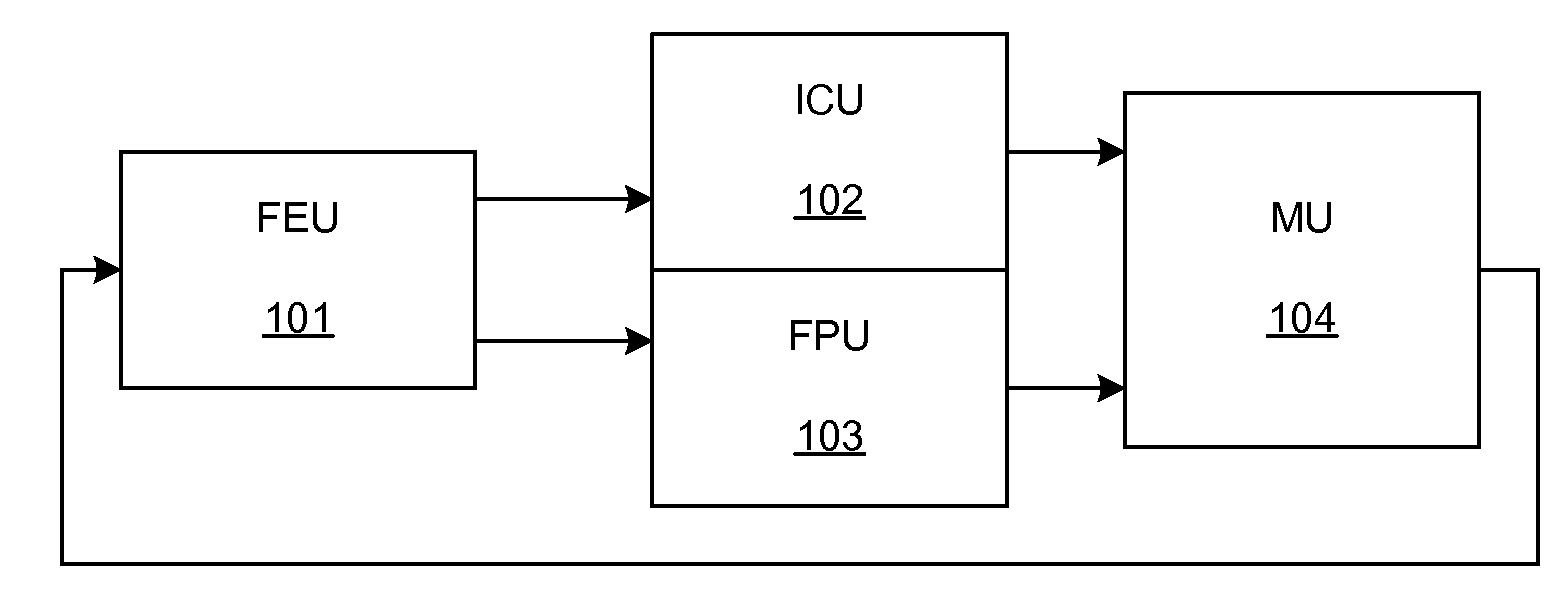
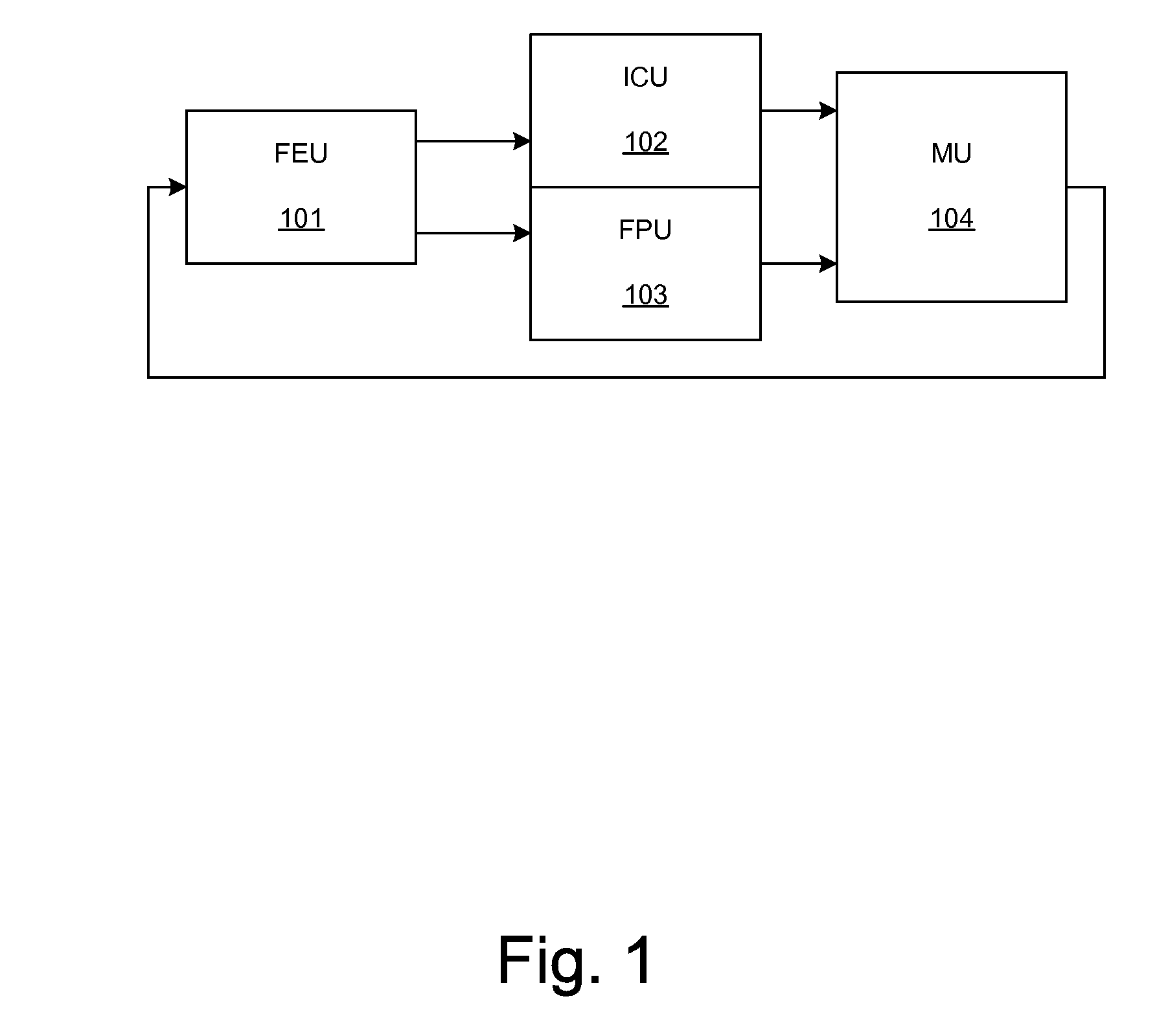
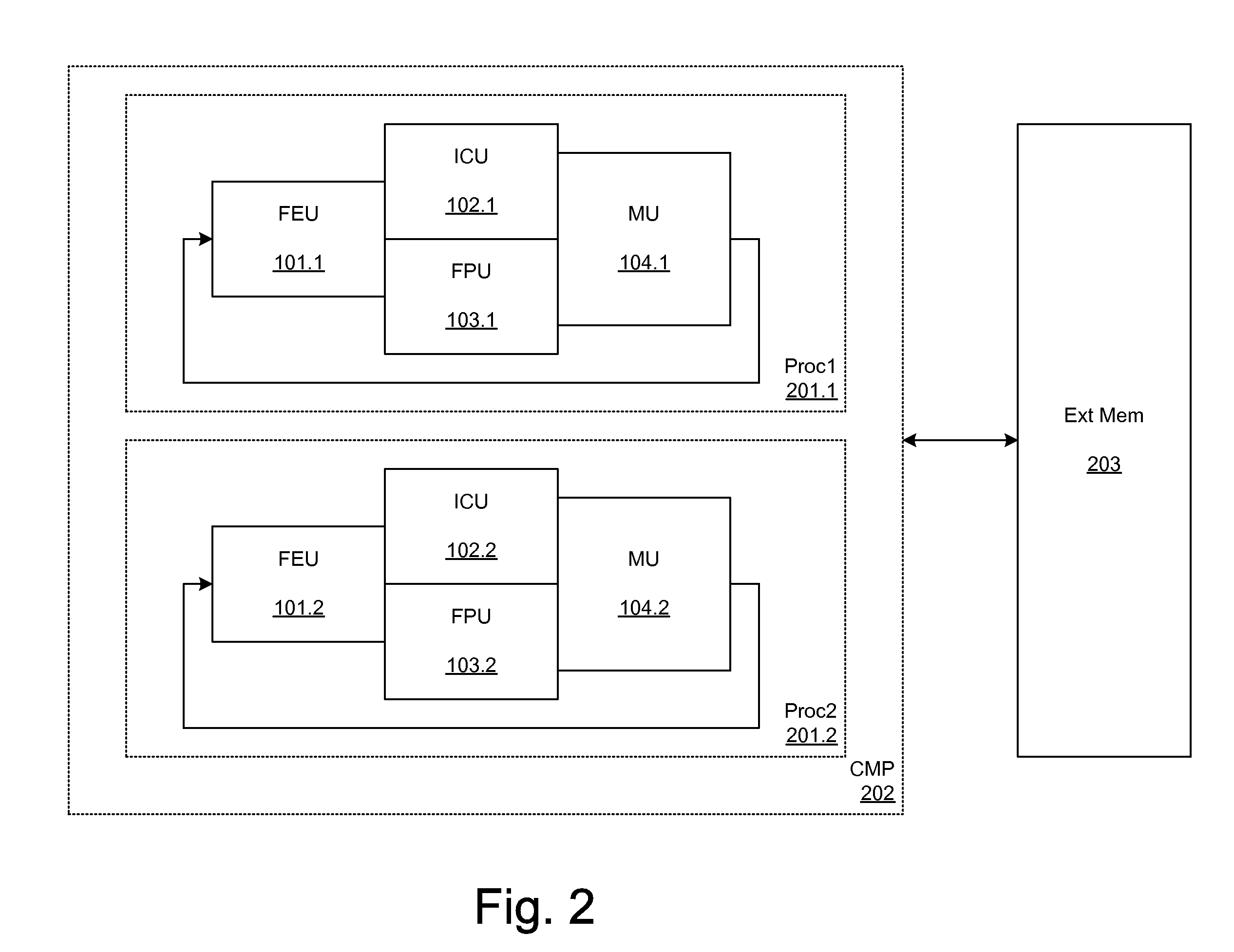
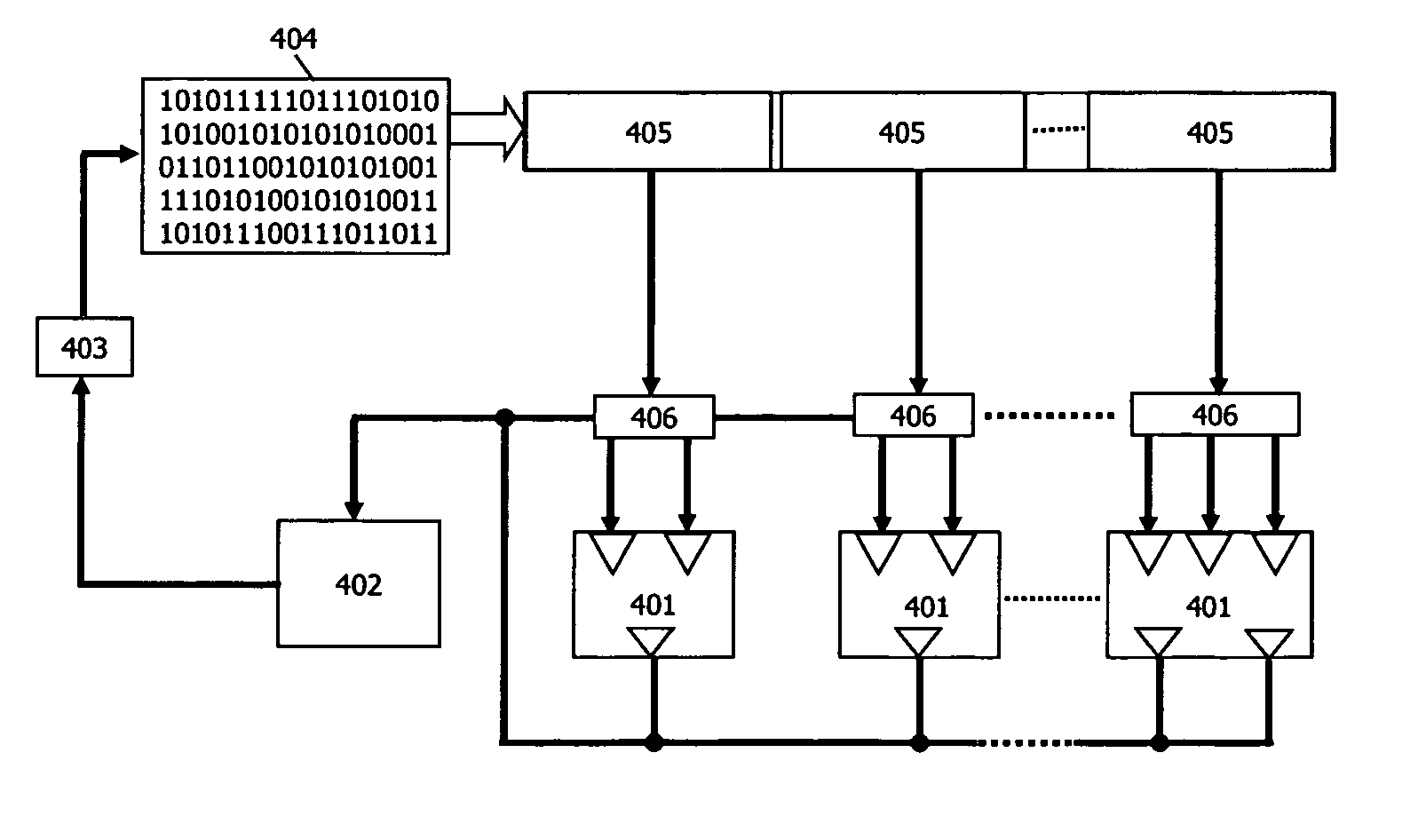
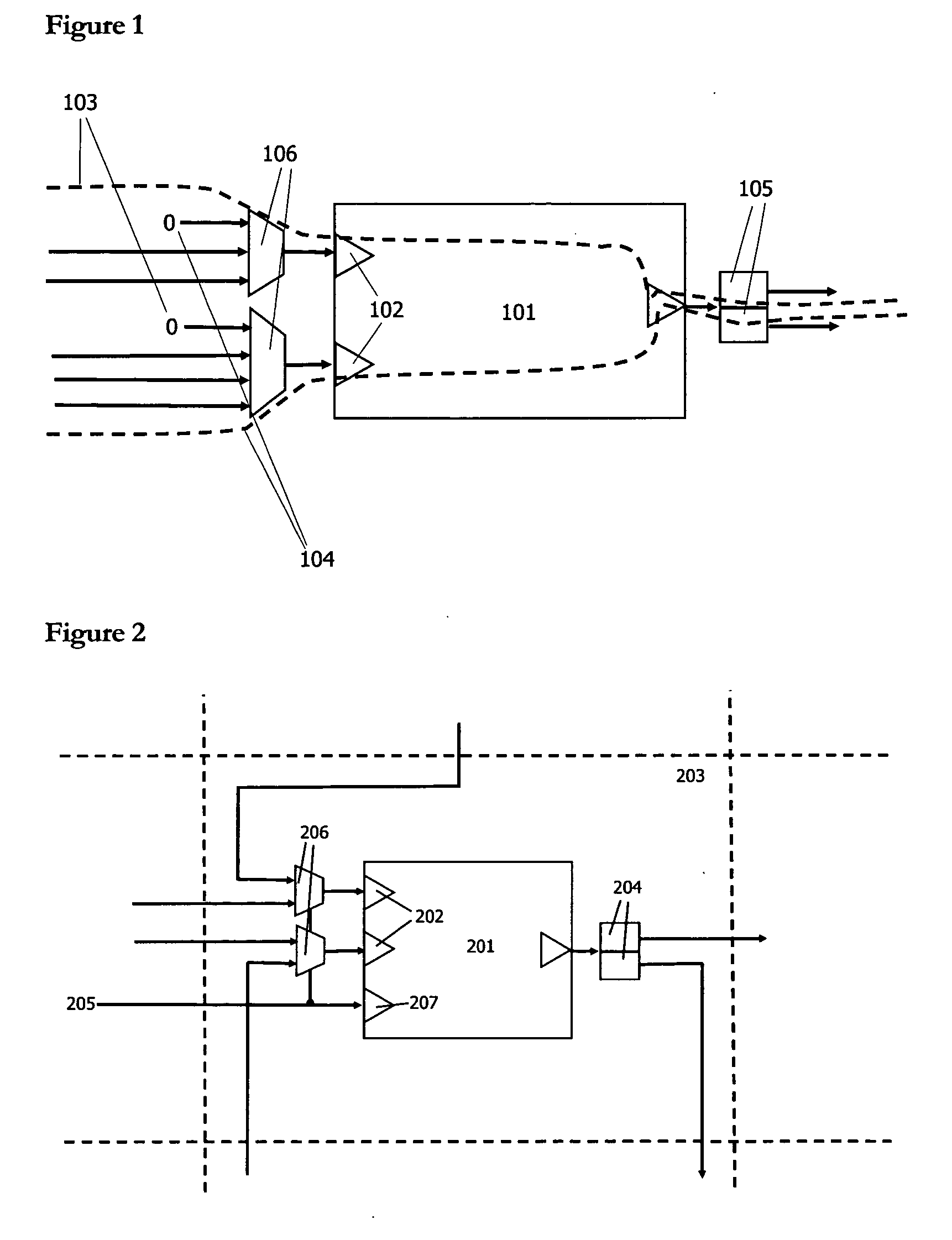
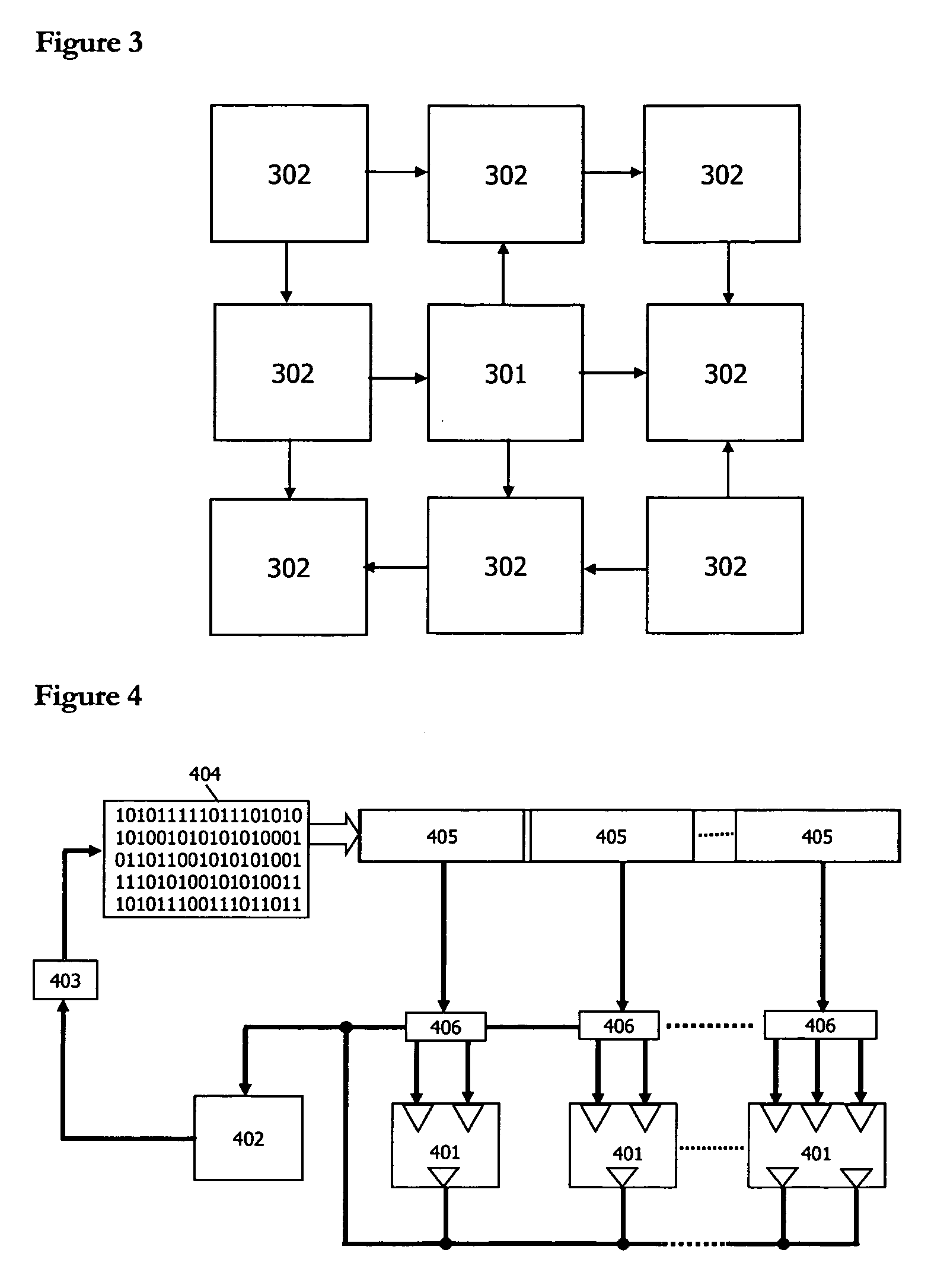
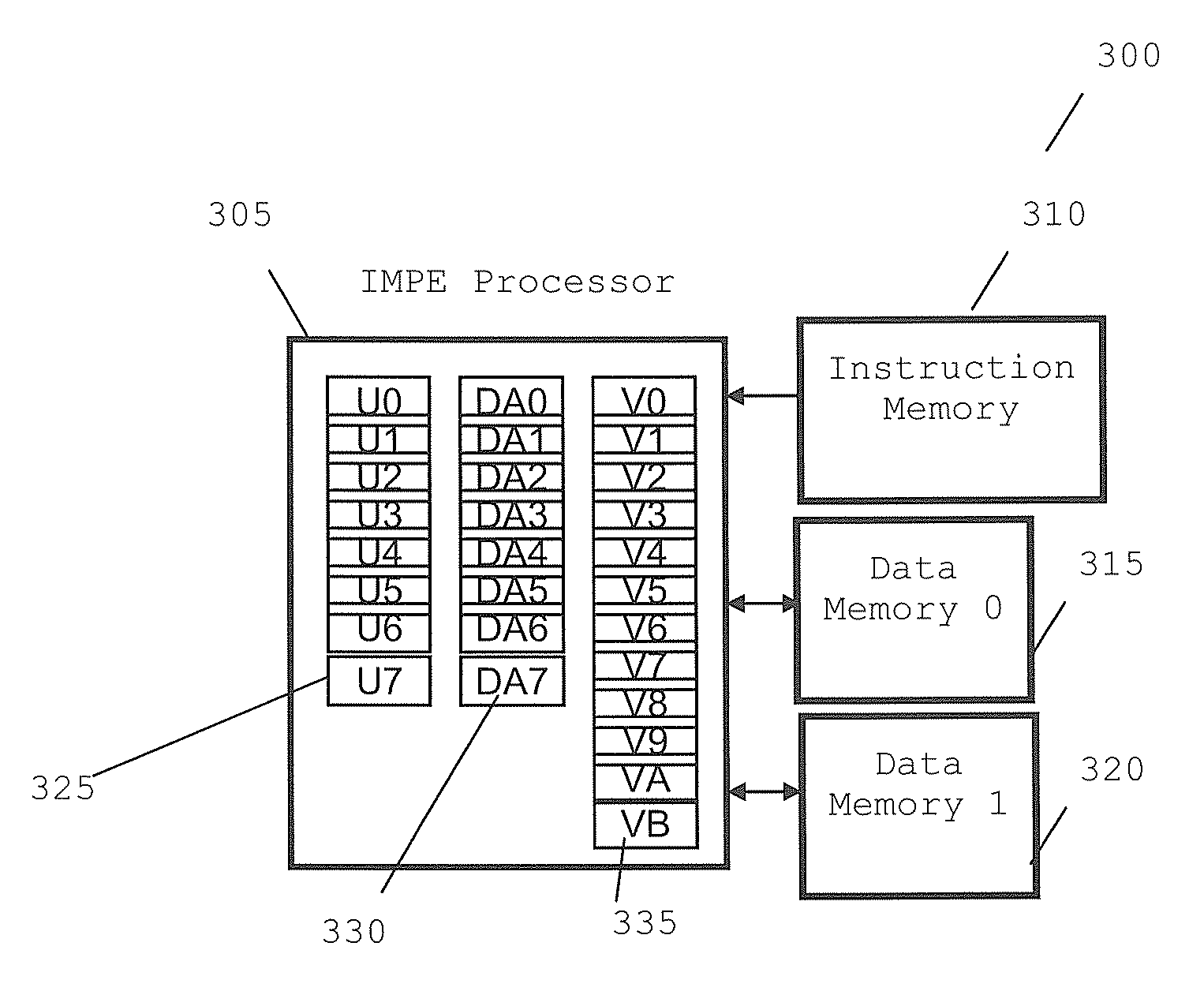
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Microprocessor architecture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
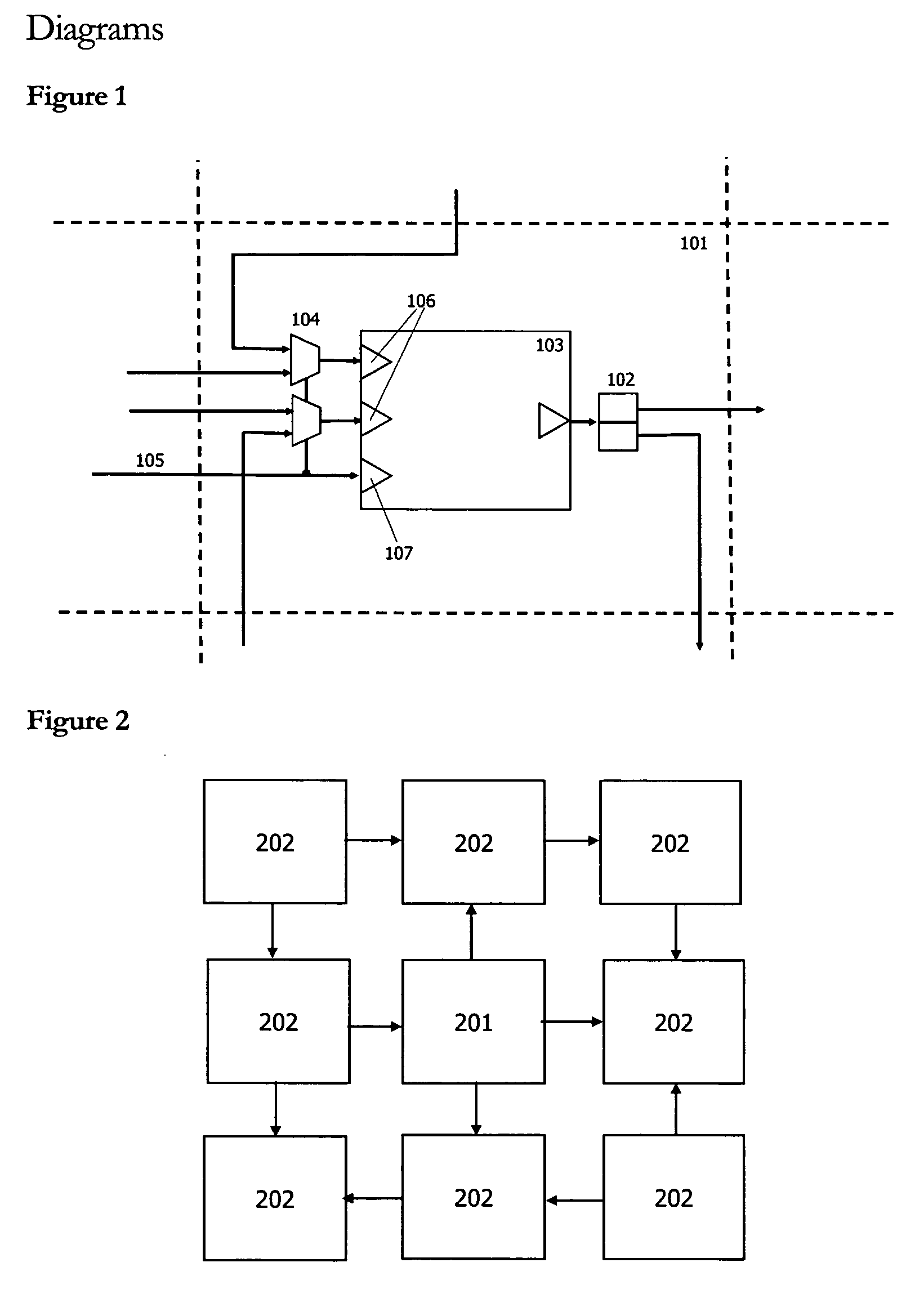
Adaptive computing ensemble microprocessor architecture
ActiveUS7389403B1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerExecution controlPower usage
