Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
239results about How to "Effective export" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
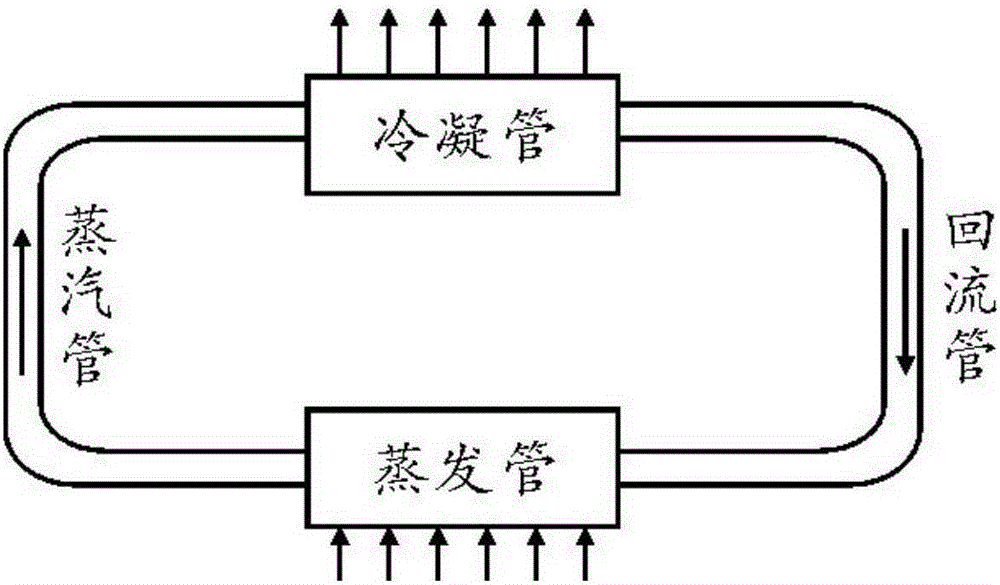
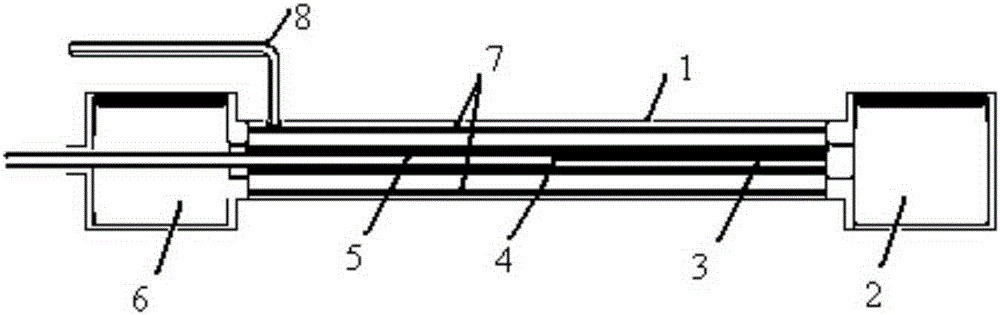
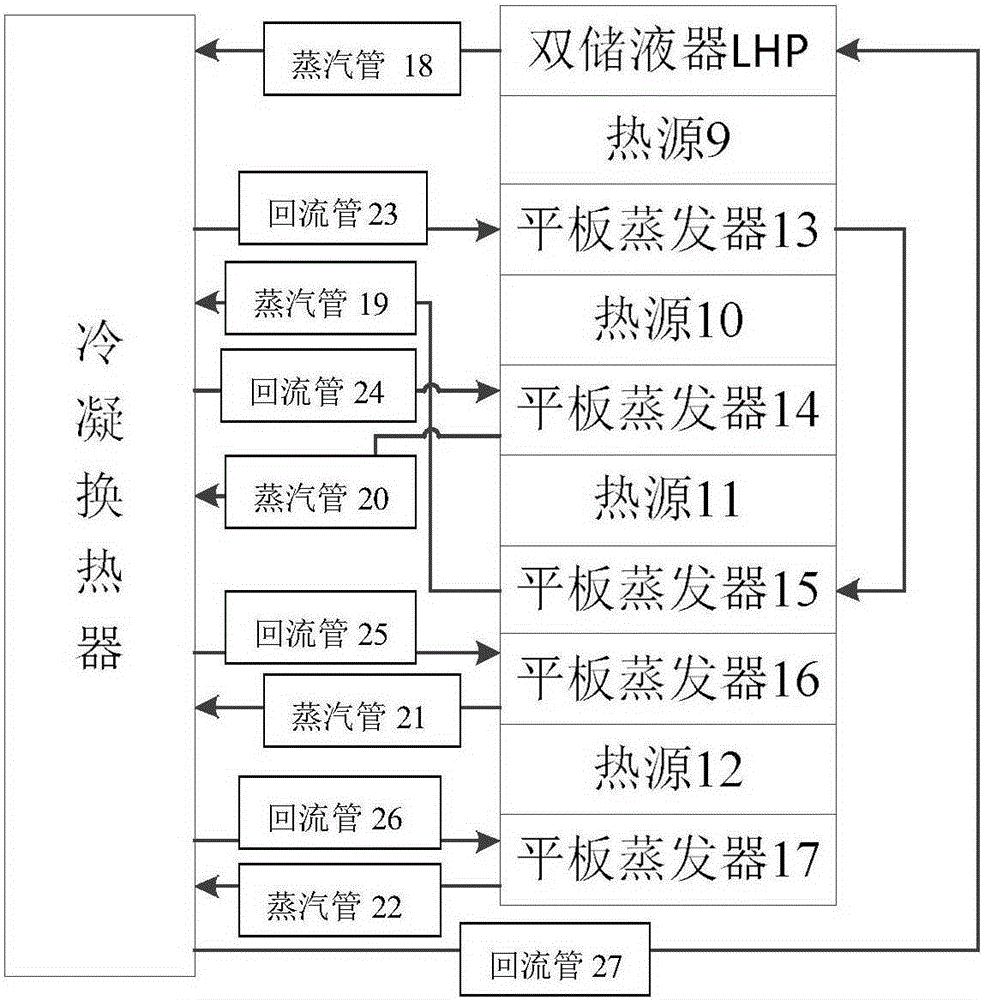
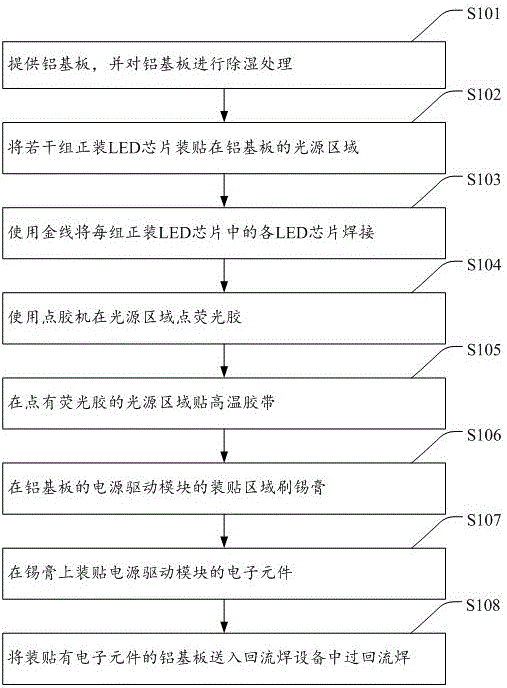
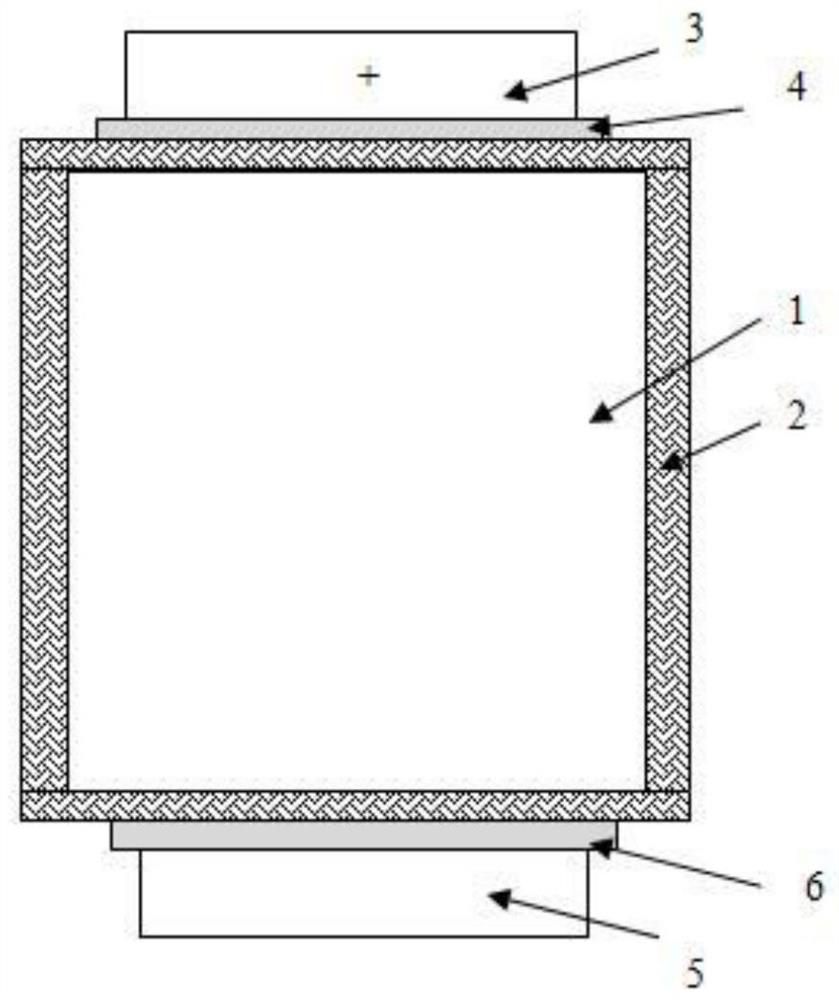
Thermal control loop heat pipe of integrated structure
InactiveCN105277028AImprove temperature uniformityImprove anti-acceleration abilityIndirect heat exchangersMicro-loop heat pipeEvaporation
The invention provides a thermal control loop heat pipe of an integrated structure. The thermal control loop heat pipe comprises a structure thermal control hollow metal pipe body filled with phase change media. The structure thermal control hollow metal pipe body is a loop heat pipe (LHP) formed by connecting a condensation pipe and an evaporator in series, the two sides of the evaporator are connected with liquid accumulators where a steam pipe and a reflux pipe pass, and the liquid accumulators on the two sides are both filled with liquid working media. After heat emitted by a heat source is absorbed by an evaporation pipe, the phase of the liquid working media is changed, the liquid working media enter the condensation pipe through the steam pipe to release heat to be condensed and flows back to the evaporation pipe through the reflux pipe, and then a complete loop heat pipe cycle is completed. According to the thermal control loop heat pipe, integration is adopted, a semiconductor refrigeration manner is used, heat emitted out of the interior of the complex structure can be effectively led out accordingly, and the application range of a heat pipe thermal control system is greatly expanded.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Touch control display device
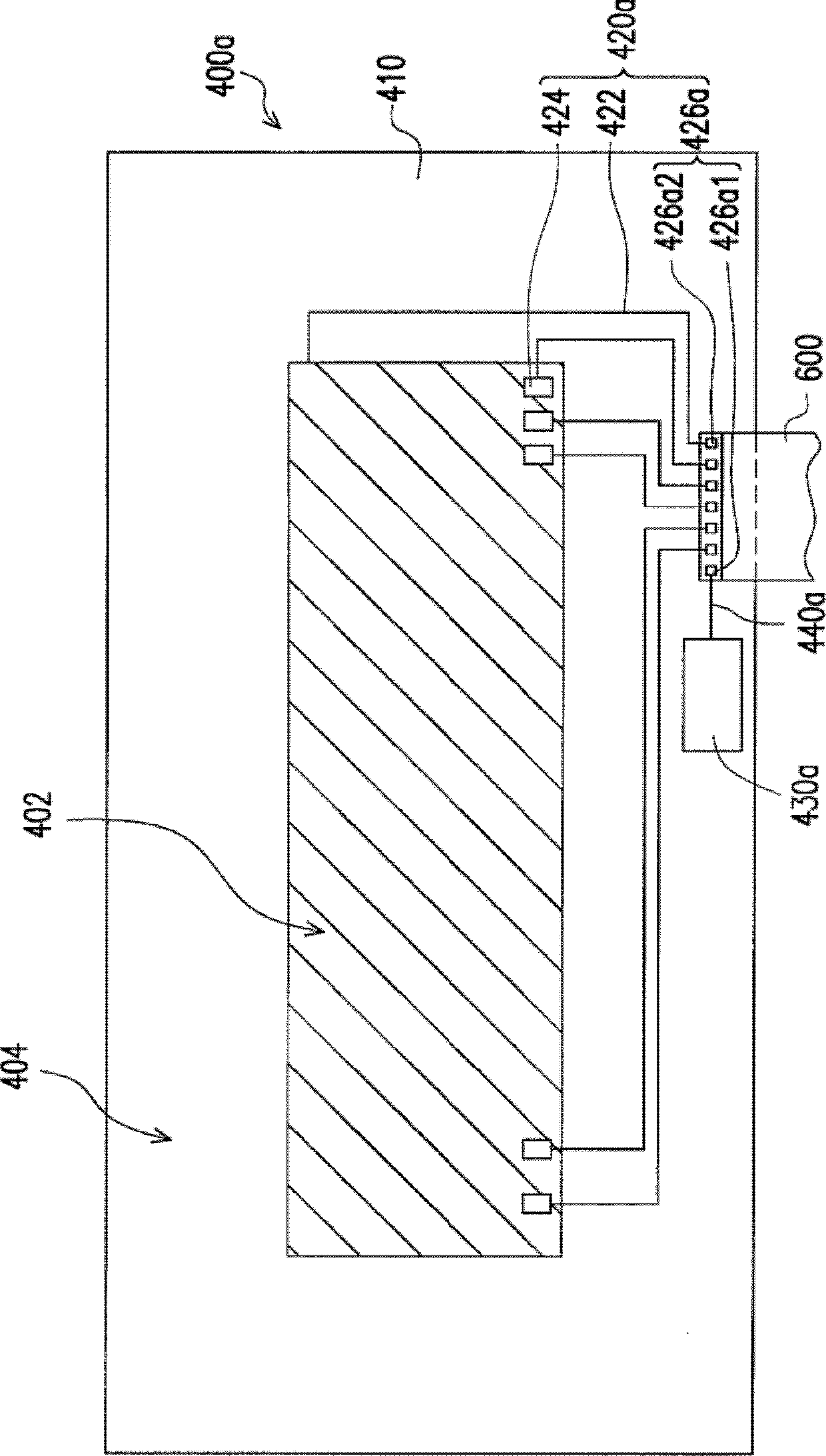
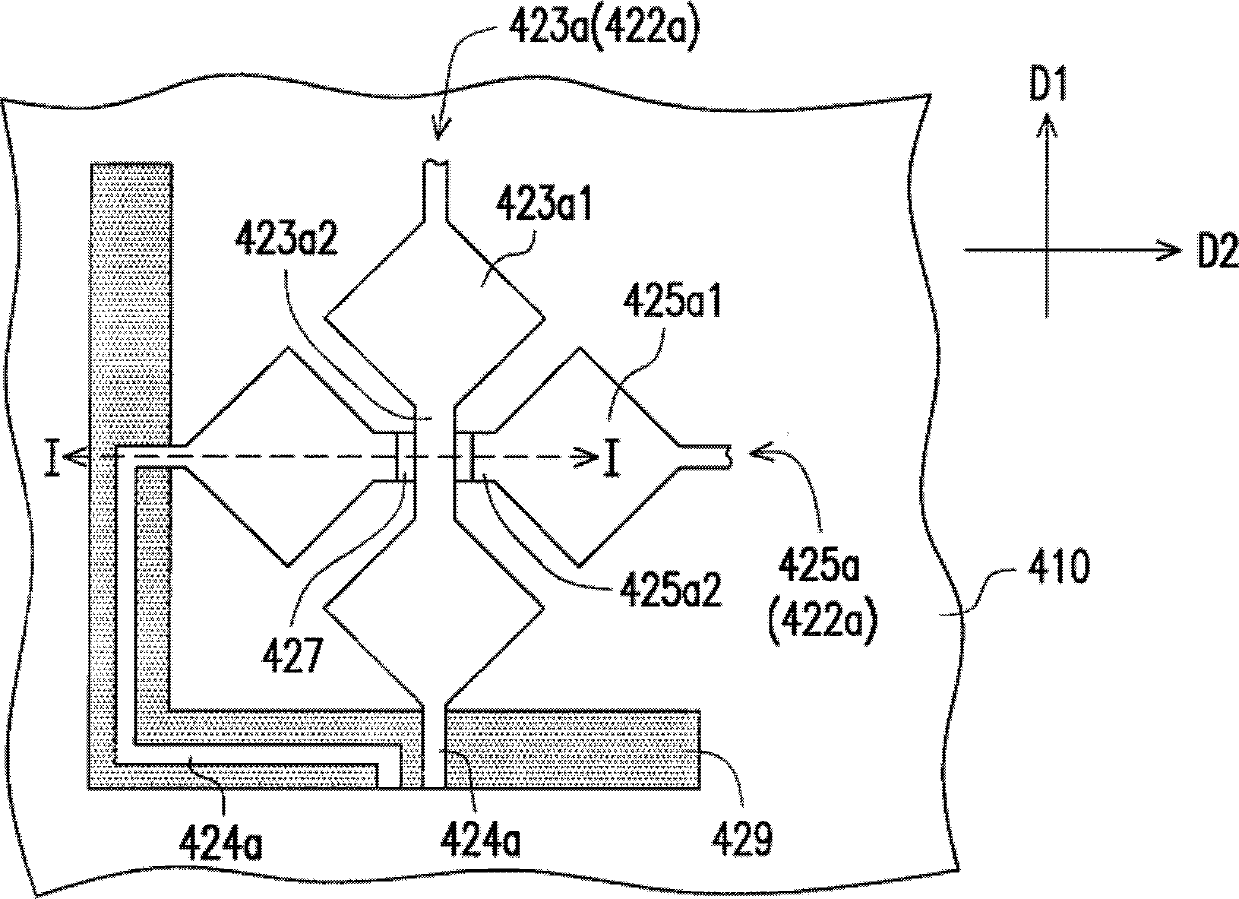
InactiveCN103294238AReduce signal interferenceEffective exportInput/output processes for data processingFlexible circuitsDisplay device
The invention discloses a touch control display device which comprises a display panel, a shading electrode layer, a touch panel, a conductive element and a flexible circuit board, wherein the display panel is covered with the shading electrode layer, and the touch panel is configured on the shading electrode layer. The touch panel comprises a baseplate, a touch control element, one or more grounding electrode and one or more metal wires; and the touch control element comprises one or more sensing electrodes, one or more transmission conducting wires and two or more connecting pads. The transmission conducting wire is electrically connected with the sensing electrode and one of the connecting pads. The metal wire is connected with the grounding electrode and the other connecting pad. The shading electrode layer is electrically connected to the metal wire or the grounding electrode of the touch panel through a conductive element. The flexible circuit board is electrically connected with the connecting pads so as to enable the sensing electrode and the metal wire to be electrically connected to the flexible circuit board.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
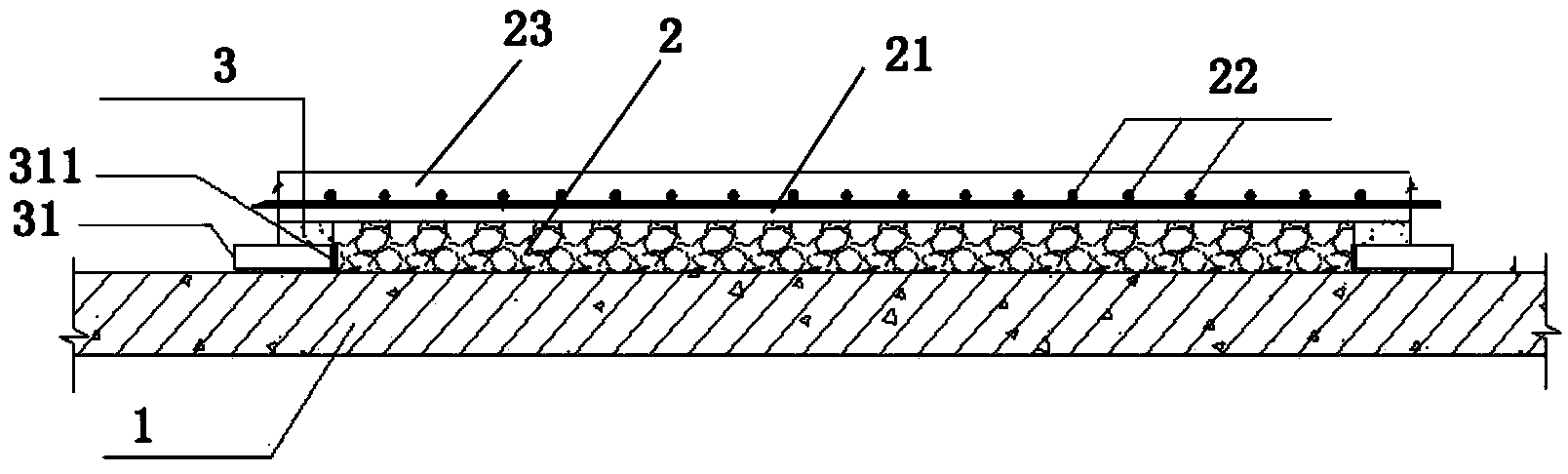
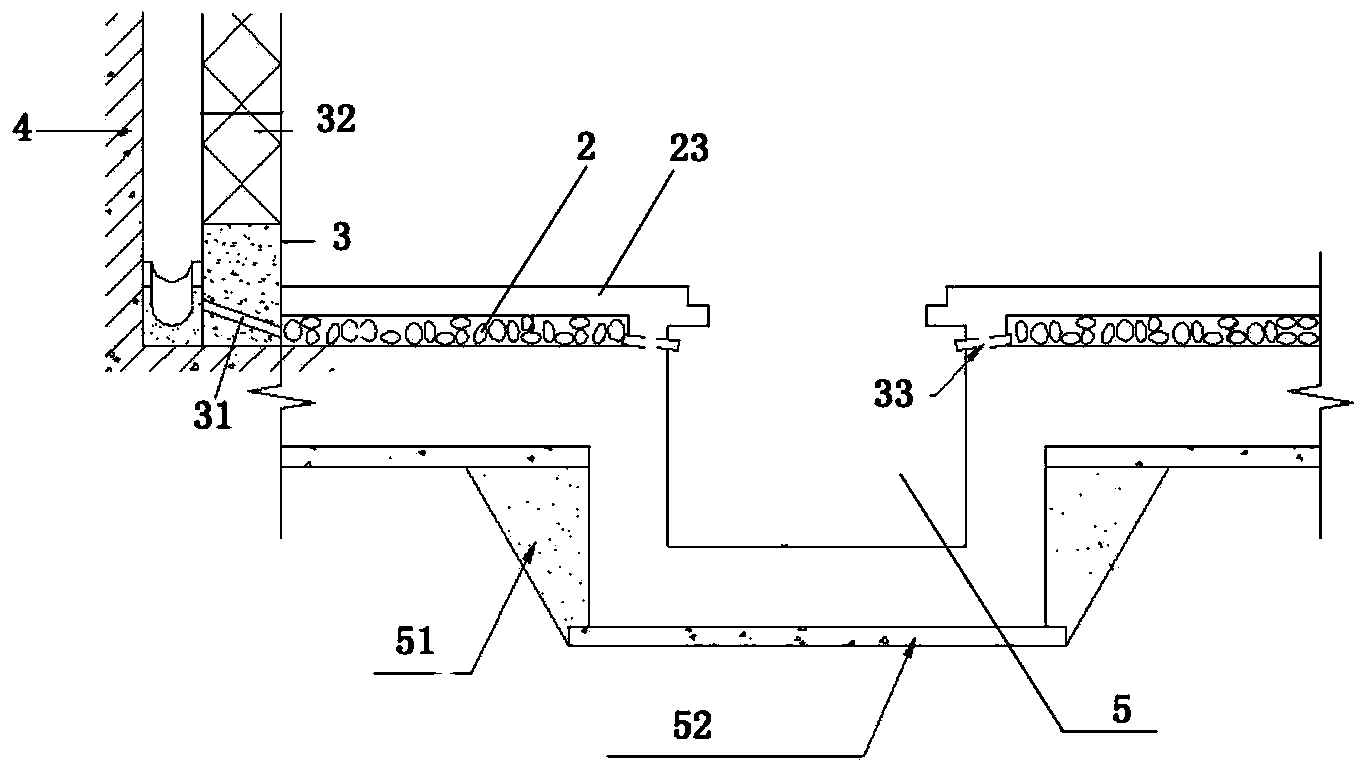
Basement bottom plate water drainage layer construction method
InactiveCN103821181ASolve common quality problemsEffective exportArtificial islandsProtective foundationBasementSurface layer
