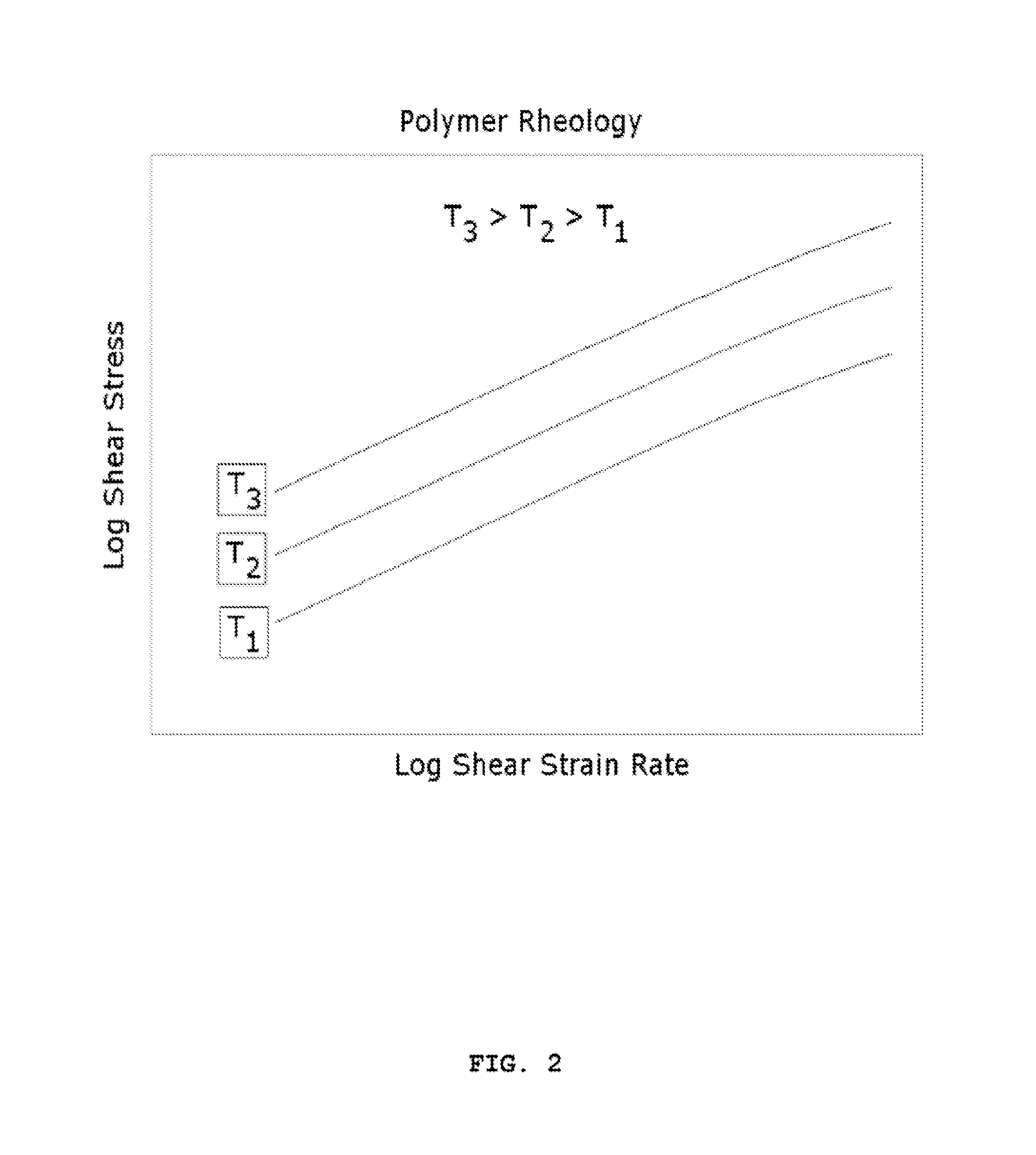
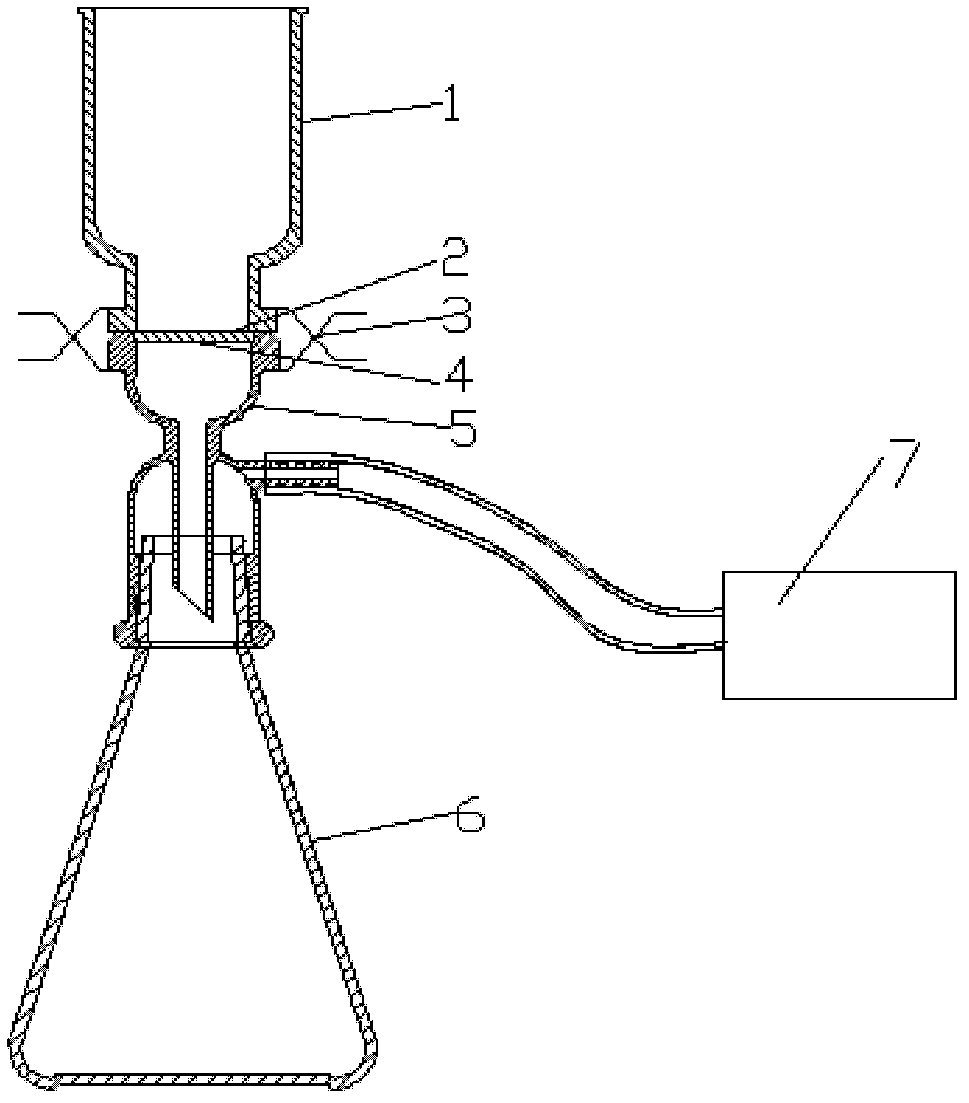
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
333 results about "Polymer matrix composite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
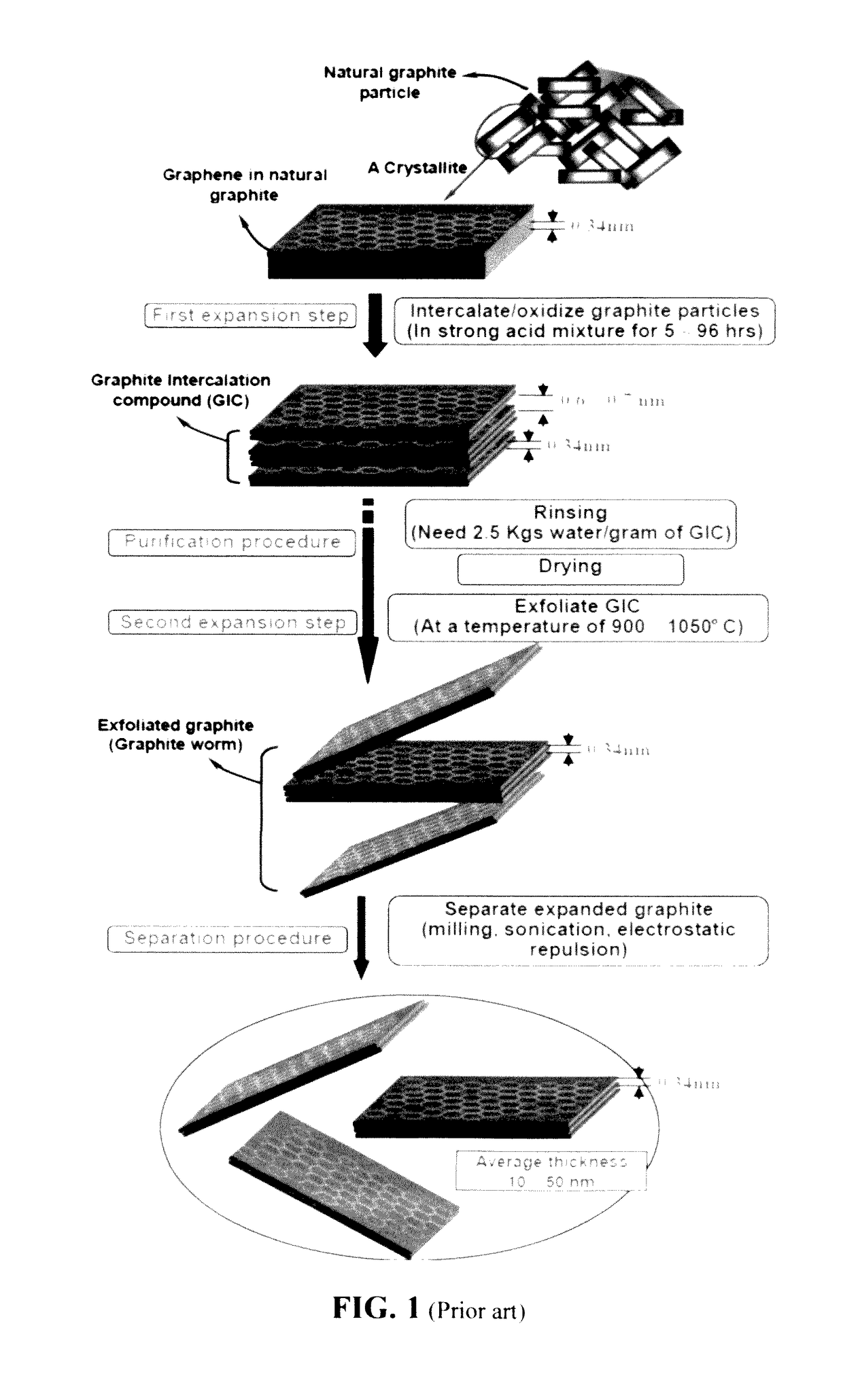
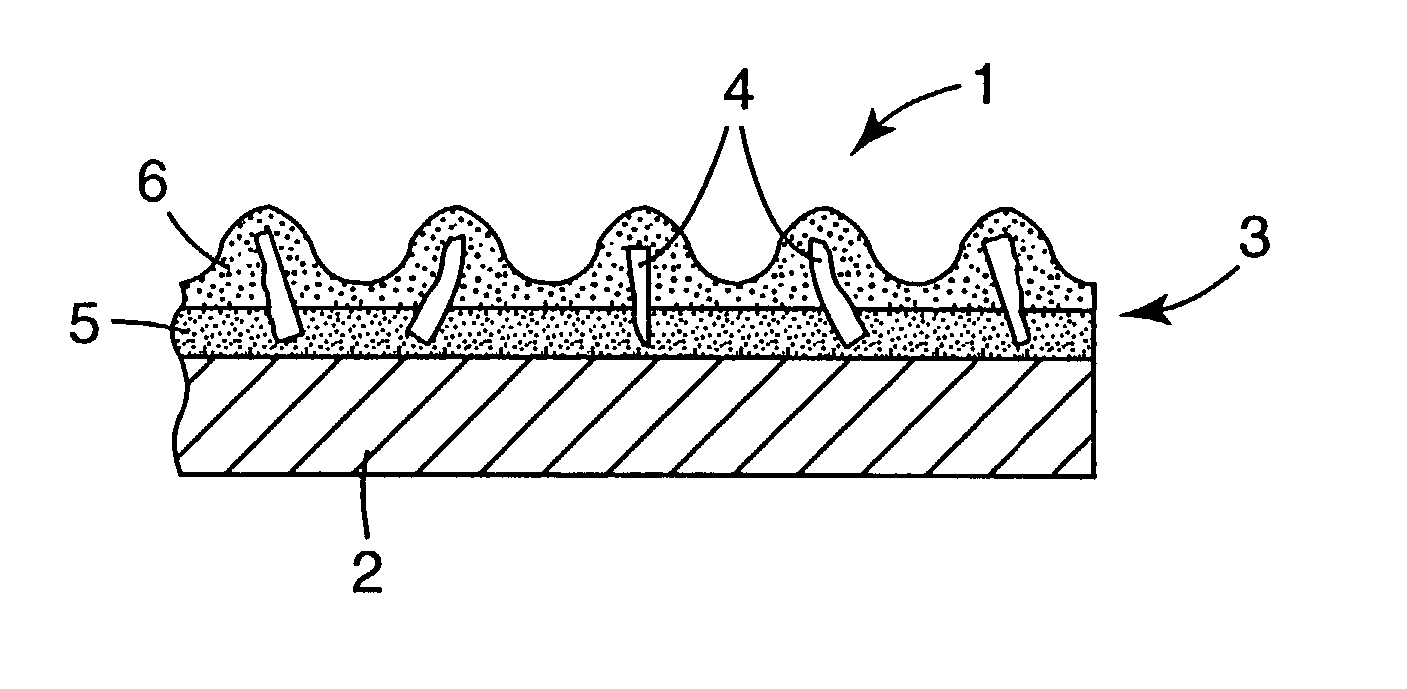
A polymer matrix composite (PMC) is a composite material composed of a variety of short or continuous fibers bound together by an organic polymer matrix. PMCs are designed to transfer loads between fibers through the matrix. Some of the advantages with PMCs include their lightweight, high stiffness and their high strength along the direction of their reinforcements. Other advantages are good abrasion resistance and good corrosion resistance.
