Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46results about How to "Avoid misregistration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
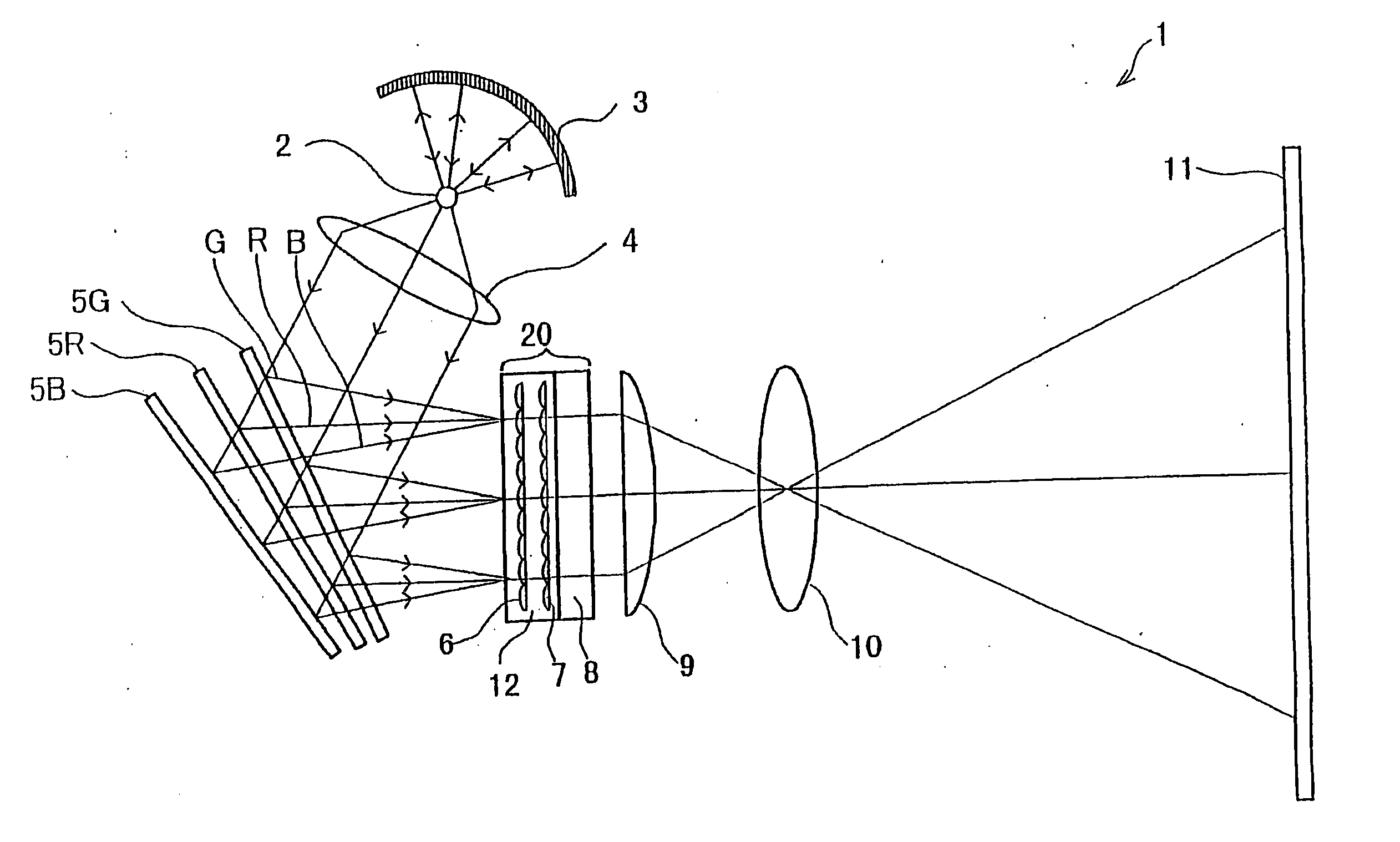
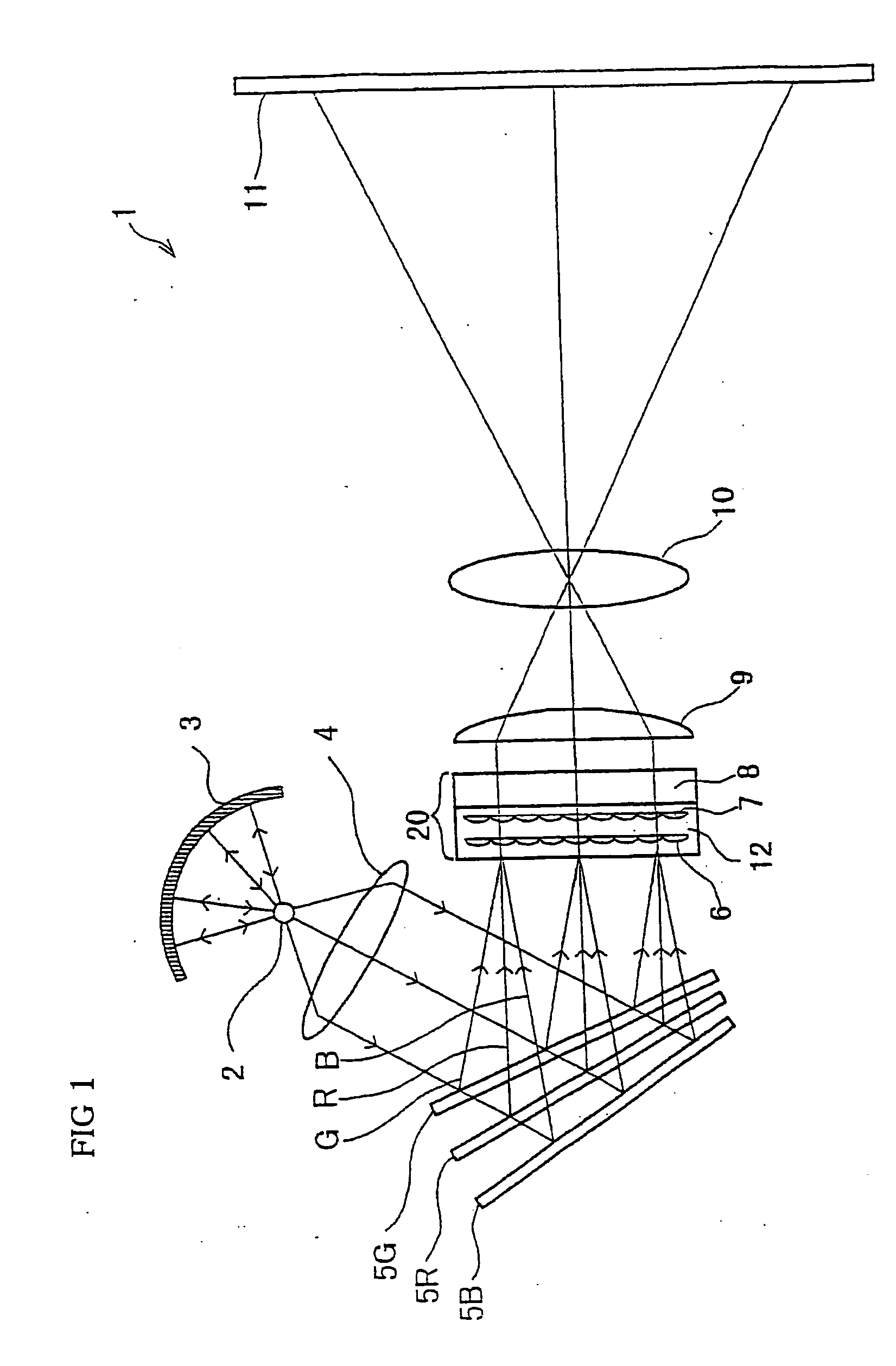
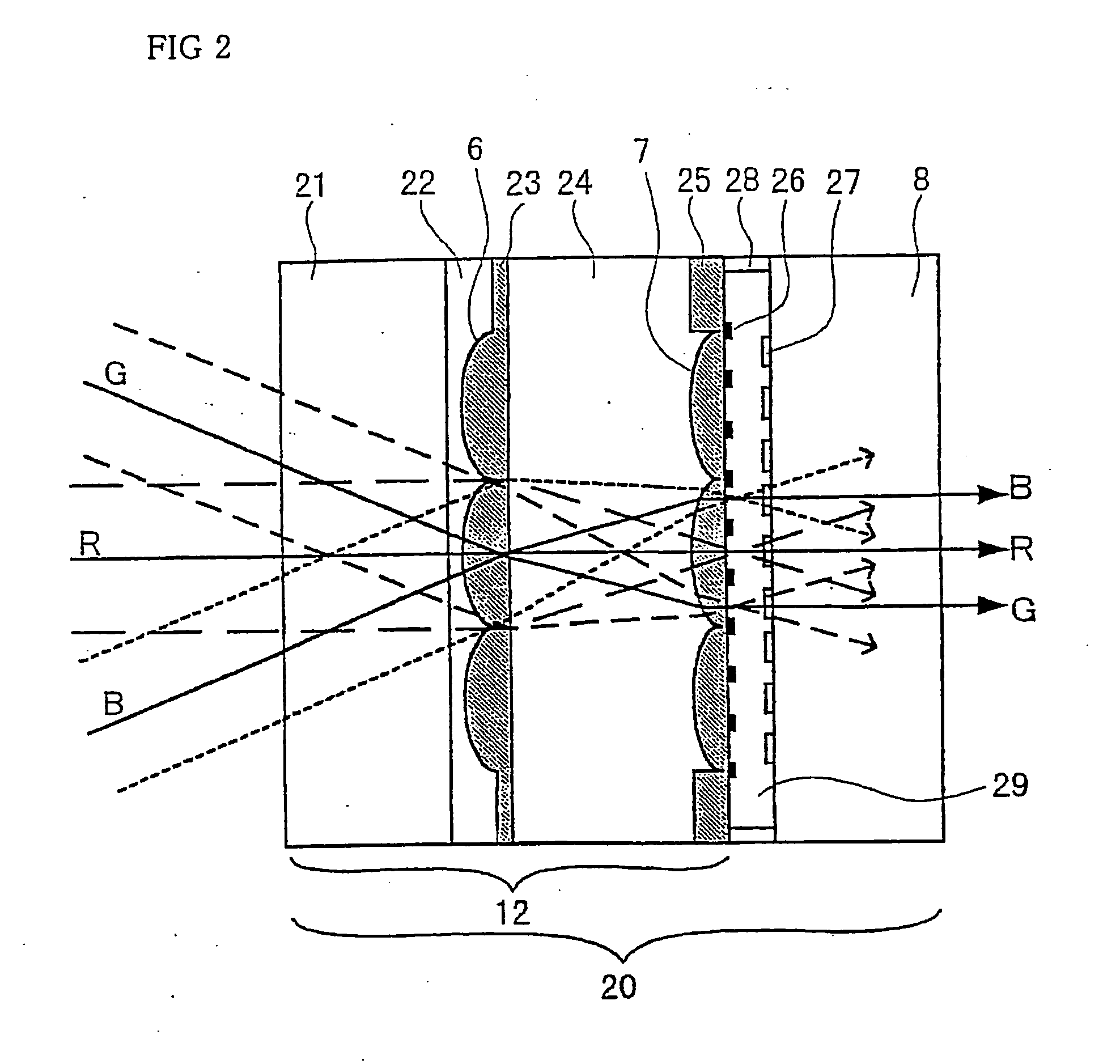
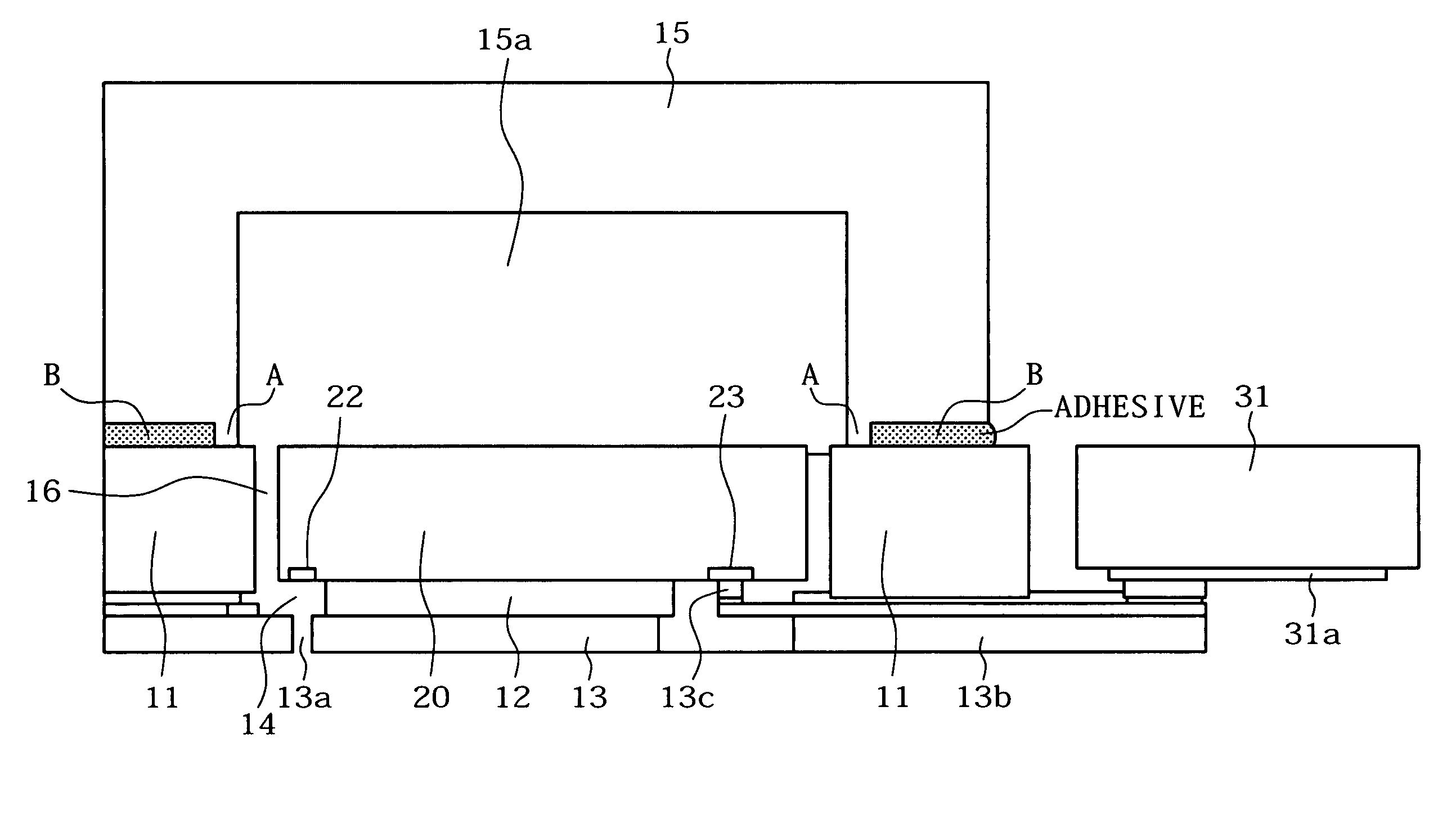
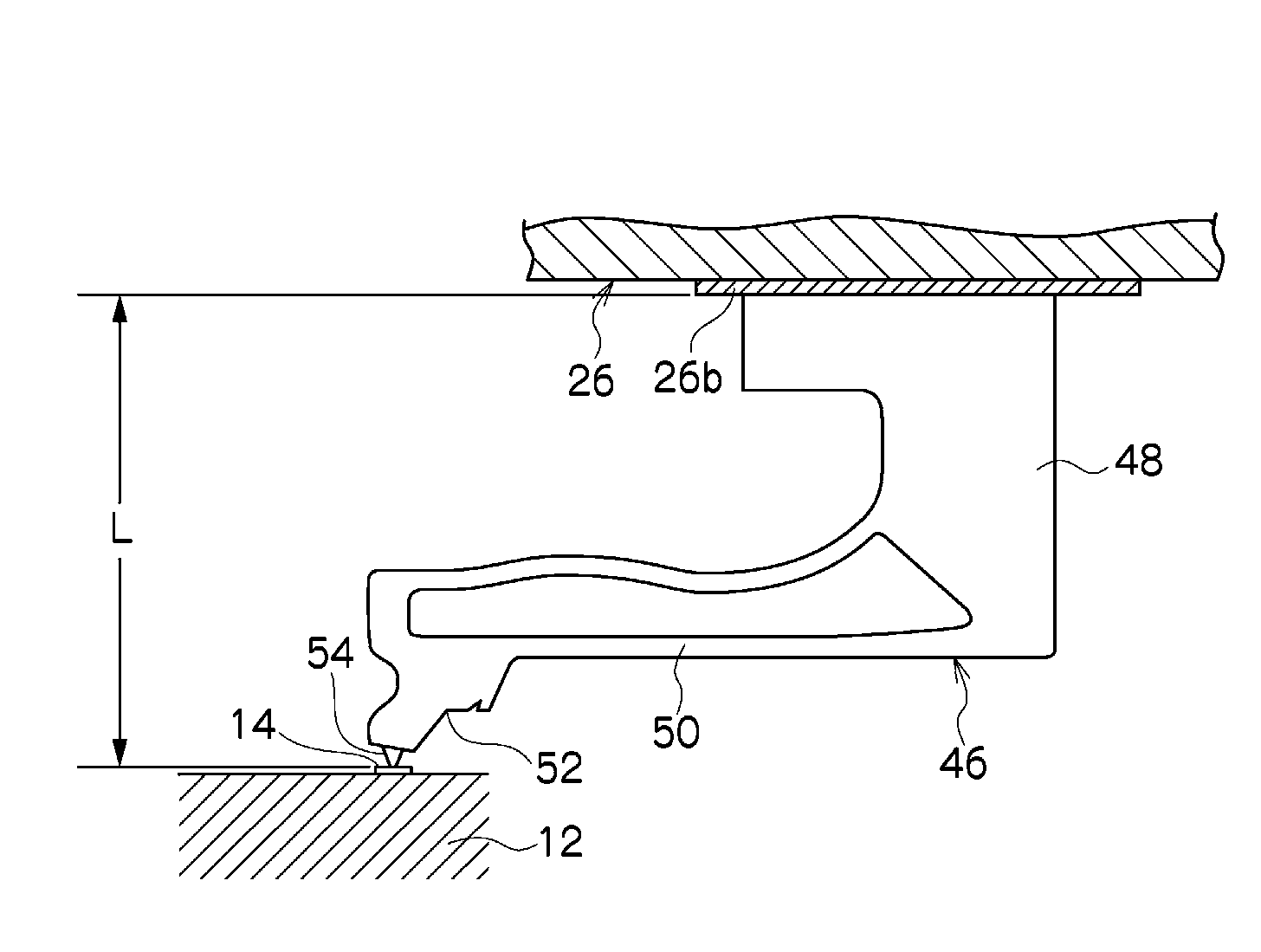
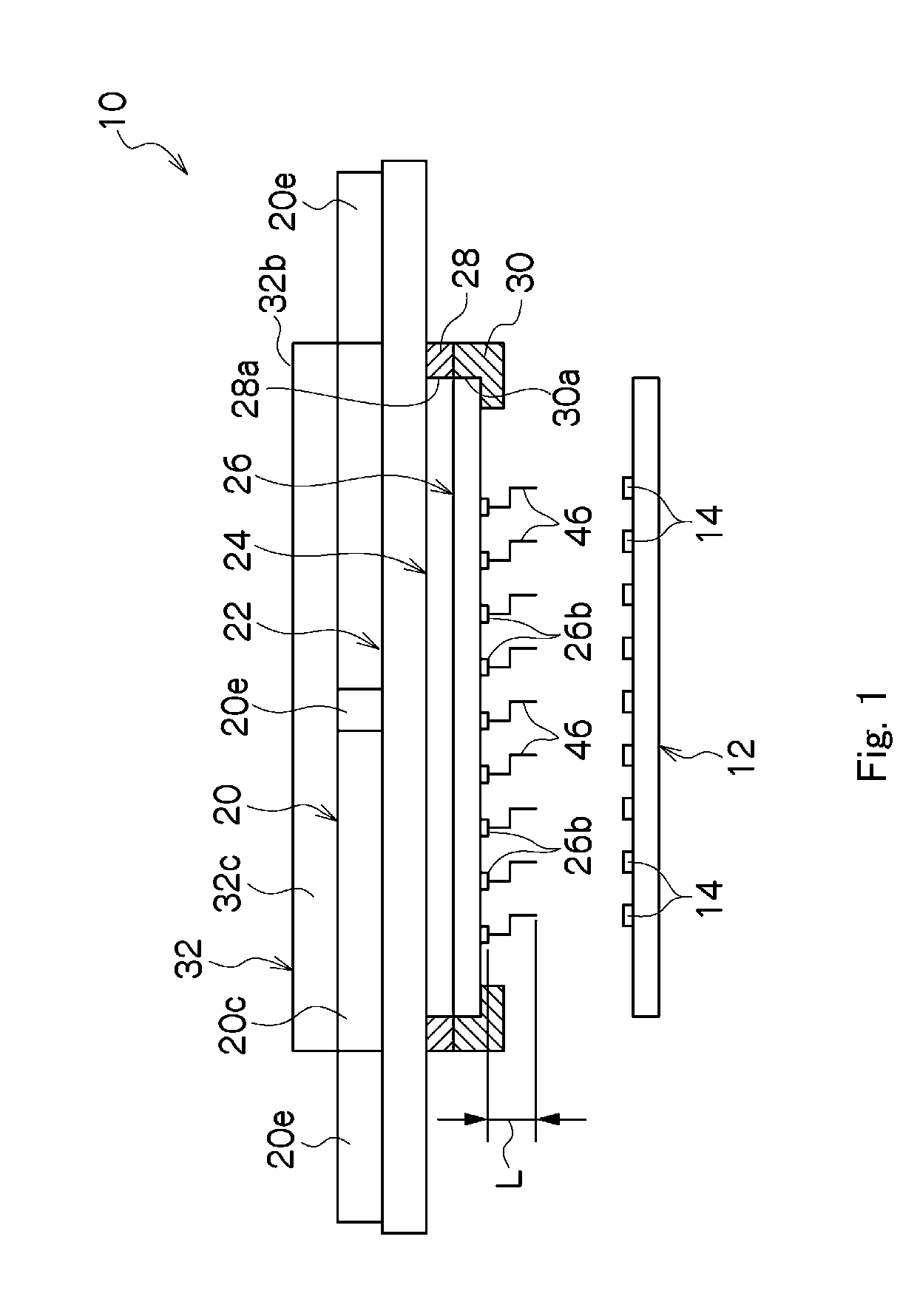
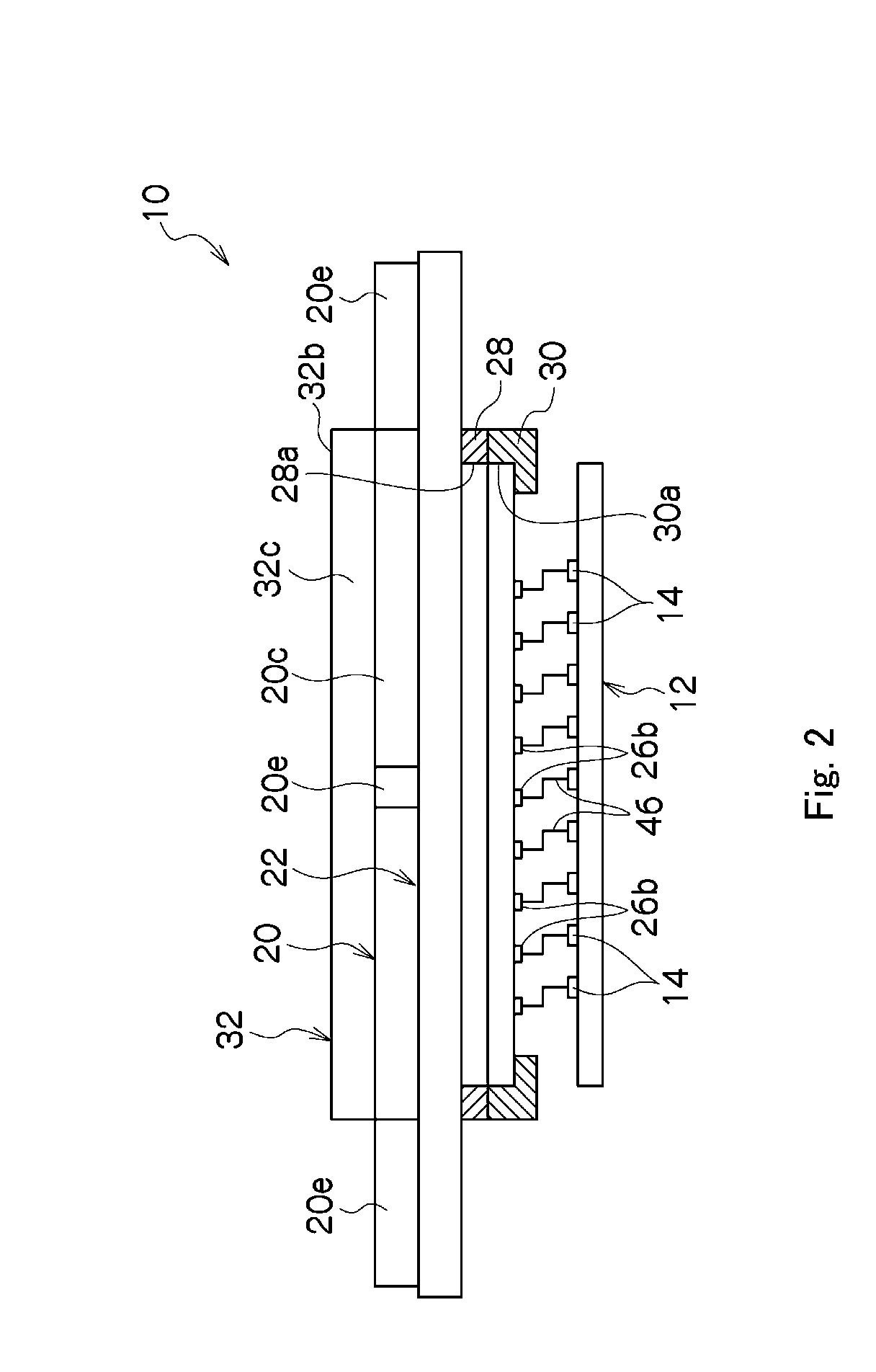
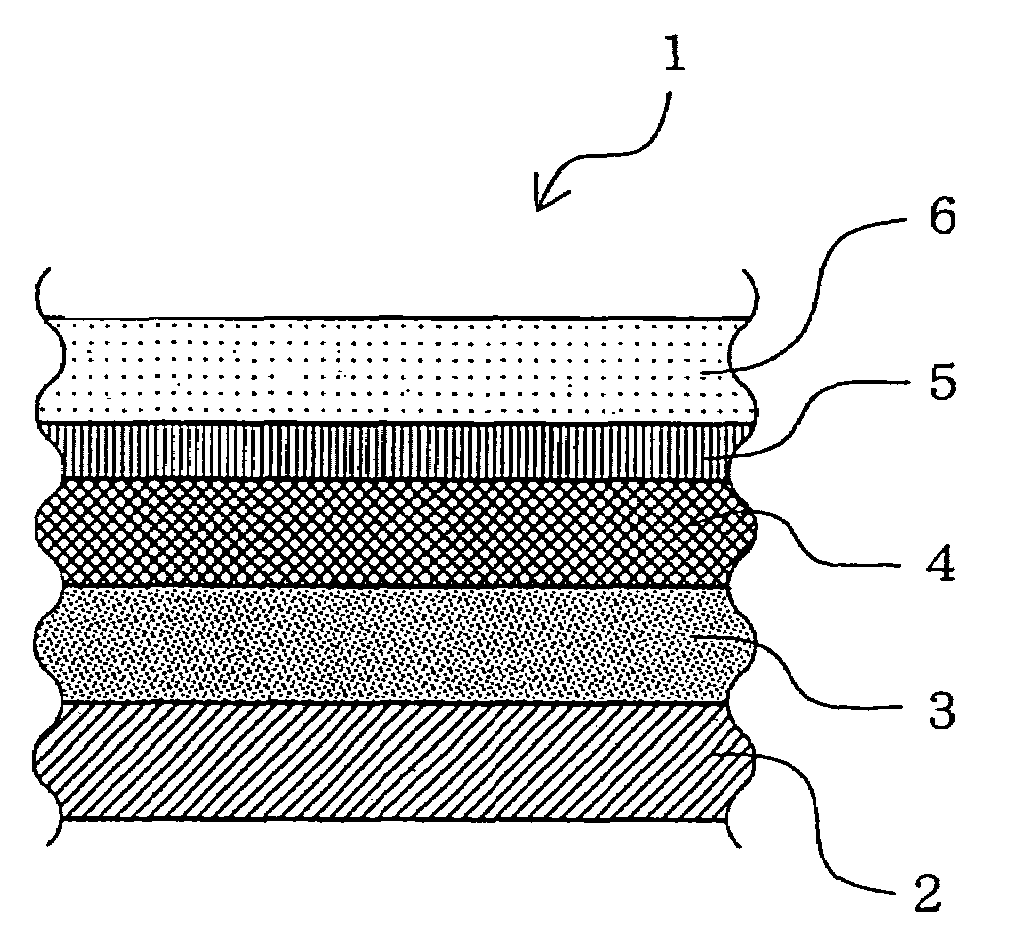
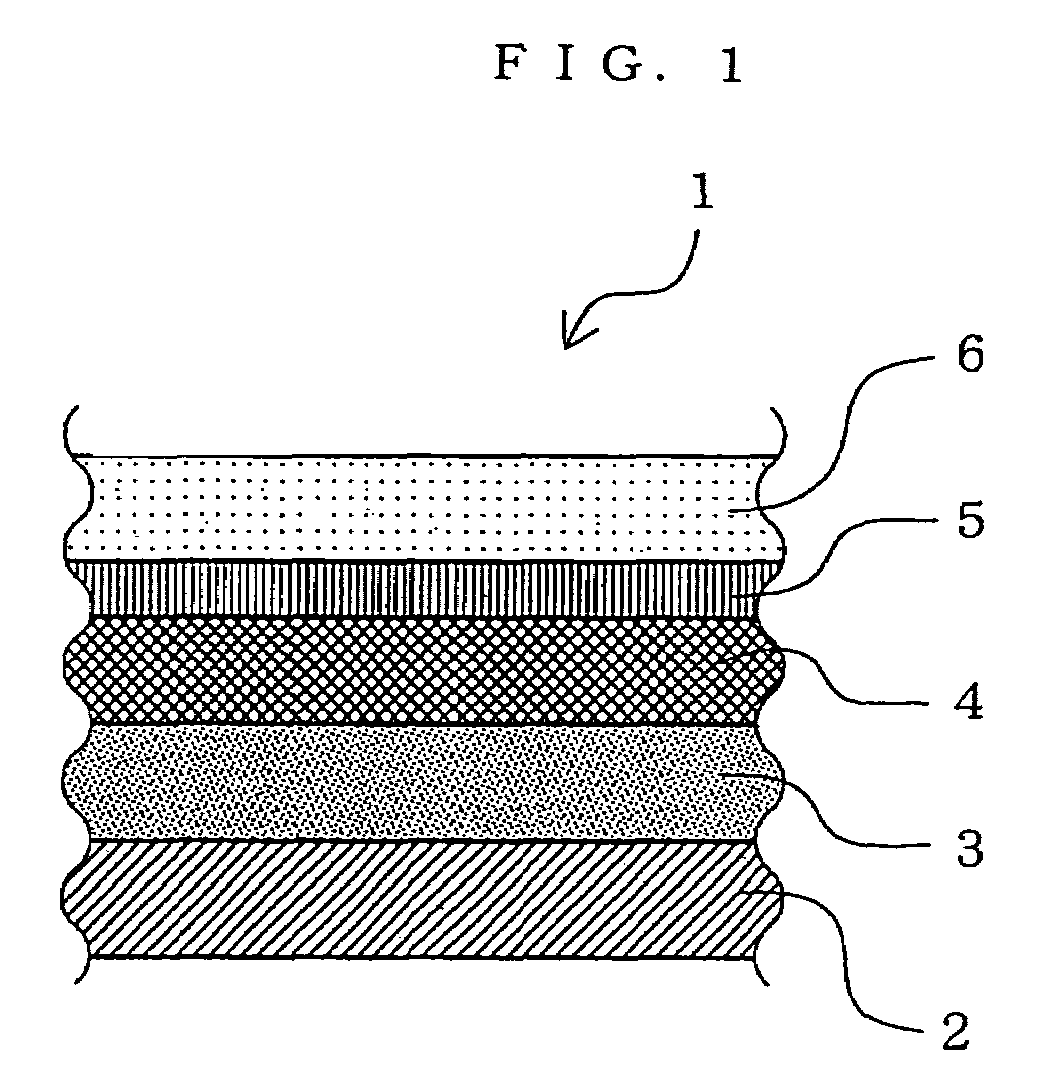
Micro-lens array substrate and production method therefor, and projection type liquid crystal display unit using those
InactiveUS20050174649A1Improve accuracyLow costOptical articlesColor television detailsLiquid-crystal displayDielectric substrate
In a micro-lens array substrate (12) that includes first and second micro-lens arrays (6, 7) respectively having a plurality of lenses, the first micro-lens array (6) is sandwiched between two inorganic dielectric substrates (21, 24), and the second micro-lens array (7) is formed on one of the two inorganic dielectric substrates (21, 24).