An Adaptive Computing Ensemble (ACE) includes a plurality of flexible computation units as well as an execution controller to allocate the units to Computing Ensembles (CEs) and to assign threads to the CEs. The units may be any combination of ACE-enabled units, including instruction fetch and decode units, integer execution and pipeline control units, floating-point execution units, segmentation units, special-purpose units, reconfigurable units, and memory units. Some of the units may be replicated, e.g. there may be a plurality of integer execution and pipeline control units. Some of the units may be present in a plurality of implementations, varying by performance, power usage, or both. The execution controller dynamically alters the allocation of units to threads in response to changing performance and power consumption observed behaviors and requirements. The execution controller also dynamically alters performance and power characteristics of the ACE-enabled units, according to the observed behaviors and requirements.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
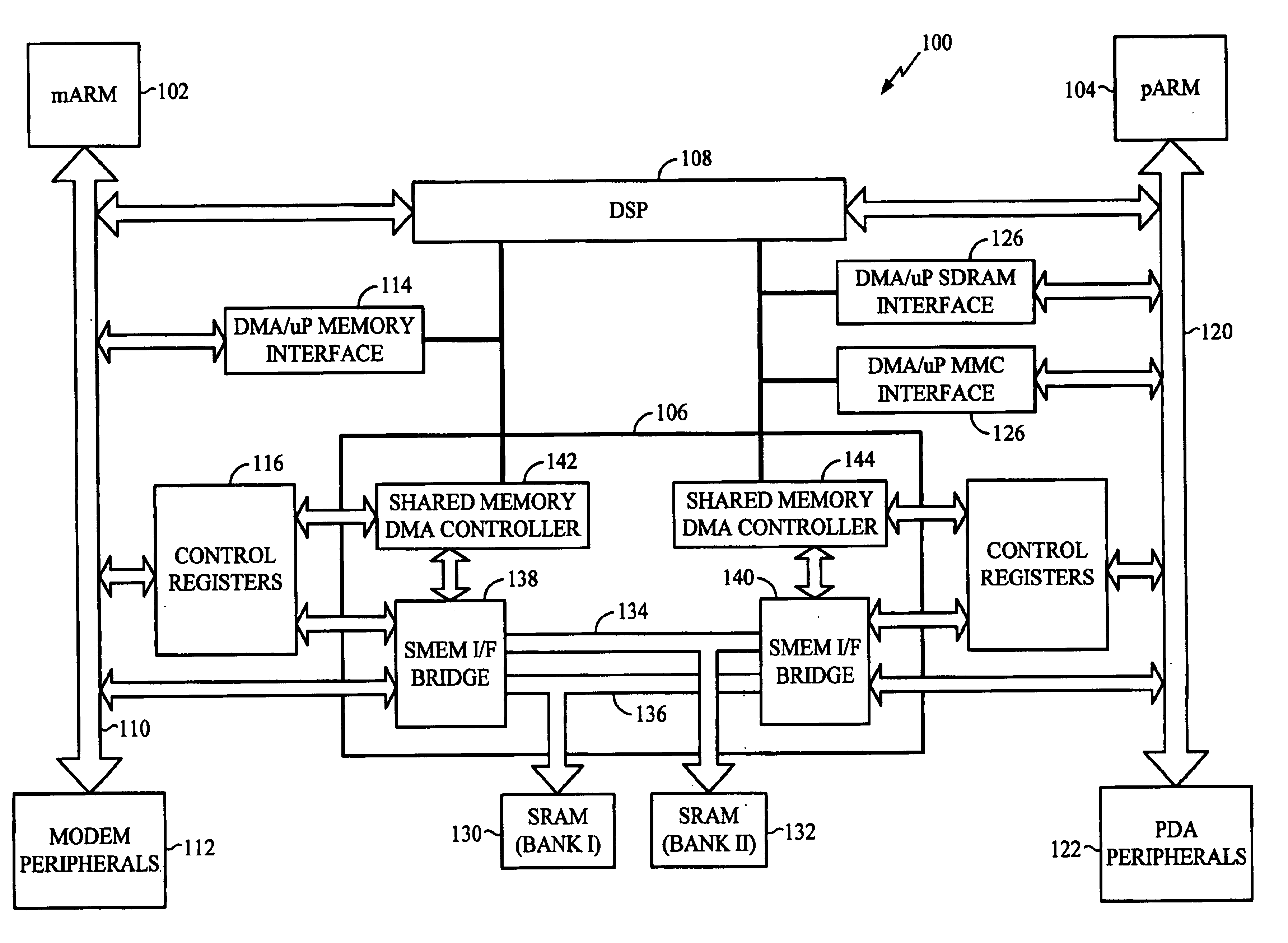
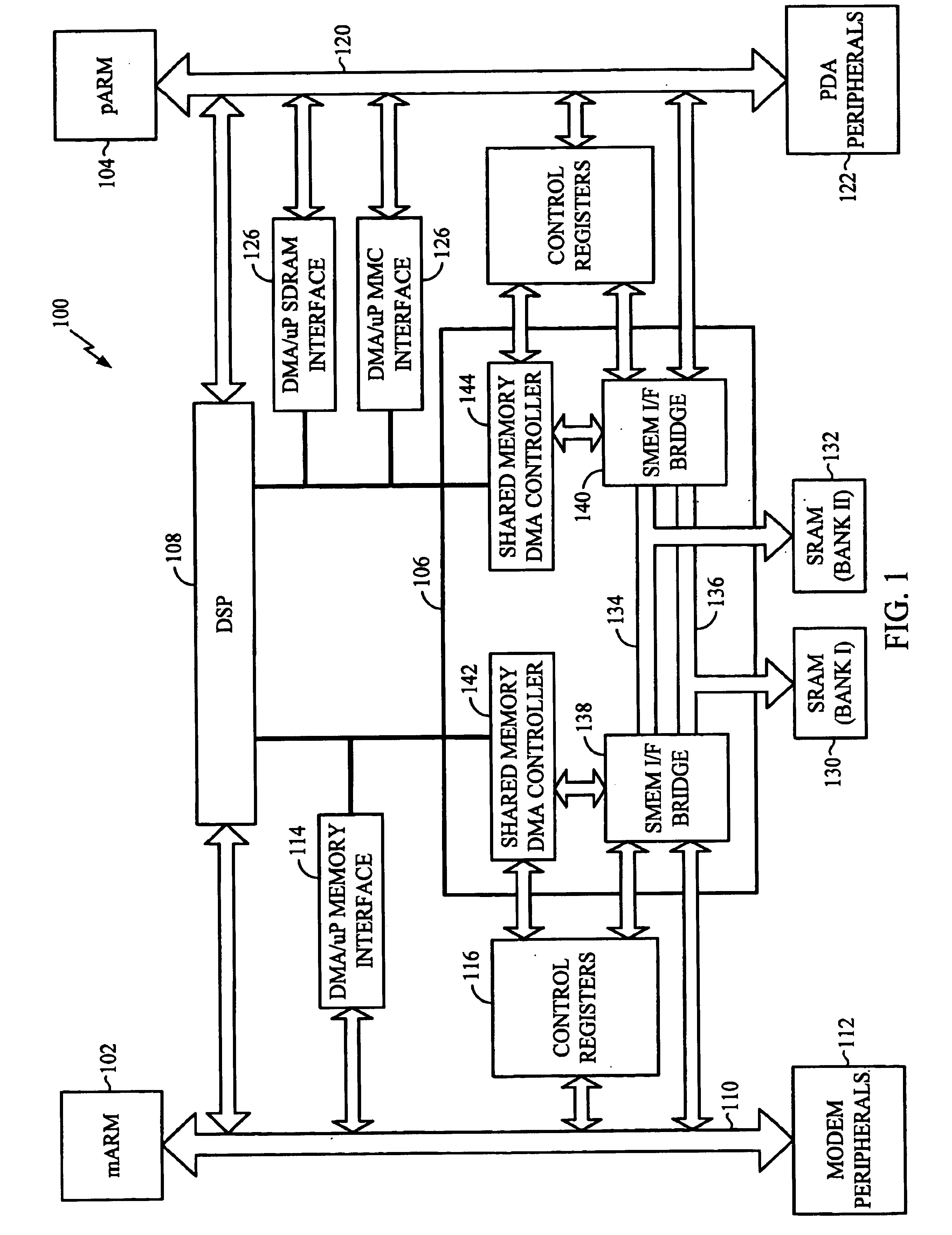
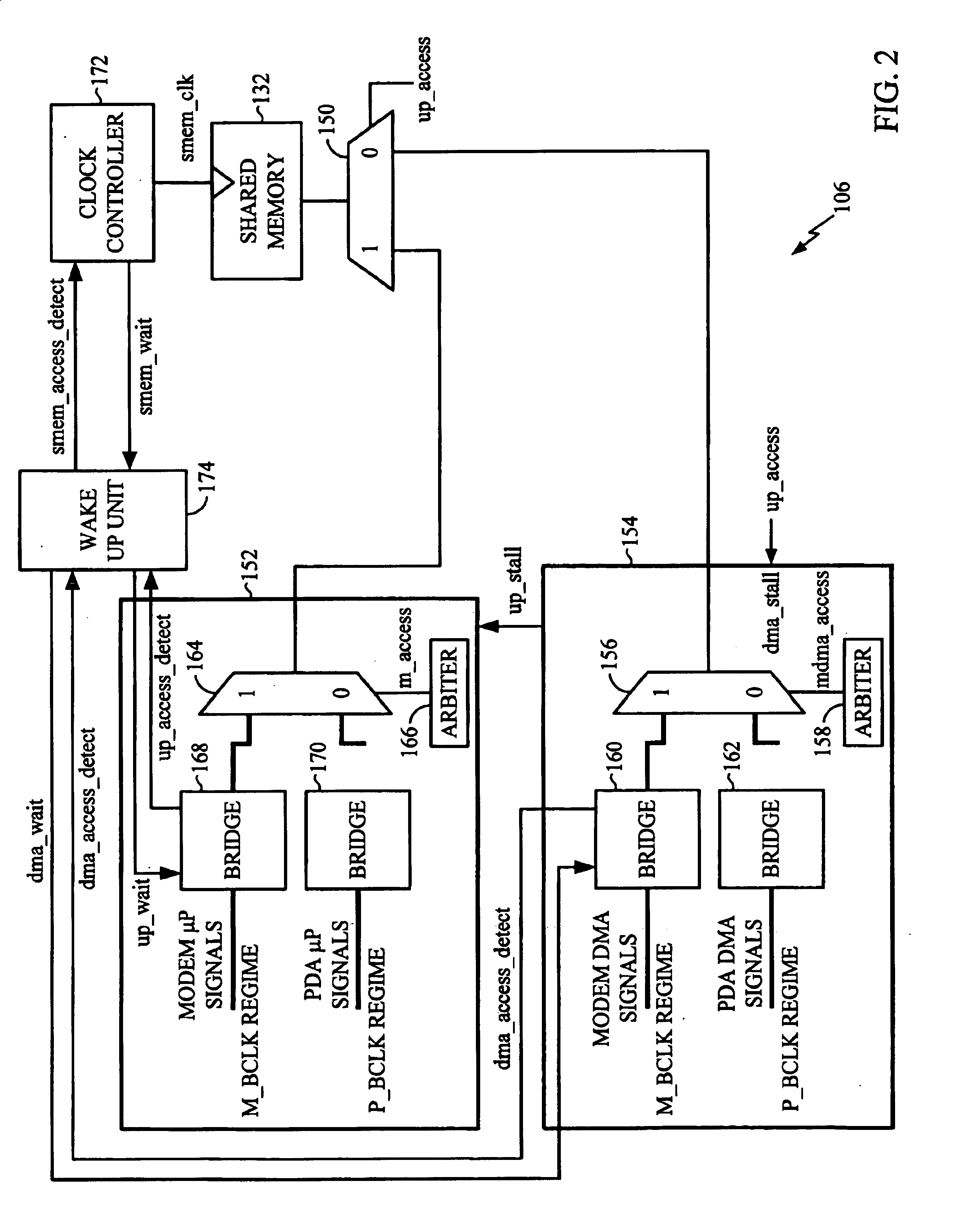
Mobile communication device having dual micro processor architecture with shared digital signal processor and shared memory
