Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "Small-angle scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Small-angle scattering (SAS) is a scattering technique based on deflection of collimated radiation away from the straight trajectory after it interacts with structures that are much larger than the wavelength of the radiation. The deflection is small (0.1-10°) hence the name small-angle. SAS techniques can give information about the size, shape and orientation of structures in a sample.
X-ray reflectometry with small-angle scattering measurement
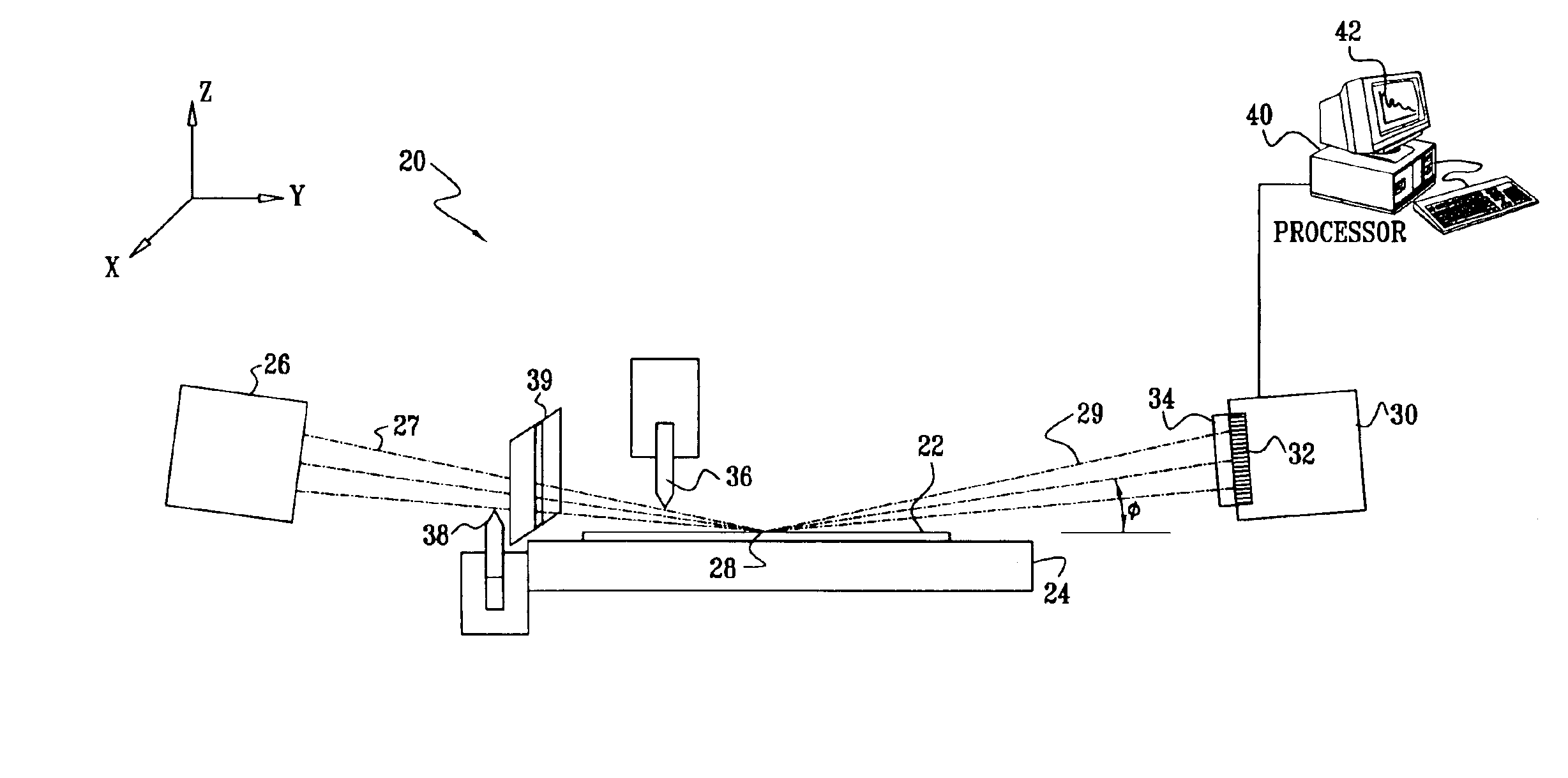
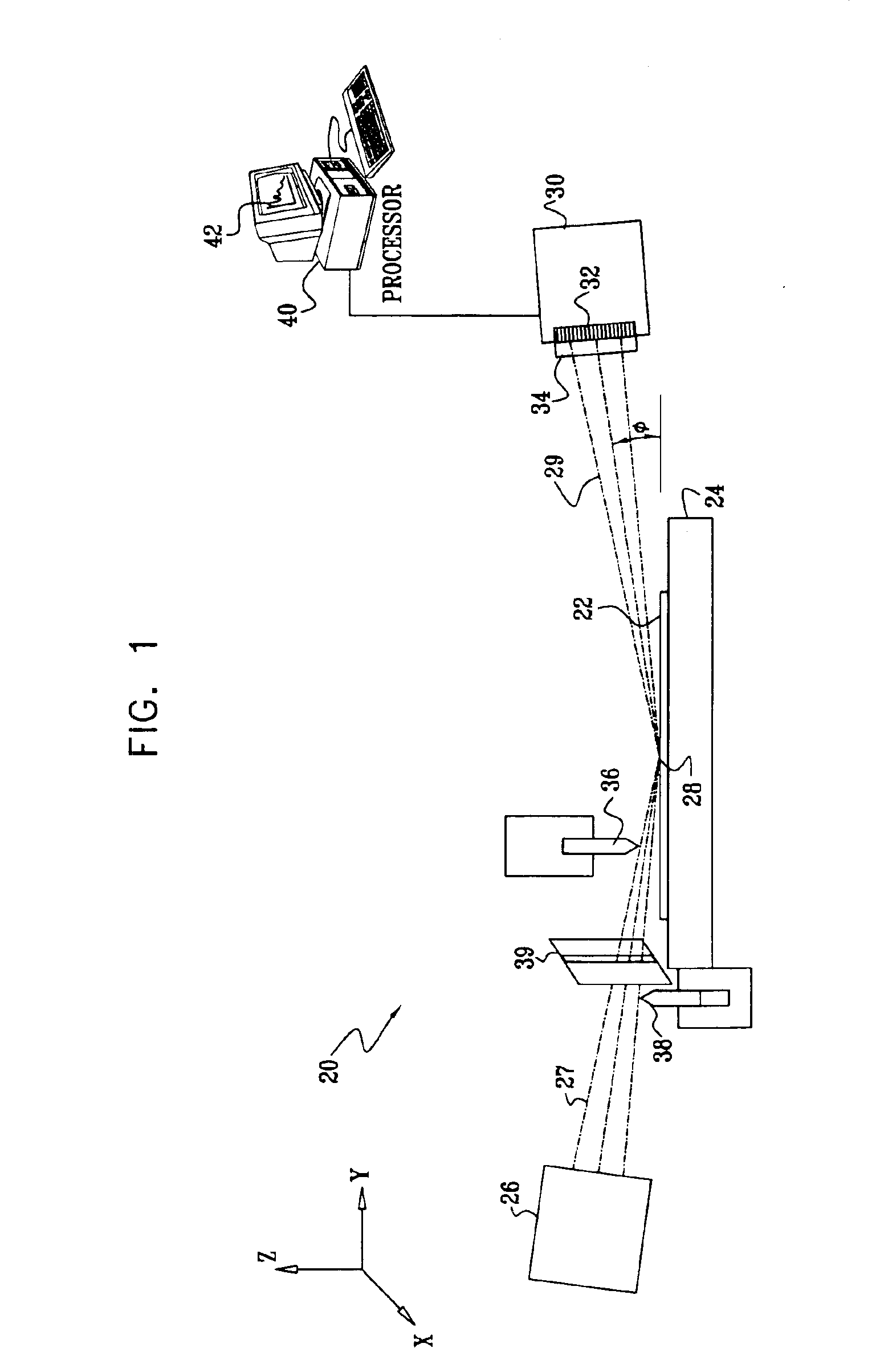
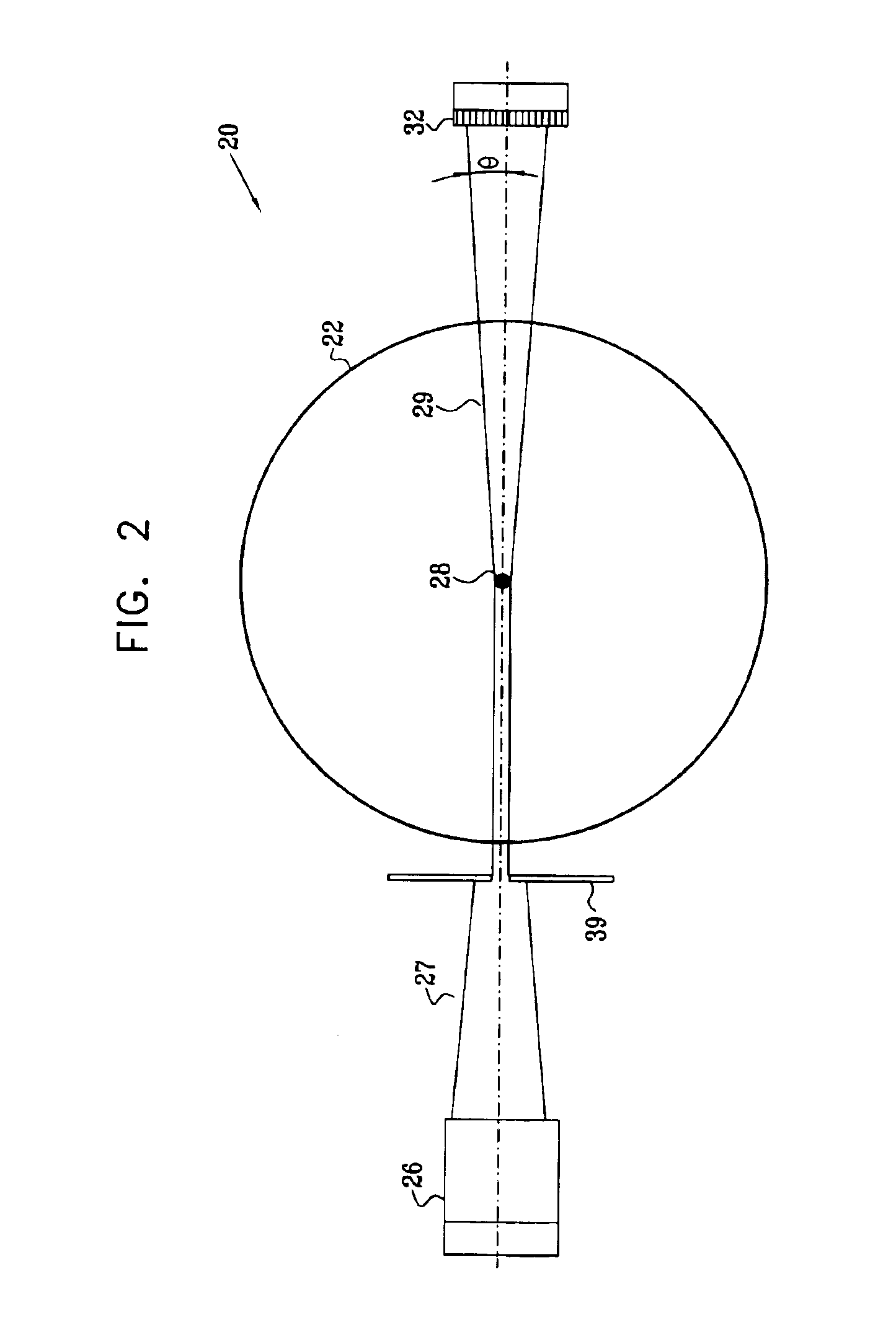
InactiveUS6895075B2Improve featuresUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionElevation angleDetector array
Apparatus for inspection of a sample includes a radiation source and an array of detector elements arranged to receive radiation from the surface due to irradiation of an area of the surface by the radiation source. The array has a first operative configuration for resolving the received radiation along a first axis perpendicular to the surface, and a second operative configuration for resolving the received radiation along a second axis parallel to the surface. A signal processor processes the signal from the detector array in the two configurations so as to determine a reflectance of the surface as a function of elevation angle relative to the surface and a scattering profile of the surface as a function of azimuthal angle in a plane of the surface.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
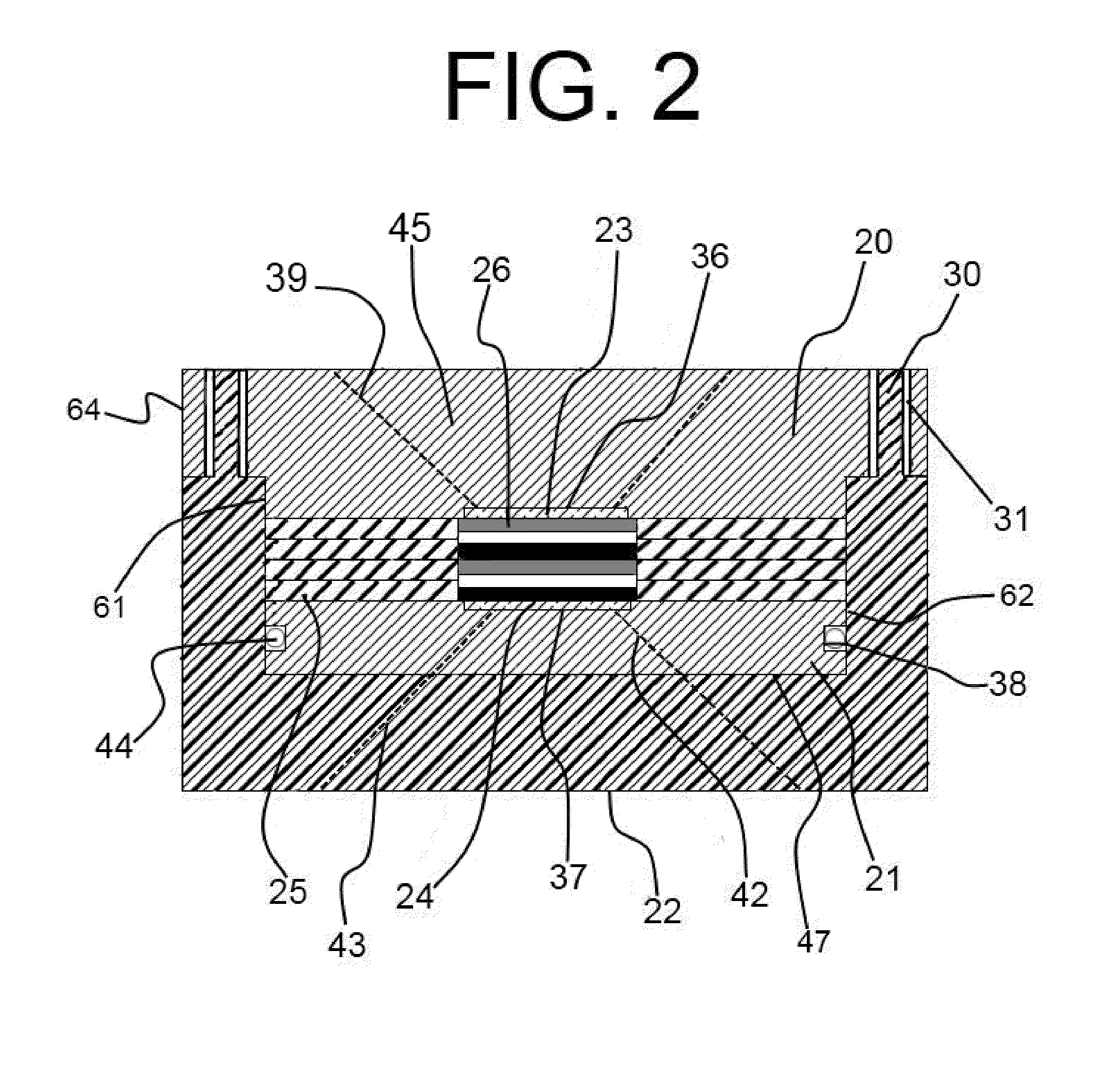
Small-angle scattering x-ray metrology systems and methods
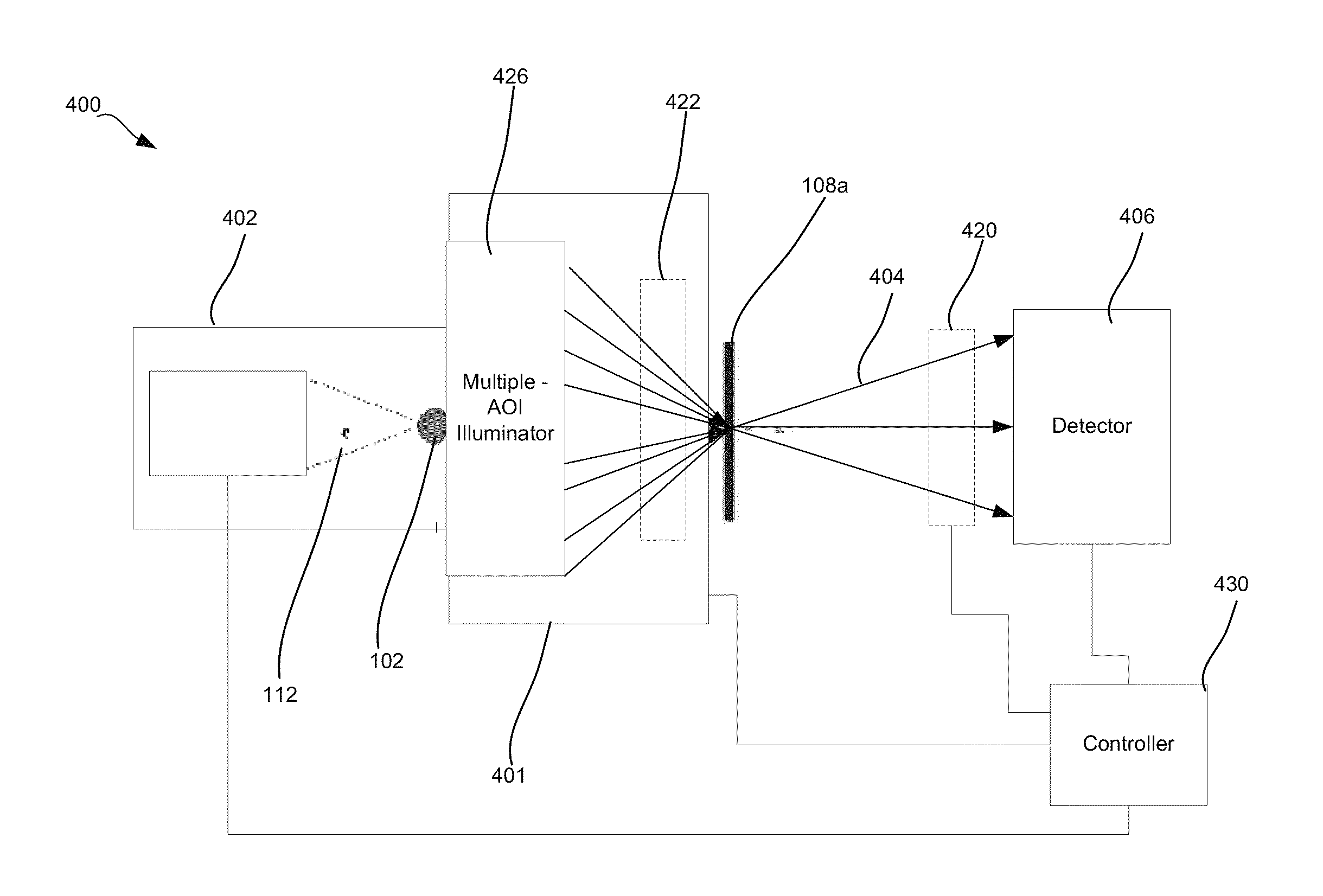