Owner:SHARP KK
Head module, liquid jetting head, liquid jetting apparatus, method of manufacturing head module, and method of manufacturing liquid jetting head
InactiveUS20050116995A1Increase manufacturing costInhibit thermal stressInking apparatusBuffer tankEngineering
A head module includes a head chip provided with an array of heat generating elements, a nozzle sheet provided with nozzles, a barrier layer for forming ink liquid chambers, a module frame adhered to the nozzle sheet to thereby support the nozzle sheet and provided with a head chip arranging hole for arranging the head chip therein, and a buffer tank which is so disposed as to cover the head chip arranging hole from a surface, on the opposite side of the surface of adhesion to the nozzle sheet, of the module frame and which is for forming a common liquid conduit communicated with all the ink chambers of the head chip.
Owner:SONY CORP
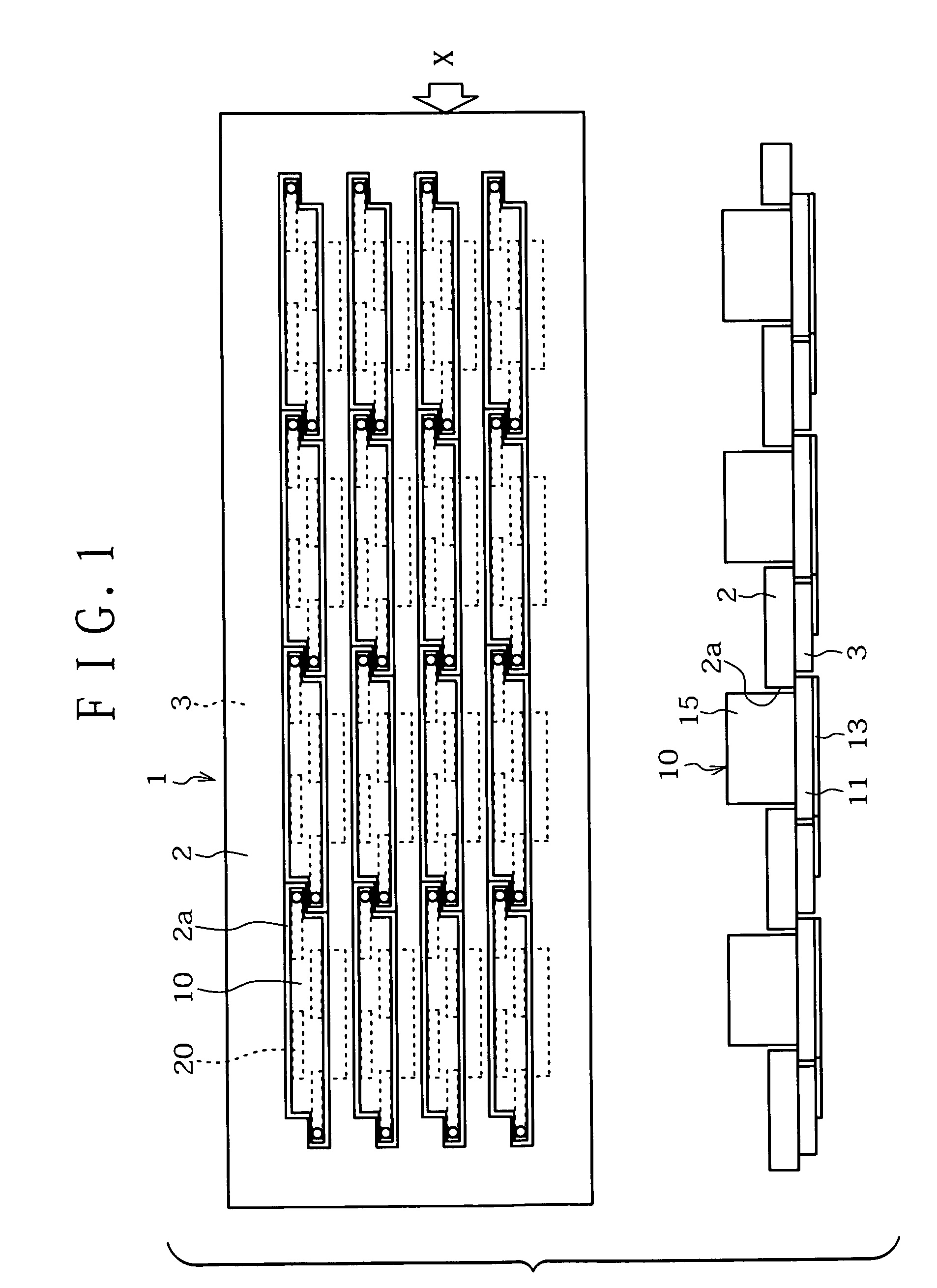
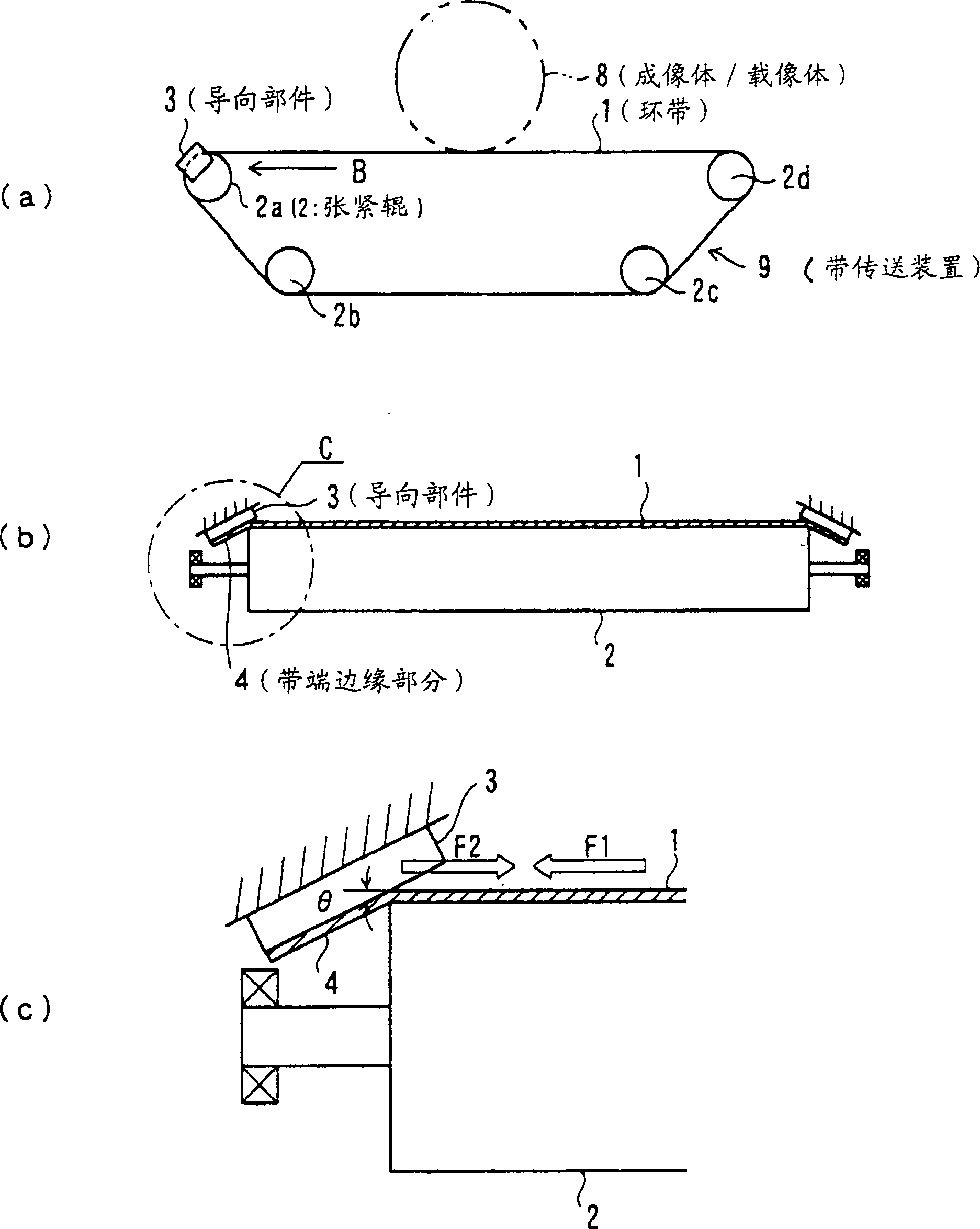
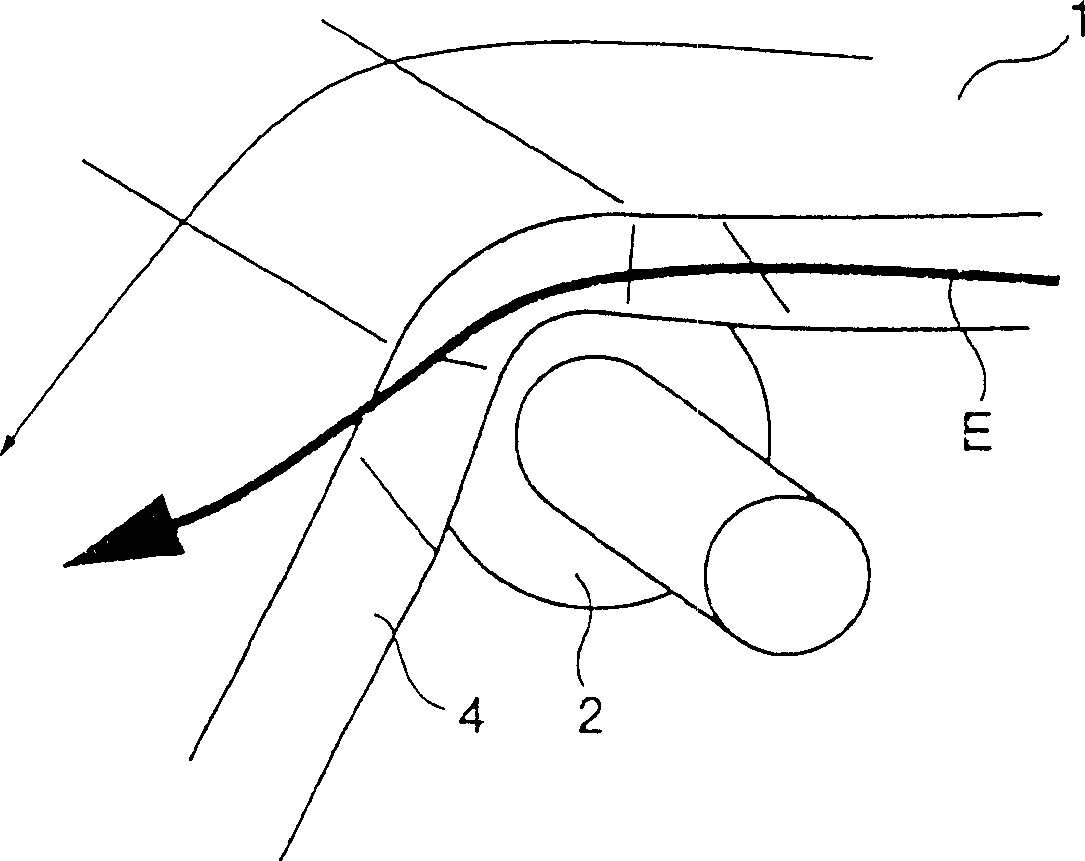
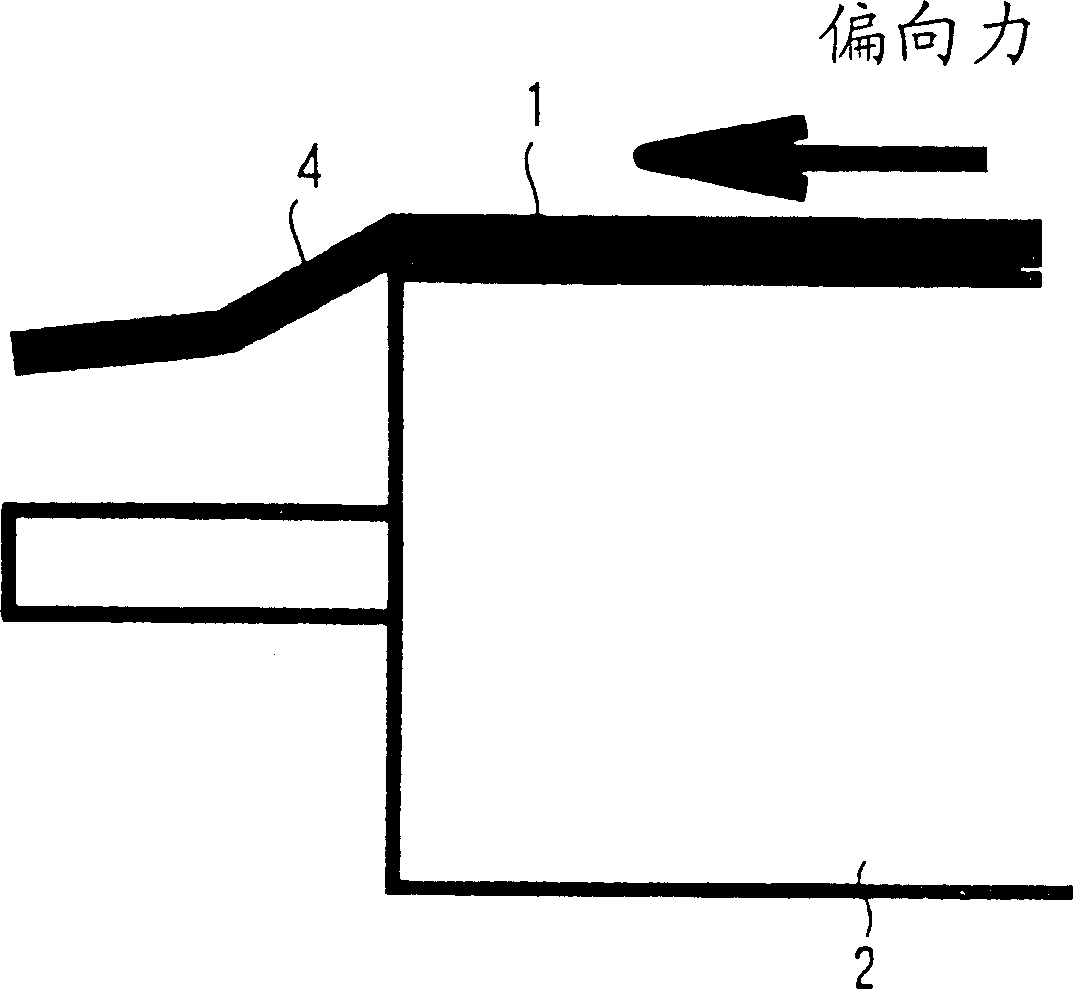
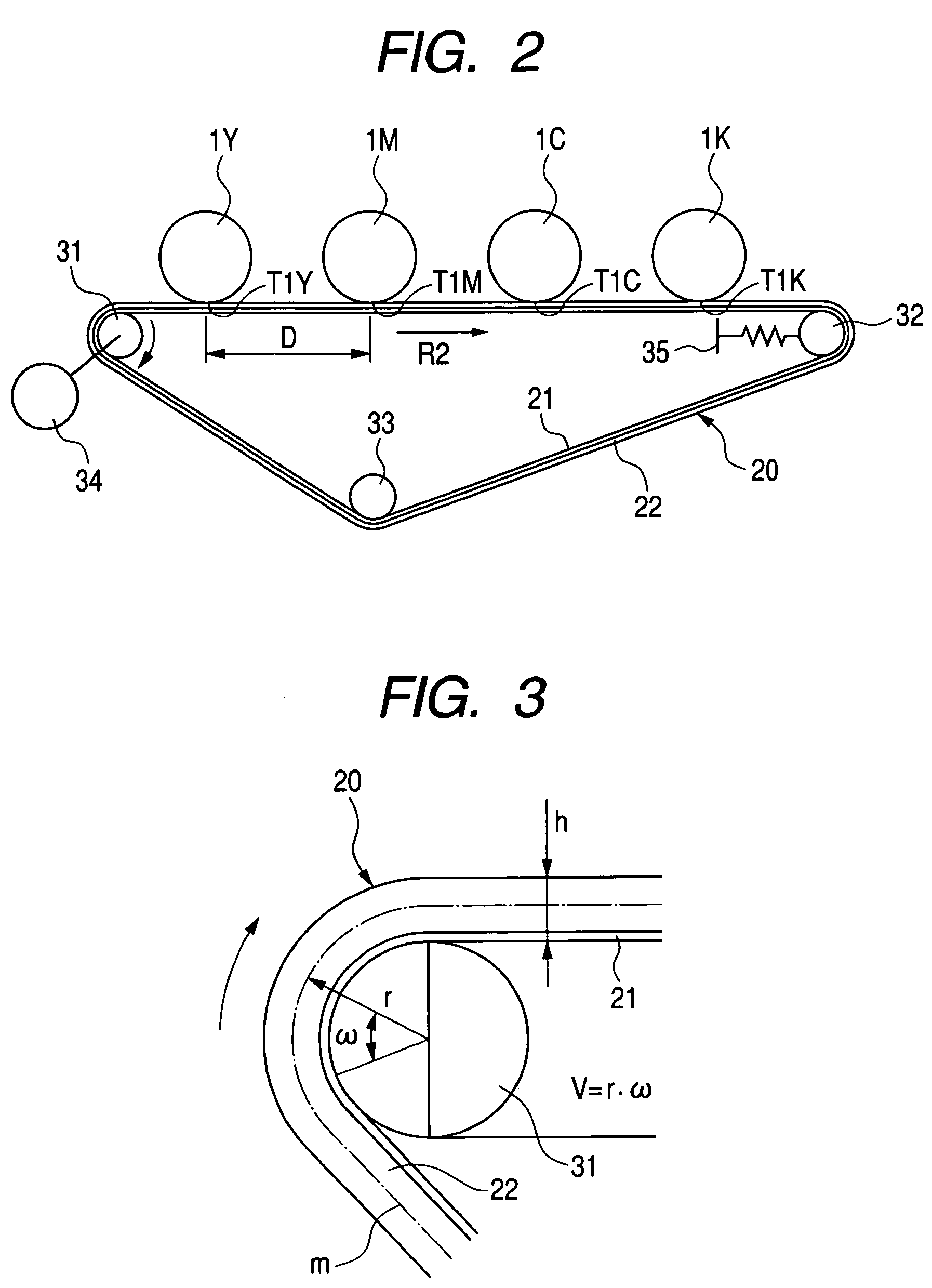
Belt transfer device and imaging equipment using the belt transfer device
InactiveCN1261831CAvoid misregistrationElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersImaging equipmentMechanical engineering
A belt transporting device for circulatingly transporting an endless belt, which is in use with an image forming apparatus, such as copying machine or a printer. The belt transporting device includes a plurality of tension rolls, an endless belt laid on the tension rolls, the endless belt having a belt-end edge part protruding from an end of one of the tension roll and a guide member provided in the vicinity of the endless belt. The guide member comes in contact with the belt-end edge part so as to bend the belt-end edge part in a tapering-off direction. The guide member regulates the shape of the belt-end edge part so that a rotary peripheral length of the belt-end edge part becomes smaller than that of an area where a rear side of the endless belt is in contact with the tension roll.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Remote sensing image registration method
InactiveCN101957991AEliminate small voidsAvoid misregistrationImage enhancementImage analysisImage mosaickingImaging processing
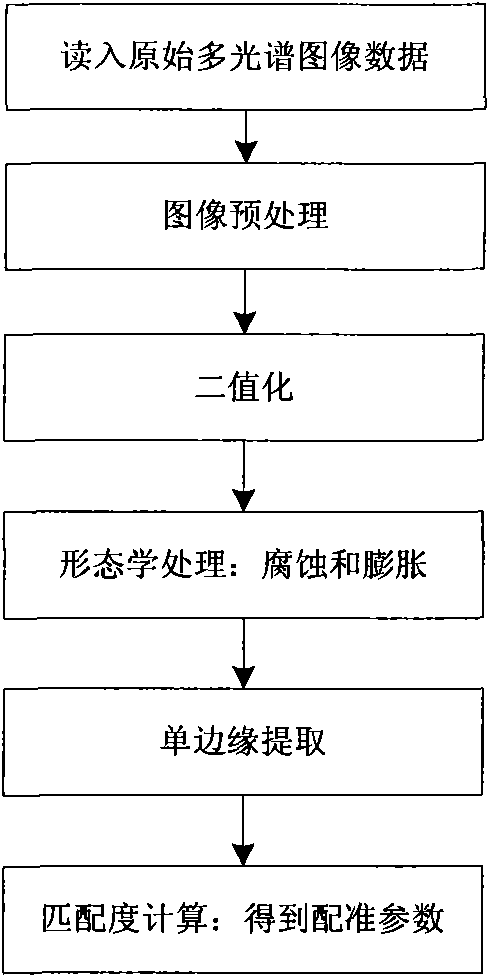
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, in particular to a remote sensing image registration algorithm. The registration algorithm comprises the following steps of: (1) reading primary remote sensing image data from a storage medium; (2) pre-processing each primary image; (3) performing binarization processing to realize image segmentation; (4) corroding and expanding the binary image; (5) extracting a monotropic edge from the eroded and expanded binary image by the Roberts cross gradient operator; (6) calculating the matching degree of the edge image and finding the optimal matching point; (7) conversing images; and (8) outputting registration information and registration images. The remote sensing image registration algorithm can be applied to multispectral data fusion and remote sensing image mosaicking.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Belt transfer device and imaging equipment using the belt transfer device
InactiveCN1445622AAvoid misregistrationElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersComputer printingStructural engineering
The present invention relates to a belt conveyor for endless conveyance of an endless belt for use with imaging equipment such as copy machines or printers. The belt conveying device includes: a plurality of tension rollers; an endless belt disposed on the tension rollers, the belt end edge portion of the endless belt protruding from the end of one of the tension rollers; and a guide member disposed close to the endless belt . The guide member contacts the belt end edge portion to bend the belt end edge portion in a tapering direction. The guide member adjusts the shape of the belt end edge portion so that the rotational circumference of the belt end edge portion is smaller than the length of the area of the back side of the endless belt that contacts the tension roller.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Control of a printing press using a torsion model
InactiveCN101024329AGood repeatabilitySimplify workRotary pressesPrinting press partsDrive motorEngineering
A method and an apparatus control a printing press having a plurality of printing units, a plurality of cylinders which are coupled mechanically to one another and a control computer for controlling at least one drive motor which drives the mechanically coupled cylinders. A torsion model is stored in the machine computer for describing the torsion state of the cylinders in the printing press which are rotatably coupled mechanically to one another, as a function of at least one measurable operating parameter or at least one variable of the printing press which is known to the machine computer. A control of the printing press is performed by the control computer on the basis of the values which are calculated by the torsion model.
Owner:HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN AG
Electrical connecting apparatus
InactiveUS20080197869A1Avoid displacementAvoid misregistrationTemperature compensation modificationElectrical testingElectricityElectrical connection
