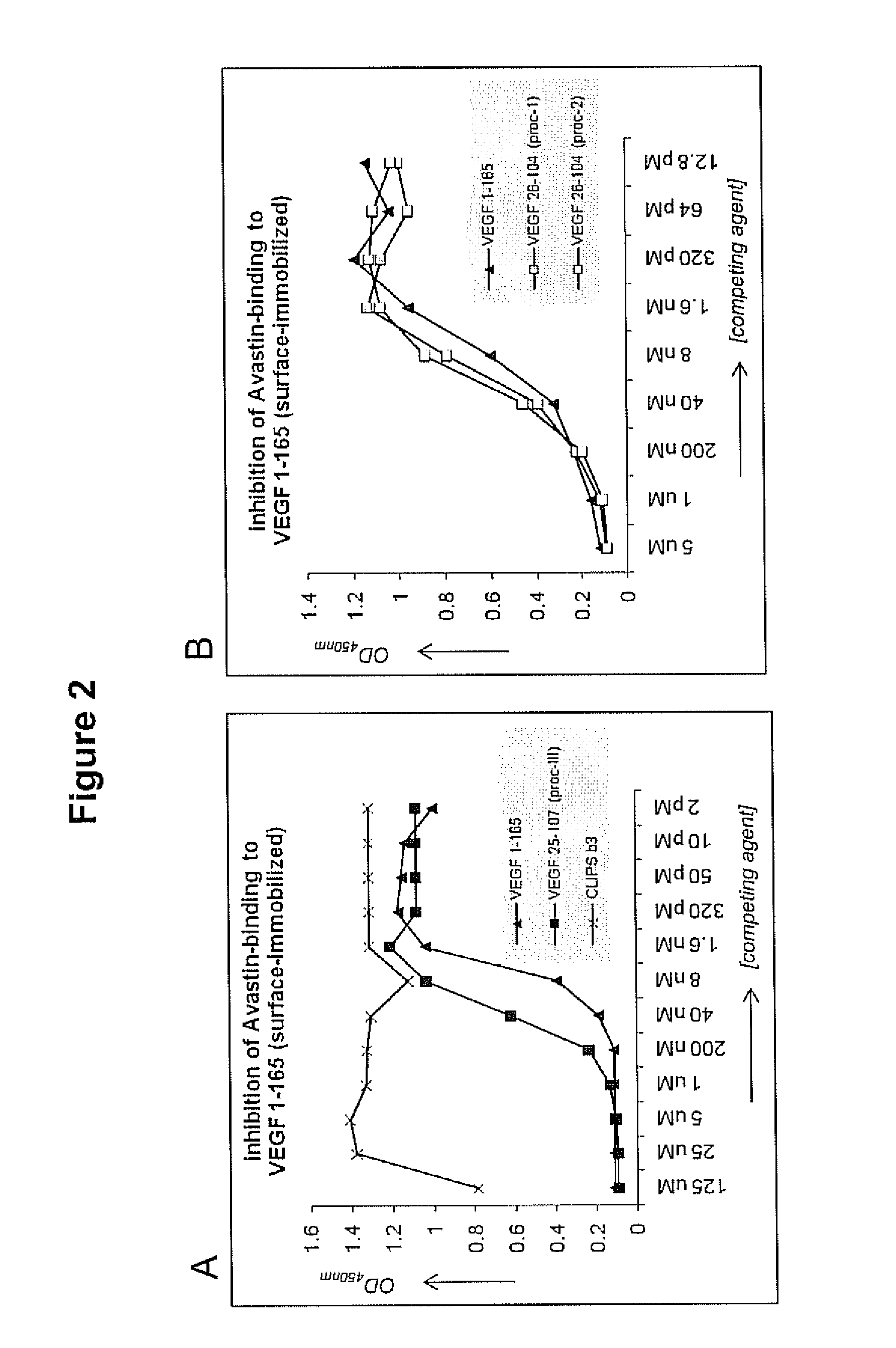
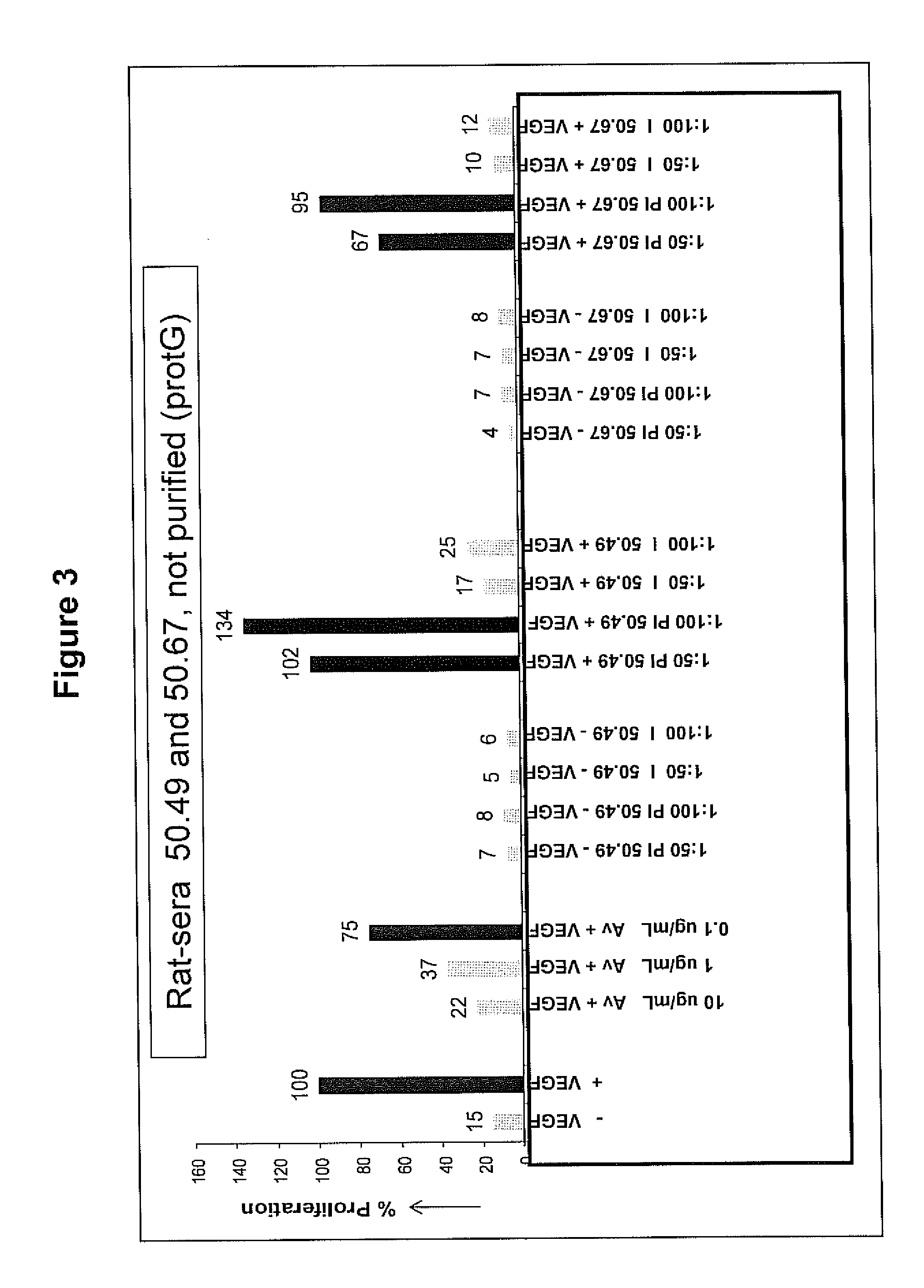
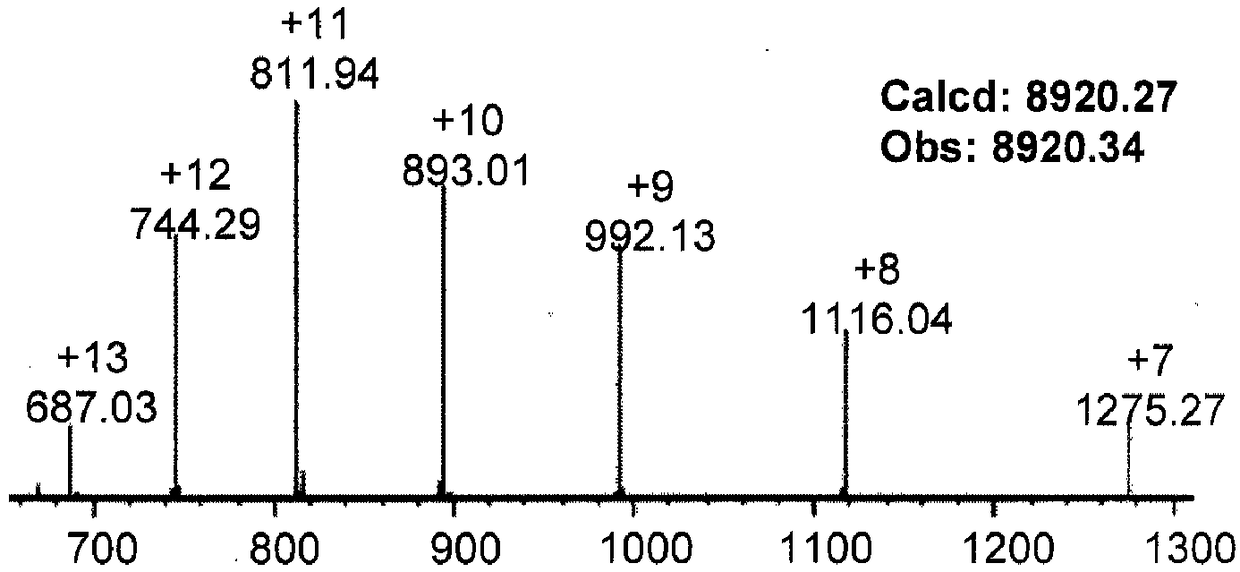
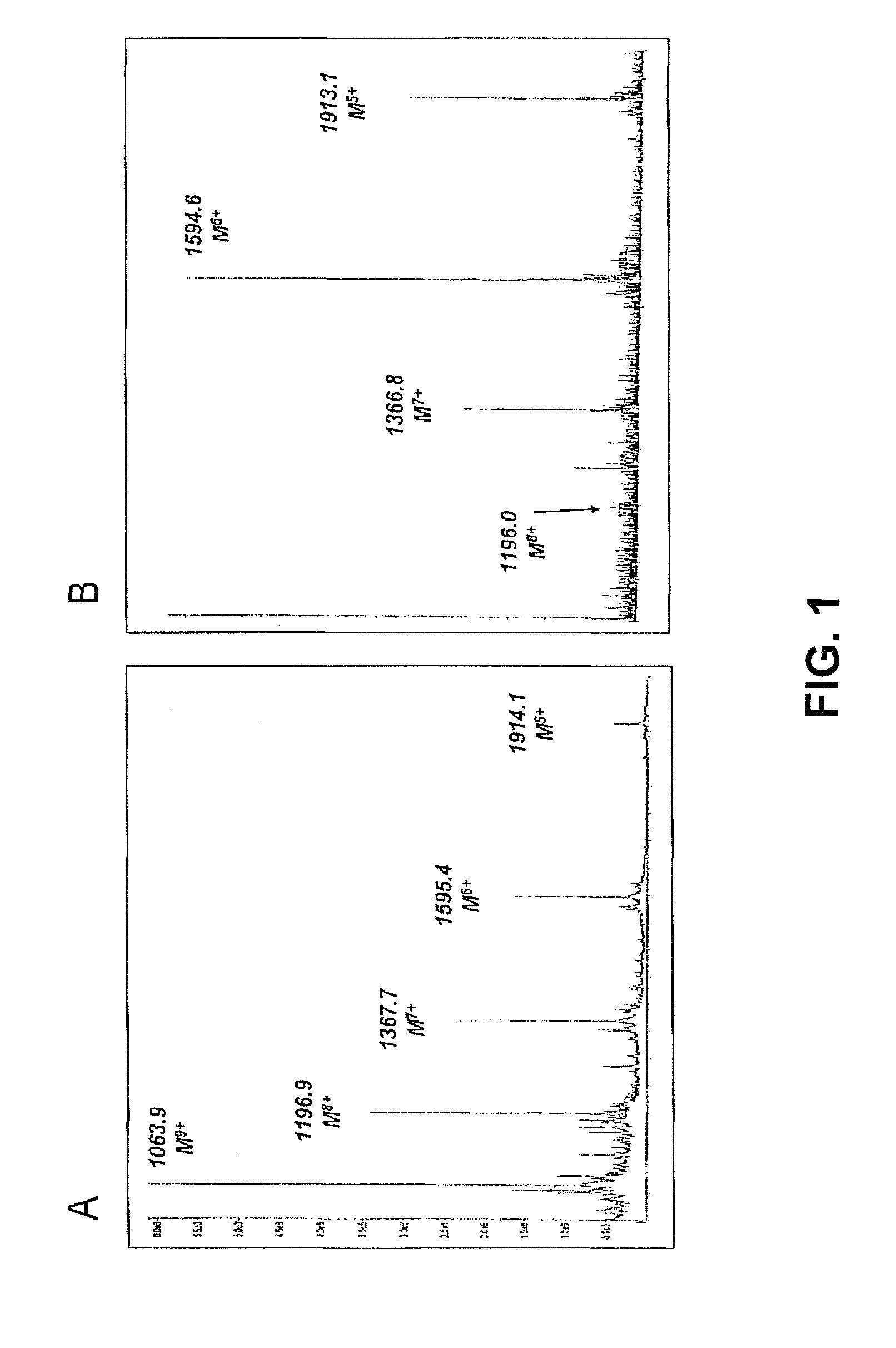
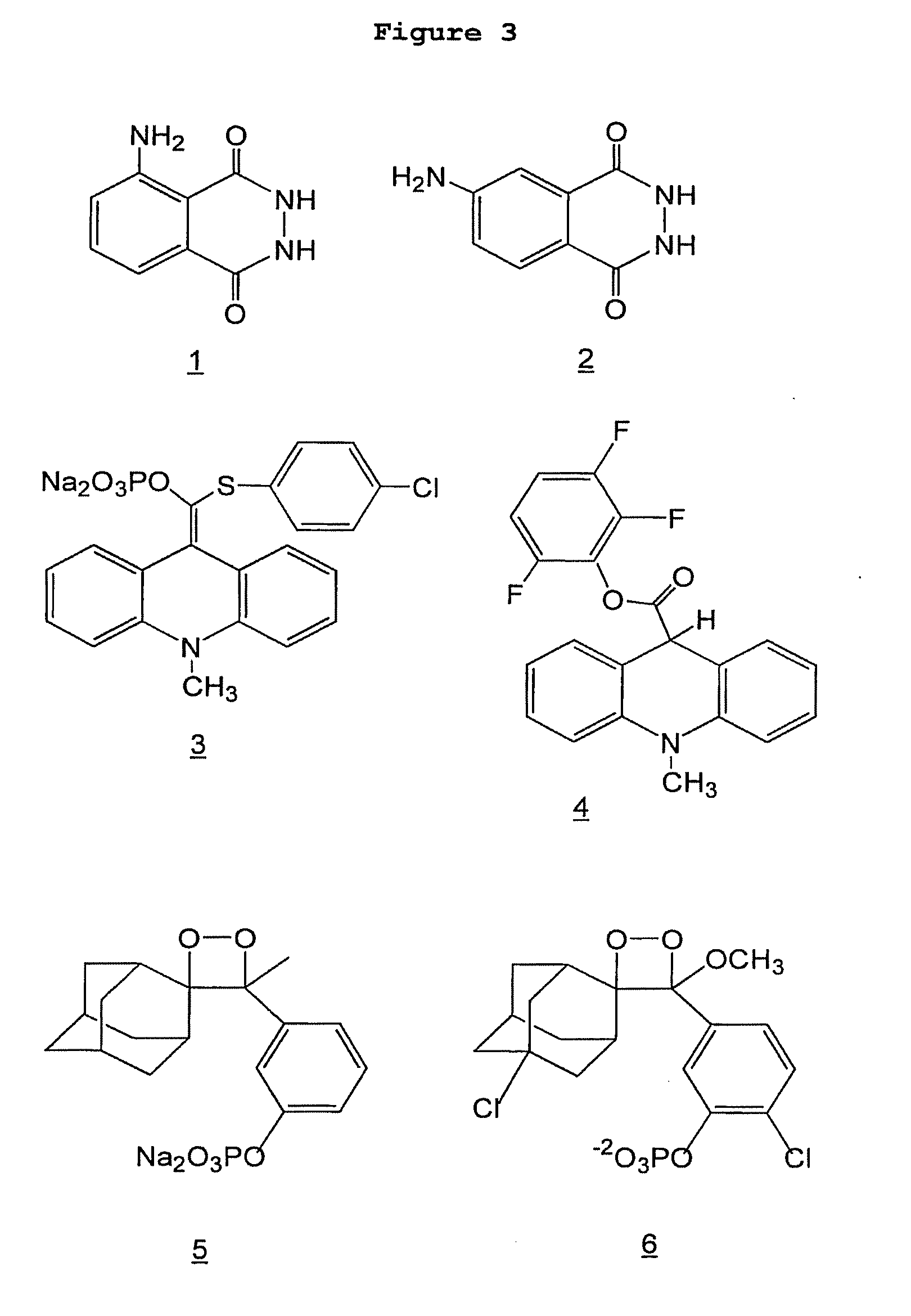
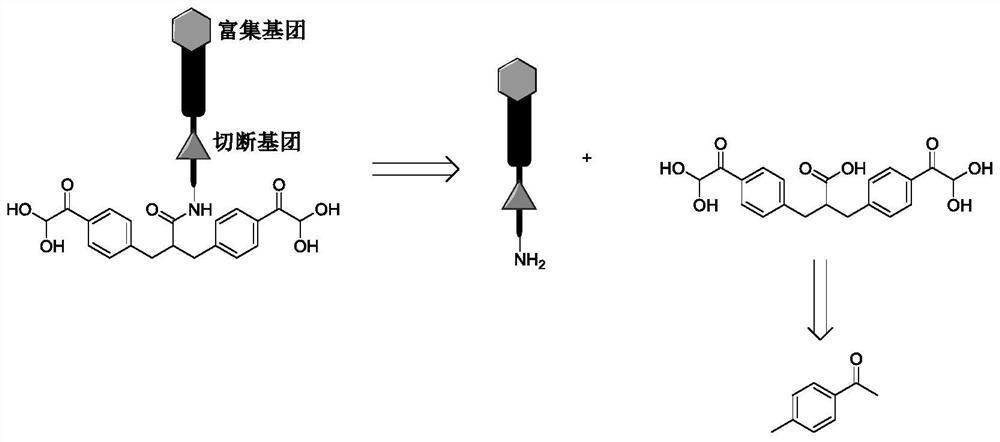
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Protein chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Chemistry of Biology: Proteins. Proteins. Proteins are organic compounds that contain the element nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are the most diverse group of biologically important substances and are often considered to be the central compound necessary for life.
