Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Phosphoproteomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phosphoproteomics is a branch of proteomics that identifies, catalogs, and characterizes proteins containing a phosphate group as a posttranslational modification. Phosphorylation is a key reversible modification that regulates protein function, subcellular localization, complex formation, degradation of proteins and therefore cell signaling networks. With all of these modification results, it is estimated that between 30%–65% of all proteins may be phosphorylated, some multiple times. Based on statistical estimates from many datasets, 230,000, 156,000 and 40,000 phosphorylation sites should exist in human, mouse, and yeast, respectively.
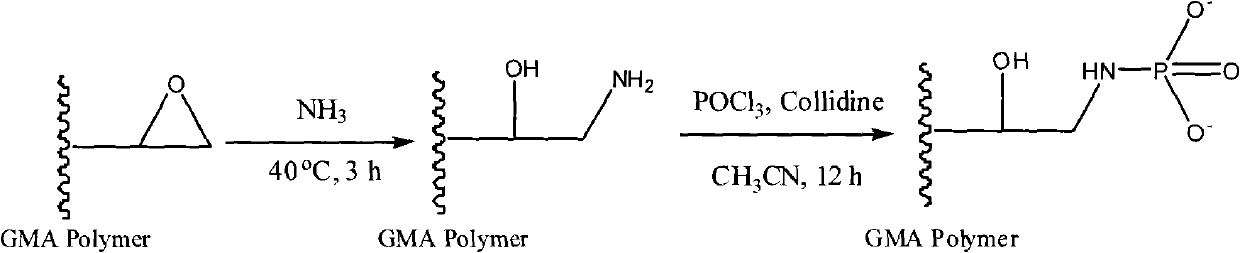
Affinity chromatography fixed phase of immobilization metal and its preparation method
InactiveCN101288844AImprove selective enrichment effectReduce non-specific adsorptionOther chemical processesSynthesis methodsMicrosphere
The invention relates to a separation and purification technique, in particular to an affinity chromatography stationary phase of immobilized metal and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the stationary phase is shown in the drawing; wherein, the particle size of GMAPolymer micro-sphere is 10nm-50um; the GMAPolymer micro-sphere is poly-methacrylic acid glycidyl esters micro-sphere. By carrying out amination and phosphoric esterification, a synthesis method of the high-performance poly-methacrylic acid glycidyl ester-group novel affinity chromatography stationary phase is gained and used for the research in phosphorylation proteomics and highly-selective separation, enrichment and purification of phosphopeptide by the chelation with zirconium ions and iron ions; meanwhile, compared with the traditional stationary phase, the affinity chromatography stationary phase reduces the nonspecific adsorption on the non-phosphopeptide.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid treatment method for phosphoproteome sample
InactiveCN104949864AQuick analysisPromote lysisPreparing sample for investigationHigh concentrationPretreatment method
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
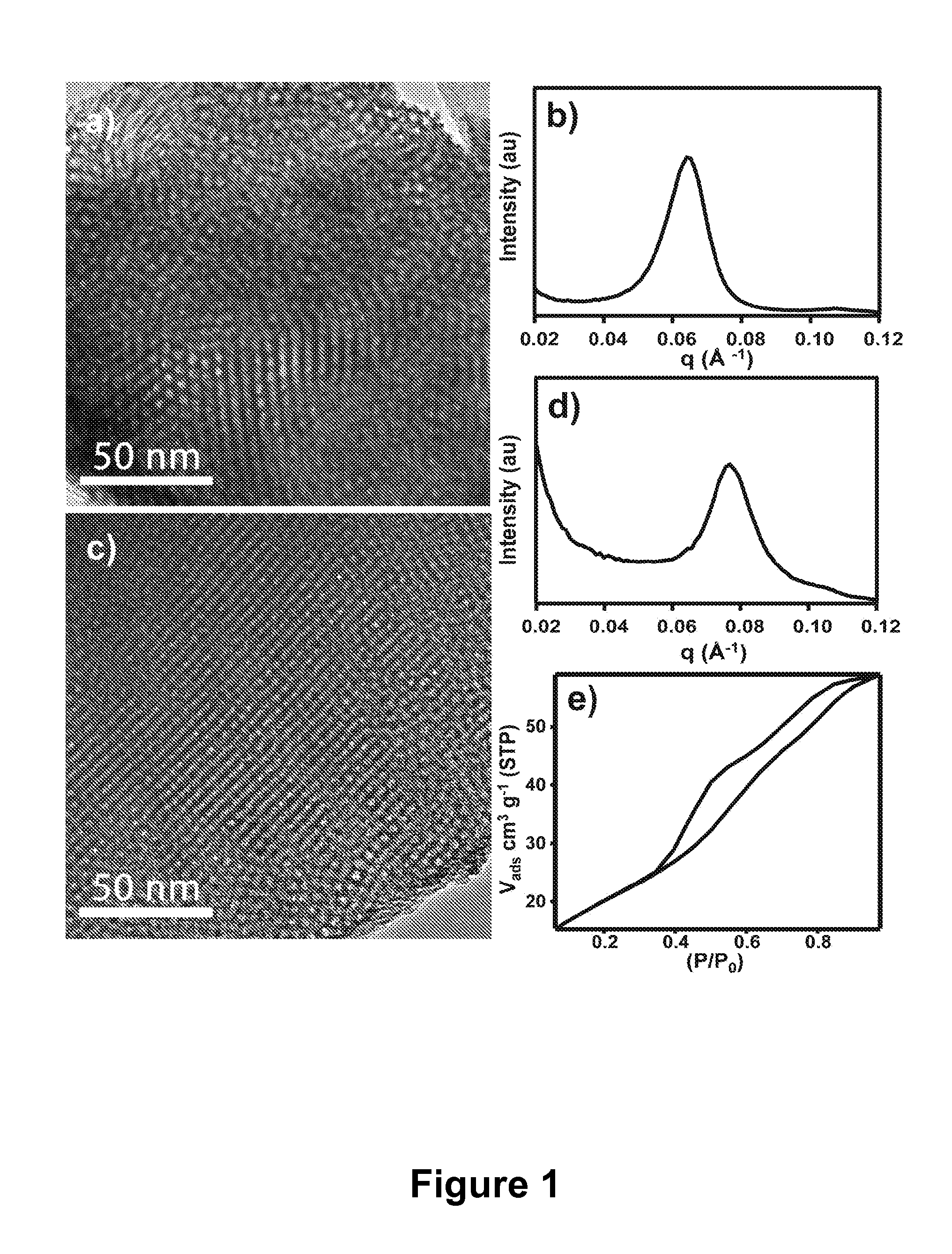
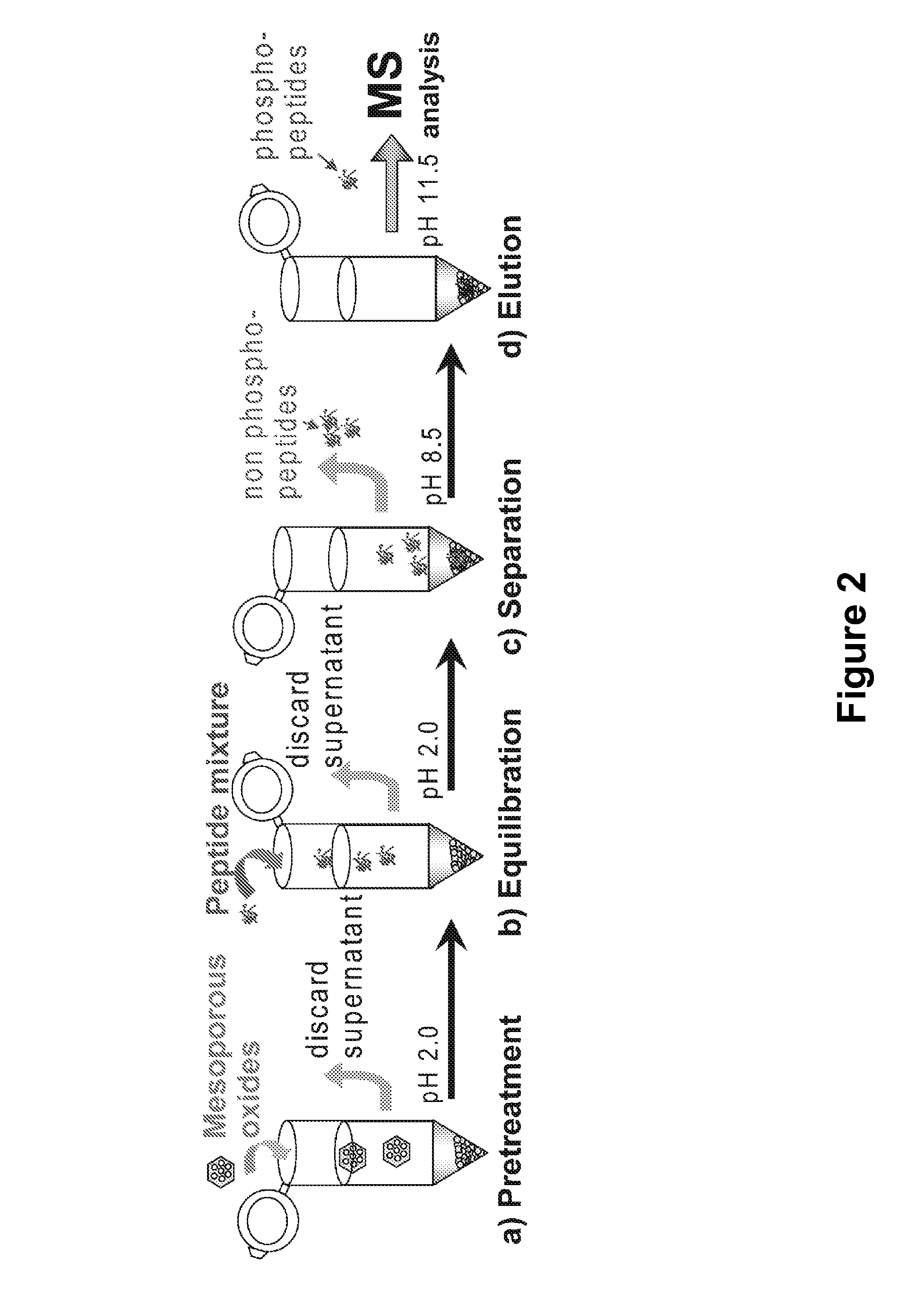
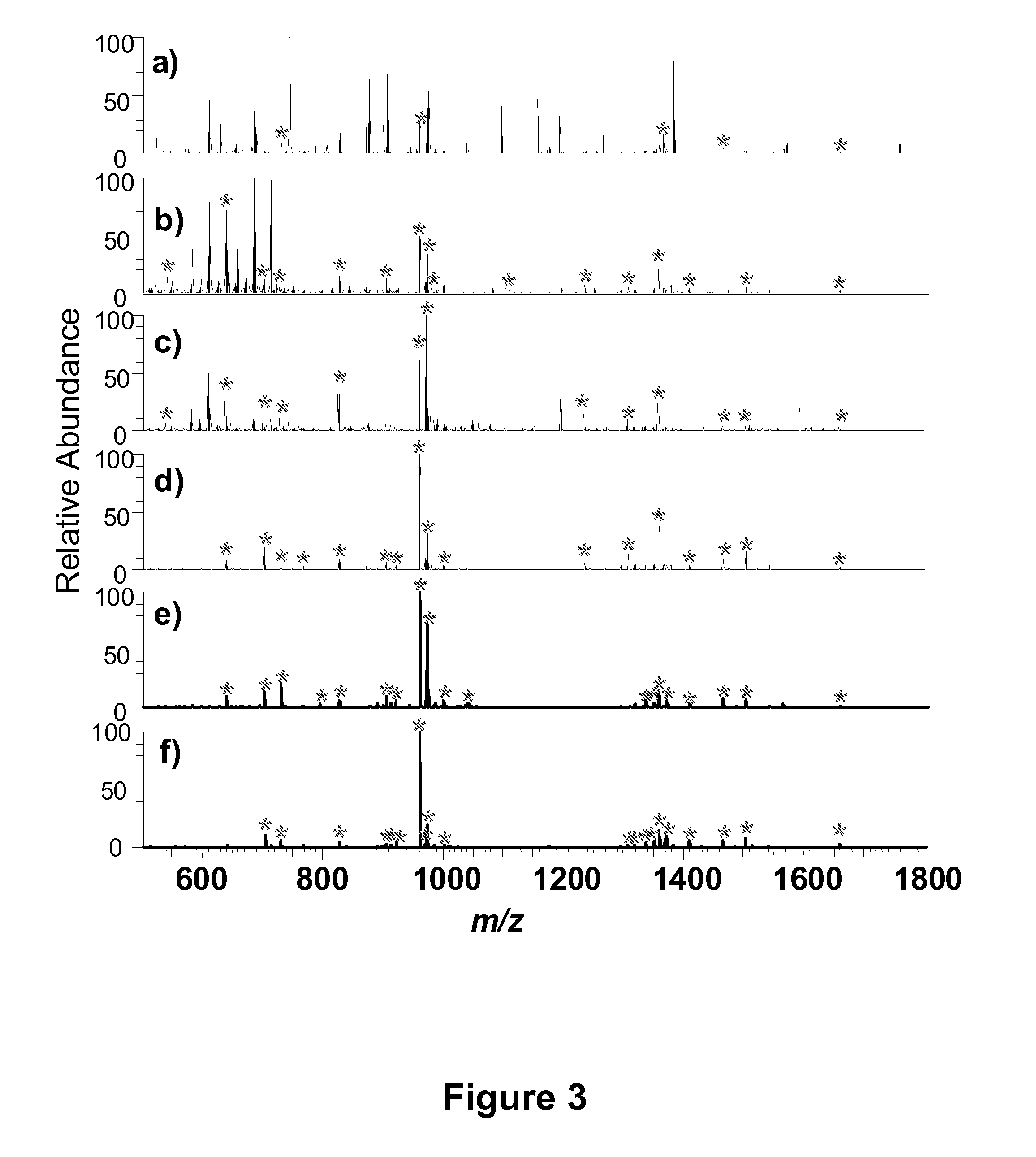
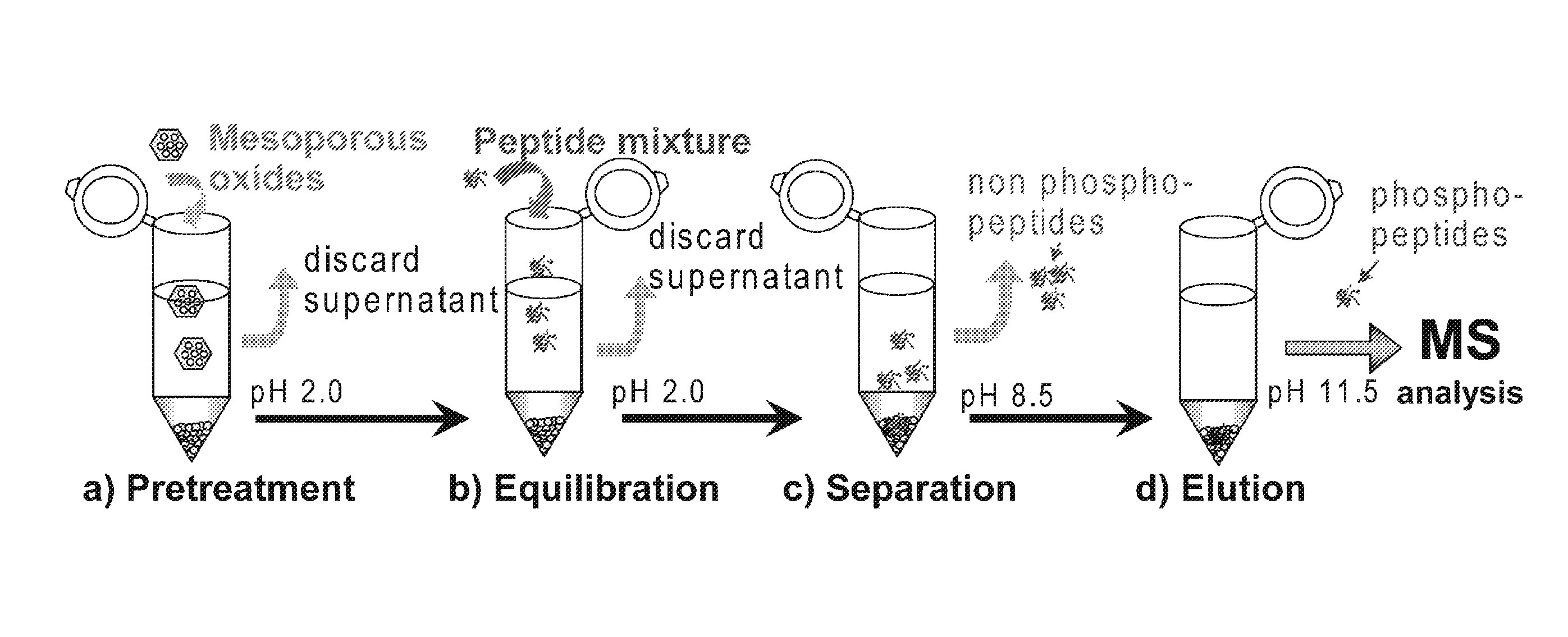
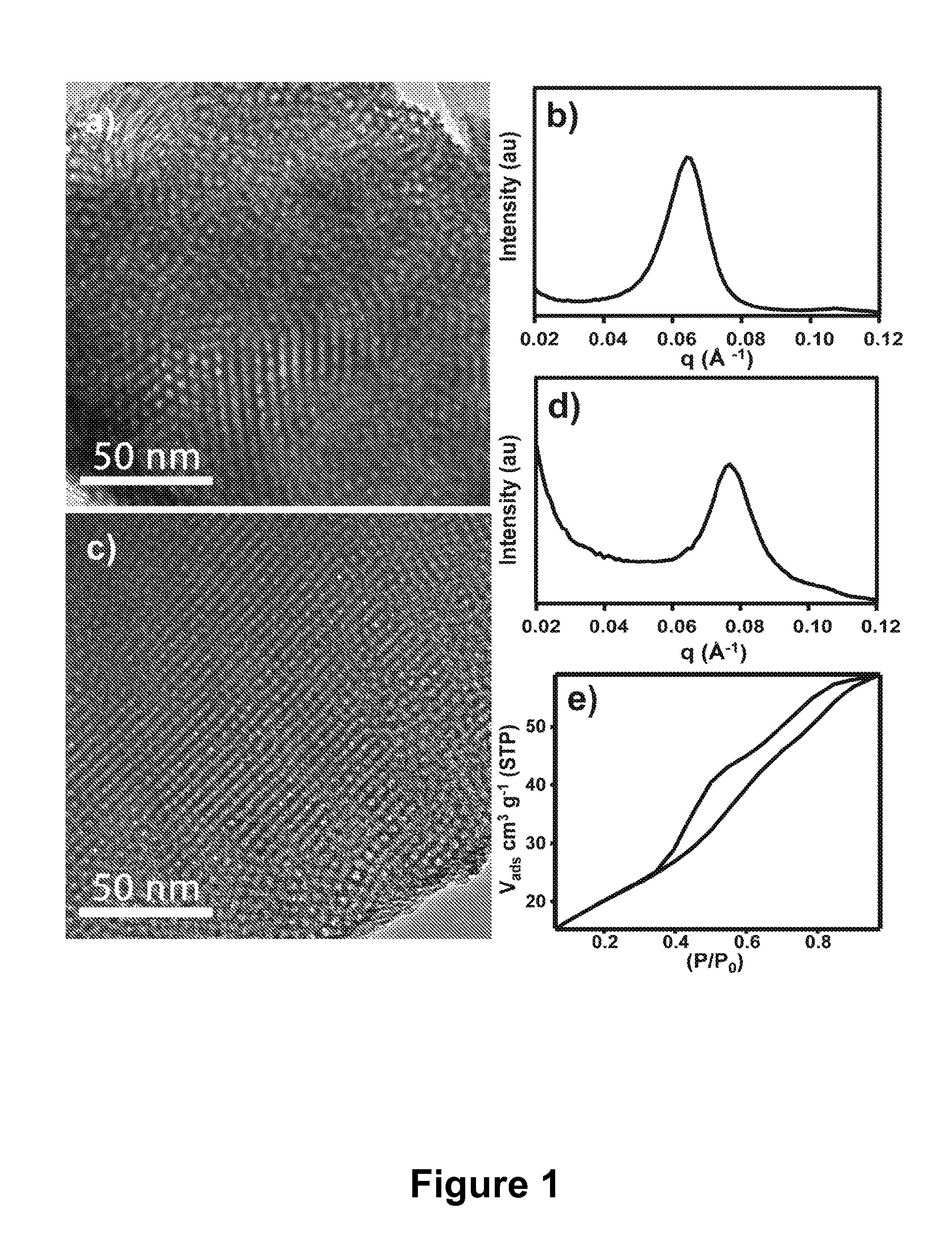
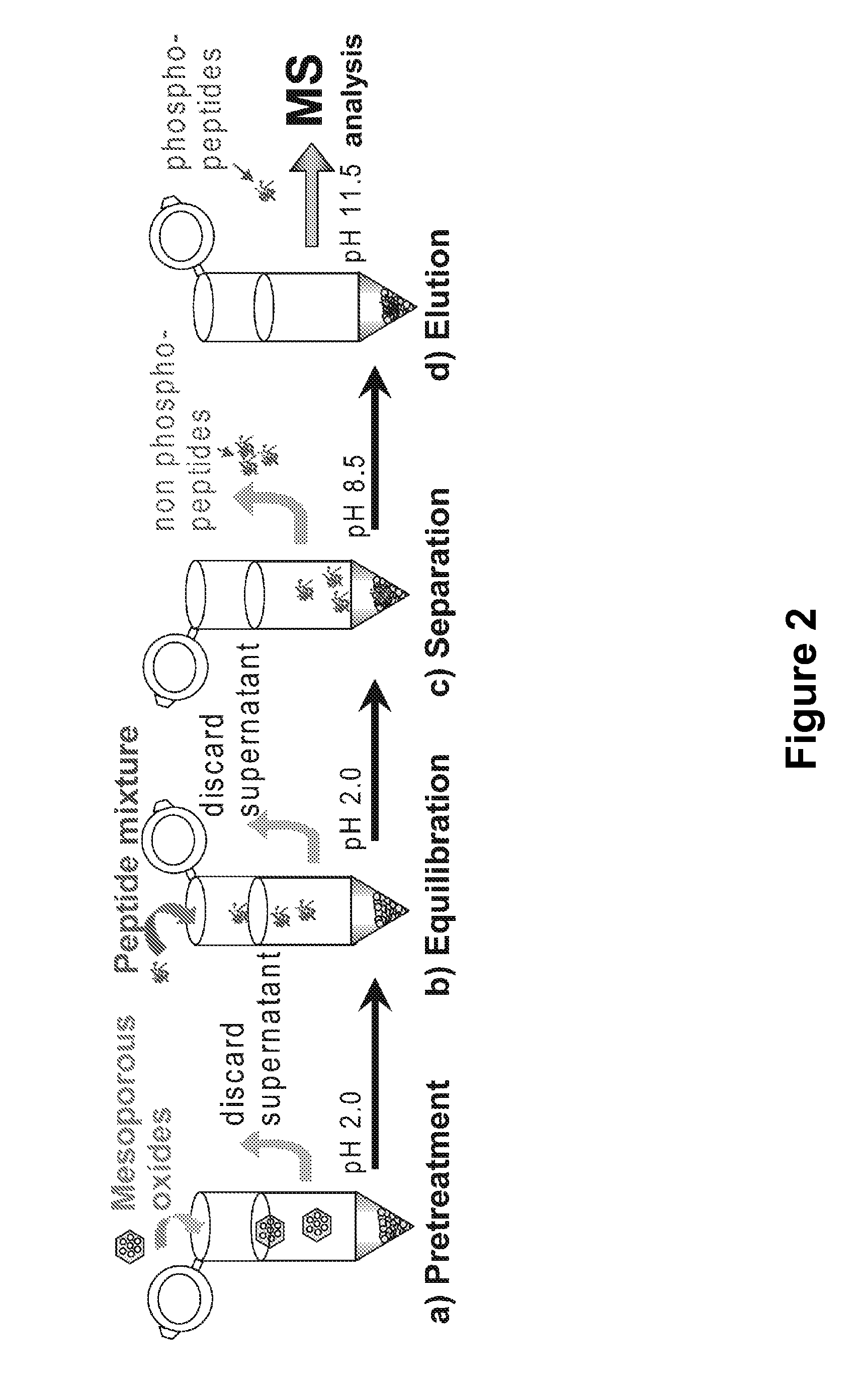
Mesoporous metal oxide materials for phosphoproteomics
ActiveUS20100093102A1Strong specificityIncrease load capacityComponent separationPeptide preparation methodsPhosphoric acidMesoporous material
The present invention provides methods and materials for isolating, purifying, and / or enriching the concentration of compounds having one or more phosphate groups and / or derivatives thereof, including but not limited to phosphorylated peptides and / or phosphorylated proteins. In some aspects, the present invention provides nanostructured enrichment materials, such as metal oxide mesoporous materials, that selectively and reversibly bind with phosphorylated compounds with high specificity and are capable of controlled release of phosphorylated compounds bound to their active surfaces. Mesoporous materials of the present invention also provide enrichment materials having large active surface areas that provide for higher loading capacities for phosphorylated peptides and proteins relative to conventional affinity based methods. Nanostructured metal oxide mesoporous enrichment materials of the present invention are also compatible with implementation via a variety of separation platforms including flow through separation systems, elution based separation systems, column chromatography and affinity chromatography.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Tyrosine phosphoproteomics analysis method of tyrosine phosphopeptide
InactiveCN108414606AStrong specificityEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationOmicsTrifluoroacetic acidElution
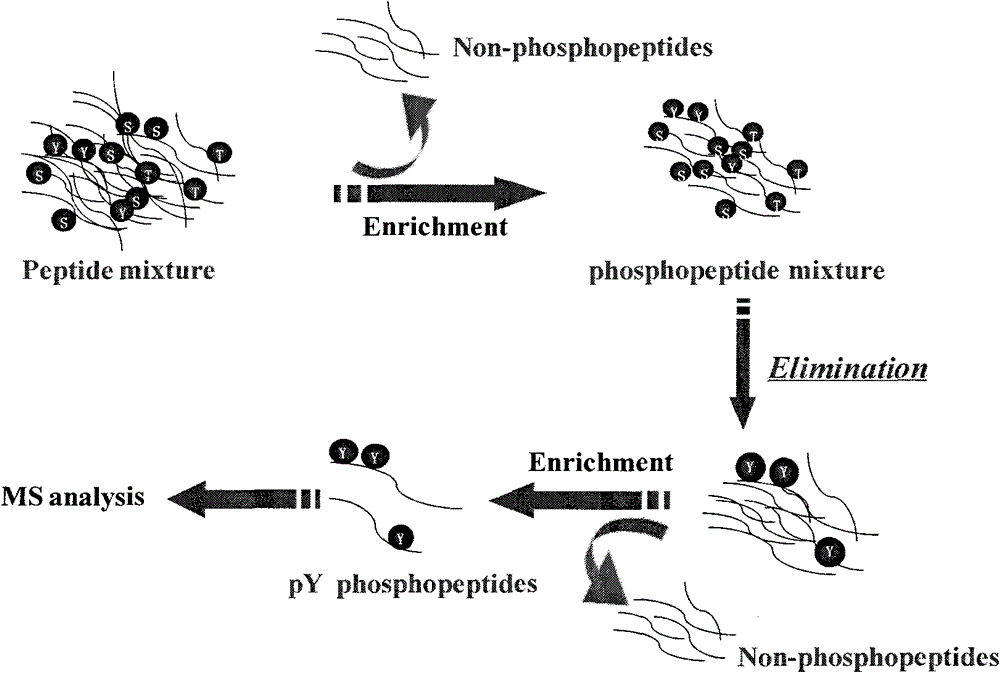