To restrain misregistration of tips due to change in temperature, an electrical connecting apparatus is used for connection of a tester, and electrical connection terminals of a device under test to undergo electrical test by the tester. The electrical connecting apparatus comprises a probe board having a plurality of probe lands on its underside; and a plurality of contacts having tip portions to be brought into contact with a base end portion fixed at the respective probe lands and the connection terminals of the device under test. The measure from the tip of each contact and the probe land ranges from 1.1 to 1.3 mm, and the coefficient of thermal expansion of the probe board is greater than the coefficient of thermal expansion of the device under test within the range from 1 to 2 ppm / ° C.
Owner:NIHON MICRONICS
Heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet and method for processing adherend using the heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet
InactiveUS7635516B2Reduce debrisHigh elastic modulusFixed capacitor dielectricLaminating printed circuit boardsShear modulusFoaming agent
Disclosed is a heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet that can prevent the deformation of a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer caused by pressurization, further reduce chipping in grinding and cutting processes, be easily peeled off from a processed article after processing, and can be easily applied to an adhered at ordinary temperature. The heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet includes a substrate, and a heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer arranged on or above at least one side of the substrate, the heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer containing a foaming agent and having a shear modulus (23° C.) in an unfoamed state of 7×106 Pa or more. The adhesive sheet further includes a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer being arranged on or above heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer, wherein the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer has a shear modulus (23° C.) of less than 7×106 Pa and a thickness of 0.01 to 10 μm.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
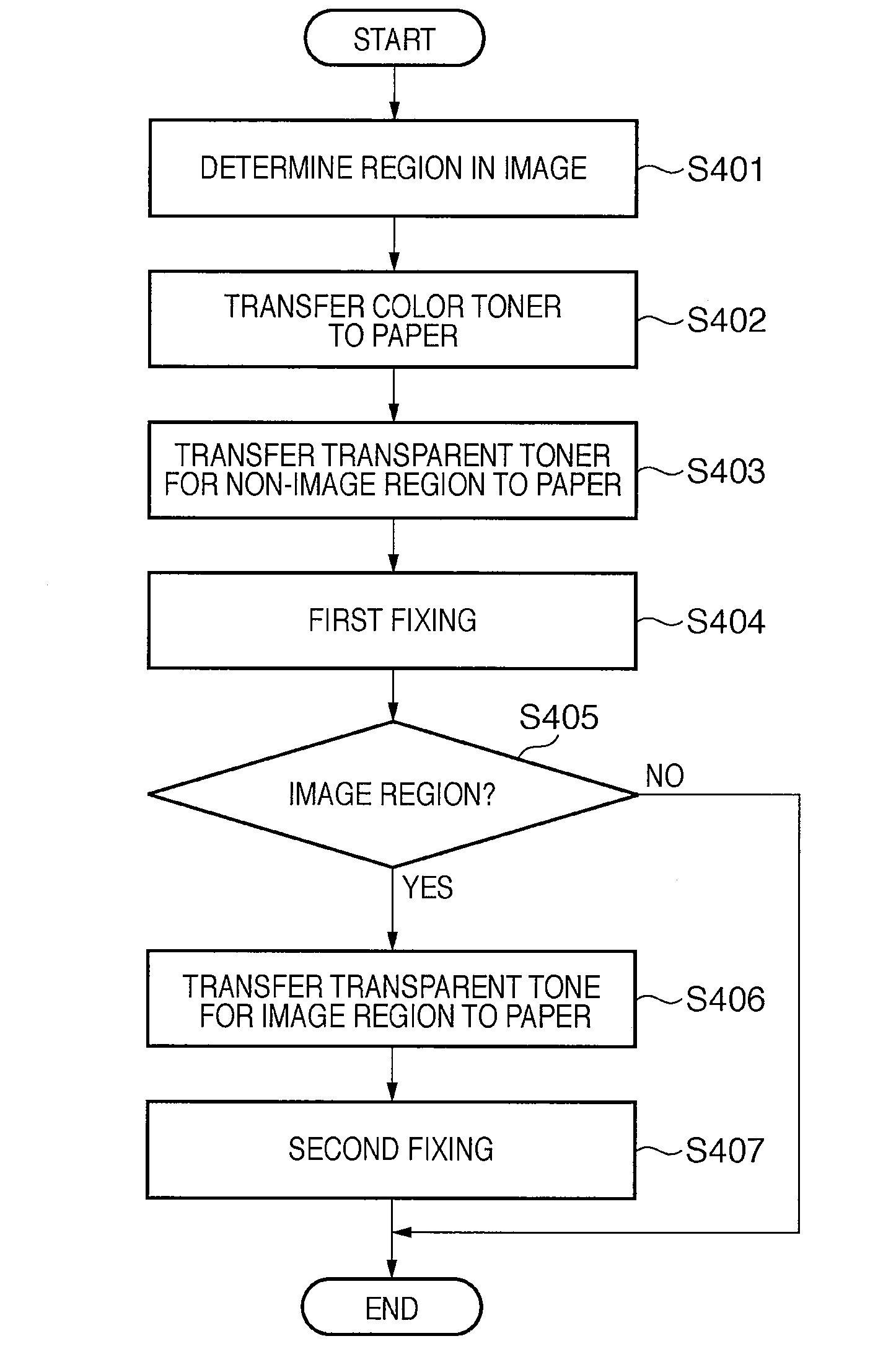
Image forming apparatus, control method therefor, program, and storage medium
ActiveUS20090067863A1Avoid misregistrationEliminate gloss irregularityElectrographic process apparatusImage formationComputer science
An image forming apparatus equipped with an image forming unit capable of image formation using color toner and transparent toner includes, a determining unit adapted to determine whether each pixel of image data belongs to an image region or a text region; a control unit adapted to control the image forming unit by switching between transfer of a toner image to the image region and transfer of a toner image to the text region; a fixing unit adapted to fix the toner image formed on recording material; and a transport unit adapted to discharge the recording material on which the toner image is fixed or re-feed the recording material to the image forming unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of adjusting measurement position of radiation thermometer and heat treatment apparatus
ActiveUS20180269085A1Easy to adjustAvoid misregistrationRadiation pyrometryFurnace componentsRadiation thermometerEngineering
A pyrometer holder is mounted to an outer wall of a chamber while holding a lower radiation thermometer. The front end of the lower radiation thermometer is brought into abutment with a mounting portion of the pyrometer holder, and a bottom plate is brought into abutment with the rear end of the lower radiation thermometer. A tension spring is tensioned between the bottom plate and the mounting portion to prevent the lower radiation thermometer from falling off or misregistration. An angle adjusting mechanism adjusts the angle of the radiation thermometer with respect to the outer wall of the chamber, with the front end of the radiation thermometer serving as a supporting point. Thus, the measurement position of the lower radiation thermometer is adjusted.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Automatic register method, system and equipment based on machine vision
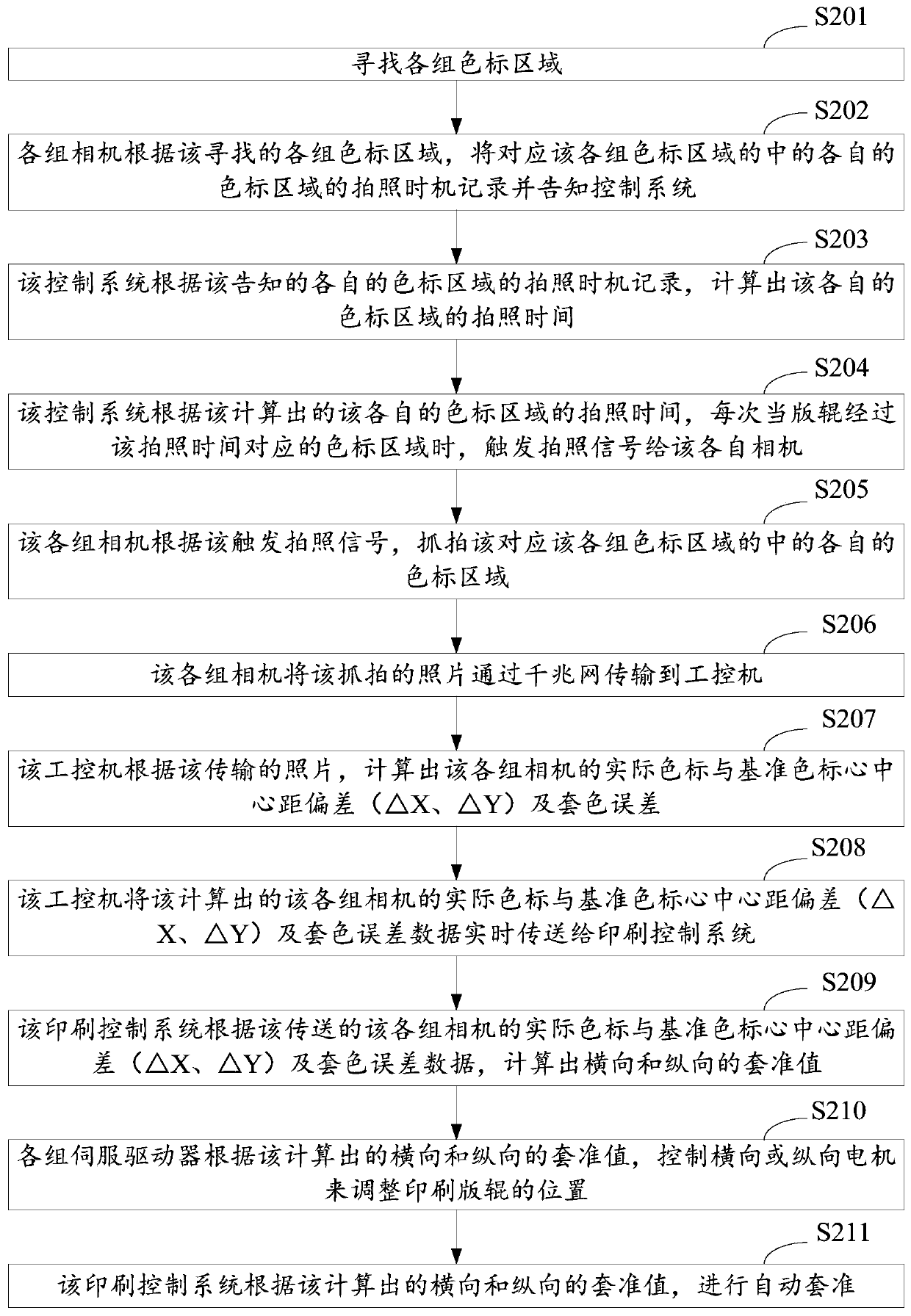
ActiveCN110091590ARealize automatic registrationPrecise registrationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMachine visionControl system
The invention discloses an automatic register method, system and equipment based on machine vision. The automatic register method based on machine vision includes the following steps: an industrial control computer transmits calculated center distance deviation ([delta]X and [delta]Y) of actual color codes and reference color codes of all groups of cameras and register error data to a control system, the control system calculates transverse and longitudinal register values according to the transmitted center distance deviation ([delta]X and [delta]Y) of the actual color codes and the referencecolor codes of all the groups of the cameras and the register error data, and the control system carries out automatic register according to the calculated transverse and longitudinal register values. Through the method, the recognition of color code images by shooting can be realized by using the machine vision, an actual position is calculated for the automatic register, the register is accurate, and the problem of inaccurate register caused by color code printing can be avoided.
