Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112results about How to "Increase energy content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
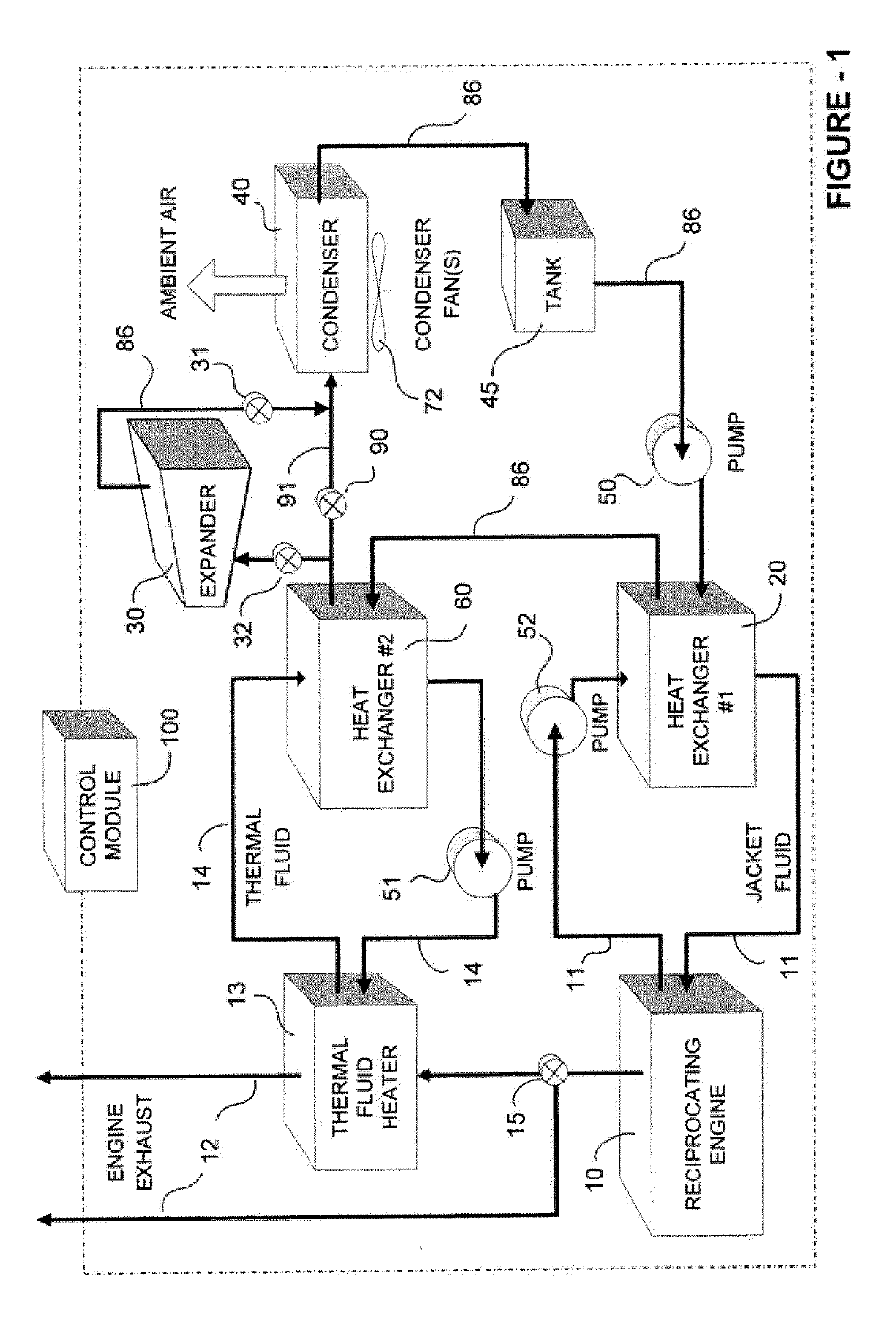
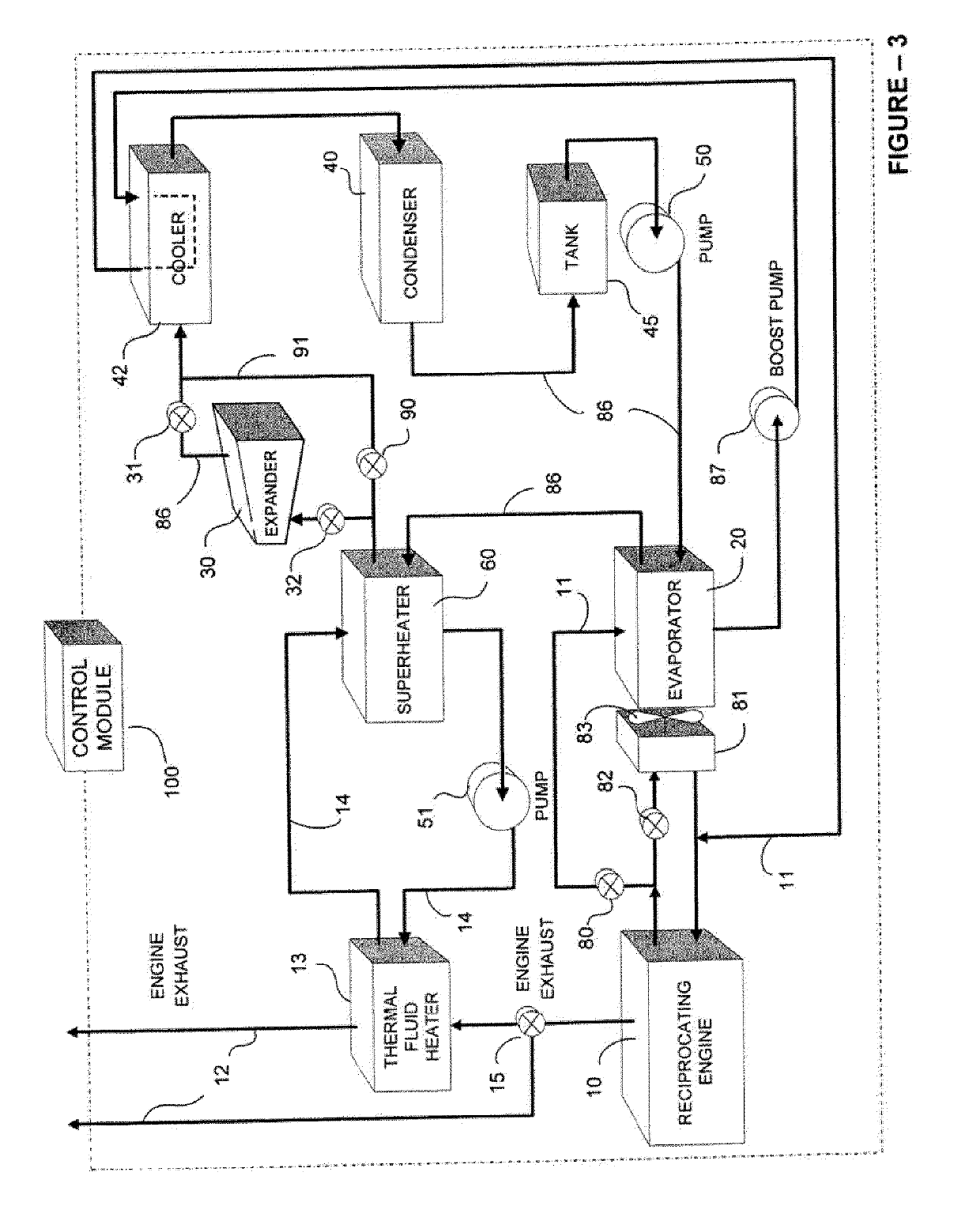
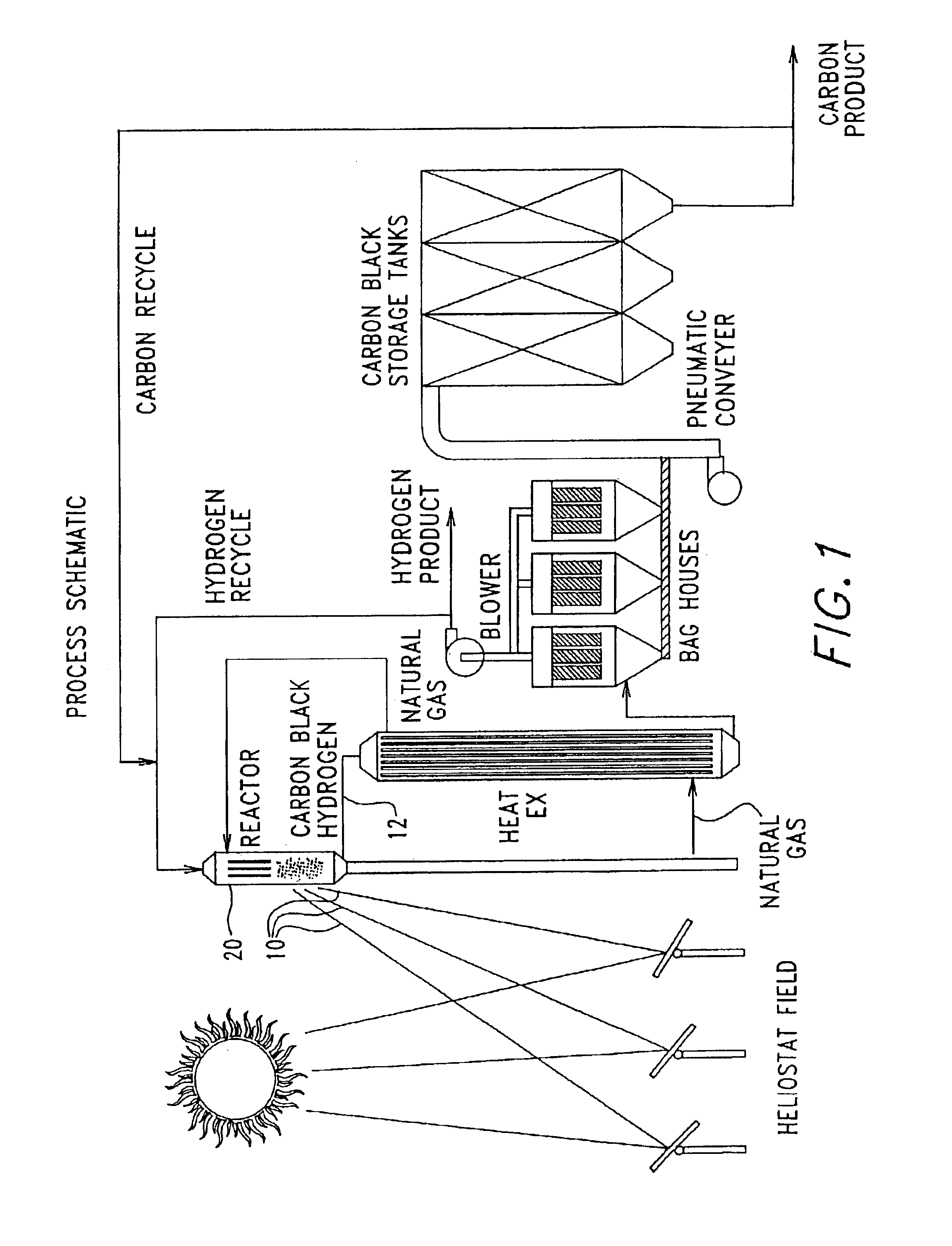
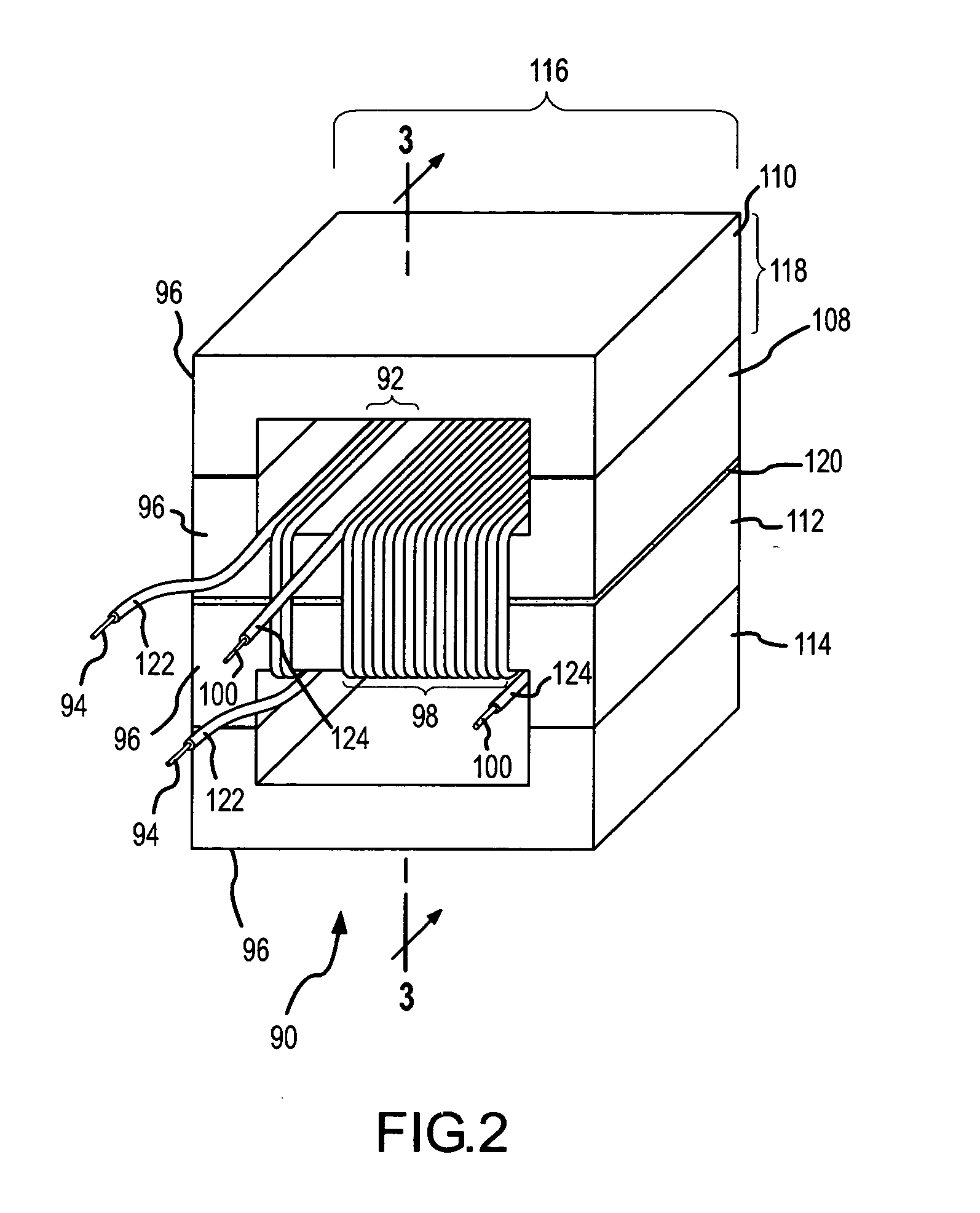
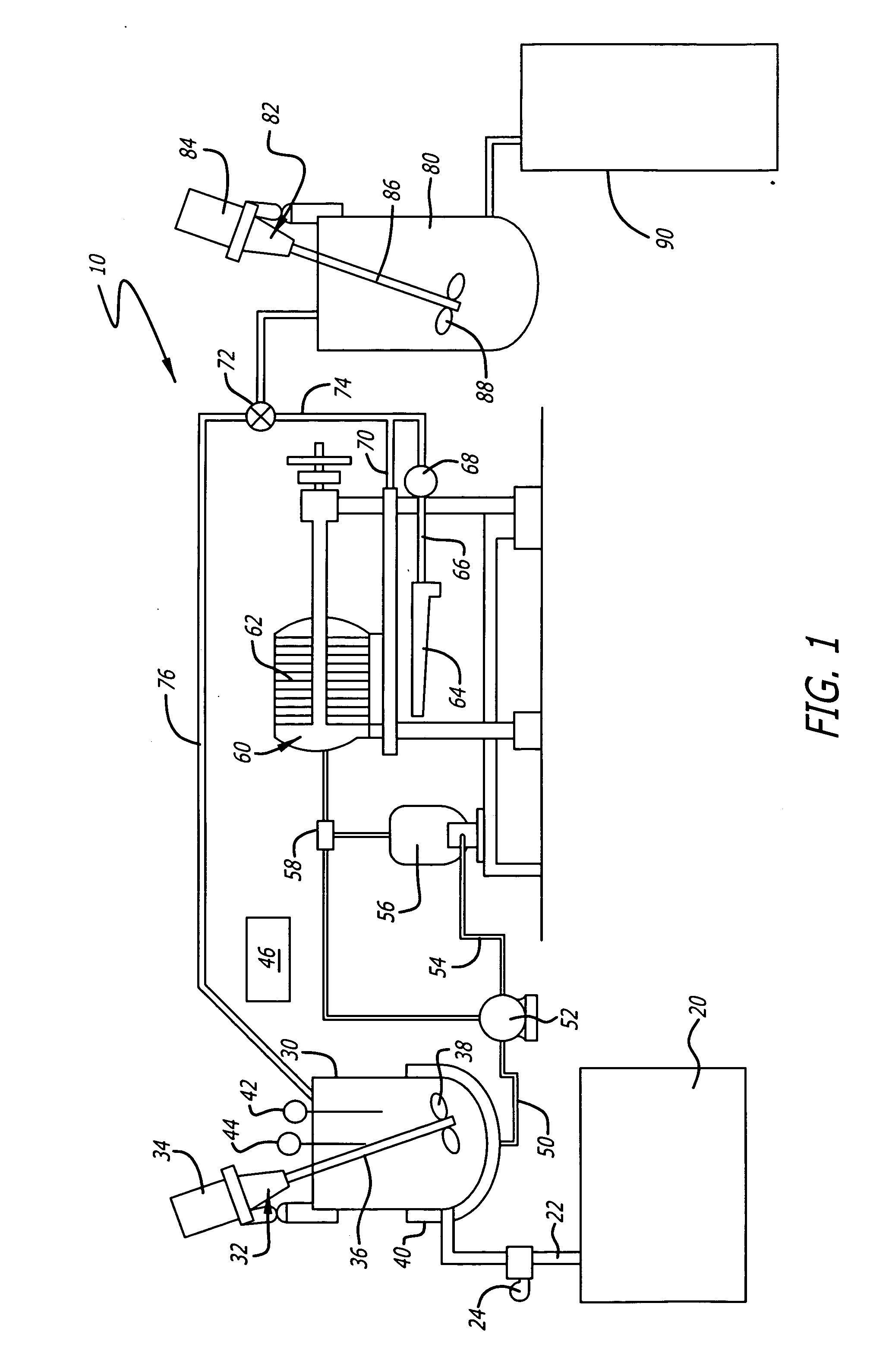
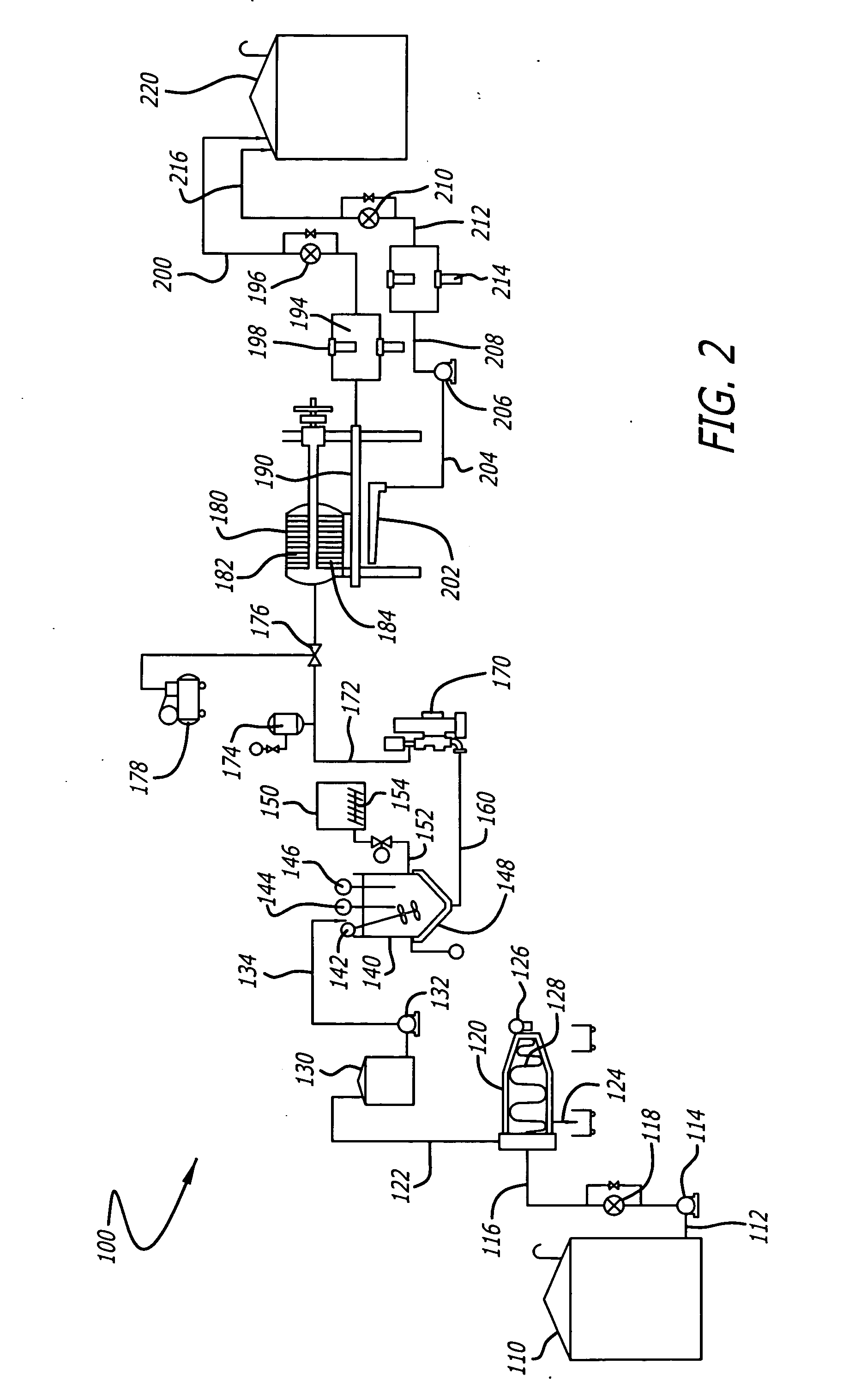
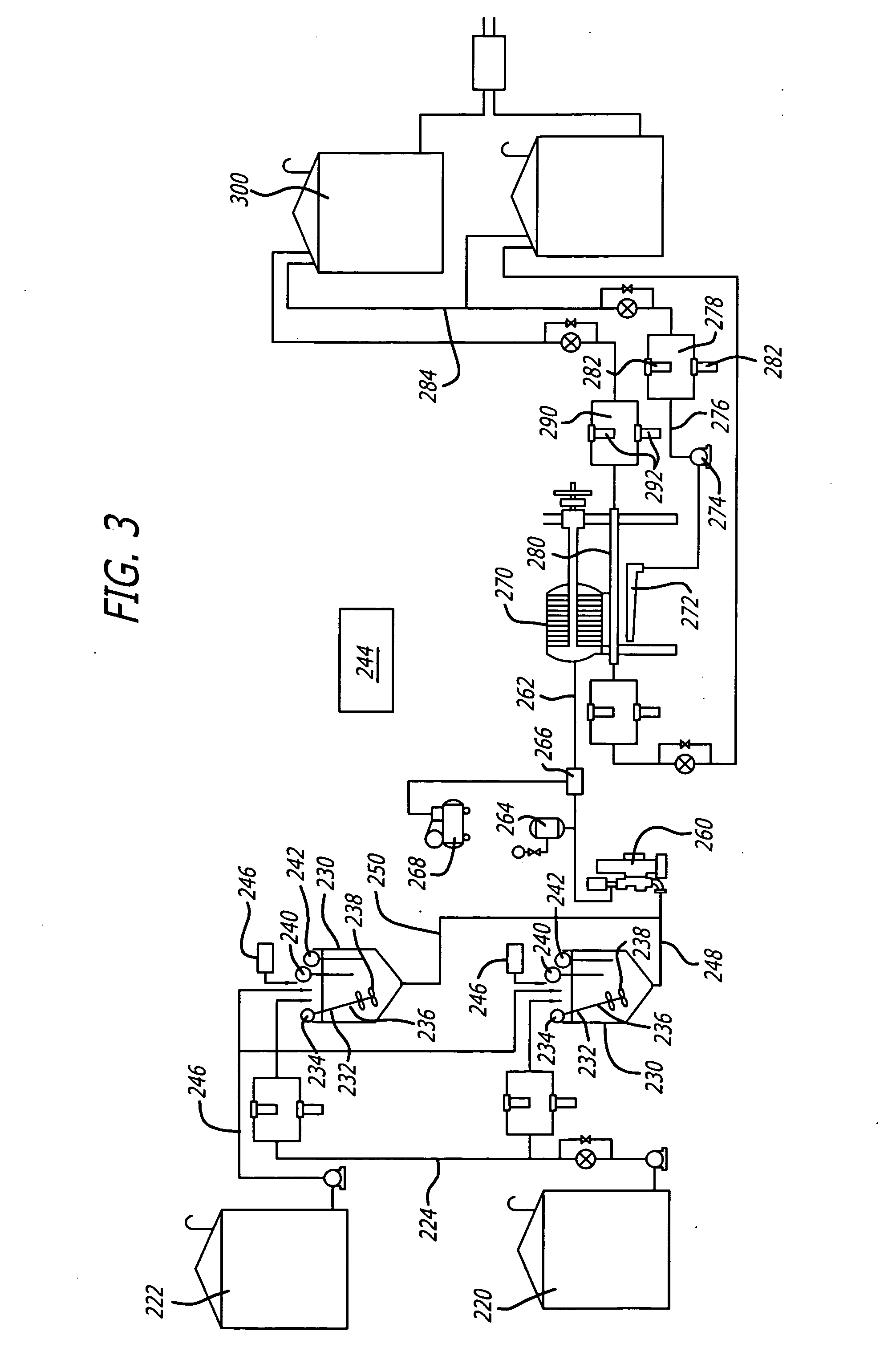
Supplementary Thermal Energy Transfer in Thermal Energy Recovery Systems
ActiveUS20090320477A1Maximize power generationIncrease energy contentSteam engine plantsMechanical energyEngineering
A system for controlled recovery of thermal energy and conversion to mechanical energy. The system collects thermal energy from a reciprocating engine (for example, from engine jacket fluid) and may also collect further thermal energy from a natural gas compressor (for example, from compressor lubricating fluid). The collected thermal energy is used to generate secondary power by evaporating an organic propellant and using the gaseous propellant to drive an expander in production of mechanical energy. Secondary power is used to power parasitic loads, improving energy efficiency of the system. A supplementary cooler may provide additional cooling capacity without compromising system energy efficiency.