The present invention relates to a method for deep analysis of tyrosine phosphoproteomics based on competitive elution of affinity tyrosine phosphopeptide on a superbinder SH2. Specifically in the elution process of tyrosine phosphopeptide enrichment, a biotin-containing tyrosine phosphopeptide capable of strongly interacting with a superbinder SH2 is used as a competitive reagent to replace the traditional trifluoroacetic acid, the tyrosine phosphopeptide acting with the superbinder SH2 is sequentially eluted according to the intensity of the interaction, and the competitive reagent being notbound to the superbinder SH2 is bound by corresponding avidin so as not to affect the subsequent identification and analysis of the tyrosine phosphopeptide sample. According to the present invention,the method has advantages of rapidness, sensitivity, low cost and the like, can easily achieve the deep analysis of tyrosine phosphoproteomics, and can further provide the information of the interaction between the tyrosine phosphopeptide and the superbinder SH2.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for purifying tyrosine phosphopeptide
InactiveCN102199189AAchieve purificationStrong specificityPeptide preparation methodsPhosphoric acidPhosphopeptide
The invention discloses application of a beta-elimination and Michael nucleophilic addition method in study of phosphoproteomics, in particular a method for purifying tyrosine phosphopeptide. The method comprises the following steps of: eliminating phosphate modification groups on non-tyrosine phosphopeptide in protein hydrolysate by using beta-elimination and Michael nucleophilic addition; and enriching the tyrosine phosphopeptide which is not subjected to the elimination reaction by using a phosphoeptide enriching material. By utilizing the high specificity of the beta-elimination and Michael nucleophilic addition, the tyrosine phosphopeptide is purified from a complicated protein hydrolysate sample in high selectivity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for accumulating cotton phosphorylated protein
InactiveCN101967181ALow priceImprove efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a method for accumulating cotton phosphorylated protein, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the steps of extracting cotton total protein and utilizing the Al(OH)3 affinity chromatography to accumulate cotton phosphorylated protein. By using the method, 12mu g of phosphorylated protein can be accumulated from 1mg of cotton total protein so that the accumulation efficiency is more than 6 times of that of the imported Qiagen kit. The two-dimensional electrophoresis technology and the phosphorylated protein specific dye ProQ DiamondTM (Invitrogen) dyeing test prove that the phosphorylated protein accumulated by the method has no non-phosphorylated protein. The method can replace the expensive imported kit, be used to accumulate phosphorylated protein efficiently and specificly and be widely used in researches such as phosphorylated proteomics and cellular signal.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
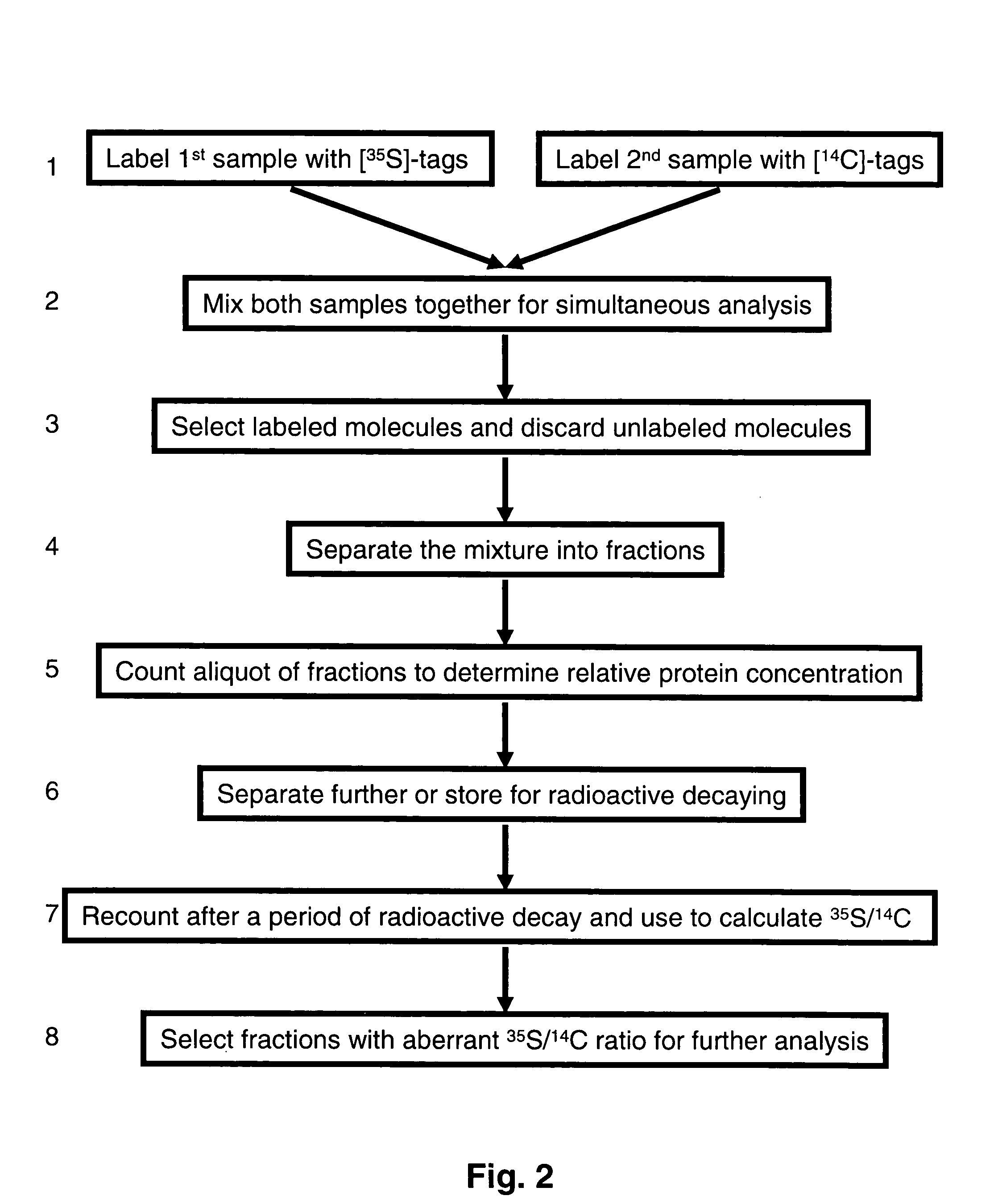
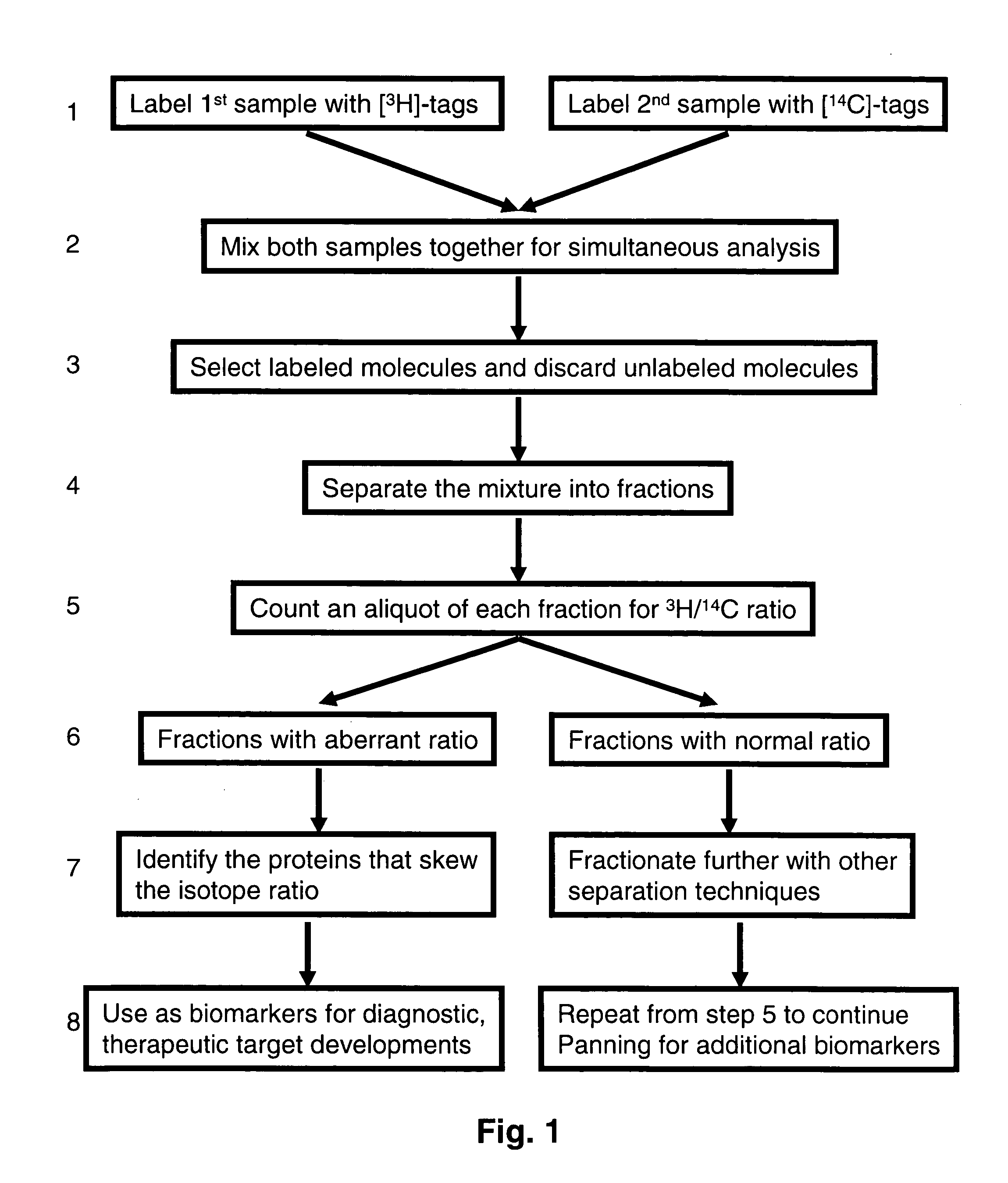
Methods and reagents for differential proteomic analysis
InactiveUS20050074794A1Easy to analyzeSimple methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsEpigenome
Methods and reagents for labeling molecules of interest in a plurality of samples, and then combining and selecting labeled molecules away from unlabeled molecules for use in simultaneous co-assaying analysis. The reagents comprise labeling means of distinguishable radioactive isotopes which remain with the labeled molecules. Additionally, the reagents also comprise selection means which can be affinity tags, beads, or immobilized surface which may remain or be cleaved off through cleavable linkers. A set of labeling reagent can be used to label a plurality of samples, combine them before or after selecting / enriching for labeled molecules and co-assay together for reliable comparison. This invention has many applications in comparing and panning for differentially abundant molecules or differential modification of molecules for proteomics, glycomics, phospho-proteomics, metabolomics, epi-genomics . . . studies.