The invention discloses a basement bottom plate water drainage layer construction method. According to the method, a grait layer is paved at the basement bottom layer part, the self discharge function of the grait layer is utilized for realizing the water drainage, the traditional single water blocking mode is broken, water seeped from the outer wall and the bottom plate of the basement is firstly gathered to an anti-seeping wall water drainage ditch and is then gathered to a water collecting well through entering the water drainage layer to flow freely, and finally, the water is pumped and discharged into a municipal pipe network through an automatic water discharge pump. The water drainage layer is used as an isolation layer between the bottom plate structure and a decoration surface layer, seeped water can be effectively guided out, the dryness of the use surface layer is maintained, a good water drainage effect is reached, and the common quality problem of the basement outer wall and bottom plate seepage is effectively solved.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN CONSTR GROUP
Heat-conducting and wave-absorbing rubber material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106751910AHigh temperature resistantLow temperature resistanceHeat-exchange elementsCross-linkRubber material
The invention discloses a heat-conducting and wave-absorbing rubber material and a preparation method thereof. The heat-conducting and wave-absorbing rubber material is prepared from the following substances in parts by weight: 100 parts of a rubber matrix, 50-600 parts of heat-conducting powder, 50-400 parts of wave-absorbing powder, 0-2 parts of a release agent and 0.5-2 parts of a cross-linking agent. The heat-conducting and wave-absorbing rubber material has the properties of high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, high voltage resistance, ozone aging resistance, radiation resistance, weather resistance, physiologically inert property, high permeability and solvent resistance, and especially has outstanding high temperature resistance, so that the possibility is provided for preparation of the heat-conducting and wave-absorbing material; the heat-conducting and wave-absorbing rubber material can be directly applied between a heat dissipation room and a metal housing, and heat energy can be effectively exported; and meanwhile, the heat-conducting and wave-absorbing rubber material has electromagnetic shielding and electromagnetic noise wave absorbing properties, so that a good solving scheme is provided for electronic communication products in heat conduction and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:DALIAN DONGSHIN MICROWAVE TECH
Wavelength conversion apparatus and light emitting device
InactiveCN103794704AHigh thermal conductivityReduce the temperatureSpectral modifiersSemiconductor devicesPhysicsThermal conductivity
The invention brings forward a wavelength conversion apparatus for absorbing exciting light and emitting excited light. The wavelength conversion apparatus comprises a wavelength conversion layer and a heat-conduction substrate. To be specific, the wavelength conversion layer includes wavelength conversion particles and first heat-conduction particles, wherein the wavelength conversion particles and the first heat-conduction particles are mixed uniformly. The heat conductivity coefficient of the first heat-conduction particle is higher than 10W / m.K; and the