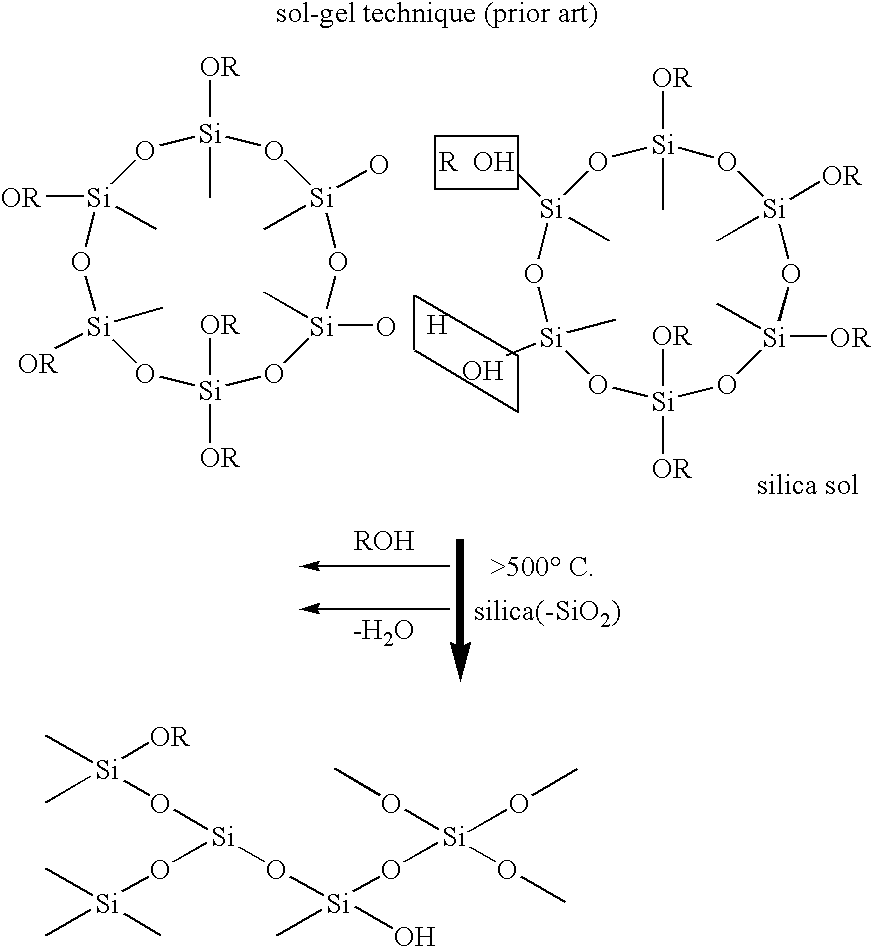
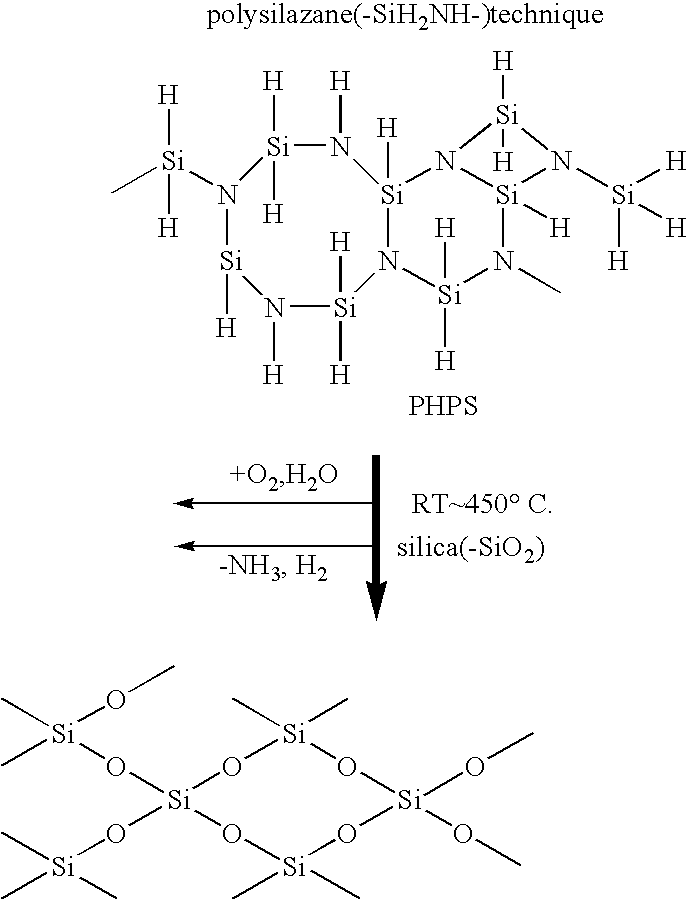
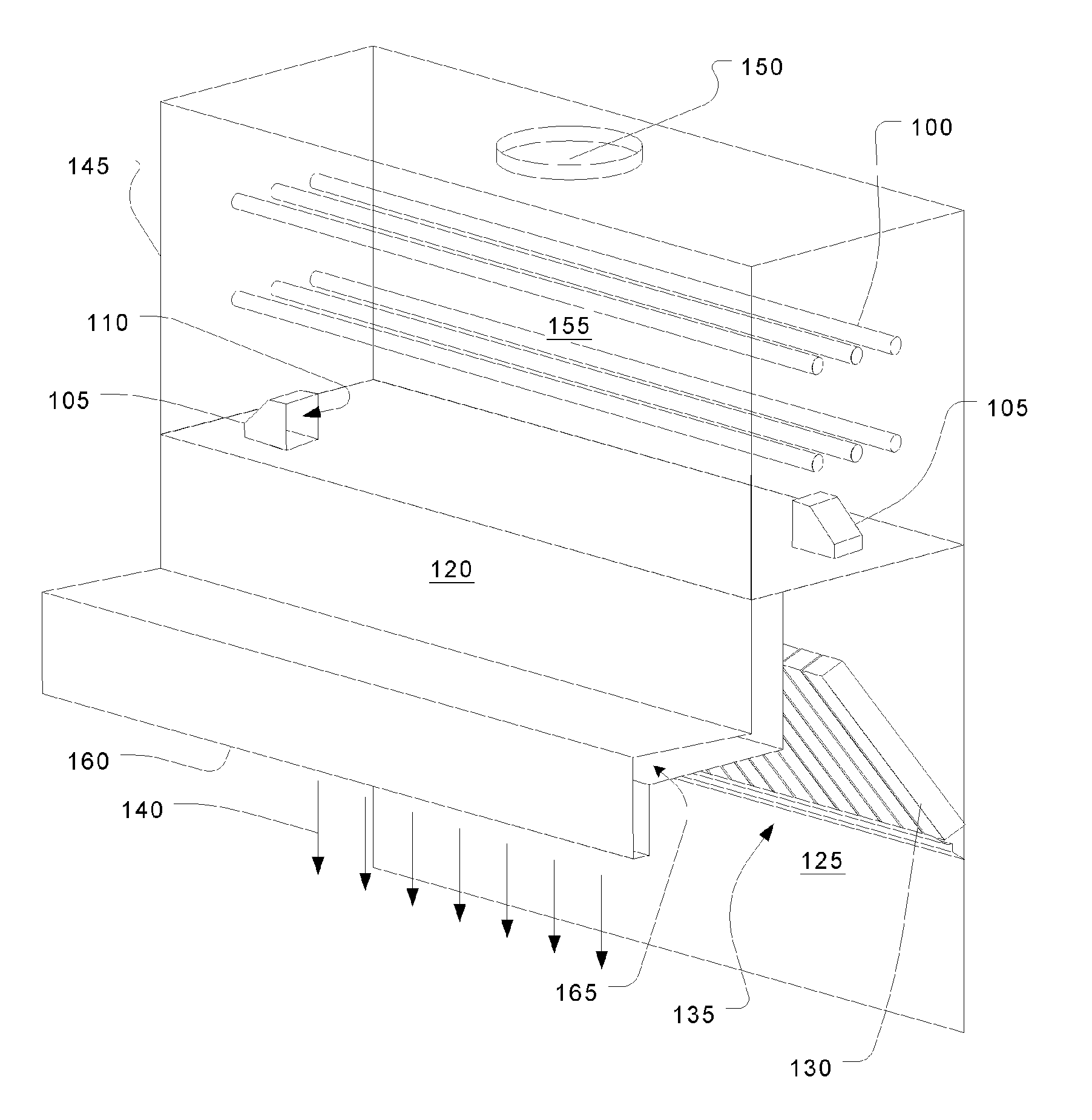
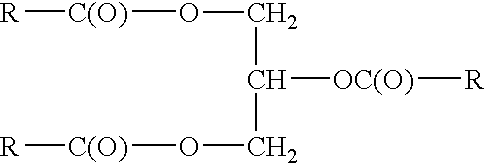
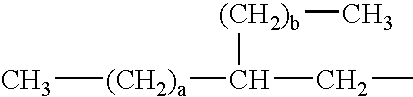
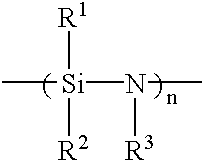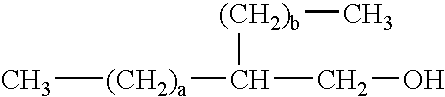Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "UV degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Many natural and synthetic polymers are attacked by ultraviolet radiation, and products using these materials may crack or disintegrate if they are not UV-stable. The problem is known as UV degradation, and is a common problem in products exposed to sunlight. Continuous exposure is a more serious problem than intermittent exposure, since attack is dependent on the extent and degree of exposure.
