Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Register transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
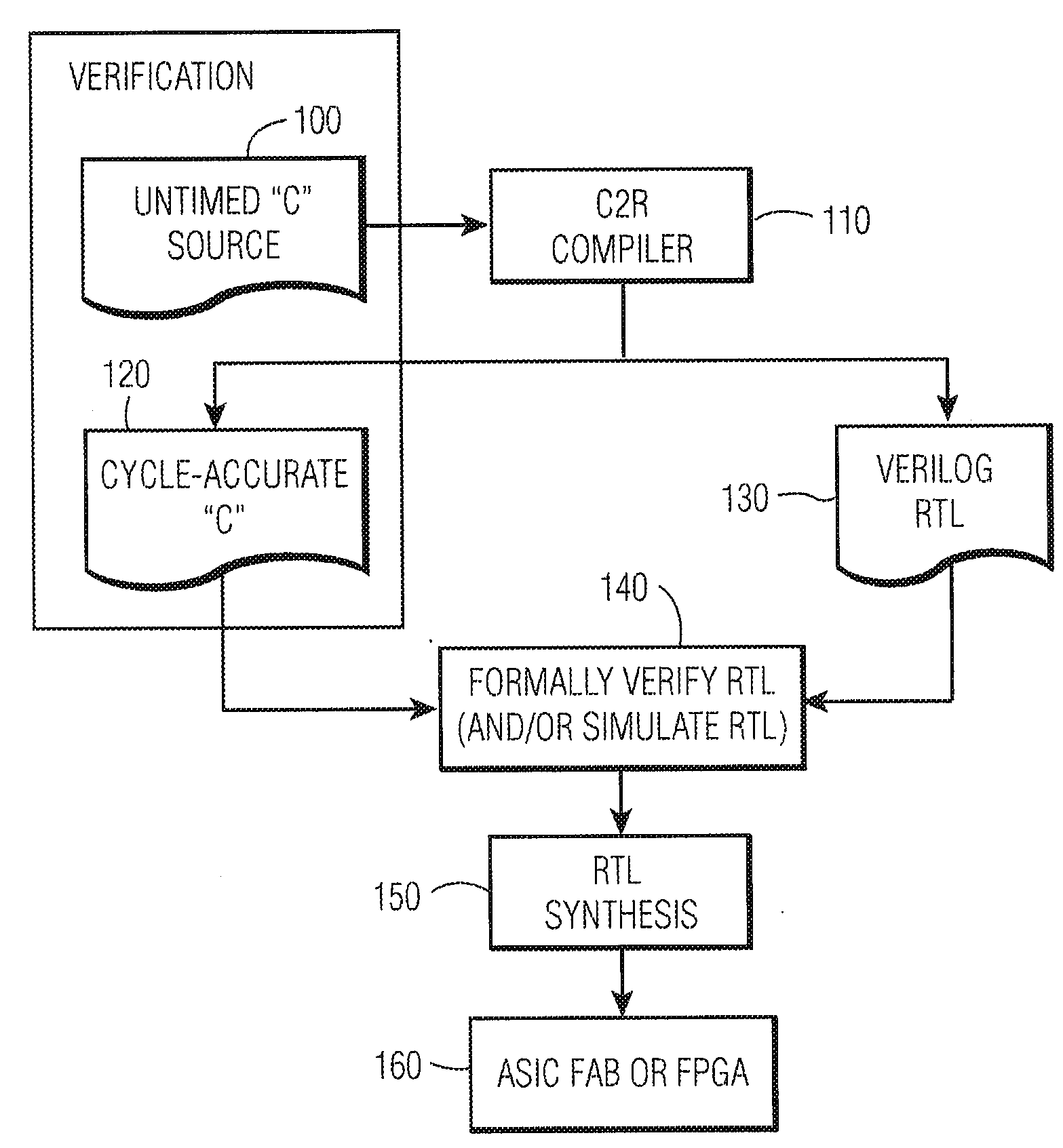
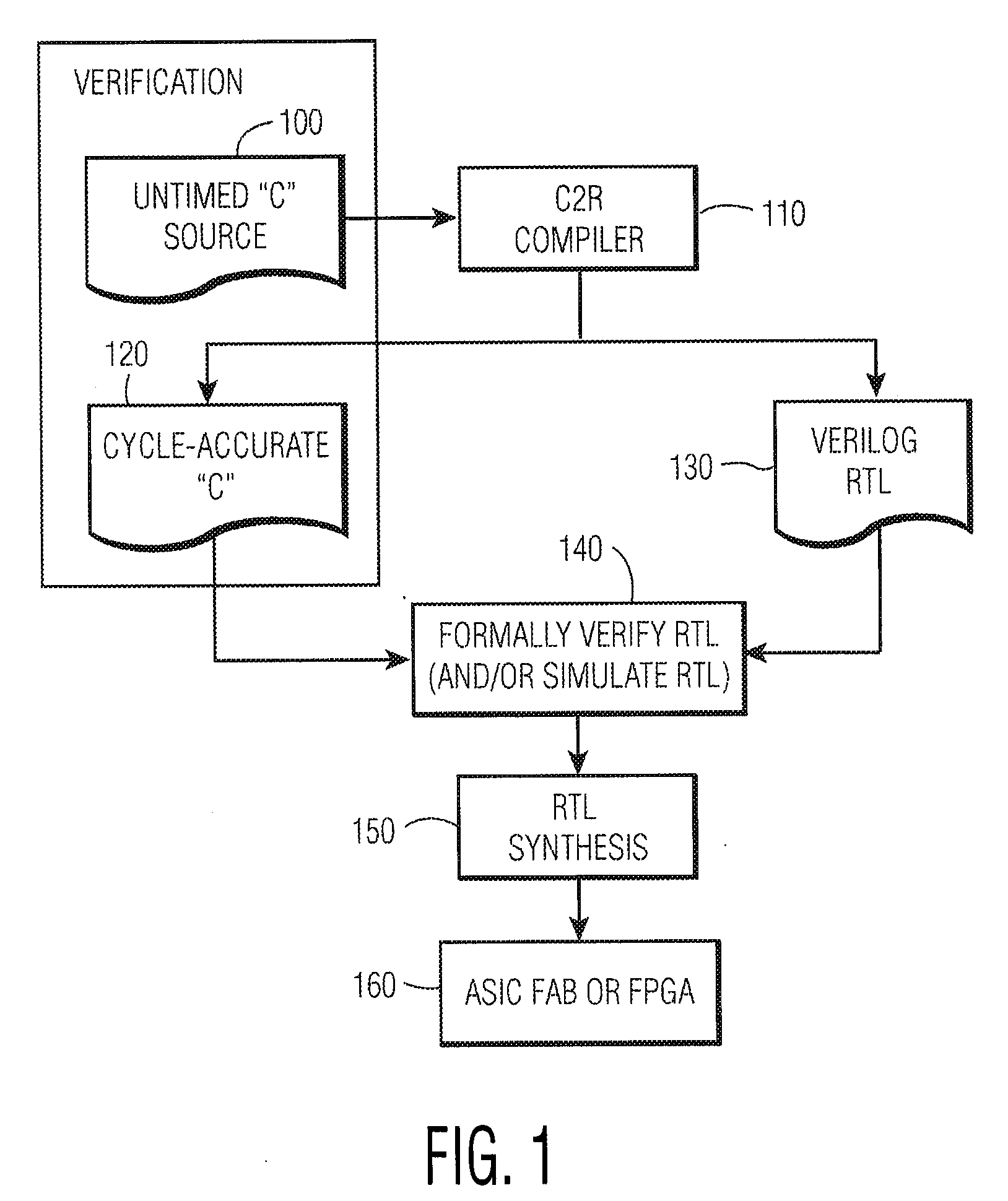
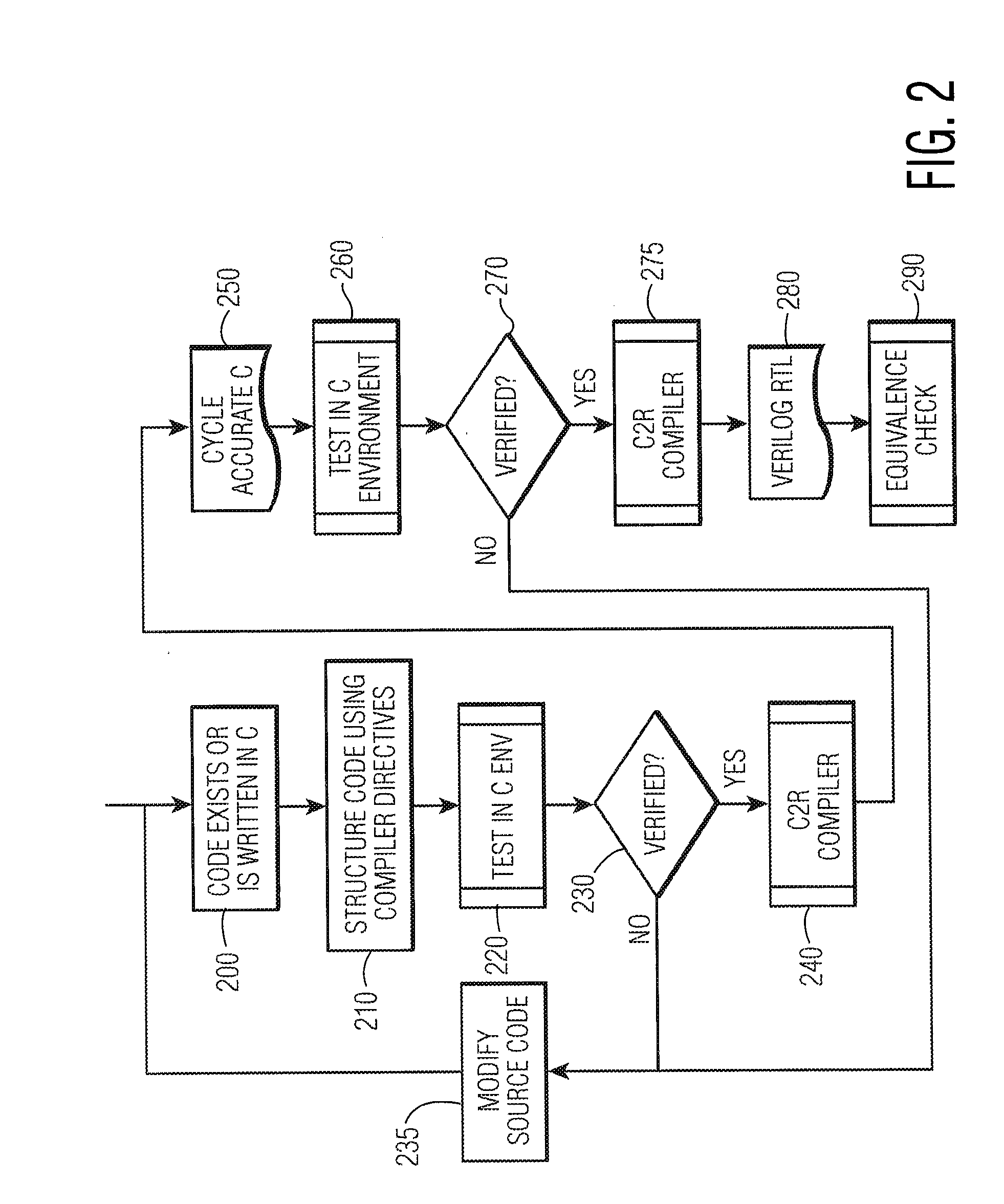
System and method for converting software to a register transfer (RTL) design
ActiveUS20090144690A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designComputer architectureProcessor register
A method for converting a C-type programming language program to a hardware design, where the said program is an algorithmic representation of one or more processes. The C-type programming language program is compiled into a hardware description language (HDL) synthesizable design. The compiler categorizes variables as using either implicit memory or custom memory. Different accessor functions are used depending on which type of memory is used. The programming language may use ANSI C and the HDL may be Verilog Register Transfer Level (RTL). The hardware device generated from the HDL synthesizable design may be an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) or a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA).
