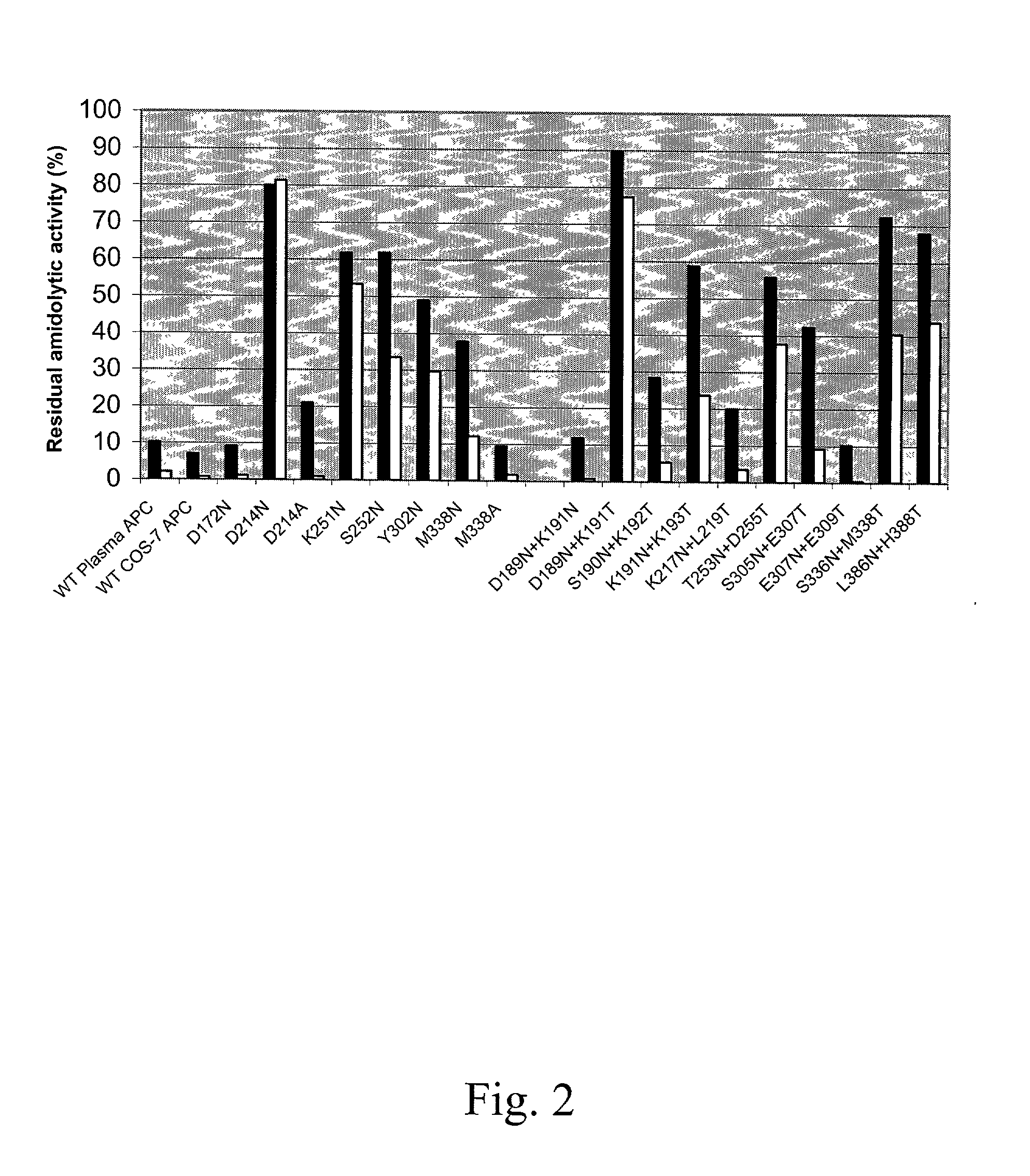
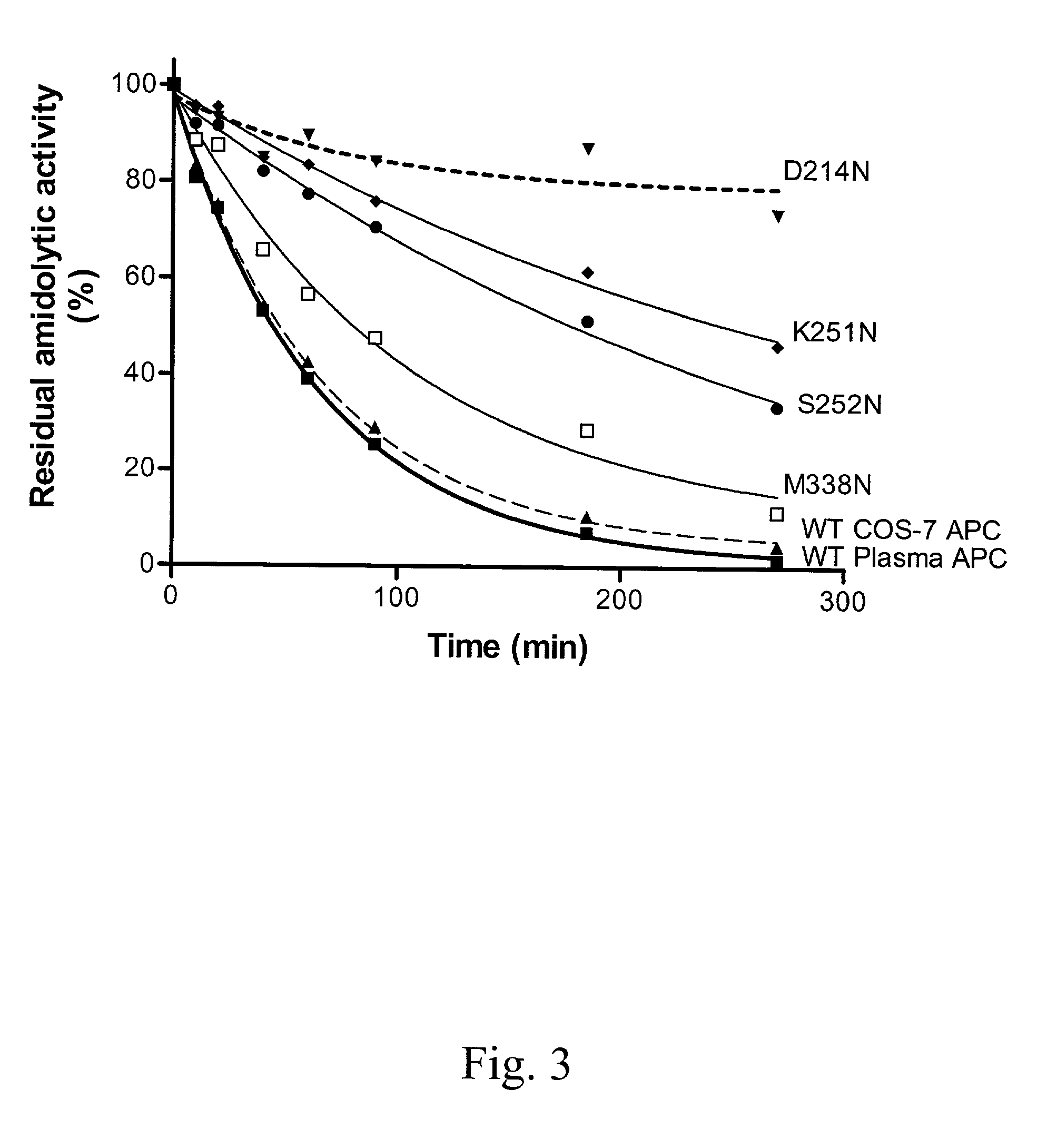
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "N-Glycosylation Site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A glycosylation site is an amino acid residue within a peptide that accepts oligosaccharide via amide linkage, specifically through amide nitrogen of asparagine via N-acetylglucosamine, as one of the post-translational modifications.
Factor vii or viia polypeptide variants
The present invention relates to novel polypeptide variants of factor VII (FVII) or factor VIIa (FVIIa) polypeptides, where said variants comprise an amino acid substitution in position 10 and 32 and where said variants further comprise a sugar moiety covalently attached to an introduced in vivo N-glycosylation site located outside the Gla domain. Such polypeptide variants are useful in therapy, in particular for the treatment of a variety of coagulation-related disorders, such as trauma.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Factor VII or VIIa Polypeptide Variants
InactiveUS20060270002A1Improve bioavailabilityIncrease the areaFungiBacteriaFactor VIIaAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to novel polypeptide variants of factor VII (FVII) or factor VIIa (FVIIa) polypeptides, where said variants comprise an amino acid substitution in position 10 and 32 and where said variants further comprise a sugar moiety covalently attached to an introduced in vivo N-glycosylation site located outside of the Gla domain. Such polypeptide variants are useful in therapy, in particular for the treatment of a variety of coagulation-related disorders, such as trauma.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Factor VII or VIIa Polypeptide Variants
InactiveUS20060270001A1Improve bioavailabilityIncrease the areaFungiBacteriaFactor VIIaAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to novel polypeptide variants of factor VII (FVII) or factor VIIa (FVIIa) polypeptides, where said variants comprise an amino acid substitution in position 10 and 32 and where said variants further comprise a sugar moiety covalently attached to an introduced in vivo N-glycosylation site located outside of the Gla domain. Such polypeptide variants are useful in therapy, in particular for the treatment of a variety of coagulation-related disorders, such as trauma.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Factor VII or VIIa Polypeptide Variants
InactiveUS20060270000A1Improve bioavailabilityIncrease the areaFungiNervous disorderFactor VIIaDisease
The present invention relates to novel polypeptide variants of factor VII (FVII) or factor VIIa (FVIIa) polypeptides, where said variants comprise an amino acid substitution in position 10 and 32 and where said variants further comprise a sugar moiety covalently attached to an introduced in vivo N-glycosylation site located outside of the Gla domain. Such polypeptide variants are useful in therapy, in particular for the treatment of a variety of coagulation-related disorders, such as trauma.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method for selective enrichment and identification of N-linked glycopeptide
InactiveCN106483294AMaterials are cheap and readily availableGood dispersionPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingMicrosphereSide chain
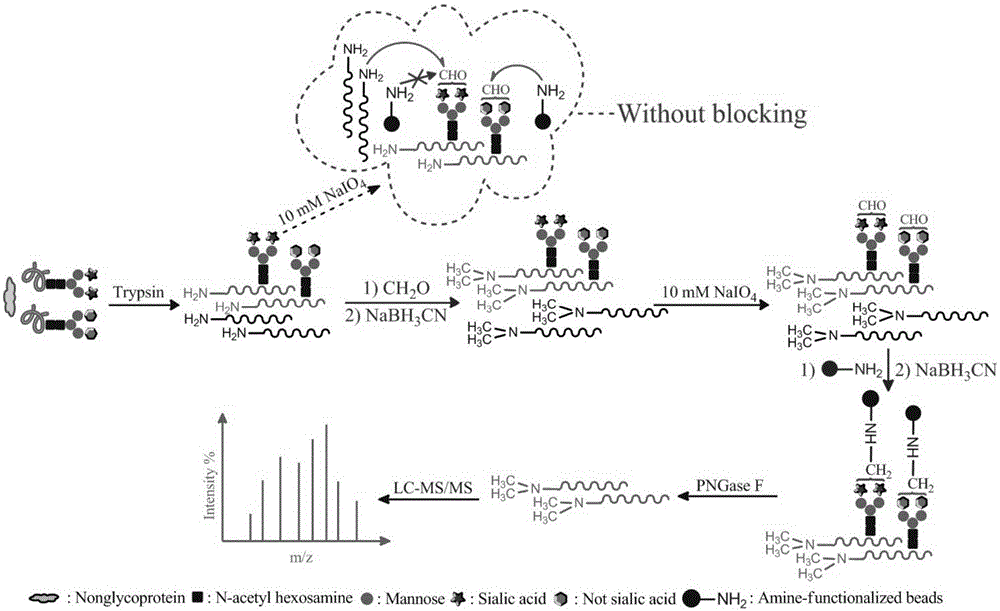
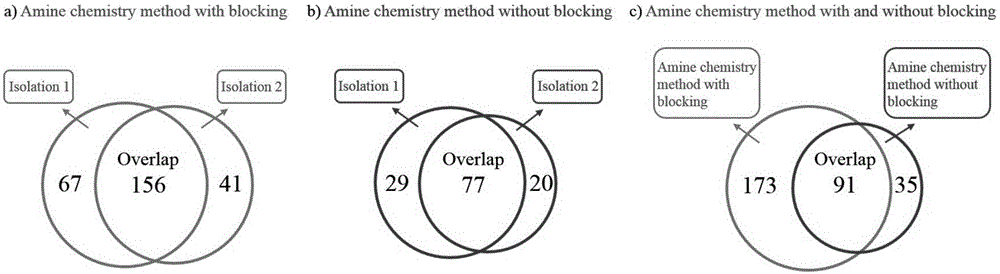
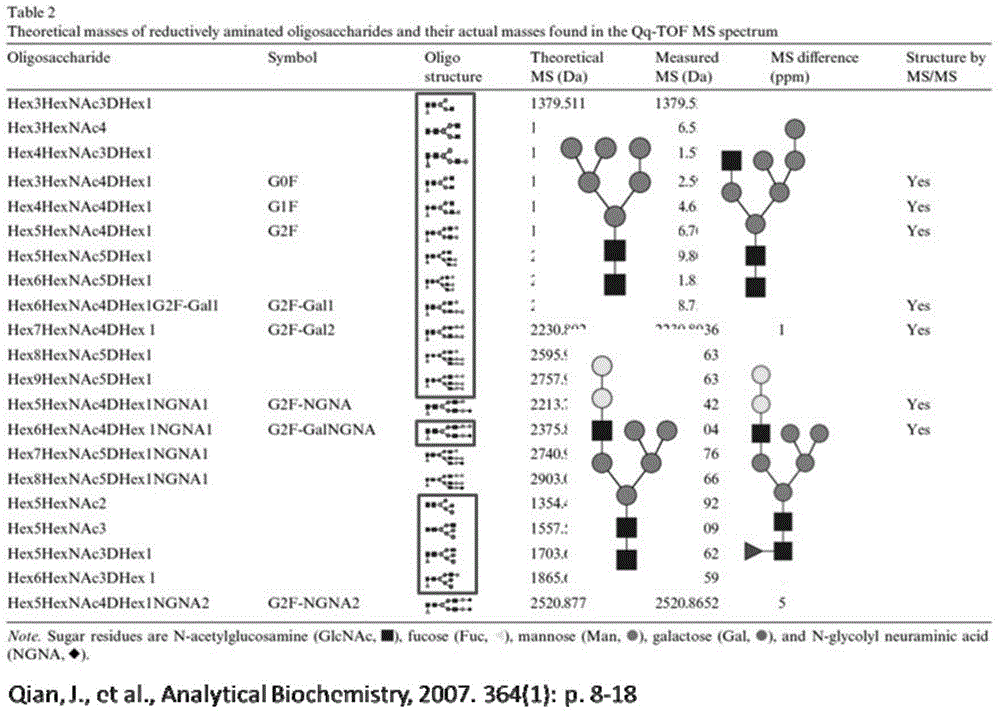