Owner:JUCHYMENKO VICTOR
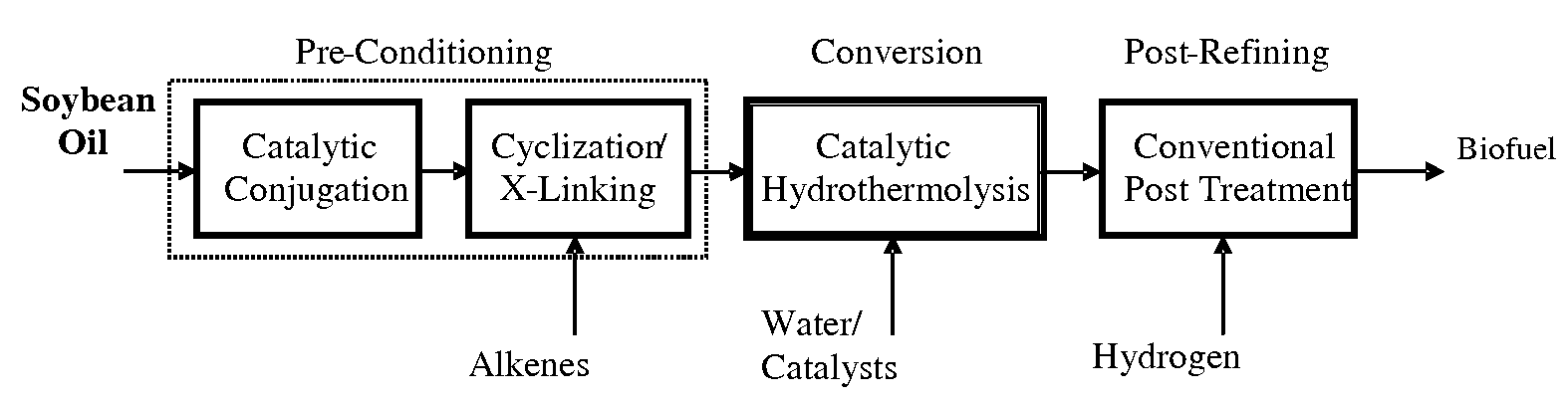
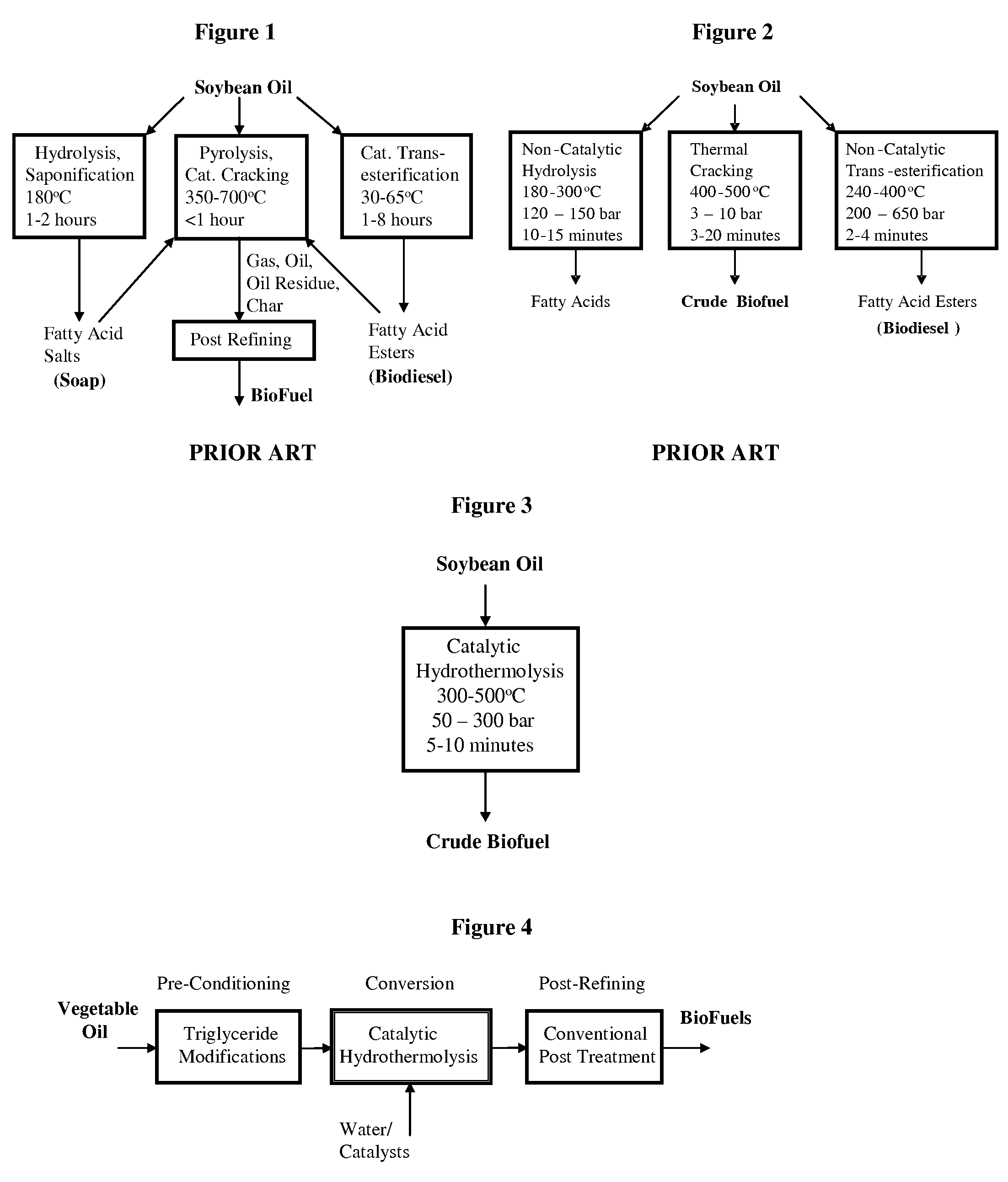
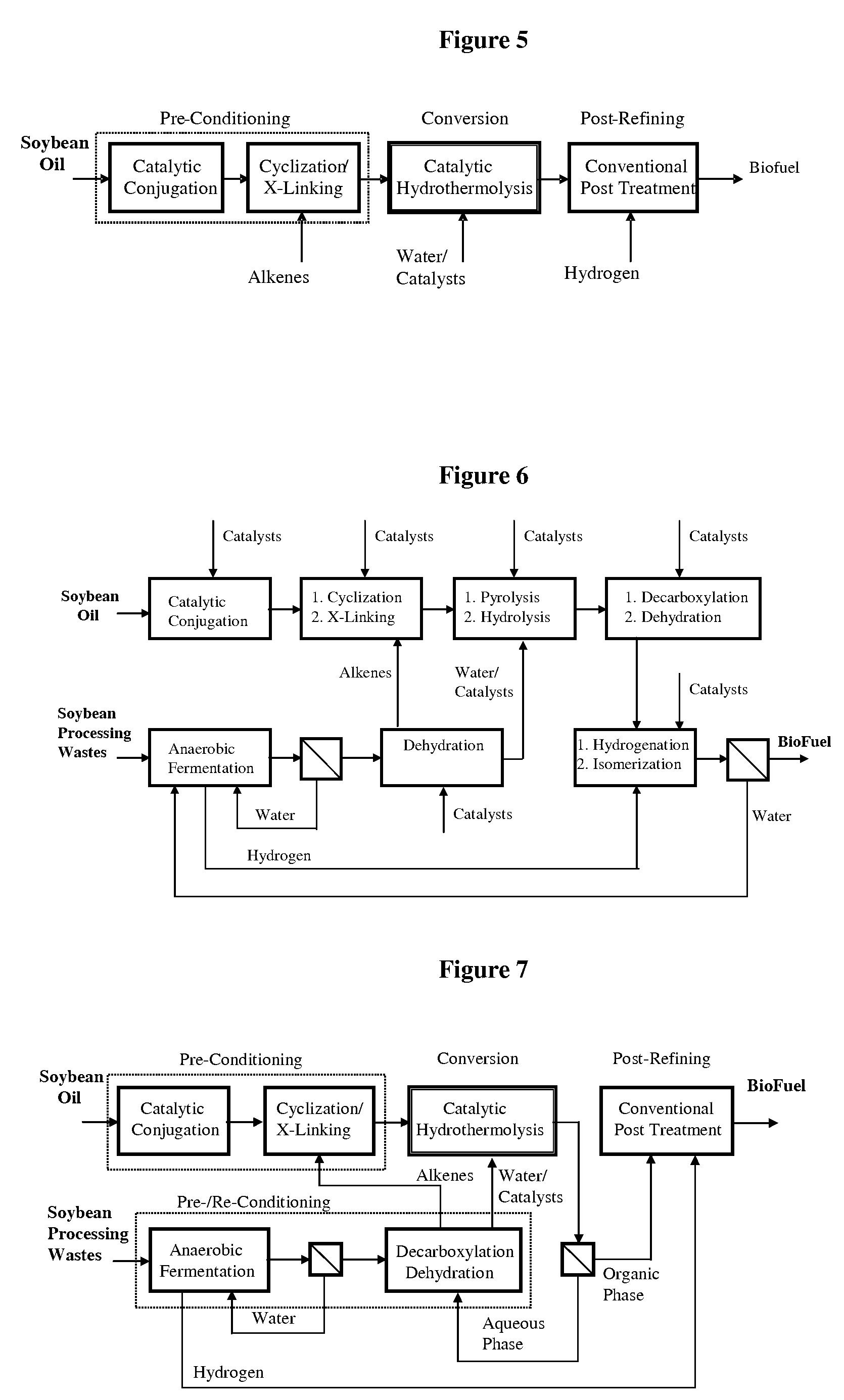
Method of converting triglycerides to biofuels
ActiveUS7691159B2Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkIsomerization
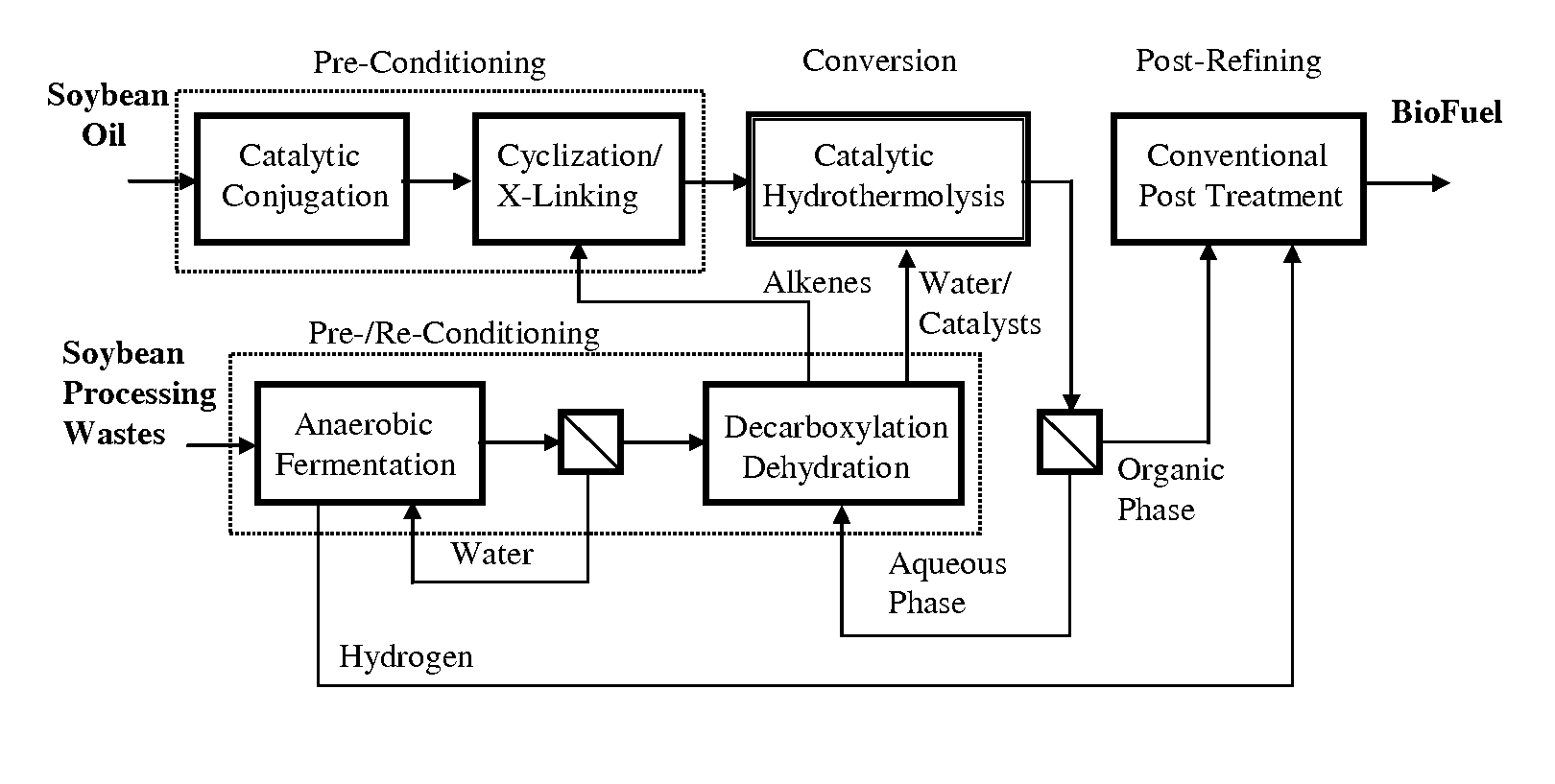
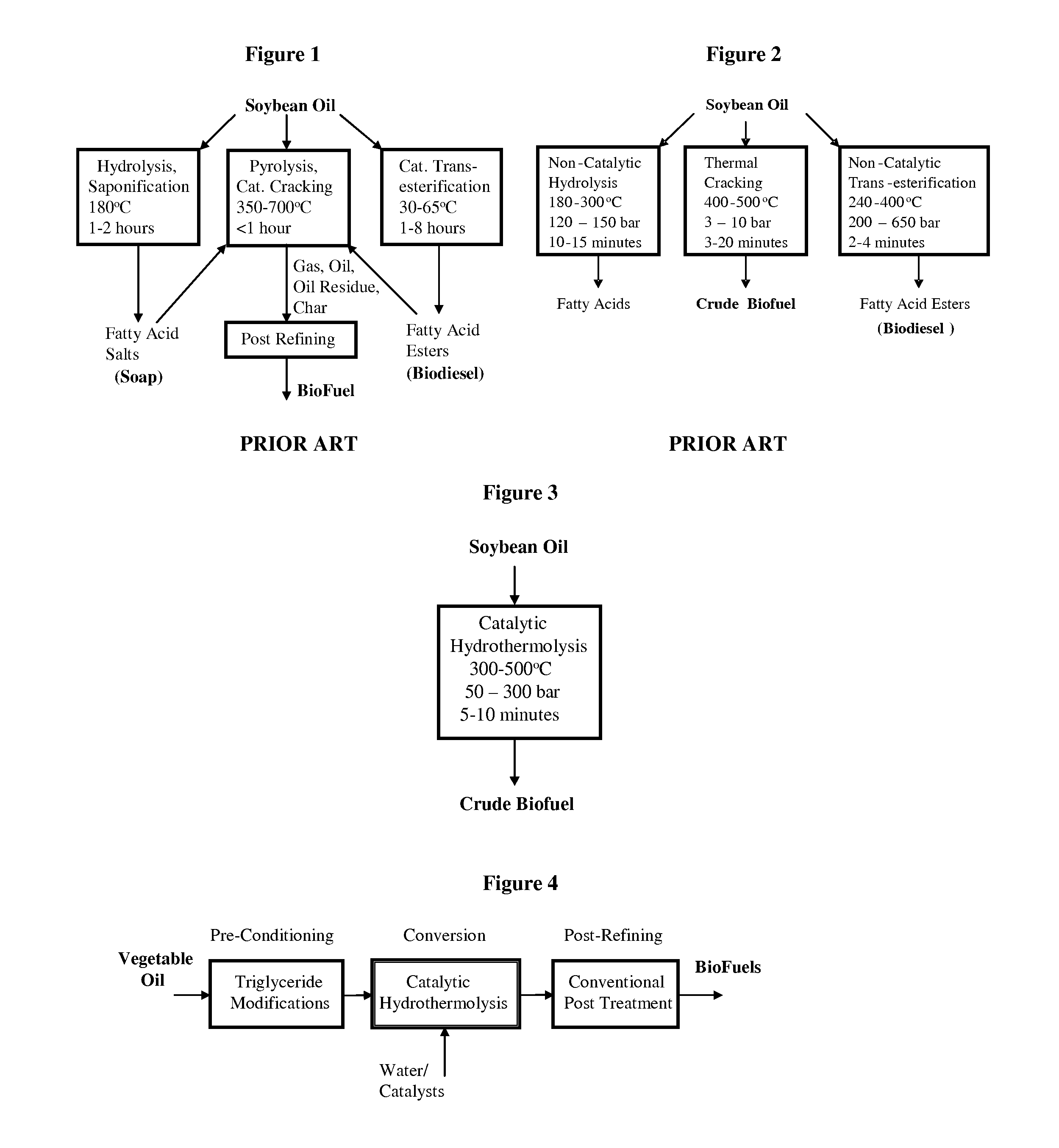
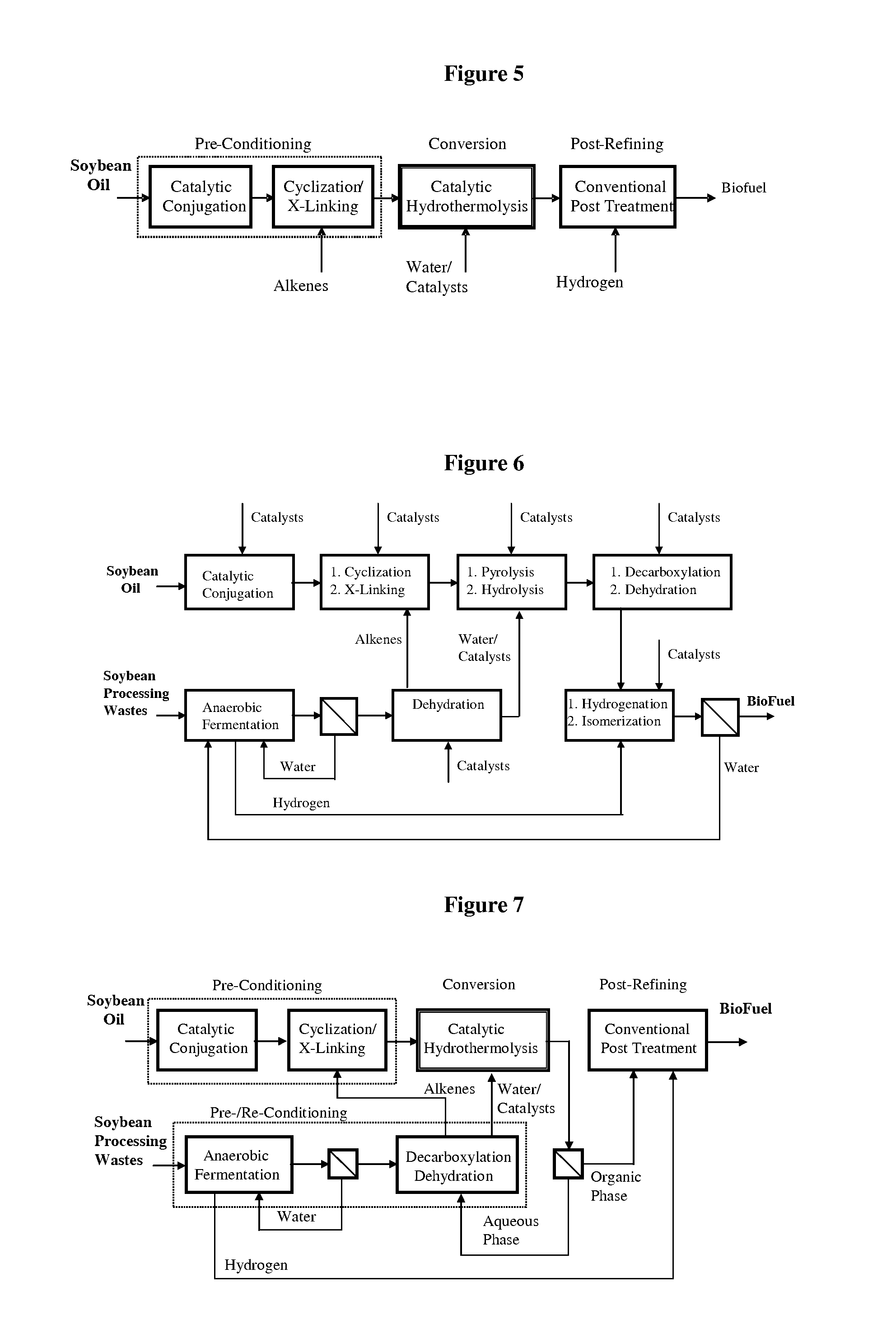
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Method and apparatus for controlled contraction of soft tissue
InactiveUS20050187599A1Reduces cell necrosisReduce Shrinkage ProblemsElectrotherapyCatheterThermal energyMedicine
An apparatus for effecting change in at least a portion of a selected site of a collagen containing tissue that is at least partially adjacent to a fluid medium. The apparatus includes an energy delivery device configured to deliver a level of energy to the selected site of the collagen containing tissue. The energy delivery device includes a distal portion where a sensor is positioned. The sensor provides a signal indicative of the thermal energy content of at least the selected site of the collagen containing tissue and the adjacent fluid medium to a feedback control unit. The signal is received by the feedback control system which adjusts the level of energy supplied to the energy delivery.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Fuels for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS6858048B1Emission reductionSafer land environmentLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesKeroseneOctanol
Mixed alcohols can be used as a fuel additive in gasoline, diesel, jet fuel or as a neat fuel in and of itself. The mixed alcohols can contain C1-C5 alcohols, or in the alternative, C1-C8, or higher, alcohols in order to boost energy content. The C1-C5 mixed alcohols contain more ethanol than methanol with amounts of propanol, butanol and pentanol. C1-C8 mixed alcohols contain the same, with amounts of hexanol, heptanol and octanol. A gasoline-based fuel includes gasoline and the mixed alcohols. A diesel based fuel includes diesel and the mixed alcohols. A jet fuel includes kerosene and the mixed alcohols. The neat fuel of the mixed alcohols has an octane number of at least 109 and the Reid Vapor Pressure is no greater than 5 psi. The gross heat of combustion is at least 12,000 BTU's / lb.
Owner:STANDARD ALCOHOL COMPANY OF AMERICA
Method of Converting Triglycerides to Biofuels
ActiveUS20080071125A1Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationBiofuelsIsomerizationPtru catalyst
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Solar thermal aerosol flow reaction process
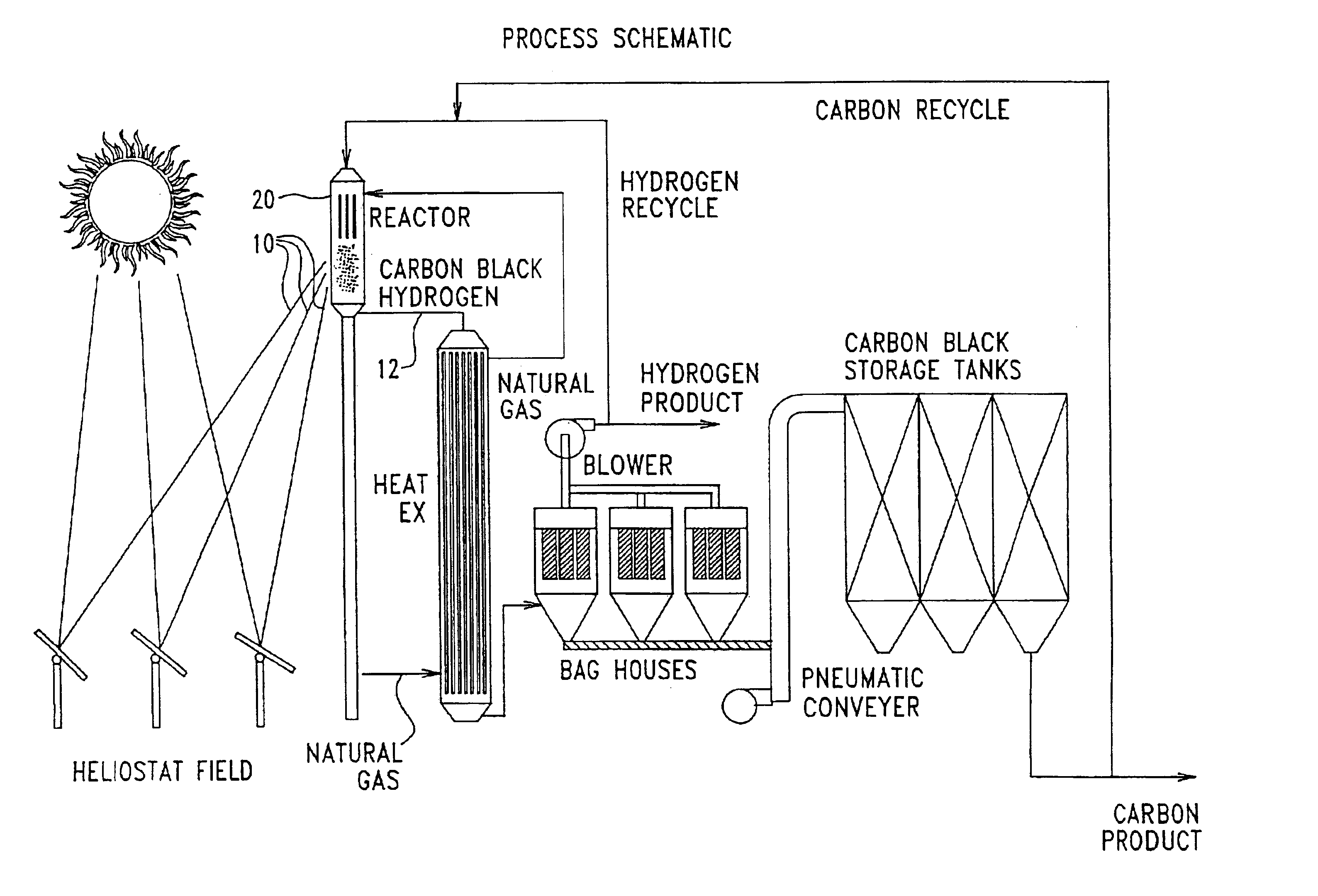
InactiveUS6872378B2Short stayCost-effectiveSolar heating energyHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesForming gasChemical reaction
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Generation of plants with altered oil content
InactiveUS20060277630A1Maximize oil contentIncrease valueOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesP PHENOTYPENucleic acid
The present invention is directed to plants that display an altered oil content phenotype due to altered expression of a HIO103.1 nucleic acid. The invention is further directed to methods of generating plants with an altered oil content phenotype.
