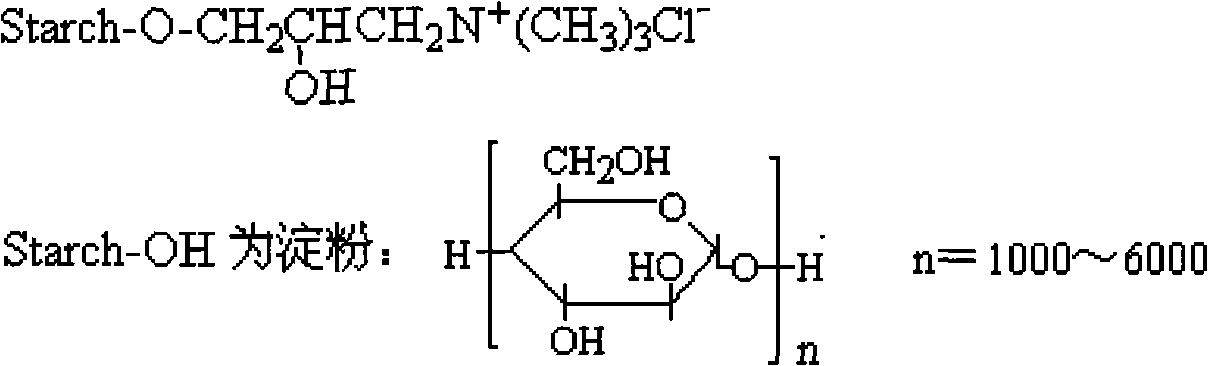
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Starch grain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant storage body for amylose and amylopectin, 1-100um in diameter. Also contains small amounts of enzymes, amino acids, lipids and nucleic acids. The shape of the grain varies widely amongst species, but is often spherical or disk-shaped. [GOC:jl, PMID:11217978]
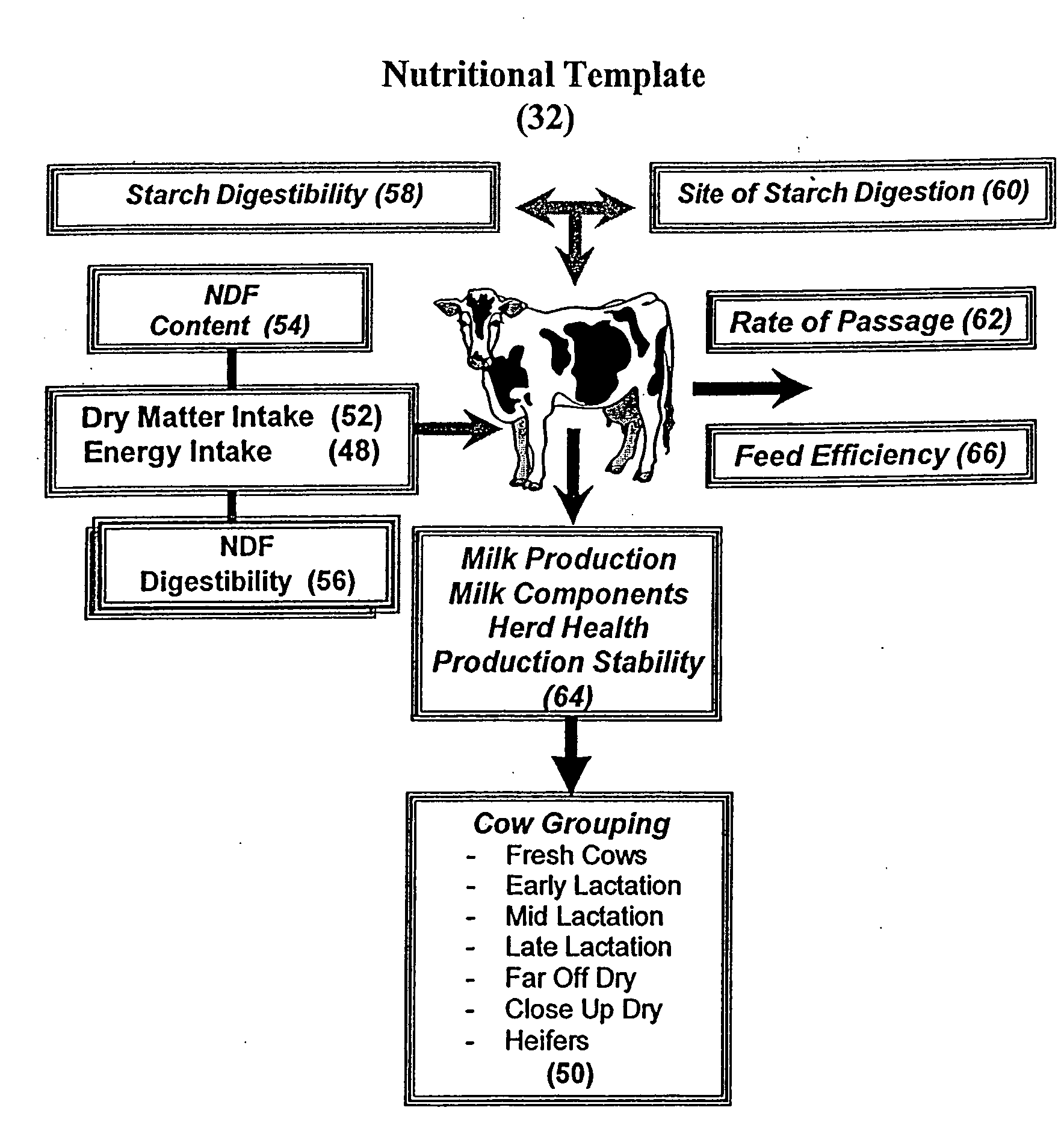
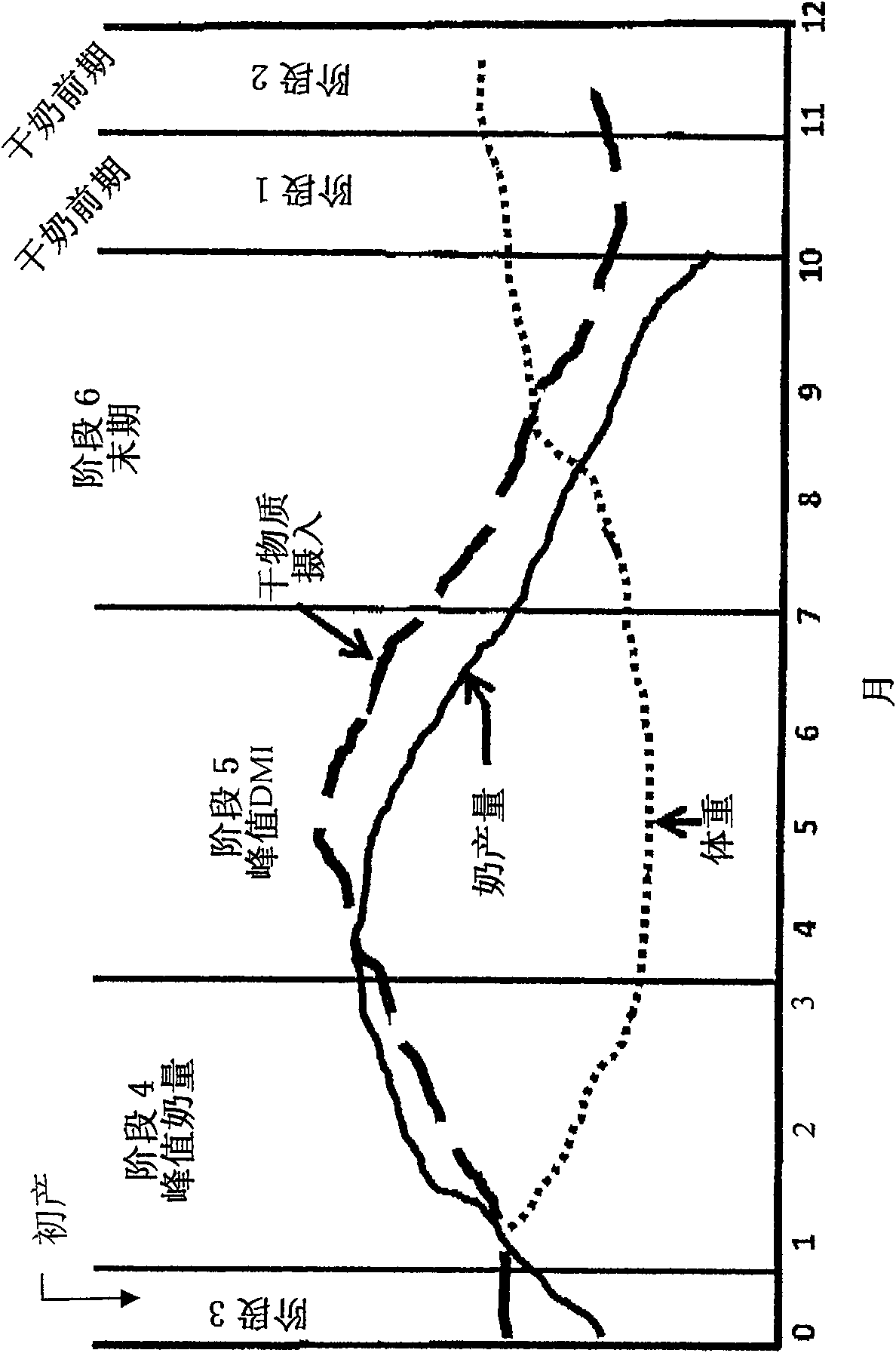
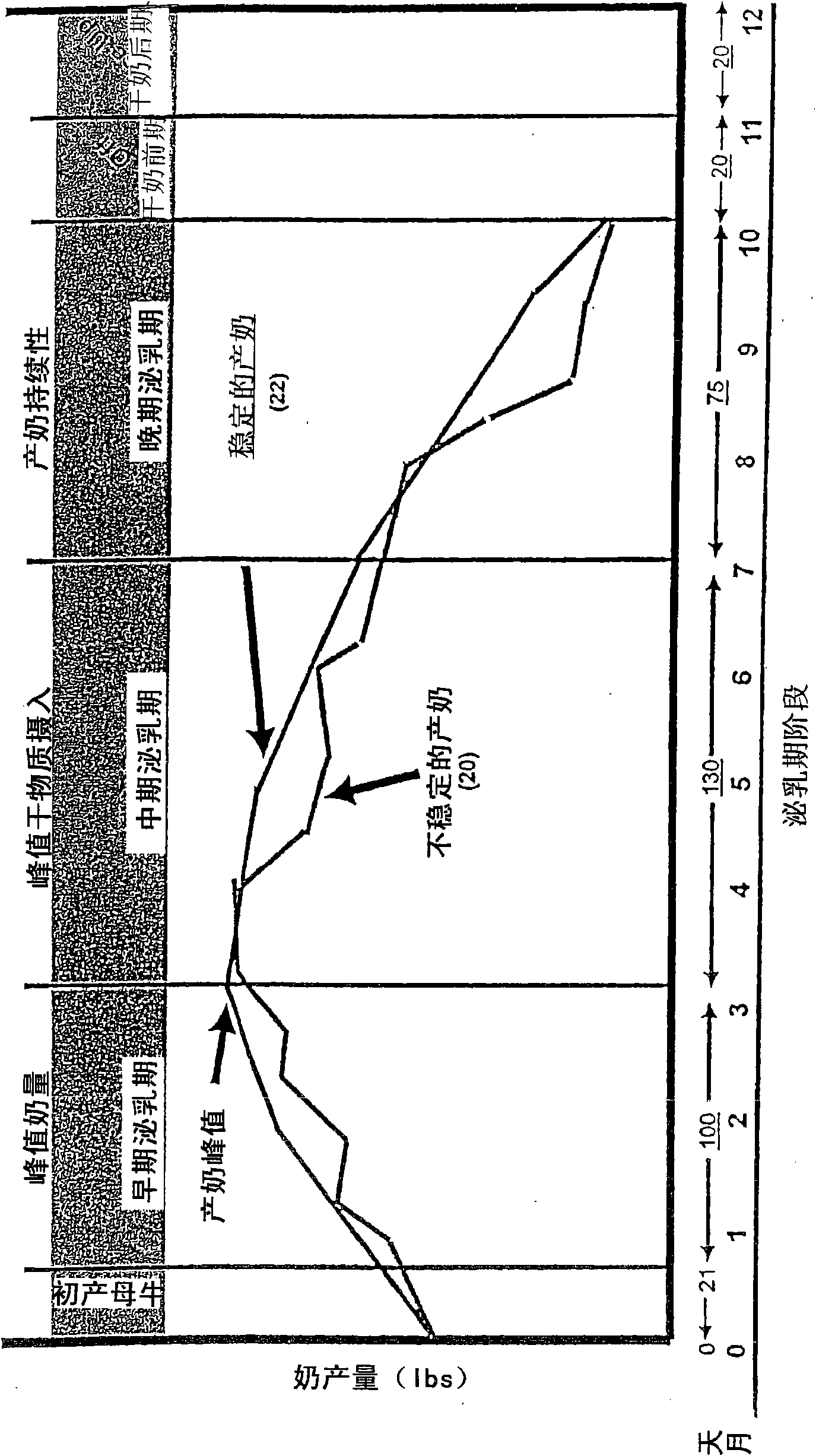
Feed delivery system for enhancing ruminant animal nutrition
InactiveUS20080215167A1Precisely formulatedImprove production stabilityAnimal feeding stuffSpecial data processing applicationsAgricultural scienceAnimal Foraging
A feed delivery system for a dairy farm wherein a third-party supplier of the system can provide the dairy farm with lists of approved hybrids for the feed components, necessary information inputs for practicing the feed method, and all or a portion of its component needs for the feed ration corresponding to a feed ration that contains: at least one primary forge source selected from the group consisting of brown midrib corn silage, dual-purpose corn silage, leafy corn silage, and grass silage; a secondary forage source selected from the group consisting of dual-purpose corn silage, alfalfa haylage, alfalfa dry hay, grass silage, and alfalfa / grass mix; a corn grain of floury and / or vitreous endosperm starch grain into which normal dent corn or mutt corn may be blended in order to achieve a predetermined level of in vitro starch digestibility; such grain component being further processed to produce a specific particle size of the blended starch. The feed delivery system can also provide the dairy farm with real-time characterizations of at least some of its feed ingredients, and re-penning strategies for maximizing the milk productivity of the cows.
Owner:NUTRI INNOVATIONS LLC
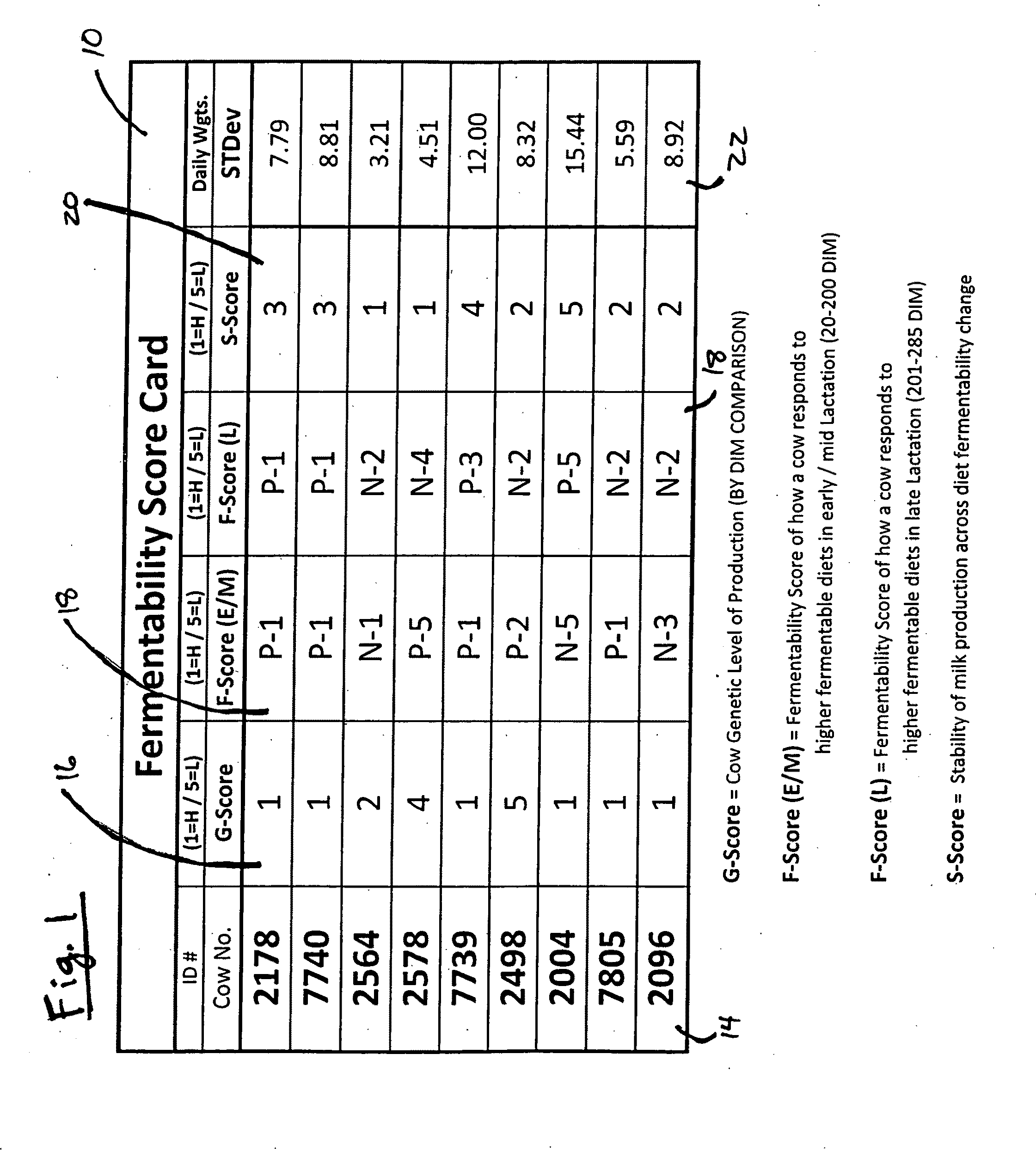
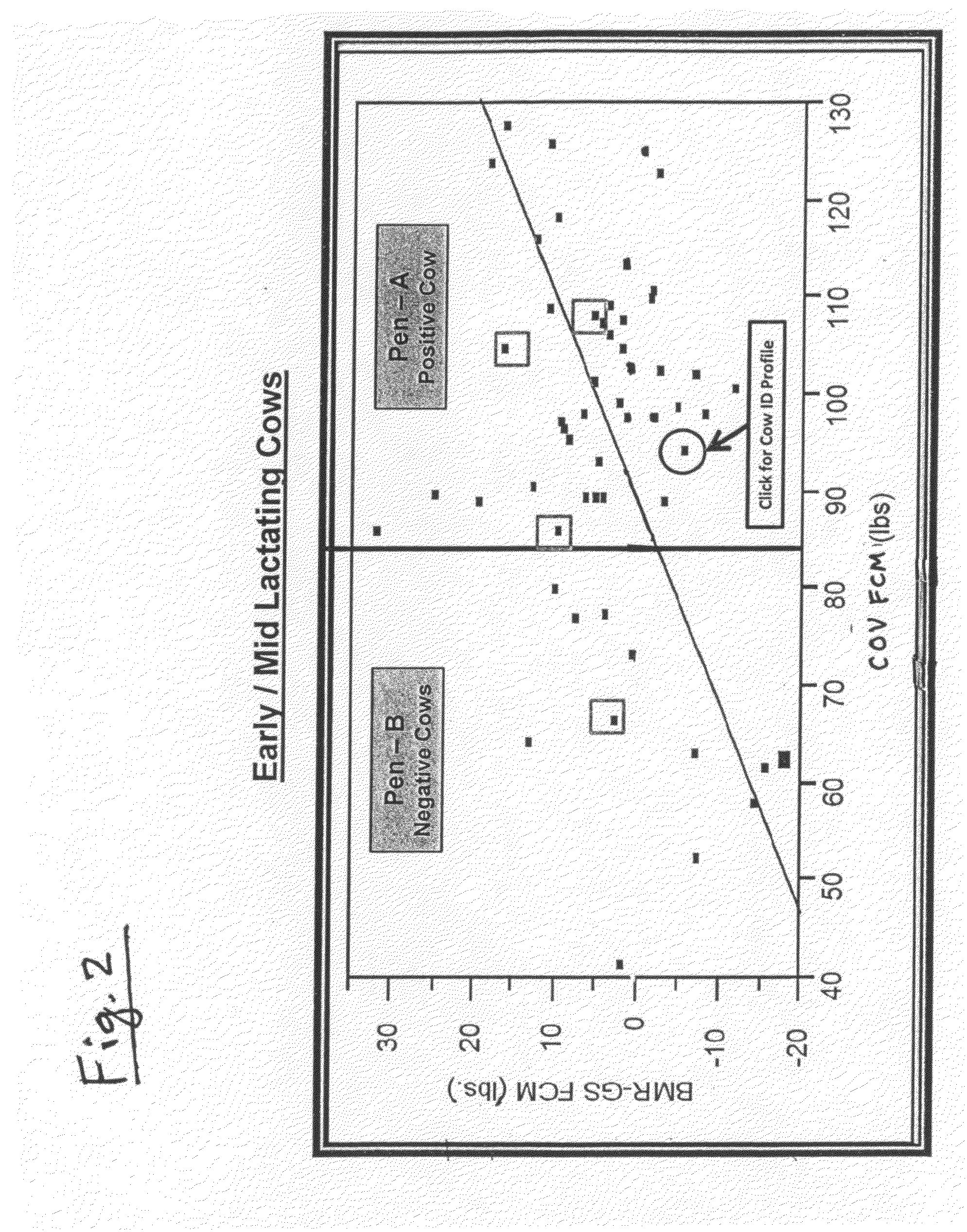
System for real-time characterization of ruminant feed rations
InactiveUS20090092715A1Improve energy efficiencyHealth be optimizedMaterial analysis by optical meansAnimal feeding stuffAgricultural scienceAdditive ingredient
Owner:NUTRI INNOVATIONS LLC
Method for preparing starch nanocrystal