Owner:厦门微控科技有限公司
Thermal transfer image receiving sheet
InactiveUS6365546B1Improve accuracyImprove printing qualityPattern printingAblative recordingReciprocating motionImage formation
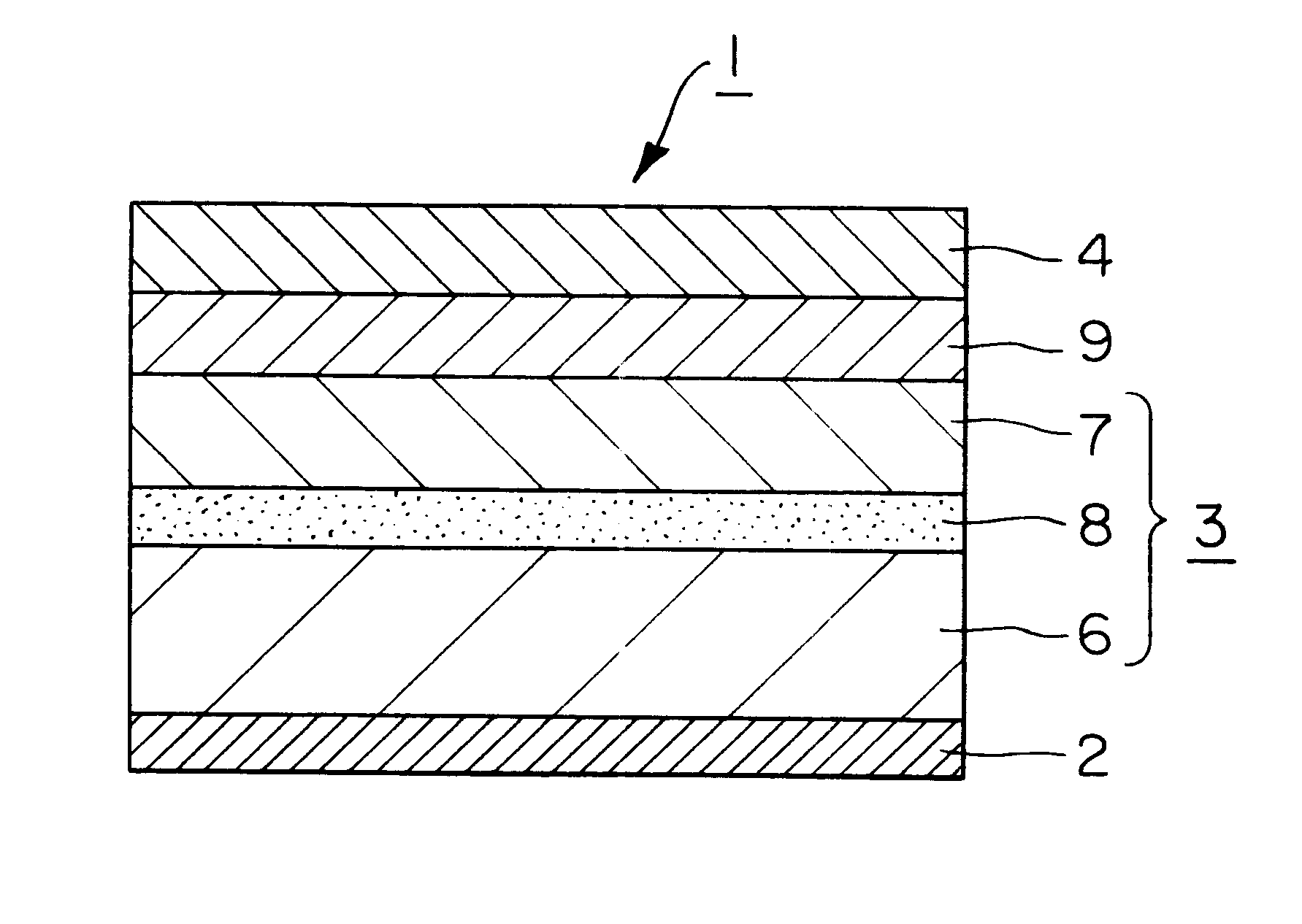
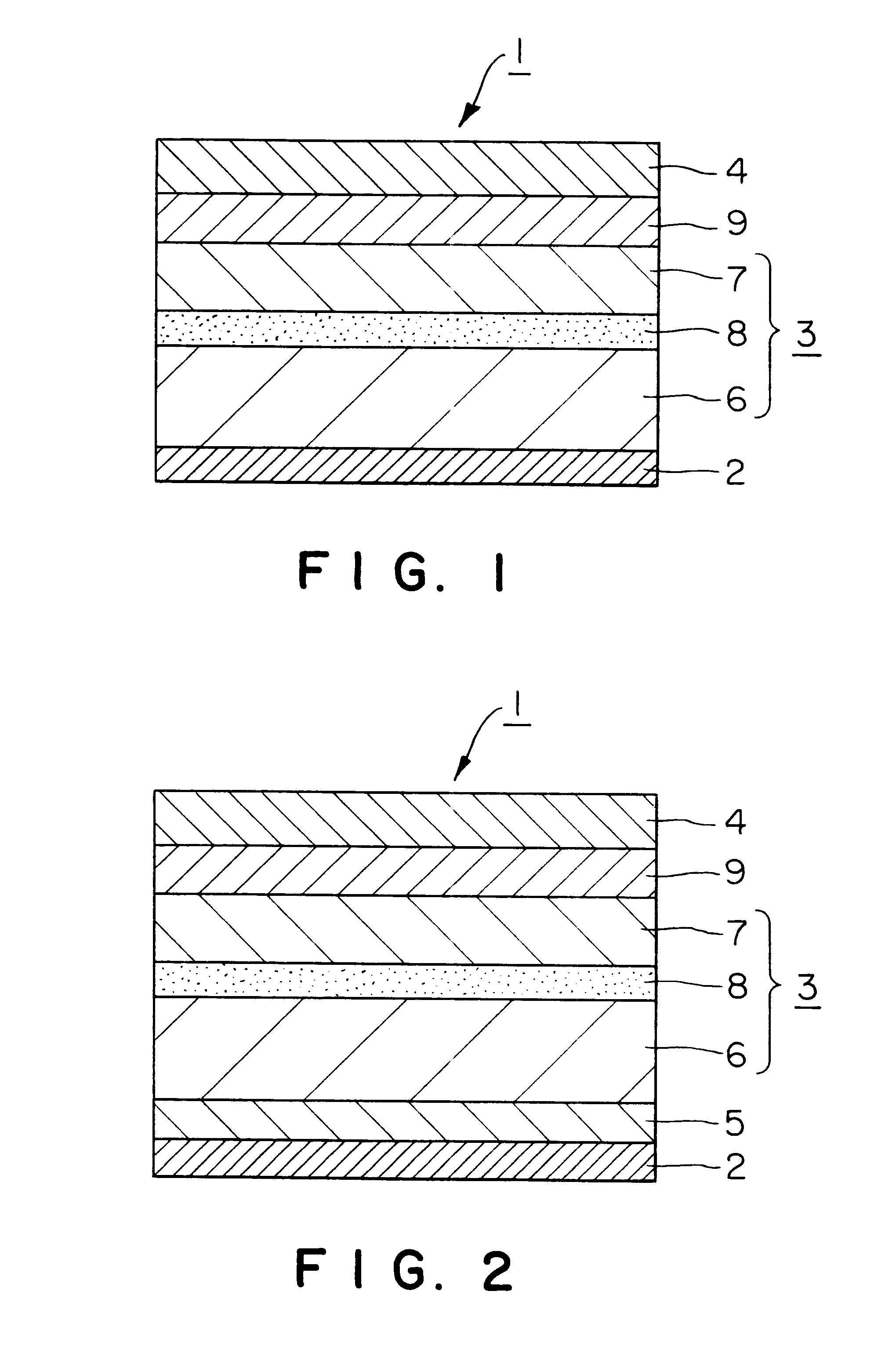
A thermal transfer image receiving sheet is provided which, when used with various printers, can be carried with improved accuracy, can form an image without misregistration, can prevent a trace of a spike of a metallic roller in the printer from reaching the image receiving surface and hence can form an image having quality not significantly influenced by the trace of the spike.The thermal transfer image receiving sheet 1 comprises a substrate 3, a receptive layer 4 provided on at least one side of the substrate 3, and a grip layer 2 provided on the other side of the substrate 3. In this case, the grip layer 2 is constituted by an unstretched synthetic resin layer having a softening point of 110° C. or above. This constitution permits a spike of a metallic roller in a printer to satisfactorily bite the unstretched synthetic resin layer having a softening point of 110° C. or above as the grip layer 2. This prevents slippage between the metallic roller and the thermal transfer image receiving sheet 1 at the time of a reciprocation for image formation and hence can prevent misregistration. Therefore, the thermal transfer image receiving sheet can be carried with improved accuracy, and a thermally transferred image can be formed without misregistration.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Optical device and projection device
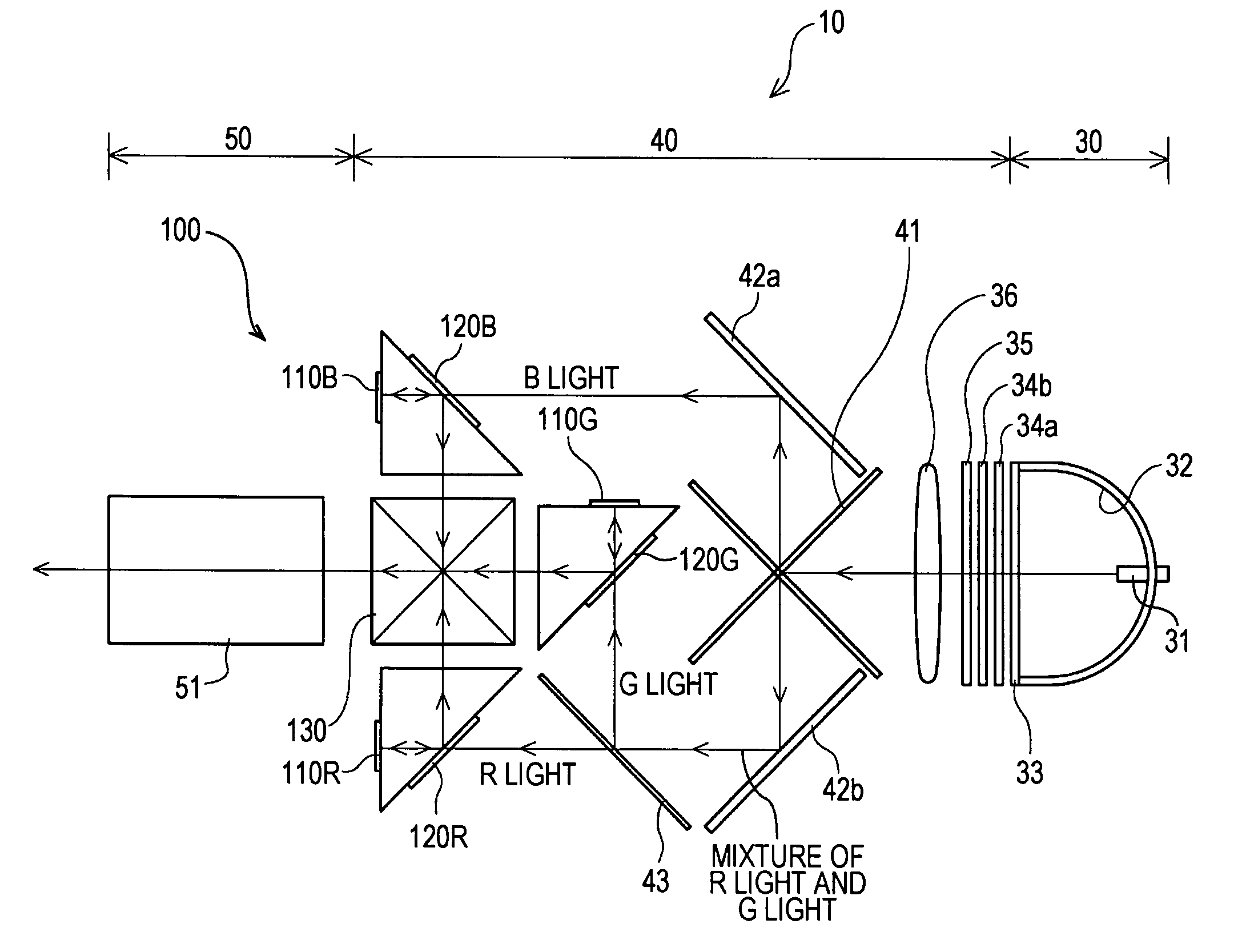
InactiveUS8480239B2Cutting safetyAvoid misregistrationProjectorsColor photographyImage signalOptical polarization
Owner:SONY CORP
Image forming apparatus which prevents misregistration
Owner:CANON KK
Method for manufacturing microwave power device by using double level polysilicon device structure
InactiveCN101950722AImproved power output characteristicsHighly integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutocollimationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a microwave power device by using a double level polysilicon device structure. The method of the invention adopts a deep groove isolation technique and inhomogeneous thermal design, realizes the acinaceous cellular structure, adopts outer base region composite plate to carry out photoetching, vertically etches a monox dielectric layer and outer base polycrystalline silicon to obtain the outer base region window of the ratio change of the length and the like, and forms a compound L-shaped side wall capable of adjusting the length of an emitting electrode by means of autocollimation in the outer base region window. In the invention, the emitting electrode polycrystalline silicon composite plate is adopted to carry out photoetching, the emitting electrode polycrystalline silicon and the dielectric layer are vertically etched by utilizing autocollimation, the selective side wall protection technology is combined, under the scale of the deep submicron, and the polycrystalline silicon refractory metallic silicide with low film resistivity is realized by means of autocollimation, thereby avoiding the short circuit connection of two types of polycrystalline silicon leads, reducing the restriction of parasitic components of the interconnected leads on improving the characters of the microwave power device under the graph scale of submicron and deep submicron, thereby improving the overall performance of the microwave power device and the microwave performance thereof.
Owner:WUXI JINGKAI TECH
Image forming apparatus, control method therefor, program, and storage medium
ActiveUS8208827B2Avoid misregistrationReduce irregularitiesElectrographic process apparatusComputer graphics (images)Image formation
An image forming apparatus equipped with an image forming unit capable of image formation using color toner and transparent toner includes, a determining unit to determine whether each pixel of image data belongs to an image region or a text region; a control unit to control the image forming unit by switching between transfer of a toner image to the image region and transfer of a toner image to the text region; a fixing unit to fix the toner image formed on recording material; and a transport unit to discharge the recording material on which the toner image is fixed or re-feed the recording material to the image forming unit.