Owner:PROTEOMYX
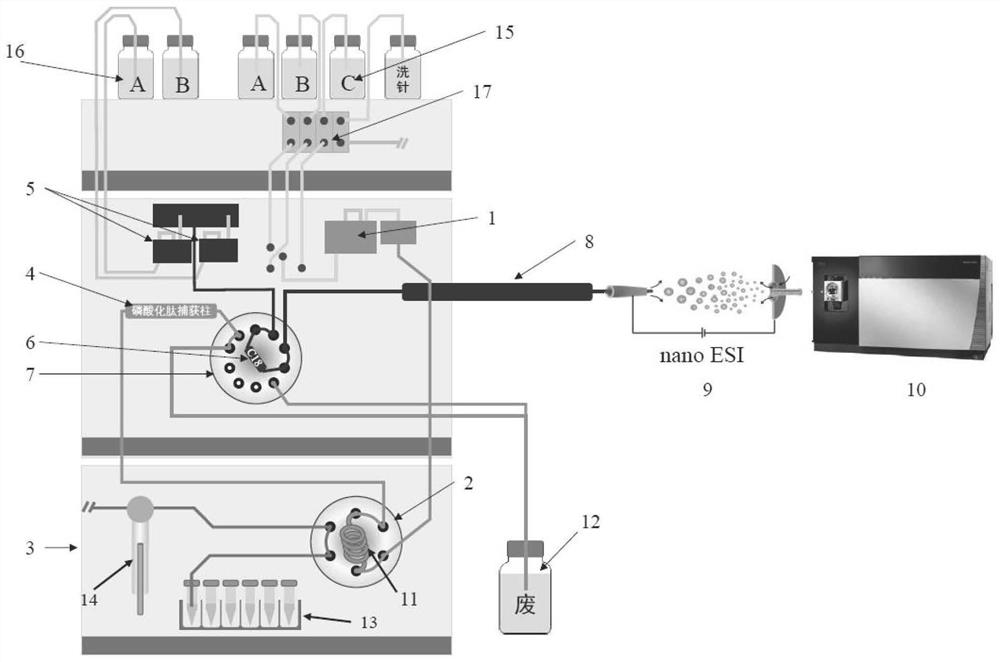
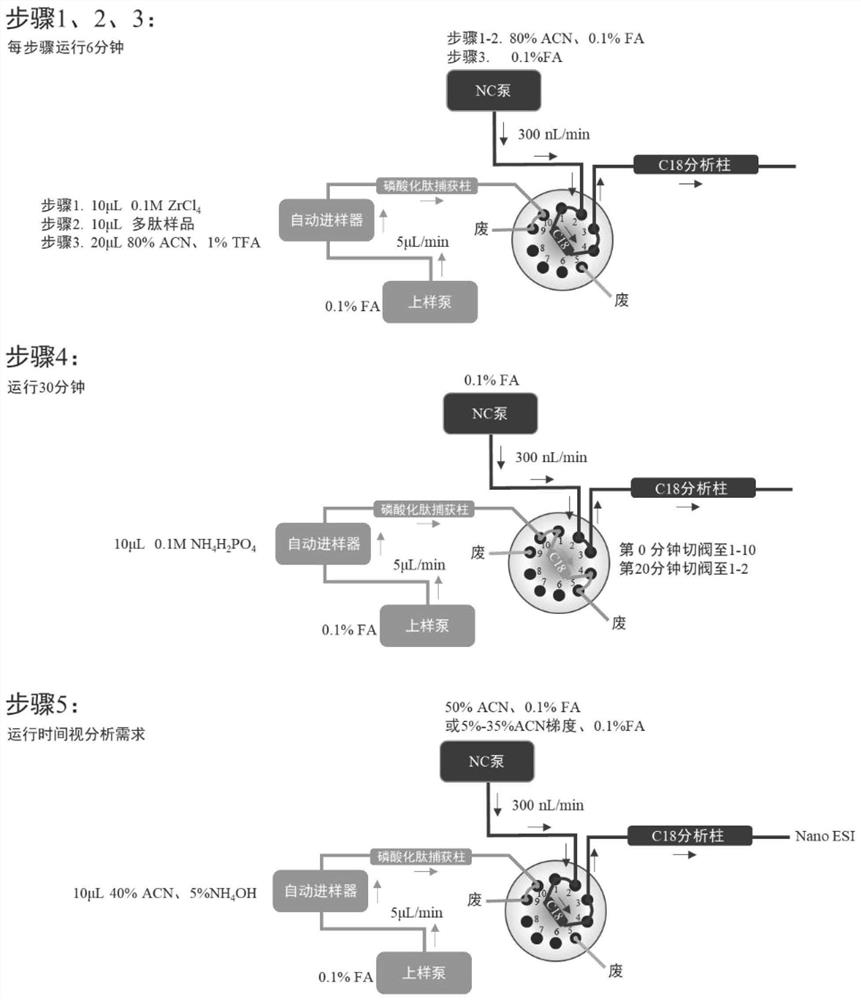
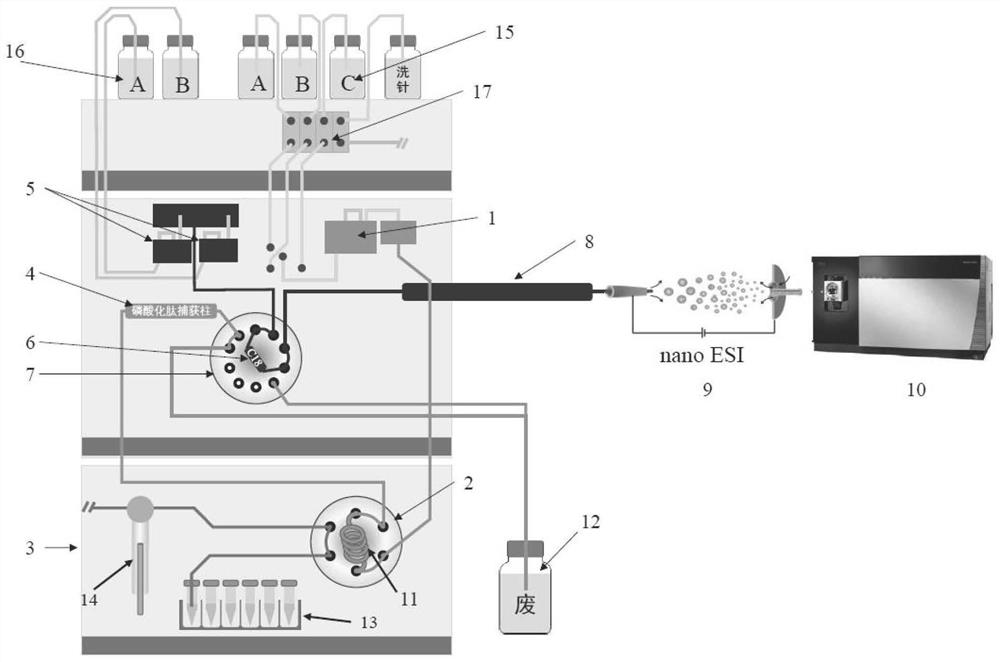
Online automatic analysis device and analysis method for phosphorylated proteomics
ActiveCN113607868AImprove consistencyAnalysis does not affectComponent separationLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopyPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses an online automatic analysis device and an analysis method for phosphorylated proteomics. The device is a liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer, the liquid chromatograph comprises a phosphorylated peptide capture column and an analytical column, and the phosphorylated peptide capture column is an ATP modified immobilized metal ion affinity chromatographic column; and potassium water glass, gamma-glycidyl ether oxypropyl trimethoxy silane and water-dissolved adenosine disodium triphosphate are mixed and stirred, then formamide dissolved with water is added and stirred to obtain a reaction solution, a chromatographic column is filled with the reaction solution, then the reaction solution filling the chromatographic column is subjected to a reaction curing, washing is performed, and the ATP modified immobilized metal ion affinity chromatographic column is obtained. The device has the primary advantage that researchers are liberated from complicated manual operations such as metal ion loading, sample loading, washing, elution, desalting, drying and redissolving required by enrichment of phosphorylated peptides, so that the experiment efficiency is improved.
Owner:AGRO BIOLOGICAL GENE RES CENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
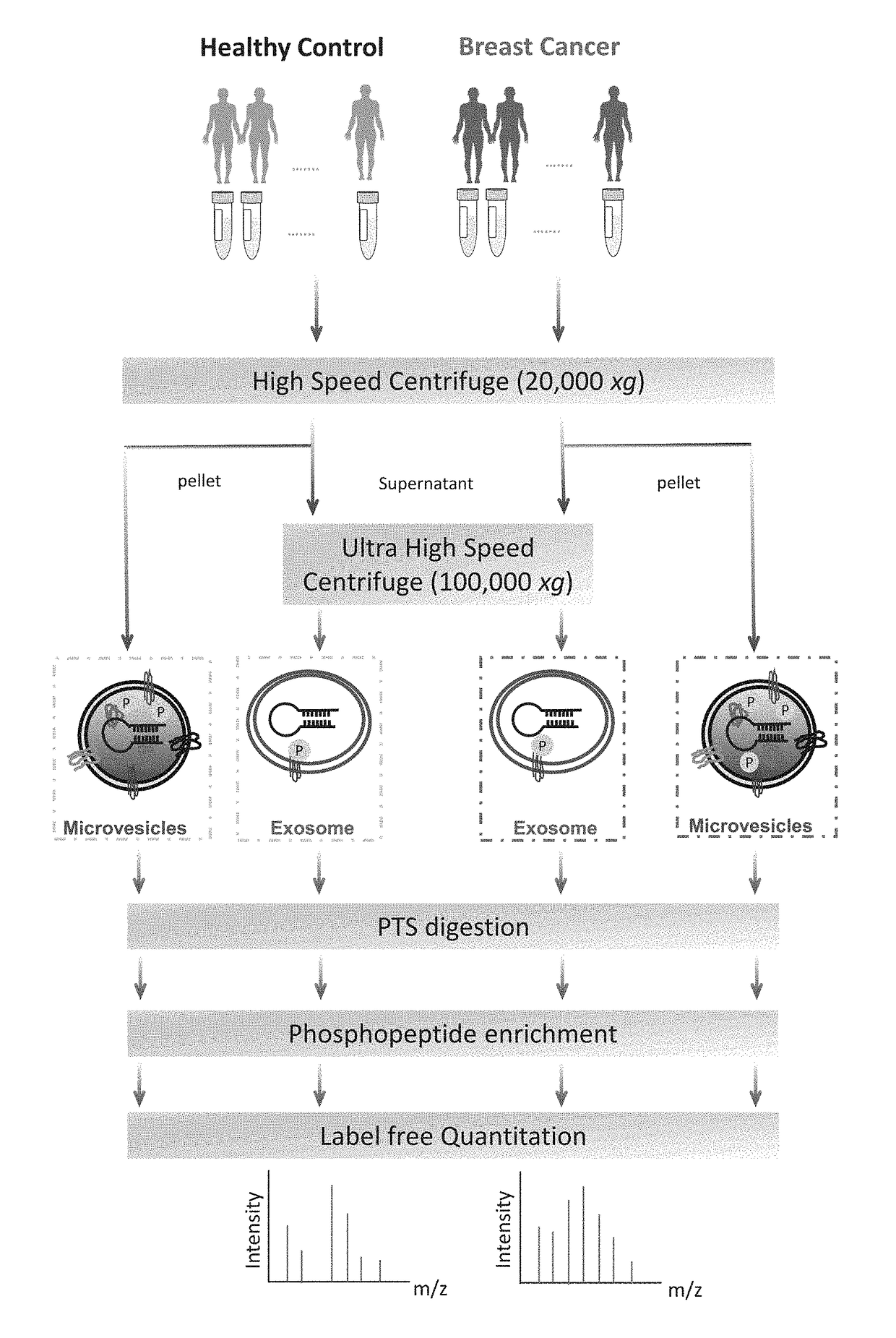
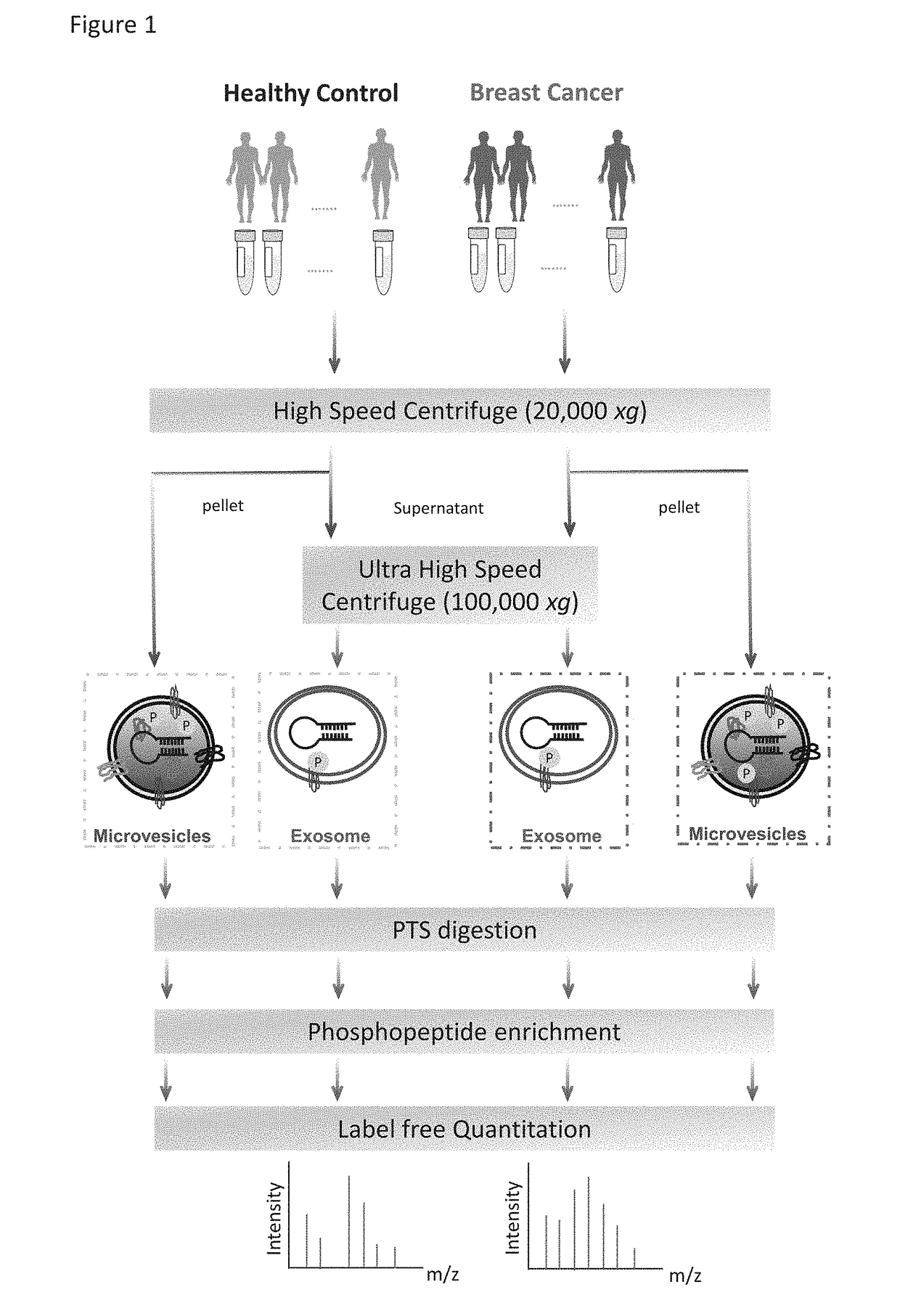
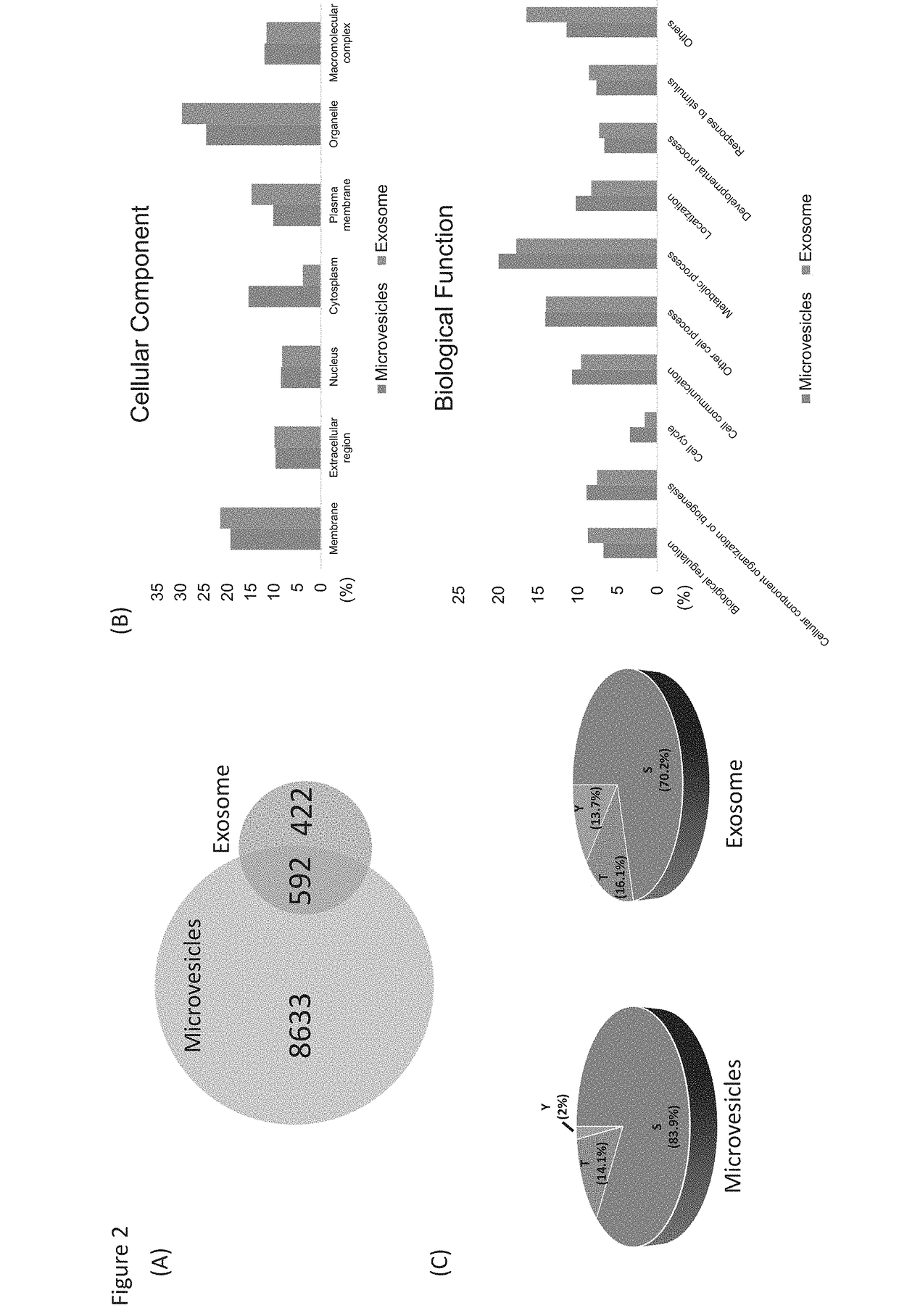
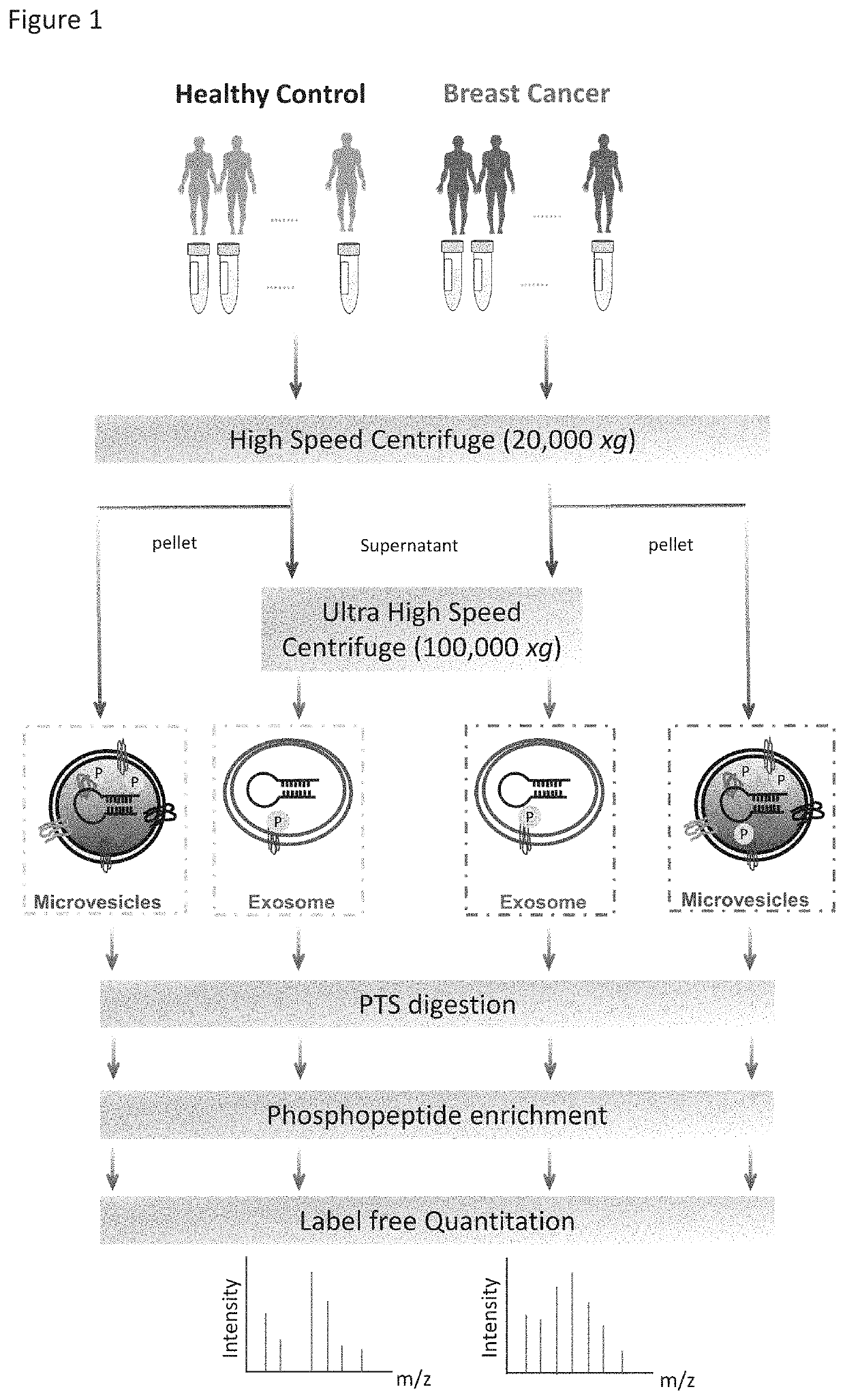
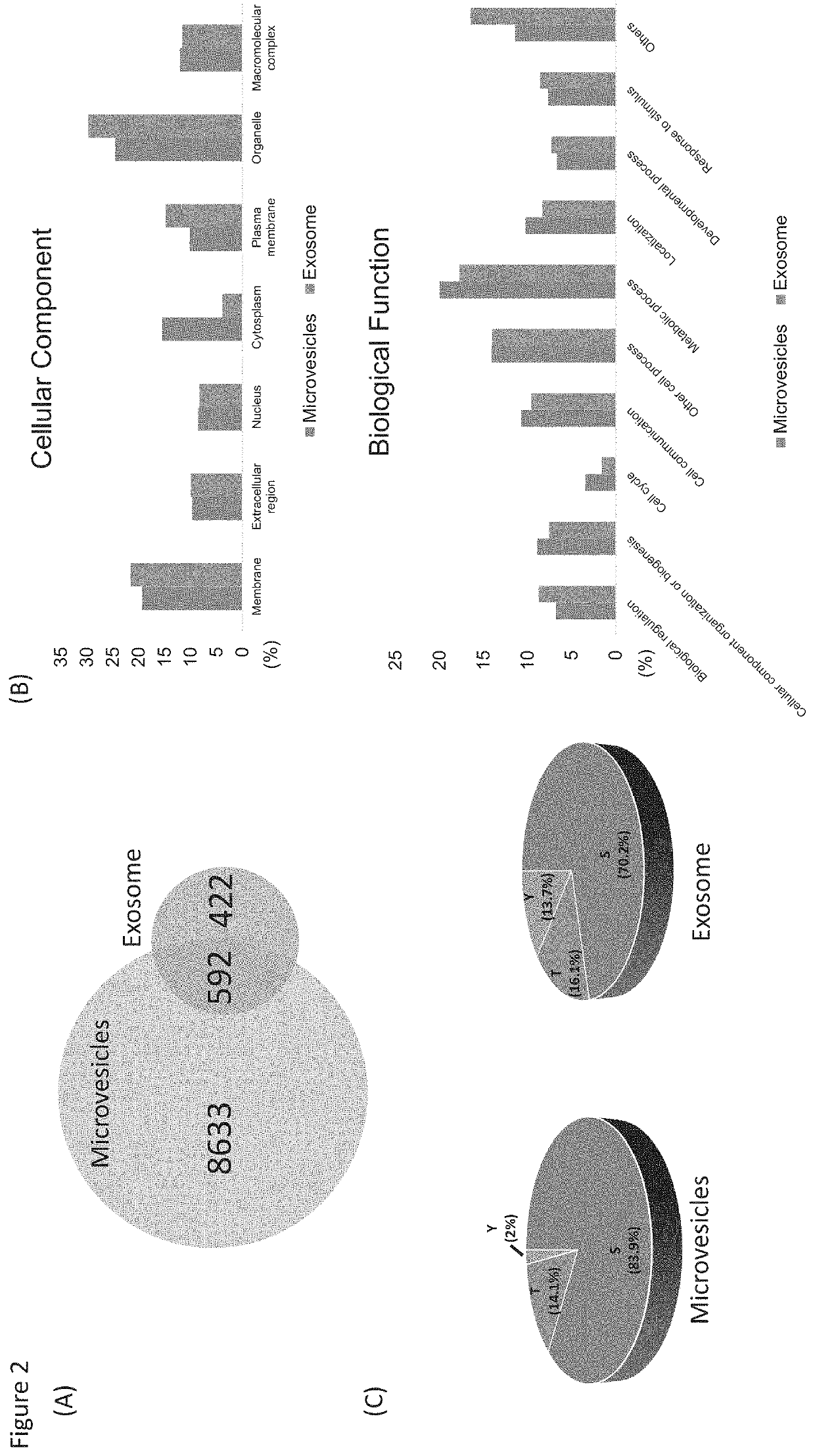
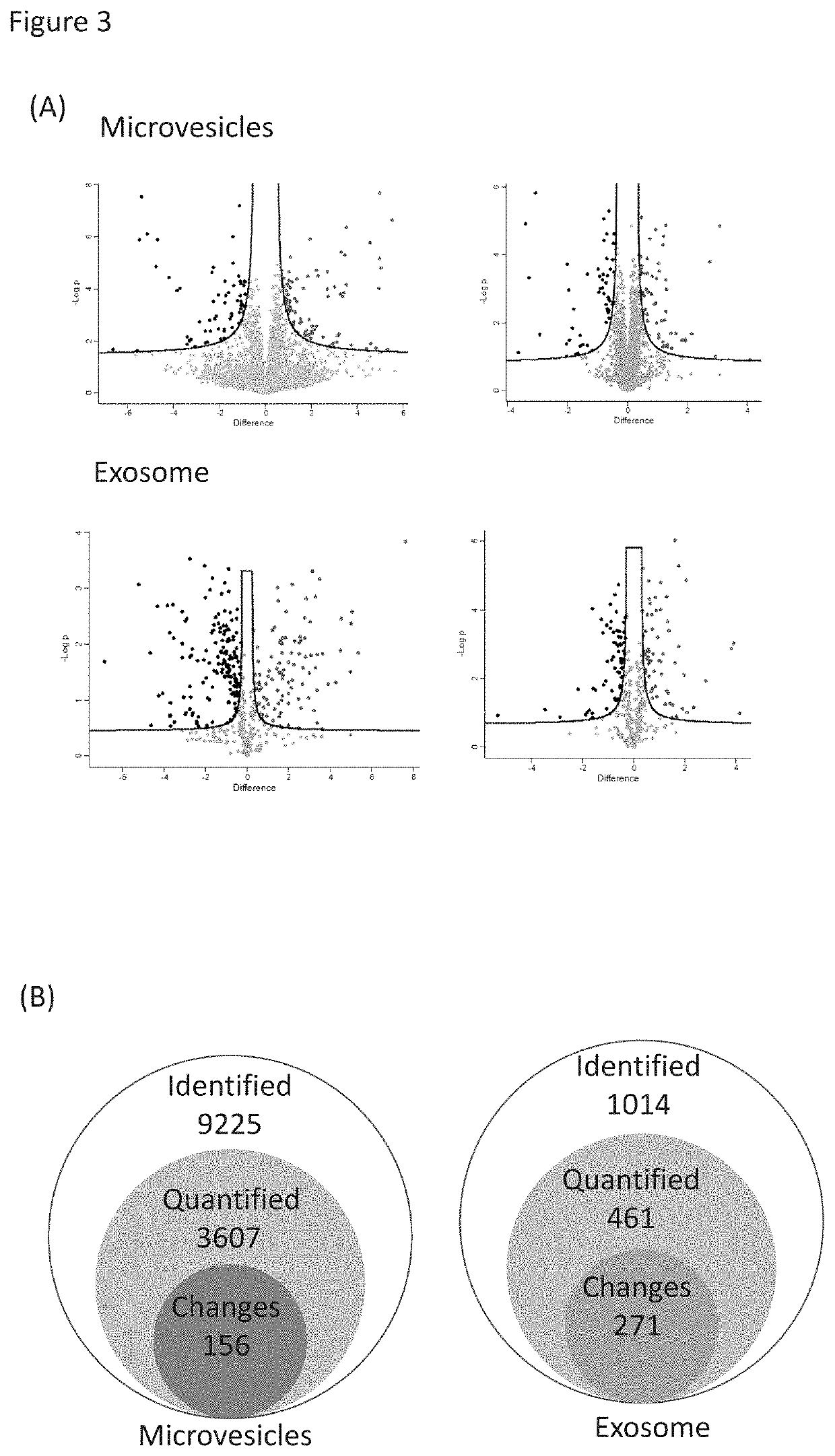
Phosphoproteins in Extracellular Vehicles as Candidate Markers for Breast Cancer
The state of protein phosphorylation and glycosylation can be key determinants of cellular physiology such as early stage cancer, but the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in biofluids for disease diagnosis remains elusive. Here we demonstrate, for the first time, a strategy to isolate and identify phosphoproteins / glycoproteins in extracellular vehicles (EVs) from human plasma as potential markers to differentiate disease from healthy states. We identified close to 10,000 unique phosphopeptides