size D2 of the first heat-conduction particle is less than or equal to 0.5 times of the size D1 of the wavelength conversion particle and is larger than or equal to 0.05 times of the D1. The wavelength conversion layer is tightly attached to the surface of the heat-conduction substrate. According to the invention, gaps among the wavelength conversion particles are filled with the first heat-conduction particles with the specific particle sizes, thereby effectively improving the thermal conductivity of the wavelength conversion layer. Therefore, heat emitted by the wavelength conversion particles can be effectively conducted to the surface of the wavelength conversion layer and then is dissipated through the heat-conduction substrate, so that the temperature of the wavelength conversion layer is effectively reduced.
Owner:吴震
Integrated COB light source with power drive
ActiveCN105072776AEffective exportNo mismatchElectric light circuit arrangementMaterial resourcesEngineering
The invention discloses an integrated COB light source with a power drive. The integrated COB light source comprises an aluminum substrate. A light source module and a power drive module are arranged on the aluminum substrate. The light source module comprises a plurality of LED chip sets. The power drive module is arranged around the light source module, and has the same number of drive control ends as the LED chip sets. The LED chip sets are covered with fluorescent powder. The power drive module lights up the corresponding LED chip set according to the change of input voltage. By adopting the aluminum substrate, heat generated by the light source and electronic components can be dissipated effectively, and the heat dissipation performance is good. As the light source module and the power drive module are arranged on the same substrate, power source and light source mismatch is avoided. Moreover, the assembly process is simplified, the product yield is improved, and the cost of manpower and material resources is reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN FURI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flame-retardant heat conductive insulation silicone rubber product for power equipment and preparing method of flame-retardant heat conductive insulation silicone rubber product
ActiveCN106046799AReduce intensityLow thermal conductivitySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationSmall animalInsulation layer
The invention discloses a flame-retardant heat conductive insulation silicone rubber product for power equipment. The flame-retardant heat conductive insulation silicone rubber product comprises a bonding layer and a heat conductive insulation layer, wherein the bonding layer is arranged below the heat conductive insulation layer, the thickness of the bonding layer ranges from 0.05 mm to 0.1 mm, the thickness of the heat conductive insulation layer ranges from 0.5 mm to 3.5 mm, and the heat conductive insulation layer comprises a silicon rubber insulation layer. The invention further discloses a preparing method of the silicon rubber product. The obtained silicon rubber product is easy to construct and capable of being tightly attached to power equipment, heat generated in the running process of power equipment can be effectively led out, and human casualty accidents caused by pollution flashover, condensate flashover, small animal short circuiting and naked busbars in transformer substations are also effectively eliminated.
