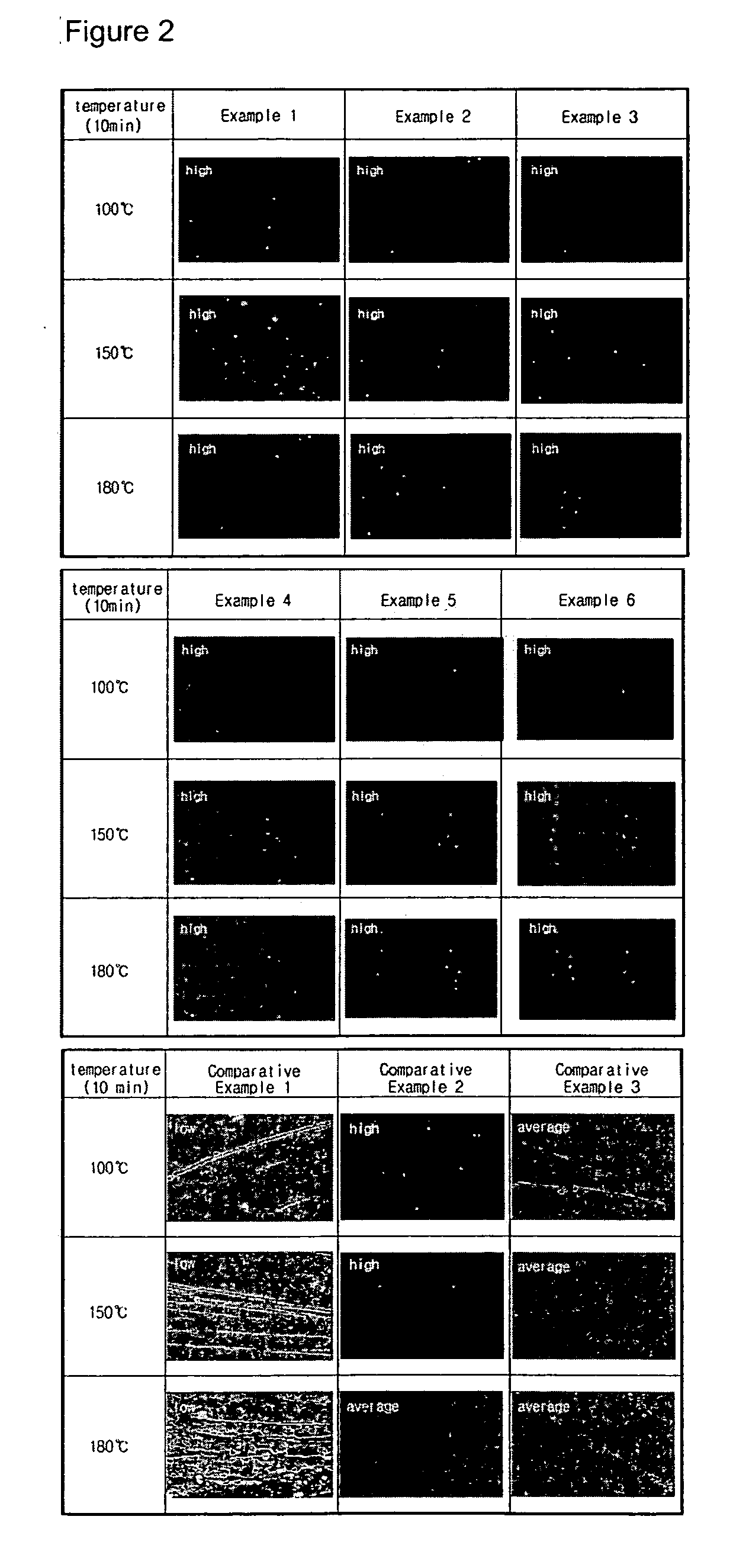
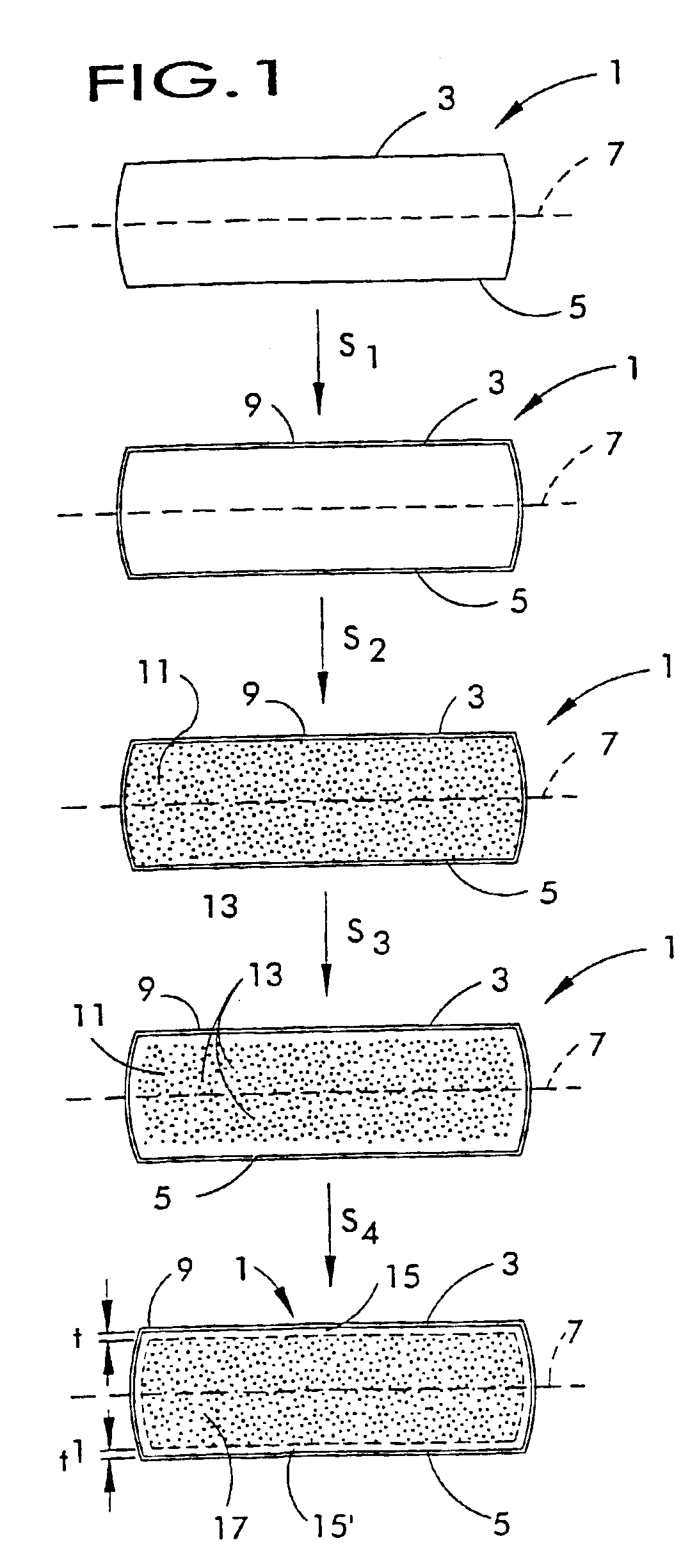
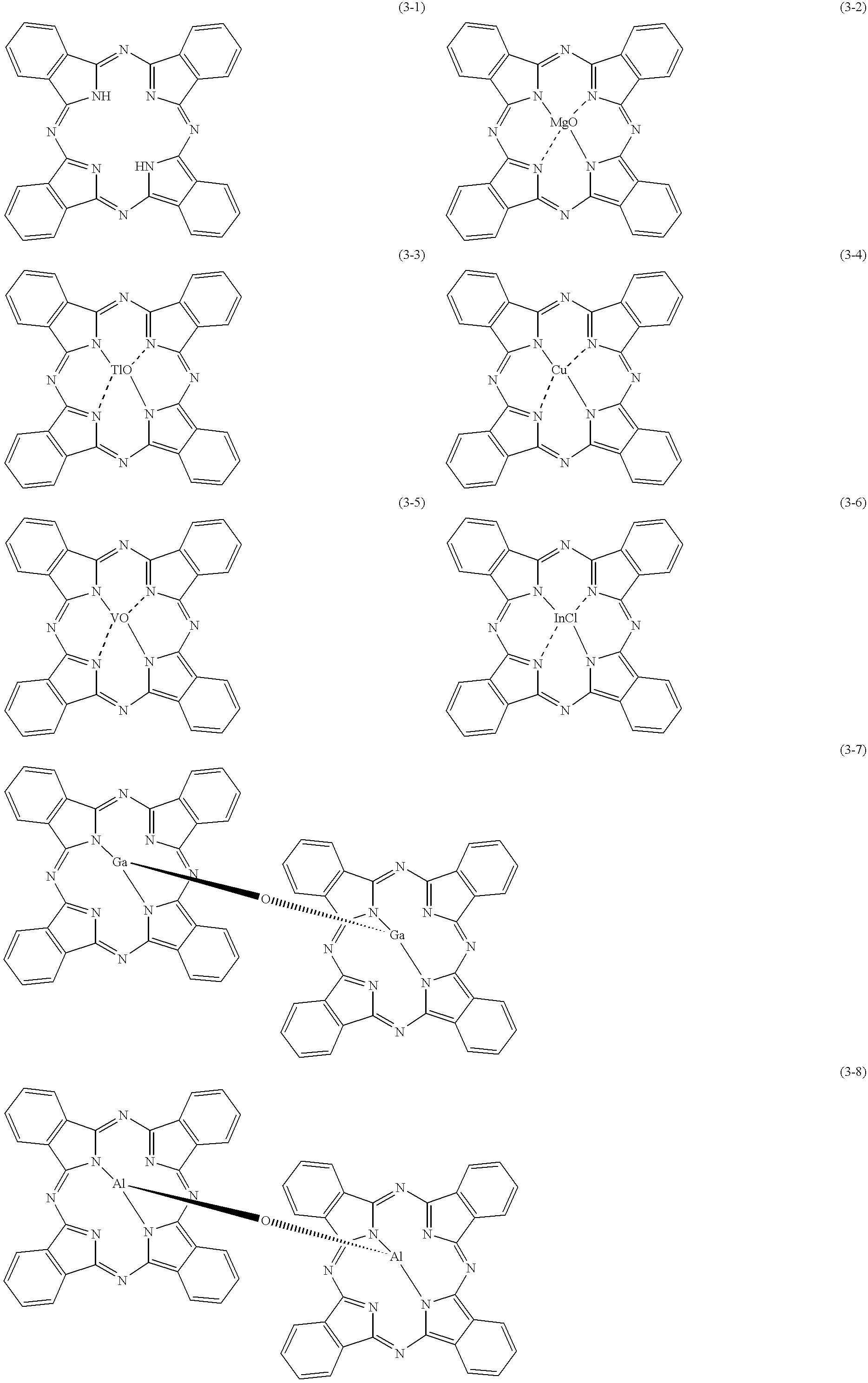
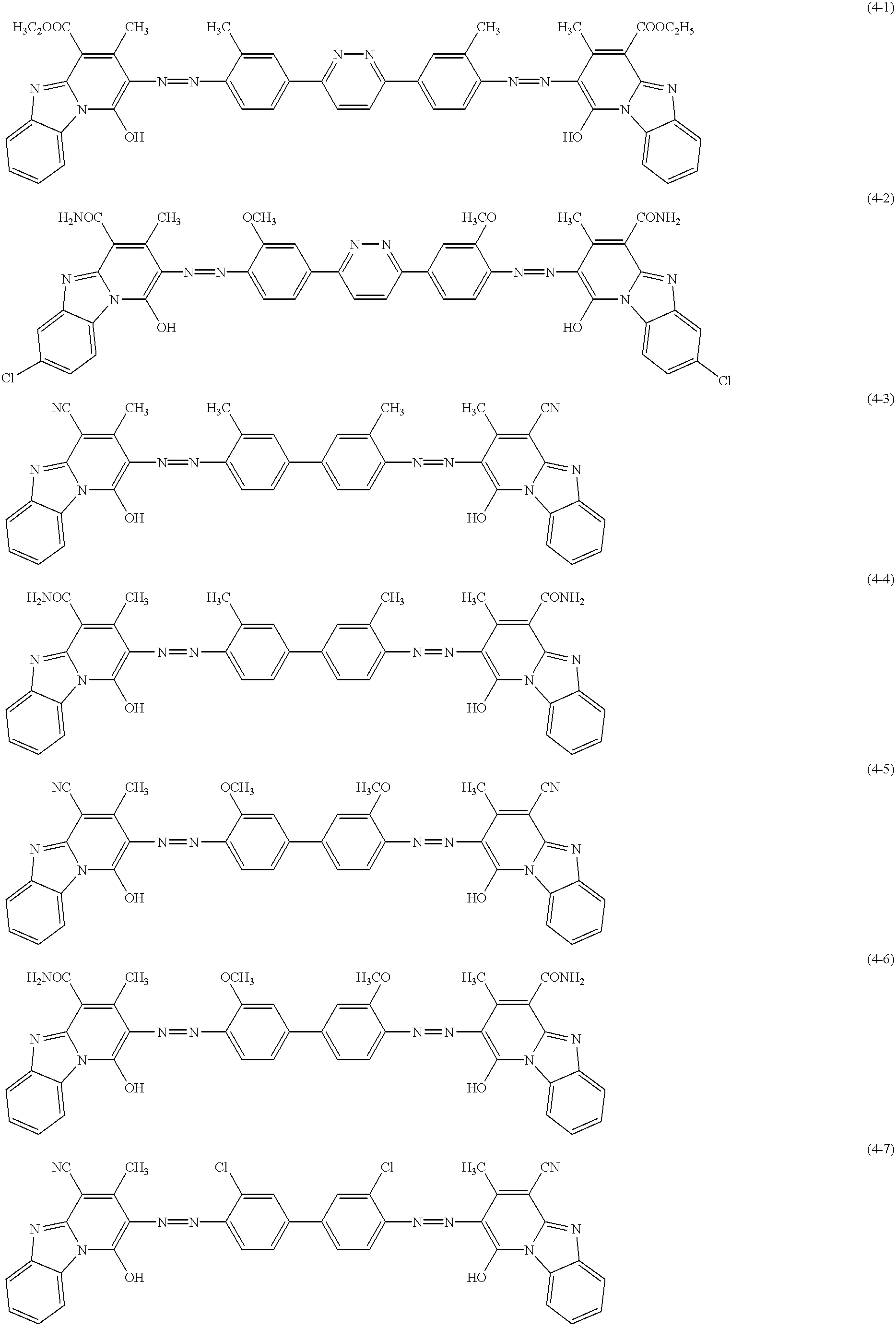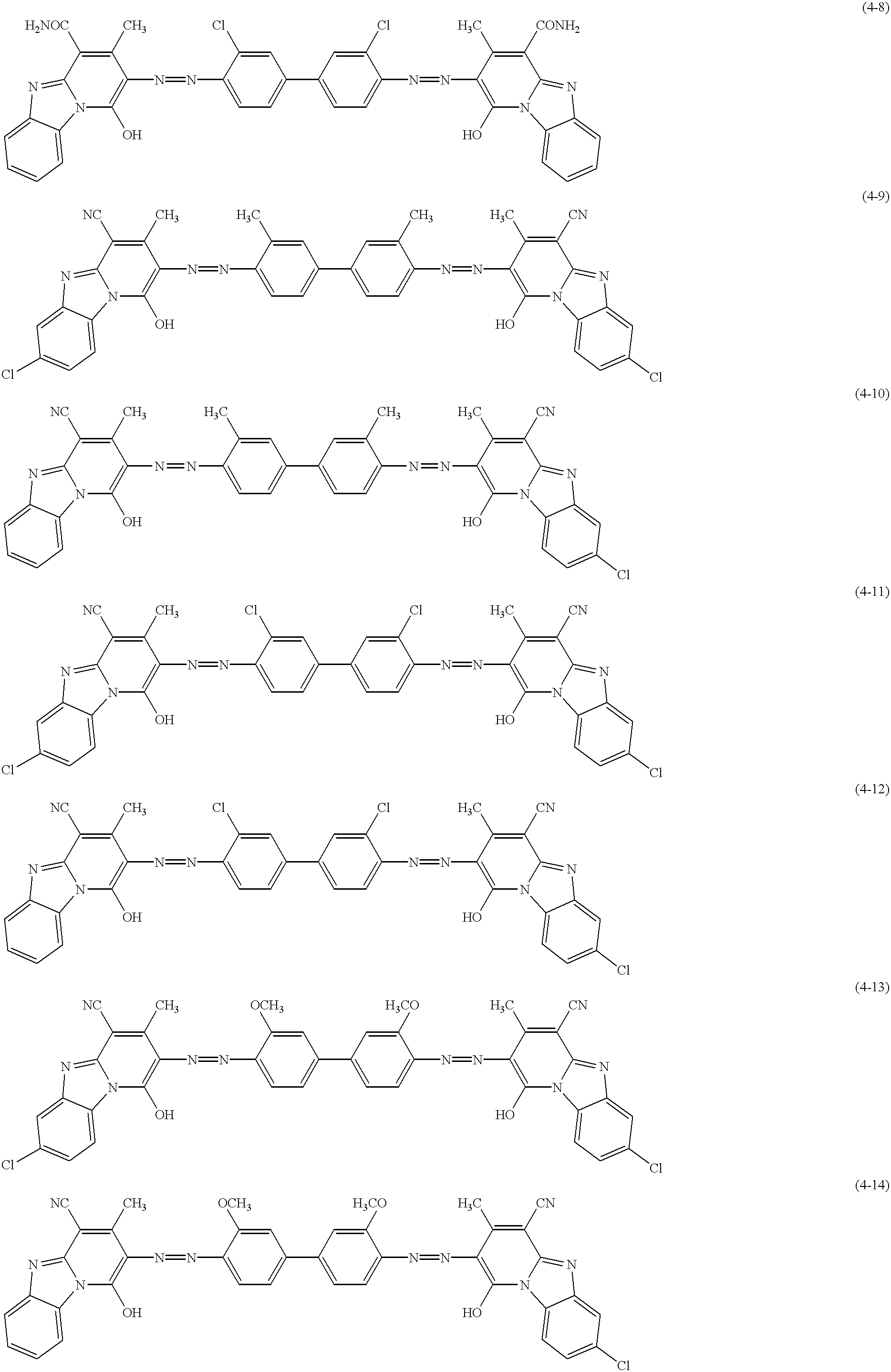Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
139 results about "Vacancy defect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
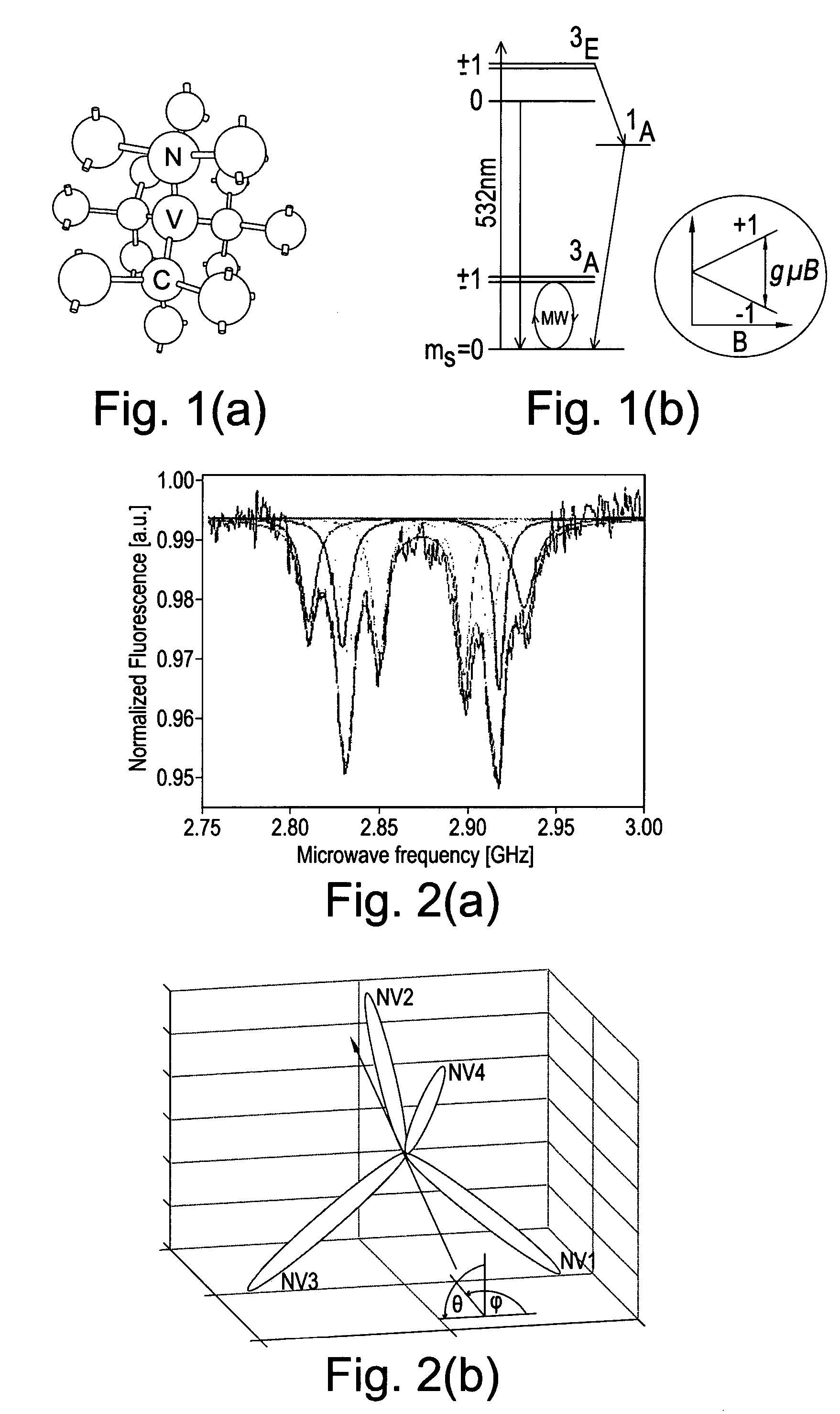
In crystallography, a vacancy is a type of point defect in a crystal. Crystals inherently possess imperfections, sometimes referred to as crystalline defects. A defect in which an atom is missing from one of the lattice sites is known as a "vacancy" defect. It is also known as a Schottky defect, although in ionic crystals the concepts are not identical. Vacancies occur naturally in all crystalline materials.