Owner:EXELIXIS PLANT SCI INC
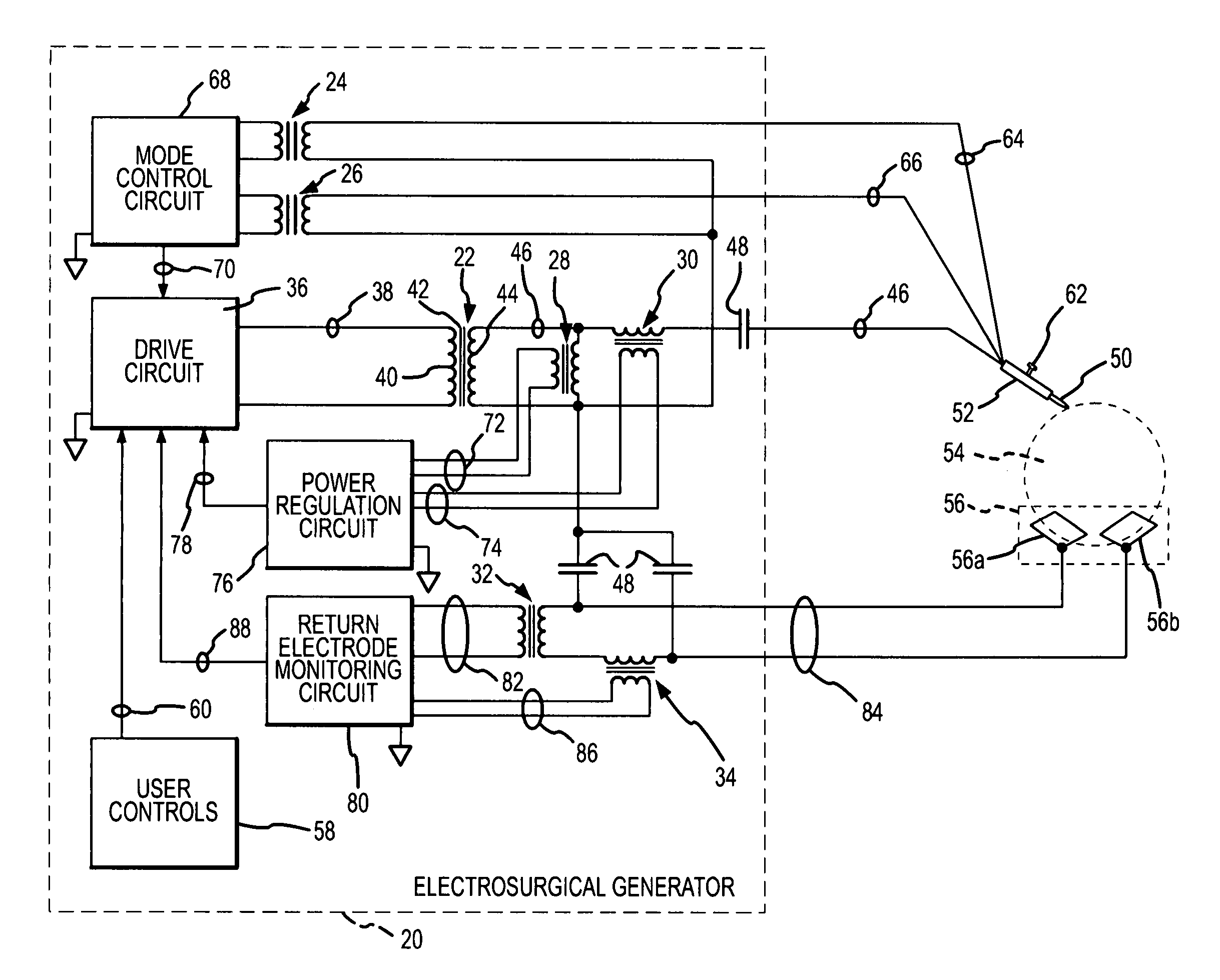
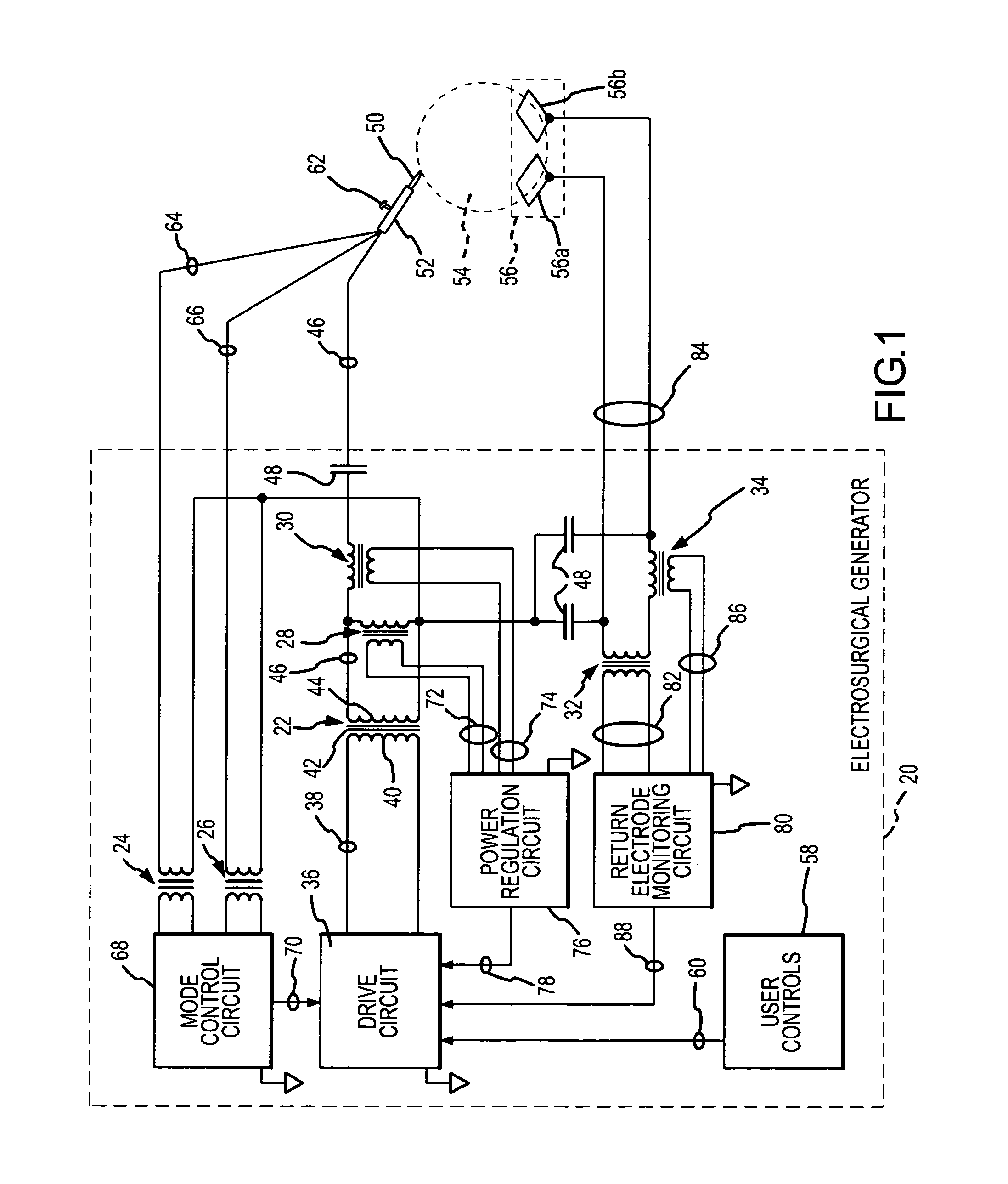
Electrosurgical generator and method using a high permeability, high resistivity transformer
InactiveUS20080071260A1Increase insulation thicknessReduce parasitic capacitanceSurgical instruments for heatingFrequency spectrumTransformer
A transformer which conducts or responds to a high voltage, high frequency electrosurgical output waveform has a core with a permeability in the range of 500-2000 and a resistivity in the range of 90,000-1,000,000 ohm centimeters and insulation on the secondary high voltage winding of at least 800 VAC per 0.001 inch thickness. The permeability and resistivity of the core enhance energy conversion, reduce parasitic capacitance to enhance the high frequency spectral energy content of the electrosurgical output waveform while simultaneously reducing leakage current, reducing the size of the transformer, enhancing manufacturing reproducibility and enhancing the ability to pass a high voltage safety test.
Owner:CONMED CORP
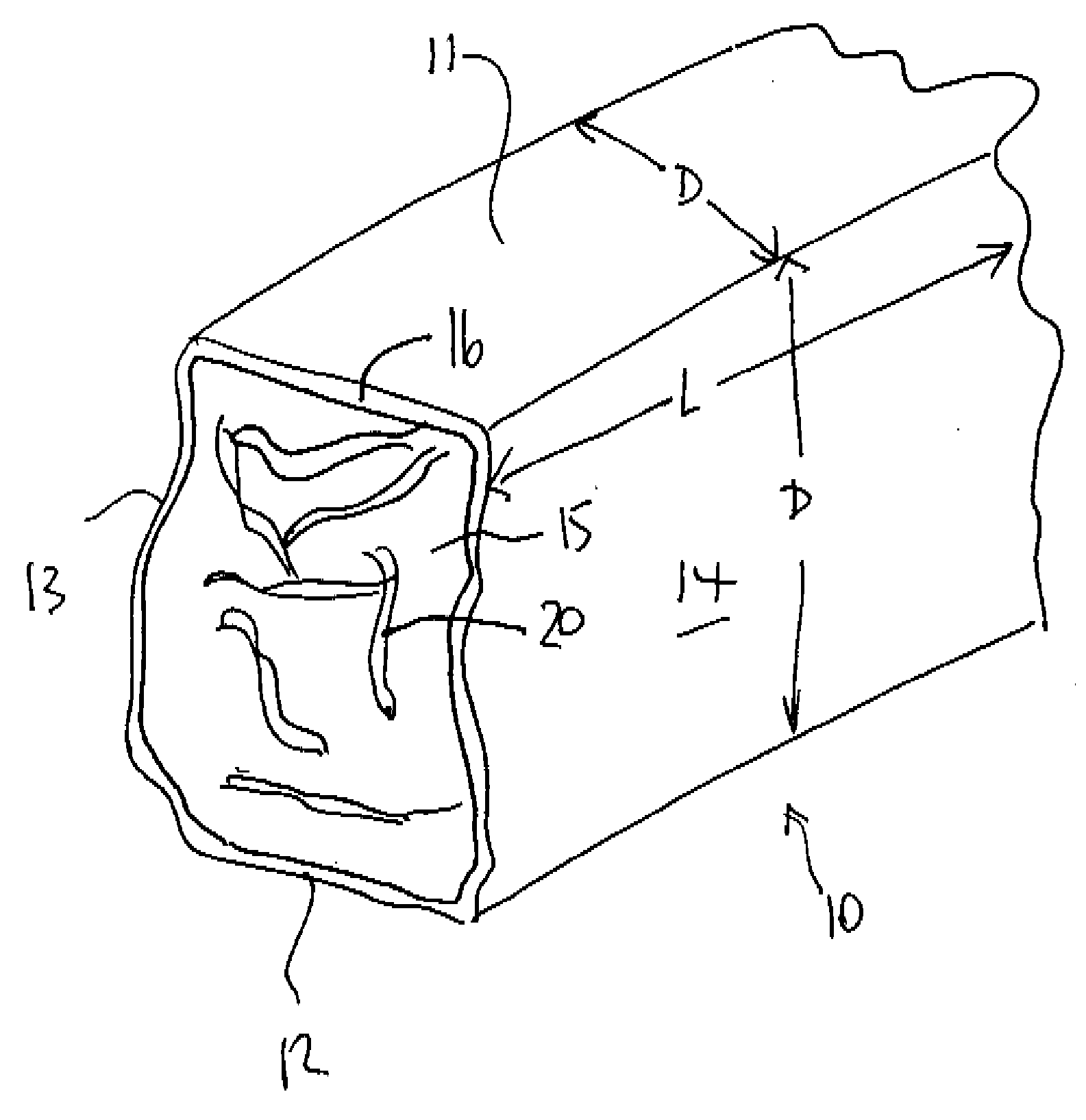
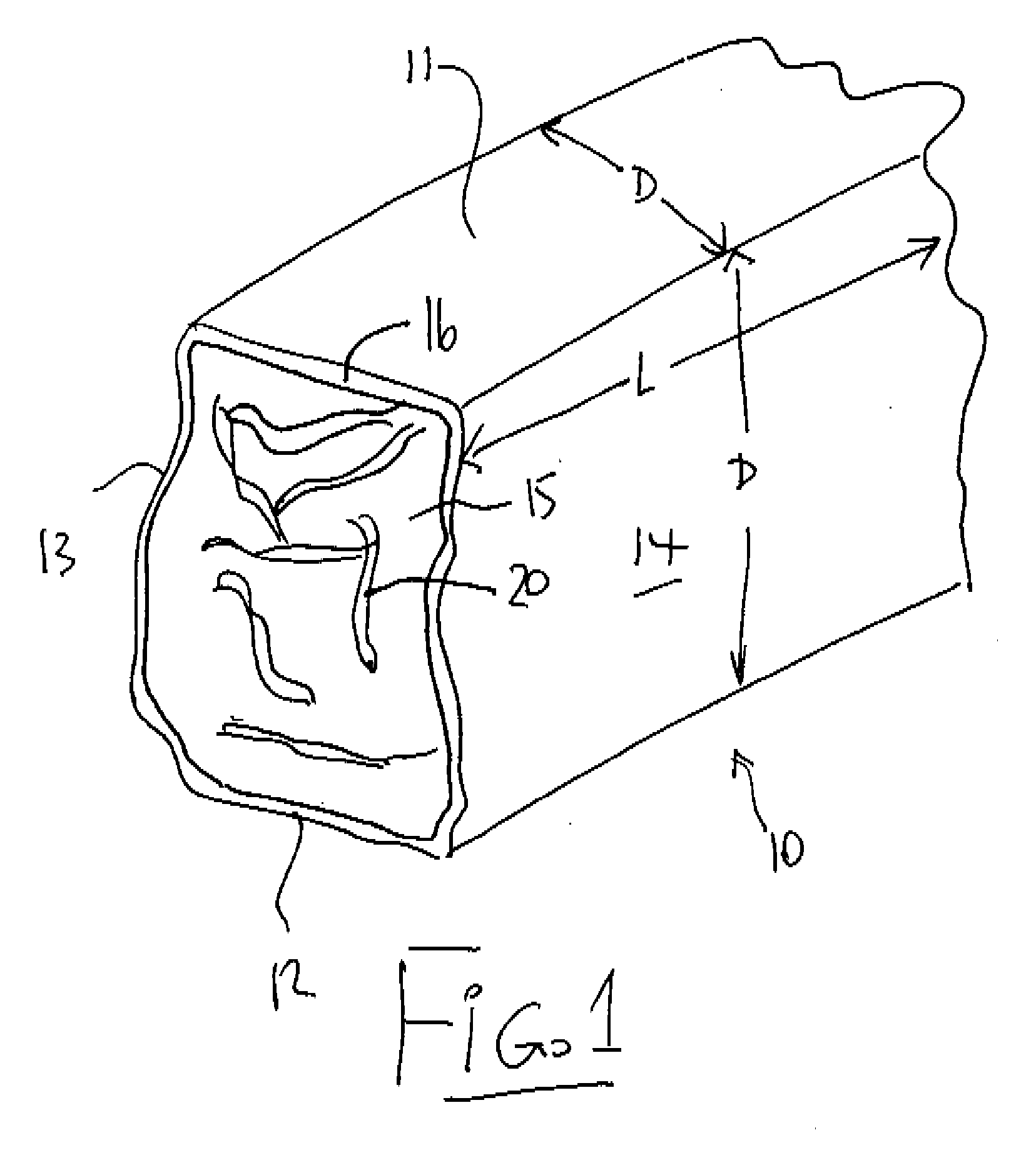
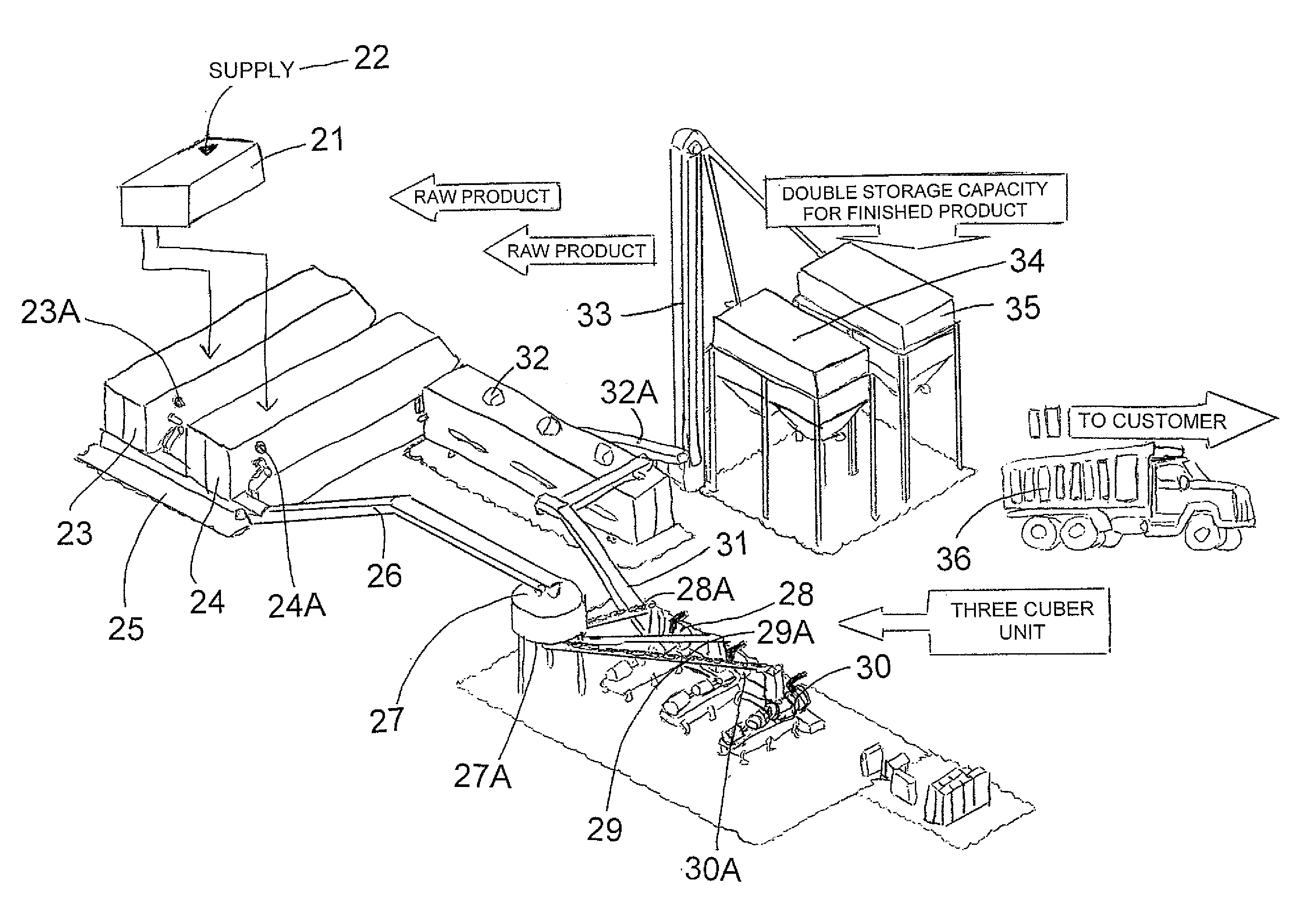
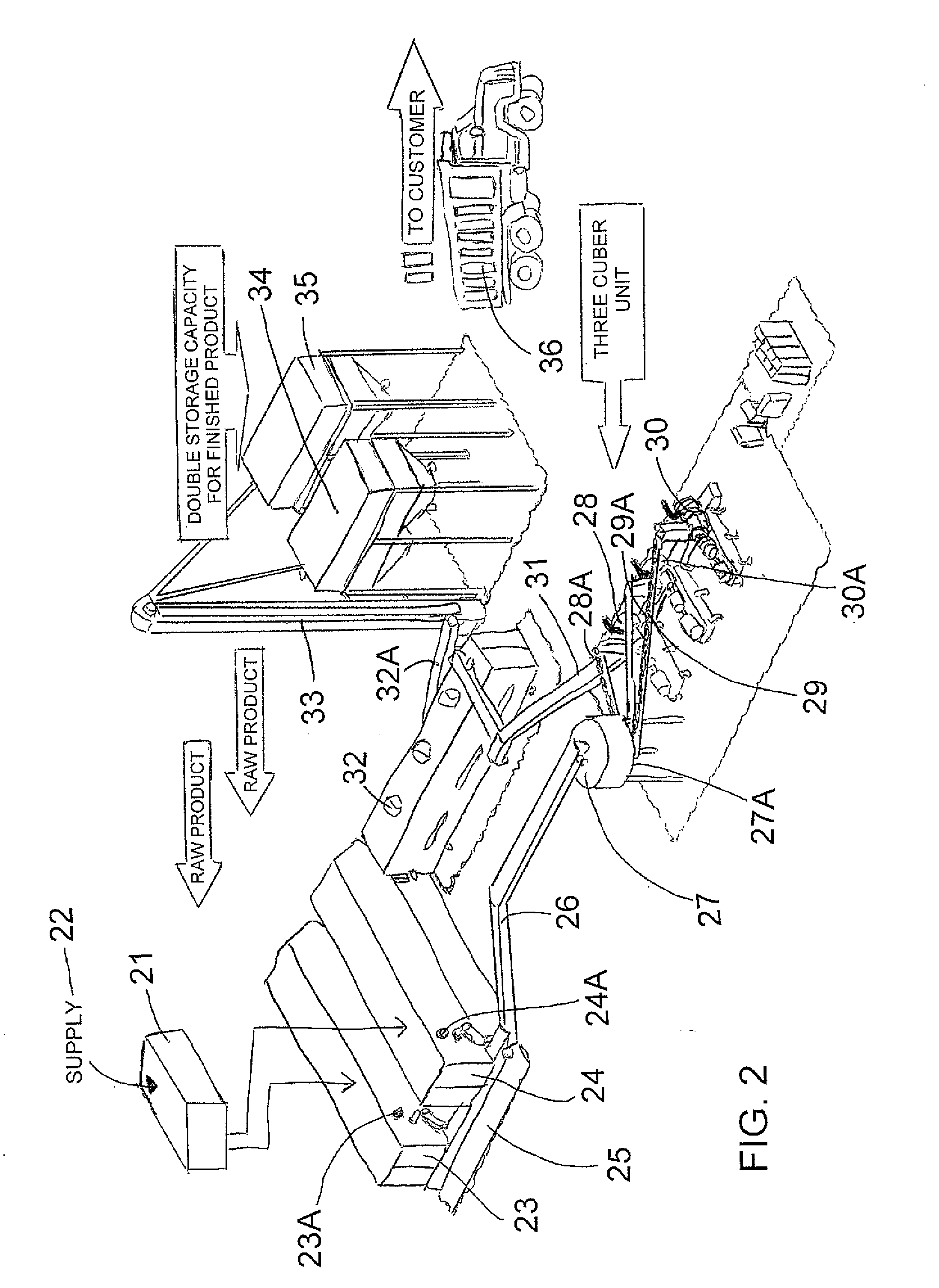
Plant biomass solid fuel
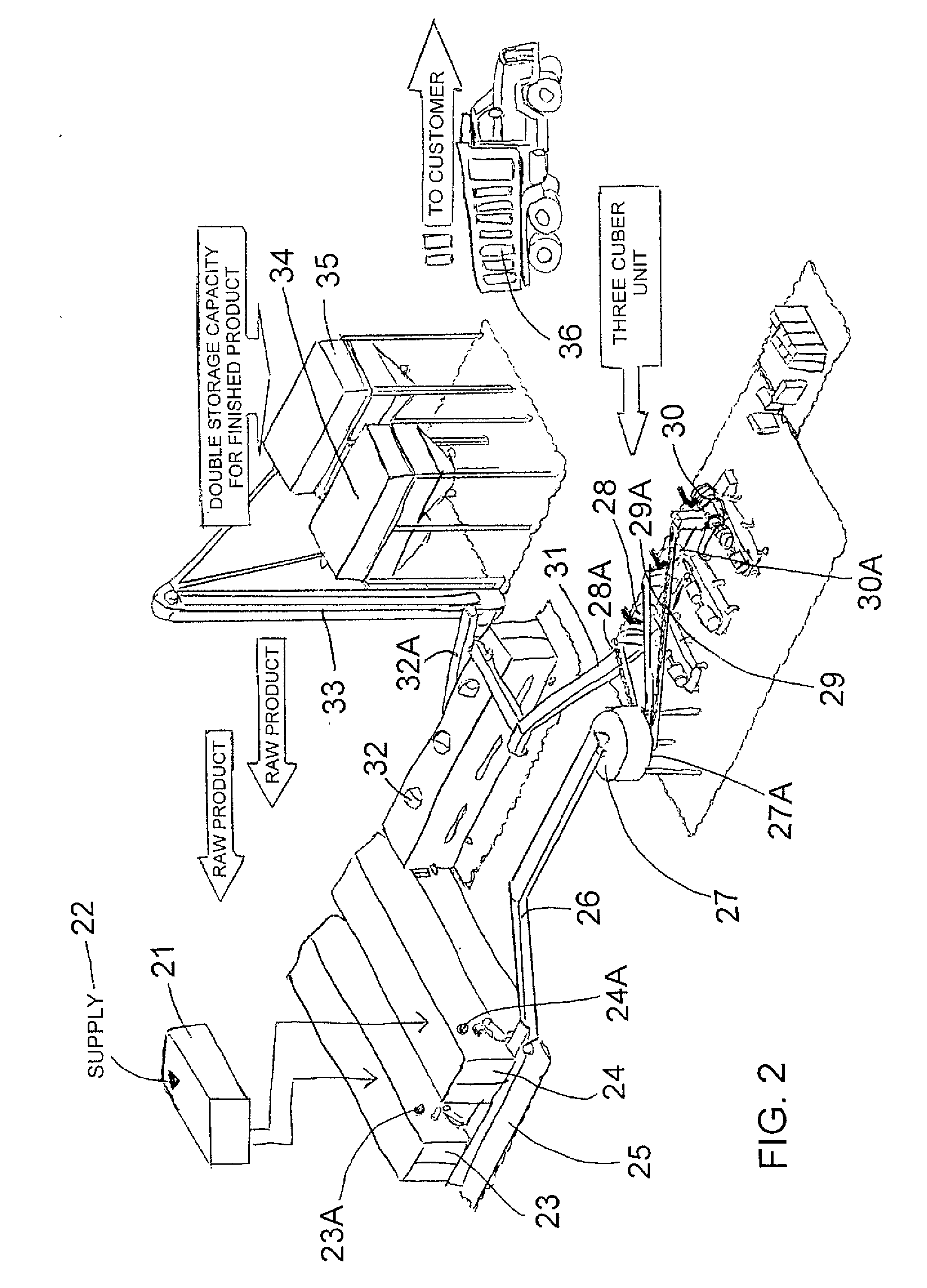
A solid fuel is formed in a cuber to form body pieces formed of materials extruded through a die with a density greater than 35 lbs / cu ft; an energy content greater than 6500 BTU / lb; transverse dimensions less than 1.5 inches; and a length less than 4 inches; from plant biomass material which contains components when extended of greater than 1.0 inch. Primarily the materials are paper or other cellulose product and crop residue such as wheat straw. The cellulose and lignin from these materials act without additional binders as binders and encasing materials. The moisture content is maintained at a target value by mixing selected quantities of the materials without drying. The cubing machine has a feeding system where the space between the inner rotor and outer casing is smaller than 4 inches and the height of the outer flight is less than 1 inch.