The invention relates to a method for selective enrichment and identification of N-glycosylation sites in a biological sample based on a reductive amination reaction of amino and aldehyde groups and application of the method to proteomic analysis of N-glycoprotein. The method comprises the following steps: taking a biological sample containing glycoprotein, carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis by using trypsin and then blocking the terminated amino group and side-chain amino group of a peptide fragment by using formaldehyde; then oxidizing a sugar chain on glycopeptide by using a sodium periodate solution so as to produce an aldehyde group; then enriching oxidized glycopeptide with amino microspheres and carrying out treatment with peptide glycosidase PNGase F; and carrying out mass spectrometry on released N-glycopeptide so as to obtain proteome information of N-glycoprotein in the sample. The method can be used for proteomic analysis of glycosylation and can acquire identification results of corresponding glycoprotein, glycopeptide and glycosylation sites at the same time. The method is simple and highly efficient and has high throughput in identification of N-glycosylation sites on glycoprotein.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polynucleotides encoding S99T interferon gamma polypeptide variants and means of expression
InactiveUS20050249703A1High degreeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotidePolynucleotide
Owner:PERSEID THERAPEUTICS
Modified DNA molecule, recombinant containing the same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6936707B2Good effectImproving immunogenicityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenModified dna
There is provided a DNA molecule derived from a prokaryotic cell in which at least one of the DNA regions encoding NXB (N is asparagine, X is any amino acid other than proline, and B is serine or threonine) has been modified so that no N-glycosylation occurs during the expression in a eukaryotic cell, and since the DNA molecule has been modified at the N-glycosylation site, it produces a non-N-glycosylated protein, which thereby exhibits a high immunogenicity when, for example, it is allowed to produce, in a eukaryotic cell, an antigen protein derived from a prokaryotic cell.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Protein C or activated protein C-like molecules
InactiveUS20050095668A1Improve stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The present invention relates to novel conjugates between polypeptide variants of protein C and a non-polypeptide moiety, such as PEG or sugar moieties. In particular, the present invention provides novel protein C conjugates having an increased resistance to inactivation by e.g. human plasma and α1-antitrypsin. Consequently, such conjugates have an increased in vivo half-life. Preferred examples include protein C conjugates, wherein at least one additional in vivo N-glycosylation site has been introduced. The conjugates of the invention are useful for treating a variety of diseases, including septic shock.
Owner:MAXYGEN +1
Method for increasing lipase expression through glycosylation modification as well as mutant enzyme and application thereof
ActiveCN104762277ADoes not affect growthIncrease enzyme activityFungiHydrolasesExtracellular proteinsPeptide sequence
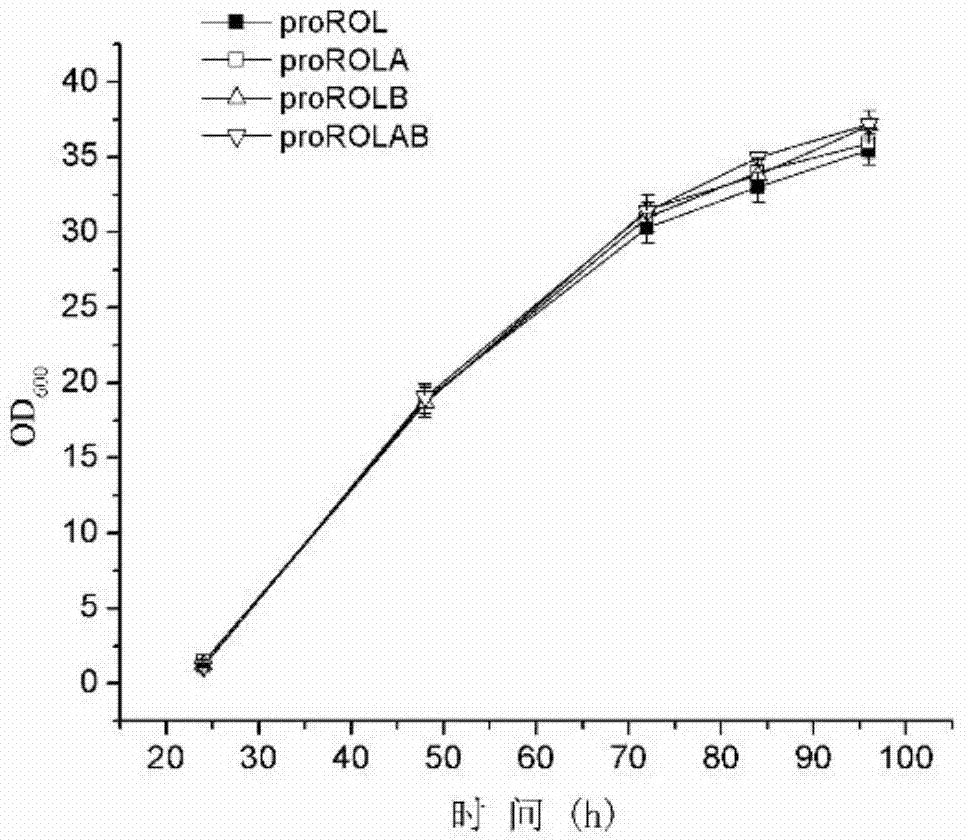
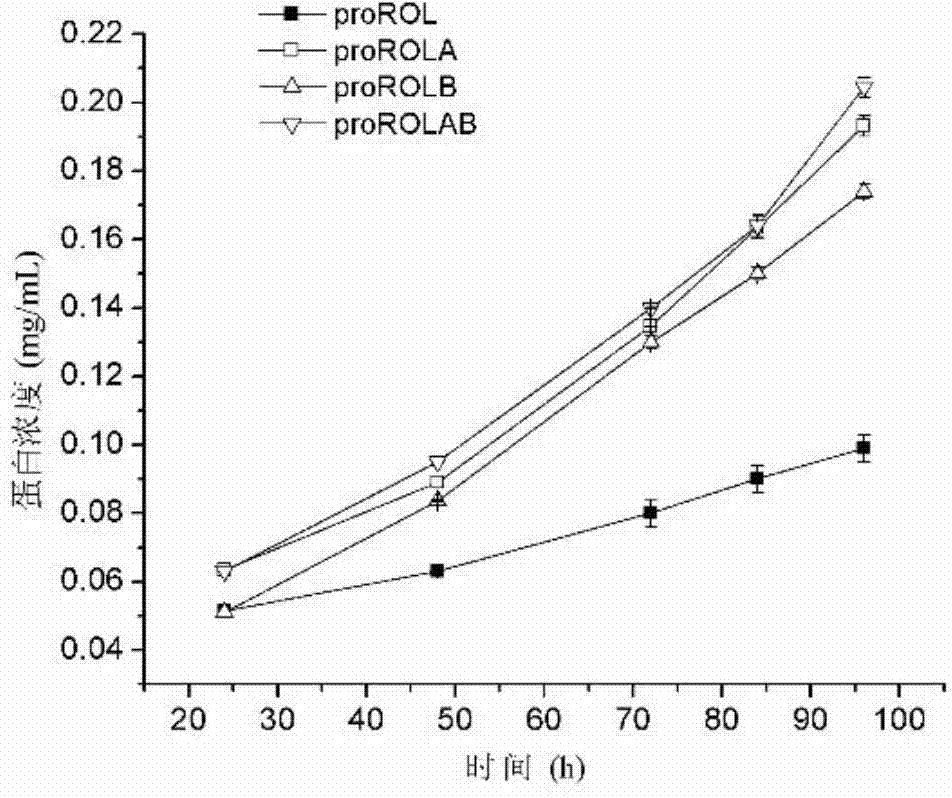
The invention discloses a method for increasing lipase expression through glycosylation modification as well as a mutant enzyme and an application thereof and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The N-glycosylation mutation is performed on a leading peptide sequence of rhizopus oryzae lipase, the SAS and / or NT amino acid are / is respectively modified to an N-glycosylation site NGT and / or NLT, the extracellular protein concentrations of the obtained mutant enzyme proROLA, proROLB and proROLAB are increased by 211%, 188% and 233% compared with those of the un-glycosylated proROL, the enzyme activities when culturing in a fermentation tank are respectively 8210 U.mL<-1>, 8457 U.ml<-1> and 9366 U.mL<-1>, and the un-mutated proROL extracellular enzyme activity is almost zero. The rhizopus oryzae lipase provided by the invention has obviously increased lipase enzyme activity and can be used in the fields such as food, chemical engineering and biological energy source.
