Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
308results about "DC level change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
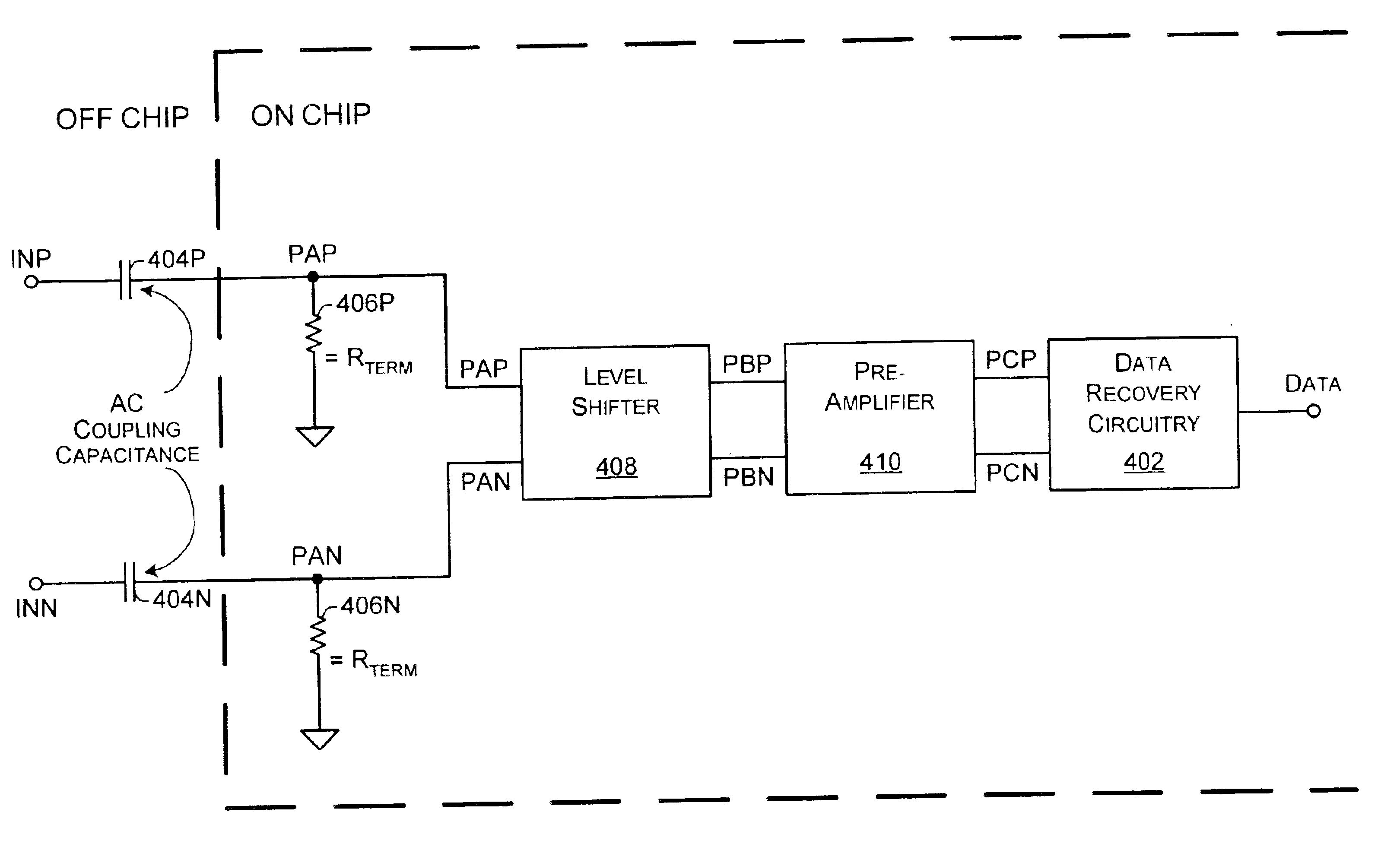
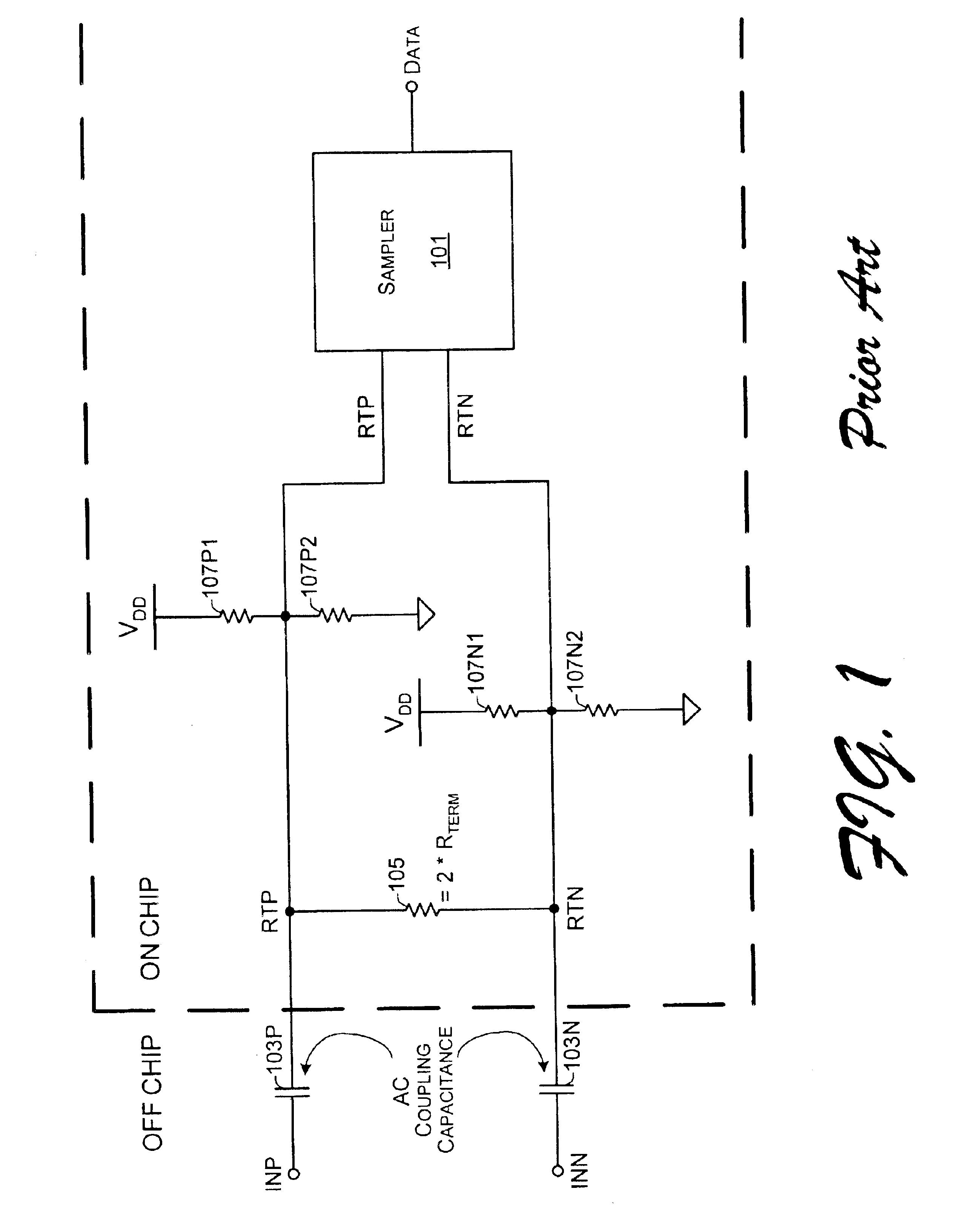
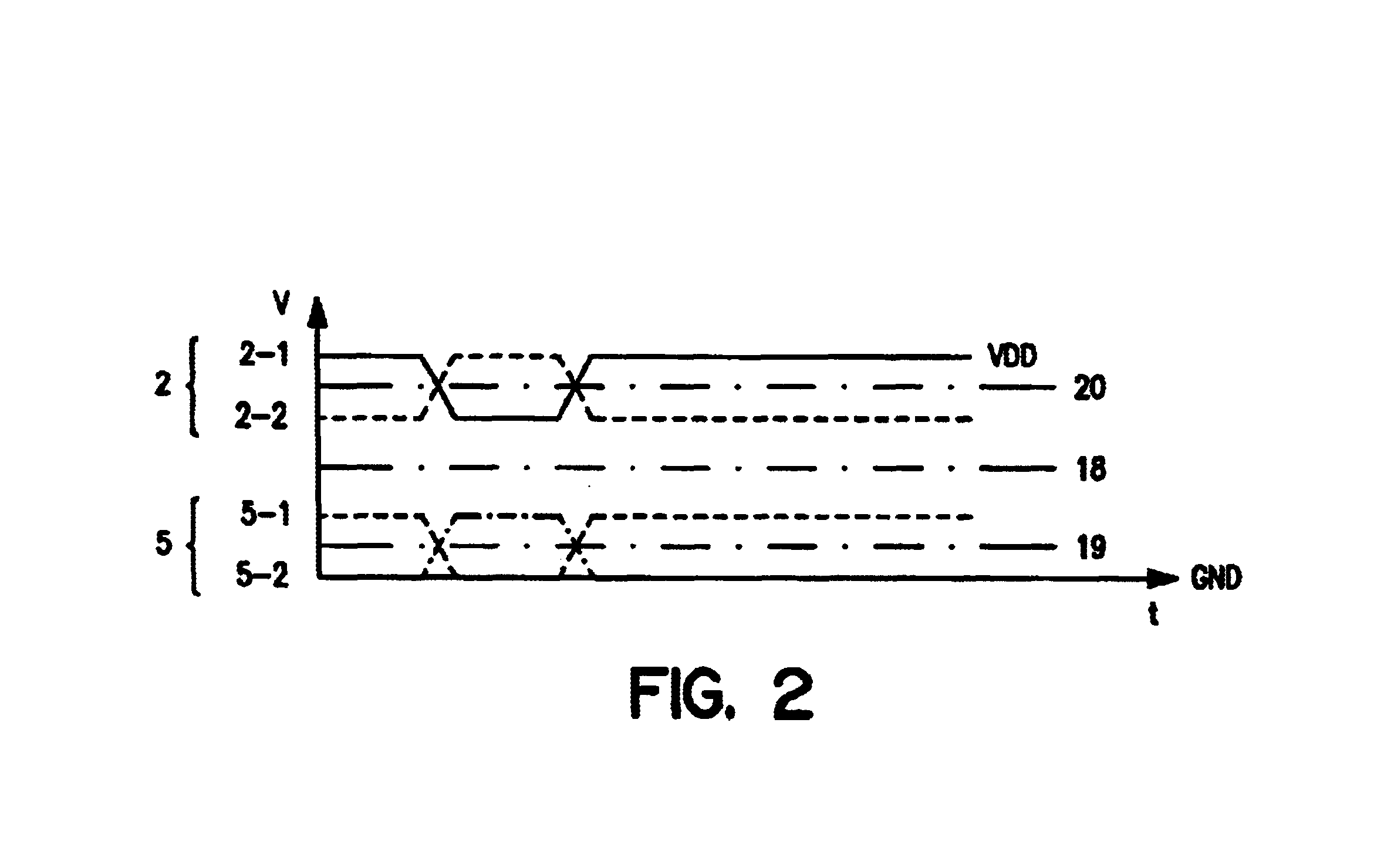
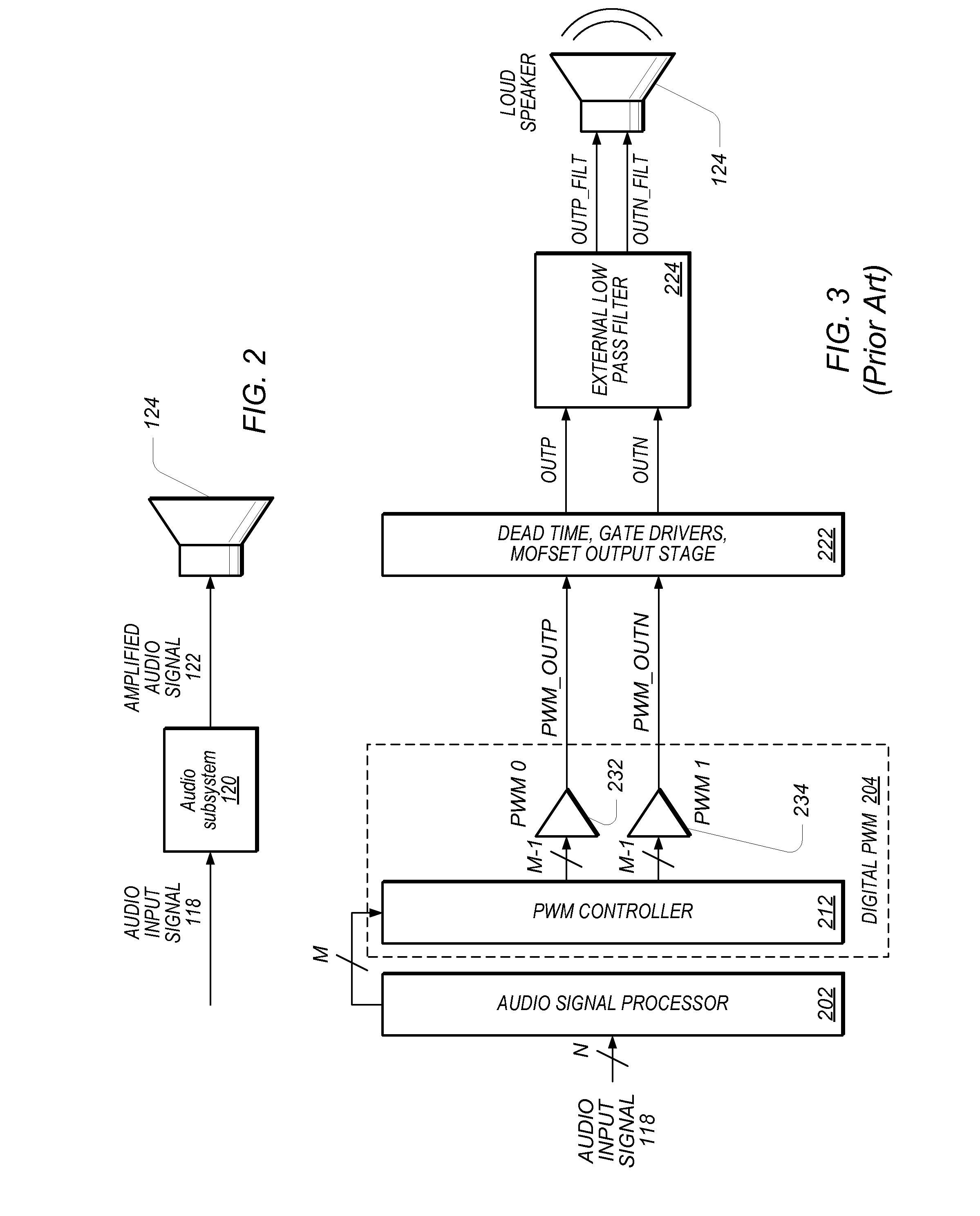
Method and apparatus for signal reception using ground termination and/or non-ground termination
InactiveUS6856169B2Reliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsAbove groundInput selection
Receiving units with inputs that may be ground-terminated and with inputs that are selectively ground-terminated or non-ground terminated are enabled with signal level shifting and a termination mode selection input. In a first exemplary implementation, a receiving unit is capable of having ground-terminated inputs. However, common mode voltage of the signal that is input to decoding data recovery circuitry is above ground because the input signal may be level shifted in between the ground-terminated inputs and the decoding data recovery circuitry. In a second exemplary implementation, a mode selection is accomplished by switching a voltage divider into operation and bypassing a level shifter for a non-ground terminated mode. For a ground terminated mode, the voltage divider is switched out of operation and the level shifter is switched into operation for its signal output to be decoded. Pre-amplification may also be employed to improve signal strength.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
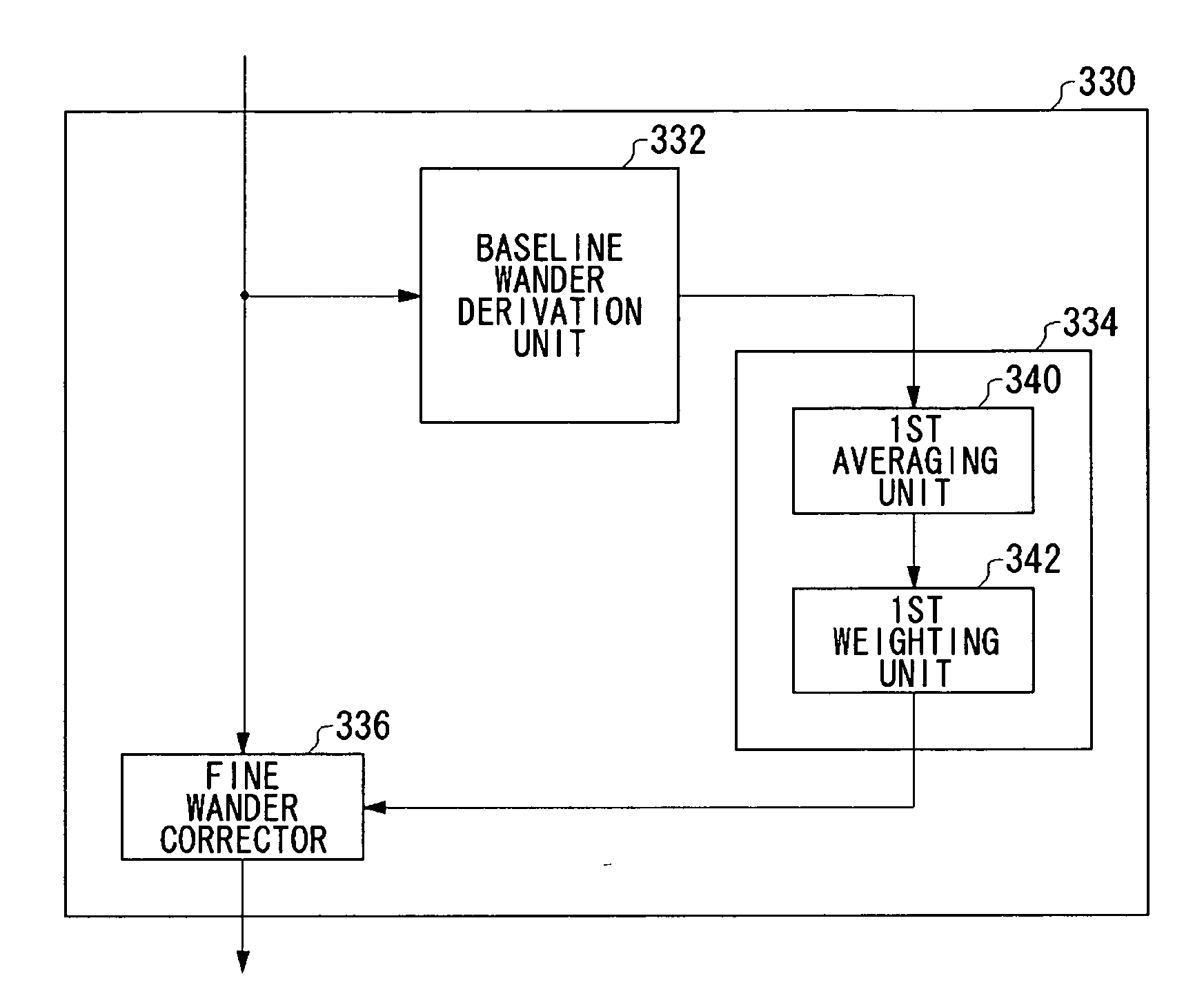
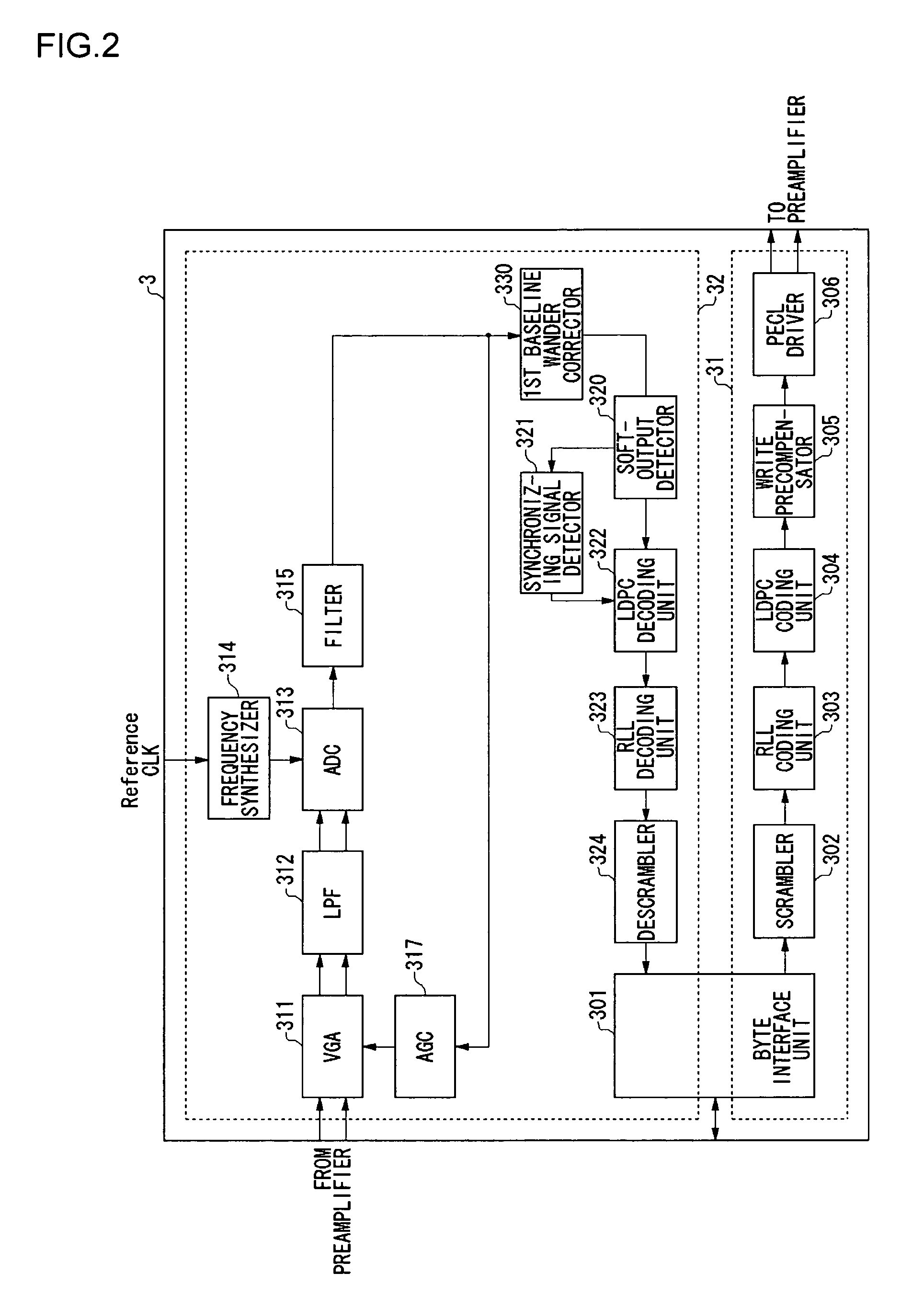
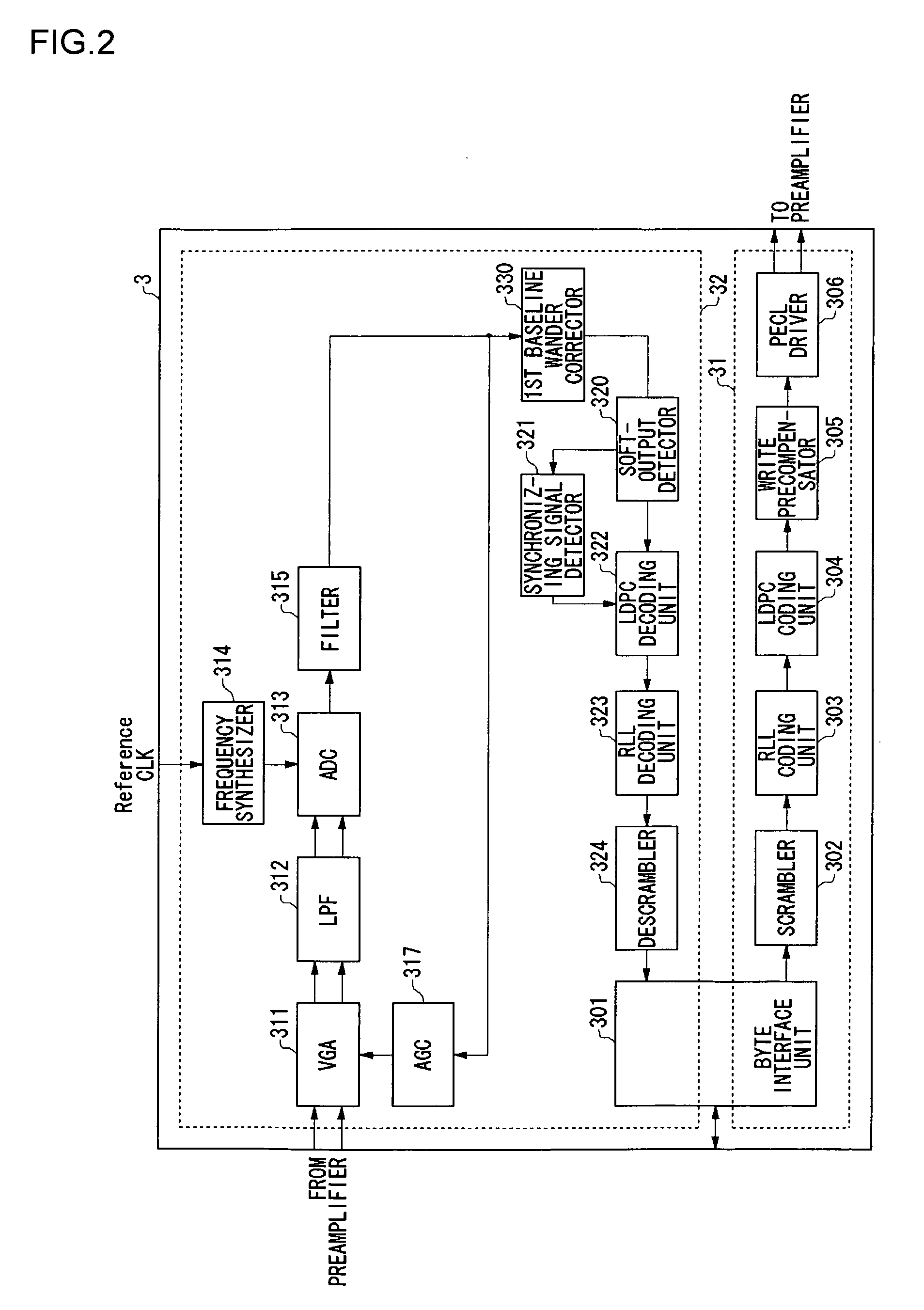
Signal processing apparatus, signal processing method and storage system
InactiveUS20070104300A1Effective correctionCorrecting baseline wander efficientlyError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal onArtificial intelligence
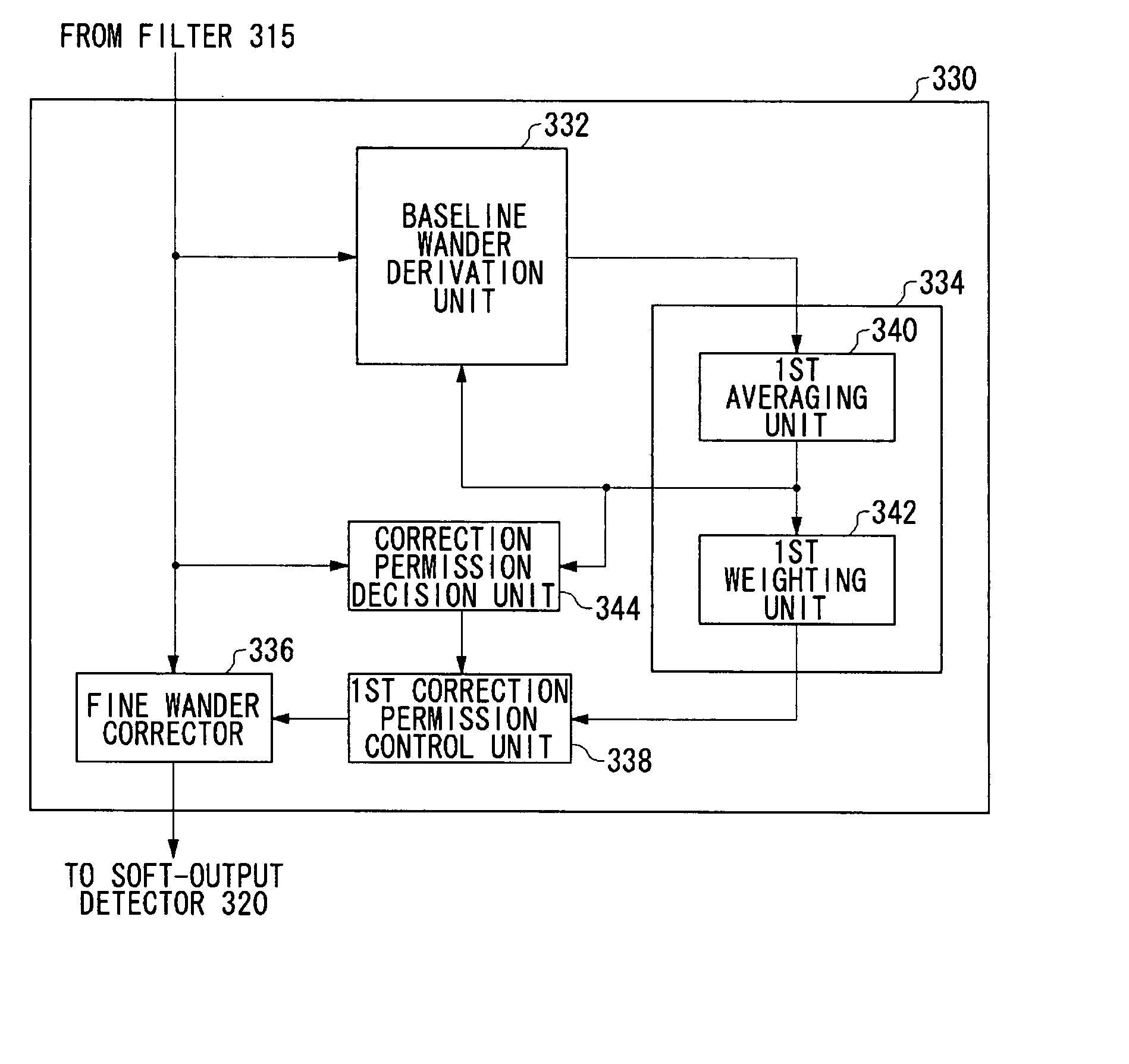
A baseline wander correcting unit is provided in a processing path in which a predetermined processing is performed on an input signal. The baseline wander correcting unit includes a baseline wander derivation unit which derives an amount of wander of baseline of a signal on which the predetermined processing has been performed, and an adjustment unit which adjusts an amount of wander of the baseline derived by the baseline wander derivation unit and outputs a baseline correction amount, so that the baseline wander correcting unit corrects the baseline wander by a feedforward control. The correction by the feedforward control ensures the baseline wander in the event of an instantaneous wander.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Differential to single-ended logic converter
InactiveUS6924668B2Easy to implementMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEngineeringSignal transition
The present invention is a converter stage for converting a differential logic input signal and a corresponding common mode differential logic signal each having a first single-ended logic signal and a complementary second single-ended logic signal into a single-ended logic output signal. The converter stage comprises a first and a second differential stage each having a first and a second MOS transistor and a first and second current source for the differential stages. According to the invention the current sources are controlled by the voltage level which is centered between the mid-potentials of the common mode level differential logic signal and the mid-potential of the differential logic input signal.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