Owner:北京天衣鼎嘉工程技术有限公司
Method for identifying transformer sympathetic inrush current based on intelligent substation territory information
ActiveCN103259250AShould surge current be effectiveEffective exportEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHarmonic phaseEngineering
Disclosed is a method for identifying transformer sympathetic inrush current based on intelligent substation territory information. The method includes the following steps: (1) judging whether a transformer is in a no-load shutdown state, (2) judging whether the phenomenon of no-load transformer switching-in exists, (3) acquiring line current of the switching-in side of the transformer which is switched in without load, acquiring line current of primary and secondary sides of other operating transformers, and calculating differential current of the primary and secondary sides of the operating transformers, (4) continuously calculating the secondary harmonic component of the operating transformers and carrying out timing from the moment of no-load switching-in till the secondary harmonic component is larger than m% and fundamental waves exceed by n% of rated current, (5) comparing the secondary harmonic phase of the switched-in transformer and the secondary harmonic phase of operating transformers, and (6) increasing the constant value of differential protection starting current of the operating transformers to k1 times of an original starting value and carrying out timing, and setting the constant value to be the original starting value and returning the process to the step (1) when one of three conditions is met. According to the method for identifying the transformer sympathetic inrush current based on the intelligent substation territory information, during the sympathetic inrush current, protection can still be effectively carried out when internal fault of the transformers occurs; after the sympathetic inrush current, differential protection action characteristics can return to original action states quickly.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
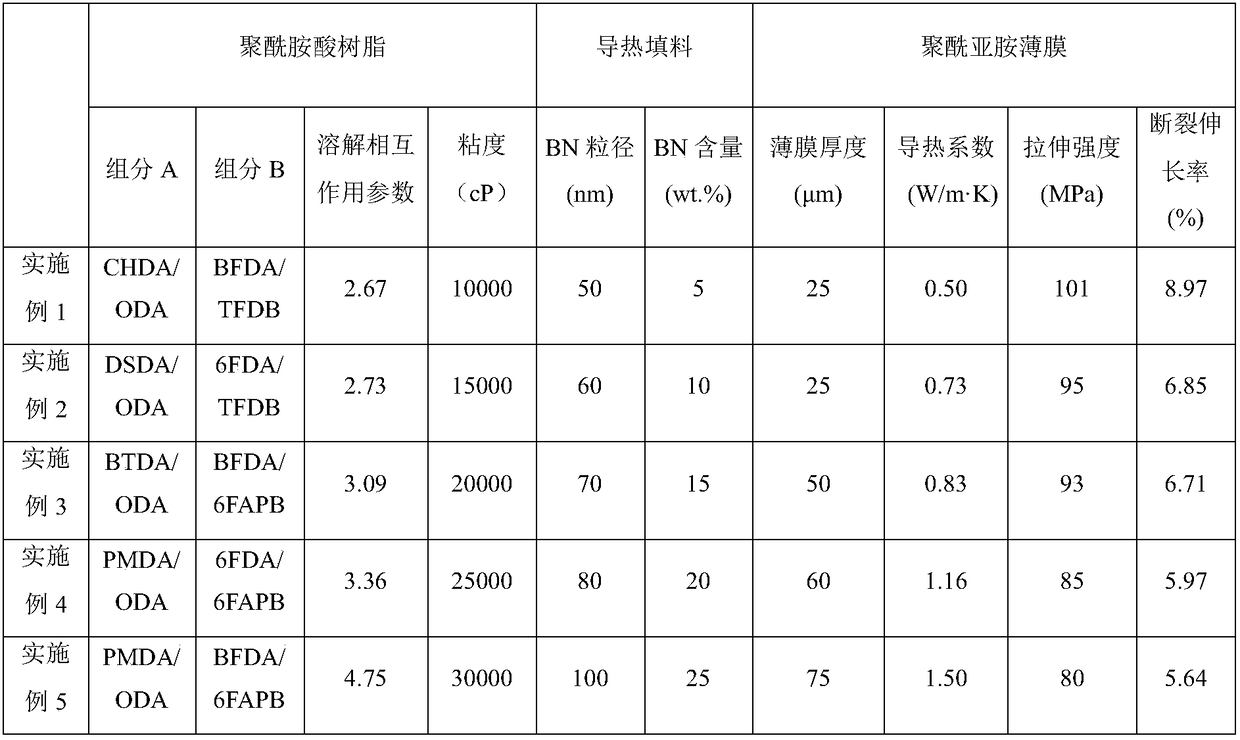
High thermal conductivity polyimide film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108610631AGood mechanical propertiesEffective exportHeat-exchange elementsPolyamic acidElectronic component
The invention relates to a high thermal conductivity polyimide film and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of polyimide films. According to the high thermal conductivity polyimide film, the problems that an efficient heat conduction channel is difficulty constructed by an existing doping method at low filling volume of thermal conductive filler and mechanical properties and the thermal conductivity of the polyimide film cannot be simultaneously obtained are solved. The film comprises a polyimide resin A, polyimide resin B and the thermal conductive filler; the thermal conductive filler is dispersed in A phase; a solution interaction parameter difference of polyamic acid resin A and polyamic acid resin B is 2.5 to 5.0; the heat conduction channel of the polyimide film is continuous and is perpendicular to the plane of the film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a thermal conductive filler solution doped with the polyamic acid resin A and a thermal conductive filler solution doped with the polyamic acid resin B; mixing the two solutions; coating a substrate with the mixed solution; heating in the procedures; carrying out thermal imidization and stripping to obtain the high thermal conductivity polyimide film. The high thermal conductivity polyimide film and the preparation method thereof can be used for insulated heat dissipation of electronic components.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Room-temperature mold-curing heat-conducting wave-absorbing rubber material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106751881AHigh temperature resistantLow temperature resistanceRubber materialPolymer science
The invention discloses a room-temperature mold-curing heat-conducting wave-absorbing rubber material and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises the following substances in parts by weight: 100 parts of rubber matrix, 50-400 parts of heat-conducting powder, 50-400 parts of wave-absorbing powder, 0.5-5 parts of catalyst, 1-10 parts of crosslinking agent and 0-60 parts of diluter. The room-temperature mold-curing heat-conducting wave-absorbing rubber material has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, radiation resistance and weather resistance, provides possibility for preparing the heat-conducting wave-absorbing material, has the advantages of low production cost and energy saving, can be directly used between a heat dissipation chamber and a metal shell, can effectively dissipate heat energies, has electromagnetic shielding and electromagnetic clutter absorbing properties, and thus, provides a favorable solution for electronic communication products in heat conduction and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:DALIAN DONGSHIN MICROWAVE TECH
Power battery heat management system
PendingCN107959090AImprove efficiencyEffective exportSecondary cellsCell component detailsPower batteryHeat management
The invention relates to a power battery heat management system, and belongs to the technical field of power batteries. The power battery heat management system comprises a battery box, a temperatureadjustment device, a controller, a power supply switch and a plurality of semiconductor chilling plates. The temperature adjustment device is connected with the battery box, the semiconductor chillingplates are arranged on the temperature adjustment device and connected with a power supply end of the battery box through the power supply switch, the controller is connected with the power supply switch and used for controlling the power supply switch, so that the semiconductor chilling plates refrigerate, a plurality of phase change components and a plurality of battery components are arrangedin the battery box, and a temperature sensor connected with the controller is arranged in each phase change component. The temperature adjustment device comprises a hollow plate and a plurality of heat pipes, the hollow plate is filled with cooling liquid under a vacuum state, one end of each heat pipe is communicated with the hollow plate, and the other end of each heat pipe is closed and inlaidinto the battery box. The power battery heat management system has the advantages of simple structure, high cooling efficiency, easiness in control, light weight, low cost, excellent performance and the like.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Colored resin composition, color filter, liquid crystal display device, organic el display device
ActiveCN103430099AFormation effect is goodExcellent developabilityMonoazo dyesDisazo dyesLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
The purpose of the invention is to provide a display having high image quality; to provide a colored resin composition with which it is possible to prevent a reduction in image quality of the display; and to provide a color filter having excellent pixel color purity and transmittance, as well as a high-quality liquid crystal display device and an organic EL display device, by using such a colored resin composition. The invention relates to a colored resin composition comprising (A) a dye, (B) a solvent, (C) a binder resin, and (D) a chain transfer agent that contains a specific compound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Method for preparing anti-reflection layer and anti-reflection surface, photoelectric conversion device used by same
InactiveCN102110739AImprove anti-reflection effectCoated evenlyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIonWavelength
The invention relates to a method for preparing an anti-reflection layer. The method comprises the following steps of: forming a metallic film on the passivation layer; heat-treating the metallic film to enable the metallic film to self-assemble into metallic nanometer particles; removing partial region of the passivation layer by using the metallic nanometer particles as a shield to form a sub-wavelength anti-reflection structure, wherein the section area of the sub-wavelength anti-reflection structure increases along the thickness direction of the passivation layer; and removing the metallic nanometer particles. Besides, the invention also provides the prepared sub-wavelength anti-reflection structure and a reflection ratio thereof. Since the sub-wavelength anti-reflection structure provided by the invention has a good anti-reflection effect, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the photoelectric conversion device can be improved. In addition, since the sub-wavelength anti-reflection structure is made on the passivation layer, the possibility of semi-conductor layer damage caused by reactive ions etching can be reduced; and then the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the photoelectric conversion device is improved.
