Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Phylogenetic profiling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
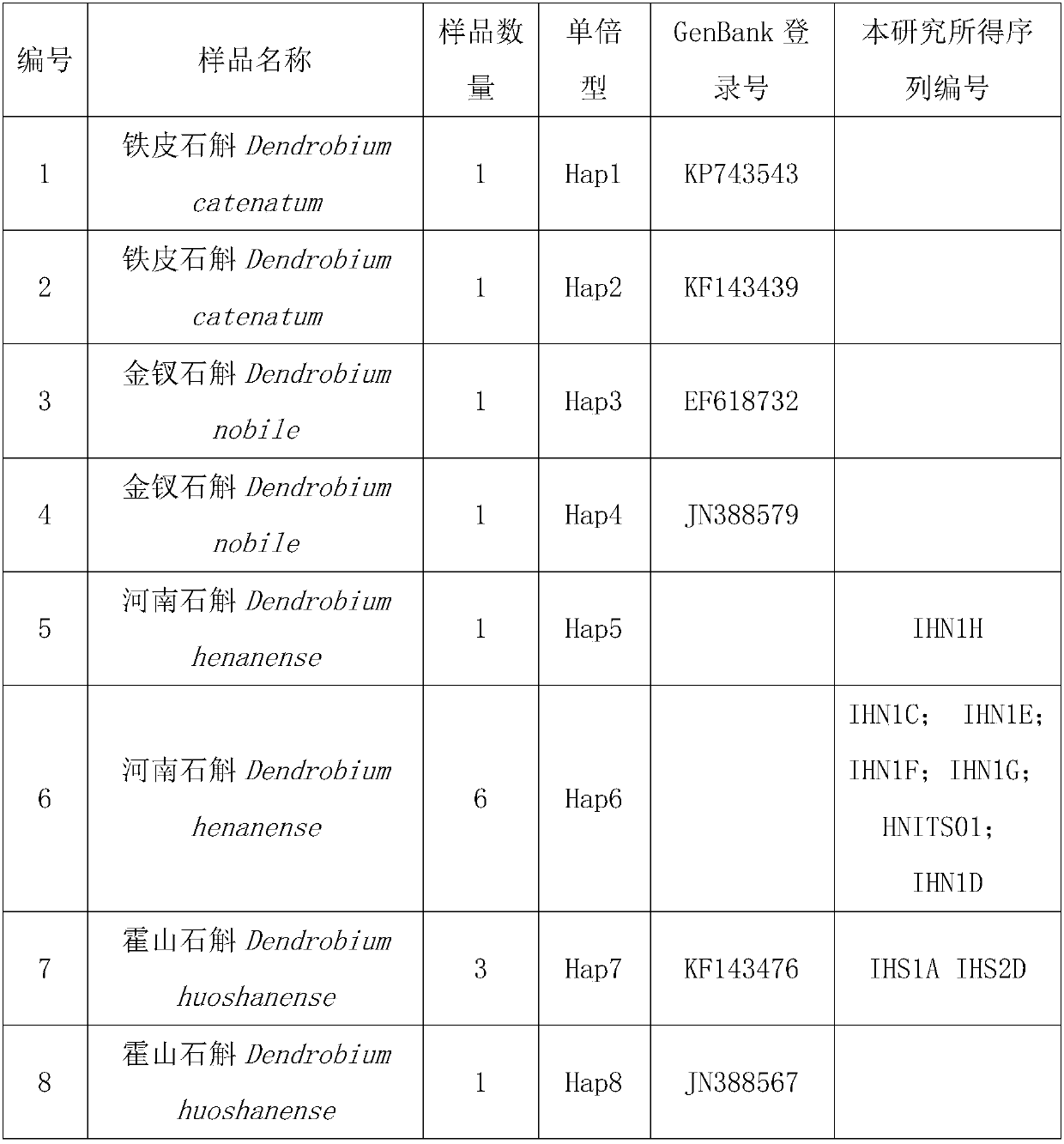
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phylogenetic profiling is a bioinformatics technique in which the joint presence or joint absence of two traits across large numbers of species is used to infer a meaningful biological connection, such as involvement of two different proteins in the same biological pathway. Along with examination of conserved synteny, conserved operon structure, or "Rosetta Stone" domain fusions, comparing phylogenetic profiles is a designated "post-homology" technique, in that the computation essential to this method begins after it is determined which proteins are homologous to which. A number of these techniques were developed by David Eisenberg and colleagues; phylogenetic profile comparison was introduced in 1999 by Pellegrini, et al.
Methods and systems for phylogenetic analysis
InactiveUS20120165215A1ConfidenceNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTaxonBiological Taxon
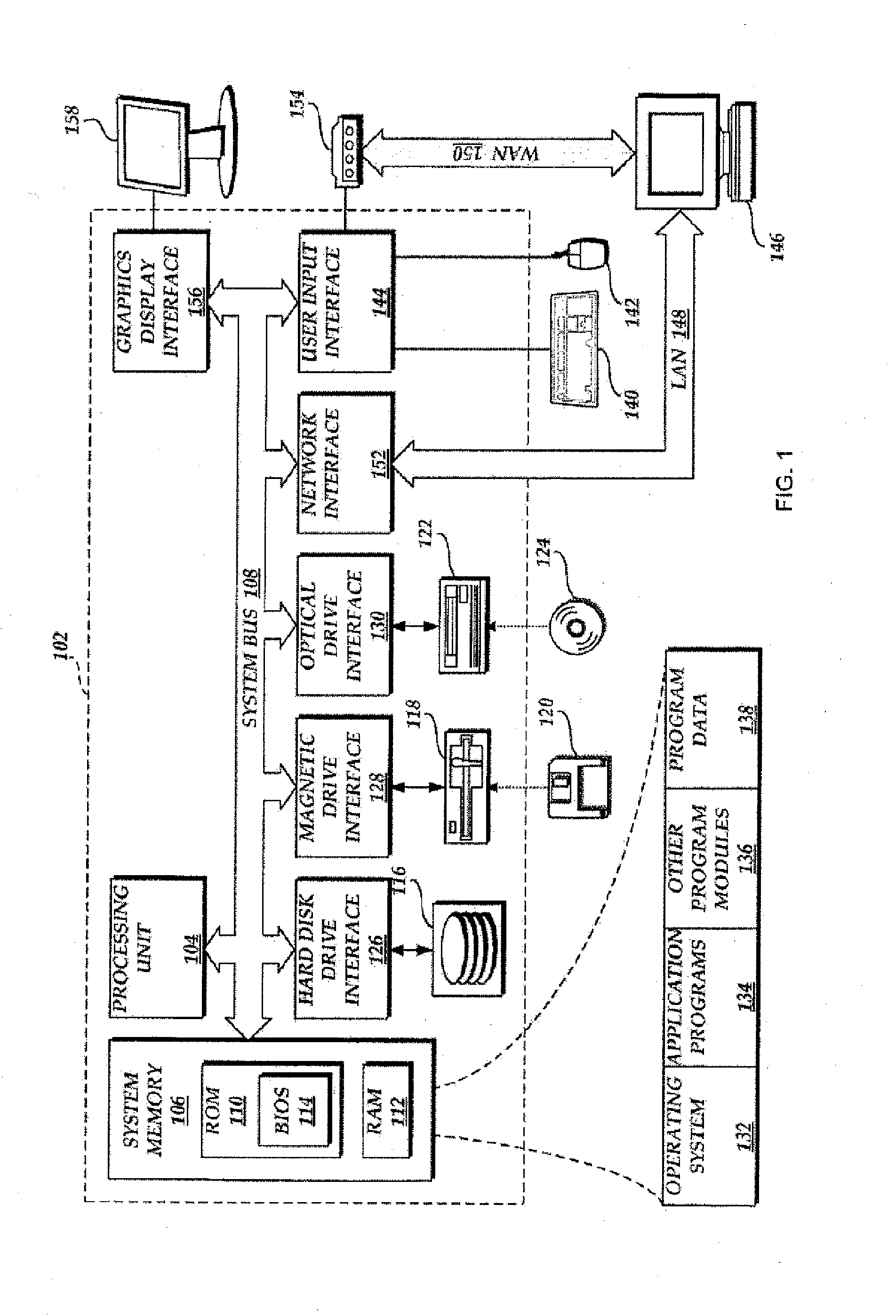
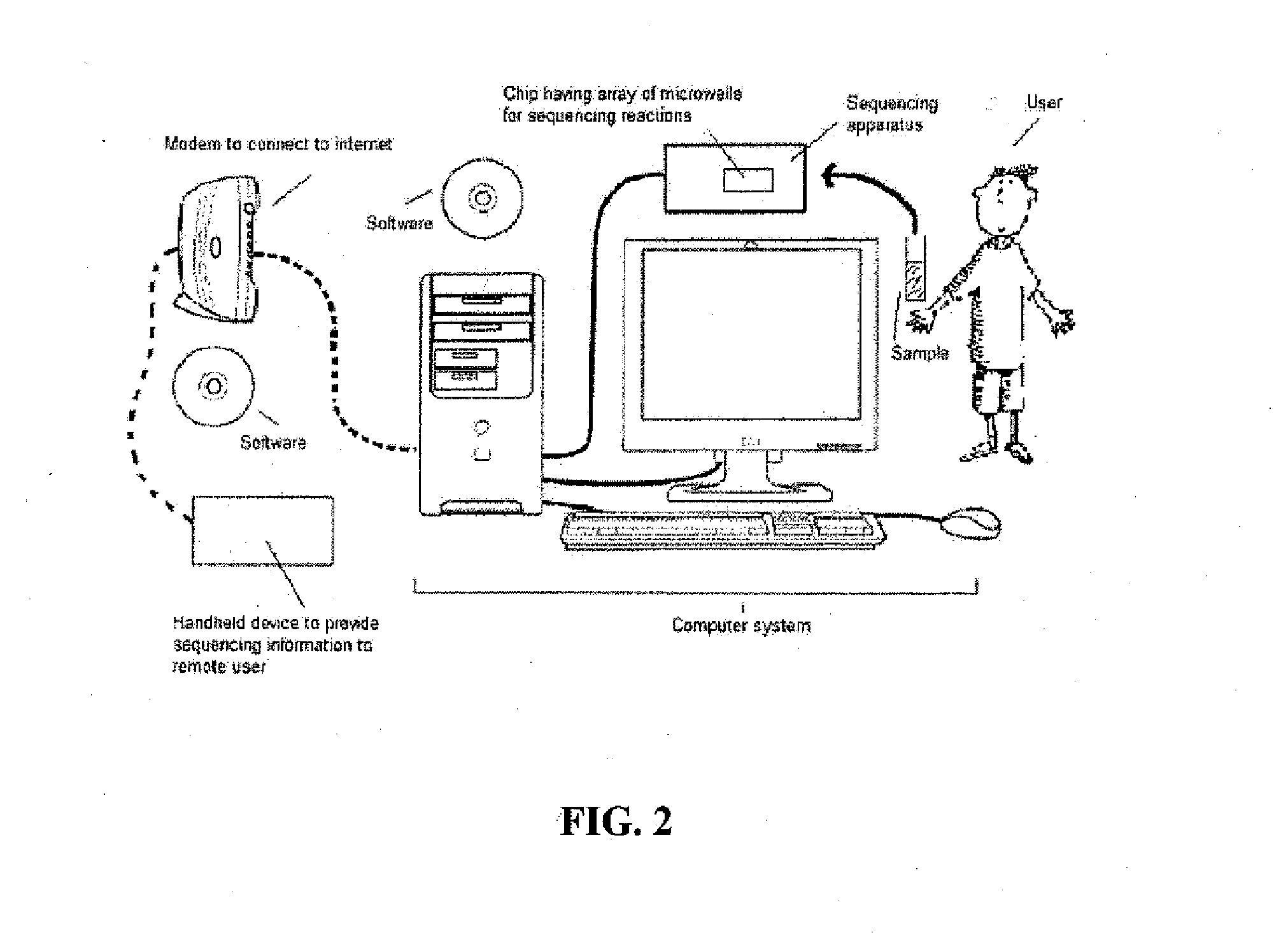
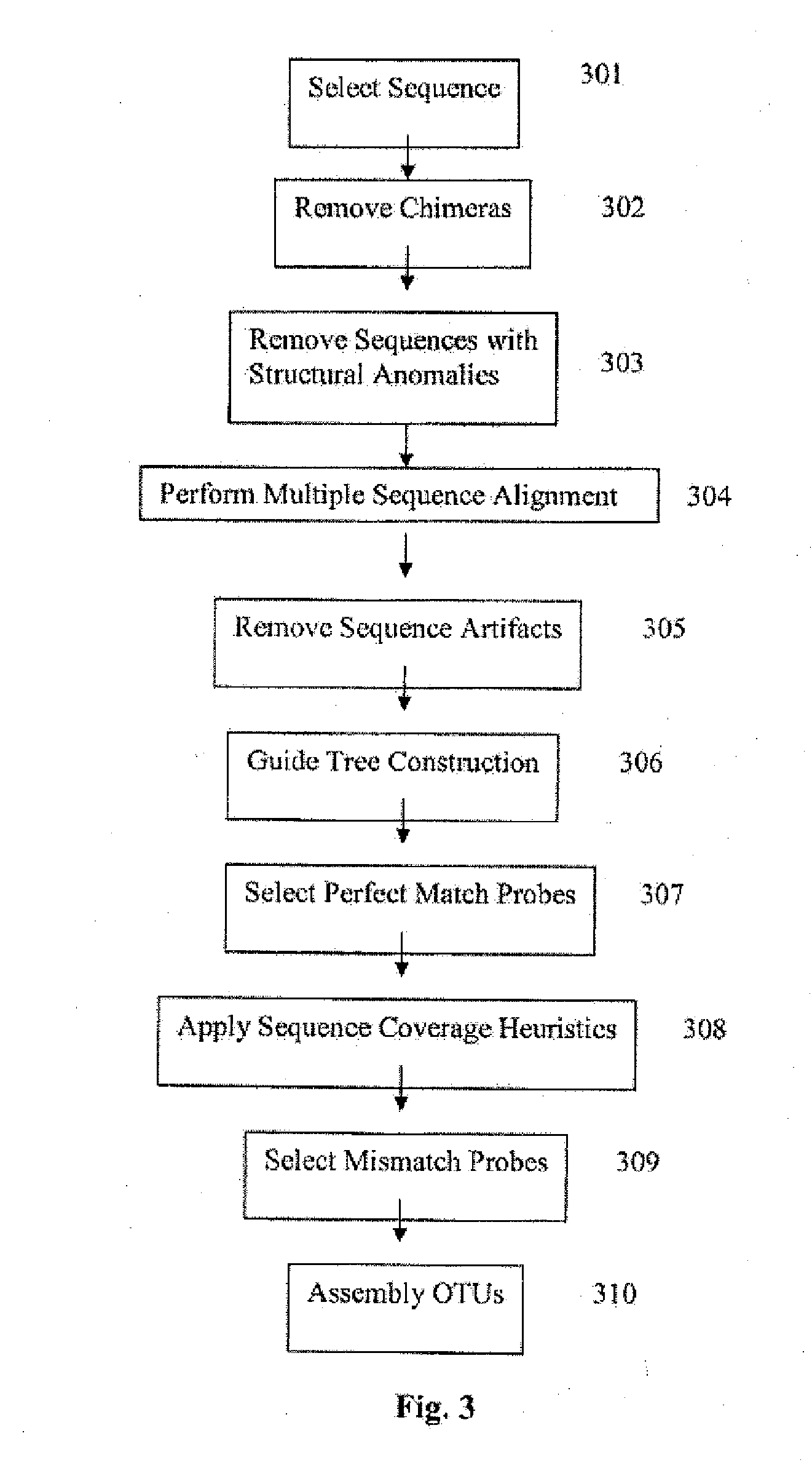
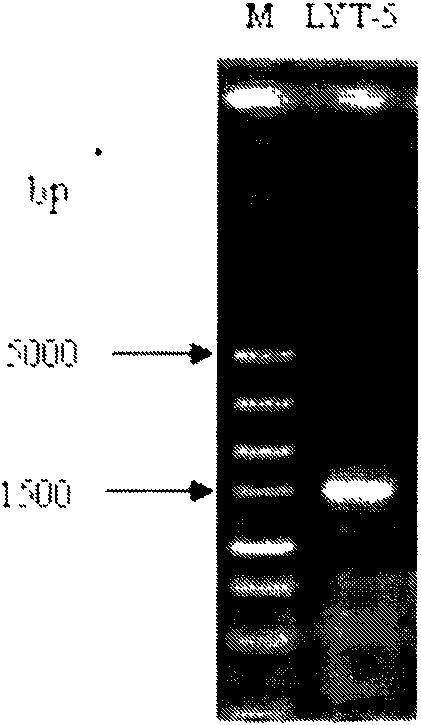
The present invention discloses methods and systems for designing and using organism-specific and / or operational taxon unit (OTU)-specific probes. The methods and systems allow for detecting, identifying and quantitating a plurality of biomolecules or microrganisms in a sample based on the hybridization or binding of target molecules in the sample with the probes. Some embodiments provide methods of selecting an oligonucleotide probe specific for a node on a clustering tree. Other embodiments provide methods of selecting organism-specific or OTU-specific oligonucleotide probes for use in accurately detecting a plurality of organisms in a sample with high confidence. Some embodiments provide methods and systems to detect the presence of a rare OTU in a sample.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