Al2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2/HfO2 materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS7507268B2Facilitates formation and homogeneityEliminates and minimizes heat transferPigmenting treatmentGlass drawing apparatusFiberThermal insulation
Al2O3—Y2O3—ZrO2 / HfO2 ceramics (including glasses, crystalline ceramics, and glass-ceramics) and methods of making the same. Ceramics according to the present invention can be made, formed as, or converted into glass beads, articles (e.g., plates), fibers, particles, and thin coatings. The particles and fibers are useful, for example, as thermal insulation, filler, or reinforcing material in composites (e.g., ceramic, metal, or polymeric matrix composites). The thin coatings can be useful, for example, as protective coatings in applications involving wear, as well as for thermal management. Certain ceramic particles according to the present invention can be are particularly useful as abrasive particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Plastic rail system and other building products reinforced with polymer matrix composites
InactiveUS20040009338A1Reduce air pressureBalustersSynthetic resin layered productsBuilding productUltimate tensile strength
Polymeric building materials are provided which include a composite reinforcement comprising continuous filaments of fibers substantially oriented in at least a first direction within a polymeric matrix. The composite reinforcement includes a higher tensile strength and a lower rigidity than aluminum. The building material further includes a capstock polymeric material disposed substantially over the composite reinforcement. The building material is resistant to heat deformation and corrosion. This invention also includes methods for constructing such polymeric composite building materials, including in the preferred embodiments, pultrusion and extrusion steps.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Discontinuous conductive filler polymer-matrix composites for electromagnetic shielding
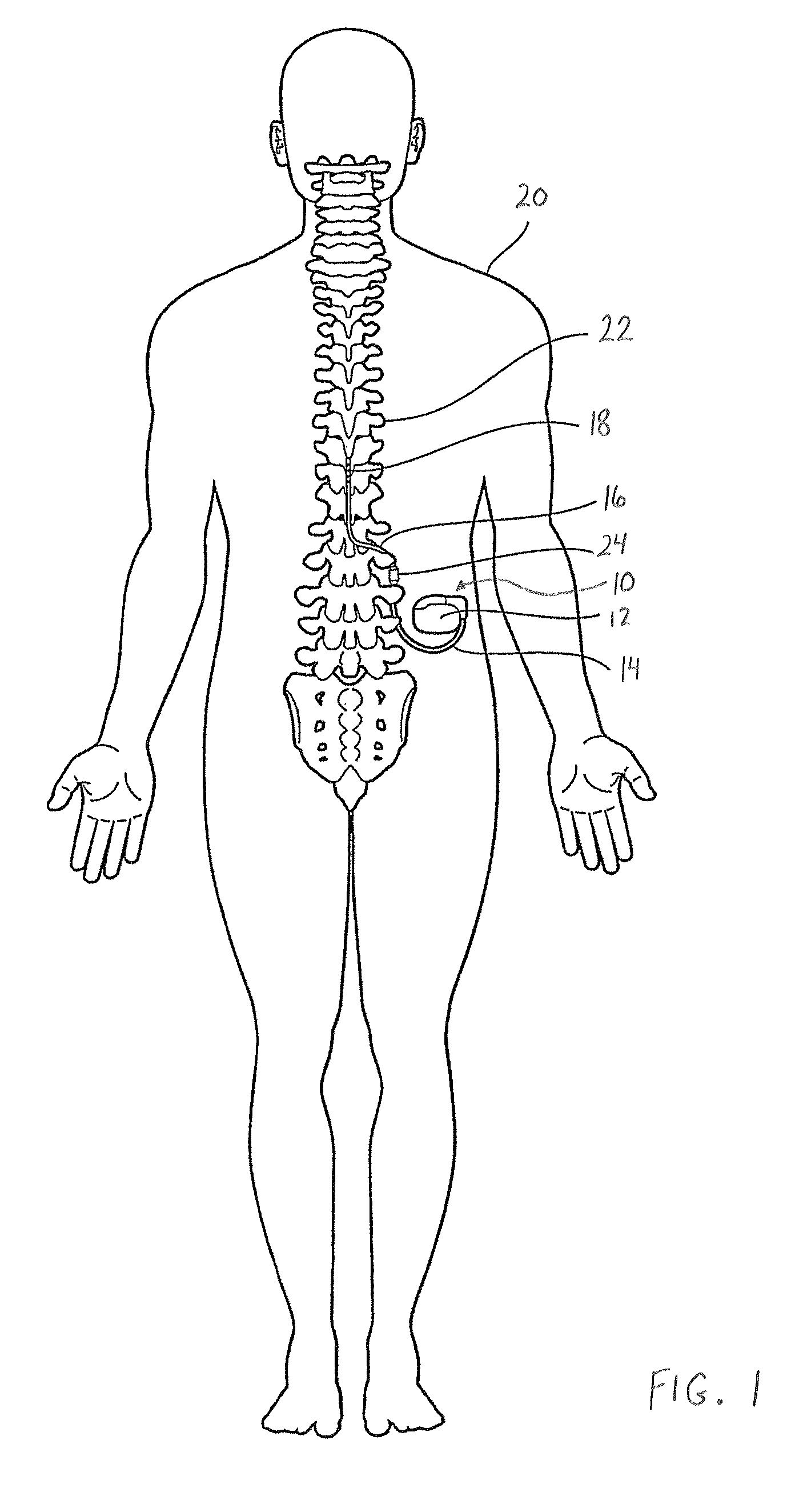
A medical electrical lead having a conductor assembly covered by an insulating layer, and a shield covering positioned adjacent or proximate to at least a portion of the insulating layer in order to shield the conductor assembly from one or more electromagnetic fields. The shield covering is formed of a polymer-matrix composite. The polymer-matrix composite includes a polymeric resin having discontinuous conductive fillers provided therein. The discontinuous conductive fillers include one or more of nano-sized metal structures and nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures. The nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures can have a coating formed of one or more metals. The nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures can be formed of carbon. In turn, the nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures can include one or more of carbon nanofibers, carbon filaments, carbon nanotubes, and carbon nanoflakes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Al2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2/HfO2 materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030110708A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationPigmenting treatmentGlass drawing apparatusFiberThermal insulation