Owner:EXAR CORP
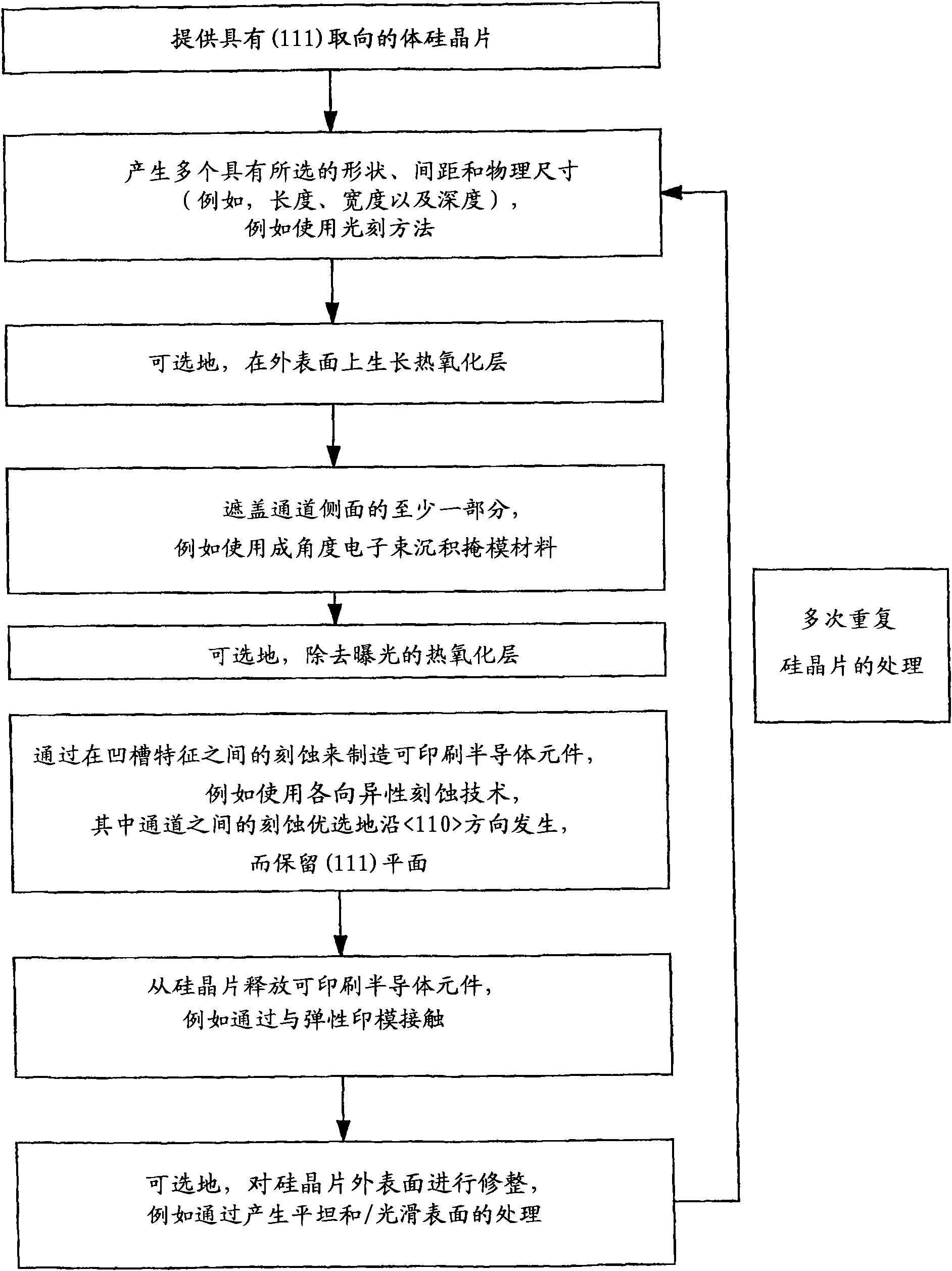
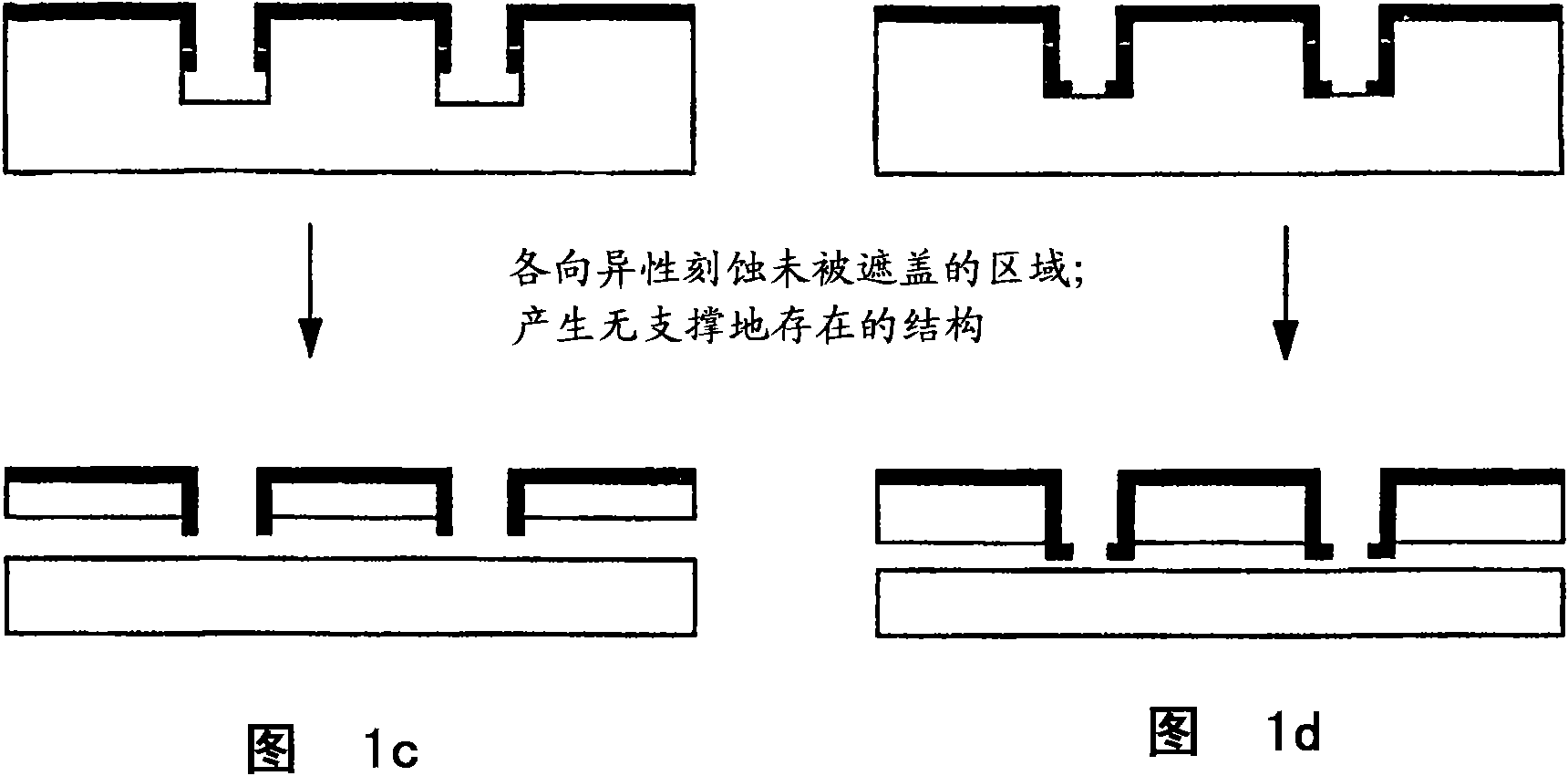
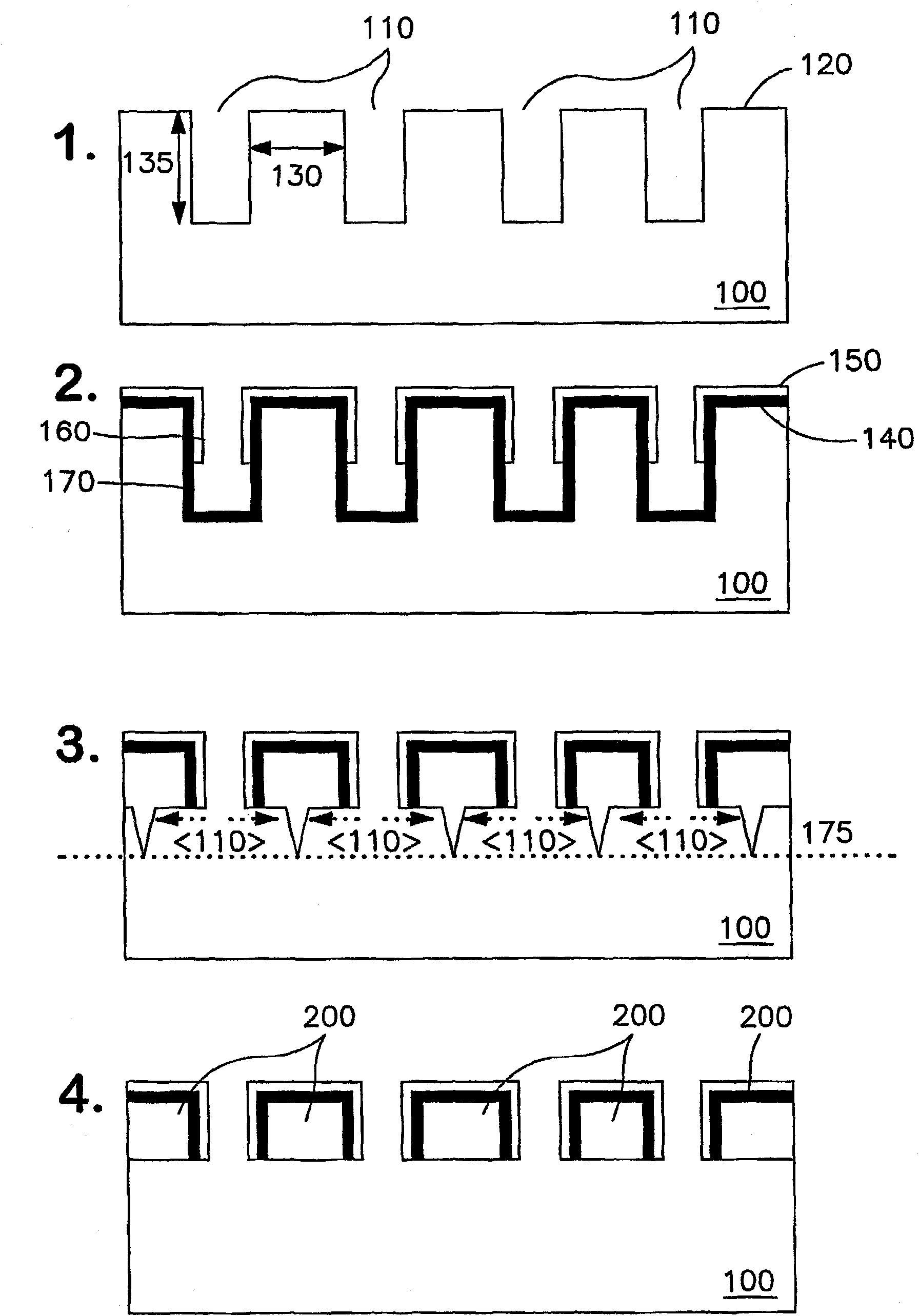
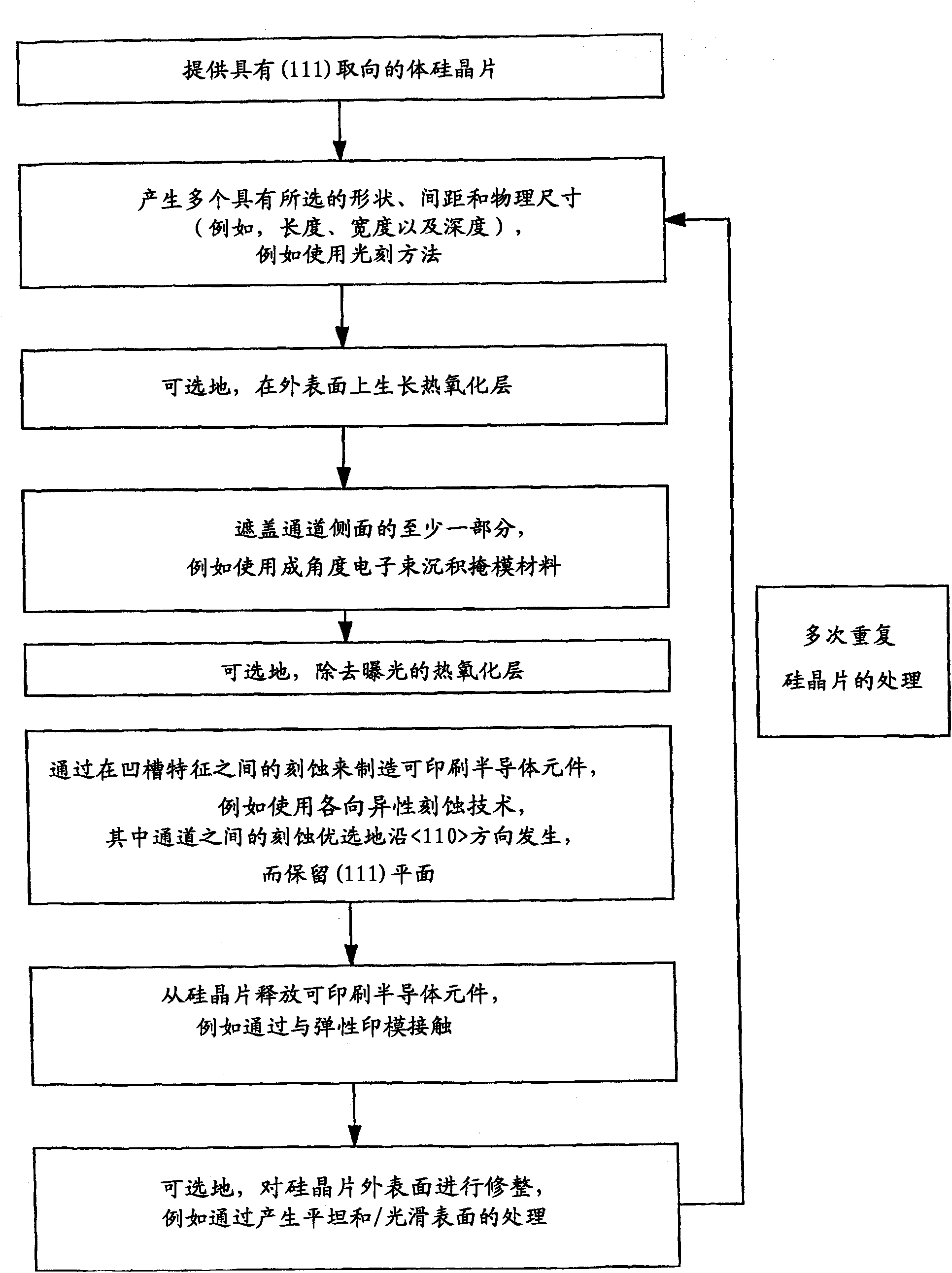
Printable semiconductor structures and related methods of making and assembling
ActiveCN101632156APrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSpatial OrientationsSemiconductor structure
The present invention provides a high yield pathway for the fabrication, transfer and assembly of high quality printable semiconductor elements having selected physical dimensions, shapes, compositions and spatial orientations. The compositions and methods of the present invention provide high precision registered transfer and integration of arrays of microsized and / or nanosized semiconductor structures onto substrates, including large area substrates and / or flexible substrates. In addition, the present invention provides methods of making printable semiconductor elements from low cost bulk materials, such as bulk silicon wafers, and smart-materials processing strategies that enable a versatile and commercially attractive printing-based fabrication platform for making a broad range of functional semiconductor devices.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
System and method for converting software to a register transfer (RTL) design
ActiveUS7904850B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designComputer architectureTerm memory
A method for converting a C-type programming language program to a hardware design, where the said program is an algorithmic representation of one or more processes. The C-type programming language program is compiled into a hardware description language (HDL) synthesizable design. The compiler categorizes variables as using either implicit memory or custom memory. Different accessor functions are used depending on which type of memory is used. The programming language may use ANSI C and the HDL may be Verilog Register Transfer Level (RTL). The hardware device generated from the HDL synthesizable design may be an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) or a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA).