Owner:GAUTHIER STEPHANE +4
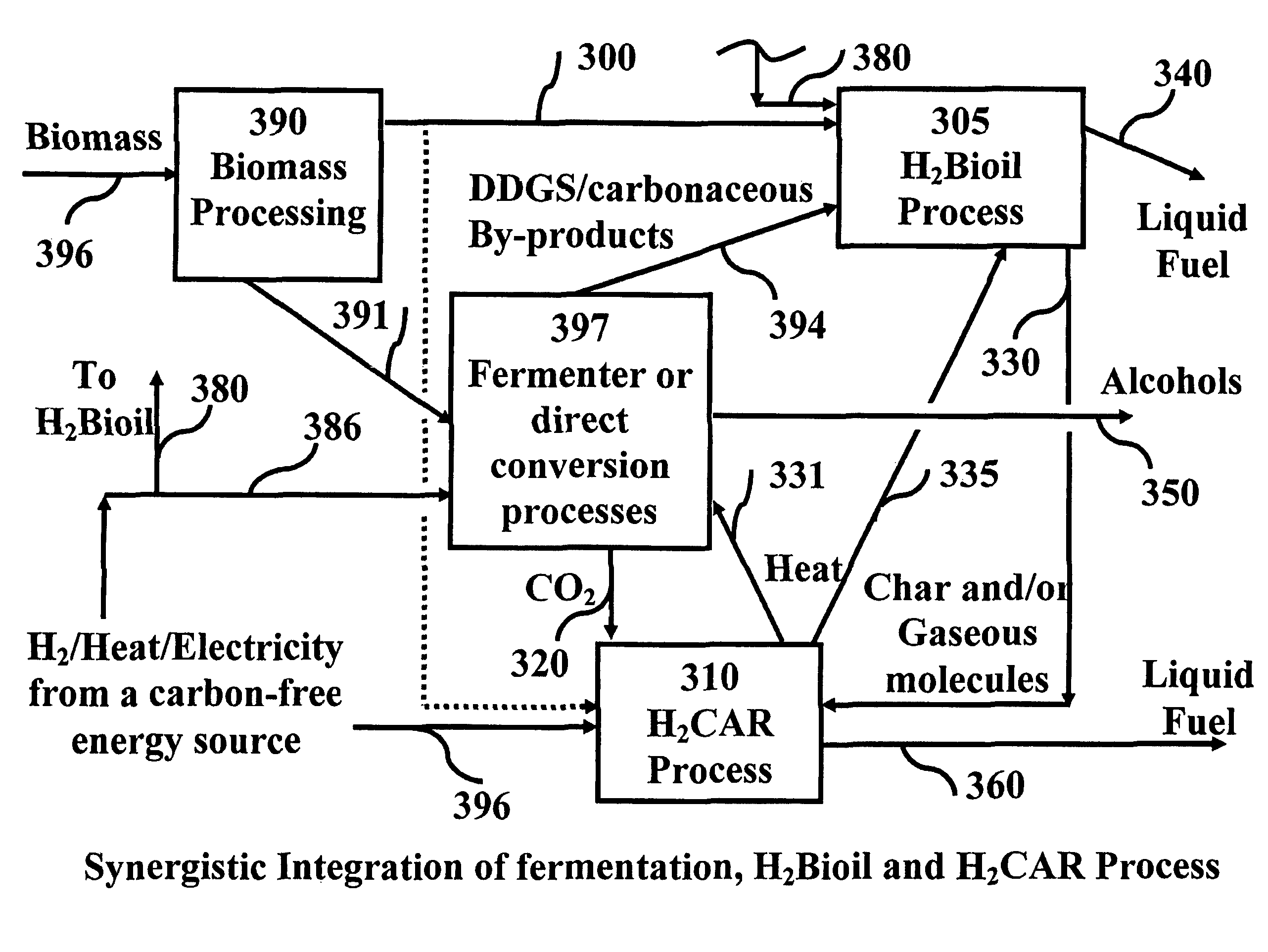
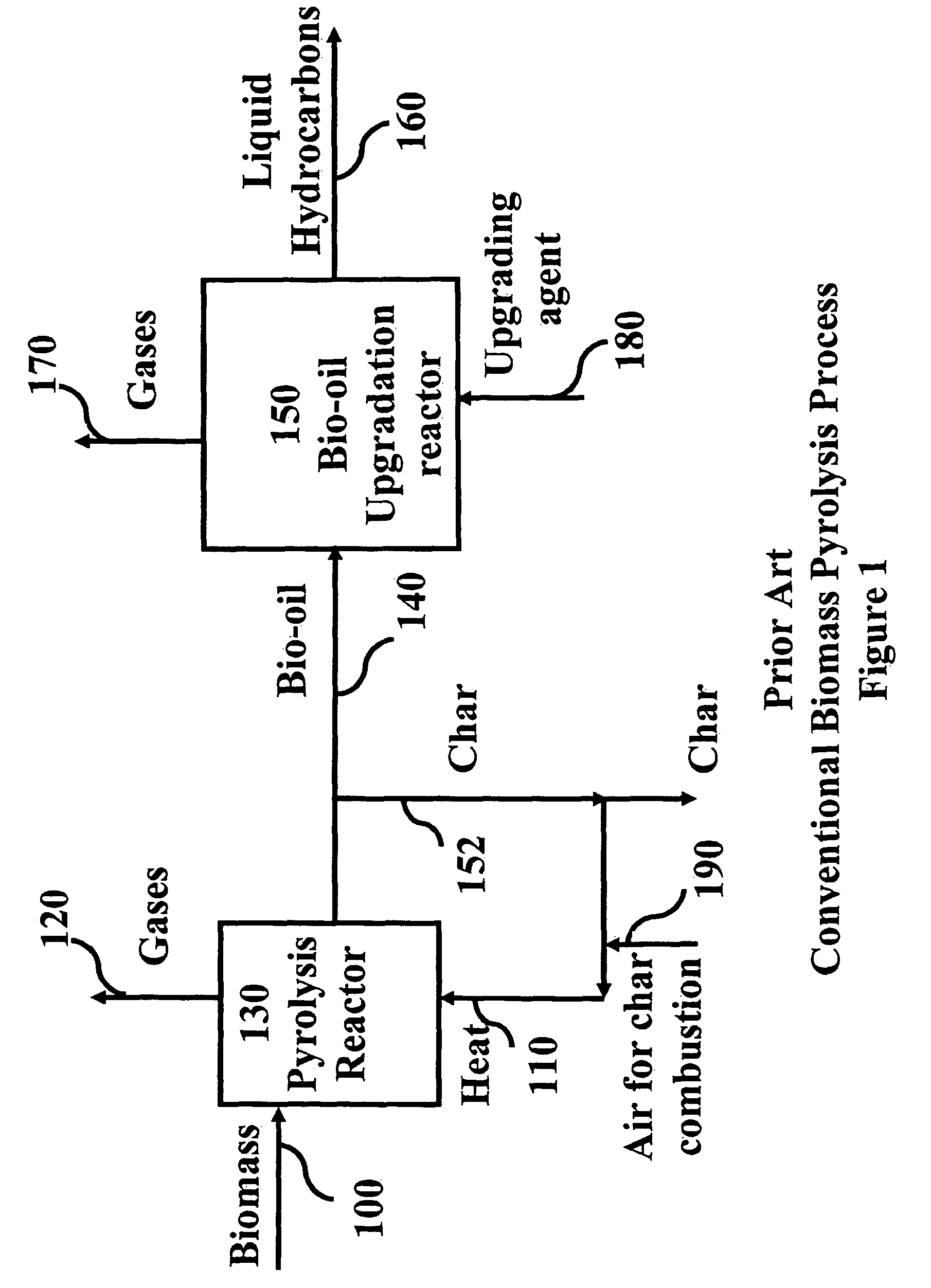
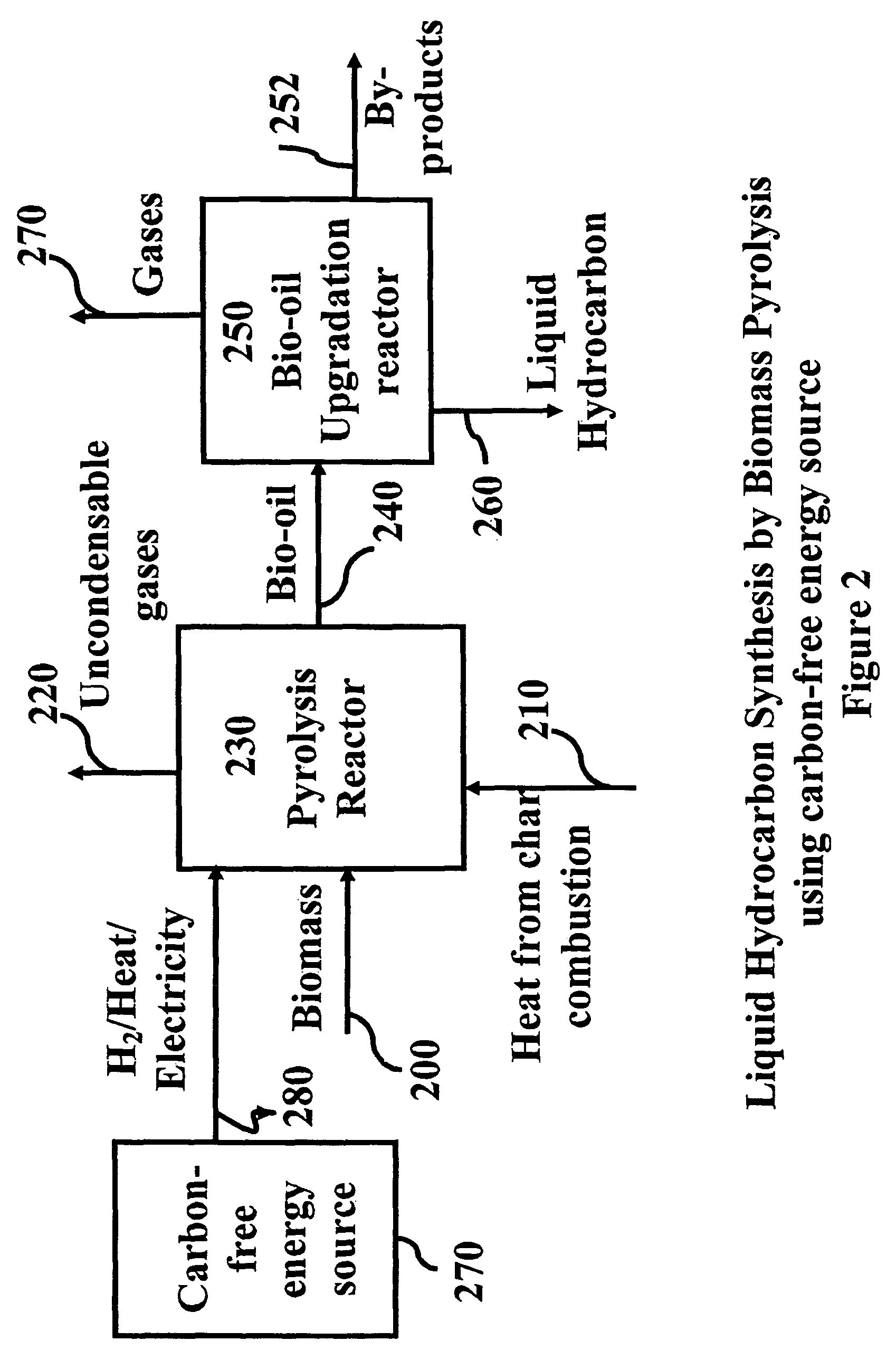
Process for producing liquid hydrocarbon by pyrolysis of biomass in presence of hydrogen from a carbon-free energy source
ActiveUS8217211B2Yield maximizationInhibition formationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlkaneHydrogen
In at least one embodiment of the present invention, a method for producing liquid hydrocarbons from biomass is provided. The method comprises pyrolizing the biomass with hydrogen (H2) to form bio-oil. The bio-oil comprises alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, aromatics, hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof. The H2 is formed from a carbon-free energy source.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for manufacture of plant biomass solid fuel
InactiveUS20090056206A1Enhance cube durability and energy contentHigh qualityBiofuelsSolid fuelsBiomassCellulose
A solid fuel is formed in a cuber to form body pieces formed of materials extruded through a die with a density greater than 35 lbs / cu ft; an energy content greater than 6500 BTU / lb; transverse dimensions less than 1.5 inches; and a length less than 4 inches; from plant biomass material which contains components when extended of greater than 1.0 inch. Primarily the materials are paper or other cellulose product and crop residue such as wheat straw. The cellulose and lignin from these materials act without additional binders as binders and encasing materials. The moisture content is maintained at a target value by mixing selected quantities of the materials without drying. The cubing machine has a feeding system where the space between the inner rotor and outer casing is smaller than 4 inches and the height of the outer flight is less than 1 inch.
Owner:PRAIRIE BIO ENERGY
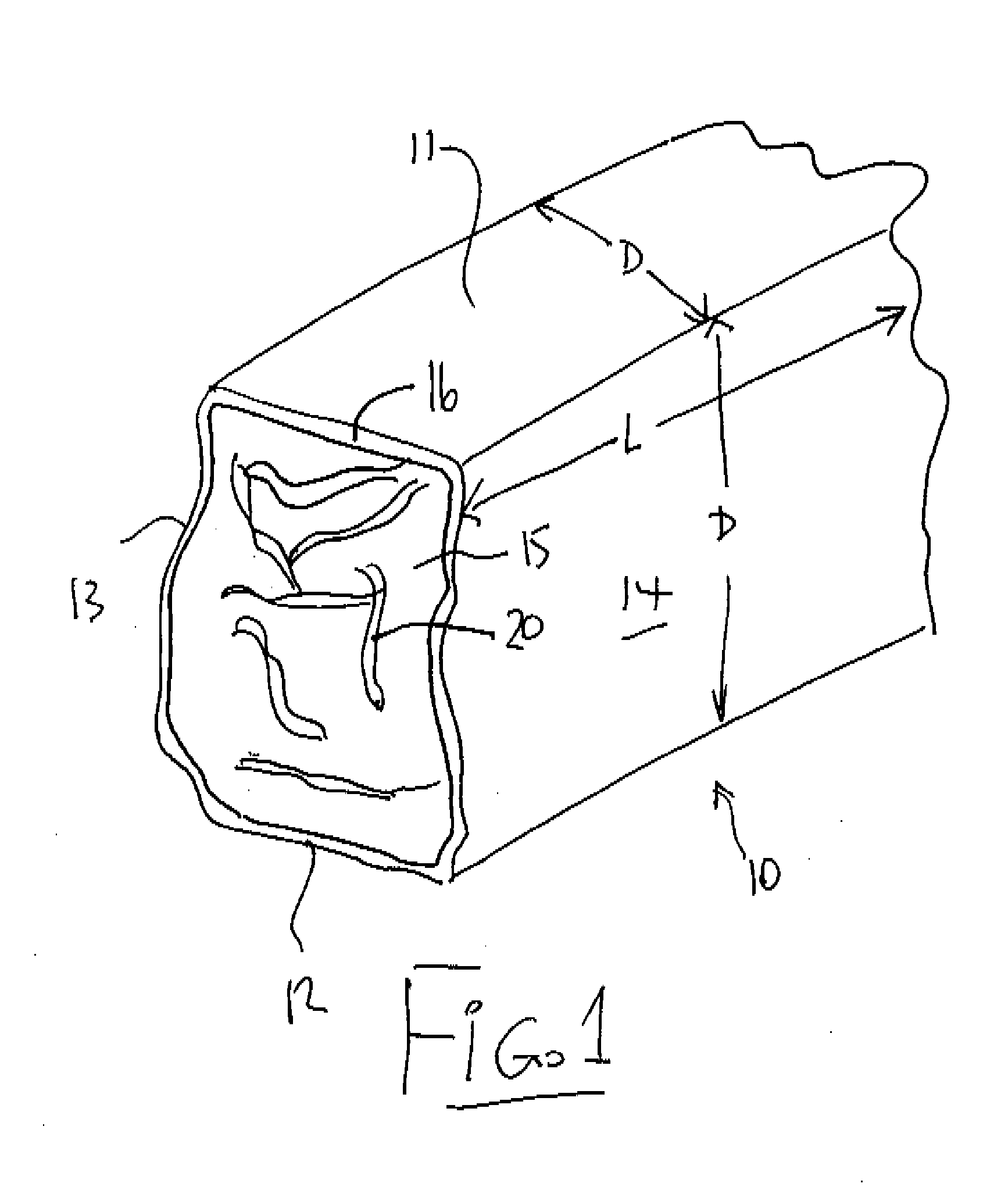
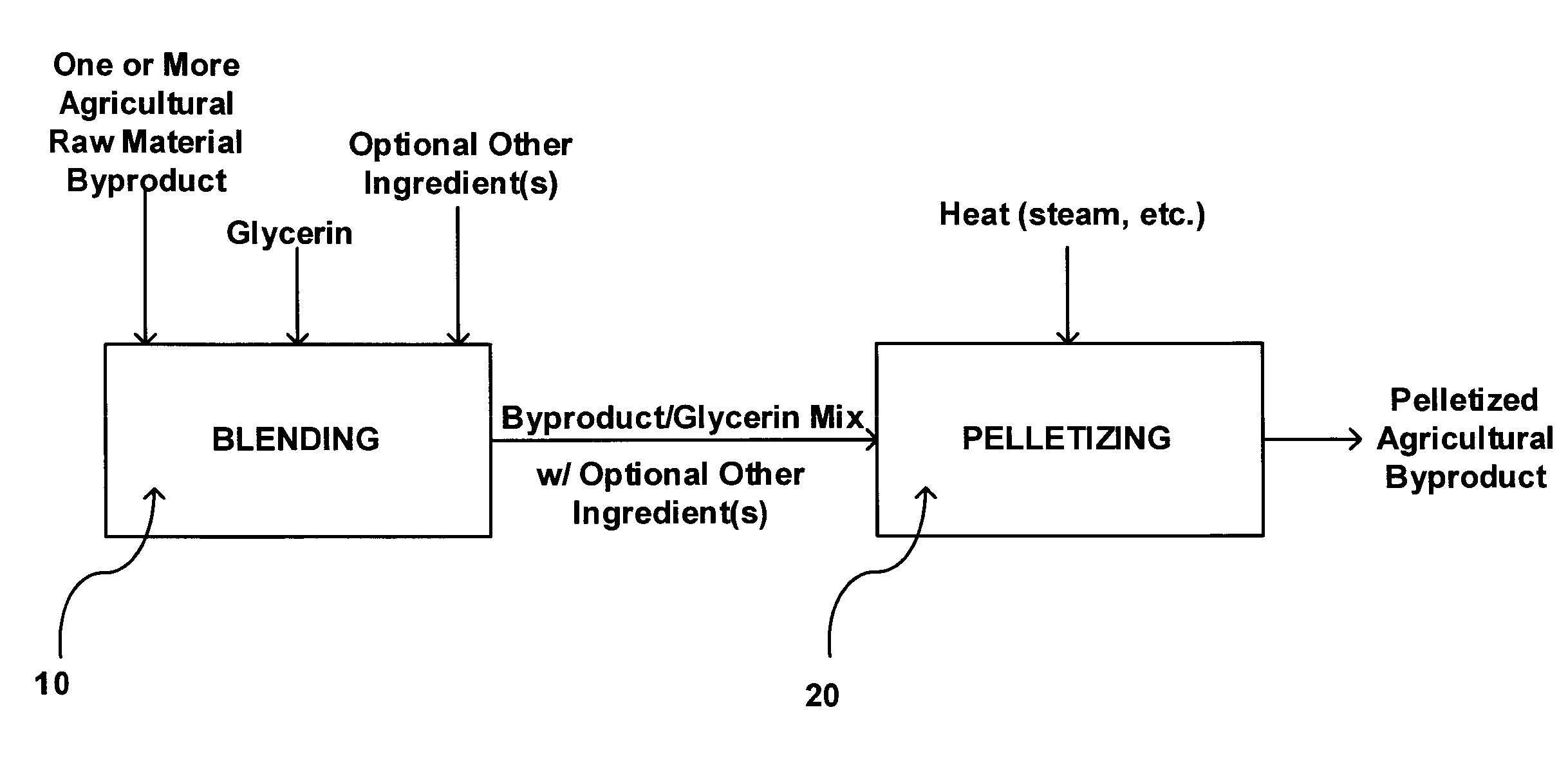
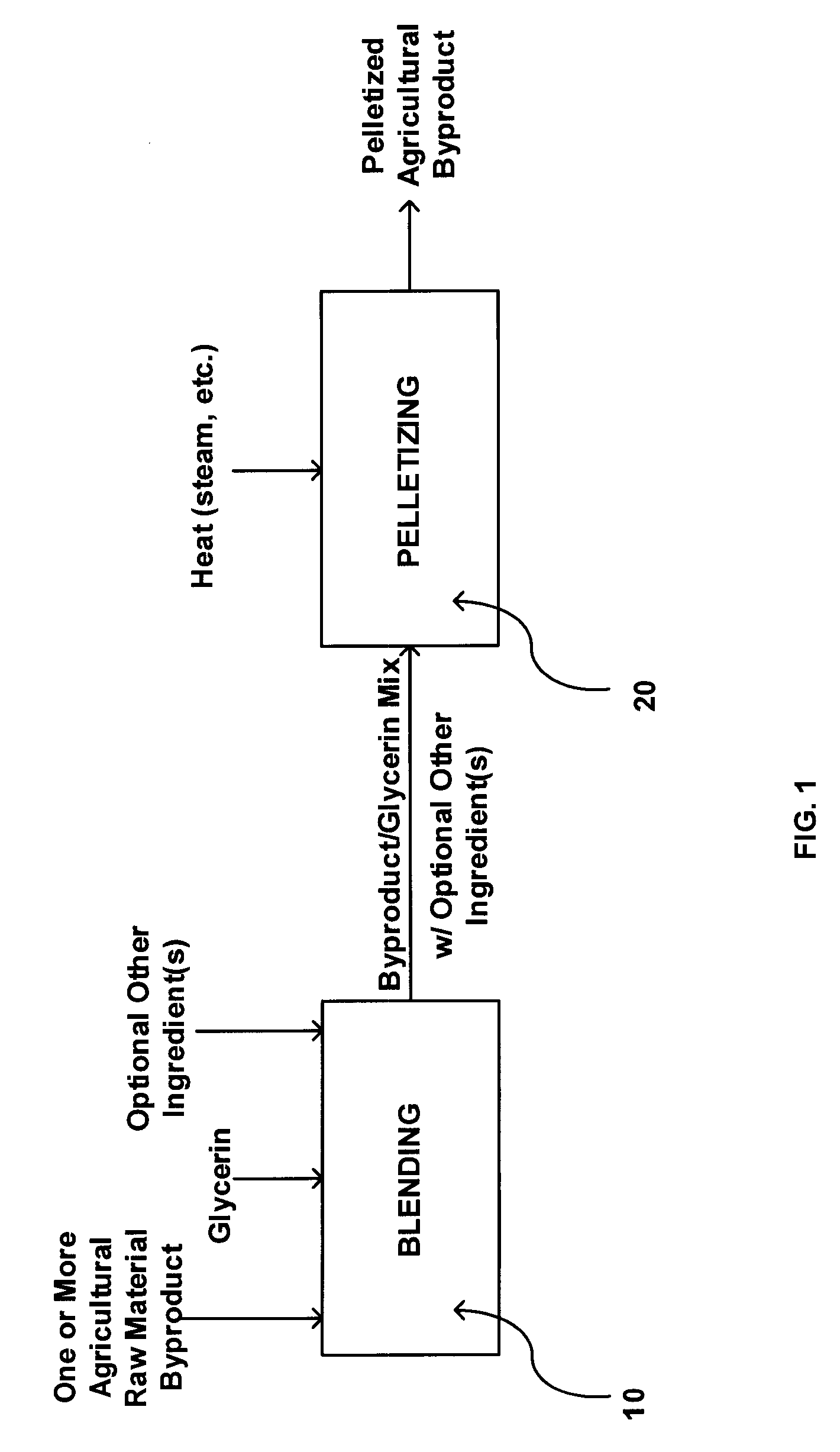
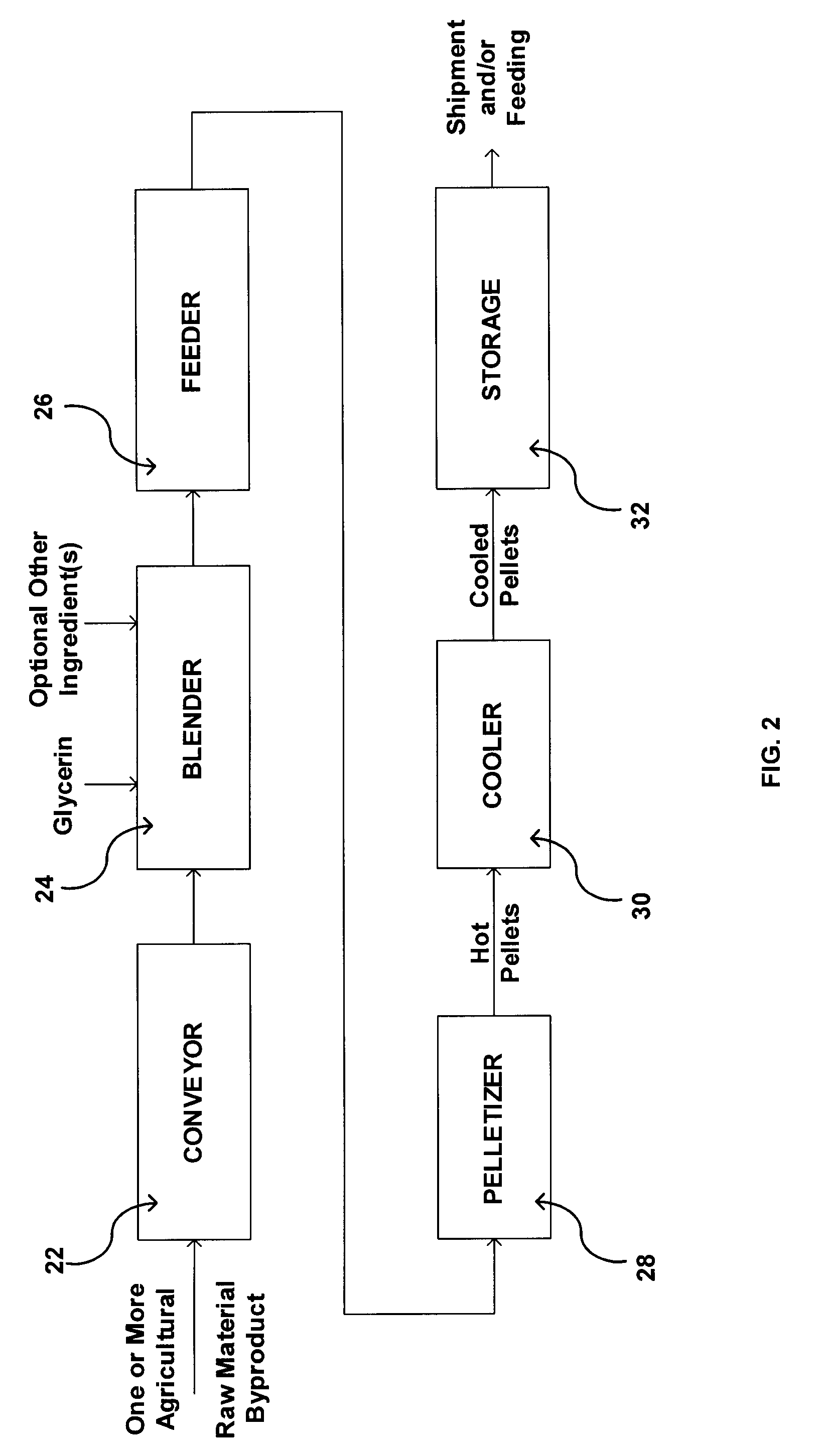
High density, energy component-added pelletized agricultural processing byproducts for animal feed
InactiveUS20070172540A1Improve feeding qualityHigh densityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffHigh densityGlycerol
An animal feed in pellet form including one or more agricultural raw material byproduct and a glycerin binder. The animal feed may also include nutritional additives, vitamins, minerals, antibiotics, hormones and sweeteners in effective amounts. Further provided is a process for preparing an animal feed product, including providing one or more agricultural raw material byproduct; blending the one or more agricultural raw material byproduct with a quantity of glycerin; and pelletizing the blended agricultural raw material byproduct and glycerin into pellets. The glycerin may be present at a concentration effective to bind the blended one or more agricultural raw material byproduct and glycerin into a stable pellet, and may also be present at a concentration effective to improve the shelf life of the one or more byproduct.