Al2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2 / HfO2 ceramics (including glasses, crystalline ceramics, and glass-ceramics) and methods of making the same. Ceramics according to the present invention can be made, formed as, or converted into glass beads, articles (e.g., plates), fibers, particles, and thin coatings. The particles and fibers are useful, for example, as thermal insulation, filler, or reinforcing material in composites (e.g., ceramic, metal, or polymeric matrix composites). The thin coatings can be useful, for example, as protective coatings in applications involving wear, as well as for thermal management. Certain ceramic particles according to the present invention can be are particularly useful as abrasive particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
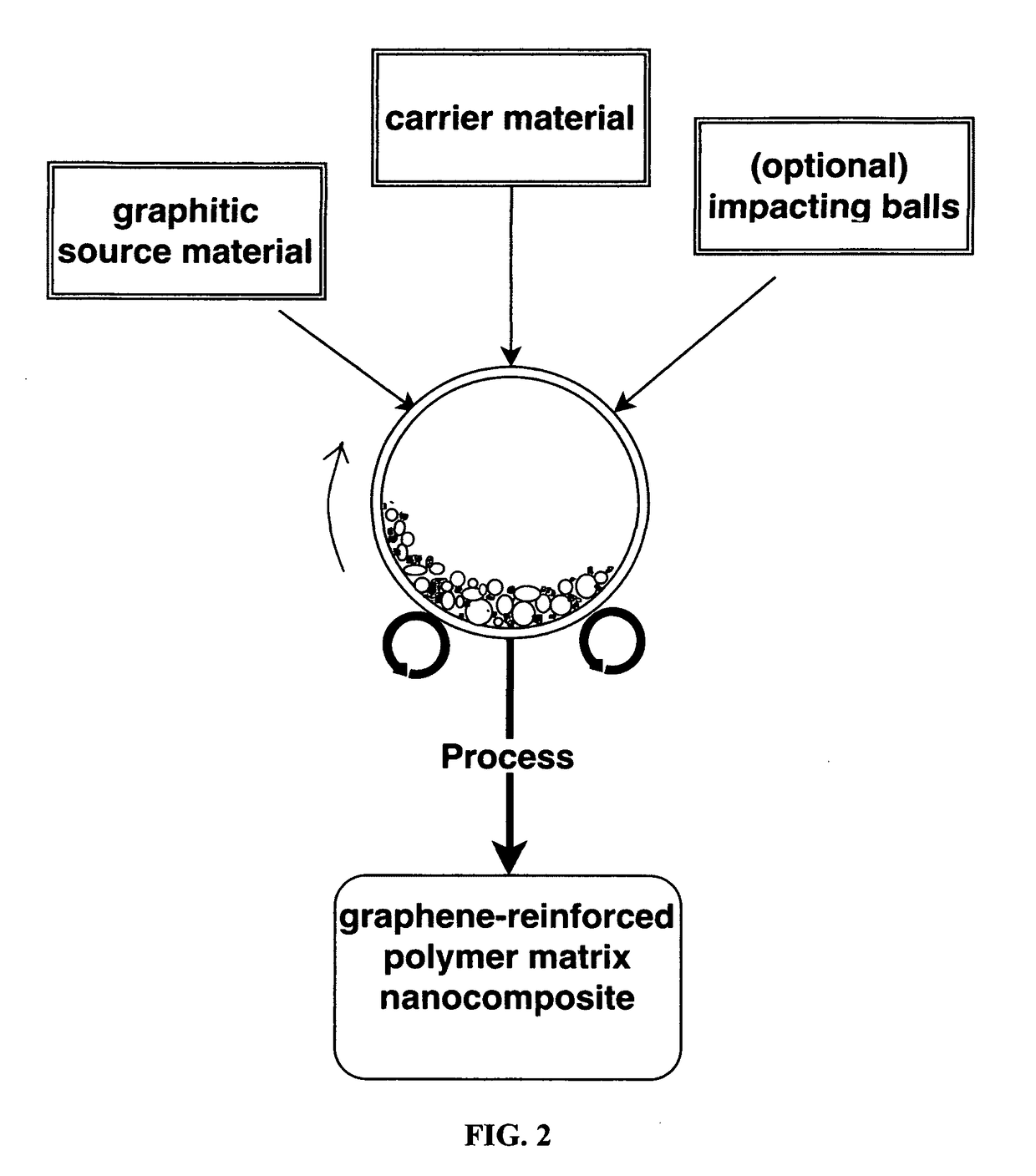
Chemical-free production of graphene-reinforced polymer matrix composites
ActiveUS20170166722A1Optimization propertiesOptimize throughputAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsPolymer scienceGraphite
Provided is a simple, fast, scalable, and environmentally benign method of producing a graphene-reinforced polymer matrix composite directly from a graphitic material, the method comprising: (a) mixing multiple particles of a graphitic material and multiple particles of a solid polymer carrier material to form a mixture in an impacting chamber of an energy impacting apparatus; (b) operating the energy impacting apparatus with a frequency and an intensity for a length of time sufficient for peeling off graphene sheets from the graphitic material and transferring the graphene sheets to surfaces of solid polymer carrier material particles to produce graphene-coated or graphene-embedded polymer particles inside the impacting chamber; and (c) forming graphene-coated or graphene-embedded polymer particles into the graphene-reinforced polymer matrix composite. Also provided is a mass of the graphene-coated or graphene-embedded polymer particles produced by this method.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Graphene filled polymer matrix composite material and its preparation method
ActiveCN103087404AImprove conductivityImprove thermal conductivityIn situ polymerizationMechanical property
The invention discloses a graphene filled polymer matrix composite material. The composite material is prepared through using 90-99 parts by weight of a thermoplastic resin, 0.1-10 parts by weight of a graphene microchip, 0.01-1 part of a coupling agent, and 1-10 parts of a lubricant. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the graphene filled polymer matrix composite material. Compared with other carbon system filled composite materials, the graphene filled polymer matrix composite material has the advantages of easy processing, easy forming, less filler filling amount, wide raw material source, environmental protection and the like. The composite material has the characteristics of excellent electric conductivity, excellent thermal conductivity, good mechanical properties, good dimensional stability, good weather resistance and the like; and compared with present technologies for preparing a graphene / polymer composite material through in-situ polymerization or solution polymerization, the melt blending method for preparing the graphene filled polymer matrix composite material in the invention has the advantages of continuous production, suitableness for the large-scale production, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
Al2O3-rare earth oxide-ZrO2/HfO2 materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030126803A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesFiberThermal insulation