Owner:EXAR CORP
Method for determining dynamic function call relation based on register transfer languages
The invention discloses a method for determining a dynamic function call relation based on register transfer languages, mainly aiming to solve the problems in design that a call relation of a function pointer and a loadable module function cannot be analyzed through a static function call relation. The method includes: detecting function call executing events during system operation, if call instructions are detected, analyzing function names corresponding to function entry addresses called through the instructions, performing statistics on number of the instructions and outputting the function names, call occurrence time, subordinate process numbers, subordinate threading numbers, subordinate stack top pointers and module numbers prior to storing to a trace data file; if the detected instructions are return instructions, outputting time, the subordinate process numbers, the subordinate threading numbers and the subordinate stack top pointers to the track data file; processing the track data file to acquire the data format with predetermined standard, transmitting the track data file to a static function call relation generating device so as to generate a dynamic function call graph describing the function call relation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
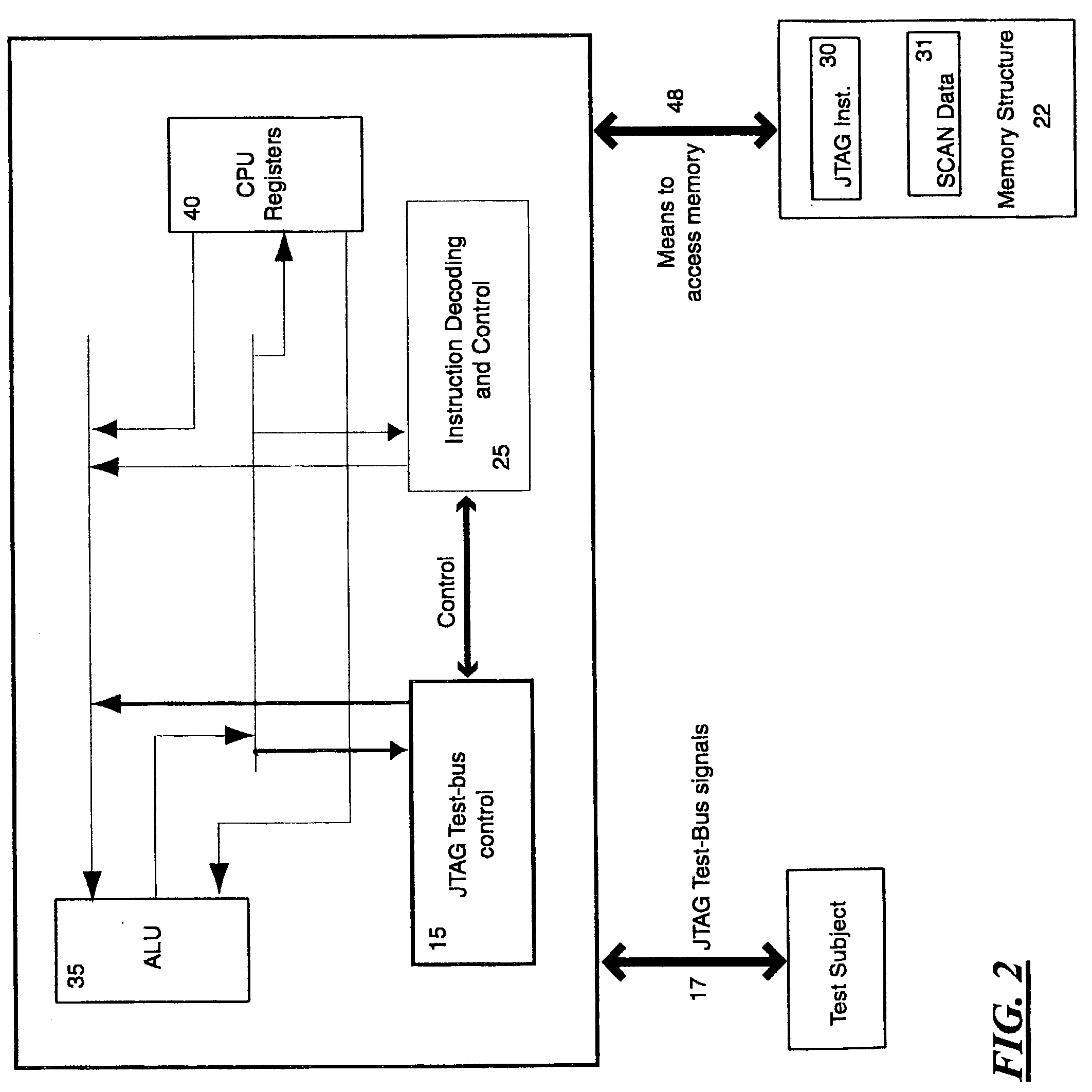
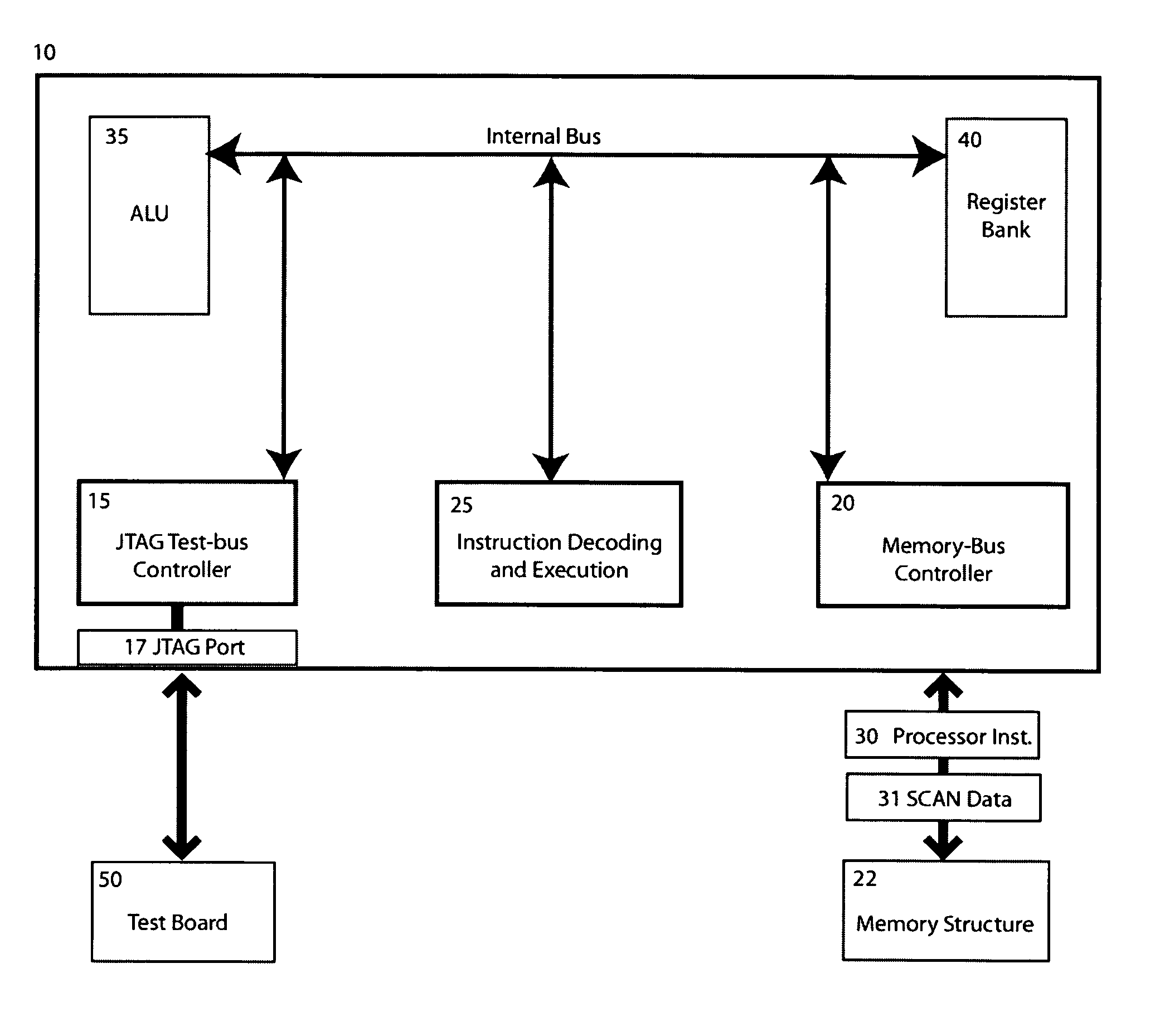
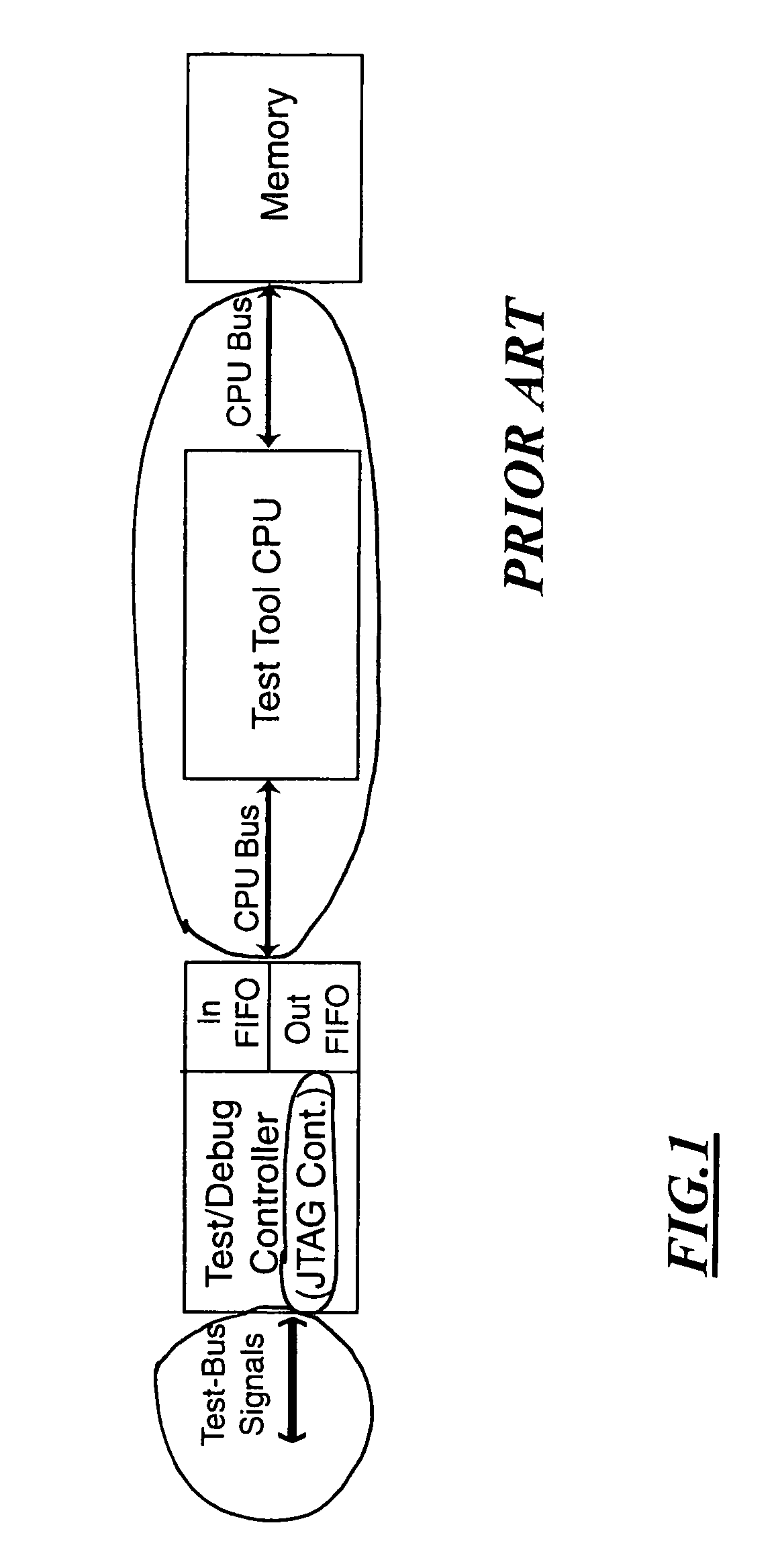
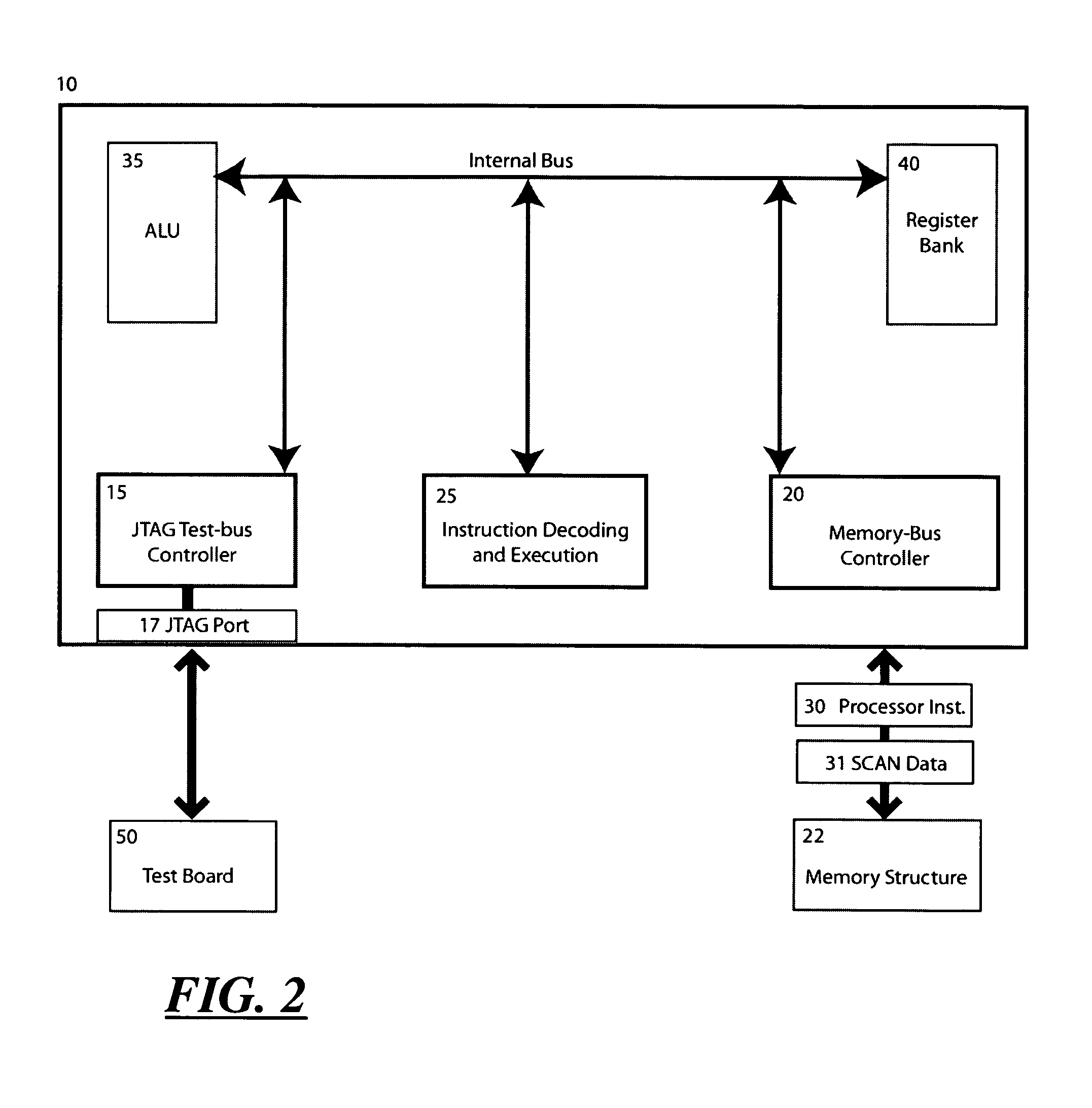
Test and debug processor and method
InactiveUS20030061020A1Solve the slow test speedSufficient speedElectronic circuit testingSoftware testing/debuggingProcessor registerLogical operations
A Test and debug processor that can execute JTAG scans without the involvement of an external CPU or dedicated hardware. The processor includes a JTAG-bus controller logic, a JTAG port coupled to the JTAG-bus controller logic, memory capable of storing JTAG instructions, and an instruction decoding unit capable of fetching or requesting JTAG instructions from the memory. During use, the JTAG scan functions are encoded in instructions that are natively executable by the processor hardware without software interpretation. The instructions are then stored in a memory structure, fetched and executed directly by the processor. The instruction could optionally include the end-state of the bus after the operation, information about the bit count of the data to be scanned, information about the location of the data to be sent out of the JTAG port and also the location to store the received information from the test subject. Optionally, the test processor can directly access any memory location to fetch or store test data objects. This is achieved by adding a memory-bus interface to the processor allowing it to be the memory bus master. Also the test-processor can have the ability to decode and execute arithmetic and logic operation by adding an ALU the processor. The processor can also have the ability to execute register transfer operations to execute functions such as JUMP to control the run path.
Owner:MICHAEL SAM
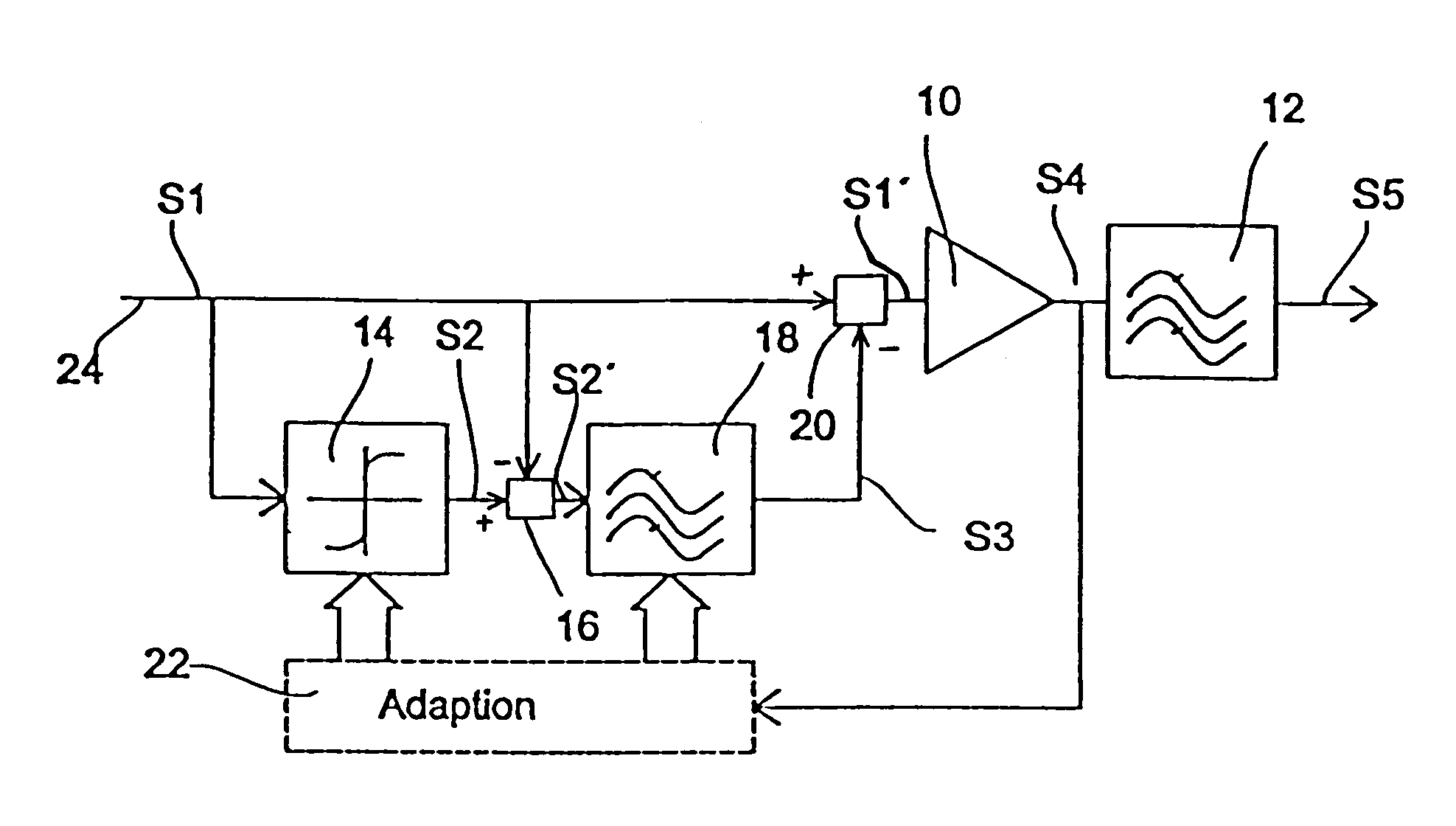
Device and method for predistorting a transmission signal to be transmitted via a nonlinear transmission path
InactiveUS7170951B1Spurious emission can be reducedLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersTime extensionFrequency spectrum
A device for predistorting a transmission signal to be transmitted over a nonlinear transmission path comprises an estimator for determining an error signal depending on the transmission signal and a previously registered transfer characteristic of the nonlinear transmission path. The error signal represents an estimate of an error generated due to the nonlinearity of the trans-mission path. A time-dispersive element is provided to produce a correction signal by a temporal extension of the error signal. A combiner is provided to combine the transmission signal and the correction signal. As a result of the temporal extension of the error signal, an error signal segment in the frequency spectrum of a transmission signal transmitted by the nonlinear transmission path is shifted away from the useful frequency range of the transmission signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Flash memory device capable of improving read performance