Aluminum oxide material for optical data storage
InactiveUS6846434B2Increase of write/read rateHigh data storage densityPolycrystalline material growthPhotosensitive materialsVacancy defectDopant
The present invention provides aluminum oxide crystalline materials including dopants and oxygen vacancy defects and methods of making such crystalline materials. The crystalline materials of the present invention have particular utility in optical data storage applications.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
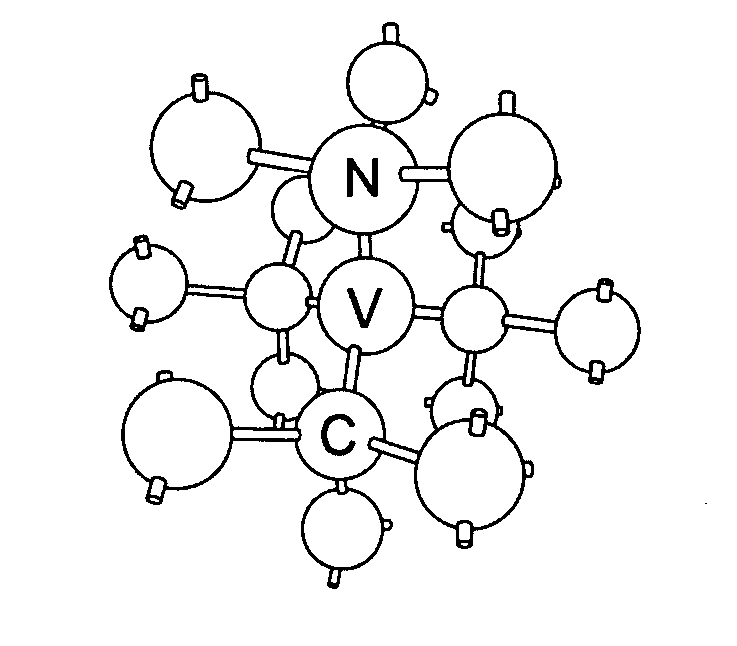
Diamond sensors, detectors, and quantum devices
ActiveUS20140061510A1Improve light outcoupling efficiencyEnhanced couplingPolycrystalline material growthUltra-high pressure processesVacancy defectPreferential alignment
A single crystal synthetic CVD diamond material comprising: a growth sector; and a plurality of point defects of one or more type within the growth sector, wherein at least one type of point defect is preferentially aligned within the growth sector, wherein at least 60% of said at least one type of point defect shows said preferential alignment, and wherein the at least one type of point defect is a negatively charged nitrogen-vacancy defect (NV−).
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
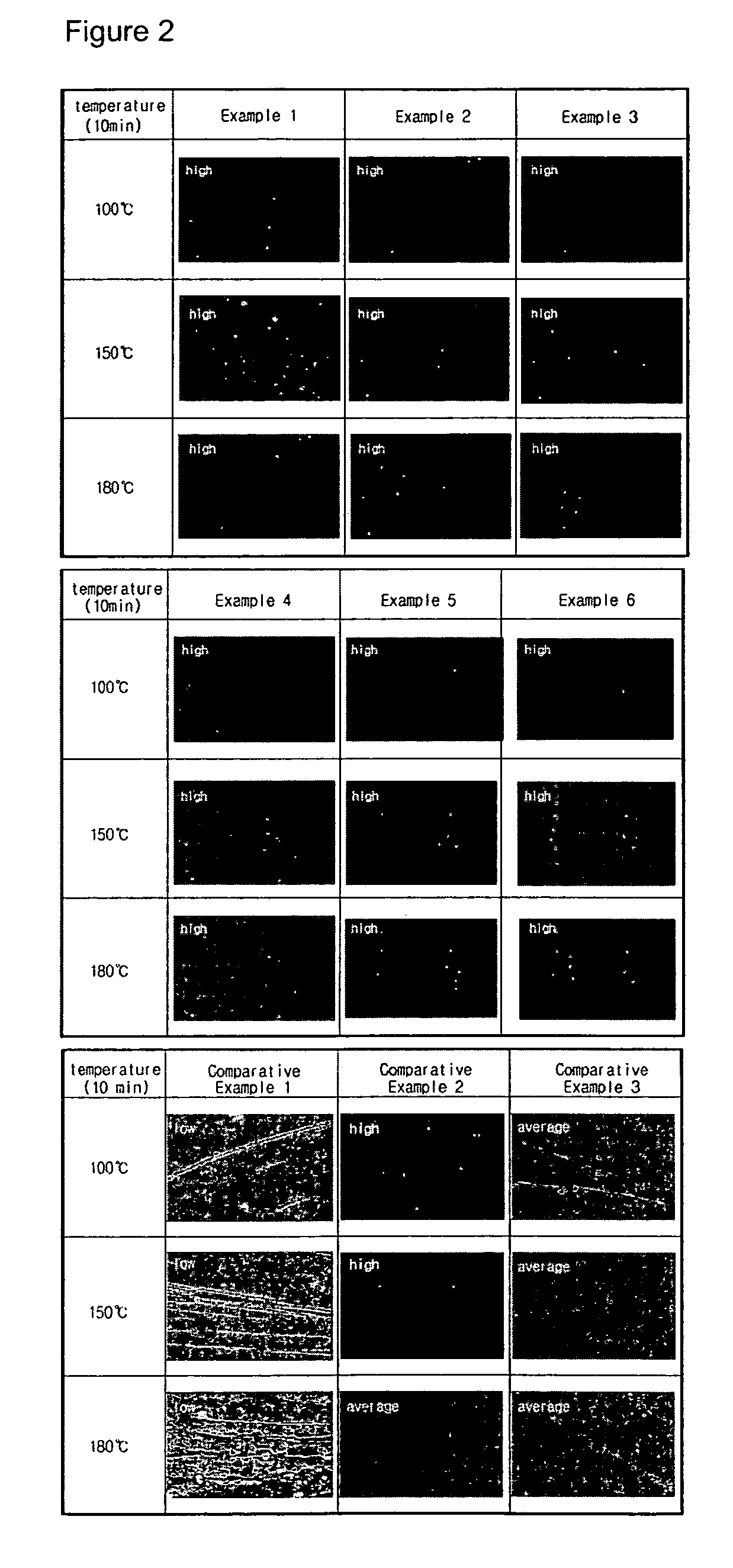
Single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material
ActiveUS20140335339A1Improve optical qualityReduce concentrationPolycrystalline material growthSynthetic resin layered productsPhotoluminescenceSingle crystal
A single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material comprising: a total as-grown nitrogen concentration equal to or greater than 5 ppm, and a uniform distribution of defects, wherein said uniform distribution of defects is defined by one or more of the following characteristics: (i) the total nitrogen concentration, when mapped by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm using an analysis area of 10 μm or less, possesses a point-to-point variation of less than 30% of an average total nitrogen concentration value, or when mapped by SIMS over an area equal to or greater than 200×200 μm using an analysis area of 60 μm or less, possesses a point-to-point variation of less than 30% of an average total nitrogen concentration value; (ii) an as-grown nitrogen-vacancy defect (NV) concentration equal to or greater than 50 ppb as measured using 77K UV-visible absorption measurements, wherein the nitrogen-vacancy defects are uniformly distributed through the synthetic single crystal CVD diamond material such that, when excited using a 514 nm laser excitation source of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at room temperature using a 50 mW 46 continuous wave laser, and mapped over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm with a data interval less than 10 μm there is a low point-to-point variation wherein the intensity area ratio of nitrogen vacancy photoluminescence peaks between regions of high photoluminescent intensity and regions of low photolominescent intensity is <2× for