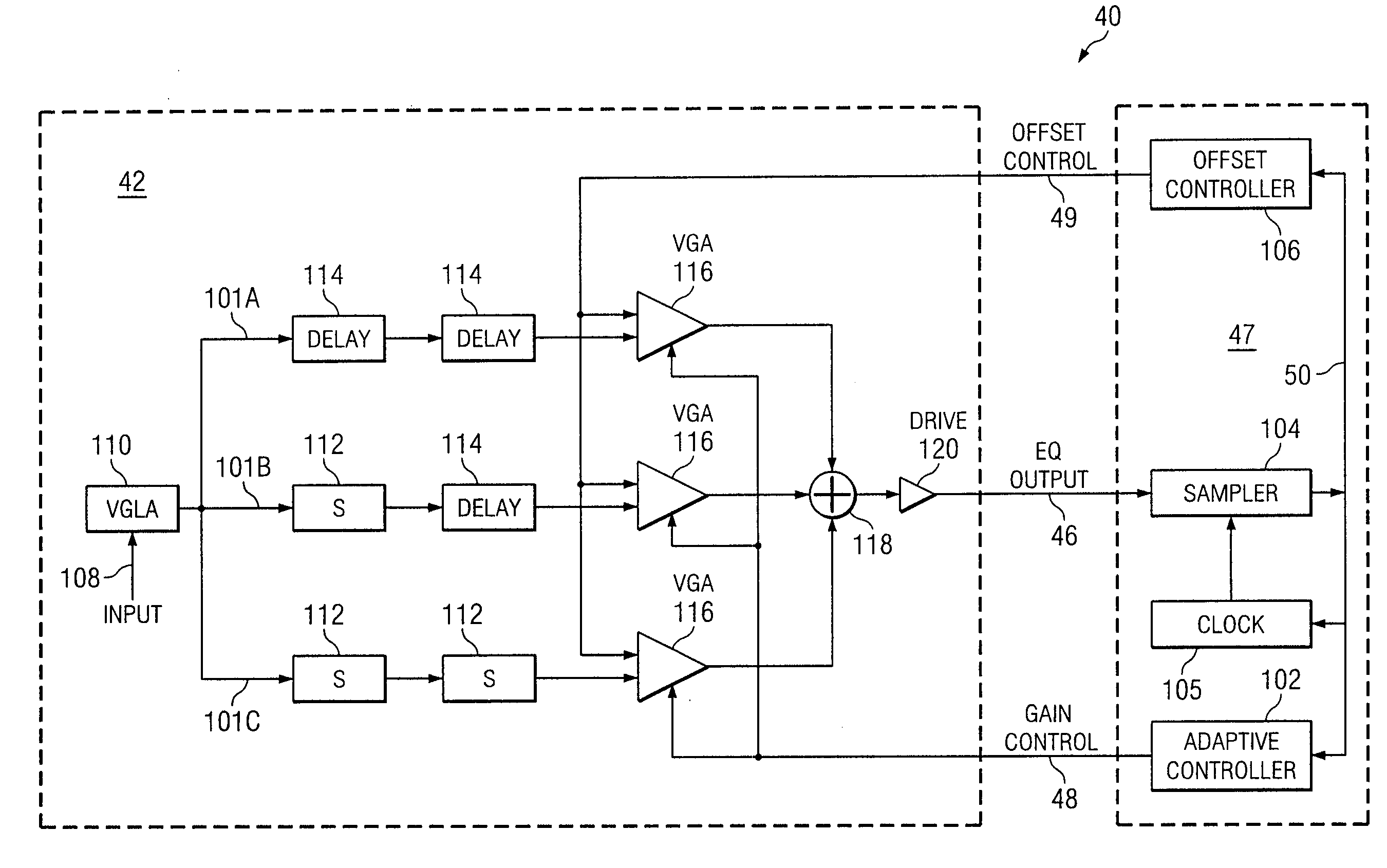
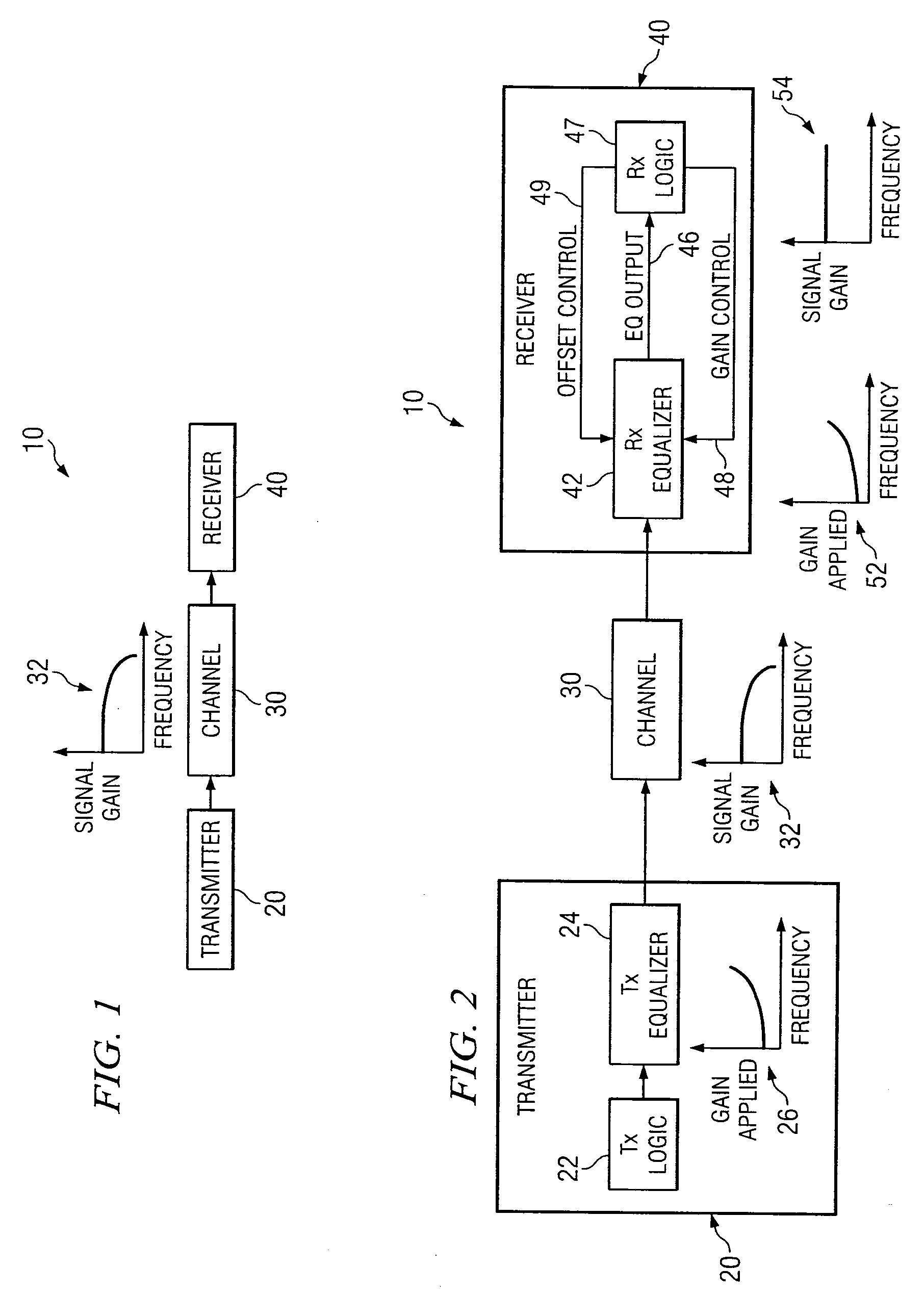
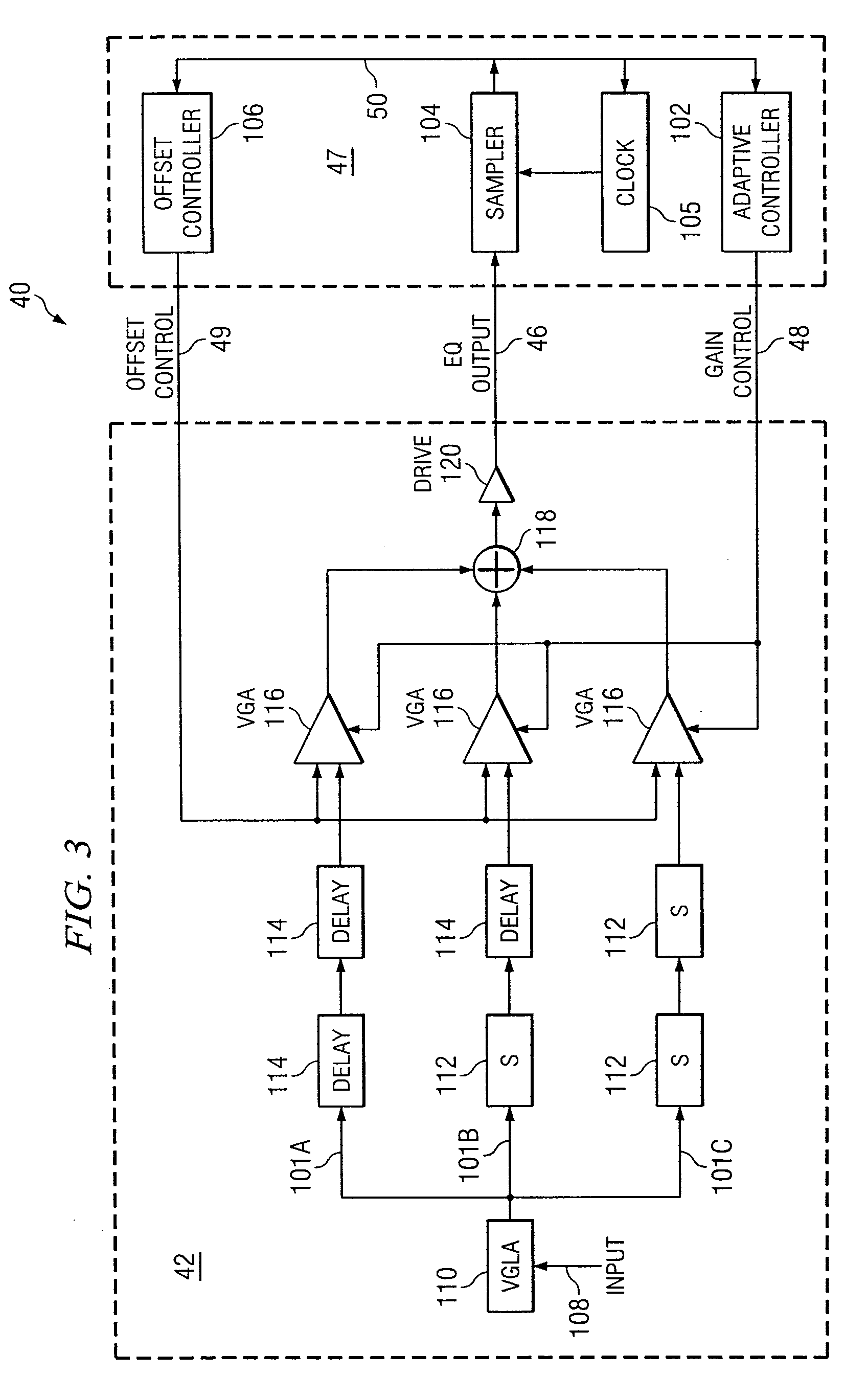
System and Method for the Adjustment of Compensation Applied to a Signal
InactiveUS20070280342A1High sensitivityPrevent lockMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringData value
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for adjusting a signal includes applying at least one of a loss compensation for frequency-dependent distortion and an offset compensation for DC-offset distortion to a signal before or after the distortion occurs to generate an output signal, the output signal comprising even phase and odd phase. The method also includes selecting either the even phase or the odd phase at which to begin sampling. The method further includes, using a clock signal, beginning at the selected phase, sampling the output signal to generate a plurality of data values and an error value, the error value indicating residue of the distortion based on the sampling of the output signal. The method also includes adjusting none, one, or more of the loss compensation and the offset compensation applied to the signal based on the sampled error value. The method further includes, after adjusting the at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation applied to the signal based on the sampled error value, selecting either the even phase or the odd phase at which to begin the next sampling.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System and method of transistor switch biasing in a high power semiconductor switch
A circuit and method are provided for switching in a semiconductor based high power switch. Complementary p-type based transistors are utilized along insertion loss insensitive paths allowing biasing voltages to alternate between supply and ground, allowing for negative voltage supplies and blocking capacitors to be dispensed with, while improving performance.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC +1
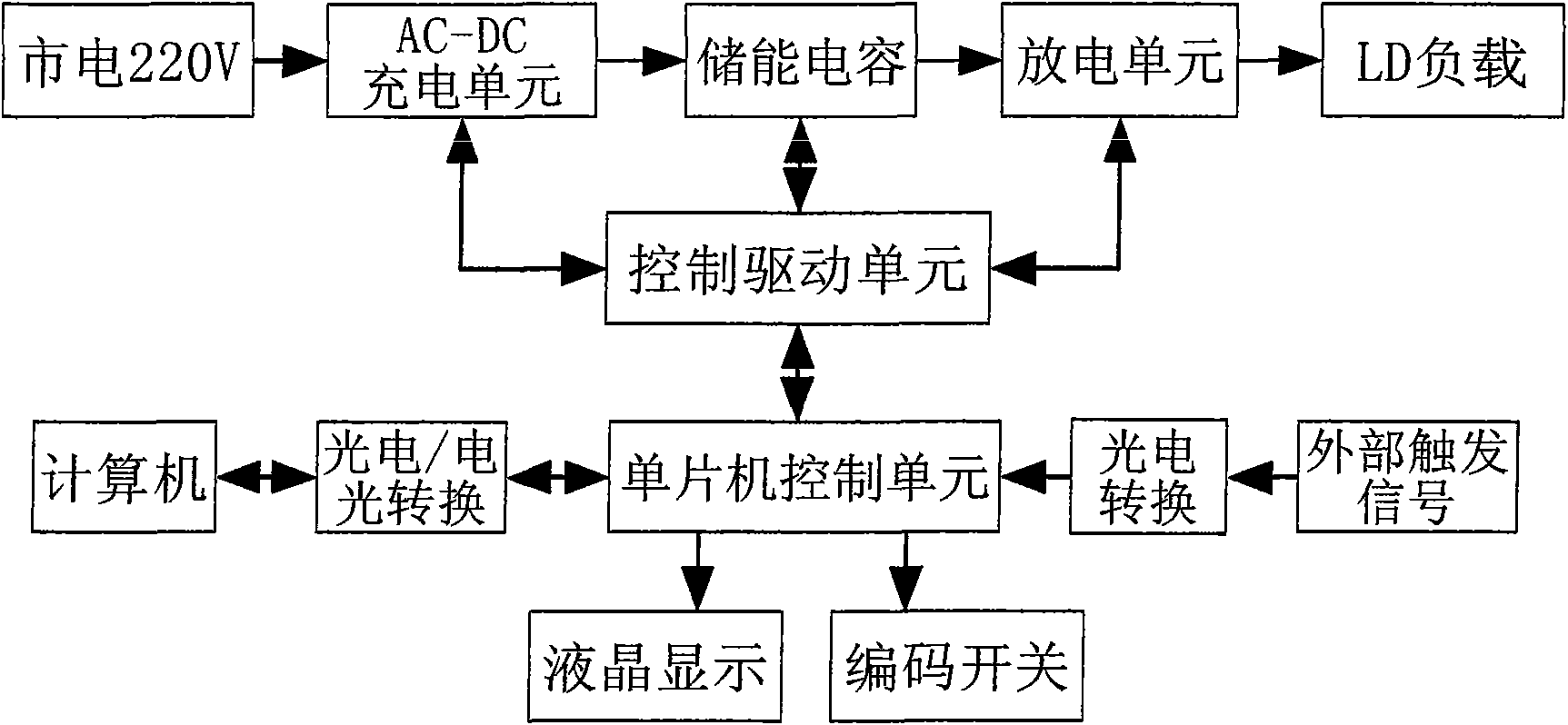
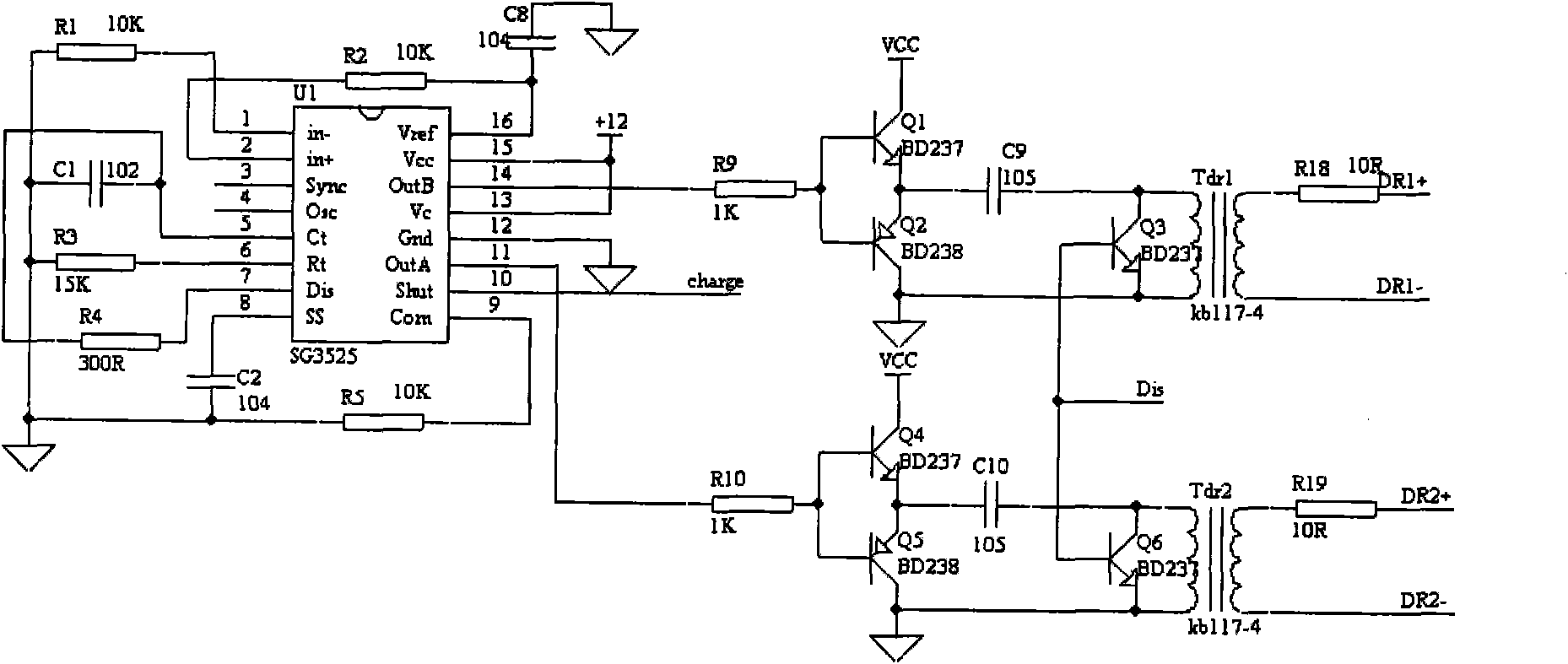
Large-current pulse LD laser driving power supply
InactiveCN101567519ARealize power supplyAchieving AdaptivenessProgramme controlLaser detailsCapacitanceEngineering
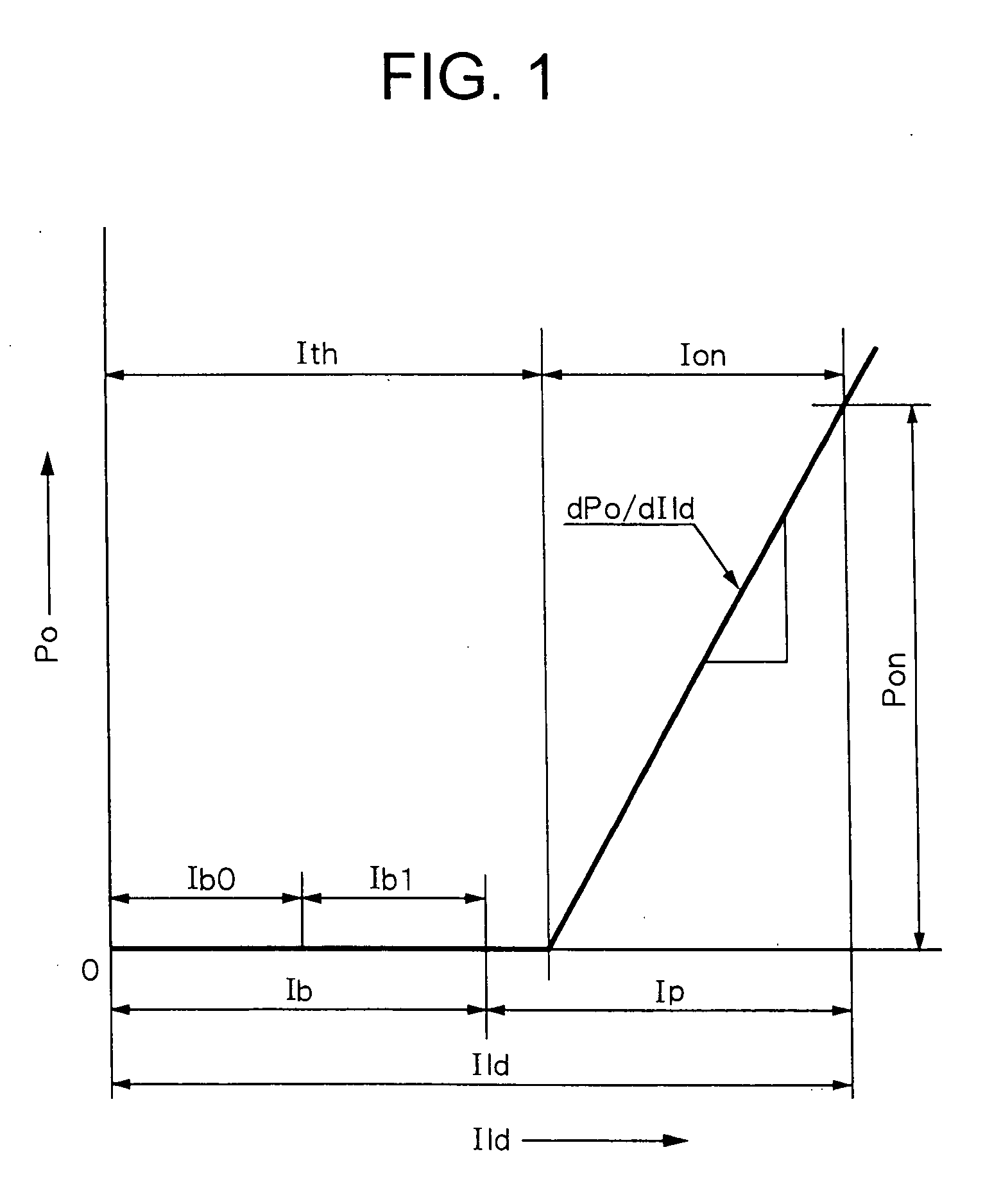
The invention provides a large-current pulse LD laser driving power supply, comprising a discharging unit; the discharging unit comprises a bias circuit used for calculating the voltage reduction of external loads, and the bias circuit comprises a first MOS tube, a first resister, a second resister, a first variable resister and a first capacitor; the drain of the first MOS tube is connected with the cathode terminal of external load; the source of the first MOS tube is grounded by the first resister; the grid of the first MOS tube is connected with the first variable resister by the second resister so as to obtain a constant voltage value; the grid of the first MOS tube is also grounded by the first capacitor so as to stabilize the voltage. The large-current pulse LD laser driving power supply realizes large-current power supply to the load, realizes the self-adaptability of the external load, realizes the constant current charging to the energy-storage capacitor, is beneficial to improving the charging efficiency and protecting the energy-storage capacitor and realizes the protection of the multi-path protection circuit on the LD load and the power supply.
