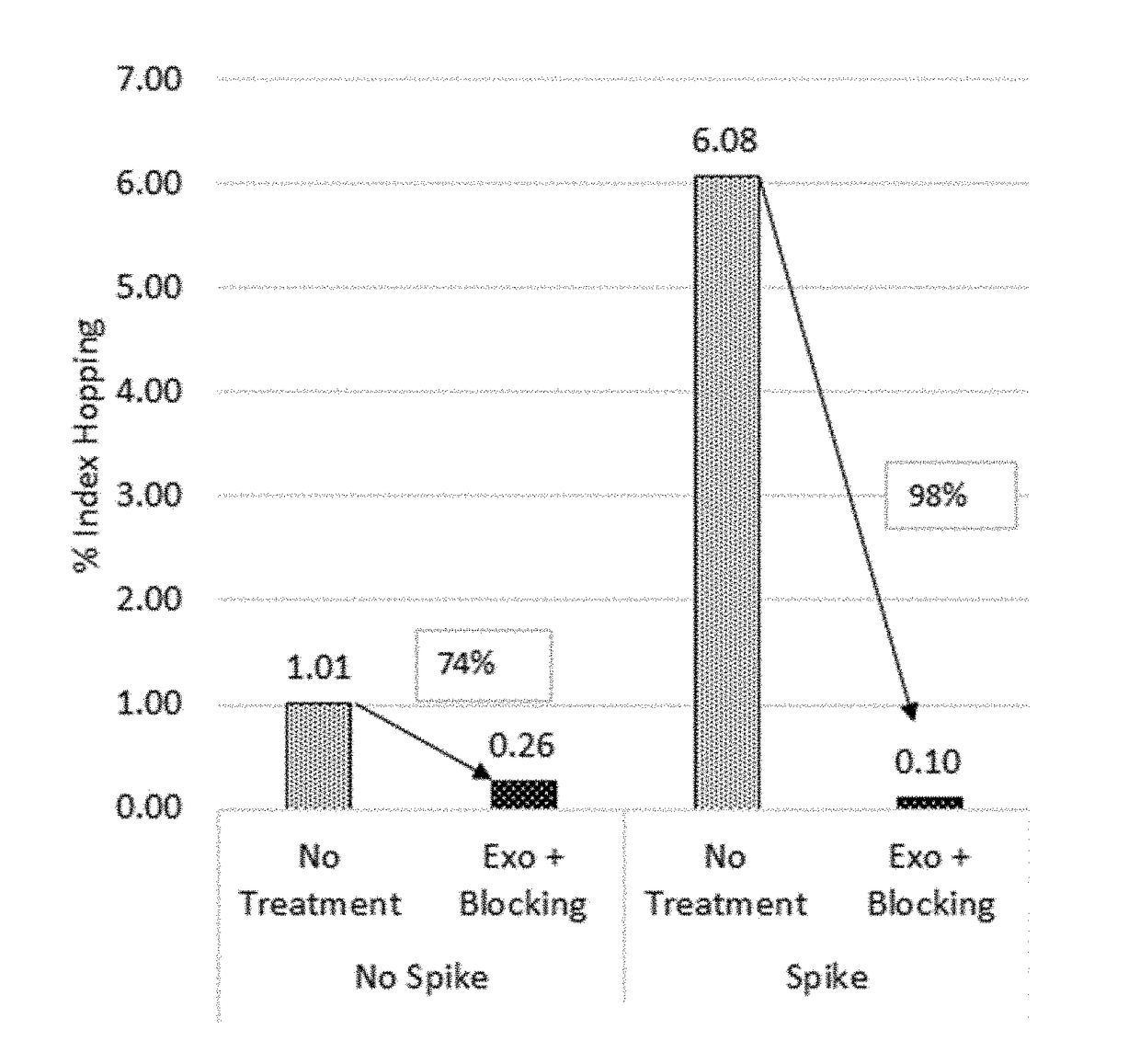
ActiveUS20180305753A1Narrowing activity of exonucleaseIndex can be reduced and eliminatedNucleotide librariesLibrary tagsNucleotideLibrary preparation
The present invention is concerned with compositions and methods for improving the rate of correct sample identification in indexed nucleic acid library preparations for multiplex next generation sequencing by exonuclease treatment and optionally blocking the 3′ ends of pooled indexed polynucleotides from multiple samples prior to amplification and sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Method of stabilizing reagent for amplifying or detecting nucleic acid and storage method
InactiveUS20050059000A1Run cost be reduceRapidly and conveniently detectMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBiologyTrue positive rate
A method of stabilizing a reaction reagent for highly sensitively and specifically amplifying a target nucleic acid in a sample with the use of a chimeric oligonucleotide primer and a method of storing the same over a long time; and a method of highly sensitively detecting a pathogenic microorganism and a virus.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Pharmaceutical composition with antiobesity action
ActiveCN102423374AAppetite suppressantInhibit digestionMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsDrugs prescriptionsTraditional Chinese medicine
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition with antiobesity action. The pharmaceutical composition is prepared from 3-6 parts of oolong, 1-3 parts of pomegranate bark, 2-4 parts of lotus leaf and 1-2 parts of balsam pear; in addition, 1-2 parts of apple or 1-2 parts of passionflower and 1-2 parts of citrus aurantium can be added; and meanwhile, the raw materials can be replaced by corresponding plant extracts. The pharmaceutical composition is prepared through taking sufficient consideration to the combination of the theories and the experiments of the traditional Chinese medicine, is not the simple combination of the raw materials, but the combination of different weight-reducing mechanisms; through the compatibility of the raw materials and a lot of comparative experiments, the formulation has the antiobesity action outdistancing that of a single drug prescription, and an effect that the sum of one plus one is greater than two is achieved; and furthermore, the traditional Chinese medicines are adopted as the raw materials, so that the pharmaceutical composition with the antiobesity action is safe and reliable and has an outstanding curative effect.
Owner:GUILIN NATURAL INGREDIENTS CORP
Antiobesity agent using hen's egg antibody against digestive enzymes
InactiveUS20060182730A1Increased substrate specificityImprove securityEgg immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsANTIOBESITY AGENTSBiology
Objects of the present invention are to provide an agent for inhibiting a digestive enzymes and an antiobesity agent having digestive-enzyme-inhibiting activity with high substrate specificity and having high safety. Provided is a composition comprising eggs produced by hens immunized with digestive enzymes or fragments thereof, or the processed products thereof, and containing 2 or more types of digestive enzymes.