Owner:SPRING FOUND OF NCTU
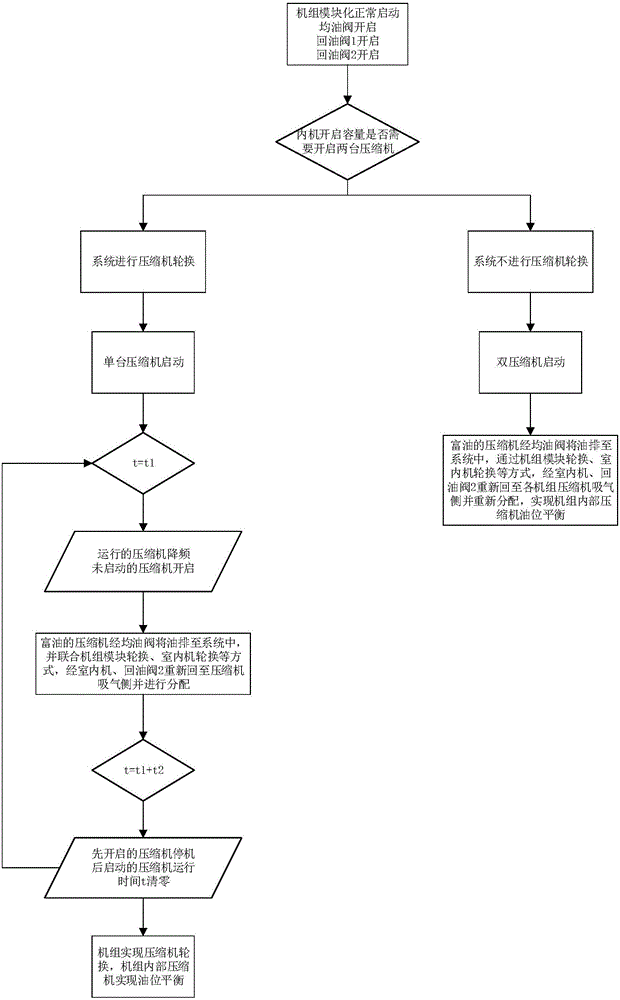
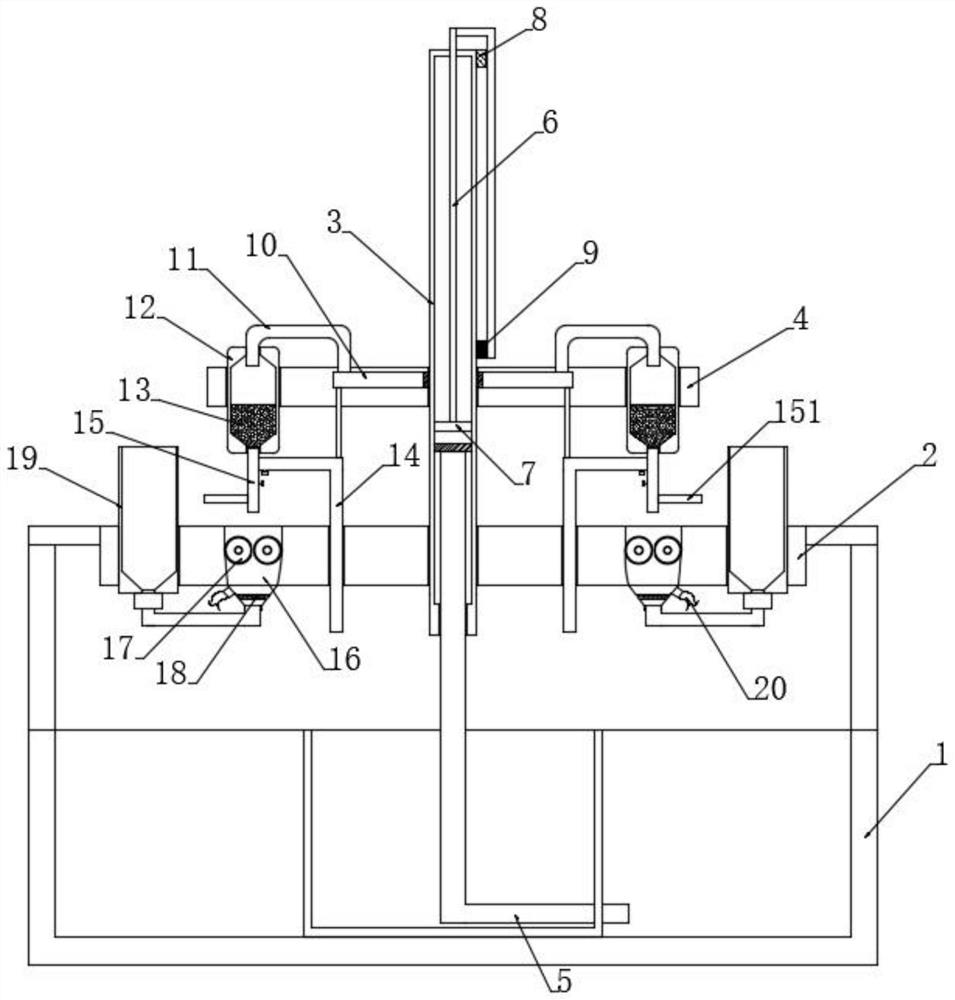
Oil balancing and returning air conditioning unit and control method thereof
ActiveCN106440572AEvenly distributedAddressing uneven distributionRefrigeration componentsVapor–liquid separatorAir conditioning
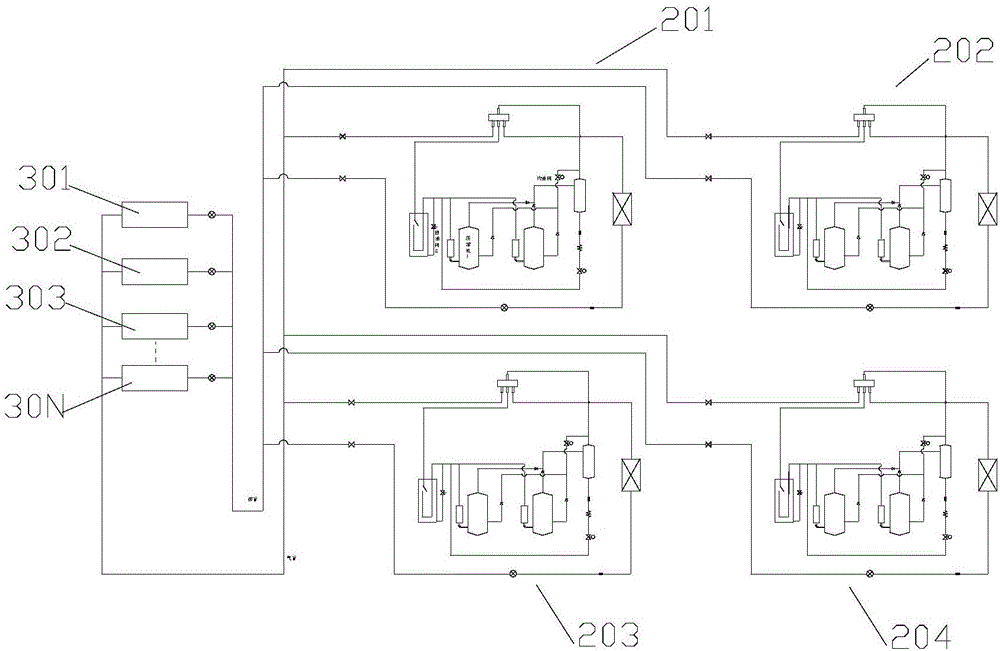
The invention provides an oil balancing and returning air conditioning unit and a control method thereof. The oil balancing and returning air conditioning unit comprises outdoor units (201, 202, 203, 204) and indoor units (301, 302, 303, 304), each outdoor unit comprises more than two compressors (101, 102) which are arranged in parallel, air suction pipes (401,402) of each of the compressors are converged and connected to a gas-liquid separator (5), and exhaust pipes (601, 602) of each of the compressors are converged and connected to an oil separator (7), wherein each compressor is also provided with oil balancing holes (801, 802) used for discharging oil inside the compressor and oil balancing pipes (901, 902) connected with the oil balancing holes, and the oil balancing pipes of each of the compressors are converged and connected to a refrigerant outlet end of the oil separator (7). By using the oil balancing and returning air conditioning unit, oil in the compressors which are rich in oil can be effectively and uniformly distributed into each compressor and each outdoor unit through the oil balancing pipes, so that the problems of oil quantity distribution nonuniformity and oil level unbalance are solved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
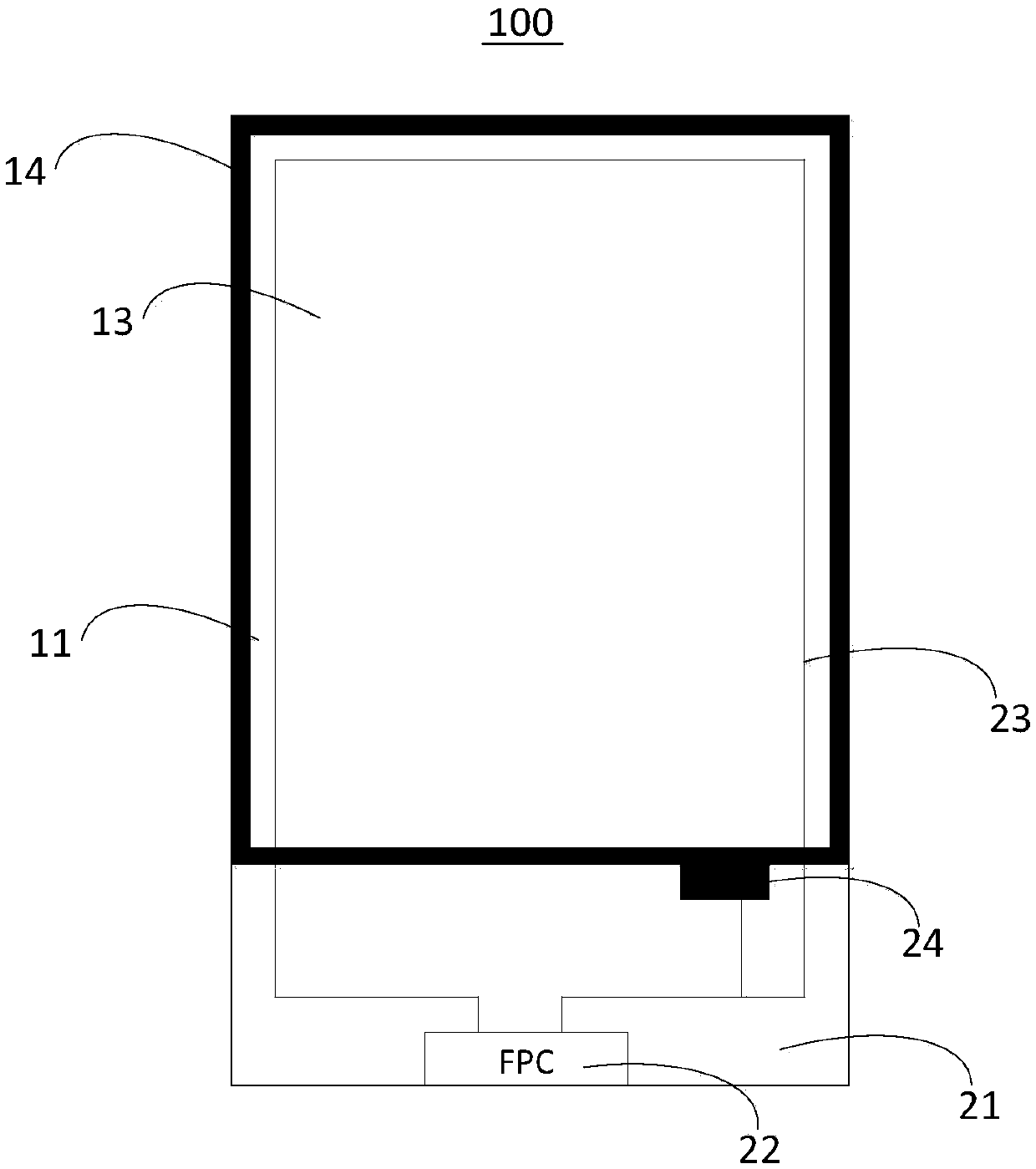
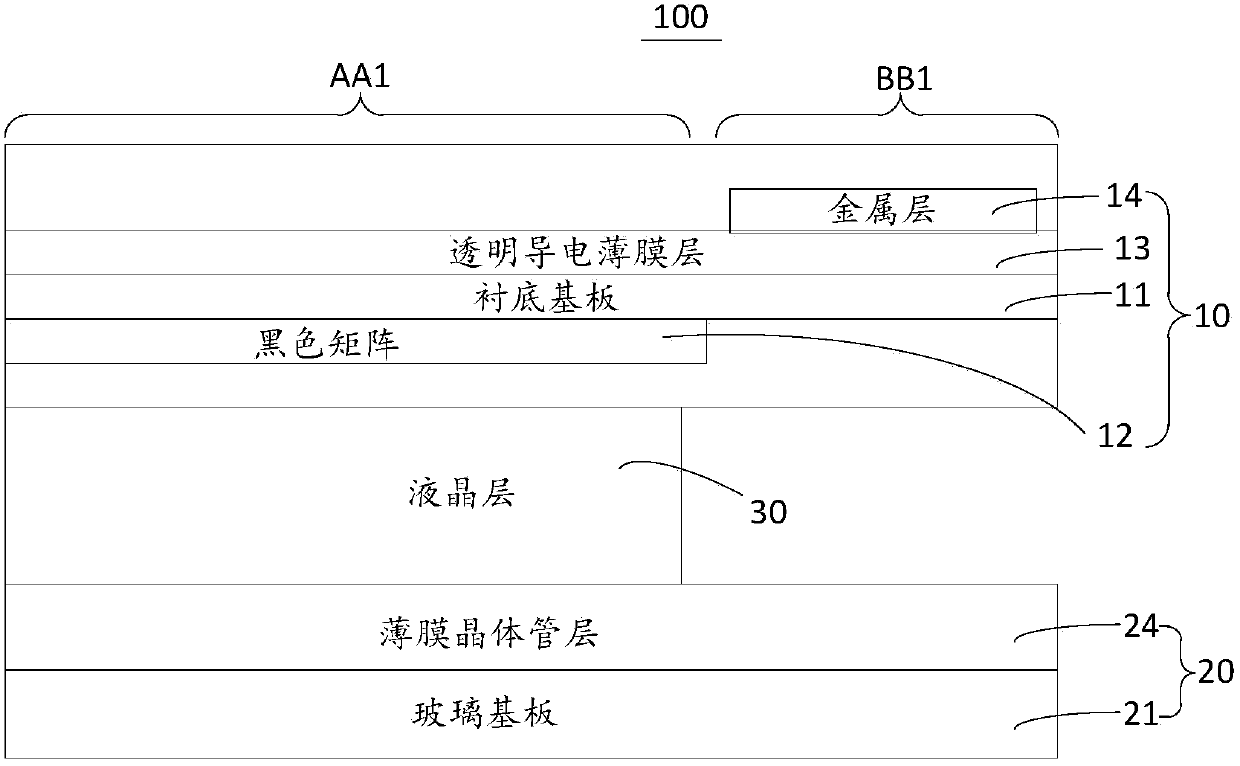
Color film substrate and liquid crystal panel
InactiveCN105954922AEffective exportImprove conductivityNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayColor film
The invention discloses a color film substrate and a liquid crystal panel. The color film substrate comprises a base substrate, a black matrix, a transparent conductive film layer and a metal layer; the base substrate comprises a display region and a non-display region; the black matrix and the transparent conductive film layer are oppositely arranged at both sides of the base substrate; the metal layer and the transparent conductive film layer are arranged at the same side; the metal layer is positioned in the non-display region of the base substrate, wherein the metal layer is used for being connected with an earth connection point. In the mode, according to the color film substrate and the liquid crystal panel which are disclosed by the invention, electrostatic charges on the color film substrate can be effectively led out, a better electrostatic shielding effect can be taken, and anti-static electricity capacity of the color film substrate is improved.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
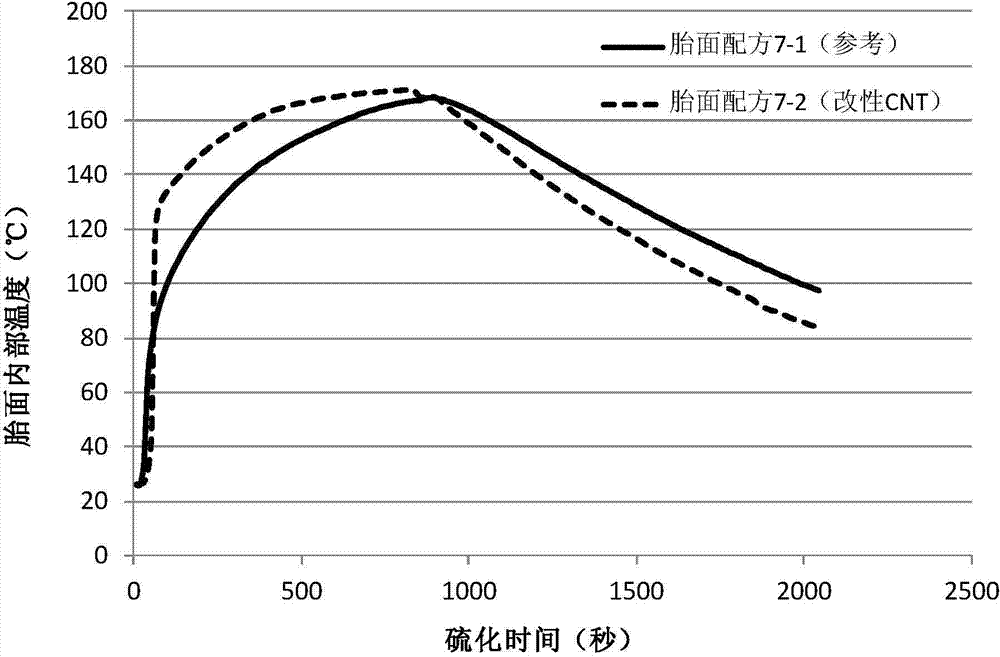
Rubber composition and tire same
ActiveCN104262698ALower volume resistivityExtended service lifeSpecial tyresCarbon nanotubeBackbone chain
The invention relates to a rubber composition and a tire containing the same, providing a rubber composition. The rubber composition comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of diene rubber, 20-120 parts of white carbon black, 0-50 parts of carbon black and 2-30 parts of surface-modified carbon nanotubes, wherein the molecule of a modified group at least contains an unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond or triple bond; the number of carbon atoms of the molecule is greater than or equal to 2; and the unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond or triple bond is on a main chain or a branch chain. The invention also provides the tire containing the rubber composition.