in EVs by isolating from small volume of plasma samples. Using label-free quantitative phosphoproteomics, we identified 144 phosphoproteins in plasma EVs that are significantly higher in patients diagnosed with breast cancer than in healthy controls. Several novel biomarkers were validated in individual patients using Paralleled Reaction Monitoring for targeted quantitation. Similarly a group of glycoproteins in plasma EVs are identified. The study demonstrated that the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in plasma EV as disease biomarkers is highly feasible and may transform cancer screening and monitoring.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
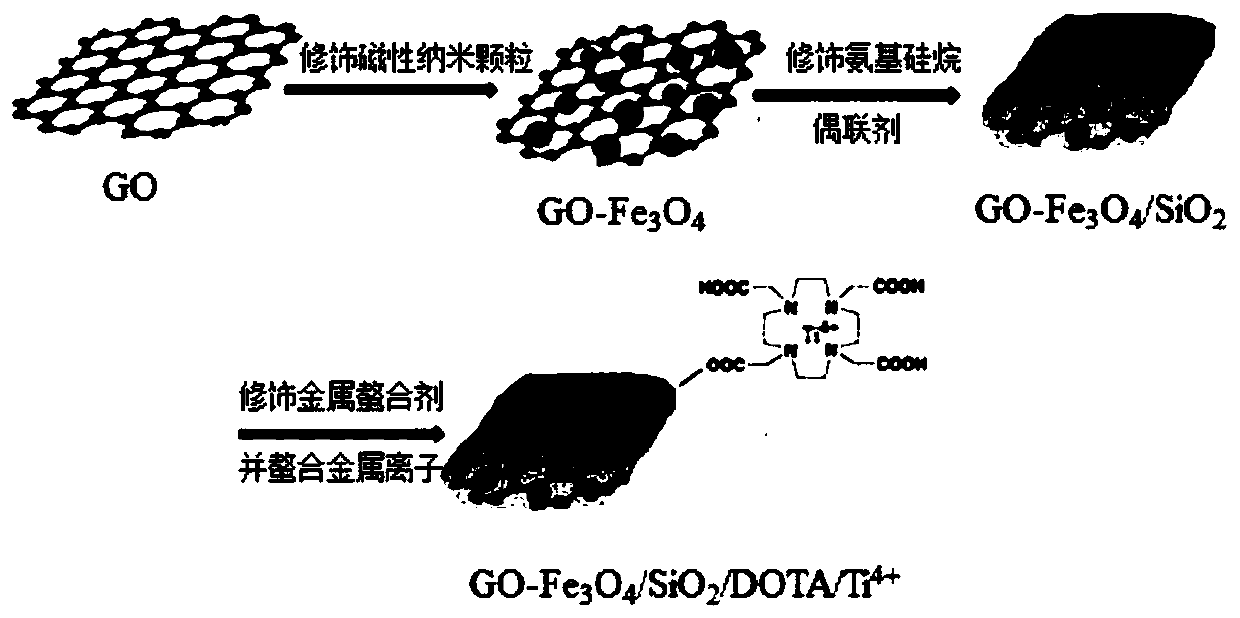
Method for extracting exosome in urine and method for analyzing proteomics and phosphorylation proteomics of exosome
InactiveCN110487946AHighly Specific ExtractionHigh recovery rateComponent separationPhosphatePhosphorylation
The invention discloses a method for extracting an exosome in urine and a method for analyzing proteomics and phosphorylation proteomics of the exosome. The invention firstly provides a magnetic nanomaterial with metal ions chelated on the surface. The magnetic nano material is prepared according to the steps of modifying magnetic nano particles on the surface of graphene oxide to obtain a product 1; coating the surface of the product 1 with a silicon dioxide layer to obtain a product 2; modifying the surface of the silicon dioxide layer of the product 2 with a silane coupling agent with amino to obtain a product 3; modifying the surface of the product 3 with a metal chelating agent to obtain a product 4; and chelating metal ions on the surface of the product 4. The magnetic nano materialcan be used for extracting the exosome in urine, and can be used for proteomics analysis or phosphorylation proteomics analysis of the exosome. According to the invention, phosphate radicals exposedon the surface of a membrane phospholipid bilayer of the exosome are combined with the metal ions through a double-coordination chemical effect, the high-specificity extraction of the urine exosome isrealized by combining an electrostatic adsorption effect at the same time, the extraction speed is high, and the recovery rate is high.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
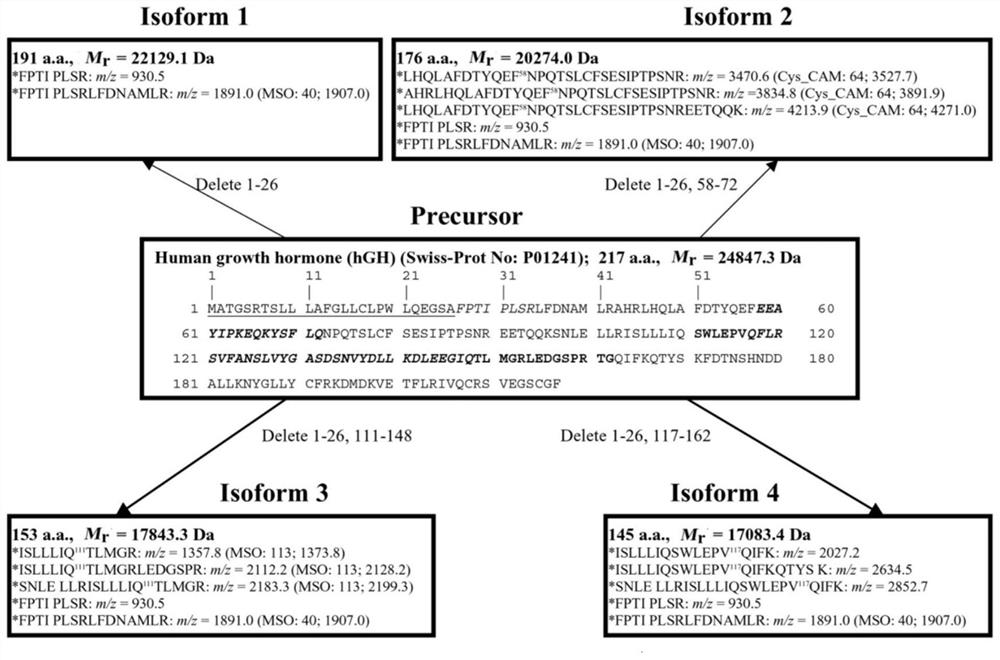
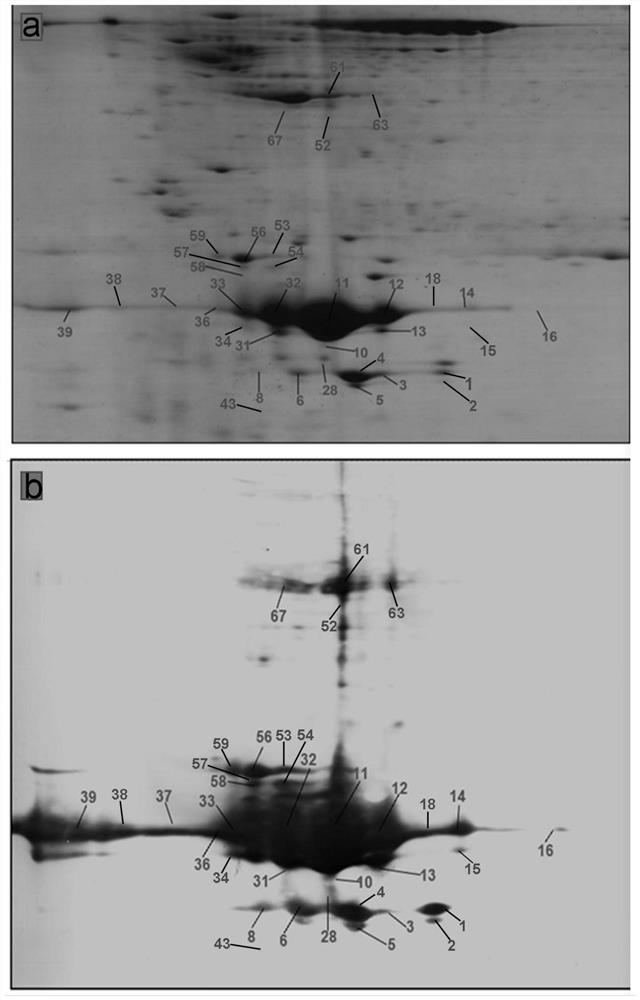
Method for identifying existence form biomarker spectrum of human growth hormone protein