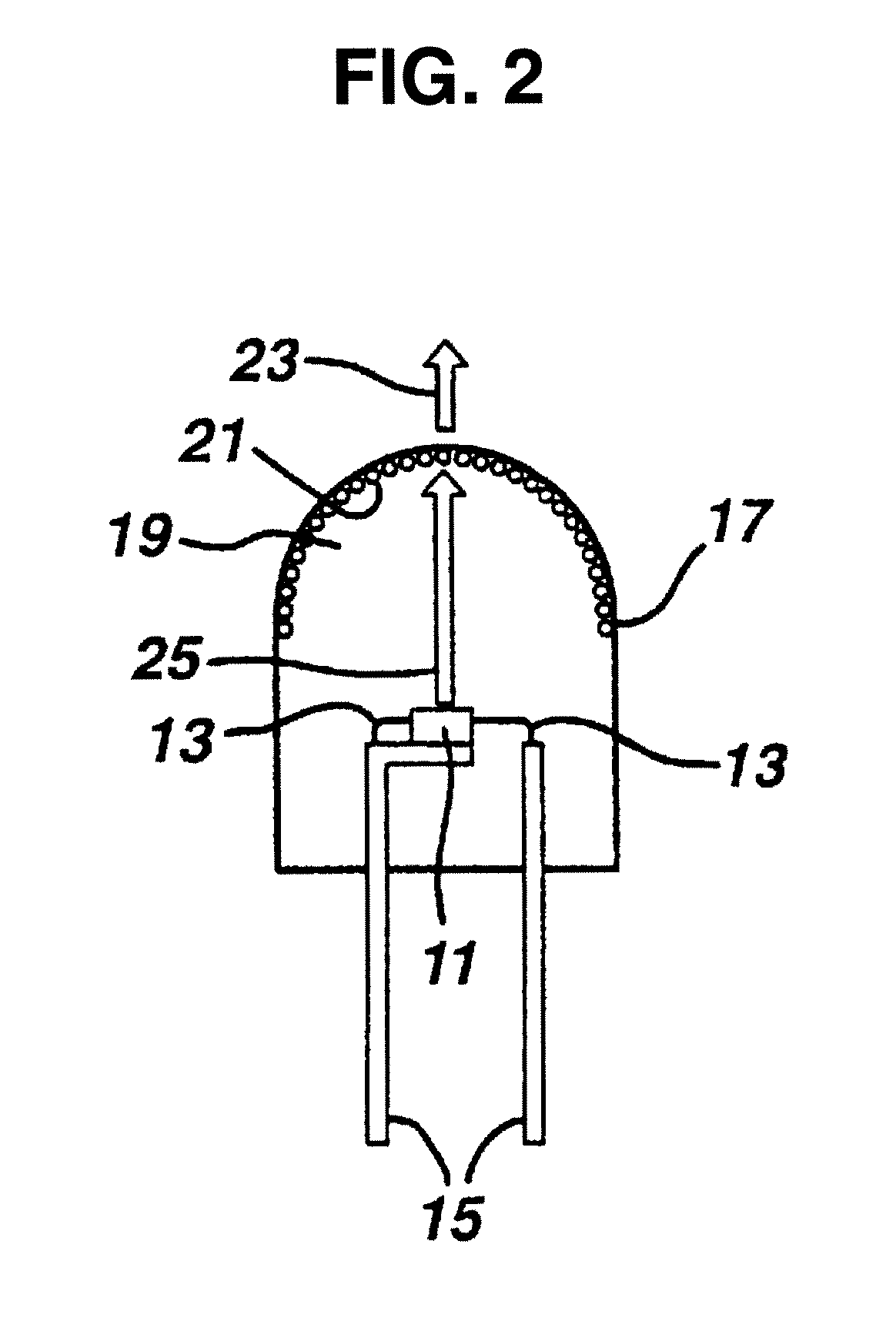
Light emitting device
InactiveUS6781148B2Electroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesUltravioletMoisture absorption
The invention aims to provide a light emitting device comprising a base material or protective member which has improved light transmittance, heat resistance, passivation (gas barrier, oligomer release prevention and minimized outgassing), anti-water or moisture-absorption, stability against chemical degradation, dimensional and shape stability, anti-surface-reflection, electrical insulation, UV degradation resistance, and weather resistance, and is highly productive due to possible film formation under atmospheric pressure, and hence, a light emitting device featuring high reliability, ease of manufacture and low cost. The object is attained by a light emitting device comprising a base material (1) having flexibility, light transparency and heat resistance, a lower electrode (4) having light transmittance, a light emitting layer (4), and an upper electrode (4) formed on the base material, the device further comprising a silica film and / or a siliceous film (3) which is formed on the substrate side as viewed from the light emitting layer (4) or on opposite sides of the substrate by applying polysilazane and subjecting it to oxidative treatment.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
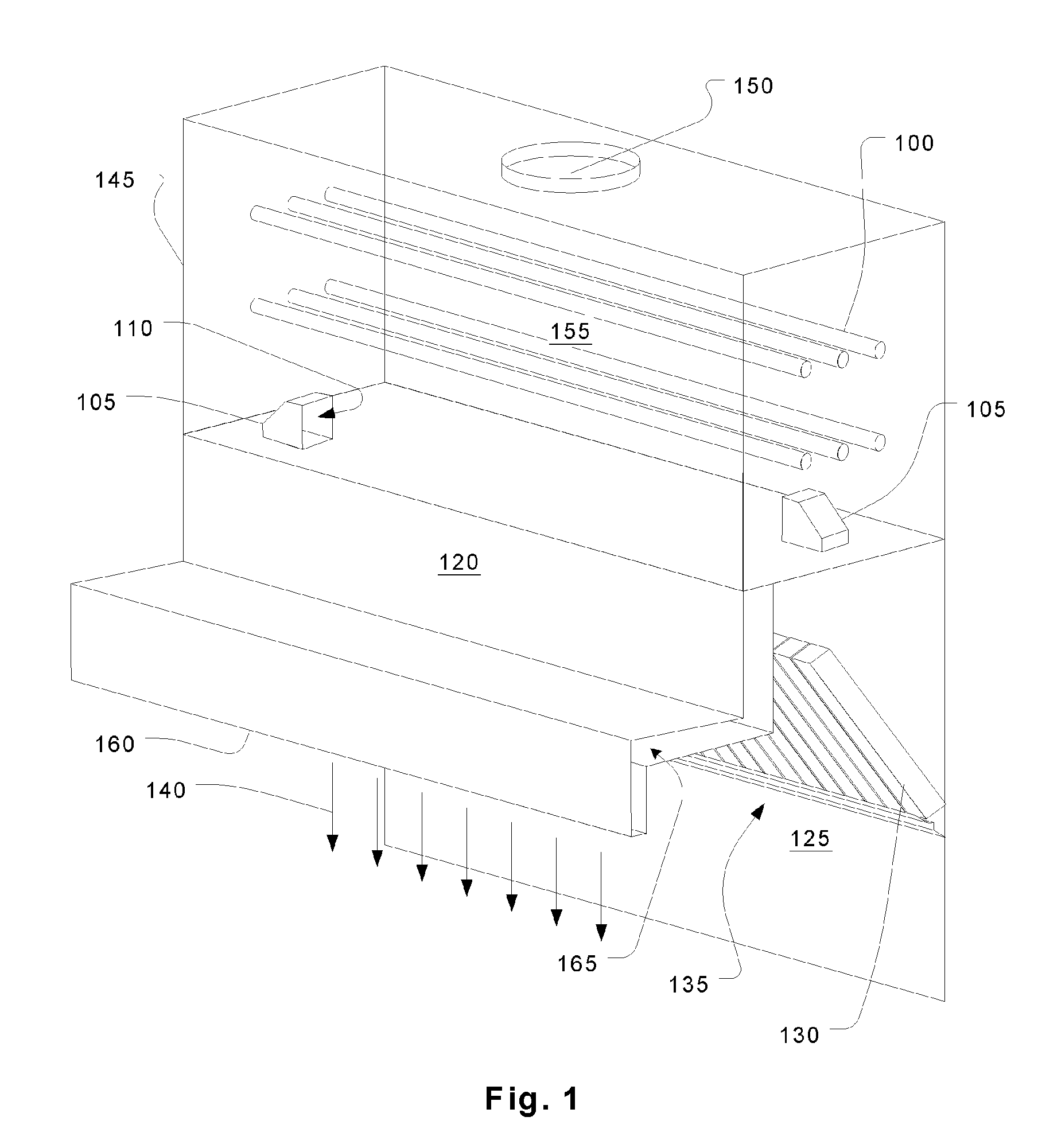
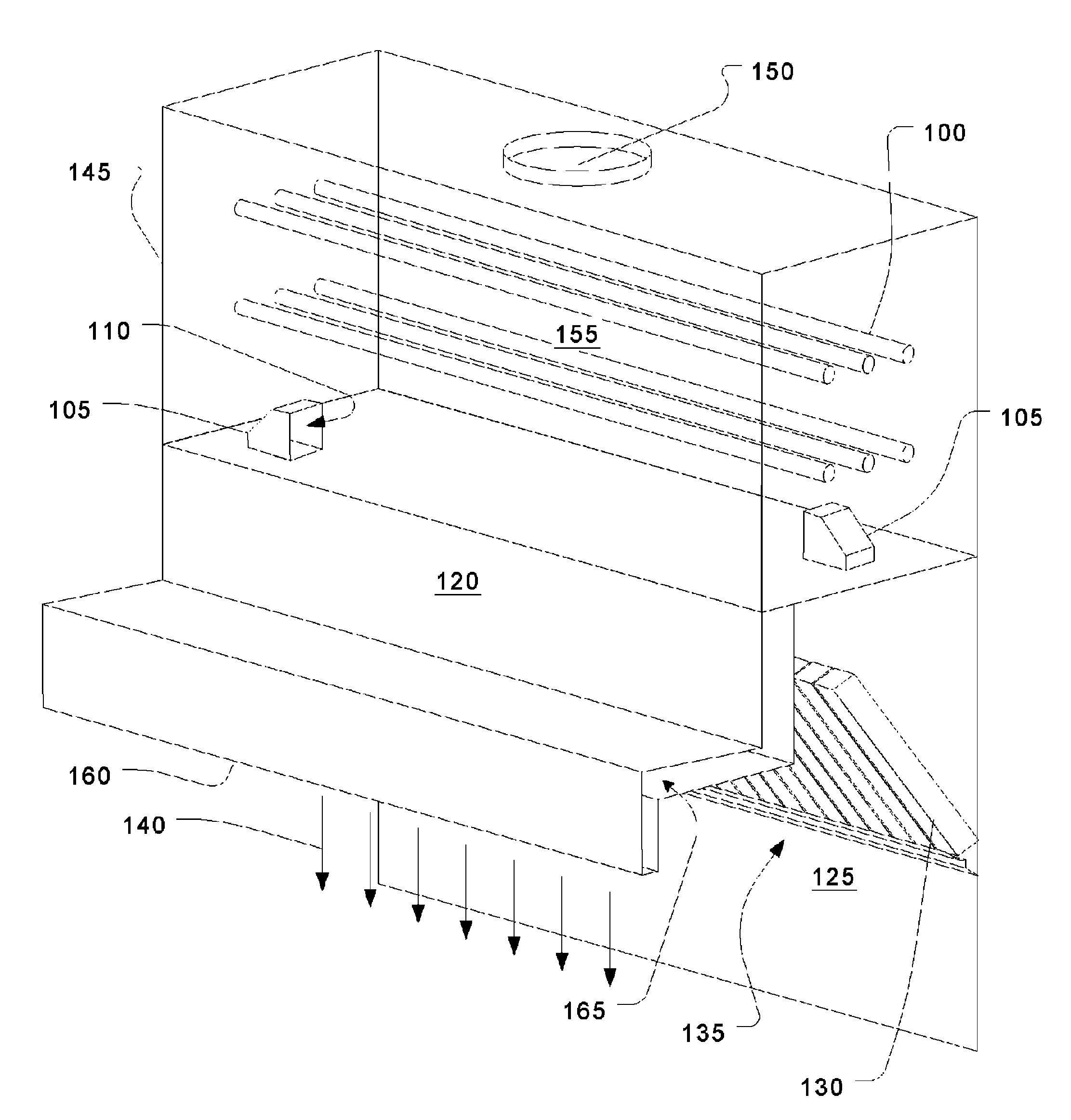
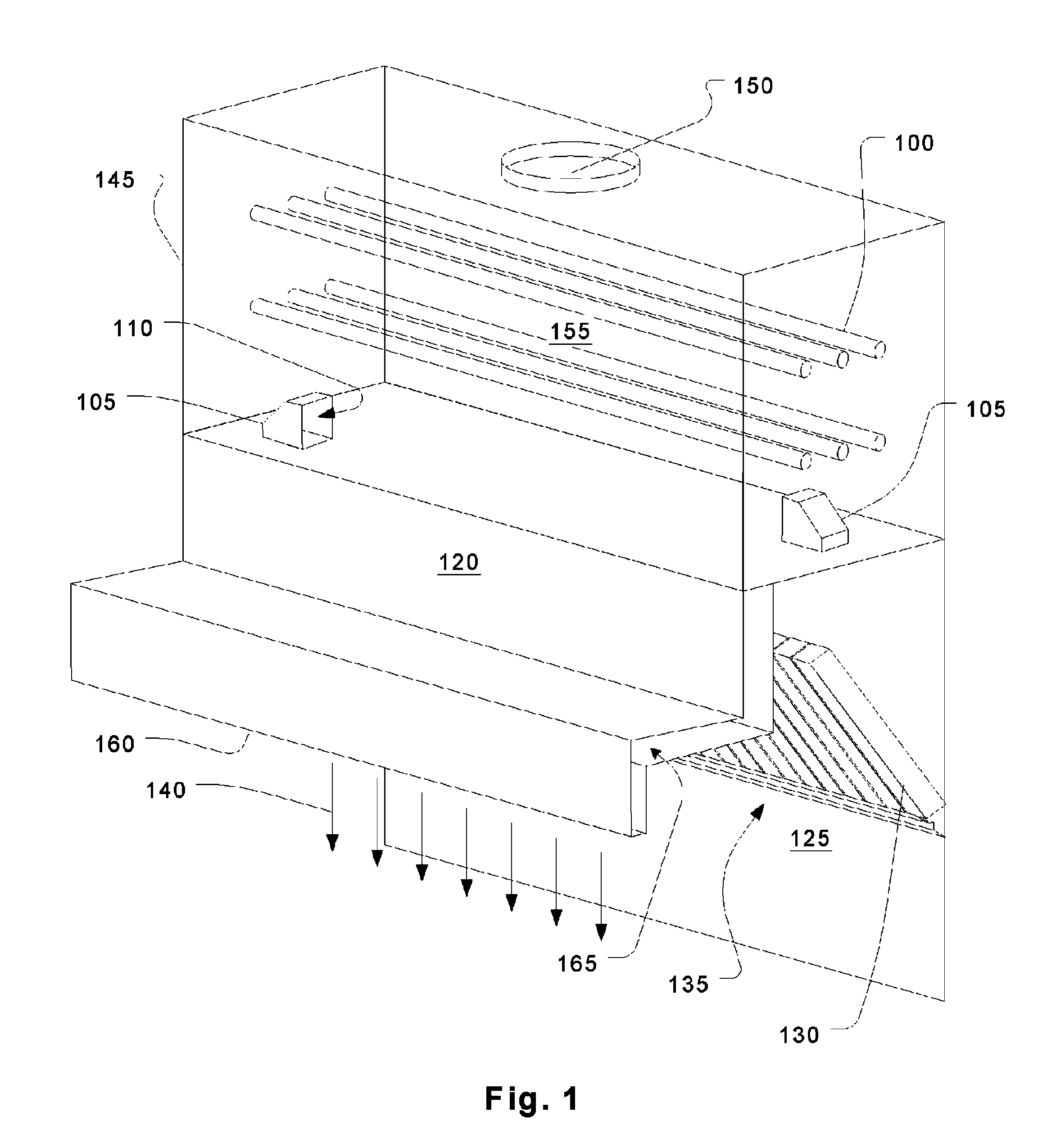
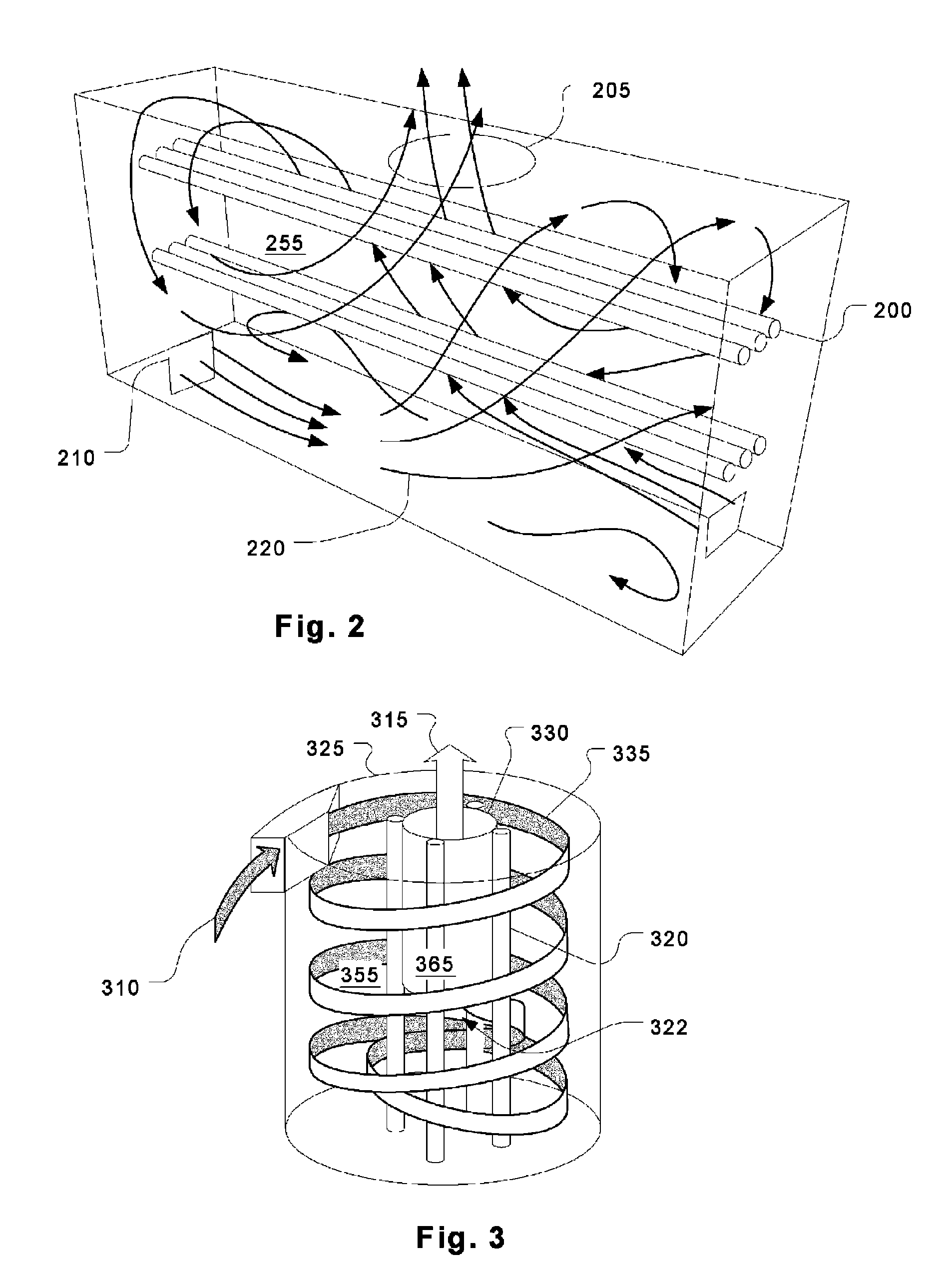
Fume treatment method and apparatus using ultraviolet light to degrade contaminants
ActiveUS20060219235A1Increase minimum dwell timeSpeed up the flowCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesStream flow
An ultraviolet treatment chamber for treating exhaust streams, particularly those containing organic particulates, utilizes ultraviolet light energy very efficiently. This is done by setting up a circulating flow in a treatment plenum so that all of the effluent experiences a substantially uniform residence time without the need for baffles or other flow controllers that would block the ultraviolet light.