either the 575 nm photoluminescent peak (NV0) or the 637 nm photoluminescent peak (NV); (iii) a variation in Raman intensity such that, when excited using a 514 nm laser excitation source (resulting in a Raman peak at 552.4 nm) of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at room temperature using a 50 mW continuous wave laser, and mapped over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm with a data interval less than 10 μm, there is a low point-to-point variation wherein the ratio of Raman peak areas between regions of low Raman intensity and high Raman intensity is <1.25×; (iv) an as-grown nitrogen-vacancy defect (NV) concentration equal to or greater than 50 ppb as measured using 77K UV-visible absorption measurements, wherein, when excited using a 514 nm excitation source of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at 77K using a 50 mW continuous wave laser, gives an intensity at 575 nm corresponding to NV0 greater than 120 times a Raman intensity at 552.4 nm, and / or an intensity at 637 nm corresponding to NV− greater than 200 times the Raman intensity at 552.4 nm; (v) a single substitutional nitrogen defect (Ns) concentration equal to or greater than 5 ppm, wherein the single substitutional nitrogen defects are uniformly distributed through the synthetic single crystal CVD diamond material such that by using a 1344 cm−1 infrared absorption feature and sampling an area greater than an area of 0.5 mm2, the variation is lower than 80%, as deduced by dividing the standard deviation by the mean value; (vi) a variation in red luminescence intensity, as defined by a standard deviation divided by a mean value, is less than 15%; (vii) a mean standard deviation in neutral single substitutional nitrogen concentration of less than 80%; and (viii) a colour intensity as measured using a histogram from a microscopy image with a mean gray value of greater than 50, wherein the colour intensity is uniform through the single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material such that the variation in gray colour, as characterised by the gray value standard deviation divided by the gray value mean, is less than 40%.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
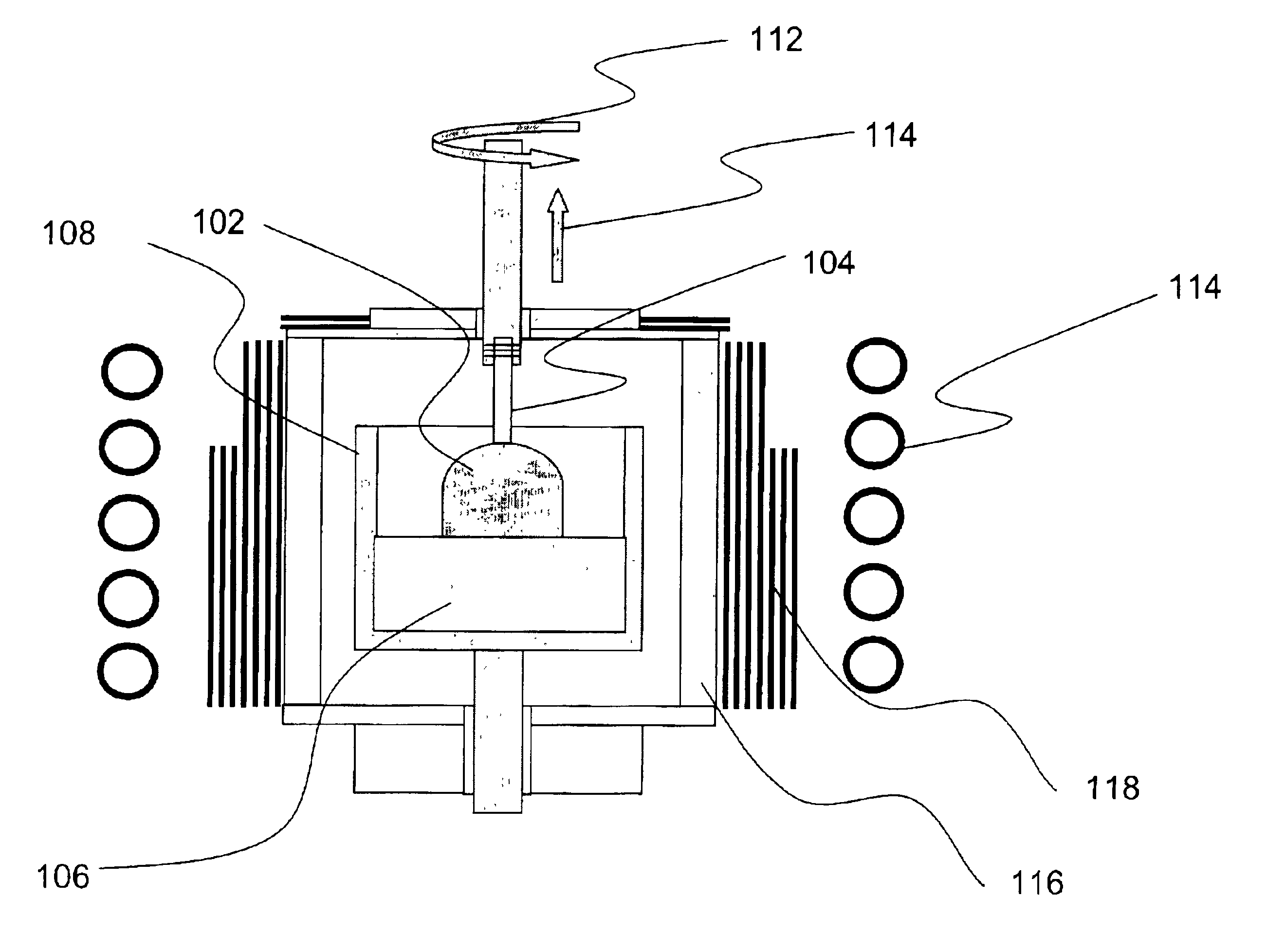
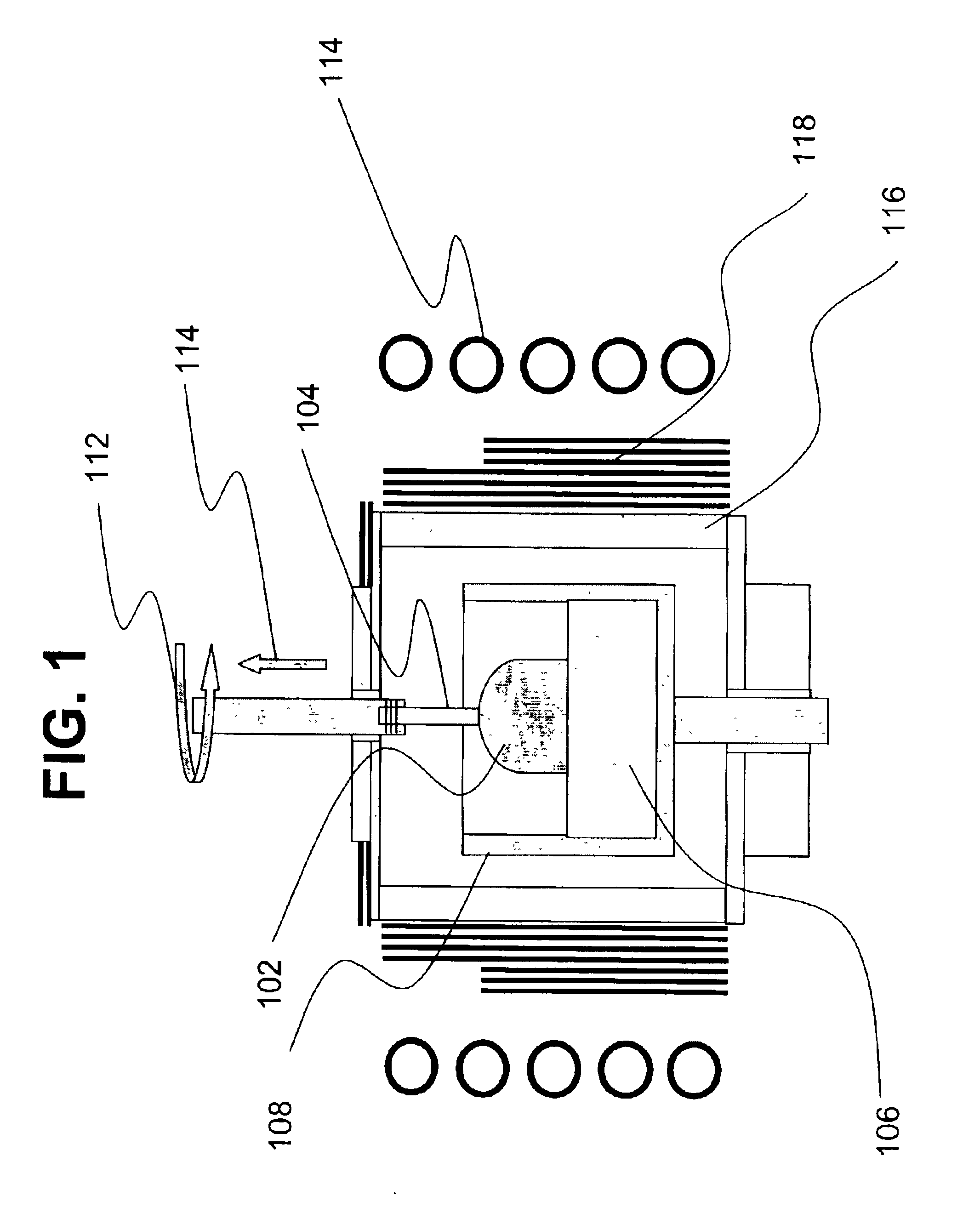
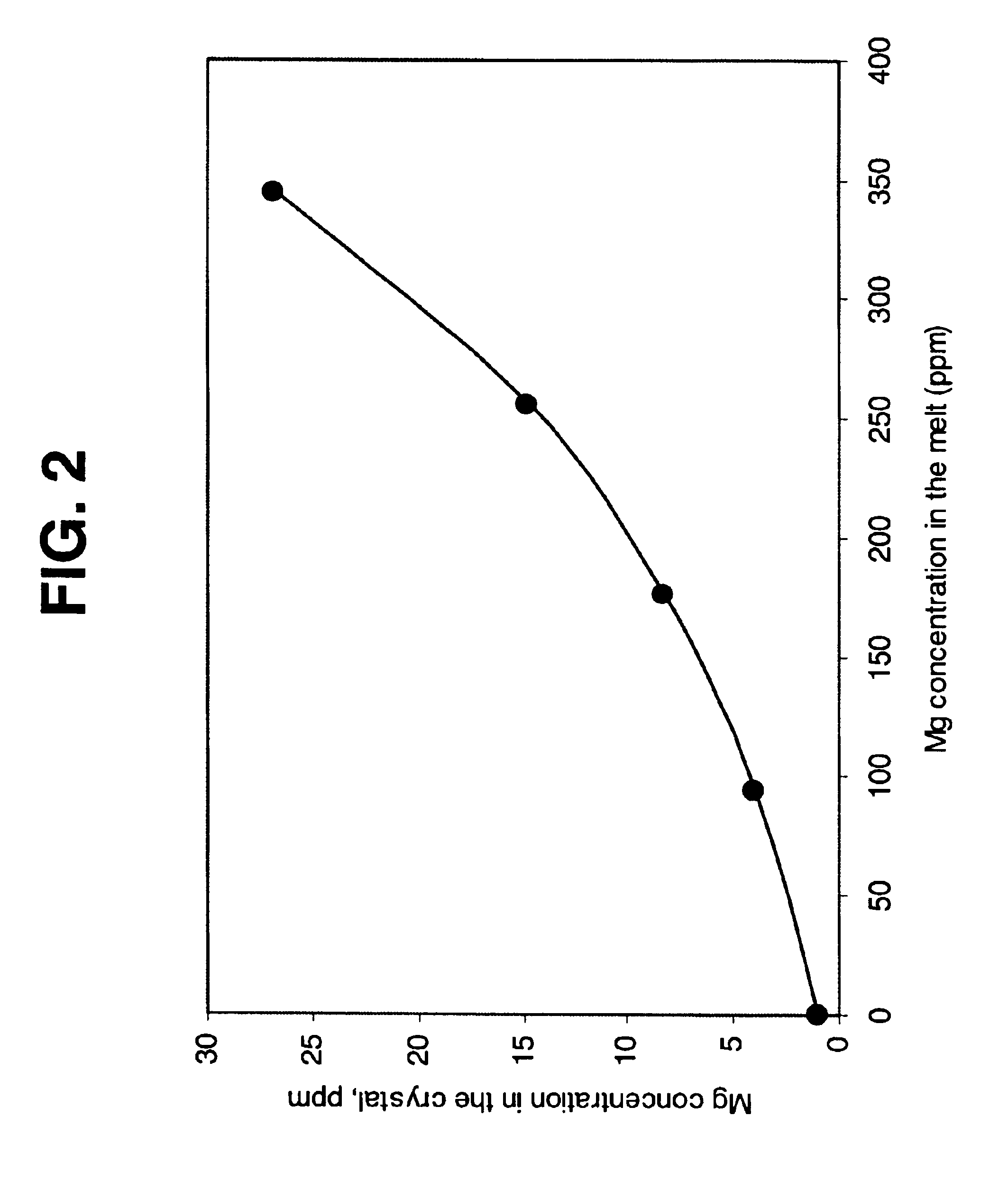
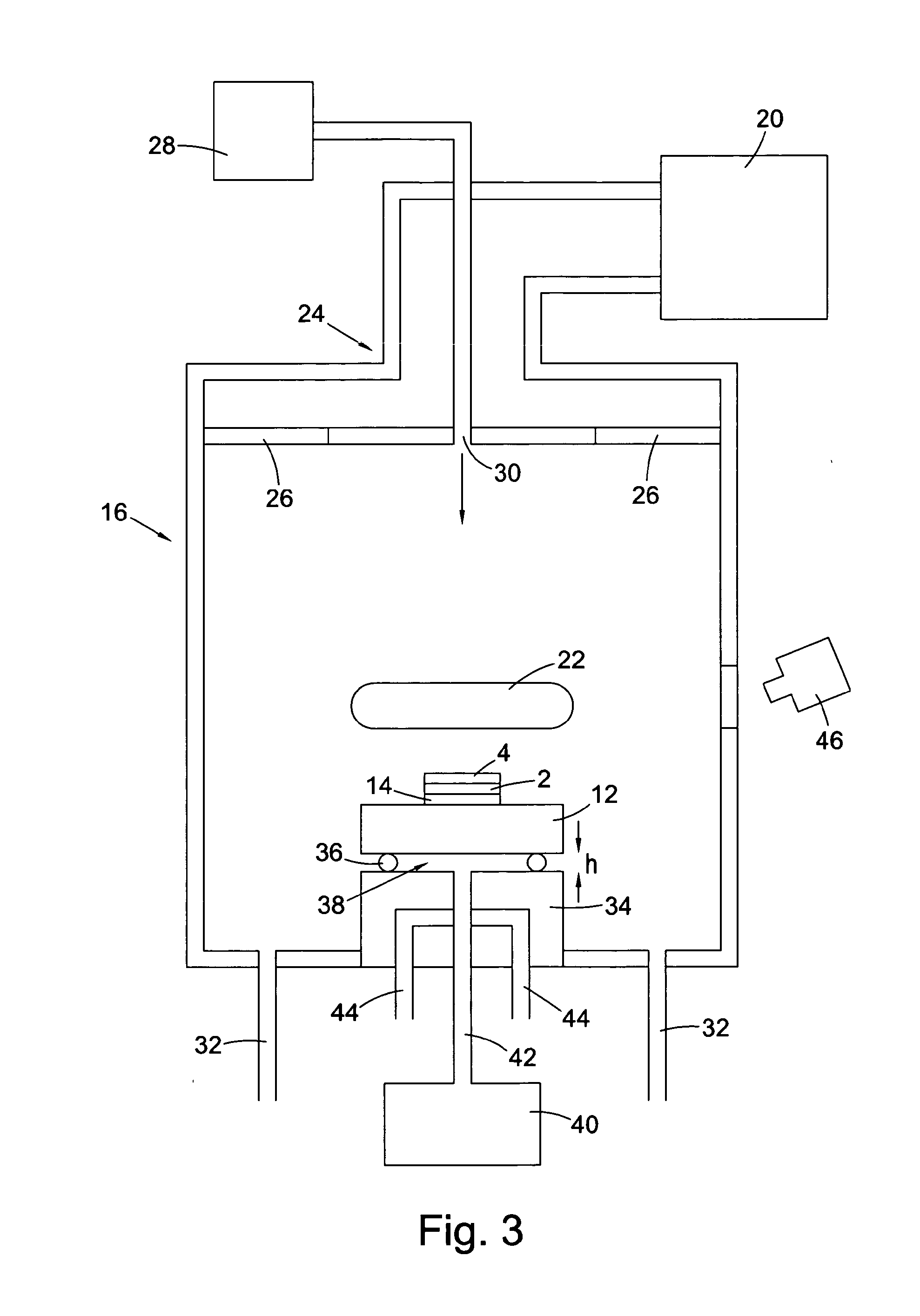
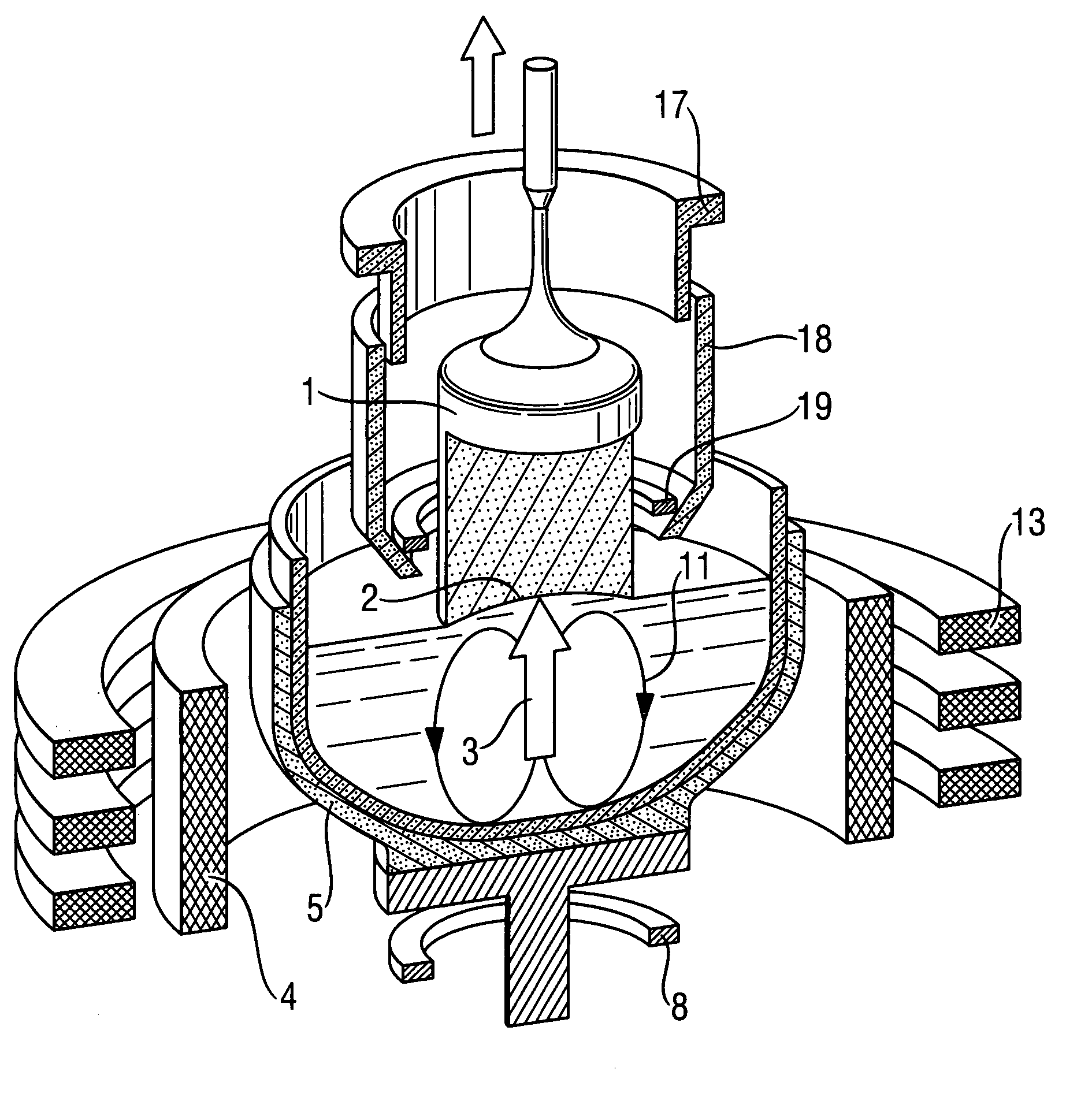
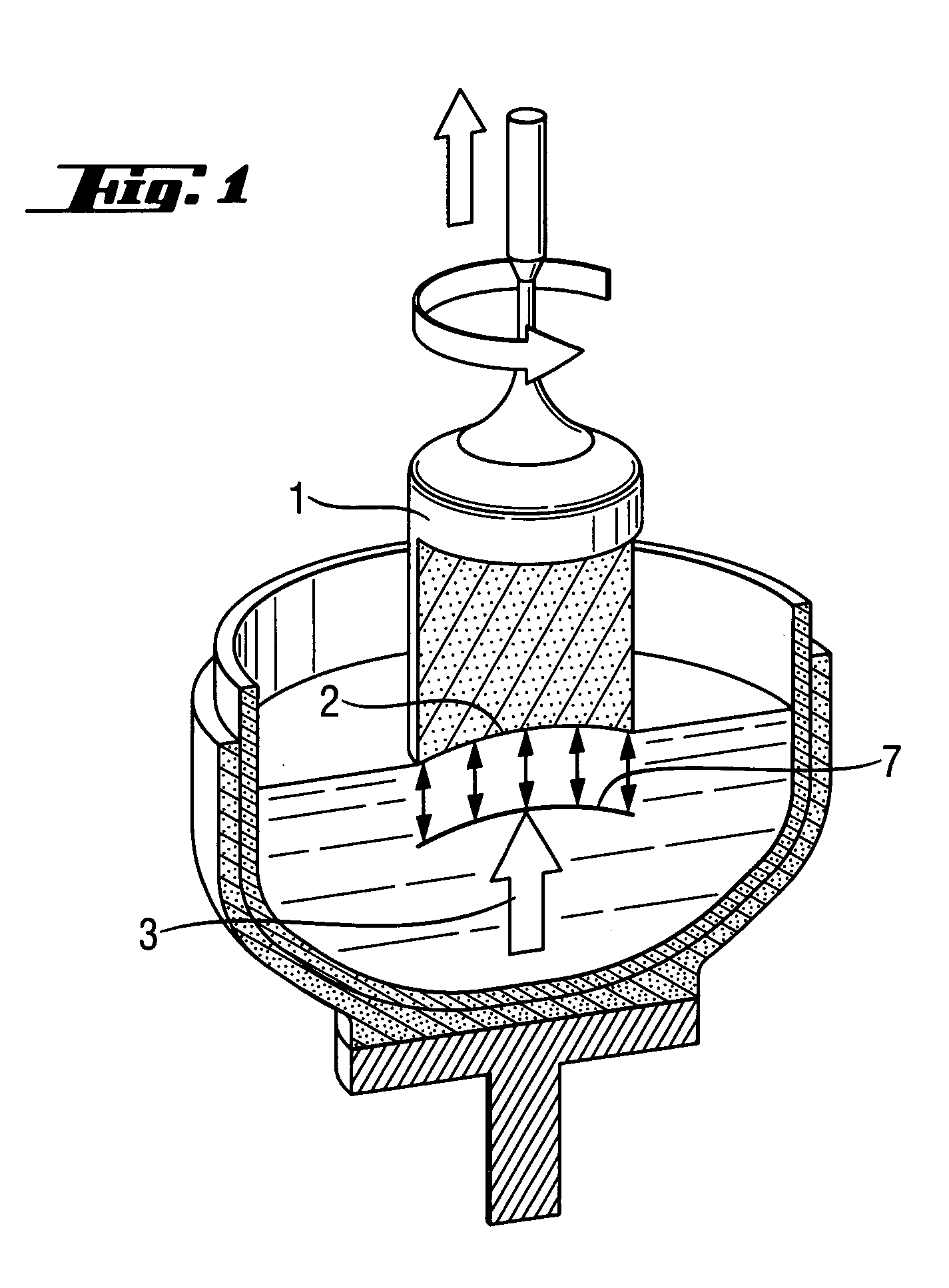
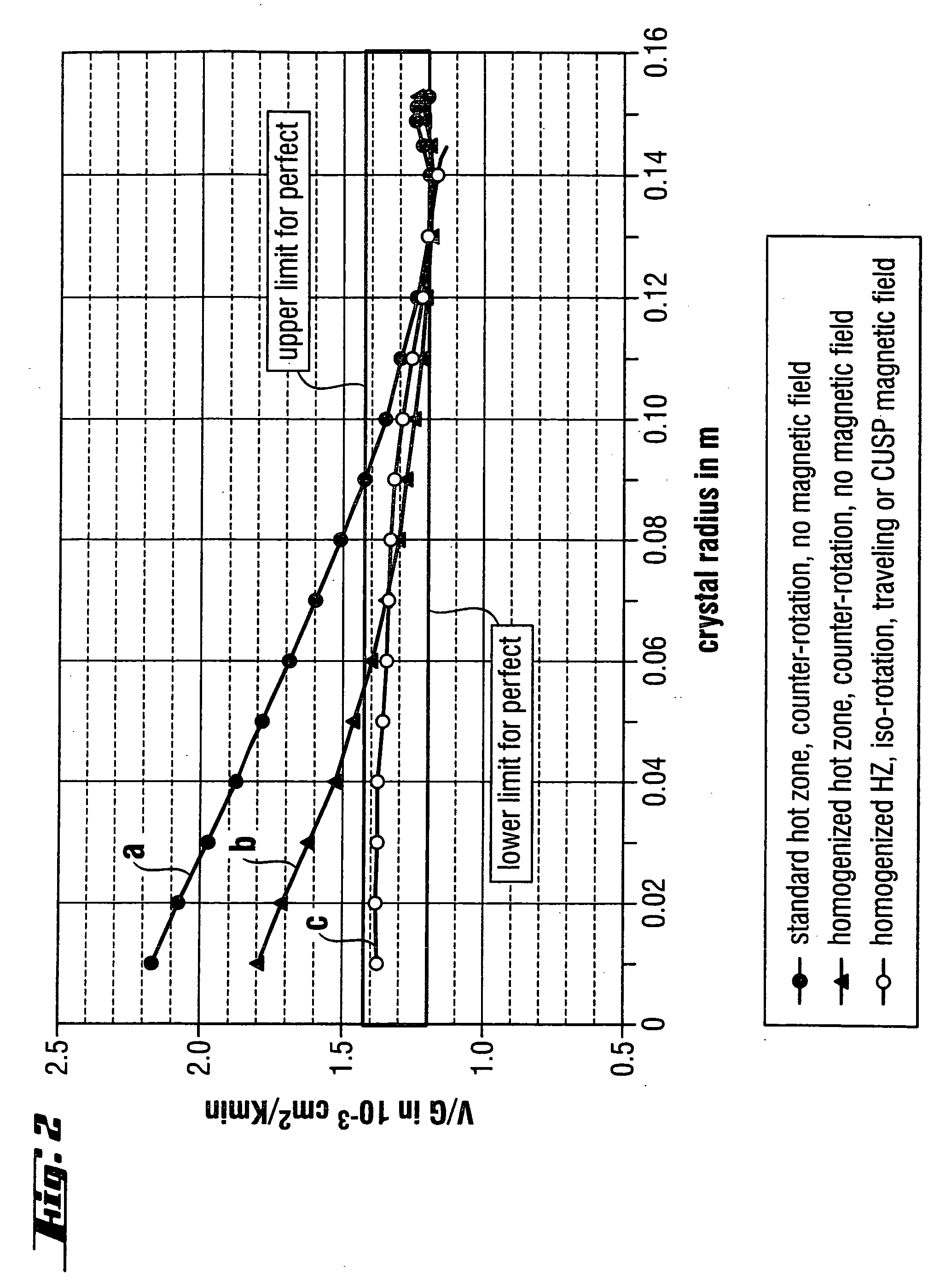
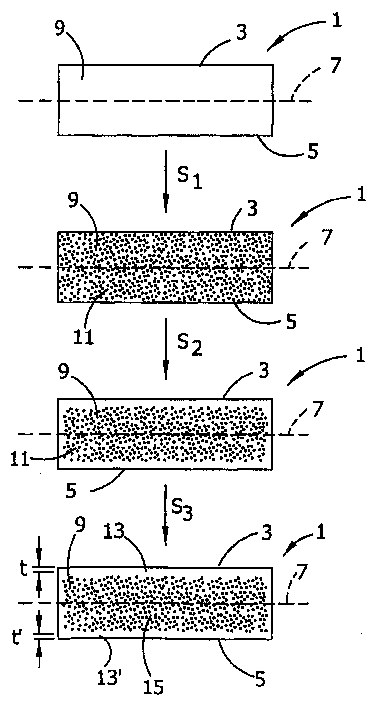
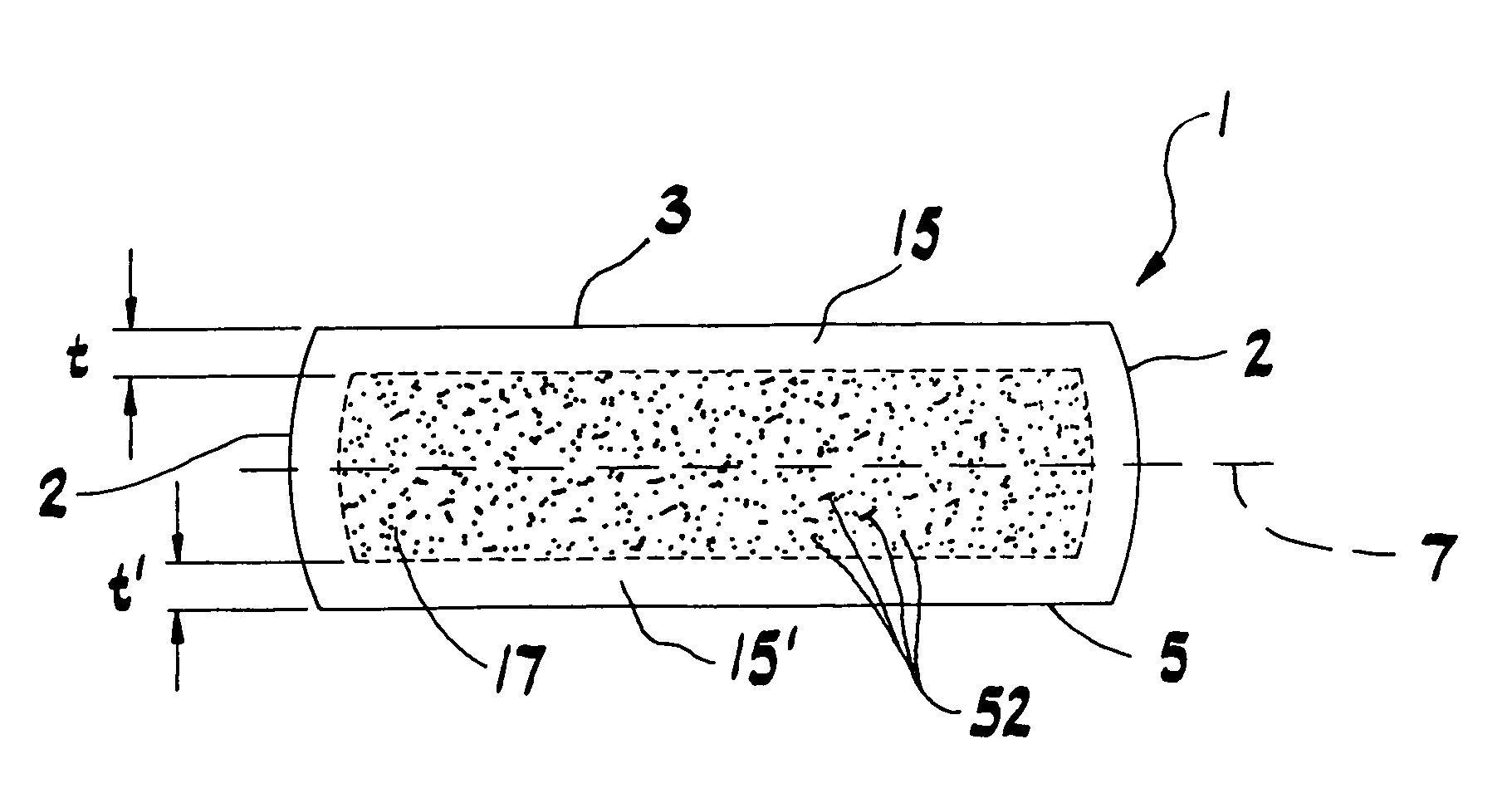
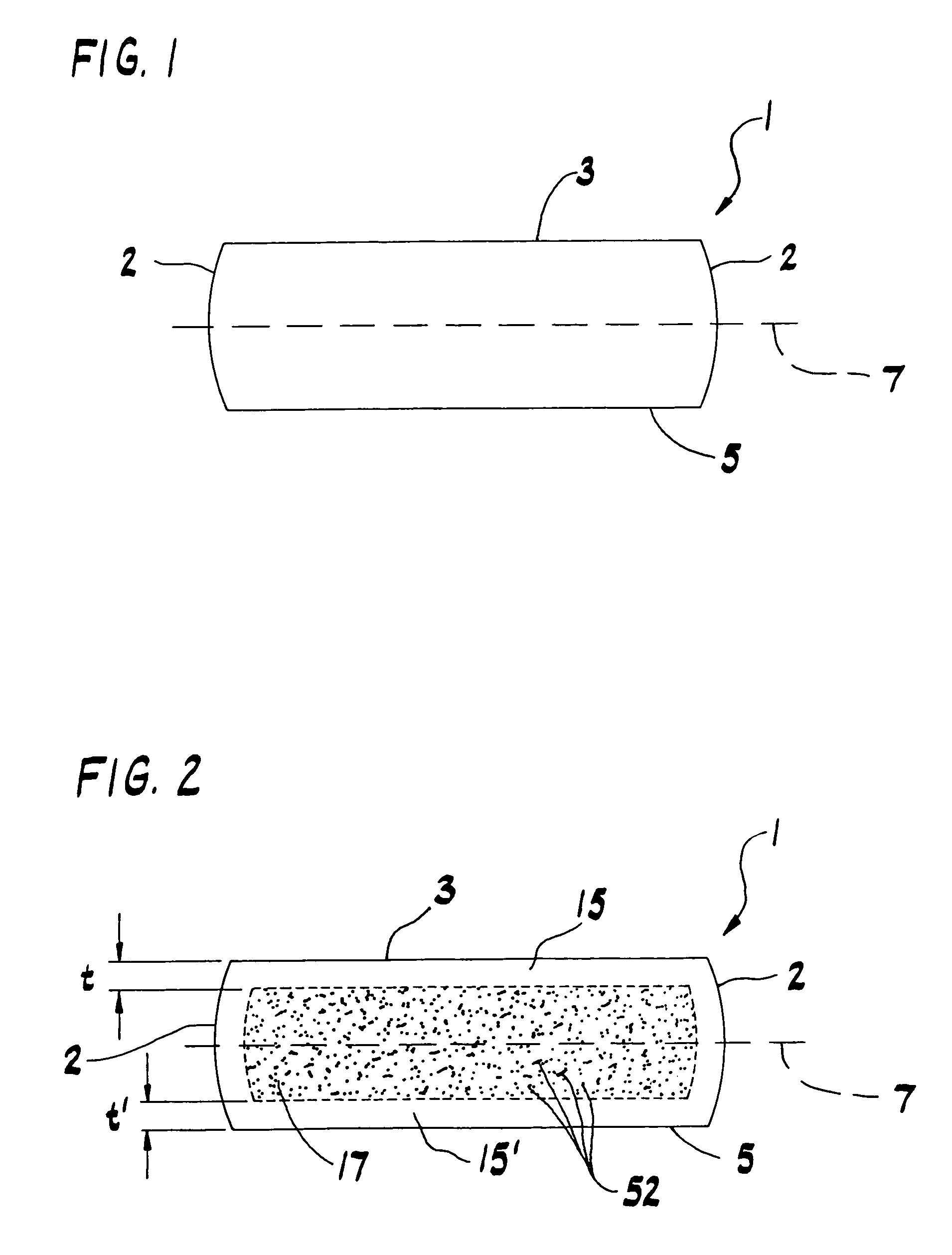
Method and device for the production of a silicon single crystal, silicon single crystal, and silicon semiconductor wafers with determined defect distributions
InactiveUS20040192015A1Increase productionMinimize thermal dissipationPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateVacancy defectHeat flux