The invention discloses a method for preparing starch nanocrystal, and belongs to the field of modified starch processing. The method is based on the principle that lipid layers in waxiness corn starch grains have resistance for acid, the starch is prompted to be crushed because of homogenization treatment under a certain pressure, the lipid is prompted to be digested through Soxhlet extraction by using an alcohol-water solution, a pore structure from outside to inside is formed, then the resistance to the acid is eliminated, and the penetration of the acid inside the starch is prompted under a negative pressure condition so as to accelerate hydrolysis of the starch grains in an amorphous area. The method specifically comprises the following steps: homogenously crushing the starch grains under a pressure of 50-150 MPa, degreasing the crushed starch by using a 70-90% methanol-water solution, and accelerating hydrogen ions in sulfuric acid to rapidly penetrate into the starch grains to be subjected to restrictive hydrolysis under a 0.06-0.1MPa negative pressure condition, so as to prepare the nanocrystal. Through the technical measures, the hydrolysis period of the starch is shortened to be 48-72 hours, the starch nanocrystal yield is greatly improved to be 19-25%, and the particle size distribution is 20-300nm.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Production of malt
Production of malt is carried out by immersing for wheat grain, germinating and drying. It can supply sufficient hydrolase for saccharification to decompose protein into soluble nitrogen; it can supply alpha-amino-nitrogen and dissolve albuminous cell wall to degrade starch grain. It's controllable, has better physical-bio-chemical reaction and quality.
Owner:邱虎
Method for preparing amorphous starch grain not containing cross-linked chemical bond using alcohol solvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing amorphous starch grain containing no cross bond with alcohol, comprising following steps: dispersing starch or converted starch into alcohol solution at constant temperature to prepare homogenous starch milk, heating or adding strong basic for amorphous treatment, washing, filtering, disintegrating, drying and sifting with 80-120 mu screen got amorphous starch. The method can also comprises following steps: dispersing starch or converted starch into water or salt solution to prepare starch milk, then treating starch milk for amorphous, dispersing amorphous starch with alcohol or washing, filtering, disintegrating, drying and sifting with 0-120 mu screen. The prepared starch grain retains gelatinization property of original starch grain, and can be widely used in foodstuff, paper making, weaving, building material, chemical industry, pharmacy, oil, environmental protection, agriculture, forestry and mining industry.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