Owner:OTSUKA MATERIAL SCI & TECH SHANGHAICO LTD
Cooling system for power device of ship
InactiveCN103879538AAvoid downtimeEffective exportPropulsion based emission reductionPropulsion power plantsPropellerWater tanks
The invention relates to a cooling system for a power device of a ship. The cooling system is arranged on the power device of the ship. A power source is arranged at one end of the power device. The power source is connected with a heat exchanger. A propeller is arranged at the other end of the power device. The propeller is connected with the power source. The cooling system for the power device of the ship further comprises a circulation system. The circulation system is arranged on the power device. The circulation system comprises a heat-absorbing portion and a cooling portion. The heat-absorbing portion is arranged on the heat exchanger. The cooling portion is arranged on the outer surface of the power device in a surrounding mode. The cooling system further comprises a cold water tank used for storing sea water. A water inlet of the cold water tank is connected with a water inlet formed in the ship. The cooling system further comprises a waste heat recovery device. The waste heat recovery device is connected with the cooling portion. The cooling system for the power device of the ship has the advantages of being capable of saving energy, environmentally friendly, simple in structure, high in cooling efficiency and capable of recycling waste heat.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGSHOUHU SHIP & LIGHT BOAT MFG
Semi-conductive polyolefin shielding material for high-voltage direct-current cable
InactiveCN103709478AHas ultra-smooth surface propertiesGood physical propertiesPower cables with screens/conductive layersLow-density polyethylenePolyolefin
The invention provides a semi-conductive polyolefin shielding material for a high-voltage direct-current cable. The semi-conductive polyolefin shielding material comprises the following components in parts by mass: 100 parts of LDPE (low-density polyethylene), 1-2 parts of CPE (chlorinated polyethylene), 0.5-1.5 parts of BaTiO3, 8-15 parts of conductive potassium titanate whisker, 0.2-0.6 parts of stearic acid, 1-2.5 parts of cross-linking agent and 0.1-0.5 part of antioxidant. The semi-conductive polyolefin shielding material prepared from the components has the characteristic of ultra-smooth surface, and is good in physical performance and excellent in comprehensive performance. The current can be effectively conducted, a good effect of homogenizing an electric field is achieved, and the problem of partial discharge or insulation breakdown caused by serious electric field concentration probably brought by the surface defect of a semi-conductive shielding layer is solved. By attracting an ionized charge and an injected charge into a deep trap, the charges are prevented from being accumulated in a partial area, so that space charge accumulation in a cable insulation material is suppressed, and the electric conductivity of the cable insulation material is reduced.