A method for the production of a silicon single crystal by pulling the single crystal, according to the Czochralski method, from a melt which is held in a rotating crucible, the single crystal growing at a growth front, heat being deliberately supplied to the center of the growth front by a heat flux directed at the growth front. The method produces a silicon single crystal with an oxygen content of from 4*10<17 >cm<-3 >to 7.2*10<17 >cm<-3 >and a radial concentration change for boron or phosphorus of less than 5%, which has no agglomerated self-point defects. Semiconductor wafers are separated from the single crystal. These semiconductor wafers have may have agglomerated vacancy defects (COPs) as the only self-point defect type or may have certain other defect distributions.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Diamond sensors, detectors, and quantum devices
ActiveUS8686377B2Convenient lightingHigh strengthDiamondNanoopticsVacancy defectPreferential alignment
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Alignment film for LCD using photoreactive polymer and LCD comprising the same
ActiveUS20060159865A1Improve thermal stabilityIncrease ratingsLiquid crystal compositionsRoad vehicles traffic controlVacancy defectPolycyclic compound
The present invention provides a composition for forming a liquid crystal alignment film, which comprises a photoreactive polymer including a multicyclic compound having a photoreactive group on a main chain thereof. The present invention also provides a liquid crystal alignment film produced using the composition, and a liquid crystal display including the liquid crystal alignment film. The photoreactive polymer including the multicyclic compound on the main chain thereof has a high glass transition temperature, thus thermal stability is excellent. Since lattice vacancy is relatively large, the photoreactive group is capable of moving relatively freely in the main chain of the polymer, thus it is possible to improve a slow photoreaction rate, which is considered a disadvantage of a conventional polymer material.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Graphene membrane with regular angstrom-scale pores
InactiveUS8979978B2Uniform pore sizeMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesVacancy defectPore diameter
Technologies are generally described for perforated graphene monolayers and membranes containing perforated graphene monolayers. An example membrane may include a graphene monolayer having a plurality of discrete pores that may be chemically perforated into the graphene monolayer. The discrete pores may be of substantially uniform pore size. The pore size may be characterized by one or more carbon vacancy defects in the graphene monolayer. The graphene monolayer may have substantially uniform pore sizes throughout. In some examples, the membrane may include a permeable substrate that contacts the graphene monolayer and which may support the graphene monolayer. Such perforated graphene monolayers, and membranes comprising such perforated graphene monolayers may exhibit improved properties compared to conventional polymeric membranes for gas separations, e.g., greater selectivity, greater gas permeation rates, or the like.
