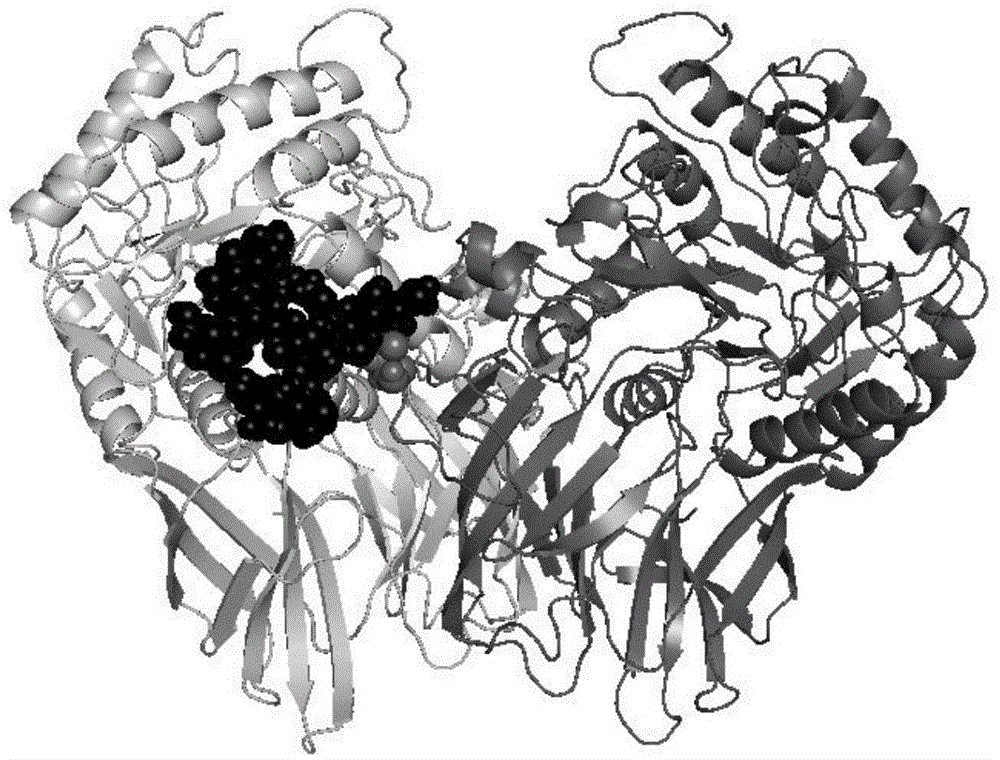Method of improving enzymatic thermostability via artificially designed glycosylation modification
A technology of thermal stability and glycosyl modification, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of reduced heat resistance, low efficiency of enzymatic properties, limited improvement of enzymatic properties, etc., to simplify the preparation process and thermal inactivation of enzyme molecules. The effect of raising the threshold and reducing the cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1: Rational design of N-glycosylation modification sites
[0017] 1. Knock out potential glycosylation sites
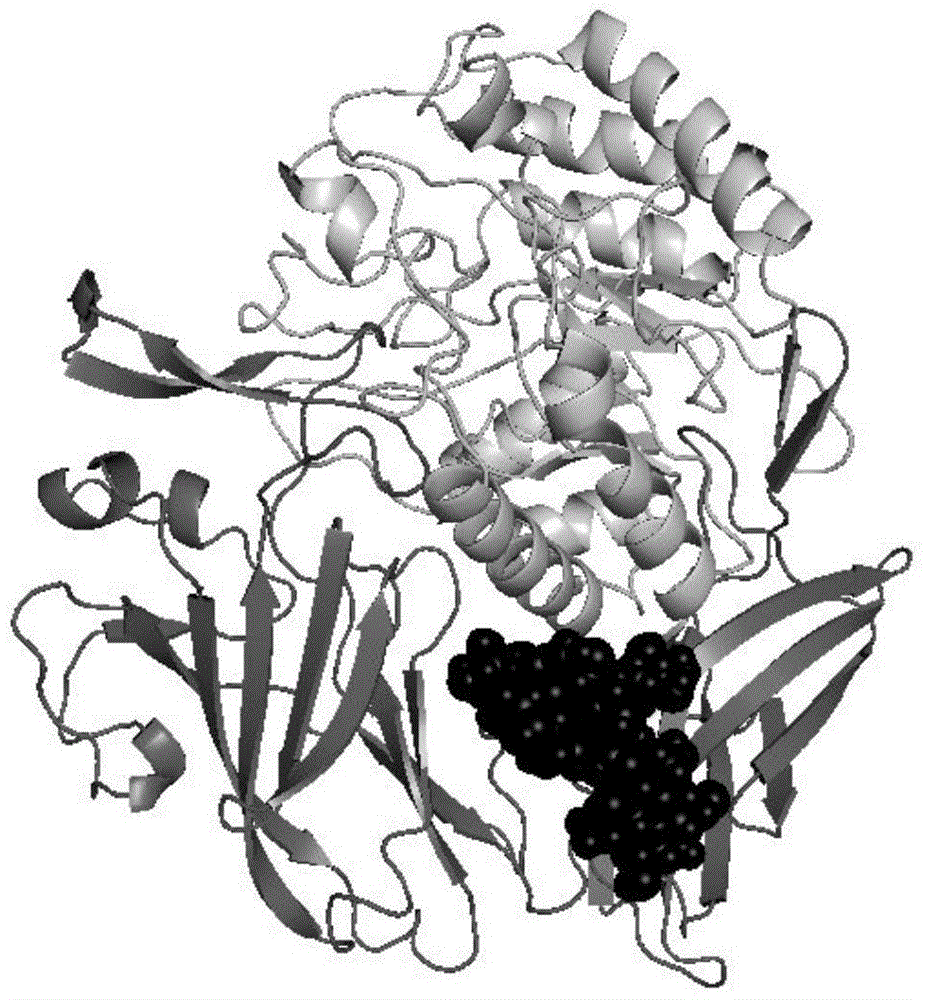
[0018] Taking β-D-glucuronidase PGUS (Genbank registration serial number EU095019) as the verification object, the online software NetNGlyc was used to analyze its primary amino acid sequence, and the sequon Asn-X-Ser / Thr find out the potential glycosylation sites of PGUS, and use the site-directed mutagenesis method to mutate the amino acid residues Asn of the potential glycosylation sites N28, N231, N383 and N594 to Gln to obtain mutations of aglycosylation modification sites Enzyme PGUS-UN.