Owner:BEIJING GK LASER TECH
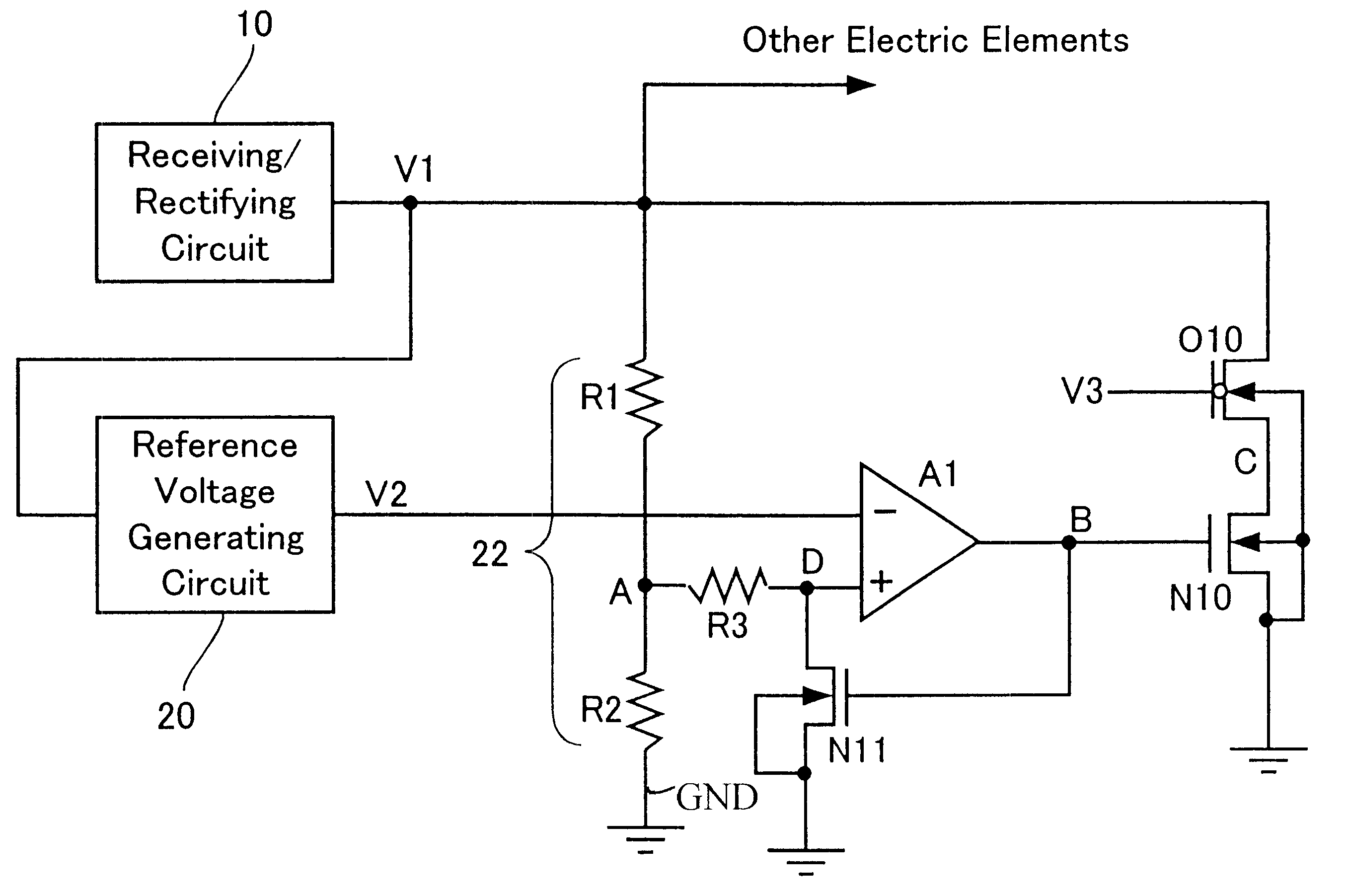
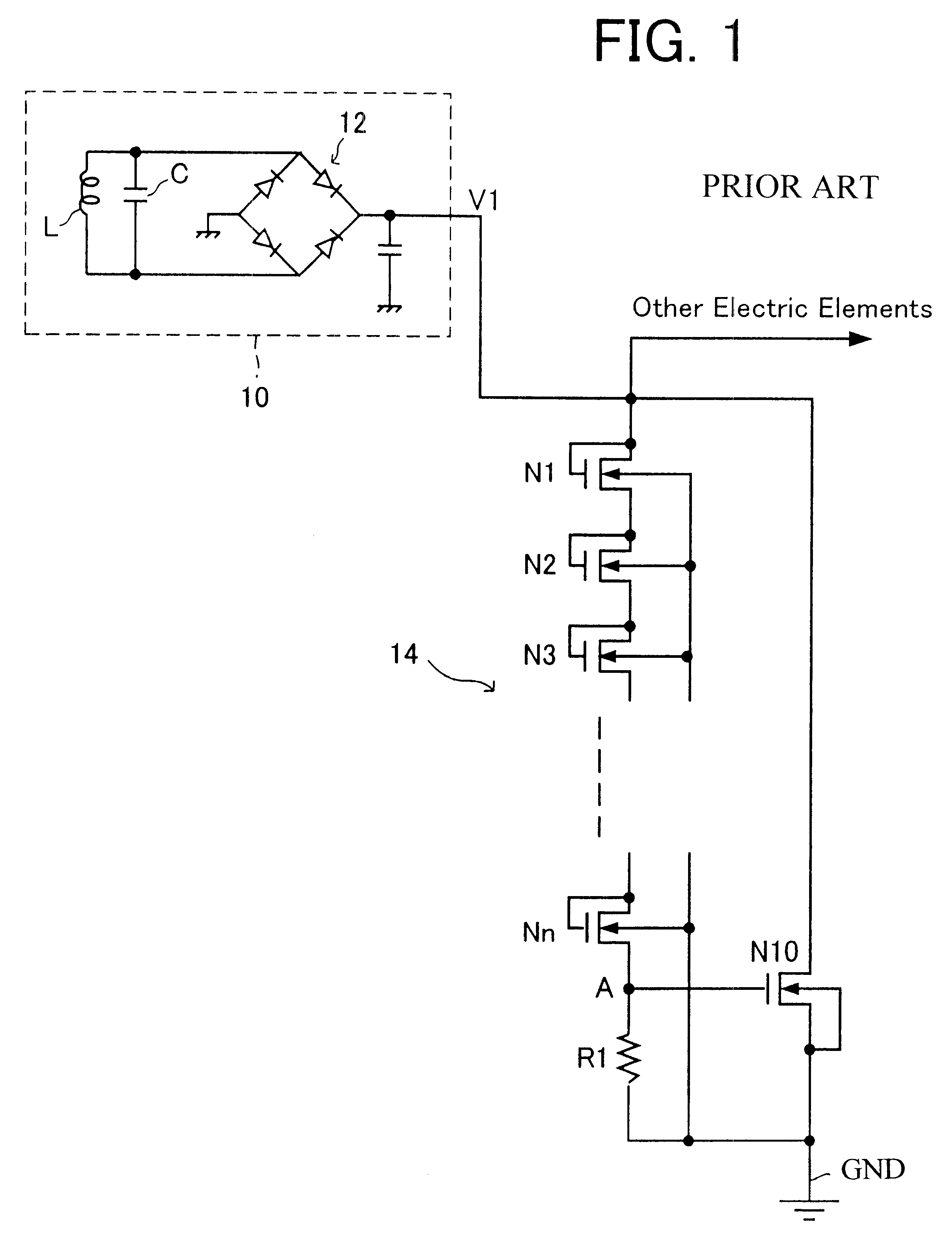
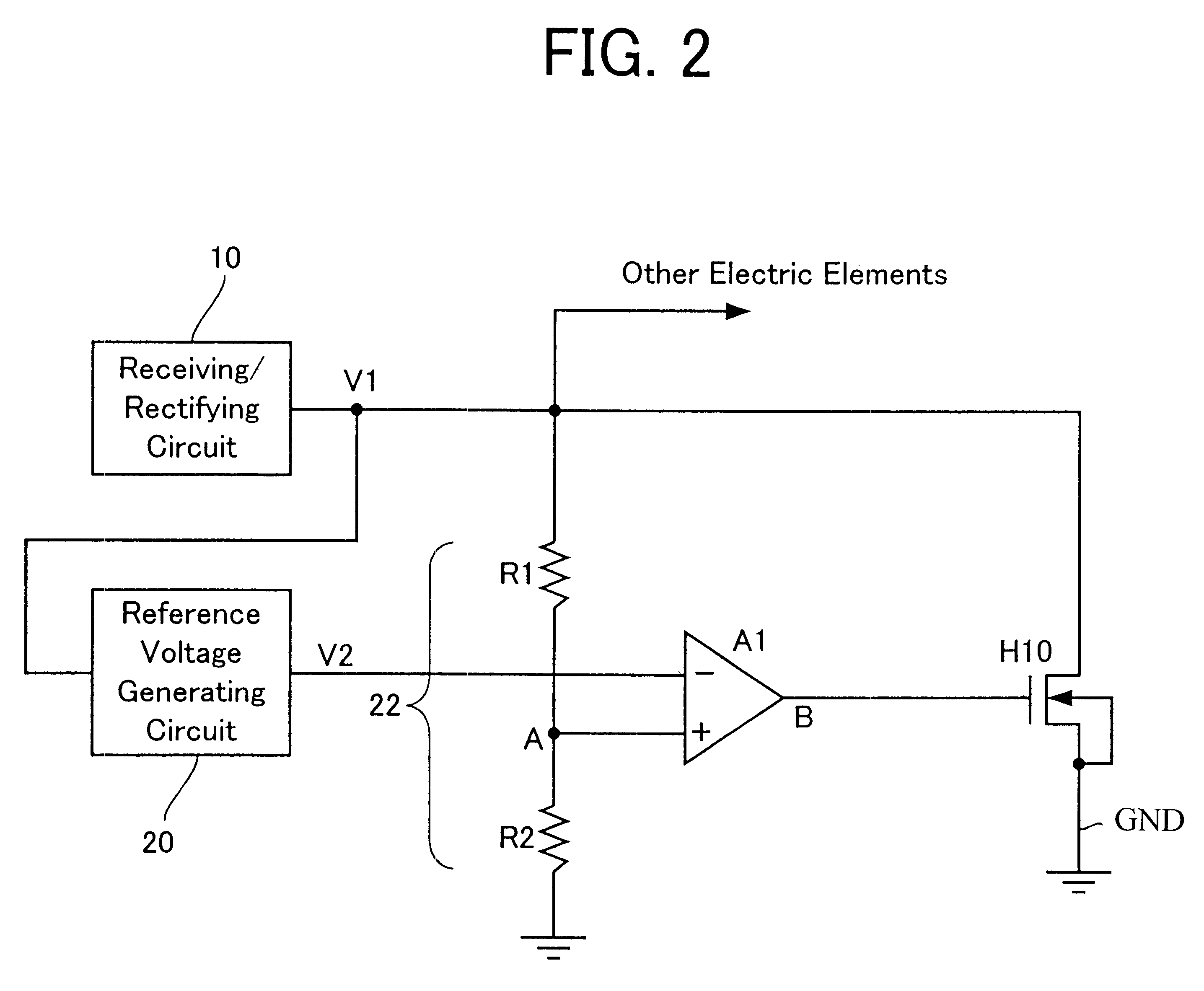
Noncontact interface circuit and method for clamping supply voltage therein
InactiveUS6630858B1Accurate startCircuit arrangementsCo-operative working arrangementsVoltage referenceInterface circuits
A supply voltage is divided to provide a divided supply voltage. The divided supply voltage is compared with the reference voltage. The supply voltage is controlled based on the result of comparison so that the supply voltage does not exceed a predetermined breakdown voltage.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Display device having an improved voltage level converter circuit
InactiveUS6930666B2Supply capability is decreasedIncrease currentPower reduction in field effect transistorsPulse automatic controlCapacitanceLow voltage
A display device has a driver including a level converter formed of polysilicon MISTFTs. The level converter includes first, second and third N-channel MISTFTs (NMISTFTs) and first, second and third P-channel MISTFTs (PMISTFTs). Gate and first terminals of the first NMISTFT and PMISTFT, and a gate terminal of the third PMISTFT are coupled to an input terminal via a capacitance. Second terminals of the second NMISTFT and PMISTFT, and a gate terminal of third NMISTFT are coupled to the input terminal via a capacitance. A first terminal of the third PMISTFT, and second terminals of the first NMISTFT and PMISTFT are coupled to a high voltage. A second terminal of the third NMISTFT, gate and first terminals of the second NMISTFT and PMISTFT are coupled to a low voltage. A second terminal of the third PMISTFT and a first terminal of the third NMISTFT are connected to an output terminal.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Signal processing apparatus, signal processing method and storage system
ActiveUS20070104301A1Effective correctionCorrecting baseline wander efficientlyMultiple-port networksError preventionArtificial intelligenceFeedback control
A signal processing apparatus includes a first baseline wander correcting unit, provided in a processing path in which a predetermined processing is performed on an input signal, which corrects baseline wander by a feedforward and a second baseline wander correcting unit, provided anterior to the first baseline wander unit, which corrects the baseline wander by a feedback control. The first baseline wander correcting unit derives an amount of baseline wander. Further, it calculates a value corresponding to an average value of the amount of derived baseline wander and fine-adjusts a correction amount of baseline. Then it corrects the baseline wander by using the fine-adjusted baseline amount. The second baseline wander correcting unit calculates a value corresponding to an average value of the amount of baseline wander derived by the baseline wander derivation unit and coarse-adjusts a correction amount of baseline, and corrects the baseline wander by using the coarse-adjusted baseline amount. The fine correcting by the first baseline wander correcting unit and the coarse correcting by the second baseline correcting unit ensure efficient correction of baseline wander.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
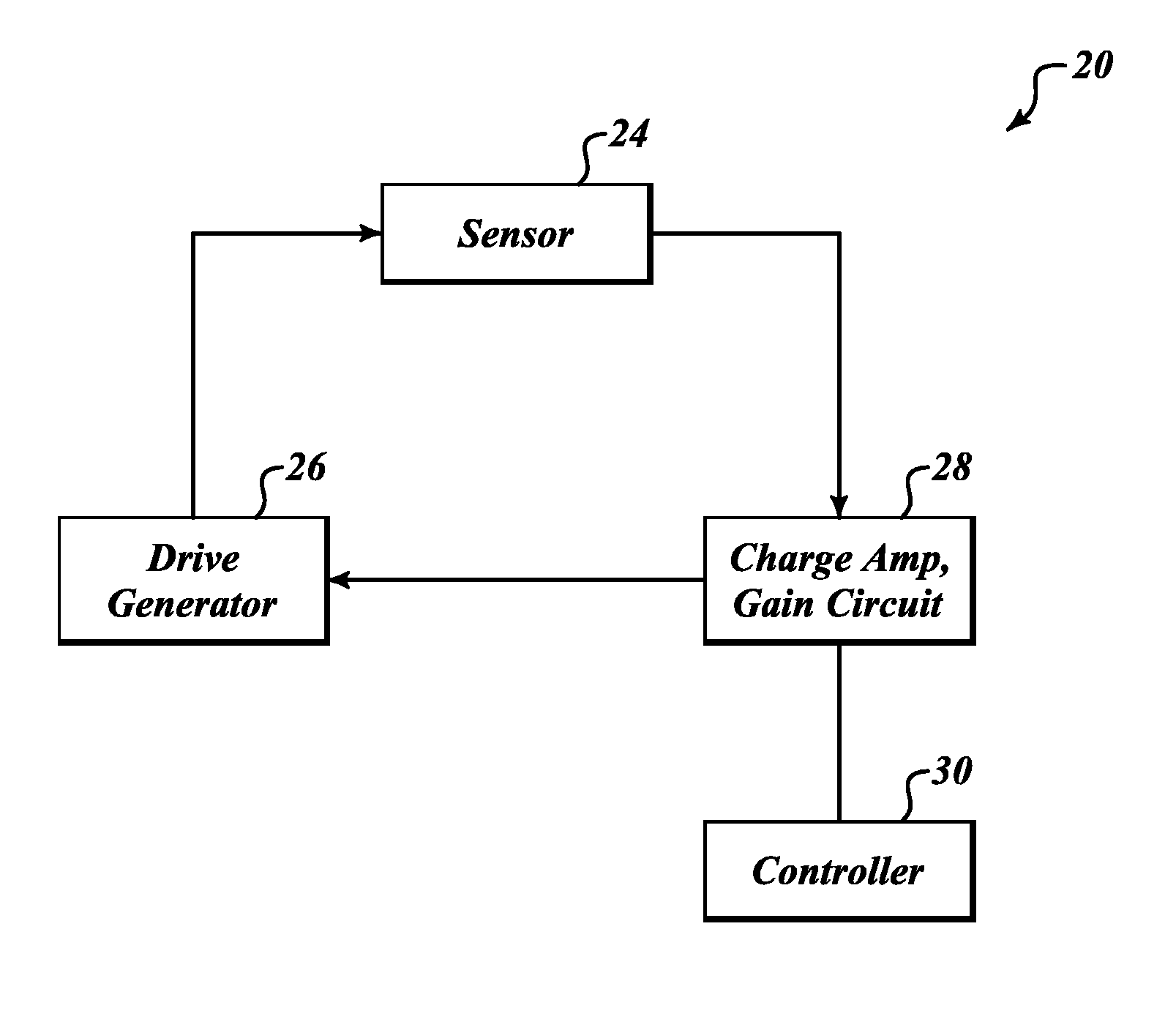
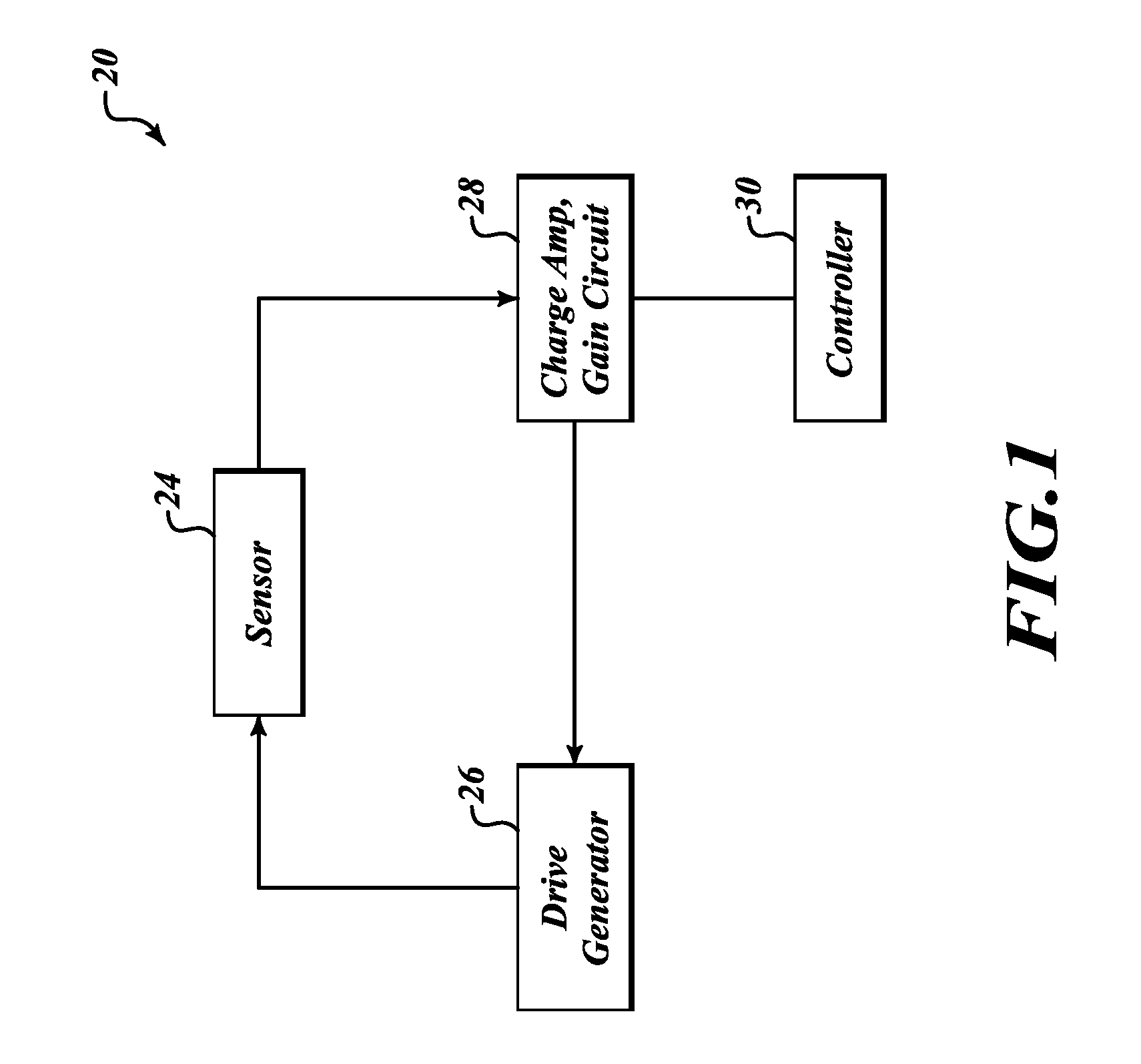
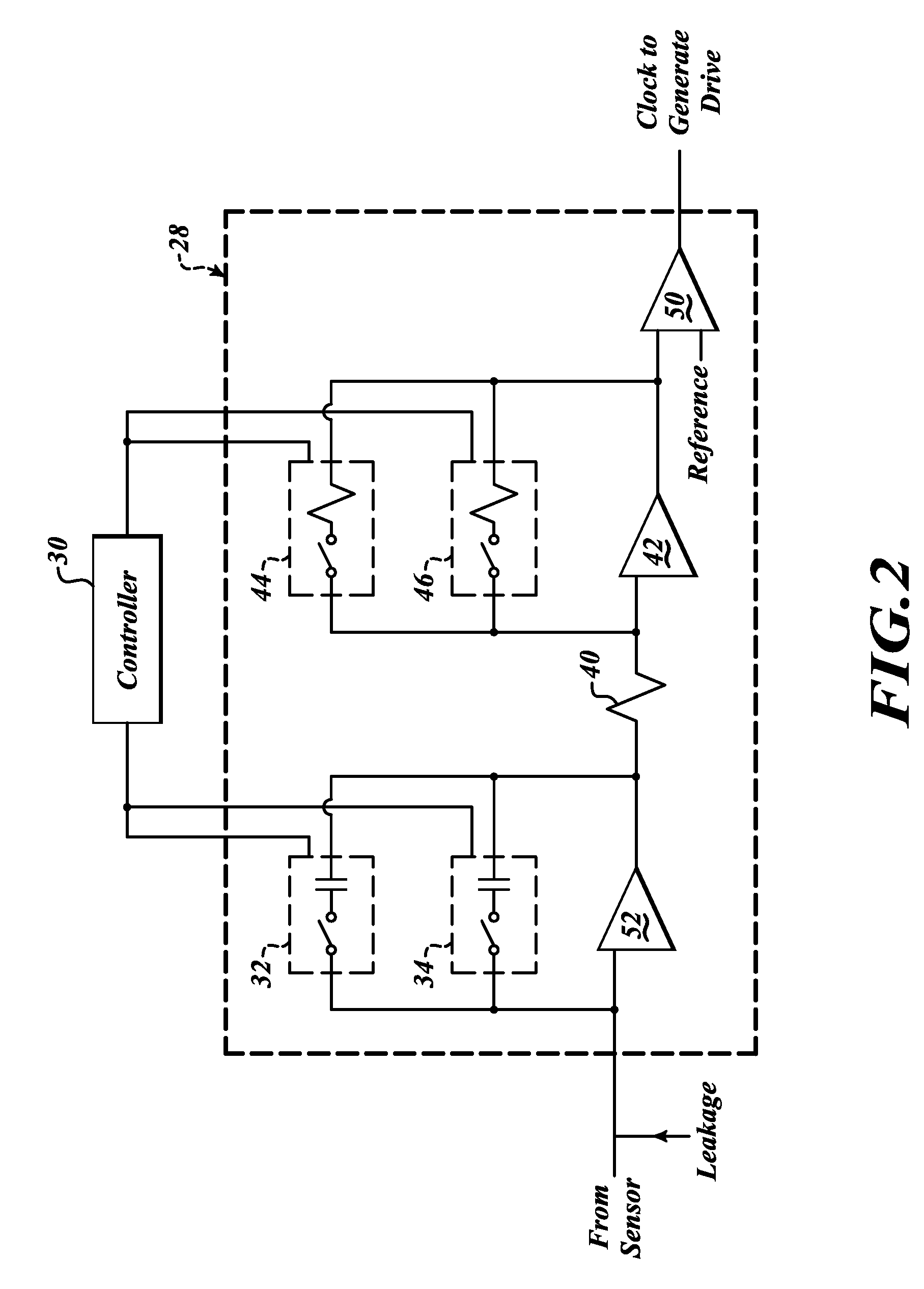
Systems and methods to overcome DC offsets in amplifiers used to start resonant micro-electro mechanical systems
ActiveUS7859352B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAudio power amplifierEngineering
Systems and methods for insuring successful initiation of a resonating micro-electro mechanical systems (MEMS). An example system includes a resonating sensor, a drive device, a charge amplifier, and a voltage gain circuit. At start up, the charge amplifier and voltage gain circuit receives signals from the resonating sensor, compensates this signal for DC offsets, and generates a clock signal for the drive, thus placing the resonating sensor in a steady state operating mode. The circuit includes a plurality of gain switches that are toggled to produce a glitch in the signal associated with the received signal. The glitch overcomes the DC offset. A comparator generates the clock signal for the drive device if a signal associated with the received signal exceeds a reference signal.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Output Power Limiter in an Audio Amplifier
InactiveUS20130089223A1Reduce widthControl output powerAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersEngineeringFeedback control