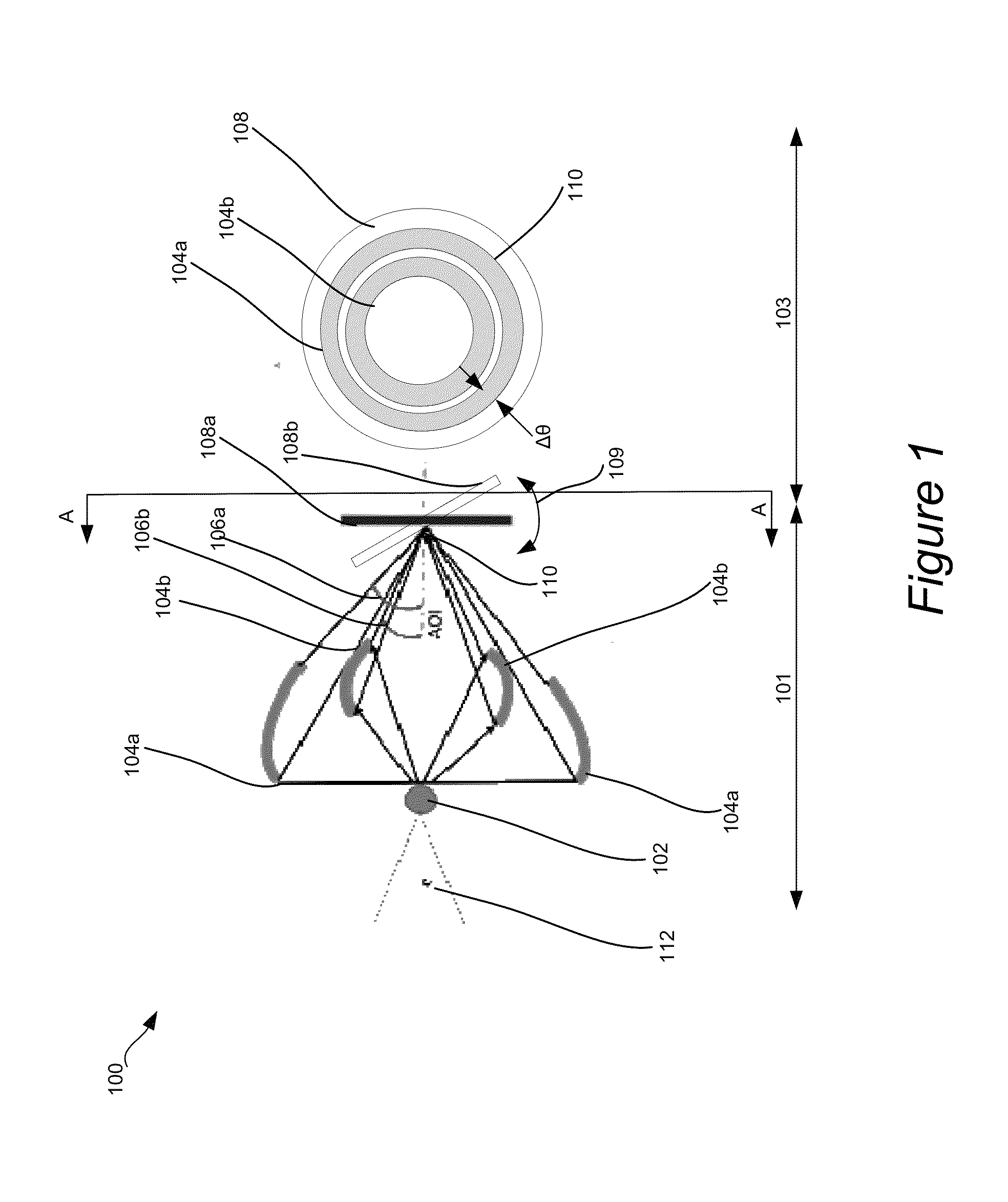
ActiveUS20150110249A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationTesting semiconductor materialsSoft x rayMetrology
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for performing small angle x-ray scattering metrology. This system includes an x-ray source for generating x-rays and illumination optics for collecting and reflecting or refracting a portion of the generated x-rays towards a particular focus point on a semiconductor sample in the form of a plurality of incident beams at a plurality of different angles of incidence (AOIs). The system further includes a sensor for collecting output x-ray beams that are scattered from the sample in response to the incident beams on the sample at the different AOIs and a controller configured for controlling operation of the x-ray source and illumination optics and receiving the output x-rays beams and generating an image from such output x-rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
Transmission-geometry electrochemical cell for in-situ scattering and spectroscopy investigations
ActiveUS20140093052A1Continuous measurementContinuous monitoringMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSecondary cellsSpectroscopyX-ray
The present invention relates to a test chamber that can be used to perform a variety of X-ray and neutron spectroscopy experiments including powder diffraction, small-angle scattering, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and pair distribution functions, such chamber comprising a first electrode with an X-ray transparent window; a second electrode with an X-ray transparent window; a plurality of insulating gaskets providing a hermetic seal around the sample and preventing contact between said first and second electrodes; and an insulating housing into which the first electrode is secured.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