Owner:GHEN CORP
Carbohydrate based cellulase inhibitors as feeding stimulants in termites
InactiveUS20080107619A1Increase feed rateIncrease termite mortalityBiocideAnimal repellantsEndoglucanase activityDigestion
A method, composition and system for controlling termites wherein single carbohydrate-based compounds are used as both cellulase inhibitors and feeding stimulants. Di-saccharides, cellobioimidazole (CBI), fluoro-methyl cellobiose (FMCB), and mono-saccharides, fluoro-methyl glucose (FMG) and analogs thereof inhibit termite cellulose digestion, which leads to starvation or stimulates termite feeding to cause mortality. CBI, FMCB and FMG were tested against enzyme fractions that represented endogenous (foregut / salivary gland / midgut) and symbiotic (hindgut) termite cellulases in vitro and in vivo. Feeding stimulation by di-saccharides results in greater cellulase inhibitor intake throughout midrange concentrations (1 mM-10 mM), which is associated with significant termite mortality. In contrast, the monosaccharide inhibitor, FMG did not stimulate feeding, but did inhibit feeding at concentrations above 1 mM, causing mortality. With modification to create longer β-glycosidic chain lengths, the cellulase inhibitors identified herein can also be targeted to endoglucanase activity for increased efficacy and use as novel termite control compositions.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Controlled release formulations of enzymes, microorganisms, and antibodies with mucoadhesive polymers
InactiveUS20050281795A1Satisfies needDigestionPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsMicroorganismWater soluble
There is provided a composition comprising at least one mucoadhesive polymer that is capable of forming a hydrogel and at one least water soluble polymer, and one or more enzymes, microorganisms, or antibodies. The formulation forms a hydrogel in aqueous solution that has mucoadhesive properties and that is capable of releasing the enzymes, microorganisms, or antibodies over an extended period of time and / or of entrapping enzymes, microorganisms, or antibodies within the hydrogel that is active for an extended time.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME USA CO LTD +1
Quantitative standard for mass spectrometry of proteins
ActiveUS9063149B2Easy to handleAvoidance of biasPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass spectrometry imaging
This invention relates to a method of determining the absolute amount of a target polypeptide in a sample using mass spectrometry.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Quantitative standard for mass spectrometry of proteins
ActiveUS20140072991A1Easy to handleAvoidance of biasPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSpectroscopyMass spectrometry imaging
The present invention provides a method of determining the absolute amount of a target polypeptide in a sample, said method comprising the following steps: (a) adding (aa) a fusion polypeptide to said sample, said fusion polypeptide comprising (i) at least one tag sequence and (ii) a subsequence of the target polypeptide; and (ab) a known absolute amount of a tag polypeptide comprising or consisting of said tag sequence according to (aa) to said sample, wherein said fusion polypeptide on the one hand is mass-altered as compared to said target polypeptide and said tag polypeptide on the other hand, for example, said fusion polypeptide on the one hand and said target polypeptide and said tag polypeptide on the other hand are differently isotope labeled; (b) performing proteolytic digestion of the mixture obtained in step (a); (c) subjecting the result of proteolytic digestion of step (b), optionally after chromatography, to mass spectrometric analysis; and (d) determining the absolute amount of said target polypeptide from (i) the peak intensities in the mass spectrum acquired in step (c) of said fusion polypeptide, said tag polypeptide and said target polypeptide and (ii) said known absolute amount of said tag polypeptide.Furthermore provided is a fusion polypeptide for the quantification of a target polypeptide by mass spectroscopy, wherein: said fusion polypeptide consists of 35 to 455 amino acid residues and comprises (i) a target region, which is a fragment of the target polypeptide, and (ii) a tag region, which is not a fragment of the target polypeptide, said target region consists of 15 to 205 amino acid residues and comprises at least two signature regions; said tag region consists of 20 to 250 amino acid residues and comprises at least two signature regions; and each signature region has the structure Y-Z-X4-28-Y-Z, wherein all Y:s are selected from one of (i)-(iv), wherein (i) is R or K, (ii) is Y, F, W or L, (iii) is E and (iv) is D and each X and each Z are independently any amino acid residue, provided that the Z:s are not P if the Y:s are selected from (i)-(iii); and each signature region comprises at least one amino acid residue comprising a heavy isotope.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Synbiotic feed additive for growing and fattening of pigs, and preparation method and application
InactiveCN108719637AGood for healthPrevent proliferationAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsLean meatIsomaltooligosaccharide
The invention discloses a synbiotic feed additive for growing and fattening of pigs. The synbiotic feed additive is prepared from composite probiotic agents, maltodextrin, isomaltooligosacharide, glucose, citric acid, composite vitamins, composite trace elements, charcoal, attapulgite, leguminosae, dioscorea opposita, poria cocos, atractylodes macrocephala rhizomes, dried unripe fruits of citrus aurantium, common vladimiria roots, Chinese thorowax, dried ripe fruits of crataegus pinnatifida, oblongleaf kadsura stems or roots and bidens pilosa. The invention further provides an application method of the additive. During the growth and fattening period of pigs, the synbiotic feed additive for growing and fattening of pigs is added to a feed according to the addition quantity of the synbioticfeed additive to the body weight of fattening pigs being 0.1-5% for feeding. Through adoption of the synbiotic feed additive for growing and fattening pigs and the application method disclosed by theinvention, the weight increment speed of the body weight of the pigs can be increased, the lean meat proportion is increased, the nutrients are comprehensive, the feed feeding quantity can be reduced, the utilization rate of the feed can be increased, the growth speed of the pigs is high, the meat quality is bright red, tender in nature and good in mouth feel, the economic benefits are increased,and the synbiotic feed additive has good application prospects.