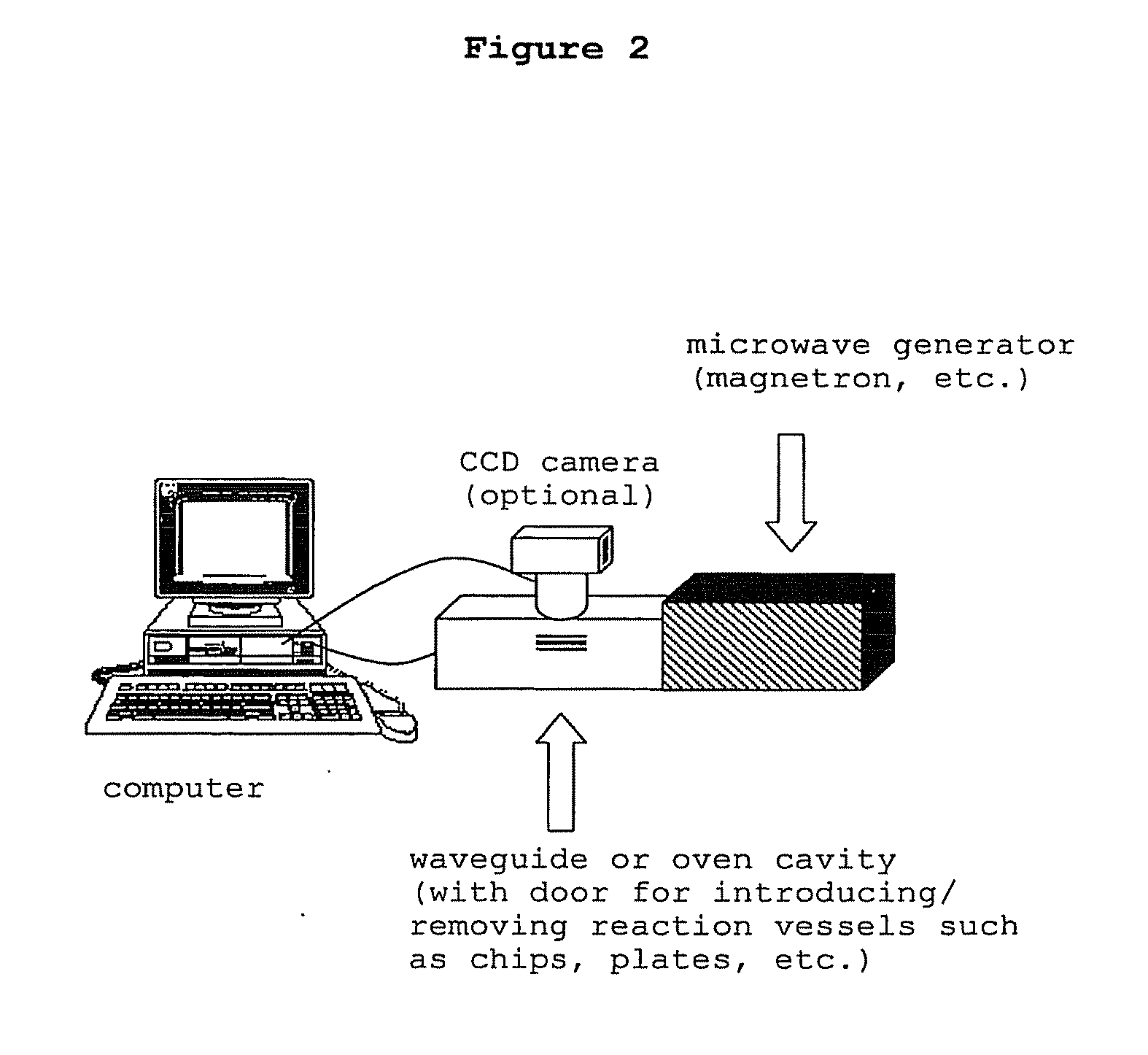
Directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS20030082633A1Promote resultsImprove adsorption capacityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical reactionChemical transformation
The present invention concerns a novel means by which chemical preparations can be made. Reactions can be accelerated on special chips using microwave energy. The chips contain materials that efficiently absorb microwave energy causing chemical reaction rate increases. The invention is important in many small scale chemical transformations including those used in protein chemistry and in combinatorial chemistry.