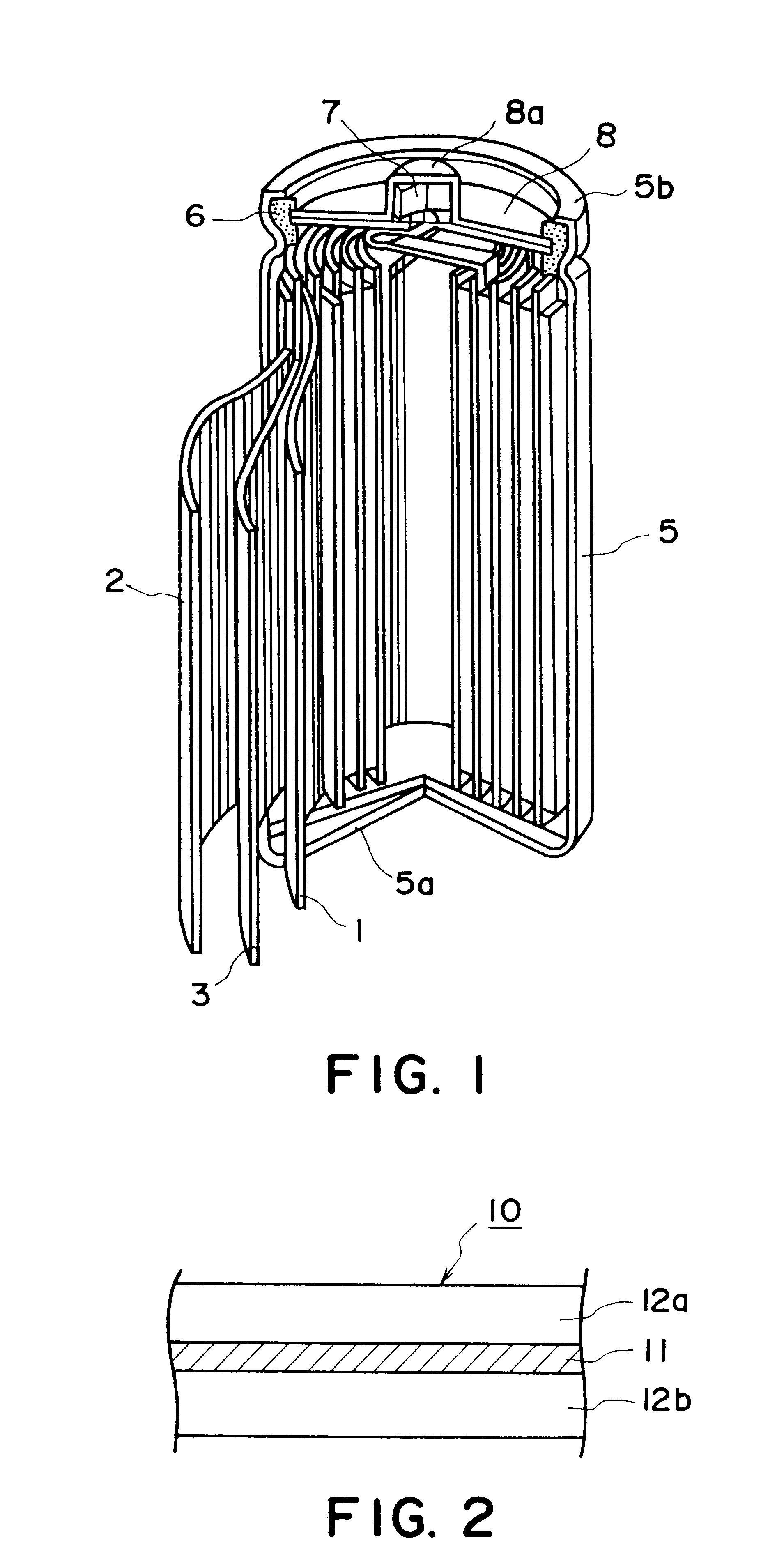
Carbonaceous electrode material for secondary battery
InactiveUS6569570B2Efficient use ofLarge capacityConductive materialCarbon preparation/purificationX-rayPhotochemistry
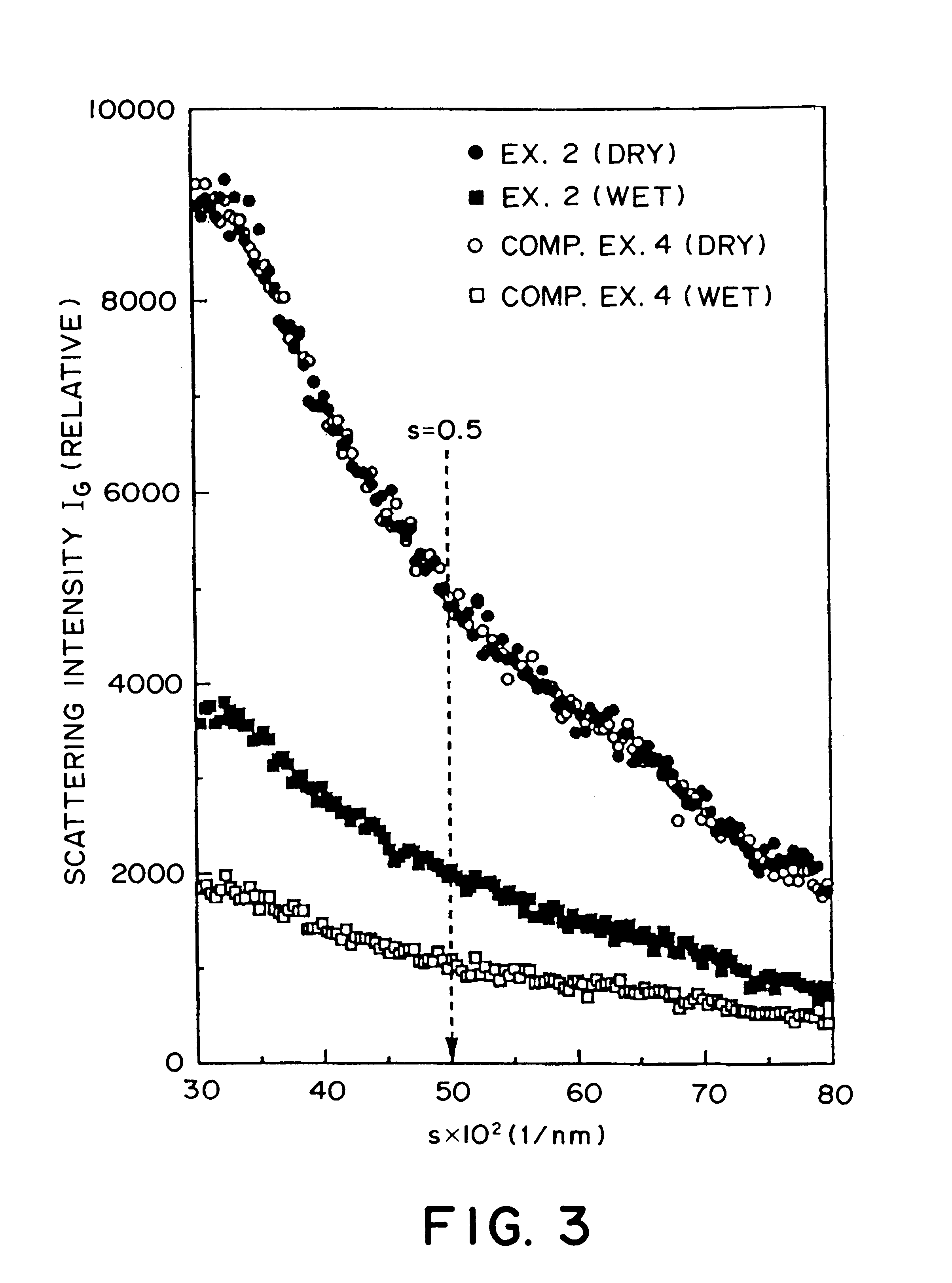
A carbonaceous electrode having improved capacities for doping and dedoping of a cell active substance, such as lithium, and suitable for a non-aqueous secondary battery, is constituted by a carbonaceous material obtained by carbonizing an aromatic condensation polymer formed by condensation of an aromatic compound having a phenolic hydroxy group and an aldehyde. The carbonaceous material is characterized by an atomic ratio H / C between hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms of below 0.1, a carbon dioxide adsorption capacity of at least 10 ml / g, and an X-ray scattering intensity ratio IW / ID of at least 0.25, wherein IW and ID represent scattering intensities as measured in a wet state and a dry state, respectively, at a parameter s=2.sin theta / lambd of 0.5 nm-1, wherein theta denotes a scattering angle and lambd denotes a wavelength of X-rays in X-ray small-angle scattering measurement.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Medical imaging system
ActiveUS20140169522A1Accurate measurementImage enhancementImage analysisSoft x rayDifferential phase