InactiveUS20080235442A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInitControl logic
A flash memory device, related system ad method are disclosed. The memory device includes a memory cell array a page buffer receiving read data, wherein the page buffer includes a main register transferring read data to a cache register during an read operation, and a control logic block controlling operation of the page buffer during the read operation, such that initialization of the main register continuously extends beyond a time period during which read data is transferred from the main register to the cache register.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flexible Microprocessor Register File
InactiveUS20080082798A1Minimal powerSave powerRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsProcessor registerByte
Architectures and methods for viewing data in multiple formats within a register file. Various disclosed embodiments allow a plurality of consecutive registers within one register file to appear to be temporarily transposed by one instruction, such that each transposed register contains one byte or word from multiple consecutive registers. A program can arbitrarily reorganize the bytes within a register by swapping the value stored in any byte within the register with the value stored in any other byte within the same register. Indirect register access is also provided, without additional scoreboarding hardware, as an apparent move from one register to another. The functionality of a hardware data FIFO at the I / O is also provided, without the power consumption of register-to-register transfers. However, the size of the FIFO can be changed under program control.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and apparatus for verification of memories at multiple abstraction levels
InactiveUS6848084B1Efficient verificationSimulated more efficientlyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureProcessor register
This invention relates to method and apparatus for verification of circuit designs containing memories. At a register transfer abstraction level, verification of a circuit design requires showing that the register transfer language (RTL) abstraction of the design is logically equivalent to the design implementation represented at the logic (e.g., gate and / or flip-flop) and / or the transistor (e.g. implementation verification) abstraction levels, as well as logic simulation of the design RTL embedded in a system-level test bench for verification at the system-abstraction level.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
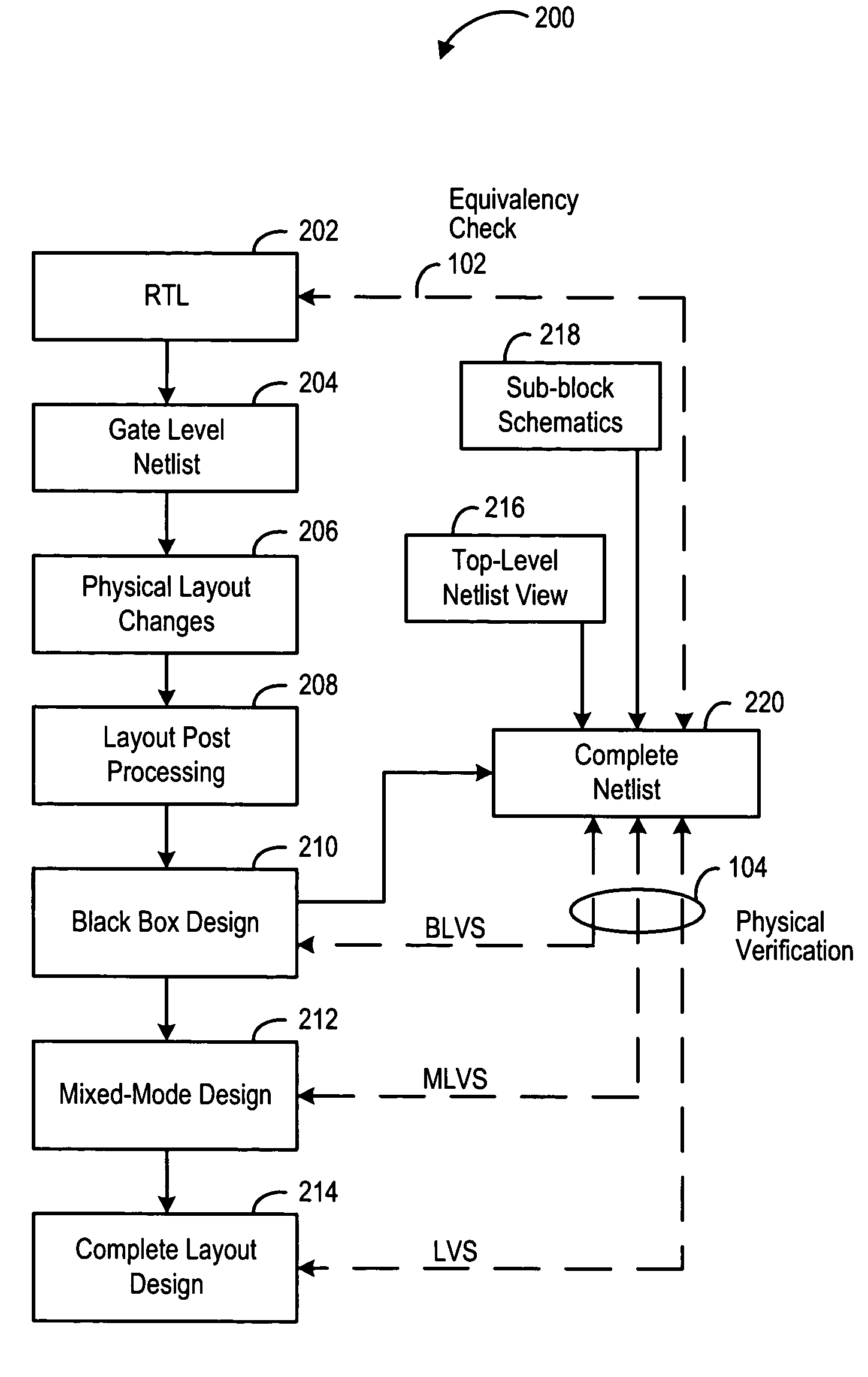
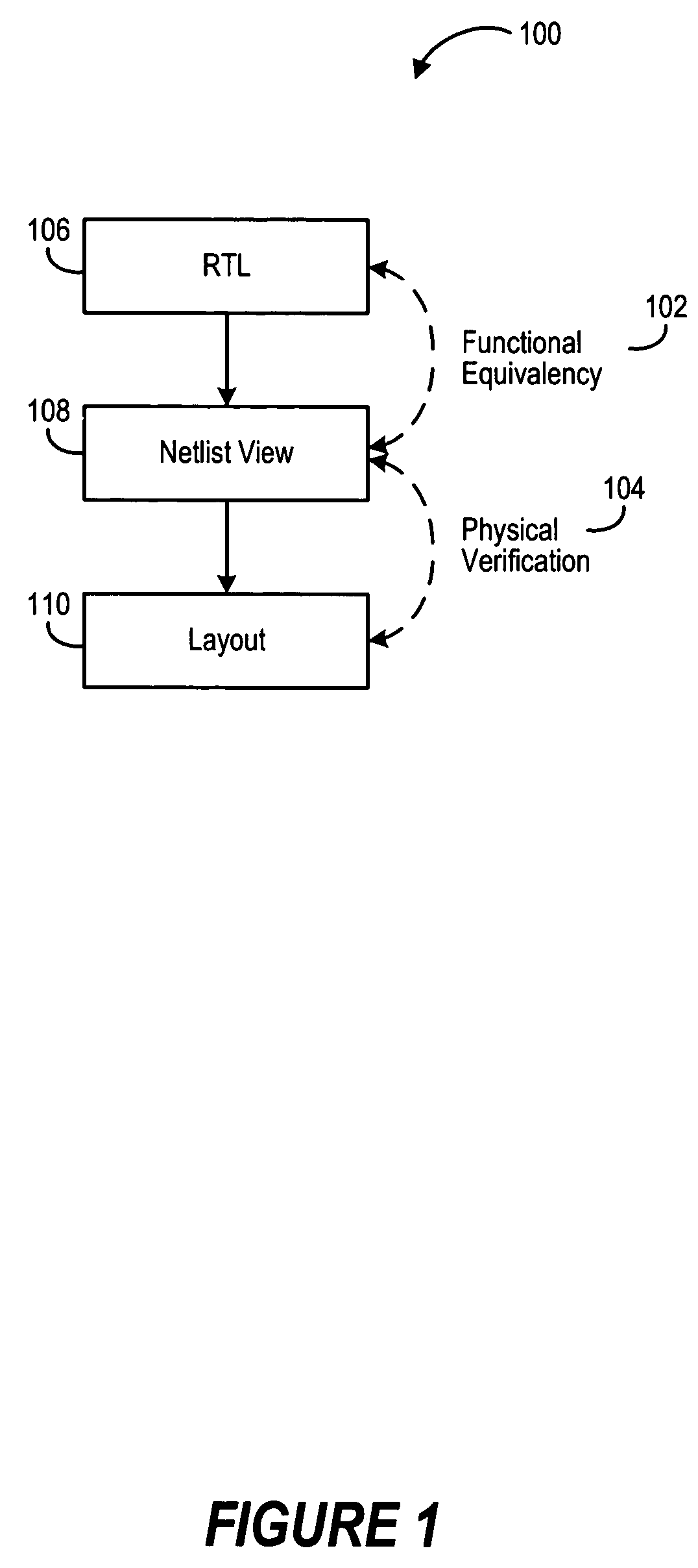
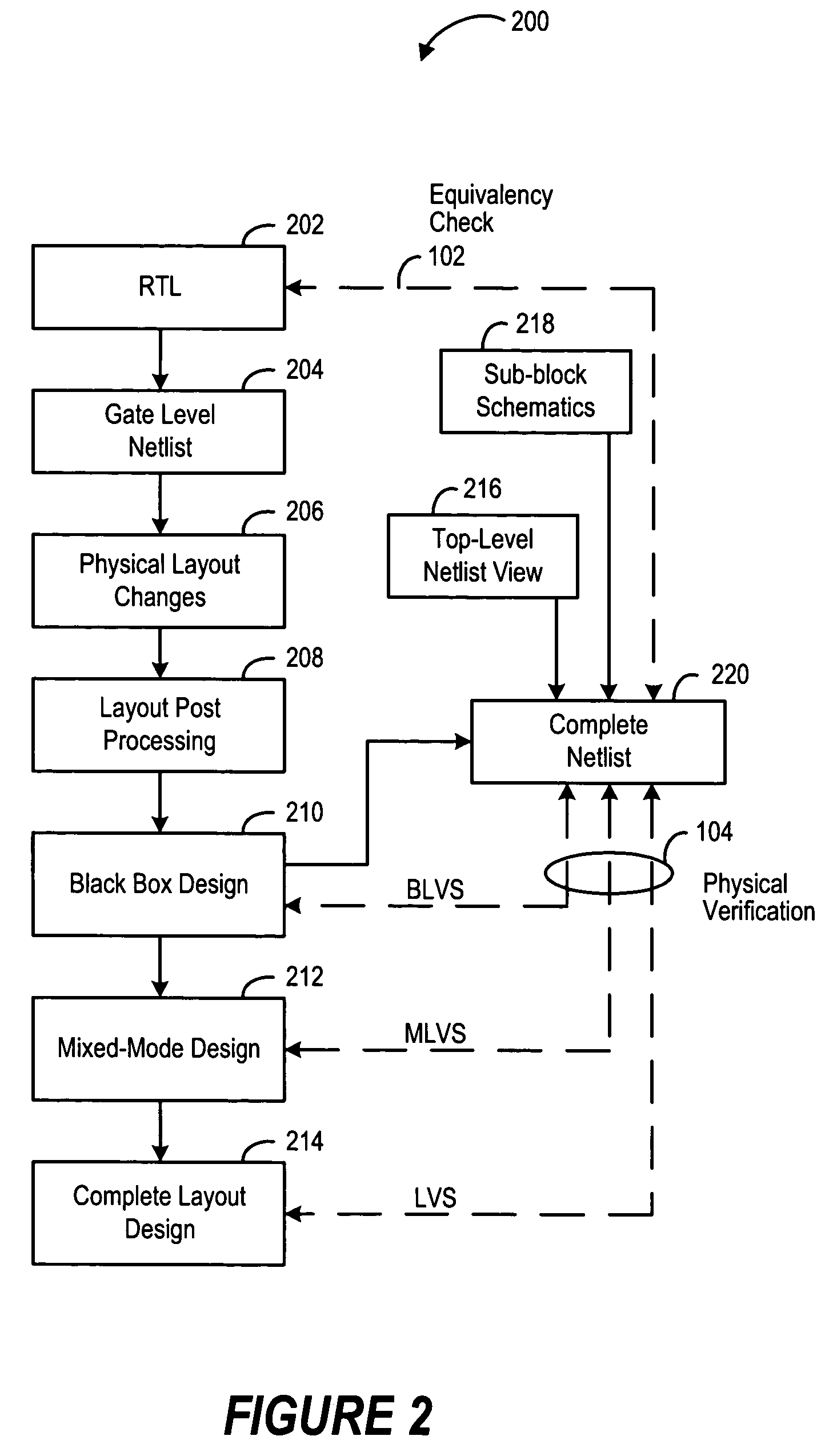
Fullchip functional equivalency and physical verification
ActiveUS7404161B2Efficient modificationStay connectedCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPhysical verificationComputer science
A method for maintaining equivalency between the reference Register Transfer Logic (RTL) and the physical layout design of an integrated circuit by way of maintaining a reference netlist derived from symbolic connectivity.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System for controlling operational characteristics of buffer group where capture registers receive control signals in parallel and update registers transfer control signals to buffer group
InactiveUS6044417AEnergy efficient ICTReliability increasing modificationsControl signalProcessor register