Owner:WUXI JIANGNAN CABLE
System-level packaging structure with internal heat dissipation device
InactiveCN109860131AReduce thermal resistanceImprove cooling conditionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHeat sinkEngineering
The invention discloses a system-level packaging structure with an internal heat dissipation device. Heat sinks are arranged on chips, and the heat sinks and a cover board are connected and adopt thesame material, so that besides an original downward heat dissipation channel which passes through a substrate shell of the chip, a heat dissipation channel from the heat sinks to the cover plate directly is also added. By adopting the packaging structure, the local heat source in a SiP module is provided with heat dissipation channels in the upper direction and the lower direction, so that the heat on the heat source of the chip can be effectively guided out, the heat resistance is reduced, and the heat dissipation condition is improved.
Owner:XIAN MICROELECTRONICS TECH INST
High-color-rendering high-power LED (light emitting diode) encapsulation structure and manufacture method of high-color-rendering high-power LED encapsulation structure
InactiveCN103050606AImprove thermal conductivityImprove cooling effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHigh colorEngineering
The invention relates to a high-color-rendering high-power LED (light emitting diode) encapsulation structure and a manufacture method of the high-color-rendering high-power LED encapsulation structure. The high-color-rendering high-power LED encapsulation structure comprises a high-heat-conduction base plate, a high-heat-conduction material block, a high-power LED chip and an encapsulation assembly, wherein a blind hole is arranged in the high-heat-conduction base plate, the high-heat-conduction material block is arranged in the blind hole and is glued into a whole with the high-heat-conduction base plate through high-heat-conduction bonding agents. The high-color-rendering high-power LED encapsulation structure and the manufacture method have the advantages that the structure that the high-heat-conduction base plate and the high-heat-conduction material block which is arranged in the blind hole of the high-heat-conduction base plate and is tightly matched with the high-heat-conduction base jointly form a high-power LED chip heat radiation base is adopted, the whole heat conduction and heat radiation performance of the heat radiation base is excellent, and heat generated by the high-power LED chip can be fast conducted out of the work region and is radiated through the heat radiation base, so the temperature can be effectively lowered, the stability and the reliability of the high-power LED chip are greatly enhanced, the high-power LED chip can continuously work for a long time at high current, and the service life is long.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Energy-saving easy-to-open fridge
InactiveCN104613717AImprove sealingPrevent leakageDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusIceboxMechanical engineering
The invention relates to an energy-saving easy-to-open fridge. The energy-saving easy-to-open fridge comprises a box body and a fridge door, wherein an air guide ring is arranged in the fridge door, is tightly adhered to the fridge door, and is distributed on the four side edges of the inner wall of the fridge door; an air inlet pipe is connected to a position beside the air guide ring; a handle is movably mounted on the fridge door through a tension spring mechanism; an air ventilation cylinder which is communicated with the air guide ring is also arranged in the fridge door; a piston which can translate along the inner wall of the air ventilation cylinder is mounted in the air ventilation cylinder and is fixedly connected with one end of an elastic steel pipe; the elastic steel pipe is fixedly connected with a fridge body after extending out of the fridge door along the axis of the air ventilation cylinder; air openings which are communicated with the outside are formed in the air guide ring at equal intervals; each air opening directly faces the side wall of the fridge body. The fridge is low in material cost, can achieve a very good sealing effect, and can be opened and closed easily.
Owner:陈芊羽
U-shaped pipe LED lamp
InactiveCN104075165AEffective exportImprove thermal conductivityPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsLight headLED lamp
The invention discloses a U-shaped pipe LED lamp which comprises a lamp cap and a lamp body, wherein the lamp body comprises a multi-surface columnar radiating body surrounded by a plurality of heat dissipation single bodies and side surface lamp panels with LED lamp beads; a side surface light-transmittable shade is mounted on the side surface of each heat dissipation single body; a top surface lamp panel with LED lamp beads is mounted at the top of the heat dissipation single body; a top light-transmittable shade is mounted on the top surface lamp panel; a mounting cover is arranged between the radiating body and the lamp cap; a power module is placed on the upper end surface of the mounting cover; electrode spring plates connected with the power module are arrayed on the lower end surface of the mounting cover; each electrode spring plate comprises two side edges; the middle parts of the two side edges are bent relatively to form compressive surfaces; the arranging positions of the all side surface lamp panels are corresponding to the arranging positions of all the electrode spring plates; all the side surface lamp panels extend to the lower part of the mounting cover and extend into the compressive surfaces formed by all the electrode spring plates. The U-shaped pipe LED lamp has the advantages that the assembly and manufacture are simple, the radiating effect is good and the conductivity is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAXINJIE TECH
Battery having a cooling plate and motor vehicle having a corresponding battery
ActiveCN102859785AFixing is simple and fastSimplify the installation processSecondary cellsPropulsion by batteries/cellsMotorized vehicleElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention relates to a battery which has at least one battery module (16) having a lower face, a cooling plate (10) having an upper face (20) and a fixing system for the at least one battery module (16), which is arranged on the upper face (20) of the cooling plate (10) and connected to the cooling plate (10). The fixing system has at least one fixing strap (12, 12'). By means of the at least one fixing strap (12, 12'), the at least one battery module (16) is fixed on the cooling plate (10) in such a way that the lower face of the battery module (16) is in direct contact with the upper face (20) of the cooling plate (10). The invention further relates to a motor vehicle having said battery.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
Flexible package lithium carbon fluoride primary battery
PendingCN112038650AEffective exportQuick exportOrganic electrolyte cellsCell component detailsElectrolytic agentElectrical battery
The invention discloses a flexible package lithium carbon fluoride primary battery, which is composed of a plurality of cylindrical pole groups, a non-aqueous electrolytic solution, a glue-containingelectrode lug and a soft shell, wherein the plurality of cylindrical pole groups are connected in parallel, each cylindrical pole group is of a multi-electrode lug or foil-electrode lug structure andcan be used for quickly guiding flow and conducting heat, positive and negative electrode sheets and a diaphragm are tight and wound so as to achieve tight contact between positive and negative electrodes and the diaphragm in the whole discharge process, the F / C atomic ratio in carbon fluoride is in gradient distribution in material particles, and the F / C atomic ratio of the outermost layer is close to 0, so that the problem that a conventional lithium carbon fluoride battery cannot discharge at high power is solved. According to the invention, the square lithium carbon fluoride battery adoptsthe soft package light shell, has the characteristics of high specific energy and high safety, does not deform and obviously expand in the whole discharge process, and does not need to adopt a high-strength shell and a clamp for limitation in the use process, so that the difficulty of combined application is greatly reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN JUYUAN NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Industrial wastewater quality detection device and use method thereof
InactiveCN111811888AImprove the effect of water quality detectionEasy to detect and handleWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationChemistrySorbent
The invention discloses an industrial wastewater quality detection device and a use method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater detection. Waste water in a waste water storage pool is guided into a sampling adsorption cylinder for adsorption treatment through cyclic and repeated extraction of the sampling cylinder; a heavy metal adsorbent filled in the sampling adsorption cylinder is used for adsorbing heavy metals in the wastewater; after the adsorption work is more complete, the heavy metal adsorbent is introduced into a desorption cavity below the sampling adsorption cylinder for desorption treatment; the grinding mechanism is matched to effectively crush the heavy metal adsorbent into adsorbent particles; a proper amount of acid solution or dissolving solution is used to wash and desorb the adsorbent particles; finally, an acid pickling desorption solution or a dissolving desorption solution is acquired and guided into a detection cylinder so that technicians can detect and treat heavy metal ions in the wastewater conveniently; and meanwhile, multiple sets of contrast detection are set, a data analysis range is enlarged, and a wastewater quality detection effect is effectively improved.