A medical imaging system includes an X-ray imaging apparatus and an image processor. The X-ray imaging apparatus is provided with a Talbot or Talbot-Lau interferometer and includes an X-ray source, an X-ray detector, and a subject table. The image processor generates a differential phase image, and optionally, one or both of an X-ray absorption image and a small-angle scattering image of the subject on the basis of the image signal of the subject. The image processor specifies a location of an edge of a bone in the joint on the basis of at least one of the generated images; and detects an edge of a cartilage in the joint in the differential phase image on the basis of the specified location of the bone edge to quantitatively measure a feature of the cartilage.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
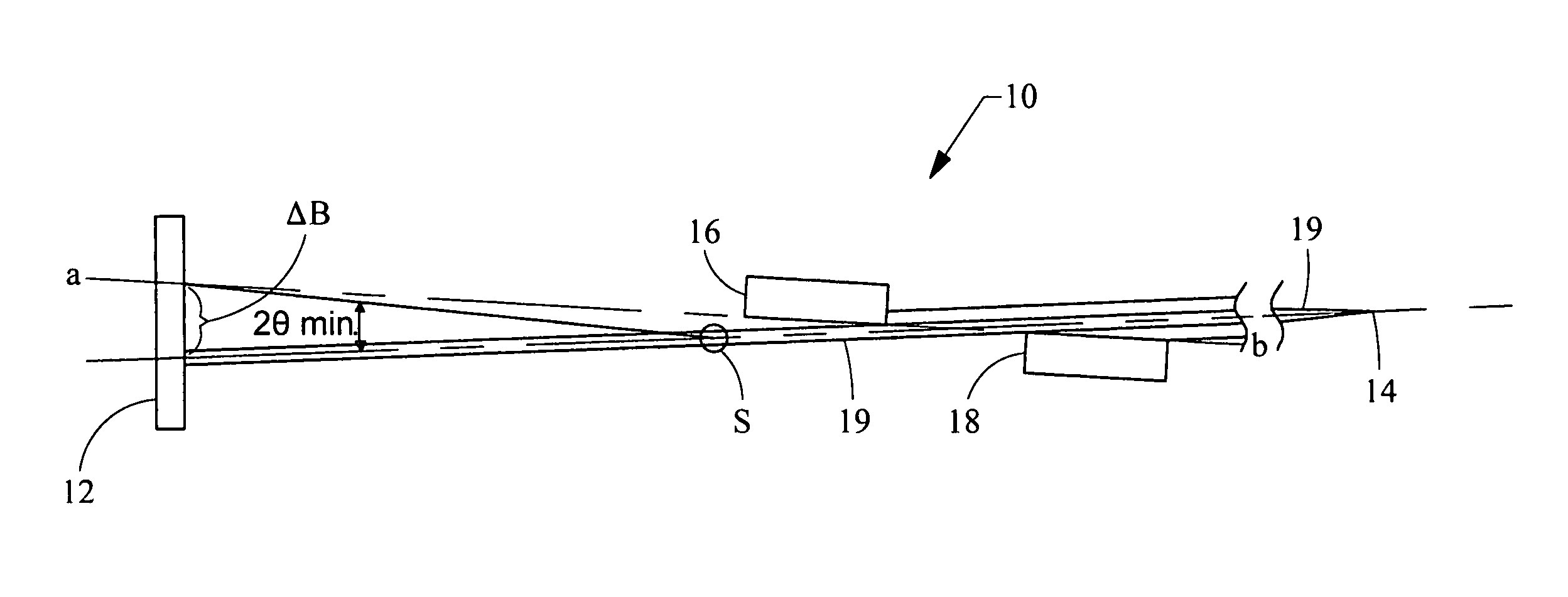
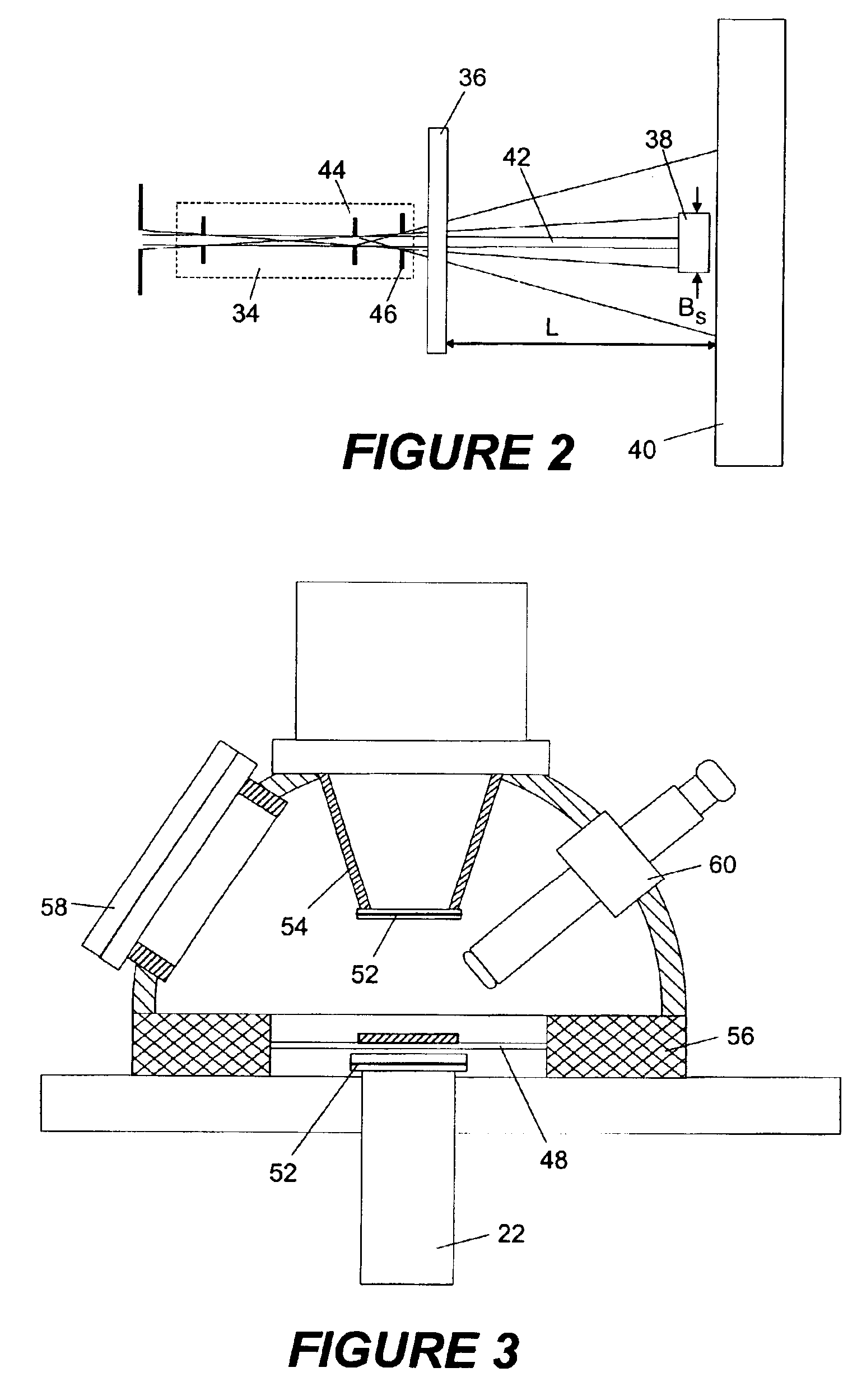
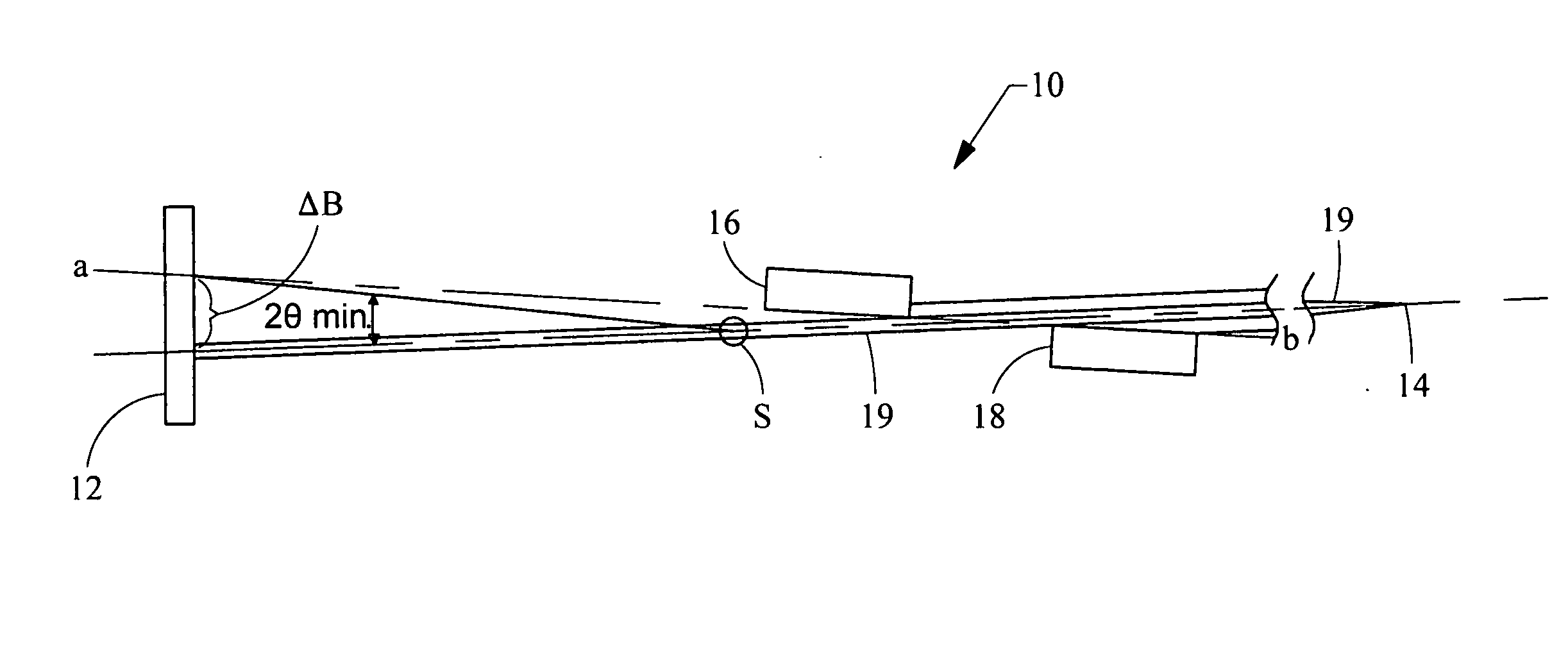
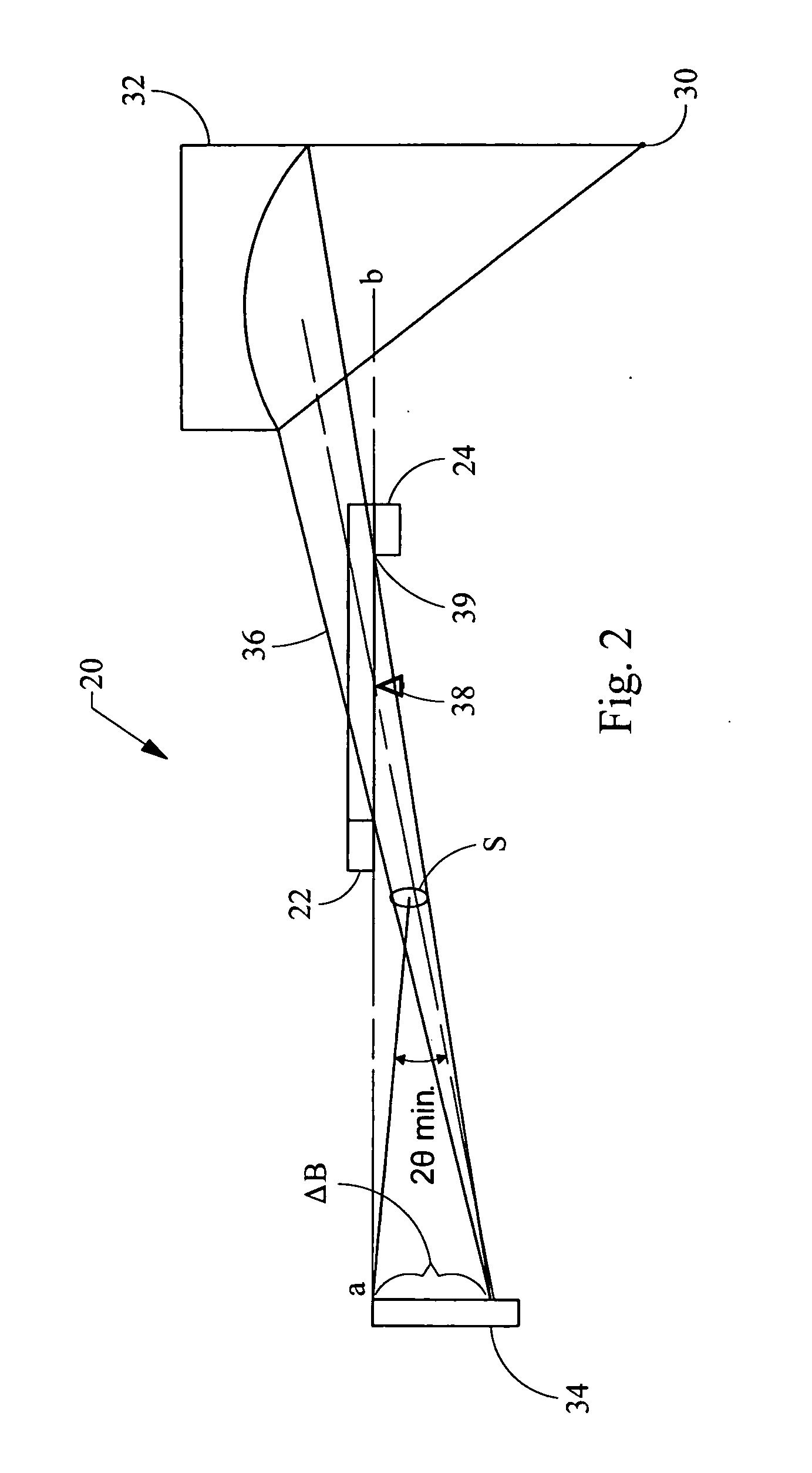
Two-dimensional small angle x-ray scattering camera
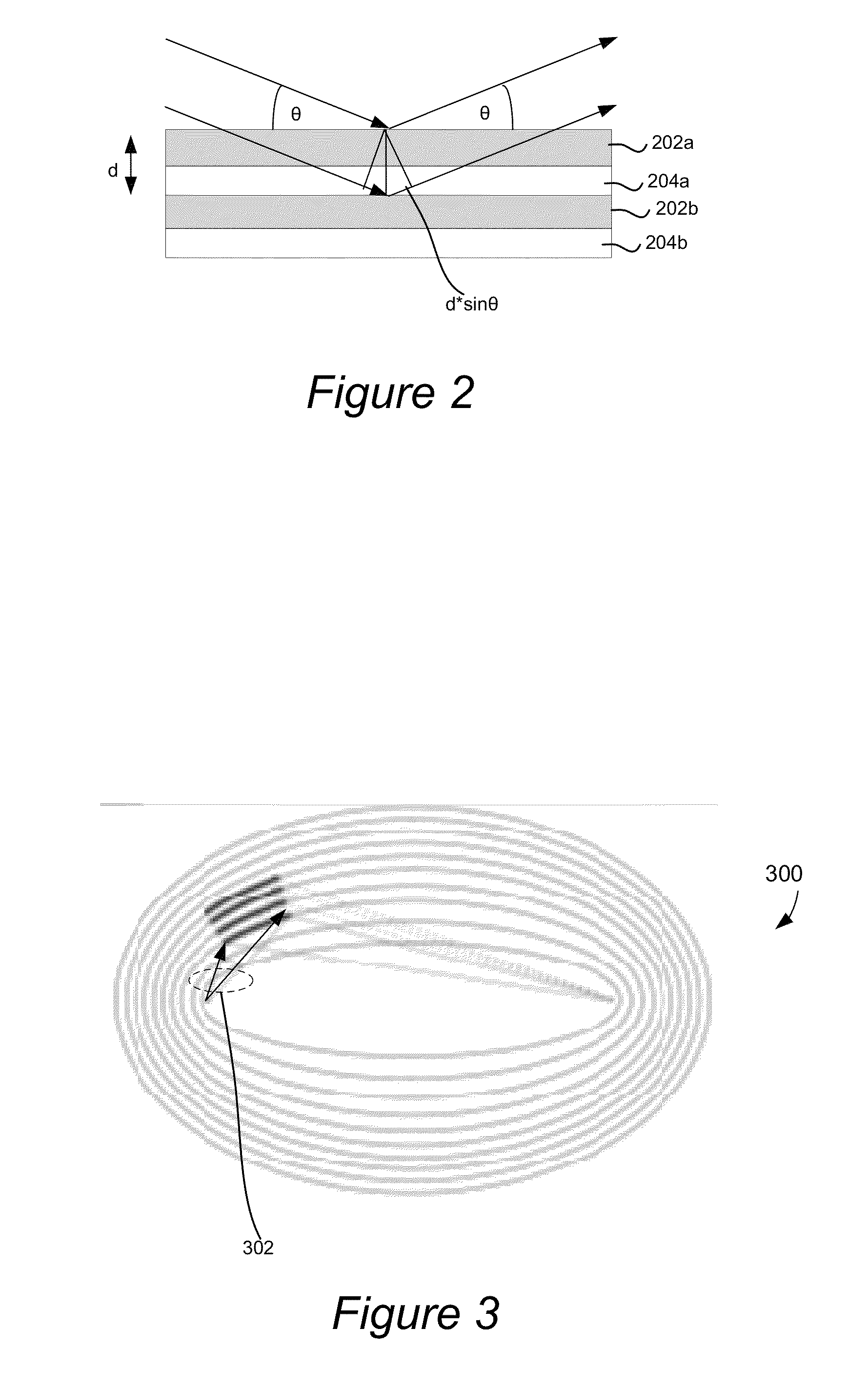
ActiveUS7139366B1Wide range of anglesHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSmall-angle X-ray scatteringLight beam
A two-dimensional x-ray scattering camera includes a source, an optic, a detector, and a pair of collimating blocks. The source emits x-ray beams that are reflected by the optic towards a sample. The detector detects scattering from the sample, the pair of collimating blocks is positioned between the optic and the detector to collimate the beam. A bottom surface of one block is substantially parallel a top surface of the other block, and the blocks are rotatable relative to the beam about a pivot. The system forms a two-dimensional beam that is symmetric about the primary beam axis at the detector position, regardless how the beam is collimated by the collimating blocks. The system therefore eliminates smearing and can be used for anisotropic small angle scattering at high resolution and low Qmin.