An output power limiter system (PLS) for audio amplifiers may be designed as a feedback control system for protection of the load and / or quality of the audio experience. The PLS may use comparator to sense the output current, compare it to a specified threshold, and assert a signal when the output current reaches and exceeds the specified threshold. The output signal from the comparator may enable a counter that is clocked with a high frequency clock to begin counting to measure the pulse-width of the comparator output. The output of the counter may be averaged through a fast attack and slow release infinite impulse response (IIR) filter having programmable settings to generate a rate of attenuation or rate of release that adjusts a gain correction in terms of decibels (dB). The output of the IIR filter may then be used for attenuating the output current.
Owner:MEYERTONS HOOD KIVLIN KOWERT & GOETZEL P C
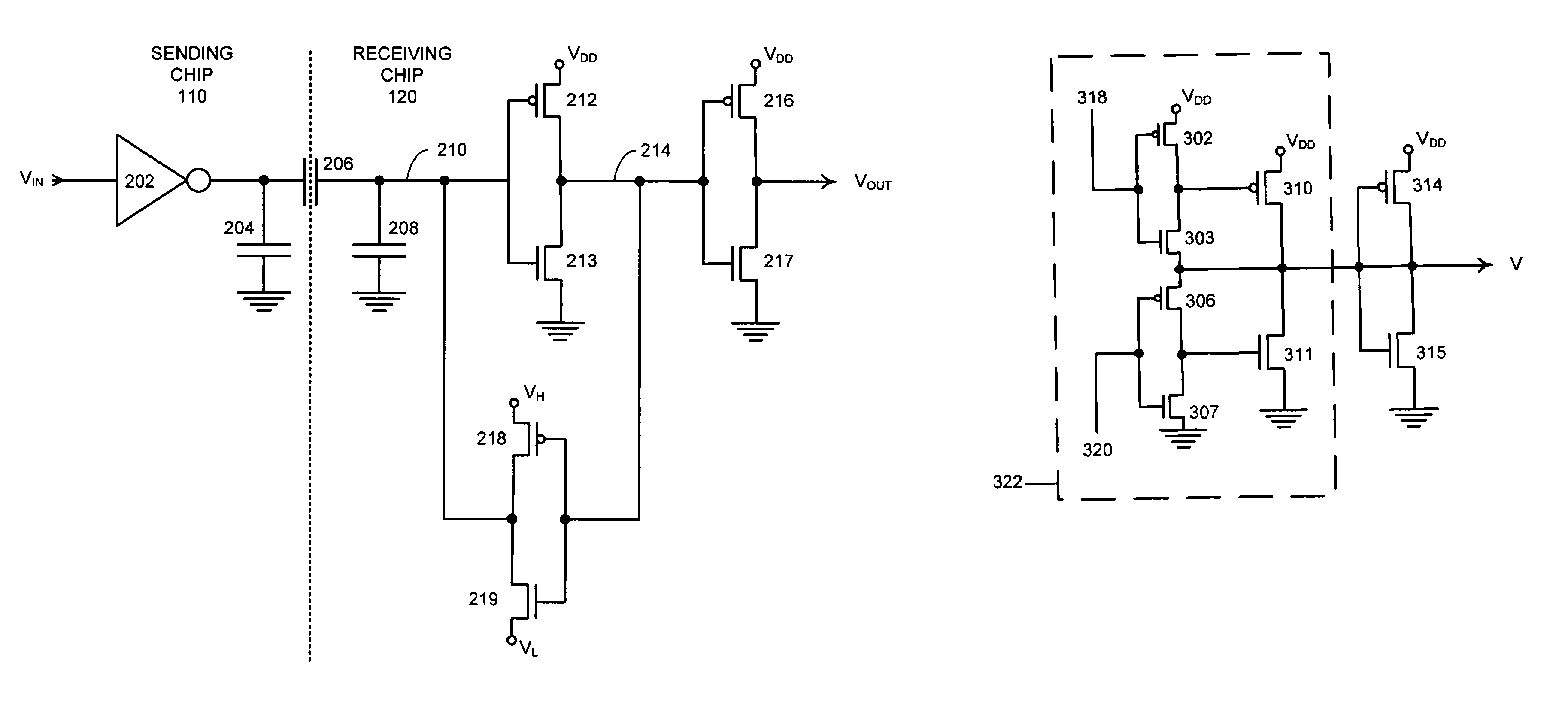
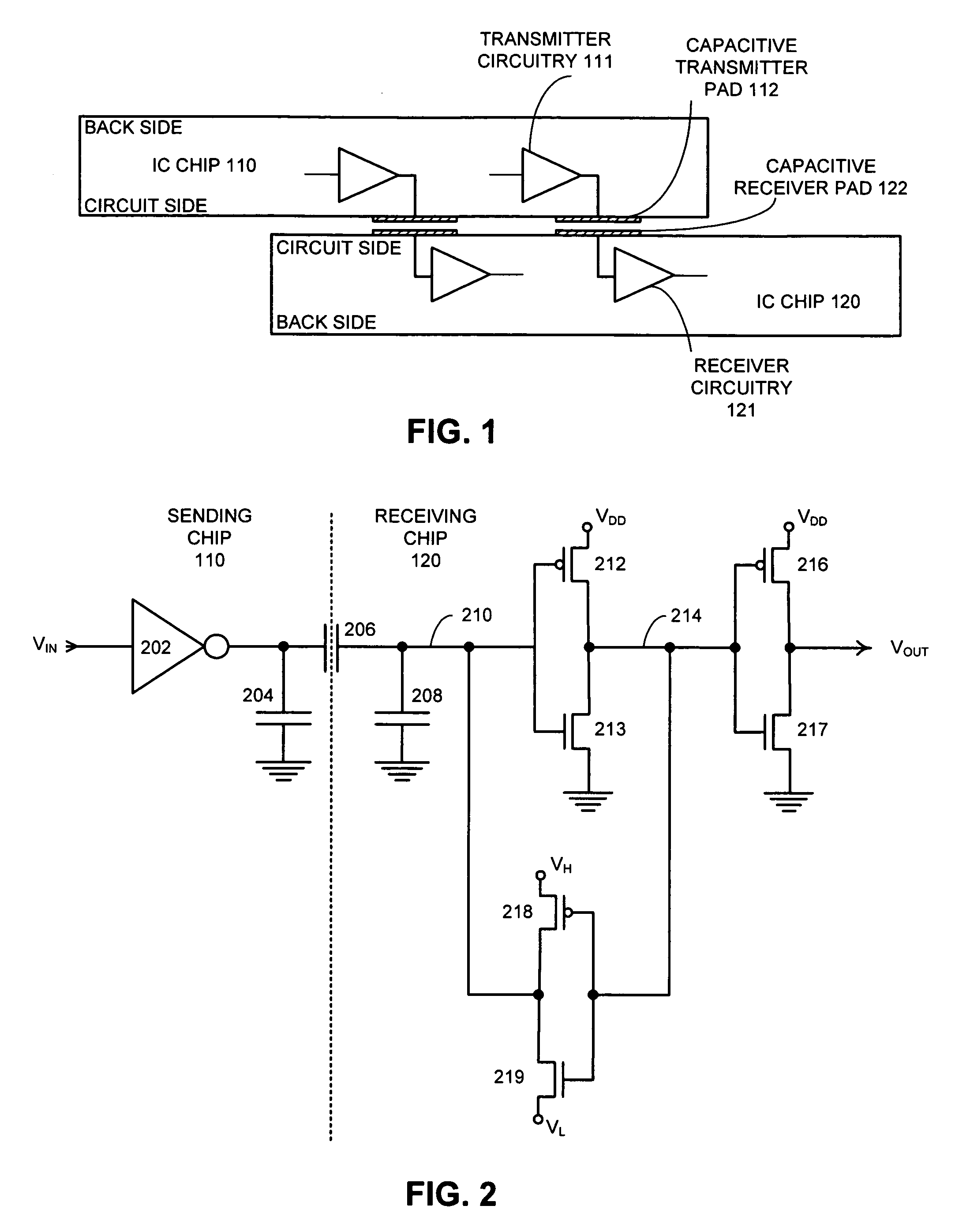
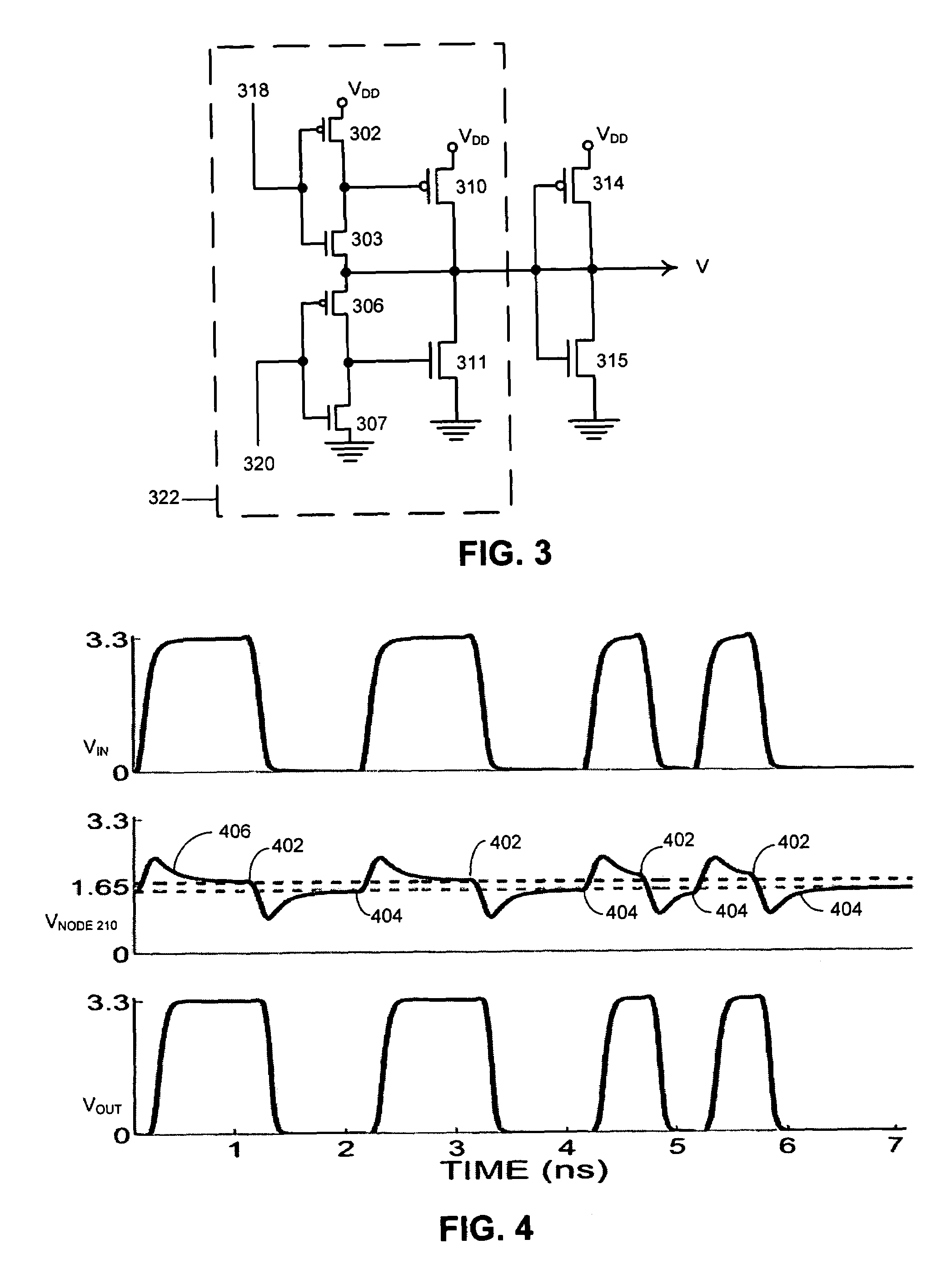
Sense amplifying latch with low swing feedback
InactiveUS6987412B2Pulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceSignal on
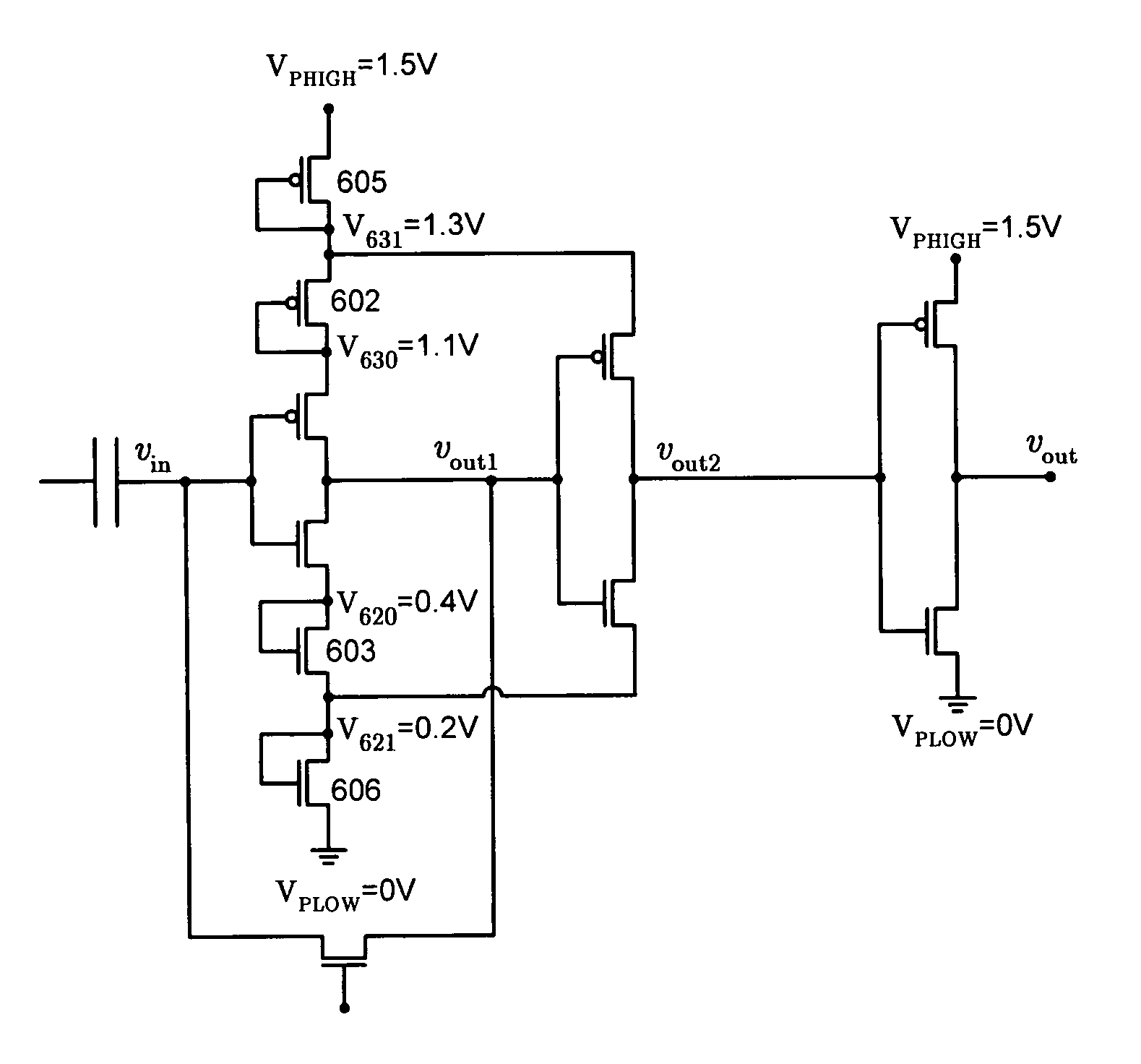
A system is presented for latching and amplifying a capacitively coupled inter-chip communication signal that operates by receiving an input signal on a capacitive receiver pad and feeding the input signal through an inverter to produce an output signal. The output signal is fed back through a weakened inverter to produce a feedback signal that is fed into an input of the inverter to form a latch for the input signal. The weakened inverter is biased to produce a feedback signal that swings between a high bias voltage, VH, and a low bias voltage, VL. VH is set slightly higher than the switching threshold of the inverter, and VL is set slightly lower than the switching threshold. This feedback signal causes the input signal to reside within a narrow voltage range near the switching threshold of the inverter, thereby making the inverter sensitive to small transitions in the input signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
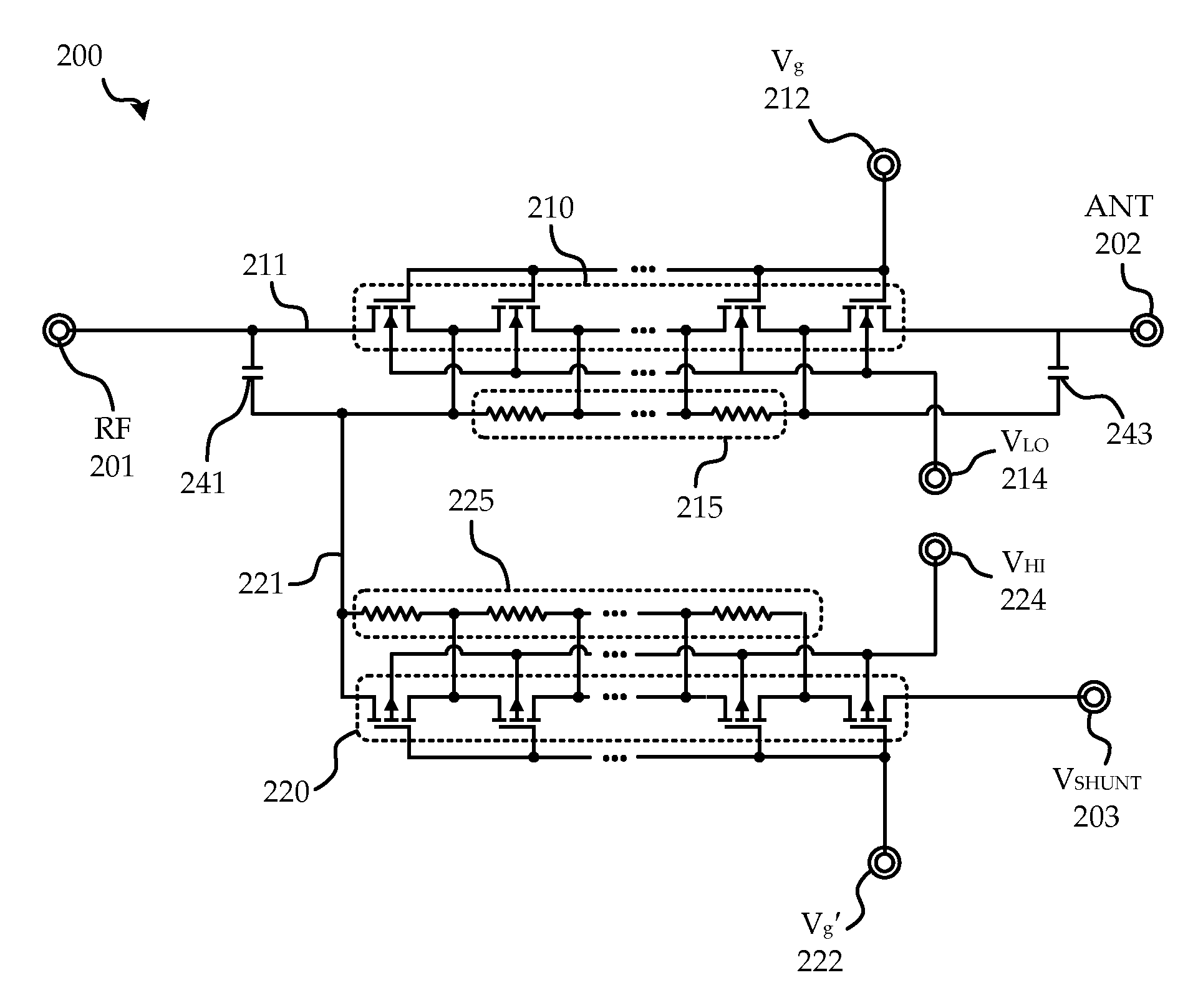
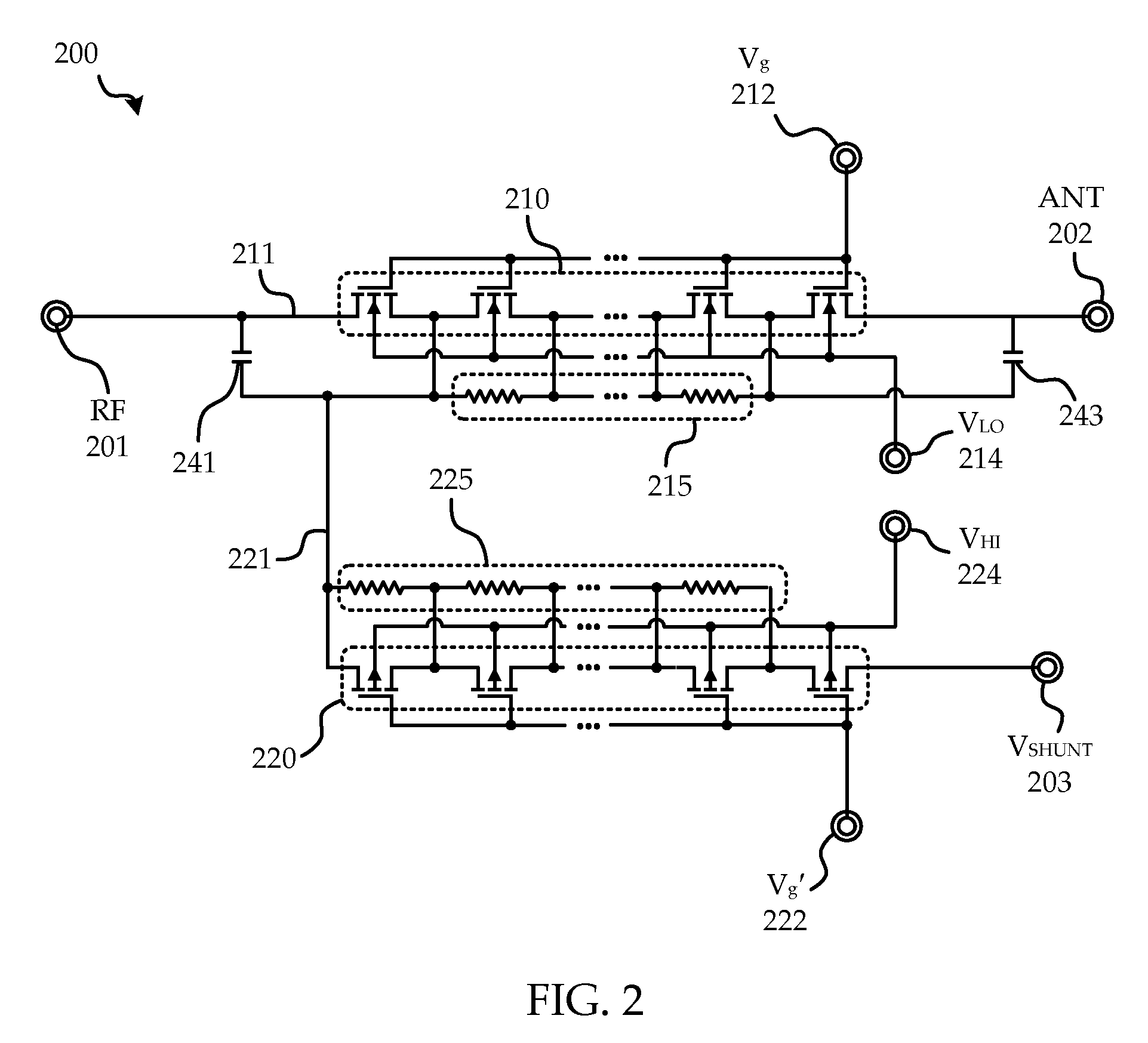
Phase calibration circuit and method for multi-channel radar receiver
ActiveUS20160033625A1Eliminate offsetPulse automatic controlDC level changePhase responseRadar systems
This invention describes circuits and methods which can allow multiple radar receiver chips to be adjusted to have very low phase offset between them. Multiple receiver chips are used in frequency-modulated carrier-wave (FMCW) radar systems for beamforming to enable angle-of-arrival measurements. FMCW radar systems are widely used in collision-avoidance and adaptive cruise control systems in vehicles, which today are operating in the 76-81 GHz frequency band. In a multi-receiver system, each receive element must have a well-controlled phase response which can be calibrated over process, voltage, and temperature. Without calibration, phase offsets can result in erroneous beamforming receiver measurements. The inventive circuit provides a technique to adjust the phase of multiple receivers across multiple chips using a single local oscillator reference and built-in-test circuitry which consist of phase shifters, a multi-frequency nonlinear phase detection circuit, and power coupling circuits.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for amplifying capacitively coupled inter-chip communication signals
ActiveUS6972596B1Reduce power consumptionSave powerReliability increasing modificationsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceCMOS
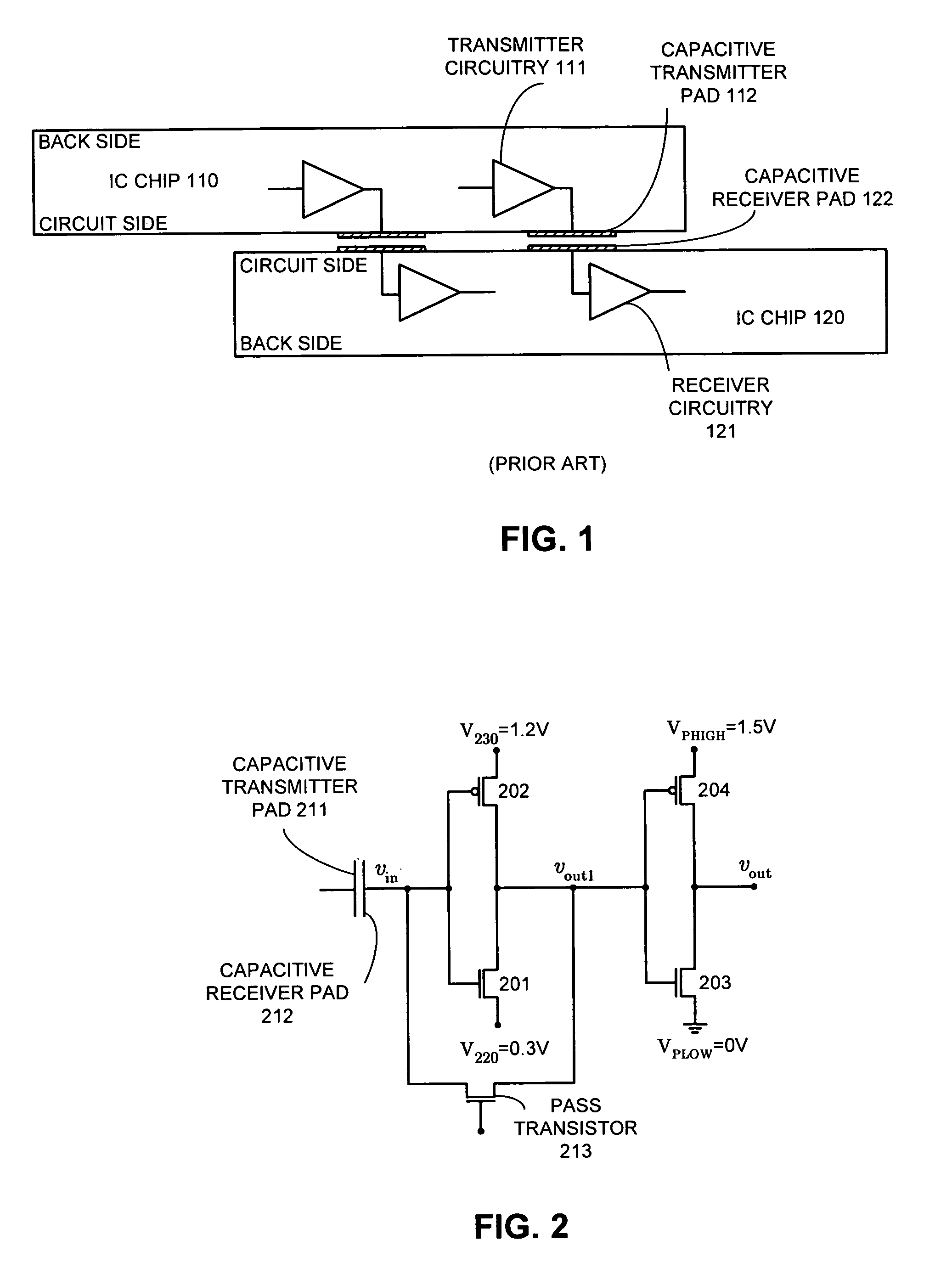
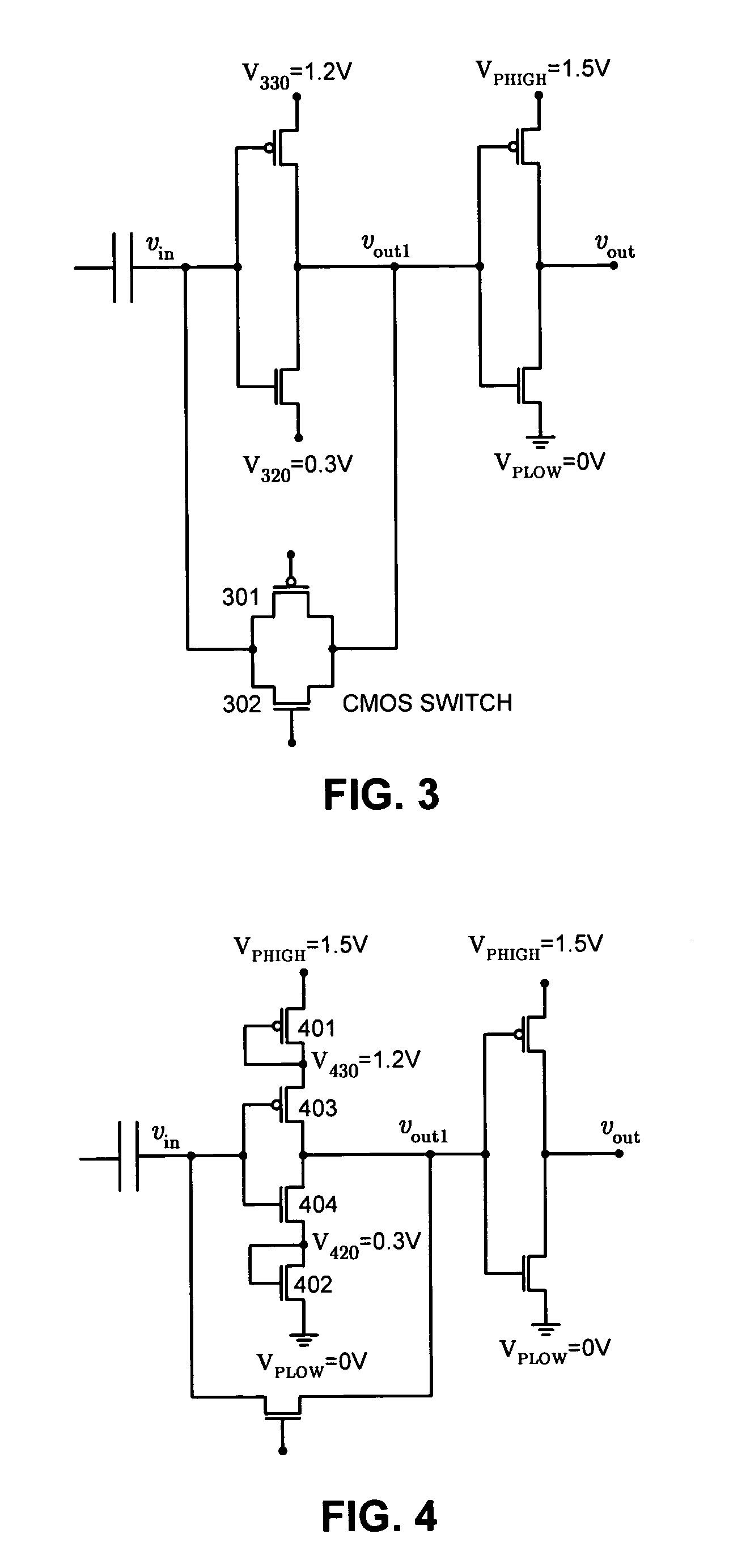
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that amplifies capacitively coupled inter-chip communication signals. During operation, the system transmits a signal through a capacitive transmitter pad and receives a corresponding input signal through a capacitive receiver pad. The system amplifies the input signal by feeding it through a number of cascaded CMOS inverters operating from ever-increasing power supply voltages from the first to the last inverter. The system periodically initializes the input voltage of the first CMOS inverter by: suspending data transmission on the capacitive transmitter pad and setting the voltage on the capacitive transmitter pad to a middle point between a voltage that represents logic “1” and a voltage that represents logic “0”, coupling the output of the first CMOS inverter to its input through a switch, and, after the input voltage of the first CMOS inverter stage substantially stabilizes at the switching threshold, uncoupling the output of the first CMOS inverter stage from the input of the first CMOS inverter stage and then resuming data transmission on the capacitive transmitter pad.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Shift register and driving method thereof