Owner:FARMERS UNION IND
Process for generating a hydrocarbon feedstock from lignin
The present invention discloses processes for generating a hydrocarbon feedstock for biofuels synthesis from lignin via hydroprocessing. Embodiments of the present invention can occur in a refinery setting or in a paper mill setting. Embodiments of the present invention can utilize the separated lignin or the entire black liquor solution.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for using biogenic carbon dioxide derived from non-fossil organic material
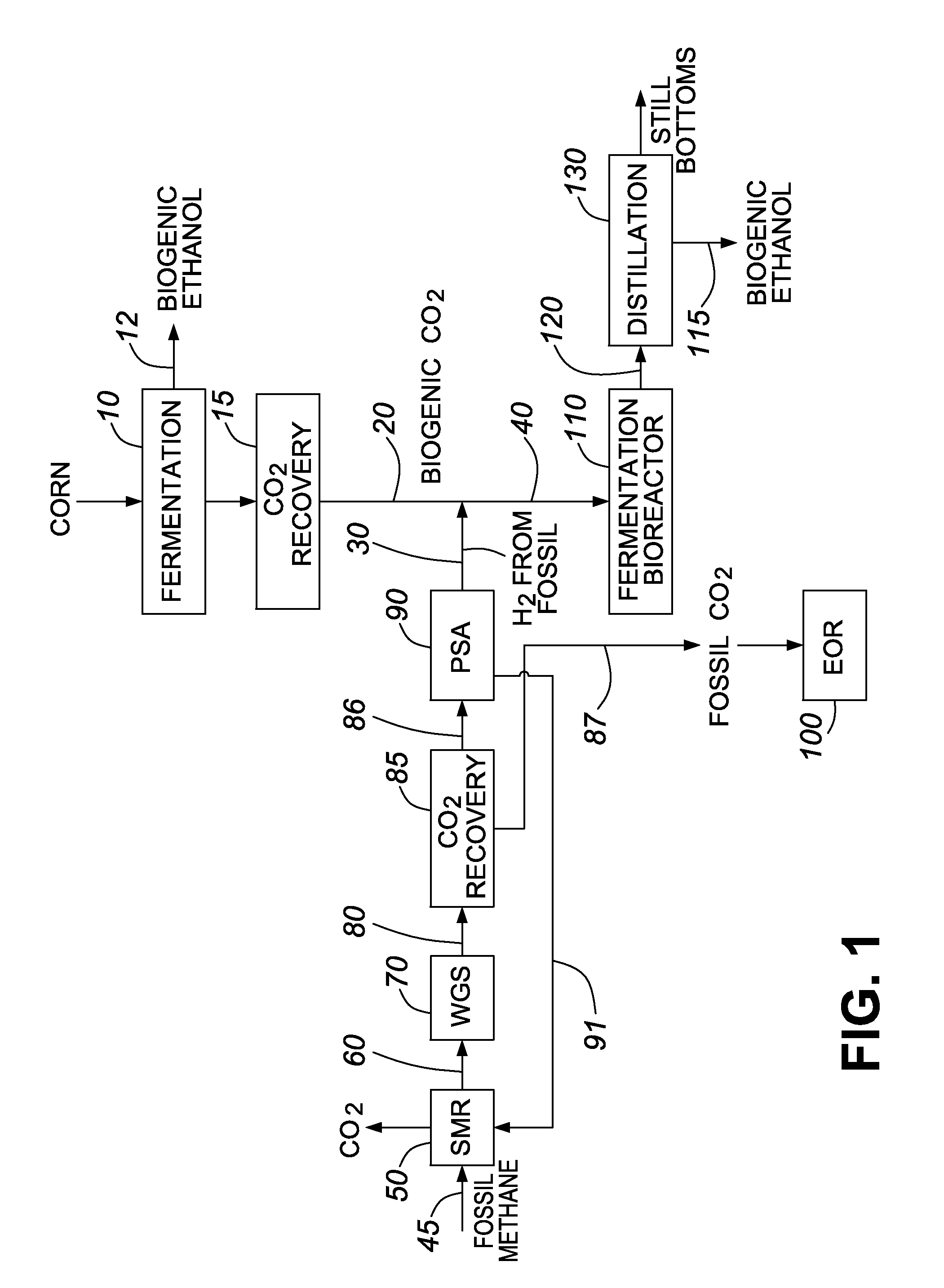
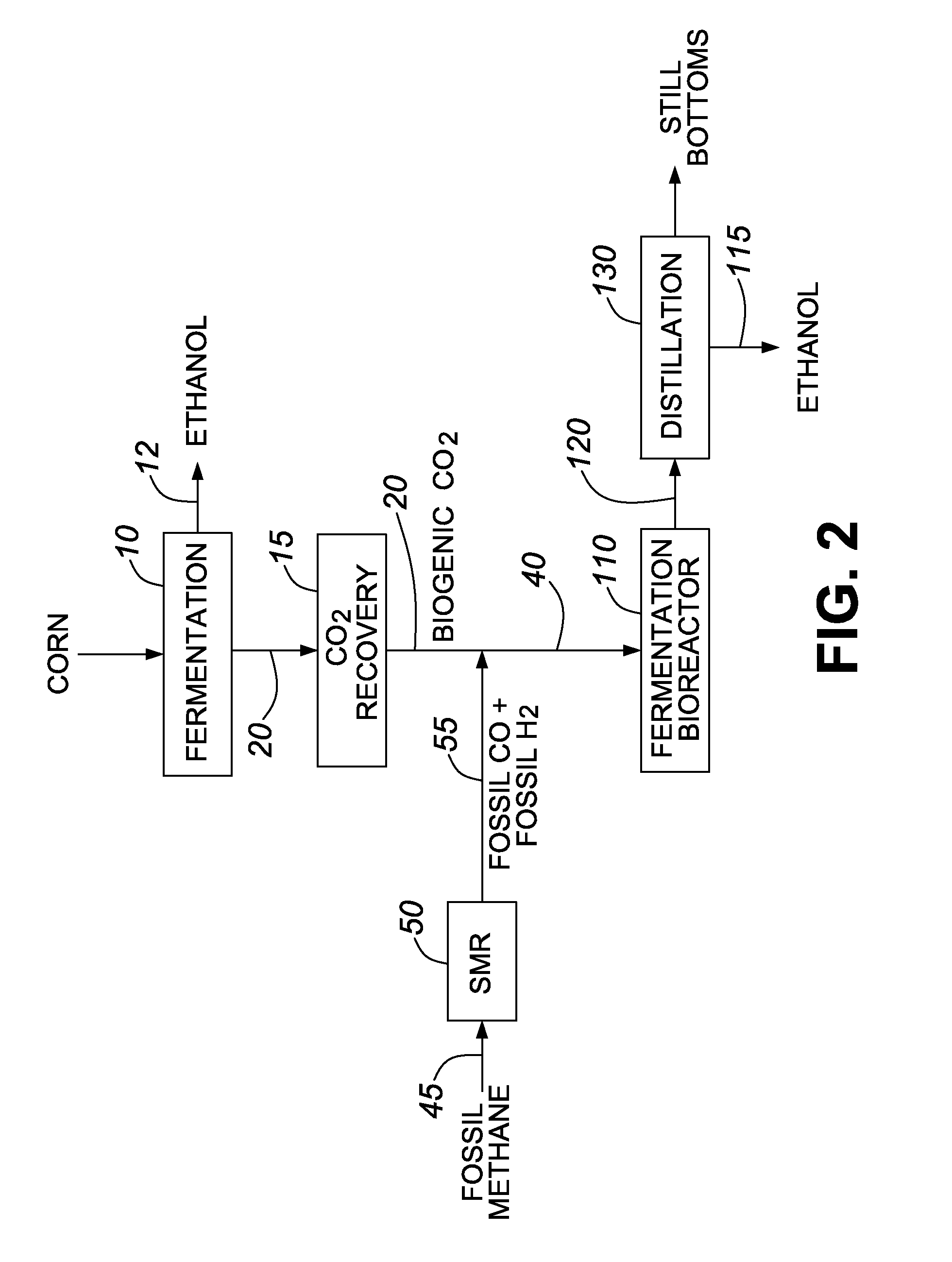
ActiveUS9108894B1Improve production yieldProduce moreCarbon compoundsBiofuelsEnergy productsHydrogen
The present disclosure provides a process for forming a biogenic carbon-based fuel or a fuel intermediate from biogenic carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The hydrogen is sourced from a process that produces hydrogen and fossil carbon dioxide from a fossil-fuel hydrocarbon and separates the fossil carbon dioxide from the hydrogen. The process may further comprise carrying out or arranging for one or more parties to carry out at least one step that contributes to a reduction in the GHG emissions of the biogenic carbon-based fuel, or a fuel made from the fuel intermediate, of at least 20% relative to a gasoline baseline. In various embodiments this includes (a) introducing the fossil carbon dioxide underground, and / or (b) using a biogenic carbon-based product selected from a chemical and energy product produced from the non-fossil organic material to displace the use or production of a corresponding fossil-based product. Methods of using the present invention to enable fuel credit generation are also described.
Owner:IOGEN CORPORATION
Biofuel conversion process
InactiveUS20060236595A1Increase energy contentEfficient conversionBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsVegetable oilKerosene
A process, method, apparatus and materials for efficient conversion of waste vegetable oils into biofuel that does not use methanol as a reactant or catalyst. The resulting biofuel is mixed with kerosene or heavy oil to form a stable diesel fuel grade fuel that is mixable with diesel fuel. In addition, the process and apparatus are also applicable to the conversion of virgin vegetable oils and other waste or virgin oils, such as used motor oil, into fuels or fuel additives.
Owner:NAKAMURA NORIKAZU
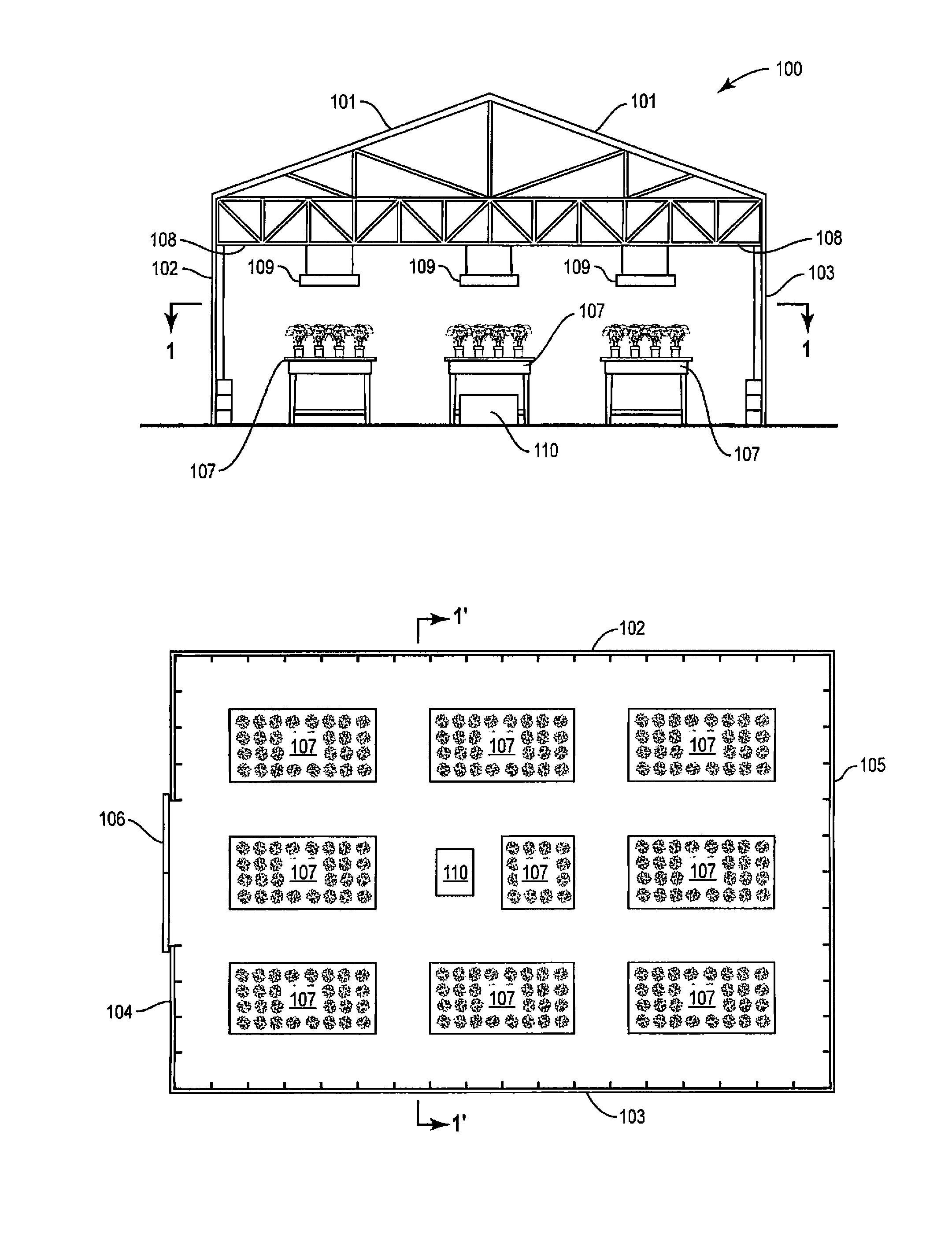
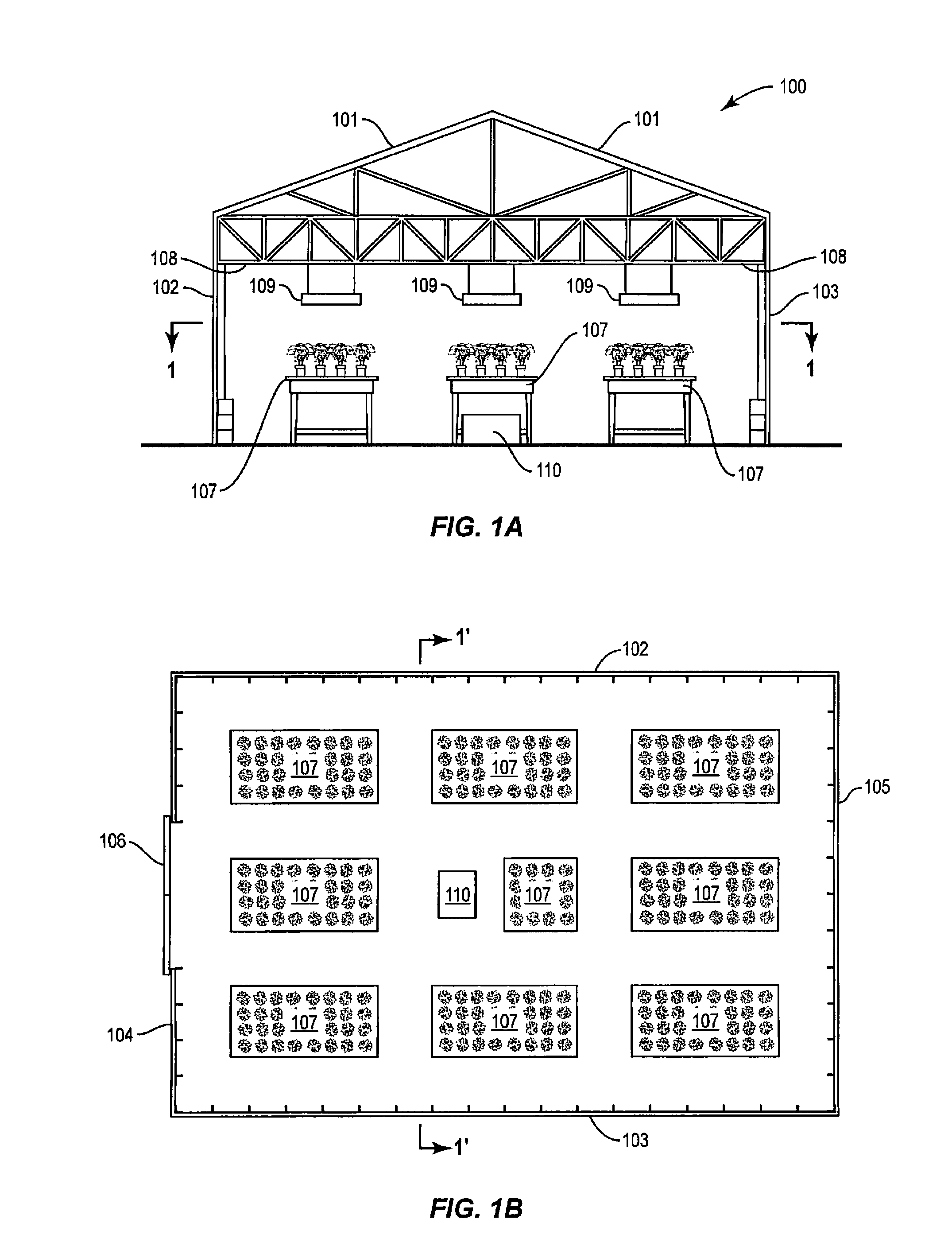
Plant cultivation system and method
InactiveUS20150264871A1Increase energy contentLow costClimate change adaptationGreenhouse cultivationFuel cellsGreenhouse
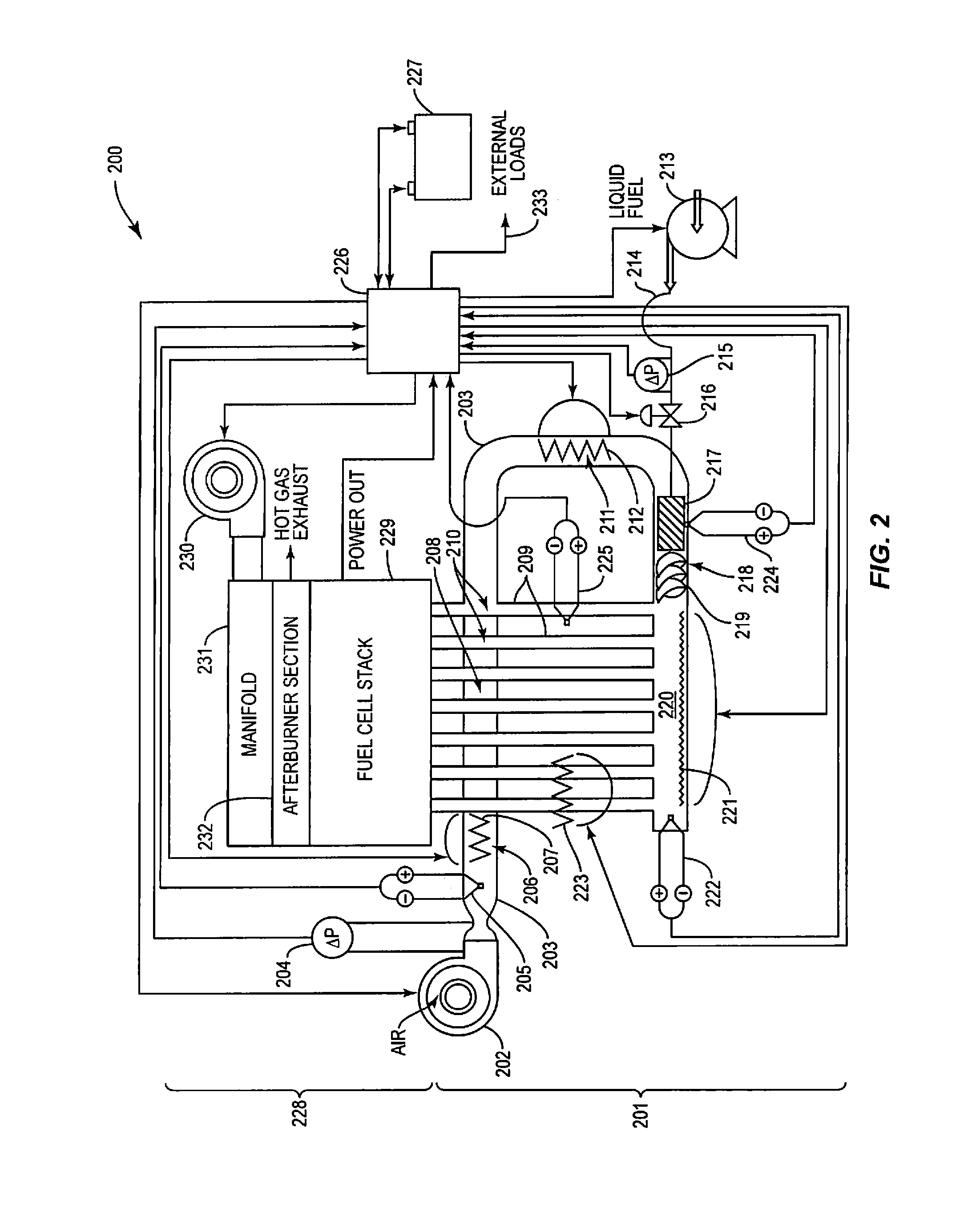
The electrical power, carbon dioxide and heating requirements of an enclosed plant cultivation system and method, for example, a greenhouse and greenhouse plant cultivation method, are provided by a solid oxide fuel cell.
Owner:WATT FUEL CELL CORP
Low Energy Food Product
InactiveUS20080187645A1Improve textureIncrease energy contentEdible oils/fats ingredientsEdible oils/fats with reduced calorie/fat contentFatty acid compositionFatty acid ester
The present invention relates to an emulsified food product comprising water, from 0 to 5% by weight triglycerides, from 0.5 to 60% by weight plant sterol and / or stanol fatty acid ester, wherein the fatty acid composition of the plant sterol and / or stanol fatty acid ester comprises from 0 to 7% by weight saturated fatty acids, and optionally one or more emulsifiers, wherein the weight ratio of emulsifier(s) to the sum of plant sterol and / or stanol fatty acid ester and triglycerides, if present, is between 0-0.10:1. The invention also relates to a method for preparing such a food product.
Owner:RAISIO NUTRITION LTD
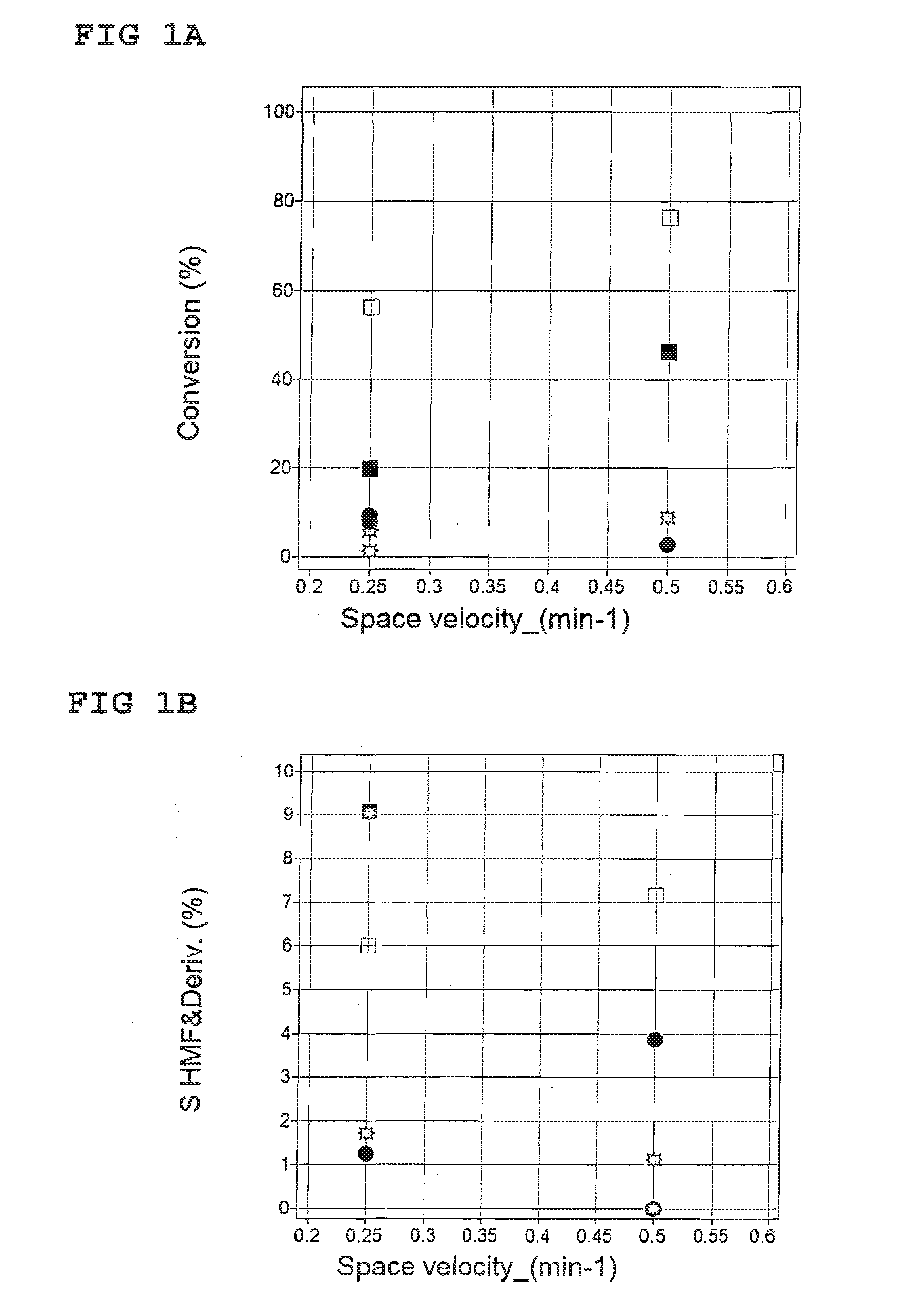
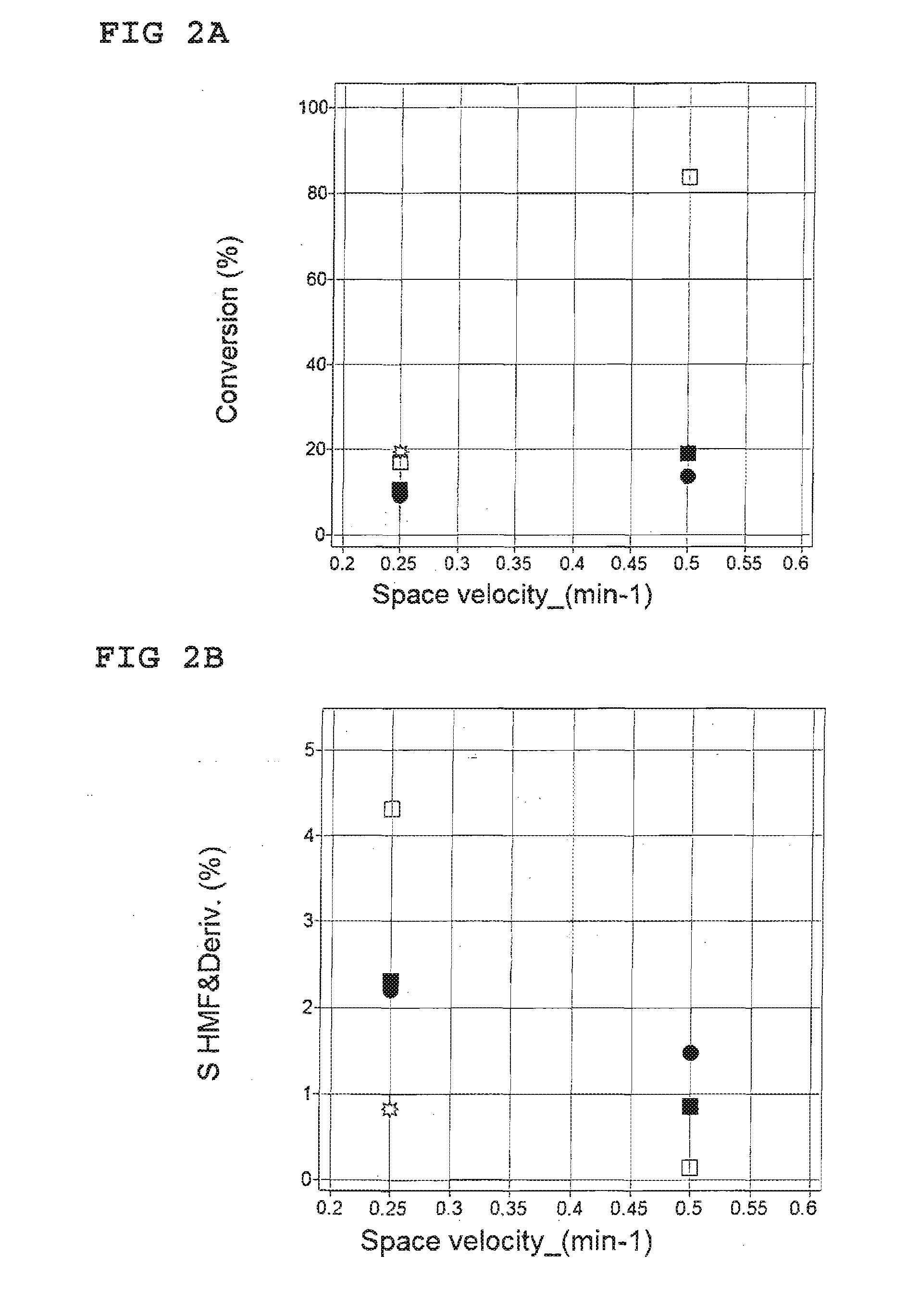
Method for the synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural ethers and their use
Owner:FURANIX TECH BV
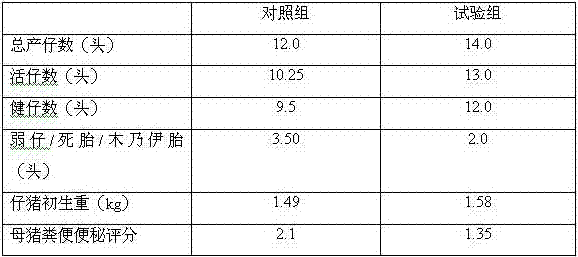
Gongtai special mixed feed for late pregnancy of pregnant sows and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105433000AMeeting nutritional needsIncrease nutritionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceDL-methionine
The invention provides a Gongtai special mixed feed for late pregnancy of pregnant sows and a preparation method thereof. The feed of the invention comprises the following raw materials (by weight): 30-40 parts of corn, 20-25 parts of wheat bran, 10-20 parts of soybean meal, 0-10 parts of vinasse protein, 0-10 parts of rice bran meal, 0-2.5 parts of soybean oil, 0-1 part of white sugar, 1-1.3 parts of fine ground limestone, 0.5-1 part of calcium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3-0.4 part of salt, 0.2-0.3 part of an acidifier, 0-0.15 part of choline chloride, 0-0.08 part of L-lysine, 0-0.06 part of DL-methionine, 0-0.06 part of threonine, 0-0.1 part of sodium butyrate, 0-0.12 part of a mildew inhibitor, 0-0.1 part of Novasil, 0-0.02 part of a flavouring agent, 0.5-1.5 parts of a vitamin premix and 0.5-1.5 parts of a microelement premix. Based on the newest sows nutrition theory and by combination of production reality, feed energy, protein level, vitamin, mineral elements, dietary fiber and other ingredients are designed reasonably, and problems such as sow body overweight, fetal oversize, prolonged labor, constipation and the like which are caused by existing lactation feeds for Gongtai are overcome.