Owner:OSMIC
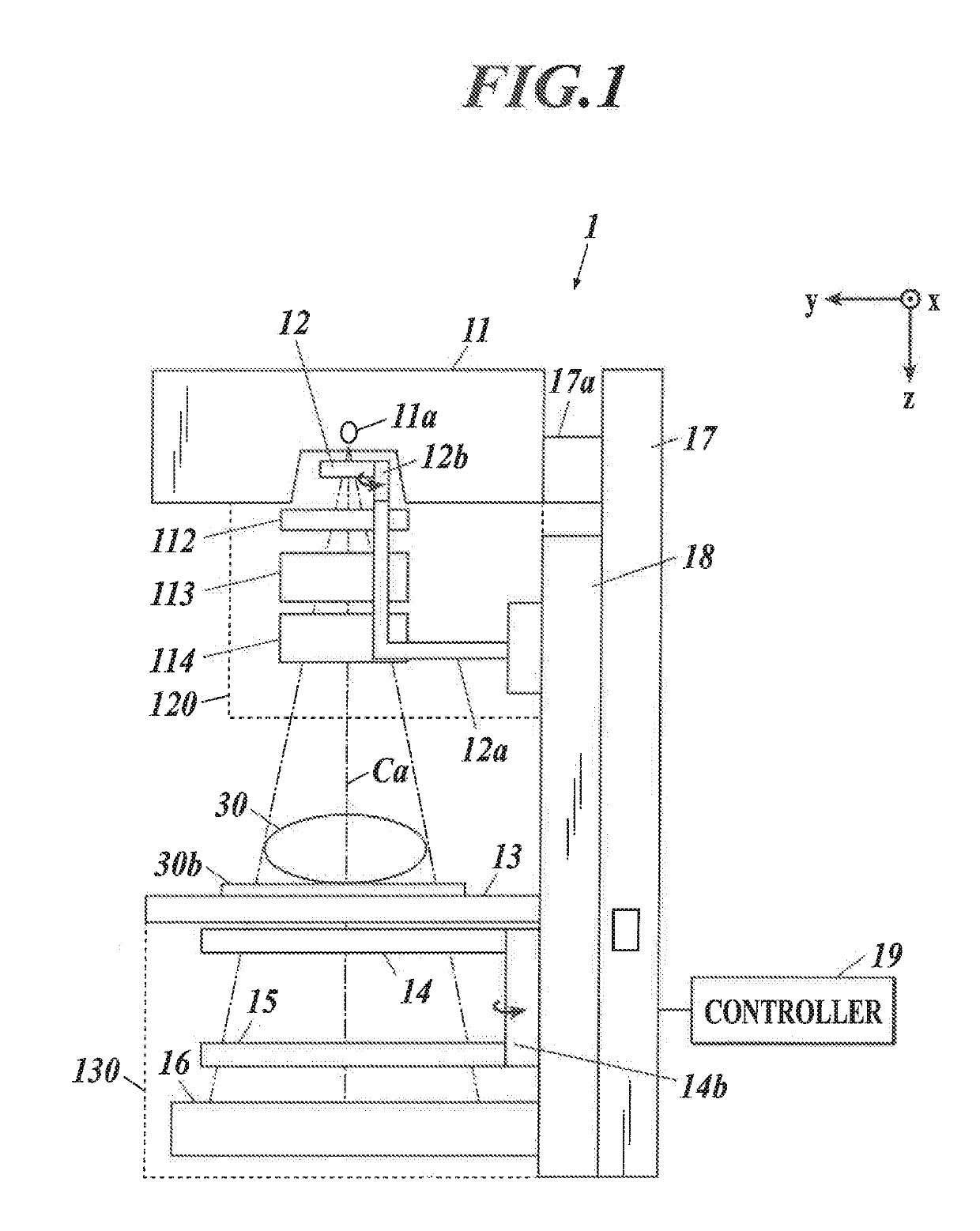
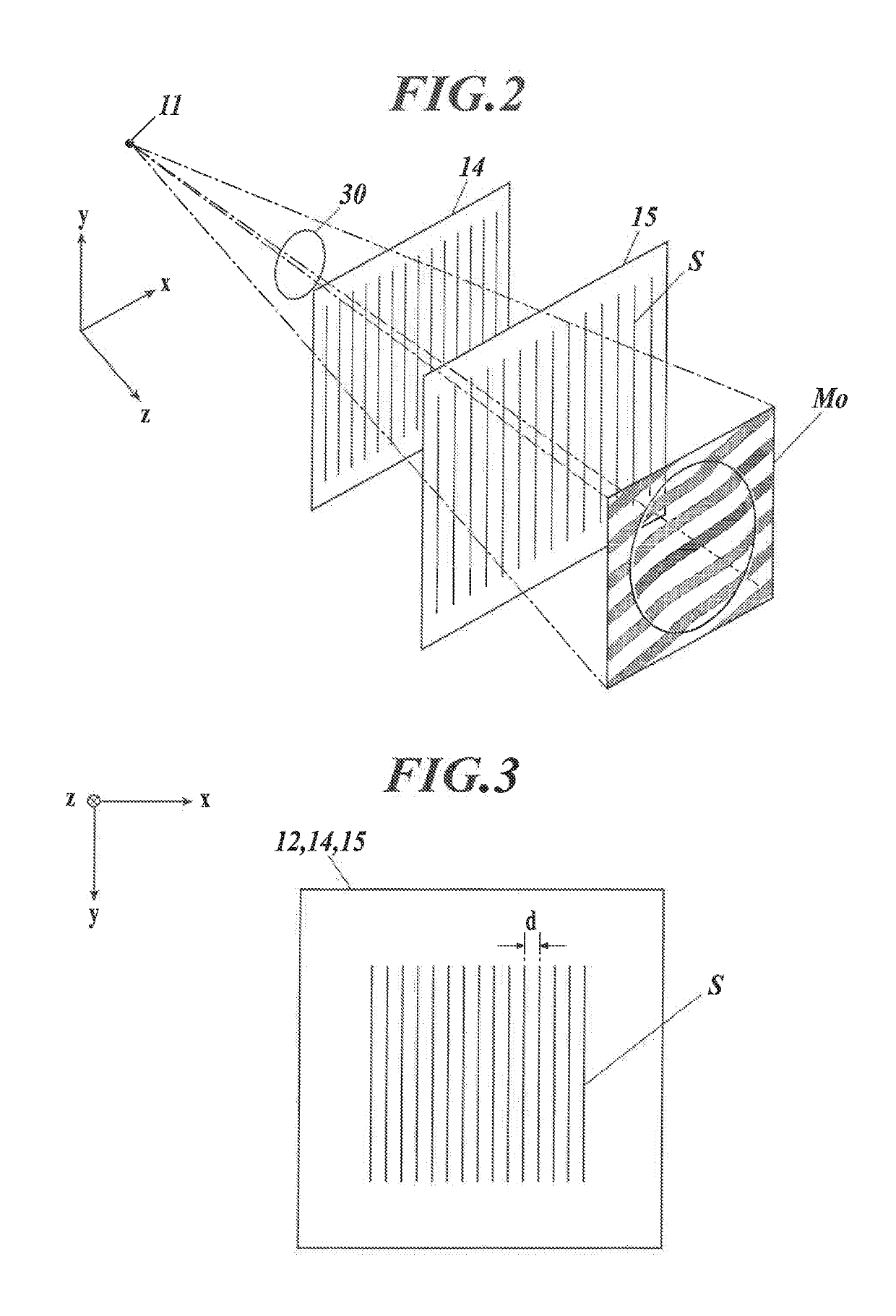
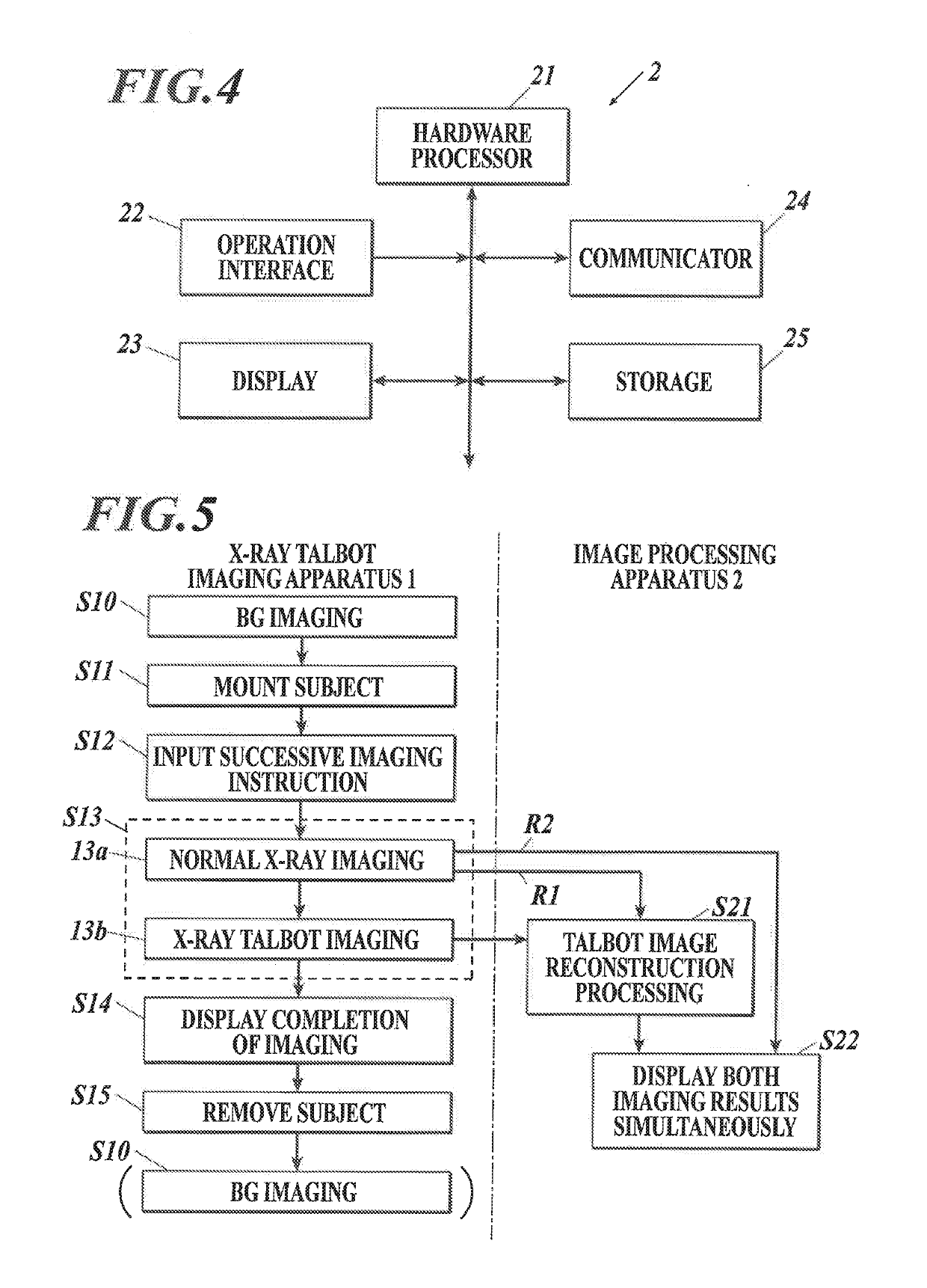
X-ray imaging system
ActiveUS20190261935A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsForeign body detectionSoft x rayDifferential phase
An X-ray imaging system includes an X-ray Talbot; imaging apparatus and an image processing apparatus. The image processing apparatus generates reconstruction images from the moire image taken by the X-ray Talbot imaging apparatus. The reconstruction images include a differential phase image, an absorption image and a small-angle scattering image. The X-ray imaging system performs X-ray Talbot imaging and normal X-ray imaging. X-ray Talbot imaging includes setting an exposure energy of the X-ray Talbot imaging apparatus to a first exposure energy and taking the moire image with the X-ray detector. Normal X-ray imaging includes setting the exposure energy of the X-ray Talbot imaging apparatus to a second exposure energy and taking an absorption contrast image with the X-ray detector by normal X-ray imaging.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Optical arrangement for a flow cytometer
ActiveUS7800754B2Easy to separateImprove performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansIndividual particle analysisFlow cellFluorescence
An optical system suited to high sensitivity measurement of small particles as they travel through a point of detection in a flow cell. The system consists of components along two optical axes, preferably but not necessarily, at approximately the Brewster angle to one another. The first axis incorporates a flow cell, high numerical aperture light collection lens, spatial filtering and optical detectors. The second axis incorporates a radiation source (typically a laser or arc-lamp) and beam shaping optics. The two axes are positioned at an angle sufficient to enable collection of small angle light scatter near the edge of the collection lens and to allow collection of medium and large angle light scatter through the centre and opposite side of the collection lens. The invention enables spatial filtering in the image plane of the collection lens to exclude radiation from the dominating sources of unwanted scattering in the flow cell, and also allows the use of a high numerical aperture lens to collect radiation scattered and fluoresced by the sample particles.
Owner:OJK CONSULTING
Vertical small angle x-ray scattering system
InactiveUS6956928B2Distance minimizationUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSmall-angle X-ray scatteringX-ray
A small angle x-ray diffraction scattering system has a vertical orientation, allowing for simplified analysis of liquid samples. The system may function in a beam-up or a beam-down configuration. An x-ray source provides an initial x-ray beam that is directed vertically along a primary beampath to a sample located on a sample support. The small angle scattered x-ray energy travels through a secondary beampath to a detector. The primary and secondary beampaths may be evacuated and separated from a sample chamber by fluid seals. Beam conditioning optics and a collimator may be used in the primary beampath, and a beamstop used in the secondary beampath. The sample chamber may have a microscope or camera, which may be movable, for observing the sample, and a translation stage for moving the sample in at least two dimensions.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
Hot stage for small-angle scattering experiment
InactiveCN104833687AEvenly heatedAvoid influenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayEngineering
The present invention provides a hot stage for small-angle scattering experiment. The hot stage includes an intake passage, a sealed window, a translucent window, an exhaust passage, a heating layer package wall, a heating layer, a sample chamber and a sample clamp layer. The hot stage for small angle scattering experiment has thermal station temperature in the range of -40 to 1200 DEG C; and the connecting lines between two end ports of the sample chamber and the edges of the transparent window have included angle of 4- 90 DEG with the axial parallel of the sample chamber. Surrounding heating on the sample chamber by the heating layer ensures uniform heating of the sample, and avoids the effects of the heating layer on neutron and X-ray path. The sealed window and translucent window uses quartz glass, sapphire or Kapton film with high transmittance of neutrons and X-rays, so as to achieve high transmittance of neutrons and X-ray, and ensure normal operation of the neutron and X-ray small-angle scattering experiments.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Method of evaluating ion-exchange film, method of evaluating organic sample and X-ray measuring apparatus
Disclosed herein is a method of evaluating the performance of an ion-exchange film. In the method, small-angle scattering curves for the ion-exchange film are obtained by an X-ray measuring apparatus that can detect X-rays scattered at small angles with respect to the axis of an X-ray applied to film. From the positions of the peaks on the small-angle scattering curves and the X-ray intensities at these peaks, the molecular structure of the ion-exchange film is determined, thereby to evaluate the performance of the ion-exchange film.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Negative active material for secondary battery, process for producing same, and negative electrode and lithium-ion battery both obtained using same
The present invention relates to: a negative active material for secondary batteries which comprises a silicon oxide-based composite material, attains a high battery capacity, and has excellent charge / discharge cycling characteristics; a process for producing the negative active material; and a negative electrode and a lithium-ion battery both obtained using the negative active material. The silicon oxide-based composite material has a new structure and is directly obtained by burning, in an inert gas atmosphere, a polysilsesquioxane having a specific structure. The yielded silicon oxide-based composite material has graphitic carbon and is represented by the general formula SiOxCy (0.5<x<1.8, 1<y<5). In an examination by the X-ray small-angle scattering method, the composite material gives a spectrum which shows scattering in the range of 0.02 Å-1<q<0.2 Å-1. In an examination by Raman spectroscopy, the composite material gives a spectrum which shows scattering at 1,590 cm-1 (G band; graphite structure) and at 1,325 cm-1 (D band; amorphous carbon), the peak intensity ratio of crystalline carbon and amorphous carbon (ID / IG ratio) being in the range of 2.0-5.0. The silicon oxide-based composite material is used as a negative active material to form a negative electrode therefrom, and the negative electrode is used to form a lithium-ion secondary battery.