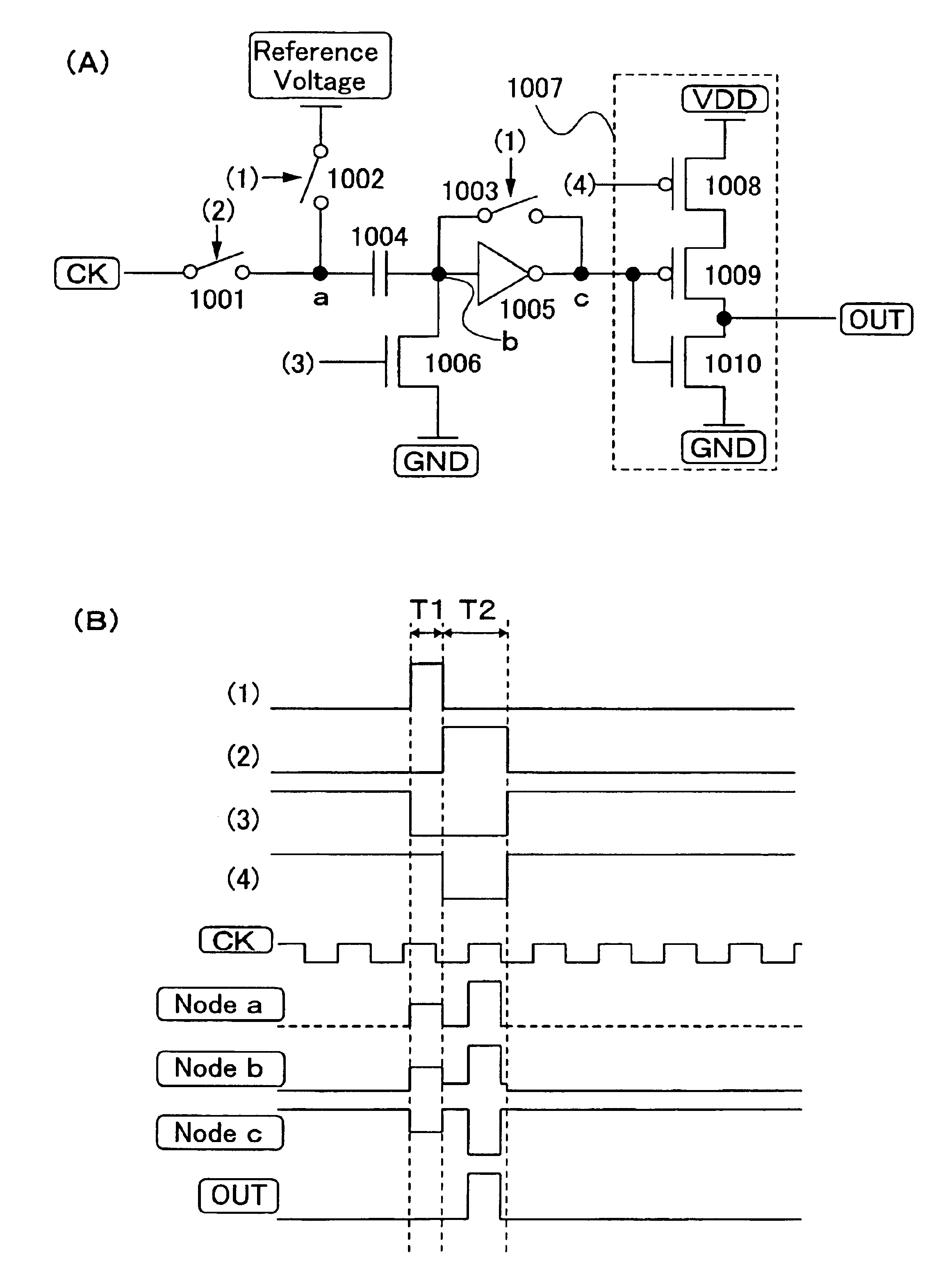
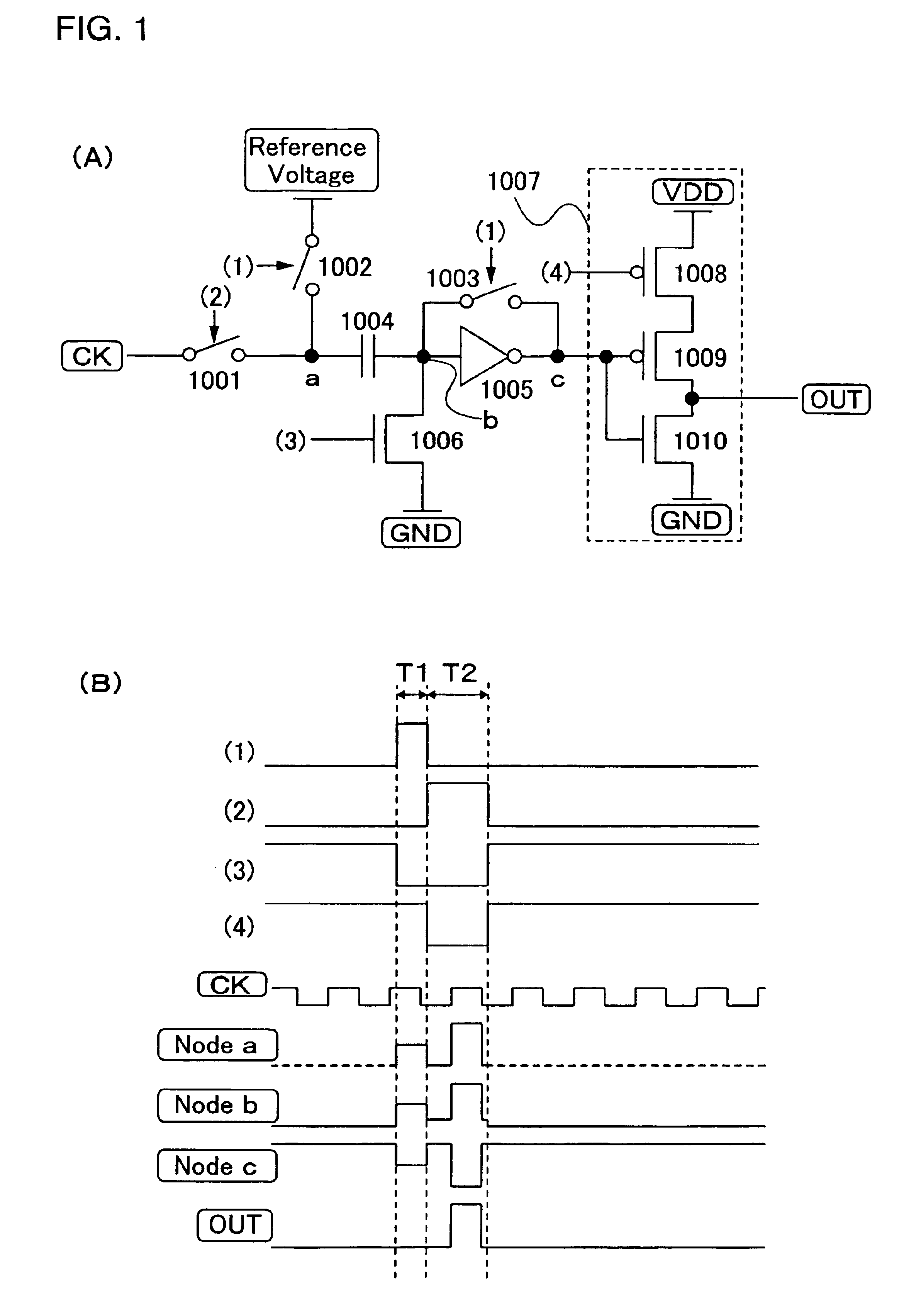
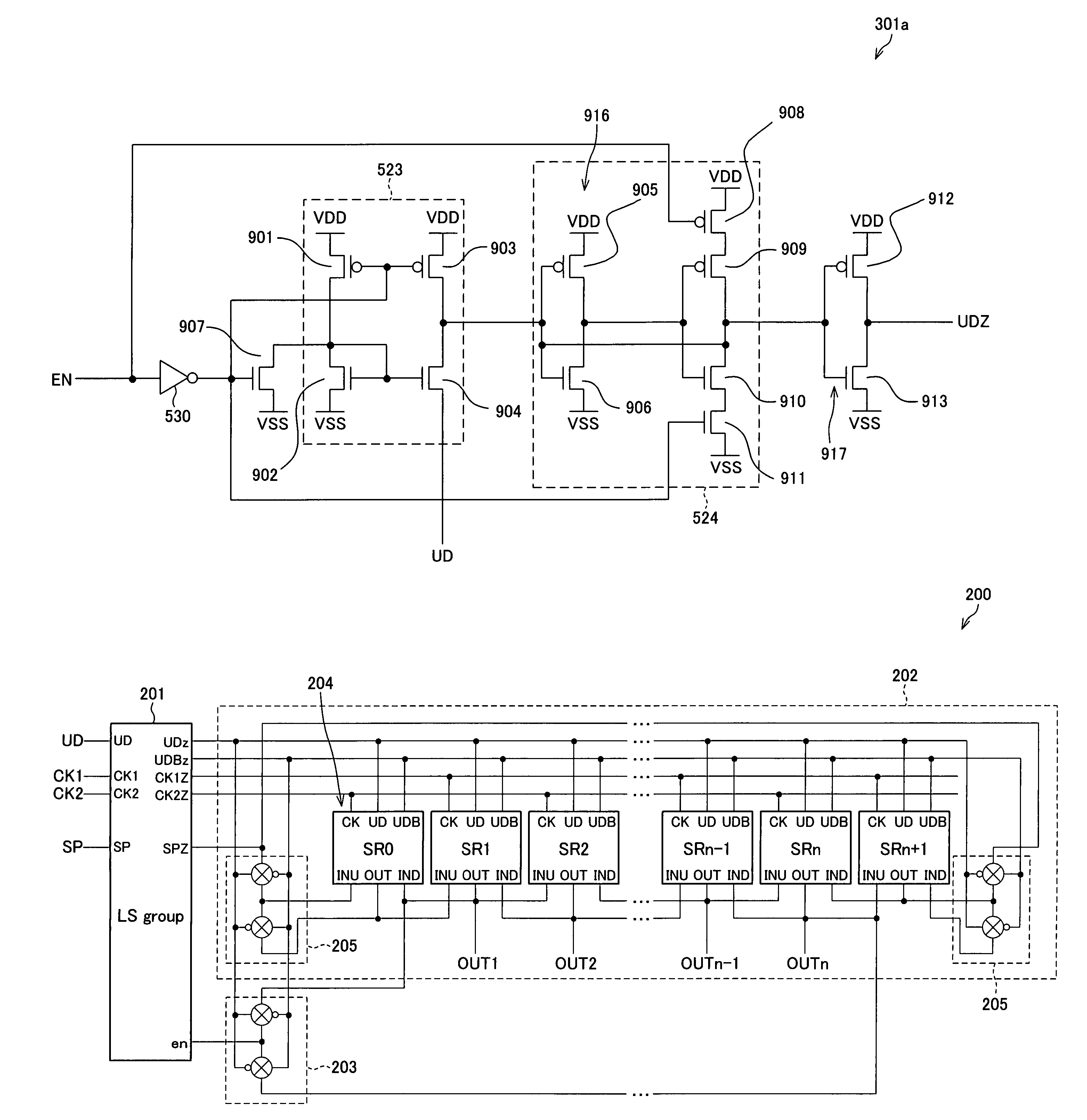
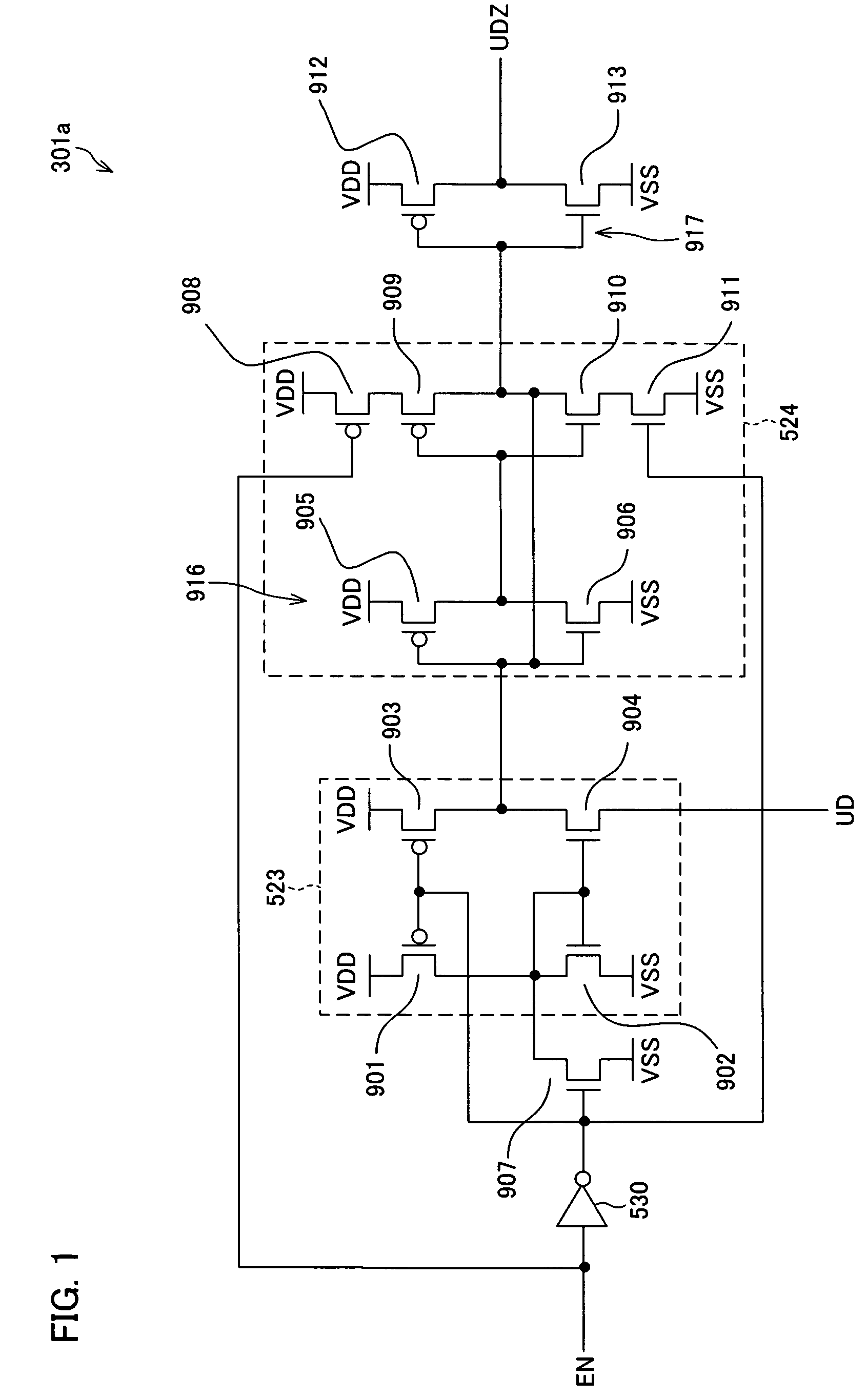
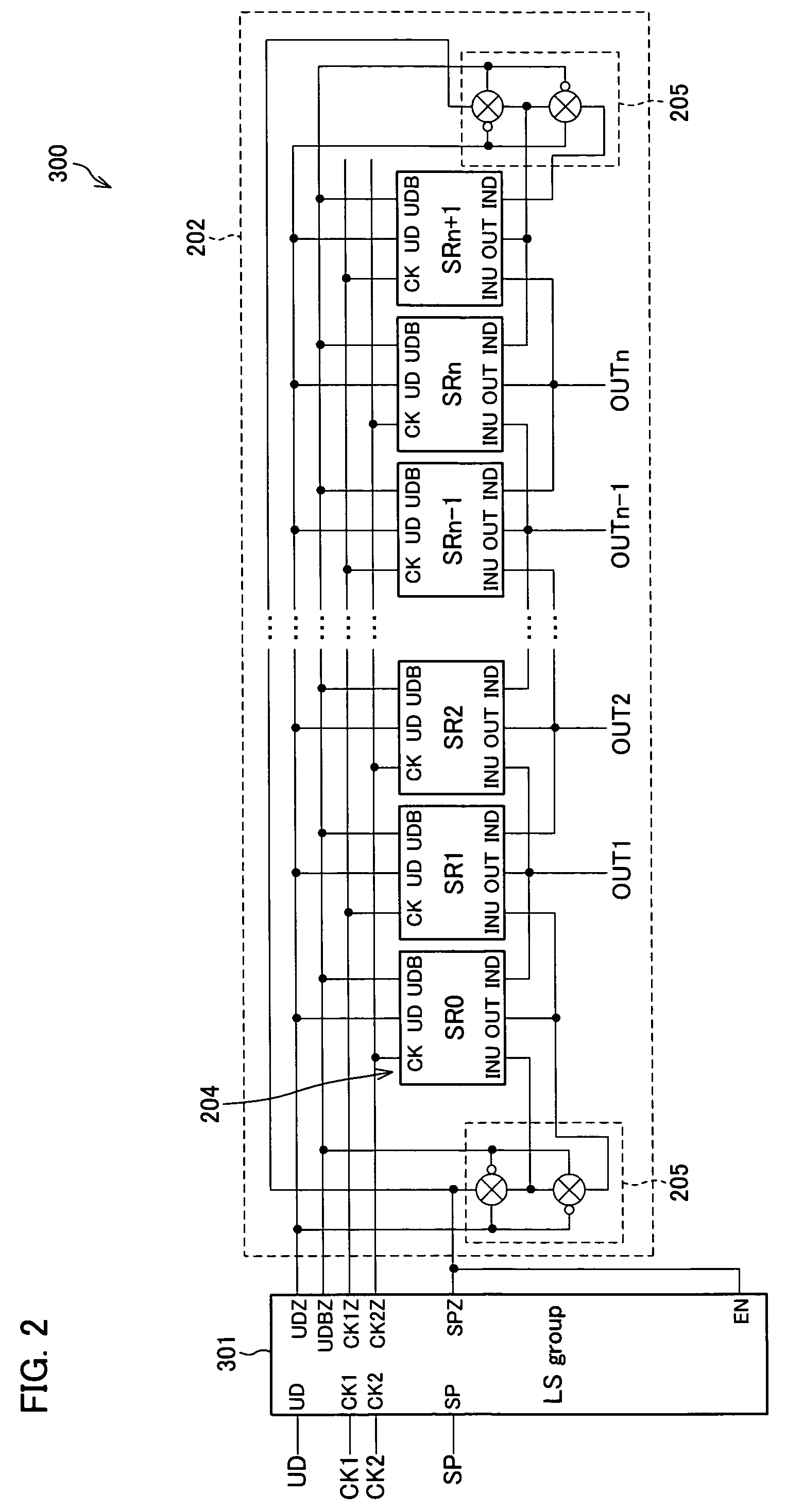
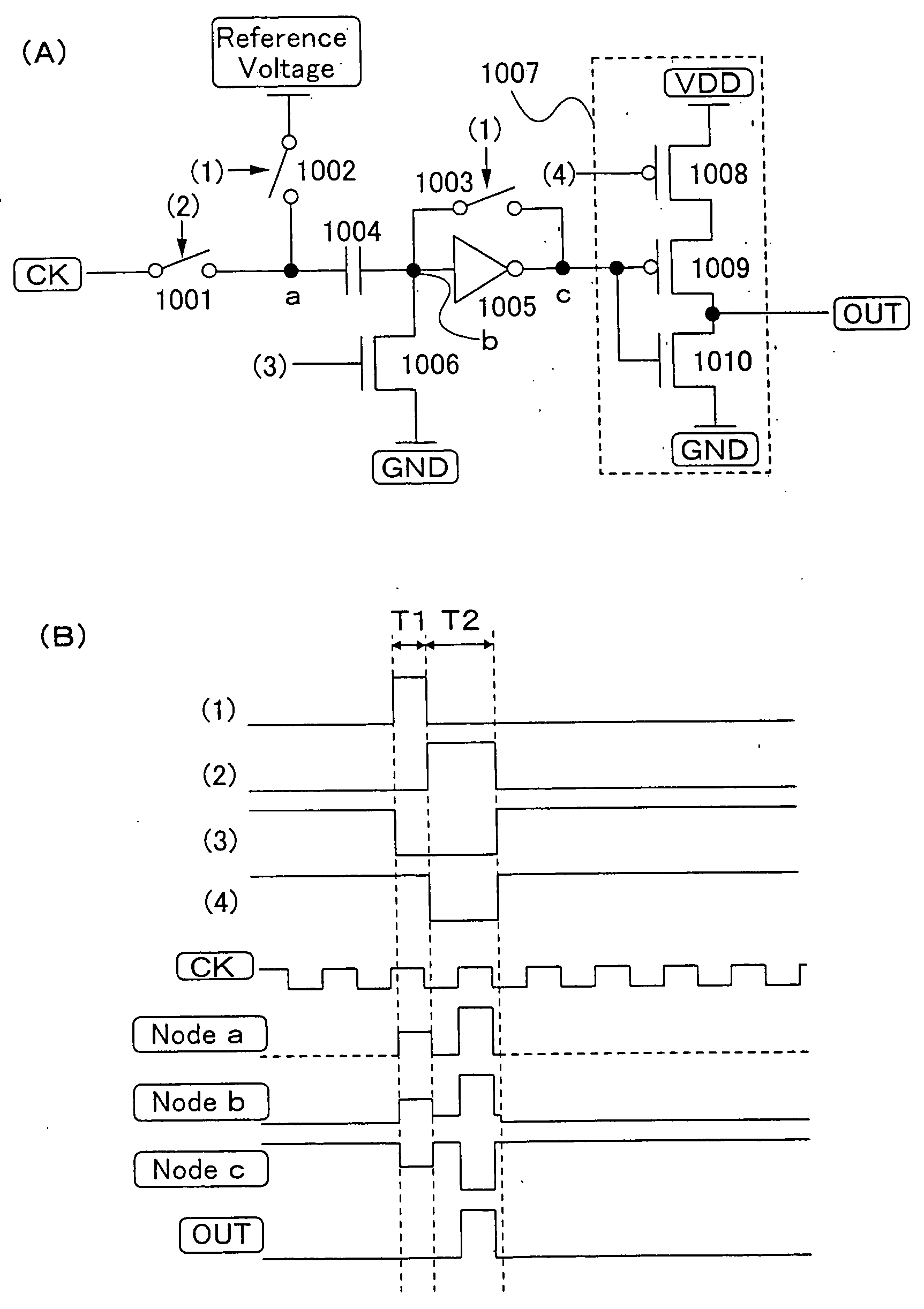
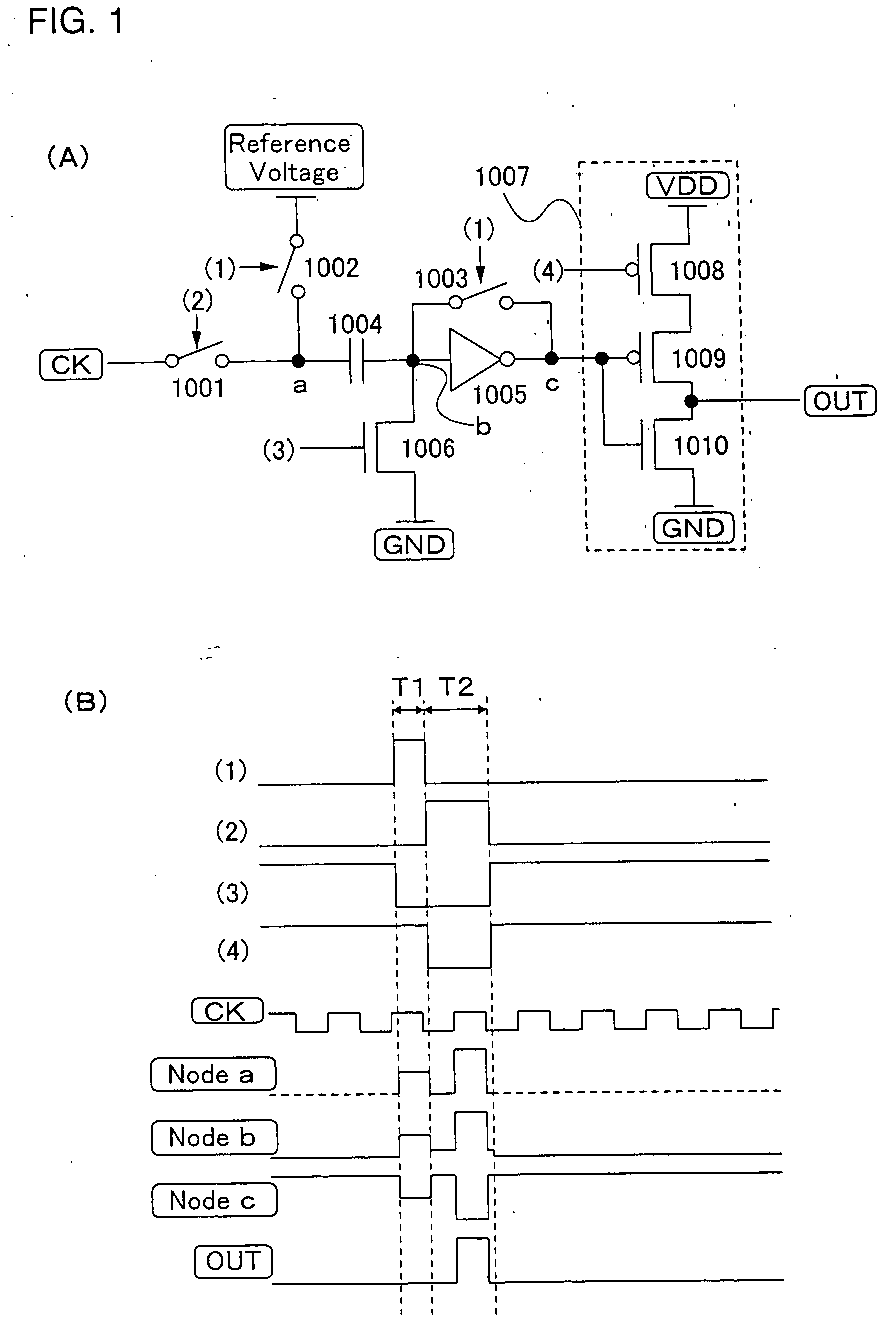
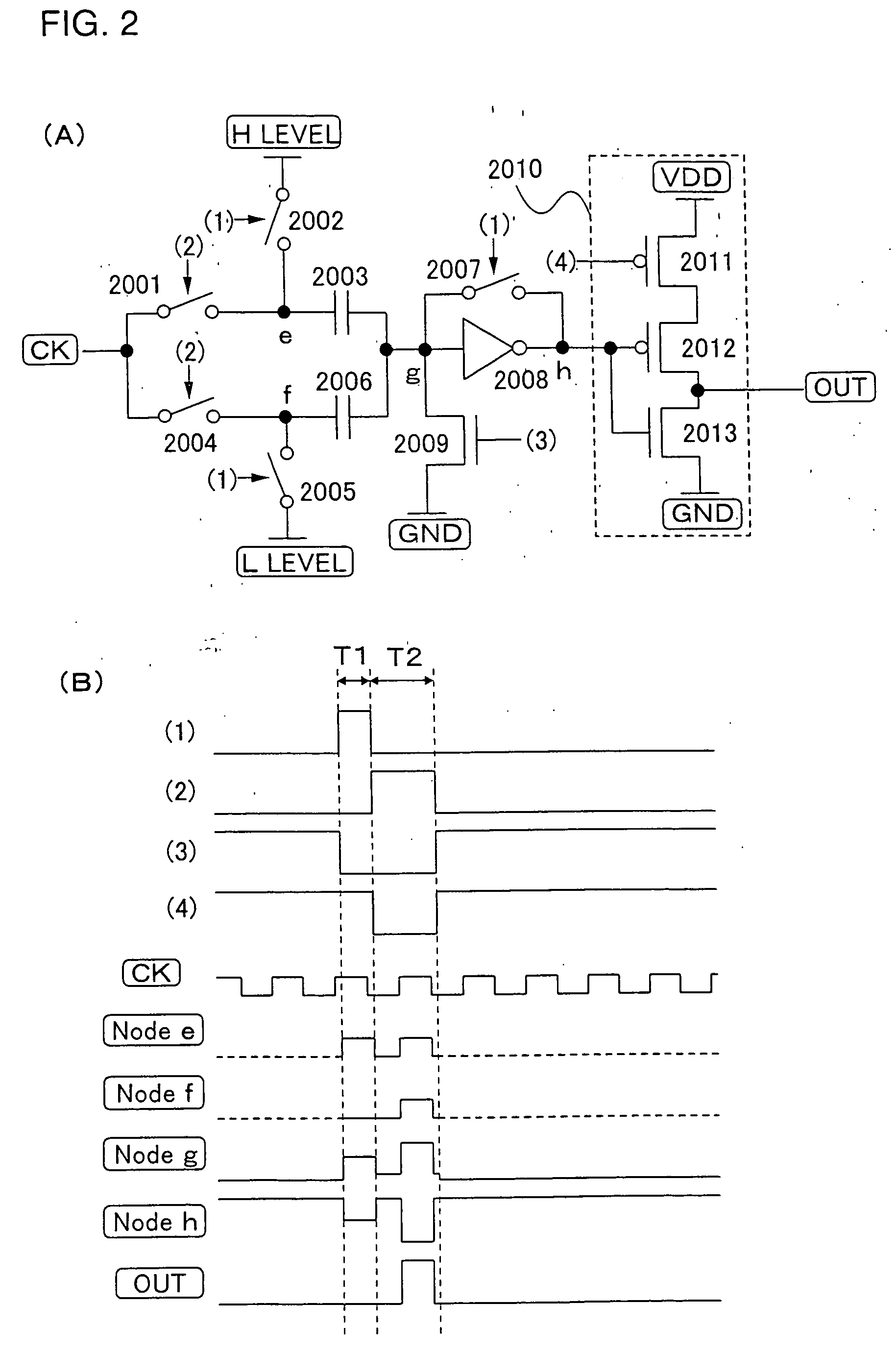
ActiveUS6870895B2Reduce power consumptionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsStatic indicating devicesPower inverterShift register
A low power consumption shift register which inputs a CK signal with a low voltage with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors. In the invention, an input portion of an inverter is set at a threshold voltage thereof and a CK signal is inputted to the input portion of the inverter through a capacitor means. In this manner, the CK signal is amplified, which is sent to the shift register. That is, by obtaining the threshold potential of the inverter, the shift register which operates with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors can be provided. A level shifter of the CK signal is generated from an output pulse of the shift register, therefore, the low power consumption shift register having the level shifter which flows a shoot-through current for a short period can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Attenuating Non-Linear Noise in An Amplifier with Alternating DC -offset Correction
InactiveUS20130088294A1Increase valueReduce the valueHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlSignal qualityAudio power amplifier
An amplifier may include two or more pulse-width modulators controlling respective sets of switches to produce an amplified version of a source signal. A positive DC-offset based on the source signal may be applied to the pulse-width modulator controlling one respective set of switches, and an equal value negative DC-offset may be applied to the pulse-width modulator controlling the other respective set of switches, to provide an effective offset between the respective points in time of the rising / falling edges of the different pulse-width modulated control signals. The addition of alternating positive and negative DC-offset values doesn't affect the output load, and doesn't degrade the signal. The DC-offsets may be added at a frequency selected to be beyond the signal baseband, and the value of the small input signal level may be determined using an RMS level comparator or similar measurement technique.
Owner:MEYERTONS HOOD KIVLIN KOWERT & GOETZEL P C
DC cancellation apparatus and method
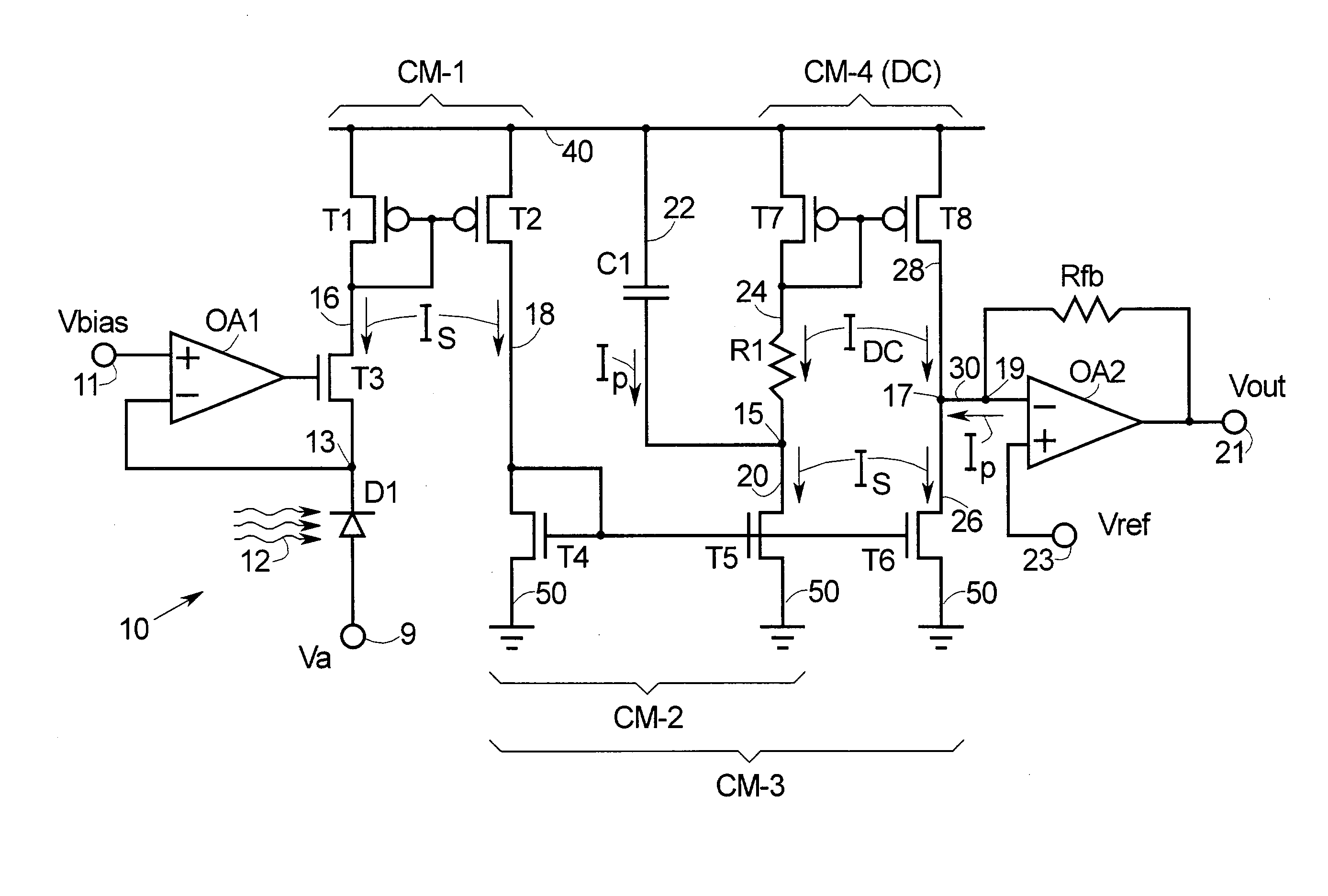
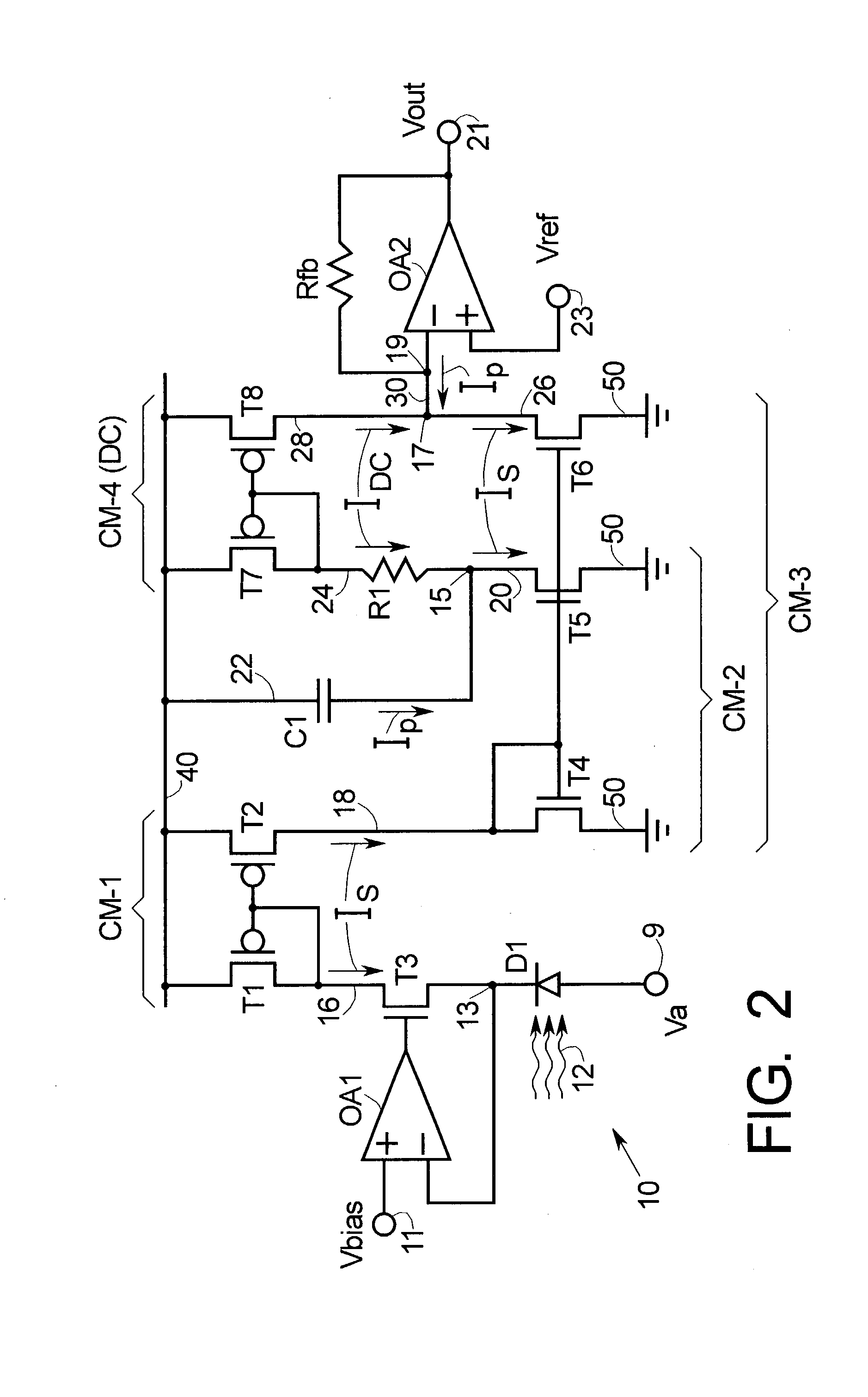
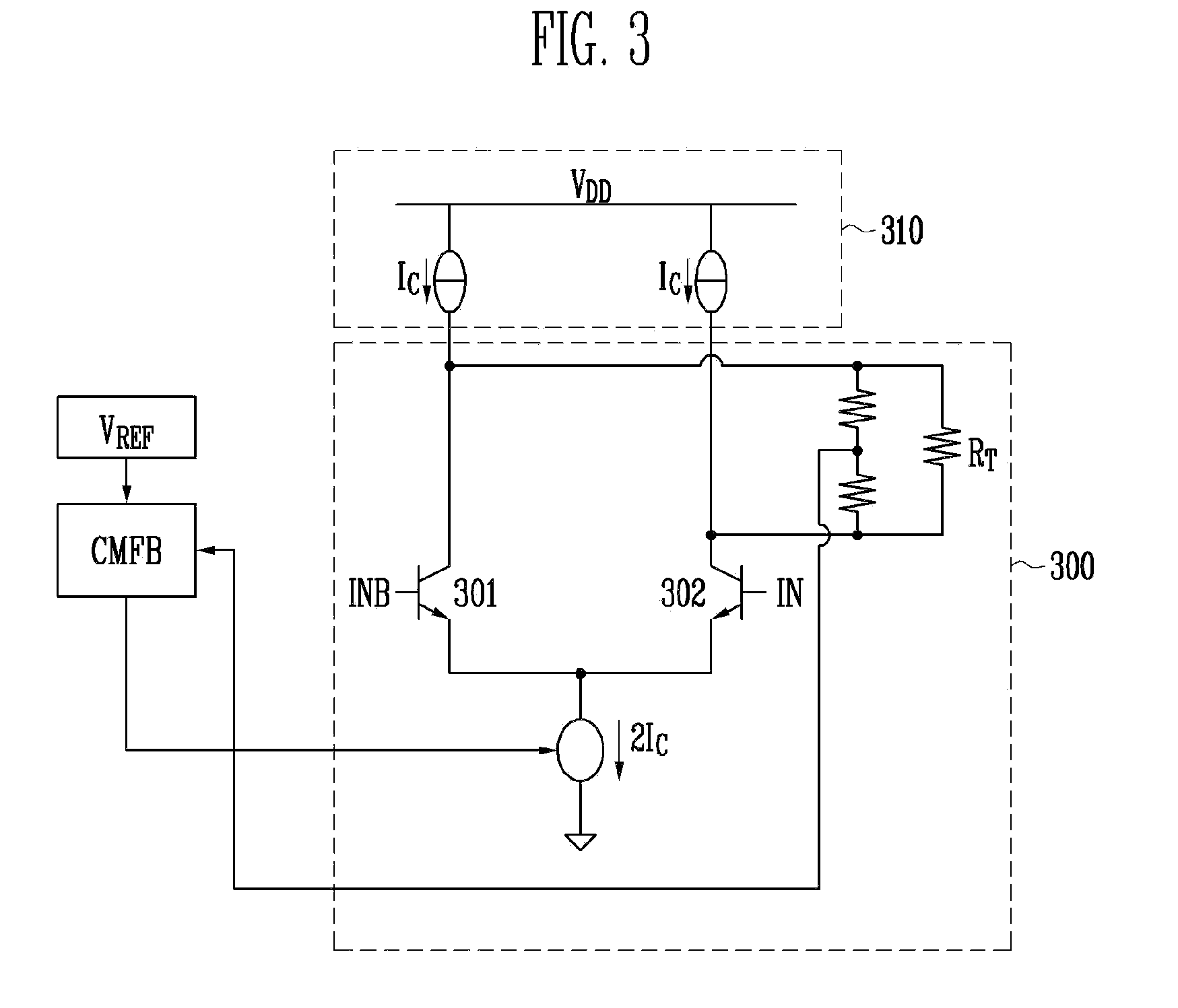
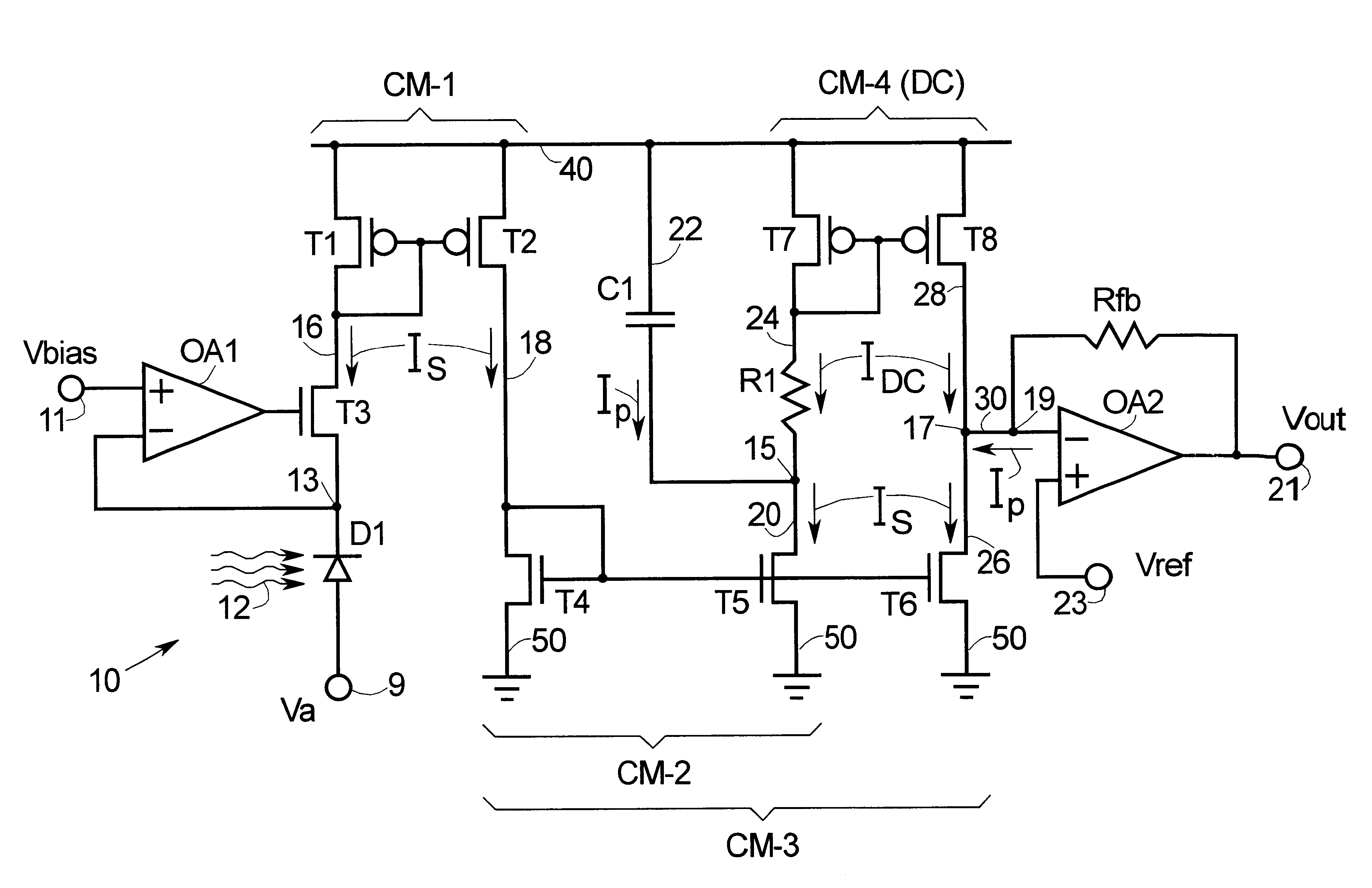
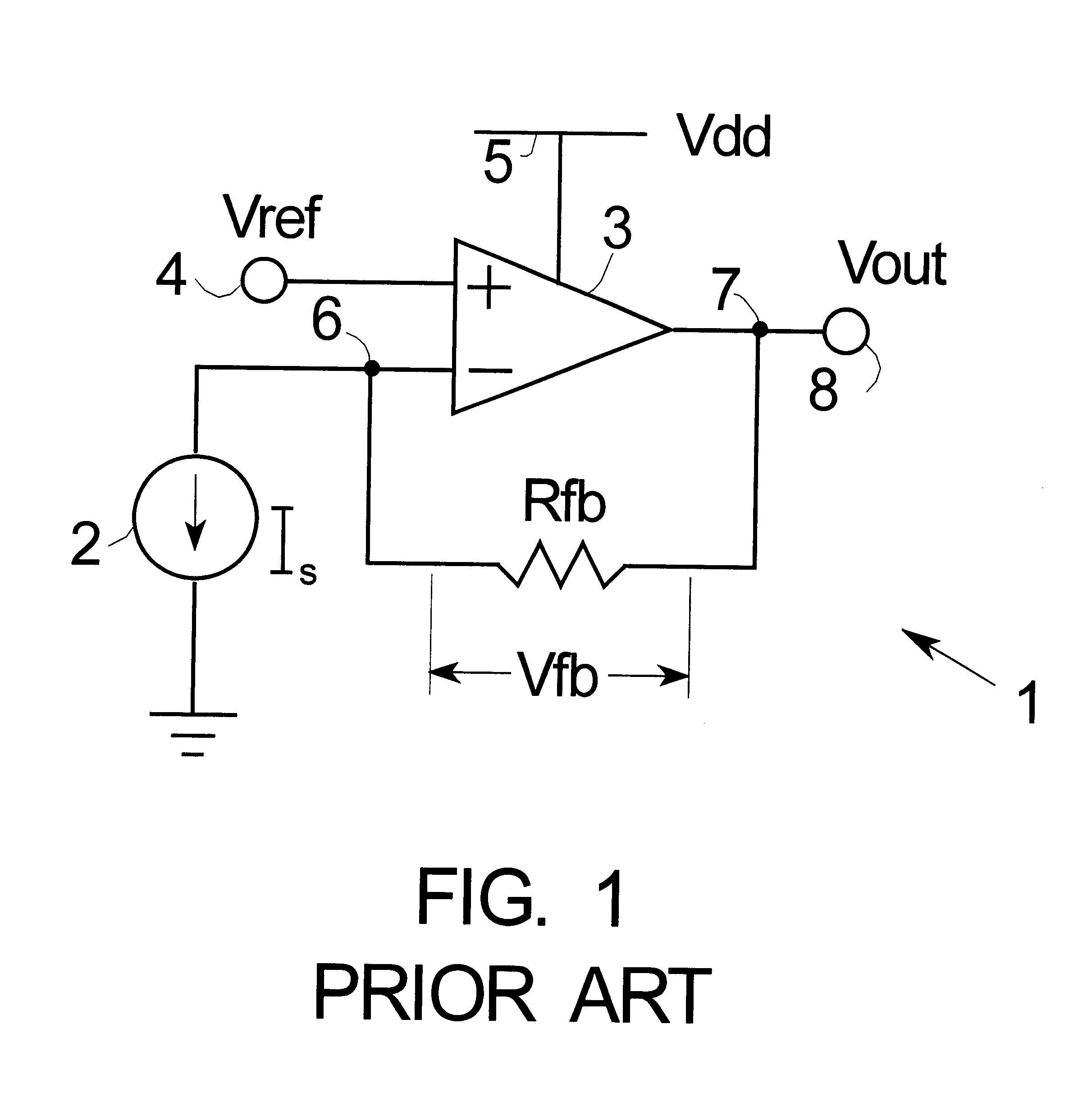
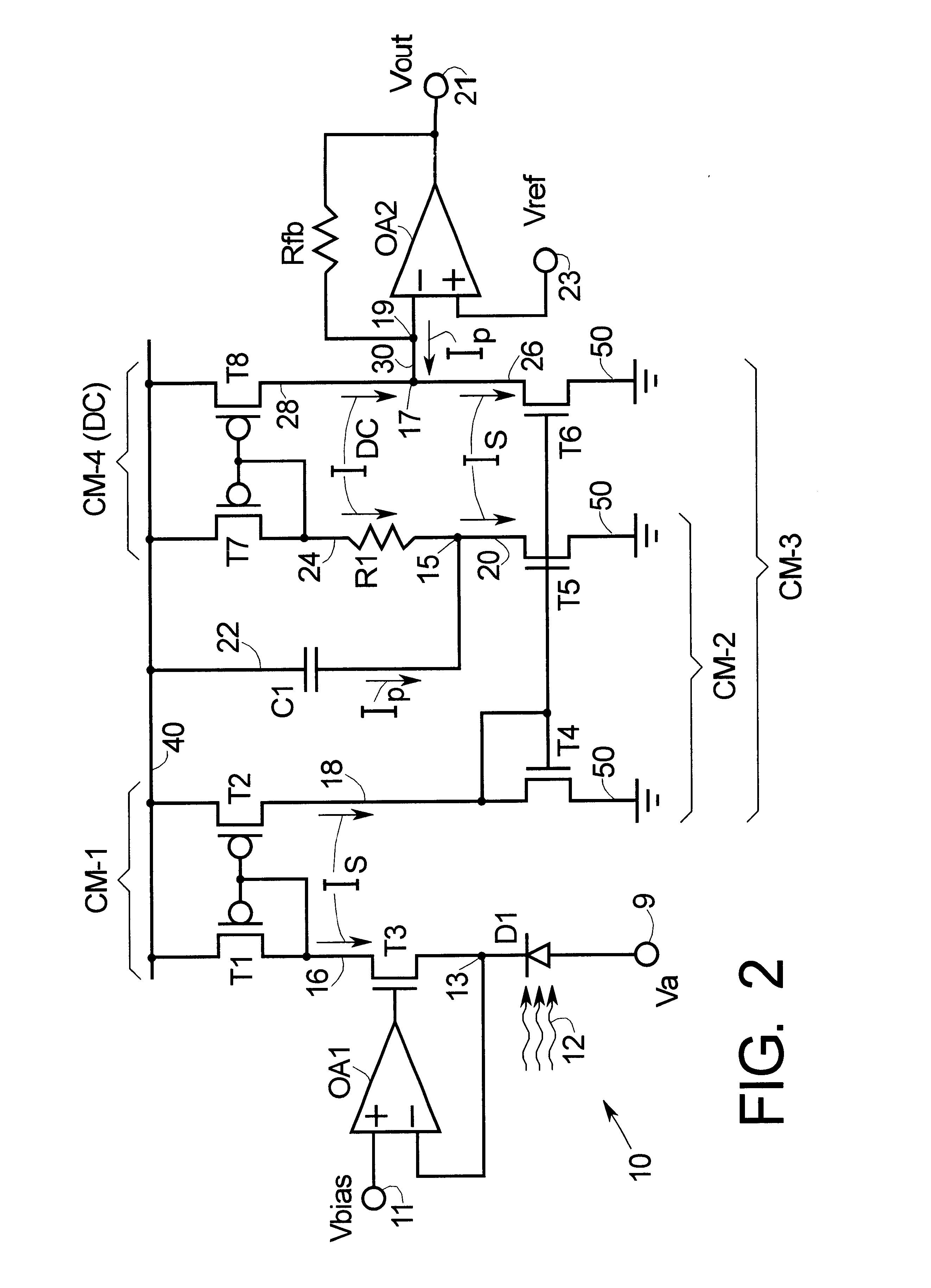
Methods and apparatus are provided for separating DC and AC components of a composite signal Is=Idc+Iac from a current source, e.g., a photodiode current source. Four current mirrors CM-1 . . . CM-4 are used with common branches and overlap. CM-1 through CM-3 mirror Is and CM-4 mirrors Idc where Iac has been removed by a frequency selective branch. Outputs of the Cm-3 and Cm-4 are combined at a node to provide a signal proportional substantially only to Iac. Complementary devices are used where Cm-1 and Cm-4 are of one type and Cm-2 and Cm-3 are of opposite type. The arrangement allows detection of AC signals (e.g., pulses) that are orders of magnitude smaller than the DC background. An I-to-V converter with a large feedback resistance is used at the output to produce a comparatively large voltage output proportional to Iac.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Level shifter and display device using same
ActiveUS7209130B2Reduce power consumptionLow mobilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLevel shiftingShift register
A level-shifter is combined with a bi-directional shift register. The level shifter turns a start signal of the bi-directional shift register to be an enable signal, and (i) activates a level shifting section by supplying a stationary current, during a period in which the enable signal is HIGH, while (ii) deactivates the level shifting section by cutting off the stationary current, during a period in which the enable signal EN is LOW. With this, it is possible to reduce unnecessary current consumption by a level shifter provided for a signal which does not frequently change, such as a shifting direction switching signal for which the bi-directional shift register is provided. At the same time, when such a signal changes, the change is followed with no time lag.