Owner:MIRARI BIOSCI
Directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS7348182B2Improve adsorption capacityFast bindingImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical reactionChemical physics
The present invention concerns a novel means by which chemical preparations can be made. Reactions can be accelerated on special chips using microwave energy. The chips contain materials that efficiently absorb microwave energy causing chemical reaction rate increases. The invention is important in many small scale chemical transformations including those used in protein chemistry and in combinatorial chemistry.
Owner:MIRARI BIOSCI
Chromatographic method for mutation detection using mutation site specifically acting enzymes and chemicals
InactiveUS6027898AHighly reproducibleEasy to implementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChromatographic separationRetention time
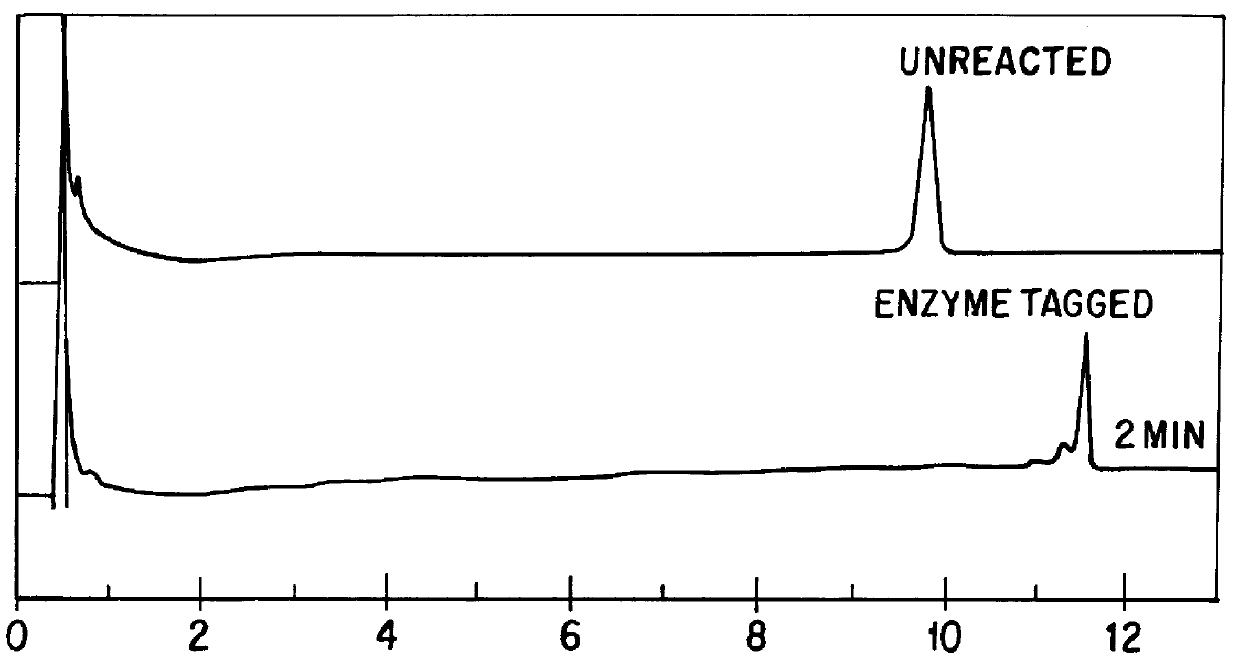
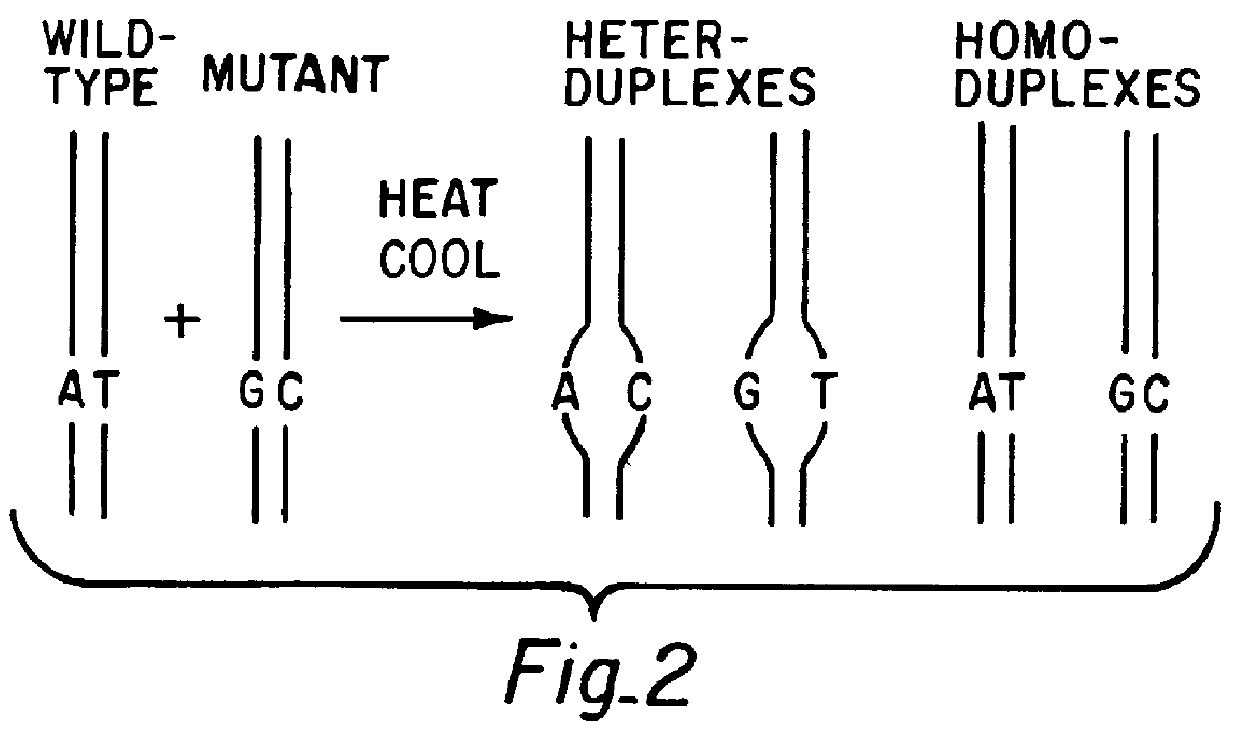
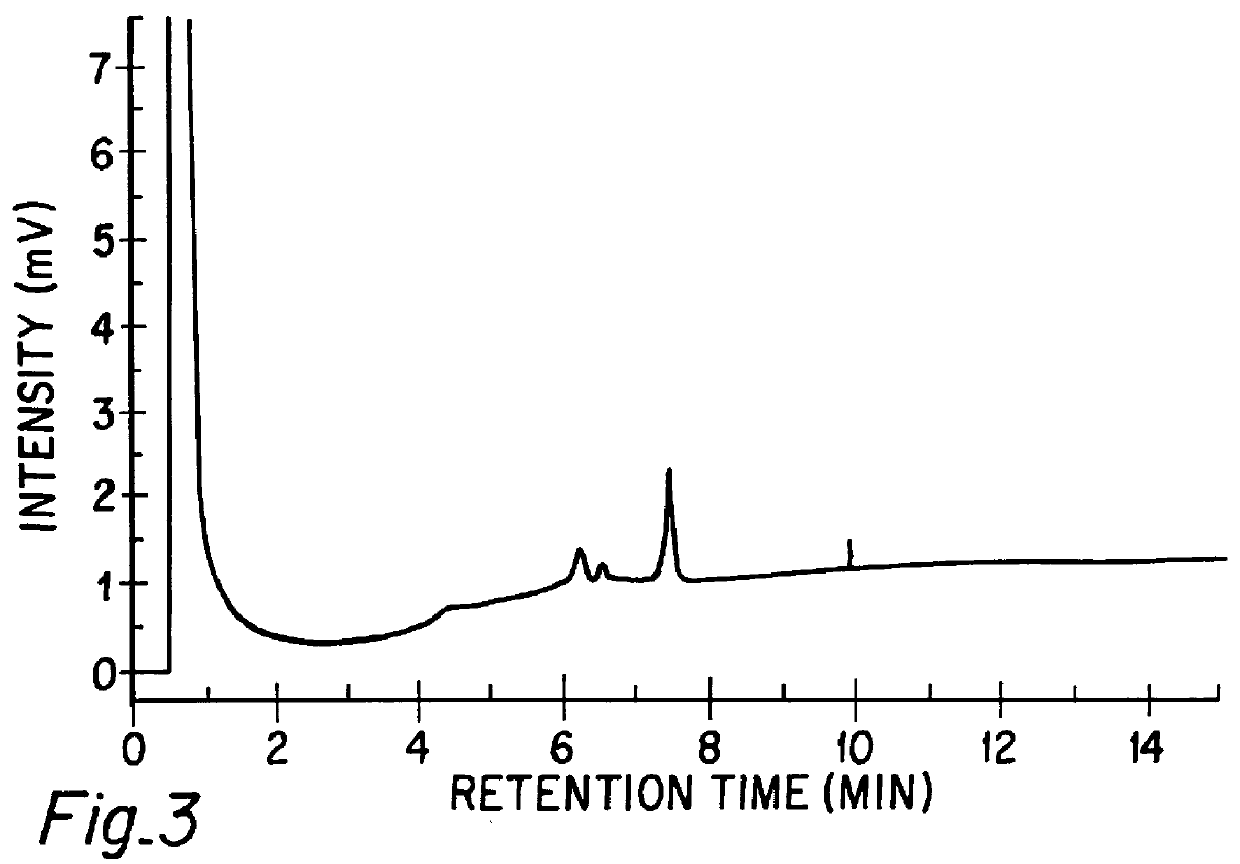
A method for analyzing a sample of double stranded DNA to determine the presence of a mutation therein comprises contacting the sample with a mutation site binding reagent, and chromatographically separating and detecting the product. The chromatographic separation can be performed using Matched Ion Polynucleotide Chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, ion exchange chromatography, or reverse phase chromatography. The mutation site binding reagent can be an enzyme or a non-proteinaceous chemical reagent. In one embodiment, a mutation site binding reagent binds to the site of mutation and alters the chromatographic retention time. In another embodiment, a mutation site binding reagent cleaves at the site of mutation, resulting in an increase in the number of fragments.