Owner:JNC CORP +1
In situ pressure loading device for neutron small-angle scattering
InactiveCN104849148AAvoid occlusionReduce radiationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFrame basedBall screw
The invention provides an in situ pressure loading device for neutron small-angle scattering. The in situ pressure loading device can conduct pressure loading for tested samples in the neutron beam direction and control stress and strain of the samples. The in situ pressure loading device comprises a power drive assembly, a transmission gear assembly, a ball screw assembly, a high-accuracy measurement assembly, a clamp assembly, a fixed machine frame base assembly and a shielding layer. The in situ pressure loading device is characterized in that a plurality of assemblies, which are of hollow structures, on a neutron beam line allow direct passing of neutrons, and a clamp is made of sapphire materials with high neutron transmittance, so as to achieve the pressure loading of the samples in the neutron beam direction. The in situ pressure loading device is matched with a neutron small-angle scattering spectrometer for use, conducts in situ detection on the microscopic deformation, damage and break processes of the tested samples in the mechanical use environment, and provides an effective and reliable means for study on further disclosure of the mechanical property and the damage and break mechanism of materials.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
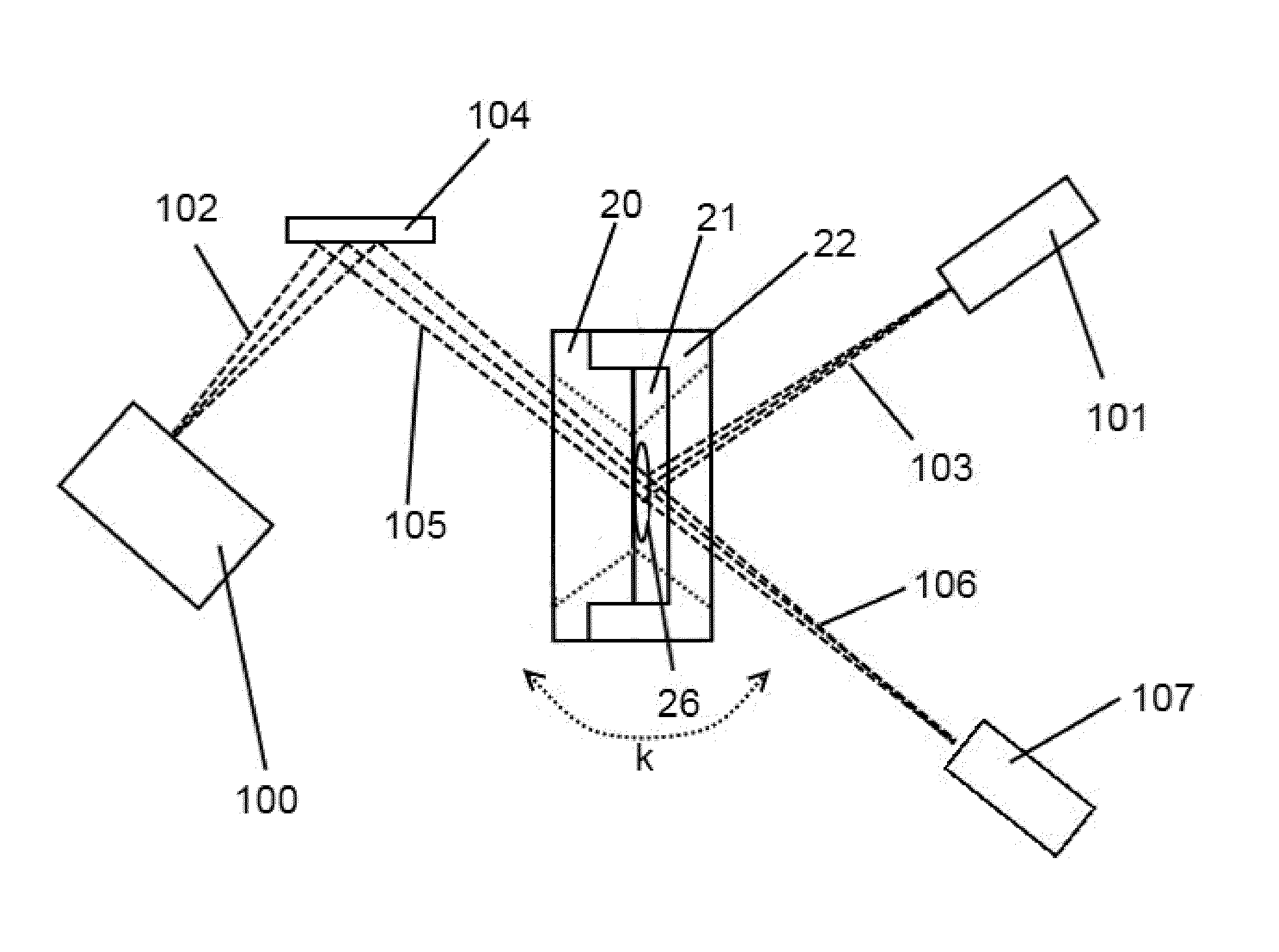
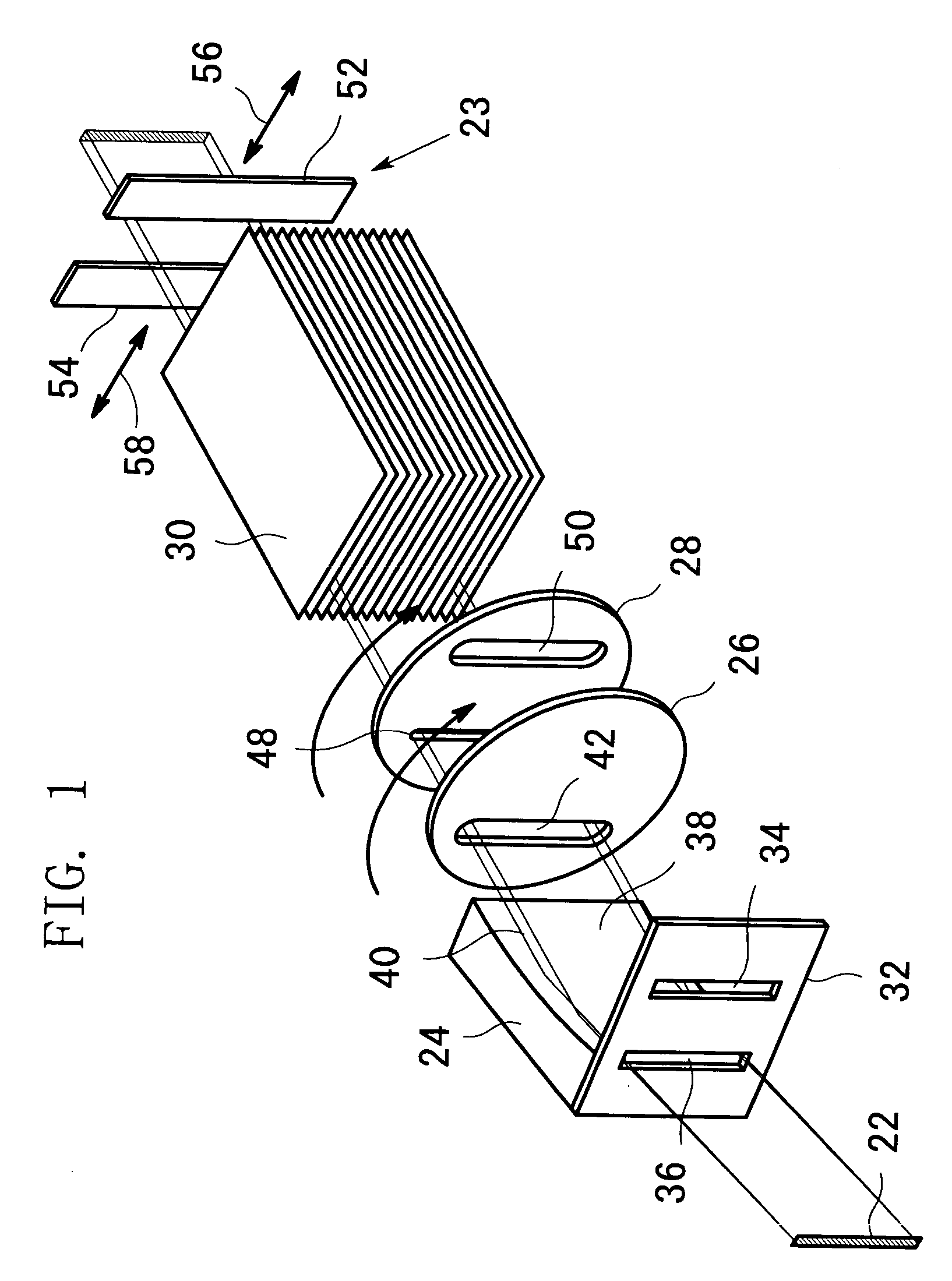
X-ray optical system for small angle scattering
ActiveUS6990177B2Easy to switchLarge intensityHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersParallel beamCable harness
An X-ray optical system for small angle scattering has a parabolic multilayer mirror and, so that switching to other X-ray incident optical systems for X-ray analysis can be easily performed. A parabolic multilayer mirror, an optical-path selecting slit device, a small-angle selecting slit device and a Soller slit are arranged between an X-ray source and a specimen-side slit. An X-ray beam having passed through the first aperture of an aperture slit plate is interrupted by the optical-path selecting slit. An X-ray beam having passed through the second aperture of the aperture slit plate is reflected at the reflecting surface of the multilayer mirror to become a parallel beam. This parallel beam passes through an aperture of the optical-path selecting slit device. The beam width is restricted by a narrow slit of the small-angle selecting slit device.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
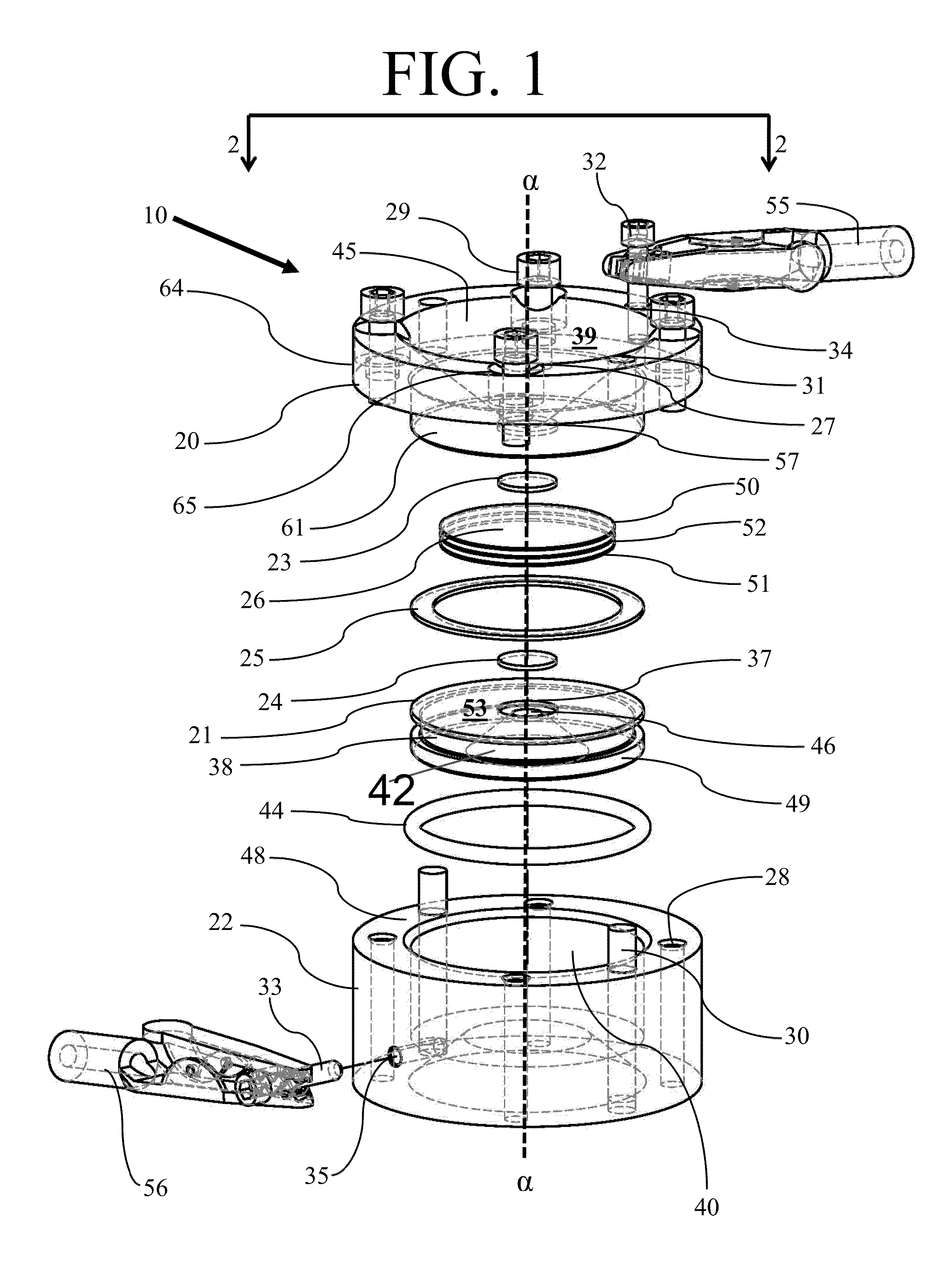
Sample reservoir for carrying out in-situ characterization on crystallization process of molecular sieve based catalyst, and use method thereof
ActiveCN101629915AWide range of applicationsRealize in situ online characterizationThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansWaxX-ray absorption fine structure
A sample reservoir for carrying out in-situ characterization on crystallization process of a molecular sieve based catalyst comprises a reservoir body, a press ring, a sealing pad, a window piece, a reservoir cover, a fastening element, an inner core and a thermocouple component. The sample reservoir allows X rays to pass through and studies the crystallization process of the molecular sieve based catalysts in an in-situ online manner by using XAFS (x-ray absorption fine structure), XRD (X-ray diffraction), SAXS (small angle X-ray scattering), SAXS / WAXS (small angle X-ray scattering and wide angle X-ray scattering) under the conditions of 0-300 DEG C and 0-3 MPa. The change of the catalyst structure is monitored during the processes.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High strength polyethylene fiber
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
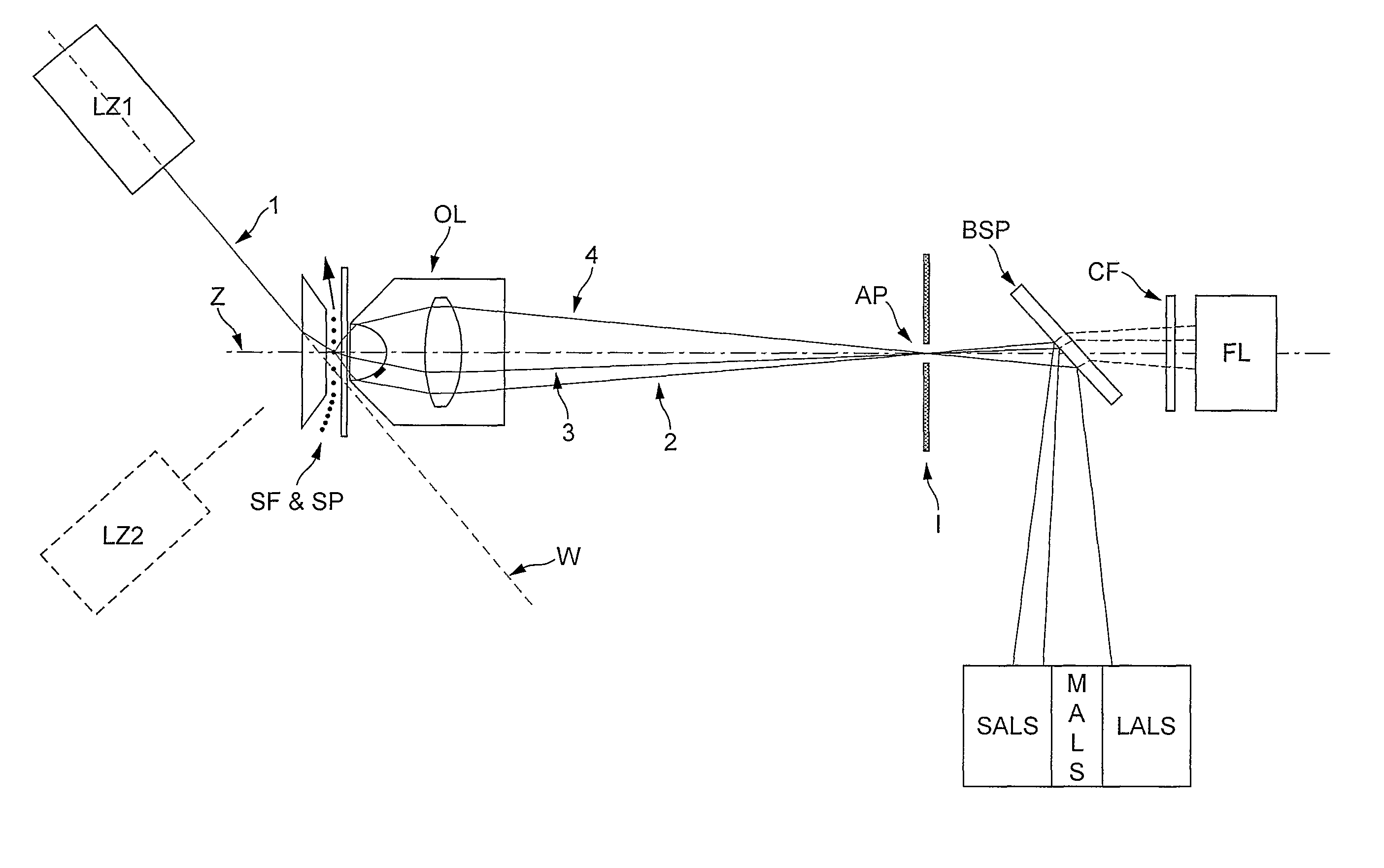
Single-beam double-lens laser particle analyzer
The invention discloses a single-beam dual-lens laser particle size analyzer, which adopts an emanative laser beam as the light source and arranges two lenses before and after a sample pool; wherein, the lens after the sample pool simultaneously has two functions, one is to change the emanative laser beam into parallel light (secondary collimation), and the other is to receive the backward large-angle scattered light (aggregation). The lens before the sample pool is used to receive the forward scattered light. Photodetectors are respectively arranged on the focal planes of the two lenses to receive the forward and backward scattered signals, so that the forward and backward scattered light can be simultaneously received; the forward scattered light and the backward scattered light are respectively treated, and a small-angle scattered light and large-angle scattered light combined treatment technology is introduced, so that the test range of the laser particle size analyzer can reach 0.01-2000 micron. Through the effect of the unique design of the single-beam optical path reaching the multi-beam optical path, the invention is characterized by large test range, simple structure, small size, low cost and high measurement accuracy.