Owner:成都永晟昌清洁服务有限公司
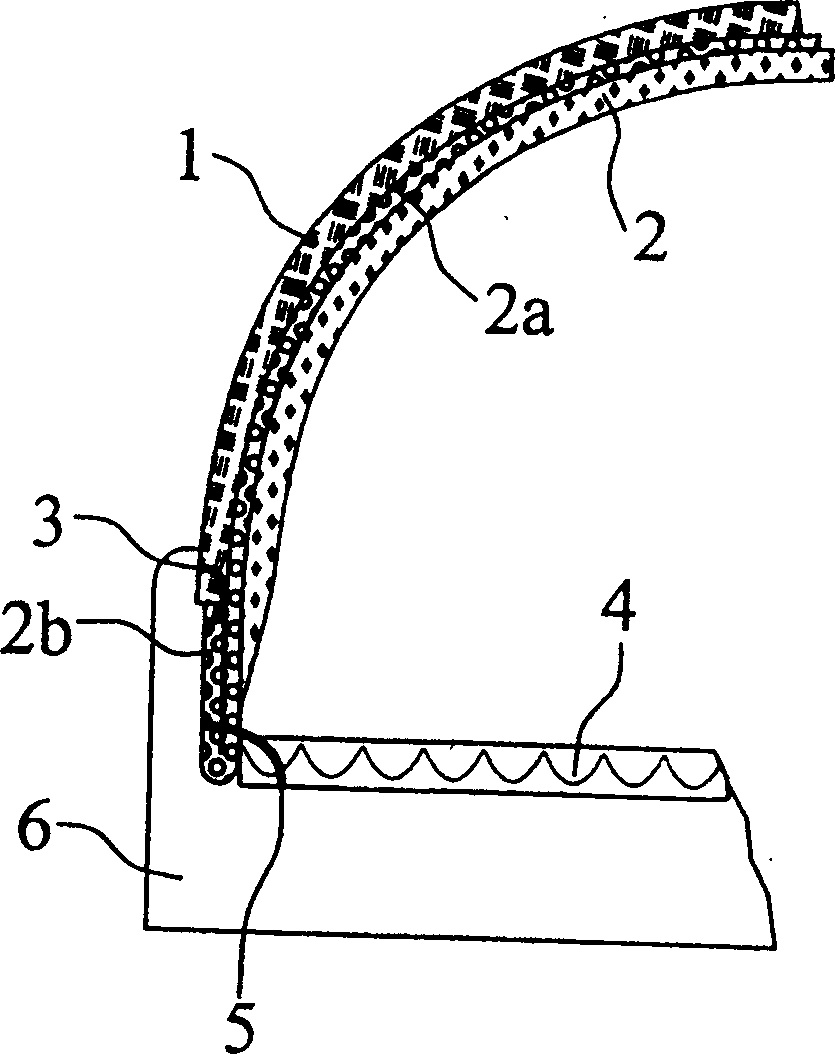
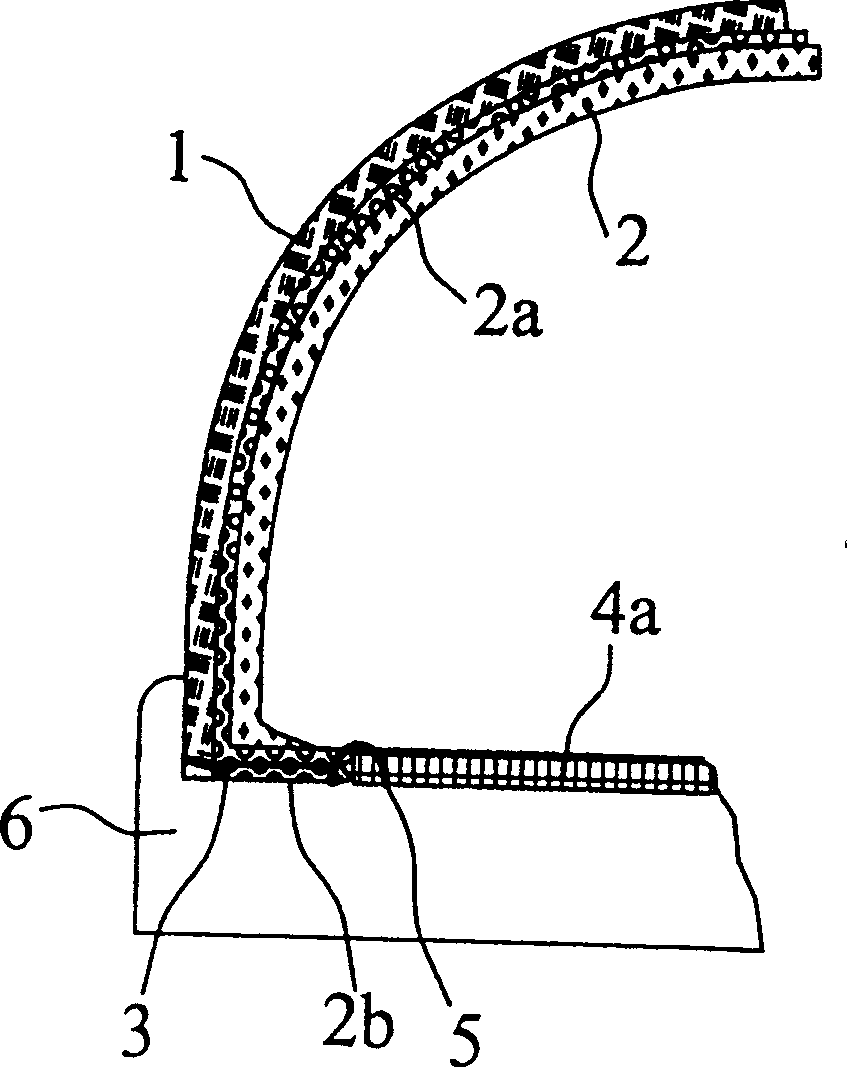
Waterproof shoe structure with folded interior upper
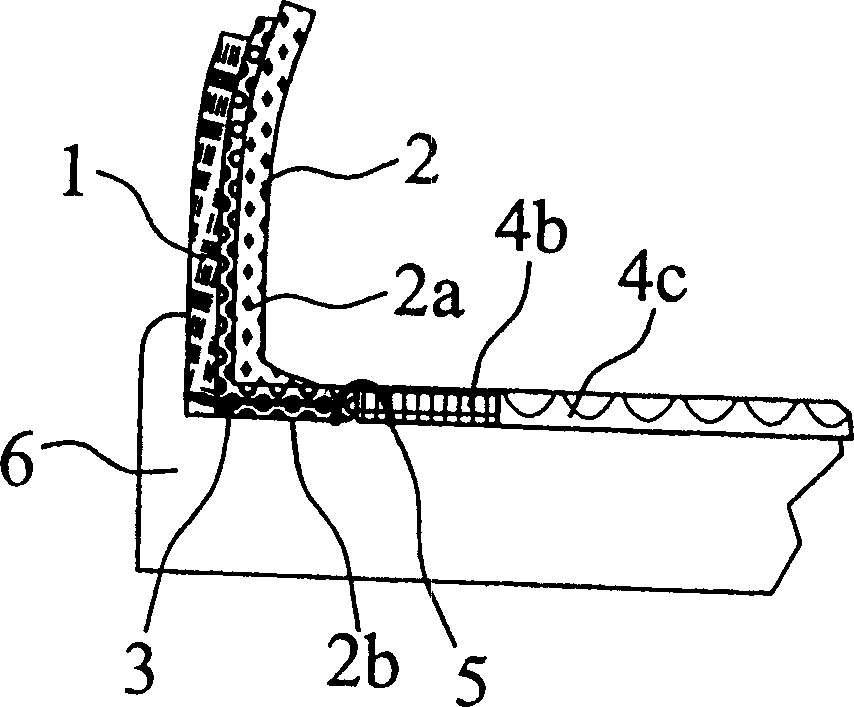
A waterproof shoe structure having an exterior upper (1), an interior upper including a waterproof, water vapor permeable functional layer (2a) arranged adjacent to the exterior upper (1) and a lining (2) facing the shoe interior, an insole (4, 4a, 4c) and an outsole (6), wherein the interior upper has a lower end region (2b) that extends at least for the most part beyond the lower end of the exterior upper, and which is joined on the one hand to the exterior upper (1) and on the other hand to the insole (4, 4a, 4c). The lower end region of the interior upper that extends beyond the exterior upper (1) is folded outwards in such a way that the functional layer in the entire end region (2b) is turned back on itself, and the interior upper has a lower edge arising from this folding, that the free end of the outwardly folded interior upper is joined to the exterior upper (1), and that the lower edge of the interior upper is joined to the insole (4, 4a, 4c).
Owner:SYMPATEX TECH GMBH
A wind channel heat radiator
InactiveCN101080159ALow costSimple structureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsUltrasound attenuationEngineering
This invention relates to an air ducted radiator including a radiation plate with several air ducted radiation vanes arranged in definite distance, in which, upper and lower air ducts are set on the radiation vanes to form convection while working and lead out the working heat of the Led effectively, reduce attenuation, increase the luminescent efficiency and prolong the life of the Led.
Owner:SHANGHAI LONGGUANG SHENJING OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
Radiating structure of electronic assemblies
ActiveCN101674719AReduce manufacturing costEffective exportPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringCopper
The invention relates to a radiating structure of electronic assemblies, which comprises a radiating fin, an aluminum radiating base arranged on the radiating fin and at least one electronic assembly arranged on the aluminum radiating base, wherein at least one copper column heat conductor is arranged on the aluminum radiating base via a mold in a forcibly-pressed manner with the position corresponding thereto, so that heat conduction for the electronic assemblies can be realized, thus achieving the advantages of low manufacturing cost, fast production, reduced manufacturing procedures, good environmental friendliness and high radiating efficiency.
Owner:DONG GUAN HAN XU HARDWARE & PLASTIC TECH CO LTD
Self-cleaned solar cell assembly with high conversion rate
InactiveCN105140325AHigh mechanical strengthHigh light transmittancePhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationPolyesterElectrical battery
The invention relates to a self-cleaned solar cell assembly with a high conversion rate. The self-cleaned solar cell assembly comprises toughened glass, an EVA adhesive film, a single crystalline silicon solar cell slice, an EVA adhesive film, a backplane, an aluminum-alloy frame, and a DC junction box, and is characterized in that the toughened glass, the EVA adhesive film, the single crystalline silicon solar cell slice, the EVA adhesive film, and the backplane are successively laminated to form an assembly laminated member; the assembly laminated member is subjected to sealed packaging by using the aluminum-alloy frame and silica gel; the single crystalline silicon solar cell slice is electrically connected with the DC junction box after being welded on a busbar; the toughened glass is low-iron ultra-white toughened glass with a light-receiving surface plated with a hydrophobic antireflection film; the backplane is an aluminum-alloy backplane with double surfaces plated with anode oxide films; a small polyester film is arranged between the aluminum-alloy backplane and the busbar exposing the upper EVA adhesive film; and water leakage holes are arranged on both ends of a long side of the aluminum-alloy frame.
Owner:高金刚
LED (light emitting diode) ceramic COB (chip on board) light source fluorescent lamp and preparation method thereof
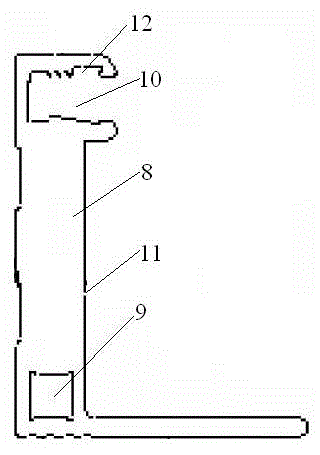
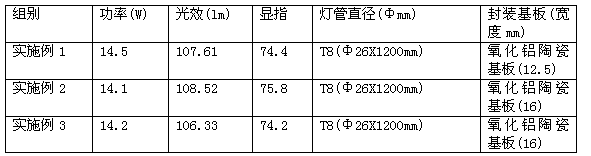
InactiveCN103236491AImprove insulation performanceGood thermal conductivitySolid-state devicesCircuit susbtrate materialsColor rendering indexPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses an LED (light emitting diode) ceramic COB (chip on board) light source fluorescent lamp and a preparation method thereof. A high-heat-conduction ceramic substrate is used for replacing the traditional metal packaging substrate, a multi-chip integration COB chip module applied to a fluorescent lamp bar is additionally used, and therefore the LED ceramic COM light source fluorescent lamp has the advantages of high lighting effect, high reliability and high quality; and a non-isolated power supply and all PC (personal computer) shells can be selected to lower the production cost so as to achieve the best cost performance. According to the LED ceramic COM light source fluorescent lamp disclosed by the invention, when the color temperature is 5700-6300K, a color rendering index exceeds 70, and the whole lamp lighting effect exceeds 1001m / w. The obtained fluorescent lamp has the advantages of low energy consumption, long service life and high lighting effect, and the production and application requirement scan be satisfied.
Owner:YANCHUANG PHOTOELECTRIC TECH GANZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com