Owner:EMPIRE TECH DEV LLC
Food Product Vacancy Reduction System
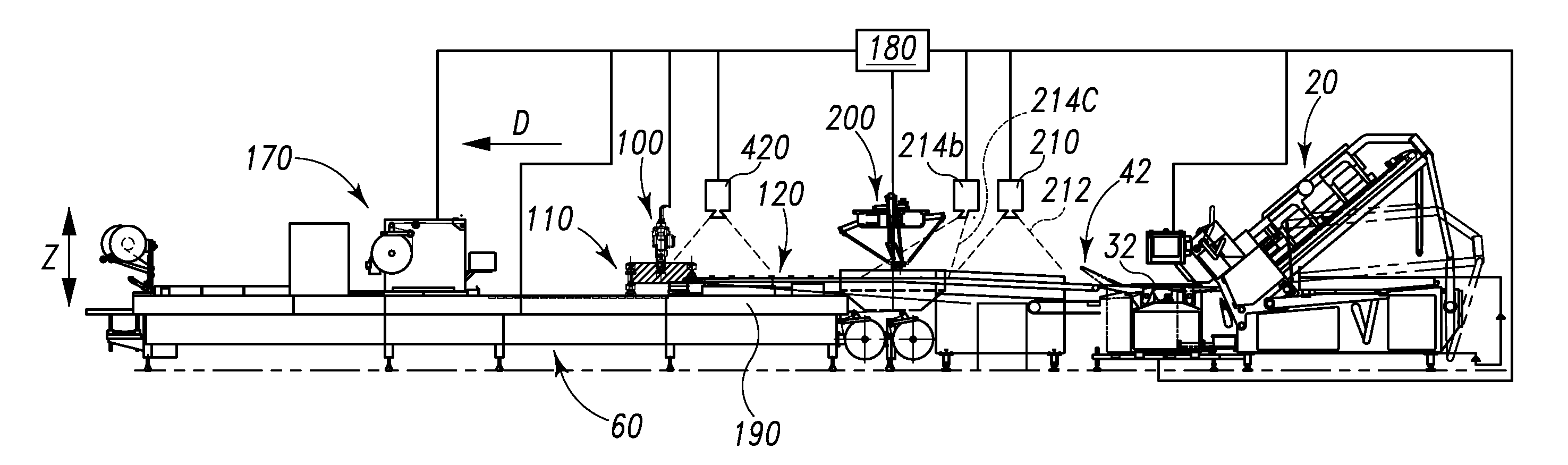
A food handling system having a vacancy reduction system. The vacancy reduction system includes the main conveyor, a food product parking station, a vacancy detector, a robot, and a controller. The vacancy detector is configured to detect a vacant food product position on the main conveyor. The robot has a working range for moving between the parking station and the main conveyor. The controller is signal-connected to the vacancy detector. The controller is configured to receive a signal from the vacancy detector indicating a vacant food product position on the conveyor. The controller is signal-connected to the robot and has control instructions for instructing the robot to move the food product from the food product parking station to the vacant food product position on the main conveyor.
Owner:PROVISUR TECHNOLOGIES INC
Epitaxial silicon wafer with intrinsic gettering and a method for the preparation thereof
A wafer is characterized in that the wafer has a non-uniform distribution of crystal lattice vacancies, wherein the concentration of crystal lattice vacancies in the bulk layer are greater than the concentration of crystal lattice vacancies in the front surface layer. In addition, the front surface of the wafer has an epitaxial layer, having a thickness of less than about 2.0 μm, deposited thereon. A process comprises heating a surface of a wafer starting material to remove a silicon oxide layer from the surface and depositing an epitaxial layer onto the surface to form an epitaxial wafer. The epitaxial wafer is then heated to a soak temperature of at least about 1175° C. while exposing the epitaxial layer to an oxidizing atmosphere comprising an oxidant, and the wafer is cooled at a rate of at least about 10° C. / sec.
Owner:SUNEDISON SEMICON LIMITED UEN201334164H
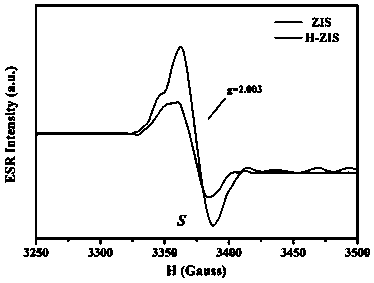
Surface sulfur vacancy defect mode structure-enriched sulfur-indium-zinc photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109569657ALow costKeep shapePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionElectron holeVacancy defect
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor photocatalysis and particularly relates to a surface sulfur vacancy defect mode structure-enriched sulfur-indium-zinc (ZnIn2S4) photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the surface sulfur vacancy defect mode structure-enriched sulfur-indium-zinc photocatalyst is characterized in that after high-temperature and high-pressure hydrogenation, a large number of sulfur vacancy defect mode structures are formed on the surface of the sulfur-indium-zinc photocatalyst. Compared with unmodified sulfur-indium-zinc photocatalysts, the surface sulfur vacancy defect mode structure-enriched sulfur-indium-zinc photocatalyst has a large number of the sulfur vacancy defect mode structures on the surface, surface sulfur vacancy defects can form photo-generated carrier capturing 'traps', separation of photo-generated charges can be effectively promoted, compounding of photo-generated electron-hole pairs can be reduced, and further the photocatalytic hydrogen production performance is greatly improved. The surface sulfur vacancy defect mode structure-enriched sulfur-indium-zinc photocatalyst and the preparation method thereof provide a new idea and a new way for designing and developing novel efficient visible light catalysts.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
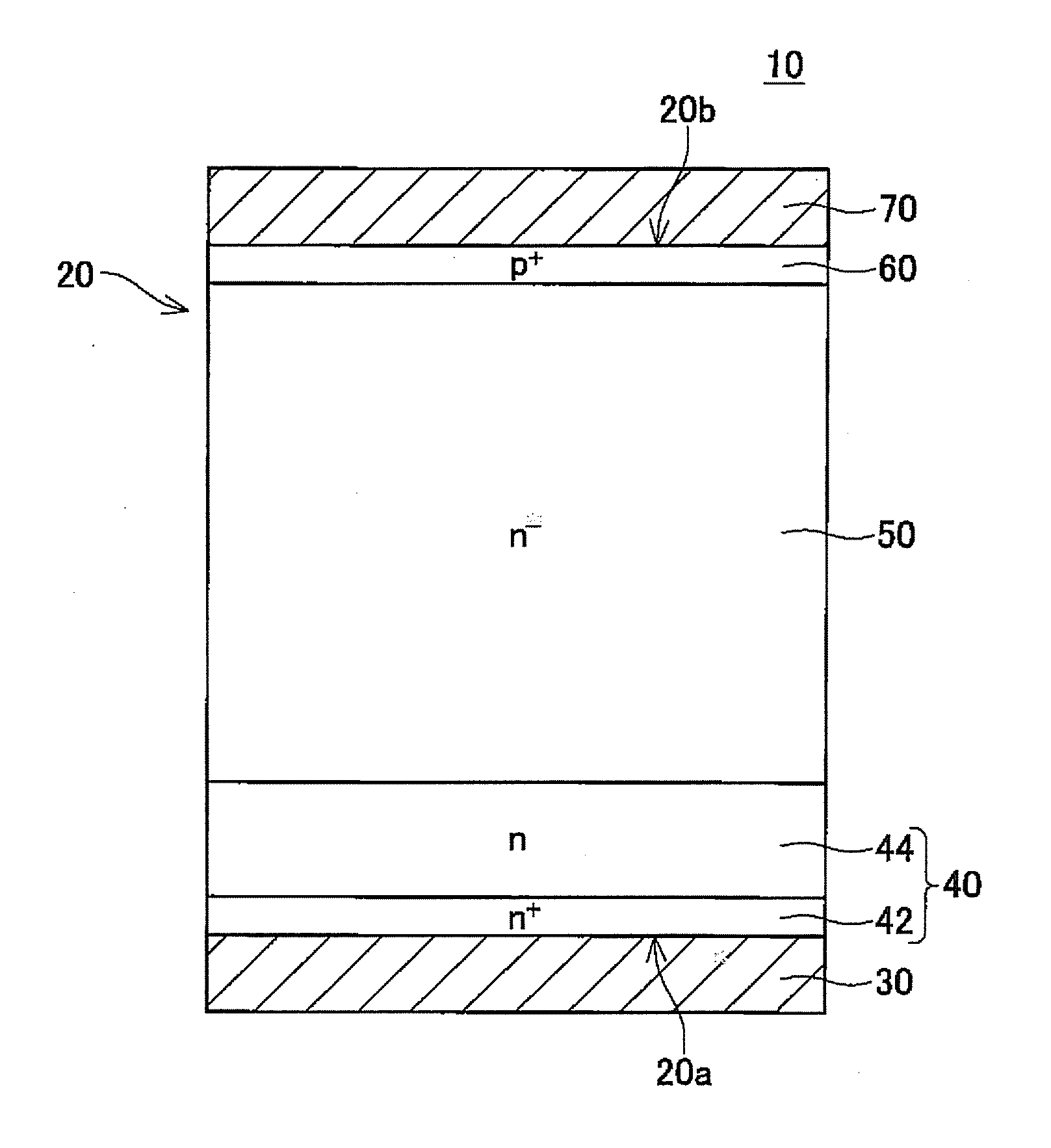
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110140243A1Reduce reverse recovery chargeSoftening of recovery currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesVacancy defectOxygen vacancy