New method for preparing rice gluten milk powder and rice gluten milk by using crushed rice
The invention relates to a new method for preparing rice gluten milk powder and rice gluten milk by using crushed rice and belongs to the technical field of natural protein separation and extraction as well as deep processing. According to the characteristic that starch grain in rice endosperm is combined with proteosome, physical high-pressure homogenized splitting method is adopted for splitting the thin cell wall of amyloplast, and the split starch and protein are centrifugalize according to the difference of specific weight, and the protein in light phase is concentrated, formulated and formed to prepare the milk powder and fluid milk. The method completely maintains the physicochemical property of natural rice protein, is high in extraction rate, concise in process and low in cost and avoids the three wastes.
Owner:铜陵峰元科技发展有限公司
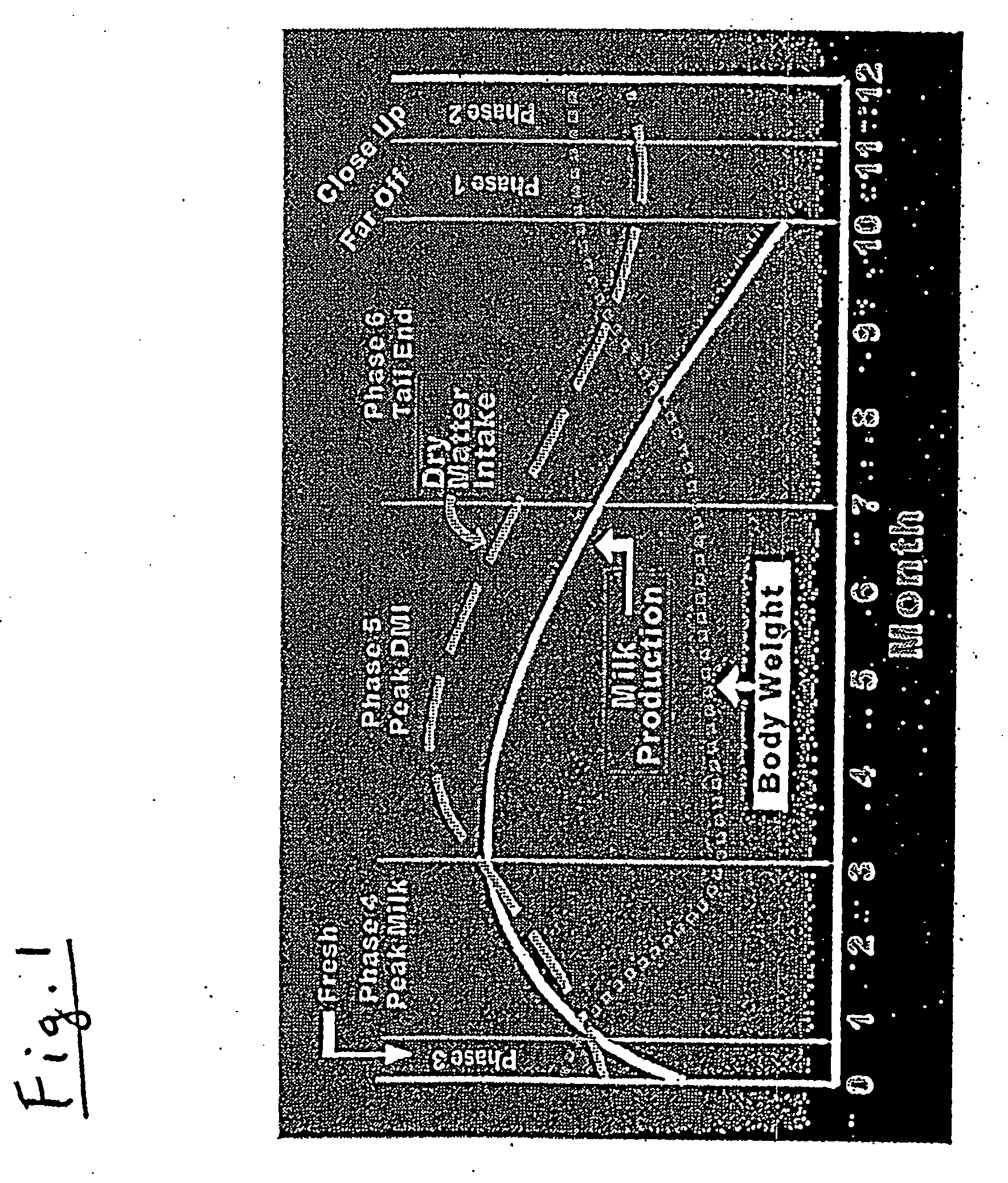
Method and feed for enhancing ruminant animal nutrition
InactiveUS20080145476A1Improve production stabilityImprove the level ofAnimal feeding stuffAgricultural scienceAnimal Foraging
A method for feeding a ruminant animal a feed ration for enhancing its milk production stability across a multiple-stage lactation cycle is provided according to the invention. The feed ration should contain: at least one primary forge source selected from the group consisting of brown midrib corn silage, dual-purpose corn silage, leafy corn silage, and grass silage; a secondary forage source selected from the group consisting of dual-purpose corn silage, alfalfa haylage, alfalfa dry hay, grass silage, and alfalfa / grass mix; a corn grain blend of opaque / floury and vitreous / hard endosperm starch grain into which normal dent corn or mutt corn may be blended in order to achieve a predetermined level of in vitro starch digestibility; such blended grain component being further processed to produce a specific particle size of the blended starch. A feed ration prepared in accordance with this method optimizes the ruminal environment inside the cow that consumes the feed ration for producing the enhanced milk production stability.