Owner:ADS BIOTEC INC
Total-fibroin albumen composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention pertains to the field of textile fiber processing and chemical technology of protein, in particular to a whole silk fibroin protein composite and a preparation method thereof. The invention adopts inorganic salt solution to preprocess degummed silk of directional arrangement which is taken as a reinforced layer, and then adopts concentrated regenerated silk fibroin aqueous solution to cast the degummed silk to form film, thus obtaining a whole silk fibroin protein composite with high performance. The whole silk fibroin protein composite has further optimized mechanical property after being processed by alcoholic solvents. Both the substrate and fiber phase of the composite are originated from fibroin protein, with good biocompatibility, are easy adhesive for cells and are biodegradable. Therefore, the composite has extensive application prospect in the field of medicine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of metal chelating agarose gel
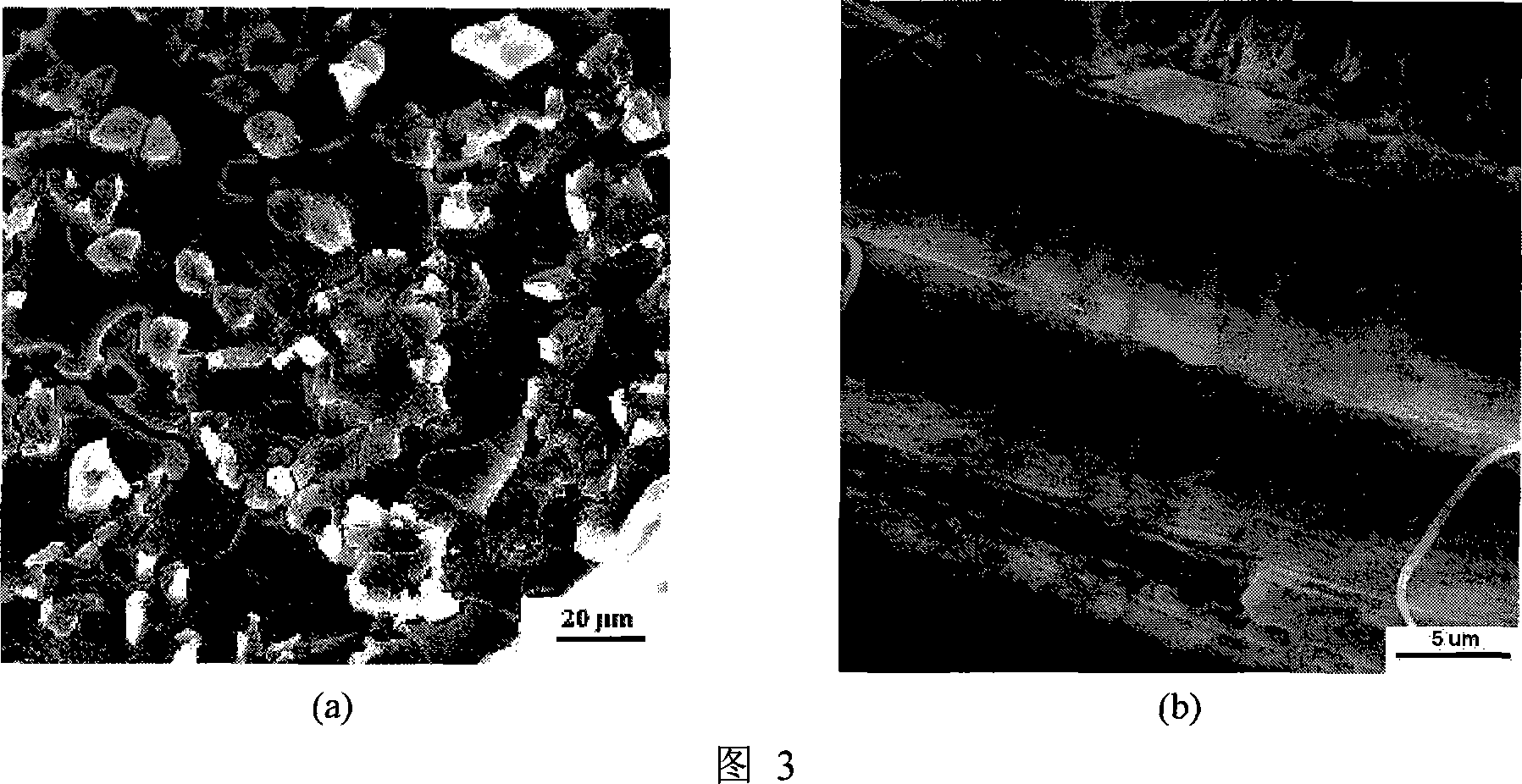
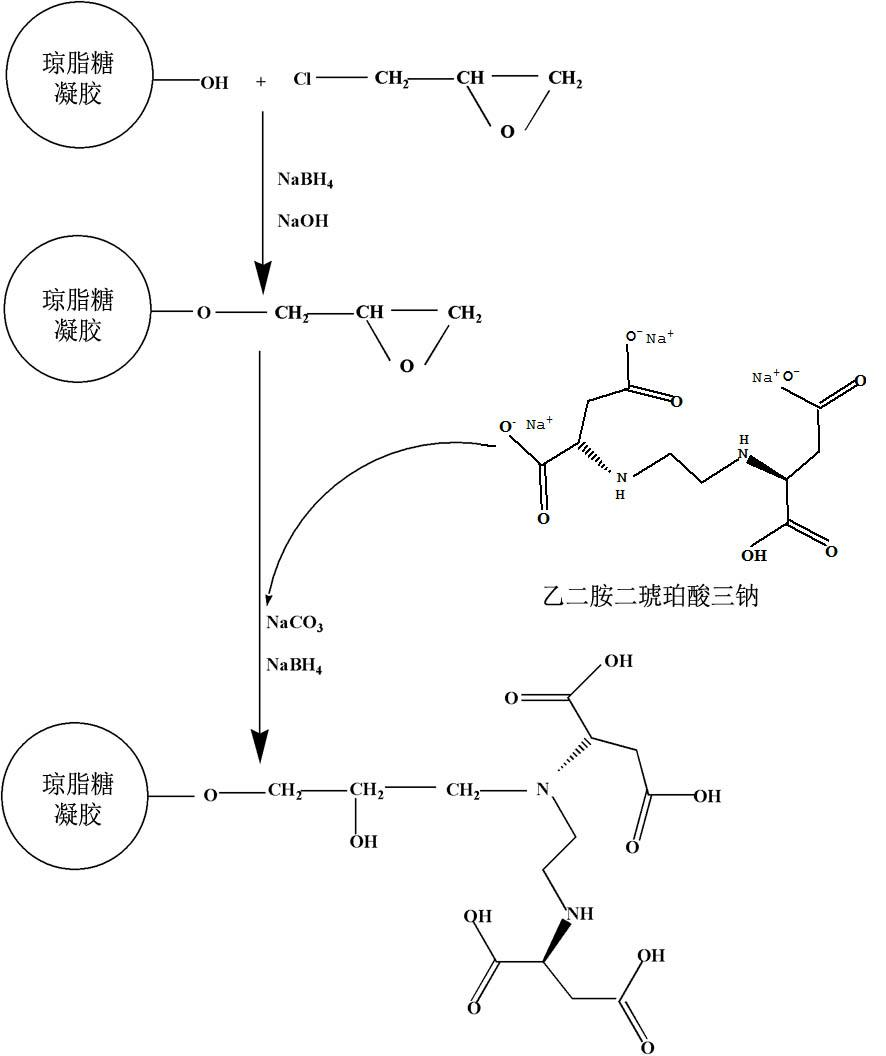
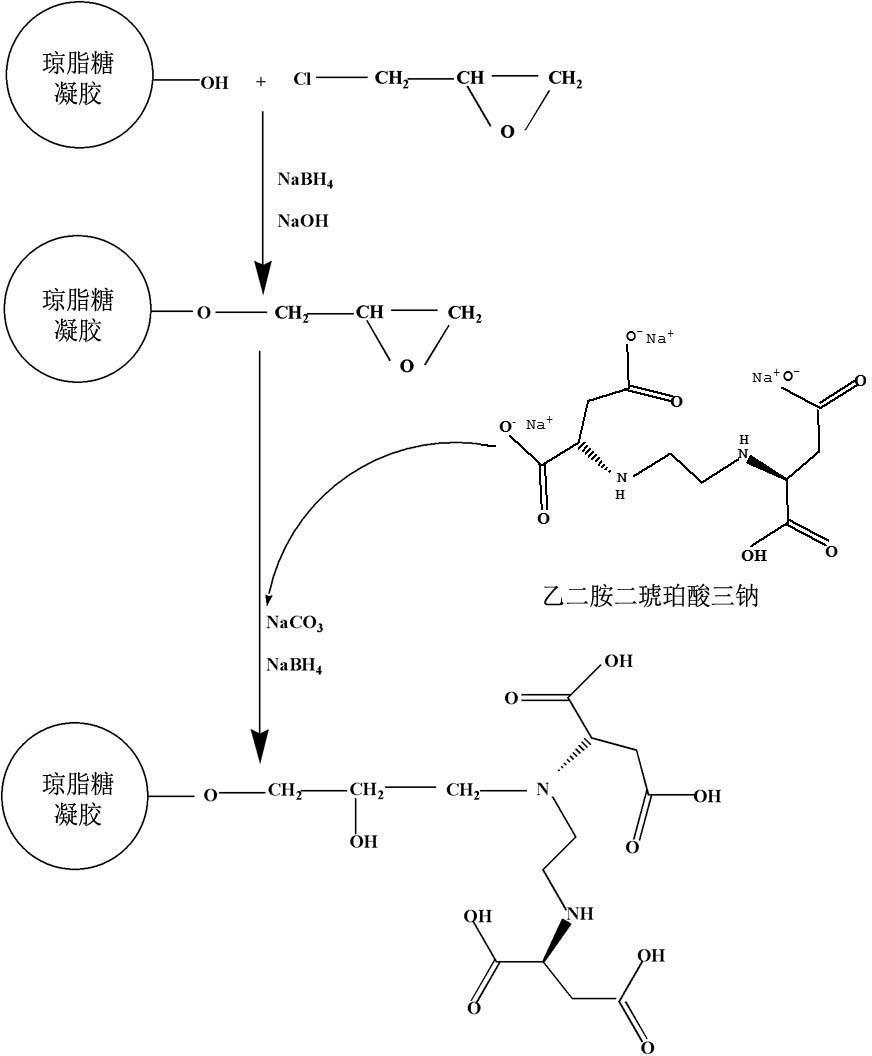
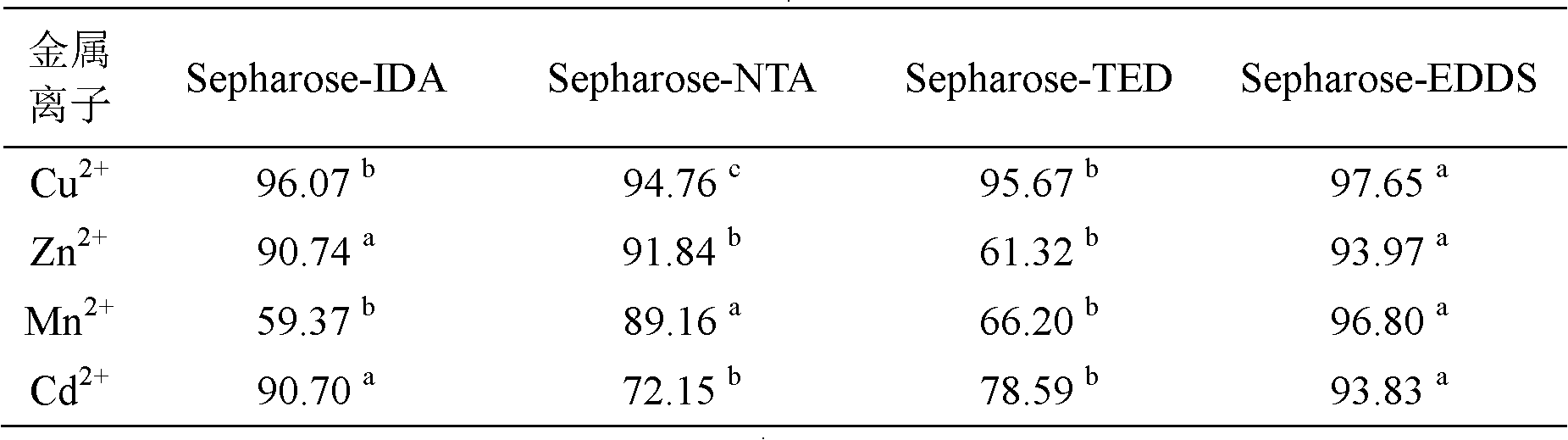
InactiveCN102432696ASimple preparation processEasy to usePeptide preparation methodsEthylenediamineProtein Sciences
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of metal chelating agarose gel, and belongs to the field of protein chemistry. The method for preparing the metal chelating agarose gel comprises the steps of activating and coupling. An agarose chelating medium with 6 ligands is formed by connecting ethylene diamino-disuccinic acid to sepharose. The metal chelating agarose gel can be applied to the removal of metal ions such as Cu, Zn, Mn, Cd and the like in a protein solution, and has high binding ability and binding capacity, and the removal rate reaches 93 percent. The preparation process is simple, easy to scale up and convenient to use; and the metal chelating agarose gel can be better applied to the removal of the heavy metal ions in the research of plant proteins which grow in a complex heavy metal polluted environment, and can also be applied to other protein scientific research in which metal ions are required to be removed.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
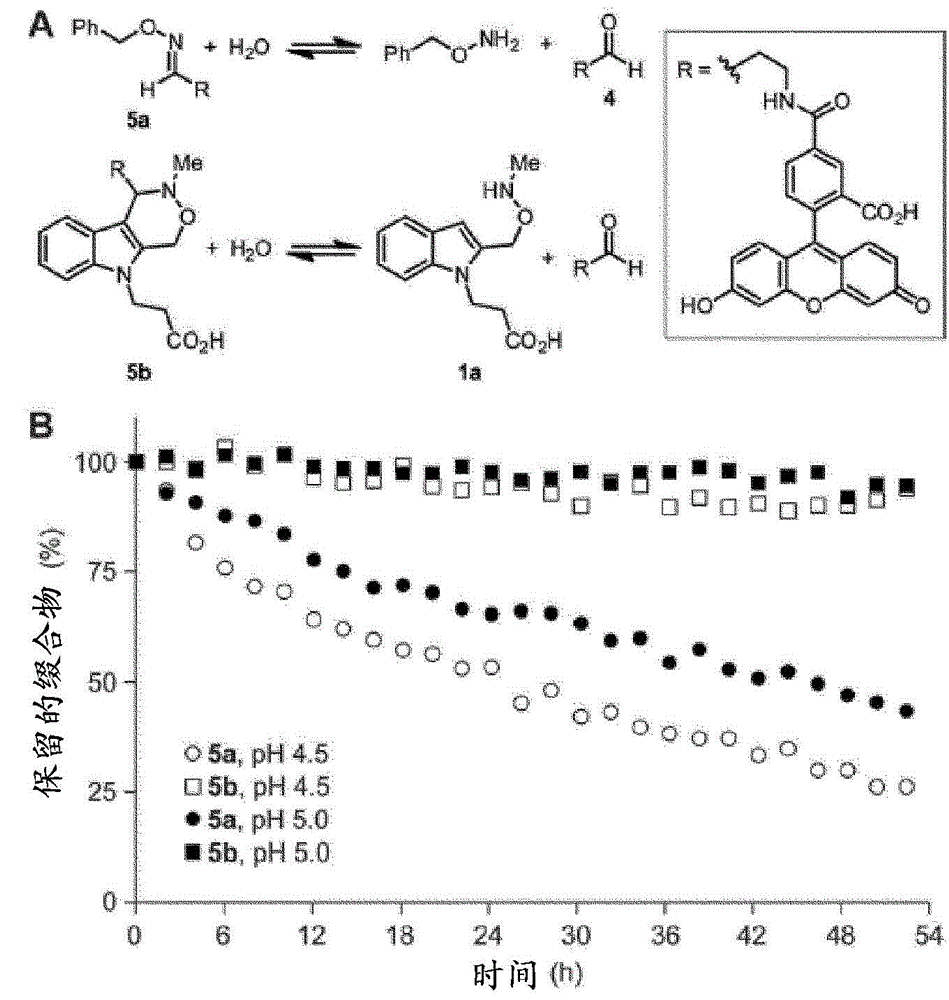
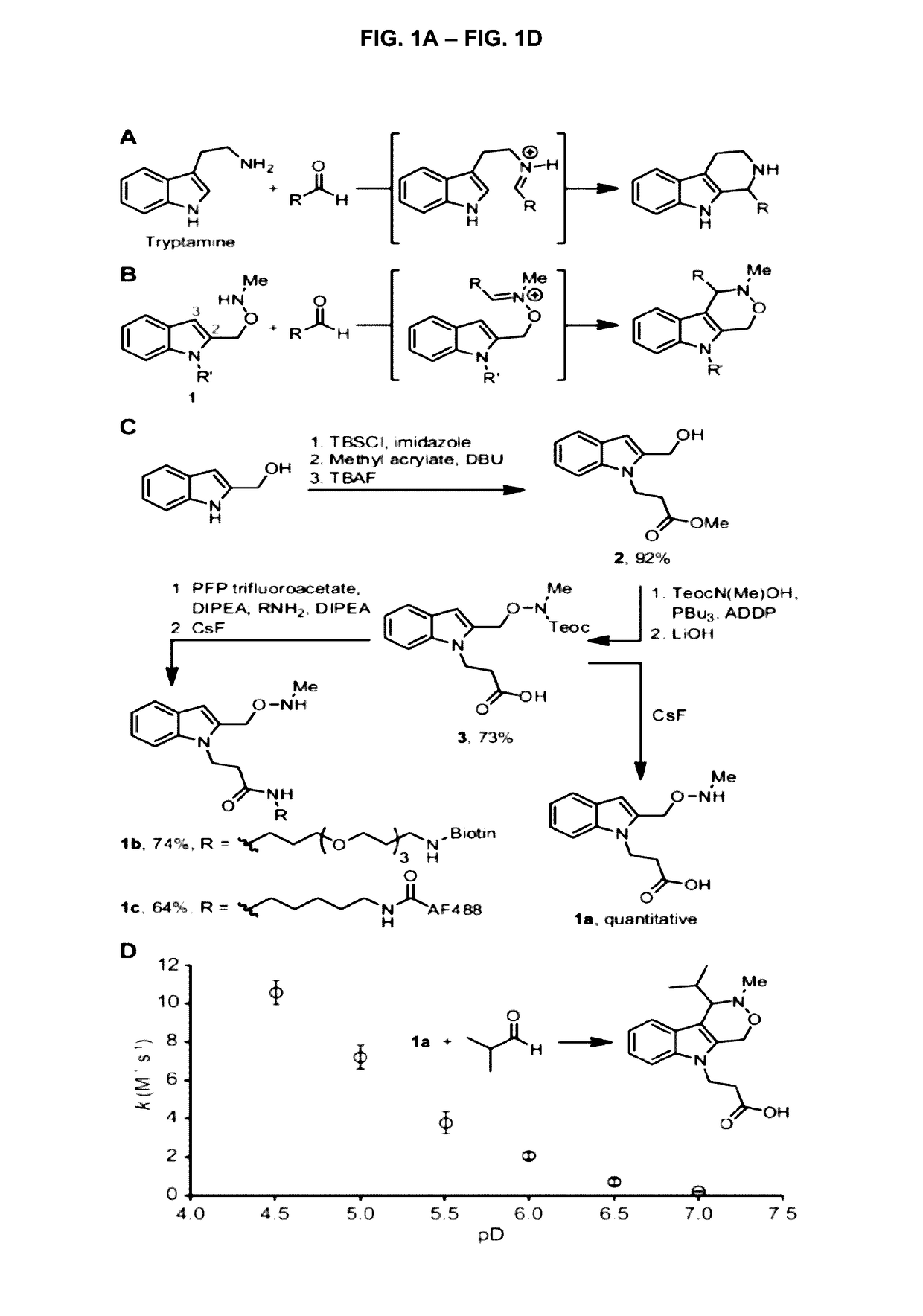
Pictet-spengler ligation for protein chemical modification
Aldehyde- and ketone-functionalized proteins are promising new substrates for the development of chemically modified biotherapeutics and protein-based materials. Their reactive carbonyl groups are typically conjugated with a-effect nucleophiles, such as substituted hydrazines and alkoxyamines, to generate hydrazones and oximes, respectively. However, the resulting C=N linkages are susceptible to hydrolysis under physiologically relevant conditions, which limits their utility in biological systems. Here we introduce a Pictet-Spengler ligation that is based on the classic Pictet-Spengler reaction of aldehydes and tryptamine nucleophiles. The ligation exploits the bioorthogonal reaction of aldehydes and alkoxyamines to form an intermediate oxyiminium ion; this intermediate undergoes intramolecular C-C bond formation with an indole nucleophile to form an oxacarboline product that is hydrolytically stable. The reaction was utilized for site-specific chemical modification of glyoxal- and formylglycine-functionalized proteins, including an aldehyde-tagged variant of the therapeutic monoclonal antibody Herceptin. In conjunction with techniques for site-specific introduction of aldehydes into proteins, the Pictet-Spengler ligation offers a new means to generate stable bioconjugates for medical and materials applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for synthesizing alpha-amino acid
ActiveCN108675937AAvoid expensiveAvoid dangerOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationElectron donorHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing an alpha-amino acid, and belongs to the fields of organic chemistry, medicinal chemistry and protein chemistry. The method uses sunlight or visible light as an energy source, is added with an electron donor, and uses carbon dioxide and an imine compound as raw materials for synthesizing the alpha-amino acid at normal temperature and normal pressure. The method adopts cheap and readily available raw materials, uses extremely mild reaction conditions, avoids expensive and dangerous high-pressure reaction devices by using a carbon dioxide gas at the normal pressure, can use clean and infinite sunlight as the energy source, and eliminates subsequent purification operations by automatically separating out products from a system in a solid form after completing the reaction and simply filtering to obtain a target product.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Tyrosine bioconjugation through aqueous Ene-like reactions