In one aspect of the present invention, a bus buffer is provided. The bus buffer includes at least one buffer group having first and second groups of control input terminals. The first and second groups of control input terminals control different operational characteristics of the buffer group. The bus buffer includes first and second capture registers and first and second update registers. The data output terminals of the first update register are connected to the first group of control input terminals. The data output terminals of the second update register are coupled to the second group of control input terminals. The data input terminals of the first and second update registers are coupled to the data output terminals of the first and second capture registers, respectively. The bus buffer includes a new settings register having data output terminals coupled to the data input terminals of the capture registers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
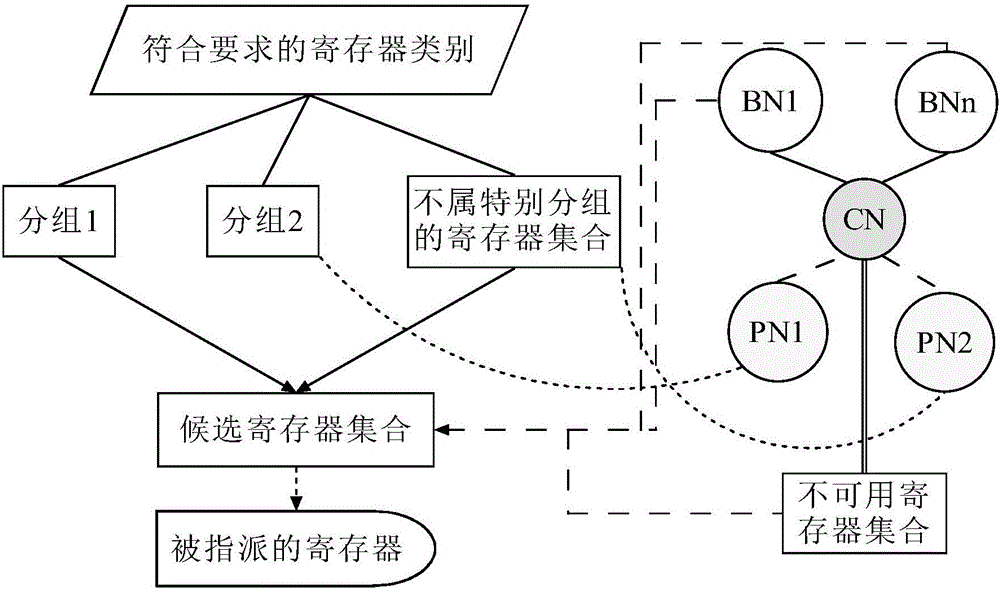
Vector VLIW architecture diagram coloring register grouping allocation method
ActiveCN105912304AQuality improvementReduce overflowMachine execution arrangementsProcessor registerBasic block
A vector VLIW architecture diagram coloring register grouping allocation method comprises the following steps: S1, data model constructing; S2, network constructing and attribute analysis; S3, conflict analysis; S4, register merging: traversing the instructions of all basic blocks, not processing an instruction if the instruction is not a register transfer instruction, or, analyzing and processing the instruction according to the register category and grouping attribute; S5, conflict graph trimming: pressing all the nodes in a conflict graph into one stack according to the requirements of the register category and grouping attribute; and S6, physical register assigning: popping up the nodes in the stack in turn, and assigning a register meeting the requirements of the register category and grouping to a network corresponding to each node when the node is popped up, so as to enable any two nodes in conflict to get different registers. The method has the advantages of simple principle, easy implementation, and realization of effective register resource allocation in the global level of process.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
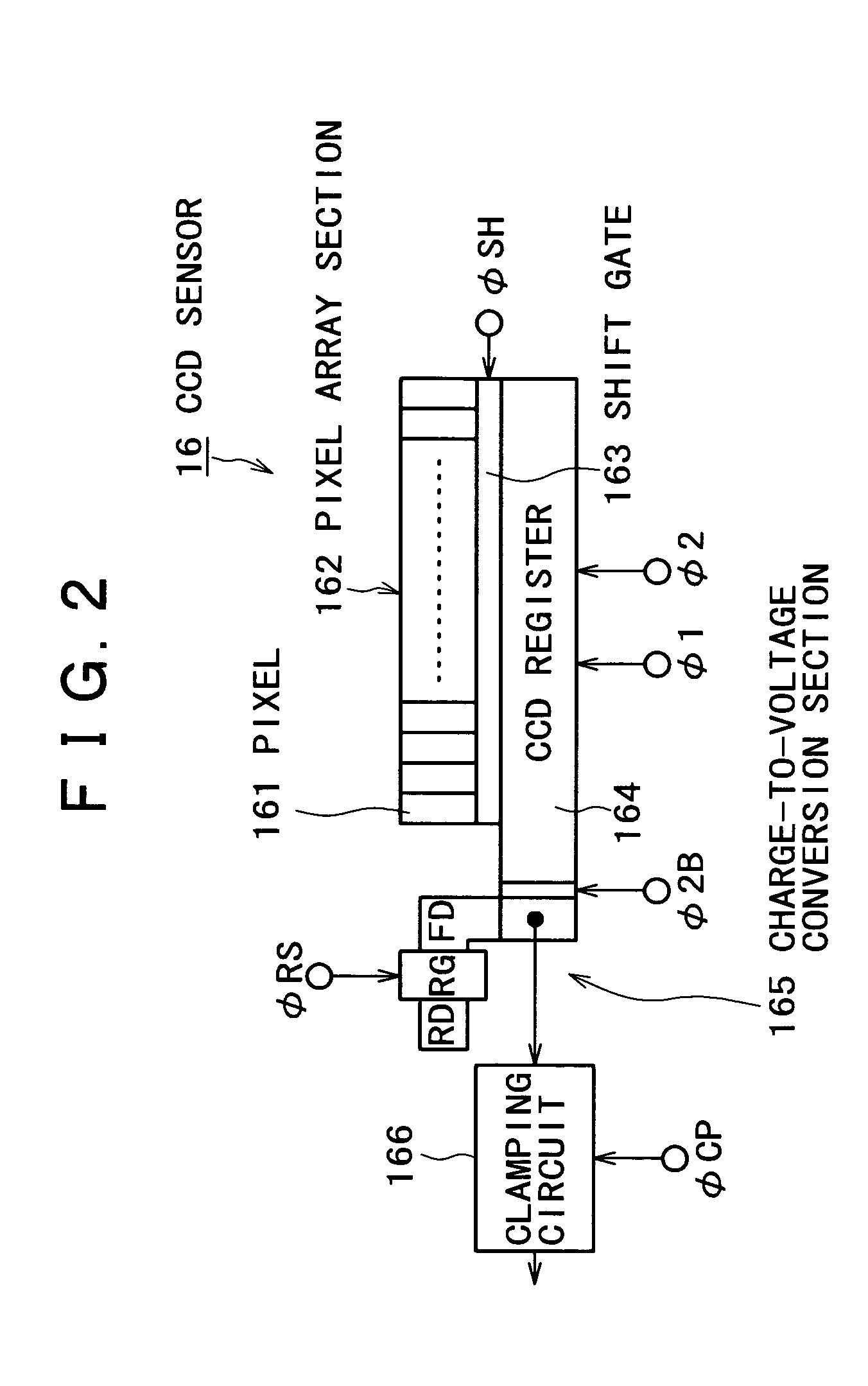
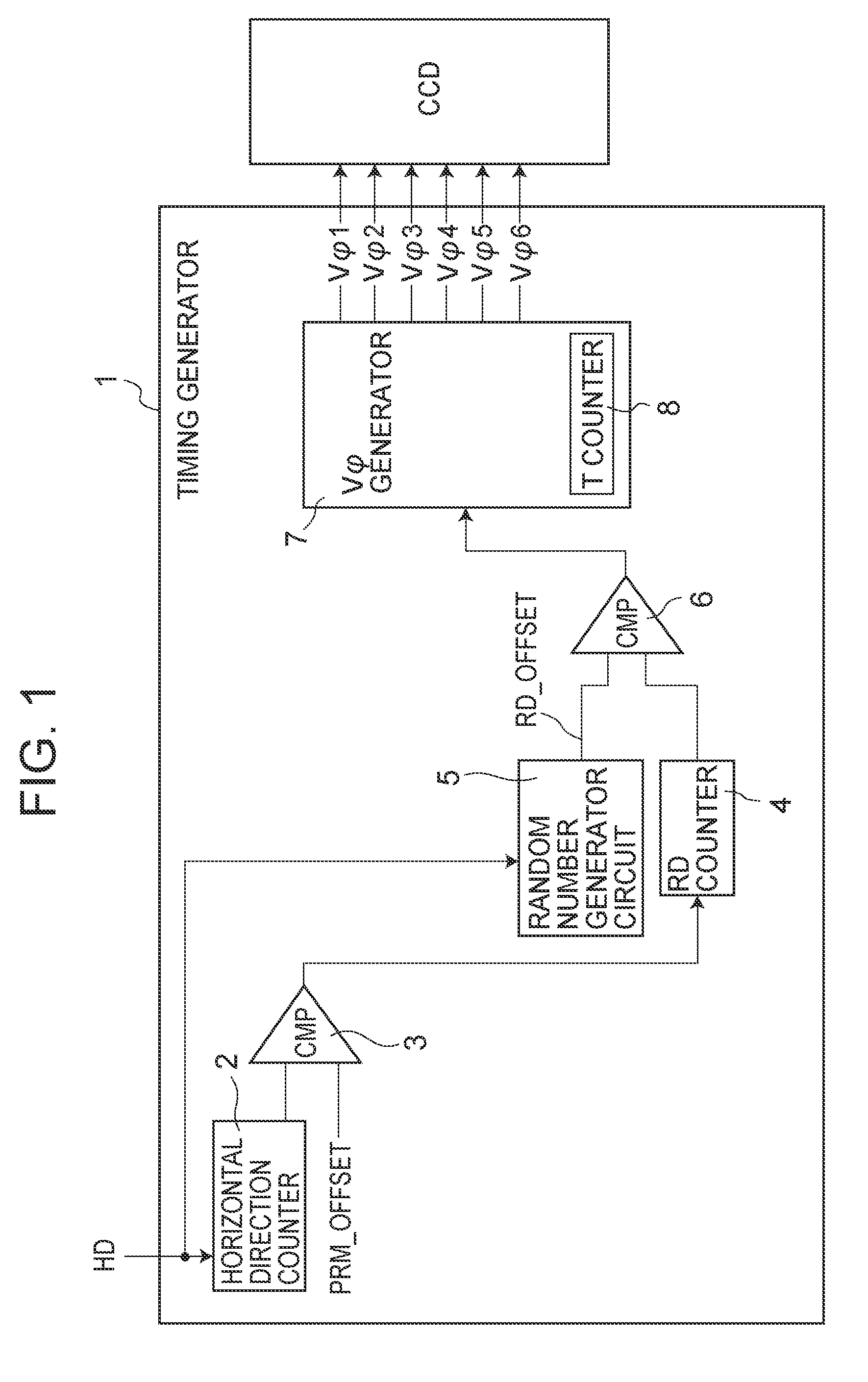
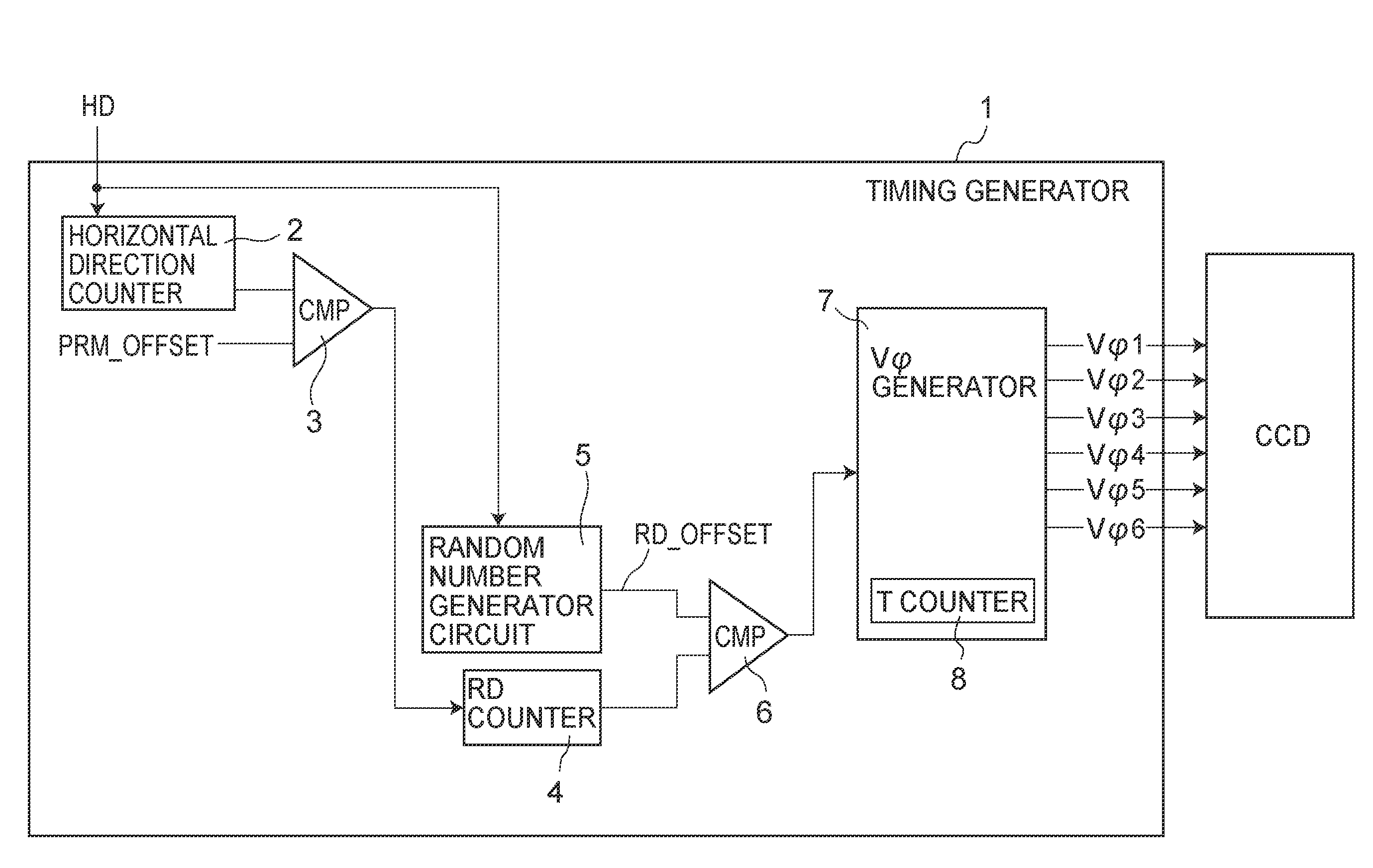
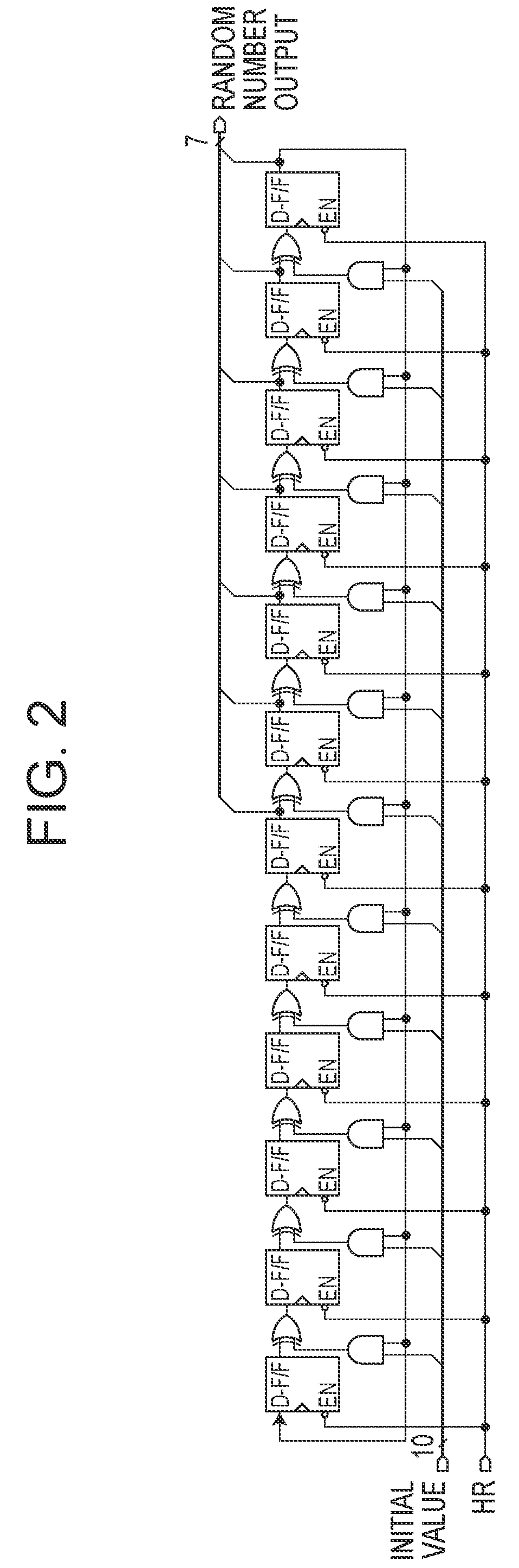
Image reading apparatus
InactiveUS7800787B2Television system scanning detailsSolid-state devicesProcessor registerTransducer
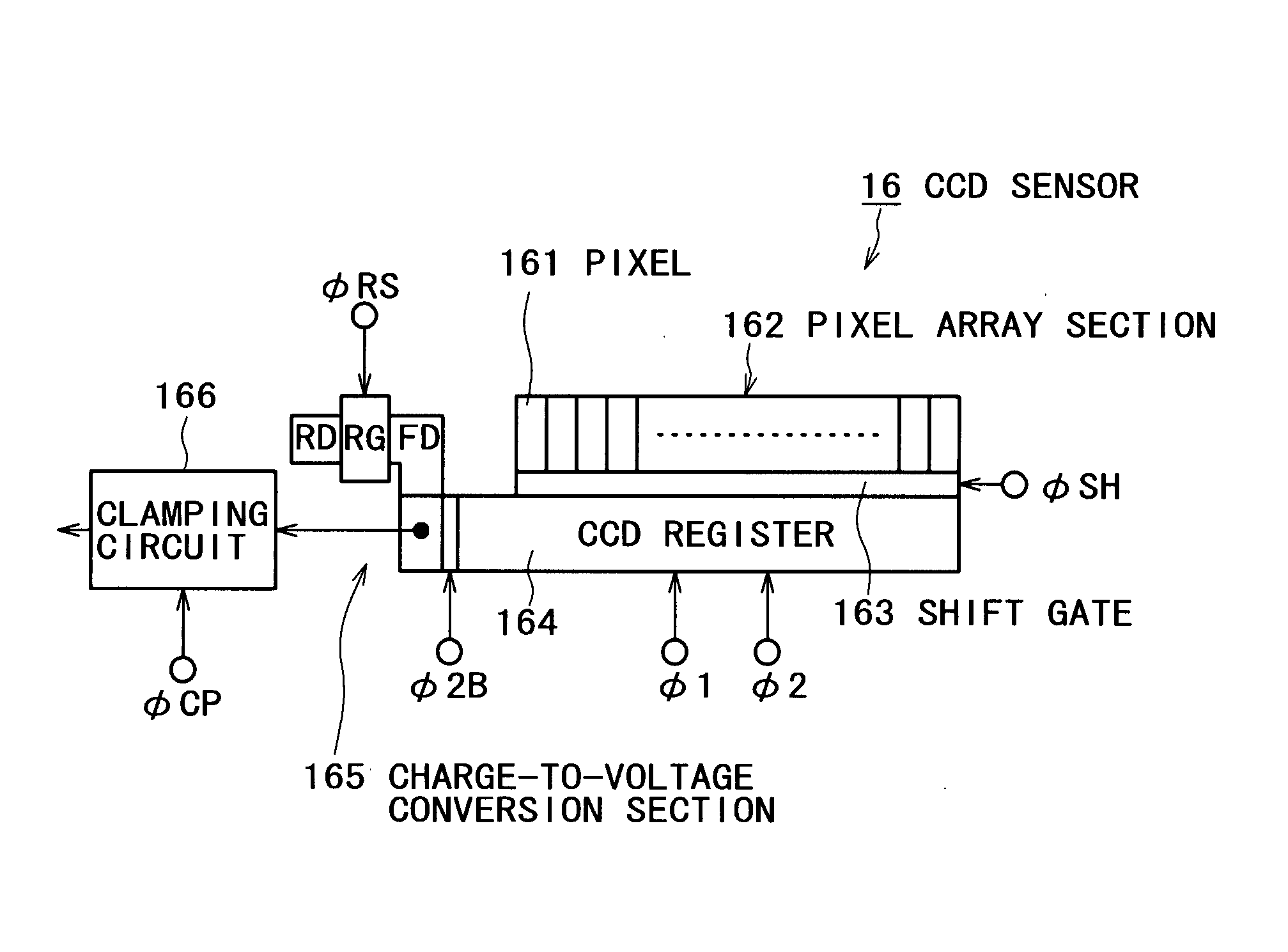
An image reading apparatus includes a solid-state image sensor having a pixel array section in which pixels each including a photoelectric transducer are arrayed, a charge transfer register that transfers a signal charge transferred from each of the pixels of the pixel array section, and an output section that converts the signal charge transferred by the charge transfer register into an electrical signal and outputs the electrical signal; a driving unit that drives the charge transfer register according to a first timing signal, and the output section according to a second timing signal; and a power supplying unit that supplies power of different power systems to a circuit portion handling the first timing signal and a circuit portion handling the second timing signal of the driving unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
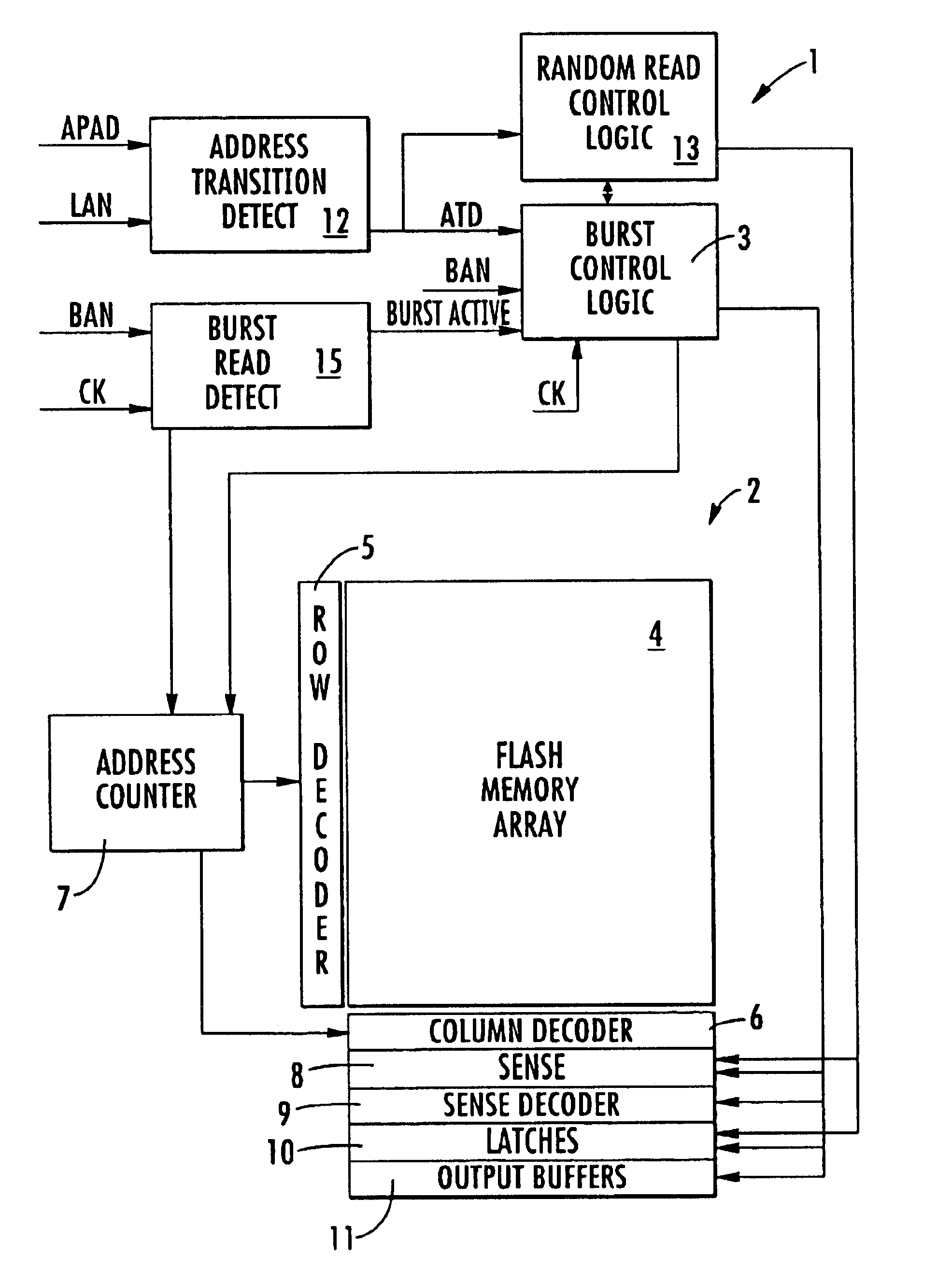
Non-volatile memory device with burst mode reading and corresponding reading method
A read control circuit and a reading method for an electronic memory device integrated on a semiconductor includes a non-volatile memory matrix with associated row and column decoders connected to respective outputs of an address counter. An address transition detect (ATD) circuit detects an input transition as the memory device is being accessed, and read amplifiers and attendant registers transfer the data read from the memory matrix to the output. The read control circuit includes a detection circuit to which is input a clock signal and a logic signal to enable reading in the burst mode. A burst read mode control logic circuit is connected downstream of the detection circuit. The method includes accessing the memory matrix in a random read mode, detecting a request for access in the burst read mode, and executing the parallel reading of a plurality of memory words during a single period of time clocked by the clock signal.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Transfer pulse generator circuit and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20080246870A1Mitigate recognition of imageHard to visually recognizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPulse controlEngineering