The invention provides a method for identifying a human growth hormone protein existence form biomarker spectrum, which comprises the following steps: collecting human growth hormone secreting pituitary adenoma and normal pituitary tissue samples, respectively extracting tissue proteins, carrying out two-way gel electrophoresis, western blot and coomassie brilliant blue staining, scanning a visual PVDF membrane and a two-way gel into a digital image, digesting corresponding two-way gel protein spots with trypsin, purifying, and identifying a GHP biomarker spectrum through mass spectrum identification and bioinformatics analysis; and identifying post-translational modifications and shear variations on GHP by using quantitative phosphorylated proteomics, ubiquitinated proteomics, and acetylated proteomics analysis in combination with bioinformatics. According to the invention, the GHP change mode between the growth hormone secreting pituitary adenoma and normal pituitary tissues can be identified, 46 kinds of GHPs are identified in the growth hormone secreting pituitary adenoma, 35 kinds of GHPs are identified in the normal pituitary tissues, and 11 kinds of GHPs only appear in the growth hormone secreting pituitary adenoma tissues.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
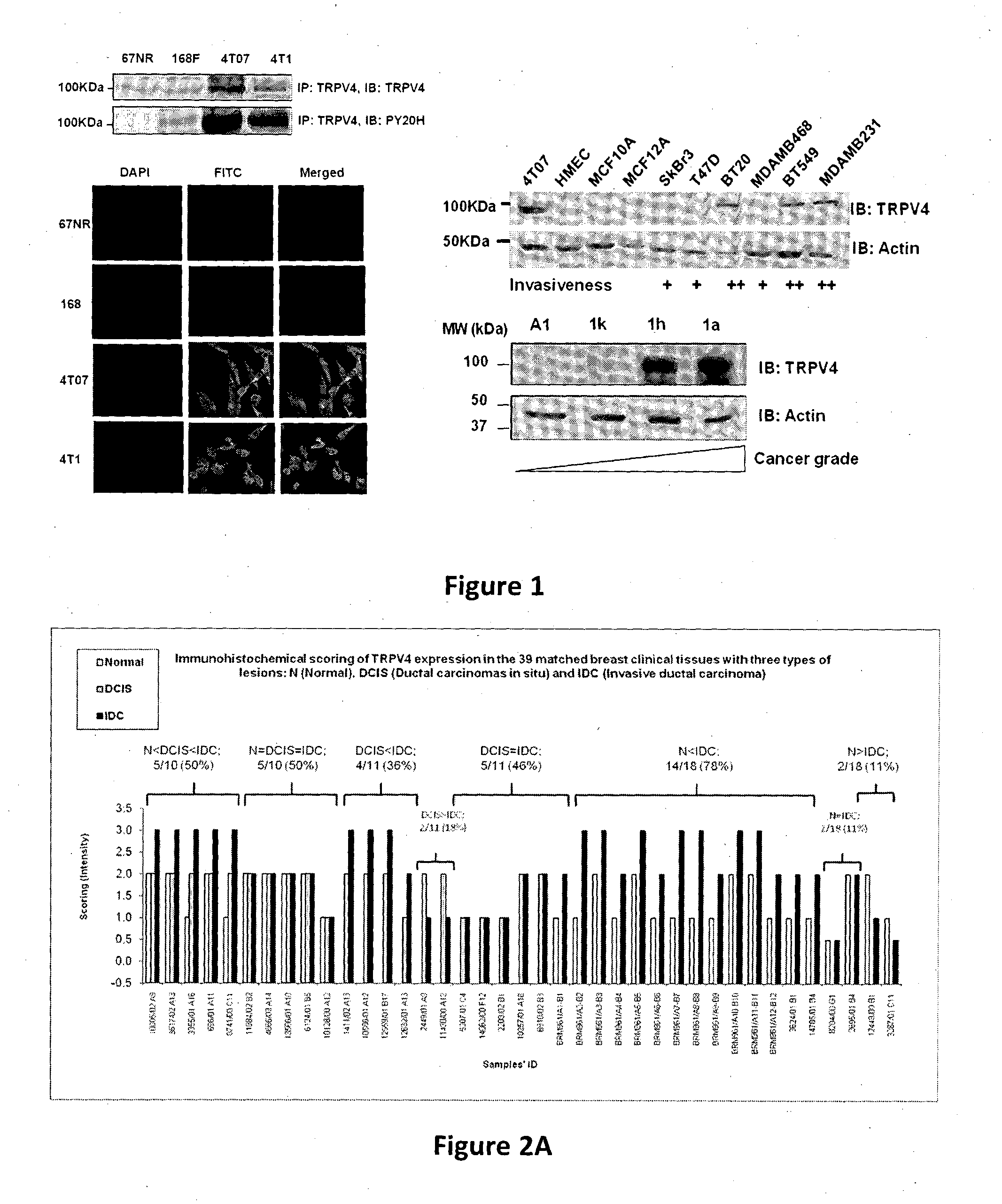
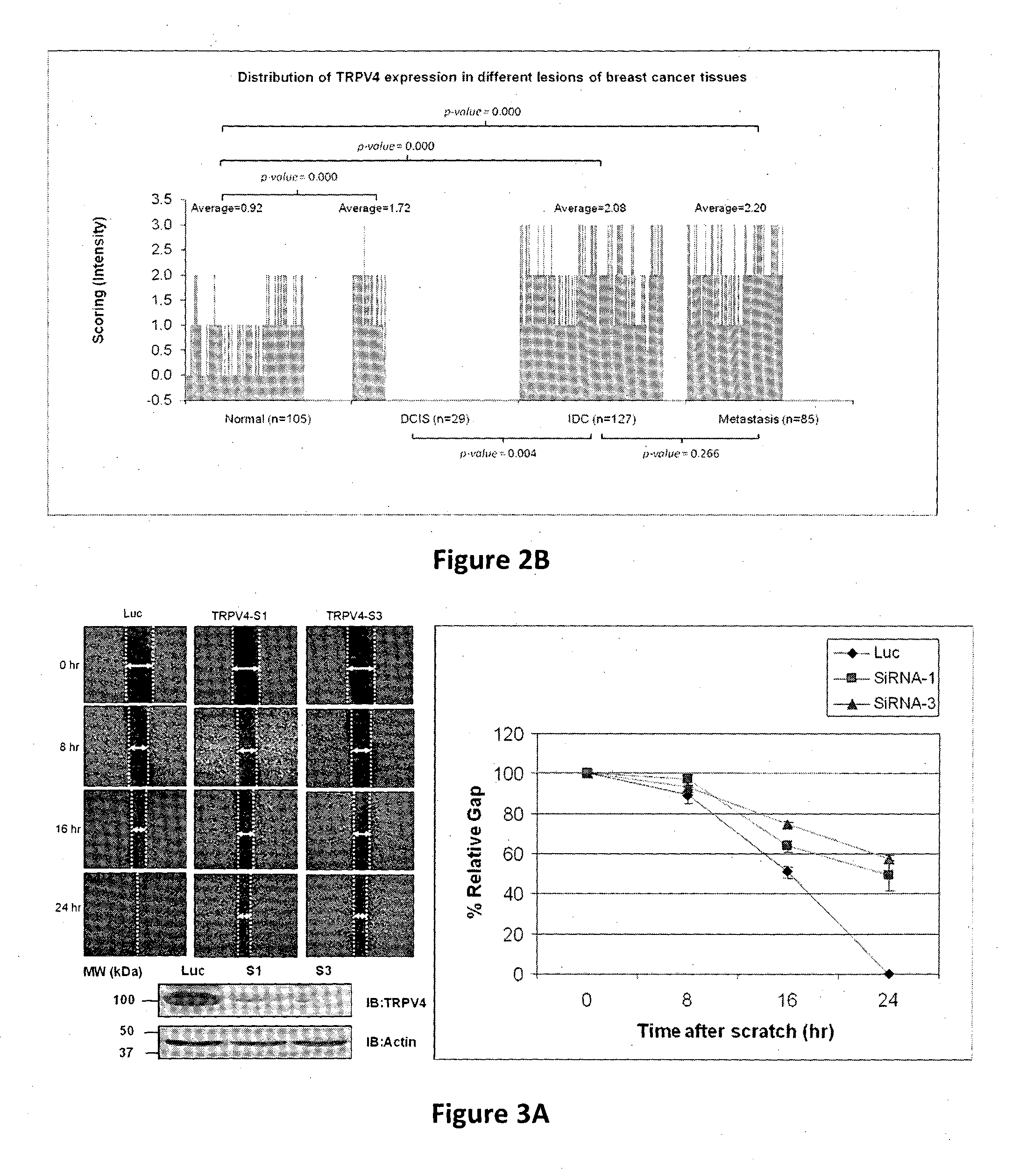
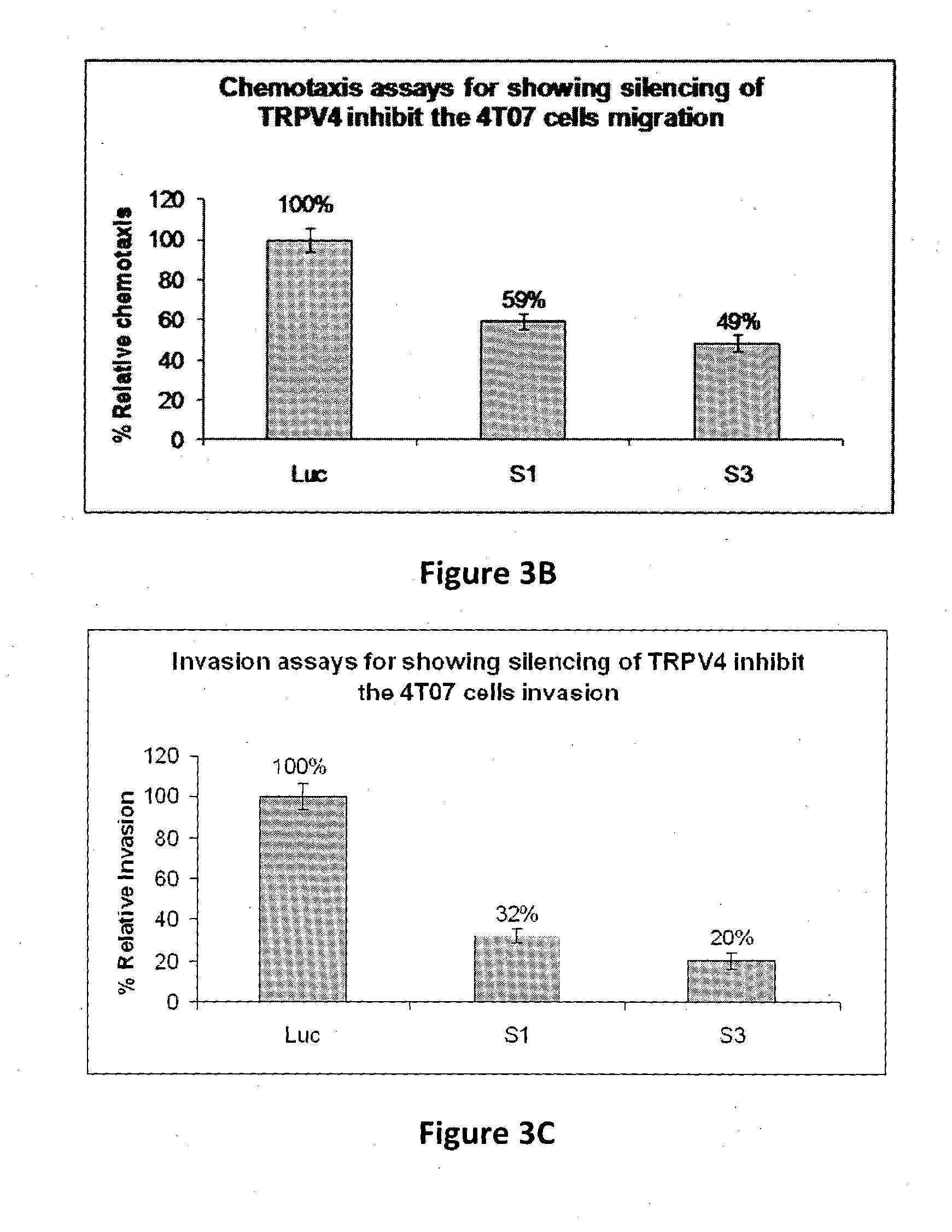
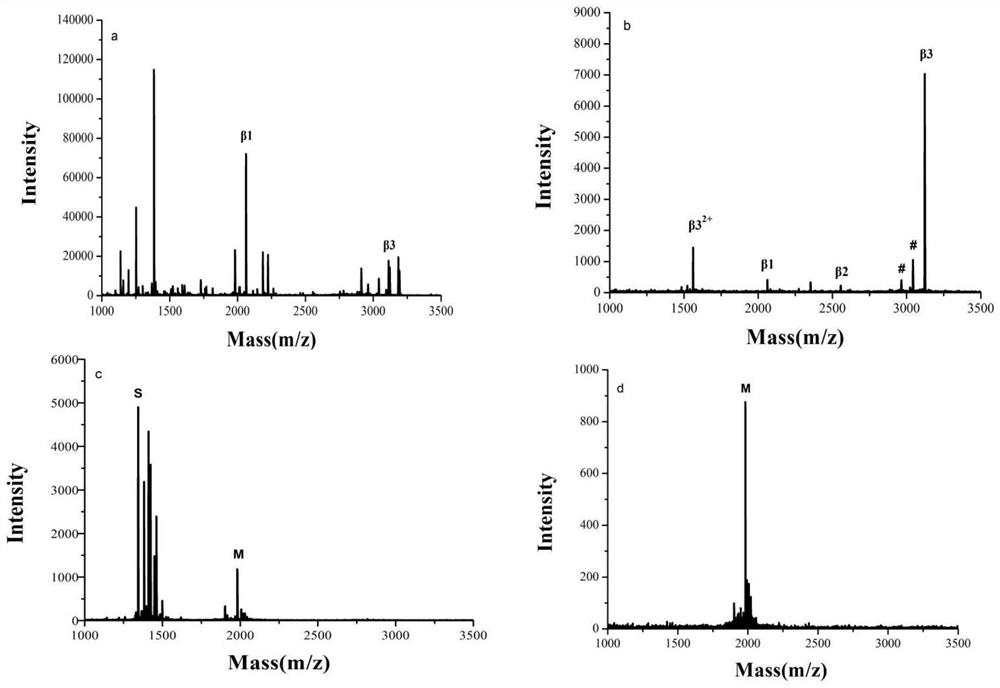
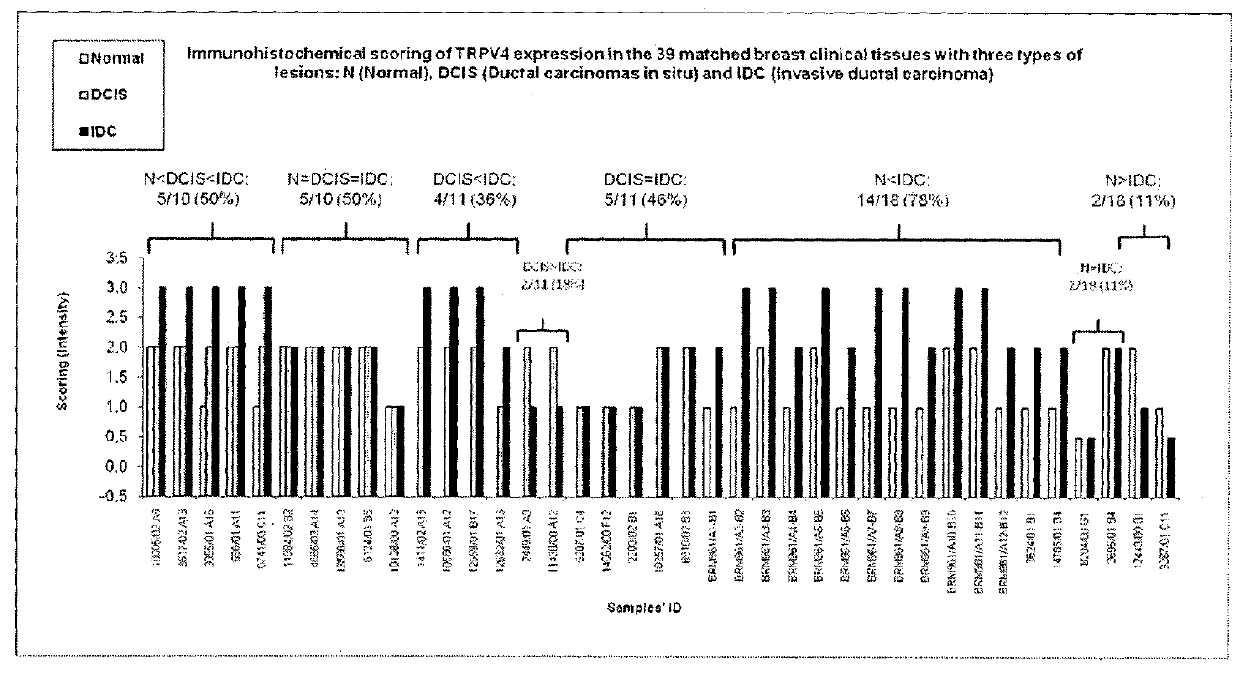
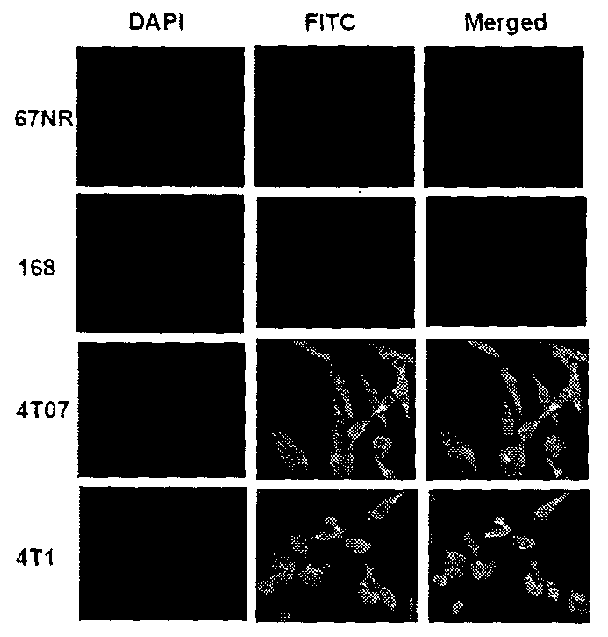
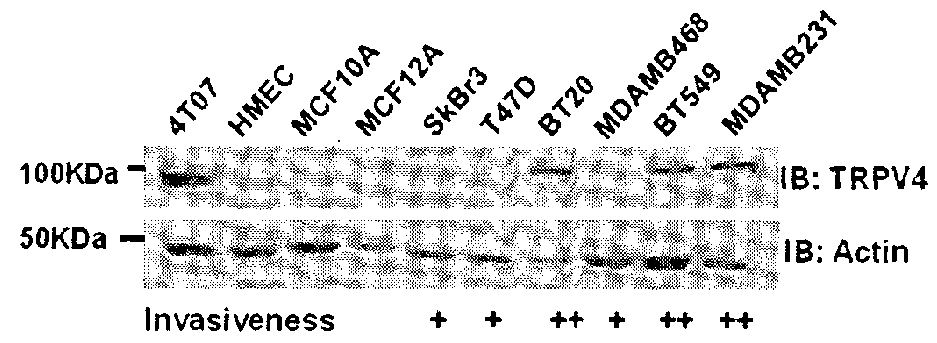
Protein involved in detection of cancer metastasis and a treatment thereof
InactiveUS20140199330A1High copy numberSsRNA viruses negative-senseCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCell PlasticityLymphatic Spread
Using phosphoproteomics, we profiled the phosphorylation levels of hundreds of proteins concurrently across an isogenic model of breast cancer metastasis. Among them is TRPV4, a calcium channel that we found to be overexpressed in invasive breast tumors compared to ductal carcinoma in situ, a pre-neoplastic lesion and normal tissues. TRPV4 was also found to be elevated mostly in invasive breast cancer cell lines and less so in non-invasive breast cancer cell lines. These data led us to hypothesize that TRPV4 confer early traits of metastatic cancer cells. Functional studies revealed that silencing of TRPV4 expression diminished breast cancer cell migration and invasion significantly but not proliferation. Silencing expression of TRPV4 in