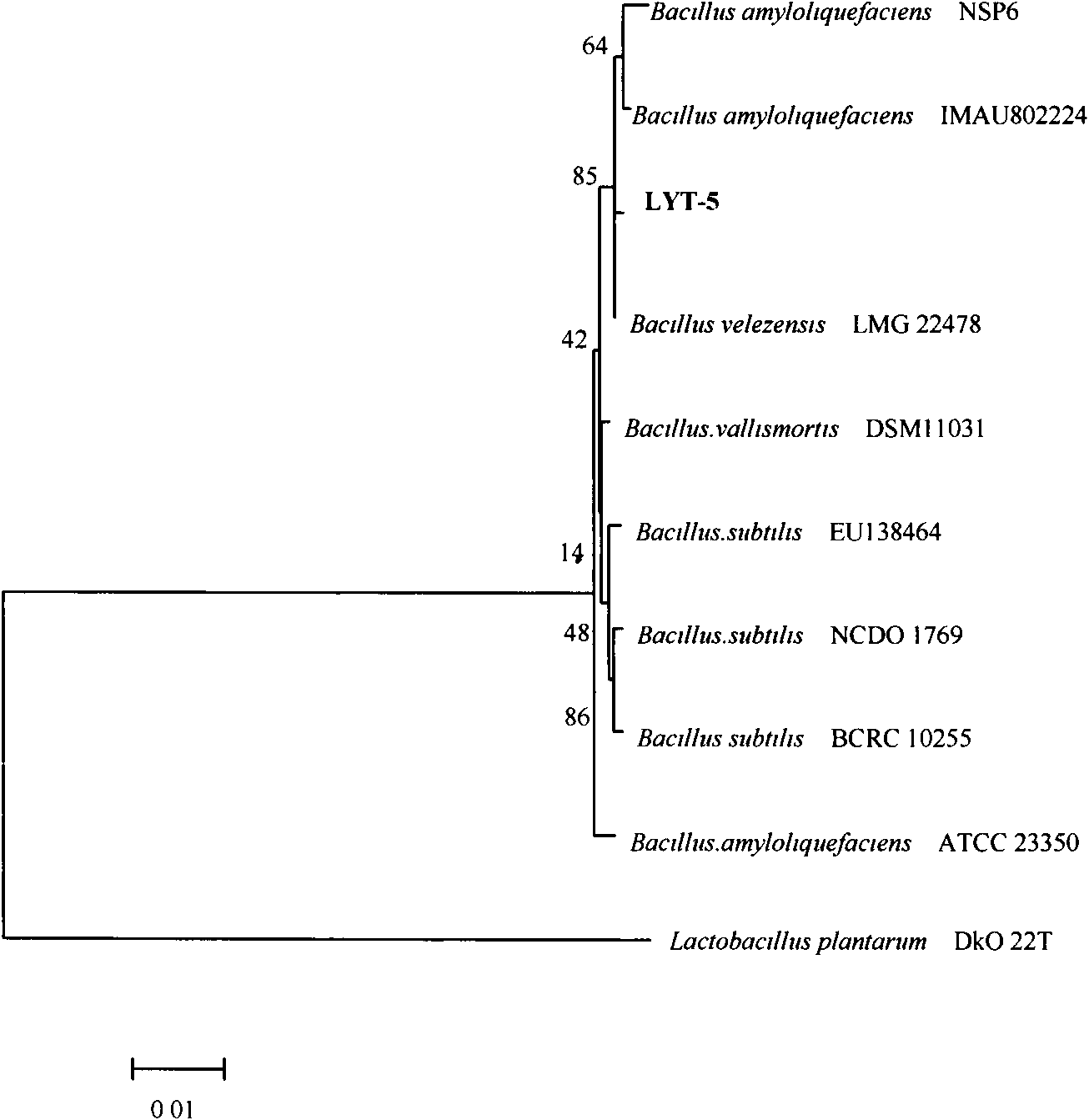
A kind of Bacillus velesi and its application in the antagonism of tomato fusarium wilt
InactiveCN102286412AHigh antibacterial activityIncrease productionBiocideBacteriaPhylogenetic profilingMicrobiology
The invention discloses a Bacillus velezensis CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4992 and application thereof in tomato blight antagonism bacteria. A farmland soil sample on which tomatoes are planted for years in Xinjiang Fukang is subjected to antagonism bacteria screening to obtain a strain with stronger bacteriostatic activity; the strain is further screened and domesticated and bred; and the obtained strain is subjected to morphological specificity and 16S rRNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) sequencing and system development analysis. The antagonism of the fermentation broth of the strain has outstanding technical effect on solving the tomato blight antagonism bacteria and has wide application field.
Owner:新疆万康诚一肥业有限公司
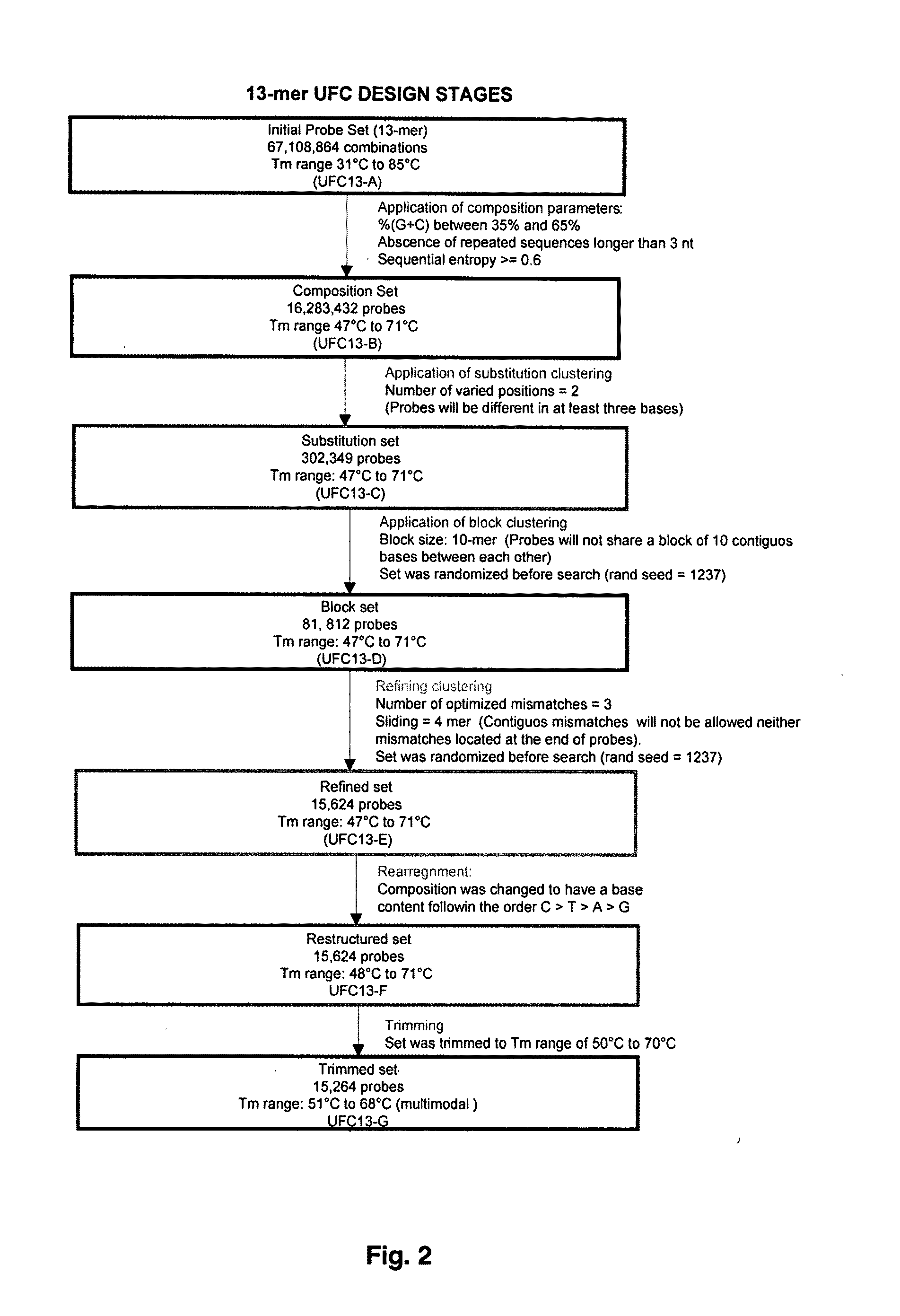
Universal fingerprinting chips and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110105346A1Avoid formingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideOrganism
The present invention discloses a designing strategy for constructing a set of probes useful for analyzing all or most prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. A set of capture probes with optimal fingerprinting properties and highly representative of all possible sequences of an organism can be selected by six sequential steps. Fingerprinting potential of such probes is validated by phylogenetic analysis, which generates results that strongly correlate with phylogenetic trees produced by sequence alignment. The probes generated by the instant methods can be used for detecting an organism, for establishing phylogenetic relationships between different organisms, for detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms and a wide variety of other applications that require genetic analysis.