Owner:NUTRI INNOVATIONS LLC
Method for detecting low-quality starch-doped potato starch fast
InactiveCN105044014AQuick checkImprove predictive performanceParticle size analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsPotato starchElectron microscope
The invention discloses a method for detecting low-quality starch-doped potato starch fast. The method comprises the following steps: qualitatively distinguishing whether sweet potato starch, tapioca, corn starch and wheat starch are doped in potato starch or not through electronic microscope imaging and starch grain shape and grain size analysis; quantitatively analyzing the doping quantity of low-quality starch doped in the potato starch through infrared spectroscopic analysis. Test results show that the method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting the low-quality starch doped potato starch is simple, fast and high in forecasting capability and stability, thereby having an excellent market application prospect.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Technique for reducing in-vivo decomposition and absorption speed of starch
InactiveCN103519162AIncrease the rate of hydrolysisFood ingredient as thickening agentAlgae medical ingredientsBiotechnologyStarch breakdown
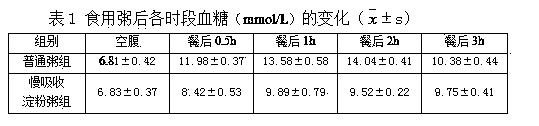
The invention relates to a technique for reducing in-vivo decomposition and release speed of starch, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: pulverizing starch food raw materials into fine powder or directly using starch,, adding a thickener and water, stirring uniformly to form a soft material, putting in a double screw extruder, extruding with a mold to obtain granules, and drying for later use; or drying the soft material, and pulverizing into fine powder for later use. The technique is characterized in that the edible thickener is added into the starch to reconstruct the physical structure of the starch granules, so that the starch decomposition is retarded, and the blood sugar after eating can not increase rapidly but is in a stable state, thereby lowering the postprandial blood sugar, lowering various complications initiated by blood sugar fluctuations after eating, and enhancing the life quality of diabetics.
Owner:JIANGXI SHI FANG SHI FANG CHINESE MEDICINE FOOD
Waxy wheat flour milling technological method
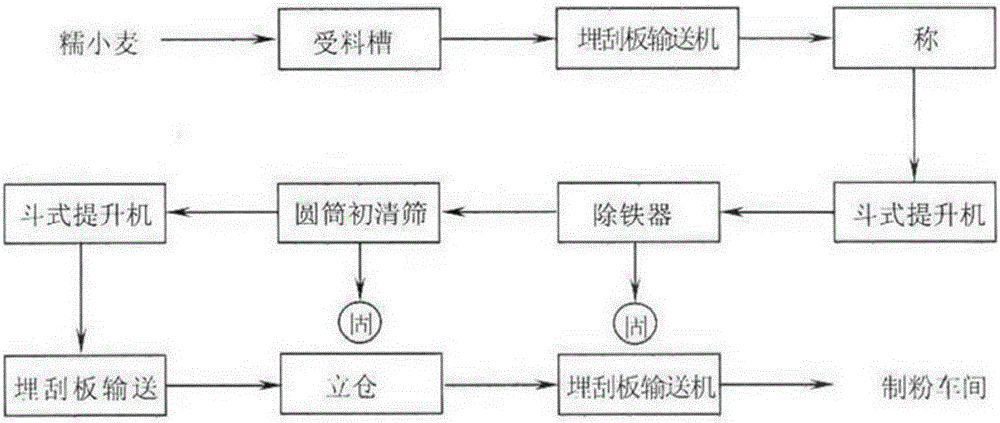
The invention discloses a waxy wheat flour milling technological method. The method comprises the following steps of (1) wheat cleaning; (2) wheat wetting including secondary wheat wetting; and (3) break milling and flour purification. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that damage to starch particles and protein can be reduced in the wheat flour milling process by means of the technological method, the flour yield can be increased, and energy consumption can be reduced.
Owner:丽江心联欣粮油贸易有限公司 +2
Separation and purification process of wheat flour starch granule
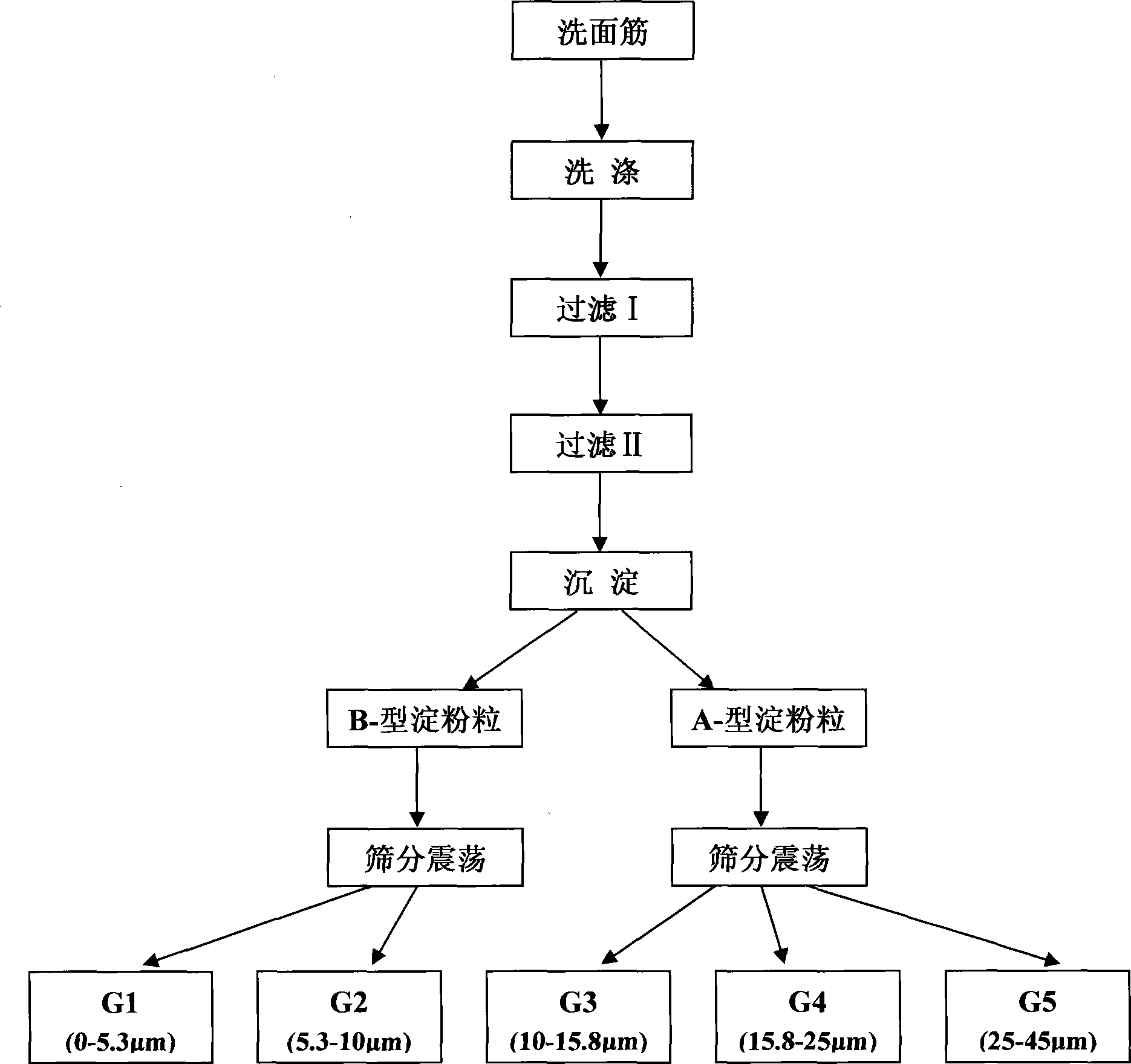
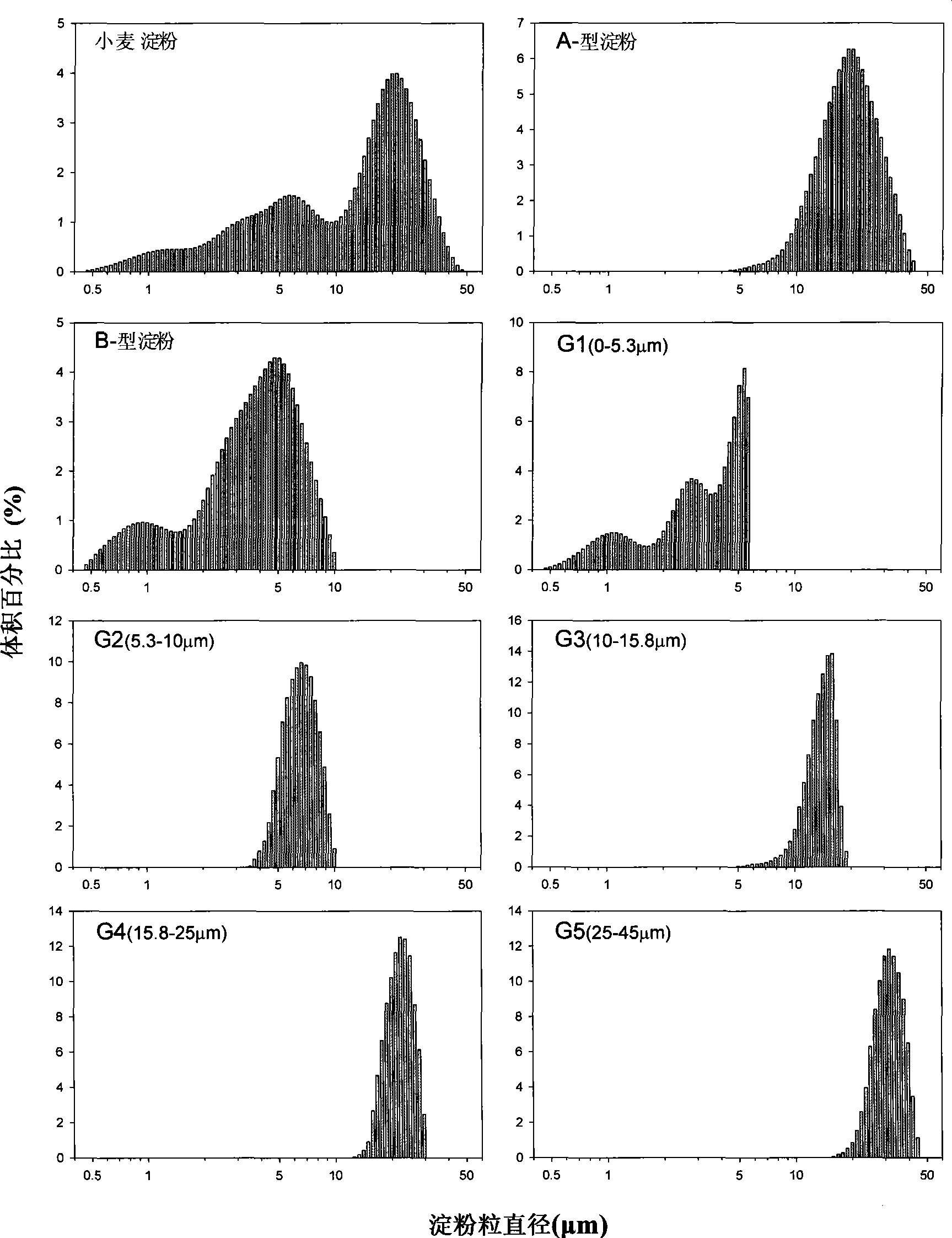
The invention relates to a separation and purification process for wheat flour starch grains, which belongs to the field of farm product deep processing. The separation and purification process comprises the following three technological flows: purifying wheat flour starch grains; separating A- and B- starch grains; and subdividing the A- and B- starch grains, wherein the technological process of purifying the wheat flour starch grains is to wash off protein through a gluten washer, wash and filter through deionized water, and filter and refine through absolute ethyl alcohol; the technological process of separating the A- and B- starch grains is to precipitate the wheat starch grains suspending in the deionized water and take the suspension liquid on the upper layer; and the technological process of subdividing the A-, B- starch grains is to screen the A-, B- starch grains suspending in the deionized water through a sieve with certain specifications and use a sieving machine for oscillation. The separation and purification process has the extraction efficiency of wheat flour starch grains above 99 percent, and has the advantages of simple technological processes, and good repeatability and reproducibility, thereby enabling researchers and engineers to have an accurate understanding of the size characteristic of the starch grains and the impact of the size characteristic on related products. The product can be also applied to scientific research and industrial production.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Stable liposoluble nutrient microcapsules as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106666731AHigh temperature resistanceImprove pressure resistanceFood ingredient functionsSpray GranulationAntioxidant