A transfer pulse generator circuit for outputting a vertical register transfer pulse includes transfer pulse control means for controlling to set rise and fall timings of the vertical register transfer pulse to desired timings in a predetermined period.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and methods for increasing bandwidth in an infiniband switch
A switch for use with an InfiniBand network. The switch includes a hub that redirects packets from a first InfiniBand device to a second InfiniBand device, a buffer that receives packets from the first InfiniBand device, and plurality of ports for transferring the data to the hub. A plurality of registers are coupled to the buffer for storing data from the packets. A switch network for selectively connecting the registers to the ports such that each register transfers a different portion of the data to a selected port.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
Test and debug processor and method
InactiveUS7428661B2Fully testedEnough timeElectronic circuit testingSoftware testing/debuggingTemporal informationProcessor register
Owner:MICHAEL SAM
Method for determining static function call relations based on register transfer language
InactiveCN103744678ADescribe the calling relationshipCall relationship is clearSpecific program execution arrangementsRegister-transfer levelRegister transfer
The invention discloses a method for determining static function call relations based on a register transfer language, and aims to provide a method to clearly describe function call relations among functions, files and modules in a software system. The method includes unloading compiled intermediate results generated in the source code compiling process in a manner of register transfer files, and acquiring function call relation files according to the compiled intermediate results; according to the function call relation files, adopting functions, files or modules as nodes, adopting the numbers of function call among functions, the files or the modules as edges, and generating function call graphs among the functions, the files or the modules to describe the function call relations; according to the function call relations files, generating function call relation lists to describe the function call relations.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Printable semiconductor structures and related methods of making and assembling
The present invention provides a high yield pathway for the fabrication, transfer and assembly of high quality printable semiconductor elements having selected physical dimensions, shapes, compositions and spatial orientations. The compositions and methods of the present invention provide high precision registered transfer and integration of arrays of microsized and / or nanosized semiconductor structures onto substrates, including large area substrates and / or flexible substrates. In addition, the present invention provides methods of making printable semiconductor elements from low cost bulk materials, such as bulk silicon wafers, and smart-materials processing strategies that enable a versatile and commercially attractive printing-based fabrication platform for making a broad range of functional semiconductor devices.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Image reading apparatus
InactiveUS20050146756A1Stable levelTelevision system scanning detailsSolid-state devicesProcessor registerTransducer