Owner:TAIXING YIMING BIOLOGICAL PRODS
Interferon gamma polypeptide variants
InactiveUS20020192183A1Renal clearance is reducedHigh molecular weightSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsInterstitial lung diseaseDisease
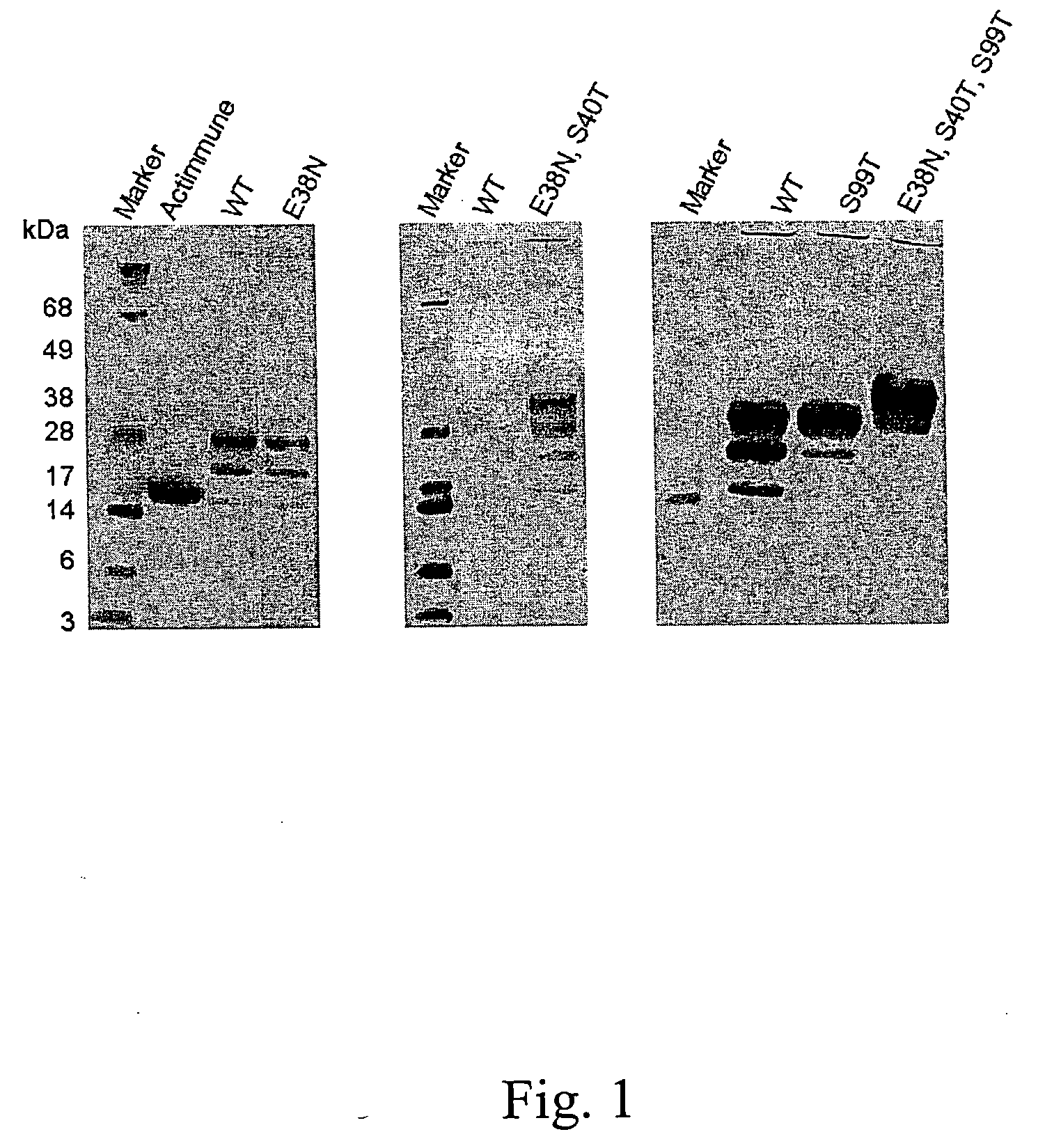
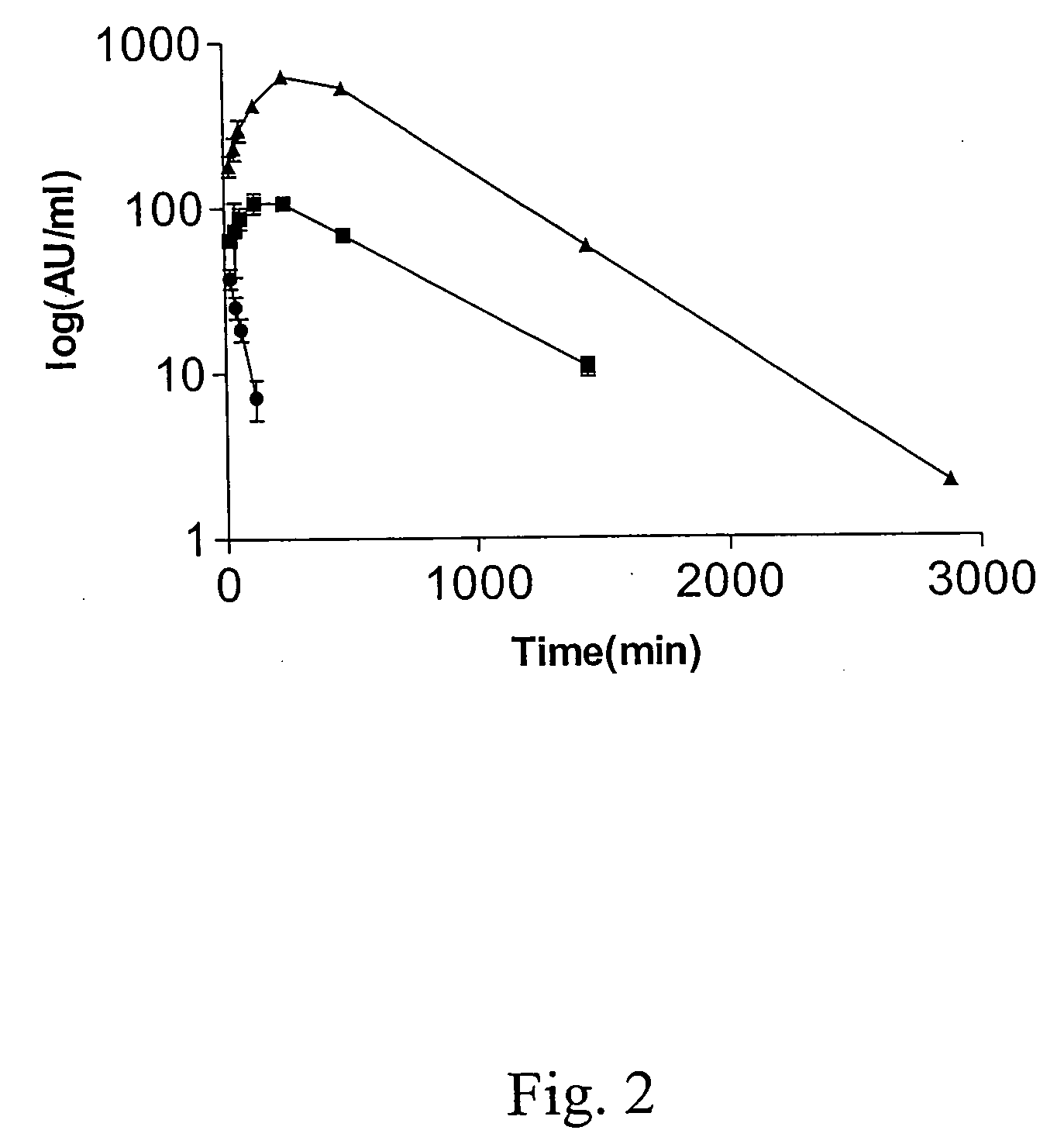
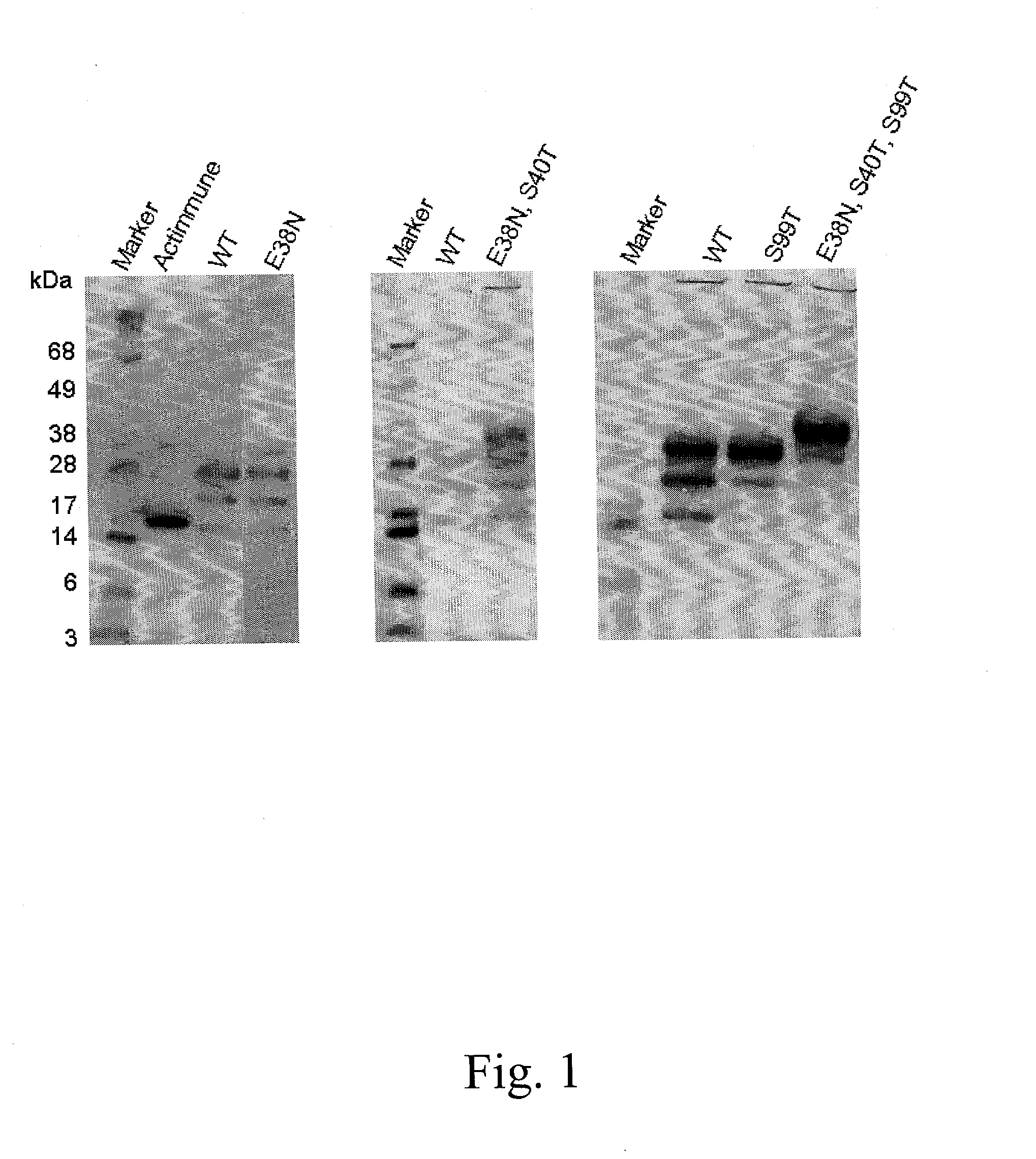
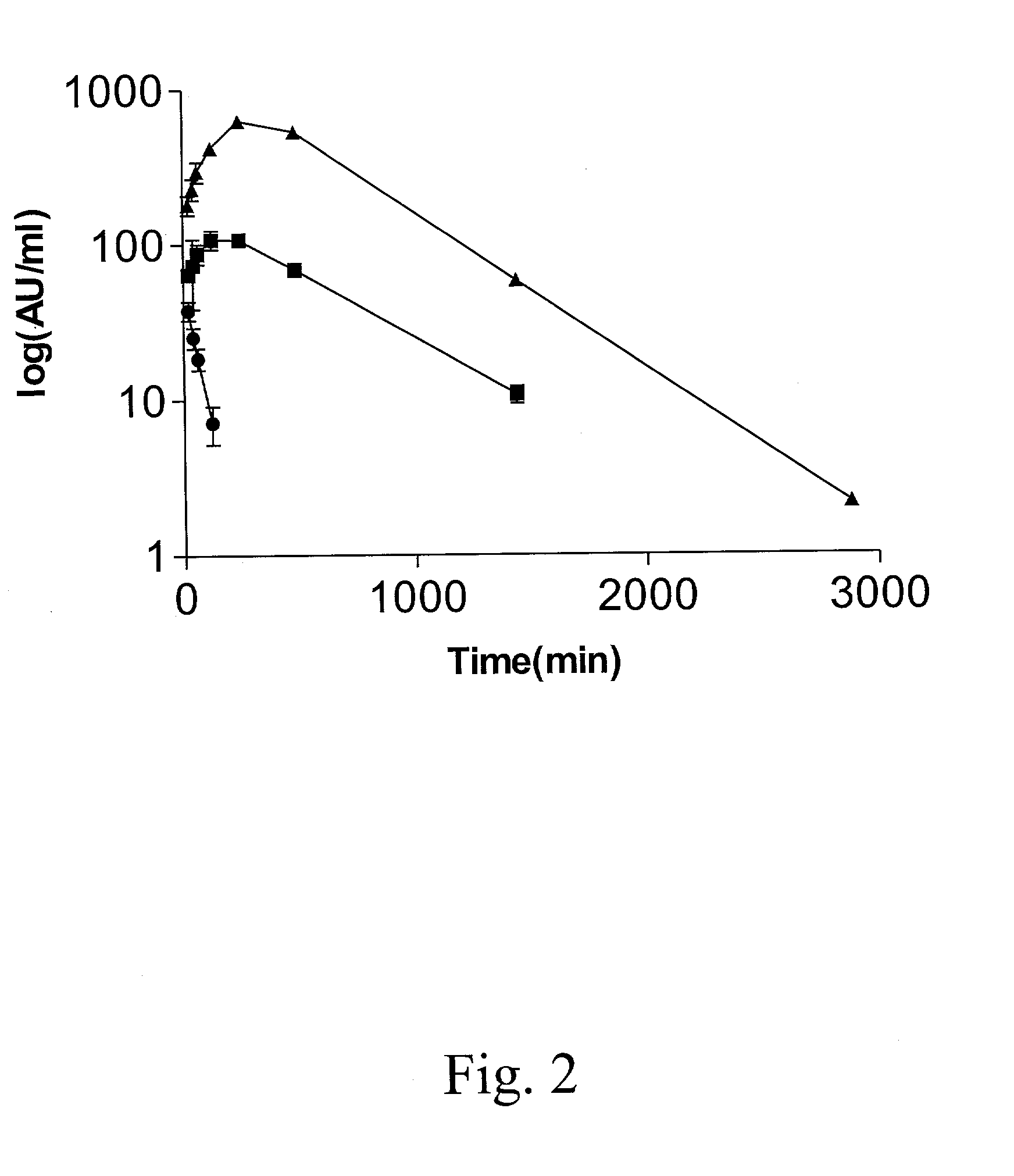
The present invention relates to novel interferon gamma polypeptide variants having interferon gamma (IFNG) activity, methods for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptide variants and their use in the treatment of diseases, in particular for the treatment of interstitial pulmonary diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. These novel polypeptide variants all comprise the substitution S99T as compared to the amino acid sequence of huIFNG or fragments thereof. By performing this mutation the naturally occurring N-glycosylation site present at position 97 is significantly better utilized. Preferably, the variants comprise further modifications, e.g. in order to increase the AUC of such variants when administered subcutaneously.