metastatic breast cancer cells also reduced the number and size of metastatic colonies in mice. This supports the notion that TRPV4 is an attractive drug target to curb metastasis. Further experimentations suggested that the functional effect of TRPV4 on breast cancer cellular processes was associated with regulation of intracellular Ca2+, cell plasticity and expression of cell-cell adhesion proteins such as beta-catenin and E-cadherin. The latter two events have obvious implications in cancer invasion and intravasation / extravasation. We have also made novel observations that activation of TRPV4 by PDD led to activation of AKT and FAK pathways, both shown to be important to cell migration. In particular, downregulation of E-cadherin and b-catenin following TRPV4 activation has been shown to be mediated by the AKT pathway. Collectively, our data suggest that activation of Ca2+ dependent cascades and pathways associated with cell migration mediate TRPV4 function in breast cancer metastasis.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
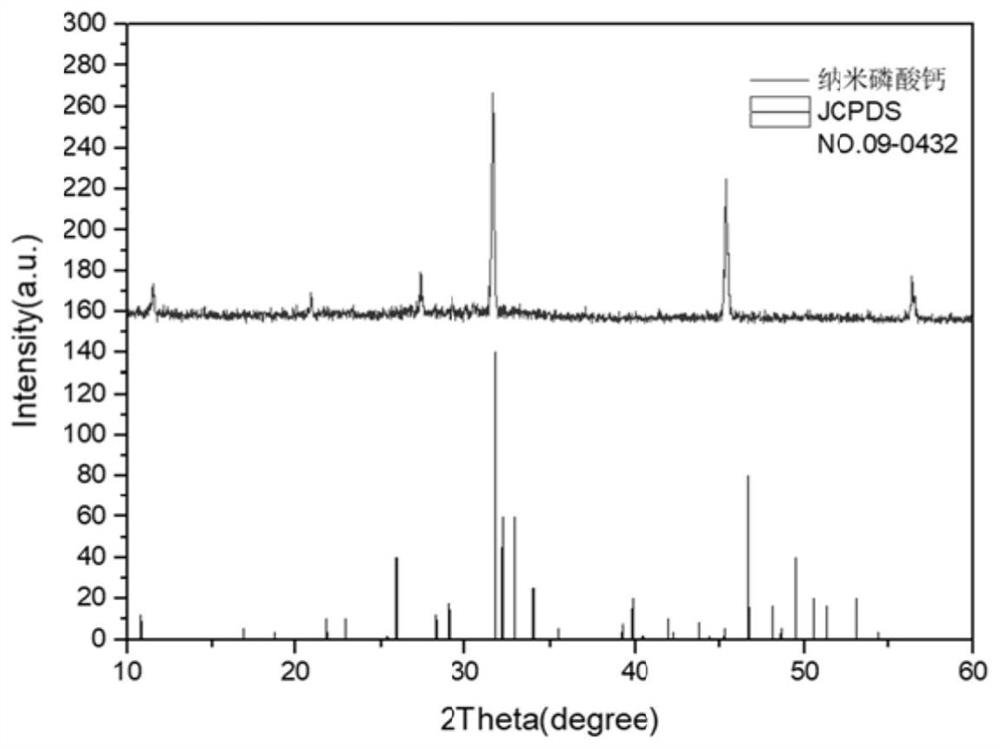
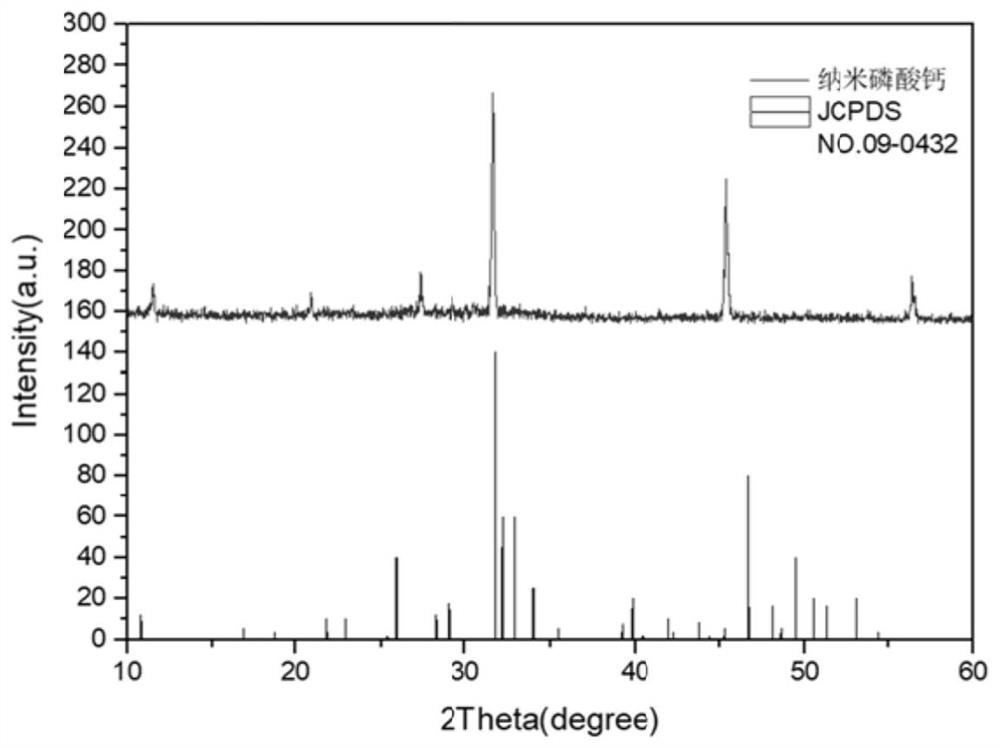
Preparation method, product and application of nano-calcium phosphate for polyphosphopeptide enrichment and phosphorylation site identification
ActiveCN112499607BEasy to prepareLow costPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCalcium biphosphatePhosphate
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and reagents for differential proteomic analysis
InactiveUS7175986B2Easy to analyzeSimple methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsEpigenome
Methods and reagents for labeling molecules of interest in a plurality of samples, and then combining and selecting labeled molecules away from unlabeled molecules for use in simultaneous co-assaying analysis. The reagents comprise labeling means of distinguishable radioactive isotopes which remain with the labeled molecules. Additionally, the reagents also comprise selection means which can be affinity tags, beads, or immobilized surface which may remain or be cleaved off through cleavable linkers. A set of labeling reagent can be used to label a plurality of samples, combine them before or after selecting / enriching for labeled molecules and co-assay together for reliable comparison. This invention has many applications in comparing and panning for differentially abundant molecules or differential modification of molecules for proteomics, glycomics, phospho-proteomics, metabolomics, epi-genomics . . . studies.