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of stable liposoluble nutrient microcapsules. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1) an oil phase is subjected to spray granulation by a fluidized bed, and microcapsules coated with starch granules are formed; 2) the temperature is increased to a dry temperature, an alkali solution is added to the fluidized bed by spraying, so that starch and grease on the surfaces of the microcapsules are gelatinized and saponified at the same time, a compact protective film is formed, and the stable liposoluble nutrient microcapsules are obtained, wherein the oil phase is a grease solution or a grease dispersion liquid containing liposoluble nutrients and an antioxidant. The preparation method performs gelatinization and saponification under the flow dry condition simultaneously, a formed dual protection film containing gelatinized starch and saponified grease is more compact, and the microcapsules are more stable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +2
Method for quantitatively discriminating true or false lily bulb powder
InactiveCN101261212AImprove clarityFast and accurate identificationMaterial analysis by optical meansSpecific gravity measurementMass ratioImaging analysis
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively discriminating genuine and fake lily powder, which is characterized in that: Swiss dyeing solution is adopted to dye the lily and adulterated starch, and the difference on microscopic characteristic of starch grain morphology can be clearly observed by a common microscope, thus accurately qualitatively discriminate the kinds of lily and adulterated starch; a random continuous sampling mode is adopted and image analysis software and a statistical method are used for measuring and calculating the volume and grain quantity of the lily and the adulterated starch; a density bottle method is used for measuring the density of the grain; the adulteration rate of the lily powder can be calculated according to the mass ratio; and therefore the quantitative index of the adulteration rate of the lily powder can be gained quantitatively. The method for quantitatively discriminating genuine and fake lily powder has the advantages of low experiment condition requirement, simple and quick operation, low cost and accurate result.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Utilization of bamboo rat faeces as dictyophora indusiata cultivation material
InactiveCN104230398ATurn waste into treasureSimple preparation processClimate change adaptationExcrement fertilisersBiotechnologyPennisetum purpureum
In the nature, dictyophora indusiata grows on bamboo humus, and nutrition is obtained in a way that rotten bamboo organic matters are decomposed by mycelia. Bamboo rats also known as Mangli, Zhuli and the like belong to mammalia rodentia rhizomyidae rhizomys, and are named because staple food is bamboo. The bamboo rats are rich in nutritional value and high in economic effect, and are bred in a large scale at present. At present, a crude feed for artificially feeding the bamboo rats mainly comprises bamboo (accounting for 50% of the feed), other crude feeds comprise neyraudia reynaudiana, saccharum arundinaceum, miscanthus floridulus, pennisetum purpureum and pennisetum sinese roxb seeds, and a fine feed is starch grains (accounting for 10% of the feed). The feeds are digested to form feces through bamboo rat unique digestive tracts and digestive enzymes. The bamboo rat feces contains cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin obtained from microorganism and enzyme decomposition and conversion, and also contains a certain amount of proteins, starch, wax, fat and resin. The feces also contains amino acids, various effective trace elements, various vitamins, saccharides, carbohydrates and the like, and is rich in nutrition. The bamboo rat feces can be supplied for dictyophora indusiata growth without stacking and fermentation, and is an important cultivation base for formation of high-quality dictyophora indusiata.
Owner:王镇
Lutein microcapsule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103565778AMask special odorHigh activitySenses disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsLuteinGranularity
The invention relates to a lutein microcapsule and a preparation method thereof, wherein the lutein microcapsule consists of a core containing a lutein crystal and an oil soluble emulsifying agent, a shell covering the core, and starch grains stuck outside the shell; the shell includes a capsule material, a water soluble emulsifying agent and a stabilizing agent, wherein dosage ratio of the lutein crystal to the oil soluble emulsifying agent to the capsule material to the water soluble emulsifying agent to the stabilizing agent is (1-30): (0.5-5): (60-95): (1-8): (0.5-5) in parts by weight. The lutein microcapsule is regular in shape, relatively uniform in granularity, good in fluidity, and excellent in both stability and activity.