Owner:HALTON GROUP LTD
Sealants for Solar Energy Concentrators and Similar Equipment
InactiveUS20090032088A1Good sealantImprove performance and longevityPV power plantsSynthetic resin layered productsFresnel lensPlastic materials
Owner:RABINOWITZ MARIO
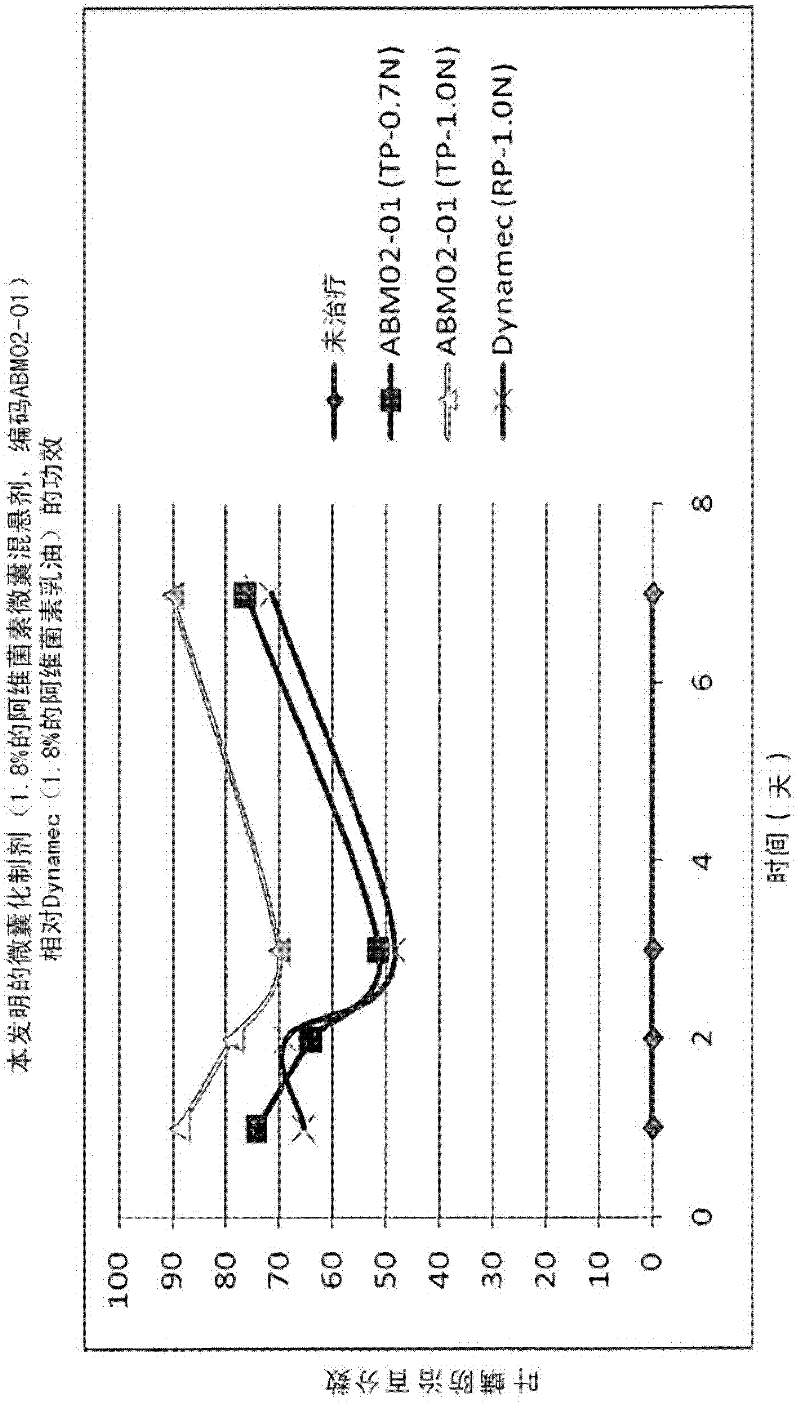
Microcapsules containing macrolide lactones abamectin, milbemectin, avermectins, milbemycins, emamectins, ivermectins and mectins in general
Microencapsulated formulations of macrolide lactones (abamectin, milbemectin, milbemycins emamectin, avermectins, ivermectins) wherein the active ingredient is protected from UV-degradation, with exceptional release characteristics resembling those of an emulsion concentrate or, if desired, of long-lasting effect; further with appropriate rheological properties, and with reduced toxicity. The invention provides a unique microencapsulation process for the chemical stability and biological activity of mectins, e.g. abamectin, and provides microcapsules of mectins to be used in formulations CS, WG / CS, ZC, EC / CS and any formulation type containing microcapsules and combination with other biologically active ingredients.
Owner:GAT MICROENCAPSULATION AG
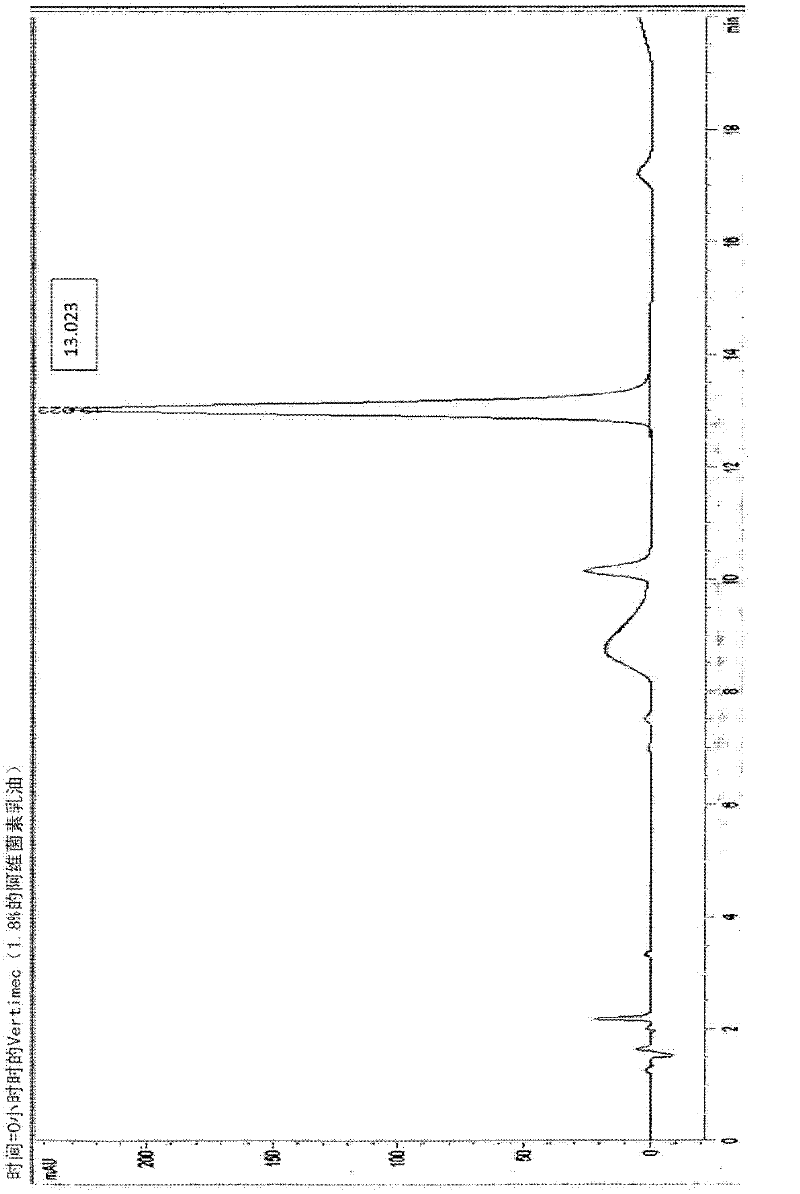
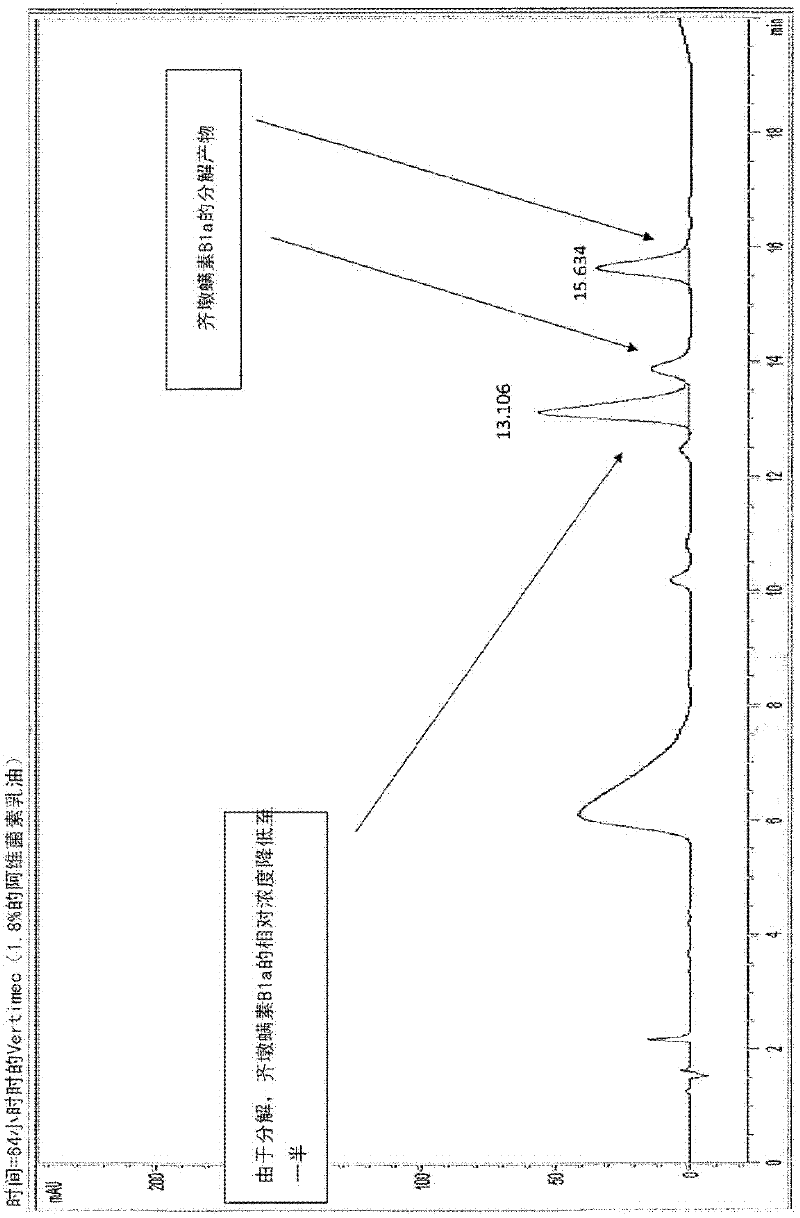
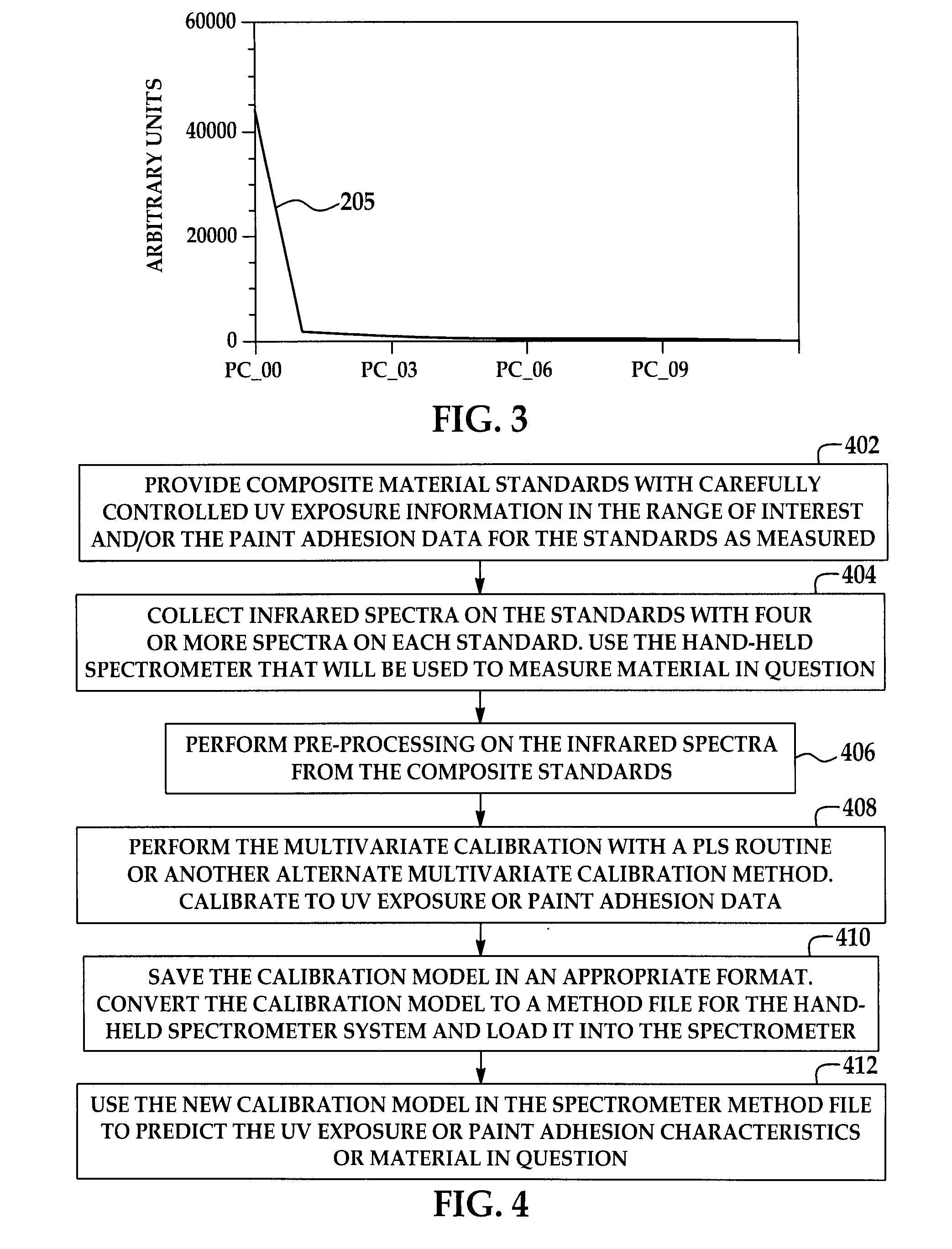
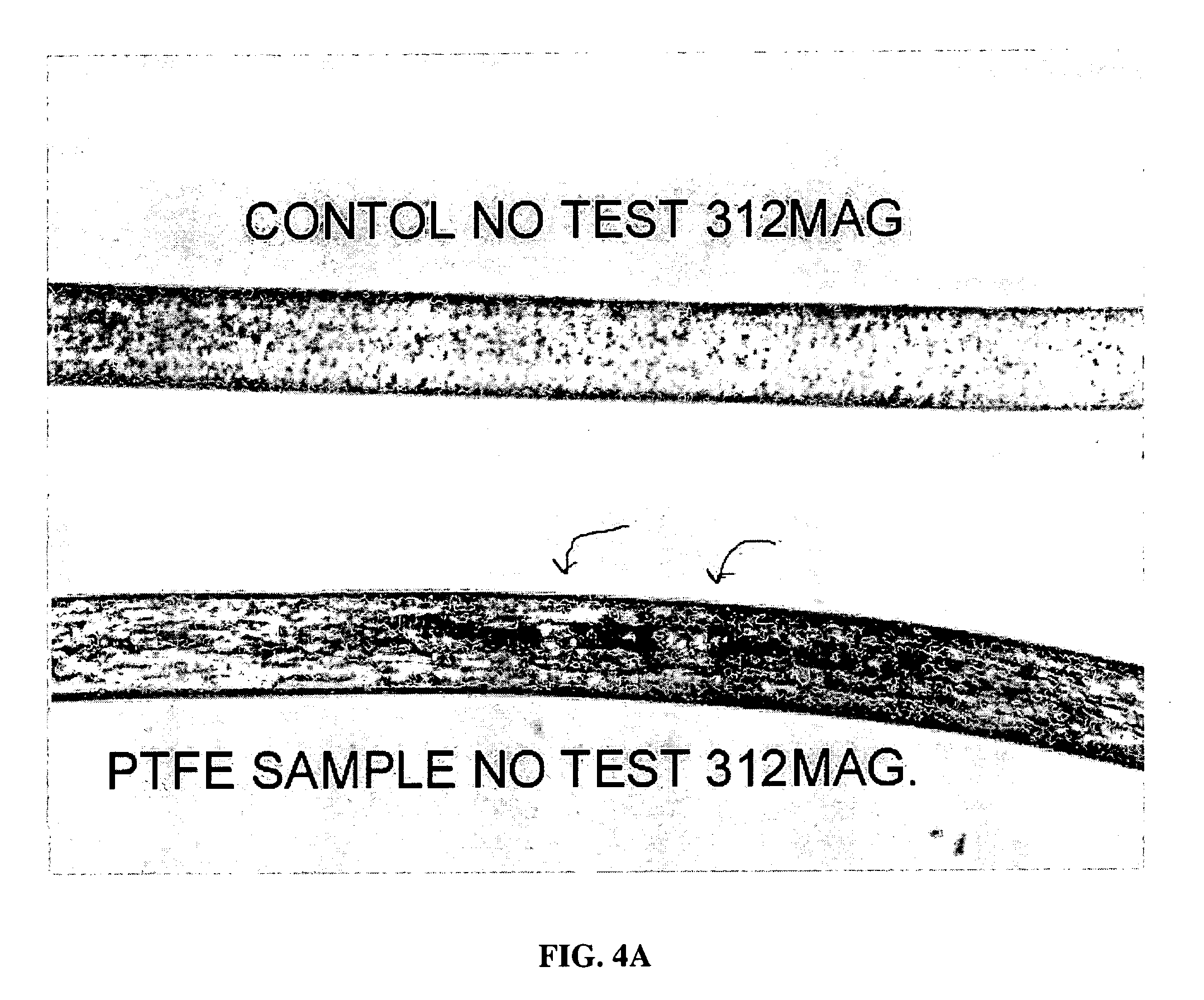
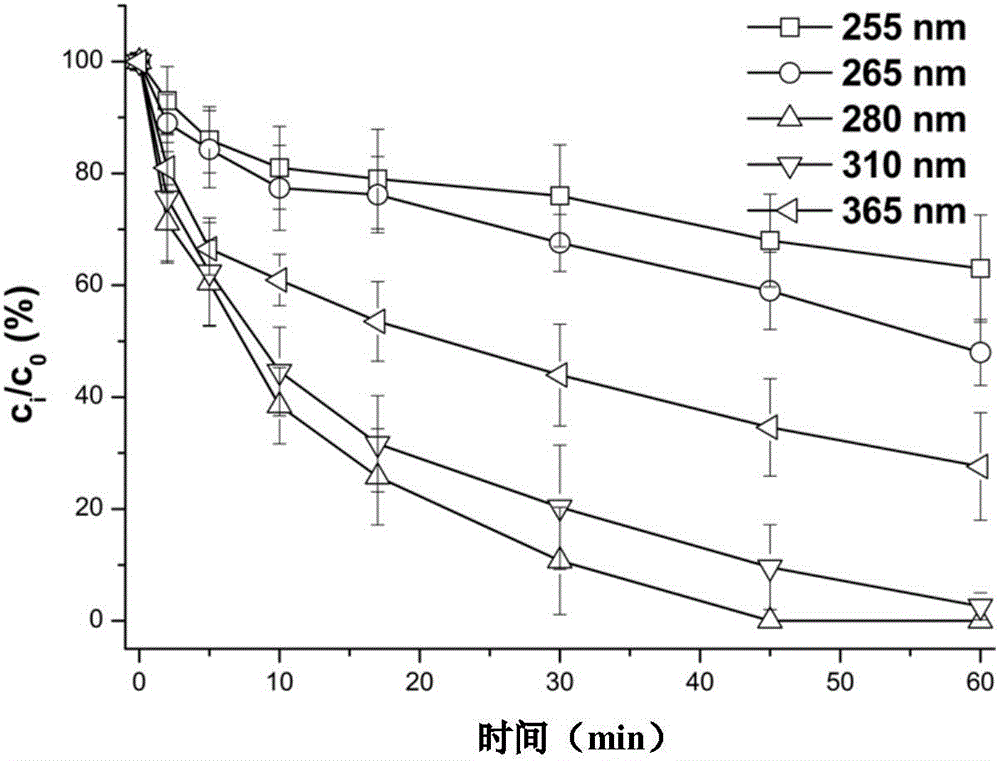
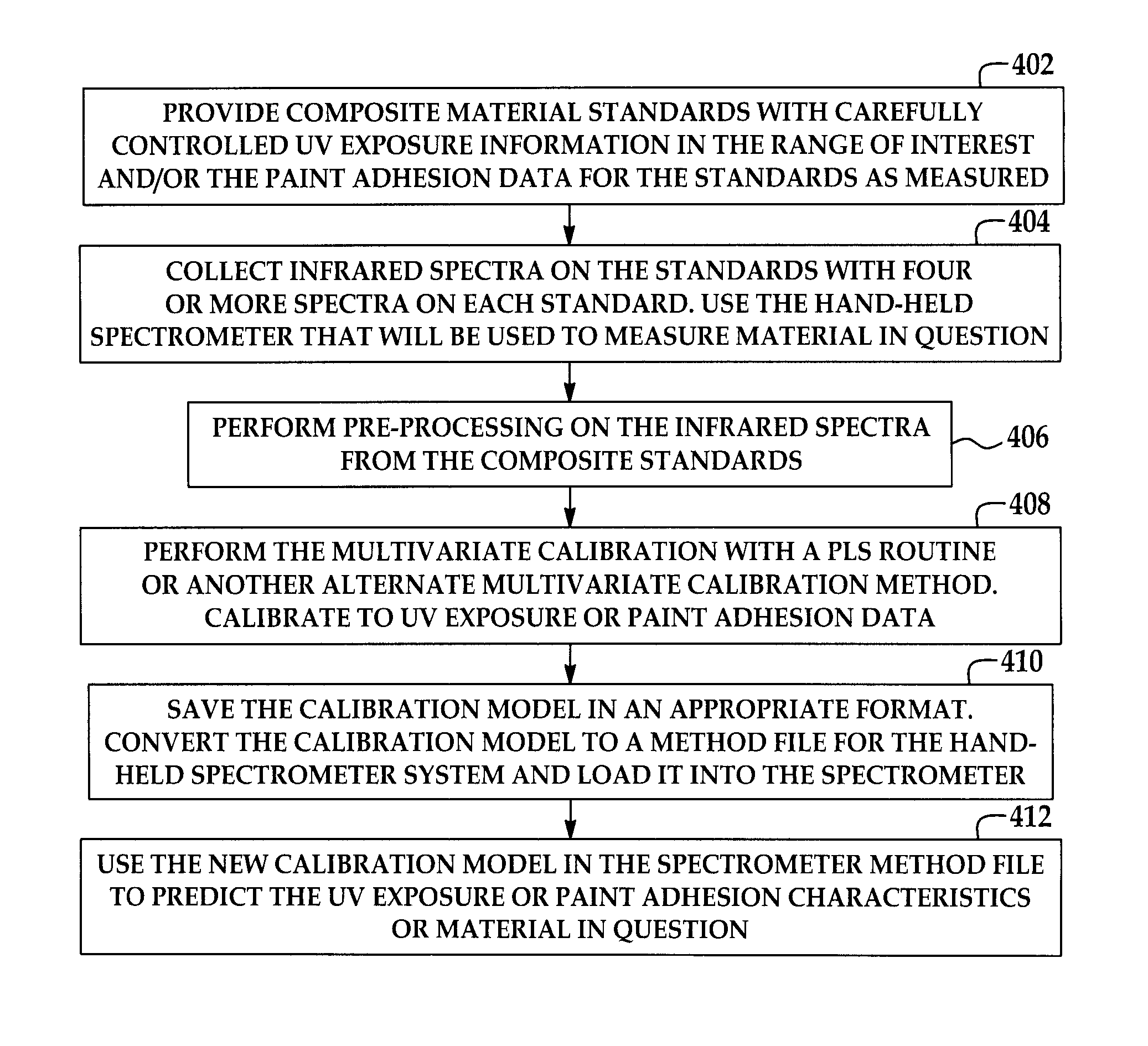
Method for performing ir spectroscopy measurements to quantify a level of UV effect
InactiveUS20090321647A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationNon destructiveMultivariate calibration