An image reading apparatus includes a solid-state image sensor having a pixel array section in which pixels each including a photoelectric transducer are arrayed, a charge transfer register that transfers a signal charge transferred from each of the pixels of the pixel array section, and an output section that converts the signal charge transferred by the charge transfer register into an electrical signal and outputs the electrical signal; a driving unit that drives the charge transfer register according to a first timing signal, and the output section according to a second timing signal; and a power supplying unit that supplies power of different power systems to a circuit portion handling the first timing signal and a circuit portion handling the second timing signal of the driving unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Horizontal register transfer pulse generation circuit and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7518648B2Poor transferReduce impactTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhase differenceProcessor register
A horizontal register transfer pulse generator includes: phase adjuster generating an output signal, from reference signal; and horizontal blanking period generator based on output signal, reference signal, and horizontal blanking pulse, wherein horizontal blanking period generator includes: delay masking pulse generator generating delay masking pulse delayed by predetermined phase relative to masking pulse generated on horizontal blanking pulse inputted into horizontal blanking period generator; and determination means determining phase difference between output signal and reference signal, when phase difference between output signal and reference signal is less than predetermined phase, horizontal blanking period generator combines masking pulse with output signal to generate horizontal register transfer pulse with horizontal blanking period, and when phase difference between output signal and reference signal is equal to or greater than predetermined phase, horizontal blanking period generator combines delay masking pulse with output signal to generate horizontal register transfer pulse with horizontal blanking period.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and device for generating RTL (Register Transfer Logic)-level IP (Intellectual Property) core
ActiveCN106709116ABest performance ratioGuaranteed performanceSpecial data processing applicationsIntellectual propertyHigh-level programming language
The invention provides a method and a device for generating an RTL (Register Transfer Logic)-level IP core, and belongs to the field of application specific integrated circuits. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, carrying out high-level synthesis on an advanced language program to obtain a plurality of behavior level IP cores; then, obtaining the compromising curve of each behavior level IP core, wherein the compromising curve is the area and task load relation curve of the each behavior level IP core; according to the compromising curve, obtaining an optimized RTL-level IP core corresponding to each behavior level IP core; and carrying out physical synthesis on all optimized RTL-level IP cores to obtain a data structure netlist. Through the method and the device for generating the RTL-level IP core, each obtained optimized RTL-level IP core has an optimal performance ratio, and an area is reduced while overall performance is guaranteed.
Owner:SHENZHEN BOJUXING IND DEV
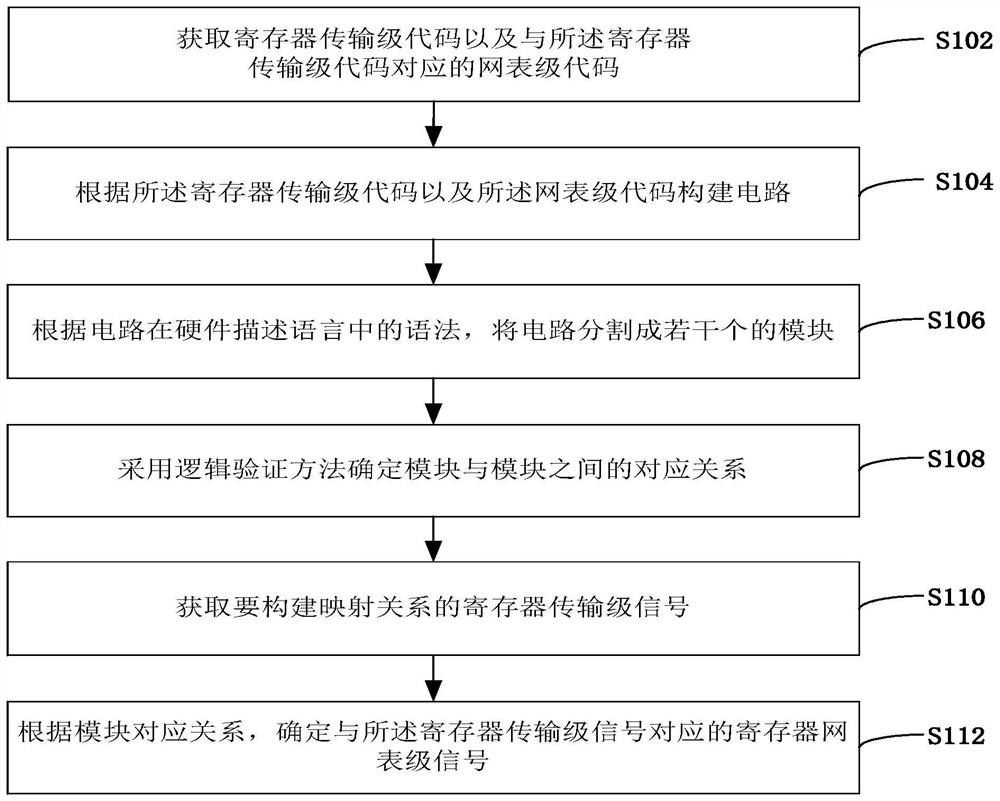
Register transfer level signal mapping construction method and device, equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN113919254AImprove versatilityShort cycleCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureHemt circuits
Owner:奇捷科技(深圳)有限公司
Transfer pulse generator circuit and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS7738022B2Hard to visually recognizeHard to visually recognize spot image noises on a screenTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPulse controlEngineering
A transfer pulse generator circuit for outputting a vertical register transfer pulse includes transfer pulse control means for controlling to set rise and fall timings of the vertical register transfer pulse to desired timings in a predetermined period.