Owner:BEATTIE KENNETH L +4
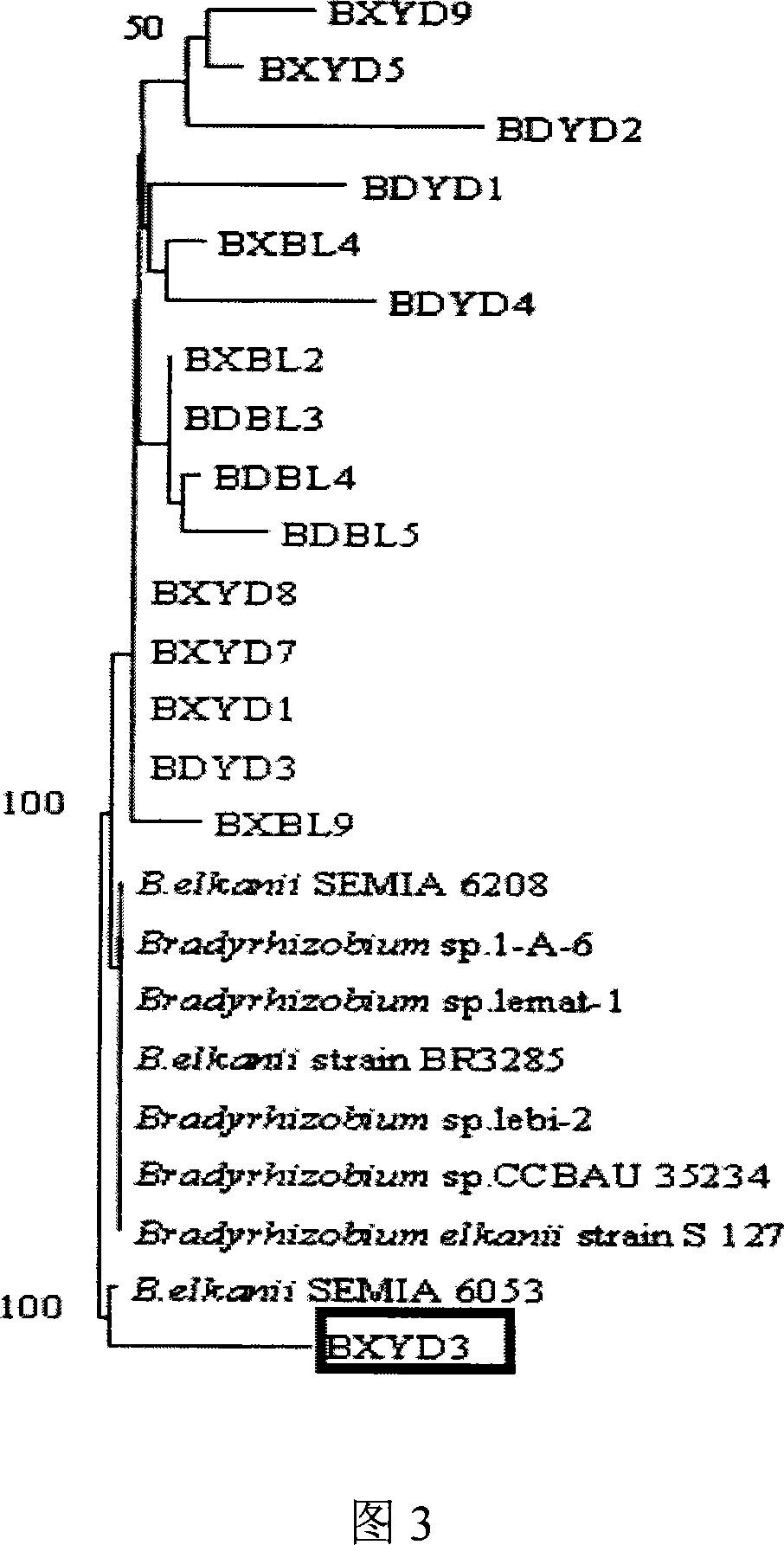
Root nodule azotobacter strain BXYD3 and uses thereof
The invention discloses a Nodule Azotobacter strain BXYD3 and the application. The strain is obtained by a way that the Rhizobia strains in the soil are respectively captured through different soybean varieties; the Rhizobia strains are separated and purified in fresh root nodules; part 16S rDNA of the strain is sequenced; the phylogenetic analysis determines that the strain is a novel Bradyrhizobium strain, which is named as Huagu 3. The Nodule Azotobacter strain BXYD3 of the invention has the characteristics of acid and aluminum tolerance and high level of nodules, which are proved by laboratory pot culture and field experiment. The inoculation of the Rhizobia strain can improve the yield of soybean more than 20 percent to 30 percent. The invention suits for the acid soil area in South China, which can be used as one of the measures for the conventional cultivation of soybean.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Contaminated soil phenanthrene and application thereof in contaminated soil restoration
The invention discloses a contaminated soil phenanthrene and an application thereof in contained soil restoration. A bacterial strain with a contaminated soil restoration function is obtained by screening the strain in kelamayi oilfield oil-contaminated soil sample; the bacteria y-8 is determined as pseudomonasgeniculata CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.6763 by further screening, domesticating and breeding, and carrying out morphological characteristic, 16SrRNA sequence determination and phylogenetic analysis to the obtained bacterial strain; according to the measured degradation property of the phenanthrene and the intensive study of the action of the phenanthrene in contaminated soil restoration, the contaminated soil phenanthrene has an outstanding technical effect in the contaminated soil restoration.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
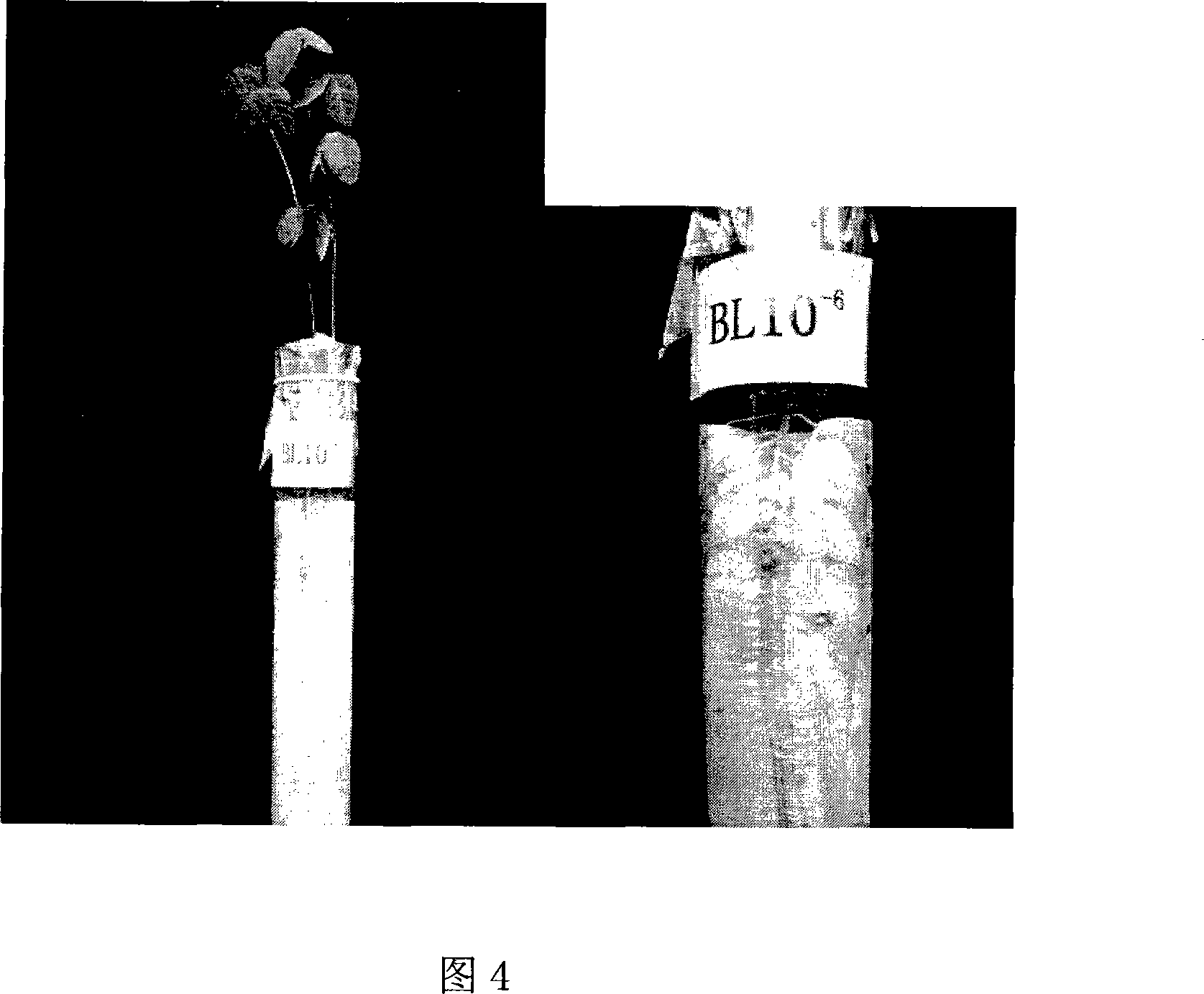
Sebacinales sp. LQcapable of promoting germination of seeds of medicinal Dendrobium officinale andDendrobium flexicauleto form seedlings and application thereof
ActiveCN110699261AThe separation method is simple and convenientLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDendrobium flexicaule
The invention discloses Sebacinales sp. LQ capable of promoting germination of seeds of medicinal Dendrobium officinale andDendrobium flexicauleto form seedlings; and the Sebacinales sp. LQ is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection under the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2019744. The invention further provides morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics of theSebacinales sp. LQ. According to the morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics, as well as nucleotide sequence and phylogenetic analysis results, the Sebacinales sp. LQ. is a fungusstrain pertaining to the Sebacinales sp.. The Sebacinales sp. LQ. can be used for promoting germination of seeds of Dendrobium officinale and seeds of Dendrobium flexicaule to form seedlings; and theSebacinales sp. LQ. has relatively high specificity. Thus, the seeds of the Dendrobium officinale and the seeds of the Dendrobium flexicaule can be separatelyinoculated with the Sebacinales sp. LQ. so as to obtain high-quality symbiotic seedlings, thereby realizing efficient cultivation of seedlings by symbiotic germination; and moreover, symbiosis can be used for seedling raising in nursery or direct seed sowing on trunks in the field. Compared with tissue culture, symbiotic culture has the advantages of being low in cost, high in survival rate in the field, free of the problem of tissue degradation and so on; and thus, the symbiotic culture has application values in obtaining of symbiotic seedlings in replacement of tissue culture.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
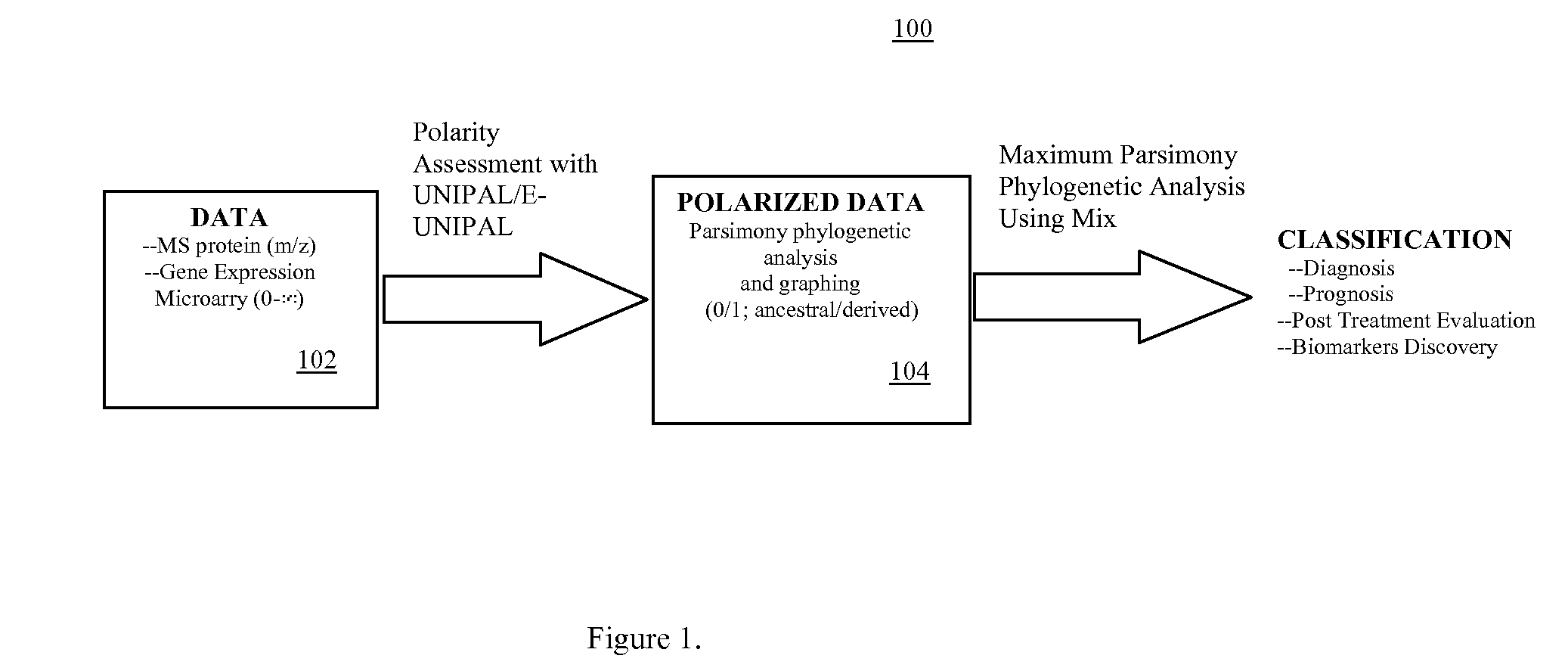
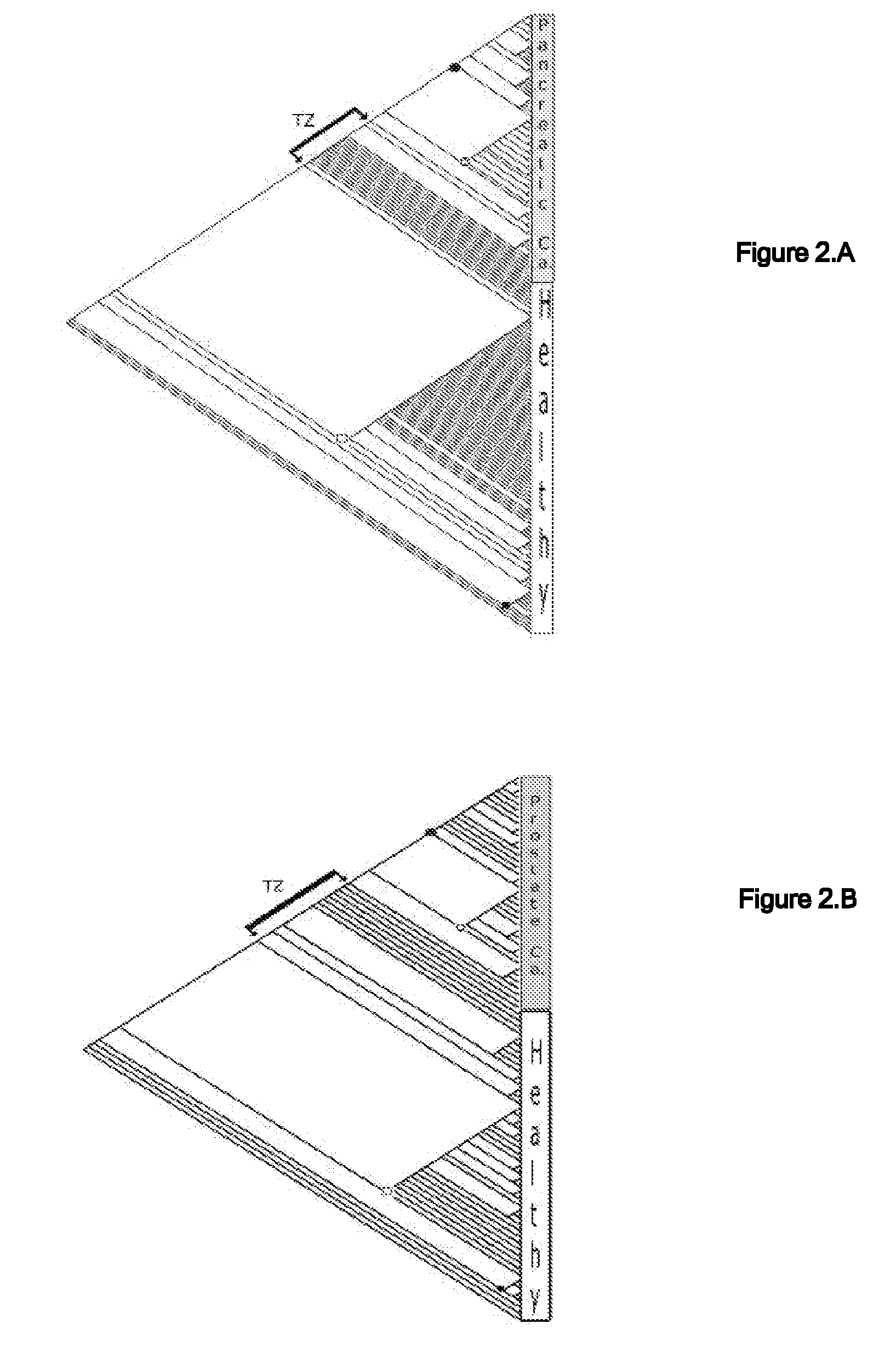
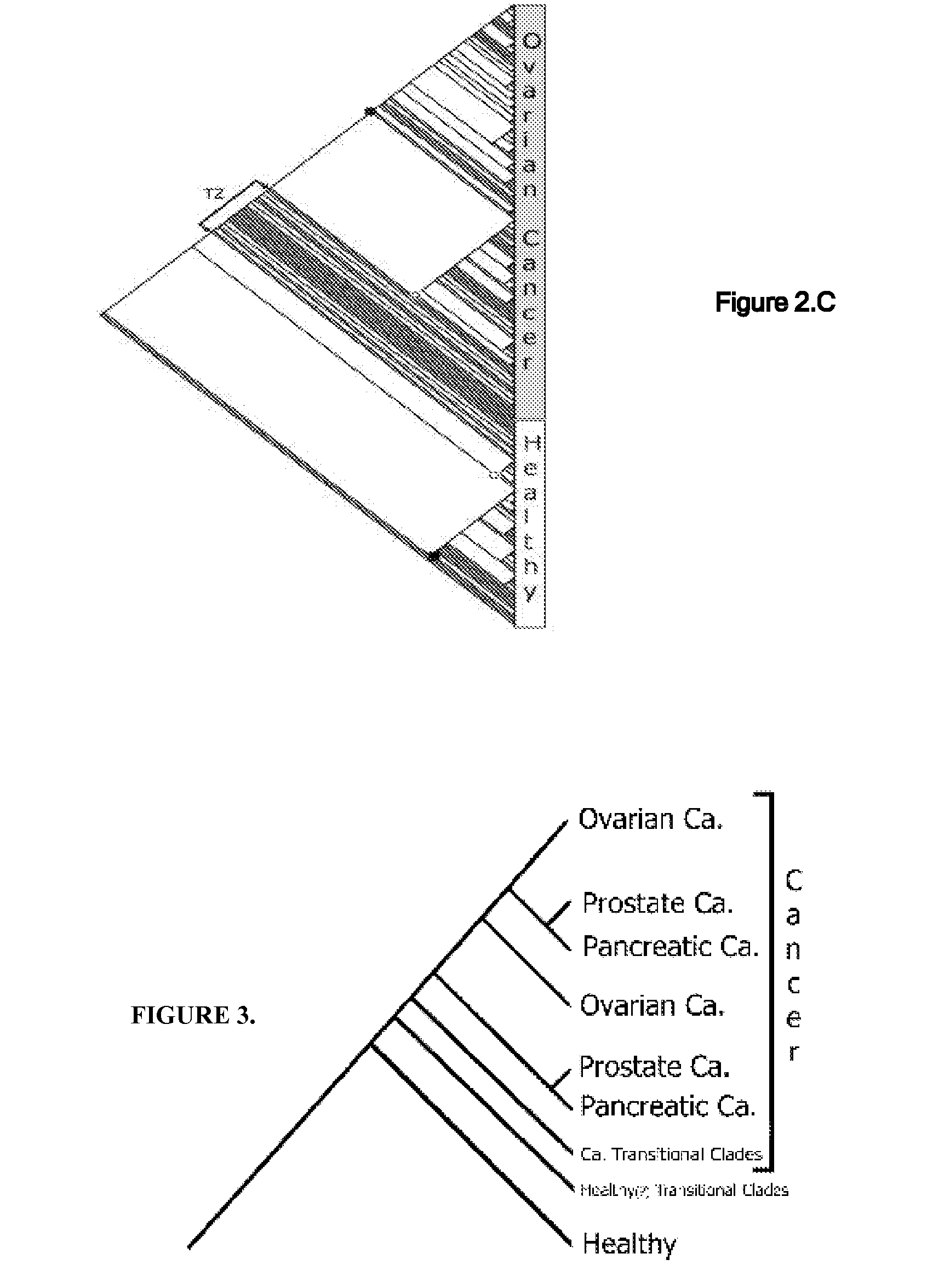
Phylogenetic Analysis of Mass Spectrometry or Gene Array Data for the Diagnosis of Physiological Conditions
ActiveUS20070259363A1Facilitates interplatform comparabilityMedical simulationMedical data miningDiseasePotential biomarkers
A universal data-mining platform capable of analyzing mass spectrometry (MS) serum proteomic profiles and / or gene array data to produce biologically meaningful classification; i.e., group together biologically related specimens into clades. This platform utilizes the principles of phylogenetics, such as parsimony, to reveal susceptibility to cancer development (or other physiological or pathophysiological conditions), diagnosis and typing of cancer, identifying stages of cancer, as well as post-treatment evaluation. To place specimens into their corresponding clade(s), the invention utilizes two algorithms: a new data-mining parsing algorithm, and a publicly available phylogenetic algorithm (MIX). By outgroup comparison (i.e., using a normal set as the standard reference), the parsing algorithm identifies under and / or overexpressed gene values or in the case of sera, (i) novel or (ii) vanished MS peaks, and peaks signifying (iii) up or (iv) down regulated proteins, and scores the variations as either derived (do not exit in the outgroup set) or ancestral (exist in the outgroup set); the derived is given a score of “1”, and the ancestral a score of “0”—these are called the polarized values. Furthermore, the shared derived characters that it identifies are potential biomarkers for cancers and other conditions and their subclasses.