A new and versatile class of cyclic diazodicarboxamides that reacts efficiently and selectively with phenols and the phenolic side chain of tyrosine through an Ene-like reaction is reported. This mild aqueous tyrosine ligation reaction works over a broad pH range and expands the repertoire of aqueous chemistries available for small molecule, peptide, and protein modification. The tyrosine ligation reactions are shown to be compatible with the labeling of native enzymes and antibodies in buffered aqueous solution. This reaction provides a novel synthetic approach to bispecific antibodies. This reaction will find broad utility in peptide and protein chemistry and in the chemistry of phenol-containing compounds.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Tyrosine Bioconjugation through Aqueous Ene-Like Reactions
InactiveUS20120289682A1Utility in preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesSide chainTyrosine
A new and versatile class of cyclic diazodicarboxamides that reacts efficiently and selectively with phenols and the phenolic side chain of tyrosine through an Ene-like reaction is reported. This mild aqueous tyrosine ligation reaction works over a broad pH range and expands the repertoire of aqueous chemistries available for small molecule, peptide, and protein modification. The tyrosine ligation reactions are shown to be compatible with the labeling of native enzymes and antibodies in buffered aqueous solution. This reaction provides a novel synthetic approach to bispecific antibodies. This reaction will find broad utility in peptide and protein chemistry and in the chemistry of phenol-containing compounds.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for separating copper proteome by using copper-chelated magnetic beads
InactiveCN105085606AGuaranteed separation effectImprove acquisition efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein solutionCoboglobin
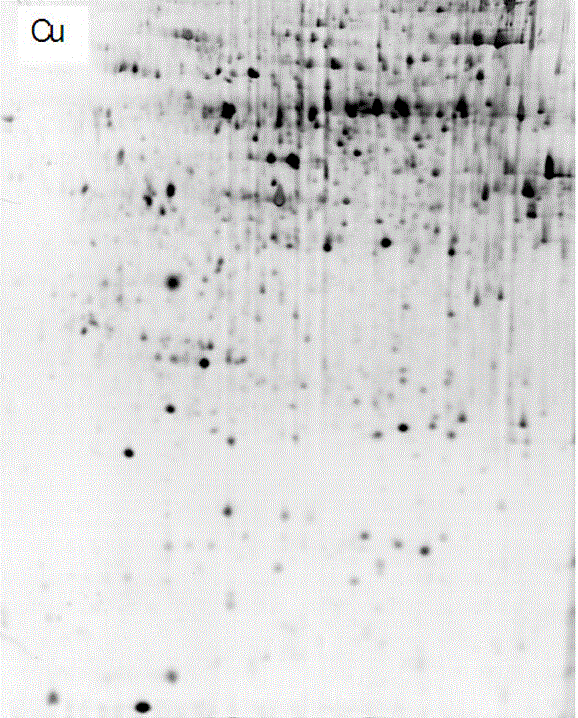
The invention discloses a method for separating copper proteome by using copper-chelated magnetic beads, and relates to the technical field of protein chemistry. The method comprises the following steps: taking a biological tissue or cell, after fully grinding with liquid nitrogen, adding protein extracting liquid, and after uniformly mixing, carrying out low-temperature centrifugation, so as to obtain a denatured protein solution; mixing the copper-chelated magnetic beads with the denatured protein solution, and incubating to obtain a magnetic bead protein mixed solution; adding a buffer solution 1 with the volume 1 time of that of the magnetic bead protein mixed solution into the magnetic bead protein mixed solution for suspension, pouring half of the supernate under the external magnetic field, and repeating for 4-5 times to obtain a mixed solution A; adding a buffer solution 2 with the volume 1 time of that of the mixed solution A into the mixed solution A, separating all the specific copper-binding proteins, namely, the copper proteome, and collecting the copper proteome under the external magnetic field. According to the method, the metalloproteome is separated under a denaturing condition by using magnetic bead-IDA, so that the procedures are greatly simplified, and the obtaining efficiency of metalloproteins is improved; a method suitable for separating the metalloproteome from the tissue or cell under the excess heavy metal treatment condition is established.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Truncated cystine-knot proteins
InactiveUS20120231000A1Negligible hormonal activityMaintain good propertiesSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCystine knotImmunogenicity
The invention relates to the fields of protein chemistry, biology and medicine. More specifically, it relates to the design and preparation of proteinmimics of members of the cystine-knot growth factor superfamily. Further, the invention relates to the use of these proteinmimics as a medicament or prophylactic agent. The invention provides proteinmimics of members of the cystine-knot growth factor superfamily, preferably for use in immunogenic and / or therapeutic compositions.