Owner:中国中化股份有限公司 +1
Technique for reducing in-vivo decomposition and absorption speed of starch
InactiveCN103519187AIncrease the rate of hydrolysisOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiotechnologyAlglucerase
The invention relates to a technique for reducing in-vivo decomposition and absorption speed of starch, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: pulverizing starch food raw materials into fine powder or directly using starch,, adding a thickener and plant extracts, adding water, stirring uniformly to form a soft material, putting in a double screw extruder, extruding with a mold to obtain granules, and drying for later use; or drying the soft material, and pulverizing into fine powder for later use. The technique is characterized in that plant the extracts capable of inhibiting alpha-glucosaccharase and edible thickener are added into the starch to inhibit the alpha-glucosaccharase and reconstruct the physical structure of starch granules, so that the starch decomposition is retarded, and the blood sugar after eating can not increase rapidly but is in a stable state, thereby lowering the postprandial blood sugar, lowering various complications initiated by blood sugar fluctuations after eating, and enhancing the life quality of diabetics.
Owner:JIANGXI SHI FANG SHI FANG CHINESE MEDICINE FOOD
Preparation method of rosin / starch based biodegradable hot melt adhesive
InactiveCN104312482AReach fillingTo achieve the double effect of reinforcementNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch adhesivesPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rosin / starch based biodegradable hot melt adhesive. The method is as below: mixing starch and a plasticizer according to the mass ratio of 1:0.2-0.5 under high speed stirring for 10-30 min, standing for 24 h, heating the mixture at 120-140 DEG C into a molten gel, and cooling and dicing to prepare thermoplastic starch grains for standby; under the protection of nitrogen, heating the rosin to 150-200 DEG C, stirring and successively adding polyols, a catalyst and an antioxidant, reacting at 240-280 DEG C for 5-10 h, cooling to 140-160 DEG C, adding the thermoplastic starch grains and a modified agent, mixing for 10-30 min, cooling and discharging to obtain the hot melt adhesive. The hot melt adhesive can reach technical standards requirements of the ordinary commercial hot melt adhesive, can degrade automatically after usage, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Micro-pore starch particles and producing method thereof
The invention provides a microporous starch grain with aperture over 5 mu m, and relatively high supporting capacity, and producing method thereof. The producing method includes: weight starch, charging water with a weight of 20-40% of the starch weight, sealed standing for 24-48 hours to make the water disperse uniformly in the starch, heating to keep temperature ranging from 55 to 90 DEG C. for 30-120 minutes, charging water to make weight ratio of starch and water to 1:2 - 4, stirring uniformly, charging amylase according to a charging amount of 450-650 per grams of starch, stirring and reacting for 2-6 hours with pH ranging from 4.5 to 5.5, temperature ranging 35-55 DEG C., spray drying after completion of the reaction, aforementioned microporous starch grain is obtained. The inventive microporous starch grain has a surface aperture of 5-10 mu m, 3-10 times large than microporous starch grain prepared by conventional technology, thus has a better supporting property, and larger supporting capacity than products of conventional technology, which makes it has better effects than products of conventional technology when applied to fields of medicament preparation, food additive, pesticide and fertilizer as carrier.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for making wheat flour for extracting vital gluten
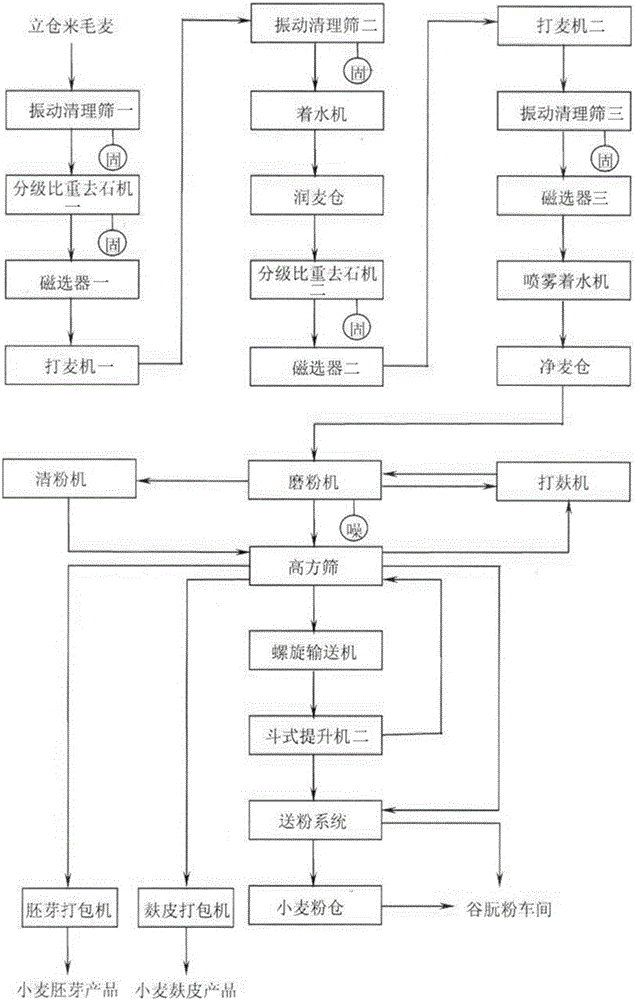
ActiveCN103028457AReduce powder contentGuaranteed qualityGrain huskingGrain polishingProcess engineeringWheat flour
The invention belongs to the processing field of flour production and particularly relates to a method for making wheat flour for extracting vital gluten. The method for making the wheat flour for extracting the vital gluten comprises the following steps of: wheat pre-washing, wheat washing and water adjusting, pure wheat flour grinding, flour mixing and post processing, wherein the pure wheat flour grinding step comprises skin grinding, core grinding, dreg grinding and tail grinding. A skin grinding system comprises a primary skin grinding port and a secondary skin grinding port. The method is characterized in that the speed ratio of the secondary skin grinding port in the skin grinding system is 2:1, namely that the speed ratio of a fast roller to a slow roller is 2:1; and grinding rollers adopted in the core grinding system, the dreg grinding system and the tail grinding system are all matt surface rollers, and the speed ratio of the matt surface rollers is 1.25:1. The wheat flour for the vital gluten, produced by the technical method meets the quality requirement for extracting the vital gluten, few gluten proteins and starch particles are destroyed, gluten is easily formed, and the separating yield rate of the vital gluten is increased by 0.8% more or less. Power consumed by the flour making method is about 5% less than power consumed by a traditional method, so that the energy saving effect is remarkable.
Owner:BINZHOU ZHONGYU FOOD
Surface treatment composition and paper or paperboard comprising a surface treatment composition
ActiveCN103154371AImprove printing propertiesImprove printing effectWater-repelling agents additionDuplicating/marking methodsChemistrySurface finishing
The present invention relates to a surface treatment composition for paper, paperboard or other fibrous webs wherein the composition comprises starch particles that comprise at least one salt. The invention further relates to a paper or paperboard being surface treated with said composition.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Purification method for 5-grade grains of lotus root starch
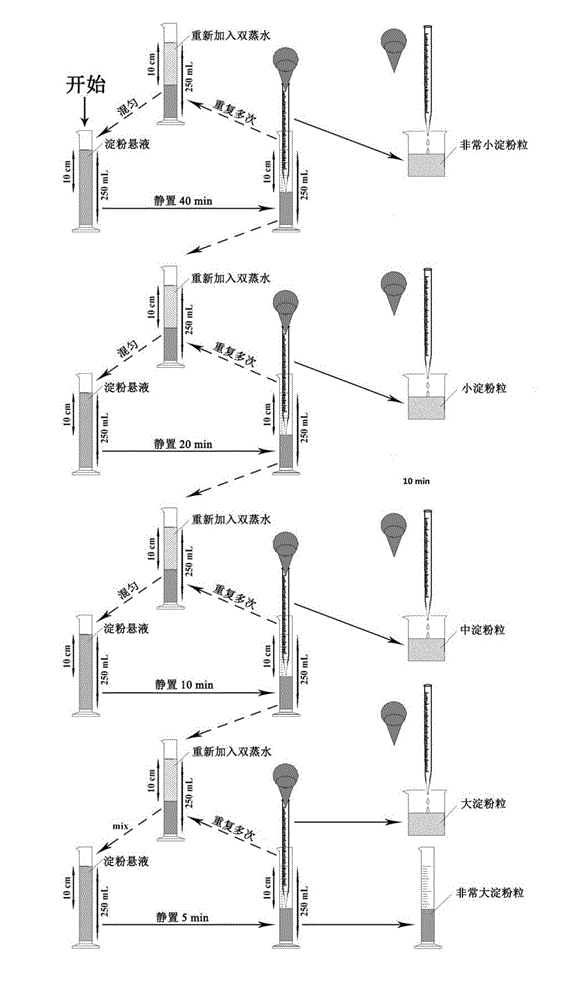
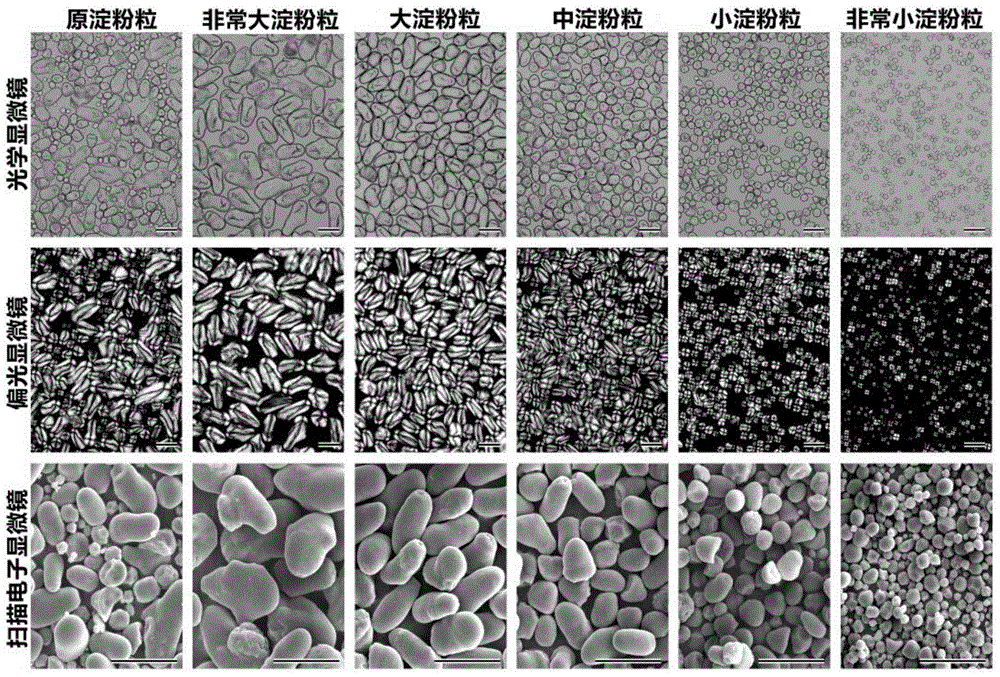
The invention discloses a purification method for 5-grade grains of lotus root starch. Lotus root starch grains are divided into five parts, namely very large (45 to 55 micron), large (35 to 45 micron), medium (25 to 35 micron), small (15 to 25 micron), and very small (0 to 15 micron) according to sizes. The method comprises the steps of starch suspension preparation, mixing, still standing for settling, supernatant suction, collection for storage and the like. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple, fast and low in cost while the purity of each grade of starch grains is high. Therefore, technical support is provided for research of the structures and performance characteristics of starch of different starch grains; the meaning for machining and application of lotus root starch grains is important.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for separating pueraria starch milk impurities
The invention relates to a method for separating pueraria starch milk impurities. The invention discloses a separating agent prepared from edible natural plant extracts, the pueraria starch milk is disturbed to precipitate starch grains within a certain period of time, and impurities including silts and the like in the pueraria starch milk are once thoroughly eliminated by a physical method. The method is used for solving the problems of difficult cleaning of coarse and uneven pueraria epidermis, peeling loss of pueraria flavone mainly reserved at the skin part and resource waste of mechanically damaged broken rootstalks. The method keeps epidermis processing, and has simple process, easy implementation, no pollution and high processing efficiency, and is widely suitable for the large-scale production of starch of underground tuber crops including pueraria and the like in small and medium enterprises to achieve the purpose of preparing pure natural green foods.