Owner:SONY CORP
Microprocessor bus structure and microprocessor
ActiveCN102043750AFast data transferImprove efficiencyElectric digital data processingAccess structureMicrocomputer
The invention relates to a common bus or bus system concerning a device in a decentralized access structure and chips adopting the common bus or the bus system, in particular to a bus structure in a microprocessor and a microprocessor adopting the bus structure. The bus in the microprocessor is in a Harvard structure, and the bus structure comprises a program bus for transmitting program commandsand a data bus for transmitting data, wherein the data bus further comprises an operand bus and at least one register transfer bus. By using the technical scheme, the bus structure provided by the invention can improve the transmission speed of data in the microcomputer, and the efficiency of the microprocessor can be effectively improved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
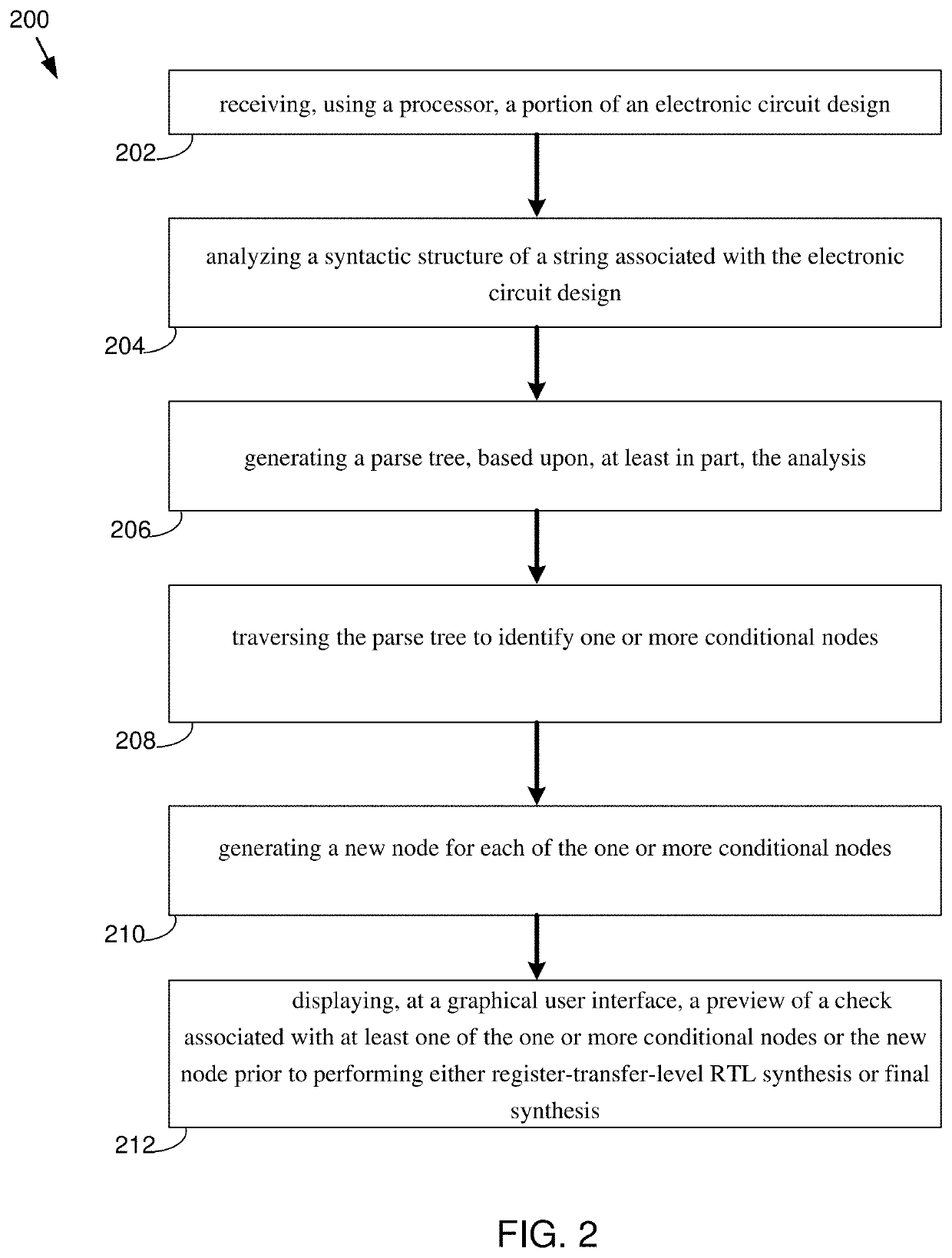
System, method, and computer program product for over-constraint/deadcode detection in a formal verification
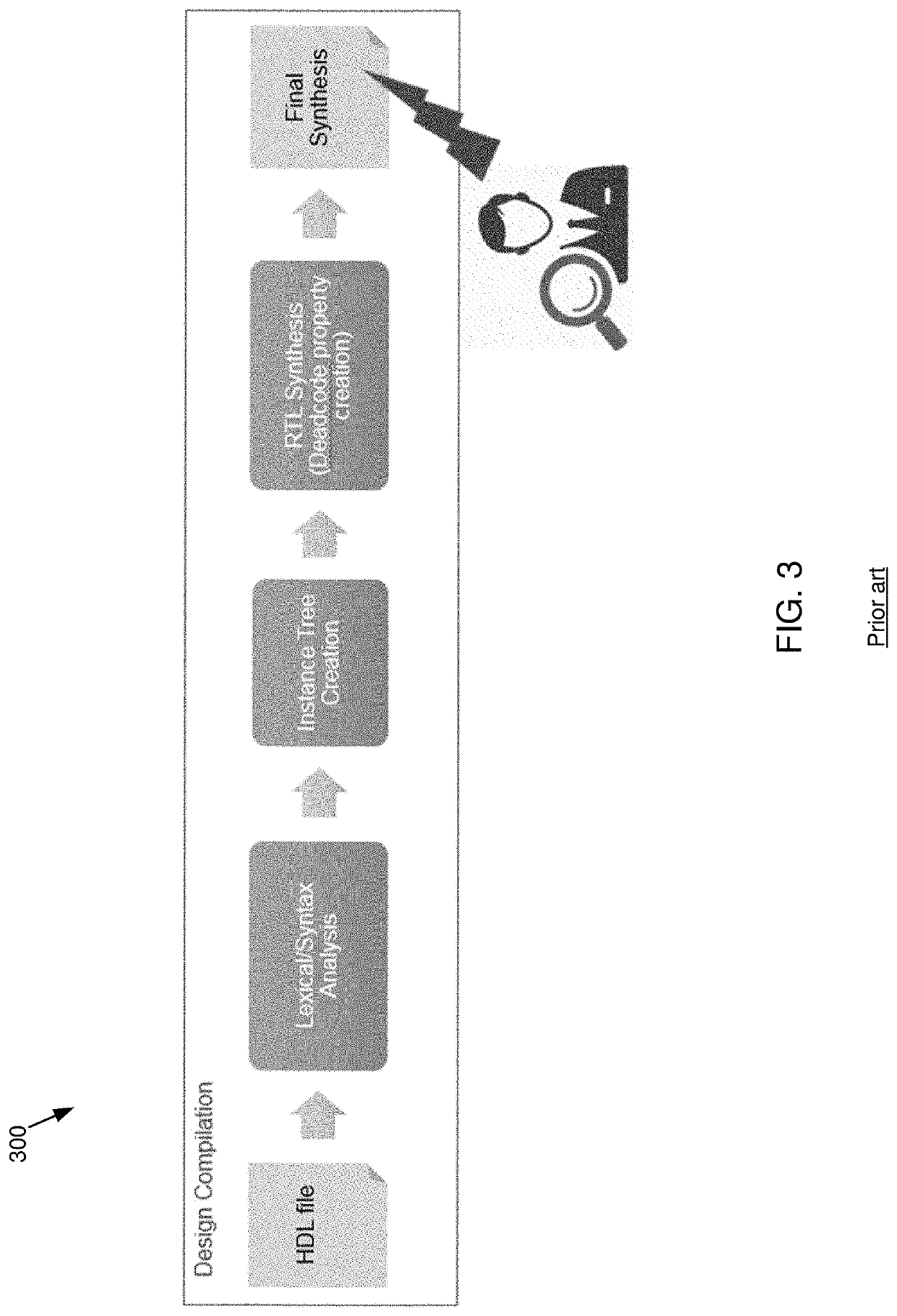
The present disclosure relates to a method for use in the formal verification of an electronic circuit. Embodiments may include receiving, using a processor, a portion of an electronic circuit design and analyzing a syntactic structure of a string associated with the electronic circuit design. Embodiments may also include generating a parse tree, based upon, at least in part, the analysis and traversing the parse tree to identify one or more conditional nodes. Embodiments may further include generating a new node for each of the one or more conditional nodes and displaying, at a graphical user interface, a check, at least one of the one or more conditional nodes or the new node prior to performing either register-transfer-level RTL synthesis or final synthesis.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Horizontal register transfer pulse generation circuit and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20060244856A1Poor transferReduce impactTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhase differenceImaging equipment
A horizontal register transfer pulse generator includes: phase adjuster generating an output signal, from reference signal; and horizontal blanking period generator based on output signal, reference signal, and horizontal blanking pulse, wherein horizontal blanking period generator includes: delay masking pulse generator generating delay masking pulse delayed by predetermined phase relative to masking pulse generated on horizontal blanking pulse inputted into horizontal blanking period generator; and determination means determining phase difference between output signal and reference signal, when phase difference between output signal and reference signal is less than predetermined phase, horizontal blanking period generator combines masking pulse with output signal to generate horizontal register transfer pulse with horizontal blanking period, and when phase difference between output signal and reference signal is equal to or greater than predetermined phase, horizontal blanking period generator combines delay masking pulse with output signal to generate horizontal register transfer pulse with horizontal blanking period.
Owner:SONY CORP
Saro: scalable attack-resistant obfuscation of logic circuits
ActiveUS20220035977A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingTheoretical computer science
A method of obfuscating a circuit design includes, in part, receiving a netlist of the circuit design, splitting the circuit design into a multitude of partitions, transforming each partitions so as to obfuscate each partition, and stitching the multitude of transformed partitions to form the obfuscated circuit. The netlist may be a register transfer level netlist. The number and the size of partitions may vary. The partitions may be distributed throughout the entirety of the design. The method may further include generating a randomized circuit associated with at least a subset of the partitions, and merging each partition with the partition's associated randomized circuit. The method may further include quantifying the amount of transformation associated with each partition. The method may further include adding a first key to at least one of the obfuscated partitions, and adding a second key to the partition's associated randomized circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Static superscale DSP cycle simulation method
ActiveCN106326521AGuaranteed cycle-accurate stateAvoid retrieval overheadSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware emulationMathematical model
The invention discloses a static superscale DSP cycle simulation method. A static superscale DSP cycle simulation system including an instruction preparation module and an instruction execution module is constructed; the instruction preparation module sets an initial value, acquires an instruction, determines the number of deferred cycles, determines the number of pause cycles and simulates clock propulsion; the instruction simulation module executes function simulation; a mathematical model of a superscale DSP cycle state is constructed from the view of time sequence; by time sequence simulation, an accurate state in a cycle when a DSP assembly line is paused; time sequence calculation mainly includes seeking of a maximum or minimum value and intersection operation which can be efficiently realized by bitwise operation; therefore, copying expense on a large number of register transfer levels and search expense on a register dependency sheet are avoided; the simulation calculation amount is relatively low, and the problems that a superscale DSP simulation method is inaccurate and relatively low in speed during DSP real-time software simulation test at the present are solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL & ELECTRONICS TECH
Printable semiconductor structures and related methods of making and assembling
ActiveCN101632156BPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSpatial OrientationsSemiconductor structure
The present invention provides a high yield pathway for the fabrication, transfer and assembly of high quality printable semiconductor elements having selected physical dimensions, shapes, compositions and spatial orientations. The compositions and methods of the present invention provide high precision registered transfer and integration of arrays of microsized and / or nanosized semiconductor structures onto substrates, including large area substrates and / or flexible substrates. In addition, the present invention provides methods of making printable semiconductor elements from low cost bulk materials, such as bulk silicon wafers, and smart-materials processing strategies that enable a versatile and commercially attractive printing-based fabrication platform for making a broad range of functional semiconductor devices.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com