[0019] 2. Using the crystal analysis structure of PGUS as a template, use SWISS-MODEL to simulate PGUS-UN at the non-glycosylation modification site, use PyMOL to display the simulation results, and analyze the B-Factor value of the local loop of the protein, The size of the protein surface groove and the secondary structure information of key parts are analy...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: Pichia expresses enzyme molecules with glycosyl modifications
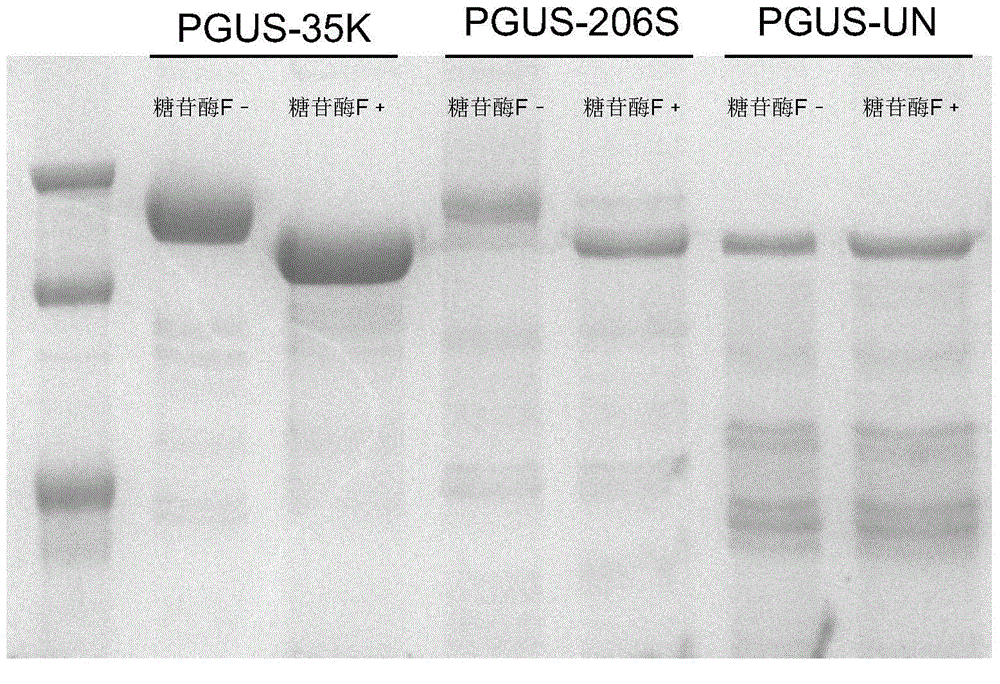
[0022] 1. Design the N-glycosylation recognition feature enhancement sequence EAS sequence at the glycosyl modification sites 35K and 206S finally determined in Example 1: Phe-X-Asn-Y-Ser / Thr (X is any one Amino acid, Y is any amino acid except Pro), using site-directed mutagenesis primers to carry out overlap extension PCR mutations corresponding to the gene sequences at 35K and 206S, and using EcoRI and NotI to perform double enzyme digestion on the PCR amplification results, after enzyme digestion The fragments were ligated to the pGAPZ a vector with the same restriction end sticky ends.
[0023] 2. Use BlnI to linearize the connected circular vector to obtain the linearized fragment and transform Pichia pastoris GS115 by electroporation, and coat the transformation product on a medium containing bleomycin resistance screening and 2% 5-bromo-4-chloro - On the 3-indolyl-β-D-glucuronide activit...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example 3: Thermal Stability Verification of Enzyme Molecules with Glycosyl Modifications
[0026] The glycosyl-modifying enzymes PGUS-35K and PGUS-206S obtained in Example 2 were placed in a 65°C water bath and incubated for 30 minutes, 60 minutes, 90 minutes, 120 minutes, 150 minutes and 180 minutes respectively. Then pipette 10 μL enzyme solution into 40 μL acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution containing 1.25 mmol / L 4-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside and pH 4.2, and react at 40°C for 5 After 2 minutes, add 200 μ L, the sodium carbonate of 0.4mol / L stops reaction, and sample solution detects the content of p-nitrophenol with microplate reader (405nm), to measure the relative enzymatic activity of β-D-glucuronidase, thereby Detect the thermal stability of glycosyl-modifying enzyme molecules, the results are as follows Figure 4 , the results showed that the artificially designed glycosyl hairpin structure PGUS-35K and glycosyl spacer structure PGUS-206S significa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com