Owner:PERSEID THERAPEUTICS
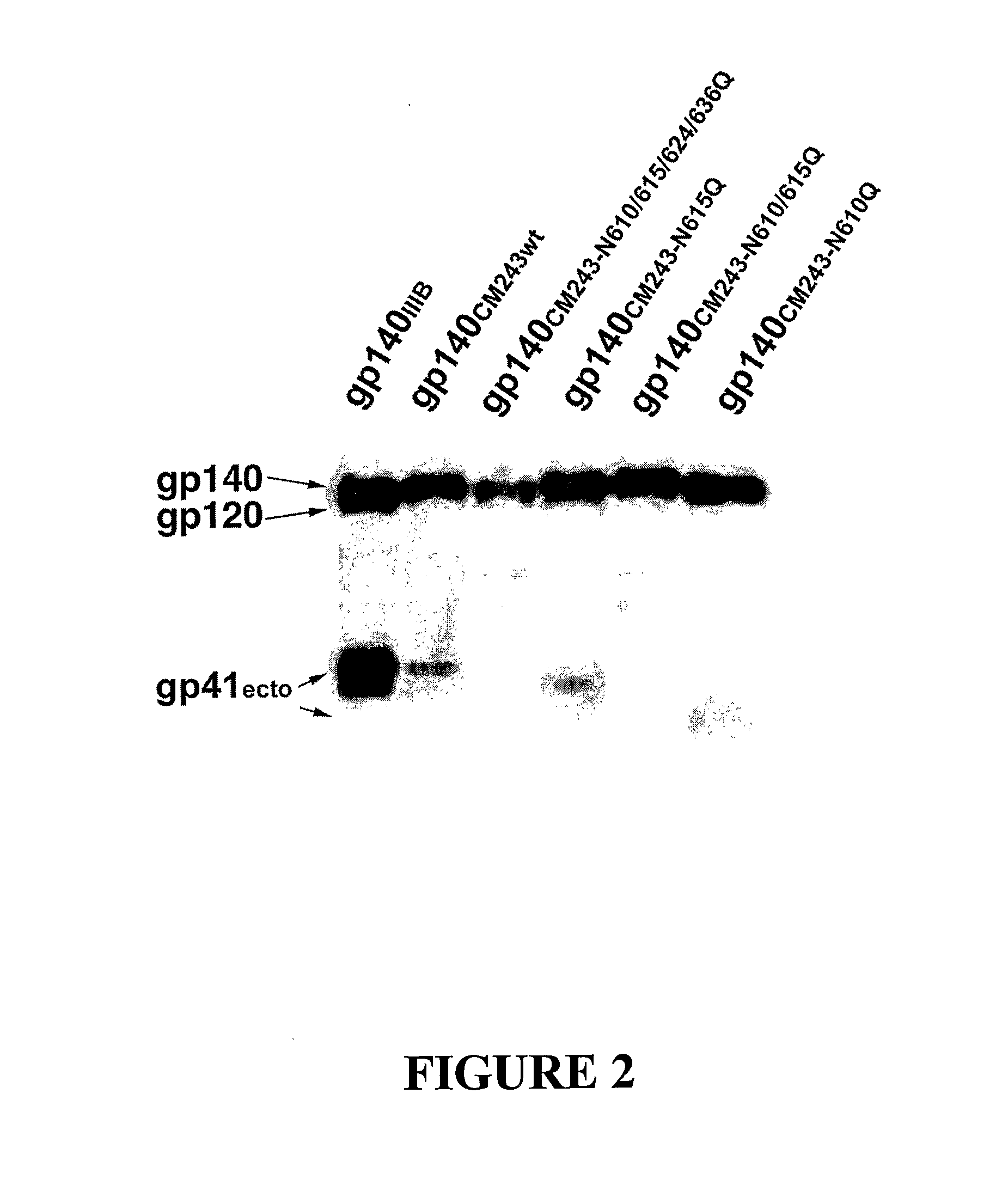
Modified HIV-1 Envelope Proteins
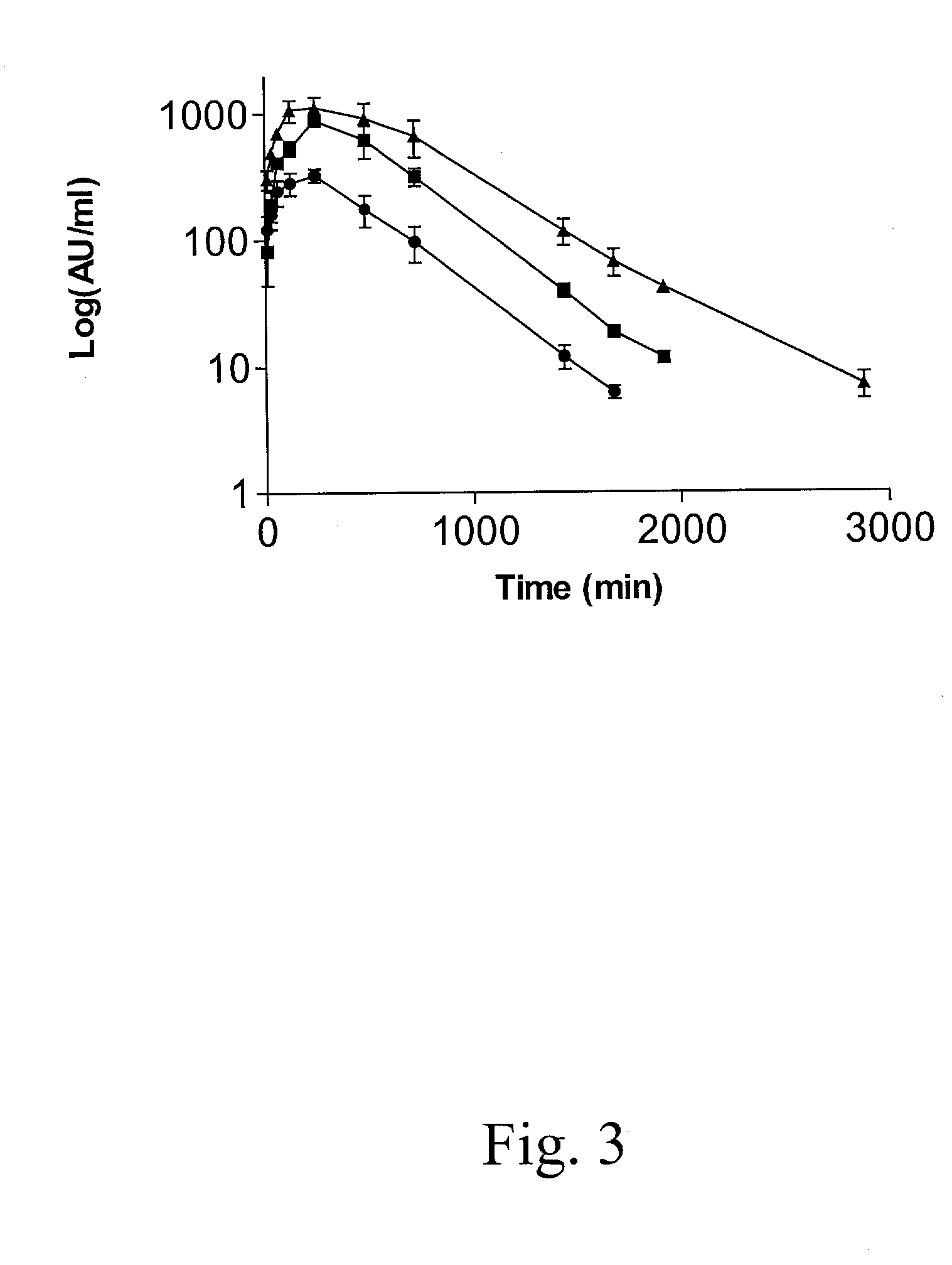
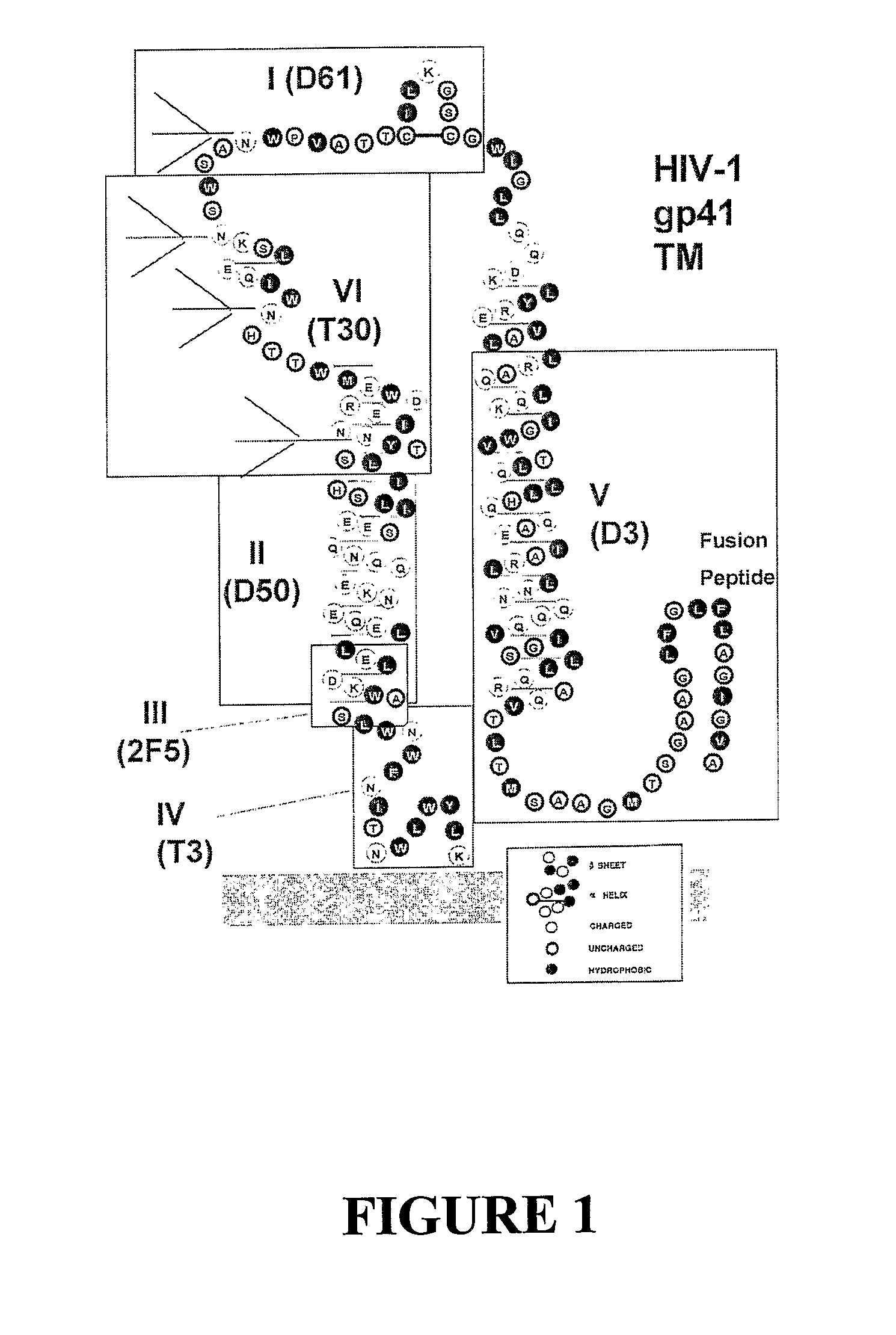
The present invention relates to modified HIV-1 envelope proteins where one or more N-glycosylation sites have been deleted or modified, which produce a broadly cross reactive neutralizing response, their methods of use and antibodies which bind to these proteins. The invention also provides for nucleic acids, vectors, antibodies and pharmaceutical compositions that comprise said modified HIV-1 envelope proteins.