Owner:TONGWEI
Production method of Anthony pig granule feedstuff
InactiveCN101390576AImprove ripenessLow costFeeding-stuffAnimal feeding stuffAnti nutritionalHeat sensitive
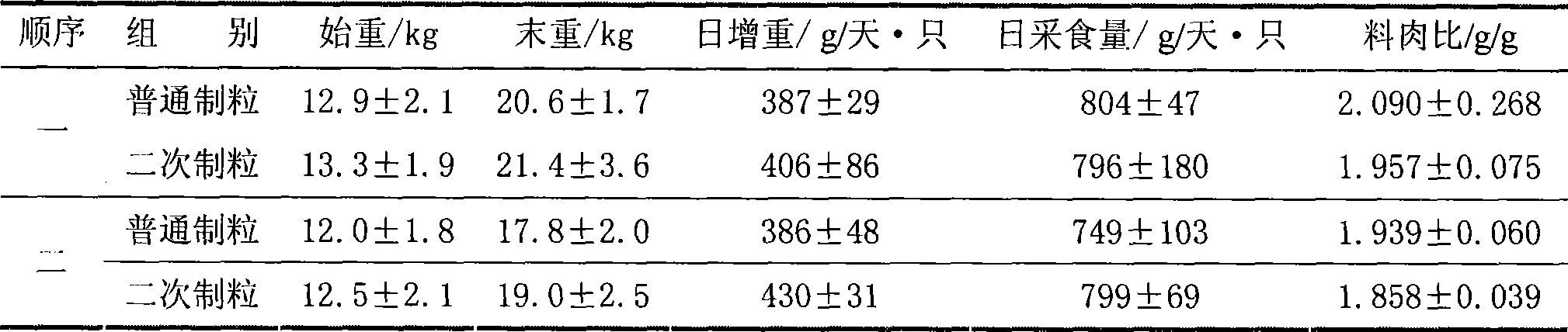
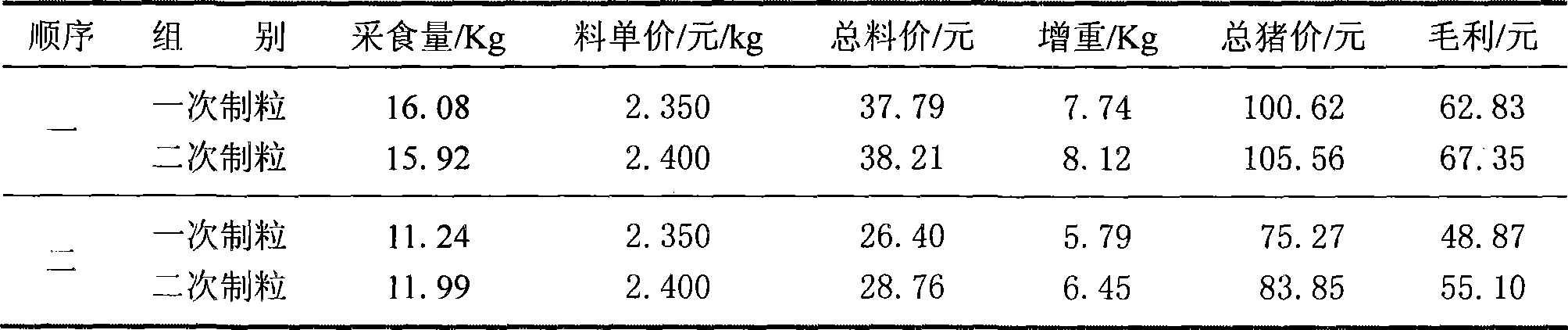
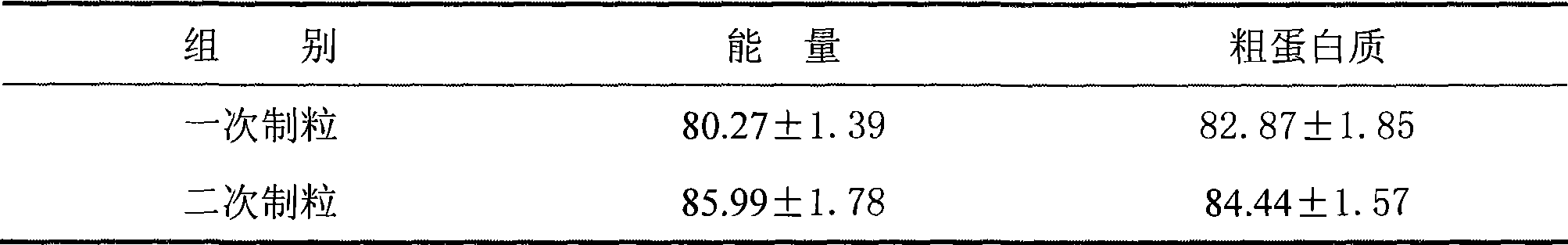
The invention relates to a production method for suckling pig pellet diet, comprises two granulation processes, wherein, the temperature in the first granulation process is more than 80 DEG C, while the temperature in the second granulation process is 50-65 DEG C. The method changes the ordinary granulation process of the existing pellet diet into the double-granulation process; the purposes of the two granulation processes are fundamentally different, wherein, the purpose of the first granulation process is to fully ripen the raw material and eliminate certain heat-sensitive anti-nutritional factors to enhance the grain digestion and absorption rate; the lowest modulation temperature for the first granulation process is 80 DEG C, while that for the second granulation process is lower and reaches 50-65 DEG C, so as to ensure smooth granulation of the power materials. The second granulation process of the double-granulation method adopts low-temperature granulation so as to reduce the high-temperature loss of vitamins and other heat-sensitive materials in the feed, decrease the production cost, improve the using effect of the feed, enhance the immunity of weaned piglets and ensure the health of the weaned piglets, thereby achieving good social values and economic values.
Owner:河南商都生物技术股份有限公司
Method for controlling percussion device, software production, and percussion device
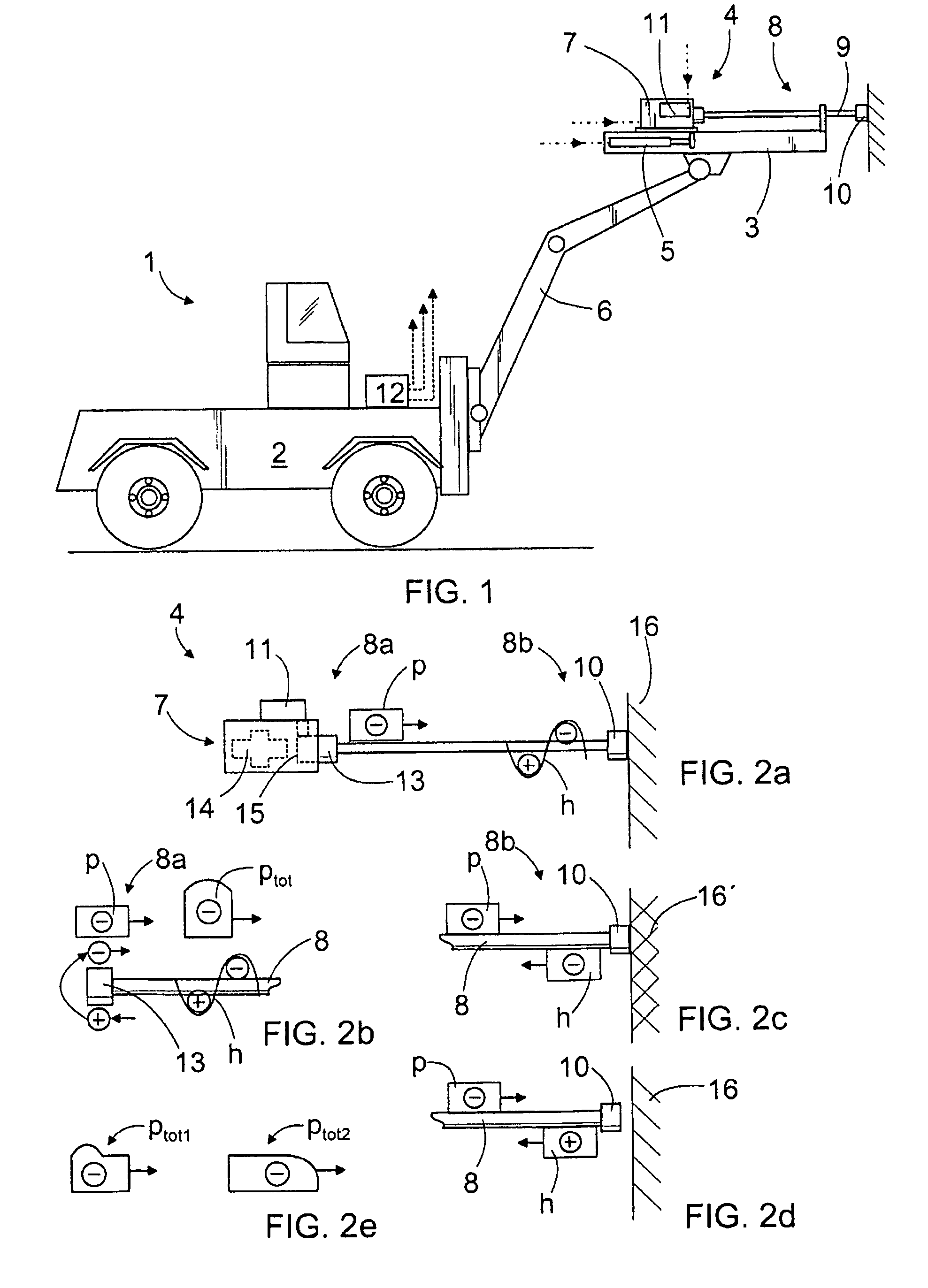
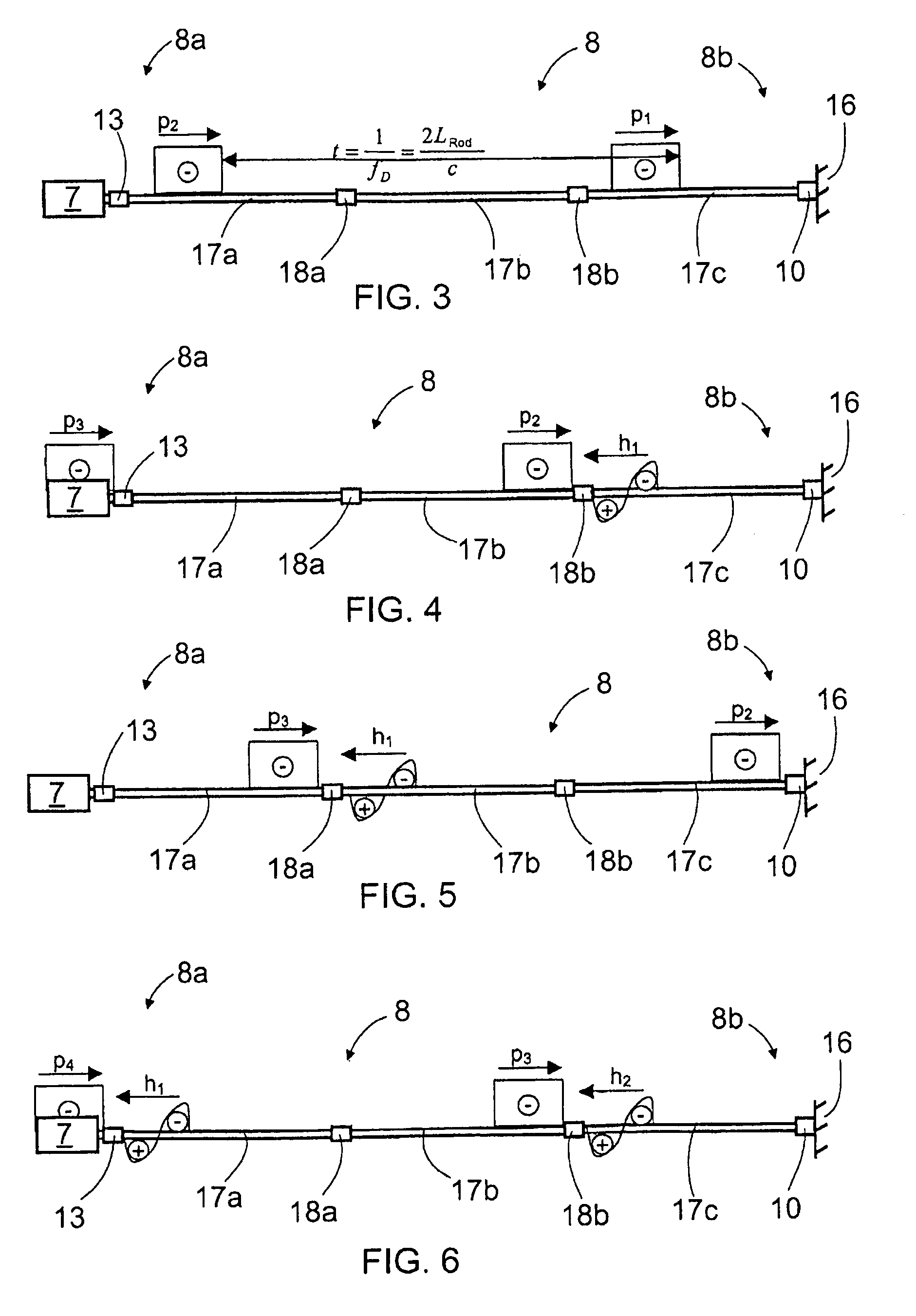
InactiveUS7717190B2Improve overall utilizationIncrease energy contentReciprocating drilling machinesConstructionsDevice formPropagation time
Owner:SANDVIK MINING & CONSTR OY
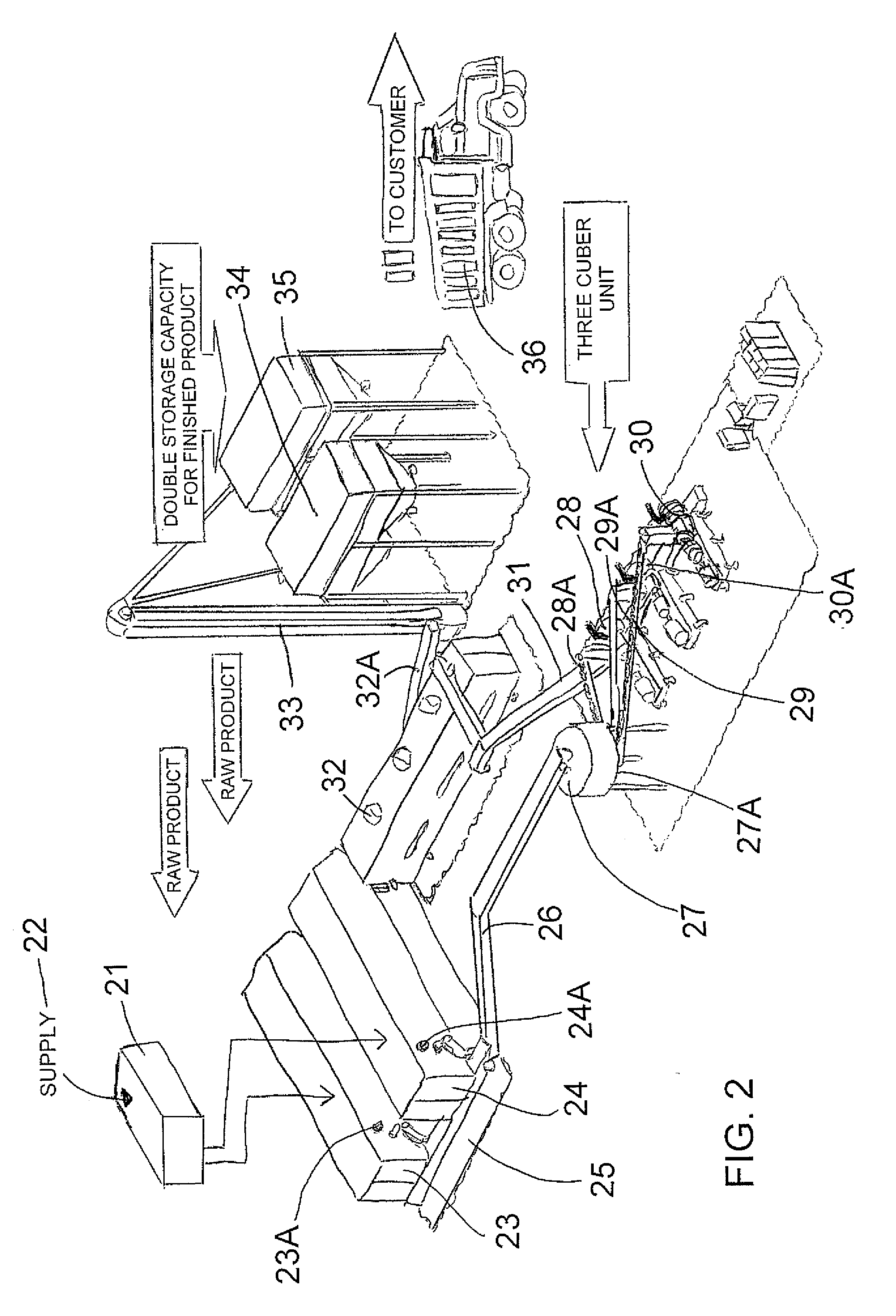
Cubing machine for manufacture of plant biomass solid fuel
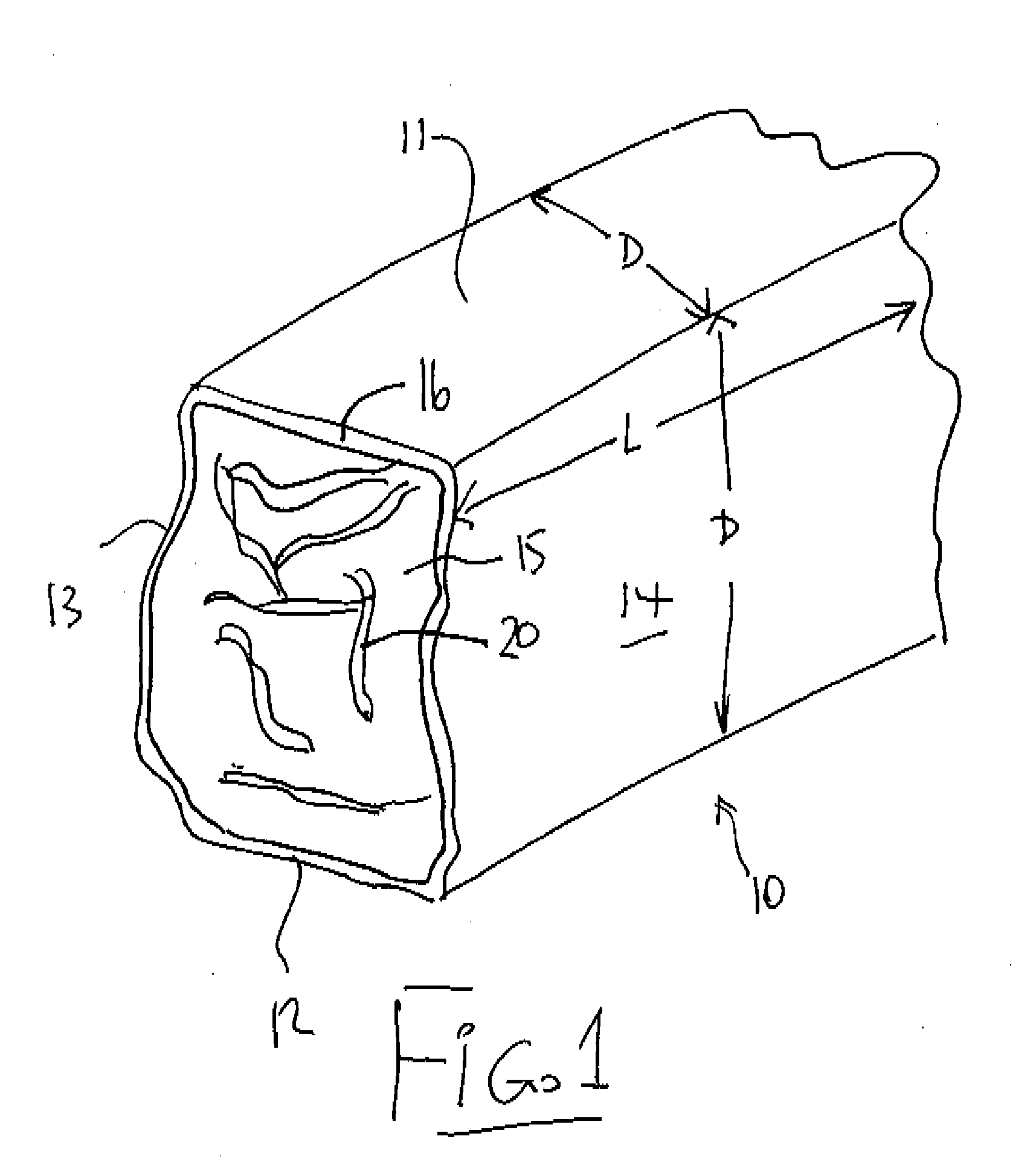
InactiveUS20090056208A1Enhance cube durabilityIncrease energy contentSolid fuelsShaping pressCelluloseSolid fuel
A solid fuel is formed in a cuber to form body pieces formed of materials extruded through a die with a density greater than 35 lbs / cu ft; an energy content greater than 6500 BTU / lb; transverse dimensions less than 1.5 inches; and a length less than 4 inches; from plant biomass material which contains components when extended of greater than 1.0 inch. Primarily the materials are paper or other cellulose product and crop residue such as wheat straw. The cellulose and lignin from these materials act without additional binders as binders and encasing materials. The moisture content is maintained at a target value by mixing selected quantities of the materials without drying. The cubing machine has a feeding system where the space between the inner rotor and outer casing is smaller than 4 inches and the height of the outer flight is less than 1 inch.
Owner:PRAIRIE BIO ENERGY
Methods and components for thermal energy storage
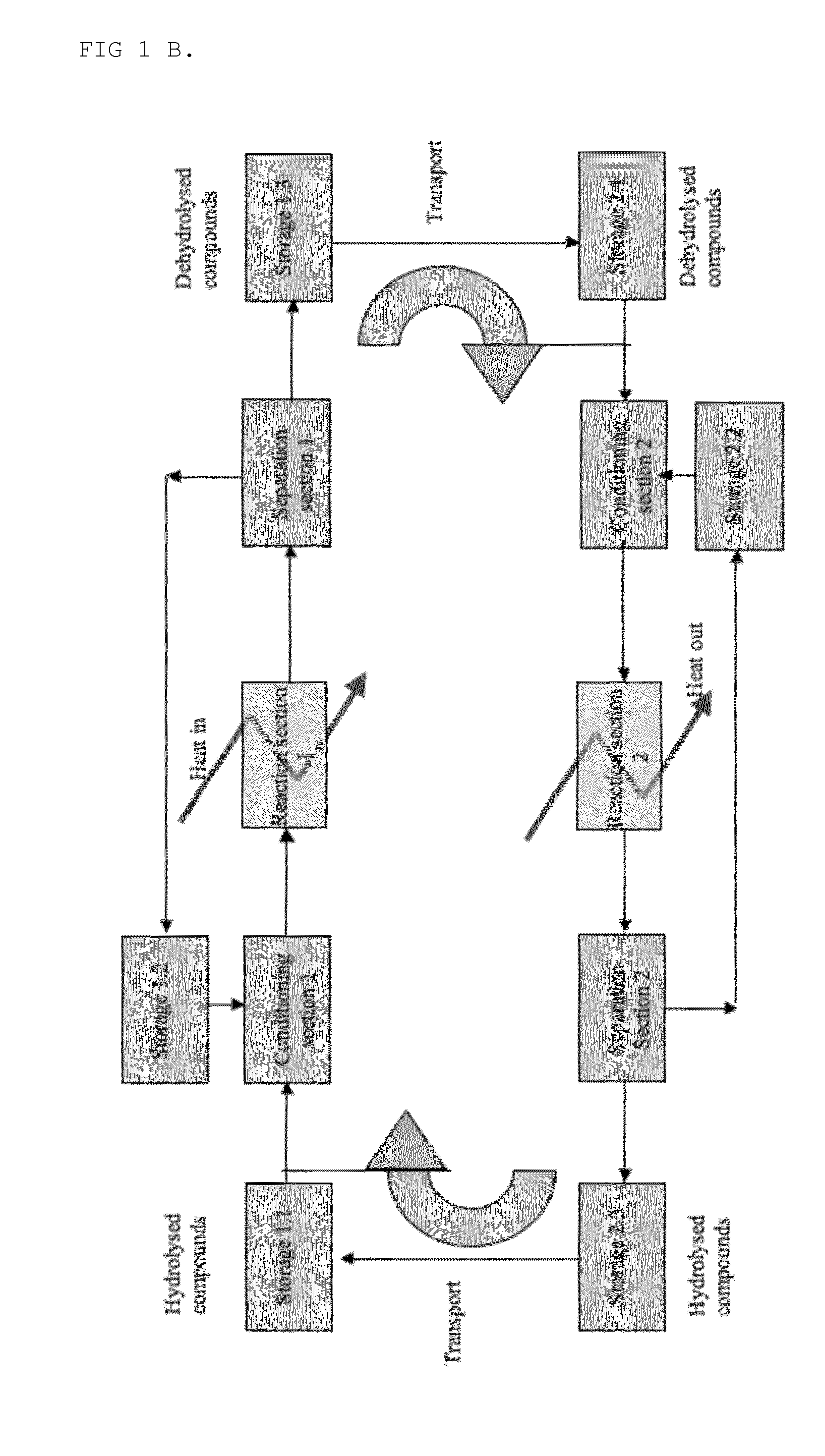
ActiveUS20130306268A1Increase heatIncrease energy contentHeat pumpsDomestic cooling apparatusThermal energyGeneration process
A method is provided for storing thermal energy or increasing the thermal energy of a heat pump using reversible chemical reactions in which inorganic oxoacid compounds and / or their salts are hydrolysed and condensed or polymerized in order to release and capture heat.The method allows thermal energy to be stored at ambient circumstances in a transportable medium and allows converting a continuous heat generation process into a discontinuous and even dislocated consumption.