Owner:汪盛明
Method for rapidly, qualitatively and quantitatively detecting five types of edible starch adulteration
InactiveCN104990945AAccurate identificationEasy to operateMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionLinear regressionViscosity
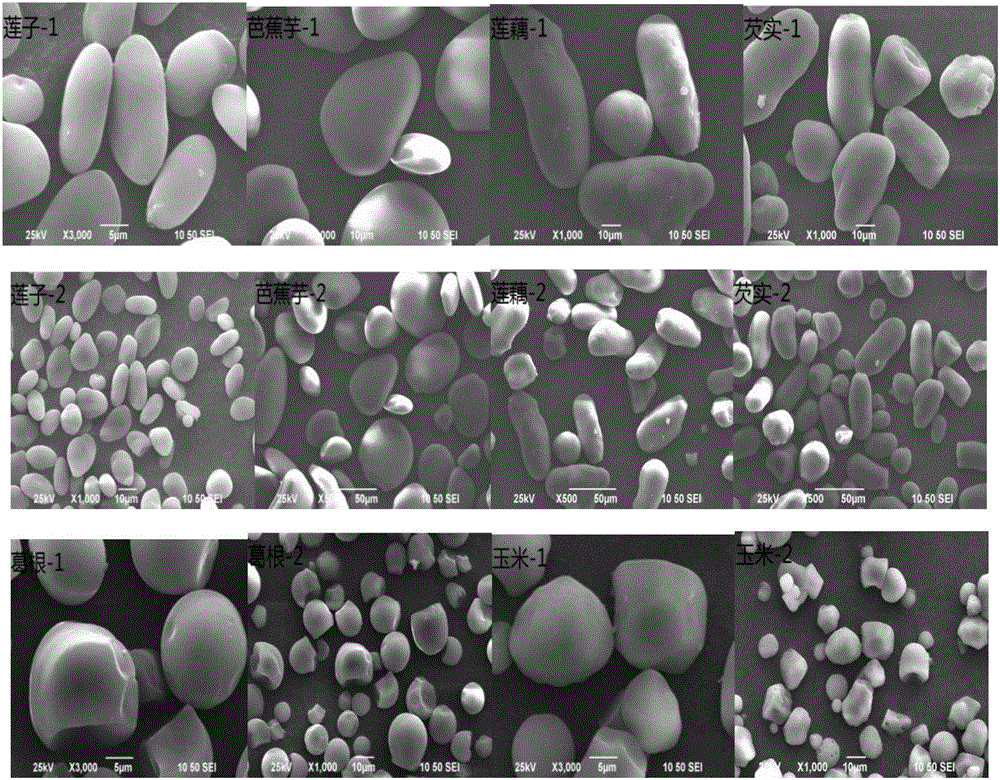
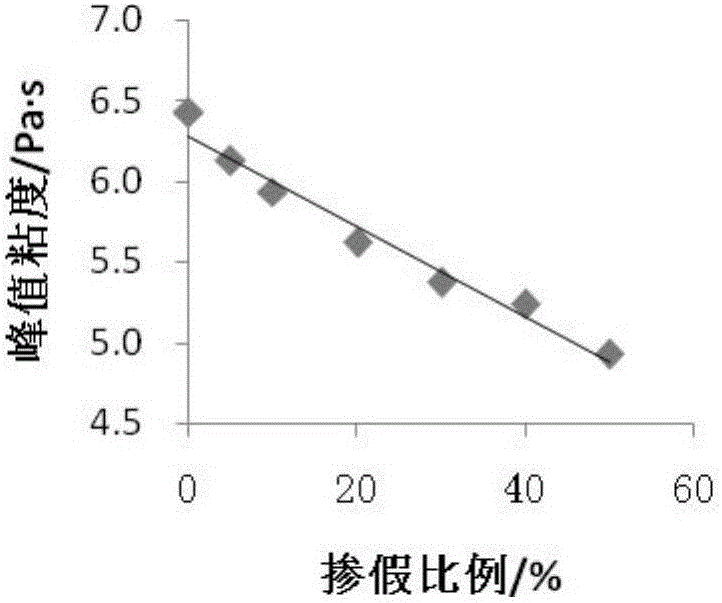
A method for rapidly, qualitatively and quantitatively detecting five types of edible starch adulteration includes the following steps of firstly, obtaining the starch grain type through a scanning electronic endoscope; secondly, obtaining the linear regression analysis equation of the peak value viscosity and the adulteration proportions of starch of different adulteration proportions through a rapid viscosity analyzer; thirdly, qualitatively and quantitatively judging edible starch adulteration. The method has the advantages that operation is easy, adulteration can be rapidly and accurately recognized at a low price, and the adulteration proportion can be rapidly judged. Experiments prove that for five types of edible starch adulteration including adulteration of pueraria starch, lotus root starch, lotus seed starch, foxnut starch and canna starch, the corn starch proportion ranges from 0% to 50%, and the deviation of accurate adulteration proportion judgment is smaller than + / -1%.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Cationic starch producing method
The invention belongs to the field of paper making technology and in particular relates to a Cationic starch producing method. The specific steps of the process of the method include etherifying agent activation and emulsification, etherification reaction, neutralization washing, dehydration, drying and finished product obtaining. Cationic starch materials produced according to the method is safe and also simply, conveniently and practically used, and has high reaction efficiency; the starch grains are not subject to pasting; the yield rate can be as high as 99 percent, and the reaction efficiency reaches 68 percent; and the property of the finished product is stable.
Owner:山东米能生物科技有限公司
Salty fresh edible fungi aromatic rice fruit and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a salty fresh edible fungi aromatic rice fruit and a preparation method thereof. The raw materials comprise the following components in percentage by weight: 5-15% of mushroom substances, 70-80% of starch grains, 5-12% of water and 2-5% of seasoning substances, wherein the starch grains are 50-60-mesh powder, the mushroom substances which comprise mushrooms and / or pleurotus eryngii are 60-120-mesh powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing and extruding the raw materials; shaping and cutting; cooling and drying to obtain extruded fruits; and spraying oil and seasoning by seasoners, and cooling, wherein the extruding condition is that a main machine is pre-heated to 50 DEG C in an area I, 150 DEG C in an area II and 160-170 DEG C in an area III; then, a main motor is started, the extruding temperature is controlled at 160-180 DEG C, and the rotary speed of the main motor is 1200r / min; the seasoners are salty fresh seasoners. The salty fresh edible fungi aromatic rice fruit is abundant in nutrition and delicious in taste.