Owner:CANON KK
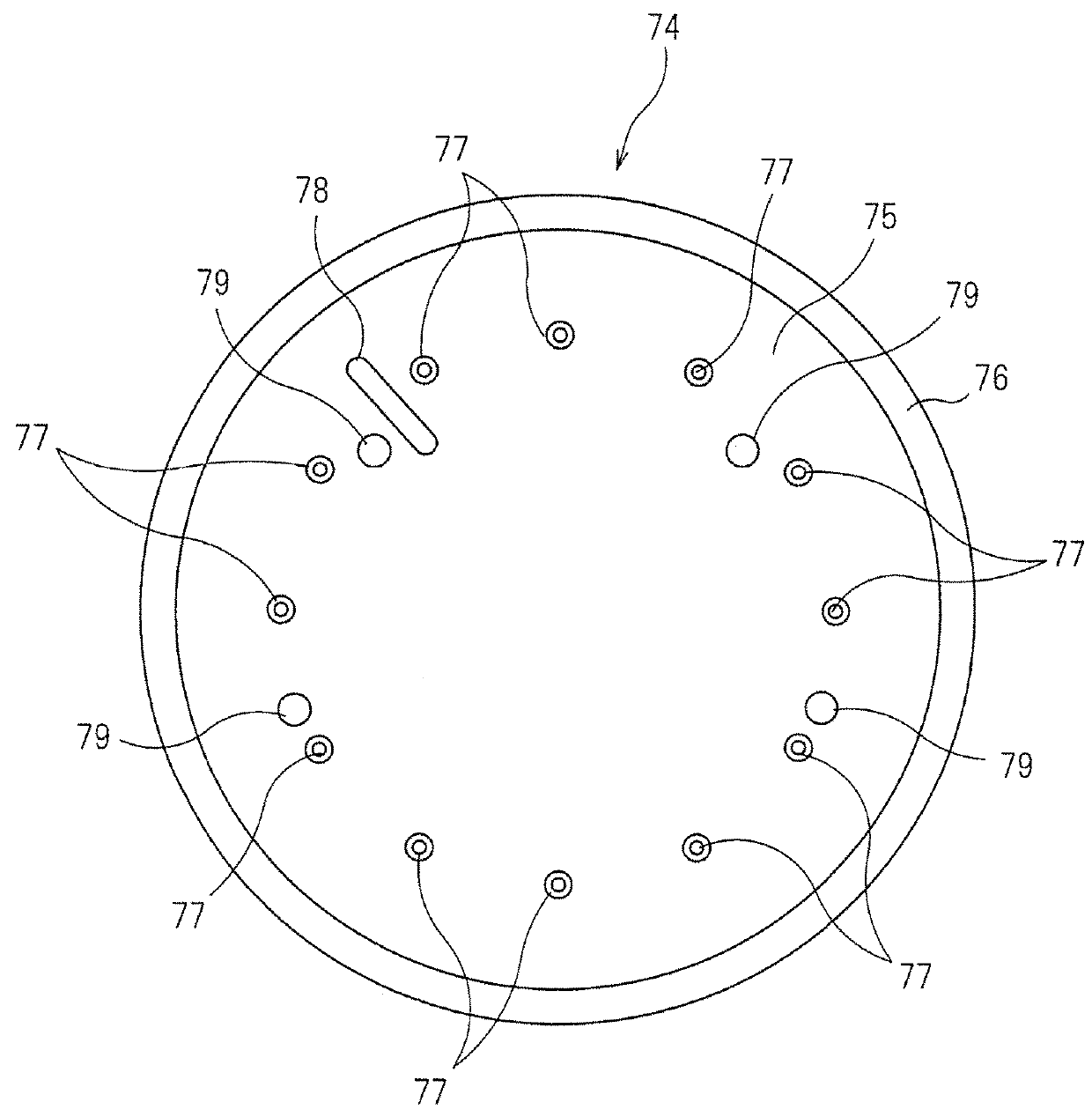
Electromagnet for use in a relay
ActiveUS8274344B2Avoid misregistrationTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsBobbinConductor Coil
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
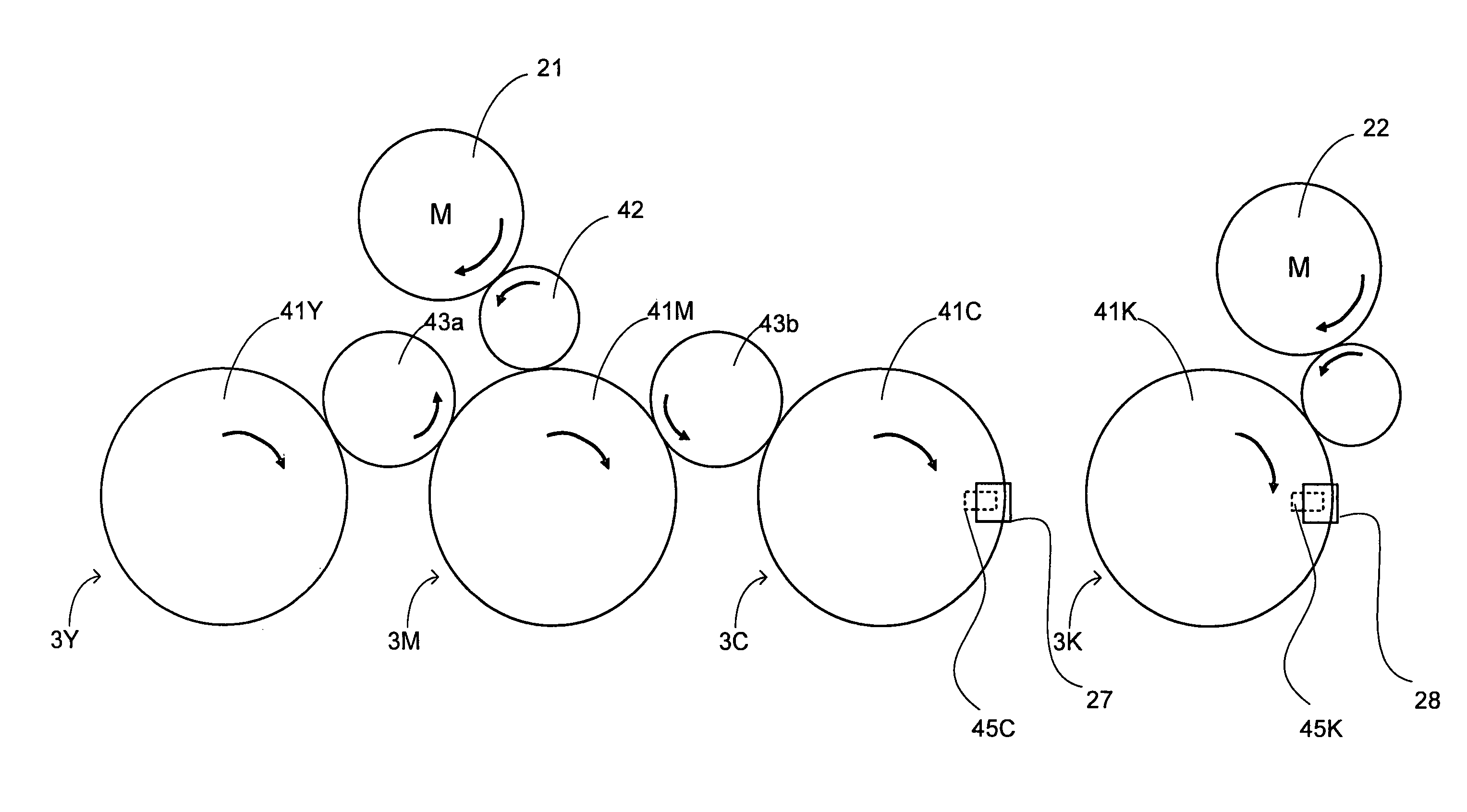
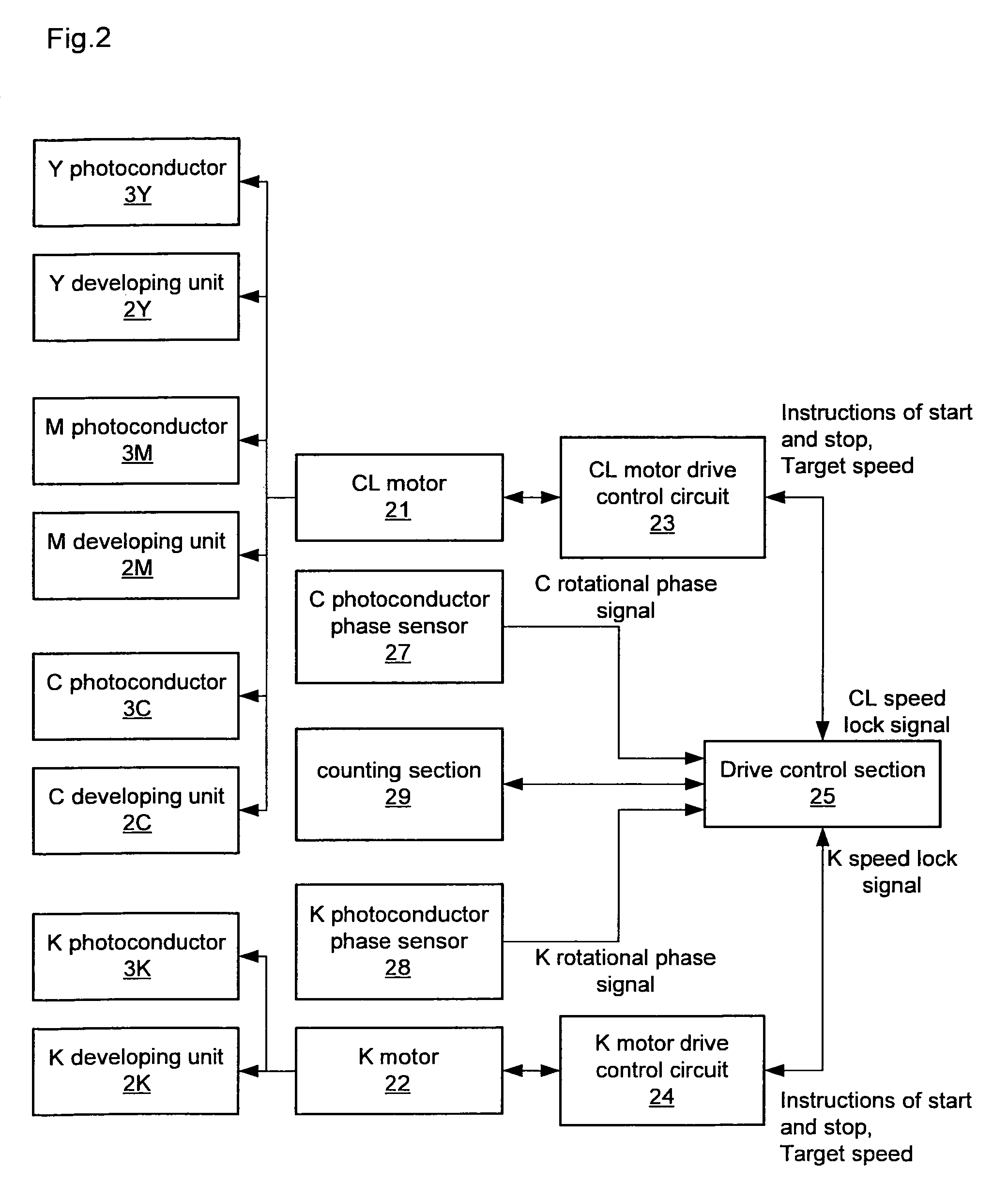
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20090311007A1Heavy loadAvoid trappingElectrographic process apparatusElectrical conductorImage formation
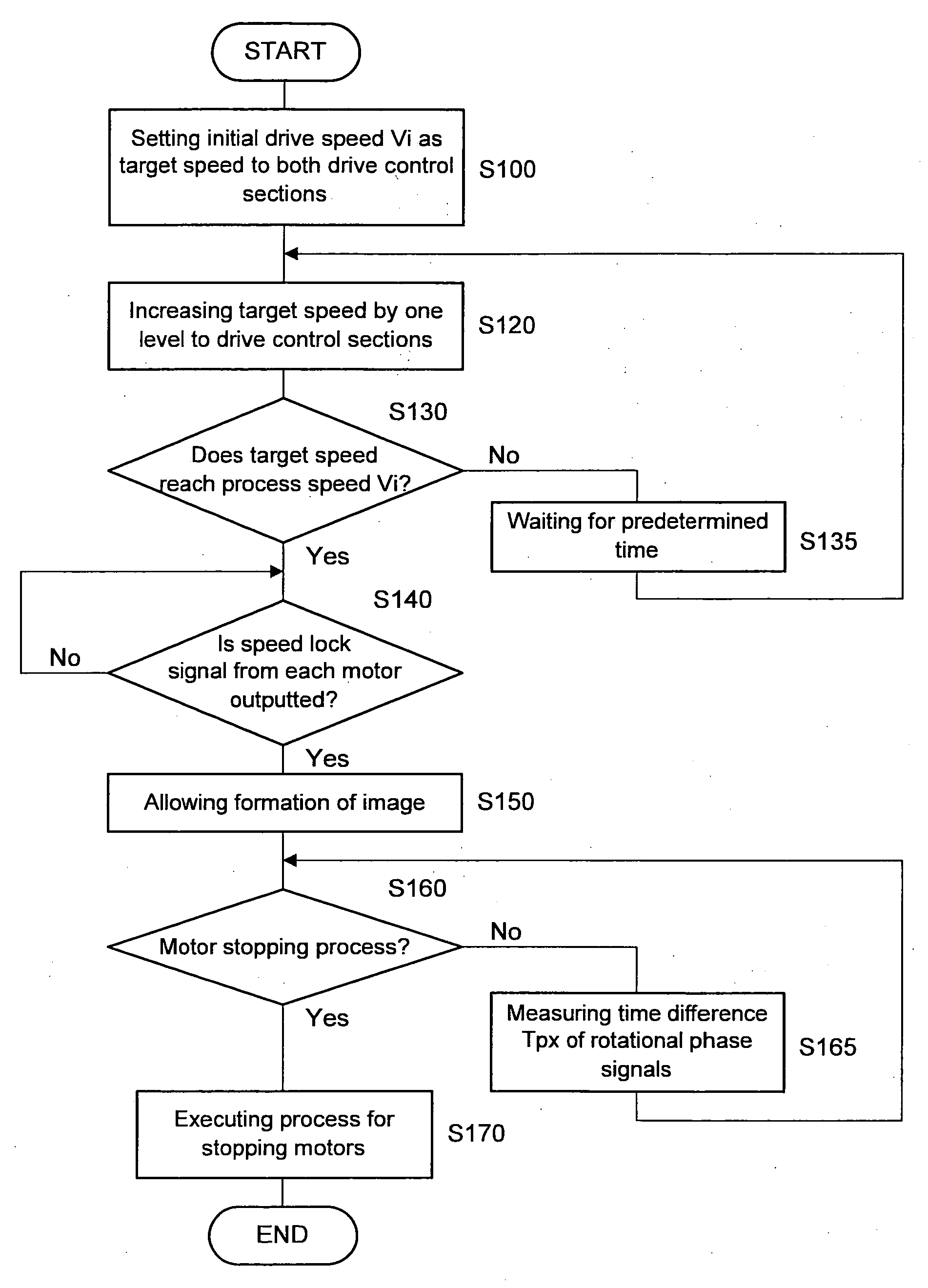
An image forming apparatus including: a first and a second photoconductor groups constituted of one or more photoconductors respectively; a first and a second drive control sections for controlling the drive of the first and the second photoconductor groups respectively to rotate the photoconductors thereof, wherein the rotational phases of the first photoconductor group and the second photoconductor group are adjusted to be matched therebetween; and the first and the second drive control sections control so that predetermined profile of a target speed is applied to the first and second photoconductor groups wherein, in the target-speed profile, the first photoconductor group starts rotating after a elapse of a predetermined startup delay time from the second photoconductor group starts rotating, and both groups end at a same final speed predetermined for full-color image formation, wherein the startup delay time is predetermined based on measurements of times needed for each of the first and the second photoconductor groups to reach a predetermined speed from starting the rotation with the target-speed profile being applied thereto.
Owner:SHARP KK
Head module, liquid jetting head, liquid jetting apparatus, method of manufacturing head module, and method of manufacturing liquid jetting head
InactiveUS20070165077A1Increase manufacturing costInhibit thermal stressInking apparatusBuffer tankSurface cover
A head module includes a head chip provided with an array of heat generating elements, a nozzle sheet provided with nozzles, a barrier layer for forming ink liquid chambers, a module frame adhered to the nozzle sheet to thereby support the nozzle sheet and provided with a head chip arranging hole for arranging the head chip therein, and a buffer tank which is so disposed as to cover the head chip arranging hole from a surface, on the opposite side of the surface of adhesion to the nozzle sheet, of the module frame and which is for forming a common liquid conduit communicated with all the ink chambers of the head chip.