Owner:广西青又青生物肥业有限公司
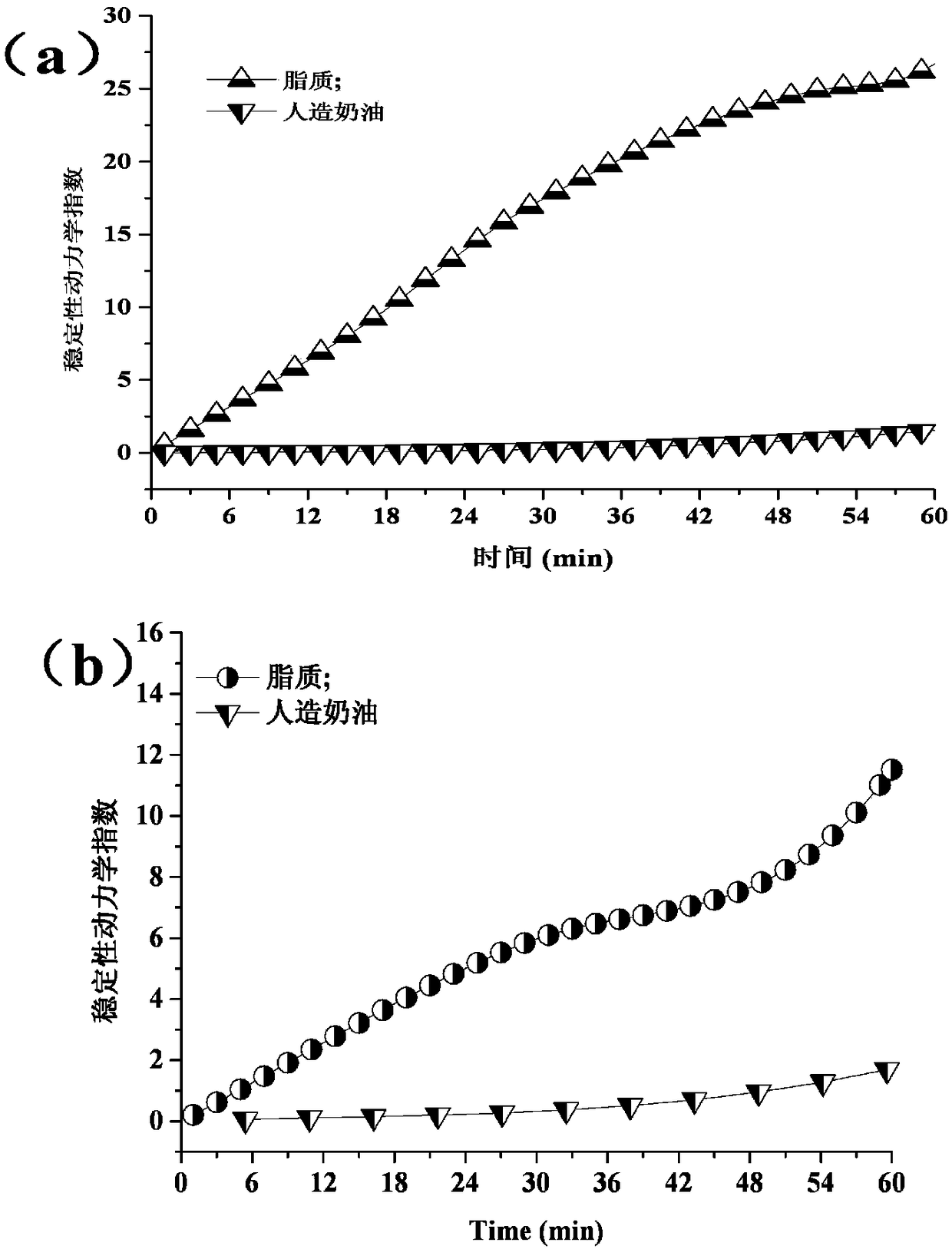
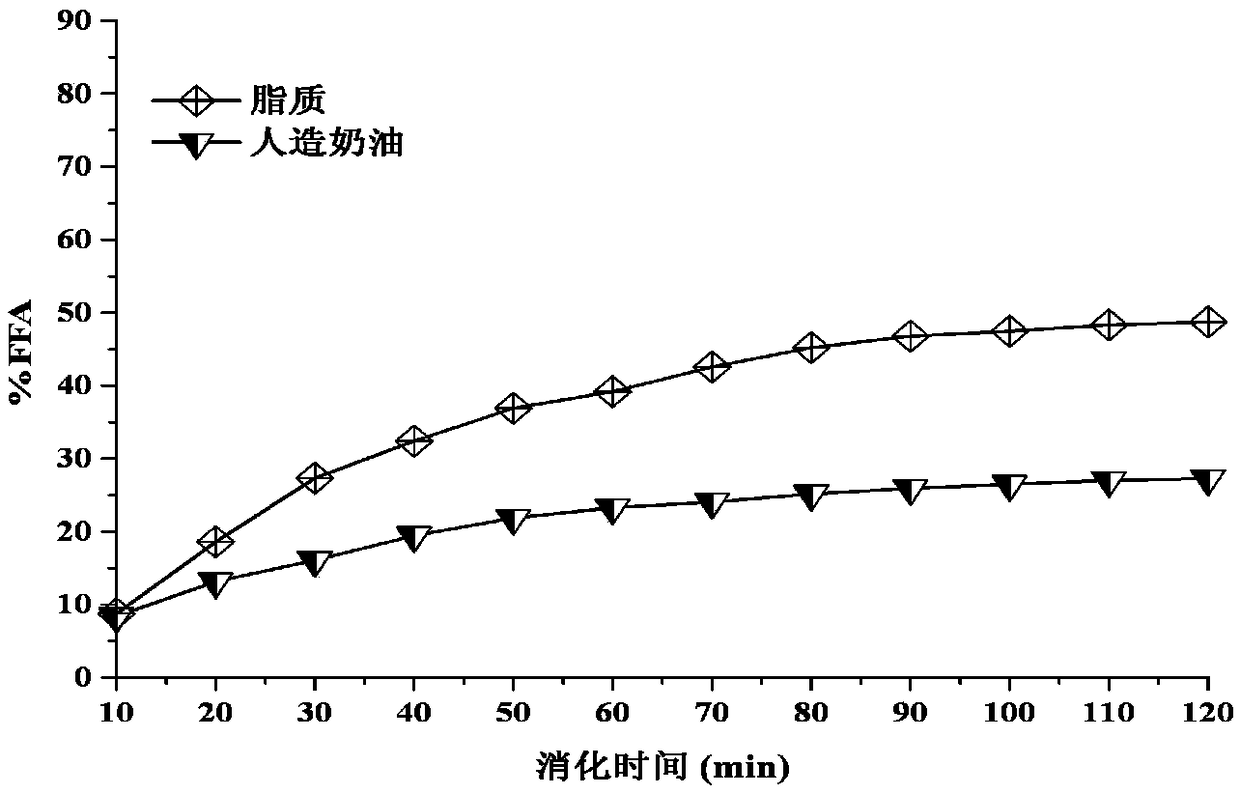
Low-fat low-lipide-digestibility artificial butter and making method thereof
The invention discloses low-fat low-lipide-digestibility artificial butter. The low-fat low-lipide-digestibility artificial butter comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-70 parts ofmicronized whey protein dispersed liquid, 10-30 parts of a xanthan gum system, and 10-60 parts of oil phase. The artificial butter not only has the characteristic of being low in fat (10-60%), but also can restrain contact of lipases and oil drops in digestive tracts of human bodies, and can prevent free fatty acids from being released, so that the lipide digestibility can be reduced. According to a method, whey protein and xanthan gum are used as raw materials, and damp and hot treatment, a micronizing technique, a compounding technique and an emulsifying homogenizing technique are adopted for preparing oil in water emulsion. The digestion suppression ratio of the artificial butter for lipide is as high as 60%. The low-fat low-lipide-digestibility artificial butter has smooth and soft mouth feel of butter, and white fine and smooth appearance, has similar processing characteristics of plasticity, stability and the like as cream sold in the market, and can be widely applied to processing of various foods through replacing cream.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methods of improving the introduction of DNA into bacterial cells
The present invention relates to methods of improving the introduction of DNA into bacterial host cells.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
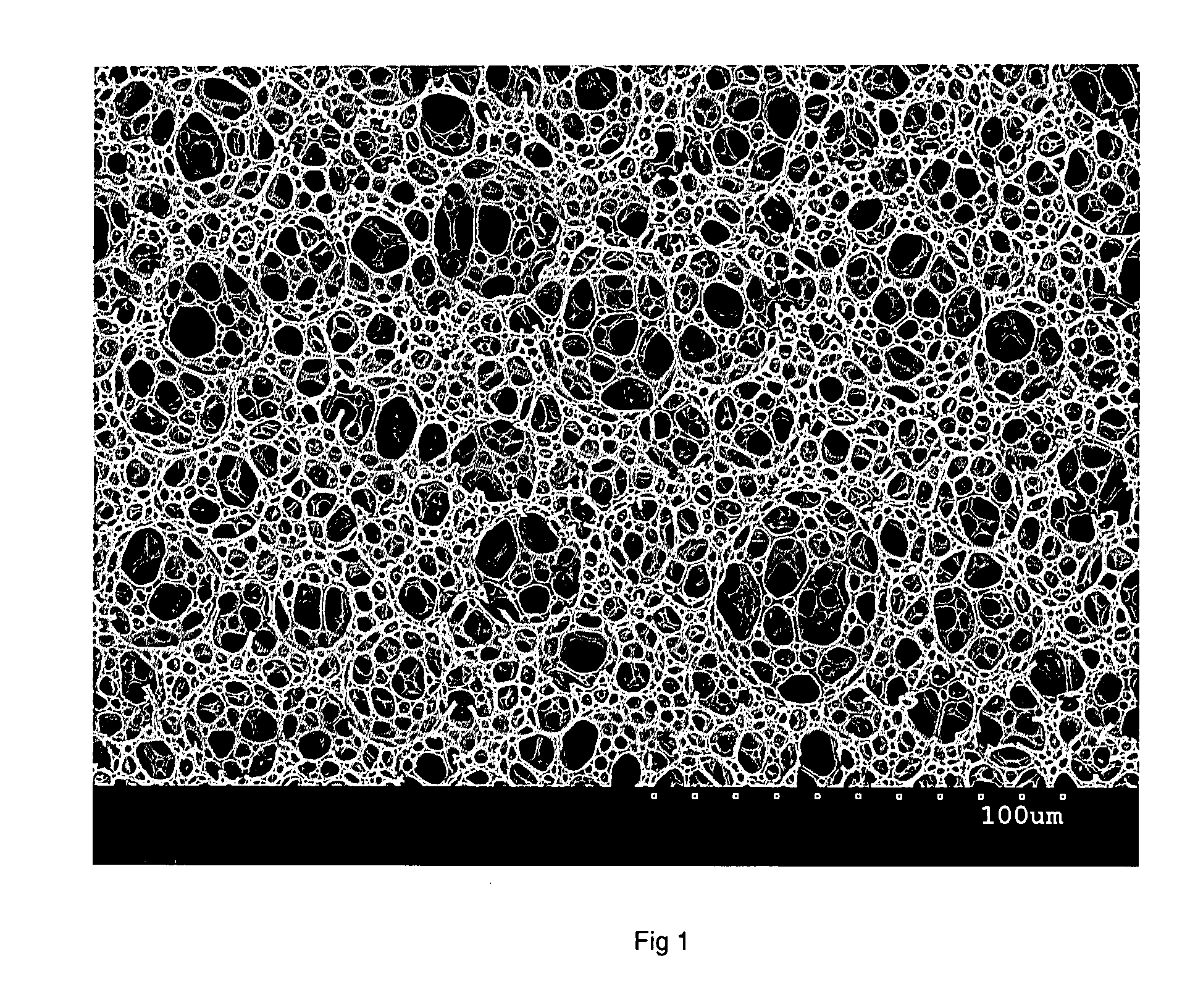
Use of non-digestible polymeric foams to sequester ingested materials thereby inhibiting their absorption by the body
InactiveUS20080075688A1Reduce the amount requiredInhibiting anal leakageDigestive systemSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsSide effectLipase inhibitors
This disclosure relates to compositions comprising an open-celled polymeric foam wherein the compositions are useful for sequestering lipophilic materials present in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby inhibiting the absorption of such lipophilic materials by the body. The disclosure further relates to compositions comprising the open-celled polymeric foam wherein the compositions are useful for ameliorating side effects associated with the use of lipase inhibitors. In a preferred embodiment, this disclosure relates to compositions comprising polymeric foam materials made from high internal phase emulsions, where such foams are useful for sequestering lipophilic materials. Further disclosed are compositions comprising open-celled polymeric foams wherein the compositions are useful for the purpose of sequestering aqueous and / or hydrophilic materials present in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby ameliorating diarrhea. Kits comprising the compositions and methods of using the compositions and kits are also described.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Composition having effects of reducing fat and blood sugar, as well as preparation and application of composition