Owner:CALORITUM NV +1
Fuel injection valve
InactiveUS20030116655A1Reduced cross sectionEasy to manufactureInternal combustion piston enginesSpray nozzlesCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
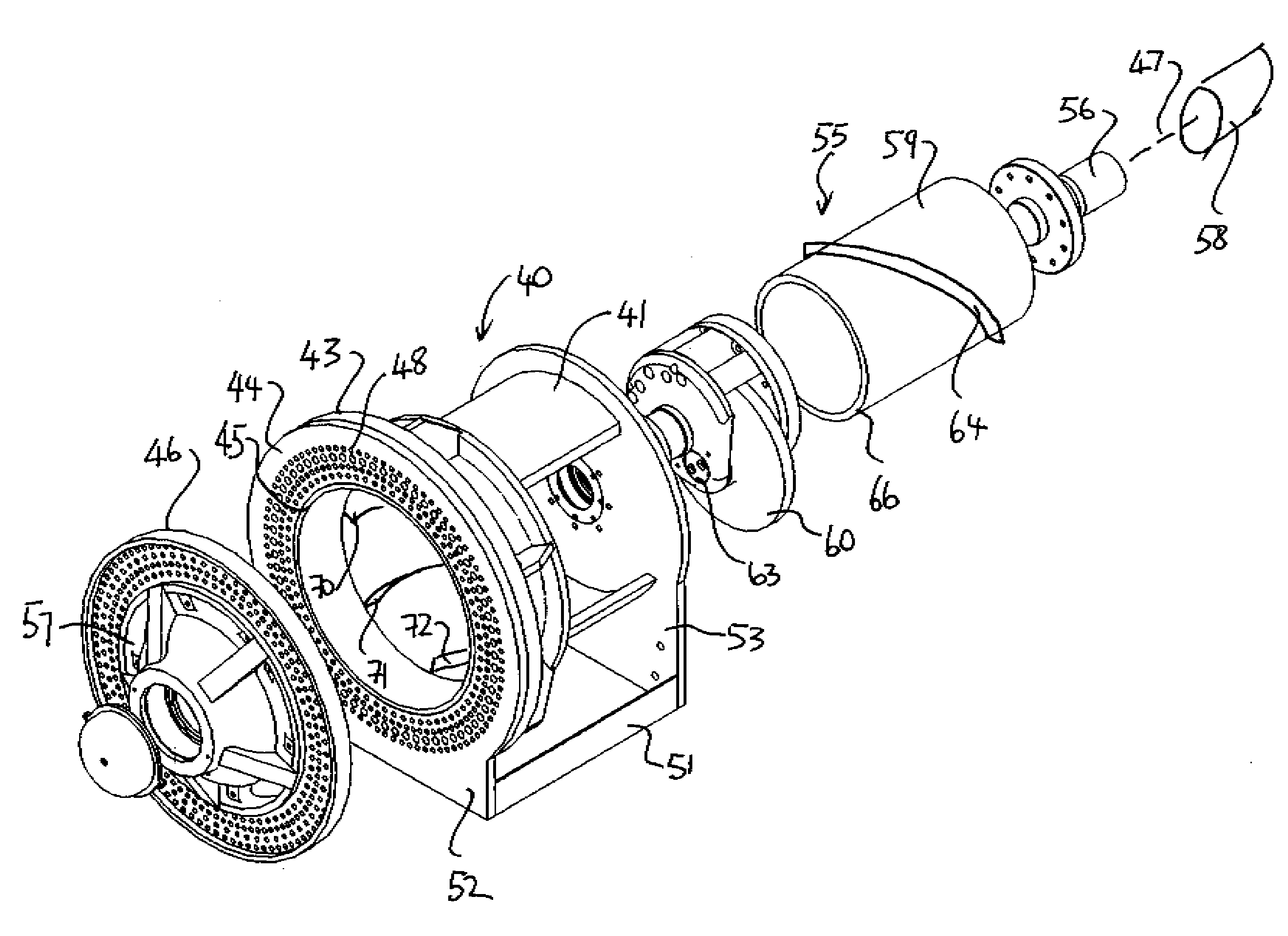
A fuel injector (1), in particular an injector for direct injection of fuel into a combustion chamber of a mixture-compressing, spark-ignition internal combustion engine has a solenoid (10), which cooperates with an armature (20), and a magnetic internal pole (13) and a magnetic external pole (9), the armature (20) being connected in a force-locking manner to a valve needle (3) for actuating of the fuel injector (1), the valve needle having on its injection end a valve-closure member (4), which cooperates with a valve seat (6). At least one permanent magnet (34) is situated in a connecting area between the internal pole (13) and the external pole (9).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Novel Hydrogen-Evolving Polymer-Capped Aluminum Nanoparticles, Composites, and Methods of Synthesis Using Lithium Aluminum Hydride
InactiveUS20150307962A1Increase energy contentLiquid surface applicatorsTransportation and packagingHydrogenNanoparticle
In some aspects, the present disclosure also provides new Al—Li3AlH6 nanocomposite materials, as well as methods of using LiAlH4 to produce Al nanoparticles, Li3AlH6 nanoparticles, or Al—Li3AlH6 nanocomposite materials.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Method for electrical flashover ignition and combustion of propellent charge, as well as propellent charge and ammunition shot in accordance therewith
InactiveUS8607704B2Increase load weightIncreased loading spaceAmmunition projectilesIncandescent ignitionElectricityCombustion
The invention relates to a method of, in the electrical ignition of a propellent charge (1) provided with an electrically conductive surface coating (5) and comprising one or more propellant components (3), ensuring that ignition and progressive combustion of the propellent charge take place. The method is characterized in that said electrically conductive surface coating, when ignition of the propellent charge is desired, is connected to an electrical high-voltage source (6), in that said high-voltage source is made to generate at least one high electrical pulse to said connected electrically conductive surface coating, and in that said at least one high electrical pulse produces an instantaneous flashover ignition of the electrically conductive surface coating of the propellent charge and of all its propellant components, simultaneously. The invention also relates to a propellent charge and to an ammunition shot comprising the propellent charge.
Owner:BAE SYST BOFORS
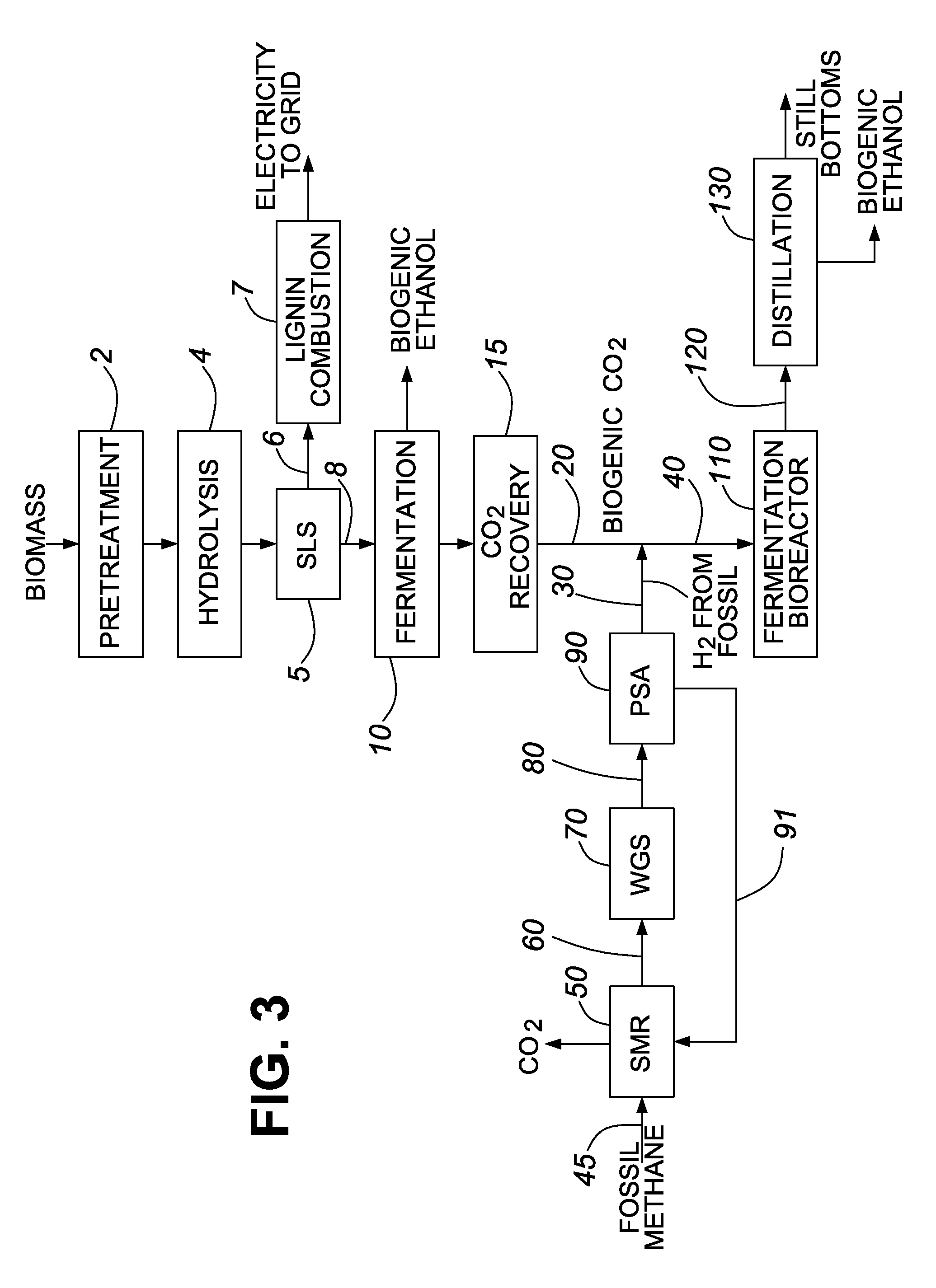
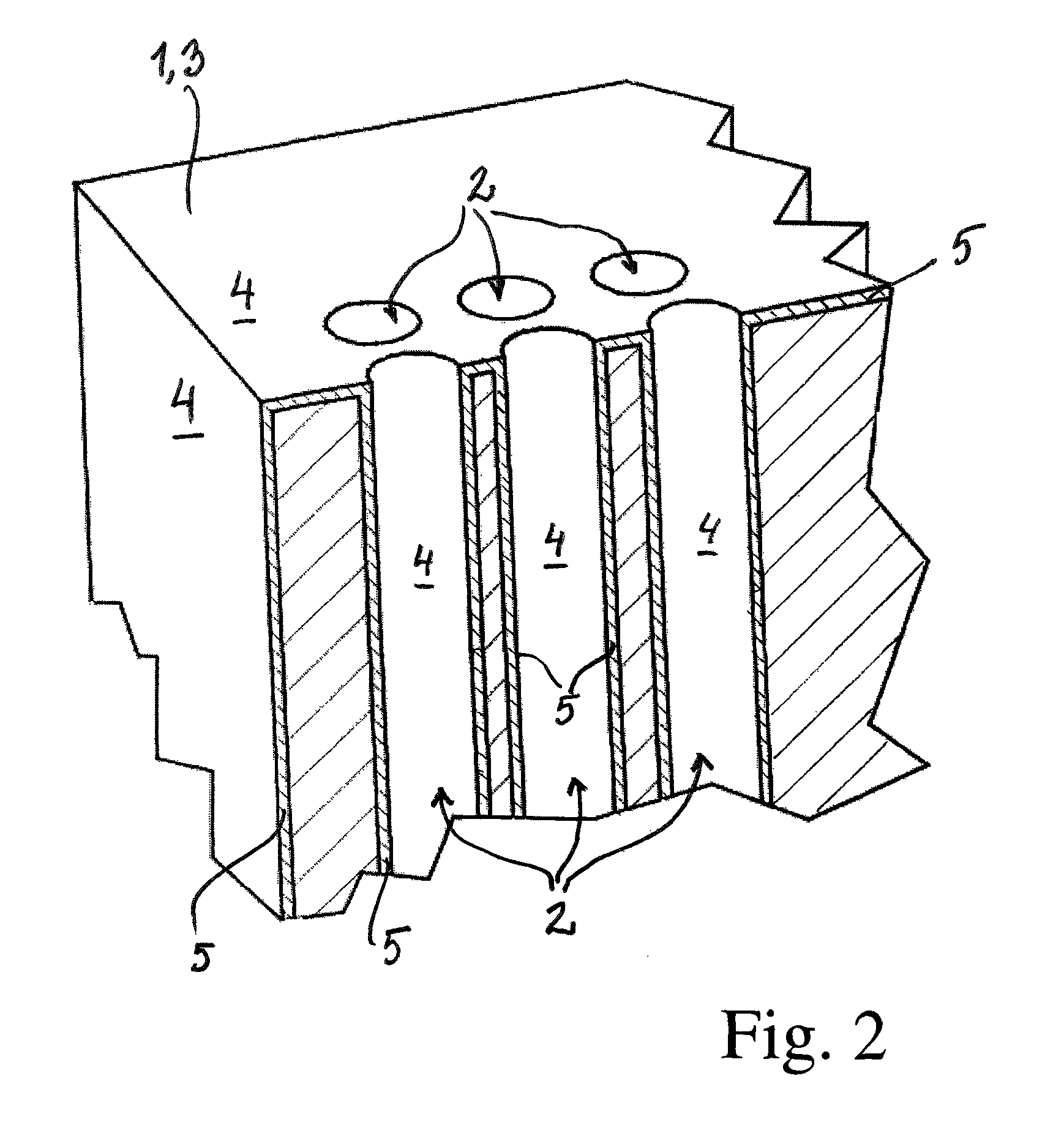
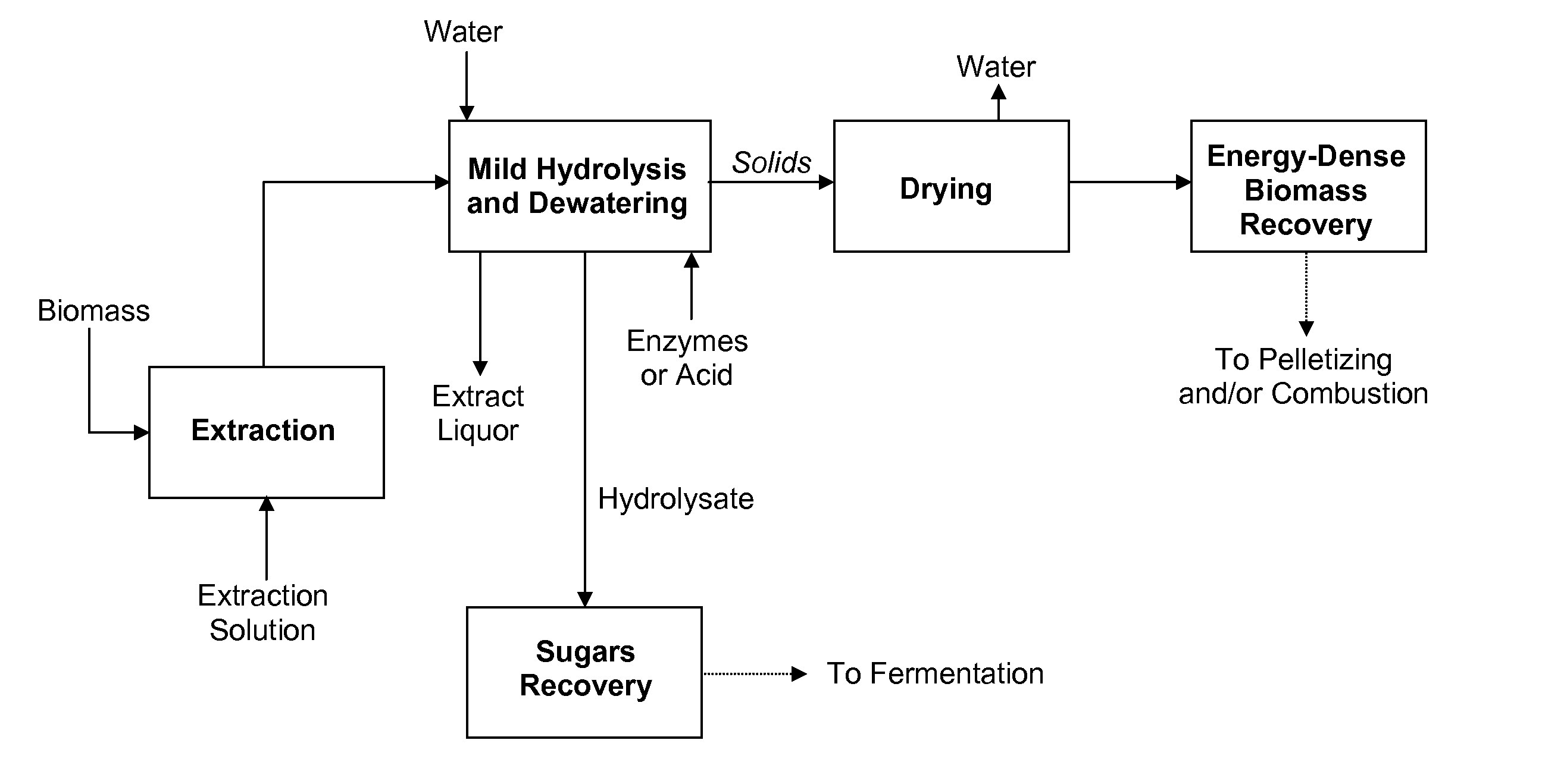
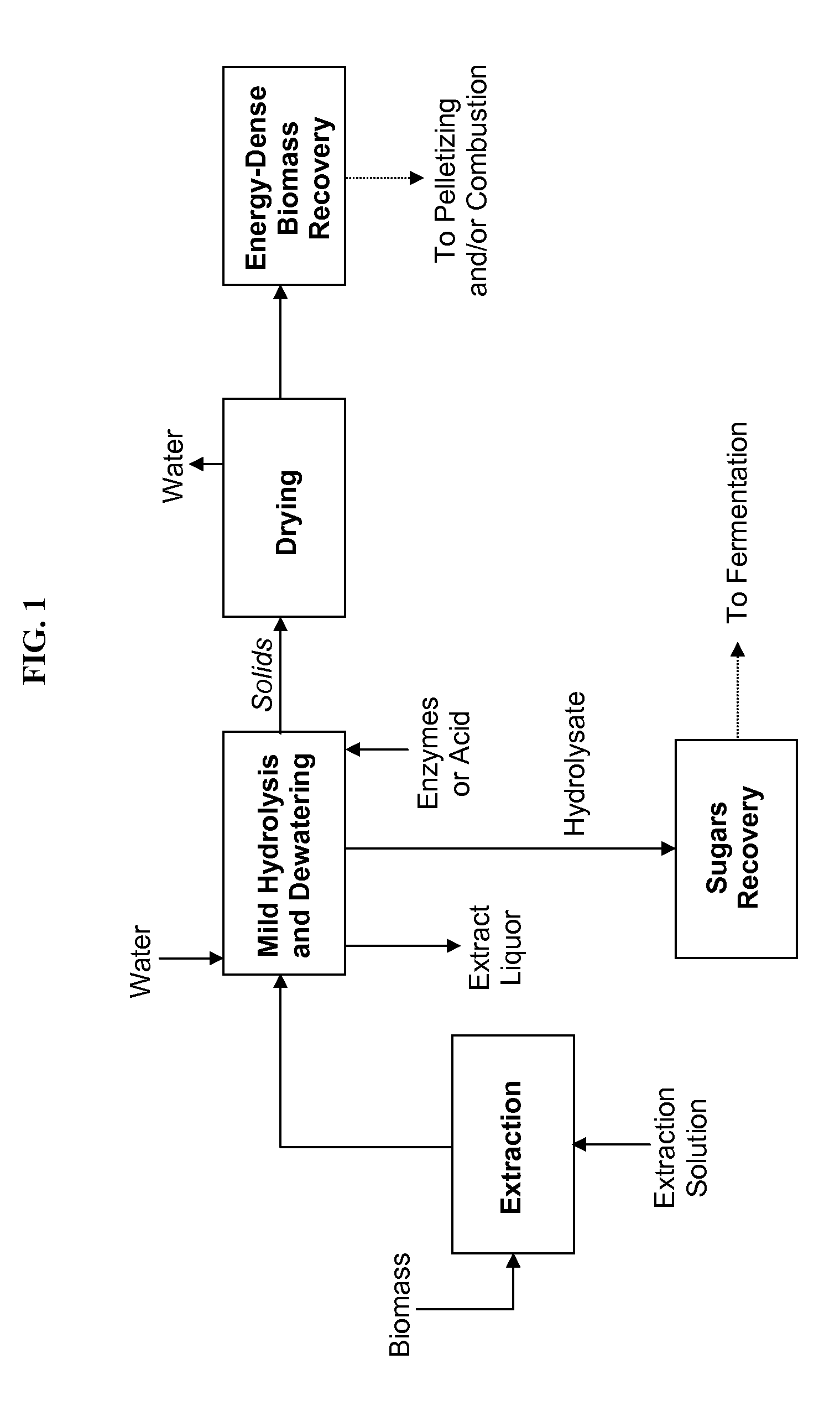
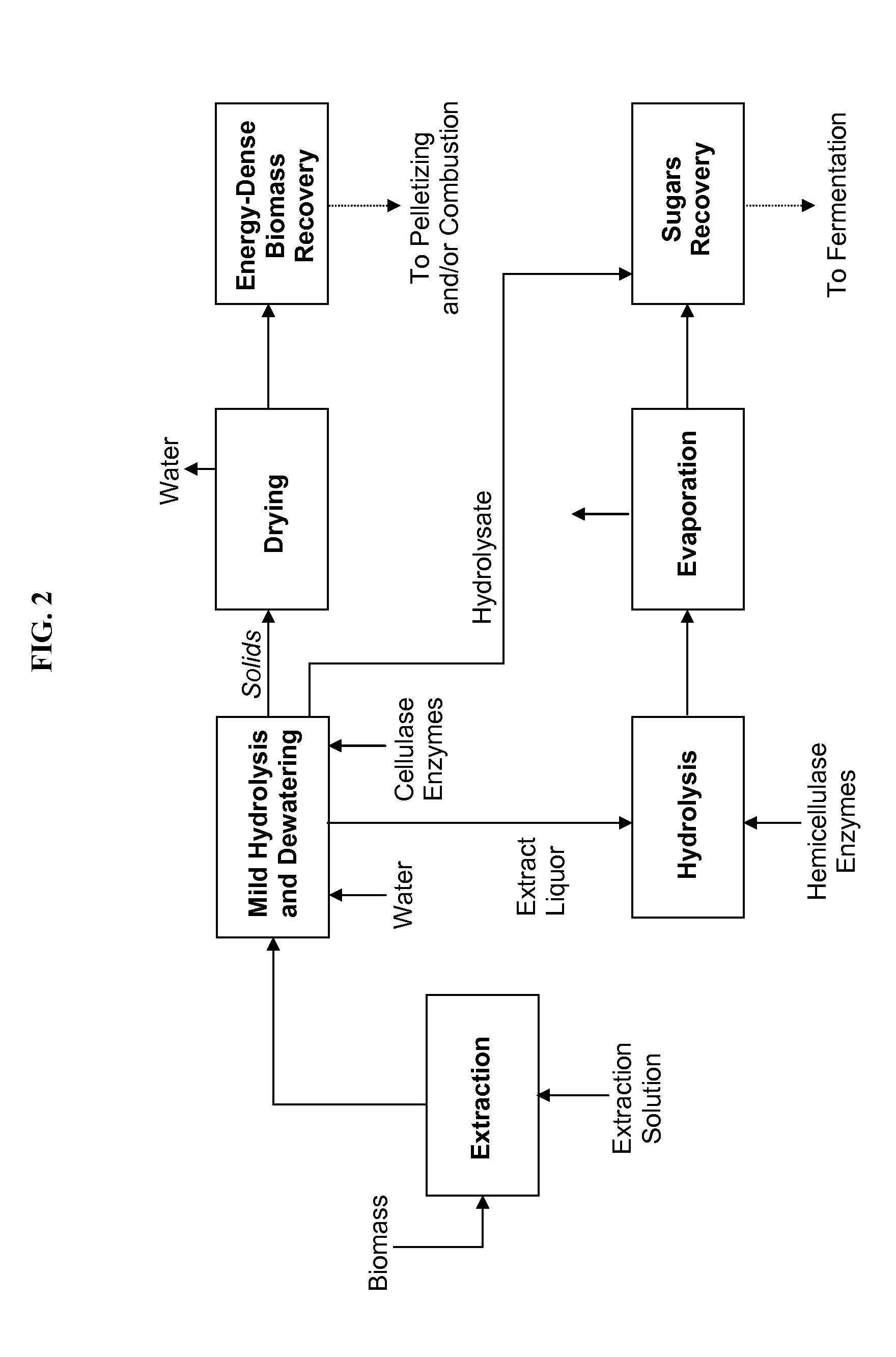
Processes and apparatus for producing energy-dense biomass for combustion and fermentable sugars from the biomass
This invention provides processes to convert biomass into energy-dense biomass for combustion, alone or in combination with another solid fuel. Some embodiments provide processes for producing fermentable sugars and energy-dense biomass from cellulosic biomass, comprising extracting the feedstock with steam and / or hot water to produce an extract liquor containing hemicellulosic oligomers, dissolved lignin, and cellulose-rich solids; separating the extract liquor, to produce dewatered cellulose-rich solids; hydrolyzing the dewatered cellulose-rich solids, thereby removing a portion of the cellulose, to produce intermediate solids (with higher energy density) and a hydrolysate; drying the intermediate solids to produce energy-dense biomass; and recovering fermentable sugars from the hydrolysate. The energy-dense biomass may be pelletized into biomass pellets, which may have a similar energy density as torrefied pellets from wood. The hemicellulosic oligomers may be further hydrolyzed to produce additional fermentable sugars. The fermentable sugars may be fermented to ethanol or another product.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