Owner:HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF THE MILITARY MEDICINE INC
Protein C or activated protein C-like molecules
InactiveUS20030018175A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The present invention relates to novel conjugates between polypeptide variants of protein C and a non-polypeptide moiety, such as PEG or sugar moieties. In particular, the present invention provides novel protein C conjugates having an increased resistance to inactivation by e.g. human plasma and alpha1-antitrypsin. Consequently, such conjugates have an increased in vivo half-life. Preferred examples include protein C conjugates, wherein at least one additional in vivo N-glycosylation site has been introduced. The conjugates of the invention are useful for treating a variety of diseases, including septic shock.
Owner:PERSEID THERAPEUTICS
Method for rapidly and comprehensively detecting oligosaccharide on medicinal monoclonal antibody N-glycosylation site
InactiveCN104597187AEasy to detectVariety/Number IncreaseComponent separationFluorescenceMonoclonal antibody
Owner:GUANGDONG ANNPO BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Cold-adapted marine yeast BoHai Sea-9145 low-temperature alkaline lipase gene, amino acid sequence and recombinant lipase
ActiveCN102363786AImprove featuresImprove temperature stabilityHydrolasesFermentationSequence signalRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention relates a gene for coding low-temperature alkaline lipase (LipY). The gene is obtained by cloning cold-adapted marine yeast (BoHai Sea-9145), which can secrete low-temperature alkaline lipase and is screened from sea mud of Bohai, by a method of combining degenerate primer polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE). The gene contains a 1206bp open reading frame (ORF), codes 401 amino acids and contains a signal peptide with 28 amino acids at the amino acid end. Each coded amino acid contains a conserved sequence (G-X-S-X-G) of the lipase and a potential N-glycosylation site. The lipase gene is cloned on an eukaryotic expression vector (pIc9K) and performs heterologous expression in Pichia pastoris (Gs115). High-activity recombinant lipase is obtained from supernate 96 hours after fermentation, wherein methanol serves as an inducer. An electrophoretic pure lipase sample is obtained by purifying the recombinant lipase by a nickel ion affinity column. The recombinant lipase has a series of advantages of high low-temperature catalytic activity, stable performance under the alkaline condition and the like, and has wide application prospect in the low-temperature catalytic fields of daily chemicals, textile, food processing and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Homogenous antibody drug conjugates via enzymatic methods
Owner:CSPC MEGALITH BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
N glycosyl transferase AaNGT and application thereof
InactiveCN107034202ATransferasesPeptide preparation methodsActinobacillus pleuropneumoniaeGlycopeptide
The invention discloses a N glycosyl transferase AaNGT. An amino acid sequence thereof is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention also discloses an application of the N glycosyl transferase AaNGT in polypeptide galactosylated modification. AaNGT is capable of supplying a simple and convenient method for the forming of glycopeptide; the capacity of AaNGT for utilizing UDP-Glc is obviously higher than that of the reported N glycosyl transferase ApNGT which is sourced from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae; the AaNGT also can transfer the special glycosyl donor UDP-GlcNH2 to the polypeptide containing N glycosylation sites, and then the other glycosyl transferases can be utilized to convert the GlcNH2 into the GlcNAc so as to form natural N glycan linking, so that a new method is supplied for the development of the glycoprotein vaccine. The invention is beneficial to the AaNGT becoming a protein modified tool enzyme.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Homogenous antibody drug conjugates via enzymatic methods
ActiveUS20170106096A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeGlutaminase
The present application in one aspect provide Fc-containing polypeptide conjugates comprising an Fc-containing polypeptide conjugated to a conjugate moiety, wherein the Fc-containing polypeptide comprises an N-glycosylated Fc region comprising an acceptor glutamine residue flanked by an N-glycosylation site and wherein the conjugate moiety is conjugated to the Fc-containing polypeptide via the acceptor glutamine residue. Also provided are methods of making such Fc-containing polypeptide conjugates by using a wildtype or engineered transglutaminases. Further provided are engineered transglutaminases specifically designed for carrying out such reactions.
Owner:CSPC MEGALITH BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 as well as expression and purification methods and application thereof
ActiveCN102351952AImprove uniformityBiologically activeFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsPichia pastorisPurification methods
The invention discloses low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 as well as expression and purification methods thereof. The low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 is protein obtained after replacing Asn in the N46 bit in the IFN-lambda1 mature peptide sequence into Gln. The blockage on the high-mannose modification process of the N-glycosylation site of the IFN-lambda1 by the Pichia pastoris is realized so that the IFN-lambda1-Nm genes are correctly expressed in the Pichia pastoris in a high-efficiency secretory way, the uniformity of the expressed recombination IFN-lambda1-Nm protein is obviously improved, the expression level is higher than 65mg / L, the purity of the expressed recombination protein after two-step column chromatography is higher than 98 percent, and the low-saccharification modified recombination IFN-lambda1-Nm protein has the same biological activity as the original Pichia pastoris expressed wild IFN-lambda1 and simultaneously has better safety. The invention provides an effective method for efficient low-cost mass production of low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 with biological activity and good uniformity, higher practical application values are realized, and the application prospects are wide.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Homogenous antibody drug conjugates via enzymatic methods
The present application in one aspect provide Fc-containing polypeptide conjugates comprising an Fc-containing polypeptide conjugated to a conjugate moiety, wherein the Fc-containing polypeptide comprises an N-glycosylated Fc region comprising an acceptor glutamine residue flanked by an N-glycosylation site and wherein the conjugate moiety is conjugated to the Fc-containing polypeptide via the acceptor glutamine residue. Also provided are methods of making such Fc-containing polypeptide conjugates by using a wildtype or engineered transglutaminases. Further provided are engineered transglutaminases specifically designed for carrying out such reactions.
Owner:CSPC MEGALITH BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
New carboxyl terminal peptide and long-acting interferon
ActiveCN106397570AExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemProtein moleculesHalf-life
The invention belongs to the field of a therapeutic biological preparation, and particularly relates to new carboxyl terminal peptide. The invention further relates to an application of the new carboxyl terminal peptide and long-acting interferon made from the carboxyl terminal peptide. Through a synergistic effect of an O-glycosylation site and an N-glycosylation site, the half life of a protein molecule fused with the carboxyl terminal peptide is prolonged, and the activity of the fused protein molecule isn't obviously affected or is enhanced.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Protein C or activated protein C-like molecules
The present invention relates to novel conjugates between polypeptide variants of protein C and a non-polypeptide moiety, such as PEG or sugar moieties. In particular, the present invention provides novel protein C conjugates having an increased resistance to inactivation by e.g. human plasma and alpha1-antitrypsin. Consequently, such conjugates have an increased in vivo half-life. Preferred examples include protein C conjugates, wherein at least one additional in vivo N-glycosylation site has been introduced. The conjugates of the invention are useful for treating a variety of diseases, including septic shock.
Owner:PERSEID THERAPEUTICS
Full-length identification and application of wingless gene of Periplaneta americana
ActiveCN106854650AImprove flight performanceEnhanced ability to prey on pestsBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameNucleotide
The invention provides a full-length cDNA of the wingless gene of Periplaneta americana and an encoded protein and cloning method thereof, and application thereof. The full-length cDNA of the wingless gene of Periplaneta americana is named as PaWg, with an accession number of KJ680328 in the GeneBank. The full-length sequence of the cDNA has a length of 1, 456 bp; the open reading frame (ORF) of the cDNA contains 1, 194 bases, coding 397 amino acids; and the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 in a sequence table. The amino acid sequence of the protein coded by the gene sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2 in the sequence table. The protein has a theoretical isoelectric point PI of 9.46 and a molecular weight of 4.4 kD and is a stable hydrophilic protein. The segment, composed of amino acids from site 1 to site 21, of the amino acid sequence of the protein is a segment of signal peptide; an enzyme site is located between site 21 and site 22; and the protein may contain two N-glycosylation sites, respectively located on asparagine at site 107 and site 343. The invention provides application of the gene, the protein and the cloning method to preparation of cockroach pesticides and biological probes and lays a foundation for research and application related to the wingless gene of Periplaneta americana.
Owner:JIANGSU OPEN UNIV
Homogenous antibody drug conjugates via enzymatic methods
The present application in one aspect provide Fc-containing polypeptide conjugates comprising an Fc-containing polypeptide conjugated to a conjugate moiety, wherein the Fc-containing polypeptide comprises an N-glycosylated Fc region comprising an acceptor glutamine residue flanked by an N-glycosylation site and wherein the conjugate moiety is conjugated to the Fc-containing polypeptide via the acceptor glutamine residue. Also provided are methods of making such Fc-containing polypeptide conjugates by using a wildtype or engineered transglutaminases. Further provided are engineered transglutaminases specifically designed for carrying out such reactions.
Owner:CSPC MEGALITH BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Modified DNA molecule, recombinant containing the same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20030059799A1Good effectImproving immunogenicityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenModified dna
There is provided a DNA molecule derived from a prokaryotic cell in which at lest one of the DNA regions encoding NXB (N is asparagine, X is any amino acid other than proline, and b is serine or threonine) has been modified so that no N-glycosylation occurs buring the expression in a eukaryotic cell, and since the DNA molecule has been modified at the N-glycosylation site, it produces a non-N-glycosylated protein, which thereby exhibits a high immunogenicity when, for example, it is allowed to produce, in a eukaryotic cell, an antigen protein derived from a prokaryotic cell.