Owner:SONY CORP
Mr imaging using shared information among images with different contrast
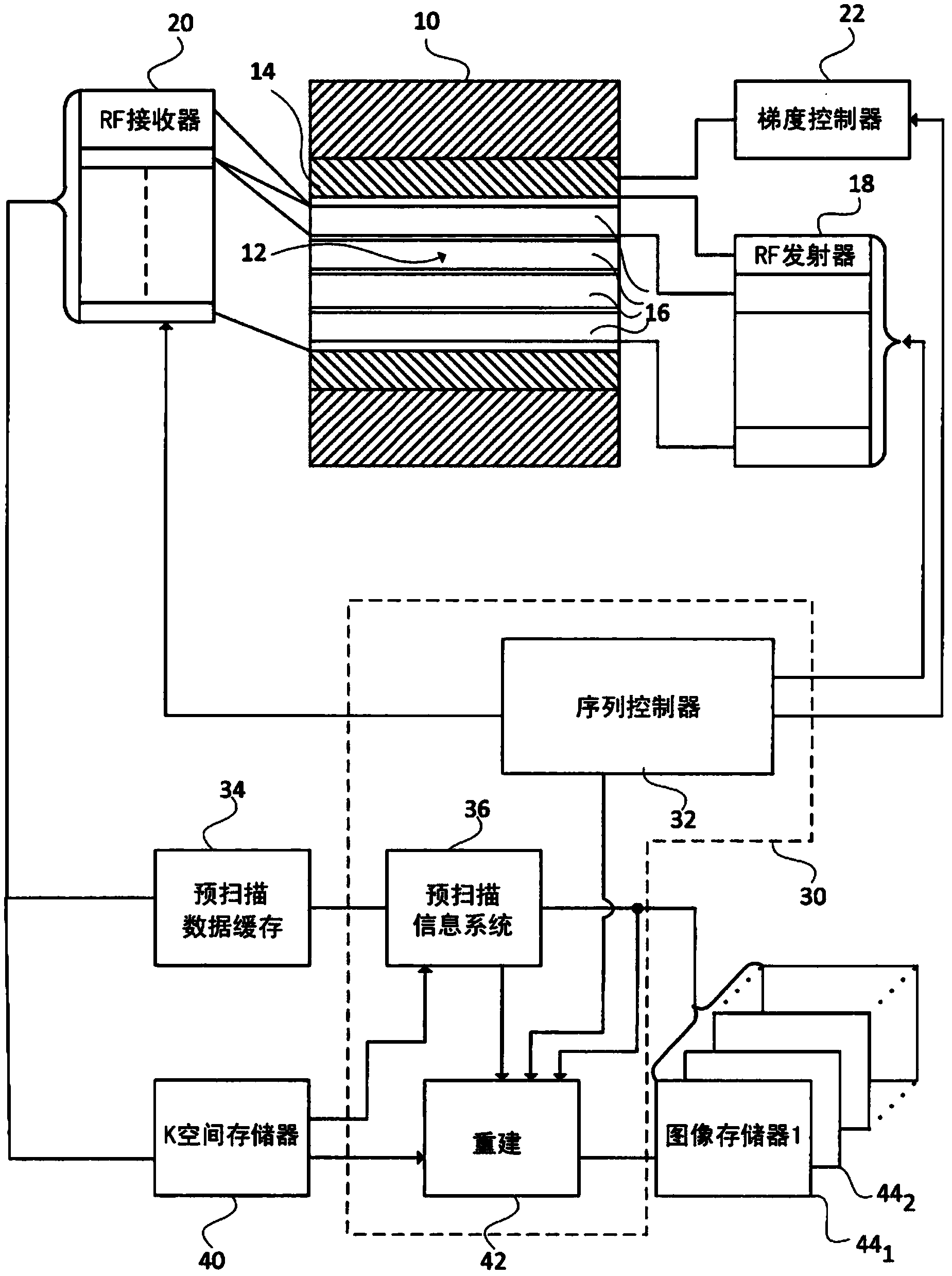
InactiveCN103930790AShorten the timePrescan reduces or eliminatesMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic gradientData store
A typical clinical MR protocol is composed of several sets of scans to acquired images with different contrast, such as T1, T2 and DWI. Currently, the acquisition and reconstruction of these images are processed individually. The proposed method treats the optimization of all acquisitions and reconstructions as one single procedure for faster and more robust MRI. The theory behind this concept is that the information such as B0, B1- field, optimized acquisition trajectory, reconstruction parameters, etc., can be shared among all scans for different contrasts since the same subject is scanned in the same system using the same RF coil.; A method of magnetic resonance imaging includes performing a first magnetic 10 resonance scan sequence which saves a data store, and performing a second magnetic resonance scan sequence which uses a data store from the first magnetic resonance scan sequence. A magnet (10) generates a B0 field in an examination region (12), a gradient coil system (14, 22) creates magnetic gradients in the examination region, and an RF system (16, 18, 20) induces resonance in and receives resonance signals from a subject in the 1 examination region. One or more processors (30) are programmed to perform a magnetic resonance pre-scan sequence to generate pre-scan information, perform a first sequence to generate first sequence data, refine the pre-scan information with the first sequence data, perform a second imaging sequence to generate second sequence data.; Further, the second sequence data is either reconstructed using the refined pre-scan information or performed using the refined pre-scan sequence information.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
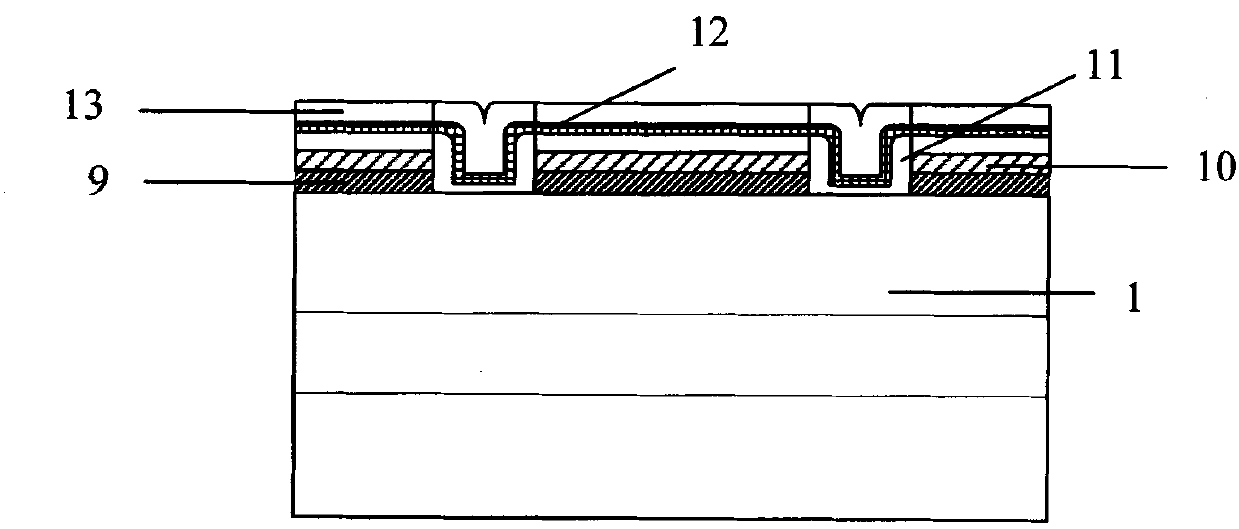
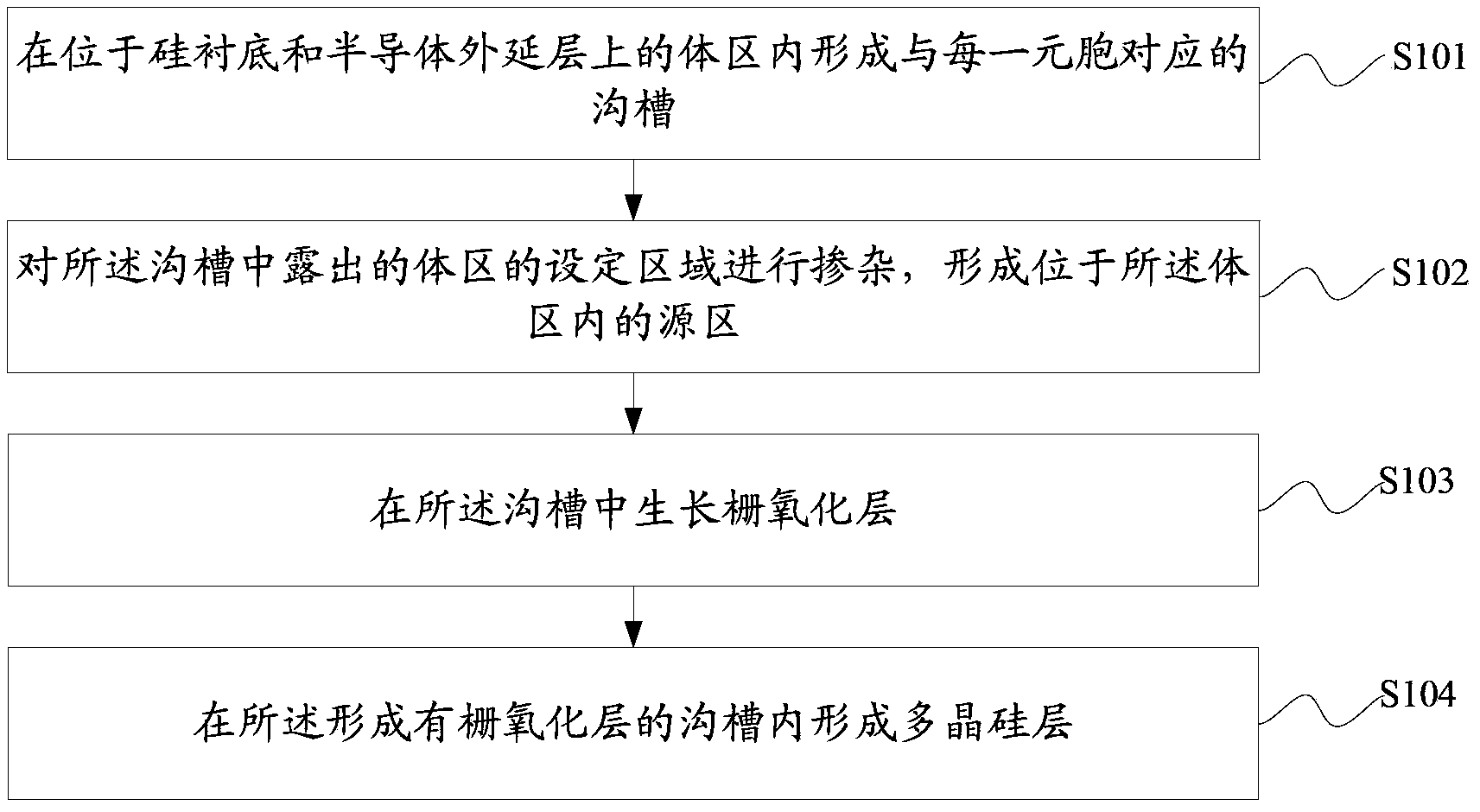
DMOS device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104241356AHighly integratedAvoid misregistrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBody areaEngineering
The invention discloses a DMOS device and a manufacturing method of the DMOS device. The DMOS device and the manufacturing method of the DMOS device are used for increasing the density of cells of the DMOS device. The method comprises the first step of forming grooves corresponding to the cells in a body area located on a silicon substrate and a semiconductor epitaxial layer, the second step of conducting doping on set areas of the body area exposed out of the grooves to form source areas located in the body area, the third step of growing a gate oxidation layer in the grooves, and the fourth step of forming a polycrystalline silicon layer in the grooves where the gate oxidation layer is formed.
Owner:FOUNDER MICROELECTRONICS INT
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS8219004B2Avoid misregistrationHeavy loadElectrographic process apparatusElectrical conductorImage formation
An image forming apparatus including: a first and a second photoconductor groups constituted of one or more photoconductors respectively; a first and a second drive control sections for controlling the drive of the first and the second photoconductor groups respectively to rotate the photoconductors thereof, wherein the rotational phases of the first photoconductor group and the second photoconductor group are adjusted to be matched therebetween; and the first and the second drive control sections control so that predetermined profile of a target speed is applied to the first and second photoconductor groups wherein, in the target-speed profile, the first photoconductor group starts rotating after a elapse of a predetermined startup delay time from the second photoconductor group starts rotating, and both groups end at a same final speed predetermined for full-color image formation, wherein the startup delay time is predetermined based on measurements of times needed for each of the first and the second photoconductor groups to reach a predetermined speed from starting the rotation with the target-speed profile being applied thereto.