Owner:PEPSCAN SYST +2
A catalyst-free hydrazone formation chemical modification method for polypeptides or proteins based on electron-deficient benzaldehydes
ActiveCN108948128ASystem feeding method is simpleEasy to manufacturePeptide preparation methodsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDihydrogen oxideBenzaldehyde
A catalyst-free hydrazone formation chemical modification method for polypeptides or proteins based on electron-deficient benzaldehydes is provided. The method includes a step shown in the description, wherein an electron-deficient benzaldehyde compound shown as a formula III, adopted as an electrophilic agent, and a polypeptide or protein shown as a formula II, adopted as a nucleophilic agent, are subjected to a hydrazone formation reaction under a condition of a water-phase buffer solution to obtain a hydrazone formation product having a structure shown as a general formula I. In the formulaIII, R is a substitute having various structures, such as methyl, a fluorescent molecular substitute and a medicine molecule substitute. The invention also provides the electron-deficient benzaldehydes shown as the formula III and polypeptides or proteins modified with the electron-deficient benzaldehydes and obtained by the method.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Truncated cystine-knot proteins
InactiveUS8772236B2Improving immunogenicityEfficiently presentedSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical drugImmunogenicity
The invention relates to the fields of protein chemistry, biology and medicine. More specifically, it relates to the design and preparation of proteinmimics of members of the cystine-knot growth factor superfamily. Further, the invention relates to the use of these proteinmimics as a medicament or prophylactic agent. The invention provides proteinmimics of members of the cystine-knot growth factor superfamily, preferably for use in immunogenic and / or therapeutic compositions.
Owner:PEPSCAN SYST +2
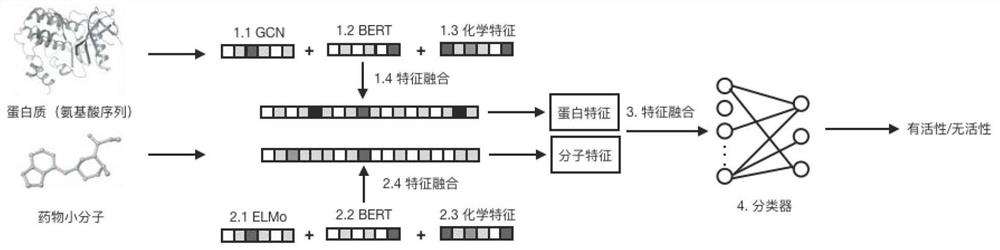
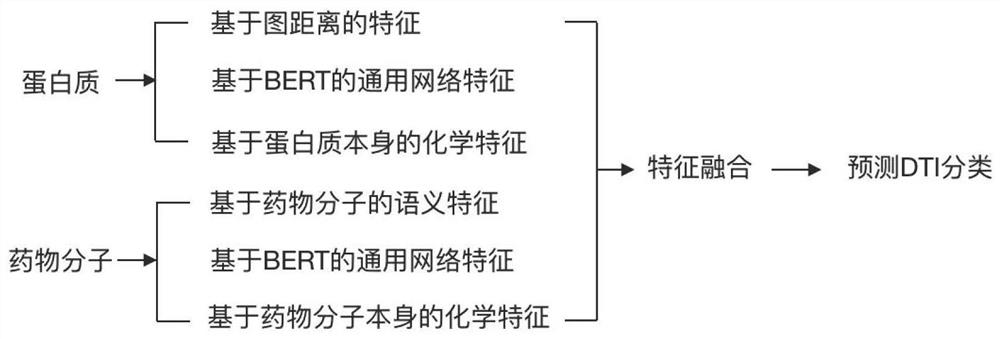
Drug small molecule-protein target reaction prediction method based on multi-dimensional information
PendingCN112331273AAccurate predictionHigh speedMolecular designChemical processes analysis/designProtein targetPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a drug small molecule-protein target reaction prediction method based on multi-dimensional information. The method comprises the following steps: (1), obtaining feature representation of a protein target, including an amino acid vector, a protein three-dimensional space structure feature and a protein chemical feature; (2), obtaining feature representations of the drug small molecules, including semantic features of the drug molecules, general network features of BERT and chemical features of the drug molecules; (3), fusing the features of protein targets and drug smallmolecules; (4), using the fused features as input of a classifier, and training the whole network in combination with labels in a training set. The fusion of three different types of features can greatly mine the potential features of drugs and proteins, and is convenient for more accurate DTI prediction. The method can improve the DTI prediction speed and accuracy at the same time, and is higherin practical value.
Owner:GALIXIR TECH (BEIJING) LTD
Separation and purification method of recombinant protein
ActiveCN113121637AEfficient removalHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionDepyrogenation
The invention belongs to the field of protein chemistry, and particularly relates to a separation and purification method of recombinant protein. The separation and purification method of recombinant protein comprises the following steps: centrifuging fermentation broth containing target recombinant protein to obtain wet thalli; carrying out primary purification treatment such as bacterium breaking, washing and renaturation; carrying out filtering through at least one tangential flow membrane, and carrying out enzyme digestion; and then, carrying out at least two times of reversed phase chromatography, depyrogenation, ultrafiltration, bottling and the like to obtain insulin glargine with the purity of 99.7%. The method can effectively remove endotoxin and reduce impurities such as polymers, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production of insulin glargine.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
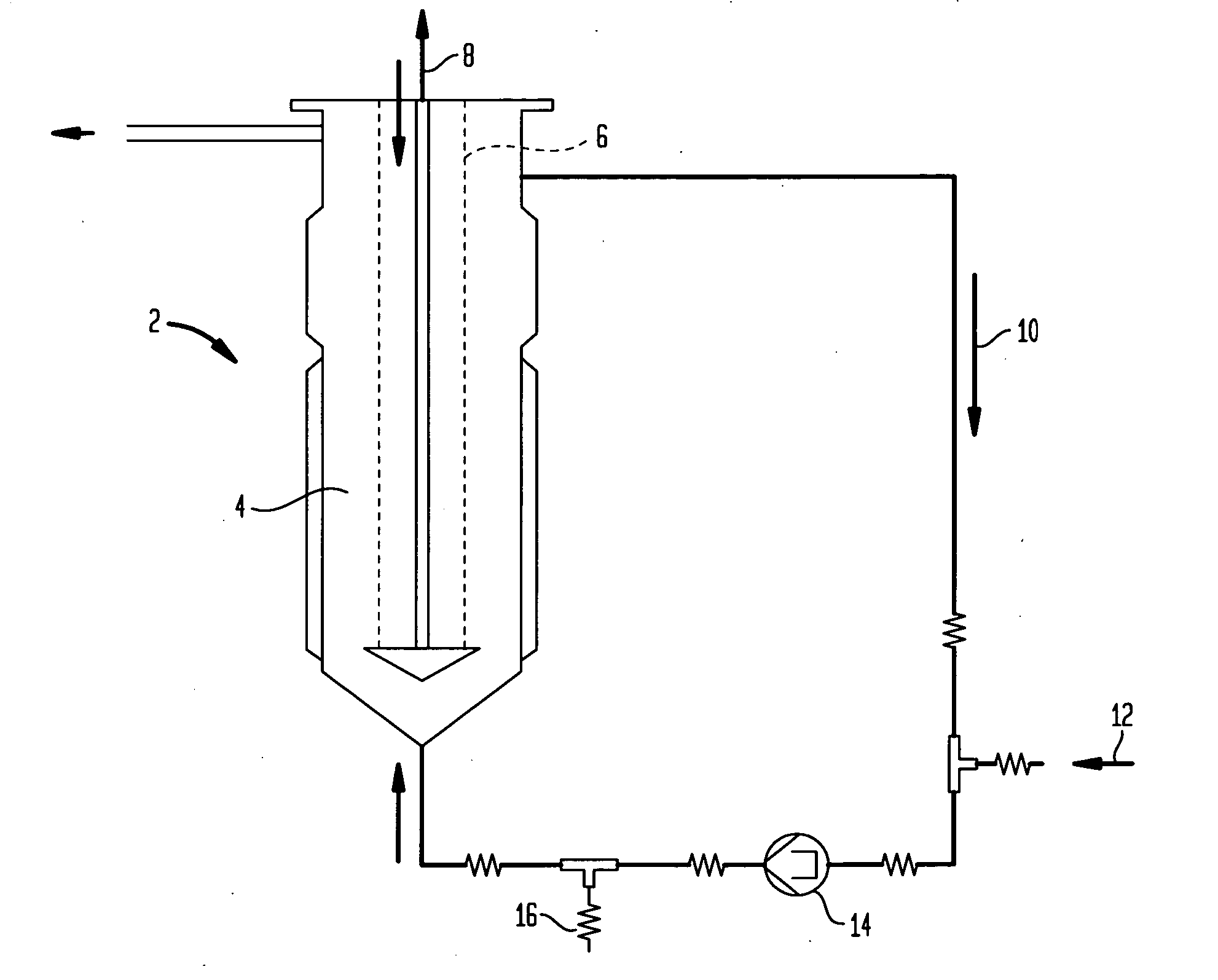
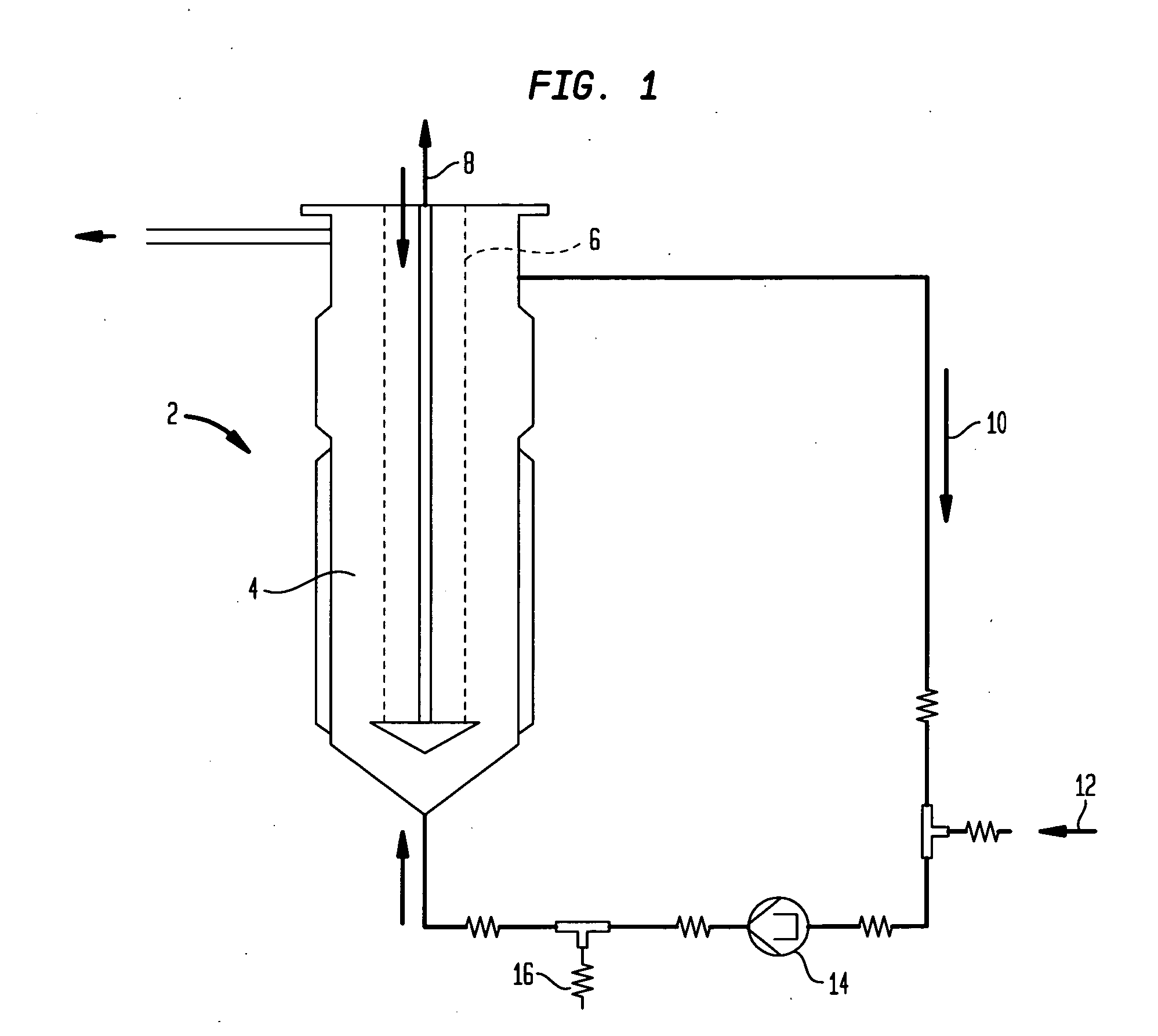
Methods and compositions for directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS20120165209A1Enhanced hybridizationDissociation—can be acceleratedImmobilised enzymesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid chemistryChemical reaction
The present invention concerns a novel means by which chemical preparations can be made. Reactions can be accelerated on special cartridges using microwave energy. The chips contain materials that efficiently absorb microwave energy causing chemical reaction rate increases. The invention is important in many chemical transformations including those used in protein chemistry, in nucleic acid chemistry, in analytical chemistry, and in the polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:MIRARI BIOSCI
High complete protein, chemical free energy enhancement and muscle rejuvenation beverage for refreshment meal replacement and enhanced Anti-inflamatory response
PendingUS20200337340A1Rapidly and highly absorbable sourceHigh activityMilk preparationNatural extract food ingredientsBiotechnologyNutritive values
A beverage composition made with low-calorie, lactose-free skim milk in liquid or dry powder form. Amelanchier alnifolia extract having Abscisic Acid is added to the skim milk in a multi-step process that utilizes CO2 to maintain the nutrient value of the extract. Crystalline fructose, natural flavorings, nutrients and carbonation are added to produce a flavorful beverage composition. A method to make a carbonated beverage composition with low-calorie, lactose-free skim milk and Amelanchier alnifolia extract includes a series of steps to preserve the nutrient value of the extract.
Owner:CLARK GEORGE H +1
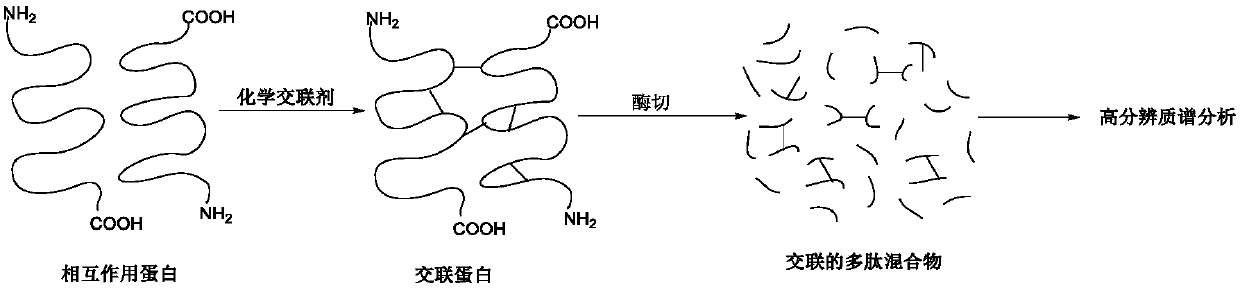
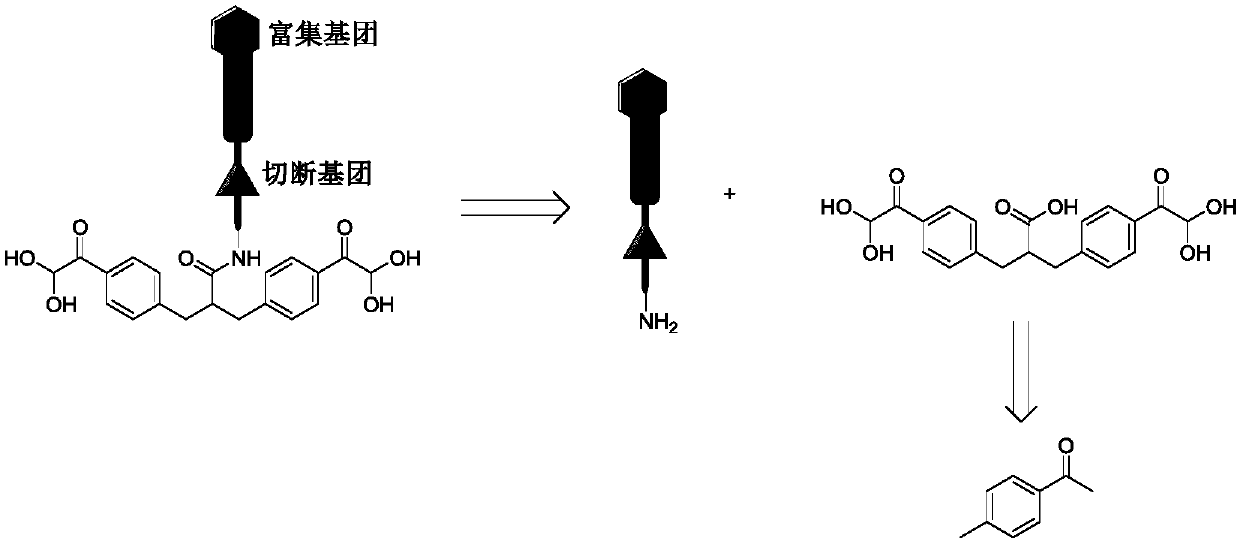
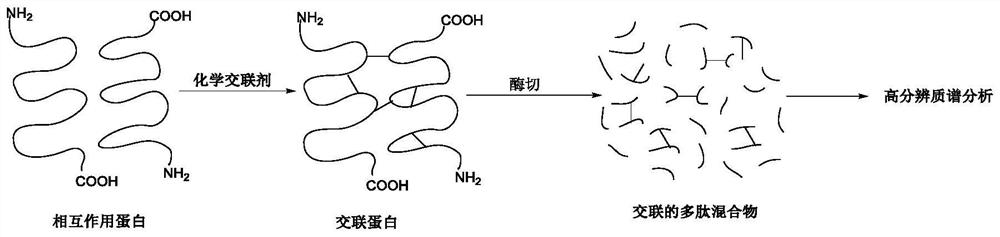