Owner:ZEON CORP
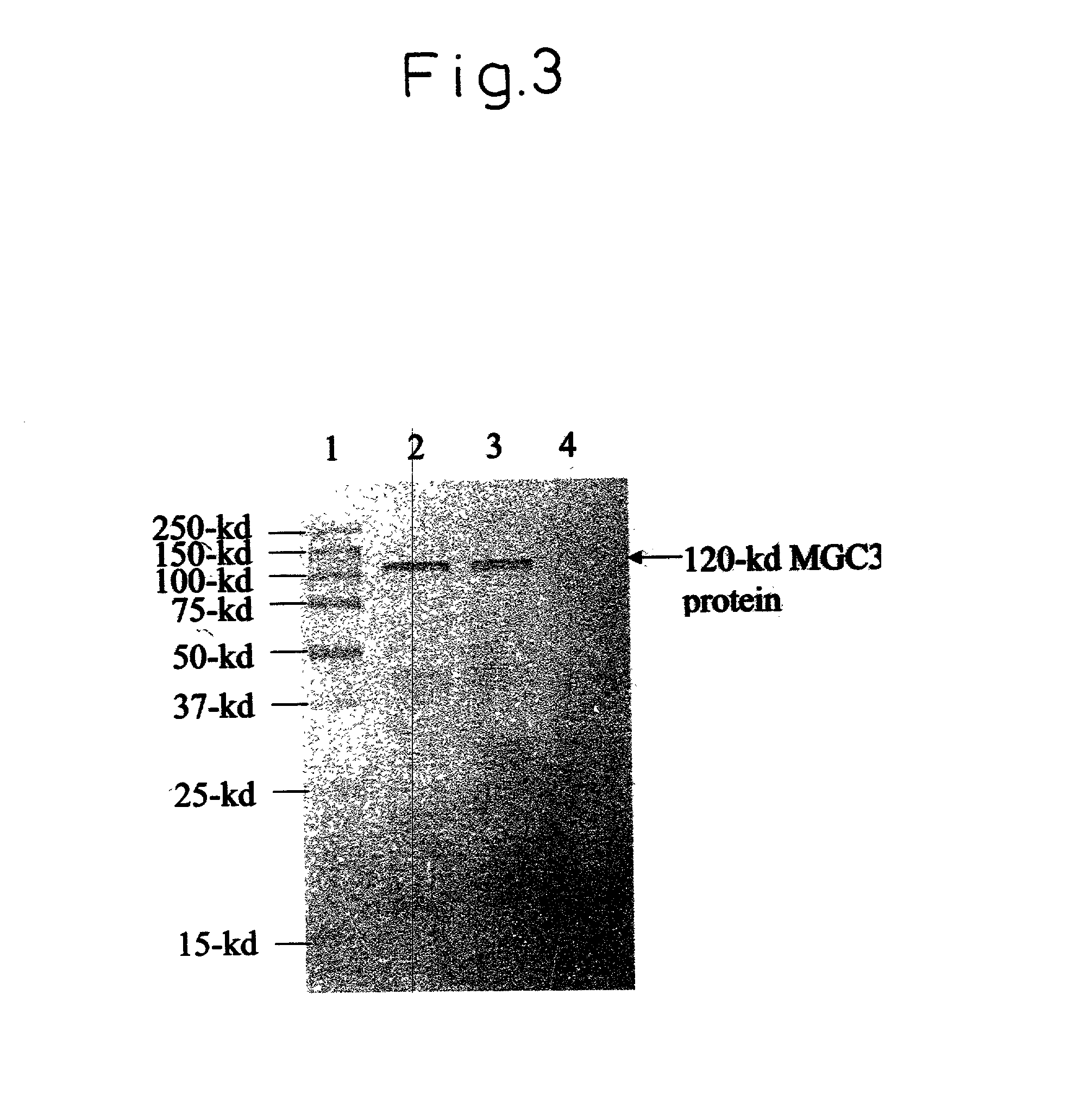
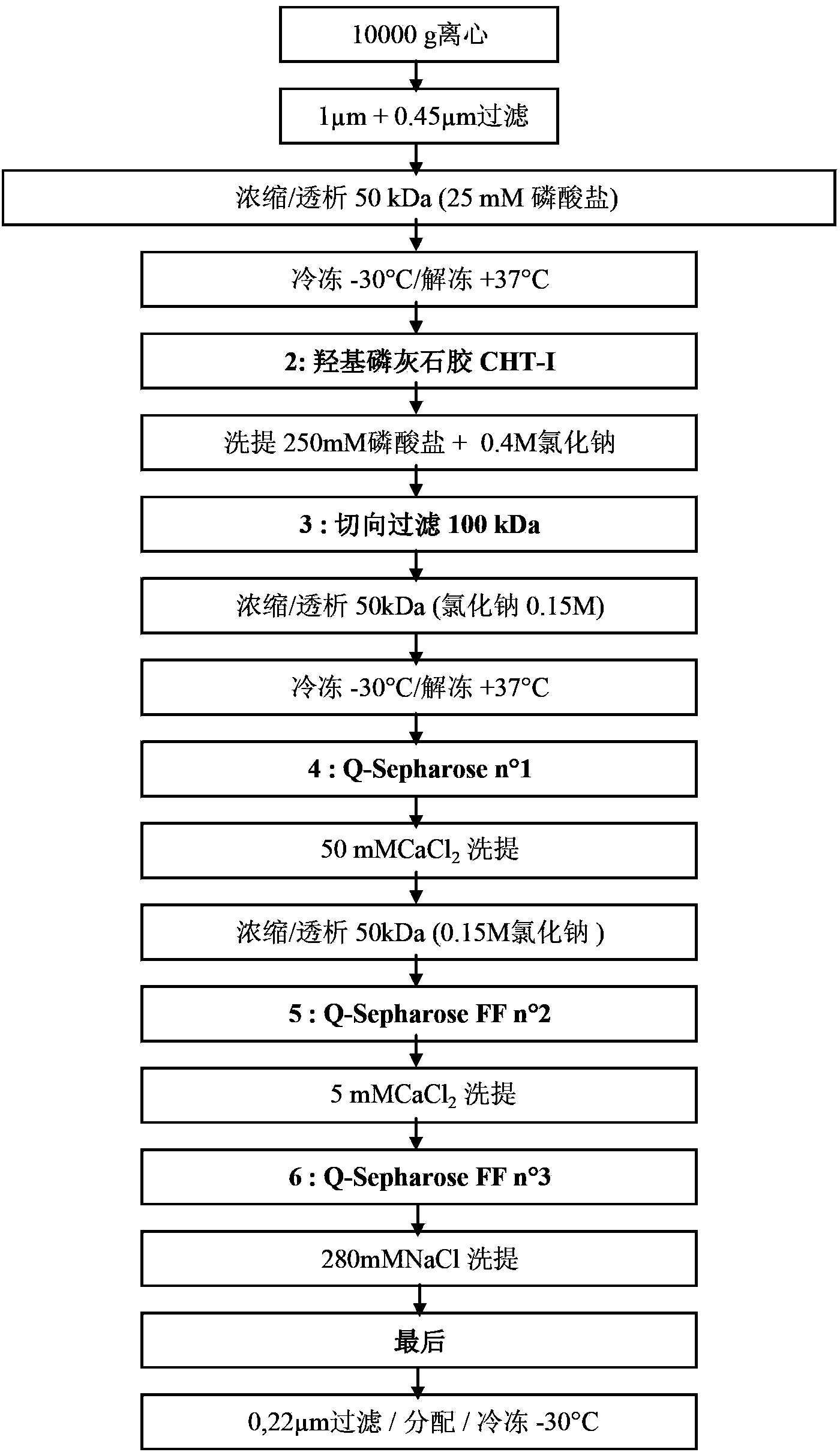
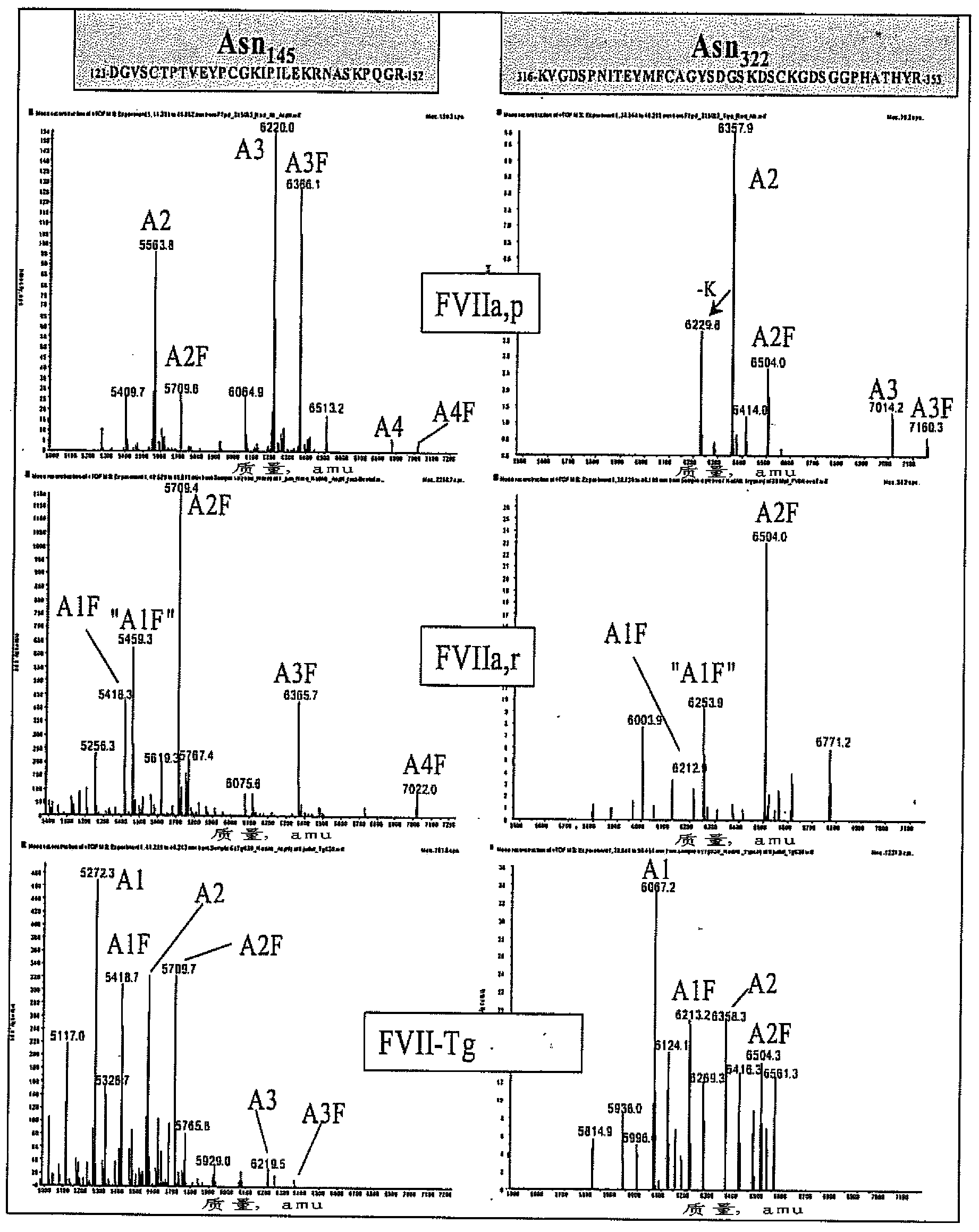
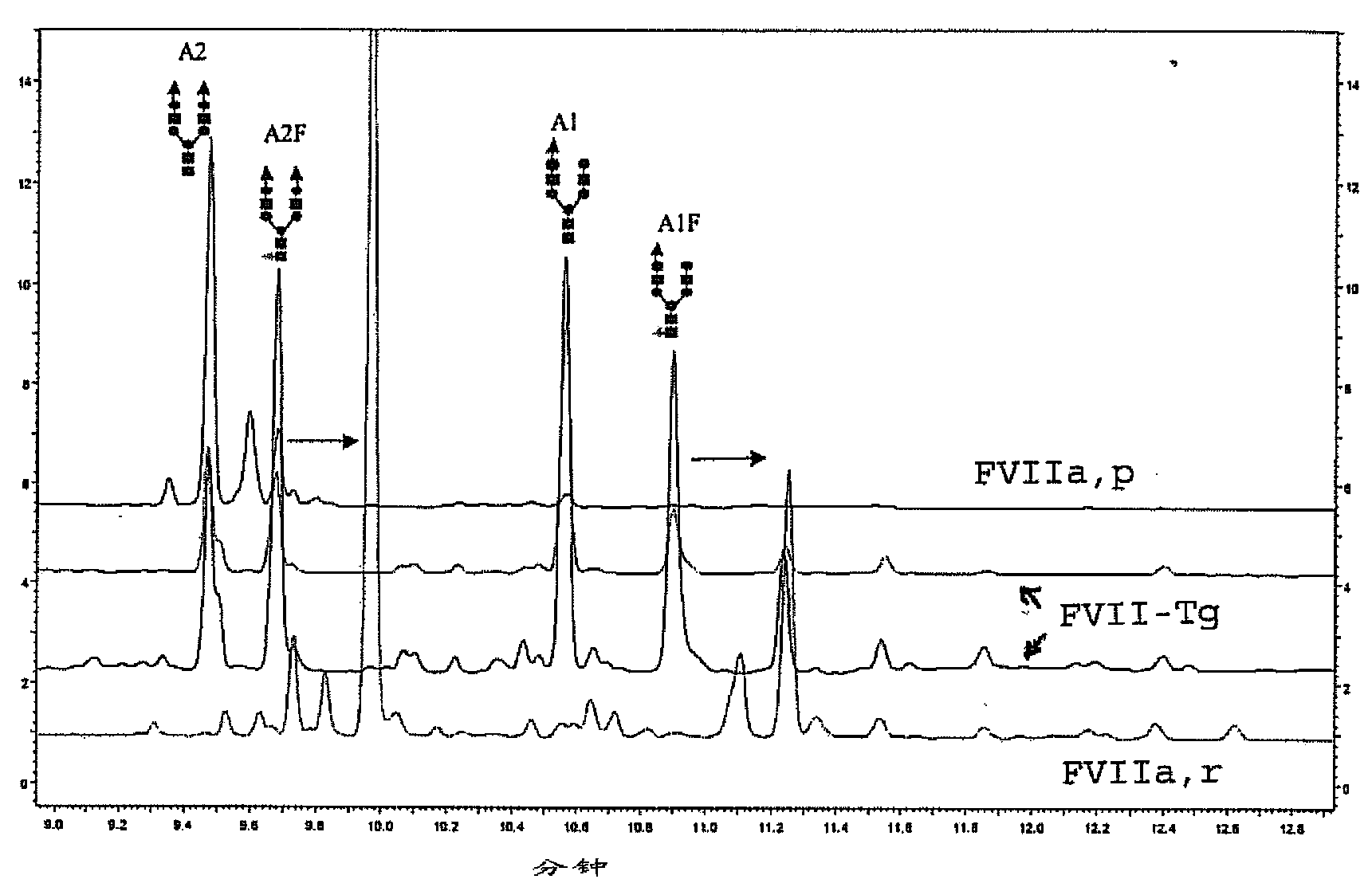
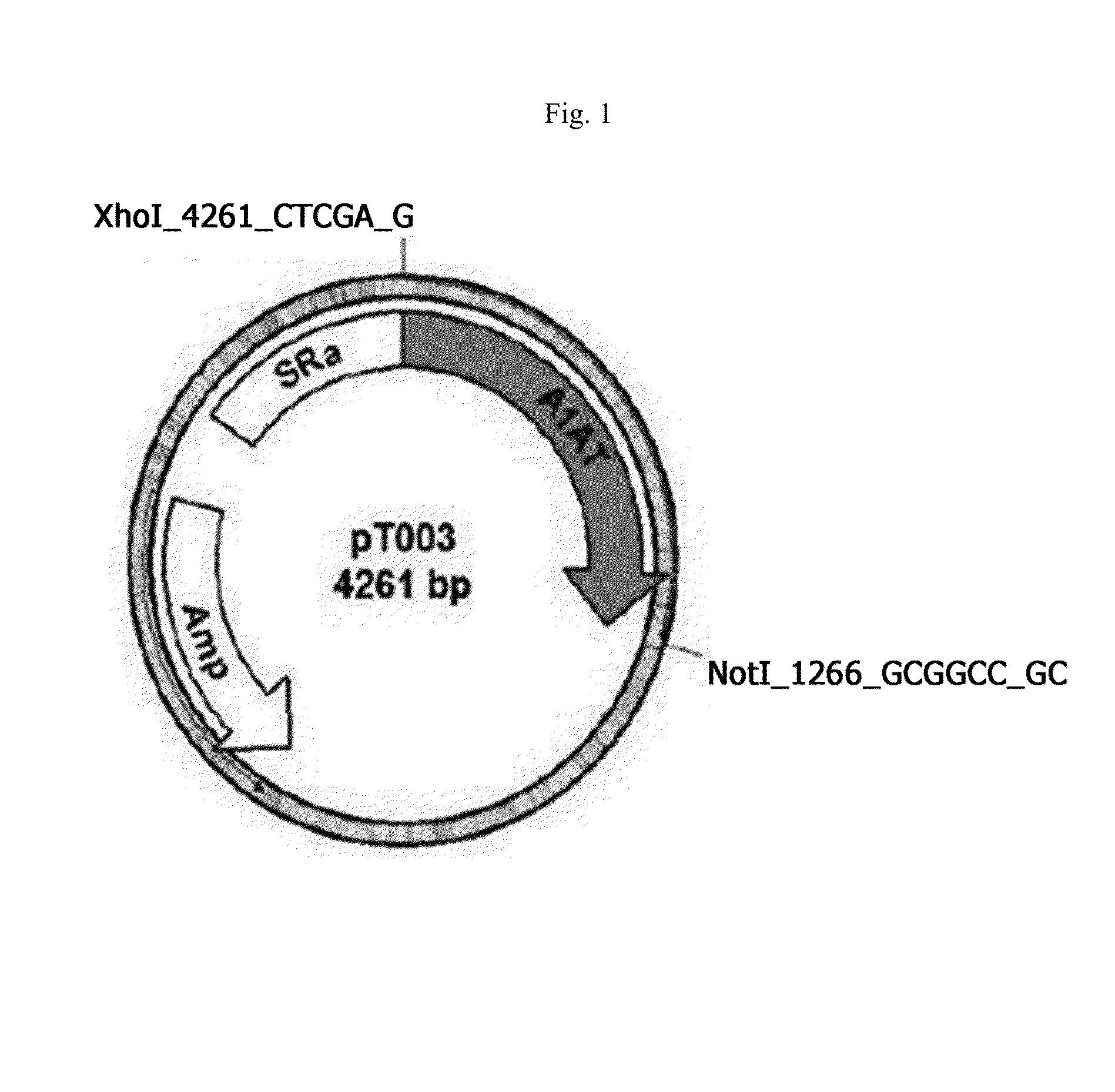
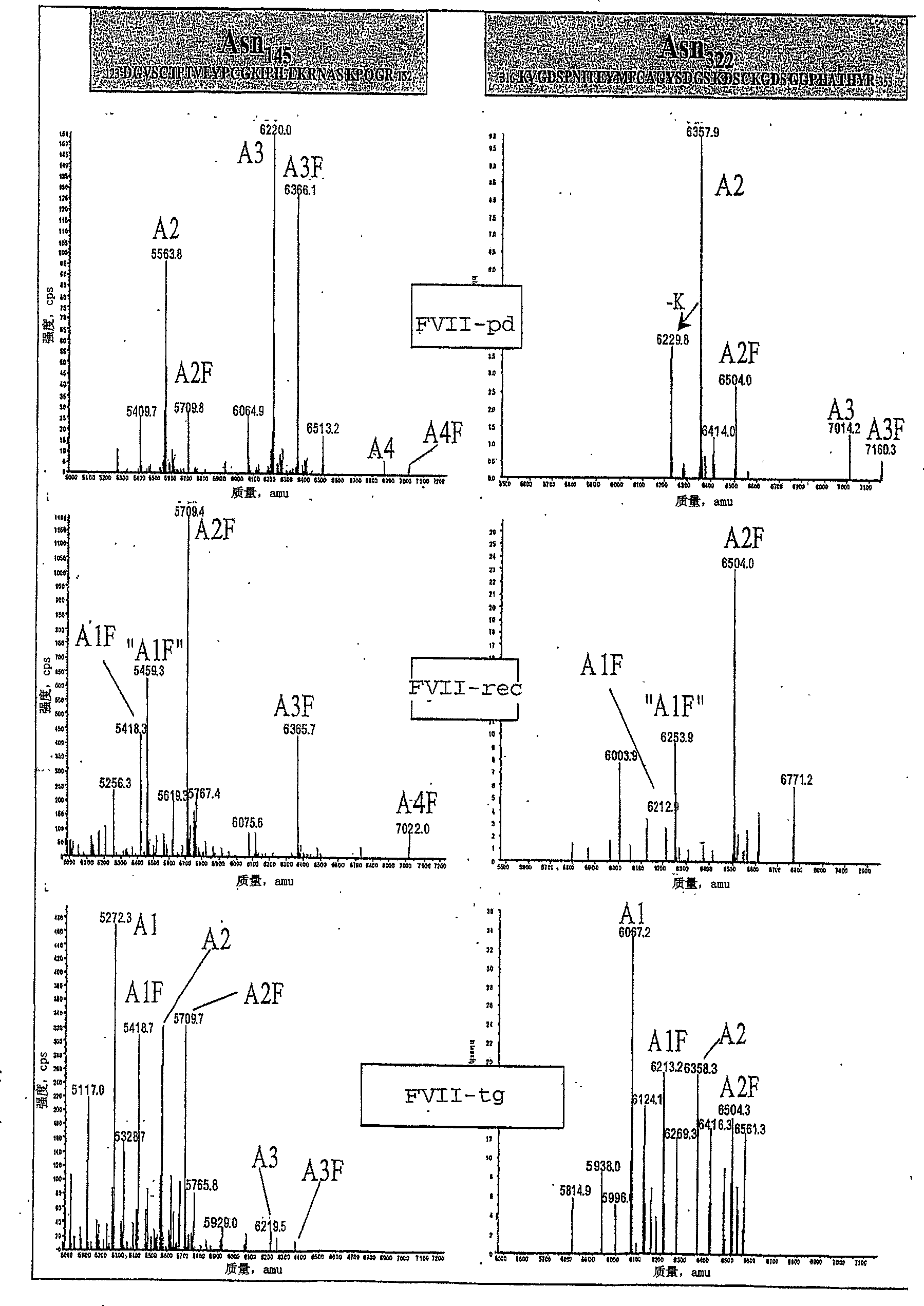
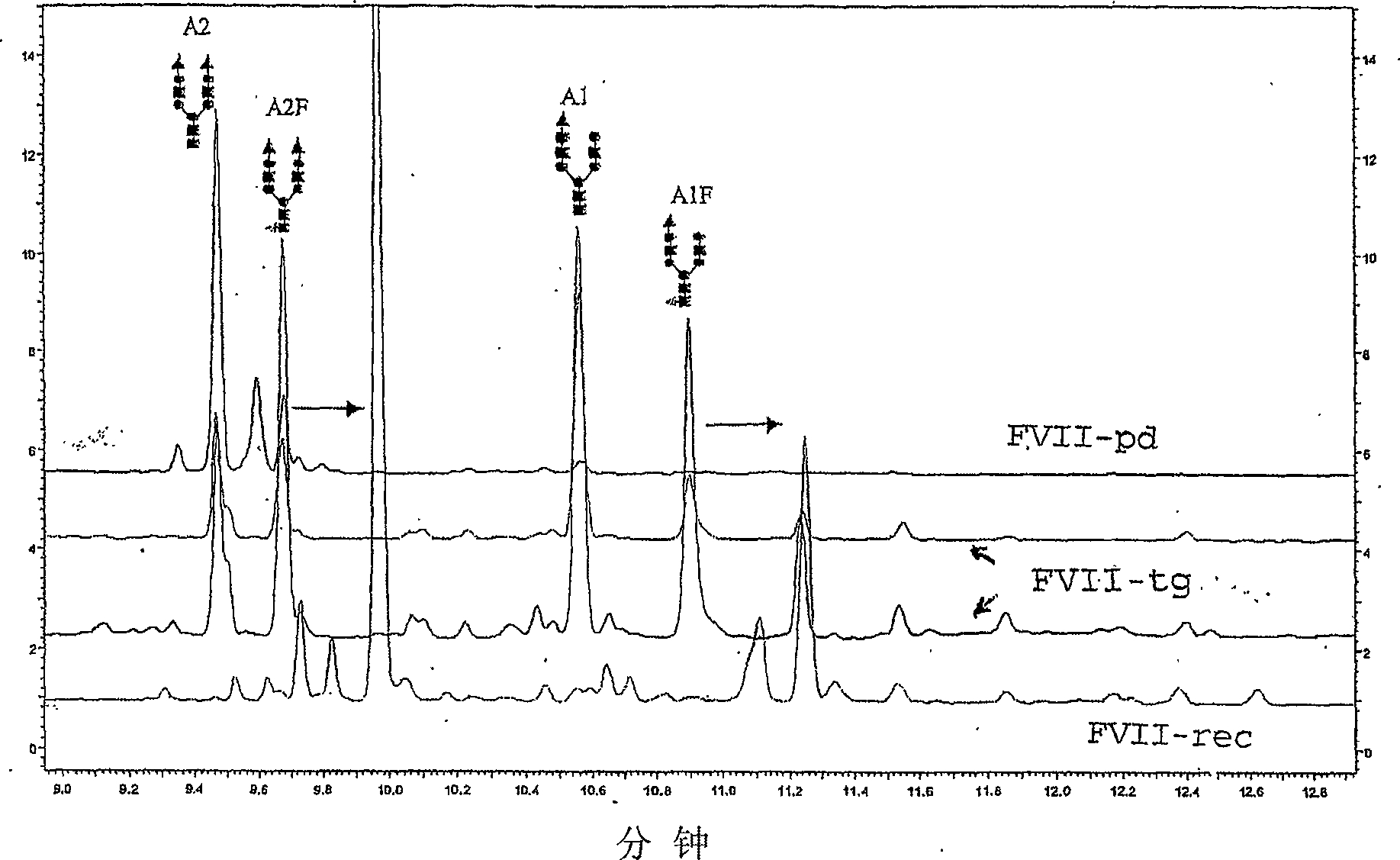
Recombinant or transgenic factor VII compound having a majority of glycan, biantennary, bisialylated and non-fucosylated forms
InactiveCN103397011AReduce frequencyReduce dosagePeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationSialic acid aldolaseFucosylation
The present invention concerns a recombinant or transgenic factor VII compound, each factor VII molecule of the compound having glycan forms linked to N-glycosylation sites, wherein among all the factor VII molecules in said compound, glycan, biantennary, bisialylated and non-fucosylated forms are in the majority. The invention also concerns such a compound for use as a medication, and a method for preparing said compound, among others.