A semiconductor device comprises a semiconductor substrate, a first electrode formed on a first main surface of the semiconductor substrate, and a second electrode formed on a second main surface of the semiconductor substrate. The semiconductor substrate includes a first region in which a density of oxygen-vacancy defects is greater than a density of vacancy cluster defects, and a second region in which the density of vacancy cluster defects is greater than the density of oxygen-vacancy defects.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Rapid-annealing method for growing large-size sapphire single-crystal with SAPMAC method
ActiveCN101580965AReduce dislocation densityReduce lattice vacanciesPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsEngineeringSingle crystal
The invention provides a rapid-annealing method for growing large-size sapphire single-crystal with the SAPMAC method. The SAPMAC method is adopted for growing sapphire single-crystal; after growing is finished, the vacuum degree of a crystal growing furnace is kept; electric power source is not cut off; heating power is lowered according to certain temperature reduction procedure until heating power is zero; and then inert gases are led in for rapid cooling. The invention has the beneficial effects that: 1. crystal dislocation density can be lowered, the lattice vacancy of crystal with big diameter and high expansion factor can be lowered, defect concentration such as distortion of lattice, dislocation and the like can be eliminated, crystal cleavage is avoided, and crystal quality and utilization factor can be improved; 2. in-situ annealing of crystal can be realized, crystal growing cycle can be shortened under the precondition of ensuring crystal quality; and 3. production cost can be lowered.
Owner:HARBIN AURORA OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
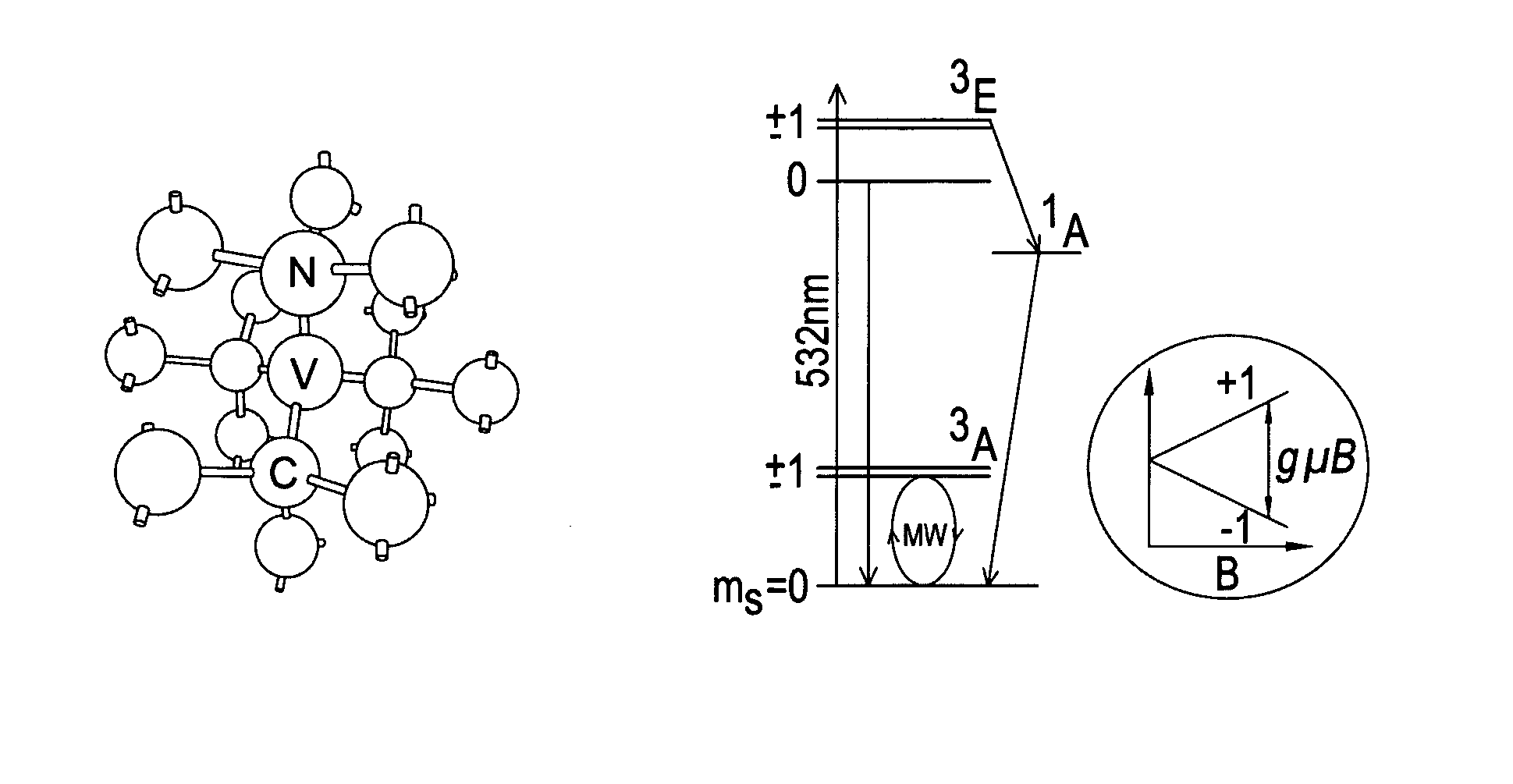
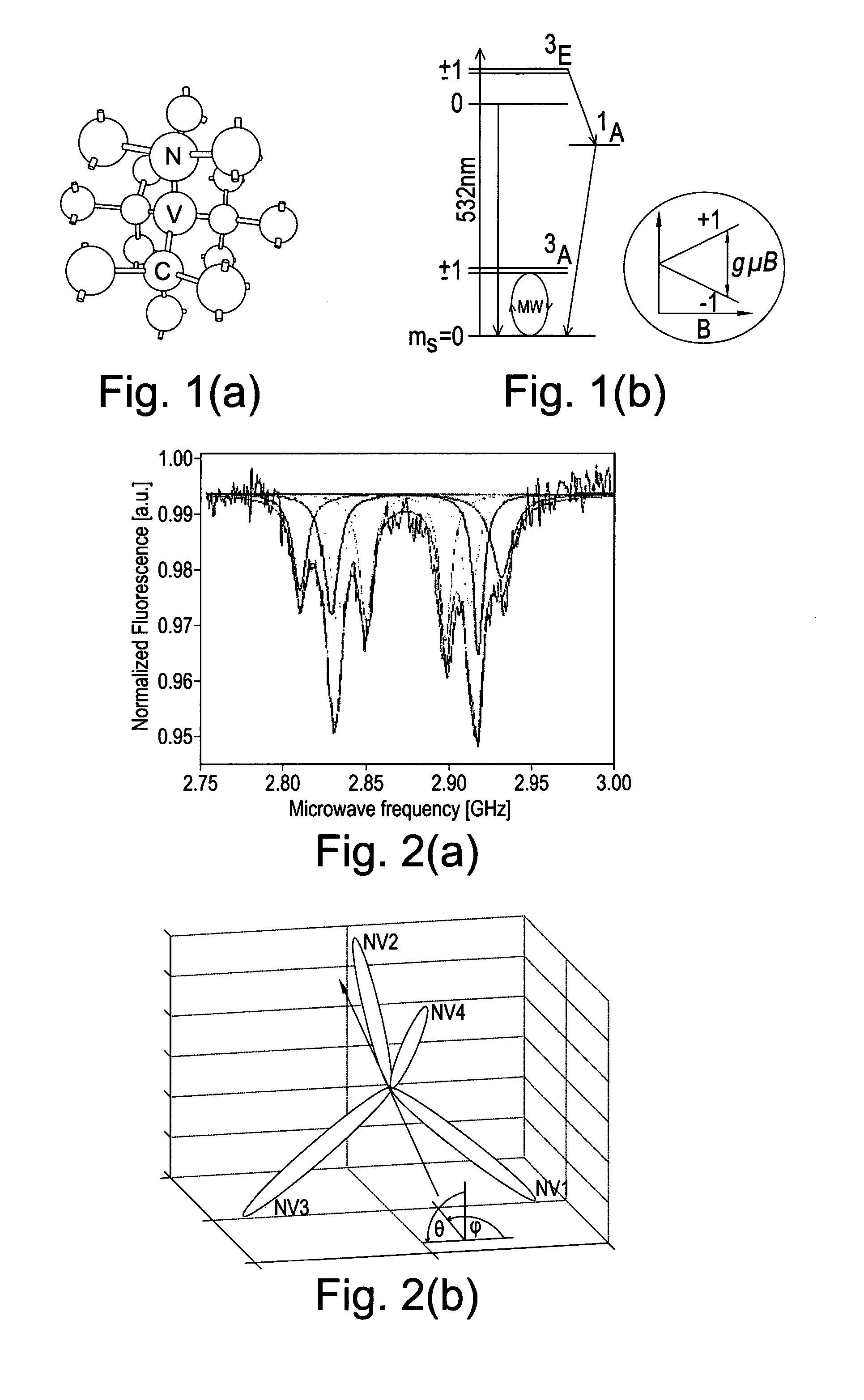
Device for achieving multi-photon interference from nitrogen-vacancy defects in diamond material
ActiveUS9335606B2Attenuation bandwidthReduce polarizationQuantum computersNanoinformaticsVacancy defectPhoton emission
A device for achieving multi-photon interference is provided based on nitrogen-vacancy defects in diamond material. Nitrogen-vacancy defects having a narrow band width and a similar emission frequency are identified within a high quality diamond material. The device has an excitation arrangement configured to individually address nitrogen-vacancy defects and optical outcoupling structures for increasing outcoupling of photons from each nitrogen-vacancy defect. A tuning arrangement is configured to tune the emission from each nitrogen-vacancy defect to reduce differences in frequency and the photons are overlapped. A detector is provided to detect the photon emissions. The detector is configured to resolve sufficiently small differences in photon detection times such that tuned photon emissions from the nitrogen-vacancy defects are quantum mechanically indistinguishable resulting in quantum interference between indistinguishable photon emissions from different nitrogen-vacancy defects.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
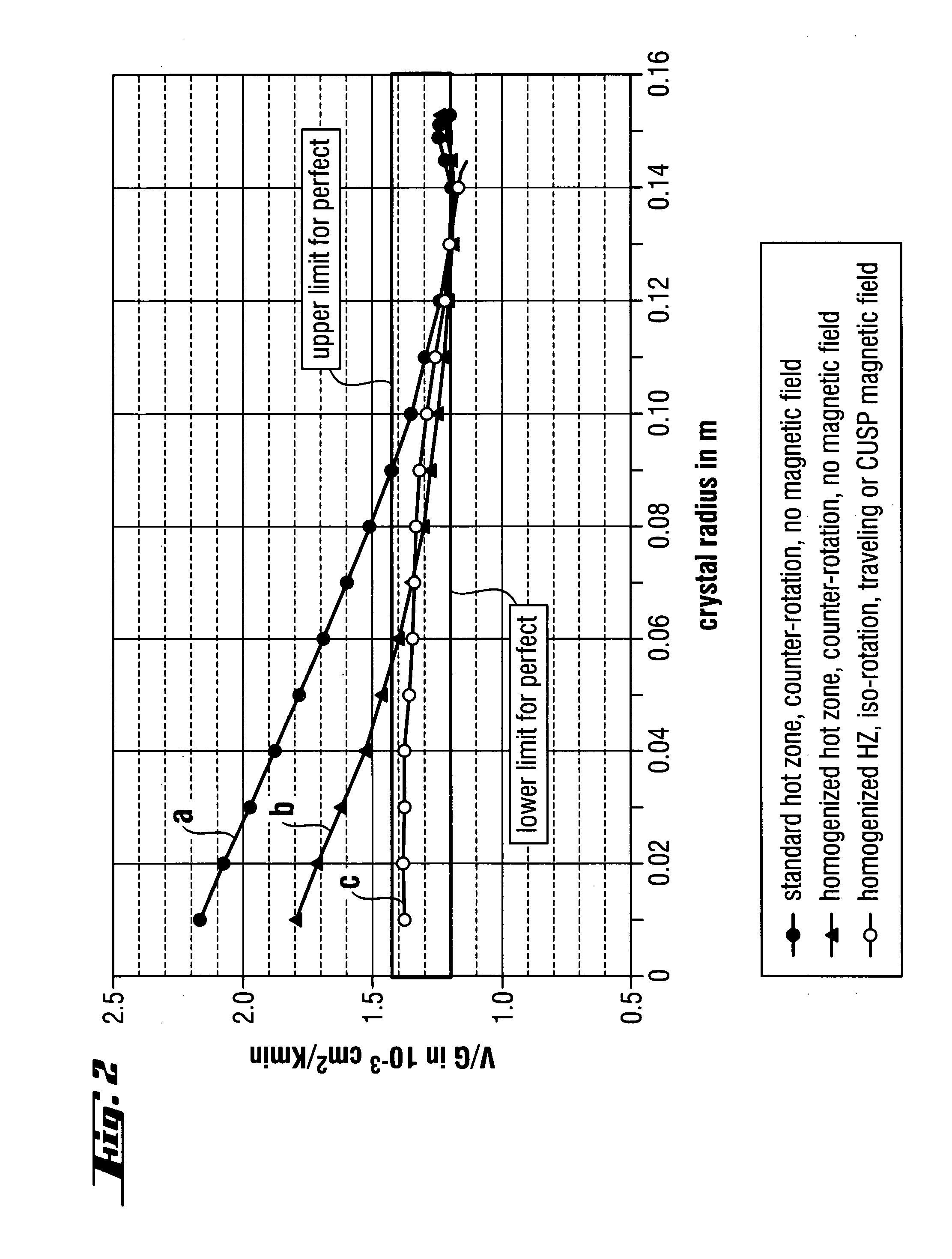
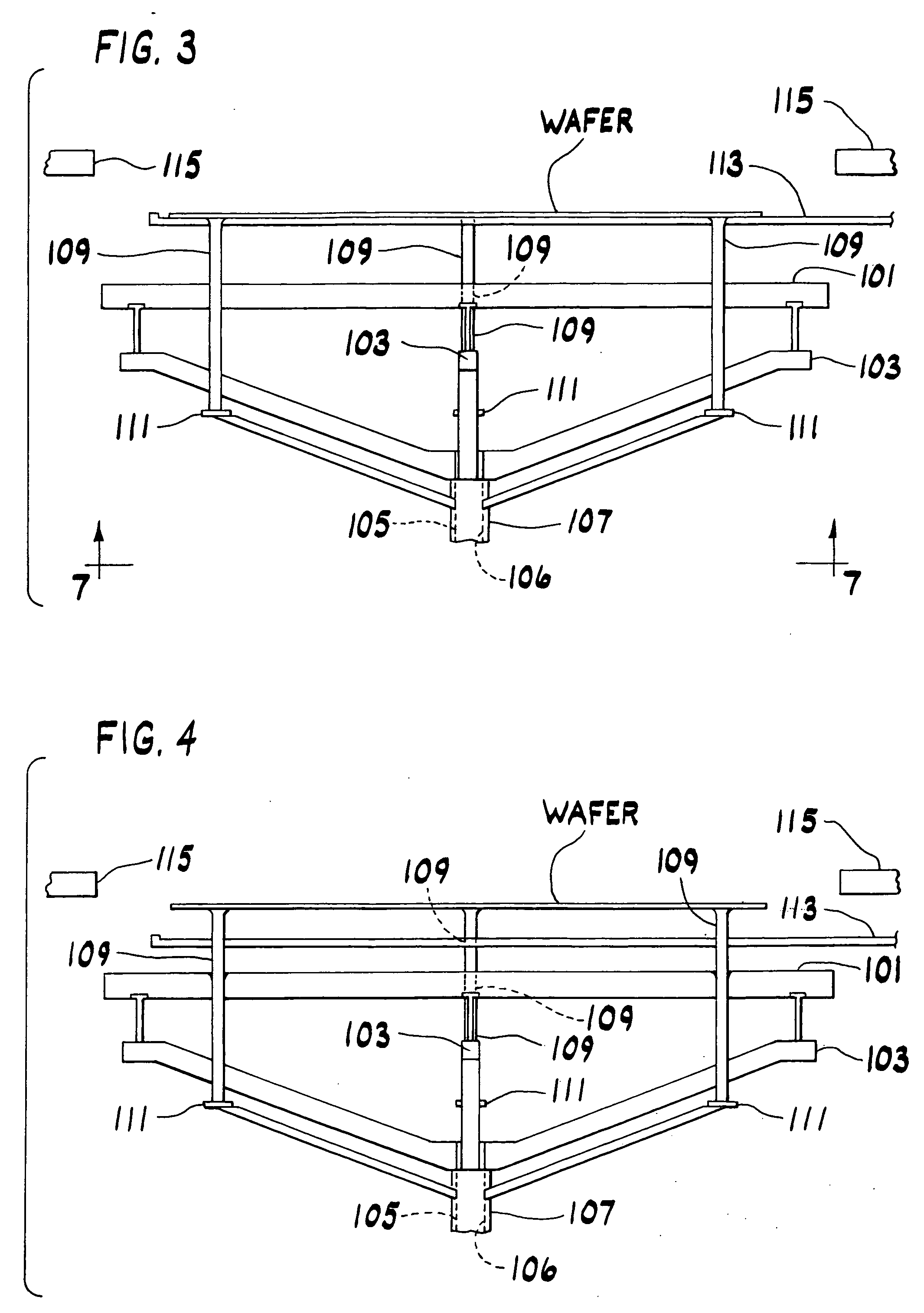
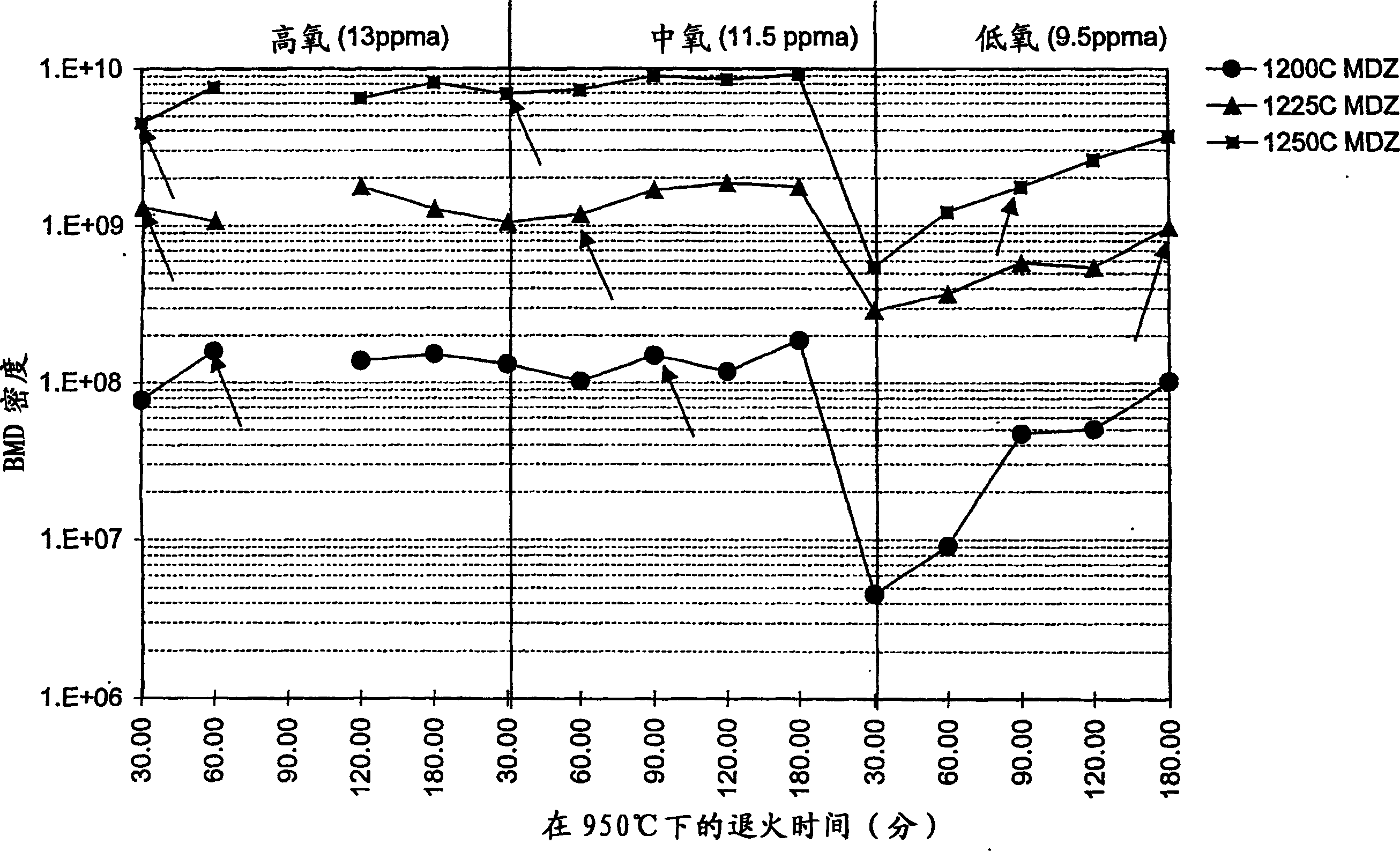
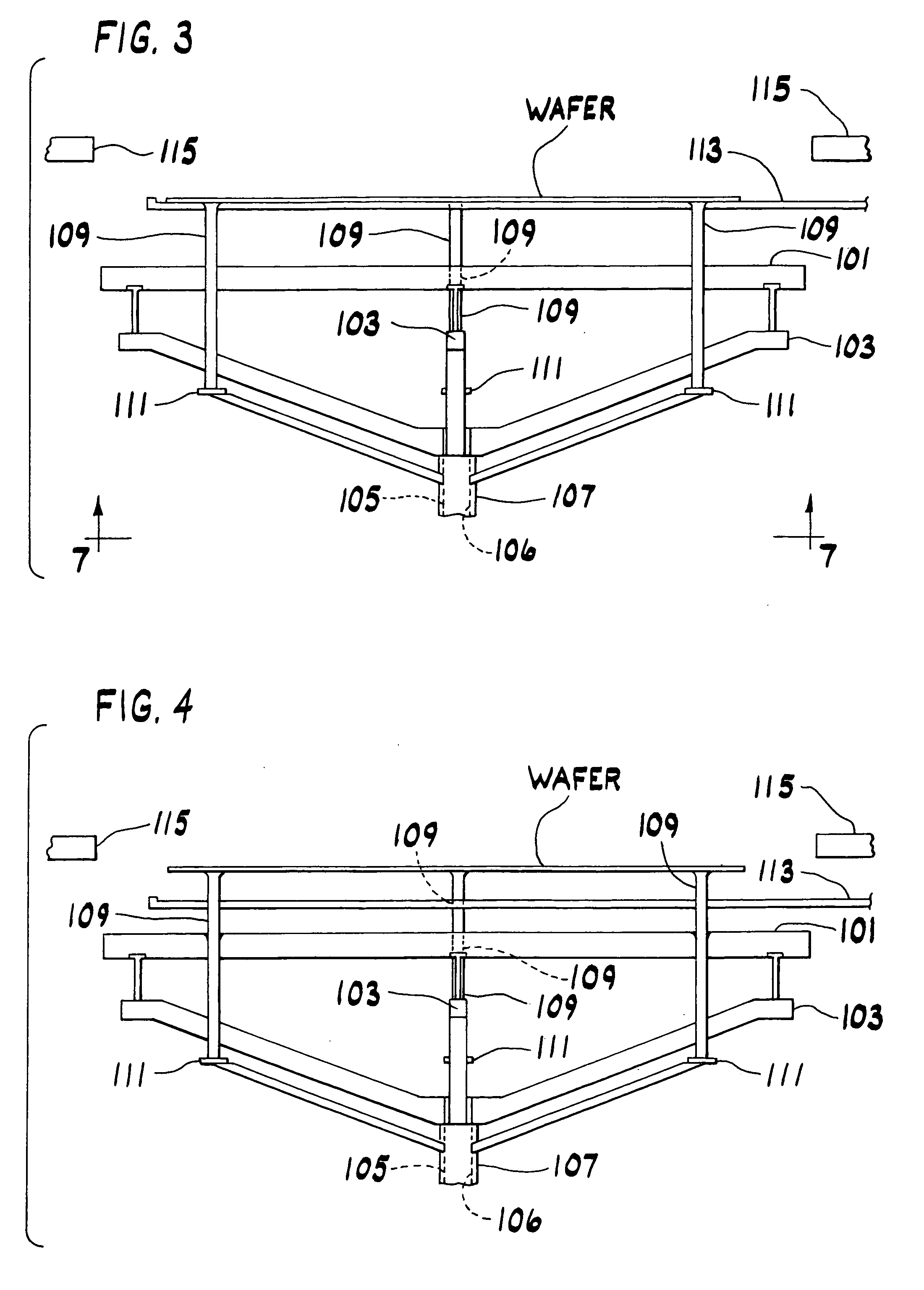
Single-crystal silicon ingot and wafer having homogeneous vacancy defects, and method and apparatus for making same
ActiveUS20050120944A1Quality improvementReduce defectsPolycrystalline material growthSiliconVacancy defectWafering
The present invention improves upon the Czochralski method for growing a single-crystal silicon ingot and provides a high quality silicon wafer having an oxide layer with superior voltage-resistance characteristics. An apparatus and method are also provided, whereby vacancy defect density and distribution are uniformly controlled. A single-crystal silicon ingot is grown under a condition where the temperature variation of the ingot is less than or equal to 20° C. / cm in the temperature range of 1000 to 1100° C.