A method of non-destructively determining the amount of ultraviolet degradation of a surface and / or paint adhesion characteristics of the surface corresponding with UV damage including determining a physical property of a composite material / surfacing film by providing a series of composite materials / surfacing films which are subjected to increasing UV light experience to create a set of UV damage standards, collecting mid-IR spectra on those standards, performing data pre-processing and then multivariate calibration on the spectra of the composite materials / surfacing films, and using that calibration to predict the UV damage for samples in question.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Protective device for plants, seedlings, and trees
InactiveUS8745920B1Reduced material requiredReduce weightPlant protective coveringsWindbreakEngineering
Disclosed is a plant protection device that combines the functionality of a solid walled style plant protector that is good for the establishment of a new plant / seedling and perforated style plant protector that is good for an established plant. The wall of a tree / plant protector and growth device has thin areas inherent in the wall that degrade faster than other parts of the same device wall. This occurs based on the weather conditions (wind / rain / cold), UV degradation, biodegradation, and other factors. Over time these areas open up, allowing air, sun light and other environmental elements to reach the plant / tree within the protector. Strategically placing the thinner areas allows for designs for different plant / tree species and applications. Applications for climatic regions—northern, aired, wetlands, etc. Other applications examples are reforestation, vineyards, windbreaks, etc. The degradation of the thin areas can be controlled by using different materials, UV stabilizer levels and other methods.