The dual microprocessor system includes one microprocessor configured to perform wireless telephony functions and another configured to perform personal digital assistant (PDA) functions and other non-telephony functions. A memory system and a digital signal processor (DSP) are shared by the microprocessors. By providing a shared memory system, data required by both data microprocessors is conveniently available to both of the microprocessors and their peripheral components thereby eliminating the need to provide separate memory subsystems and further eliminating the need to transfer data back and forth between the separate memory subsystems. By providing a shared DSP, separate DSP devices need not be provided, yet both microprocessors can take advantage of the processing power of the DSP. In a specific example described herein, the microprocessors selectively program the DSP to perform, for example, vocoder functions, voice recognition functions, handwriting recognition functions, and the like.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
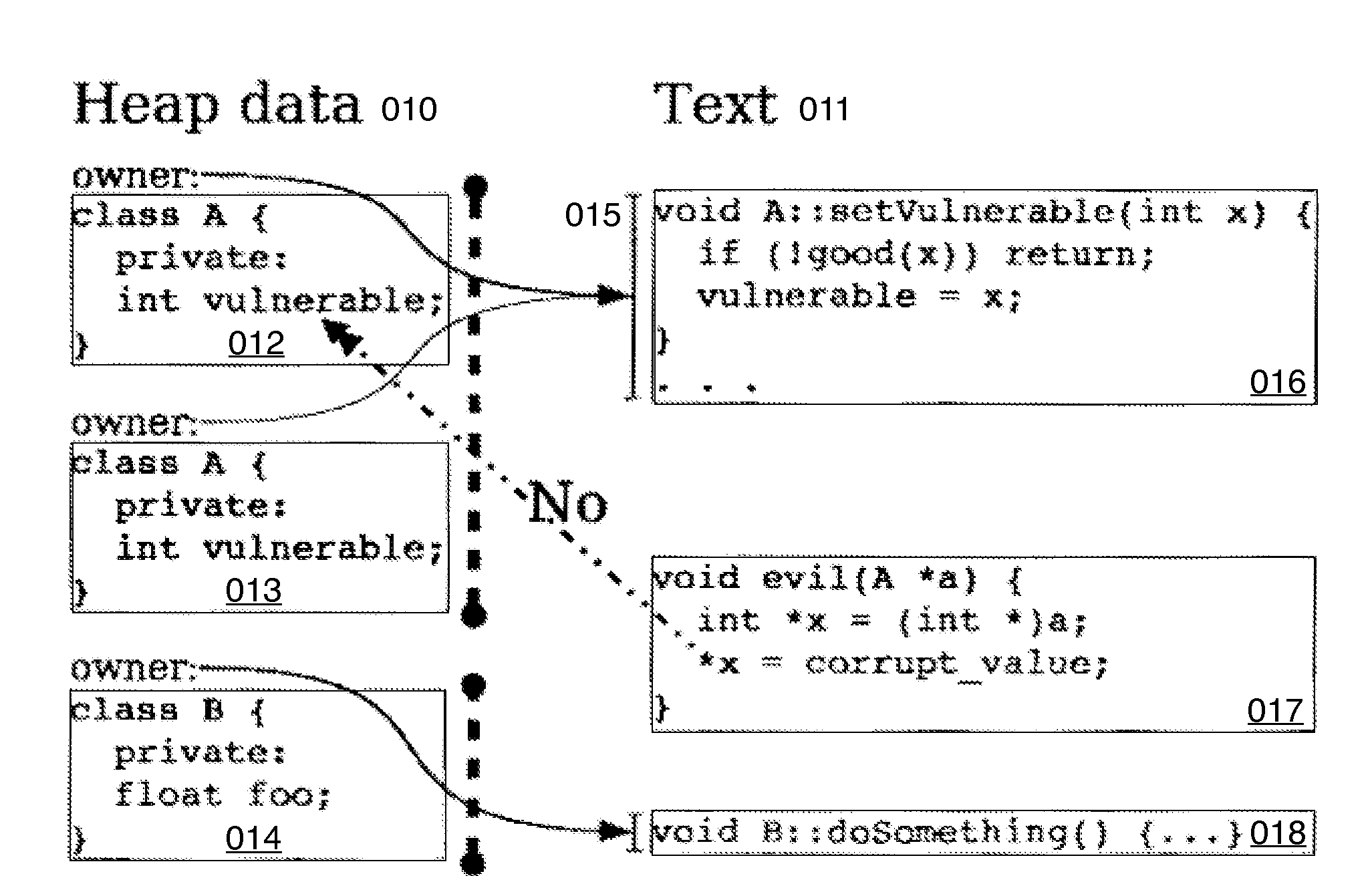
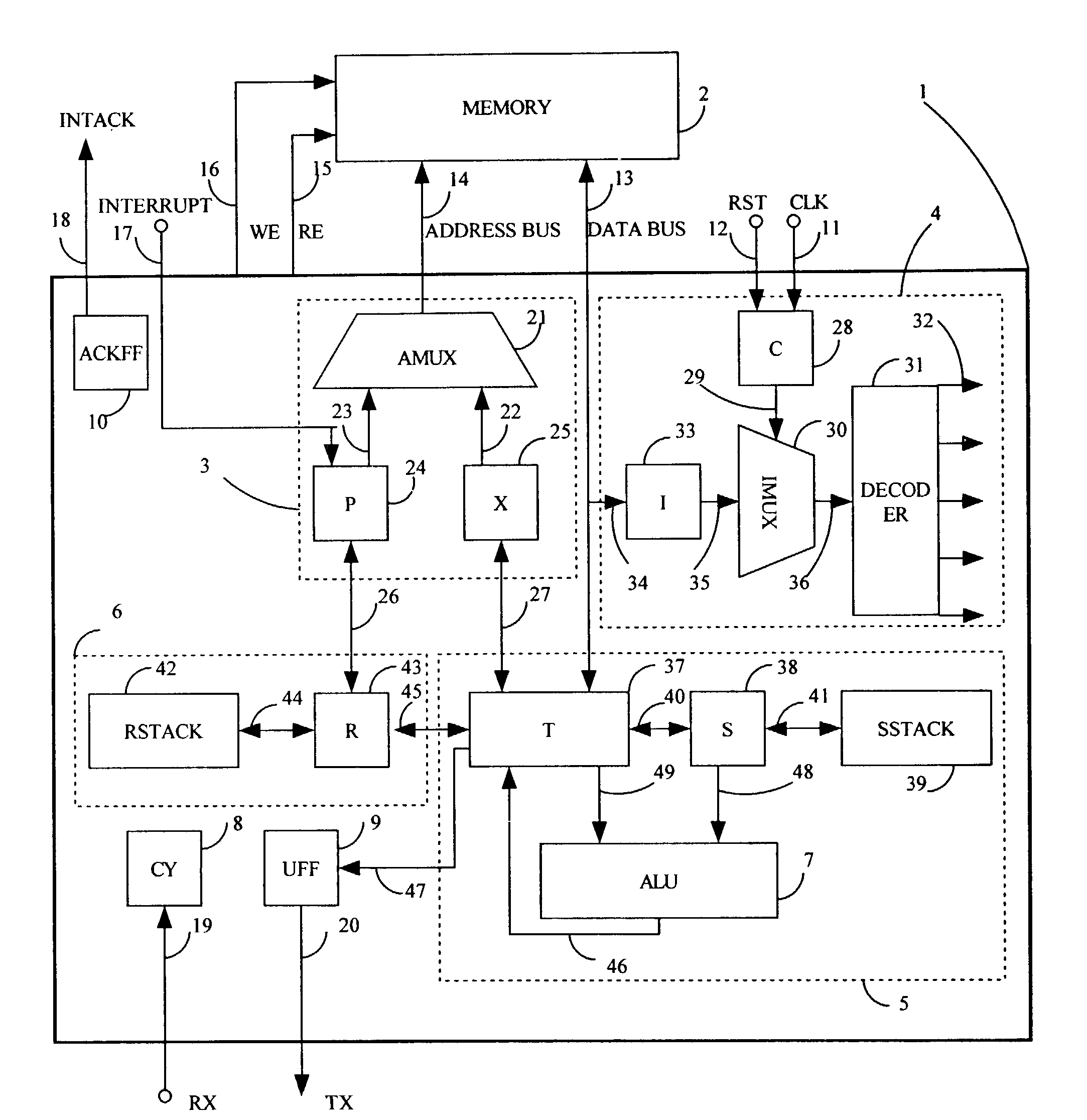
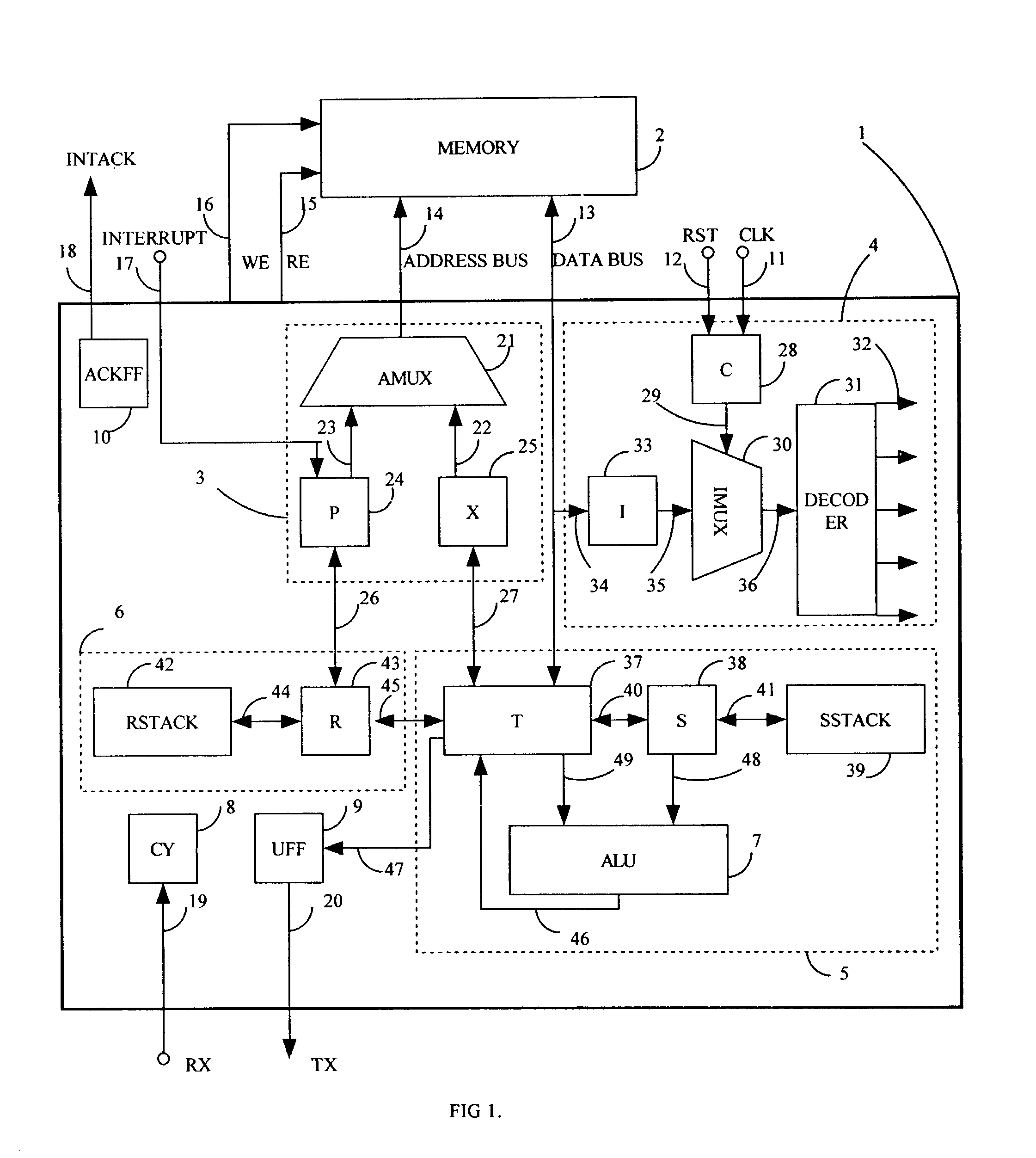
Hard Object: Hardware Protection for Software Objects
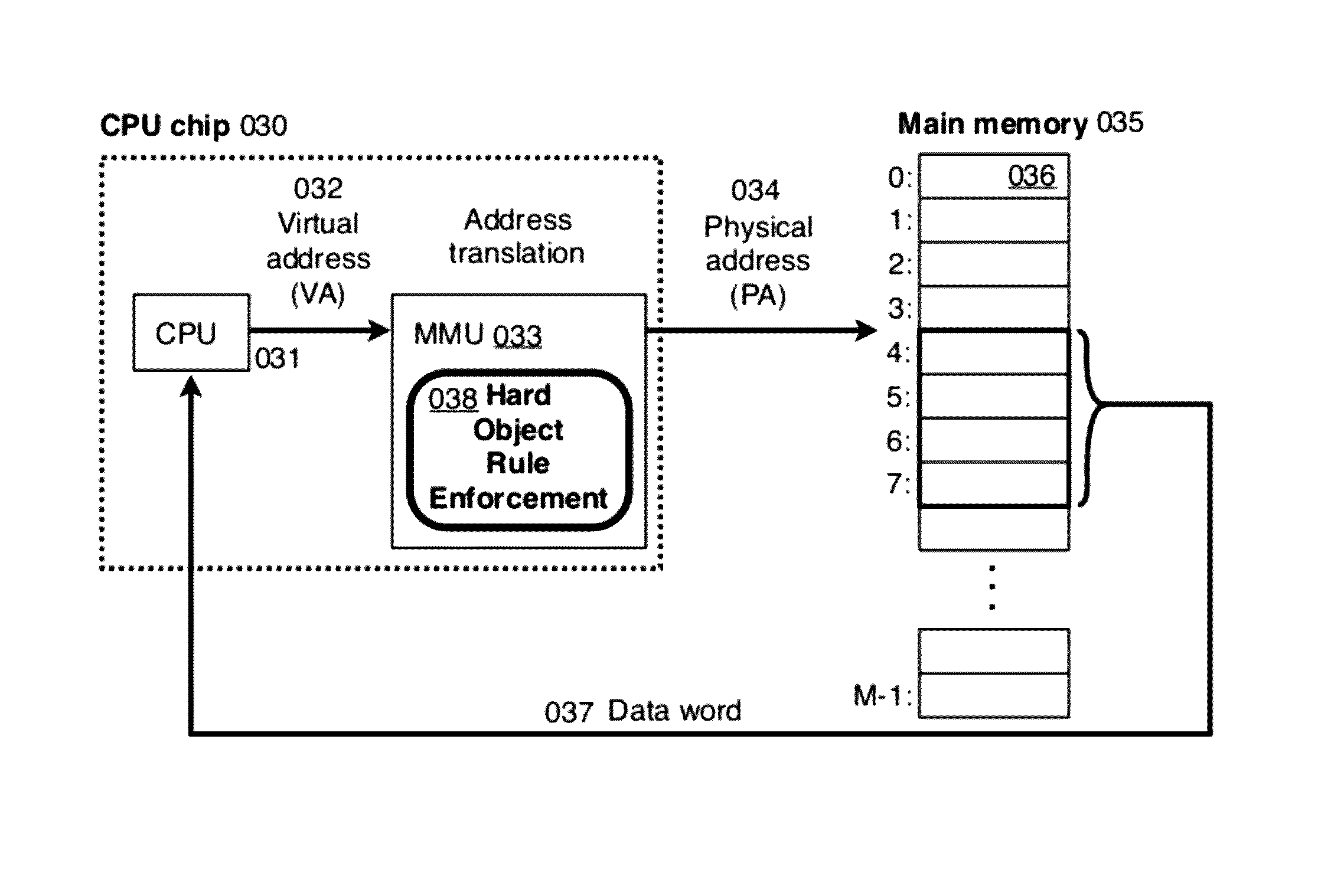
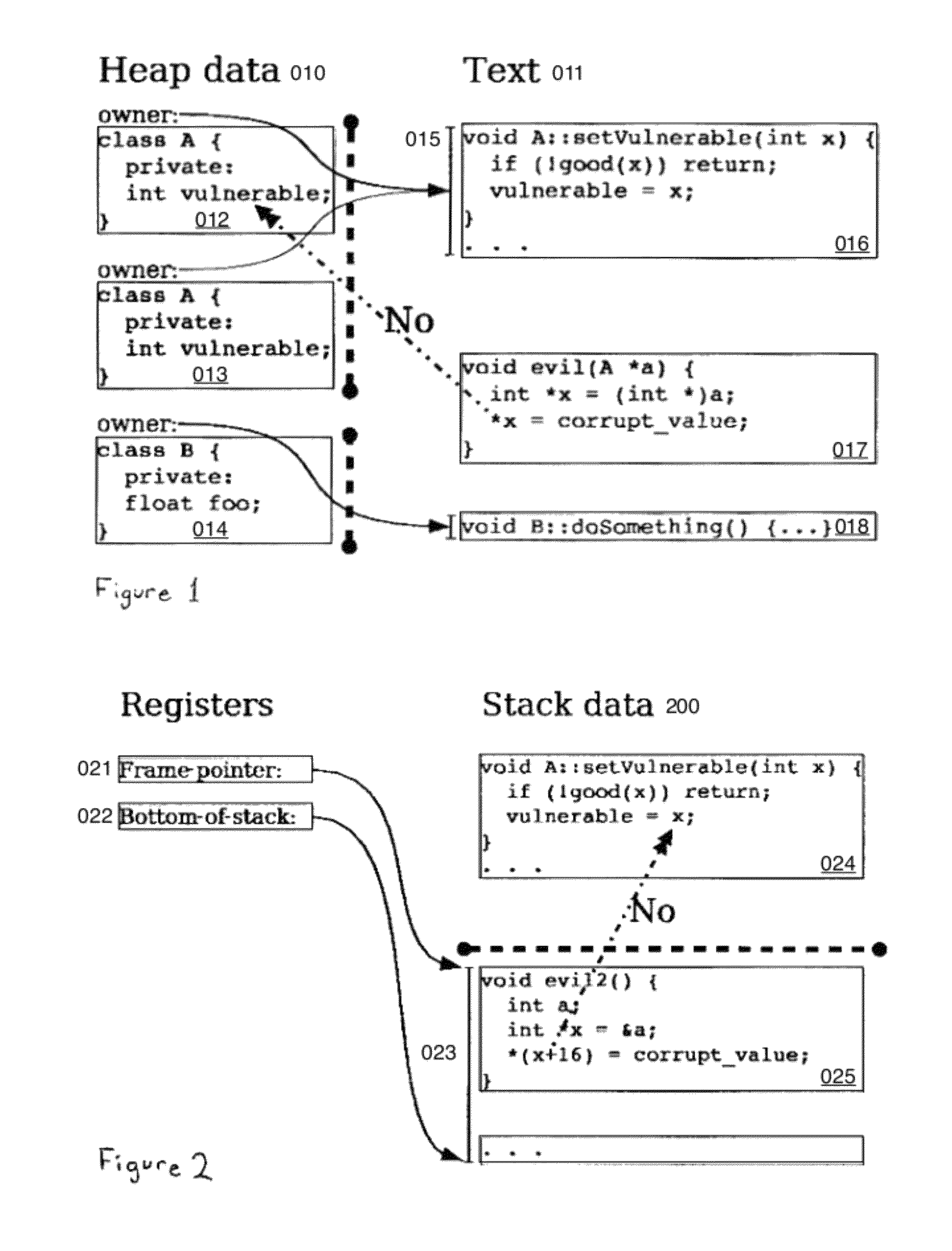