Owner:AMRI HAKIMA +2
Tracing method of cronobacter spp. in infant formula milk powder
The invention provides a tracing method of cronobacter spp. in infant formula milk powder. The method comprises the steps that by means of a multiple-locus sequence typing technology, molecular typing research is conducted on the cronobacter spp. of PIF raw materials, semi-finished products, finished products and processing environments thereof, population characteristics of the cronobacter spp. are revealed, a phylogenetic relationship of the cronobacter spp. is confirmed, phylogenetic analysis is conducted on the cronobacter spp. through bioinformatics, and therefore genetic characteristics of the cronobacter spp. in the above-mentioned environments are revealed systematically; on the basis of cronobacter spp. MLST typing, correlation analysis is conducted by taking ST of pathogenic bacteria and environmental sources as variables, key links which are most prone to pollute the cronobacter spp. in the PIF processing process and distribution rules are determined, and therefore the source of the cronobacter spp. in the infant formula milk powder is traced. The purpose of fundamentally monitoring the PIF production process and ensuring the PIF quality are achieved.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Amplification primer of tridacnidae shellfish mitochondria COI (cytochrome oxidase I) gene
InactiveCN102816762AConducive to the study of genetic diversity of speciesLow amplification efficiencyDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmDesign software
The invention relates to an amplification primer of a tridacnidae shellfish mitochondria COI (cytochrome oxidase I) gene. The known 52 tridacnidae sequences in NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) are utilized, two tridacnidae sequences obtained by amplifying a universal primer are jointly utilized, a CLUSTALW software is used for comparison analysis, a plurality of pairs of primers are designed by using a primer design software Primer Premier 5 in a determined conversation region, 43 tridacnidae individuals are repeatedly subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) experiments in a 10 mul system and are finally detected through agarose gel electrophoresis, and an efficient amplification primer of the tridacnidae shellfish mitochondria COI gene sequence is sieved. The efficient amplification primer is characterized in that CQF is 5'-GATATTGGAACCCTTTACTT-3'; and CQR is 5'-TTCAGGATTGTCCCAAGAATCA-3'. By using the tridacnidae shellfish mitochondria COI primer, the target fragments of different specifies of tridacnidae shellfishes can be efficiently amplified; and the tridacnidae shellfish mitochondria COI primer has important significance for identifying tridacnidae species and carrying out phylogenetic analysis by using a molecular method, and can provide reliable technical guidance for developing and protecting tridacnidae germplasm resources by using the molecular means.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
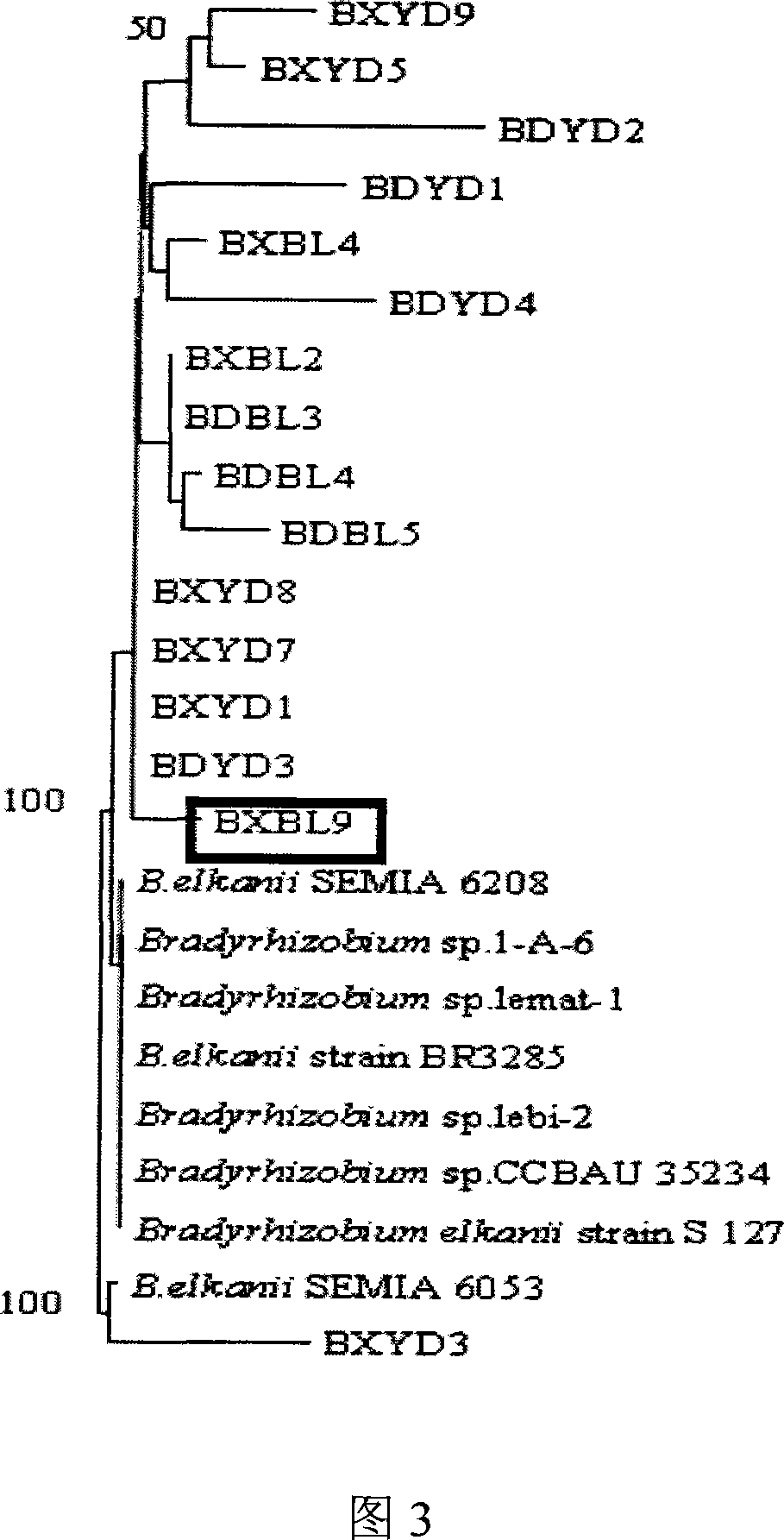
Root nodule azotobacter strain BXBL9 and uses thereof
The invention discloses a Nodule Azotobacter strain BXBL9 and the application. The strain is obtained by a way that the Rhizobia strains in the soil are respectively captured through different soybean varieties; the Rhizobia strains are separated and purified in fresh root nodules; part 16S rDNA of the strain is sequenced; the phylogenetic analysis determines that the strain is a novel Bradyrhizobium strain, which is named as Huagu 2. The Nodule Azotobacter strain BXBL9 of the invention has the characteristics of acid and aluminum tolerance and high level of nodules, which are proved by laboratory pot culture and field experiment. The inoculation of the Rhizobia strain can improve the yield of soybean more than 20 percent to 30 percent. The invention suits for the acid soil area in South China, which can be used as one of the measures for the conventional cultivation of soybean.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
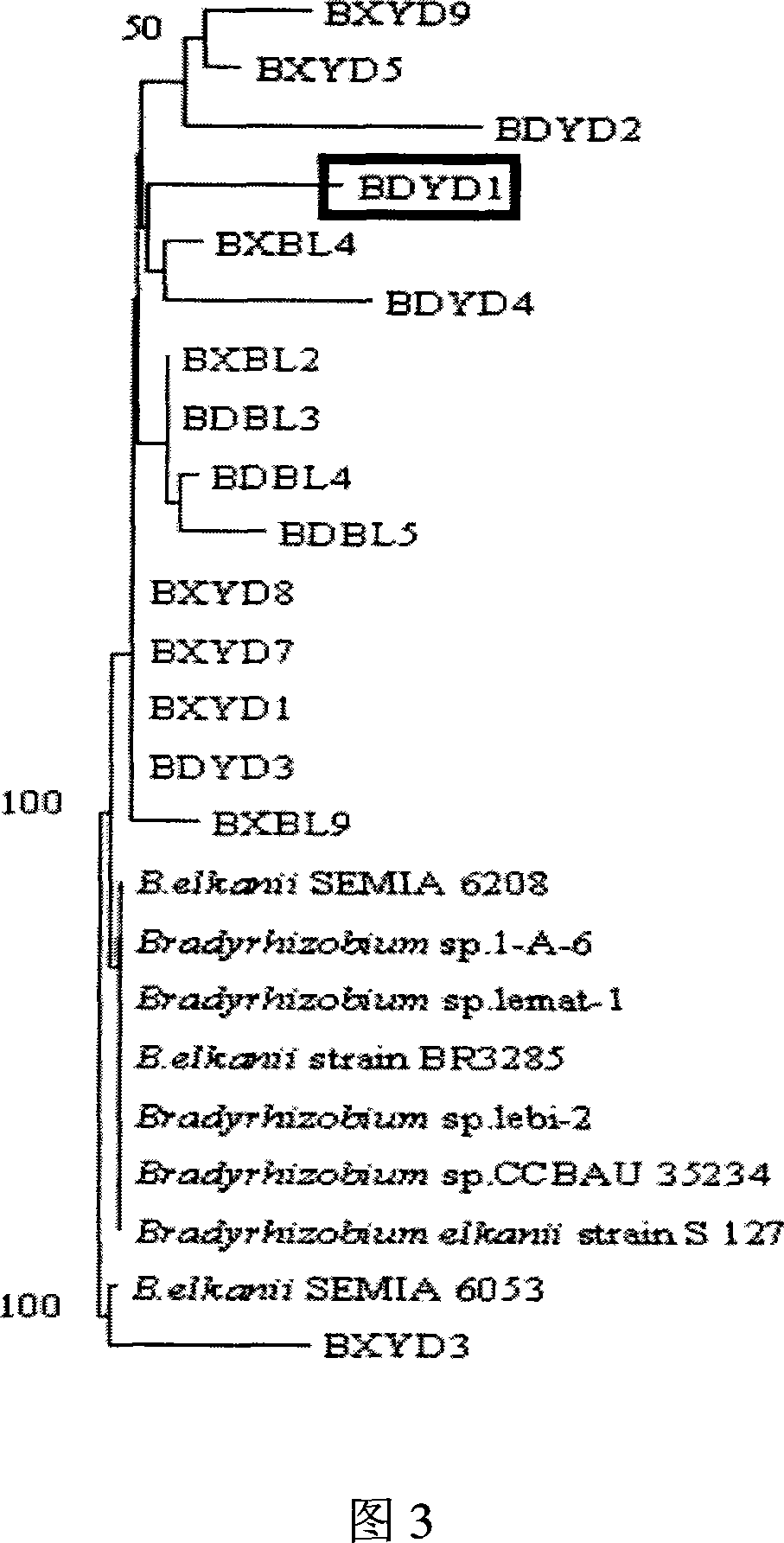
Root nodule azotobacter strain BDYD1 and uses thereof
InactiveCN101182478AIncrease useWith anodized aluminumBiocideBacteriaPlant noduleBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses a nitrogen-fixing bacterial strain BDYD1 and its application. The bacterial strain captures the rhizobia in the soil through different soybean varieties, separates and purifies the rhizobia from fresh nodules, and extracts the 16S rDNA part of the strain. The sequence was determined, and through phylogenetic analysis, it was determined to be a new strain of Bradyrhizobium (Bradyrhizobium), and it was named Huagu No. 1. The nitrogen-fixing bacterium strain BDYD1 of the present invention has been proved by laboratory potting and field back-inoculation tests that it has the characteristics of acid-resistant aluminum and high-efficiency nodulation. Inoculation of the rhizobia can increase soybean yield by more than 20-30%, and it can be applied to acid soil regions in South China , as one of the measures of conventional soybean cultivation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Root nodule azotobacter strain RY1 bacterial strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101781630AWide applicabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses a root nodule azotobacter strain RY1 bacterial strain and an application thereof. The bacterial strain (Bradyhizobium sp.RY1) is obtained from gathering fresh root nodules in main Stylosanthes guianensis planting areas in China and separating and purifying in a laboratory, the partial sequence of 16S rDNA of the bacterial strain is measured, and the bacterial strain is determined to be a new bacterial strain of Bradyrhizobium by the phylogenesis analysis and is named as Re Yan 1 (RY1). By the potted planting and the inoculation test in the laboratory, the nodule azotobacter strain RY1 bacterial strain is proven to have the characteristic of enabling the two main Stylosanthes guianensis varieties (TPRC2 and TPRC5) in China to realize the high-efficiency nodulation and achieve the high yield. Compared with the inoculation-free process, the inoculation with the root nodule can improve the yield of the Stylosanthes guianensis by more than 2 times, and can be used as one of conventional Stylosanthes guianensis culturing measures for planting the Stylosanthes guianensis.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +2