Al2O3-rare earth oxide-ZrO2 / HfO2 ceramics (including glasses, crystalline ceramics, and glass-ceramics) and methods of making the same. Ceramics according to the present invention can be made, formed as, or converted into glass beads, articles (e.g., plates), fibers, particles, and thin coatings. The particles and fibers are useful, for example, as thermal insulation, filler, or reinforcing material in composites (e.g., ceramic, metal, or polymeric matrix composites). The thin coatings can be useful, for example, as protective coatings in applications involving wear, as well as for thermal management. Certain ceramic particles according to the present invention can be are particularly useful as abrasive particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
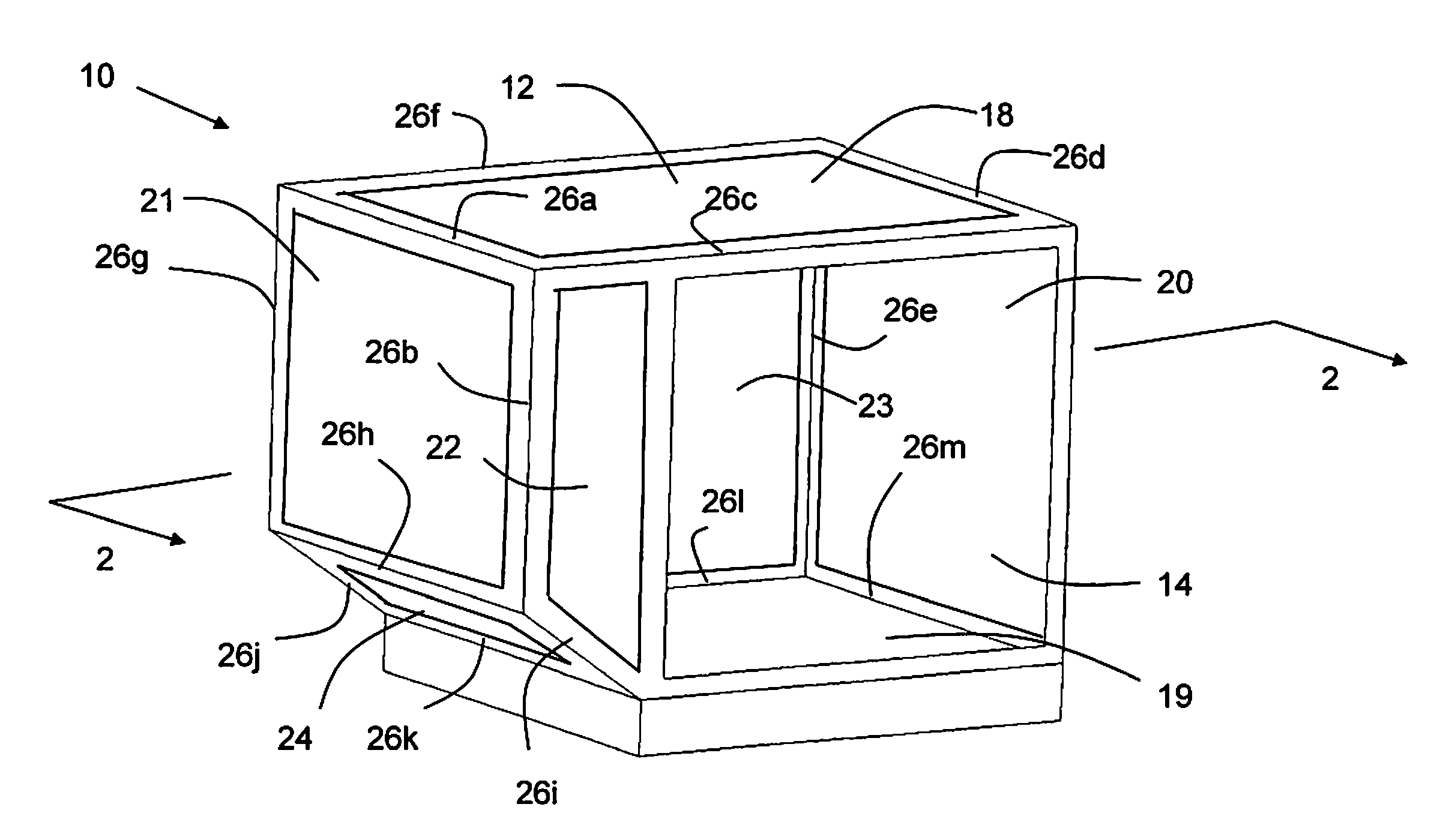
Lightweight unit load device
InactiveUS20110247958A1Reduce weightRaise the ratioSynthetic resin layered productsLarge containersUnit load deviceUnit device
A unit load device constructed from fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite materials is described. Individual panels of the unit load device may be customized with composite materials and patterns. The joints are adapted to receive the ends of the panels of the unit load device and may further be customized with fiber reinforced composite materials to strengthen the joint. Some embodiments provide for construction of a unit load device from a variety of fiber reinforcing materials utilizing a matrix of thermoplastic polymers with similar softening temperatures. Each component part within the container was designed and / or created to address the specific needs of the particular part. The unit load devices described herein provide for all composite containers with a significant weight savings from conventional unit load devices.
Owner:COMPOSITE TRANSPORT TECH
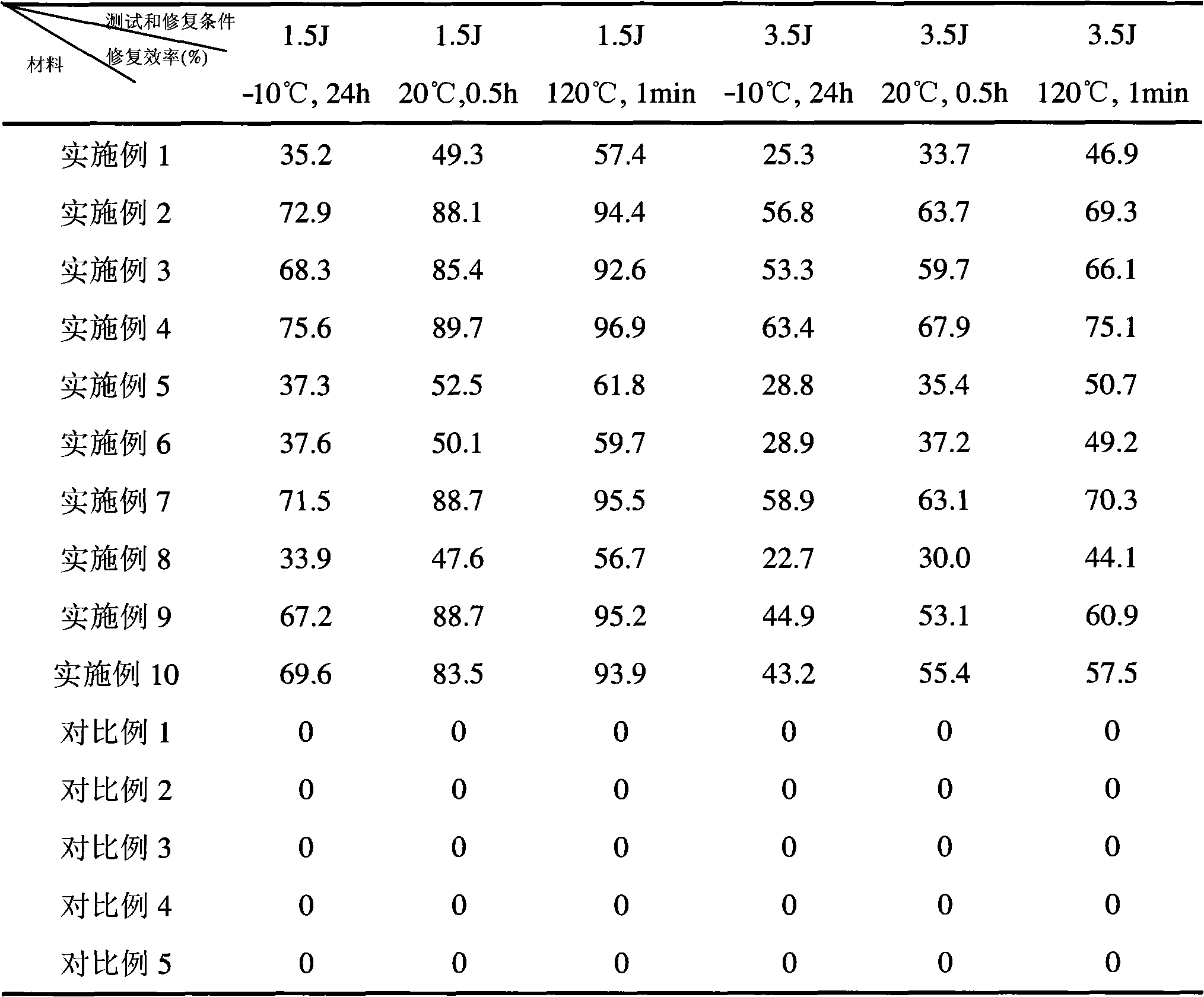
Self-repairing fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a self-repairing fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite and a preparation method thereof. In the method, a double-capsule repairing system respectively containing epoxy resin prepolymer and curing agent is evenly mixed into a resin matrix, then, the matrix curing agent and catalyst are added to be evenly mixed, the obtained mixture is used for dipping fiber reinforcing material, and at last, the self-repairing fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite is obtained by solidifying and shaping. When the self-repairing composite of the invention generates cracks or fiber unsticking damage owing to heat, force, environment corrosion and the like during processing, storing and using process, cracks pass through a restorative capsule which cracks along with the matrix to release reacting substance and quickly polymerize, thus preventing crack from expanding, repairing crack damage, keeping the mechanical property of the composites and prolonging the service life thereof. The self-repairing composite prepared by the invention can automatically finish repairing cracks at the temperature of negative 50-250 DEG C, and the repairing process totally needs no artificial intervention.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
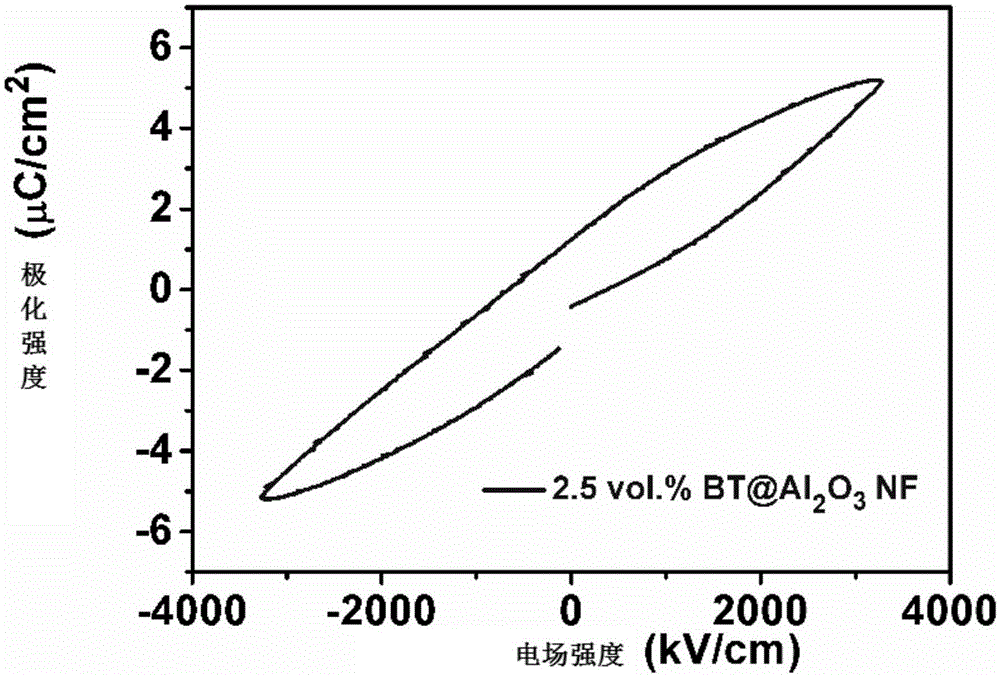
Polymer matrix composite membrane with high energy density and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102504449AHigh dielectric constantHigh breakdown field strengthInorganic material artificial filamentsFibre treatmentFiberHigh energy
The invention discloses a high-flexible polymer matrix composite membrane with high energy density and a preparation method thereof. The composite membrane is composed of a polymer matrix and core-shell structured nano-fibre dispersed in the polymer matrix; the core layer of the core-shell structured nano-fibre is ceramic fibre; the shell layer is an organic matter coated layer, wherein the mass percentage of the polymer matrix is 50-95%; and the mass percentage of the core-shell structured nano-fibre is 5-50%. The polymer matrix and the core-shell structured nano-fibre