Owner:LG SILTRON
Method and device for the production of a silicon single crystal, silicon single crystal, and silicon semiconductor wafers with determined defect distributions
ActiveUS20060292890A1Increase productionMinimize thermal dissipationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVacancy defectHeat flux
A method for the production of a silicon single crystal by pulling the single crystal, according to the Czochralski method, from a melt which is held in a rotating crucible, the single crystal growing at a growth front, heat being deliberately supplied to the center of the growth front by a heat flux directed at the growth front. The method produces a silicon single crystal with an oxygen content of from 4*1017 cm−3 to 7.2*1017 cm−3 and a radial concentration change for boron or phosphorus of less than 5%, which has no agglomerated self-point defects. Semiconductor wafers are separated from the single crystal. These semiconductor wafers have may have agglomerated vacancy defects (COPs) as the only self-point defect type or may have certain other defect distributions.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
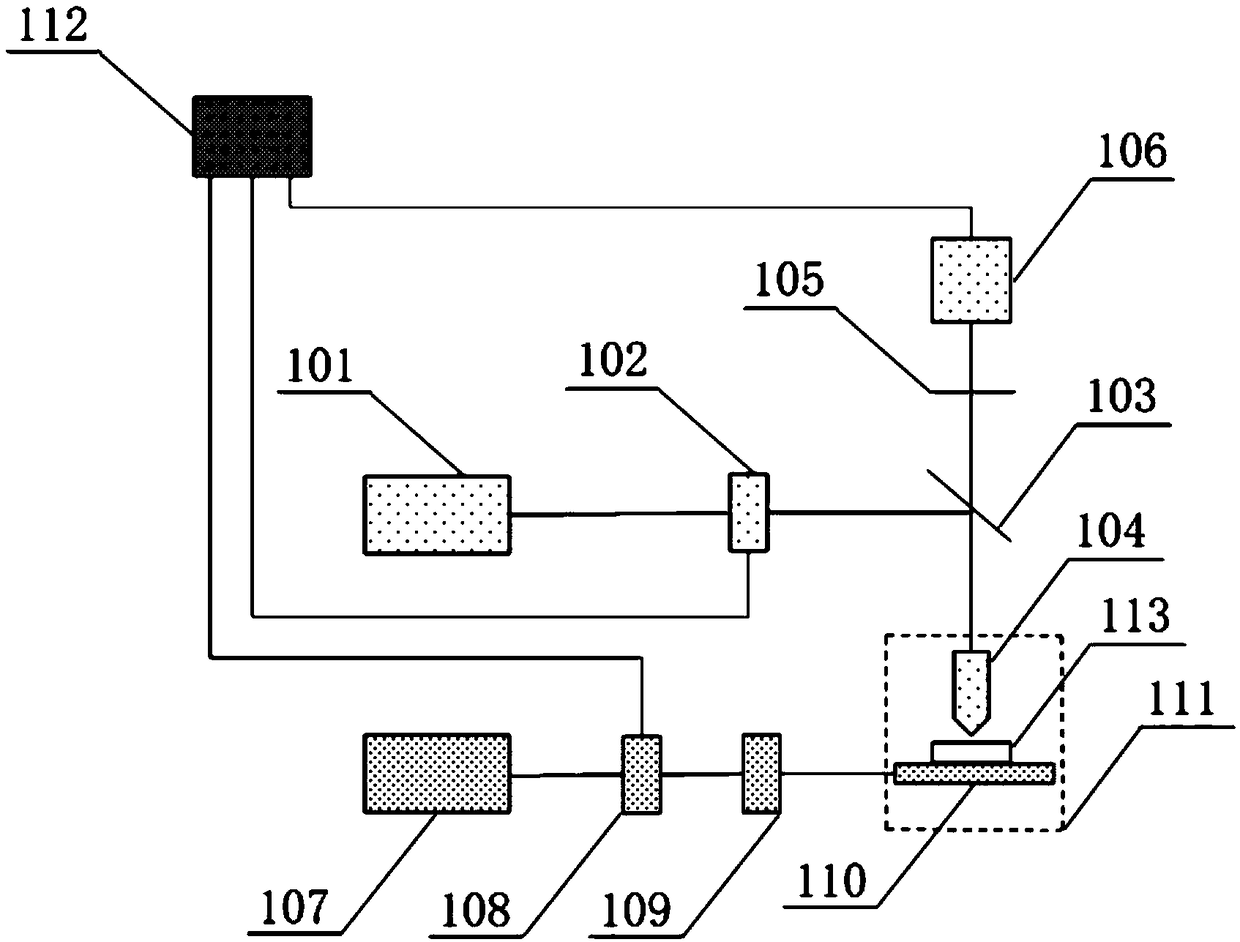
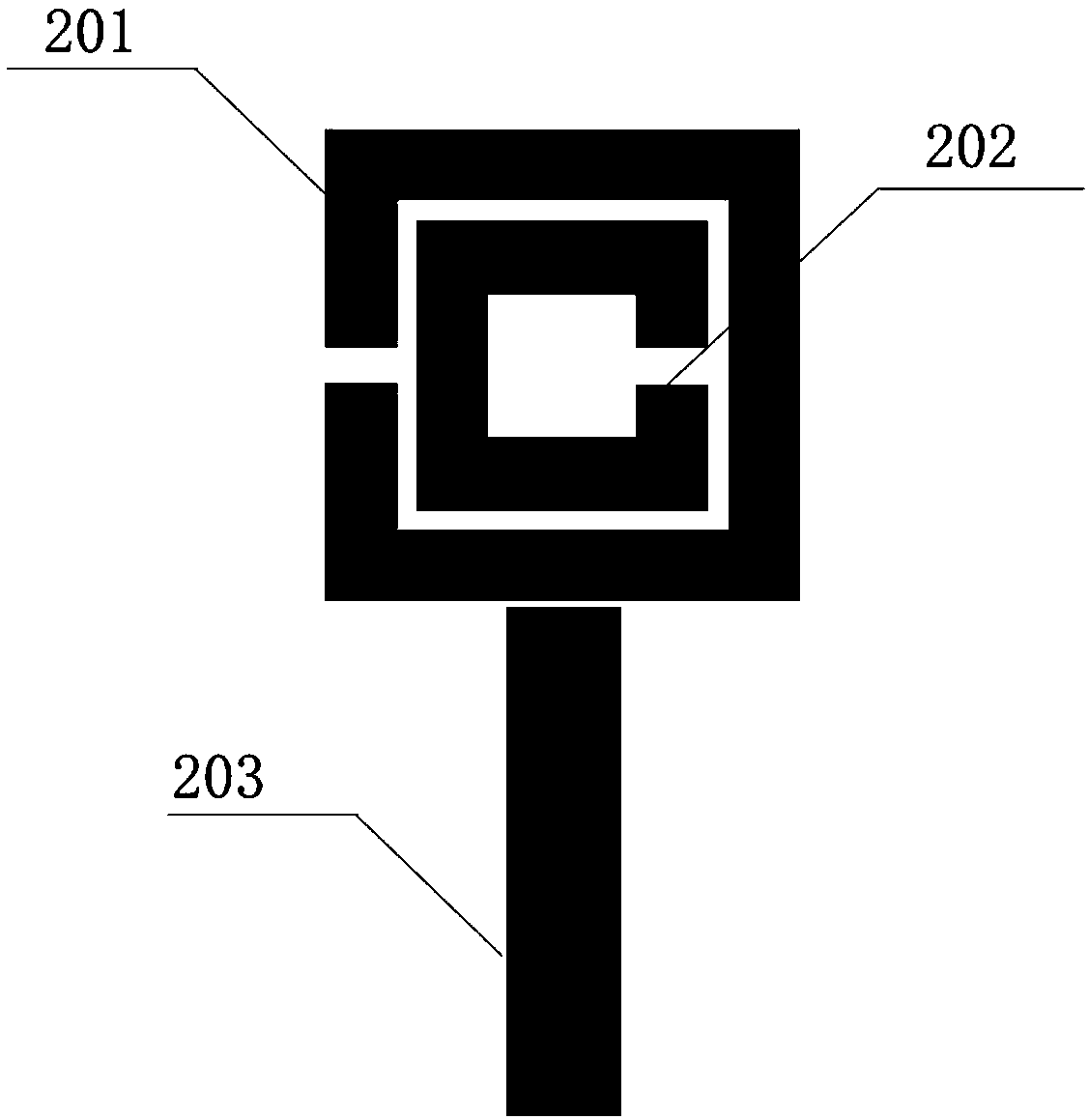
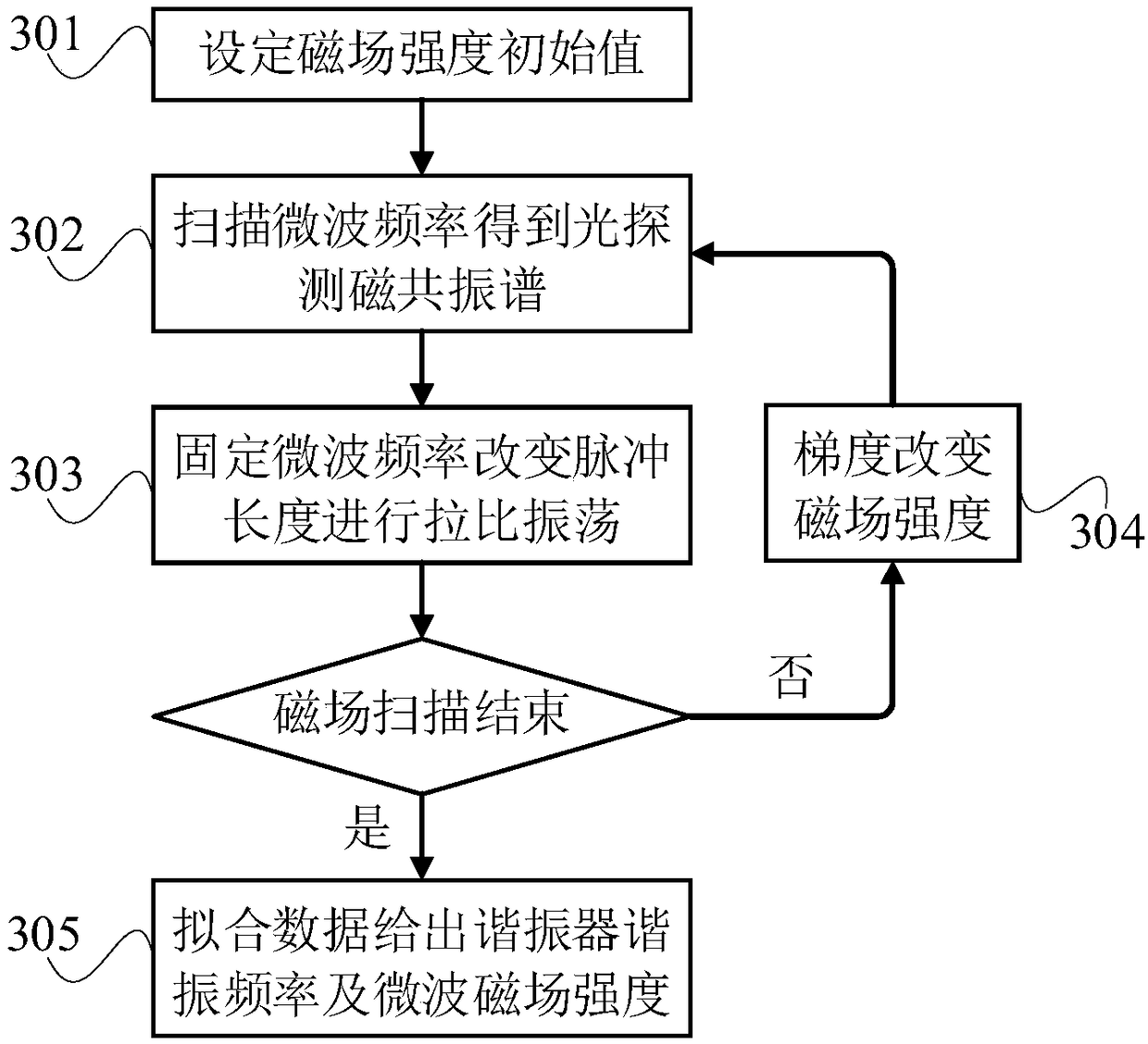
System and method for measuring resonant frequency of near-field microwave resonator
ActiveCN109061295APractical measurementAccurate measurementFrequency measurement arrangementFrequency measurementsFluorescence
The invention relates to a system and method for measuring resonant frequency of near-field microwave resonator, which utilizes electron spin resonance and diamond nitrogen vacancy defect (NV color center) to pull the oscillation frequency and the intensity of the microwave to place the diamond in a static magnetic field. In the process, the microwave pulse frequency and the magnetic field intensity are changed to perform photodetection magnetic resonance and rabbi oscillation measurement, and a series of rabbi oscillation frequencies are obtained, from which the resonator resonance frequencyis extracted. The measuring system comprises an optical module, a microwave module, a magnetic field device, a diamond and a control device, wherein the diamond is embedded with a NV color core; theoptical module can generate and guide light to the diamond, and simultaneously detect the fluorescent signal emitted by the diamond. The microwave module can generate a microwave control field and load it onto the diamond. The magnetic field device can generate a static magnetic field. The invention can measure the resonant frequency and the effective magnetic field strength of the microwave resonator practically and accurately, has high precision, and can be used under near-field conditions.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
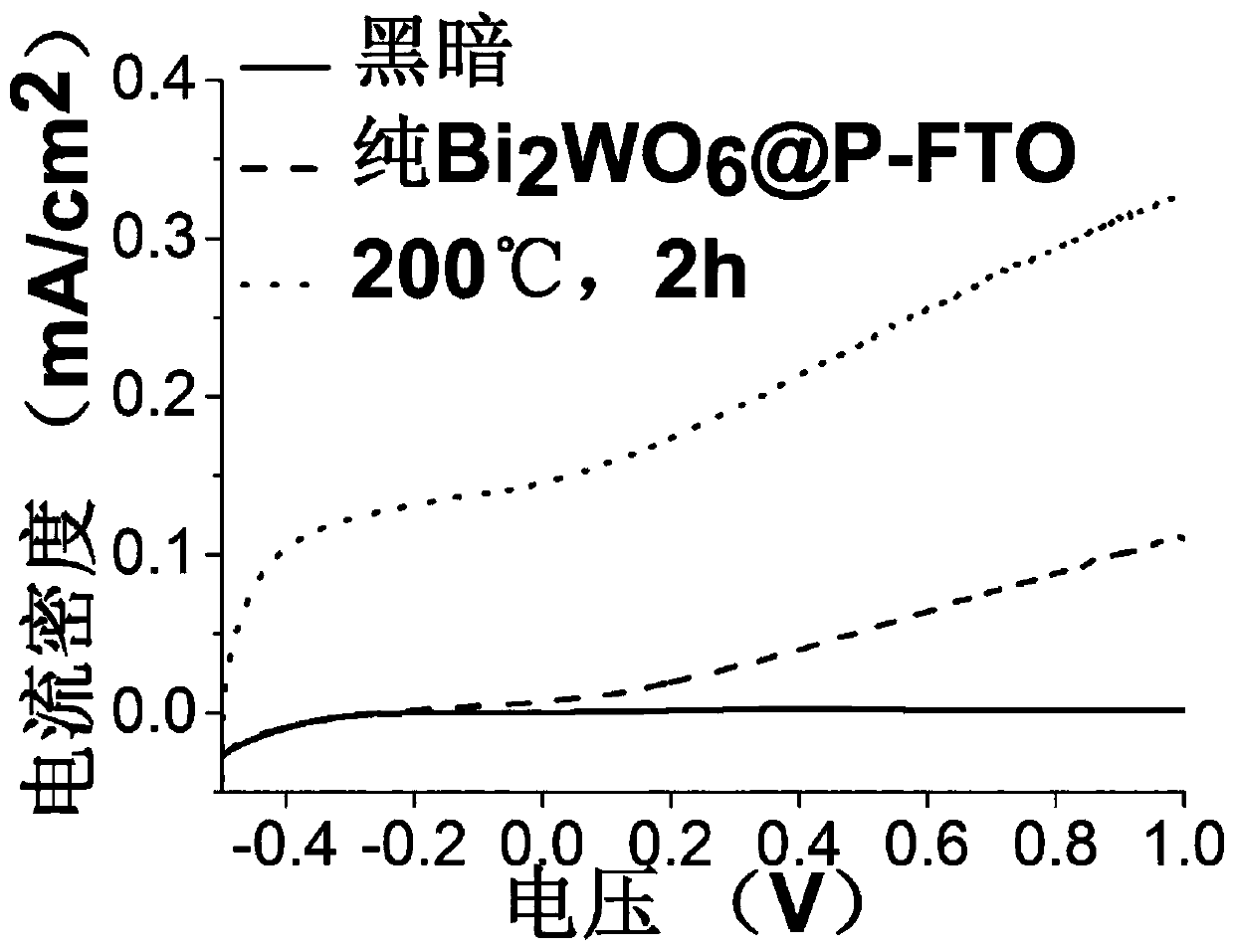
Surface oxygen vacancy defect modified bismuth tungstate photocatalyst, and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN110465286ASimple preparation processAdjustable energy levelCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogen productionTungstateOxygen vacancy
The invention belongs to the technical field of photocatalysis, and discloses a surface oxygen vacancy defect modified bismuth tungstate photocatalyst, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method comprises following steps: a sodium tungstate precursor solution and a bismuth nitrate precursor solution are mixed to obtain a bismuth tungstate precursor solution, ultrasonic treatment is carried out, the bismuth tungstate precursor solution is introduced into a high temperature reaction vessel with a conductive substrate, hydro-thermal reaction is carried out at 100 to180 DEG C, deionized water is adopted for washing, under nitrogen gas flow, drying is carried out, sintering is carried out at 450 to 600 DEG C, and an obtained bismuth tungstate film grows on the flat conductive substrate is subjected to heat processing at 150 to 400 DEG C at reductive atmosphere to obtain a finished product. The surface of the obtained surface oxygen vacancy defect bismuth tungstate film possesses more active sites, so that higher photoelectric conversion efficiency is achieved; and at the same time, existing of oxygen vacancy defects is capable of realizing micro adjustingof forbidden bandwidth Eg of the bismuth tungstate photocatalyst, narrowing Eg, and obtaining wider visible light response range.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Two-dimensional bismuth oxygen selenium atom crystal materials and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109402739ASolve the problem that the ratio is not easy to controlHigh crystal integrityPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsGas phaseSingle crystal
The invention relates to a preparation method of two-dimensional bismuth oxygen selenium atom crystals. The method comprises the following steps that a precursor containing bismuth elements and selenium elements is subjected to physical vapor deposition, a two-dimensional bismuth oxygen selenium atom crystal material is obtained, and the two-dimensional bismuth oxygen selenium atom crystal material is a tetragonal system. By adopting physical vapor deposition, the problem that the ratio of a bismuth source to a selenium source is not easily controlled in the chemical gas-phase reaction processis solved, the obtained two-dimensional bismuth oxygen selenium atom crystal material is higher in purity, vacancy defects are less, then, the electronic mobility is higher, the electronic mobility is larger than or equal to 135 cm<2> / (V s), meanwhile, compared with chemical vapor deposition, the physical vapor deposition can enable the crystal form integrity of the two-dimensional bismuth oxygenselenium atom crystal material to be higher, the crystal size is larger, the single crystal domain edge can reach the millimeter scale, the maximum single crystal domain edge is not smaller than 1.7mm, and the minimum signed crystal domain edge is not smaller than 200 micrometers.