Owner:MILLS THOMAS
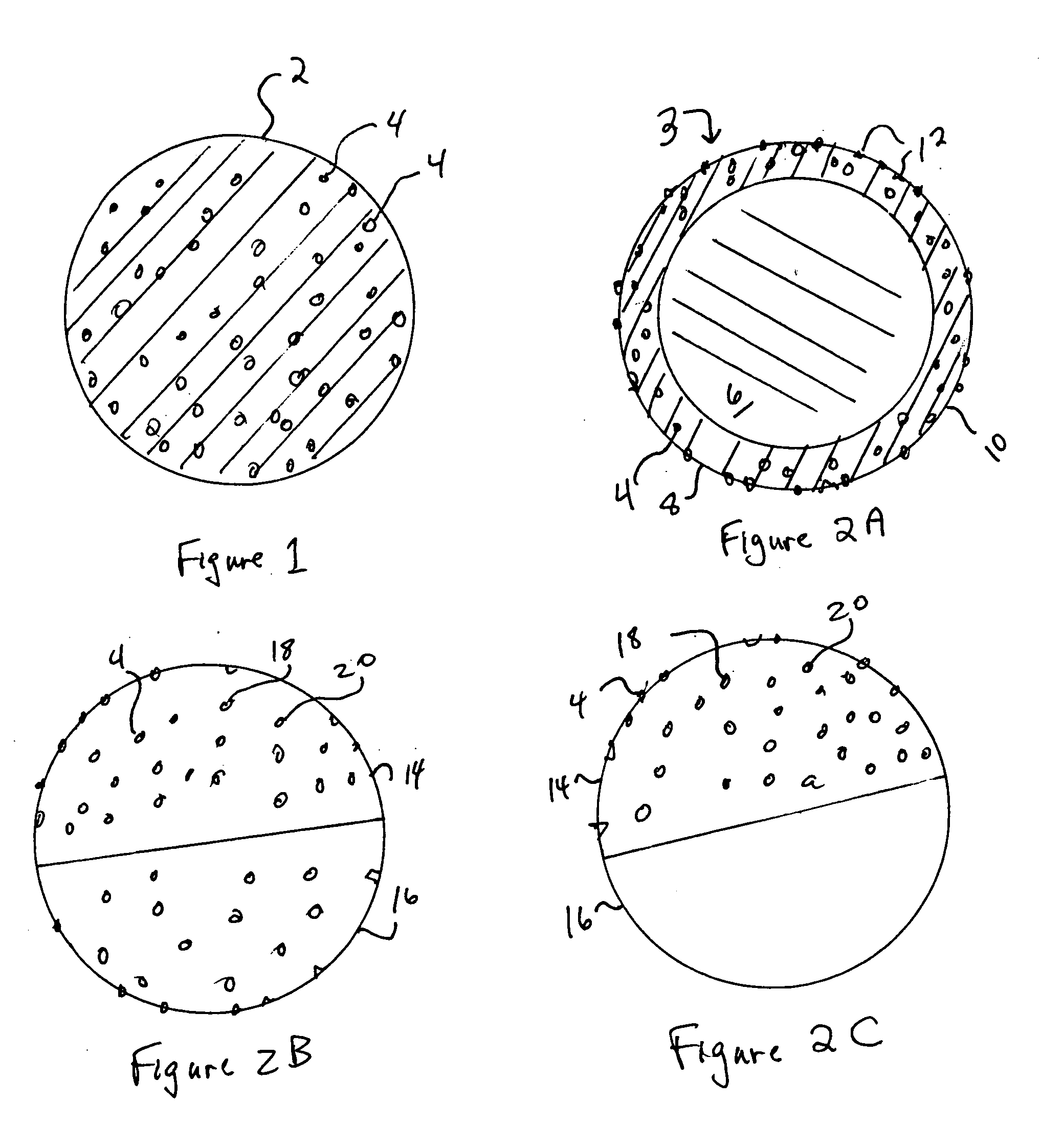
Synthetic fibers modified with PTFE to improve performance
InactiveUS20050100733A1Improve hydrophilicityImprove stain resistanceConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsYarnPolyesterUV degradation
Synthetic plastic fibers are enhanced by inclusions therein of micro-polyester particles (4), preferably sized or otherwise optimized to enhance surface (10) characteristics (abrasion resistance, hydrophilicity, coating receptiveness, increase dullness), reduce UV degradation. The synthetic plastic matrix is preferably polyester but can be any synthetic plastic. The invention is preferentially implemented in multi-component fibers (e.g. core (6)-sheath (8) bi-component fibers (3)) with the inclusions entirely or primarily in one or some, but not all such components. The PTFE inclusions, sizing, concentration, morphology can be adjusted to optimize their enhancing effects, reduce costs and enhance throughput of fiber production. Co-inclusions can be made with the PTFE including anti-microbial and / or coloring agents and with synergistic effects.
Owner:FOSS MFG CO LLC
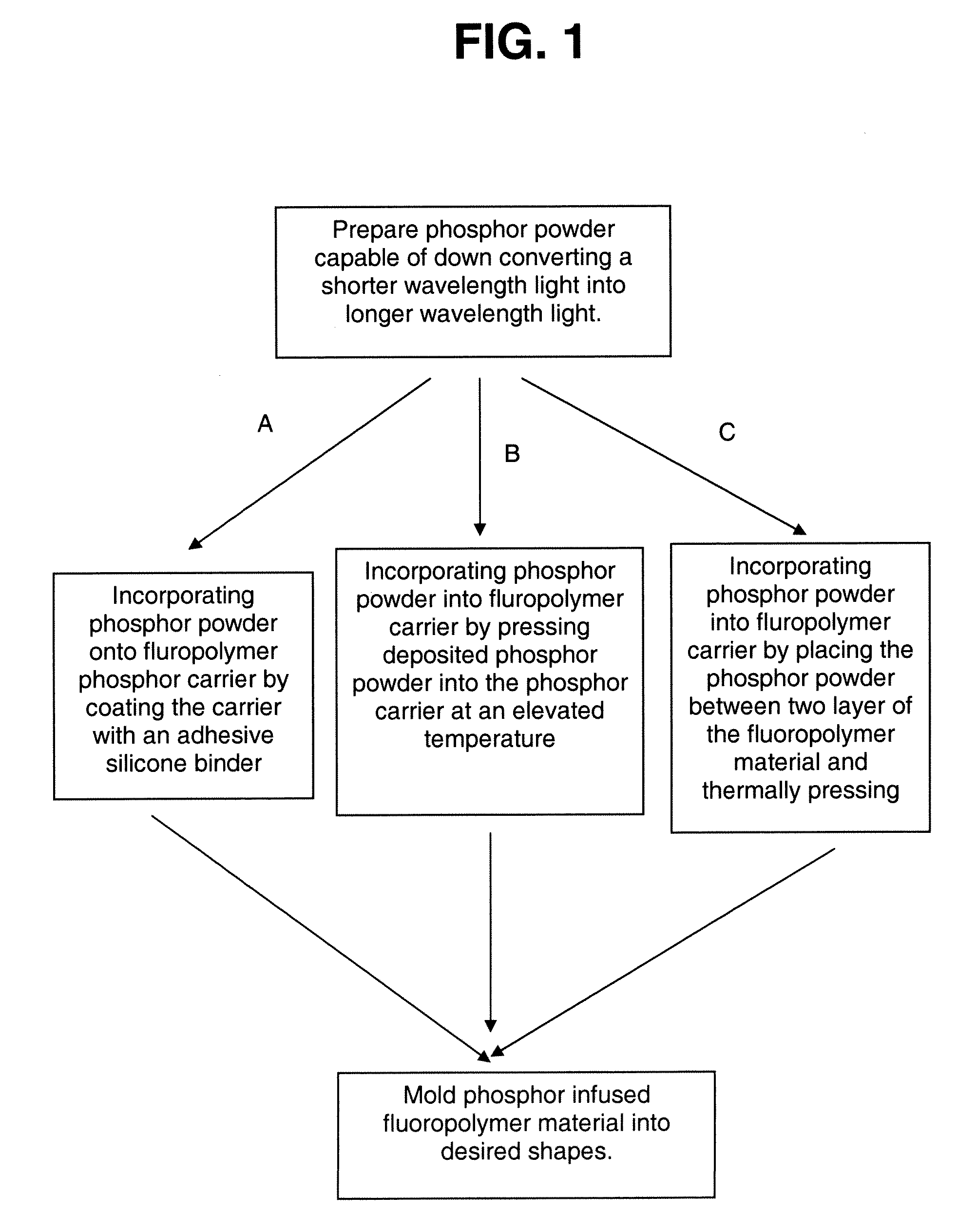
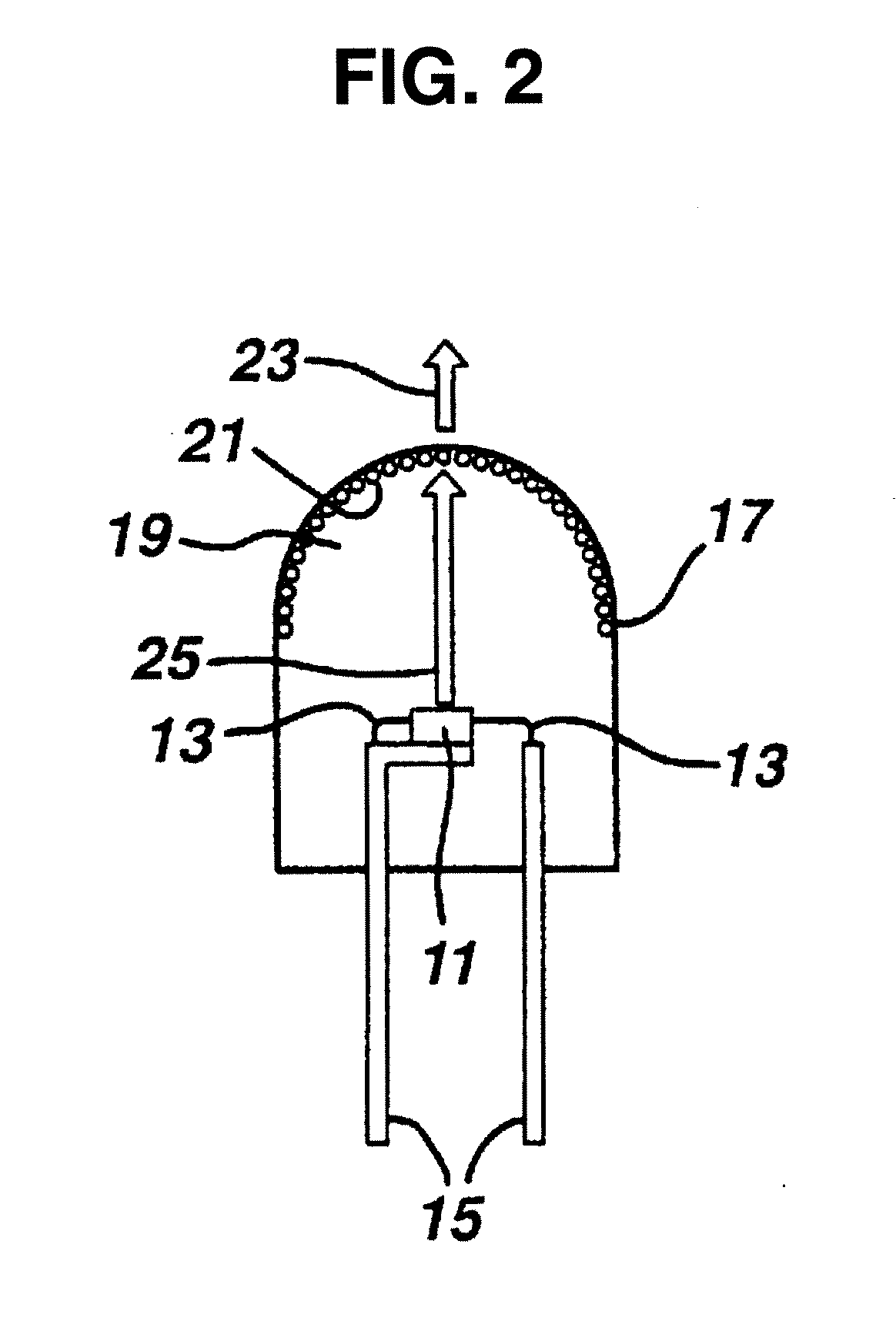
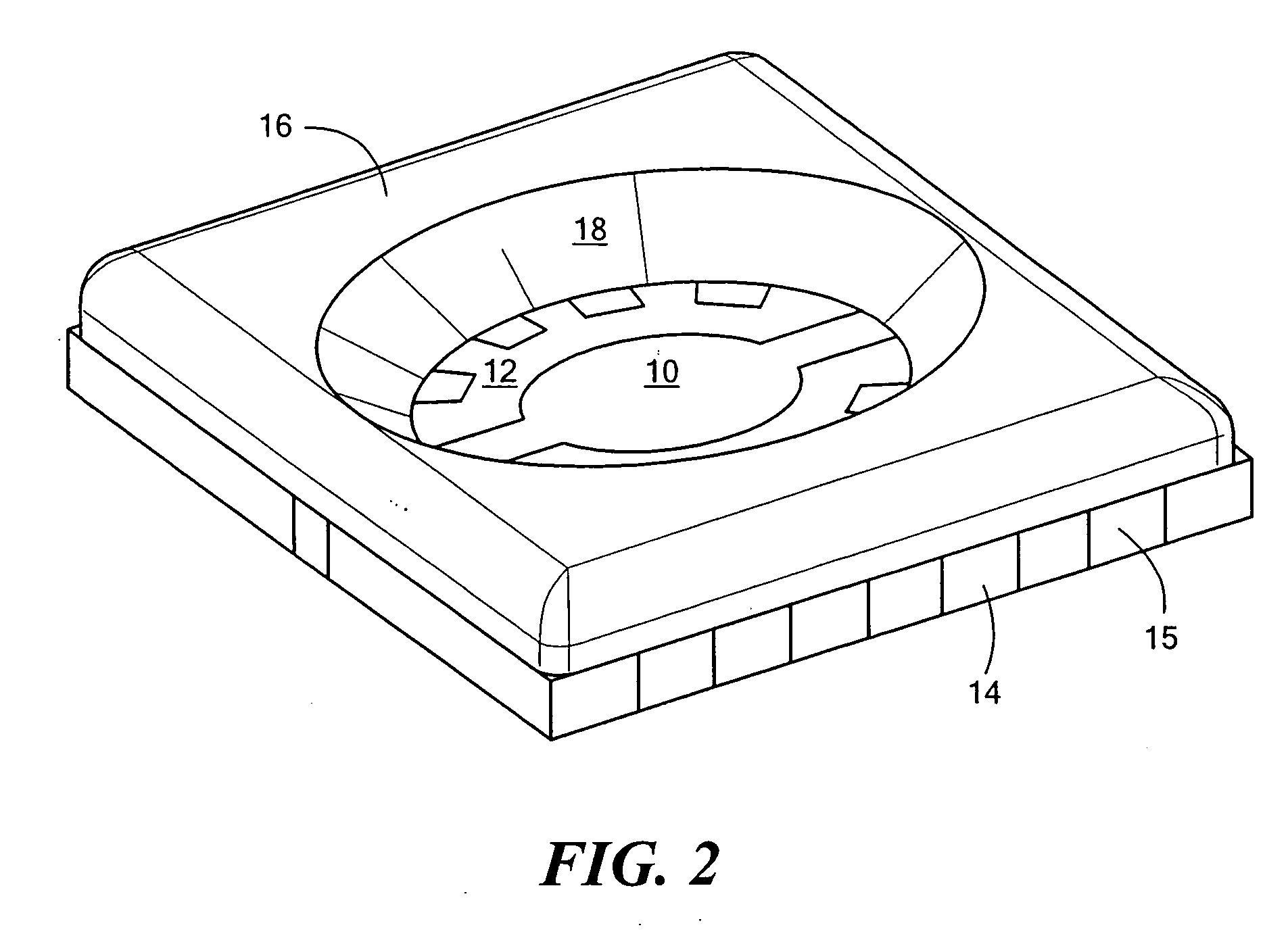
Phosphor down converting element for an LED package and fabrication method
There is provided a phosphor down converting element based on fluoropolymer resin and a method for fabricating the same. There is further provided a method for using said phosphor down converting element to generate white light from a radiation source. The method for fabricating phosphor down converting element includes preparing an appropriate phosphor powder mixture that is capable of absorbing a first band of wavelengths and emitting a second band of wavelengths being greater in length than the first bands, incorporating the phosphor powder mixture into or on a phosphor carrier element comprising a fluoropolymer material, and molding the phosphor down converting elements into useful shapes. Fluoropolymers are the most chemically inert of all plastics, can withstand both extremely high and low temperatures, and show a resistance to weavering and UV degradation, making fluoropolymers optimal for use as a phosphor carrier.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Dielectric coating and application process
InactiveUS20130048425A1Safety devices for lifting equipmentsLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringUV degradation
A method of electrically insulating one or more components of a boom assembly involves applying a seamless coating of dielectric material to an outer surface of each of one or more boom assembly components, the boom assembly components being constructed of metal or other electrically conductive material. The dielectric material is applied as a liquid and, when hardened, creates a seamless, electrically insulating barrier on the boom assembly components to which it is applied. A layer of ultraviolet radiation protective material may be applied on top of the layer of dielectric material to protect the dielectric material from ultraviolet degradation. The boom assembly components may be painted or otherwise treated prior to the application of the dielectric material.
Owner:ALTEC INDS
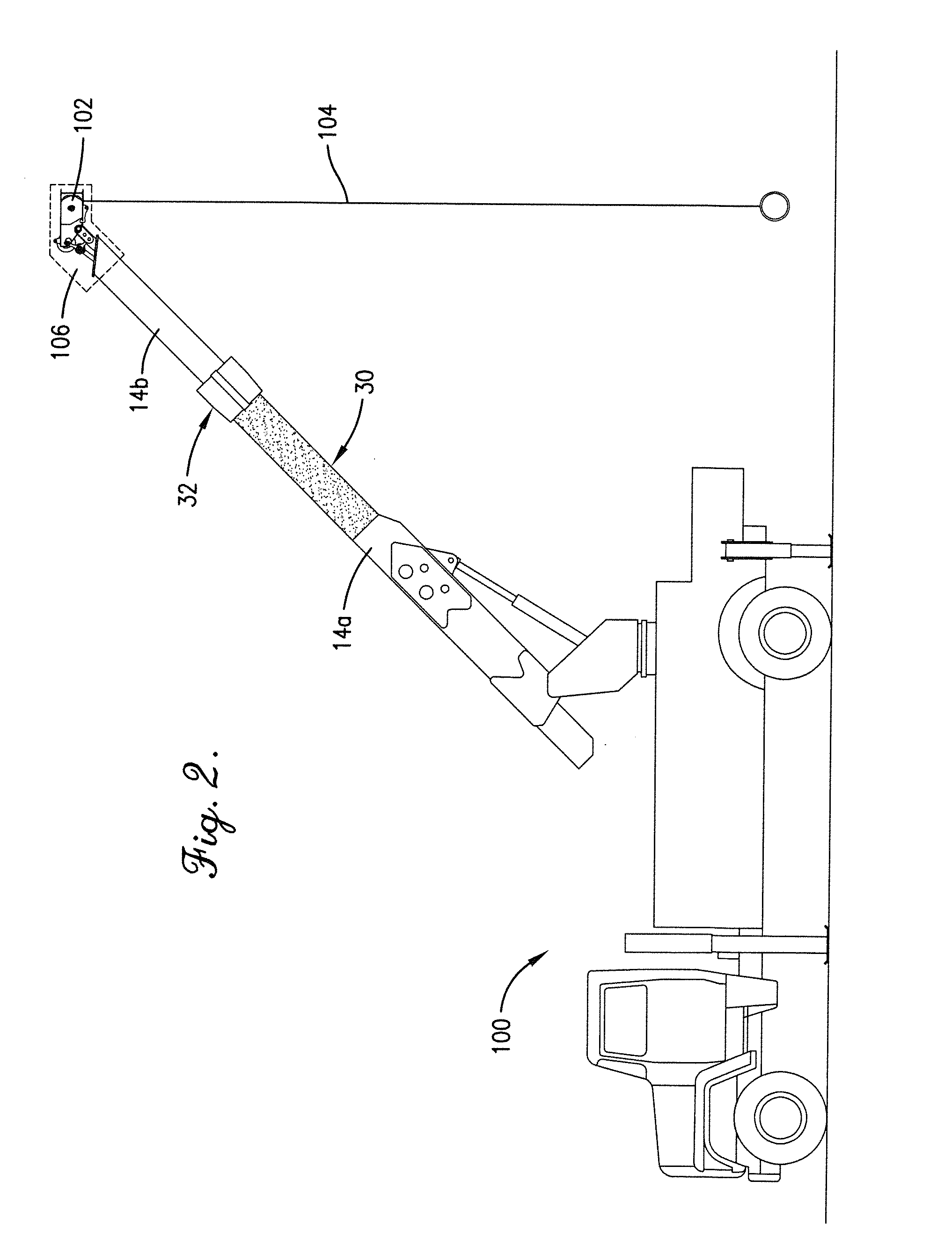
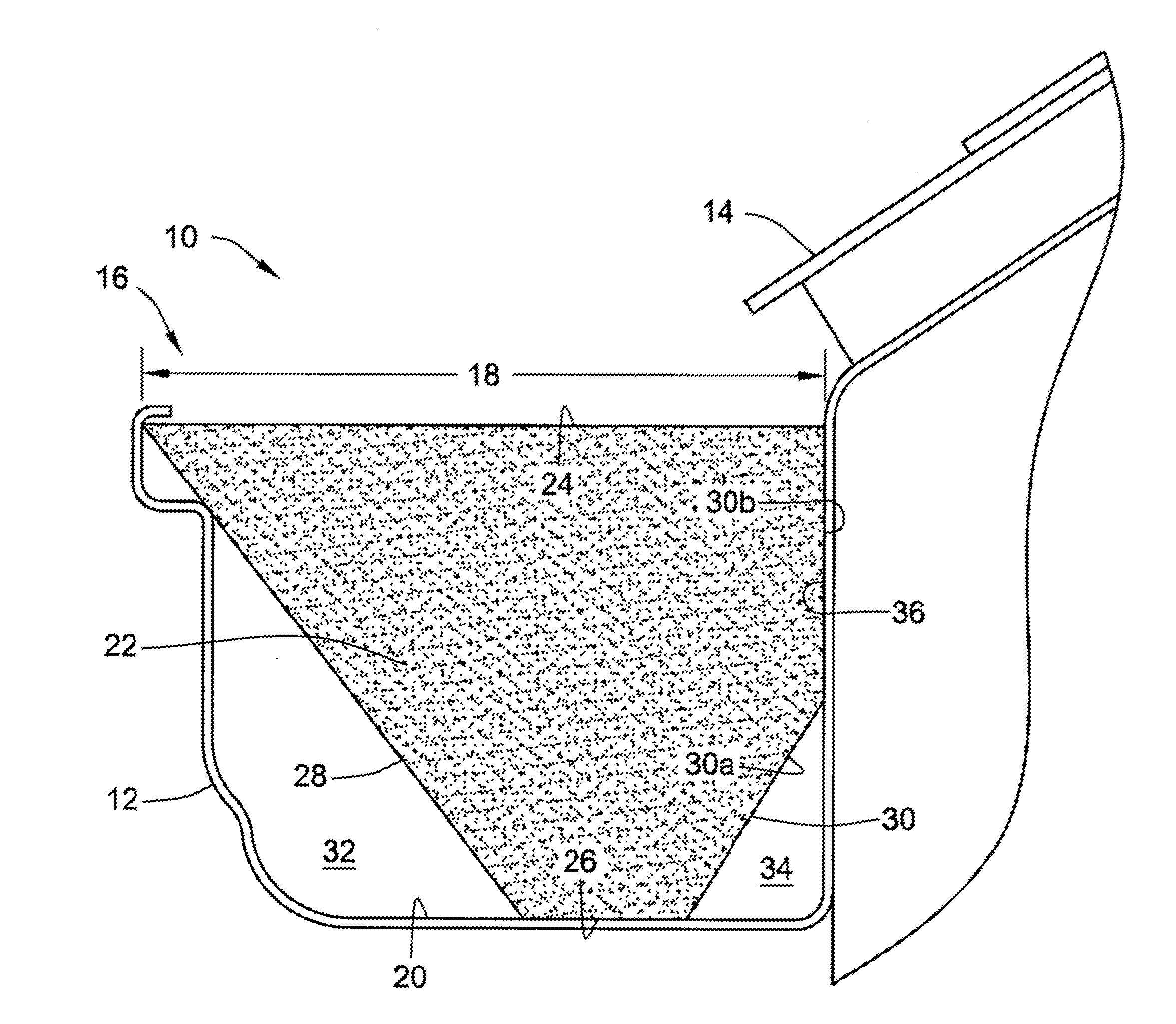
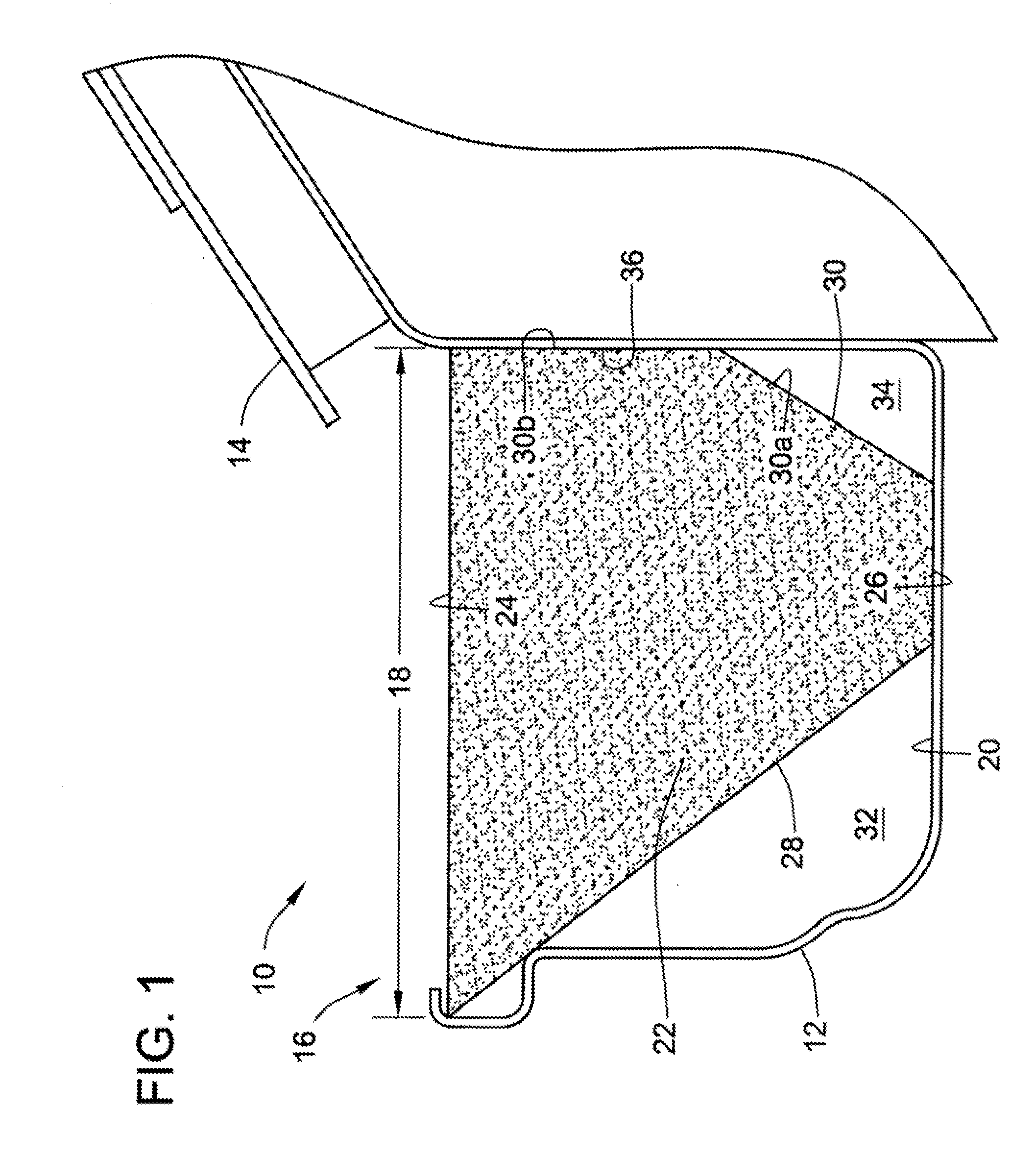
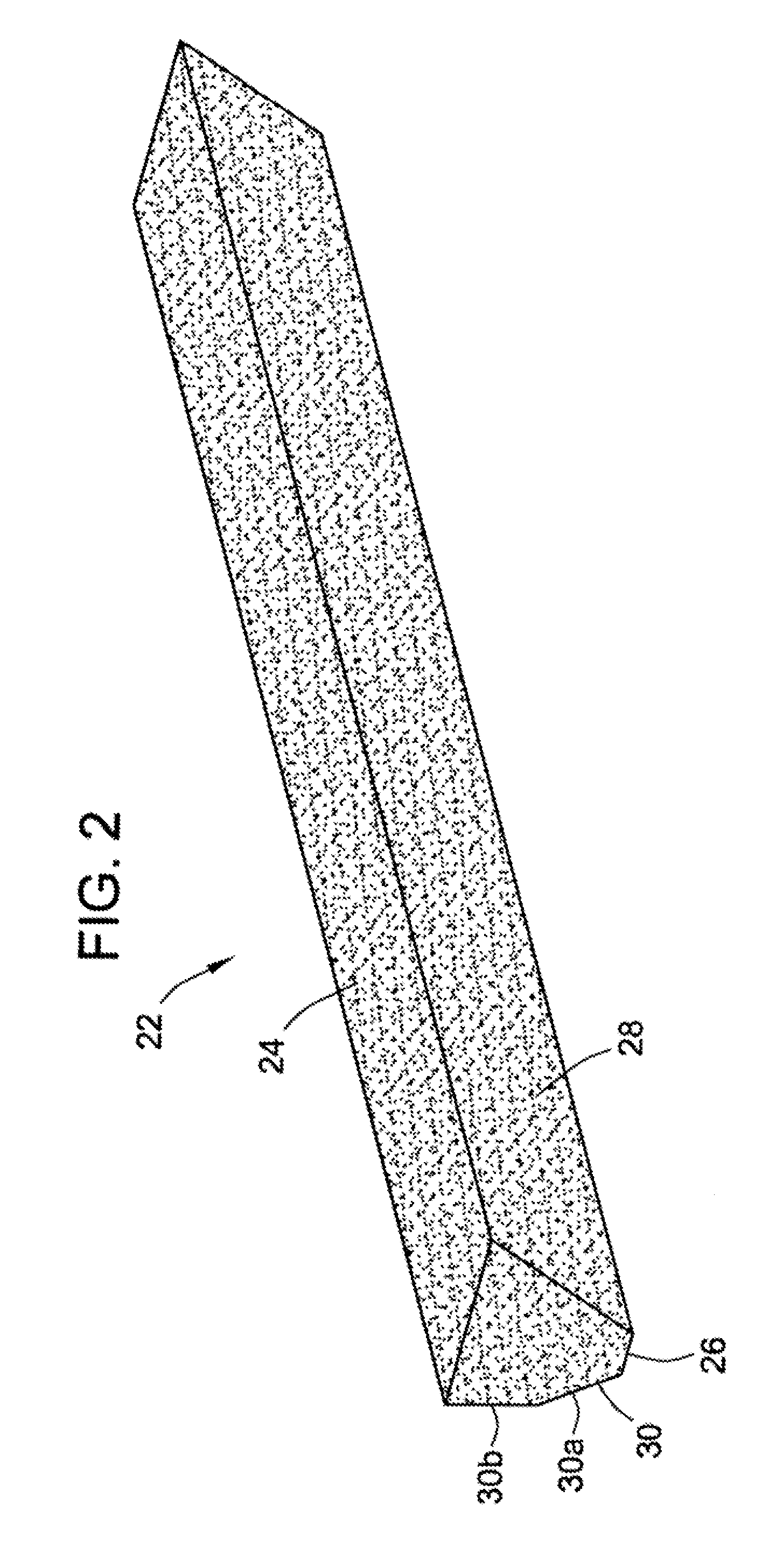
Gutter filter