Owner:PROTEOMYX
Synthesis method of nano-material with surface rich in phosphate groups and fixed with Ti < 4 + > carbon spheres and application of nano-material in phosphorylated proteomics
PendingCN114762818AImprove featuresHigh selectivityOther chemical processesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhosphorylationPhosphoric acid
The invention belongs to the field of nanotechnology, G6PNa2 is used as a carbon source, a carbon sphere material with the surface rich in phosphate groups is prepared in one step through a hydrothermal carbonization method, and then metal cations Ti < 4 + > (named as CS-Ti < 4 + >) are fixed through chelation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, adding a G6PNa2 aqueous solution with a certain concentration into a reaction kettle, putting the reaction kettle into a drying oven, reacting at 180 DEG C for 6 hours, then washing a reaction product with water and ethanol for multiple times, and obtaining a carbon sphere material rich in phosphate groups on the surface under a centrifugal condition; and then dispersing the material into a 100 mmol / L Ti (SO4) 2 solution, oscillating for 24 hours at a constant temperature at room temperature, carrying out water treatment, centrifuging, and drying at 50 DEG C to obtain a final product. The preparation process is simple, a material preparation process with an extremely short synthesis period is adopted, and a large amount of time and labor are saved; the reaction raw materials are common and no organic reagent is used.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A mini protein reactor for proteome sample preparation and its application
The invention discloses a mini protein reactor applied to preparation of a proteome sample and an application of the mini protein reactor and relates to the field of analytical chemistry. The mini protein reactor mainly comprises IMAC (immobilized metal chelating chromatography) magnetic beads and C18 beads. Smaller than 10 mu L of serum is expected to be taken as a sample for general situation analysis of proteome and can be used for translational research. According to the method, complicated sample preparation steps in proteomics are realized with a series column separation technology and include phosphoprotein pre-concentration, reduction, alkylation and digestion as well as desalination and fractionation. The method is easy to use, consumes short time (2 hours), is high in throughput,high in sensitivity (capable of detecting more than 100 phosphoprotein) and good in repeatability (R is larger than 0.99), is an effective method which can mine the most proteome data no matter fromthe number or from the variety and is speculated to be applied to technology translational research of non-labeled quantitative phosphoproteomics.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for purifying tyrosine phosphopeptide
InactiveCN102199189BStrong specificityHigh selectivityPeptide preparation methodsPurification methodsPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses application of a beta-elimination and Michael nucleophilic addition method in study of phosphoproteomics, in particular a method for purifying tyrosine phosphopeptide. The method comprises the following steps of: eliminating phosphate modification groups on non-tyrosine phosphopeptide in protein hydrolysate by using beta-elimination and Michael nucleophilic addition; and enriching the tyrosine phosphopeptide which is not subjected to the elimination reaction by using a phosphoeptide enriching material. By utilizing the high specificity of the beta-elimination and Michael nucleophilic addition, the tyrosine phosphopeptide is purified from a complicated protein hydrolysate sample in high selectivity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phosphoproteins in extracellular vesicles as candidate markers for breast cancer
The state of protein phosphorylation and glycosylation can be key determinants of cellular physiology such as early stage cancer, but the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in biofluids for disease diagnosis remains elusive. Here we demonstrate, for the first time, a strategy to isolate and identify phosphoproteins / glycoproteins in extracellular vesicles (EVs) from human plasma as potential markers to differentiate disease from healthy states. We identified close to 10,000 unique phosphopeptides in EVs by isolating from small volume of plasma samples. Using label-free quantitative phosphoproteomics, we identified 144 phosphoproteins in plasma EVs that are significantly higher in patients diagnosed with breast cancer than in healthy controls. Several novel biomarkers were validated in individual patients using Paralleled Reaction Monitoring for targeted quantitation. Similarly a group of glycoproteins in plasma EVs are identified. The study demonstrated that the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in plasma EV as disease biomarkers is highly feasible and may transform cancer screening and monitoring.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
An online automated analysis device and analysis method for phosphoproteomics
ActiveCN113607868BImprove consistencyAnalysis does not affectComponent separationLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopyAdenosine
The invention discloses an online automatic analysis device and analysis method for phosphorylated proteomics. It is a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer, and the liquid chromatography includes a phosphorylated peptide capture column and an analysis column, and the phosphorylated peptide capture column is an ATP-modified immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography column; the potassium Mix and stir water glass, γ-glycidyl etheroxypropyl trimethoxysilane and water-dissolved adenosine triphosphate disodium, then add formamide dissolved in water and stir to obtain a reaction solution, fill the reaction solution with the chromatographic column, and then fill the chromatographic column The reaction solution of the column is solidified by reaction, and then washed to obtain an ATP-modified immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography column. The primary advantage of the present invention is that researchers are freed from complex manual operations such as metal ion loading, sample loading, washing, elution, desalination, evaporation, and reconstitution required for enrichment of phosphorylated peptides, which improves experimental efficiency .
Owner:AGRO BIOLOGICAL GENE RES CENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Mini protein reactor applied to preparation of proteome sample and application of mini protein reactor
The invention discloses a mini protein reactor applied to preparation of a proteome sample and an application of the mini protein reactor and relates to the field of analytical chemistry. The mini protein reactor mainly comprises IMAC (immobilized metal chelating chromatography) magnetic beads and C18 beads. Smaller than 10 mu L of serum is expected to be taken as a sample for general situation analysis of proteome and can be used for translational research. According to the method, complicated sample preparation steps in proteomics are realized with a series column separation technology and include phosphoprotein pre-concentration, reduction, alkylation and digestion as well as desalination and fractionation. The method is easy to use, consumes short time (2 hours), is high in throughput,high in sensitivity (capable of detecting more than 100 phosphoprotein) and good in repeatability (R is larger than 0.99), is an effective method which can mine the most proteome data no matter fromthe number or from the variety and is speculated to be applied to technology translational research of non-labeled quantitative phosphoproteomics.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A rapid processing method for phosphorylated proteome samples
InactiveCN104949864BThe pretreatment method is simpleQuick changePreparing sample for investigationPhosphodiesteraseHigh concentration
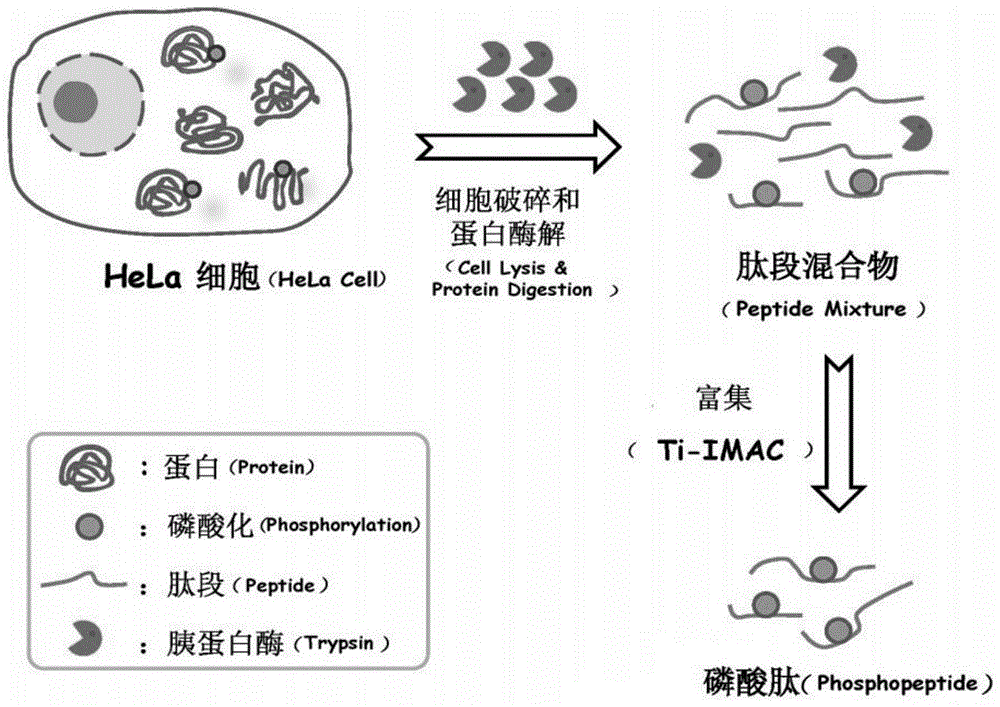
The present invention relates to a rapid processing method for phosphorylated proteome samples. Utilizing the advantage that high-concentration trypsin can promote rapid enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins, a new type of sample processing method integrating cell lysis and proteolysis is developed, and its Applied to the analysis of phosphoproteomics. Thanks to the deep mechanism of simultaneous cell lysis and proteolysis promoted by the high concentration of trypsin, the cell sample can be rapidly converted into a peptide mixture in a single step. During the enrichment of phosphopeptides, non-phosphorylated peptides As well as various other mass spectrometrically incompatible impurities, can be removed. The present invention only needs 25 minutes to realize the rapid transition from cells to peptides, and in the normal control group, the simplest method also needs at least 16 hours; The excellent coverage of mass spectrum identification proves the accuracy and efficiency of this sample pretreatment method.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation of a kind of organic monolithic small column and organic monolithic small column and application
InactiveCN107297086BHigh enrichment efficiencyExcellent enrichment efficiencyComponent separationSolid sorbent liquid separationReactive siteTitanium ion
The invention relates to the preparation of a Ti(IV)-IMAC organic monolithic small column, which is used for phosphorylated proteomics analysis of trace biological samples. The organic monolithic column material is a polymethacrylate polymer with rich pore structure, high specific surface area, and many active sites for enriching titanium ions; at the same time, due to its hydrophilic material surface, Phosphopeptide enrichment showed a strong enrichment ability. It was used in the phosphoproteomics analysis of 5g HeLa cells, and more than 1000 non-redundant phosphorylation sites were identified on average, and the enrichment specificity was as high as 92.5%. More importantly, the preparation of the Ti(IV)-IMAC organic monolithic column is simple. Compared with the packed column, it can be prepared by light-induced free radical polymerization in only a few minutes; and there is no need to prepare a stopper, The preparation time of the enrichment material is reduced to a large extent.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for accumulating cotton phosphorylated protein