Owner:TSINGHUA BERKELEY SHENZHEN INST
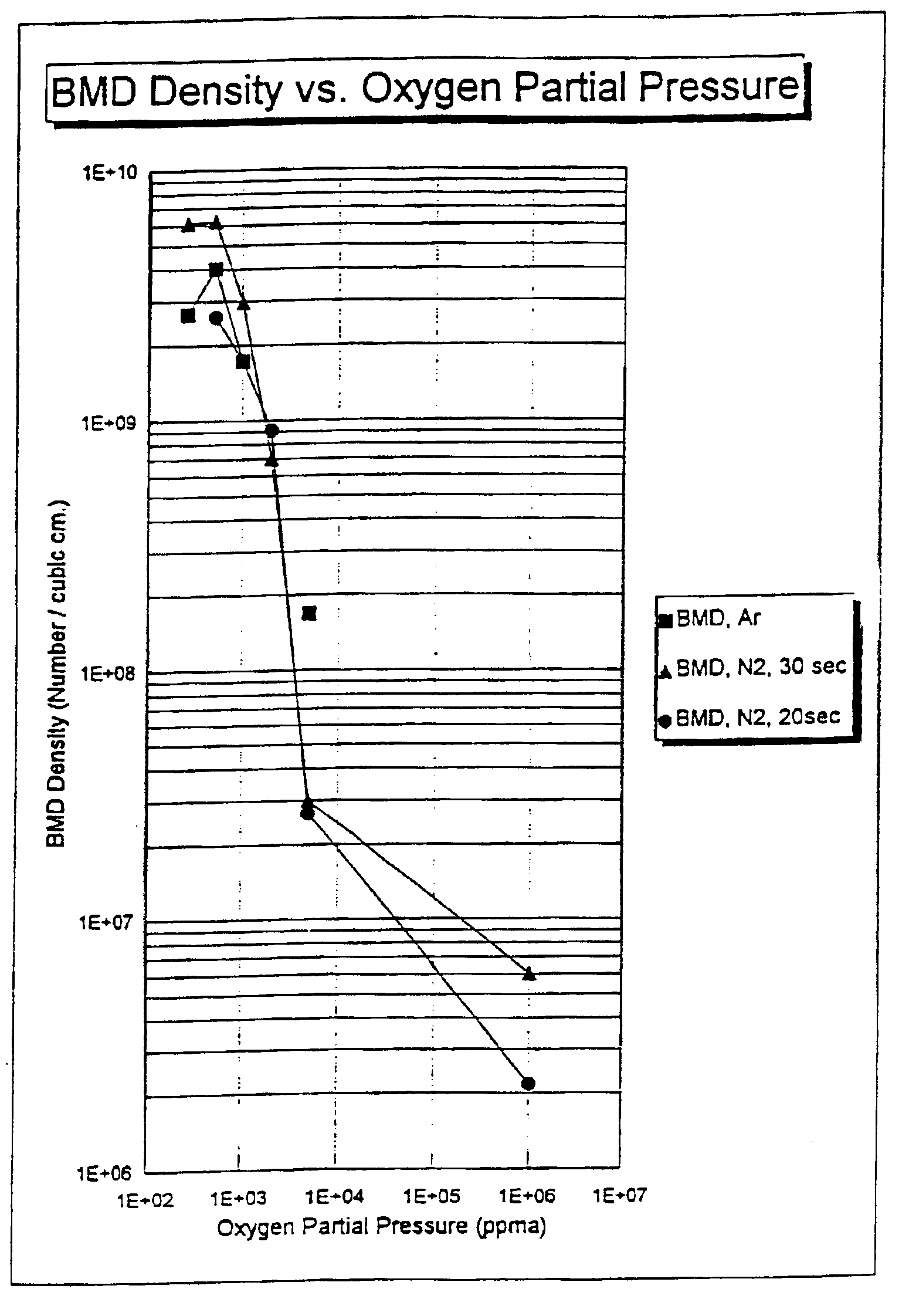
Silicon wafer having good intrinsic getterability and method for its production
Silicon wafers in the entire volume of which crystal lattice vacancies are the prevalent point defect type, have a rotationally symmetric region whose width is at least 80% of the wafer radius, crystal lattice vacancy agglomerates of at least 30 nm in a density ≦6·103 cm−3, crystal lattice vacancy agglomerates of from 10 nm to 30 nm in a density of 1·105 cm−3 to 3·107 cm−3, OSF seeds in a density of 0 to 10 cm−2, and an average bulk BMD density of 5·108 cm−3 to 5·109 cm−3, which varies at most by a factor of 10 radially over the entire silicon wafer, and a BMD-free layer on the front side, wherein the first BMD is found at a depth of at least 5 μm and on average at a depth of at least 8 μm.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Process for controlling denuded zone depth in an ideal oxygen precipitating silicon wafer
The present invention is directed to a single crystal Czochralski silicon wafer having a non-uniform distribution of lattice vacancies with peak concentration at a hypothetical In the bulk of the wafer between the central plane and a surface, such that after a heat treatment cycle in essentially any electronic device manufacturing process, the wafer forms oxygen precipitates in the bulk and a thin or shallow no-sedimentation zone.
Owner:MEMC ELECTONIC MATERIALS INC
Alignment film for LCD using photoreactive polymer and LCD comprising the same
ActiveUS7541073B2Improve thermal stabilityIncrease ratingsLiquid crystal compositionsRoad vehicles traffic controlPolycyclic compoundVacancy defect
The present invention provides a composition for forming a liquid crystal alignment film, which comprises a photoreactive polymer including a multicyclic compound having a photoreactive group on a main chain thereof. The present invention also provides a liquid crystal alignment film produced using the composition, and a liquid crystal display including the liquid crystal alignment film. The photoreactive polymer including the multicyclic compound on the main chain thereof has a high glass transition temperature, thus thermal stability is excellent. Since lattice vacancy is relatively large, the photoreactive group is capable of moving relatively freely in the main chain of the polymer, thus it is possible to improve a slow photoreaction rate, which is considered a disadvantage of a conventional polymer material.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
In-situ preparation method of photocatalyst strontium bismuth niobium oxide containing oxygen vacancy defect
InactiveCN106362729AEfficient use ofLow costHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalyst activation/preparationVacancy defectOxygen vacancy
The invention relates to an in-situ preparation method of photocatalyst strontium bismuth niobium oxide containing an oxygen vacancy defect. The method comprises the following steps of adopting a molten-salt growth method to synthesize a SrBi2Nb2O9 nanosheet, putting the SrBi2Nb2O9 nanosheet at H2 atmosphere, using ultraviolet-visible-infrared light for full-spectrum illumination, and obtaining SrBi2Nb2O9-VO. Compared with a traditional method that the oxygen vacancy defect is produced by calcining a sample at inert atmosphere or reducing atmosphere, the method for producing the oxygen vacancy defect provided by the invention is simpler, more effectively, lower in required cost, and favorable to take full advantage of sunlight. According to the method, not only can the oxygen vacancy defect be in-site produced on a catalyst, but also the catalyst can utilize the produced oxygen vacancy defect for improving the own performance in photocatalytic reducing CO2. Meanwhile, the method is hopefully applied in other oxygenous Bi-based photocatalysts.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modified TM-LDH nano material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110129815AIncrease the number ofImprove intrinsic catalytic activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationVacancy defectChemical compound
The invention provides a modified transition metal base-layer dihydroxy compound nano material, which comprises two or three transition metals, and further comprises an atomic level cation vacancy defect, the atomic level cation vacancy defect is a vacancy defect left by removing of one of the transition metals. The invention also provides a preparation method of the nano material through complexation reaction, and the preparation method can selectively remove designated metal ions to controllably form the atomic level cation vacancy defect at the atomic level, and has simple operation and mild reaction. The nano material and a water decomposition catalyst and a water decomposition electrode containing the nano material show lower decomposition water overpotential and faster hydrogen production rate, and have wide application prospect in efficient and cheap large-scale commercial water decomposition hydrogen production.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Semiconductor device and formation method therefor
ActiveCN105336660AInhibited DiffusionPrevent proliferationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesVacancy defectDielectric layer
A semiconductor device and a formation method therefor are disclosed. The formation method for the semiconductor device comprises the steps of providing a substrate including a first region and a second region; forming a groove including a first part and a second part in the substrate; forming a first barrier layer at the bottom of the first part and the surface of the side wall of the groove, wherein the first barrier layer captures lattice vacancy defects or interstitial atom defects in the substrate; forming a second barrier layer at the bottom of the second part and the surface of the side wall of the groove, wherein the second barrier layer captures lattice vacancy defects or interstitial atom defects in the substrate, and defect types captured by the first barrier layer and the second barrier layer are different; forming dielectric layers for filling the grooves; forming a first well region in the first region substrate; forming a second well region in the second region substrate, wherein the doping types of the second well region and the first well region are opposite. According to the semiconductor device and the formation method therefor, the diffusion of the doping ions in the first well region and the second well region can be effectively prevented to endow the semiconductor device with a good electrical isolation performance.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Graphene membrane with regular angstrom-scale pores
Technologies are generally described for perforated graphene monolayers and membranes containing perforated graphene monolayers. An example membrane may include a graphene monolayer having a plurality of discrete pores that may be chemically perforated into the graphene monolayer. The discrete pores may be of substantially uniform pore size. The pore size may be characterized by one or more carbon vacancy defects in the graphene monolayer. The graphene monolayer may have substantially uniform pore sizes throughout. In some examples, the membrane may include a permeable substrate that contacts the graphene monolayer and which may support the graphene monolayer. Such perforated graphene monolayers, and membranes comprising such perforated graphene monolayers may exhibit improved properties compared to conventional polymeric membranes for gas separations, e.g., greater selectivity, greater gas permeation rates, or the like.
Owner:EMPIRE TECH DEV LLC
Epitaxial silicon wafer with intrinsic gettering and a method for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS6958092B2Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsVacancy defectSurface layer
Owner:SUNEDISON SEMICON LIMITED UEN201334164H
Ideal oxygen precipitating silicon wafers and oxygen out-diffusion-less process therefor
A process for heat-treating a single crystal silicon wafer to influence the precipitation behavior of oxygen in the wafer in a subsequent thermal processing step. The wafer has a front surface, a back surface, and a central plane between the front and back surfaces. In the process, the wafer is subjected to a heat-treatment to form crystal lattice vacancies, the vacancies being formed in the bulk of the silicon. The wafer is then cooled from the temperature of said heat treatment at a rate which allows some, but not all, of the crystal lattice vacancies to diffuse to the front surface to produce a wafer having a vacancy concentration profile in which the peak density is at or near the central plane with the concentration generally decreasing in the direction of the front surface of the wafer.
Owner:SUNEDISON SEMICON LIMITED UEN201334164H
Electrophotographic photoconductor
InactiveUS6300026B1Stable and excellent charging characteristicElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeVacancy defectElectrical conductor
A photoconductor includes a conductive substrate, an undercoat layer on the substrate, and at least one photosensitive layer on the undercoat layer. The radius of vacancy type defects in each of the photosensitive layer and in the undercoat layer is o.4 nm or less. In one embodiment, the radius of vacancy type defects is measured by a positron annihilation method.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for processing graphene superlattice nano-structure with atomic force microscope
InactiveCN103787270AWidth is easy to controlSimple processing methodNanostructure manufactureMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
The invention relates to the technical field of nano processing, in particular to a method for processing a graphene superlattice nano-structure with an atomic force microscope. The method for processing the graphene superlattice nano-structure with the atomic force microscope comprises the steps that a manual vacancy defect is formed on graphene in the mode of applying pulse voltages to a needle point of the atomic force microscope, and then anisotropic etching is carried out on the graphene through a hydrogen-contained plasma. According to the method, nano hole array patterns with a period smaller than a 200 nm can be achieved on the graphene. The period of the graphene superlattice nano-structure and nanoribbon width are controllable. A processing method of the needle point of the atomic force microscope is simple and free of inducing additional pollution means, and an obtained device is clean. In addition, with the assistance of the needle point array processing technology, the method can be used for device integration and mass production of graphene nano-structure devices.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
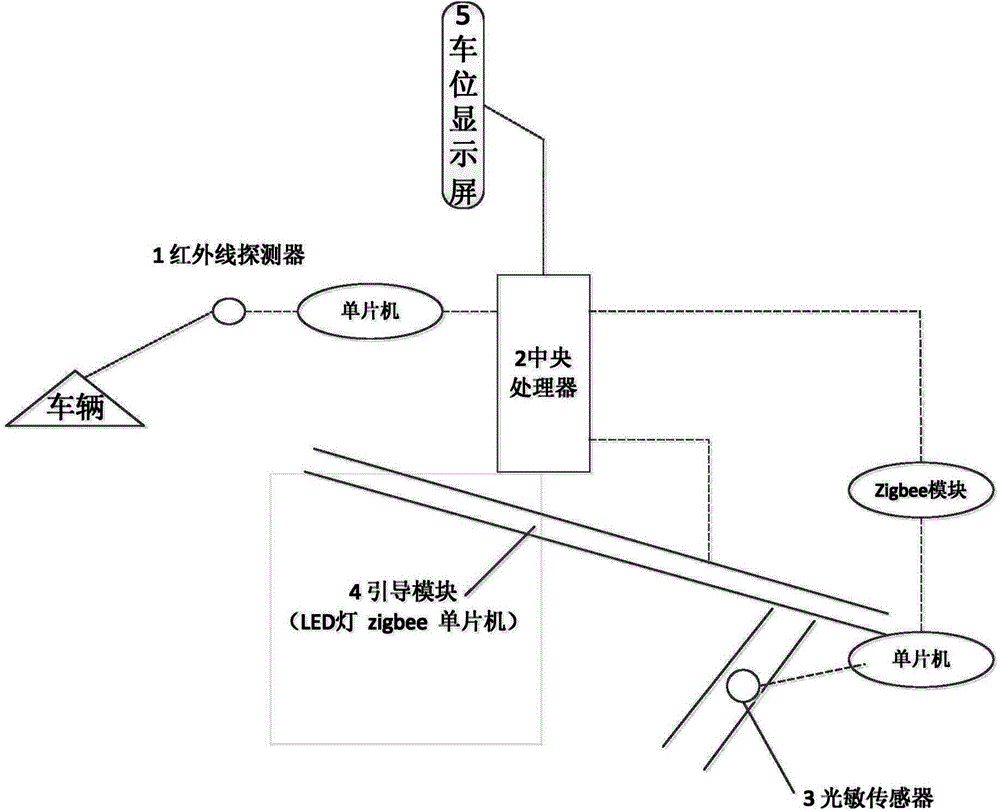
Vacancy detection and indication-based underground parking system
InactiveCN103606296ASave energyAvoid congestionArrangements for variable traffic instructionsIndication of parksing free spacesParking areaVacancy defect
Disclosed in the invention is a vacancy detection and indication-based underground parking system. Parking detection sensors that are arranged at the grounds of all parking spaces of the parking lot and are connected to a central processing unit by a single-chip microcomputer are used for transmitting parking place state to the central processing unit. And the central processing unit is also connected to a guiding module including a display screen; and according to states of all the parking places at the parking lot and the topographical condition, the central processing unit optimizes a route of a vehicle needing parking and transmits the route to the guiding module, and the route information is displayed at the display screen. The provided system can be widely applied to an underground parking lot and various garages based on light illumination. Moreover, the technical scheme is clear; the cost is low; the energy conservation and high efficiency are realized; demands of intelligence and humanization are satisfied; and innovation and practicability are both realized simultaneously.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com