InactiveCN108095113ADelayed decomposition and absorptionReduce decomposition and absorptionFood ingredient as taste affecting agentNatural extract food ingredientsSide effectBlood sugar
The invention discloses a composition having effects of reducing fat and blood sugar. The composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-50 parts of a navy bean extract, 0-20 parts of a green tea extract, 0-30 parts of L-carnitine, 0-30 parts of L-arabinose, and 0-30 parts of composite probiotics. The invention further provides a preparation and preparation method of the composition, and an application of the composition in preparation of functional foods having the effect of reducing weight. The composition has the characteristics that the composition does not influencethe appetite of consumers and does not change the food habit of the consumers, the effects of reducing blood sugar, and reducing fat and weight can be effectively realized, and the composition does not damage health of the consumers, can strengthen the exercise tolerance, can prevent cardiovascular diseases, is free from side effects, and can be used for a long term.
Owner:CHENGDU BOCHUANG BICHENG MEDICAL TECH
Synbiotic feed additive for pregnancy sows as well as preparation method and application
InactiveCN108338258AGood for healthPrevent proliferationAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsMiscarriageIsomaltooligosaccharide
The invention discloses a synbiotic feed additive for pregnancy sows. The synbiotic feed additive is prepared from a composite probiotic agent, maltodextrin, isomaltooligosacharide, glucose, citric acid, complex vitamins, radix astragali, honeysuckle flowers, bighead atractylodes rhizomes, rhizoma atractylodis, cortex magnoliae officinalis, katsumada galangal seeds, Chinese mugwort, semen cuscutae, Chinese taxillus herb and crispateleaf ardisia roots, wherein the composite probiotic agent is a mixture of enterococcus faecium, microzymes, bacillus subtilis and bacillus coagulans. The inventionfurther provides an application method of the additive. During period of pregnancy of sows, the feed additive is added to feeds according to the addition quantity that the added feed additive is 0.3-5% of the weight of the pregnancy sows for feeding. The feed additive has the efficacy of preventing miscarriage, promoting delivery, nourishing the liver, supplementing qi, resisting bacteria, diminishing inflammation, being nutritive and health-care and the like, is free from toxic and side effects, and can be used as a feed additive to be added to a feed for the pregnancy sows for feeding. The feed additive can improve the constitutions of the pregnancy sows in essence, the immunity and the stress resistance of the pregnancy sows can be improved, the spontaneous delivery rate of the sows canbe greatly increased, and improving of quality of piglets produced by the sows can be facilitated.