Chemical cross-linking agent for proteins, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107628937AAdd structural informationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationStructural chemistryCross-link
The invention relates to a chemical cross-linking agent for proteins and a preparation method thereof. The multifunctional cross-linking agent provided by the invention has excellent water-solubilityand stability, and high cross-linking efficiency, especially high cross-linking efficiency to arginine, and the multifunctional cross-linking agent is the first extensively-used specific cross-linkingagent for arginine. It is proved that the cross-linking agent has arginine selectivity; and cross-linking reactions of the multifunctional cross-linking agent with proteins of eight modes and oligomeric yeast protein compounds prove the validity of conjugation between the cross-linking agent and arginine. Combined chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometric technology is an effective and rapidly developing technology in structural chemistry and can be effectively applied to analysis of large active protein compounds without strict purification. Due to diversified structural characteristicsof the cross-linking agent, the cross-linking agent presents complementary reactivity, and arginine residues cross-linkable with the cross-linking agent are all specific.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Pictet-Spengler ligation for protein chemical modification
Owner:GERAWAN FARMING +1
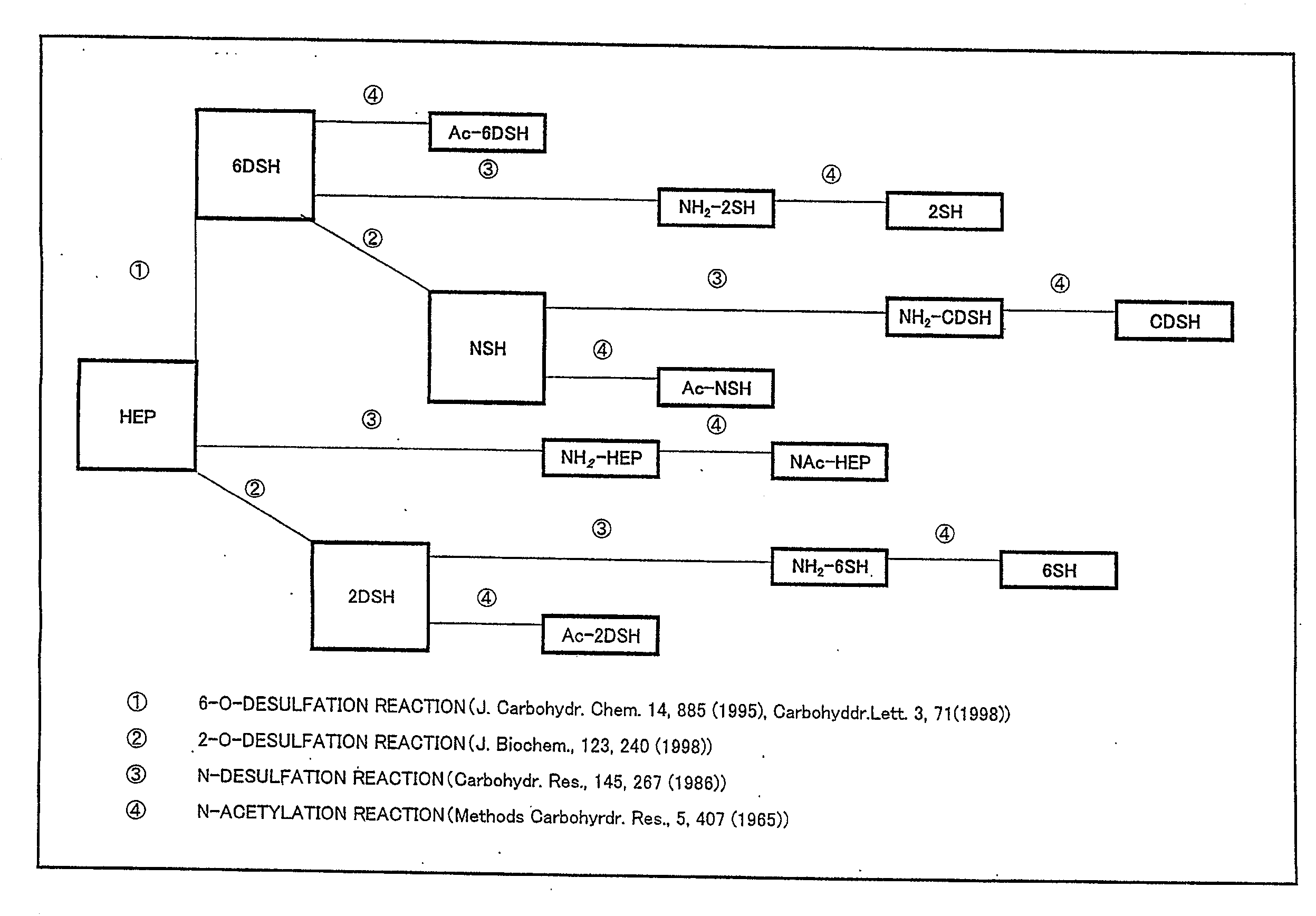
Anti-2-o-desulfated acharan sulfate antibody and its application
ActiveUS20090280502A1Efficient productionEfficient detectionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresChemical LinkageAntigen
An antibody that reacts with 2-O-desulfated acharan sulfate, a hybridoma that produces the antibody, a detection method and a detection kit to which the antibody is applied are disclosed. The antibody that reacts with 2-O-desulfated acharan sulfate can be produced by immunizing a mammal using as an antigen a substance obtained by chemically bonding a protein to 2-O-desulfated acharan sulfate.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Method for amidating polypeptides with basic aminoacid C- terminals by means of specific endoproteases
InactiveCN101268097AAvoid yield lossObvious cost advantagePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderActive enzymeCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Formulations for the synthesis of paramagnetic particles and methods that utilize the particles for biochemical applications
A set of paramagnetic particles synthesized by co-precipitation methods wherein an alkaline hydroxide solution is mixed with a metal salt solution. The alkaline hydroxide features ammonium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, or mixtures thereof. The metal salt solution features at least one ferrous salt and at least one tetravalent metal salt selected from Group 4 elements of the Periodic Table. The concentration of the ferrous salt is equal to or greater than the concentration of the tetravalent metal salt. The paramagnetic particles may be used for bioprocessing via magnetic fields. Bioprocessing, for example, may include purifying, concentrating, or detecting biomolecules of interest (e.g., nucleic acids, carbohydrates, peptides, proteins, other organic molecules, cells, organelles, microorganisms, viruses, etc.), or other magnetic field-based processes common to applications in separation science, diagnostics, molecular biology, protein chemistry, and clinical practice.
Owner:UTERMOHLEN JOSEPH GERARD
Proteins with high immunoreactivity and method for their production
InactiveUS20080075659A1Without any loss of reactivityIncrease valueAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHybrid cell preparationPurification methodsIn vivo
The invention relates to (glyco-) proteins, in particular monoclonal antibodies, which have an immunoreactivity of >81%, preferably >90%. The inventive monoclonal antibodies are produced using a fluidized bed reactor in conjunction with a conventional protein-chemical purification method or preferably with a purification method involving less column chromatography. The monoclonal antibodies thus produced are suitable, in gamma-irradiated form, e.g. Tc-99m labeled, for the in vivo diagnosis of inflammatory diseases and bone marrow metastases. In alpha- or beta-irradiated form, e.g. astatine or Re-188 or Y-90 labeled form, the inventive monoclonal antibodies can be used, for example, in the treatment of leukemia.
Owner:SCINTEC DIAGNOSTICS
Acidic beverage containing succinylated soybean protein isolate and preparation method of acidic beverage
PendingCN114391624AGood dispersionImprove stabilityFood ingredient as emulsifierBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention relates to a succinylated soybean protein isolate acidic beverage and a preparation method thereof. The invention belongs to the field of acidic protein beverages and preparation thereof. The invention aims to solve the technical problems that the soybean protein beverage is unstable and easy to flocculate under the acidic condition in the existing protein chemical modification method. The acidic beverage is prepared from succinylated soybean protein, white granulated sugar, an acidulant, a compound stabilizer, an emulsifier and water. The acidic beverage with good stability and dispersity is obtained through reasonable matching of all the components and strict regulation and control of process conditions, meanwhile, the stability under the acidic condition is further improved through the modification effect of succinylation, the preparation process is simple in process, no other chemical reagents are added, safety is high, operability is high, and the preparation method is suitable for industrial production. The method is suitable for large-scale food industrial production.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A protein chemical cross-linking agent and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107628937BAdd structural informationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationYeast ProteinsActive protein