Owner:SHARP KK
Driving apparatus of a light-emitting device
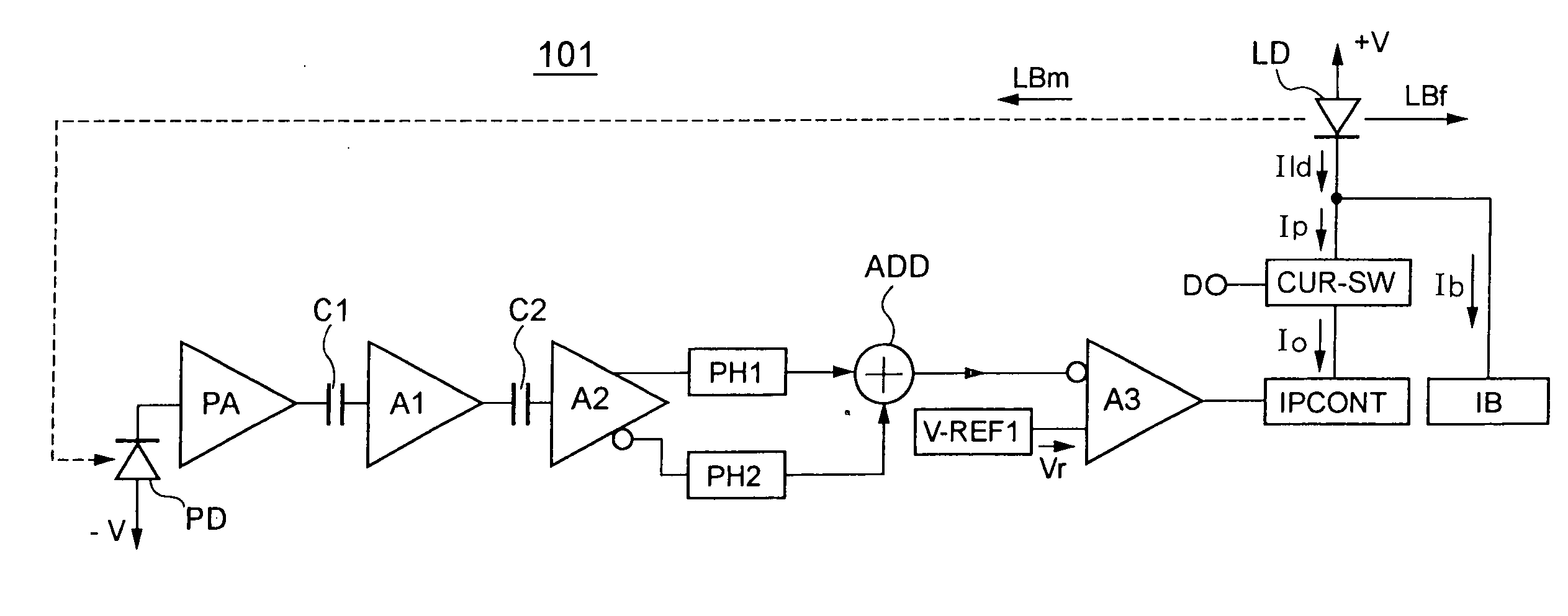
InactiveUS20050025259A1Stable controlLimit its operationMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLaser detailsDc currentNegative phase
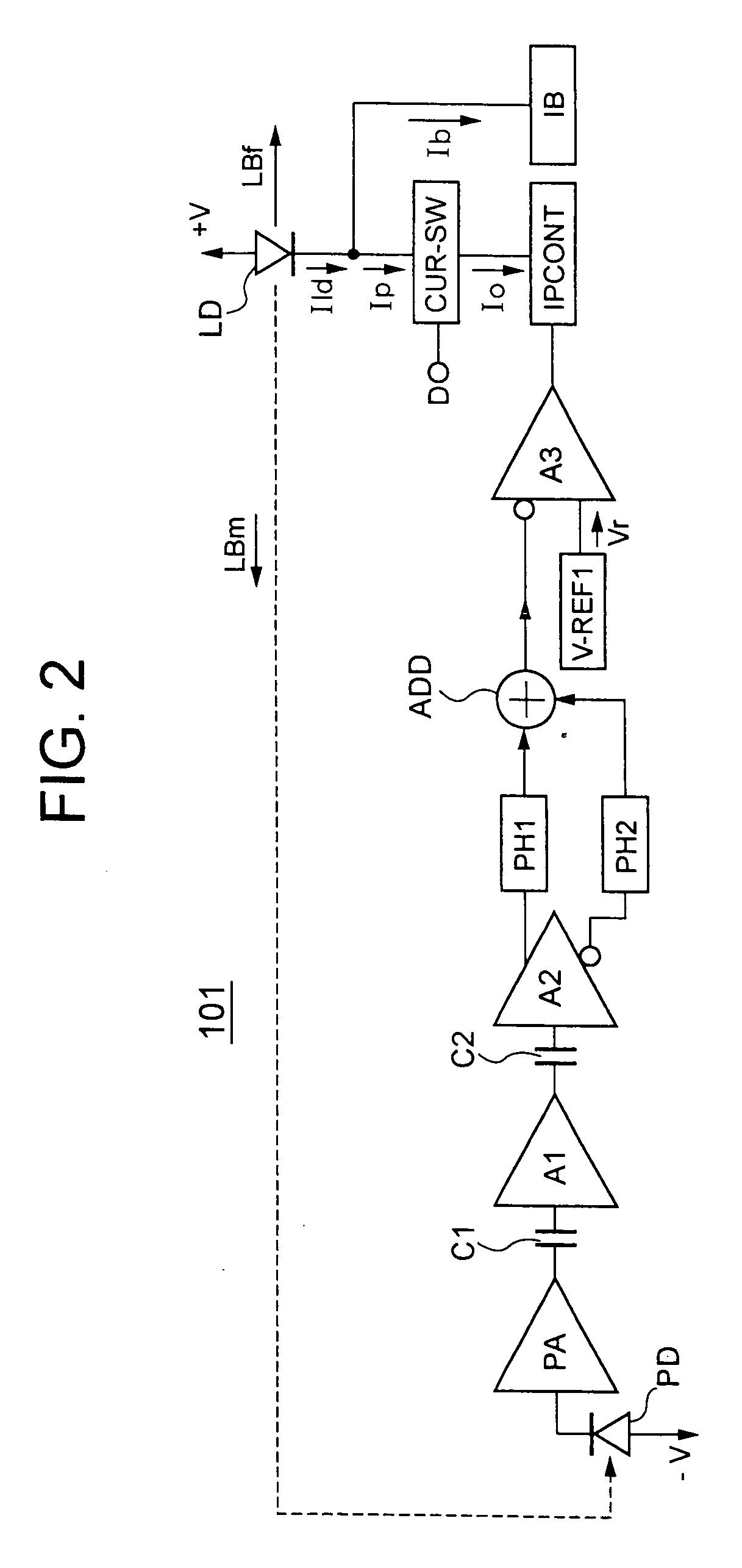
A first peak hold circuit holds a peak potential of a positive phase voltage signal output from a differential output amplifier, and a second peak hold circuit holds a peak potential of a negative phase voltage signal output from the differential output amplifier. An adding circuit adds an output signal of the first peak hold circuit and an output signal of the second peak hold circuit. A differential input amplifier amplifies and outputs a voltage difference between a reference voltage and an addition result voltage signal of the adding circuit. A current output circuit outputs a DC current based on an output voltage of the differential input amplifier. A current switch circuit converts a DC current to a pulse current so as to supply the pulse current to a laser diode.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method of fabricating bipolar transistors and high-speed lvds driver with the bipolar transistors
InactiveUS20080136464A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageDifferential signaling
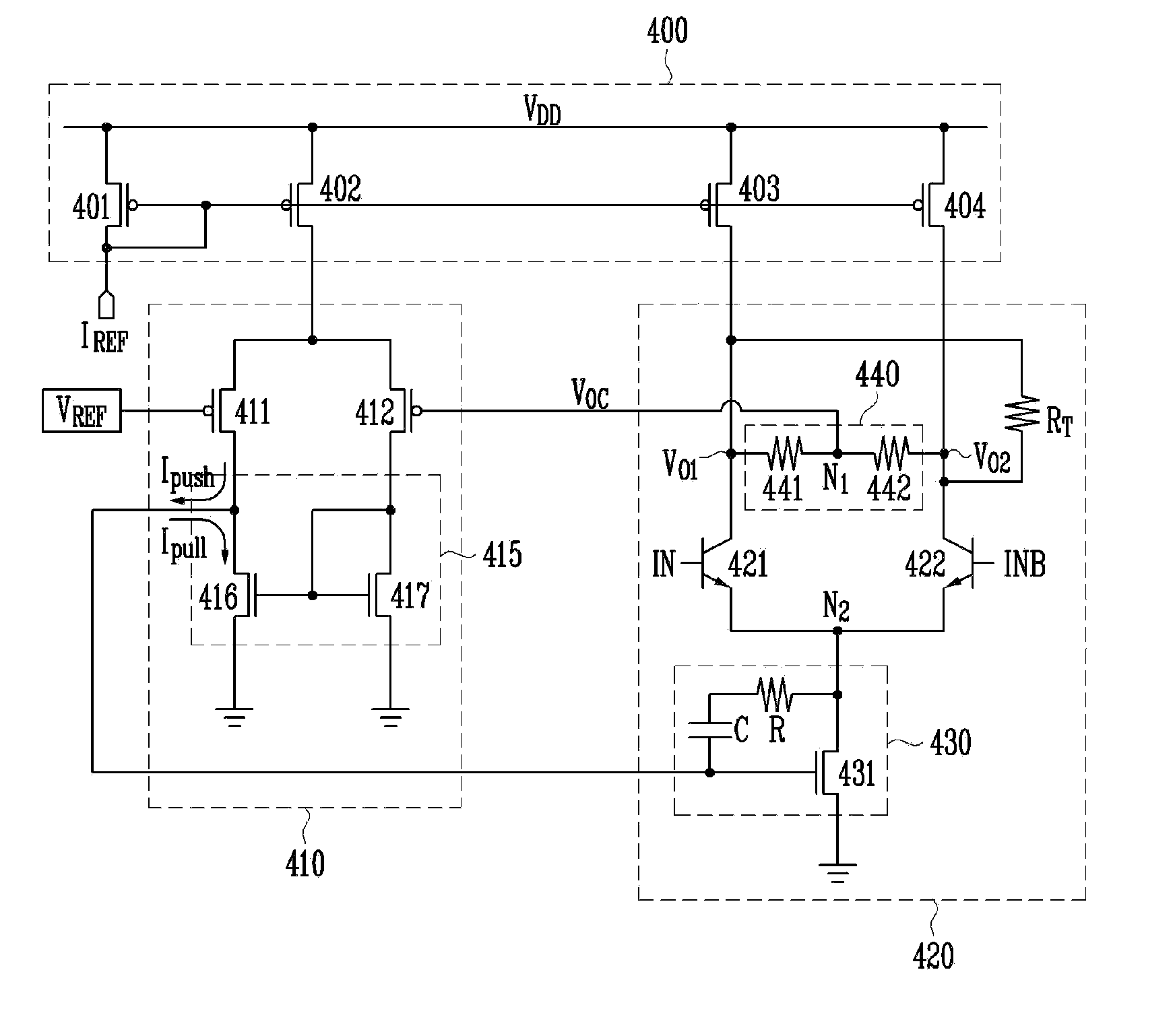
Provided is a differential signal driver capable of operating at a high speed at a low voltage of 1.8V. The differential signal driver includes: a differential-signal driving circuit for switching input differential signals and outputting a common mode voltage through first and second output nodes; and a common-mode feedback circuit for providing a predetermined current to the differential-signal driving circuit or receiving a predetermined current from the differential-signal driving circuit in response to the common mode voltage. The differential-signal driving circuit includes a common-mode voltage output circuit for connecting the first output node to the second output node and generating the common mode voltage of the differential-signal driving circuit. The differential input signals are received through two bipolar transistors.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
DC cancellation apparatus and method
Methods and apparatus are provided for separating DC and AC components of a composite signal Is=Idc+Iac from a current source, e.g., a photodiode current source. Four current mirrors CM-1 . . . CM-4 are used with common branches and overlap. CM-1 through CM-3 mirror Is and CM-4 mirrors Idc where lac has been removed by a frequency selective branch. Outputs of the Cm-3 and Cm-4 are combined at a node to provide a signal proportional substantially only to Iac. Complementary devices are used where Cm-1 and Cm-4 are of one type and Cm-2 and Cm-3 are of opposite type. The arrangement allows detection of AC signals (e.g., pulses) that are orders of magnitude smaller than the DC background. An I-to-V converter with a large feedback resistance is used at the output to produce a comparatively large voltage output proportional to lac.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
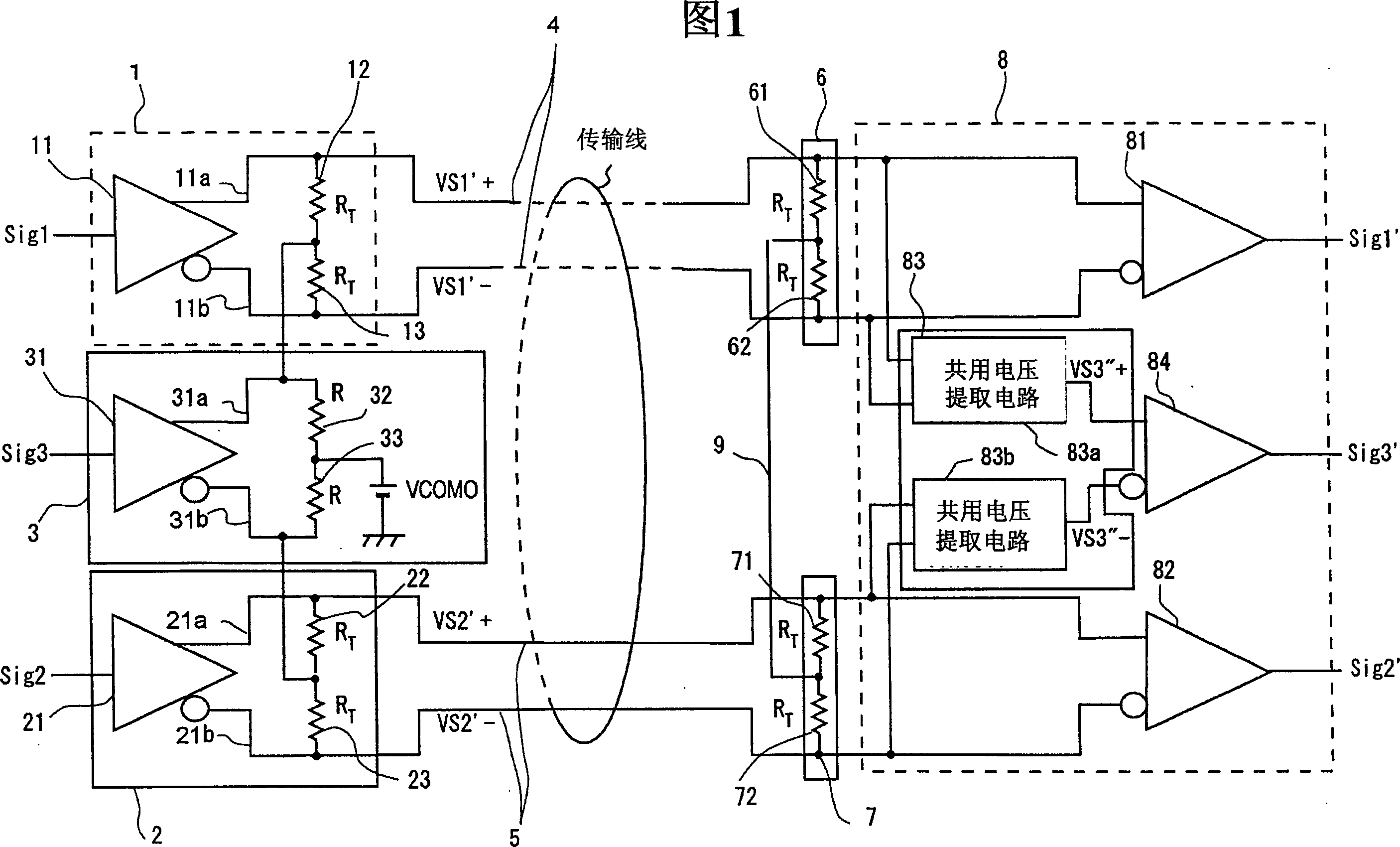
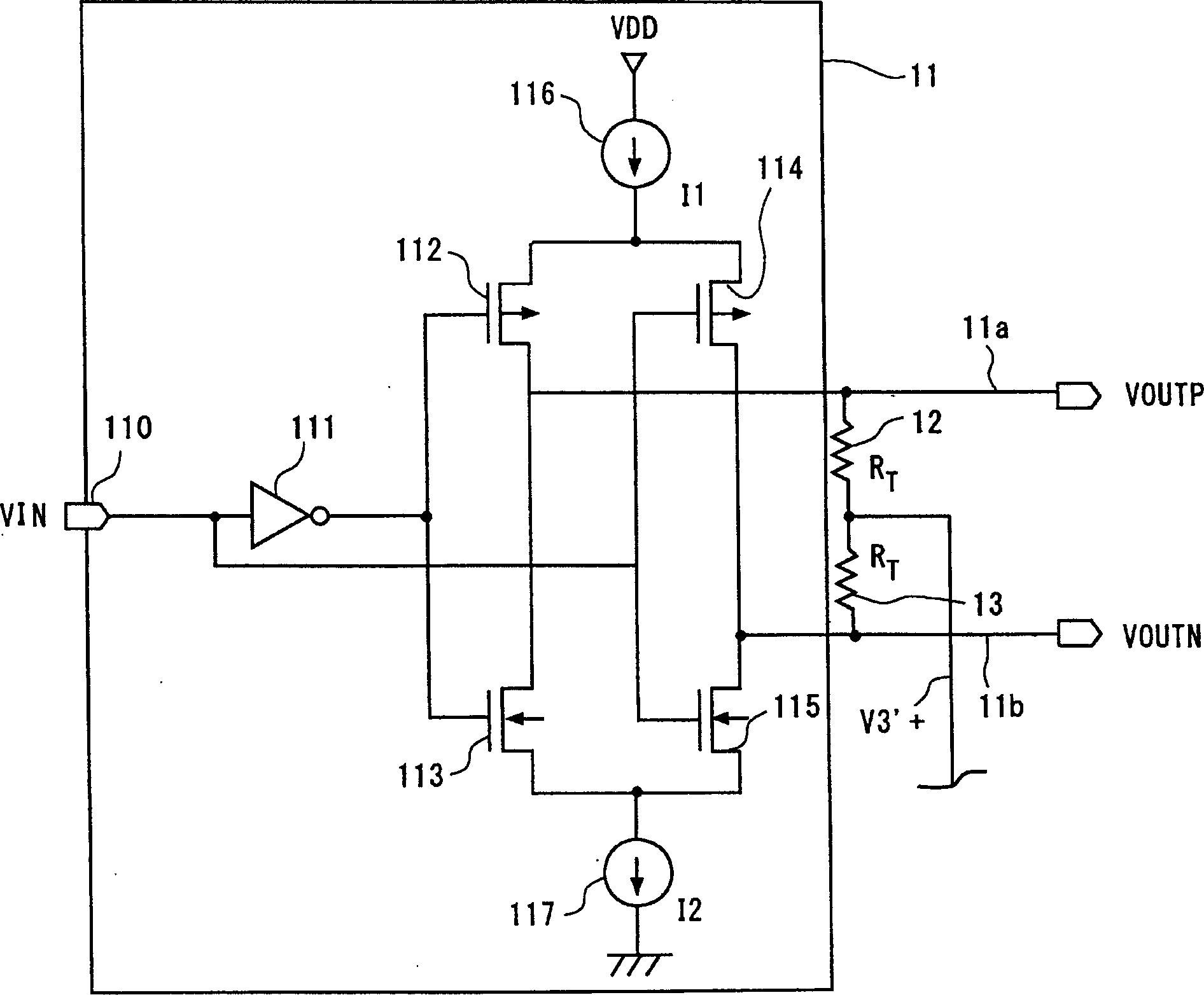
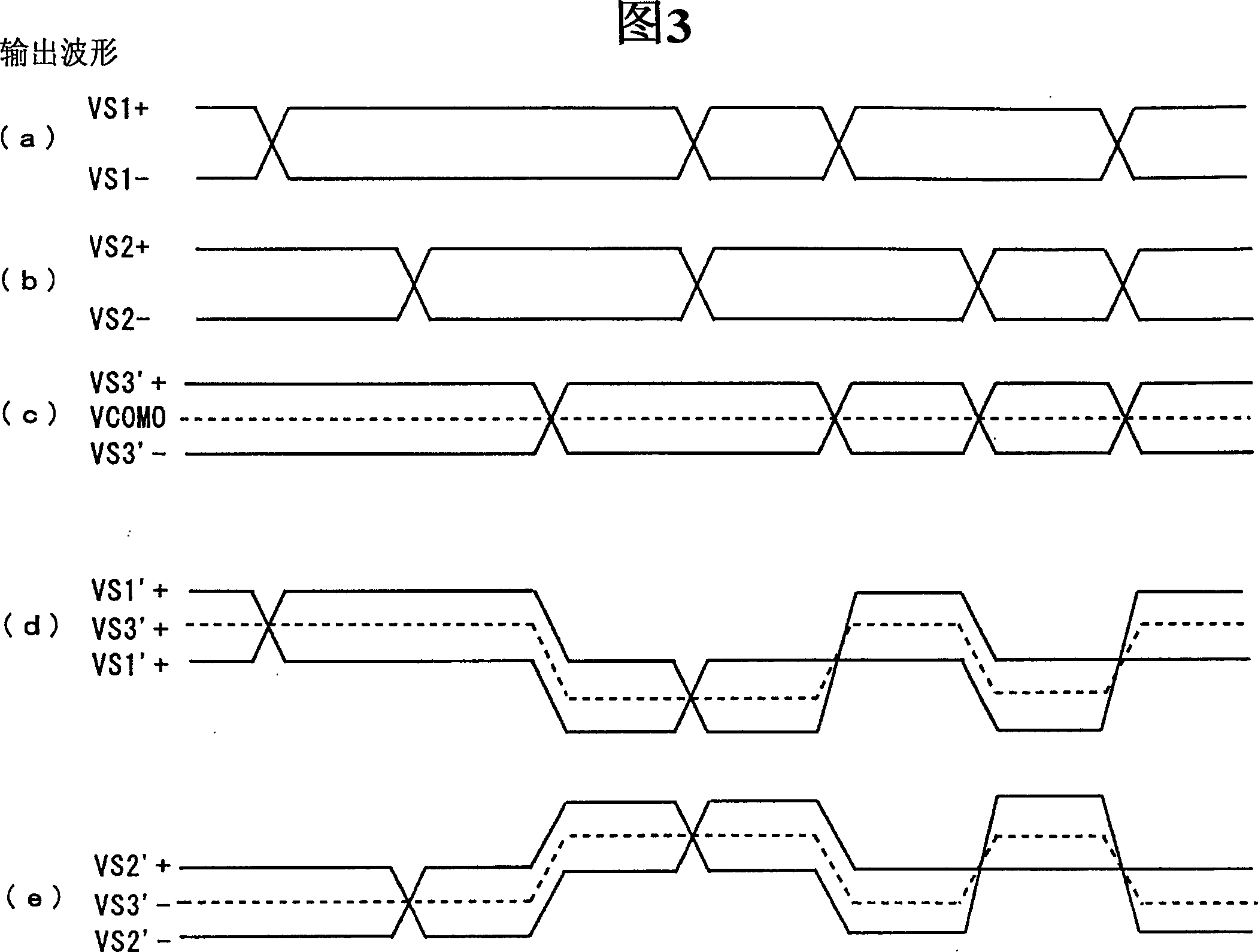
Differential signal receiving device and differential signal transmission system
InactiveCN1574800AFully understandMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLine-faulsts/interference reductionDifferential signalingEngineering
The intermediate node of the first terminator connected between a pair of signal lines transmitting the first differential signal with one side of the third differential signal as a common voltage and the intermediate node of the second terminator connected between a pair of signal lines transmitting the second differential signal with the other side of the third differential signal as a common voltage are connected by the intermediate connection. Thus, the intermediate node of the first terminator and the intermediate node of the second terminator act as a virtual ground of the third differential signal, enabling the matching of the impedance of the terminators related to the third differential signal and the impedance of the signal lines related to the third differential signal. It is thus able to prevent the reflection of the third differential signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
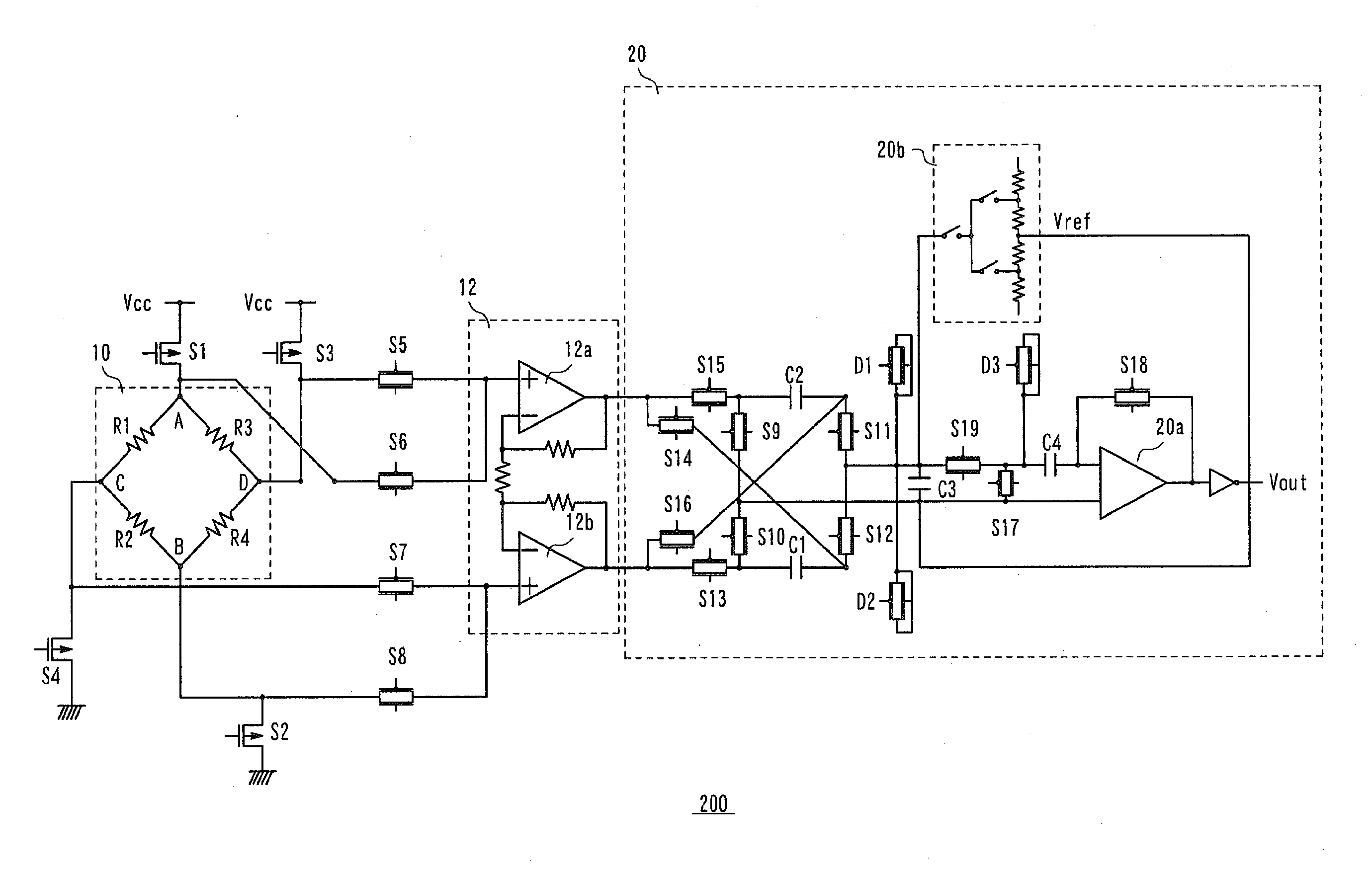
Offset cancelling circuit
InactiveUS20100308886A1Reduce impactMagnetic measurementsPulse automatic controlHall elementEngineering