InactiveCN101967181BLow priceImprove efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a method for accumulating cotton phosphorylated protein, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the steps of extracting cotton total protein and utilizing the Al(OH)3 affinity chromatography to accumulate cotton phosphorylated protein. By using the method, 12mu g of phosphorylated protein can be accumulated from 1mg of cotton total protein so that the accumulation efficiency is more than 6 times of that of the imported Qiagen kit. The two-dimensional electrophoresis technology and the phosphorylated protein specific dye ProQ DiamondTM (Invitrogen) dyeing test prove that the phosphorylated protein accumulated by the method has no non-phosphorylated protein. The method can replace the expensive imported kit, be used to accumulate phosphorylated protein efficiently and specifically and be widely used in researches such as phosphorylated proteomics and cellular signal.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
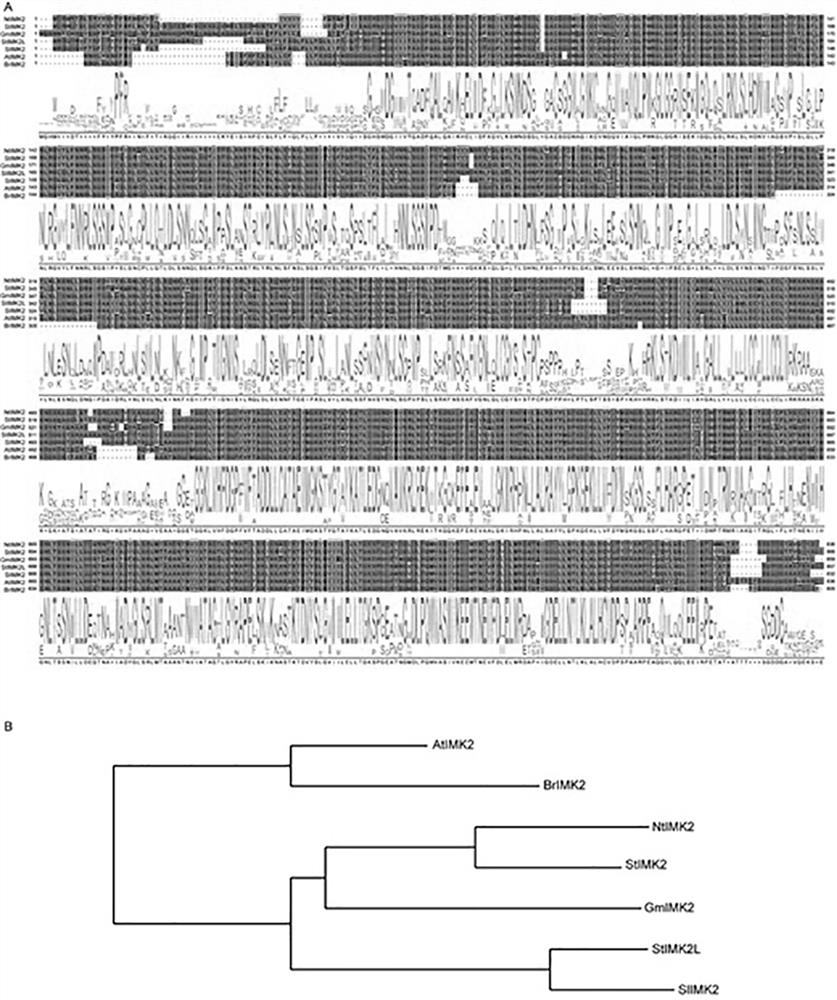
Tobacco NtIMK2 receptor protein kinase and application thereof in drought resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco genome function analysis, and particularly relates to tobacco NtIMK2 receptor protein kinase and an application thereof in drought resistance. The length of the gene is 2511bp, and the base sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. After the gene is over-expressed, the drought tolerance of a plant can be enhanced, and after the gene is silenced, the sensitivity of the plant to drought can be increased. In the early stage, on the basis of analysis of a tobacco genome, integrated analysis of multiple omics such as related phosphoproteomics, transcriptome, miRNA-seq and the like is combined, and it is found that expression of an LRR receptor kinase (RLKs) NtIMK2 gene is highly related to drought response. For further determining the function of the gene and the effect of the gene in a plant drought stress response mechanism, in the invention, the inventor preliminarily studies the function of the NtIMK2 gene in drought stress by using RNAi interference and overexpression technologies, and the result shows that when the NtIMK2 gene is overexpressed, the drought resistance of the plant can be obviously improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Affinity chromatography fixed phase of immobilization metal and its preparation method
InactiveCN101288844BImprove selective enrichment effectReduce non-specific adsorptionOther chemical processesPhosphoric Acid EstersPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a separation and purification technique, in particular to an affinity chromatography stationary phase of immobilized metal and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the stationary phase is shown in the drawing; wherein, the grain diameter of GMAPolymer micro-sphere is 10nm-50[mu]m; the GMAPolymer micro-sphere is poly-methacrylic acid glycidyl esters micro-sphere. By carrying out amination and phosphoric esterification, a synthesis method of the high-performance poly-methacrylic acid glycidyl ester-group novel affinity chromatography stationary phase is gained and used for the research in phosphorylation proteomics and highly-selective separation, enrichment and purification of phosphopeptide by the chelation with zirconium ions and iron ions; meanwhile, compared with the traditional stationary phase, the affinity chromatography stationary phase reduces the nonspecific adsorption on the non-phosphopeptide.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of nano calcium phosphate for polyphosphopeptide enrichment and phosphorylation site identification as well as product and application of nano calcium phosphate
ActiveCN112499607AEasy to prepareLow costPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCalcium biphosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of nano calcium phosphate for polyphosphopeptide enrichment and phosphorylation site identification as well as a product and application of the nano calcium phosphate, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: sequentially adding a calcium salt aqueous solution and a phosphate aqueous solution into a slightly alkaline solution, conducting stirring, and conducting drying after the reaction is finished, so as to obtain a nano calcium phosphate material. Due to strong interaction between calcium ions and phosphate radicals, nano calciumphosphate can effectively realize selective enrichment of polyphosphopeptides and identification of phosphorylation sites. Meanwhile, the calcium phosphate nano material prepared by the method is a biological functional material which is simple to synthesize, low in cost and high in stability, and has a wide application prospect in phosphorylated proteomics research.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Protein involved in detection of cancer metastasis and a treatment thereof
InactiveUS9359423B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLymphatic SpreadCell Plasticity
Using phosphoproteomics, we profiled the phosphorylation levels of hundreds of proteins concurrently across an isogenic model of breast cancer metastasis. Among them is TRPV4, a calcium channel that we found to be overexpressed in invasive breast tumors compared to ductal carcinoma in situ, a pre-neoplastic lesion and normal tissues. TRPV4 was also found to be elevated mostly in invasive breast cancer cell lines and less so in non-invasive breast cancer cell lines. These data led us to hypothesize that TRPV4 confer early traits of metastatic cancer cells. Functional studies revealed that silencing of TRPV4 expression diminished breast cancer cell migration and invasion significantly but not proliferation. Silencing expression of TRPV4 in metastatic breast cancer cells also reduced the number and size of metastatic colonies in mice. This supports the notion that TRPV4 is an attractive drug target to curb metastasis. Further experimentations suggested that the functional effect of TRPV4 on breast cancer cellular processes was associated with regulation of intracellular Ca2+, cell plasticity and expression of cell-cell adhesion proteins such as beta-catenin and E-cadherin. The latter two events have obvious implications in cancer invasion and intravasation / extravasation. We have also made novel observations that activation of TRPV4 by PDD led to activation of AKT and FAK pathways, both shown to be important to cell migration. In particular, downregulation of E-cadherin and b-catenin following TRPV4 activation has been shown to be mediated by the AKT pathway. Collectively, our data suggest that activation of Ca2+ dependent cascades and pathways associated with cell migration mediate TRPV4 function in breast cancer metastasis.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Mesoporous metal oxide materials for phosphoproteomics
ActiveUS8507287B2Strong specificityIncrease load capacityComponent separationPeptide preparation methodsPhosphoric acidMesoporous material
The present invention provides methods and materials for isolating, purifying, and / or enriching the concentration of compounds having one or more phosphate groups and / or derivatives thereof, including but not limited to phosphorylated peptides and / or phosphorylated proteins. In some aspects, the present invention provides nanostructured enrichment materials, such as metal oxide mesoporous materials, that selectively and reversibly bind with phosphorylated compounds with high specificity and are capable of controlled release of phosphorylated compounds bound to their active surfaces. Mesoporous materials of the present invention also provide enrichment materials having large active surface areas that provide for higher loading capacities for phosphorylated peptides and proteins relative to conventional affinity based methods. Nanostructured metal oxide mesoporous enrichment materials of the present invention are also compatible with implementation via a variety of separation platforms including flow through separation systems, elution based separation systems, column chromatography and affinity chromatography.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
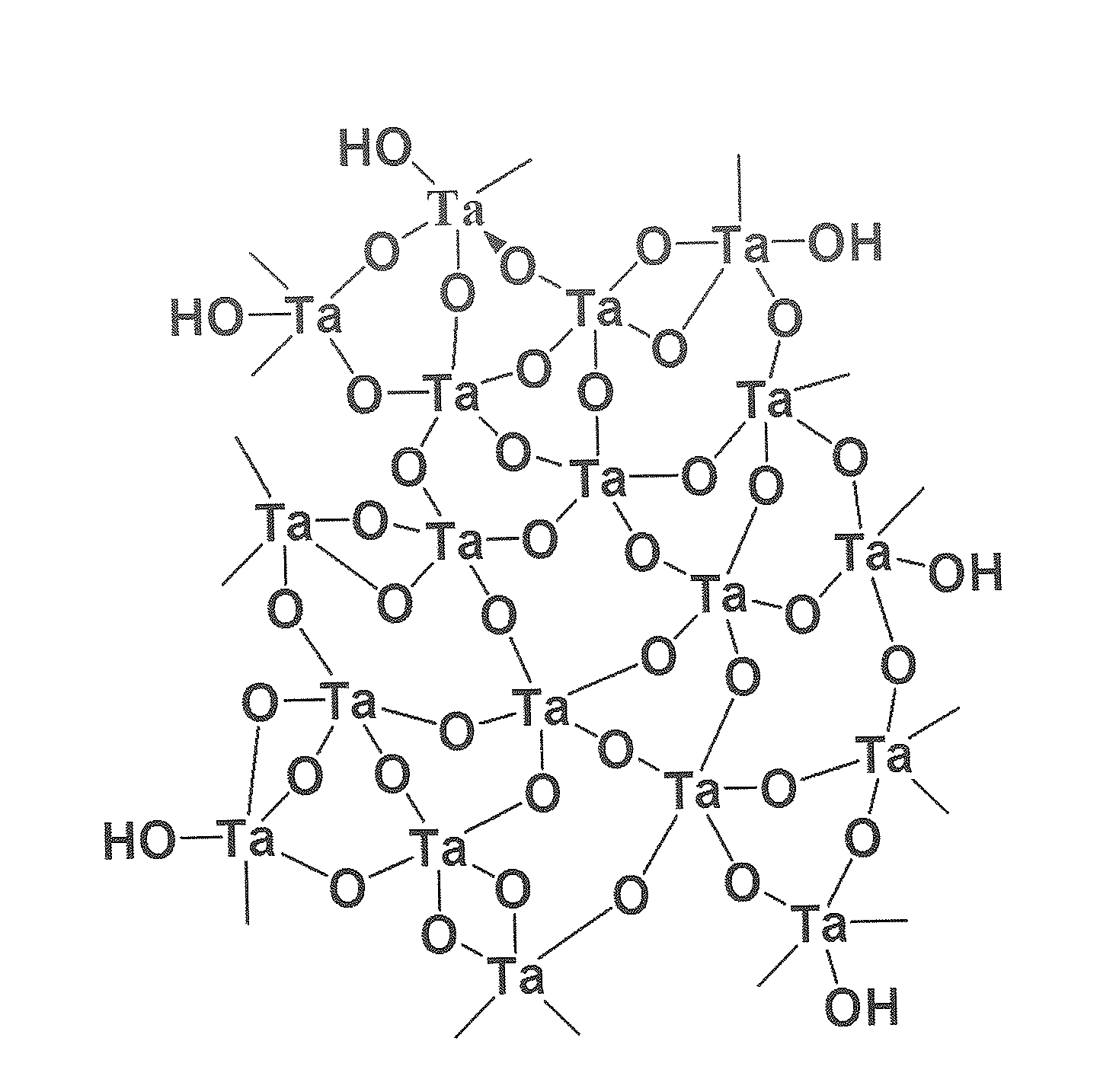
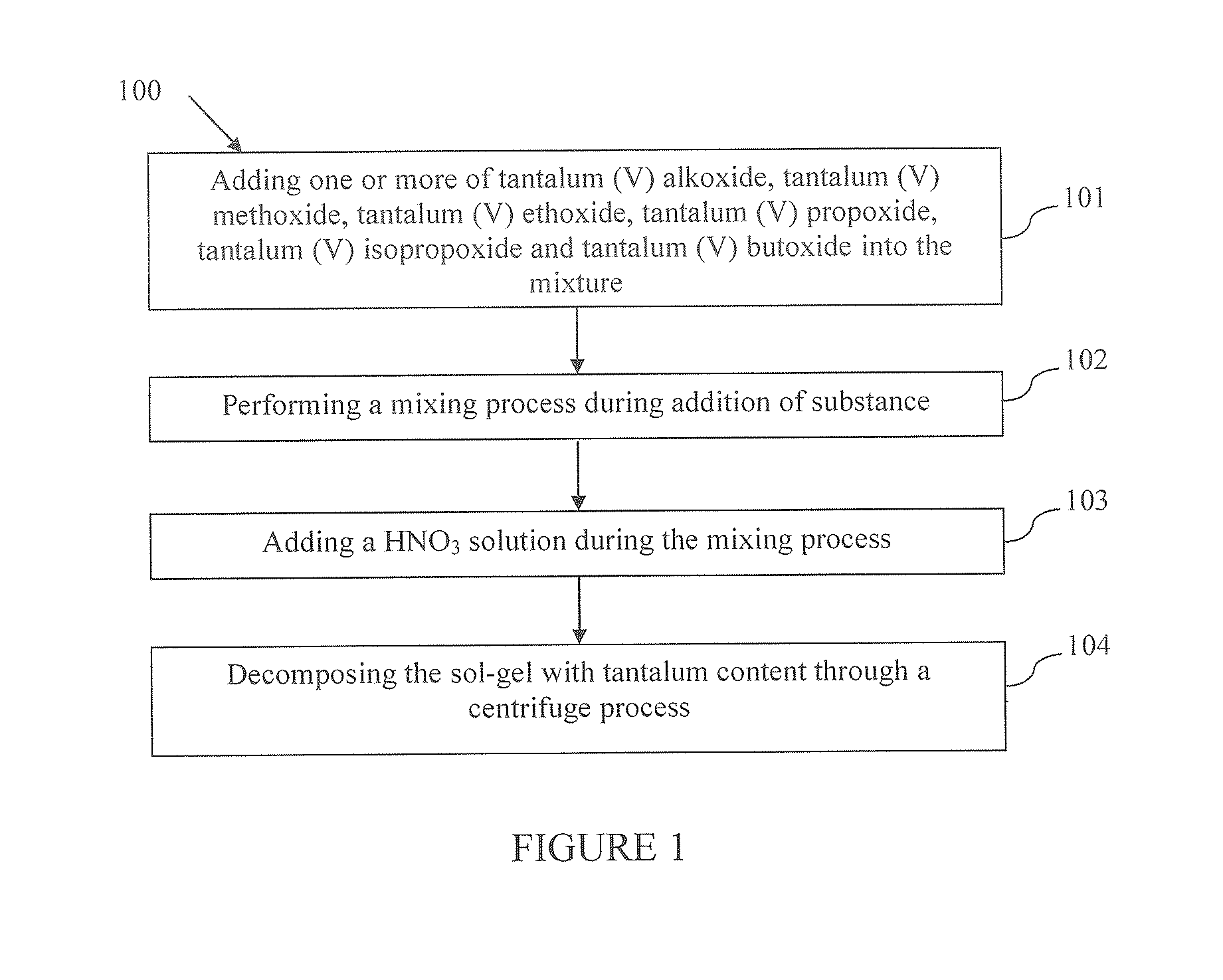
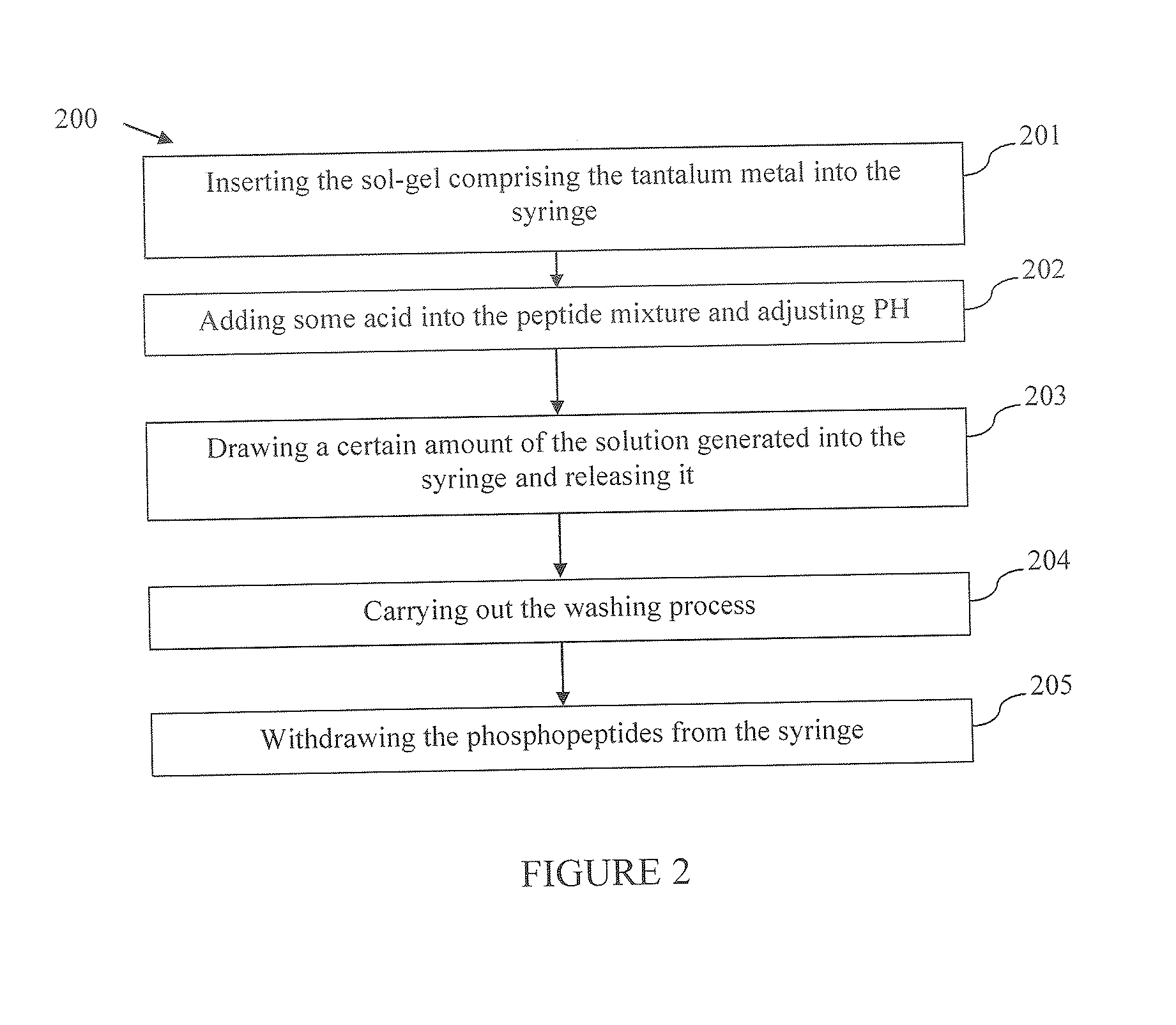
Synthesis of tantalum sol-gel and production method of microextraction syringe for the purpose of enrichment of phosphopeptides
InactiveUS20150158904A1Improve accuracyShort timePeptide/protein ingredientsOther chemical processesPhosphoric acidMass spectrometry
The present invention relates to a production method of sol-gel (100) comprising tantalum metal and a method (200) concerning use of the sol-gel produced for enrichment of phosphopeptides by means of a microextraction syringe. The syringe which is filled with the sol-gel comprising tantalum metal enables to make analysis of natural samples, that comprise low amount of phosphoprotein, with high precision and in a very short time and it shows compliance with mass spectrometric techniques. Thus, it can be used for application of fast and practical analytical methods for the analysis made in phosphoproteomics studies wherein mass spectrometric techniques are used.
Owner:SALIH BEKIR
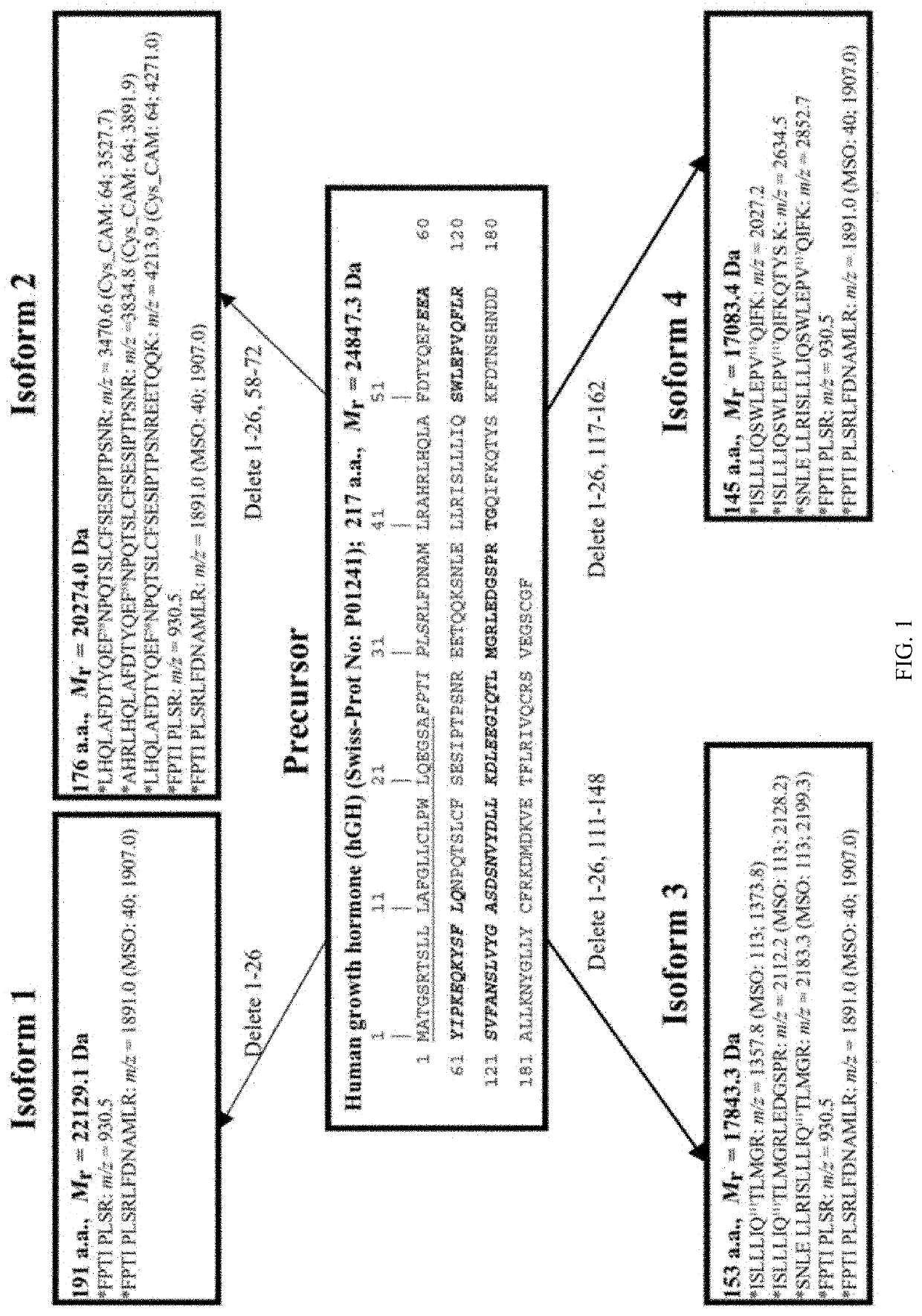
Method for Identifying Human Growth Hormone Proteoform (hGHP) Pattern Biomarker
The present disclosure provides a method for identifying a human growth hormone proteoform (hGHP) pattern biomarker. The method includes: collecting an hGH-secreting pituitary adenoma tissue sample and a normal pituitary tissue sample, and extracting tissue proteins, separately; conducting two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DGE), western blotting, and Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining, and scanning visualized polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes and 2D gels to obtain digital images; subjecting a corresponding protein in 2D gel spot to protein digestion with trypsin and purification, and conducting mass spectrometry identification and bioinformatics analysis to identify a GHP biomarker profile; and in combination with bioinformatics, using quantitative phosphoproteomics, quantitative ubiquitinomics, and quantitative acetylomics to identify post-translational modifications (PTMs) and splicing variations in GHP. The present disclosure can identify a change pattern of GHP between a GH-secreting pituitary adenoma tissue and a normal pituitary tissue. In total, 46 GHPs are identified in the GH-secreting pituitary adenoma tissue, and only 35 GHPs are identified in the normal pituitary tissue. Therefore, 11 GHPs are only present in the GH-secreting pituitary adenoma tissue.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com