A rain gutter filter apparatus and method utilize a filter element of a reticulated foam material adapted for insertion into a gutter having an open top defining a top width of the gutter. The filter element has a flat top surface with a width substantially matching the top width of the gutter, a flat bottom surface having a width less than the top width of the filter element, and front and rear surfaces extending upward from the bottom surface of the filter element to thereby form a front and a rear open passage for water on front and rear sides of the bottom surface of the filter element when the filter element is installed into the gutter. The reticulated foam material of the filter element has a composition that is flame resistant, germicidal, mold resistant, and resistant to degradation by exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Owner:AMERICAN GUTTER FILTER
Phosphor down converting element for an LED package and fabrication method
There is provided a phosphor down converting element based on fluoropolymer resin and a method for fabricating the same. There is further provided a method for using said phosphor down converting element to generate white light from a radiation source. The method for fabricating phosphor down converting element includes preparing an appropriate phosphor powder mixture that is capable of absorbing a first band of wavelengths and emitting a second band of wavelengths being greater in length than the first bands, incorporating the phosphor powder mixture into or on a phosphor carrier element comprising a fluoropolymer material, and molding the phosphor down converting elements into useful shapes. Fluoropolymers are the most chemically inert of all plastics, can withstand both extremely high and low temperatures, and show a resistance to weavering and UV degradation, making fluoropolymers optimal for use as a phosphor carrier.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Curable film-forming composition exhibiting improved resistance to degradation by ultraviolet light
InactiveUS7220793B2Improve the immunityKeep the lookPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyManganeseUltraviolet lights
A curable film-forming composition is provided comprising (i) 10 to 90 percent by weight based on the total weight of resin solids in the film-forming composition of a crosslinking agent; (ii) 10 to 90 percent by weight of a polymer containing a plurality of functional groups reactive with the crosslinking agent; and (iii) 5 to 85 percent by volume of particles having a mean particle size less than 100 nm. The particles comprise 1 to 99 percent by weight of at least one metal oxide wherein the metal is selected from zinc, titanium, cerium, manganese, bismuth, copper, zirconium and iron.A multi-component composite coating composition is also provided, comprising a pigmented basecoat and a clear coat. The basecoat and / or clearcoat may be derived from the curable film-forming composition described above.Also provided are coated substrates in which the curable coating compositions or the multi-component composite coating compositions described above are applied to a substrate and cured to form a cured coating.Further provided is a pigment comprising particles having a mean particle size less than 100 nm and comprising 1 to 99 percent by weight metal oxide wherein the metal is selected from zinc, titanium, cerium, manganese, bismuth, copper, zirconium and iron and 1 to 99 percent by weight silica. These particles may be used in the curable film-forming compositions described above.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Weather resistant plastic composites capped with polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) for outdoor exposures
InactiveUS6855402B2Low costGood weather resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolyethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