When a voltage is applied from outside such that a current flowing in a Hall element is switched, each of a plurality of capacitors is charged with an output voltage of the Hall element in each state. A dummy switching element is connected to a switching element which connects the plurality of capacitors in parallel to each other, the dummy switching element and the switching element being controlled to be switched ON and OFF exclusively with respect to each other.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
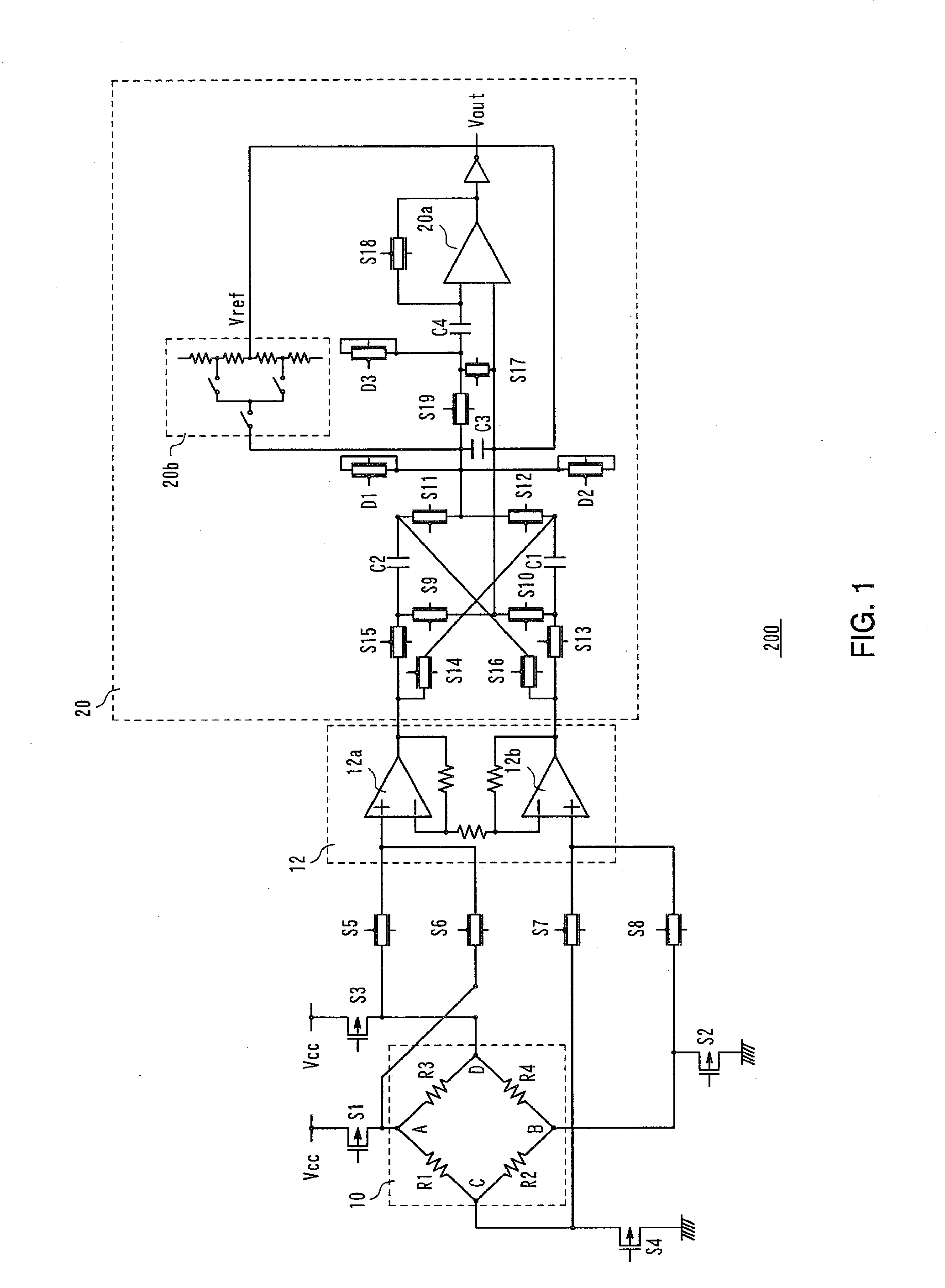
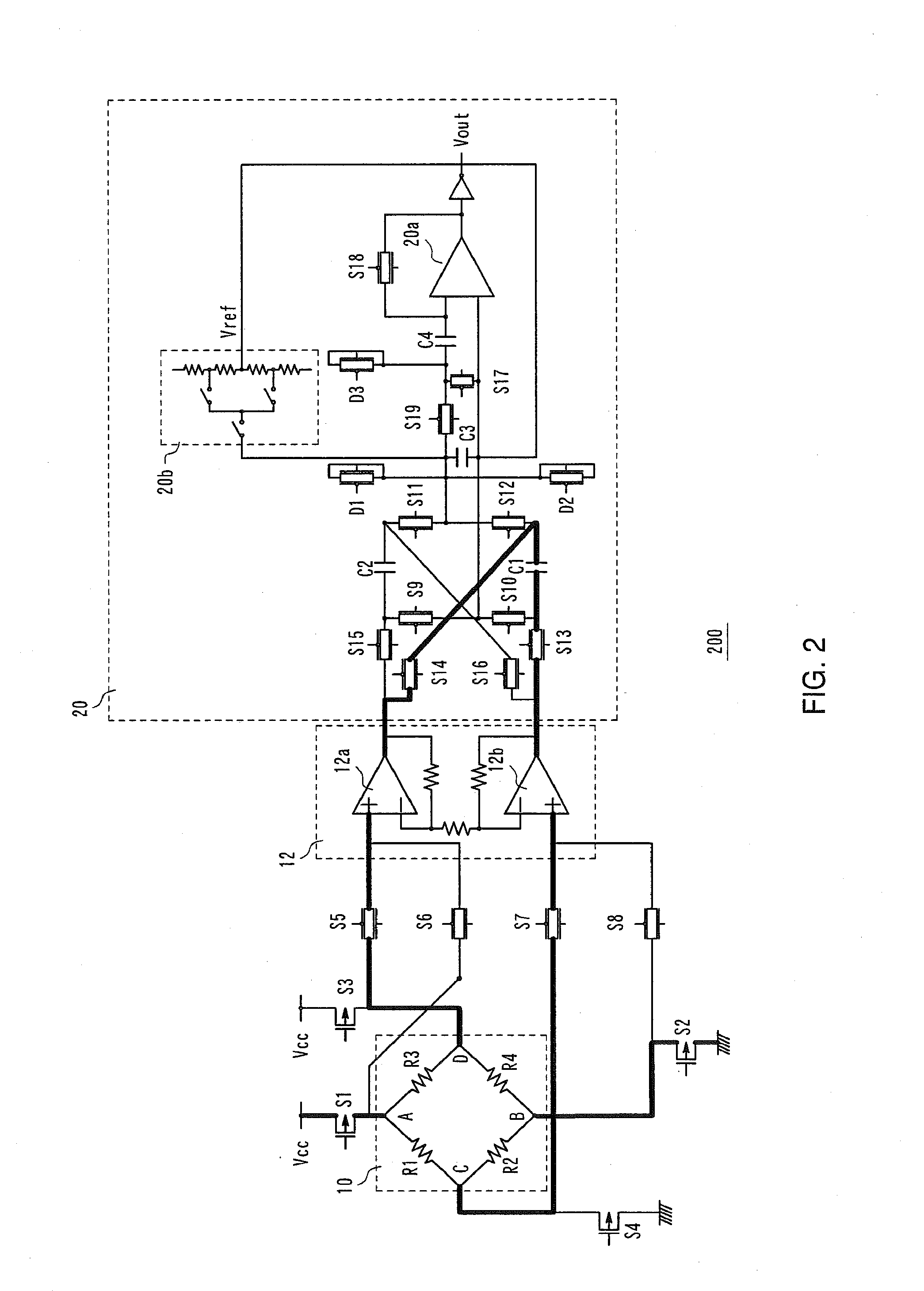
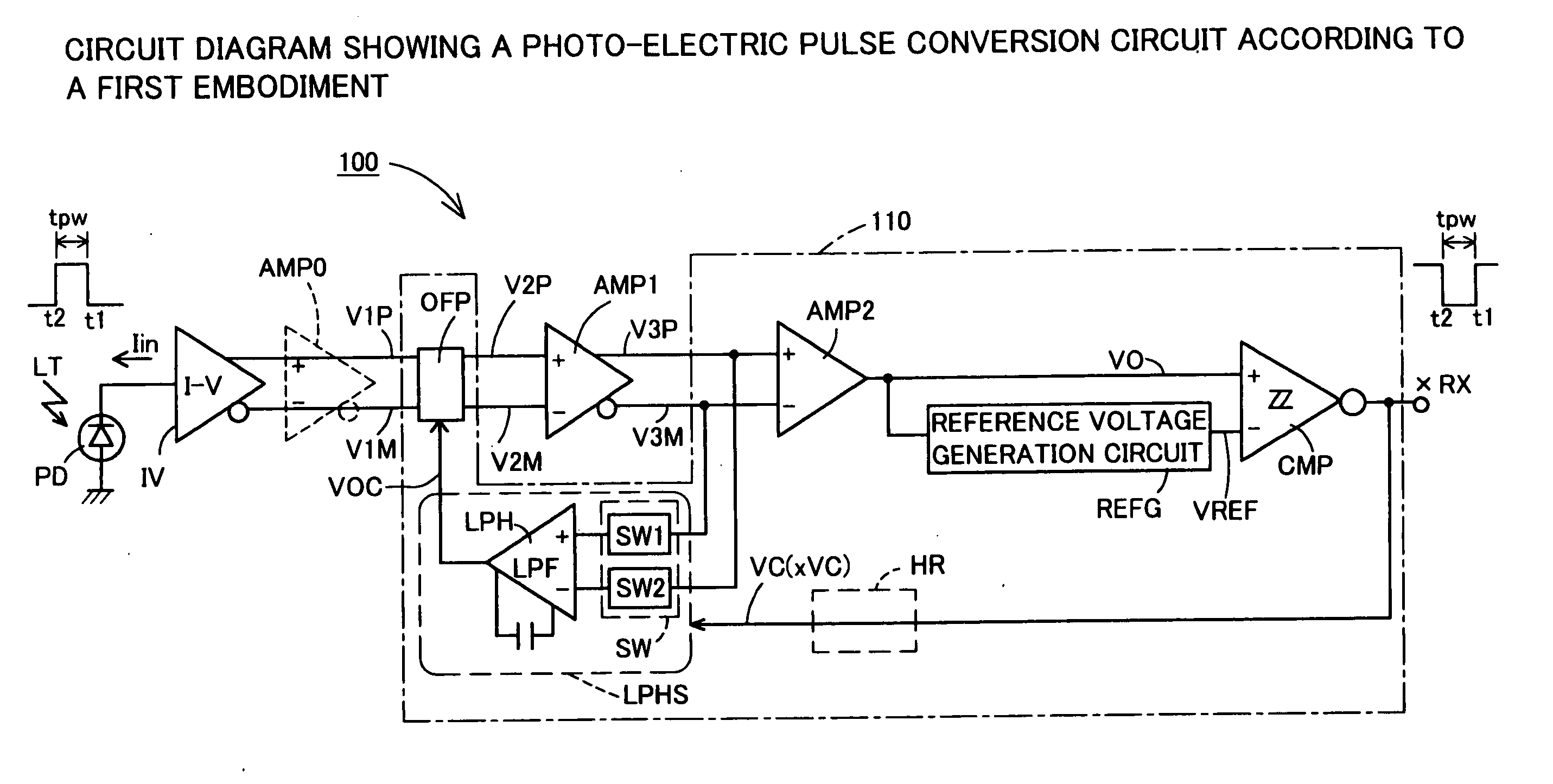
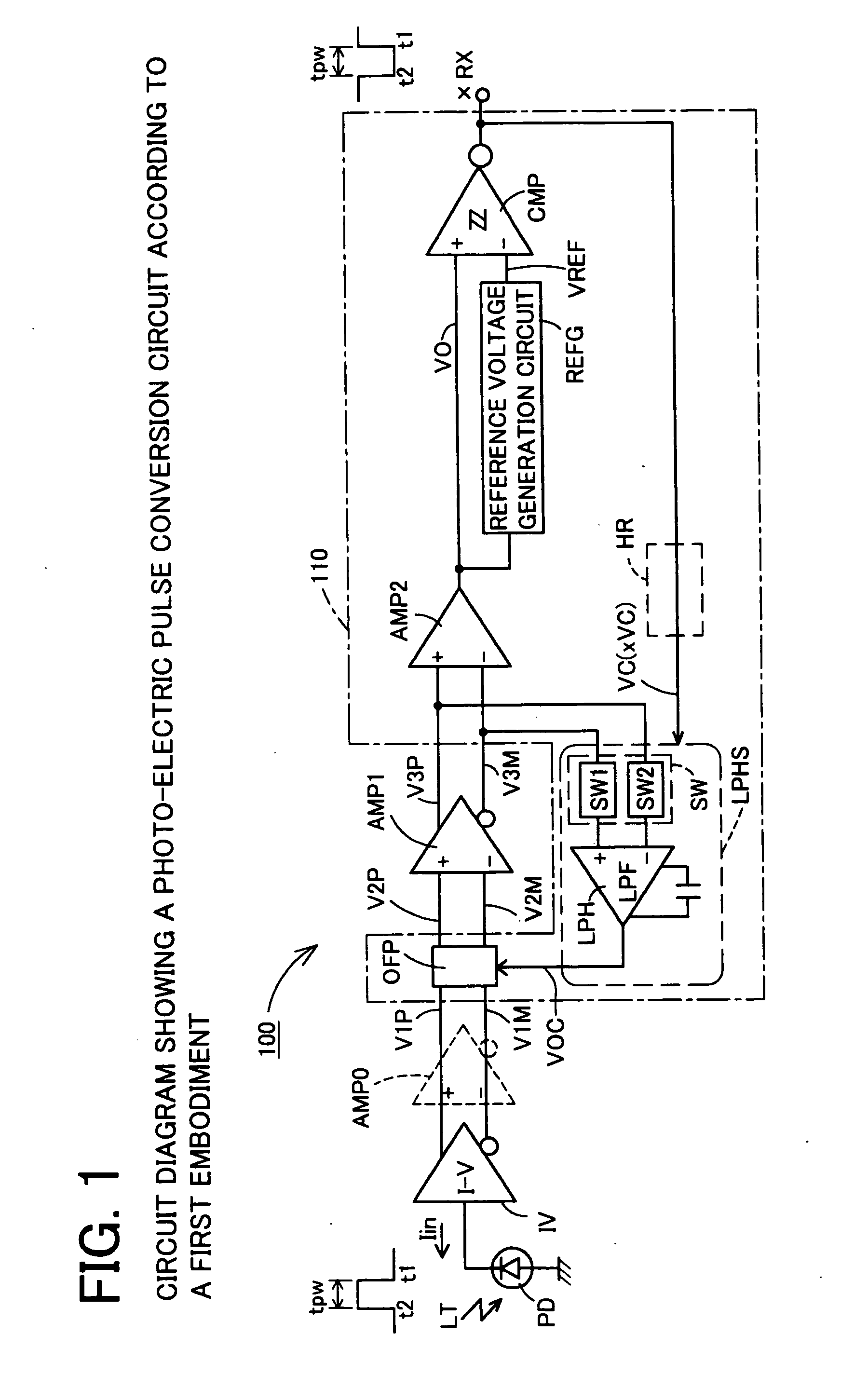
DC offset cancellation circuit, differential amplification circuit with DC offset cancellation circuit, photo-electric pulse conversion circuit, pulse shaping circuit, and pulse generation circuit
InactiveUS20050258885A1Exact widthExact reproductionDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationAmplifiers controlled by lightAc componentsNegative feedback
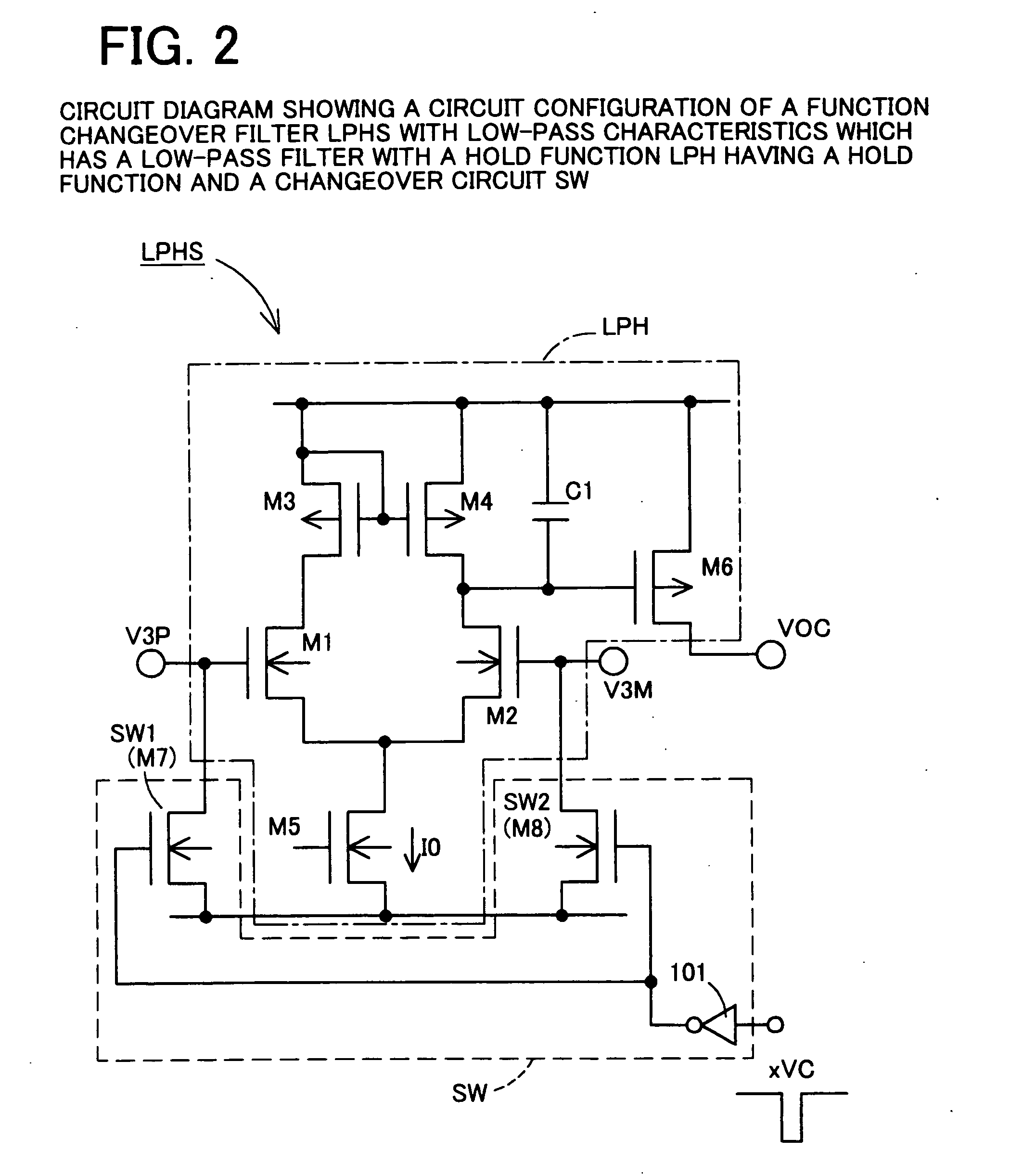
A DC offset cancellation circuit that is capable of canceling a DC offset voltage occurring between a pair of differential output signals of a differential amplification circuit, while preventing a signal waveform from being distorted due to accumulation of AC components and a photo-electric pulse conversion circuit that is capable of generating an electrical pulse signal that accurately reproduces a rise timing and a fall timing of an optical pulse signal by canceling the DC offset voltage are provided. A photo-electric pulse conversion circuit is provided with a photodiode, an I-V conversion circuit, a first differential amplification circuit having a DC offset cancellation circuit, a second differential amplification circuit, a reference voltage generation circuit, and a comparison circuit. The DC offset cancellation circuit uses a changeover circuit to change a state of a low-pass filter with a hold function in synchronization with an inversion electrical pulse signal, and performs a negative feedback of a filtered signal which is generated by subjecting third differential signals to low-pass filtration or a hold filtered signal which is a filtered signal held during changeover.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
System and method for level translation in serial data interface
ActiveUS7948270B1Maintain compatibilityHigh sensitivityAnalogue conversionElectric analogue storesSerial digital interfaceLevel shifting
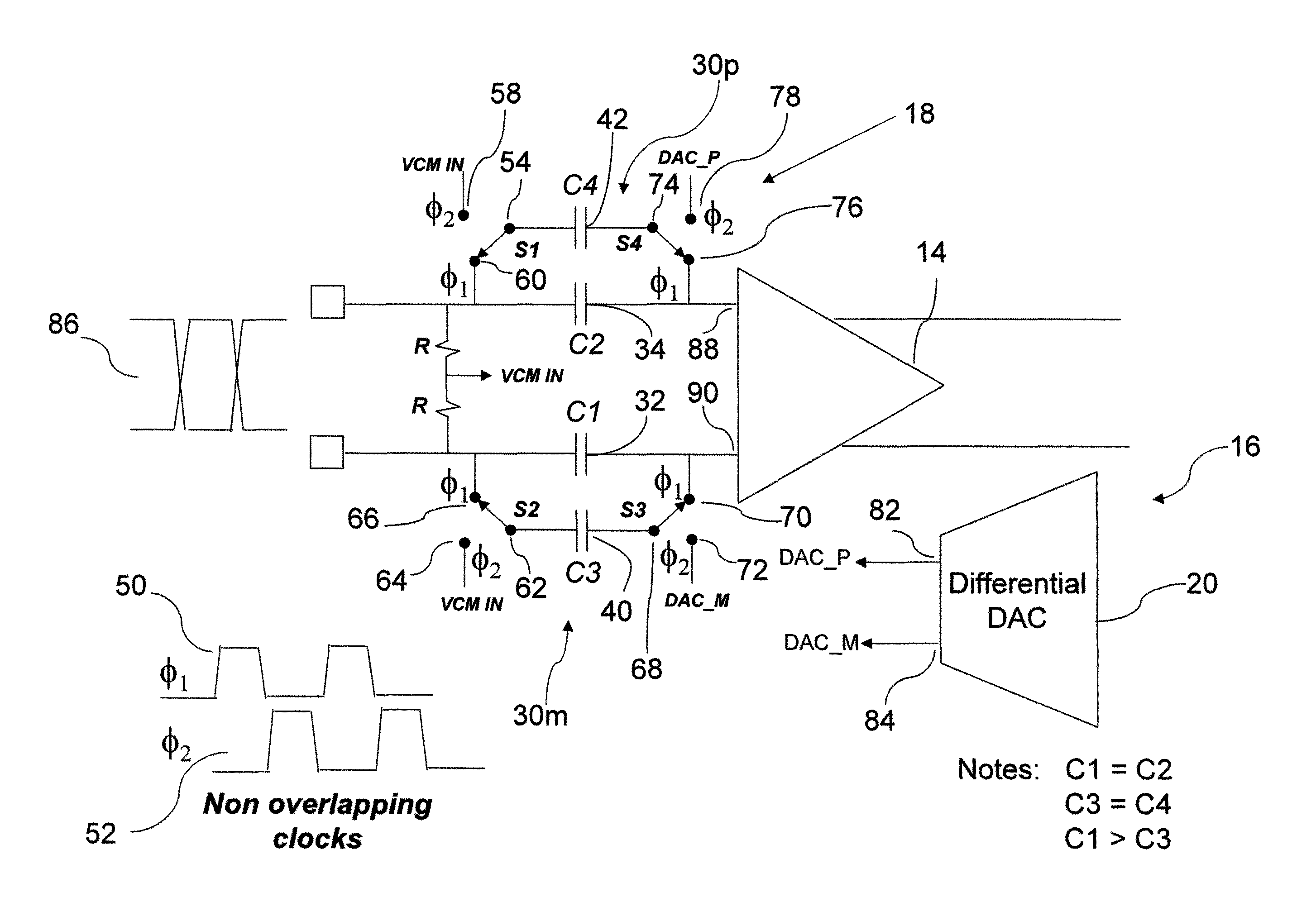
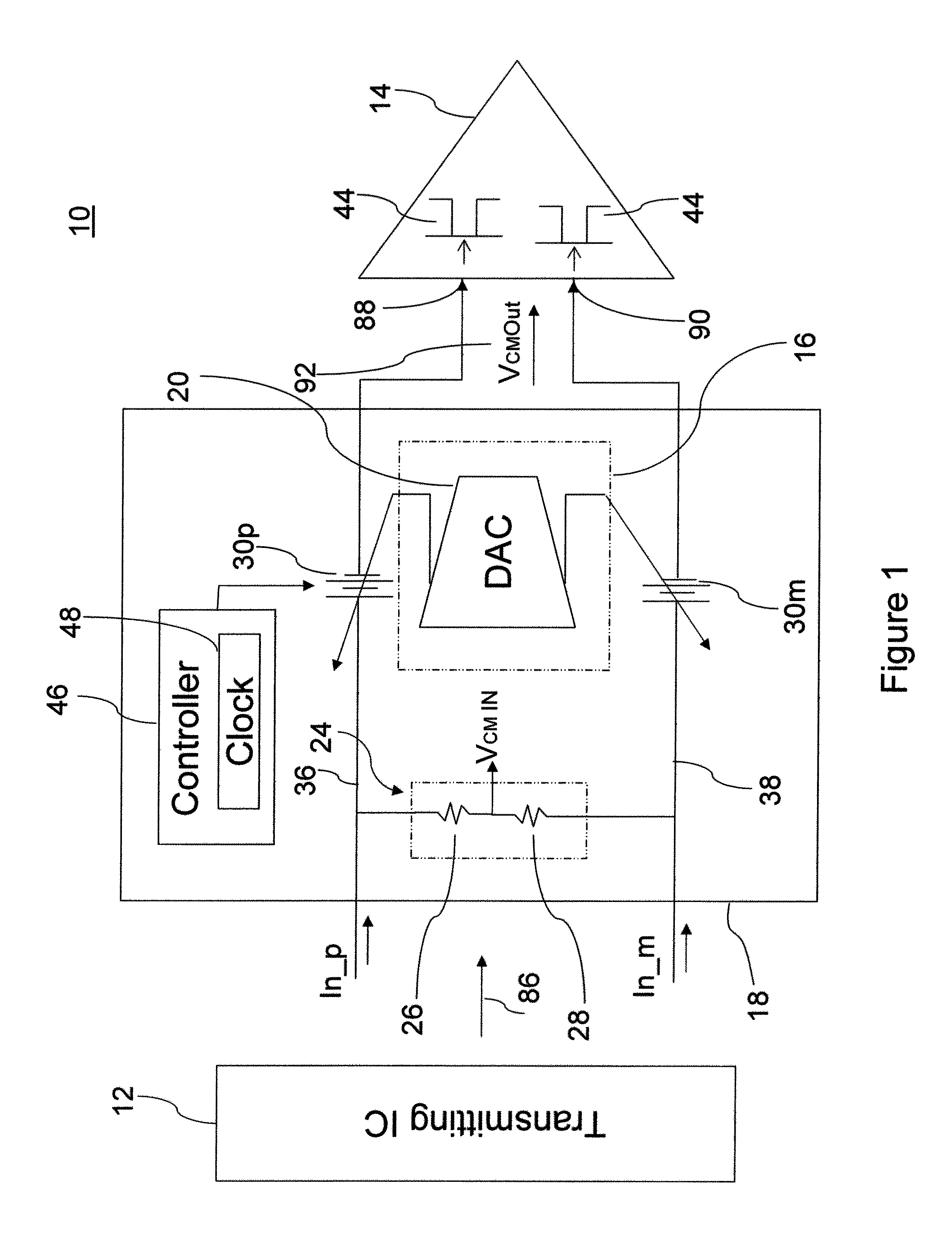
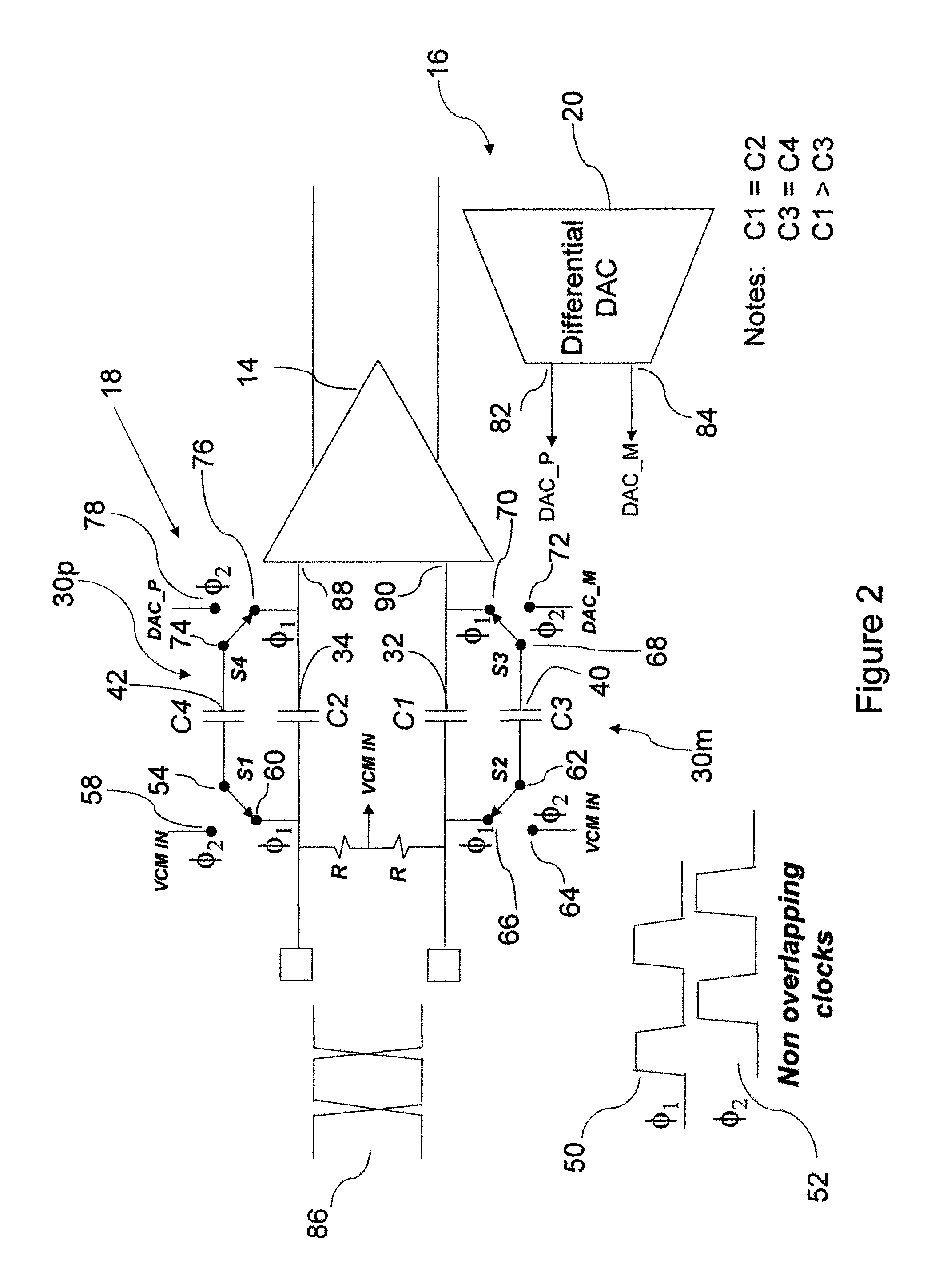
The serial interface operable, for example, to facilitate high speed differential data transfer between integrated circuits provides level shifting of an incoming data signal using a switched capacitor technique which level shifts the common mode voltage with minimal attenuation and minimal reduction of bandwidths. The serial interface also includes a DC offset correction loop of the input data receiver path. The level shifting circuit operates by sensing the incoming common mode voltage of a differential data signal with a resistor divider and sampling the difference between the measured input common mode voltage and desired input differential voltages generated by a differential DAC in the DC offset correction loop on two small capacitors. The small capacitors are switched across larger in-signal-path capacitors cyclically, so that over time a charge will build up to give the desired level shift to shift the common mode voltage of the incoming signal to the level tolerable by low voltage high speed transistors in the receiving integrated circuit.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
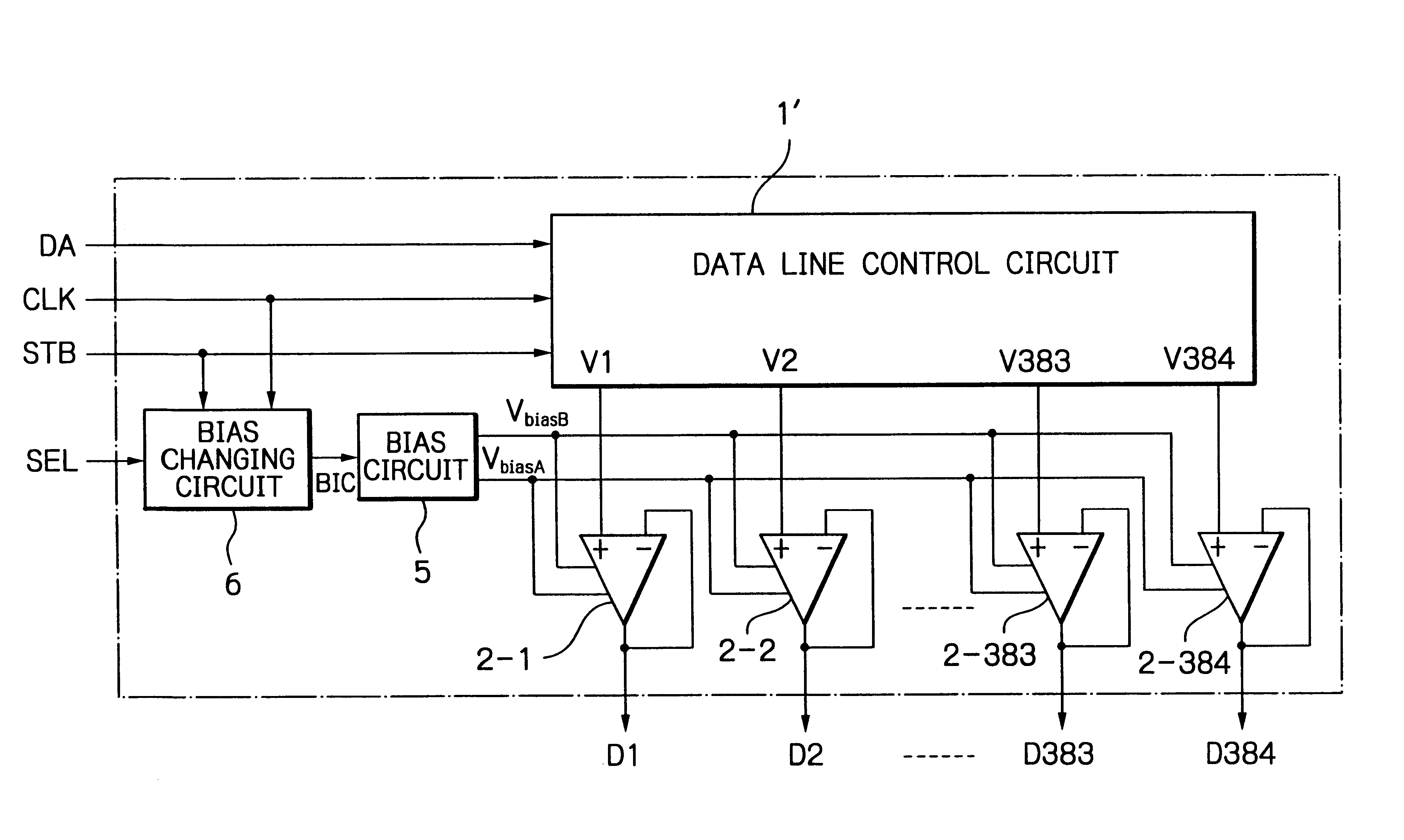
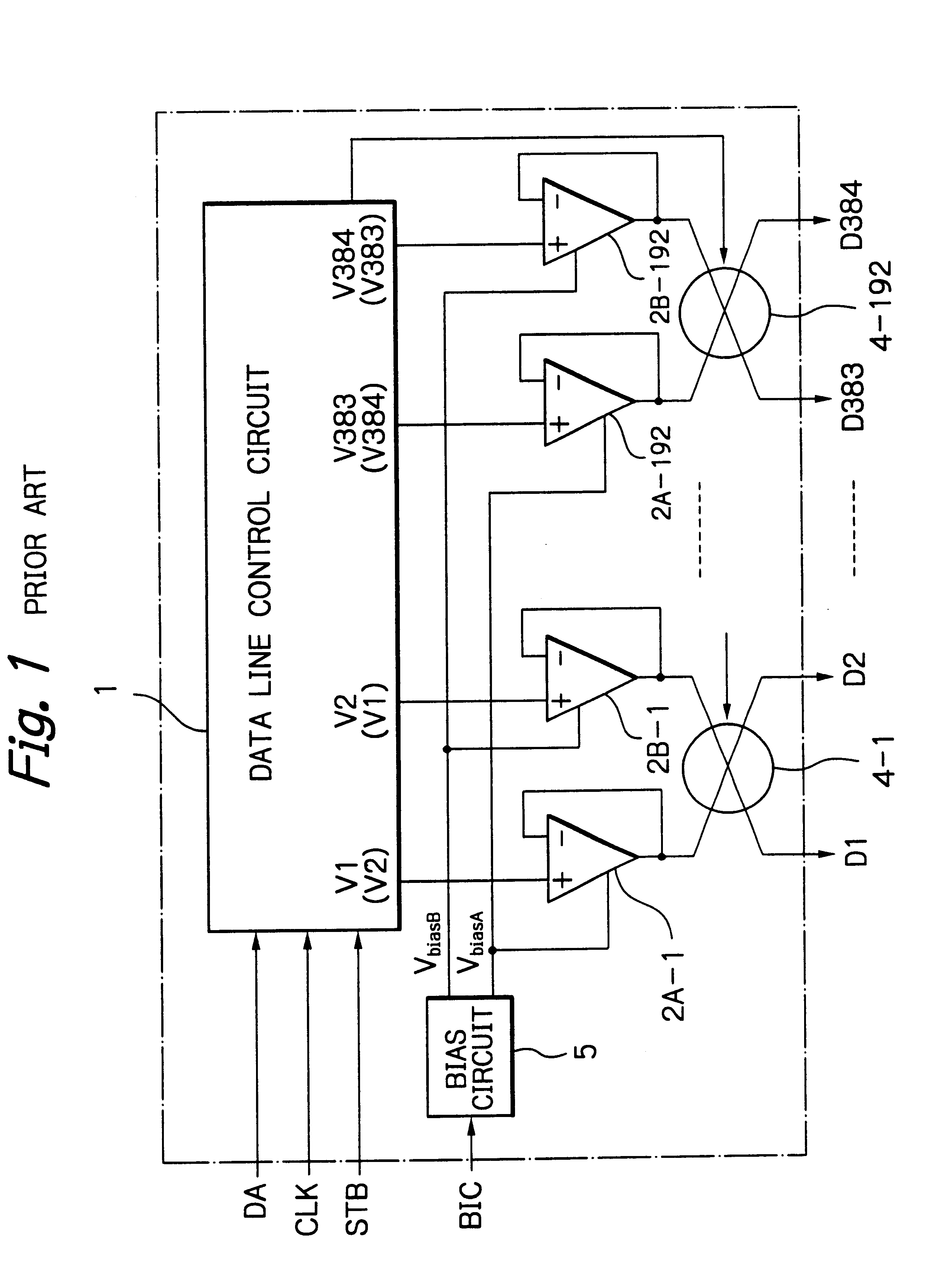
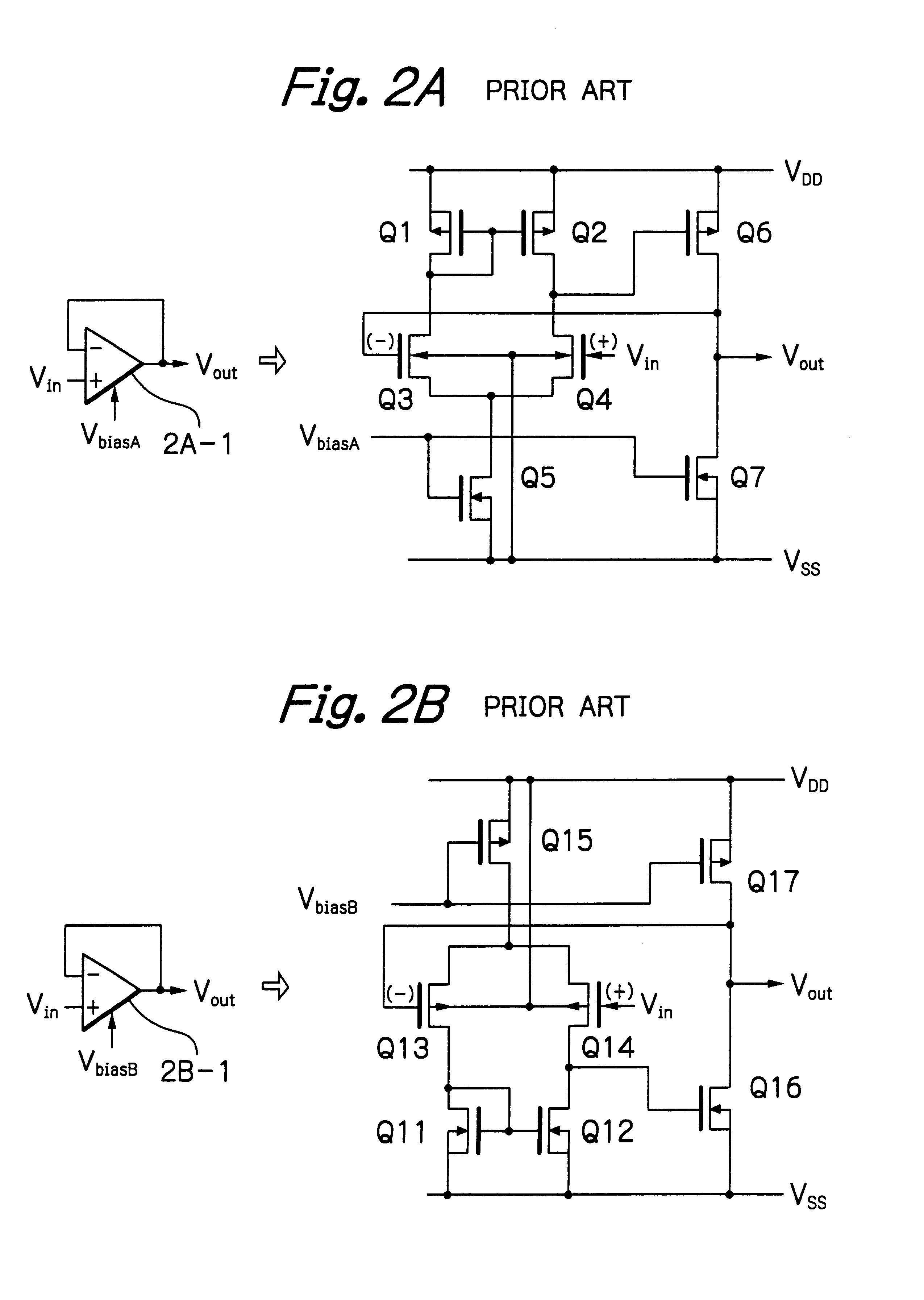
Semiconductor device capable of internally generating bias changing signal
InactiveUS6850232B2Reduce the burden onMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDigital data processing detailsAudio power amplifierControl signal
In a semiconductor device, at least one operational amplifier drives a capacitive load in accordance with a control signal. A bias changing circuit receives the control signal to generate a bias changing signal in synchronization with the control signal dependent upon a width of the control signal. A bias circuit controls a bias current flowing through the operational amplifier in accordance with the bias changing signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