Owner:广西青又青生物肥业有限公司
Weight-losing tablet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107307406AReduce synthesisReduce intakeFood shapingFood ingredient functionsWeight decreasingNutrient
The invention discloses a weight-losing tablet and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of weight-losing medicines. The weight-losing tablet is prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 20 to 25 parts of white kidney bean, 30 to 35 parts of tangerine, 20 to 25 parts of raspberry fruit, 5 to 8 parts of opuntia ficus, 5 to 8 parts of folium nelumbinis, 1 to 2 parts of xylitol, 1 to 2 parts of sorbitol, 1 to 2 parts of sucralose, 2 to 5 parts of microcrystalline cellulose, 1 to 2 parts of magnesium stearate, and 0.3 to 0.5 part of edible essence. The preparation method is characterized in that in the granulating process, a granulating device by using edible vinegar as a huddling liquid is adopted. The weight-losing tablet has the advantages that the functions of controlling body weight, decreasing body lipid and reducing weight are realized; the intestine functions are regulated; the functions of resisting oxidizing and delaying aging are realized; the glycemic index of foods is reduced, and the blood glucose value is balanced; the heat absorbing is controlled; the blood lipid is regulated, the fat settling of artery is inhibited, the multiple functions of improving the health of cardiovascular vessels and the like are realized, the health and safety effects are realized, the nutrients required by a human body are maintained, and the red-face, luster-skin, health and nature effects are realized.
Owner:HUNAN KANG QI YI BAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing peptide fragments, kit for preparing peptide fragments to be used therein, and analysis method
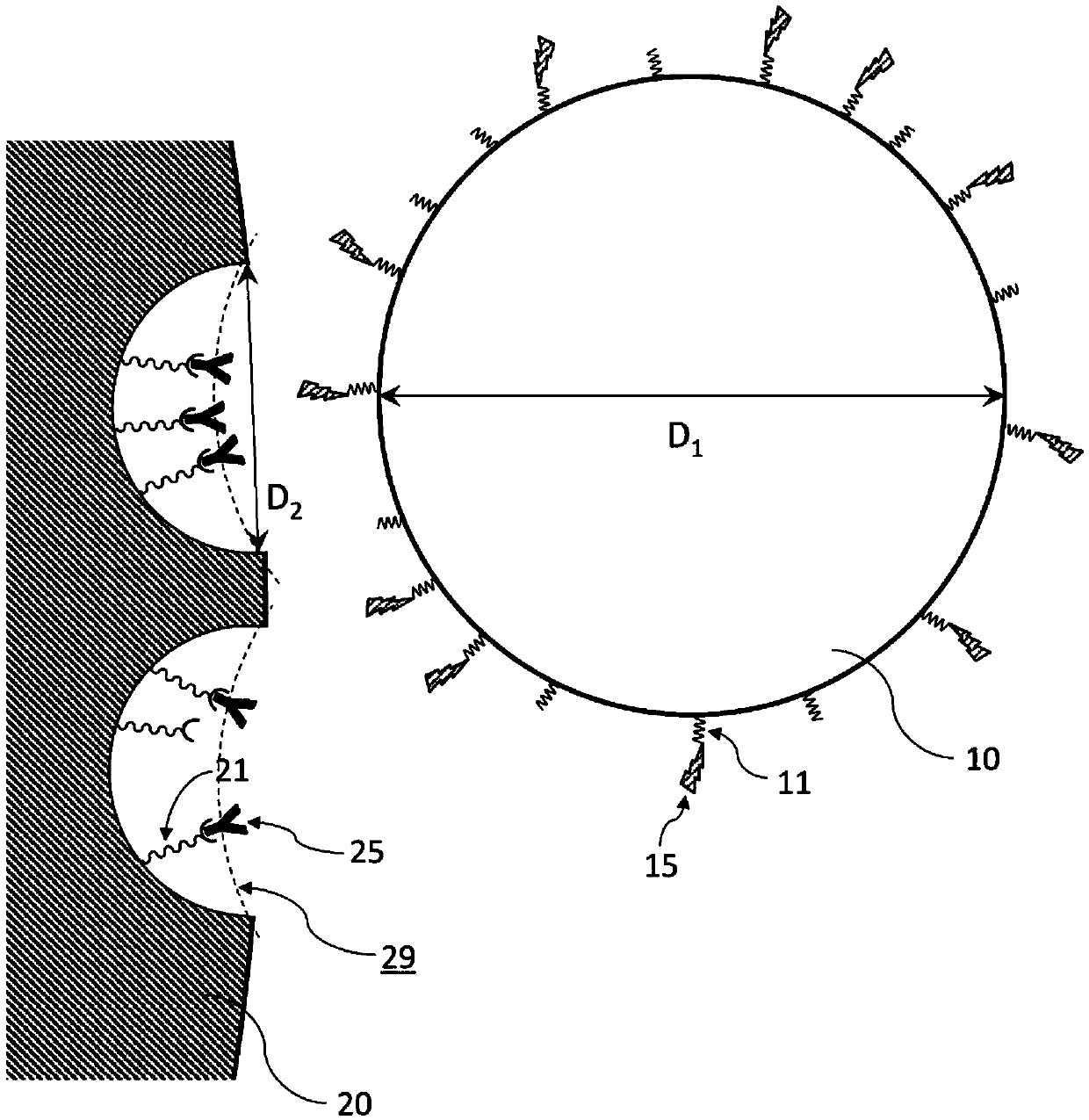
ActiveCN105518447ASimplify condition settingImprove analysis accuracyImmobilised enzymesPreparing sample for investigationViral matrix proteinProtein protein
A method for preparing peptide fragments by cleaving a protein using a protease. The method according to the present invention comprises a step for contacting, in a liquid, a porous body (20), in which the substrate protein (25) to be cleaved is immobilized in pores (29), with microparticles (10) which carry the protease (15) immobilized on the surface thereof. In the present invention, the average particle diameter of the microparticles (10) is larger than the average pore diameter of the porous body (20). According to the method of the present invention, the substrate protein (25) that is an antibody can be site-specifically cleaved. By analyzing the peptide fragments that are obtained by the above method by mass spectrometry, etc., the antibody protein can be detected or quantitatively analyzed.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Medicine combination with antiobesity effects
InactiveCN104208488AInhibit digestionAvoid absorptionPre-extraction tea treatmentMetabolism disorderCannabisAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a medicine combination with antiobesity effects. The medicine combination is made of the following raw materials, which serve as active ingredients and include, by weight part, 12-24 parts of fructus cannabis, 12-24 parts of hawthorn, 12-24 parts of lotus leaves, 9-21 parts of tea leaves, 9-12 parts of corn stigma and 9-21 parts of plantains. The medicine combination with the antiobesity effects can achieve good antiobesity effects and functions.