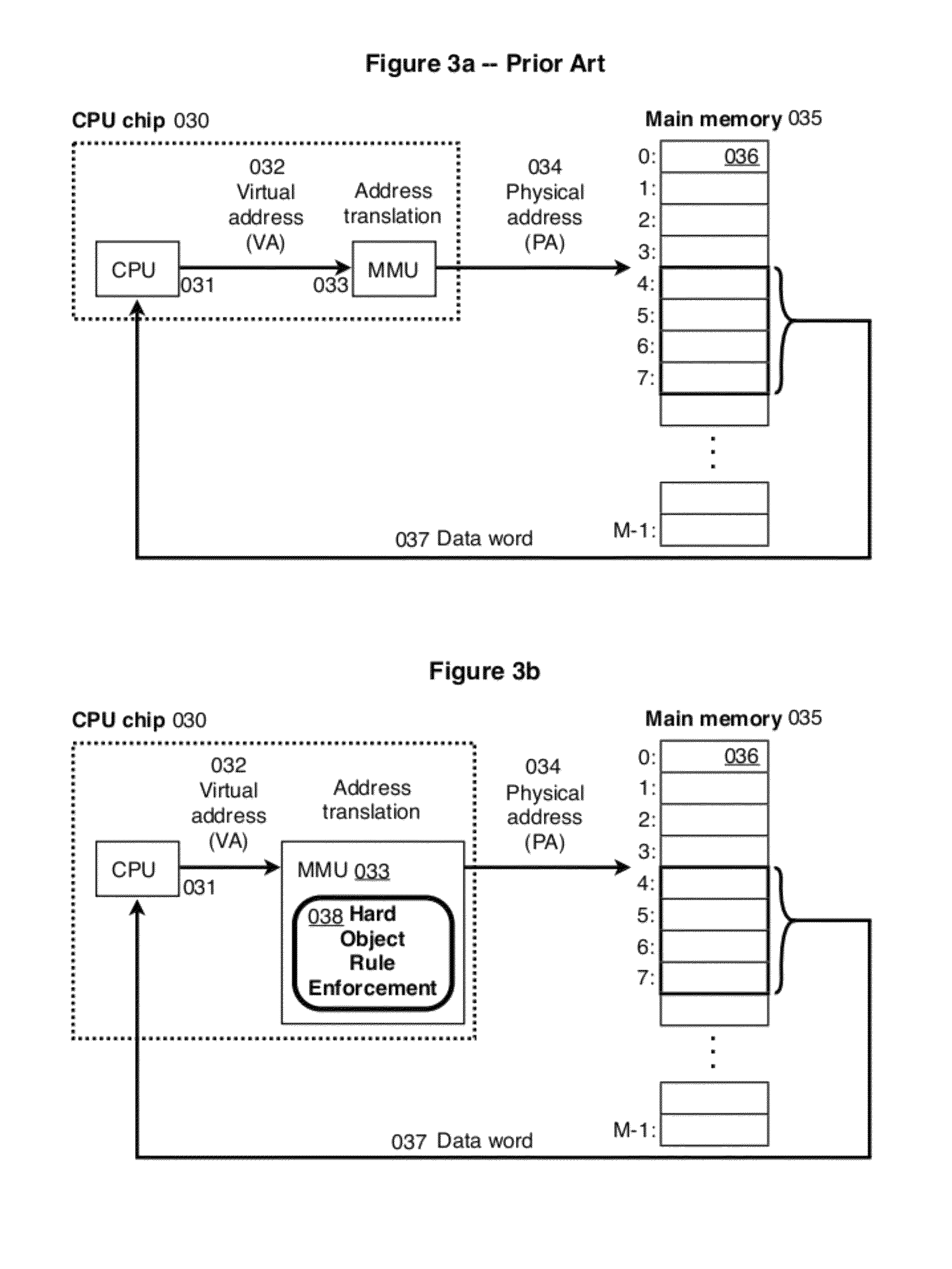
ActiveUS20080222397A1Efficiently implement enforceable separation of programDigital computer detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsProcessor registerPhysical address
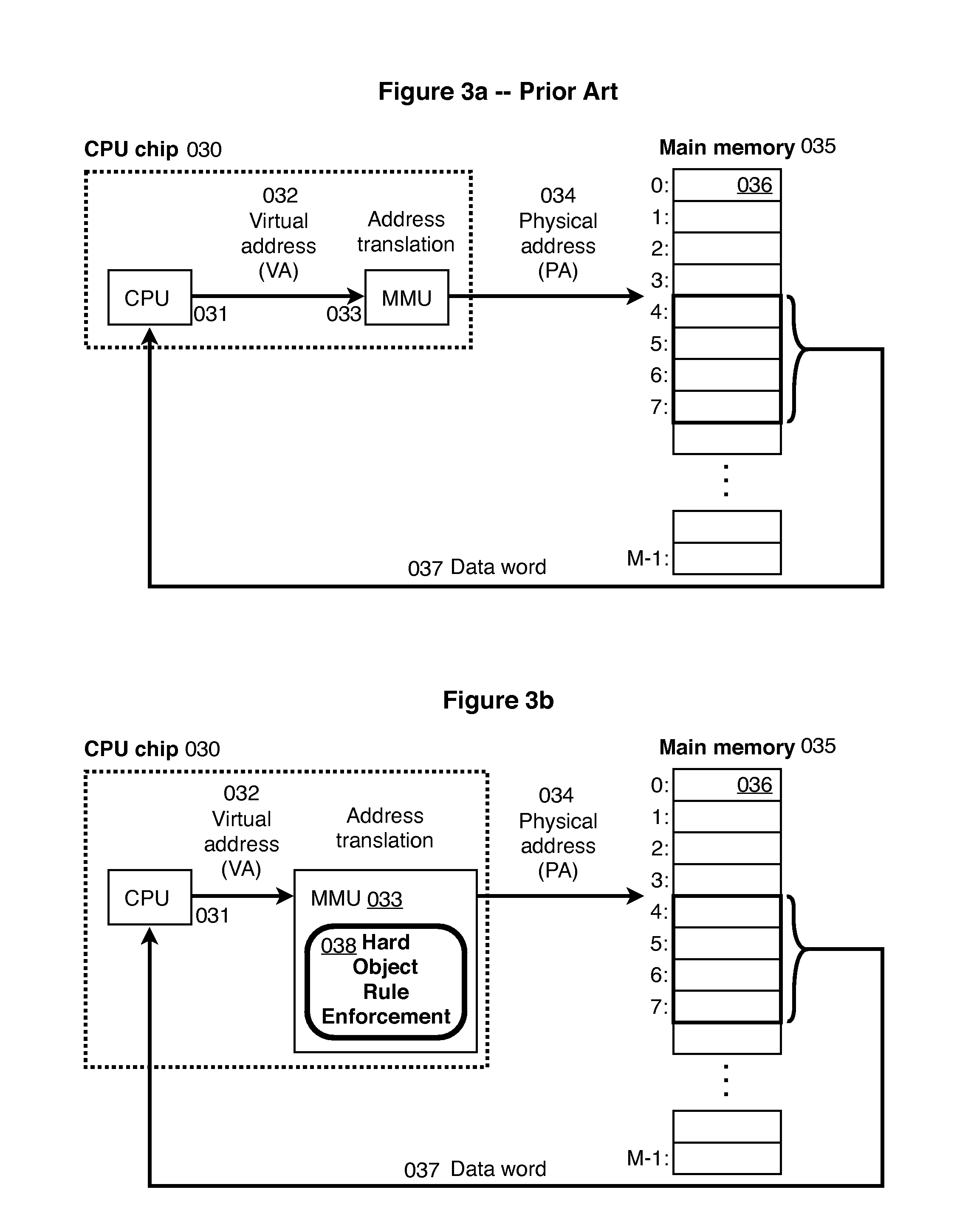
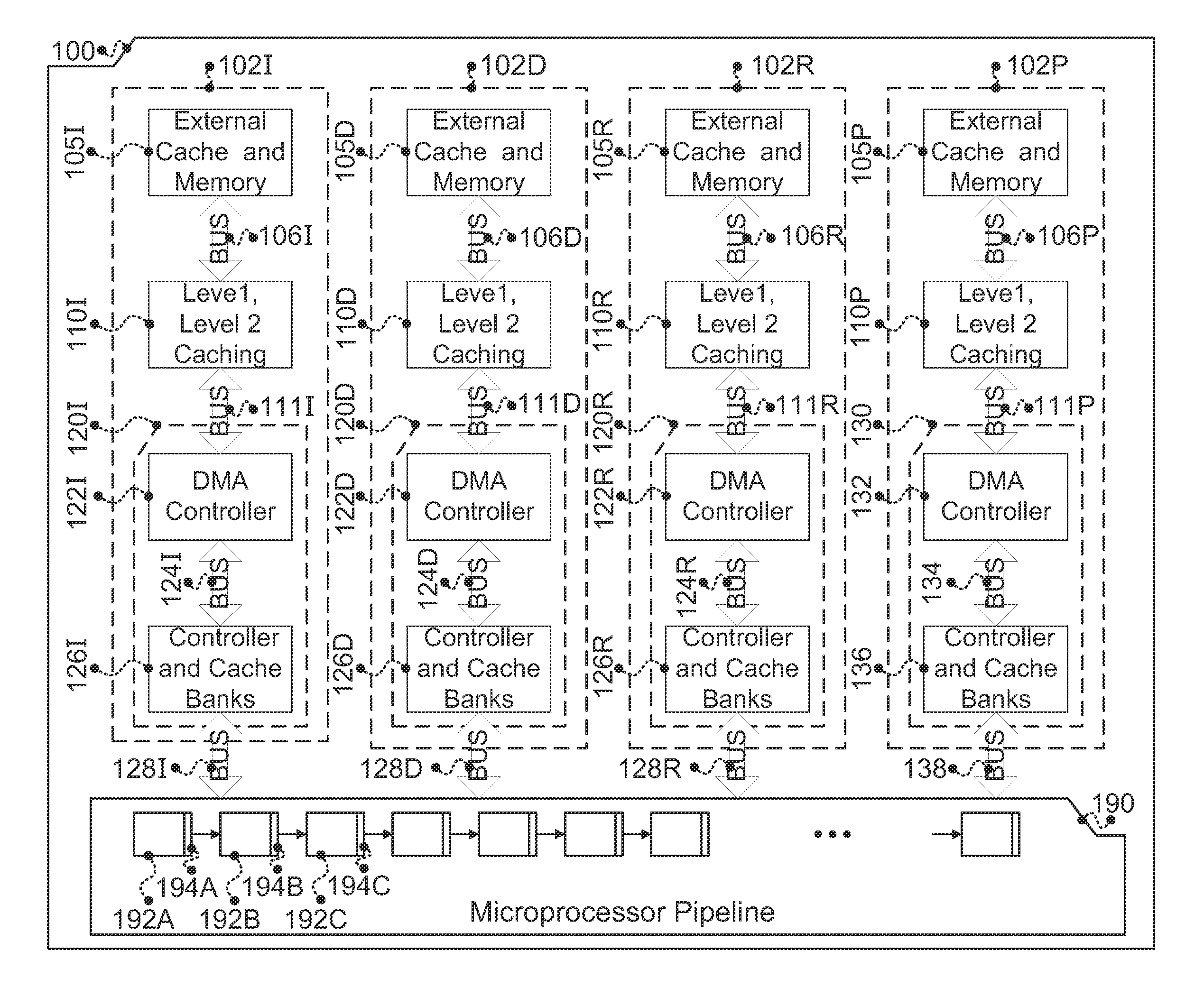
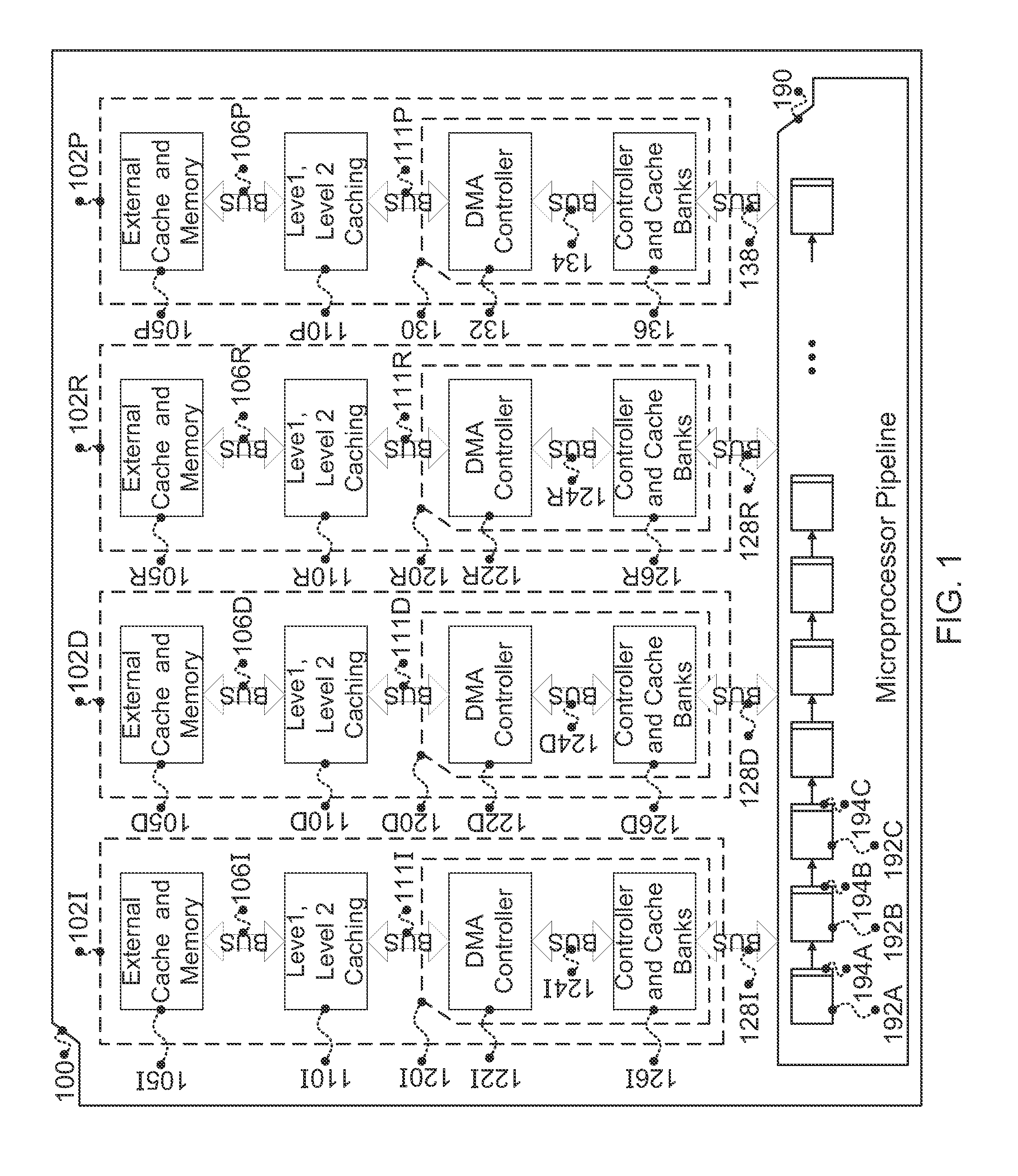
In accordance with one embodiment, additions to the standard computer microprocessor architecture hardware are disclosed comprising novel page table entry fields 015 062, special registers 021 022, instructions for modifying these fields 120 122 and registers 124 126, and hardware-implemented 038 runtime checks and operations involving these fields and registers. More specifically, in the above embodiment of a Hard Object system, there is additional meta-data 061 in each page table entry beyond what it commonly holds, and each time a data load or store is issued from the CPU, and the virtual address 032 translated to the physical address 034, the Hard Object system uses its additional PTE meta-data 061 to perform memory access checks additional to those done in current systems. Together with changes to software, these access checks can be arranged carefully to provide more fine-grain access control for data than do current systems.