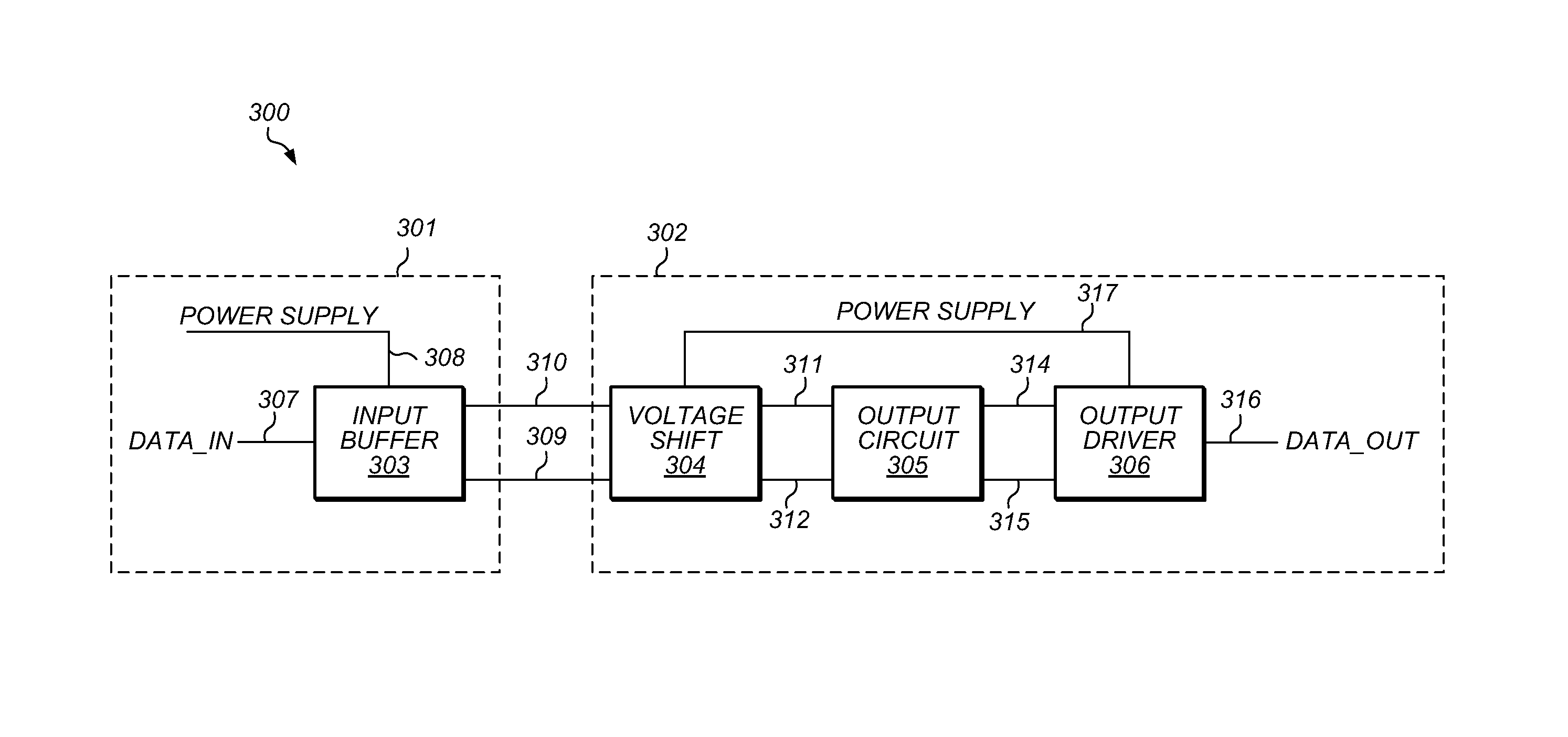
Balanced level shifter with wide operation range
Embodiments of an apparatus are disclosed that may allow for the translation of signals from one power domain to another with well-balanced rise and fall times over a wide operational range. The apparatus may include an input buffer, a voltage shift circuit, and output circuit, and an output driver. The input buffer may be configured to generate a buffered version and delayed inverted version of an external signal at a first voltage level. The voltage shift circuit may be configured to generate two internal signals at a second voltage level dependent upon the output signals of the input buffer. The output circuit may be configured to generate two output driver signals at the second voltage level dependent upon the output signals of the voltage shift circuit. The output driver circuit may be configured to generate an output signal at the second voltage level dependent on the two output driver signals.
Owner:APPLE INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS7053670B2Data signal is preventedAccurate transferMultiple input and output pulse circuitsBaseband system detailsCapacitanceDifferential signaling
Disclosed herewith is a semiconductor integrated circuit provided with a differential input circuit that can transmit data signals fast to an internal circuit free from distortion of their waveforms without increasing the subject chip in size. The differential input circuit is provided with a pair of first differential input transistors used to amplify mainly the low frequency components of those input signals and having gate terminals connected to a pair of input terminals that receive inputs of differential signals respectively, as well as a pair of second differential input transistors used mainly to amplify high frequency components of those input signals and having control terminals connected to a pair of input terminals that receive inputs of differential signals respectively through capacitance elements. The pairs of first and second differential transistors are connected to each other through a differential connection point (common source).
Owner:ABLIC INC
Apparatus for receiving wide-based pulse signal in communication channel using human body
ActiveUS20070211828A1High voltage gainReception sensitivity is degradedModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionImpedance matchingUsability
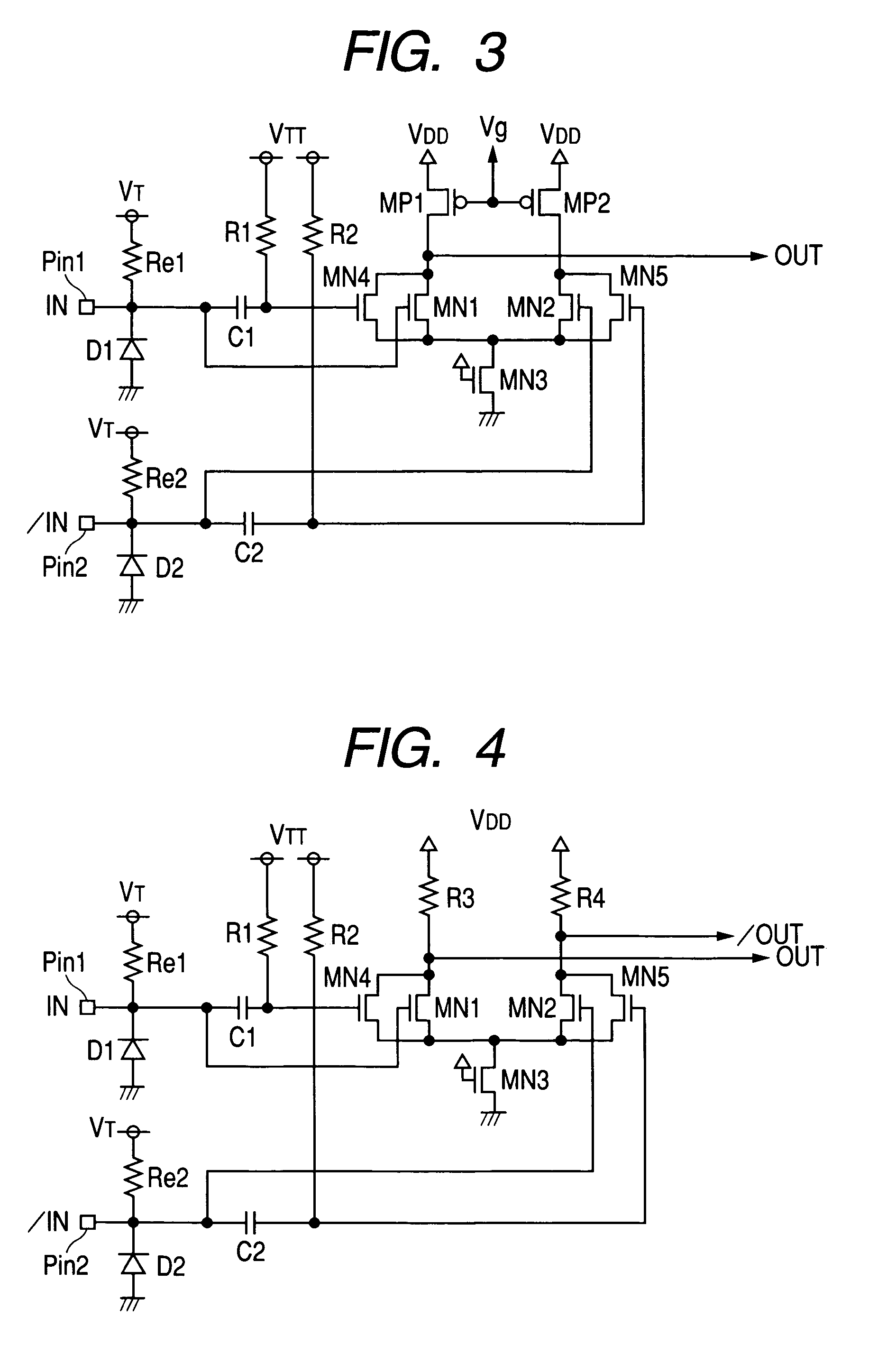
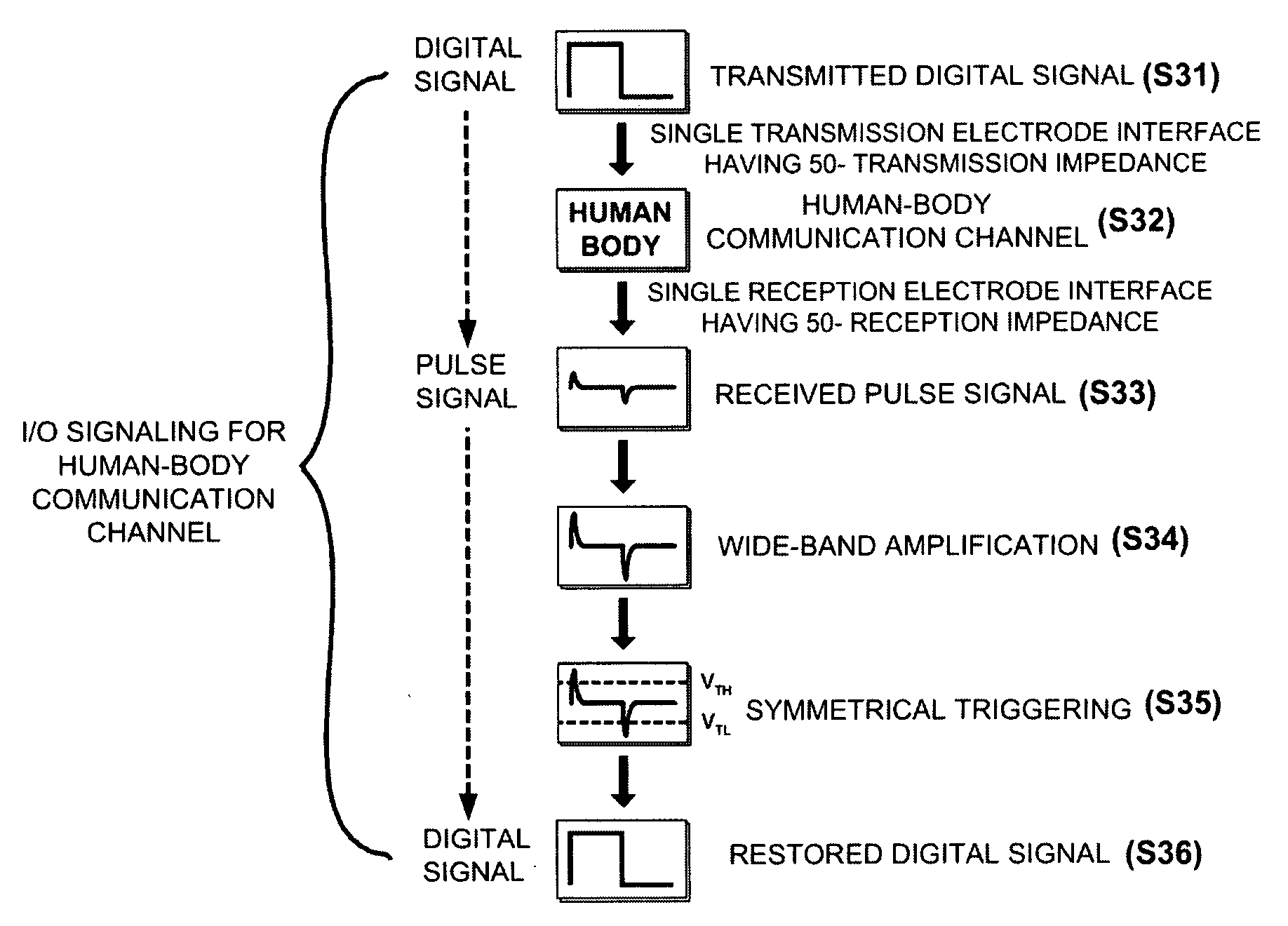
Disclosed herein is an apparatus for receiving a wide-band pulse signal in a communication channel using a human body. When a weak wide-band pulse signal, which is output from a communication channel using a human body as a data transmission medium, is restored to a digital signal, it is possible to accomplish low power consumption and high data transmission rate using a wide-band symmetrical triggering technology using 50-Ω impedance matching, wide-band amplification and symmetrical threshold voltages. In addition, since only a single signal electrode is used, it is possible to provide an apparatus having usability, wearability and miniaturization. In addition, it is possible to remove necessities of an external reference voltage to reduce area consumption and to simply adjust a feedback resistor to easily adjust the reception sensitivity according to a communication distance.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
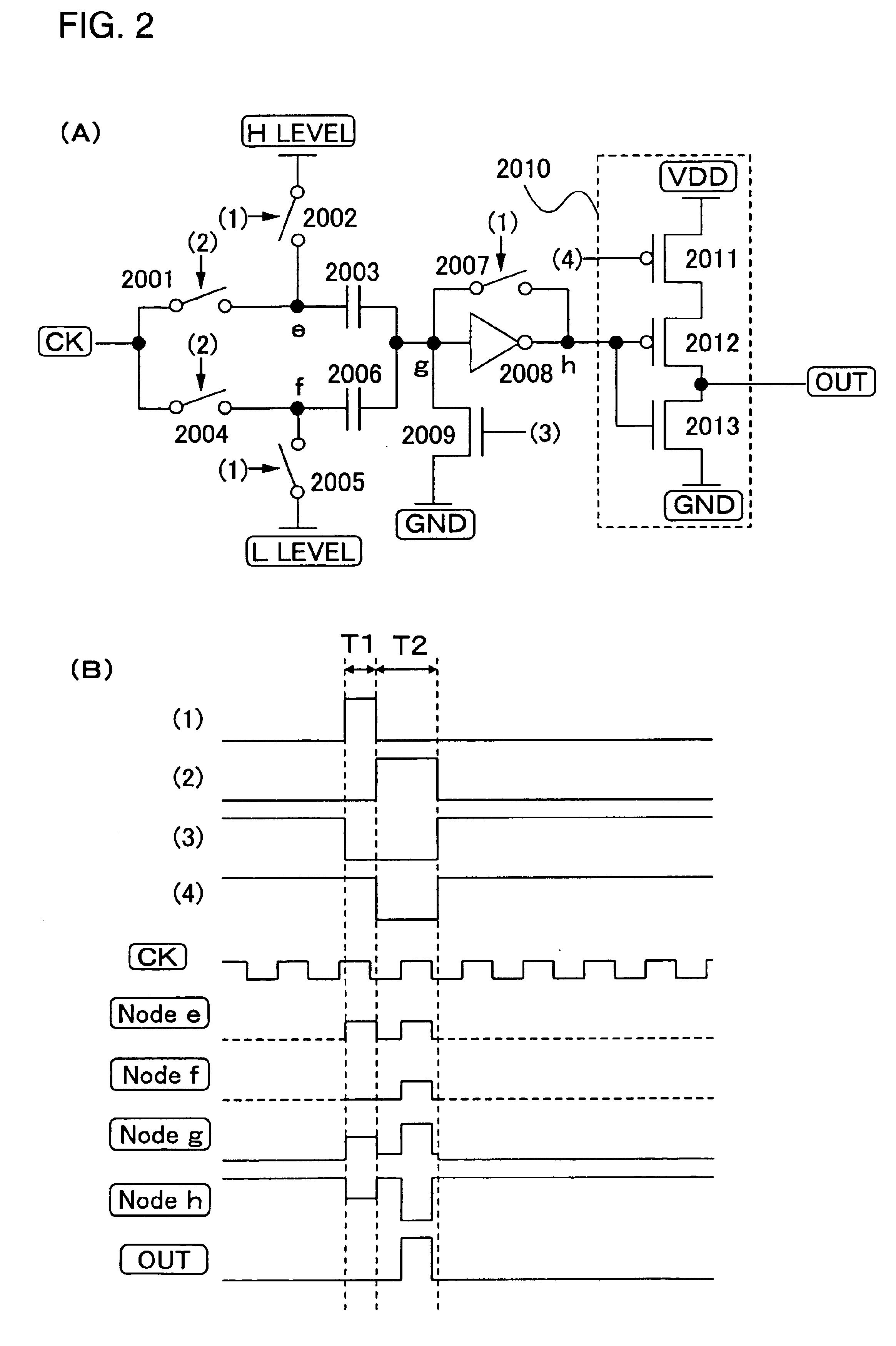
Shift register and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20050134325A1Reduce power consumptionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsStatic indicating devicesShift registerLow voltage
A low power consumption shift register which inputs a CK signal with a low voltage with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors. In the invention, an input portion of an inverter is set at a threshold voltage thereof and a CK signal is inputted to the input portion of the inverter through a capacitor means. In this manner, the CK signal is amplified, which is sent to the shift register. That is, by obtaining the threshold potential of the inverter, the shift register which operates with almost no effect of variation in characteristics of transistors can be provided. A level shifter of the CK signal is generated from an output pulse of the shift register, therefore, the low power consumption shift register having the level shifter which flows a shoot-through current for a short period can be provided
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com