Owner:上海大山合菌物科技股份有限公司
Starch / C4~C8 ring graft copolymer and prep. and use thereof
The present invention is starch / C4-C8 cyclic monomer grafted copolymer and its preparation process. Starch of corn, beans, potato and grains in grain size of 1-20 microns or modified starch in 1-60 portions and one or several C4-C8 cyclic monomer p-dioxy cyclohexanone, 1, 5-dioxy suberyl-2-one, gamma-butyrolactone, beta-butyrolactone, delta-valerolactone, epsilon-caprolactone, diglycolide and lactide in 40-99 portions react in a reaction bottle under the protection of inert gas and in the presence of catalyst in 0.01-5 portions at 60-150 deg.c for 10-48 hr to produce grafted copolymer. The unreacted monomer and homopolymer are extracted separately with solvent, the product is vacuum dried to constant weight, and the monomer converting rate, grafting rate and grafting efficiency are measured.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
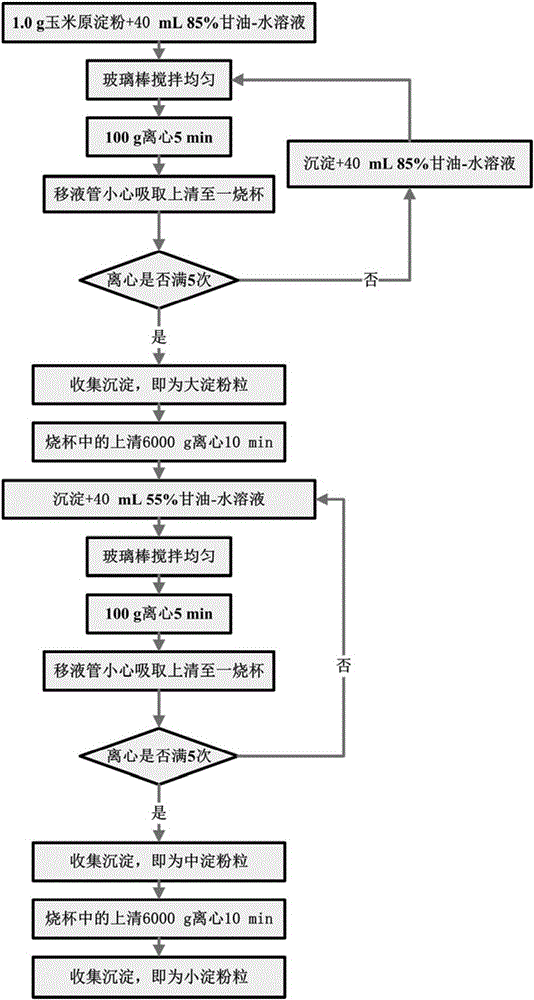
Purifying method of corn starch 3-grade particles
The invention discloses a purifying method of corn starch 3-grade particles. According to the purifying method, corn starch particles are divided into large particles (with a particle size larger than 15<mu>m), middle particles (with a particle size ranging from 10 to 15<mu>m), and small particles (with a particle size smaller than 10<mu>m). The purifying method comprises following steps: starch suspension preparation; uniform stirring; adding of 85% glycerinum-water solution and centrifugation; collection of large starch particles; adding of 55% glycerinum-water solution and centrifugation; and collection of middle and small starch particles. The purifying method is excellent in purifying effect; operation is simple and convenient; time is saved; cost is low; the purifying method is capable of providing technical support for research on physical and chemical properties of corn starch particles with different particle size, and is helpful for processing and application of corn particles.
Owner:JIANGSU FOCUS AGRICULTURE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY CO. LTD.
Method and feed for enhancing ruminant animal nutrition
InactiveCN101610681AIncrease production capacityAnimal feeding stuffMaterial analysis by optical meansAgricultural scienceNutrition
A method for feeding a ruminant animal a feed ration for enhancing its milk production stability across a multiple-stage lactation cycle is provided according to the invention. The feed ration should contain: at least one primary forge source selected from the group consisting of brown midrib corn silage, dual-purpose corn silage, leafy corn silage, and grass silage; a secondary forage source selected from the group consisting of dual-purpose corn silage, alfalfa haylage, alfalfa dry hay, grass silage, and alfalfa / grass mix; a corn grain blend of opaque / floury and vitreous / hard endosperm starch grain into which normal dent corn or mutt corn may be blended in order to achieve a predetermined level of in vitro.
Owner:NUTRI INNOVATIONS LLC
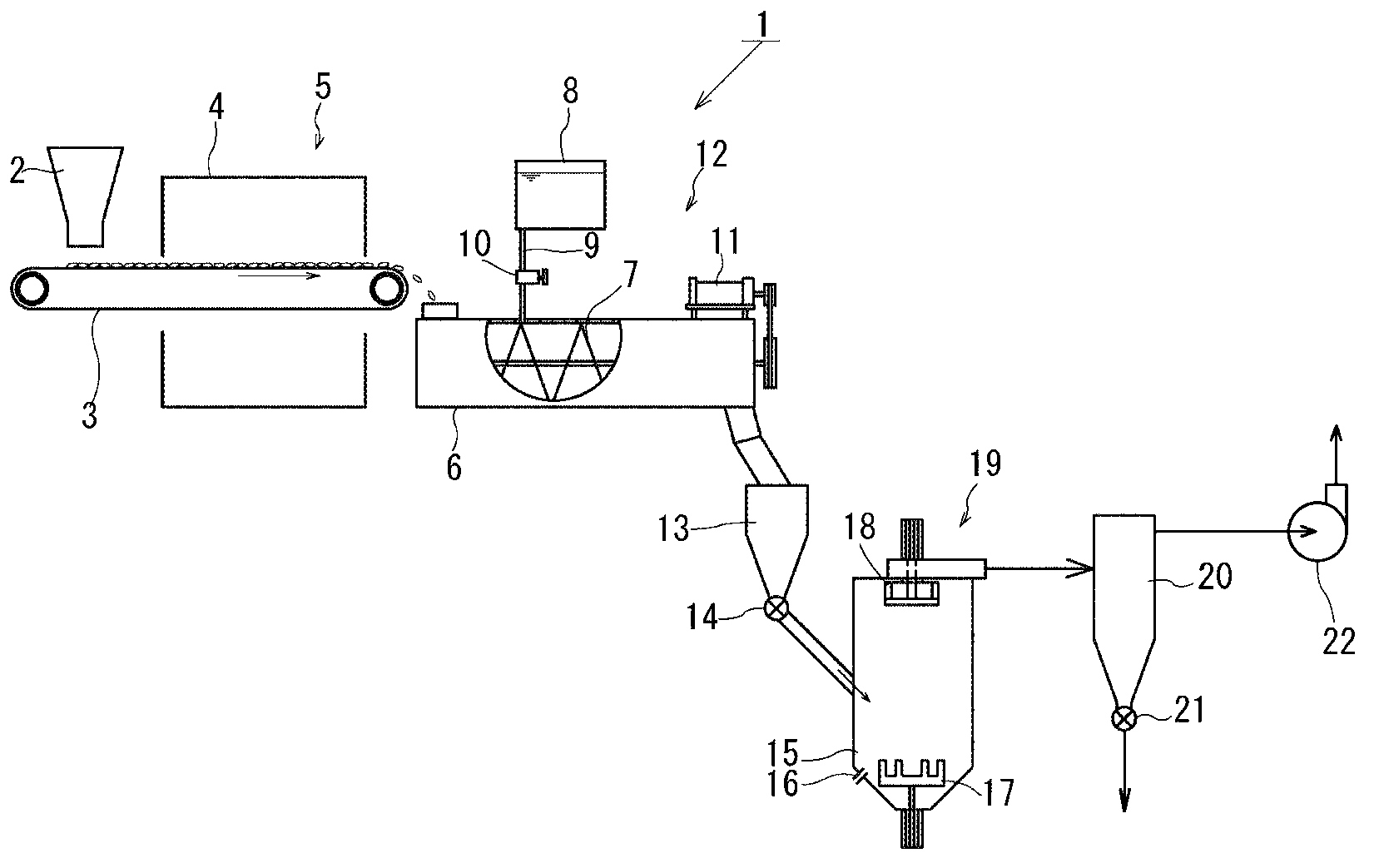
Method for producing rice powder and rice powder obtained thereby
The present invention eliminates the need for power used for roll milling by significantly reducing the hardness of rice, and provides fine rice powder with good quality even when the rice is ground only with a jet mill. The present invention includes: a preprocessing step (5) of creating a number of fine cracks on the surface of an uncooked rice grain; a water-adding step (12) of increasing the water content of the rice grain having the fine cracks formed on the surface thereof; and a grinding step (19) of grinding, with a jet mill, the rice grain having absorbed water. That is, when water is added after the fine cracks are formed on the surface of the rice grain, the swelling of a compound starch grain proceeds remarkably faster than in the case of water being absorbed gradually through a germ. The rapid swelling increases the amount of strain in the structure of a cell wall, making it easy to break the strong structure of the cell wall and significantly reducing the hardness of the rice. At the time of grinding, due to the significant reduction in the hardness of the rice, the structure of the cell wall is easily broken and even a starch grain is finely ground.
Owner:SATAKE CORP
Production method of fried broad bean
The invention discloses a production method of fried broad bean. The method comprises procedures of soaking broad beans, frying the broad beans, degreasing the broad beans, mixing and flavoring the broad beans and packaging the broad beans; and the soaking procedure comprises procedures of emulsifying, opening and pasting broad beans. According to the invention, through mainly adding an emulsifying agent to the broad beans in the broad bean soaking process, the structures of the broad beans are improved, so that more and intensive gas holes are formed in the structures; and moreover, the pasted water molecules can sufficiently enter microcrystalline structures of starch grains, starch structures of bean particles are expanded to a larger volume through the vaporized water molecules during frying; and the dried product is greatly improved in color, aroma, mouth feel and the like when compared with the traditional production method.
Owner:ANHUI TRUELOVE FOODS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com