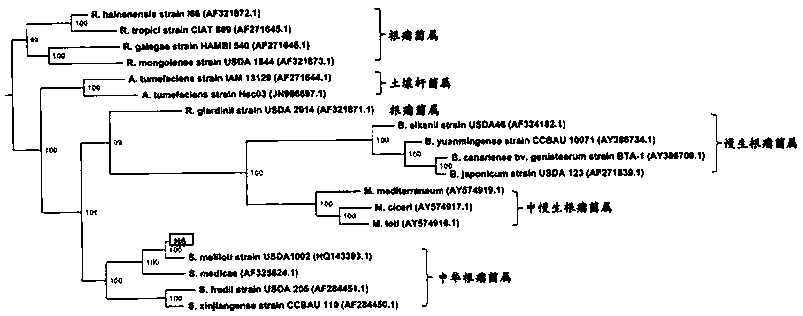
Sinorhizobium nitrogen-fixing strain H6 and application thereof
ActiveCN108841748ASalt-tolerantIncrease biomassBacteriaFabaceae cultivationPlant nodulePhylogenetic profiling
The invention relates to a sinorhizobium nitrogen-fixing strain H6 and application thereof. The sinorhizobium nitrogen-fixing strain H6 was deposited at the China Center for Type Culture Collection ofWuhan University on May 7, 2018, which is referred to as CCTCC for short, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2018255. The sinorhizobium nitrogen-fixing strain H6 is obtained by capturing rhizobia in soil by an alfalfa plant, and isolating and purifying the rhizobia from a fresh root nodule; partial 16S rDNA sequence of the strain is measured, the sinorhizobium is determined as a new strainby phylogenetic analysis, and is named H6. The sinorhizobium nitrogen-fixing strain H6 provided by the invention is proved to have the characteristics of alleviating alfalfa salt damage and fixing nitrogen efficiently by a sand culture back-test; under a salt treatment condition, the biomass of the alfalfa is increased by inoculating the rhizobia, and the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents in a plant are improved; and the sinorhizobium H6 can be applied to salinized areas such as Xinjiang and the like as one of measures for conventional cultivation of the alfalfa.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
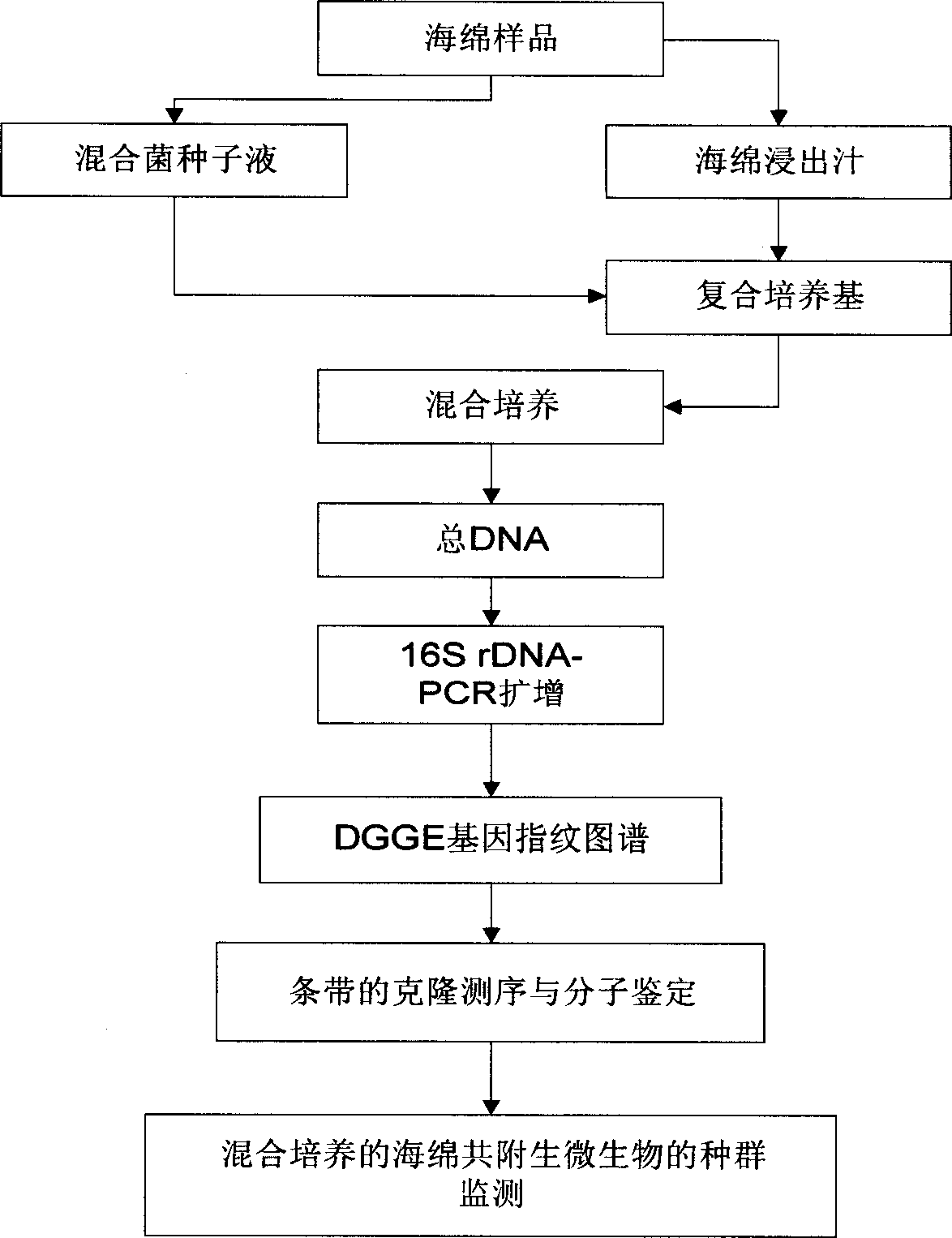
Blending culture for sponge and intergrowth microbe, culturing colony monitoring method
InactiveCN1766081AAchieve in vitro cultureDynamic monitoring of population structure changesMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementActive matterGel electrophoresis
The mixed cultivation and culturing population monitor method for sponge symbiotic microbe comprise: cleaning the epiphytic microbe on sponge surface, dipping into artificial sea water to shock and release symbiotic microbe in sponge for preparing germ liquid; extracting and preparing sponge draw-off juice with alcohol to add into seawater culture medium and prepare composite medium; inoculating to culture mixed microbe; extracting the whole DNA of cultured microbe to amplify into 16S rDNA segment less than 500bp by PCR for modified gradient gel electrophoresis and obtaining gene fingerprint pattern; realizing in-vitro monitor by callbacking fingerprint pattern strips of different time, cloning, sequencing, and homological and phylogenetic analysis to identify germ kind. This invention can improve separation and culture efficiency, and provides opposite material and technique support.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Low temperature-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae JM33 and application thereof in munake grape wine
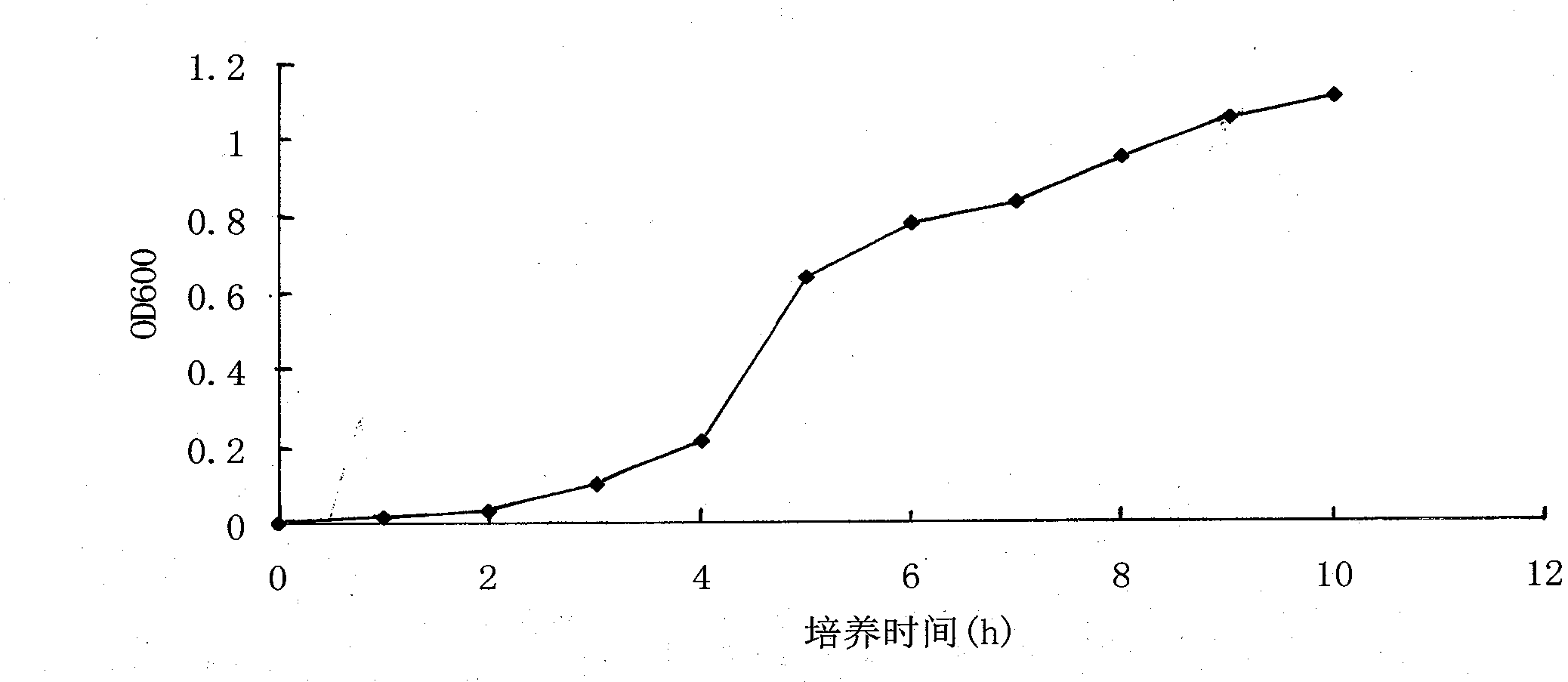
ActiveCN105199971AFruityPleasant aromaFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhylogenetic profiling
The invention low temperature-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae JM33 and application of the low temperature-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae JM33 in munake grape wine. According to the low temperature-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae JM33 disclosed by the invention, by carrying out strain separating, screening, breeding and acclimatizing on munake grapes and carrying out morphological characteristic and 26S rDNA (Ribosomal Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence determination and phylogenetic analysis on an obtained strain, a fermentation action of strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae JM33 CGMCC NO.10912 on the munake grapes is determined; the munake grape wine is prepared by fermenting the munake grapes by utilizing the Saccharomyces cerevisiae JM33 CGMCC NO.10912, the munake grape wine is straw-like yellow and is clear and transparent, the fruity flavor is strong, the taste is mellow and soft, and a special flavor of the munake grape wine is obtained.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
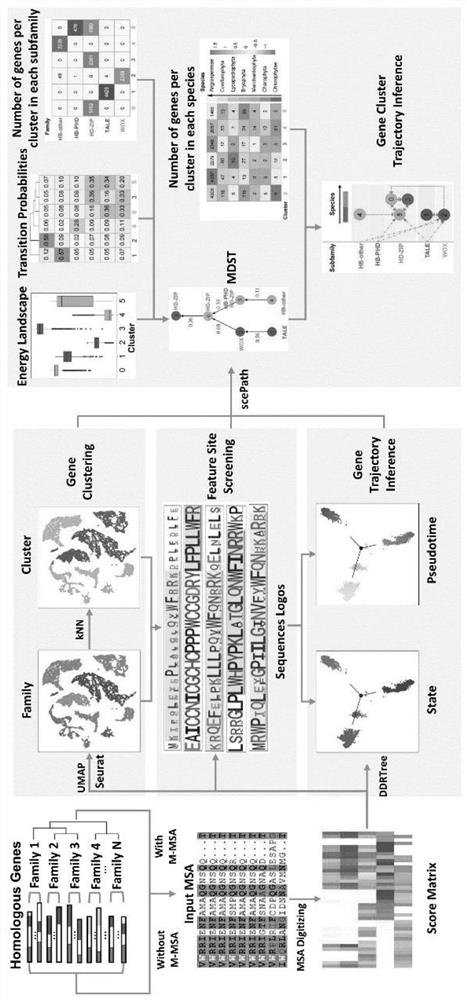
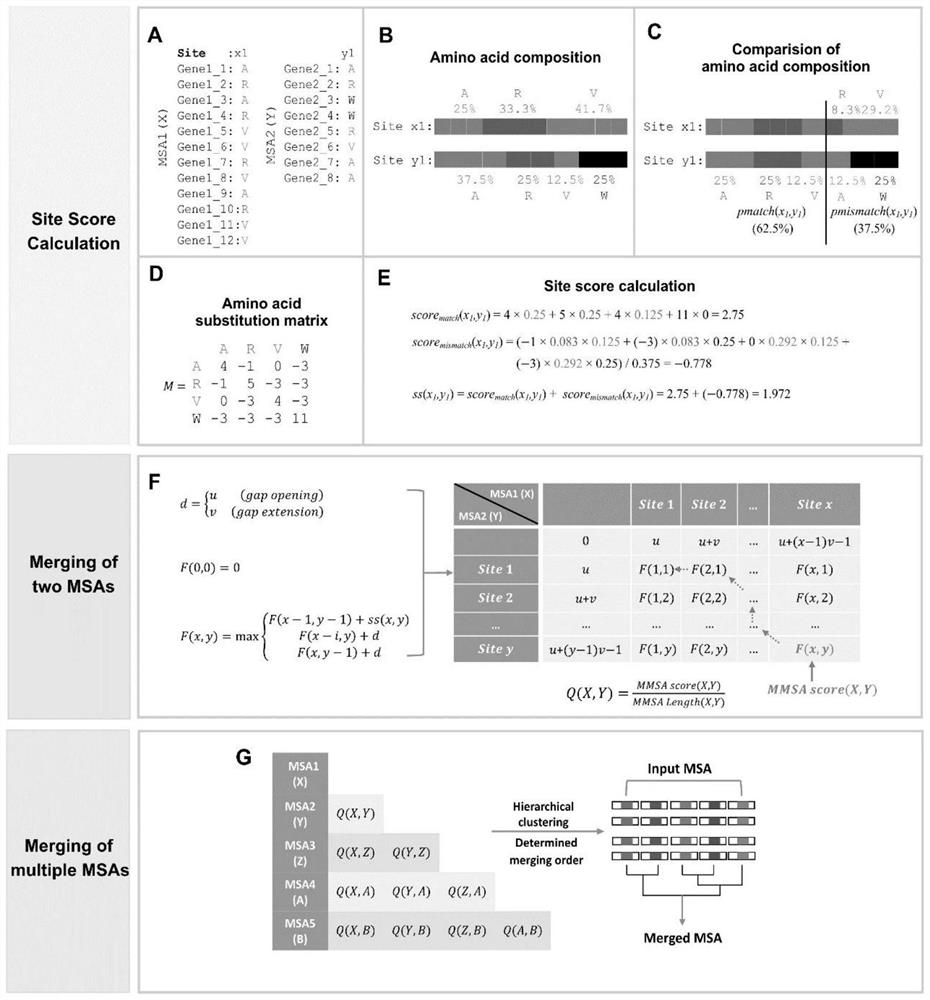
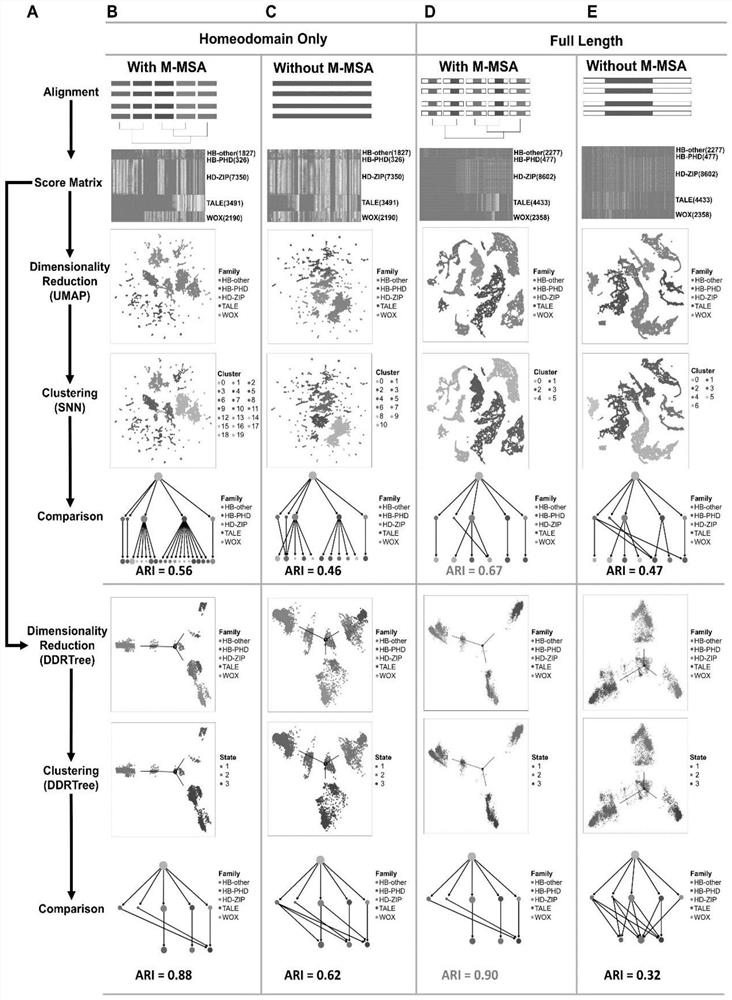
Protein family phylogenetic analysis method based on amino acid sequence alignment
PendingCN114882949AEnsure cluster stabilityClustering is fastCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsAmino acid sequence alignmentGene cluster
The invention discloses a protein family phylogenetic analysis method based on amino acid sequence alignment, which comprises the following steps: obtaining a combined multi-sequence alignment result based on an amino acid sequence alignment fusion method; digitizing a combined multi-sequence comparison result, and constructing a fractional matrix; performing dimension reduction and clustering processing on the fractional matrix to obtain an input sequence; identifying a specific site and a conserved site of the input sequence; performing quasi-time analysis on the input sequence to obtain a track sequence of the input sequence; and obtaining a development trajectory of the input sequence based on the trajectory sorting. According to the method, fractional matrix construction and dimension reduction analysis are carried out through the sequence site features, so that the clustering and evolutionary relationship between gene families is deduced, the sequence gene clustering speed is effectively increased under the condition that the sequence clustering stability is guaranteed, and a new tool and method are provided for gene phylogenetic analysis and development trajectory analysis.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Separating and screening method and applications of chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium
The invention discloses a separating and screening method and applications of chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium. The separating and screening method and applications of the chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium are realized through the steps of soil collection, culture medium preparation, chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium domestication, chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium separation, bacterial strain identification, bacterial preparation preparation and chlorpyrifos degradation by adopting the bacterial preparation. The inorganic salt culture medium taking chlorpyrifos as the unique carbon source is adopted, the chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium is domesticated in the field soil in which rice is planted throughout the year and in which the pesticide, namely, chlorpyrifos is frequently used, the degrading bacterium is separated by adopting the solid culture medium so that the single bacterial strain is obtained, the 16SrDNA sequence of the bacterial strain is subjected to sequencing, the species of the bacterial strain is identified by combining with the homology analysis and phylogenetic analysis, and then the bacterial strain is prepared into the bacterial preparation which is used for degrading chlorpyrifos.
Owner:南通市产品质量监督检验所
Geotrichum candidum and application thereof in greenhouse soil remediation
ActiveCN105154334AStrong growth and reproduction abilityFast growth rateAgriculture tools and machinesFungiPhylogenetic profilingFermentation
The invention discloses geotrichum candidum and application thereof in greenhouse soil remediation. By carrying out strain isolating, screening, breeding and domesticating on a greenhouse soil sample as well as through determination of morphological characteristics and rDNA ITS sequence of the obtained strain and through phylogenetic analysis, the effect of the strain geotrichum candidum XHS0030B CGMCC NO.9435 in greenhouse soil remediation is determined; 70-80 parts of geotrichum candidum, 30-50 parts of rhodopseudomonas palustris, 20-40 parts of candida utilis and 10-30 parts of mortierella alpina are mixed, and a mixed strain liquid is fully adsorbed in a carrier and is mixed with accessories, wherein the carrier is selected from greenhouse soil and the accessories include urine and calcium superphosphate; a greenhouse soil remediation compound is prepared by virtue of a fermentation technology; and the soil remediation compound has an outstanding technical effect in greenhouse soil remediation.
Owner:新疆惠森生物技术有限公司
Nitration brevibacillus nitrificans bacterial strain YJ1 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field, and discloses a hexadecane degradation bacterial strain YJ1 and an application thereof. A degradation bacterial strain using hexadecane as a carbon source is obtained through separating and screening. According to the shape, the physiological characteristic, the Gramstaining reaction, the 16S rDNA gene sequencing analysis and phylogenetic analysisof the bacterial strain, the bacterial strain is identified to be nitration Brevibacillus nitrificans, and is named as YJ1. The bacterial strain is preserved in the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms in the August, 2019, and the preservation No. is CGMCC NO.18418. The bacterial strain can use the hexadecane as the only carbon source, and the hexadecane can be rapidly degraded. After the initial concentration of the hexadecane is cultured at the environment of 10mg / L for 15 days, the degradation rate can achieve 66.7%. The appropriate growth condition of the bacterial strain is that the temperature is 30 DEG C, the pH is 7 and the inoculum concentration is 10%. The bacterial strain has good degradation characteristic for the hexadecane, and cannot cause secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:HUNAN HENGKAI ENVIRONMENT TECH INVESTMENT CO LTD
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof in greenhouse soil remediation
ActiveCN105154353AStrong growth and reproduction abilityFast growth rateAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaSporidiobolus pararoseusSoil remediation
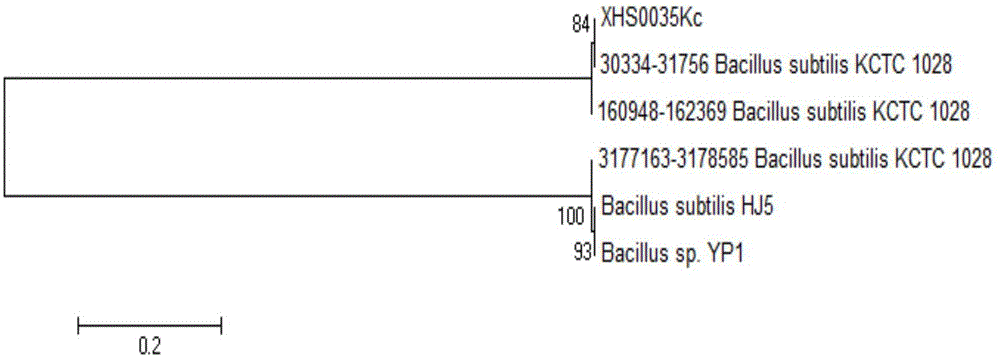
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis and application thereof in greenhouse soil remediation. By carrying out strain isolating, screening, breeding and domesticating on a greenhouse soil sample as well as through 16S rDNA sequencing and phylogenetic analysis, 70-80 parts of bacillus subtilis XHS0035Kc CGMCC NO.9434, 20-40 parts of pseudomonas fluorescens, 25-45 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus and 15-35 parts of sporidiobolus pararoseus are mixed, and a mixed strain liquid is fully adsorbed in a carrier and is mixed with accessories, wherein the carrier is selected from greenhouse soil and the accessories include urine and calcium superphosphate; a greenhouse soil remediation compound is prepared by virtue of a fermentation technology; and the soil remediation compound has an outstanding technical effect in greenhouse soil remediation.
Owner:新疆惠森生物技术有限公司
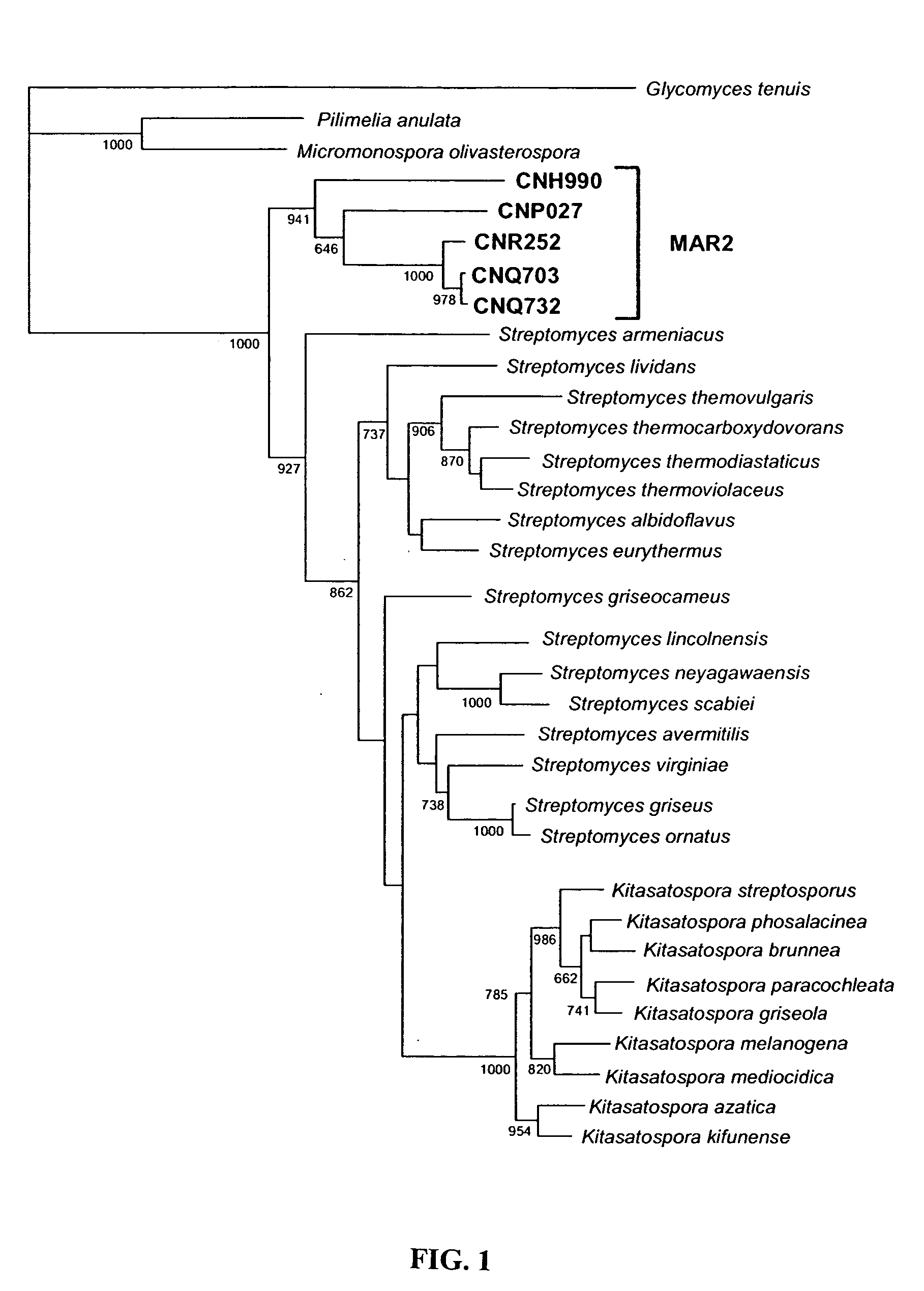
Method for the production of bioactive substances from the novel actinomycete taxon MAR2 ("Marinophilus")
The present invention provides methods for the isolation of a new group of actinomycetes and for the identification of members of this group based on characteristic nucleotide sequences and phylogenetic analyses. This group is phylogenetically distinct from all other known actinomycetes and represents a novel genus that includes multiple new species. Members of this group can be recognized by signature MAR2 nucleotides present in their 16S rRNA gene sequences and by standard phylogenetic treeing methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biological data management and phylogenetic analysis flow method
ActiveCN109493918ASolve the comparison problemNo programming skills requiredProteomicsGenomicsGenomicsInformation analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological information analysis, and discloses a biological data management and phylogenetic analysis process method. The method integrates seven programs of biological data processing and phylogenetic analysis process by using interface software without programming skills, an interface is visual and friendly, and functions of file dragging and dropping, interface memory, one-click upgrade, plug-in management and a program progress bar are provided; a codon alignment function is added to an MAFFT alignment program to solve the alignment problem of a protein gene nucleotide sequence. A batch operation function of the method can save a great amount of operation time and labors, and a multi-gene joint building function is combined to meet the requirements of big data analysis and system genomics; the method provides comprehensive mitochondrial genome bioinformatics analysis for the first time, and can save 99% of the time compared with a traditional analysis method.