are composited into the membrane by adopting a solution blending and tape casting method or a bidirectional membrane pulling method, so that a flexible polymer matrix composite material having the advantages of being good in dielectric property, high in breakdown field strength and high in energy density is obtained. The dielectric constant of the composite material can be modulated to 10-40 by adjusting the content of nano ceramic fibre; simultaneously, the dielectric loss Tan delta is kept to be less than 5%, the breakdown field strength is more than 210 kV / mm, and the energy density is 2-6 kJ / L; and the composite material is a material which can be used for capacitors and high power static energy storage.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
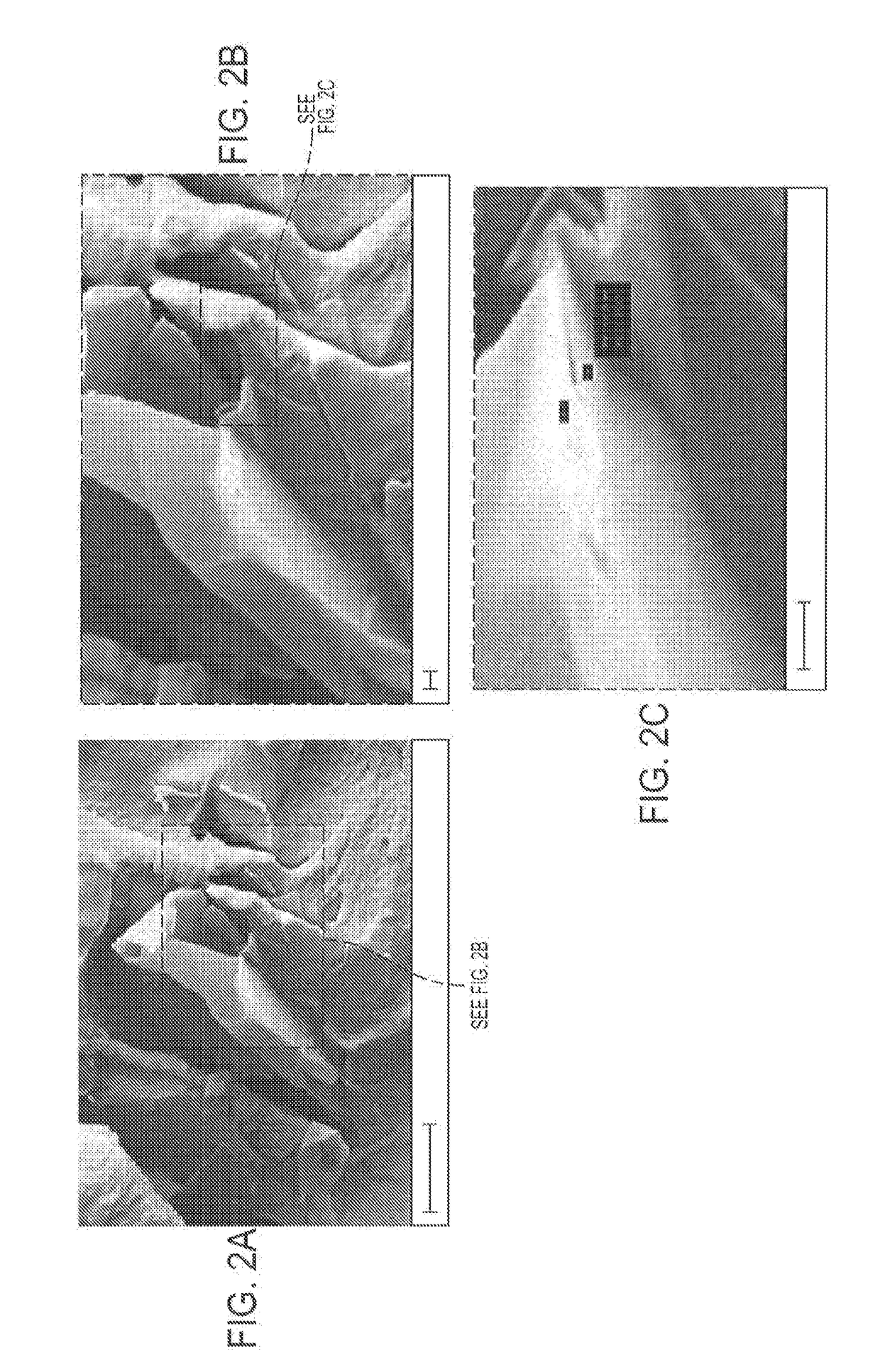
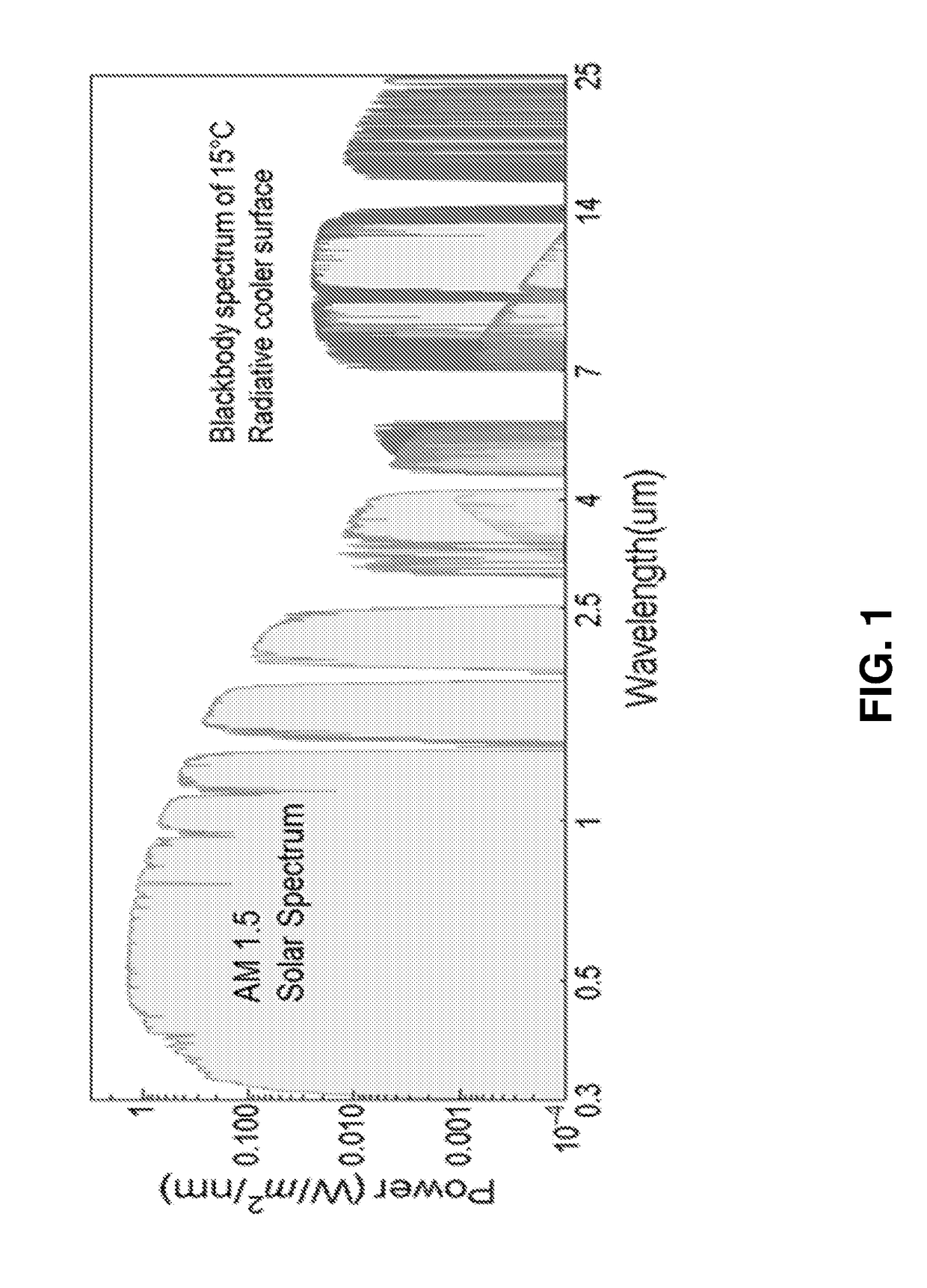
Radiative cooling structures and systems
ActiveUS20170248381A1Cheap and effectiveEasy to integrateSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsThermal radiationRadiative cooling
Polymer-based selective radiative cooling structures are provided which include a selectively emissive layer of a polymer or a polymer matrix composite material. Exemplary selective radiative cooling structures are in the form of a sheet, film or coating. Also provided are methods for removing heat from a body by selective thermal radiation using polymer-based selective radiative cooling structures.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
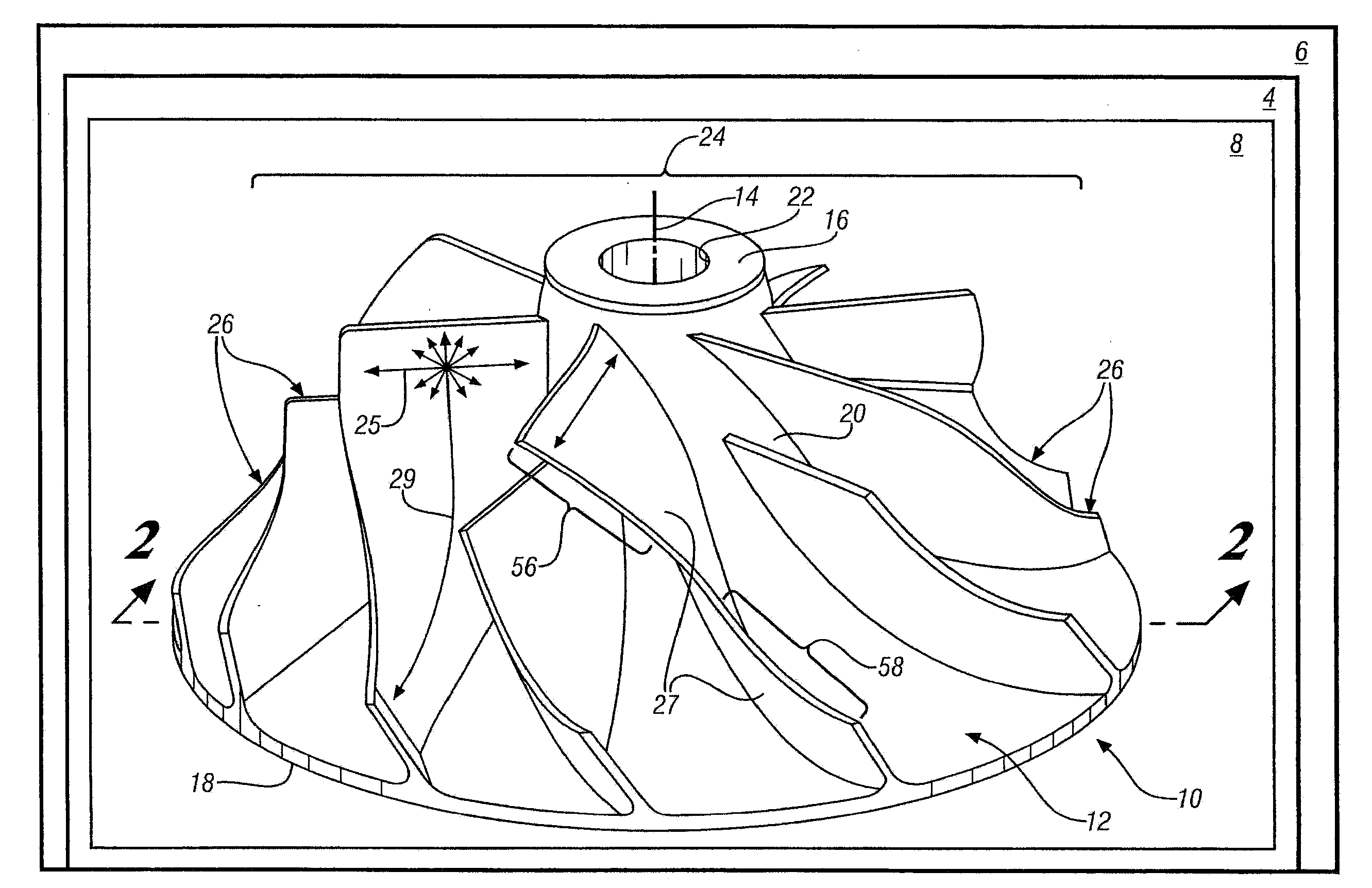
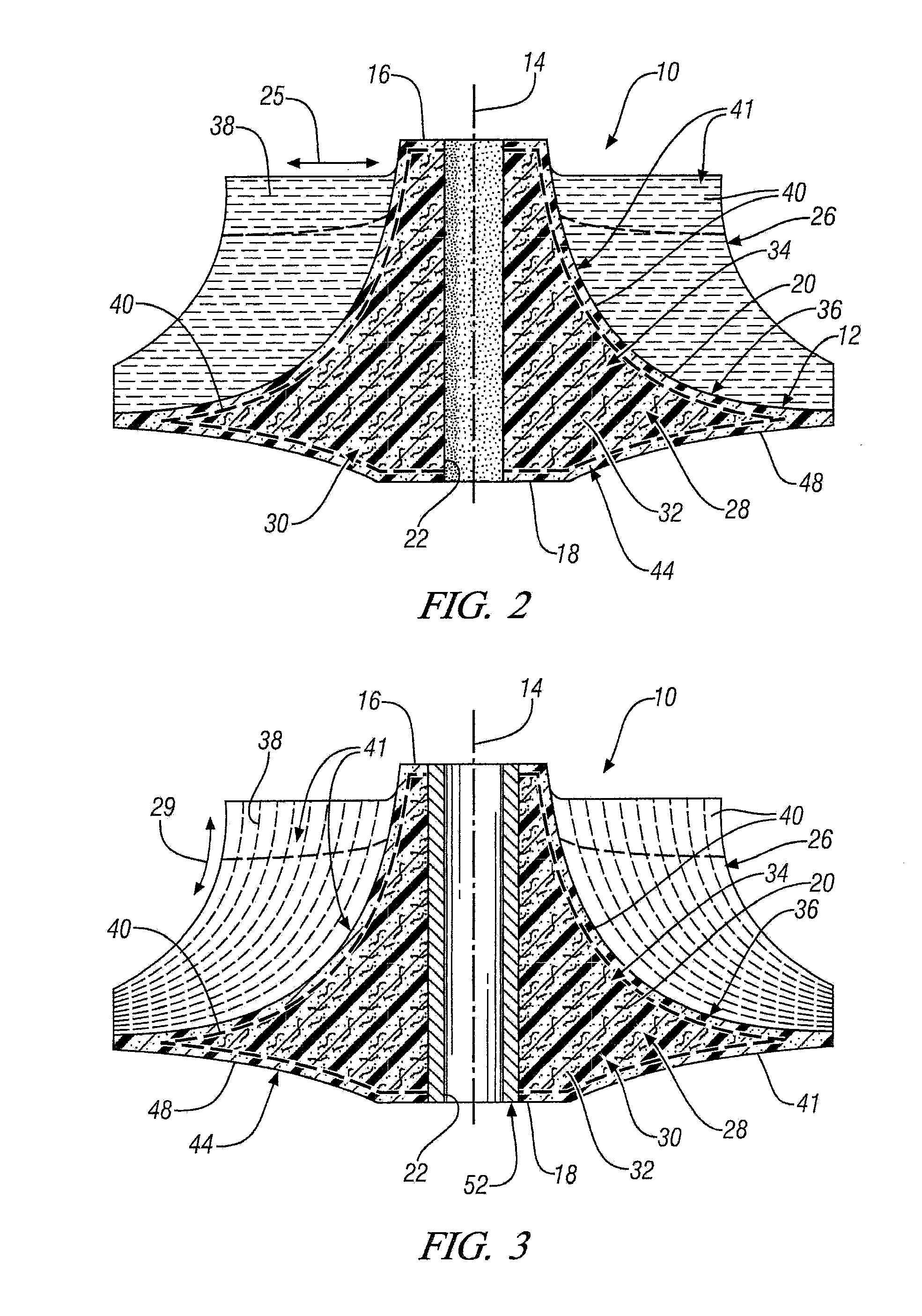
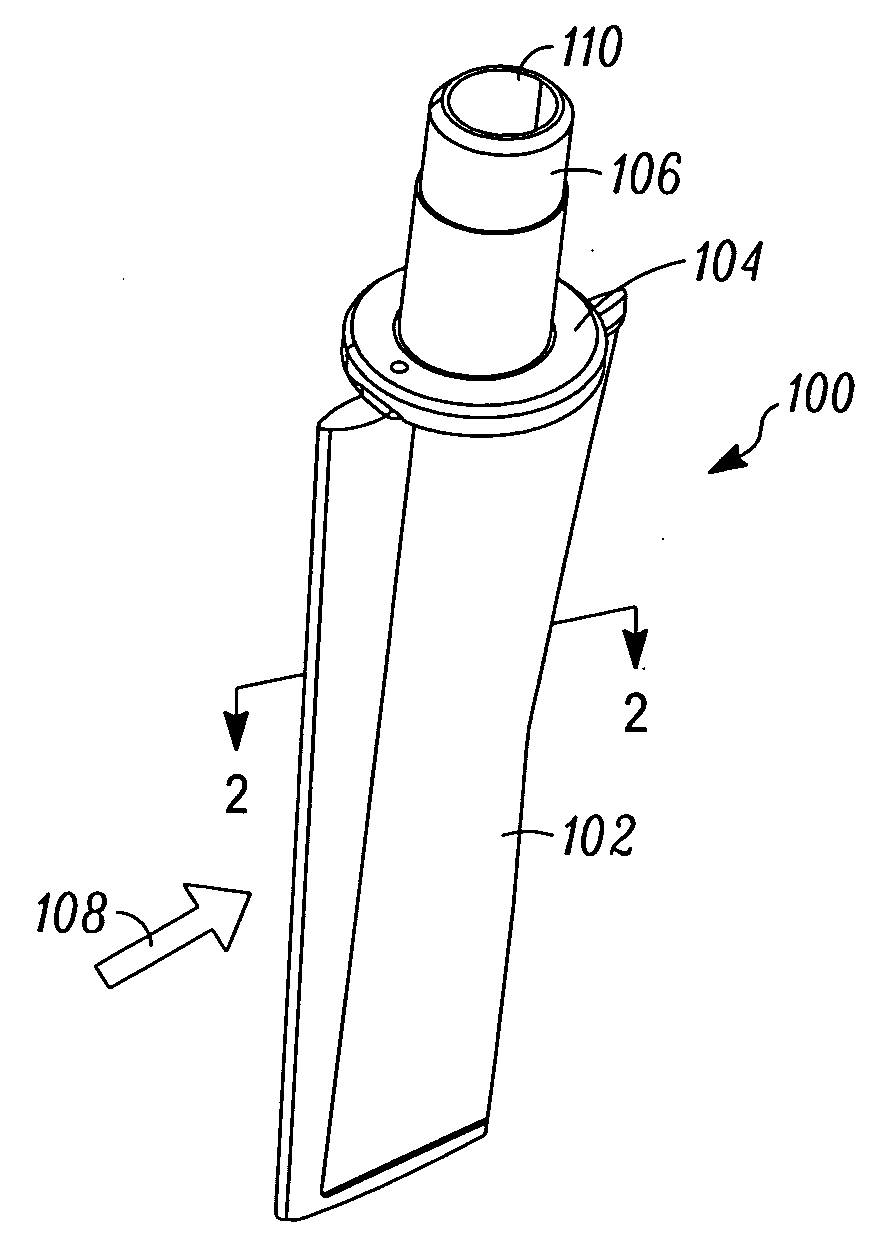
Composite Centrifugal Compressor Wheel
A centrifugal compressor wheel for a turbocharger is disclosed. The wheel includes an axially extending hub having an inlet end, an outlet end, an arcuate outer surface and a shaft bore. The wheel also includes a blade array disposed on the outer surface of the hub, the blade array comprising a plurality of circumferentially-spaced, radially and axially extending, arcuate centrifugal impeller blades disposed thereon; the hub and the blade array comprising a non-woven, discontinuous-fiber-filled, polymer matrix composite material.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
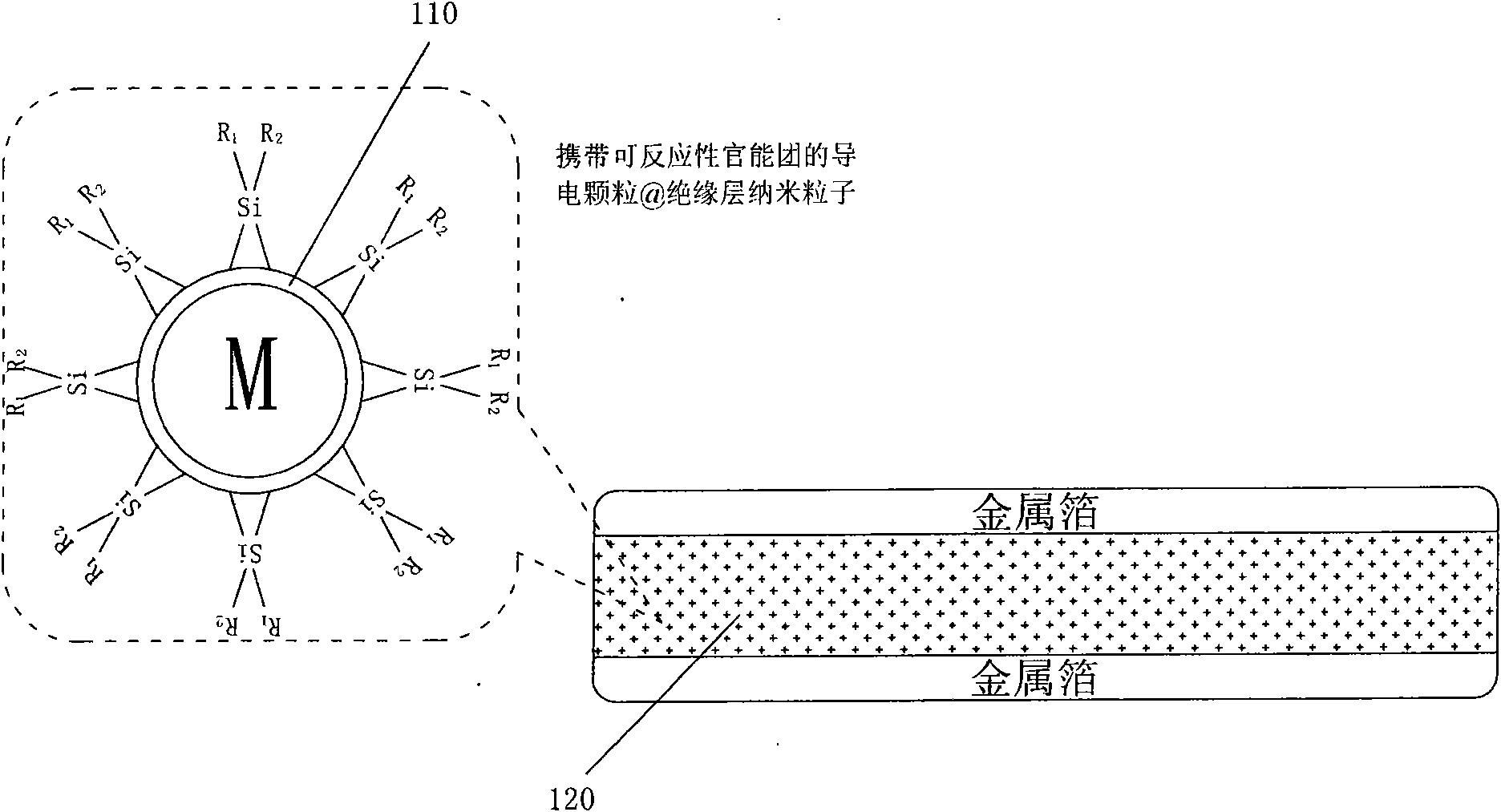
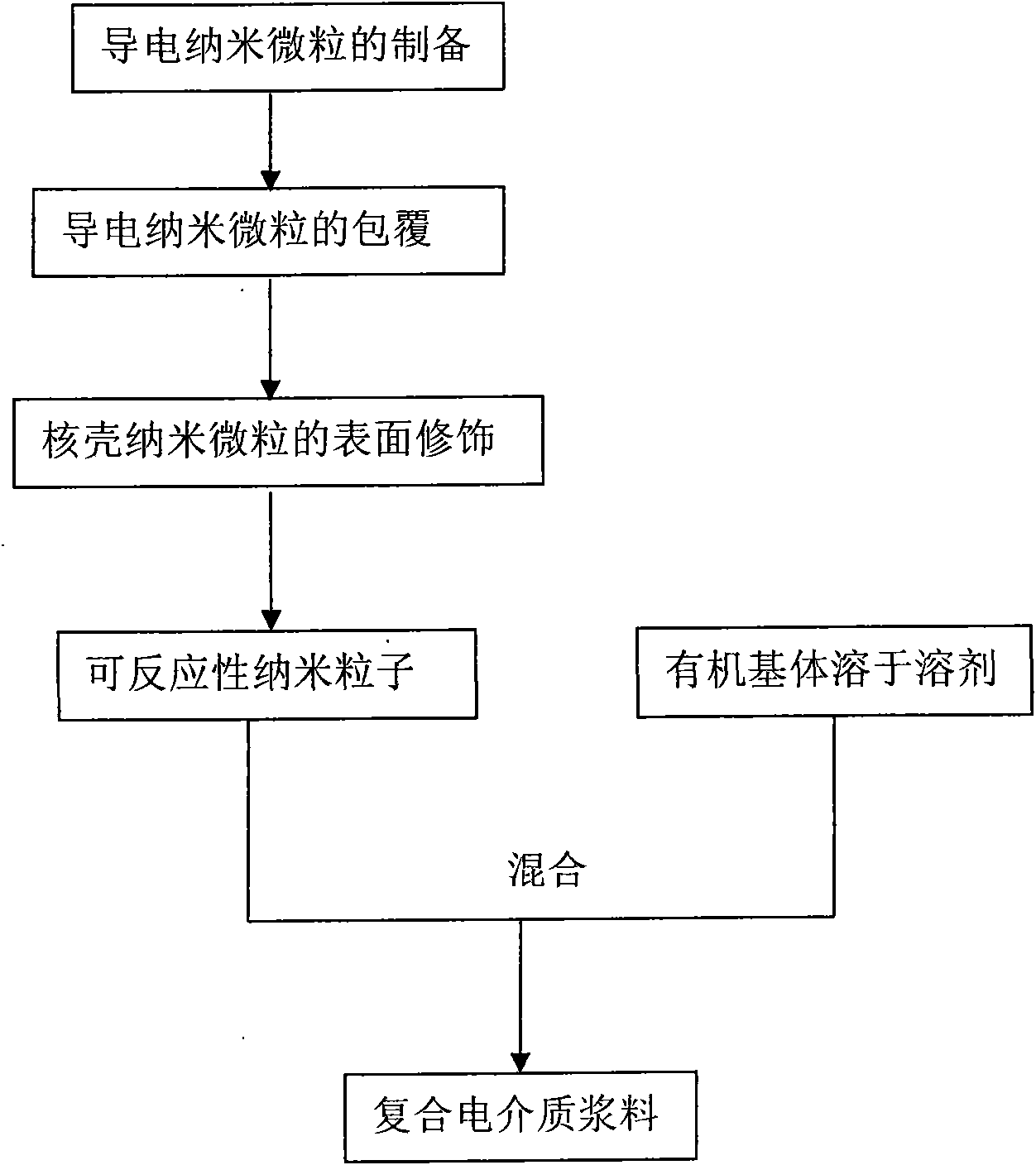
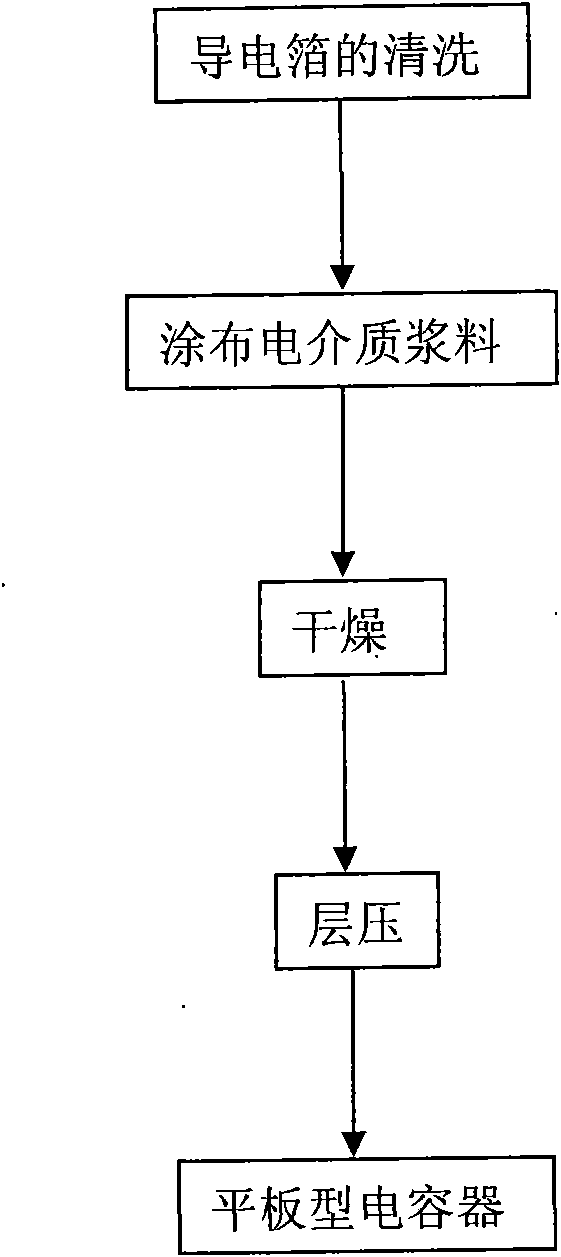
Polymer-matrix composite dielectric material and plate capacitor
ActiveCN101677033AIncrease capacitance densityHigh dielectric constantPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsFixed capacitor electrodesElectronic componentCore shell
The invention discloses a plate capacitor and polymer-matrix composite dielectric material which can be filled with reactive nano particles, belonging to the technical field of the electronic materialand the electronic component. The reactive nano particles are conductive nano particles in core shell structures, the surface of each conductive nano particle is coated with a layer of insulating coating, and the surface of the insulating coating can carry reactive functional groups. The nano particles can be organically combined with polymer through the reactive functional groups and can be evenly dispersed in the matrix of the polymer. The polymer-matrix composite dielectric material which can be filled with the conductive nano particles can be used as the dielectric layer and flexible foilsheets can be used the upper electrode and the lower electrode of the plate capacitor.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
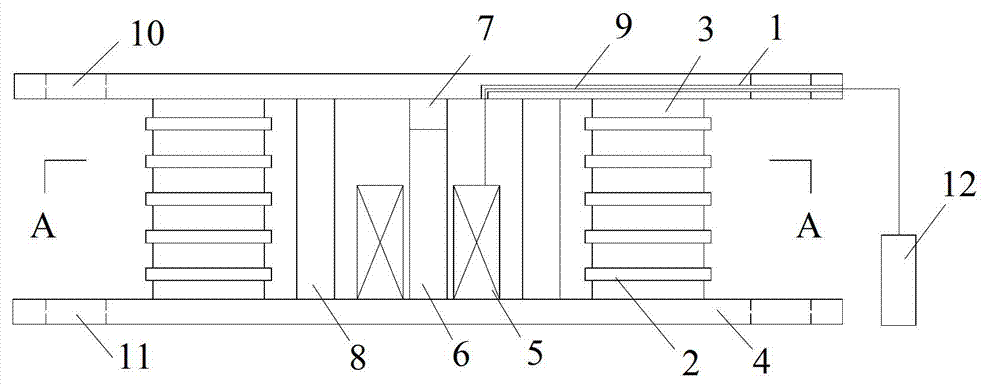
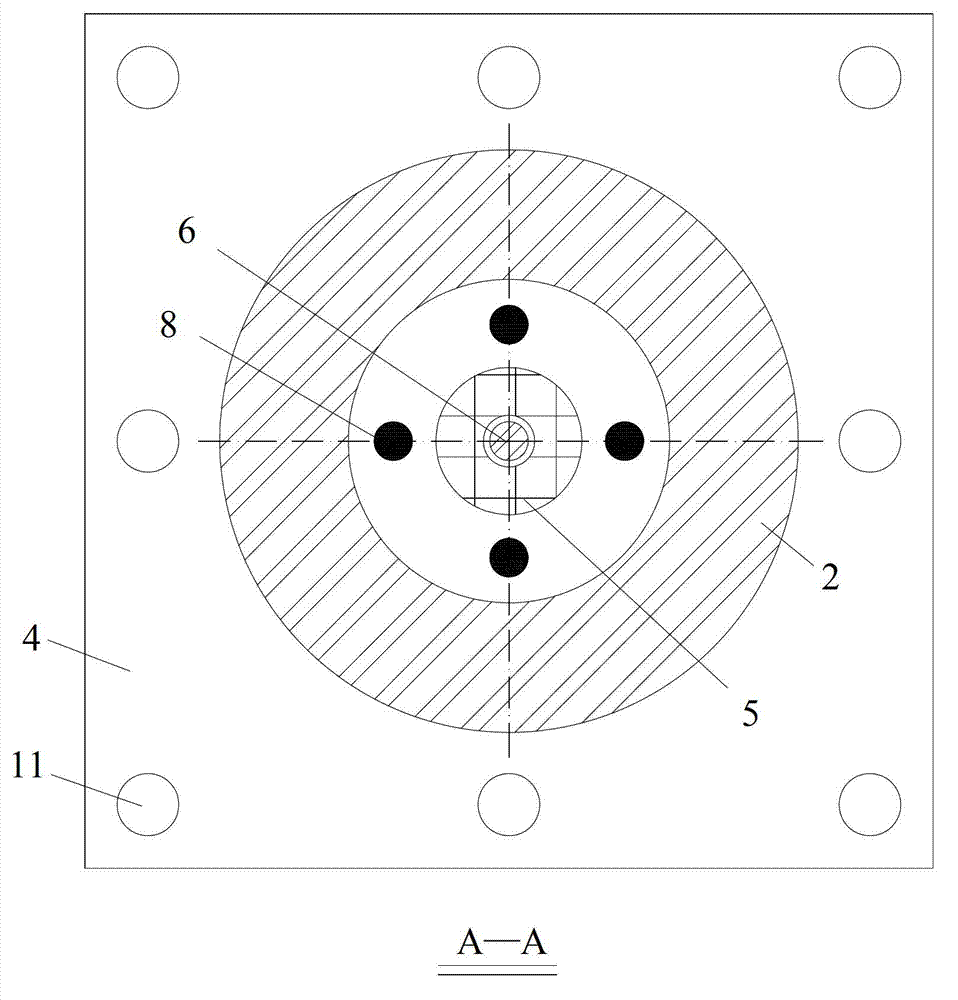
Variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat
InactiveCN102733483ASolve the problem that the stiffness can only be adjusted larger but not smallerAvoid destructionShock proofingEngineeringMagnetorheological elastomer
The invention relates to a variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat and belongs to the technical field of building structure shock absorption. The variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat is characterized by comprising an upper connecting plate (1), a lower connecting plate (4), a magnetic conduction steel plate (2), a magnetorheological elastic body (3), an excitation coil (5), a magnetic conduction iron core (6), a polymer matrix composite permanent magnet material (7), a lead core (8), a conducting wire passage (9), an upper connecting screw bolt hole (10), a lower connecting screw bolt hole (11) and a driving power supply (12), wherein the a magnetorheological elastic body (3) and the magnetic conduction steel plate (2) are in a circular ring shape or a square ring shape, the excitation coil (5) and the magnetic conduction iron core (6) are arranged inside a support seat, and the polymer matrix composite permanent magnet material (7) provides a bias magnetic field for a closed magnetic circuit. The variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat has the effects and benefits that the shock insulation and the variable rigidity are integrated, the structure is simple, the anti-interference performance is high, the two-way rigidity regulation can be realized, different horizontal rigidities can be provided for the structure according to different quake waves, and the destroy of earthquake disasters on building structures and bridge structures is effectively reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
High thermal conductance thermal interface materials based on nanostructured metallic network-polymer composites
InactiveUS20120187332A1Improve thermal conductivityLow filler loading and viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyHeat-exchange elementsNanoparticleNetwork structure
A composite structure provides high thermal conductivity as a thermal interface structure with a relatively low filler loading. The composite structure is formed by dispersing nanoparticles in a matrix at a low filler loading, and controlled sintering of the composite structure to induce agglomeration of the nanoparticles into a connected percolating thermally conducting network structure within the matrix.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Thermotropic type shape memory composite material
InactiveCN105802188ASmall mechanical propertiesImprove mechanical propertiesWoven fabricsCarbon nanotubeDual function
The invention belongs to the field of shape memory functionalized application technology of high performance polymer matrix composite materials, and provides a thermotropic type shape memory composite material. The material comprises the following components: a shape memory polymer and carbon nanotube, wherein the content of the shape memory polymer is 15-85wt%, and the content of the carbon nanotube is 85-15wt%. The carbon nanotube has excellent mechanical properties, electrical property and thermal conductance performance; the carbon nanotube can be used as an enhancer of the polymer matrix composite material, and can be used as a heating element of the thermotropic type shape memory composite material. The thermotropic type shape memory composite material needs to be heated to a certain temperature in order to realize the function thereof, the carbon nanotube of the carbon nanotube enhanced polymer matrix shape memory composite material can be directly electrified for heating, so that dual functions for enhancing and heating the shape memory composite material are realized.