Owner:丹东百特科技有限公司
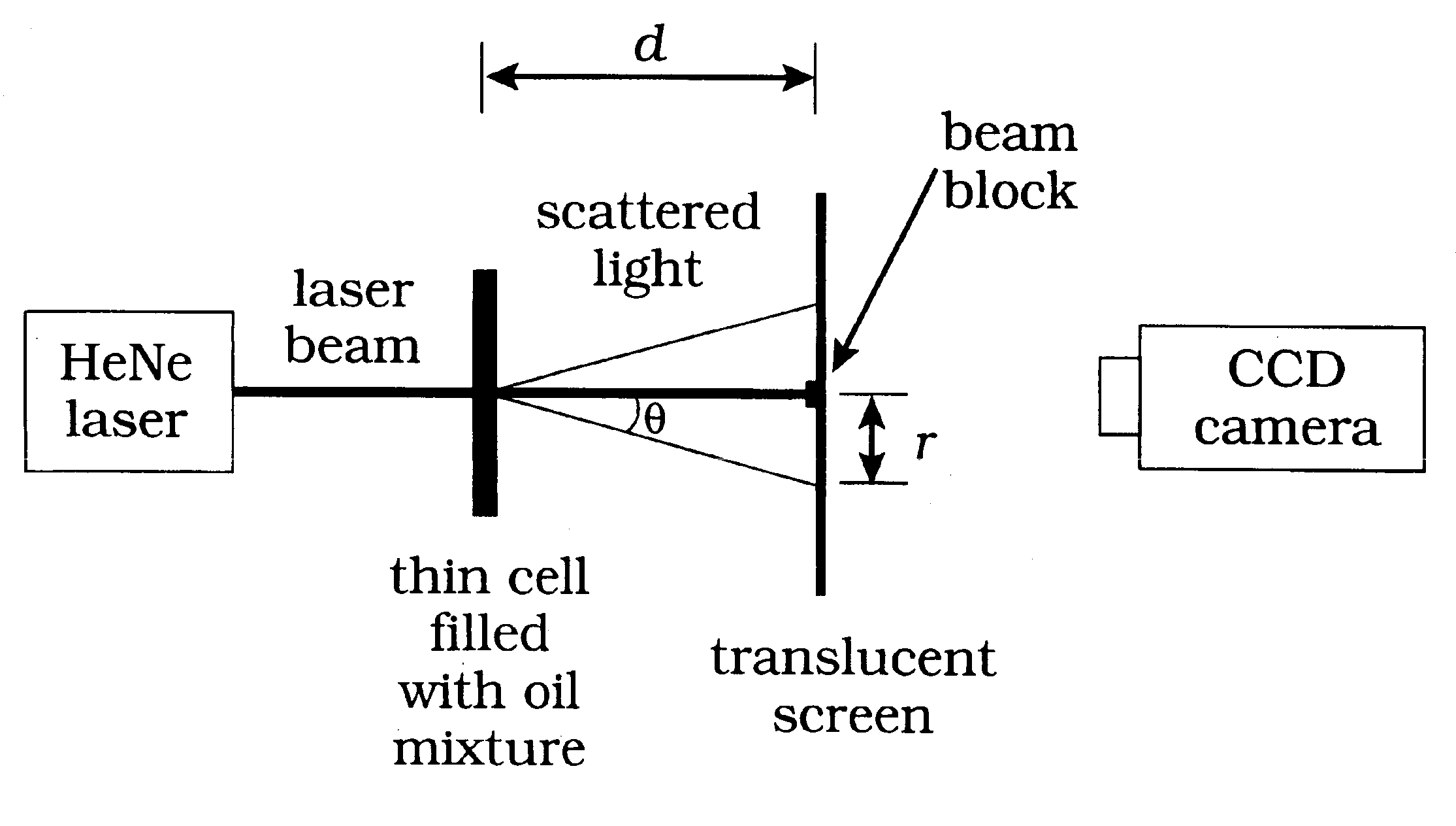
Asphaltene aggregation in petroleum oil mixtures determined by small angle light scattering
InactiveUS6839137B2Reduce sensitivityMaximum sensitivityScattering properties measurementsMaterial testing goodsSolventLaser beams
The present invention includes a method to determine if asphaltenes are soluble or insoluble in a solution. The solution may be a petroleum oil, a mixture of petroleum oils, petroleum derived oils and mixtures or similar combinations in a solvent. The invention includes the steps of illuminating the solution with a laser, measuring the small angle scattered light as a function of angle away from the laser beam, and determining if the asphaltenes are soluble or insoluble in the solution.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Medical imaging system
A medical imaging system includes an X-ray imaging apparatus and an image processor. The X-ray imaging apparatus is provided with a Talbot or Talbot-Lau interferometer and includes an X-ray source, an X-ray detector, and a subject table. The image processor generates a differential phase image, and optionally, one or both of an X-ray absorption image and a small-angle scattering image of the subject on the basis of the image signal of the subject. The image processor specifies a location of an edge of a bone in the joint on the basis of at least one of the generated images; and detects an edge of a cartilage in the joint in the differential phase image on the basis of the specified location of the bone edge to quantitatively measure a feature of the cartilage.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Medical instrument for use with a phase contrast imaging and x-ray recording system with phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20150031986A1Increase awarenessVisibility in imageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSoft x rayX-ray
A medical instrument is provided for use with a phase contrast imaging. The medical instrument includes at least one component, which has a strong small angle scattering of x-rays. Furthermore, a corresponding x-ray recording system with phase contrast imaging for recording an examination object may include such a medical instrument.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
High strength polyethylene fiber
InactiveUS20040062926A1Small differenceLow finenessSynthetic resin layered productsYarnX-rayHigh intensity
A high strength polyethylene filament, wherein said filament has a fineness of 1.5 dtex or less as a monofilament, a tensile strength of 15 cN / dtex or more and a tensile elastic modulus of 300 cN / dtex or more, and, the rate of dispersion-defective fibers cut from the filament is 2% or less, is disclosed, and a high strength polyethylene filament, wherein said filament has a tensile strength of 15 cN / dtex or more and a tensile elastic modulus of 300 cN / dtex or more, and, a long period structure of 100 Å or less is observed in an X-ray small angle scattering pattern is disclosed.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Radiation imaging system and image processing device
ActiveUS20160379353A1Reduce image qualityQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionDifferential phaseRegression analysis
A radiation imaging system includes a radiation imaging device, a reconstruction unit and a detection unit. The reconstruction unit generates at least two of a differential phase image, an absorption image and a small-angle scattering image based on periodic pattern images of a subject obtained by the imaging device. The detection unit performs regression analysis on at least two images of (a) the differential phase image, a differential absorption image of the absorption image and a differential small-angle scattering image of the small-angle scattering image or (b) a phase image of the differential phase image, the absorption image and the small-angle scattering image; calculates a value of an indicator indicating a relationship between the at least two images; and detects image quality deterioration due to change in relative position of the imaging device and the subject based on the value.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Microstructure analysis method of asphalt and modifier thereof
InactiveCN110455841AIncreased high temperature resistance to ruttingImprove low temperature cracking resistanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRoad surfaceAnalysis method
The invention relates to a microstructure analysis method of asphalt and a modifier thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microstructure analysis of modified asphalt. The problem that the microstructures of asphalt and the modifier thereof cannot be comprehensively, stereoscopically and clearly analyzed by using only one characterization method at present is solved. According to the microstructure analysis method provided by the invention, neutron small-angle scattering samples of an SBS modifier, matrix asphalt and SBS modified asphalt are prepared at first, a neutron small-angle scattering test is performed on the samples to obtain initial experimental data, and the initial experimental data are processed to obtain an absolute intensity scattering curve, and then different models are fitted through the absolute intensity scattering curves of the samples to quantitatively analyze the microstructures of the SBS modifier, the matrix asphalt and the SBS modified asphalt. Throughthe analysis of the microstructures of the asphalt and the modifier thereof, the modification mechanism of the SBS modified asphalt can be better revealed, and a relationship between the microstructure of the modified asphalt and the macroscopic properties thereof can be established, so that the performance of the SBS modified asphalt, and the service level and the service life of asphalt pavements can be better improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Two-dimensional small angle x-ray scattering camera
ActiveUS20060269045A1Wide range of anglesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSmall-angle X-ray scatteringX-ray
A two-dimensional x-ray scattering camera includes a source, an optic, a detector, and a pair of collimating blocks. The source emits x-ray beams that are reflected by the optic towards a sample. The detector detects scattering from the sample, the pair of collimating blocks is positioned between the optic and the detector to collimate the beam. A bottom surface of one block is substantially parallel a top surface of the other block, and the blocks are rotatable relative to the beam about a pivot. The system forms a two-dimensional beam that is symmetric about the primary beam axis at the detector position, regardless how the beam is collimated by the collimating blocks. The system therefore eliminates smearing and can be used for anisotropic small angle scattering at high resolution and low Qmin.
Owner:OSMIC INC
Carbonaceous electrode material for secondary battery
InactiveUS20020039686A1Efficient use ofLarge charge-discharge capacityConductive materialCarbon preparation/purificationX-raySolvent
A carbonaceous electrode having improved capacities for doping and dedoping of a cell active substance, such as lithium, and suitable for a non-aqueous solvent-type secondary battery, is constituted by a carbonaceous material obtained by carbonizing an aromatic condensation polymer formed by condensation of an aromatic compound having a phenolic hydroxy group and an aldehyde. The carbonaceous material is characterized by an atomic ratio H / C between hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms of below 0.1, a carbon dioxide adsorption capacity of at least 10 ml / g, and an X-ray scattering intensity ratio IW / ID of at least 0.25, wherein IW and ID represent scattering intensities as measured in a wet state and a dry state, respectively, at a parameter s=2.sin theta / lambd of 0.5 nm-1, wherein theta denotes a scattering angle and lambd denotes a wavelength of X-rays in X-ray small-angle scattering measurement.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
High recycling efficiency solid state light source device
ActiveUS20130070449A1Reduces light recycling efficiencyLarge aberrationNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceCollection systemWavelength conversion
A light source device includes a LED light source or a wavelength conversion material having a near Lambertian light emitting surface. The light source device includes a light recycling system to reflect small-angle lights (lights closer to the normal direction of the light emitting surface) back to the light source, and a collection system for collecting and outputting large-angle lights (lights farther away from the normal direction). The lights reflected by the light recycling system is scattered by the emitting surface in all directions, where the large-angle scattered lights are collected by the light collection system and the small-angle scattered light is reflected by the light recycling system again. A second excitation light source without wavelength conversion material or a second light source with its own wavelength conversion material may be provided, and the second light is directed to the light emitting surface by appropriate optical components.