Owner:SHARP KK
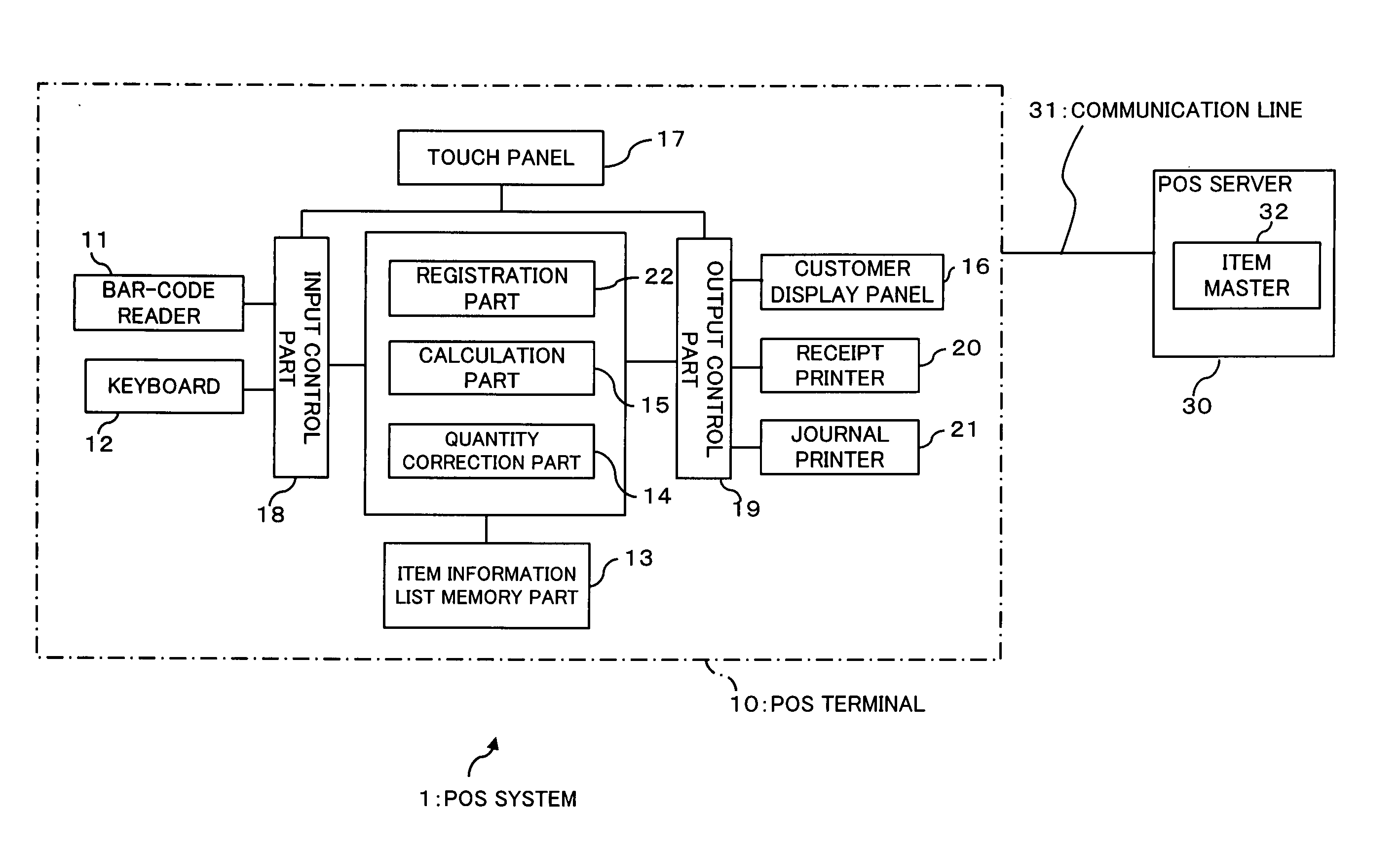
POS terminal, method of correcting a quantity, and computer-readable storage medium recording therein a program for causing a computer to correct a quantity
ActiveUS20050203803A1Easy to correctAvoid misregistrationComplete banking machinesFinancePoint of saleComputer engineering
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
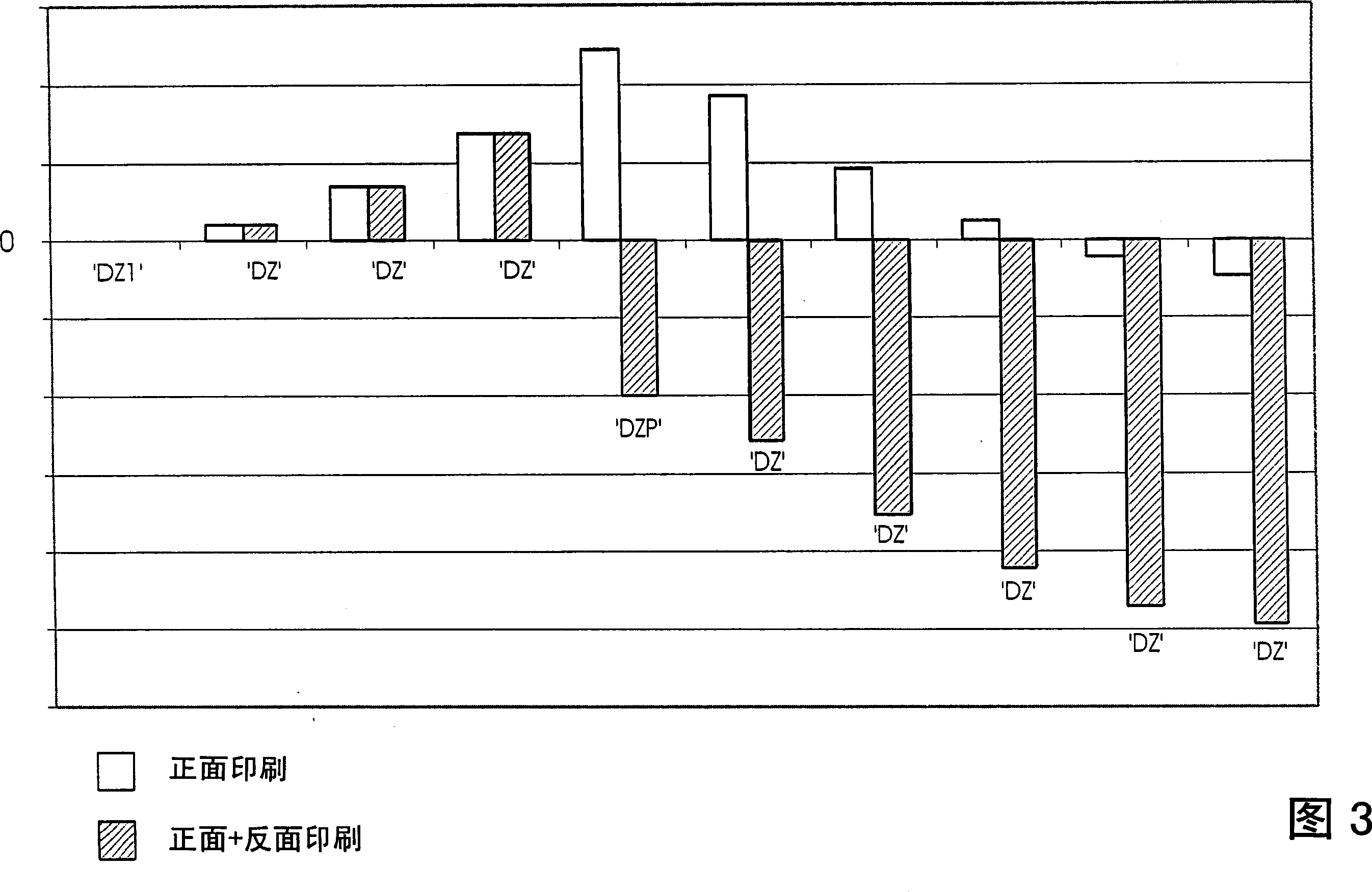
Satellite-type flexographic printing machine
InactiveCN106183364AReduce in quantityRealize automatic double-sided printingRotary letterpress machinesPrinting press partsCooking & bakingEngineering
The invention discloses a satellite-type flexographic printing machine. The printing machine comprises an unrolling unit, an unrolling correcting unit, a traction unit, a printing station, a baking oven, a rolling correcting unit and a rolling unit and also comprises an overturning correcting frame; a printing material enters the overturning correcting frame after being subjected to front printing and drying and enters the printing station again so as to be subjected to back printing after being overturned by the overturning correcting frame. By using the satellite-type flexographic printing machine, automatic double-side printing on one satellite-type flexographic printing machine is realized, the problem that halt and secondary starting are required during original double-side printing on one equipment is solved, therefore, the problems of register difference and printing tailings caused in the speed increasing and reducing processes for halt and secondary starting are also avoided, and the production efficiency and product qualification ratio are greatly increased; and meanwhile, compared with printing by using two equipment, the satellite-type flexographic printing machine has the advantages that the amount of the required operating personnel is smaller, and therefore, the labor cost can be reduced while the equipment purchasing cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN SOTECH PRINTING MACHINERY CO LTD
Micro-lens array substrate and production method therefor, and projection type liquid crystal display unit using those
InactiveUS7338754B2Prevent heat-caused misregistrationHighly accurate micro-lens array substrateOptical articlesColor television detailsLiquid-crystal displayDielectric substrate
Owner:SHARP KK
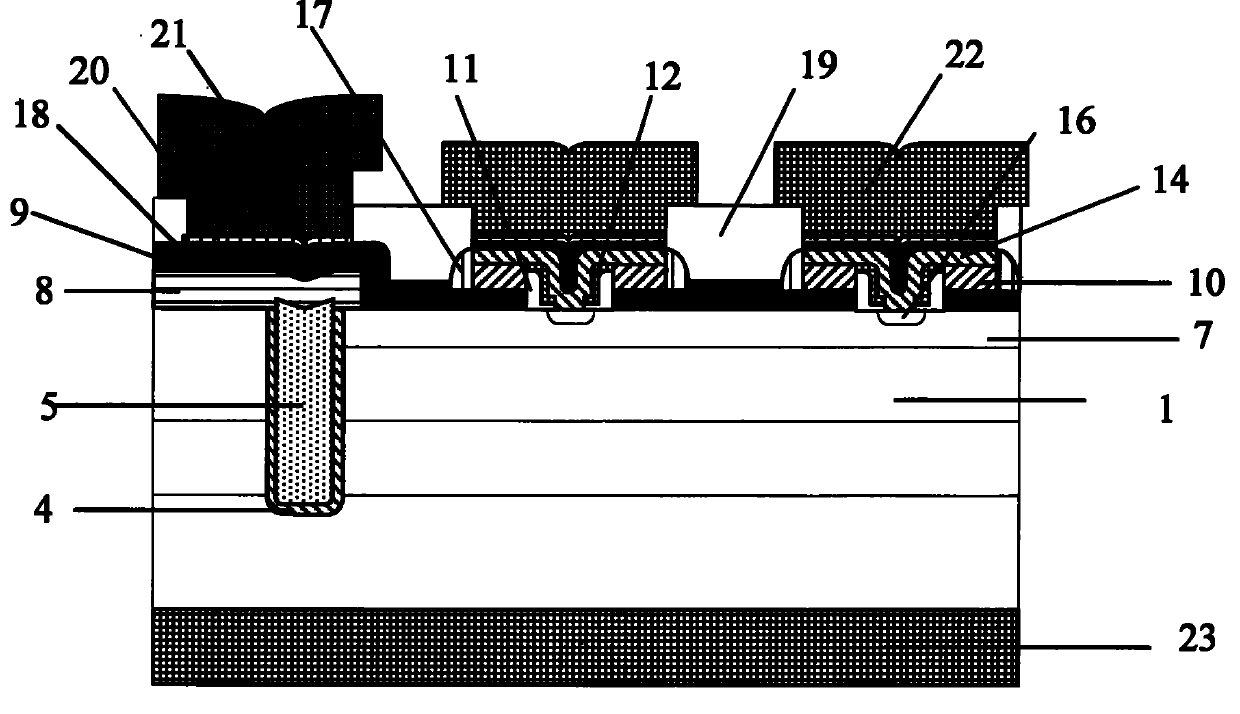
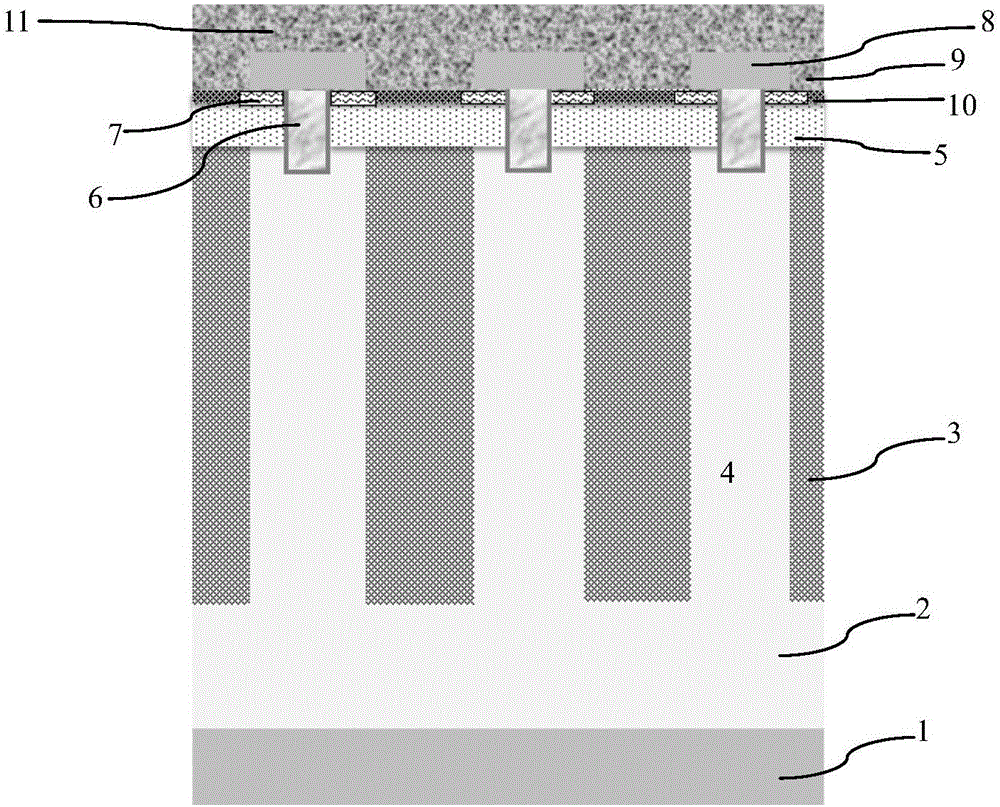
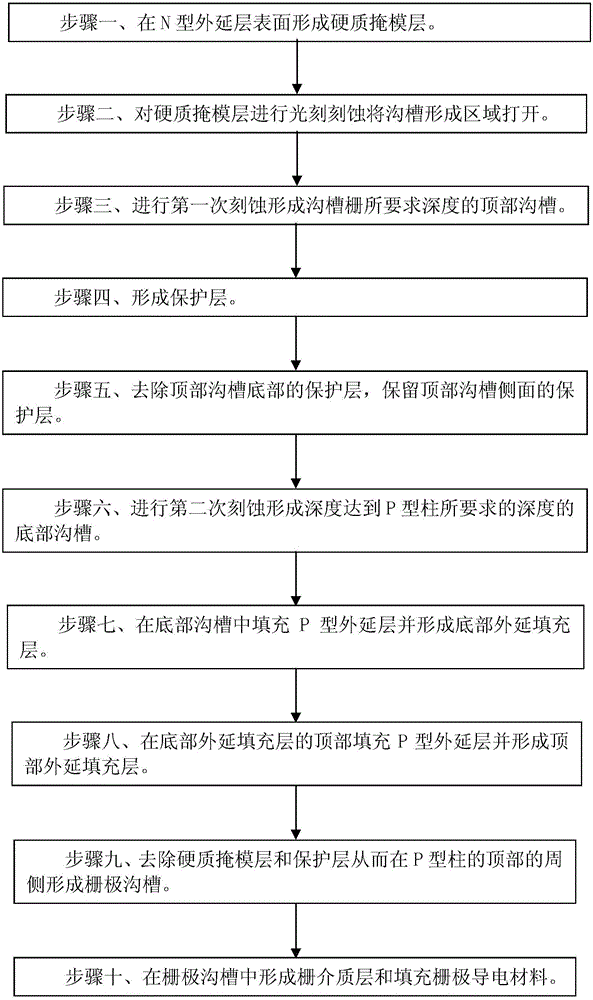
Manufacturing method for groove grid super junction MOSFET
ActiveCN105957897AEliminate misregistration problemsPrevent misregistrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETConductive materials
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a groove grid super junction MOSFET. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of forming a hard mask layer; photoetching the hard mask layer to open a groove forming area; etching for the first time to form a top groove; removing a protection layer at the bottom of the top groove, and reserving the protection layer on the side surface of the top groove; etching for the second time to form a bottom groove; filling the bottom groove with a P-type epitaxial layer to form a bottom epitaxial filled layer; filling the top of the bottom epitaxial filled layer with a P-type epitaxial layer to form a top epitaxial filled layer; removing the hard mask layer and the protection layer and thus forming a grid groove at the periphery of the top of a P-shaped column; and forming a grid dielectric layer in the grid groove and filling a grid conductive material in the grid groove. According to the manufacturing method, the registration deviation between the groove grid and the P-type column can be avoided, the technological stability can be improved and thereby the threshold voltage and breakover voltage drop of the device are more uniform, the size of the super junction unit can be smaller, and the capability of resisting unclamped inductive switching impact can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Sheet package with recloseable flap
ActiveUS7726646B2Toughening handlingEasy to printCoin-freed apparatus detailsTobacco pipesEngineeringSheet material
A sheet in accordance with the present invention includes sheets as print mediums for a printer and a package member surrounding the sheets which have been stacked up. The sheet package is configured so that the sheets can be set in the printer together with the package member exposing part of the sheets. The package member is integrally provided with a flap part which can expose part of the sheets by being opened when the sheet package is set in the printer and cover the exposed part of the sheets by being closed when the sheet package is not used.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Optical connector module
InactiveUS6851868B2Convenient registrationAvoid misregistrationCoupling light guidesEngineeringInterconnection
There is provided an optical connector module of which an optical transmission / reception wafer and an optical waveguide wafer can be registered with each other easily and accurately without misregistration. An optical transmission / reception wafer has guide pin-receiving V-grooves with a V-shaped cross-section, formed at locations preset in association with an optical transmission / reception end of an optical transmission / reception section. An optical waveguide-side connector has an optical waveguide wafer formed with guide pin-receiving V-grooves in association with the guide pin-receiving V-grooves of the optical transmission / reception wafer. Wafer registration guide pins are inserted in these guide pin-receiving V-grooves, and the optical transmission / reception wafer and the optical waveguide wafer are brought close for interconnection such that these guide pins are tightly sandwiched by the guide pin-receiving grooves.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
A printing substrate
InactiveCN101680188ALow water absorptionSmall water absorptionNon-fibrous pulp additionCoatings with pigmentsEngineeringOil absorption
The invention relates to a printing substrate for gravure and offset printing, which substrate exhibits a Cobb(wl5) water absorption value below 15 g / m<2>, preferably below 12 g / m<2>, a Cobb(o,C10) oil absorption value below 1.2 g / m2, preferably below 1 g / m<2>, and an Ink setting below 0.5, preferably below 0.3. The low water and oil absorption in combination with the quite fast ink setting of thesubstrate according to the invention gives rise to a printed substrate with improved printing qualities.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Method for manufacturing microwave power device by using double level polysilicon device structure
InactiveCN101950722BImproved power output characteristicsHighly integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutocollimationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a microwave power device by using a double level polysilicon device structure. The method of the invention adopts a deep groove isolation technique and inhomogeneous thermal design, realizes the acinaceous cellular structure, adopts outer base region composite plate to carry out photoetching, vertically etches a monox dielectric layer and outer base polycrystalline silicon to obtain the outer base region window of the ratio change of the length and the like, and forms a compound L-shaped side wall capable of adjusting the length of an emitting electrode by means of autocollimation in the outer base region window. In the invention, the emitting electrode polycrystalline silicon composite plate is adopted to carry out photoetching, the emitting electrode polycrystalline silicon and the dielectric layer are vertically etched by utilizing autocollimation, the selective side wall protection technology is combined, under the scale of the deep submicron, and the polycrystalline silicon refractory metallic silicide with low film resistivity is realized by means of autocollimation, thereby avoiding the short circuit connection of two typesof polycrystalline silicon leads, reducing the restriction of parasitic components of the interconnected leads on improving the characters of the microwave power device under the graph scale of submicron and deep submicron, thereby improving the overall performance of the microwave power device and the microwave performance thereof.
Owner:WUXI JINGKAI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com