A composite layered plastic article particularly resistant to outdoor exposure to heat, sunlight and UV degradation comprises a top surface exposed layer of PETG fused to a rigid substrate layer selected from PVC, or CPVC, or HIPS, or ABS, or ASA, or PC. The PETG layer is preferably co-extruded with the substrate layer and heat fused together to produce a laminated layered composite article. The composite layered plastic is particularly useful for color retention of dark colors and bright masstone colors, as well as pastel and white colors
Owner:POLYONE CORPORATION
Cured composite material and sand-fixing method for plant greening
InactiveCN102120933ANon-toxicSafety and environmental protectionOther chemical processesClimate change adaptationEcological environmentUltraviolet
The invention provides a cured composite material and a sand-fixing method for plant greening, a functional water soluble polyurethane composite cured material is prepared by composite reaction of a water soluble polyurethane resin chemical cured material (W-OH) and an ultraviolet degradation control agent, thereby greatly improving ultraviolet degradation resistance capability of the composite cured material, and degradation period of the composite cured material can be controlled. The ultraviolet degradation control agent comprises benzotriazole, benzophenone ultraviolet ray absorbent, and hindered amine and hindered phenol ultraviolet ray stabilizer. The cured composite material is sprayed to a sand surface with a spread plant greening composition, and a porous structured bonding layer is quickly formed on the desert surface, the bonding layer is advantaged by better air permeability, water conservation, and fertilizer-keeping characteristics, suitability for plant growth, realization of controlling more than 30 years of degradation period, and gradual realization of ecological environment remediation during sand-fixing.
Owner:JCK +1
Led reflective package
InactiveUS20080111148A1Improve aging performanceLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPlastic materialsRefractive index
An LED package which employs a high temperature plastic or polymeric material which is compatible with widely used gold-tin eutectic solder and which can replace the higher cost ceramic used in conventional LED packages. The novel LED package has a high thermal conductivity substrate, a high reflectivity for visible light and / or UV light, and good aging properties. The high temperature material is a high temperature liquid crystal polymer (LCP) having a melting temperature greater than about 340° C. and has small filler particles near the surface, the particles having a refractive index greater than about 2.0, and a size range of about 0.2 to 0.3 microns. For an LED package which is reflective to UV light, a UV stabilizer can be included in the plastic material to improve reflectivity in the ultraviolet spectrum and to protect from UV degradation of the plastic material which can be caused by UV light emitted by some LEDs.
Owner:IQLP
Easily removable UV degradable paint and process for applying the same
InactiveUS20070287766A1Mitigates and eliminates any damageImprove the environmentRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesWater insolubleWater flow
A paint is disclosed herein which comprises a binder having acid-degradable groups, and a photoacid generator that provides photogenerated acid upon exposure to UV light. The binder is water insoluble before exposure to UV light, and binder is water-removable after degradation of the acid degradable groups by the photogenerated acid. A process for applying and removing paint is further disclosed which comprises applying the paint comprising an acid degradable binder and UV sensitive photoacid generator to a surface, and hardening the paint by drying or crosslinking; and removing by exposing the paint to UV light, and directing a high pressure water stream to the exposed paint. The paint is useful as a road paint.