Owner:APPOTRONICS CORP LTD
Dedicated clamp for neutron small-angle scattering high-temperature in-site tensile test
PendingCN108760483AInhibit sheddingThe thickness can be adjusted at willMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNeutron scatteringTensile testing
The invention belongs to the field of neutron scattering experiments and especially relates to a dedicated clamp for a neutron small-angle scattering high-temperature in-site tensile test. The clamp comprises a clamp head bolt, a clamp head body and a sample fixing assembly, wherein the clamping head bolt is connected with a tensile testing machine pull rod, the clamping head bolt is fixedly connected to the clamping head body, and the clamping head body can provide axial tension for the sample fixing assembly. Therefore, the dedicated clamp for the neutron small-angle scattering high-temperature in-site tensile test disclosed by the invention has the advantages of convenience in assembling and disassembling and firmness in clamping.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Radiation imaging system and image processing device
ActiveUS9870610B2Quality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImaging processingDifferential phase
A radiation imaging system includes a radiation imaging device, a reconstruction unit and a detection unit. The reconstruction unit generates at least two of a differential phase image, an absorption image and a small-angle scattering image based on periodic pattern images of a subject obtained by the imaging device. The detection unit performs regression analysis on at least two images of (a) the differential phase image, a differential absorption image of the absorption image and a differential small-angle scattering image of the small-angle scattering image or (b) a phase image of the differential phase image, the absorption image and the small-angle scattering image; calculates a value of an indicator indicating a relationship between the at least two images; and detects image quality deterioration due to change in relative position of the imaging device and the subject based on the value.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
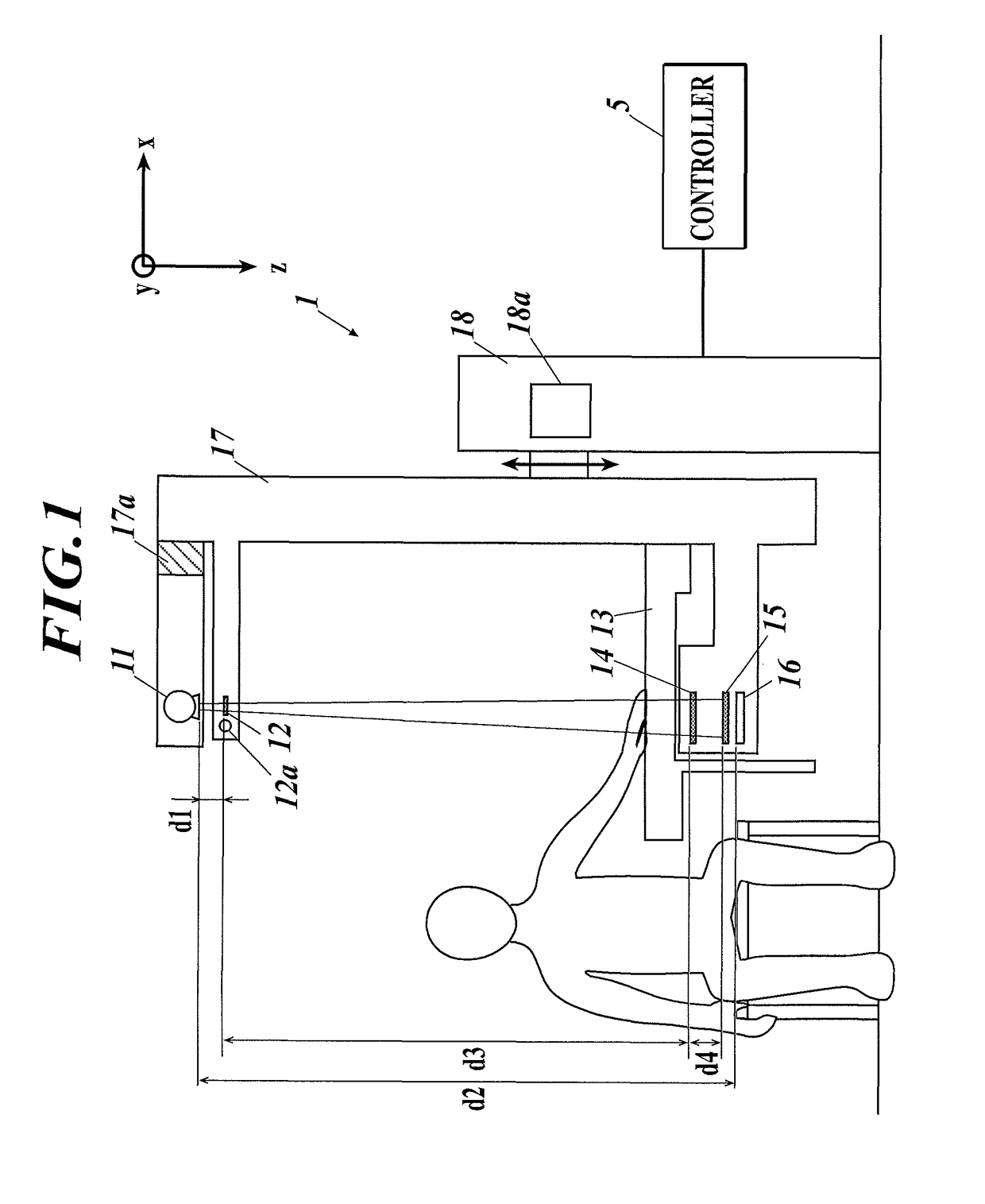
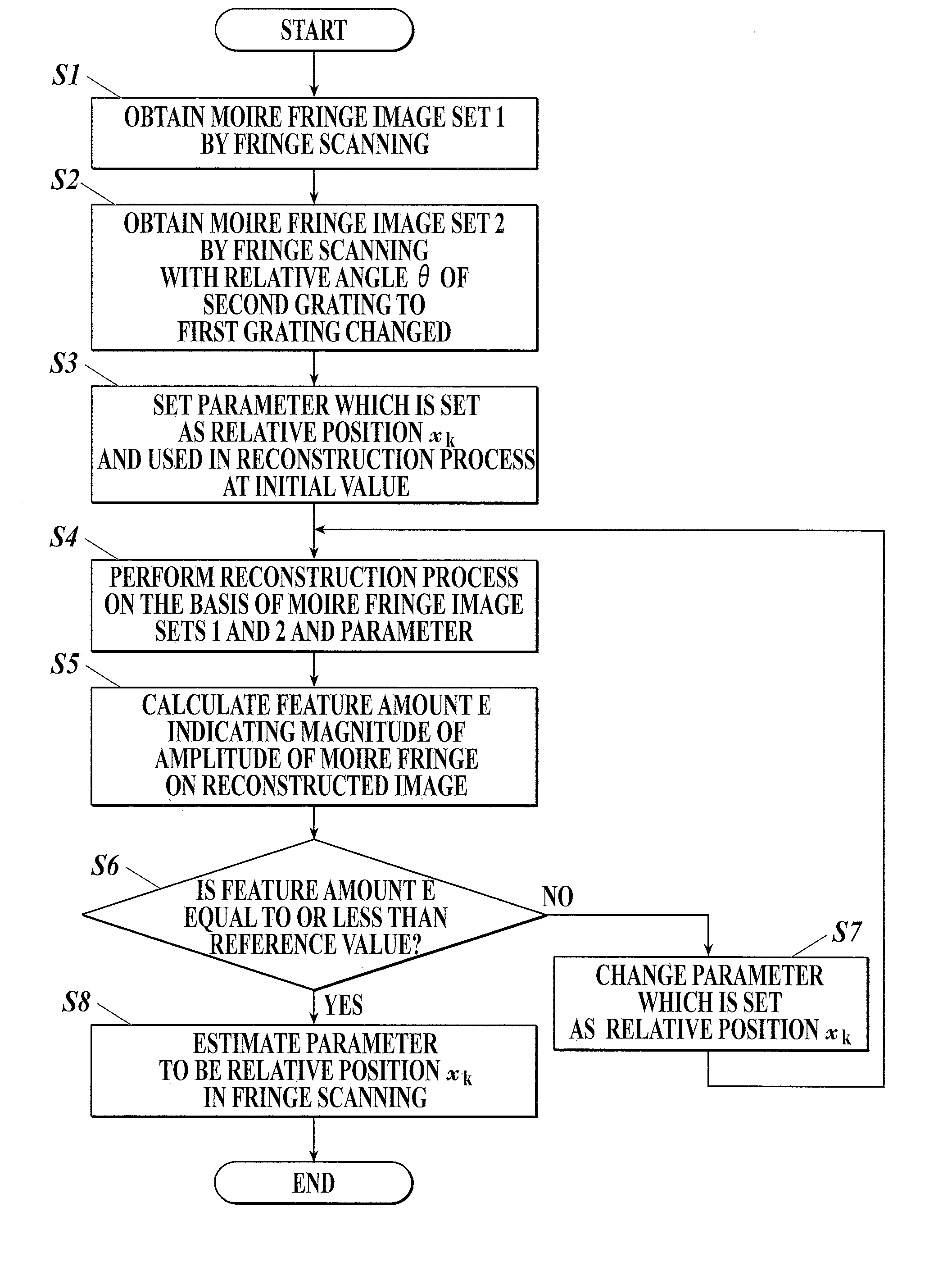
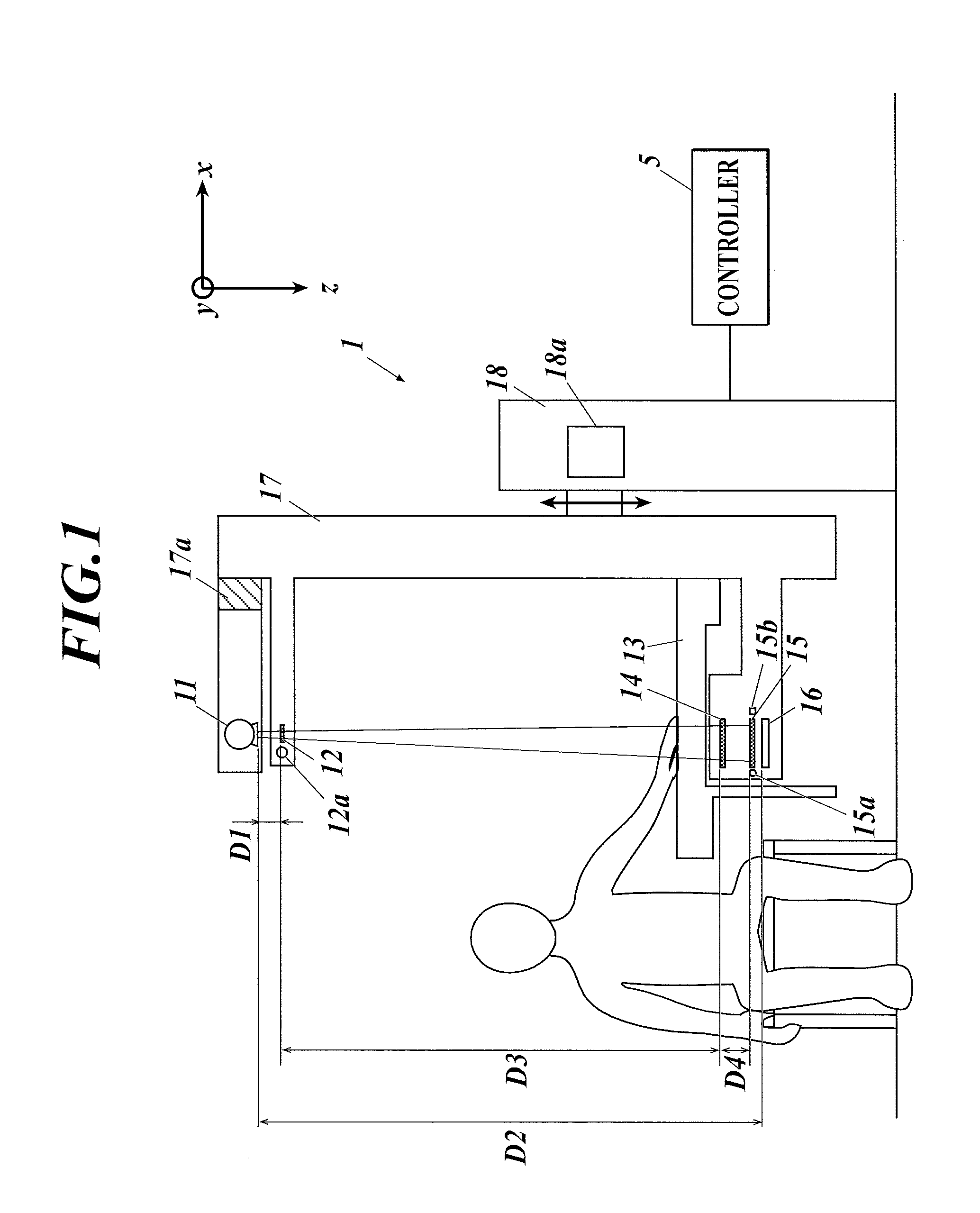
X-ray imaging system and image processing device
ActiveUS20160042533A1Low costLow imageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSoft x rayGrating
An X-ray imaging system includes an X-ray imaging device and an image processing device including a reconstruction unit and an estimation unit. The X-ray imaging device uses a Talbot or Talbot-Lau interferometer including gratings disposed in a line. The X-ray imaging device obtains sets of moire fringe images by fringe scanning multiple times between which arrangement of the gratings is changed. In the fringe scanning, one of the gratings is moved relatively to the remaining grating. The reconstruction unit generates, on the basis of the sets, a reconstructed image which is a differential phase image, an X-ray absorption image and / or a small-angle scattering image. The estimation unit estimates, on the basis of the reconstructed image, a relative position of the moved grating from a reference position of the grating at each imaging in the fringe scanning.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for removing blurring effect in X-ray scattering and diffraction experiments
InactiveCN104268421AImprove enduranceImprove angular resolutionImage enhancementComputerised tomographsSoft x rayFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a method for removing blurring effect in X-ray scattering and diffraction experiments. The method comprises the steps of measuring the distribution of straight spots on a two-dimensional detector to obtain h (x, y), measuring the scattering data of an experimental sample to obtain g (x, y), performing Fourier transform on h (x, y) and g (x, y), respectively, thereby obtaining the distribution H (u, v) of the straight spots in the reciprocal space and the distribution G (u, v) of the scattering data in the reciprocal space, performing deconvolution processing on the experimental data H (u, v) and G (u, v) by use of a Wiener filtering algorithm to obtain the Fourier transform F (u, v) of blurring effect-removed data f (x, y), performing inverse fast Fourier transform on F (u, v) to obtain the blurring effect-removed data f (x, y), and adjusting the parameter alpha according to the results of f (x, y) until the desired deconvolution result is obtained. The method for removing the blurring effect in the X-ray scattering and diffraction experiments is used for performing the deconvolution processing on the experimental data. Due to the adoption of the method, the angle resolution of the X-ray small-angle scattering data can be increased and the experimental accuracy can be improved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com