Owner:AVIC COMPOSITES
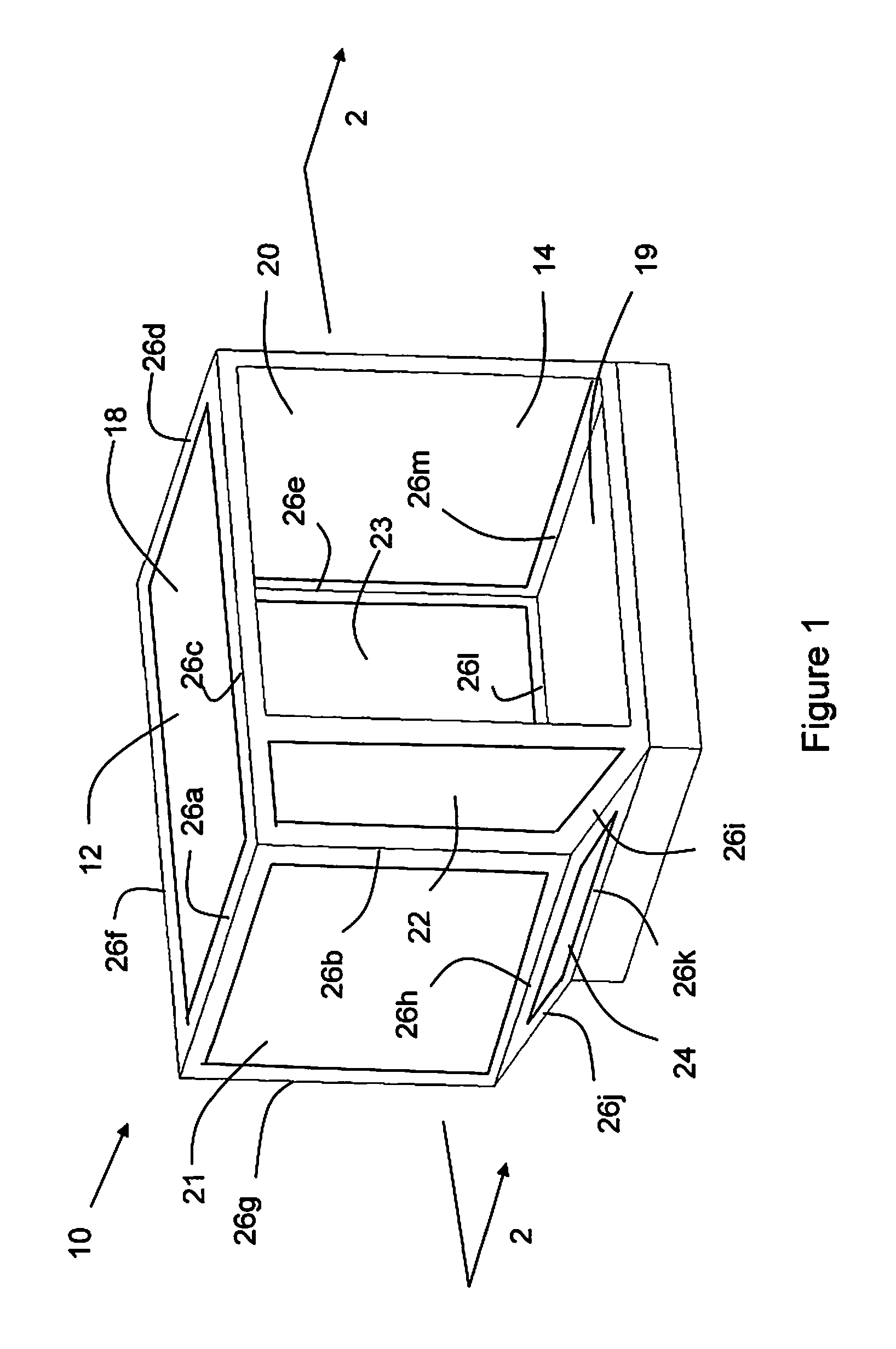
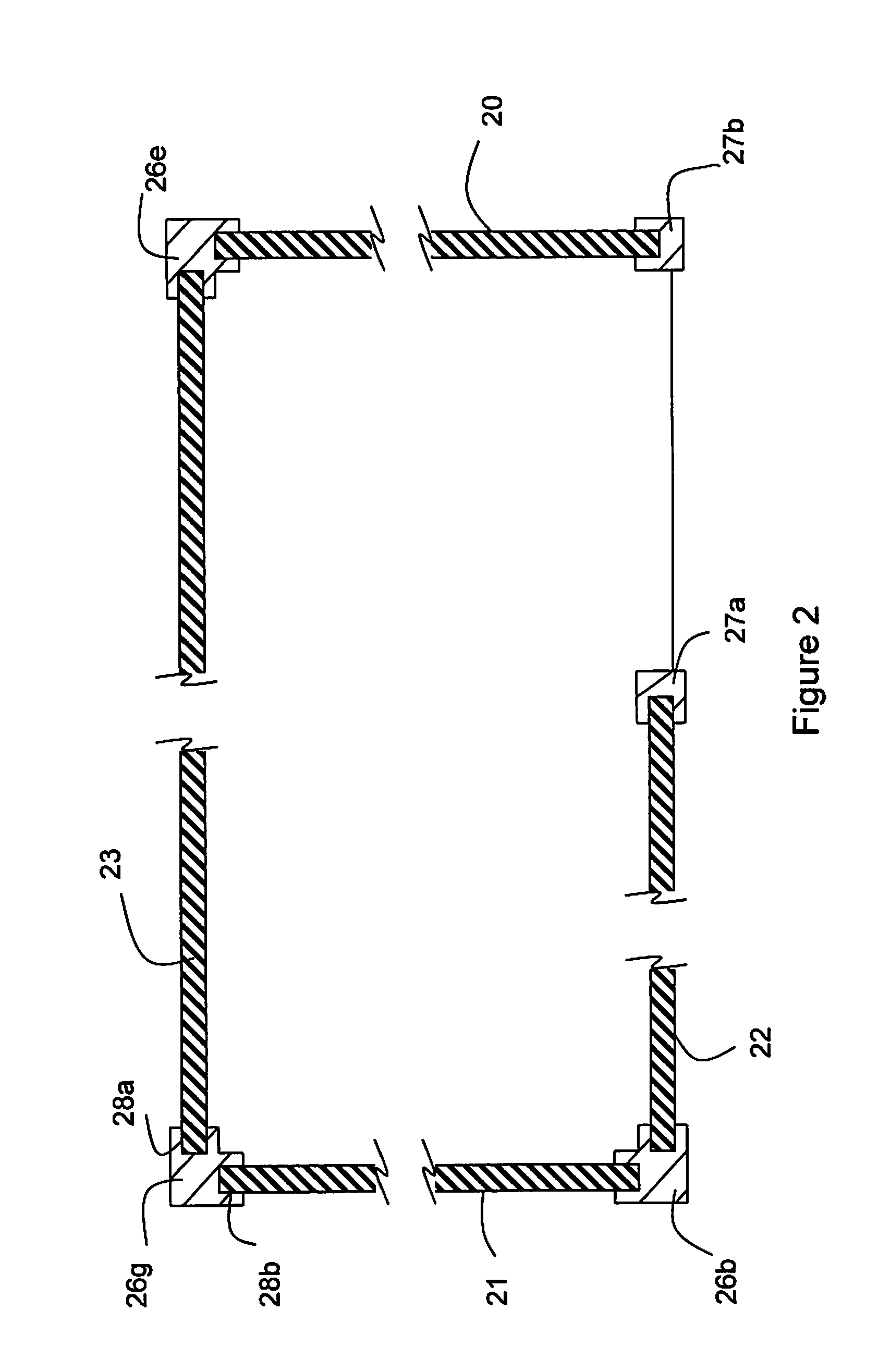
Method for Weaving Closed Structures with Intersecting Walls
ActiveUS20090149100A1Shorten manufacturing timeLow costSmallware loomsOrnamental textile articlesShell moldingTransfer molding
The present invention generally relates to a woven preform for reinforced composite materials and a method of making thereof. Specifically, the present invention is a method of machine weaving fiber preforms for polymer matrix composites that consist of closed perimeters with multiple intersecting members in their interiors. More specifically, the invention is a woven preform and a method of forming thereof with closed cells at the outer edges with continuous hoop reinforcement in each cell of the preform. The woven preform is woven flat in both the warp and weft directions, and then unfolded to achieve the final shape of the structure, and can be processed into composite structural components using known methods such as resin transfer molding or chemical vapor infiltration. Thus, complicated shapes of all sizes can be woven on a conventional loom using the instant method.
Owner:ALBANY ENGINEERED COMPOSITES
Discontinuous conductive filler polymer-matrix composites for electromagnetic shielding
ActiveUS9044593B2Internal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical conductorCarbon nanofiber
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
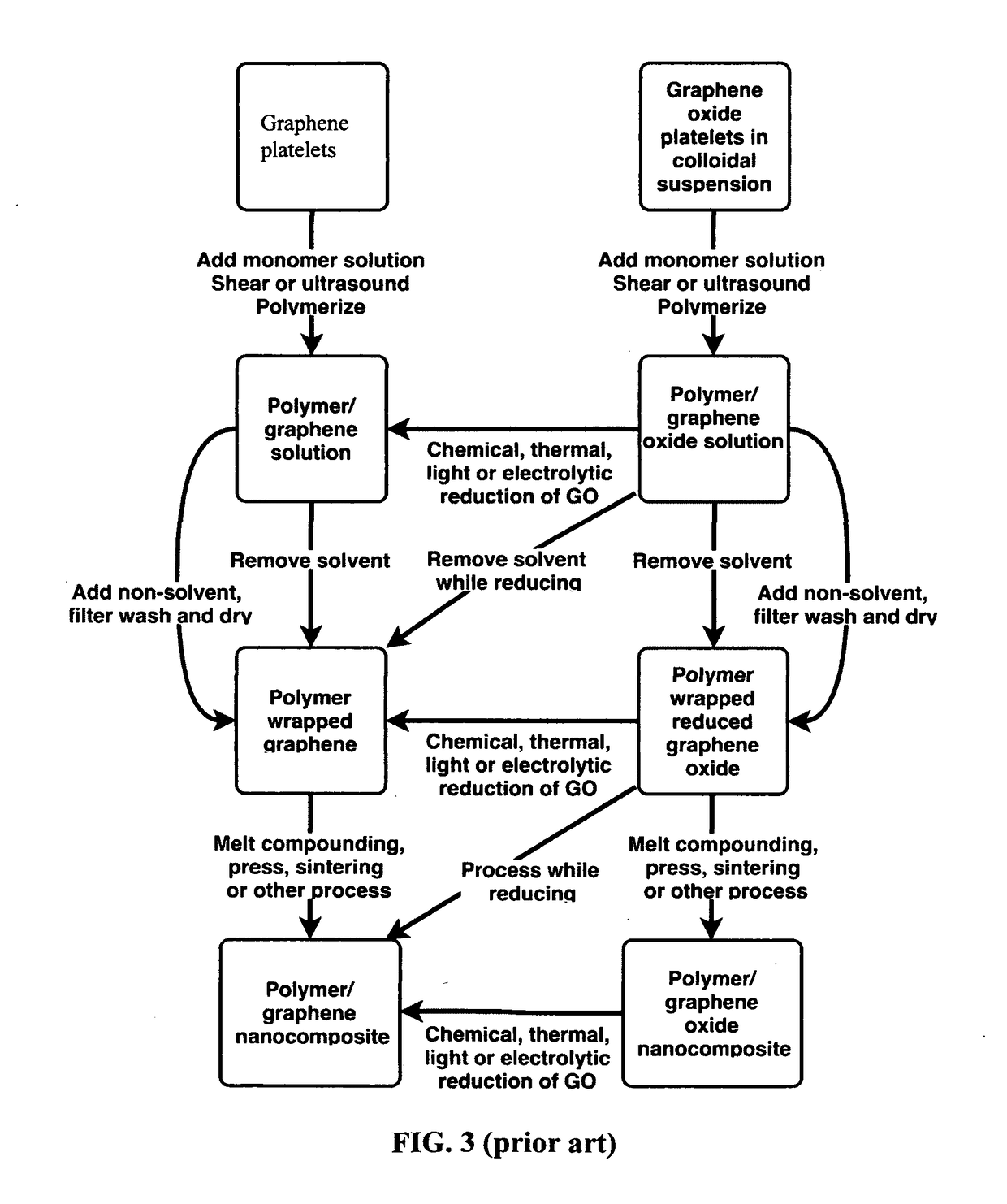
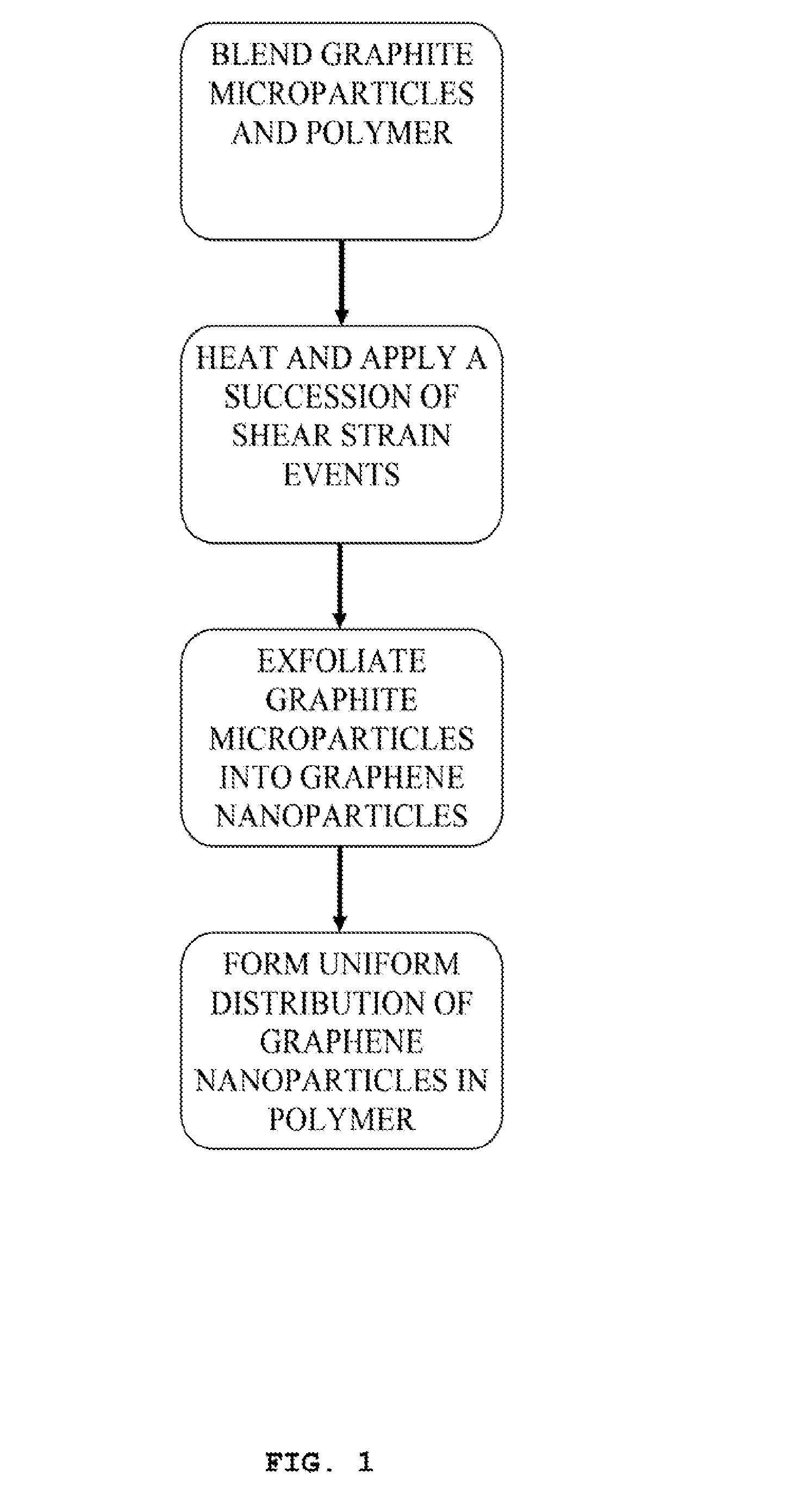
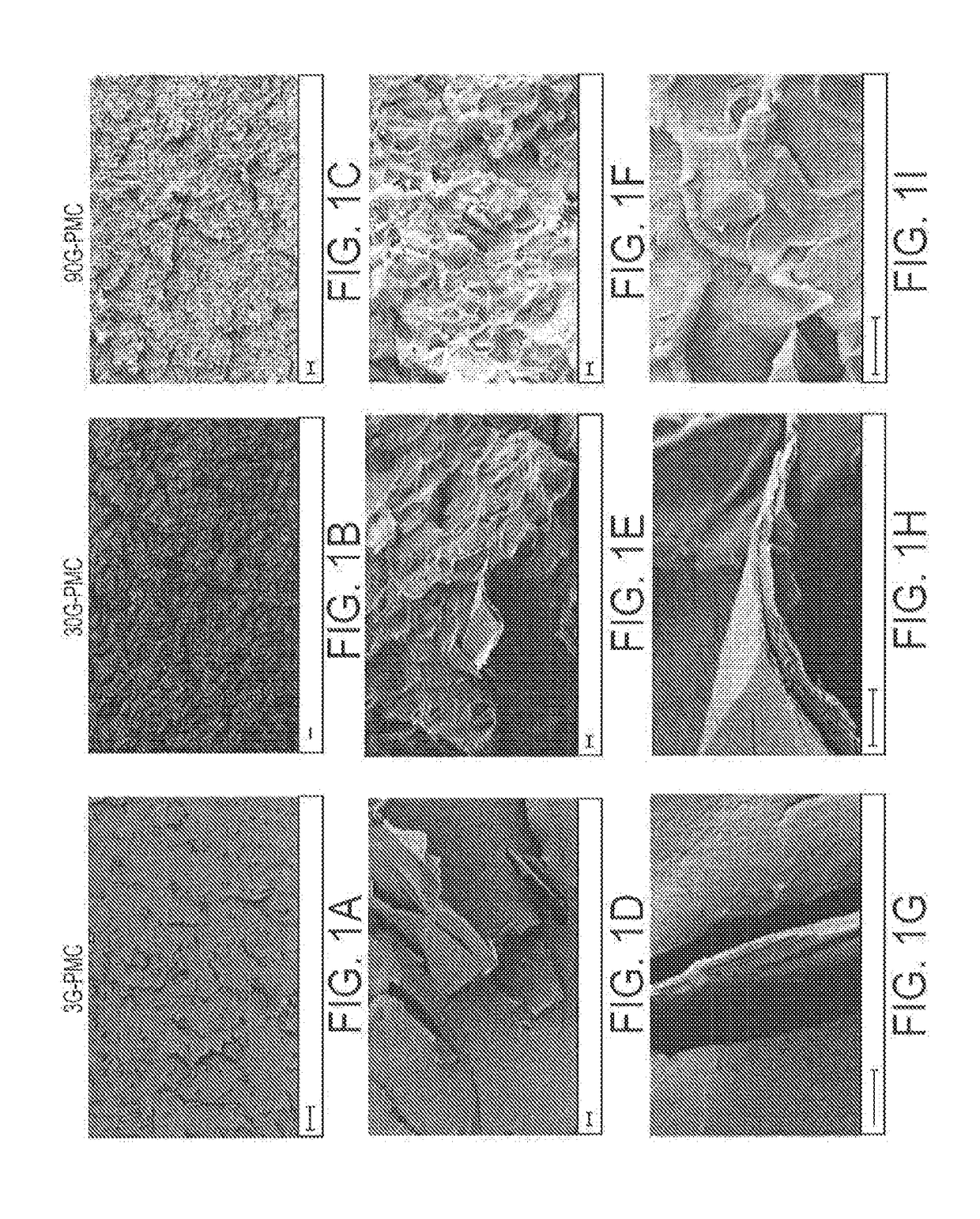
In Situ Exfoliation Method to Fabricate a Graphene-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite (G-PMC)
ActiveUS20150267030A1High bonding strengthHigh strengthLayered productsGraphenePolymer scienceMicroparticle
A method for forming a graphene -reinforced polymer matrix composite is disclosed. The method includes distributing graphite microparticles into a molten thermoplastic polymer phase; and applying a succession of shear strain events to the molten polymer phase so that the molten polymer phase exfoliates the graphite successively with each event until at least 50% of the graphite is exfoliated to form a distribution in the molten polymer phase of single- and multi-layer graphene nanoparticles less than 50 nanometers thick along the c-axis direction.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
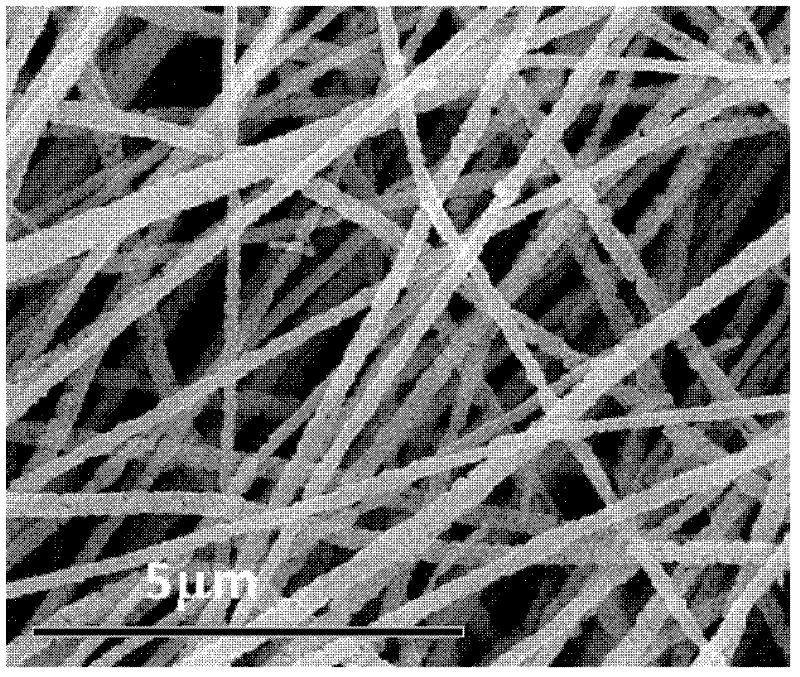
Method for preparing carbon nanometer paper enhanced conductive polymer matrix composite material
The invention provides a method for preparing a carbon nanometer paper enhanced conductive polymer matrix composite material, which is intended to solves a problem that integral mechanical properties and electroconductivity of a current carbon nanotube composite material cannot completely reaches engineering application requirements. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes or single-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide are dispersed in a plasma aqueous solution under action of supersonic waves by an anionic surfactant, after high speed centrifugation, a supernatant liquid of the carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide solution is obtained, and flexible carbon nanometer paper with thickness of 10-100mum can be prepared as an enhanced material by a vacuum filtration method. The carbon nanometer paper enhanced conductive polymer matrix composite materials can be prepared by an RTM forming or vacuum bag method, and conductivity can be raised by raising the content of the carbon nanotubes and dispersion uniformity of carbon nanotube grids in the composite material, wherein the conductivity of the nanocomposite can be raised in several orders of magnitude, and can reach 1-200S / m, thereby making the polymer matrix composite materials go into a semiconductor conductive material field from an insulator.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Graphene-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites
ActiveUS20170218141A1Improve mechanical propertiesHigh strengthGraphiteSingle layer graphenePolymer scienceSingle layer graphene
A graphene-reinforced polymer matrix composite comprising an essentially uniform distribution in a thermoplastic polymer of about 10% to about 50% of total composite weight of particles selected from graphite microp articles, single-layer graphene nanoparticles, multilayer graphene nanoparticles, and combinations thereof, where at least 50 wt % of the particles consist of single- and / or multi-layer graphene nanoparticles less than 50 nanometers thick along a c-axis direction. The graphene-reinforced polymer matrix is prepared by a method comprising (a) distributing graphite microparticles into a molten thermoplastic polymer phase comprising one or more matrix polymers; and (b) applying a succession of shear strain events to the molten polymer phase so that the matrix polymers exfoliate the graphite successively with each event until at least 50% of the graphite is exfoliated to form a distribution in the molten polymer phase of single- and multi-layer graphene nanoparticles less than 50 nanometers thick along a c-axis direction.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Radiative cooling structures and systems
ActiveUS20190086164A1Low costEasy to integrateHeat storage plantsClimate change adaptationThermal radiationRadiative cooling
Polymer-based selective radiative cooling structures are provided which include a selectively emissive layer of a polymer or a polymer matrix composite material. Exemplary selective radiative cooling structures are in the form of a sheet, film or coating. Also provided are methods for removing heat from a body by selective thermal radiation using polymer-based selective radiative cooling structures.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Polymer-matrix composite material with super-hydrophobic surface and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101830098AImprove self-cleaning effectReduce performanceNanostructure manufactureSynthetic resin layered productsFiberCarbon fibers
The invention belongs to the field of a super-hydrophobic composite material and a preparation method thereof and specifically discloses a polymer-matrix composite material with a super-hydrophobic surface and a preparation method thereof. The polymer-matrix composite material comprises a composite material body and a super-hydrophobic coating coated thereon, wherein, the composite material body is a carbon fiber or glass fiber reinforced composite material, and a microgranitic structure with the diameter of 10 mu m-30mu m is distributed on the super-hydrophobic coating; and the contact angle between the surface of the super-hydrophobic coating and water is 150-160 degrees, and the roll angle of water drops on the surface is below 10 degrees. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly preprocessing the surface of the composite material body; painting and flattening a resin system on the surface; spraying metallic oxide nano-powder on the surface of the resin system; and finally heating and curing, and then self-assembling in stearic acid ethanol solution or other similar solutions to obtain the composite material. The polymer-matrix composite material of the invention has the advantages of strong self-cleanness, strong anti-moisture absorption property, strong anti-freezing property, long service life, stable hydrophobic property and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Polymer matrix composite and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a polymer matrix composite and a preparation method thereof. The composite is a laminated film composed of a polyvinylidene difluoride matrix and a nano-fiber material dispersed in the polyvinylidene difluoride matrix. The nano-fiber material is of a core-shell structure, wherein a core layer is made of a ceramic fiber, and a shell layer is an aluminum oxide coating layer. The polymer matrix composite is prepared through the method comprises the following steps: (1) placing the ceramic fiber in mixed solution of aluminum nitrate, polyvinyl pyrrolidone and ethyl alcohol, and after uniform mixing, obtaining the nano-fiber material through sintering; (2) causing the nano-fiber material to undergo surface modification through a coupling agent, then adding the nano-fiber material into mixture of polyvinylidene difluoride and dimethylformamide, performing uniform mixing, pouring the mixture in a casting film machine to form a film through flow-casting, and performing drying to obtain the laminated film; (4) and causing the laminated film to undergo heating and heat insulation, quenching and drying, and obtaining the polymer matrix laminated film. Compared with the prior art, the polymer matrix composite has the advantages that the laminated film is high in energy density, good in energy storage efficiency, simple in preparation process and low in cost.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Erosion-protective coatings on polymer-matrix composites and components incorporating such coated composites
A stator vane is provided that includes an airfoil and a coating. The airfoil comprises a polymer matrix fiber composite having a melting point, glass transition temperature, or maximum exposure temperature that is less than about 150° C. The coating is formed over the airfoil and comprises a material that is more erosion-resistant than the polymer matrix fiber composite, where the material is the selected from a group of constituents consisting of titanium, chromium, vanadium, and zirconium, and nitrides, carbides, mixed carbonitrides, oxides, oxynitrides, oxycarbides, and oxycarbonitrides thereof. Methods for making the stator vane are provided as well.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Load-bearing structures for aircraft engines and processes therefor
InactiveUS20130119191A1Constant cross-sectional thicknessLow costPower plant constructionEfficient propulsion technologiesResin matrixEngineering
Load-bearing structures constructed from polymer matrix composite (PMC) materials, and processes for their production. The structures are produced from at least one shaped panel formed of a continuous fiber reinforcement in a thermoplastic resin matrix. The shaped panel has been thermoformed to have a substantially constant cross-sectional thickness and portions that lie in different planes and are interconnected by one or more bends. The shaped panel is machined to alter its shape, and optionally to produce multiple separate subcomponents therefrom. The machined shaped panel can constitute the entire structure, or the structure can be formed by joining the machined shaped panel with other shaped panels or by joining two or more of the subcomponents. The structure can be installed on an aircraft engine to secure components to the engine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for carrying out graft modification on graphene by virtue of styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer
The invention discloses a method for carrying out graft modification on graphene by virtue of a styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer. The method comprises the following steps: taking graphite powder as a raw material, preparing graphene oxide (GO) by utilizing an improved Hummers' process, then grafting maleic anhydride to the GO by adopting a monomer grafting way, then taking a free radical initiator, styrene and maleic anhydride as functional modification reagents, carrying out in situ polymerization, solvent washing and centrifugal separation, and drying, so that styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer grafted graphene oxide is obtained. Grafting ratio of the obtained SMAFG is 20-50%. The styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer grafted graphene oxide can be well dispersed and form stable chemical bonding in a process of preparing a styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer grafted graphene oxide / polymer matrix composite material with the polymer matrix and has the effect of better improving mechanical and thermal properties of a polymer.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Polymer matrix composite
InactiveUS20050074993A1Enhances fiber orientationLarge aspect ratioElectrode carriers/collectorsNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPolymer sciencePolymer matrix composite
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Methods for creating spatially controlled composite materials
ActiveUS8071171B1Improve performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusVariable stiffnessComposite laminates
Methods and systems for controlling a three(3)-dimensional distribution of structural reinforcement elements in a polymer-matrix composite. One embodiment of the invention provides a method that includes adding and curing a shape memory polymer in a plurality of flexible preforms attached with each other after preforming each of the flexible preforms to form a spatially controlled preform and variable stiffness material composite laminate. Here, in this embodiment, at least one of the preforms includes a flexible support formed from a patterned supporting material on a first surface of a stiff-structural sheet and the stiff-structural sheet that has been patterned on the support.
Owner:HRL LAB
Polymer-matrix composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a polymer-matrix composite material and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of preparation of electronic composite materials. The composite material is prepared from metal passivation fillers and polymer materials with different shapes, wherein the fillers are metal passivation particles and fibrous or platy metal with two grain sizes, which are matched with each other at a certain proportion, and according to the formula, the volume ratio of polymer is that the metal filler accounts for 1%-50% and the polymer accounts for 50%-99%. The composite material prepared from the metal passivation fillers with the different shapes and the polymer matrix has the advantages of high heat conductivity, low dielectric constant, low dielectric loss and the like. The preparation method has the characteristics of low heat treatment temperature, low cost and environment friendliness, and also has the characteristics of being simple to operate and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com