Owner:李成娇
Hybrid boar fodder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106819494APromote growth and developmentImprove the immunityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsSodium bicarbonateBiotechnology
The invention provides a hybrid boar fodder and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of poultry feeding. The hybrid boar fodder comprises a primary material, an auxiliary material and a fodder additive, wherein the primary material comprises corn, fish meal, bean pulp, egg powder, a biological fermentation fodder and wheat bran; the auxiliary material comprises phytase, an antioxidant, a mildew preventive, mildew decomposer, choline, sodium bicarbonate, multi-vitamins, compound organic microelement, calcium hydrophosphate, mountain flour and salt; and the fodder additive comprises coconut oil, soya-bean oil and a healthcare agent. After the hybrid boar is fed with the fodder, the quality of the seminal fluid of the hybrid boar can be increased; the technical problems of low yield and poor reproductive capacity of the hybrid boar caused by less seminal fluid, low sperm viability and teratospermia of the hybrid boar can be solved; and the technical effects of increasing the semen quality and increasing the conception rate of the hybrid boar can be achieved.
Owner:湖南赛福资源饲料科技有限公司
Collagen milk tea solid beverage and eating method thereof
The invention discloses a collagen milk tea solid beverage and an eating method thereof, and relates to the technical field of solid beverages. The collagen milk tea solid beverage comprises 13-21 parts of whole milk powder, 8-15 parts of instant black tea powder, 21-42 parts of plant fat powder, 14-35 parts of a compound solid beverage nutrition enhancer, 10-34 parts of sorbitol, 4-9 parts of N-acetylneuraminic acid, 2-6 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 0.5-3 parts of ethyl maltol, 0.5-2 parts of edible salt, 2-10 parts of sucralose, 2-7 parts of acesulfame potassium, 1-3 parts of resistant dextrin, 1-3 parts of citrus fibers, 1-9 parts of hydrolyzed fish collagen, 0.5-1 part of salmon protein powder and 3-6 parts of edible mushroom concentrated powder. The resistant dextrin, the citrus fiber, the hydrolyzed fish collagen, the salmon protein powder, the edible mushroom concentrated powder, the N-acetylneuraminic acid and other auxiliary materials are matched to prepare the beverage capable of supplementing the influencing components of the human body; the effects of accelerating body metabolism, keeping the skin moist and elastic, reducing wrinkles, inhibiting virus invasion and the like are achieved.
Owner:美蓓(北京)医学咨询有限公司
Pharmaceutical composition with antiobesity action
ActiveCN102423374BAppetite suppressantInhibit digestionMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsPEARBiotechnology
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition with antiobesity action. The pharmaceutical composition is prepared from 3-6 parts of oolong, 1-3 parts of pomegranate bark, 2-4 parts of lotus leaf and 1-2 parts of balsam pear; in addition, 1-2 parts of apple or 1-2 parts of passionflower and 1-2 parts of citrus aurantium can be added; and meanwhile, the raw materials can be replaced by corresponding plant extracts. The pharmaceutical composition is prepared through taking sufficient consideration to the combination of the theories and the experiments of the traditional Chinese medicine, is not the simple combination of the raw materials, but the combination of different weight-reducing mechanisms; through the compatibility of the raw materials and a lot of comparative experiments, the formulation has the antiobesity action outdistancing that of a single drug prescription, and an effect that the sum of one plus one is greater than two is achieved; and furthermore, the traditional Chinese medicines are adopted as the raw materials, so that the pharmaceutical composition with the antiobesity action is safe and reliable and has an outstanding curative effect.
Owner:GUILIN NATURAL INGREDIENTS CORP
A kind of slimming tablet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107307406BReduce synthesisReduce intakeFood shapingFood ingredient functionsGlycaemic indexSucrose
The invention discloses a weight-losing tablet and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of weight-losing medicines. The weight-losing tablet is prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 20 to 25 parts of white kidney bean, 30 to 35 parts of tangerine, 20 to 25 parts of raspberry fruit, 5 to 8 parts of opuntia ficus, 5 to 8 parts of folium nelumbinis, 1 to 2 parts of xylitol, 1 to 2 parts of sorbitol, 1 to 2 parts of sucralose, 2 to 5 parts of microcrystalline cellulose, 1 to 2 parts of magnesium stearate, and 0.3 to 0.5 part of edible essence. The preparation method is characterized in that in the granulating process, a granulating device by using edible vinegar as a huddling liquid is adopted. The weight-losing tablet has the advantages that the functions of controlling body weight, decreasing body lipid and reducing weight are realized; the intestine functions are regulated; the functions of resisting oxidizing and delaying aging are realized; the glycemic index of foods is reduced, and the blood glucose value is balanced; the heat absorbing is controlled; the blood lipid is regulated, the fat settling of artery is inhibited, the multiple functions of improving the health of cardiovascular vessels and the like are realized, the health and safety effects are realized, the nutrients required by a human body are maintained, and the red-face, luster-skin, health and nature effects are realized.