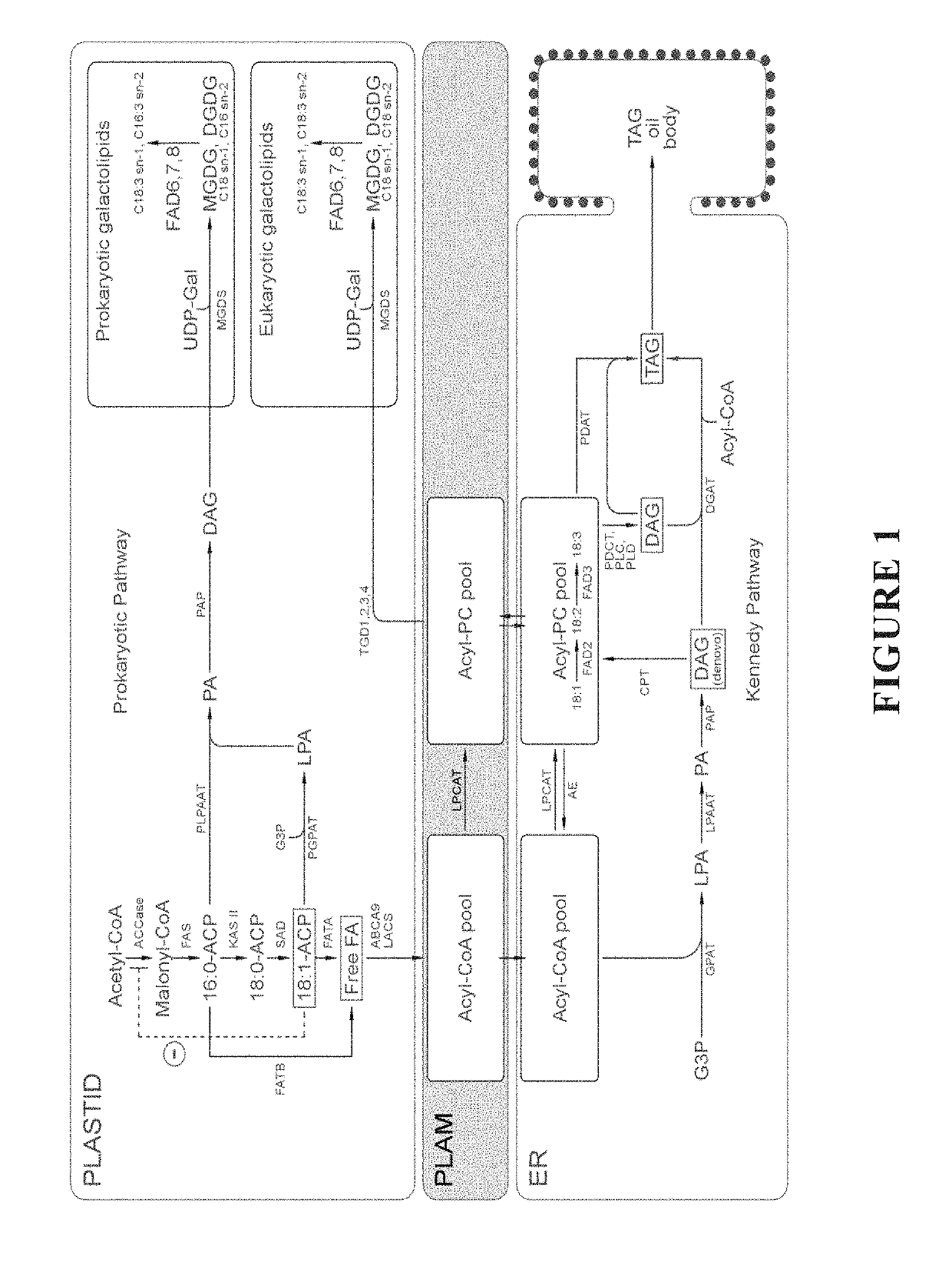
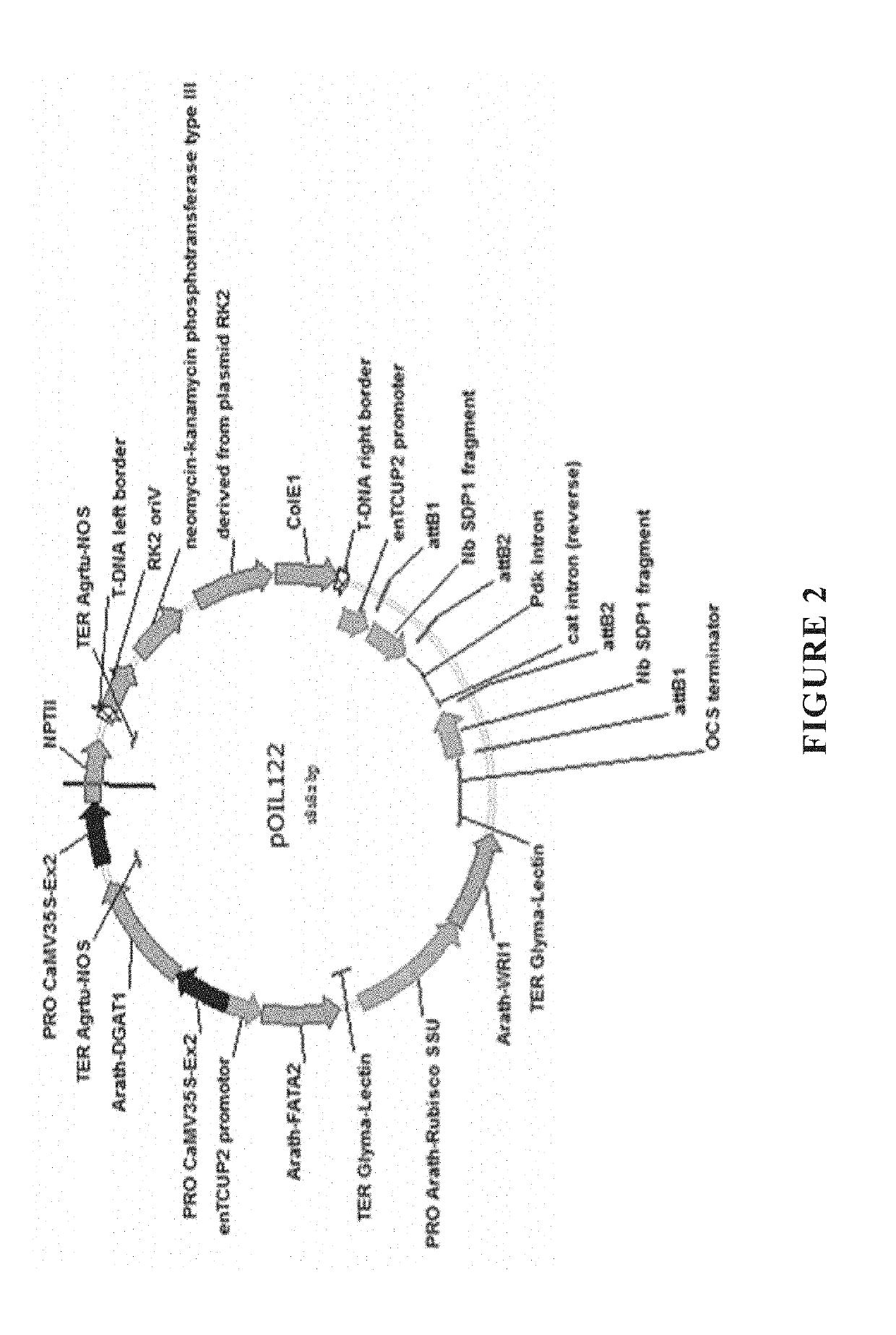
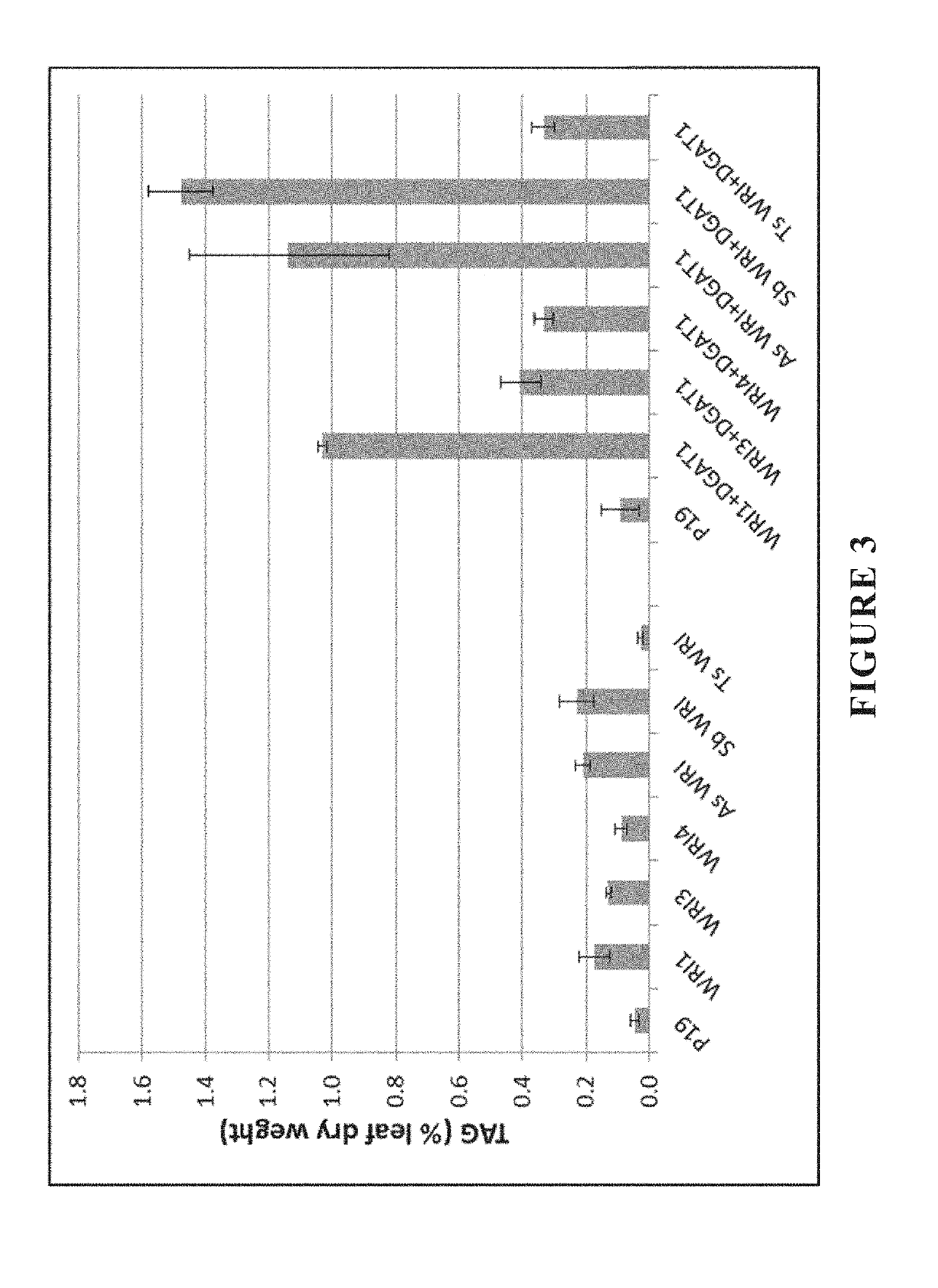
Plants producing modified levels of medium chain fatty acids
The present invention relates to methods of producing industrial products from plant lipids, particularly from vegetative parts of plants. In particular, the present invention provides oil products such as biofuel, and processes for producing these products, as well as plants having an increased level medium chain fatty acids such as lauric acid and myristic acid. In one particular embodiment, the present invention relates to combinations of modifications in a fatty acid thioesterase and one or more acyltransferases. In an embodiment, the present invention relates to a process for extracting lipids. In another embodiment, the lipid is converted to one or more hydrocarbon products in harvested plant vegetative parts to produce alkyl esters of the fatty acids which are suitable for use as a renewable biofuel.
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
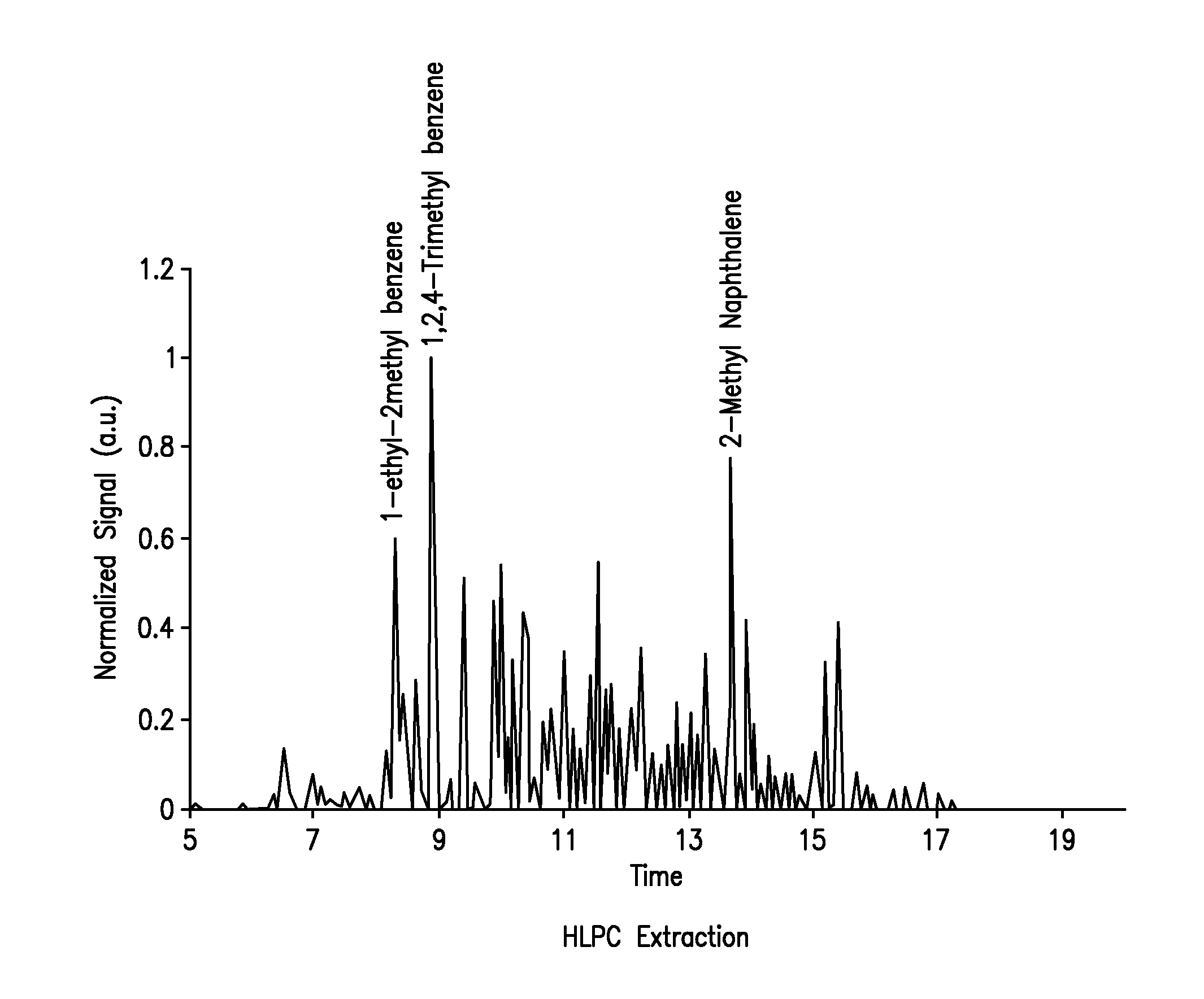
Biogenic Turbine And Diesel Fuel
ActiveUS20110230686A1Increase energy contentHydrocarbon purification/separationBiofuelsAlkaneBoiling point
The present invention provides fully renewable turbine and diesel fuels created from biomass sources. In one embodiment, the fully renewable turbine fuel is comprised of mesitylene and at least one alkane. Preferably, the turbine fuel comprises from about 50 to 99 wt % mesitylene and from about 1 to 50 wt % of at least one alkane. In another embodiment the diesel fuel comprises mesitylene, octadecane, and optionally octane or nonane. Preferably, the diesel fuel comprises from about 50 to 99 wt % mesitylene, and from about 1 to 50 wt % octadecane. These biomass derived fuels may be formulated to have a wide range of cetane values and differing freezing and boiling points. A preferred biogenic turbine fuel comprises one or more synthetic paraffinic kerosenes (SPK) and / or hydroprocessed renewable jet (HRJ) fuel; and between about 8 to 25 vol % of mesitylene. Another preferred biogenic turbine fuel is a blend of about 50% petroleum-based fuel; and about 50% of one or more of synthetic paraffinic kerosenes (SPK) and / or hydroprocessed renewable jet fuel (HRJ), and mesitylene.
Owner:SWIFT ENTERPRISES
Method for cultivating commodity pig on scale
InactiveCN101223869AIncrease energy contentIncrease dosageAnimal feeding stuffFeed conversion ratioFully developed
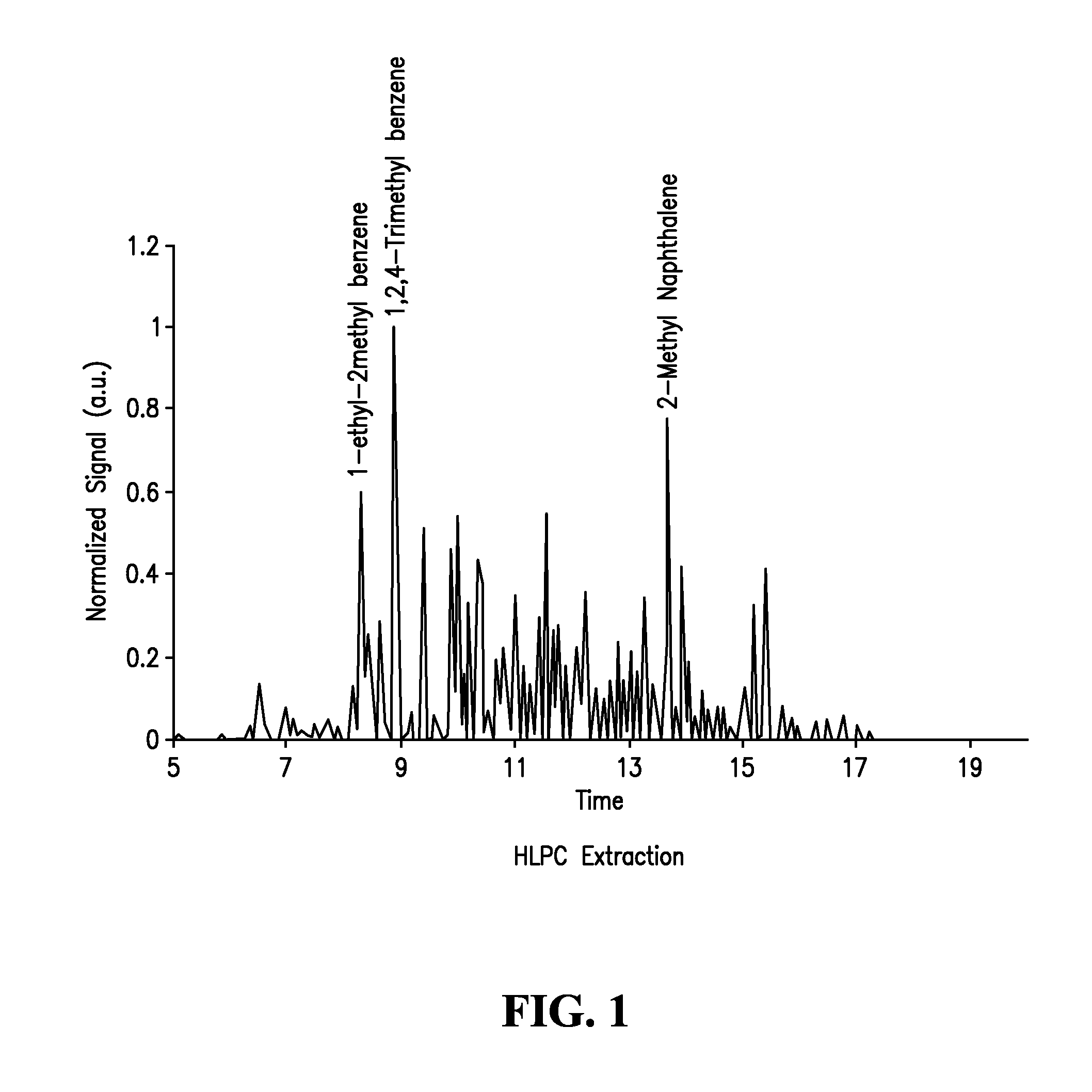
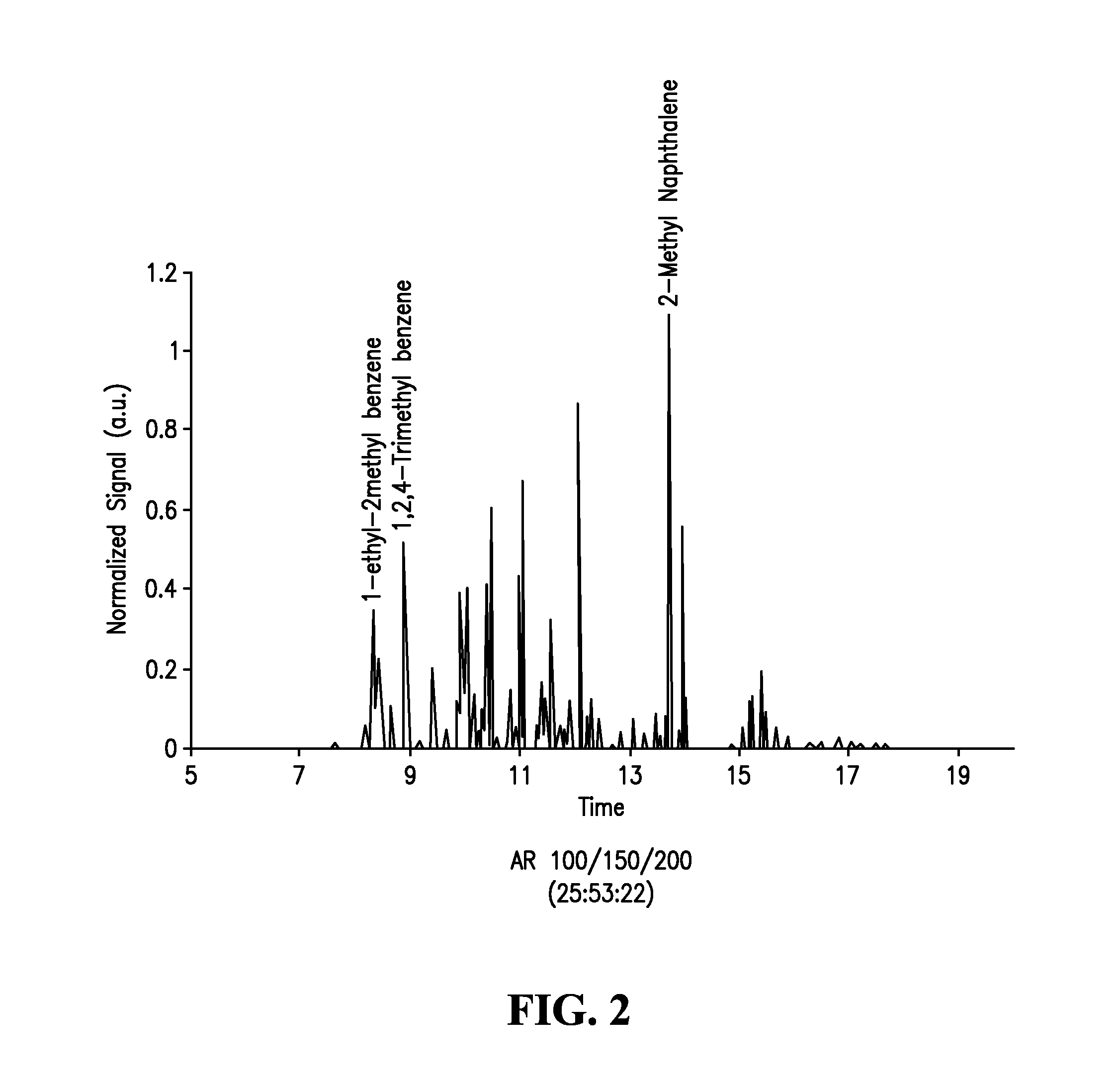
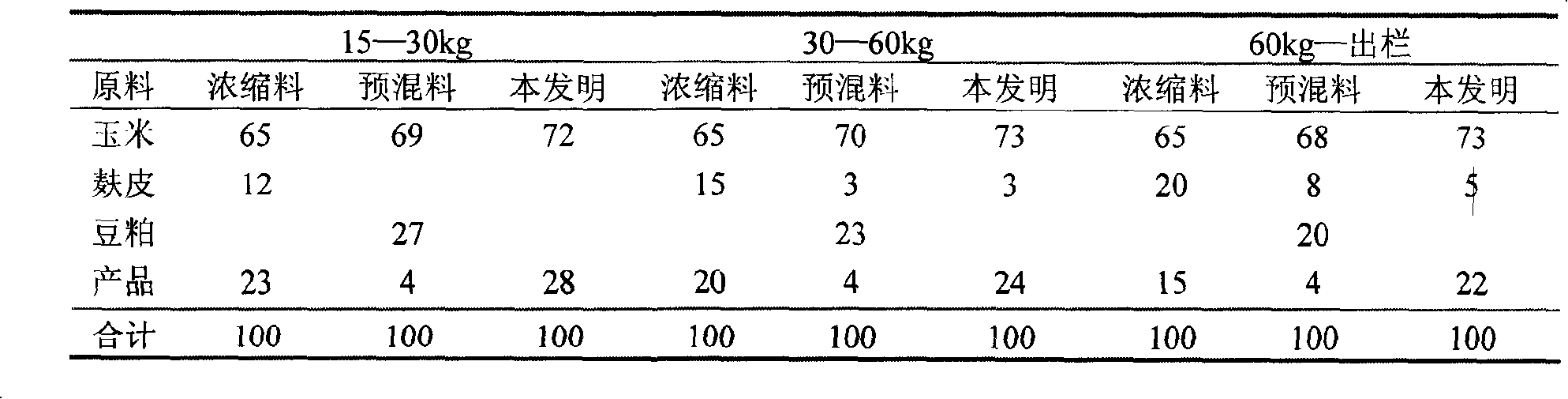
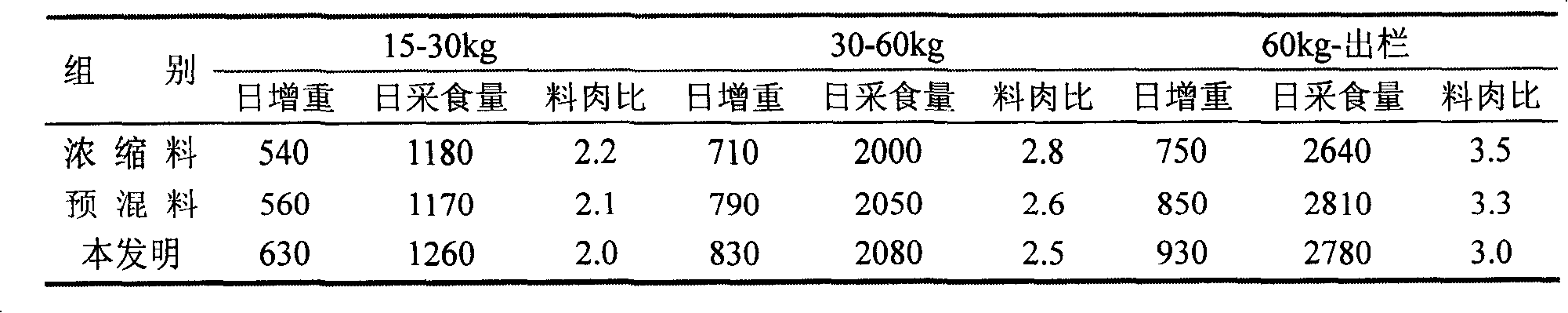
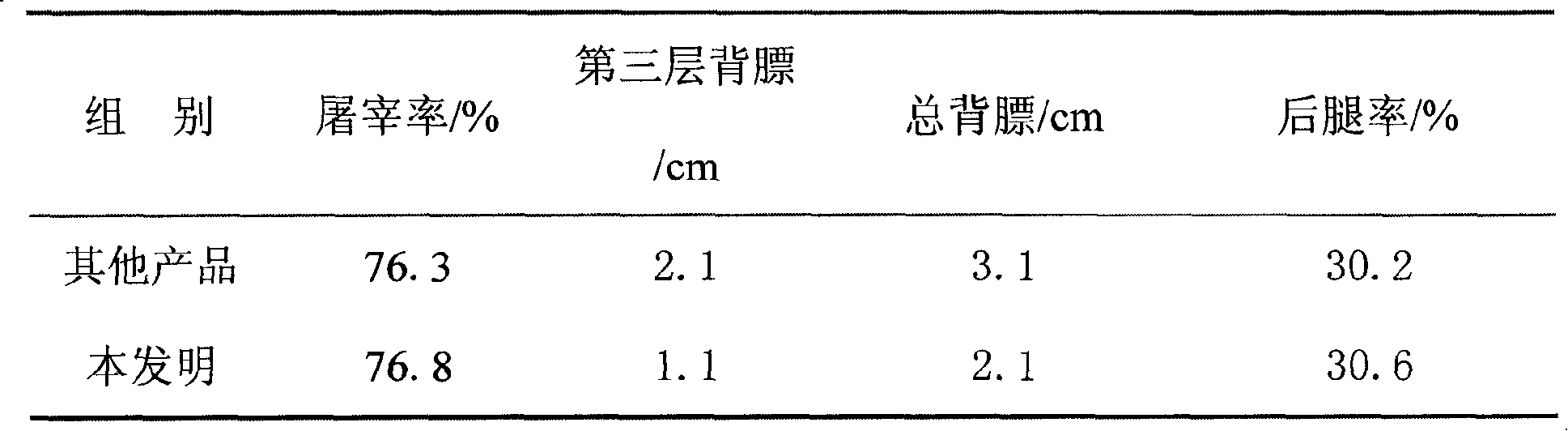
The invention relates to a commercial pig breeding method which provides different food preparations according to the different growth stages of a pig. The specific preparations are divided into the following growth stages: 15-30kg stage: the ingredients of the stage comprise 72-75wt percent of corn and 25-28wt percent of concentrate feed; 30-60kg stage: the ingredients comprise 71-73wt percent of corn, 24-25wt percent of concentrate feed and 3-5wt percent of wheat bran; 60kg to slaughtering stage: the ingredients comprise 70-73wt percent of corn, 22-24wt percent of concentrate feed and 3-5wt percent of wheat bran. The method of the invention can fully develop the pig growth potential and overcome the shortage of universal concentrate feeds; in addition, the invention increases the daily growth weight of pigs through the increasing of the complete feedstuff calories, reduces feed conversion ratio, and changes the status that the previous feedstuff focuses on protein instead of calories, which leads to poor production performance and economic benefit. The invention can also reduce the back fat thickness of commercial pigs and improve dressing percentage and lean meat ratio.
Owner:河南商都生物技术股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com