The invention relates to a chemical cross-linking agent for proteins and a preparation method thereof. The multifunctional cross-linking agent provided by the invention has excellent water-solubilityand stability, and high cross-linking efficiency, especially high cross-linking efficiency to arginine, and the multifunctional cross-linking agent is the first extensively-used specific cross-linkingagent for arginine. It is proved that the cross-linking agent has arginine selectivity; and cross-linking reactions of the multifunctional cross-linking agent with proteins of eight modes and oligomeric yeast protein compounds prove the validity of conjugation between the cross-linking agent and arginine. Combined chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometric technology is an effective and rapidly developing technology in structural chemistry and can be effectively applied to analysis of large active protein compounds without strict purification. Due to diversified structural characteristicsof the cross-linking agent, the cross-linking agent presents complementary reactivity, and arginine residues cross-linkable with the cross-linking agent are all specific.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Designing customized protein-specific buffer system
ActiveUS11001872B2Avoid changeHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementCryoprotective EffectOrganic chemistry
The present invention is related to the field of protein chemistry. In particular, mixed buffer compositions are formulated that allow an accurate identification of agent-induced changes in protein melting point temperatures. Such buffer compositions provide for methods that determine the specific effects of exogenous agents on protein stability, cryoprotective effects and / or protein quality control (e.g., synthesis and / or extraction purity validations).
Owner:CLARK SHAWN
Method for separating specific metal-binding proteins by using protein denaturation
InactiveCN105085607AAvoid Agglomeration and PrecipitationImprove acquisition efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein solutionCopper-binding protein
The invention discloses a method for separating specific metal-binding proteins by using protein denaturation, and relates to the technical field of protein chemistry. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking a biological tissue or cell, after fully grinding with liquid nitrogen, adding protein extracting liquid, and after uniformly mixing, carrying out low-temperature centrifugation, so as to obtain a denatured protein solution; replacing Ni in Ni-NTA agarose with Cu, and putting into a chromatographic column; incubating the denatured protein solution with Cu-NTA agarose, so as to ensure that the denatured proteins are fully combined with the Cu-NTA agarose; then under the low-temperature condition, injecting eluant 1, so as to renature the proteins and elute non-specific copper-binding proteins; injecting eluant 2, so as to separate specific copper-binding proteins. According to the method, the copper-binding proteins under the denaturing condition are separated by using agarose-NTA, so that the obtaining efficiency of the copper-binding proteins is greatly improved; a technology suitable for separating the specific metal-binding proteins from the biological tissue or cell under the excess heavy metal treatment condition is established.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A protein chemical cross-linking agent and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110981715BRapid responseEfficient cross-linking activityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationYeast Protein ComplexArginine
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein and its function research, in particular to a protein chemical cross-linking agent and its preparation method and application. The structure of the protein chemical cross-linking agent is shown in general formula I. The protein chemical cross-linking agent described in the present invention has the advantages of rapid reaction and no hydrolysis, and it exhibits high-efficiency cross-linking activity when applied to CXMS technology, and can realize specific recognition for arginine and lysine. The cross-linking reactions of protein chemical cross-linking agents of the present invention with six model proteins, ten protein mixtures, multi-subunit yeast protein complexes, 70S ribosomes and exosomes demonstrate that these cross-linking agents bind to lysine The effectiveness of the existing cross-linking agent is not abundant, and the existing succinimide ester cross-linking agent has many problems in the actual process of CXMS technology, such as easy hydrolysis, low selectivity and relatively slow cross-linking reaction. Wait for the question.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A catalyst-free hydrazone-linked polypeptide or protein chemical modification method based on electron-deficient benzaldehyde
ActiveCN108948128BSystem feeding method is simpleEasy to manufacturePeptide preparation methodsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPtru catalystBenzaldehyde
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A method for separating specific metal-binding proteins by protein denaturation
InactiveCN105085607BAvoid Agglomeration and PrecipitationImprove acquisition efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein solutionCopper binding
The invention discloses a method for separating specific metal-binding proteins by using protein denaturation, and relates to the technical field of protein chemistry. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking a biological tissue or cell, after fully grinding with liquid nitrogen, adding protein extracting liquid, and after uniformly mixing, carrying out low-temperature centrifugation, so as to obtain a denatured protein solution; replacing Ni in Ni-NTA agarose with Cu, and putting into a chromatographic column; incubating the denatured protein solution with Cu-NTA agarose, so as to ensure that the denatured proteins are fully combined with the Cu-NTA agarose; then under the low-temperature condition, injecting eluant 1, so as to renature the proteins and elute non-specific copper-binding proteins; injecting eluant 2, so as to separate specific copper-binding proteins. According to the method, the copper-binding proteins under the denaturing condition are separated by using agarose-NTA, so that the obtaining efficiency of the copper-binding proteins is greatly improved; a technology suitable for separating the specific metal-binding proteins from the biological tissue or cell under the excess heavy metal treatment condition is established.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com