Owner:转导精进(武汉)生物技术有限公司 +1
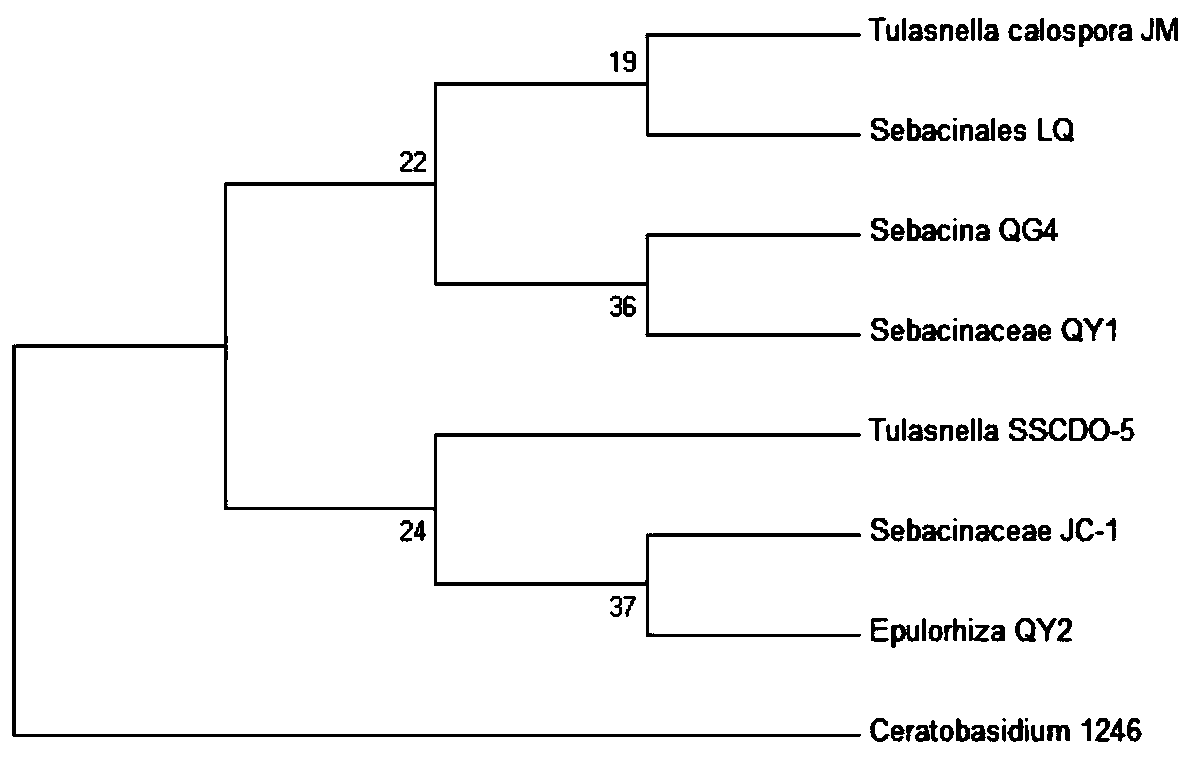
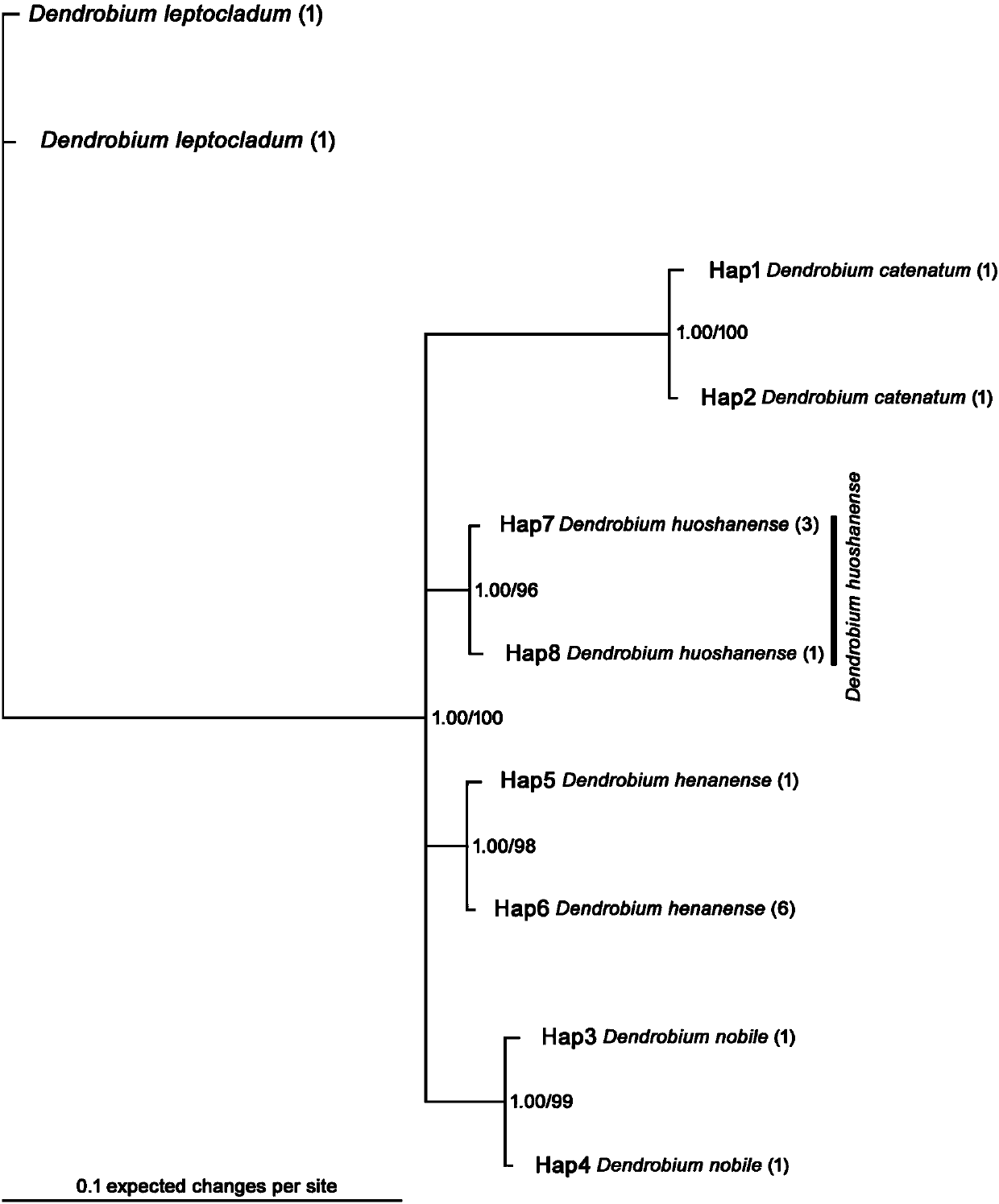
Phylogenetic tree and identification method for identifying dendrobium huoshanense or dendrobium candidum
InactiveCN107630104ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDendrobium candidumDendrobium huoshanense
The invention discloses a phylogenetic tree and an identification method for identifying dendrobium huoshanense or dendrobium candidum, and belongs to the technical field of identification of the dendrobium huoshanense or the dendrobium candidum. The phylogenetic tree uses a specific DNA sequence of each of the dendrobium huoshanense, the dendrobium candidum and some similar species as an ingroup,and two specific DNA sequences of dendrobium leptocladum as an outgroup. The specific DNA sequence of the dendrobium huoshanense is obtained by sequencing, and the specific DNA sequences of some similar species of the dendrobium huoshanense and the dendrobium leptocladum are from GenBank. Phylogenetic analysis is performed according to a Bayesian method and a simple method to establish a BI phylogenetic tree and an MP phylogenetic tree respectively. Through establishment of the phylogenetic tree of the dendrobium huoshanense, the dendrobium candidum and some similar species and through alignment sorting and comparison of the specific DNA sequences of the dendrobium huoshanense and the dendrobium candidum, the dendrobium huoshanense and the dendrobium candidum can be rapidly and accuratelyidentified and a novel method is provided for identifying the dendrobium huoshanense.
Owner:WEST ANHUI UNIV
Information processing device, information processing method, and program
InactiveCN102279907AEstimated changes in rearrangementEstimated to be stableData visualisationSequence analysisInformation processingTheoretical computer science
Provided are an information processing device, an information processing method, and a program. An information processing apparatus according to the present invention, comprising: a data acquisition unit that acquires string data representing a string of one or more characters; and a phylogenetic analysis unit that analyzes the string data acquired by the data acquisition unit to determine the string data represented by the string data. Extract homologous string fragments, and perform phylogenetic analysis based on the positional relationship and homologous relationship of the extracted homologous string fragments.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multi-target phylogenetic tree construction method based on feature hierarchy
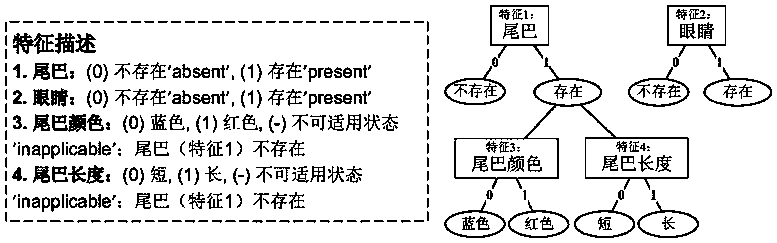
ActiveCN111462812AEasy to measureOvercome limitationsSystems biologyGenetic algorithmsComplete dataMissing data
The invention discloses a multi-target phylogenetic tree construction method based on feature hierarchy. The method comprises the steps: generating a corresponding feature hierarchy relation by combining with the feature description of form data, and estimating a missing value by combining with the dependence relation between features to obtain a complete data set; and by combining with a maximumreduction principle and a maximum likelihood principle based on an inapplicable Fitch algorithm, carrying out parallel multi-target phylogenetic tree construction, so that problems caused by inapplicable data be well measured, and the limitation of tree construction under a single principle is avoided. Compared with a traditional phylogenetic analysis method, the method of the invention has the advantages that the problem of tree structure uncertainty caused by missing data and inapplicable data can be well solved, and a basis is provided for biologists to research species evolution through various tree building principles.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Specific amplification primers of ganoderma mitochondrion rns gene and application of specific amplification primer
PendingCN110408717AEasy identificationEffectively eliminate gene interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismNucleotide
The invention discloses specific amplification primers of a ganoderma mitochondrion rns gene and application of the specific amplification primers, and relates to the field of genetic evolution. The primers comprise an upstream primer and a downstream primer, a nucleotide sequence of the upstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and a nucleotide sequence of the downstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The primers can carry out specific amplification on ganoderma species at a time in large batches, interference of genes of animals, plants and microorganisms in samples or environment is effectively eliminated, and great convenience is provided for identification, variety breeding, phylogenetic analysis and strain monitoring of the ganoderma species. The magnitude of products amplifiedby the specific amplification primers is 650-750bp, sufficient genetic loci are provided for species distinguishing and identification, it can be guaranteed that all sequences can be measured throughone sequencing reaction, species mitochondria do not need to be independently separated and extracted, and the primers have the advantages of easy operation, cost saving and convenient using.
Owner:SAAS BIOTECH & NUCLEAR TECH RES INST
Achromobacter marplatensis and application thereof
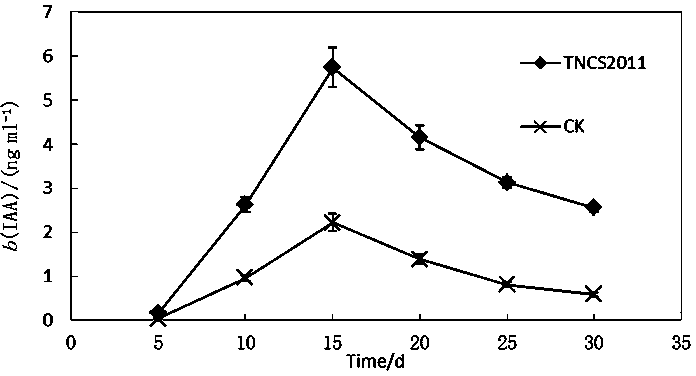
ActiveCN103642733AStrong ability to secrete IAAIncrease the sugar contentPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyEndophyte
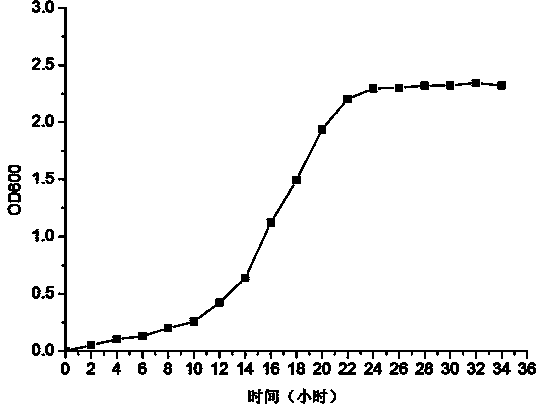
The invention discloses achromobacter marplatensis TNSC2011with a preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) No.8192 and an application thereof in sugar beet cultivation. Taxonomic status of the obtained bacterial strain is primarily determined by carrying out determination and phylogenetic analysis of morphological characteristics, physiological-biochemical characteristics and a 16 SrDNA sequence on the obtained bacterial strain; meanwhile, characteristics such as bacteriostasis rate, growth promotion and stability of fermentation liquor of the bacterium TNSC2011 are deeply researched, so that crop growth can be effectively promoted; slightly-soluble phosphate can be converted into soluble phosphate which can be biologically utilized, so that photosynthesis is improved, and the achromobacter marplatensis is proved to be an excellent endophyte with the serial number of TNSC2011; the endophyte is applied on sugar beet cultivation to obtain a good effect, so that technical effect is outstanding and application value is wide.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Specific SSR primers for malus sieversii and cultivated apple and applications of specific SSR primers
ActiveCN108660239AHigh differentiation levelLow level of differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAgricultural scienceMalus sieversii
The invention discloses specific SSR primers for malus sieversii and the cultivated apple and applications of the specific SSR primers. Based on the whole genome sequence of the cultivated apple, a functional gene sequence relevant to the stress resistance of apple is adopted as a template, and 15 pairs of SSR primers amplifying SSR target bands with specificity, stability and polymorphism in malus sieversii and the cultivated apple are screened, wherein the nucleotide sequences of the SSR primers are as shown in SEQ ID No.1-30. 8 pairs of SSR primers only capable of amplifying SSR target bands in the cultivated apple with specificity are also screened. The protein products coded by the target bands amplified by the SSR primers are known, and the SSR primers can be used for carrying out genetic diversity, polymorphis or phylogenetic analysis on the malus sieversii and cultivated apple, thus disclosing the genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of the malus sieversii and cultivated apple and the influences of the obtained genetic variation on the malus sieversii and cultivated apple in the aspects including the biological function.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
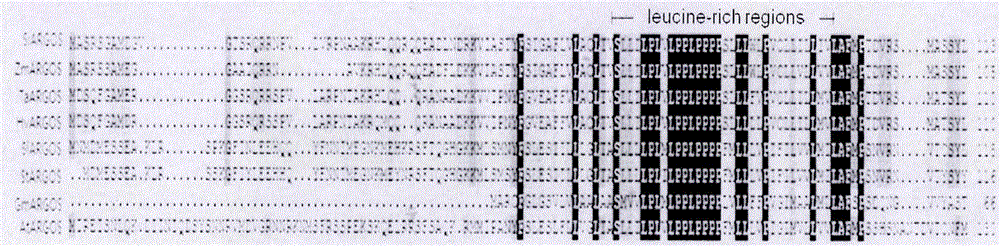
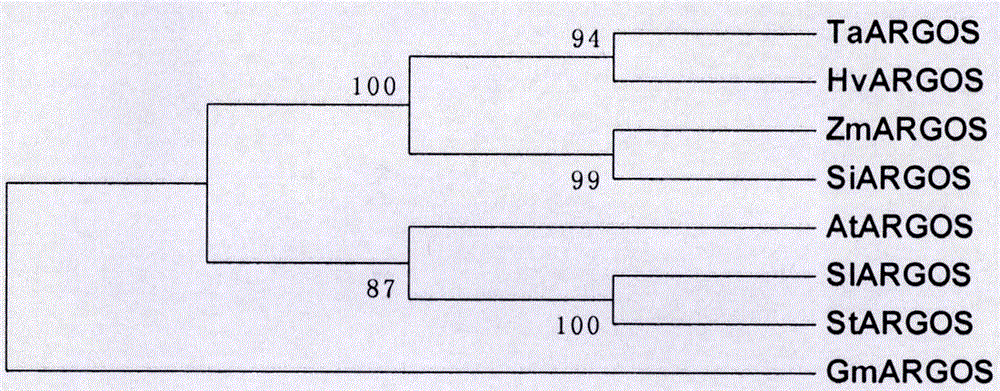
Cloning, expression analysis and functional marker development methods of millet SiARGOS gene
PendingCN107435046AHigh homologyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesSequence analysisPlant hormone
The invention discloses cloning, expression analysis and functional marker development methods of millet SiARGOS gene. Millet SiARGOS gene coding region and promoter sequence are cloned. It is found through sequence analysis that SiARGOS gene open reading frame 342bp codes 114 amino acids and the protein has crop ARGOS protein typical leucine-rich domain and promoter region 2109bp and contains various plant hormone regulation-related components such as auxin, ethene, jasmonic acid, gibberellins, etc. Phylogenetic analysis shows that millet ARGOS protein has the highest homology as corn ARGOS protein. It is found through expression analysis that SiARGOS gene has great differences in expression level of Jin 29A, K186 and their hybrid F1 roots. It is found through SiARGOS gene allelic variation analysis that one SNP exists in SiARGOS gene ORF, 19 SNPs and 2 InDels exist in the promoter region and four haplotypes are found. Three functional markers have been developed, including one CAPS marker and two SSR markers.