Owner:HUNAN KANG QI YI BAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Novel prongf mutants and uses thereof in the production of beta-ngf
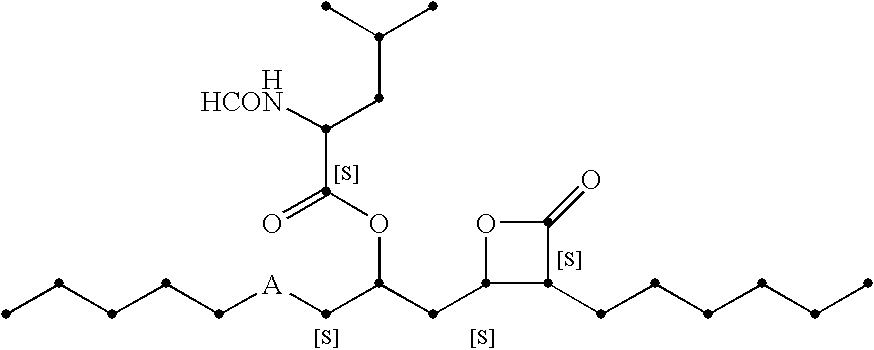
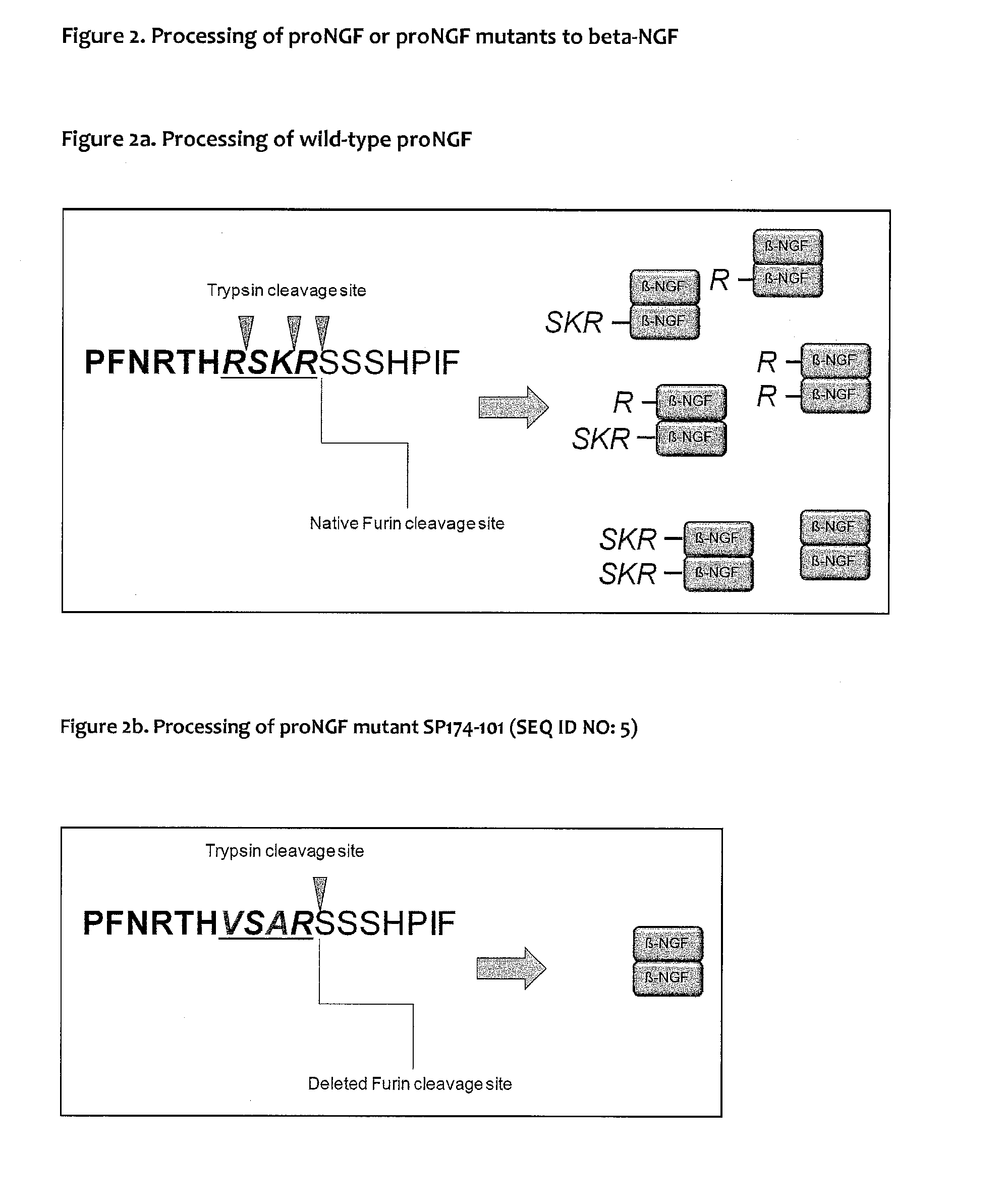
ActiveUS20150087020A1High yieldInhibit digestionSenses disorderNervous disorderNGF productionProteinase activity
The present invention relates to a proNGF mutant and to uses thereof, in particular the use of a proNGF mutant for producing human beta-NGF. The present invention discloses a method of preparing a biologically active human beta-NGF from an inactive insoluble proNGF mutant. A proNGF mutant of the invention is substituted by any amino acid but not Arg or Lys at the native protease cleavage site R1SK3R4 at least at positions R1 and K3 corresponding to positions 101 and 103 of the human wildtype proNGF sequence.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
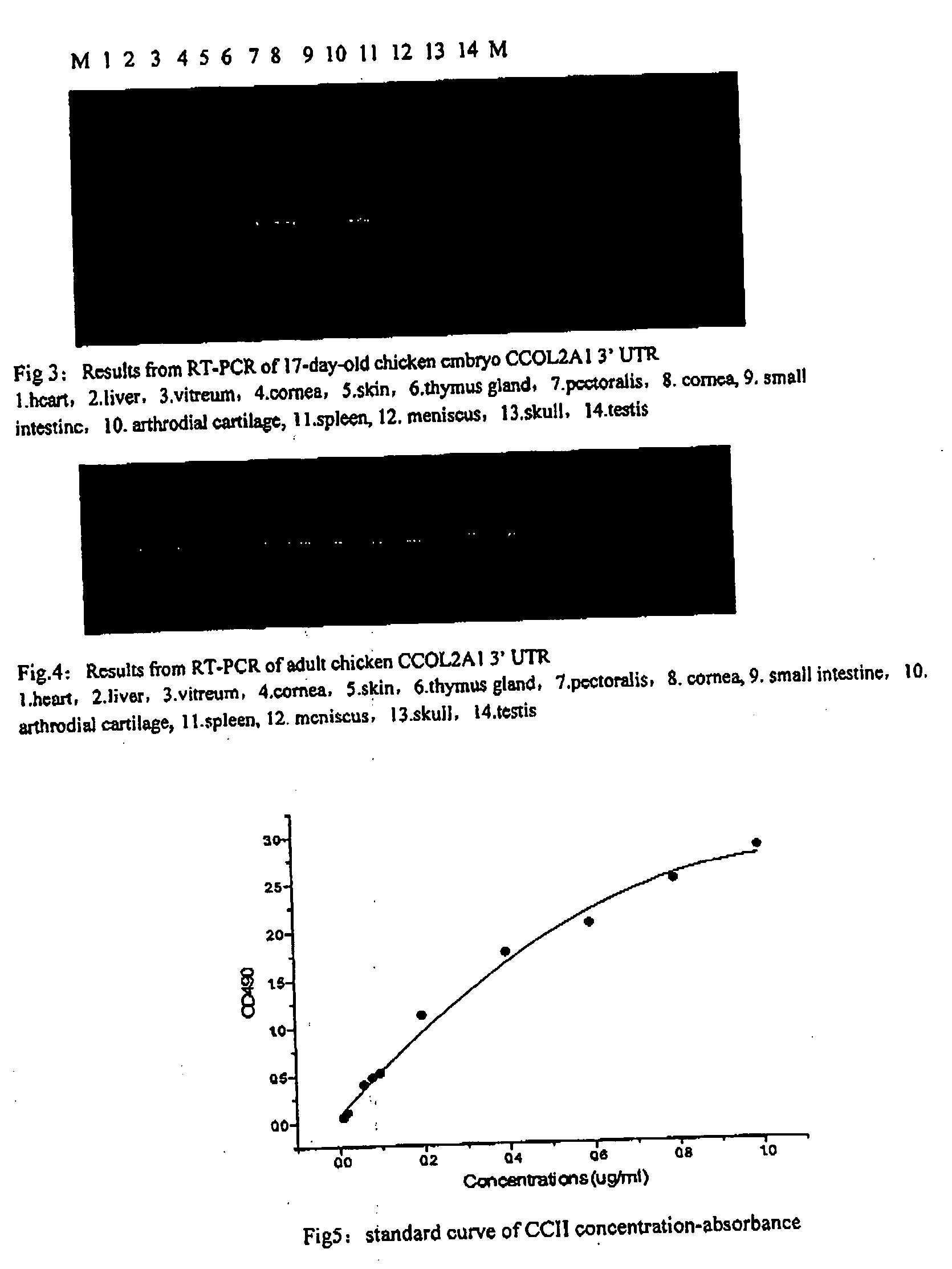
Full length polynucleotide coding chicken type II collagen and the use of it
InactiveUS20060276383A1Remarkable effectGood curative effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticFood additiveBiotechnology
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule as set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 comprising a polynucleotide sequence encoding full length chicken type II collagen (CCII), or a fragment thereof in possession of the same biological functions as well as CCII encoded thereof. It also relates to a method for producing CCII, and its use in the manufacture of a medicament for treating and / or preventing rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The invention specifically relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treating and / or preventing osteoarthritis and RA, to a food or beverage composition, and to a food additive composition, containing CCII prepared according to the method described in this invention, and the use of the nucleic acid molecules of the present application in gene therapy.
Owner:THE FIFTH MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
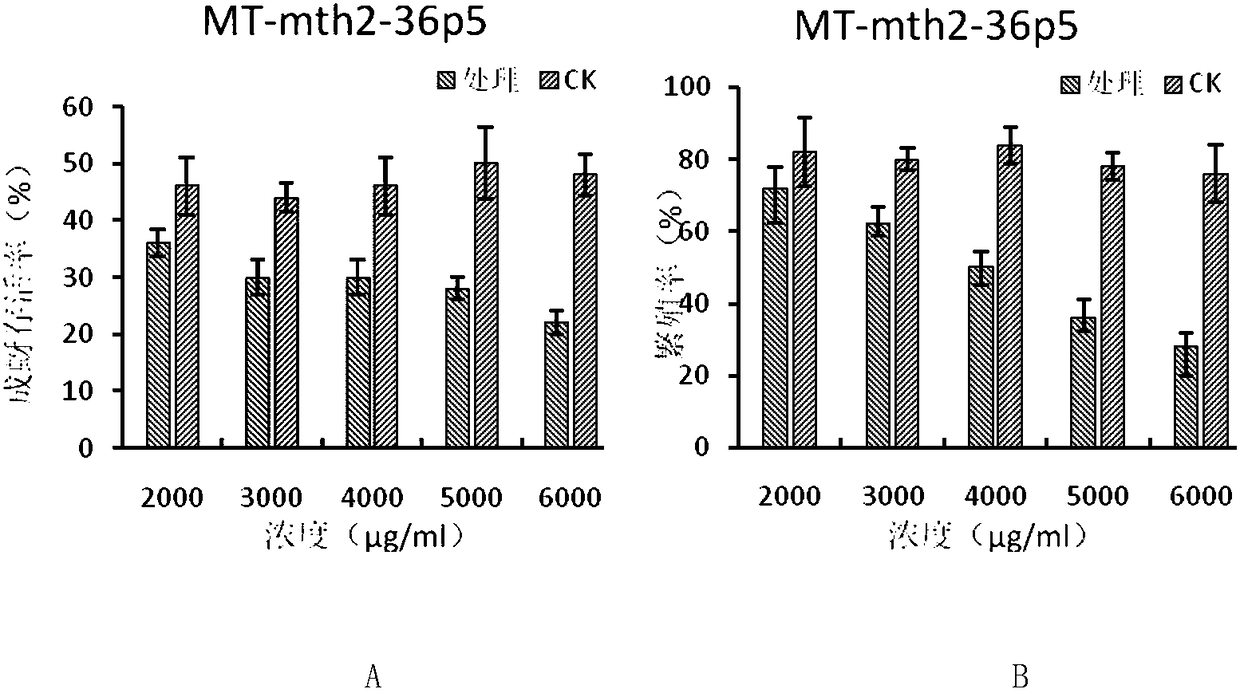
Medicago sativa trypsin inhibitor MT-mth2-36p5 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108059671AWide range of insect resistanceNarrow anti-insect spectrumBiocideProtease inhibitorsAgricultural scienceN-terminus