Owner:分馏和生物工艺法国实验室公司
Method of improving enzymatic thermostability via artificially designed glycosylation modification
ActiveCN104894091ASimple manufacturing processNo lossEnzyme stabilisationGlycosylasesSpatial structureSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention provides a method of improving enzymatic thermostability via artificially designed glycosylation modification and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method includes: subjecting a primary sequence of enzyme protein and its spatial structure to combinatory analysis, designing an N-glycosylation site on a subunit joint of the enzyme protein or on a joint of internal motifs of subunits of the enzyme protein, and utilizing site-directed mutagenesis to introduce an N-glycosylation modification feature recognition enhancer sequon so as to enable carbohydrate chains to form a specific glycosyl hairpin structure among subunits of the enzyme protein or form a specific glycosyl pad structure among the internal motifs of the subunits of the enzyme protein, thereby maximally improving the rigidity of the tertiary structure of the enzyme protein and stabilizing the spatial conformation of the enzyme protein to be free from stress of high-temperature environments. The method of enzyme protein modification has the advantages that thermostability of the enzyme protein is greatly improved, the improvement in the thermostability of the enzyme protein is under artificial control, enzyme activity is partly improved, and catalytic features of the enzyme protein are enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
N-glycosylation algin lyase mutant capable of being efficiently applied and genetic engineering bacterium construction method
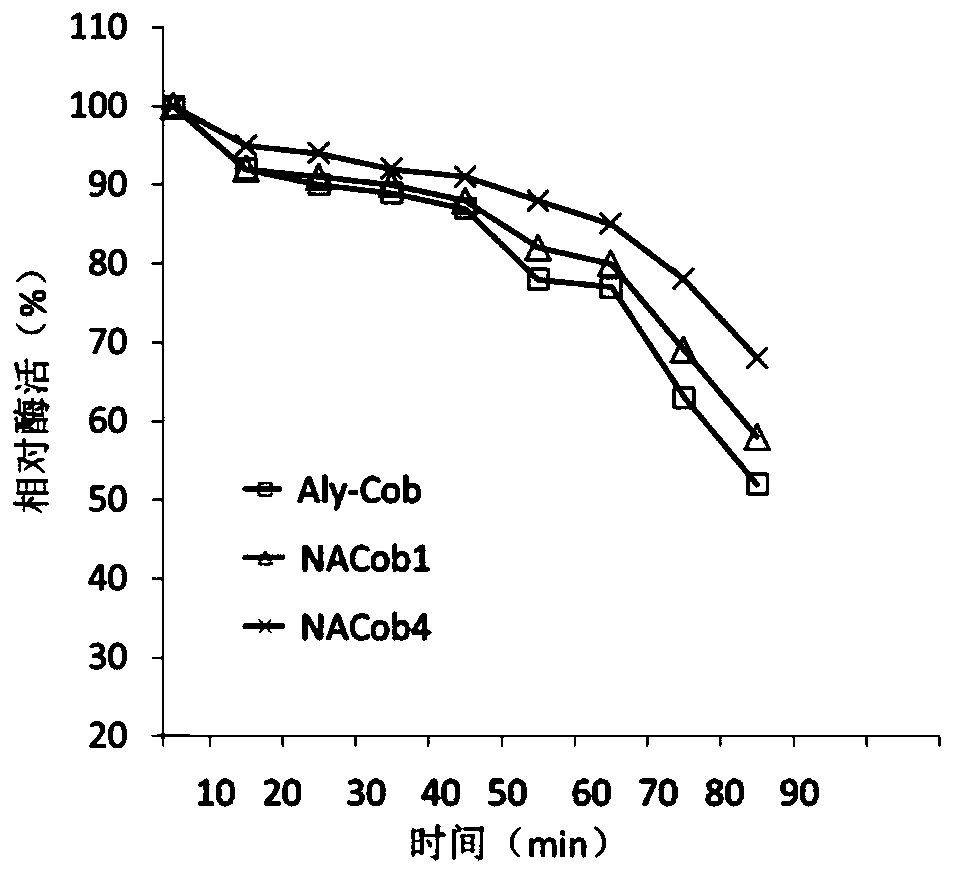
ActiveCN109852601AIncrease enzyme activityImprove stabilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionExocytosisLyase
The invention discloses a N-glycosylation algin lyase mutant capable of being efficiently applied and a genetic engineering bacterium construction method, and belongs to the technical field of biology. Based on algin lyase Aly-Cob, a DQNAT repeated sequence fragment is introduced at an N- terminal to be used as an N-glycosylation site, besides, expression carrier protein YebF is fused to be subjected to exocytosis, and further a glycosylation system pgl from campylobacter jejuni performs glycosylation modification through a sugar chain GalNAc2(Glc)GalNAc3Bac. The enzyme activity and the stability of an obtained mutant enzyme NACob are improved than those of an enzyme before glycosylation. The N-glycosylation modified algin lyase mutant provided by the invention can be widely applied to thefields of foods, medicines, agriculture and the like relevant to seaweed processing and utilizing.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
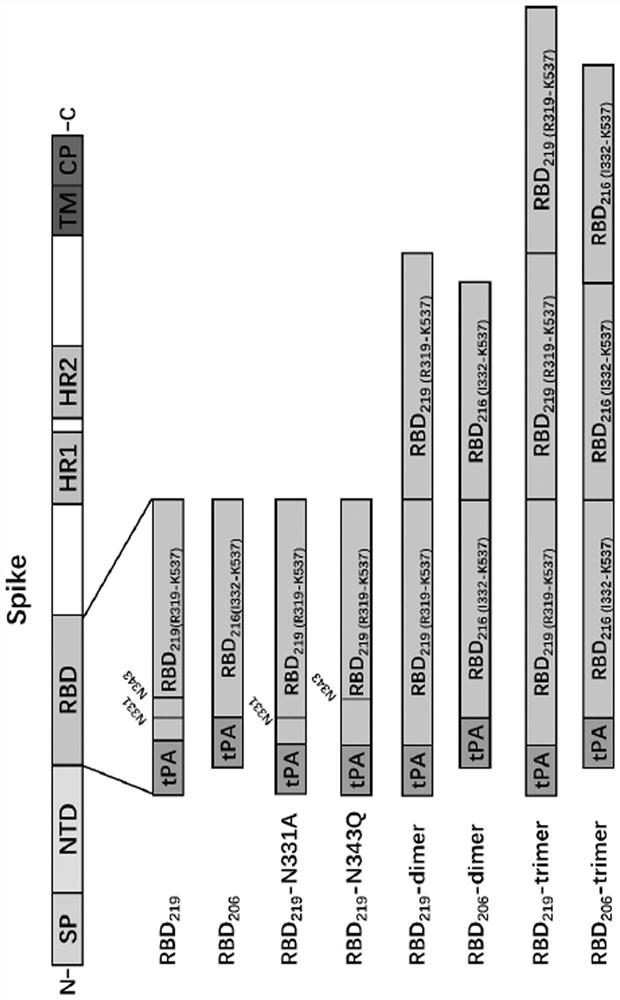
SARS-CoV-2 receptor bind region glycosylation modification antigen and application thereof
ActiveCN113637055AImprove featuresBoost neutralizing antibody levelsSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigen epitopeVariant strain
The invention discloses an SARS-CoV-2 receptor bind region (RBD) glycosylation modification antigen, which is characterized in that the N glycosylation site of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor bind region (RBD) is truncated and connected in series to form a single-chain polymer form, and natural glycosyl shielding on the surface of the RBD is reduced so as to more favorably expose antigen epitopes. Compared with a wild RBD monomer and RBD polymer form, the antigen can excite an organism to generate a higher-level SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody and a neutralizing antibody; an immune effect obtained through one-needle immunization can be equal to the immune effect of two-needle immunization of the wild type RBD monomer; and immune serum has similar neutralizing titer by aiming at an original strain and a variant strain, and shows a good cross protection effect. The invention also provides application of the glycosylation modification antigen in preparation of SARS-CoV-2 treatment and prevention drugs or vaccines.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Alpha-1 antitrypsin variant, preparation method thereof and use thereof
ActiveUS9051395B2Improve stabilityExtended half-lifeFactor VIIDipeptide ingredientsHalf-lifeBlood drug concentration
A novel alpha-1 antitrypsin variant, a method of preparing the same, and use thereof are provided. The alpha-1 antitrypsin variant has excellent stability in the body and maintains an inhibitory effect on elastase activities because the blood half-life (t1 / 2) and the area under blood drug concentration vs. time curve (AUC) are remarkably increased by adding an N-glycosylation site in animal cells through amino acid mutation between 1st and 25th positions of the N-terminus of alpha-1 antitrypsin. Therefore, the alpha-1 antitrypsin variant can be useful in preventing or treating alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Owner:ALTEOGEN
Recombinant or transgenic factor VII composition, each factor VII molecule having two N-glycosylation sites with defined glycan units
The invention concerns a recombinant or transgenic factor VII composition, each factor VII molecule of the composition having two N-glycosylation sites, wherein among all the FVII molecules of the composition the proportion of glycan units Gala1, 3Gal ranges between 0 and 40%. The invention also concerns a method for preparing such a FVII composition.
Owner:分馏和生物工艺法国实验室公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com