Owner:IBM CORP
Seed oil based coatings and their applications
InactiveUS7119135B2High viscosityIncreased durabilityInksRadiation-absorbing paintsUltravioletEngineering
A coating containing seed oil comprising the following: a seed oil used as a film forming component for the coating with at least one film forming component for the coating; at least one component to provide opacity and solar reflectivity to the coating; at least one component to provide protection to the coating from ultra-violet degradation; at least one filler component to increase the viscosity of the coating; and at least one film component that provides elongation and flexibility to the coating.
Owner:GREEN PROD
In situ exfoliation method to fabricate a graphene-reinforced polymer matrix composite
ActiveUS20160083552A1High bonding strengthHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologyPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCross-linkGraphite
A method for forming a graphene-reinforced-polymer matrix composite by distributing graphite microparticles into a molten thermoplastic polymer phase comprising one or more molten thermoplastic polymers; and applying a succession of shear strain events to the molten polymer phase so that the molten polymer phase exfoliates the graphene successively with each event, until tearing of exfoliated multilayer graphene sheets occurs arid produces reactive edges on the multilayer sheets that react with and cross-link the one or more thermoplastic polymers; where the one or more thermoplastic polymers are selected from thermoplastic polymers subject to UV degradation.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method for targeted degradation of quinolone antibiotics in water and multiband ultraviolet (UV) radiation device used for method
InactiveCN106554050ARealized by multi-band ultraviolet irradiationAdvantage UV wavelengthWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsUltravioletAntibiotic Y
The invention belongs to the field of water supply and sewerage works / environmental engineering, and discloses a method for targeted degradation of quinolone antibiotics in water and a multiband ultraviolet (UV) radiation device used for the method. The method for targeted degradation of the quinolone antibiotics in water includes the following steps that wastewater containing the quinolone antibiotics is added with a H2O2 aqueous solution and / or aqueous solution containing S2O8<2>, and then the wastewater is degraded under the multiband UV radiation action, so that a water body for targeted degradation of the quinolone antibiotics is obtained. The invention further provides the multiband UV radiation device used for the method. According to the method, the multiband UV radiation device independently designed and developed is used as the main body to be combined with the H2O2 and S2O8<2>, so that a composite UV degradation technology is formed, and the technology can be used in a water supply treatment plant or wastewater treatment plant; and electric energy serves as the driving energy, UV radiation serves as the excitation energy, the H2O2 or S2O8<2> serves as the oxidizing agent donor, efficient targeted degradation of ciprofloxacin is realized, and finally the antibacterial activity and toxicity are weakened.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Fume treatment method and apparatus using ultraviolet light to degrade contaminants
ActiveUS8002881B2Increase minimum dwell timeGood effectCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesUltraviolet lights
Owner:HALTON GROUP LTD
Gutter filter
ActiveUS20100170837A1Eliminate needEliminate damageRoof coveringArtificial water canalsReticulated foamUltraviolet
A rain gutter filter apparatus and method utilize a filter element of a reticulated foam material adapted for insertion into a gutter having an open top defining a top width of the gutter. The filter element has a flat top surface with a width substantially matching the top width of the gutter, a bottom surface having a width less than the top width of the filter element, and front and rear surfaces extending upward from the bottom surface of the filter element to thereby form a front and a rear open passage for water on front and rear sides of the bottom surface of the filter element when the filter element is installed into the gutter. The reticulated foam material of the filter element has a composition that is flame resistant, germicidal, mold resistant, and resistant to degradation by exposure to ultraviolet rays.
In situ exfoliation method to fabricate a graphene-reinforced polymer matrix composite
ActiveUS10253154B2High bonding strengthHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsAridCross-link
A method for forming a graphene-reinforced-polymer matrix composite by distributing graphite microparticles into a molten thermoplastic polymer phase comprising one or more molten thermoplastic polymers; and applying a succession of shear strain events to the molten polymer phase so that the molten polymer phase exfoliates the graphene successively with each event, until tearing of exfoliated multilayer graphene sheets occurs arid produces reactive edges on the multilayer sheets that react with and cross-link the one or more thermoplastic polymers; where the one or more thermoplastic polymers are selected from thermoplastic polymers subject to UV degradation.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Disinfecting and detoxifying meta-aramid particles
ActiveUS20110250162A1Good antimicrobialHigh detoxification activityPowder deliveryBiocideCellulose acetatePolyamide
Porous, permeable particles of meta-aramid can be chlorinated or brominated to produce antimicrobial and detoxifying particles for use in applications such as, but not limited to, nonwoven webs, paper, textiles, absorbent articles, healthcare products, paints, filter materials, powder coatings, clear coatings, molded plastic articles, binders for fibrous materials, and the like. The particles can be charged with halogen before or after incorporation into the application medium. The particles can contain blends of meta-aramid with other polymers such as, but not limited to, cellulose, cellulose acetate, polyurethane, and the like. The particles will be effective at inactivation of pathogenic and odor-causing microorganisms and toxic chemical agents. The particles, which contain N-halamine units, have unexpected resistance to ultraviolet light degradation.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Raspberry amido amines and betaines as a delivery system for natural antioxidants
The present invention relates to raspberry seed oil derivatives derived by the reaction of dimethyl amino propyl amine and cold pressed raspberry seed oil. This intermediate is subsequently reacted with sodium monochloroacetic acid to make a raspberry betaine. The choice of cold pressed raspberry seed oil as a raw material in the preparation of the compounds of the present invention is critical, since it has been found that the cold pressed raspberry seed oil contains antioxidants, antimicrobial compounds and which when reacted with a DMAPA result in products that deliver said actives to the skin and hair, resulting in protection of the skin and hair from environmental factors such as acid rain, ozone attack and UV degradation.
Owner:T C U S A
Thermoplastic containers exhibiting excellent protection to various ultraviolet susceptible compounds
InactiveUS20030155559A1Brighter clarityEffective protectionFilm/foil adhesivesOptical filtersThermoplasticUltraviolet
Novel thermoplastic articles that contain novel ultraviolet absorbing compounds that are liquid in nature, are extremely low in color (and thus permit use without the concomitant necessity of adding large amounts of other coloring agents to combat any discoloring within clear, colorless applications), are substantially non-migratory from target resins, and are highly effective in providing protection in wavelength ranges for which previous attempts at low-color ultraviolet absorbers have failed are provided. In effect, the inventive thermoplastic articles, provide excellent protection for certain vitamins, flavorings, and colorants, for example, from ultraviolet degradation, particularly above the 370 nm wavelength that is typically the high end of protection for clear thermoplastics having low migratory, colorless UV absorbers therein.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Microbiocidal Treatment Of Edible Fruits And Vegetables
Methods of controlling bacterial, yeast, and / or mold contamination of edible fruits or vegetables comprise applying thereto an aqueous microbiocidal composition stabilized against ultraviolet light-induced degradation formed from water and (A) at least one component selected from (I) a solid-state microbiocidal compound having at least one bromine atom per molecule; (II) an aqueous solution / slurry of a compound of (I); (III) a concentrated aqueous composition having an active bromine content of at least 50,000 ppm derived from water and (i) BrCl or BrCl and Br2 and (ii) overbased alkali metal sulfamate, where the relative proportions of (i) and (ii) give an atom ratio of nitrogen to active bromine greater than 0.93, and where the pH of the composition is greater than 7; (IV) a solid-state composition formed by dewatering a composition of (III), and (B) dissolved ascorbic acid or edible salt or ester thereof to inhibit ultraviolet light degradation of the solution.
Owner:ALBEMARLE CORP
Fluorescent lamp with uv-blocking layer and protective sleeve
InactiveUS20100277056A1Incadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensUltravioletEngineering
A fluorescent lamp having a protective polymeric sleeve to provide impact resistance and contain fragments if the lamp shatters. A UV-blocking layer is coated on the outside of the glass envelope of the lamp or on the inside of the sleeve to help protect the polymeric sleeve from UV degradation. The UV-blocking layer includes a UV-blocking component of Al2O3 or ZnO or SiO2 or TiO2 or mixtures thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Guerbet cranberry esters as a delivery system for natural antioxidants
The present invention relates to Cranberry seed oil derivatives derived by the reaction of a guerbet alcohol and cold pressed Cranberry seed oil. The choice of cold pressed Cranberry seed oil as a raw material in the preparation of the compounds of the present invention is critical, since it has been found that the cold pressed Cranberry seed oil contains antioxidants, antimicrobial compounds and which when reacted with a guerbet alcohol result in products that deliver said actives to the skin and hair, resulting in protection of the skin and hair from environmental factors such as acid rain, ozone attack and UV degradation.
Owner:T C U S A
Gutter filter
ActiveUS8220206B2Easy to washEasy to installRoof coveringArtificial water canalsReticulated foamUltraviolet
A rain gutter filter apparatus and method utilize a filter element of a reticulated foam material adapted for insertion into a gutter having an open top defining a top width of the gutter. The filter element has a flat top surface with a width substantially matching the top width of the gutter, a bottom surface having a width less than the top width of the filter element, and front and rear surfaces extending upward from the bottom surface of the filter element to thereby form a front and a rear open passage for water on front and rear sides of the bottom surface of the filter element when the filter element is installed into the gutter. The reticulated foam material of the filter element has a composition that is flame resistant, germicidal, mold resistant, and resistant to degradation by exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Owner:AMERICAN GUTTER FILTER
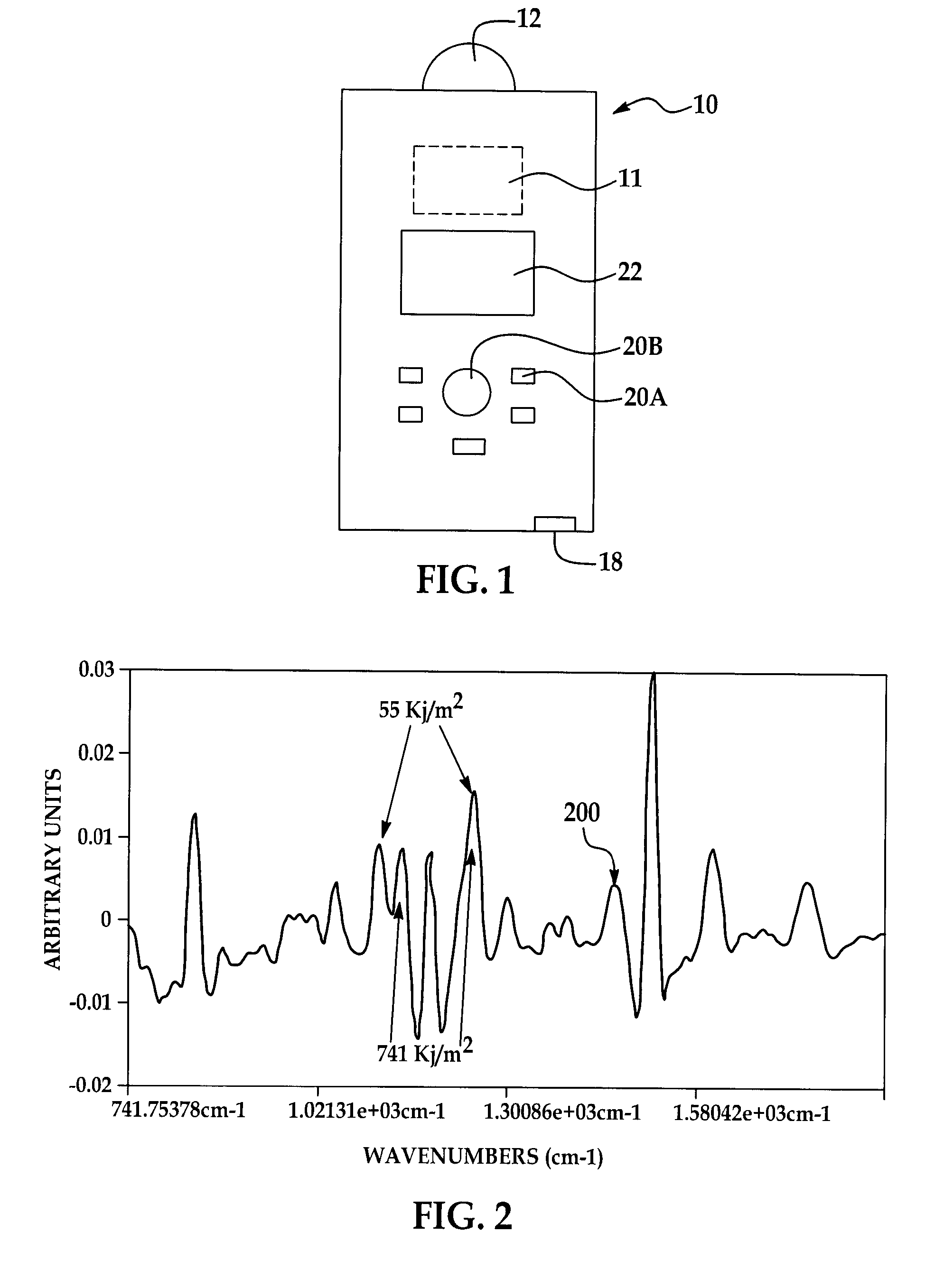
Method for performing IR spectroscopy measurements to quantify a level of UV effect
A method of non-destructively determining the amount of ultraviolet degradation of a surface and / or paint adhesion characteristics of the surface corresponding with UV damage including determining a physical property of a composite material / surfacing film by providing a series of composite materials / surfacing films which are subjected to increasing UV light exposure to create a set of UV damage standards, collecting mid-IR spectra on those standards, performing data pre-processing and then multivariate calibration on the spectra of the composite materials / surfacing films, and using that calibration to predict the UV damage for samples in question.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com