The invention discloses a medicago sativa trypsin inhibitor MT-mth2-36p5 as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The medicago sativa trypsin inhibitor MT-mth2-36p5 is a protein of a), b),c) or d), namely, a) a protein with the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2, b) a fusion protein obtained by connecting labels to the N end and / or the C end of the protein shown in the sequence 2, c) a protein with the same functions obtained by performing replacement and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2 andd) a protein with 75% or more homology as the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2 and the same functions. Experiments show that the protein has a good inhibition effect on therioaphis trifoliiand an inhibition effect on the survival rate and the reproduction rate of aphids and can be used for controlling and preventing the aphids.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Liquid state binder capable of reinforcing iron ore sintering, its preparation and its application method
The invention relates to a liquid state binder capable of reinforcing iron ore sintering, its preparation and its application method. The liquid state binder is prepared by the steps that redispersible latex powder, anionic polyacrylamide, silica sol with SiO2 having mass fraction of 30%-60% and water are mixed according to the proportion of 0.5-1.5: 1.0-2.0: 25-40: 56.5-73.5, uniformly stirred under the condition that the temperature is 50-80 DEG C and the pH value is 8-10 to prepare the product. the liquid state binder is used for sintering, the addition proportion accounts for 0.5-1.5% of total weight of the sintering raw material. Because the liquid state has the advantages of good dispersibility and strong adhesion stress, is capable of improving the granulation effect of the iron ore, raising heat stability of small granulating balls, greatly improving the permeability of a material layer during the sintering process, raising the sintering speed by 1.5-4mm / min and the utilization coefficient by 0.10-0.4t / (m<2>.h), and simultaneously ensuring the little change of the tumble strength of the sintered ore.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com