Owner:山西省农业科学院谷子研究所
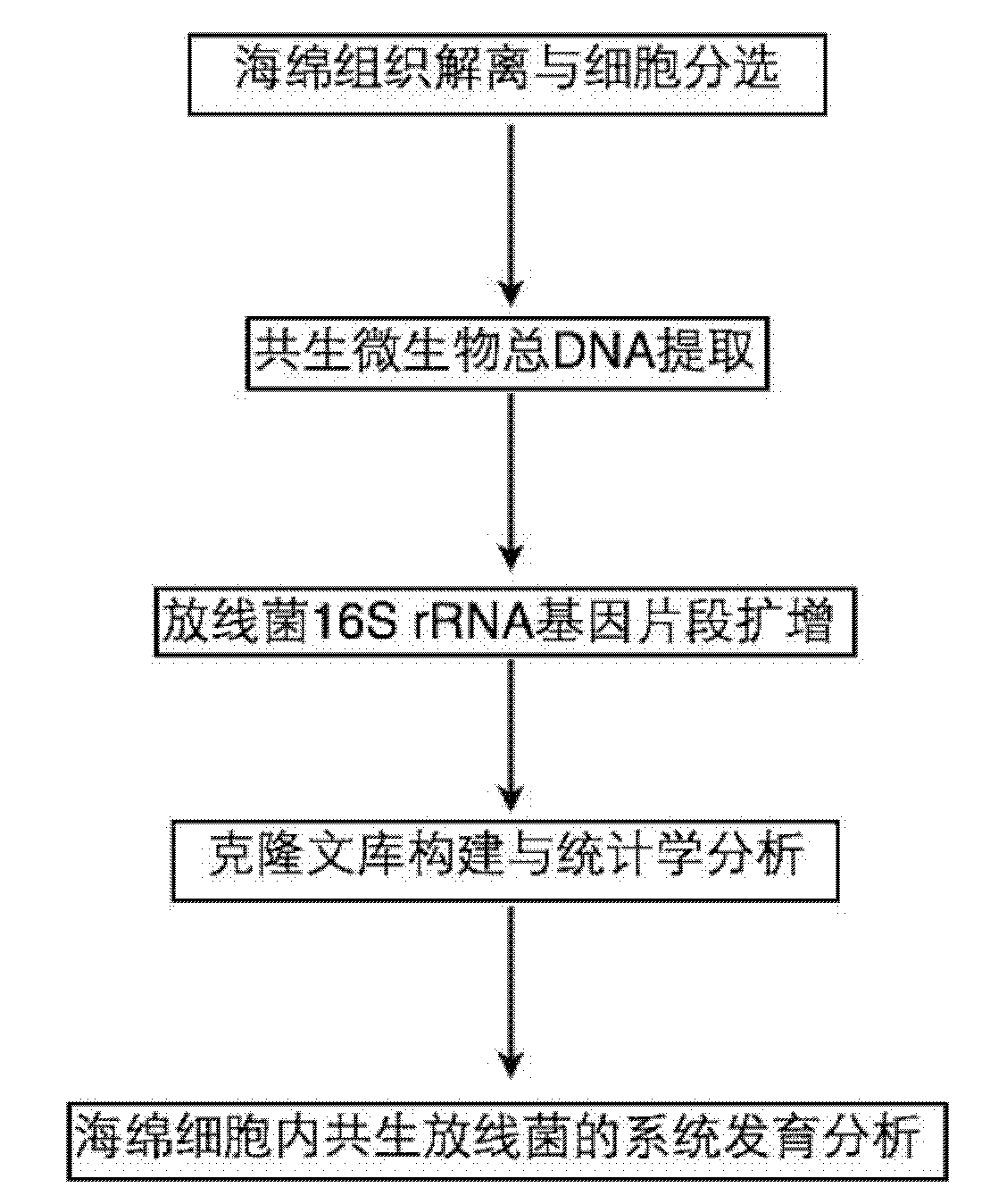
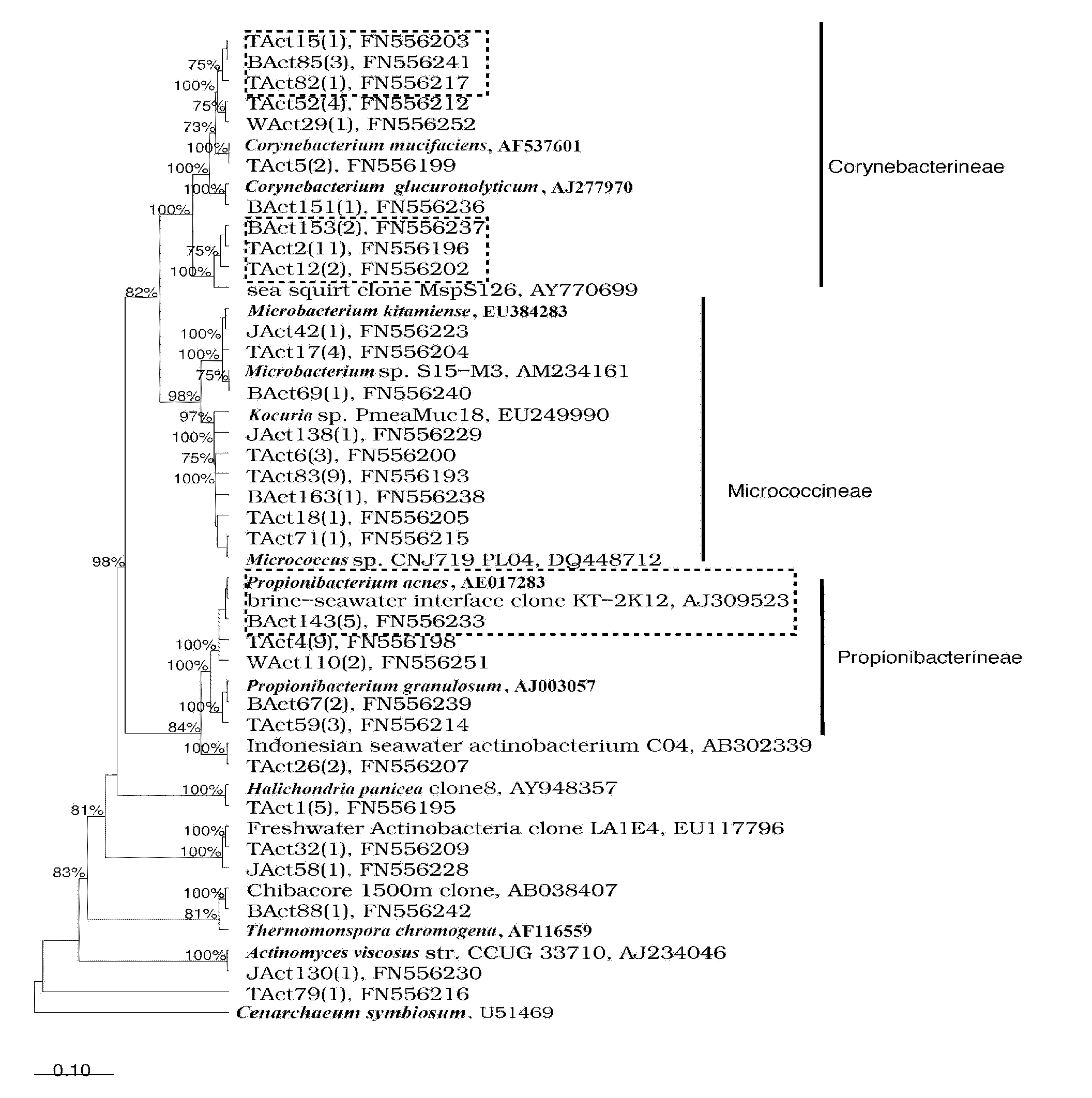
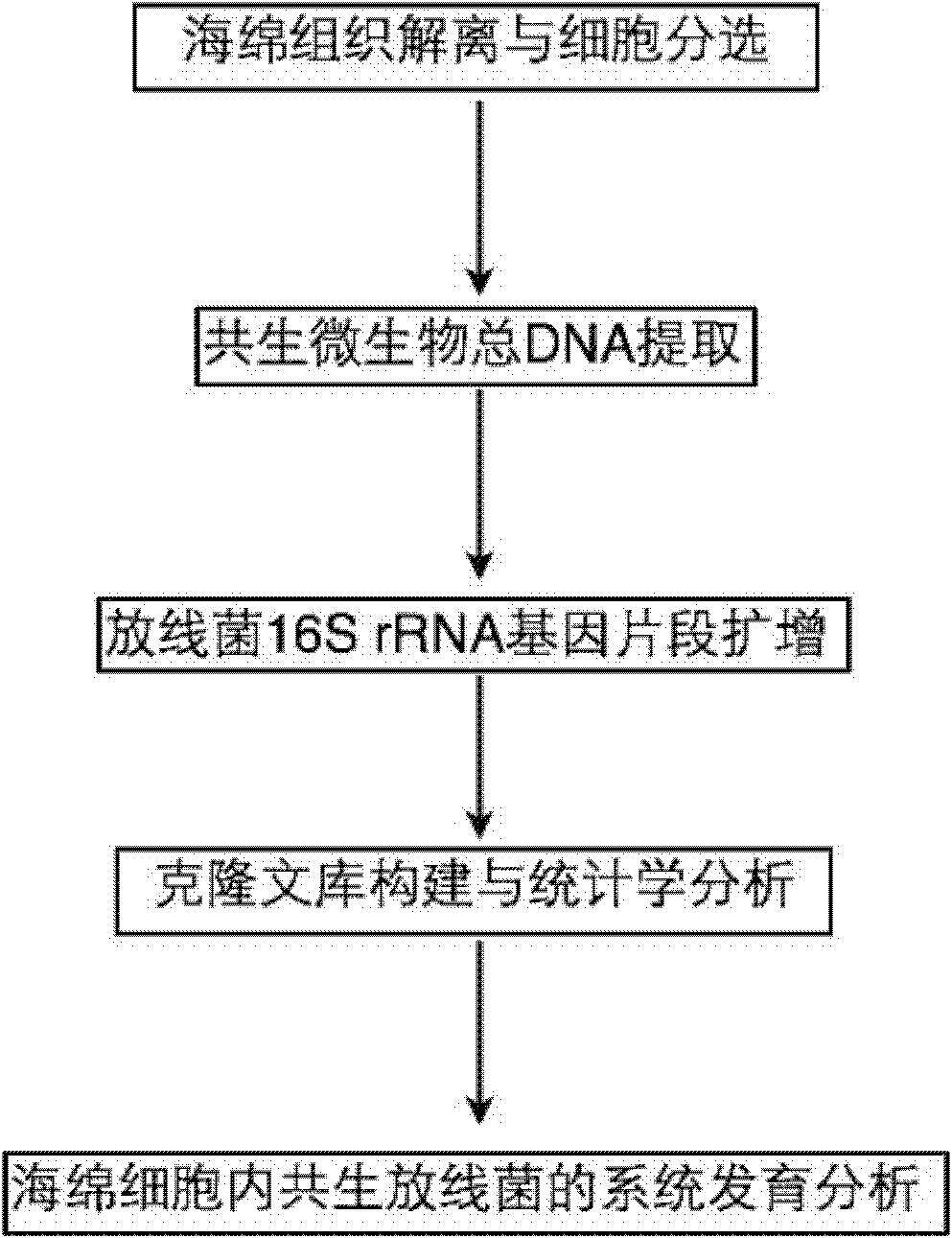
Molecule detection method of spongioblast endosymbiotic actinomycetes
InactiveCN101880713AEasy accessIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMicroorganism
The invention relates to a molecule detection method of spongioblast endosymbiotic actinomycetes, comprising the following steps of: obtaining sponge single cells by combining a mechanical method and a chemical method and extracting the total DNA in the spongioblast endosymbiotic microorganisms; amplifying the segment of an actinomycetes 16SrRNA gene through a polymerase chain reaction by using an actinomycetes species specificity primer by taking the extracted total DNA as a template; purifying the amplified product to construct and clone a library, randomly selecting positive clone for sequencing until the library is saturated, and importing a sequencing result and the closest sequence into an ARB sequence analysis software for phylogenetic analysis to finish the molecule detection of spongioblast endosymbiotic actinomycetes. The invention establishes a set of relatively comprehensive and accurate molecule detection method of spongioblast endosymbiotic actinomycetes.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com