Owner:WILKERSON DANIEL SHAWCROSS +1
Automatic configuration of a microprocessor
InactiveUS20050216701A1Fast resultsRapid productionSoftware engineeringRuntime instruction translationCoprocessorAuto-configuration
A method for automatically configuring a microprocessor architecture so that it is able to efficiently exploit instruction level parallelism in a particular application. Executable code for another microprocessor type is translated into the specialised instruction set of the configured microprocessor. The configured microprocessor may then be used as a coprocessor in a system containing another microprocessor running the original executable code.
Owner:CRITICAL BLUE
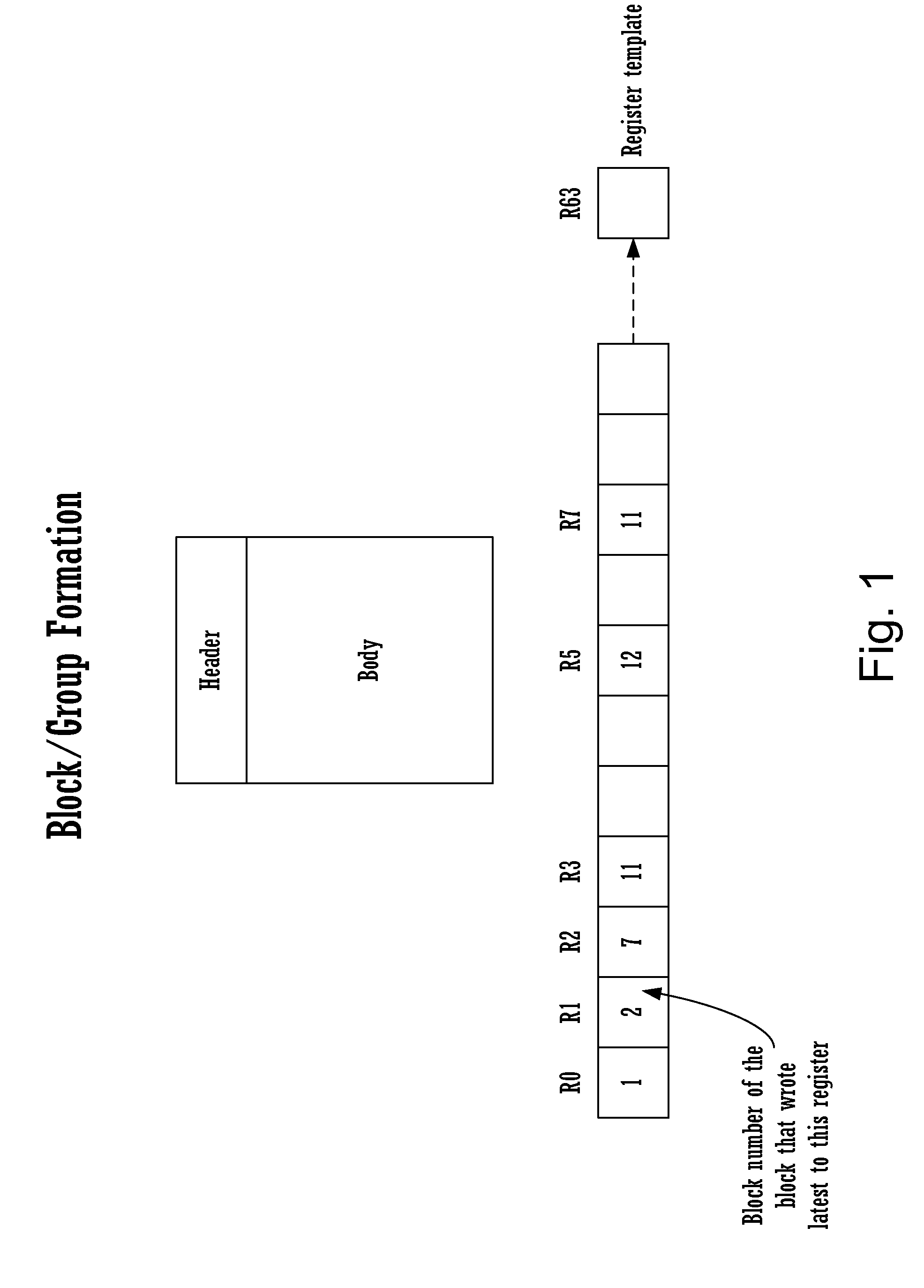
Method for executing blocks of instructions using a microprocessor architecture having a register view, source view, instruction view, and a plurality of register templates
InactiveUS20150046686A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
A method for executing blocks of instructions using a microprocessor architecture having a register view, source view, instruction view, and a plurality of register templates. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end; grouping the instructions to form instruction blocks; using a plurality of register templates to track instruction destinations and instruction sources by populating the register template with block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks, wherein the block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks indicate interdependencies among the blocks of instructions; using a register view data structure, wherein the register view data structure stores destinations corresponding to the instruction blocks; using a source view data structure, wherein the source view data structure stores sources corresponding to the instruction blocks; and using an instruction view data structure, wherein the instruction view data structure stores instructions corresponding to the instruction blocks.
Owner:INTEL CORP
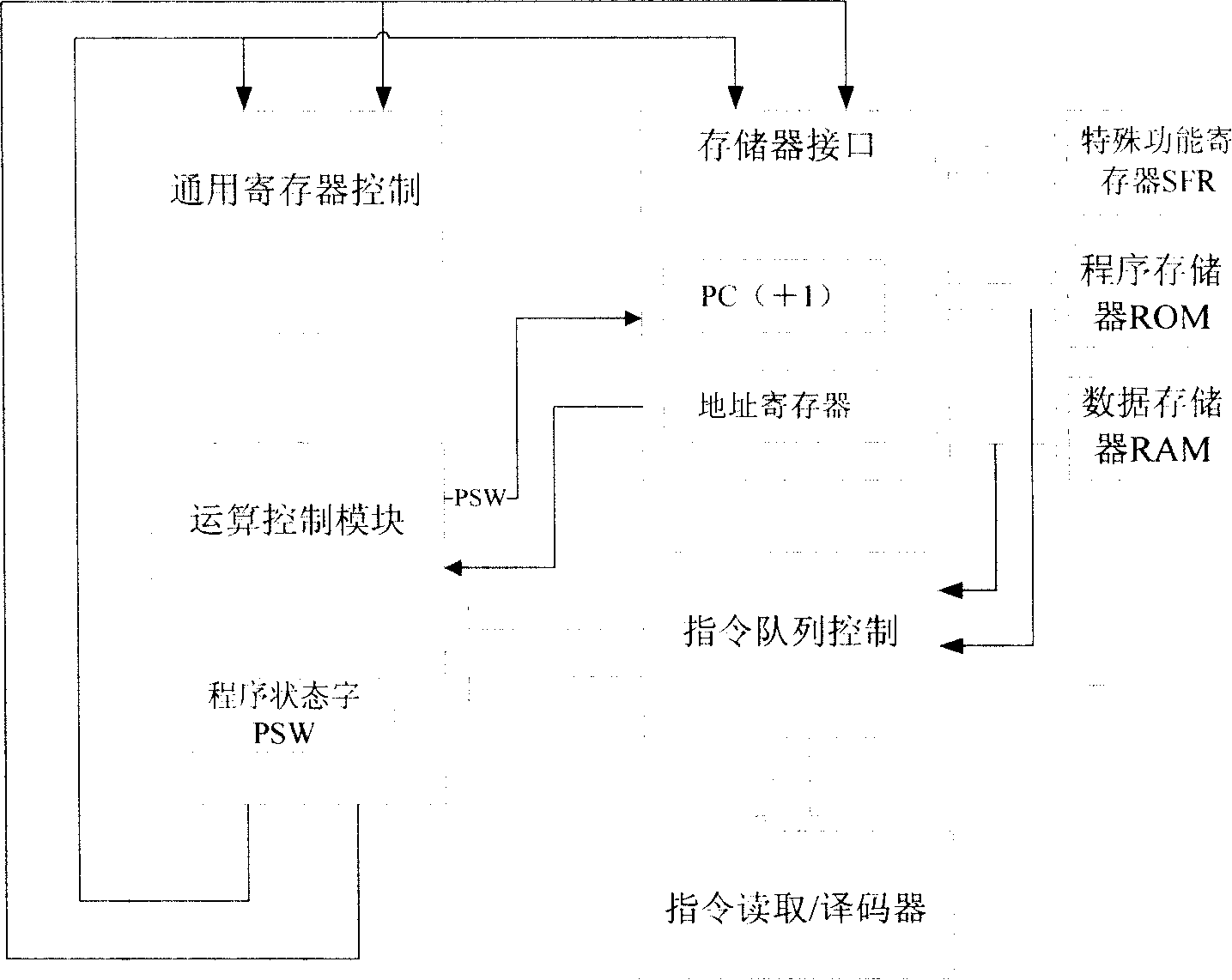
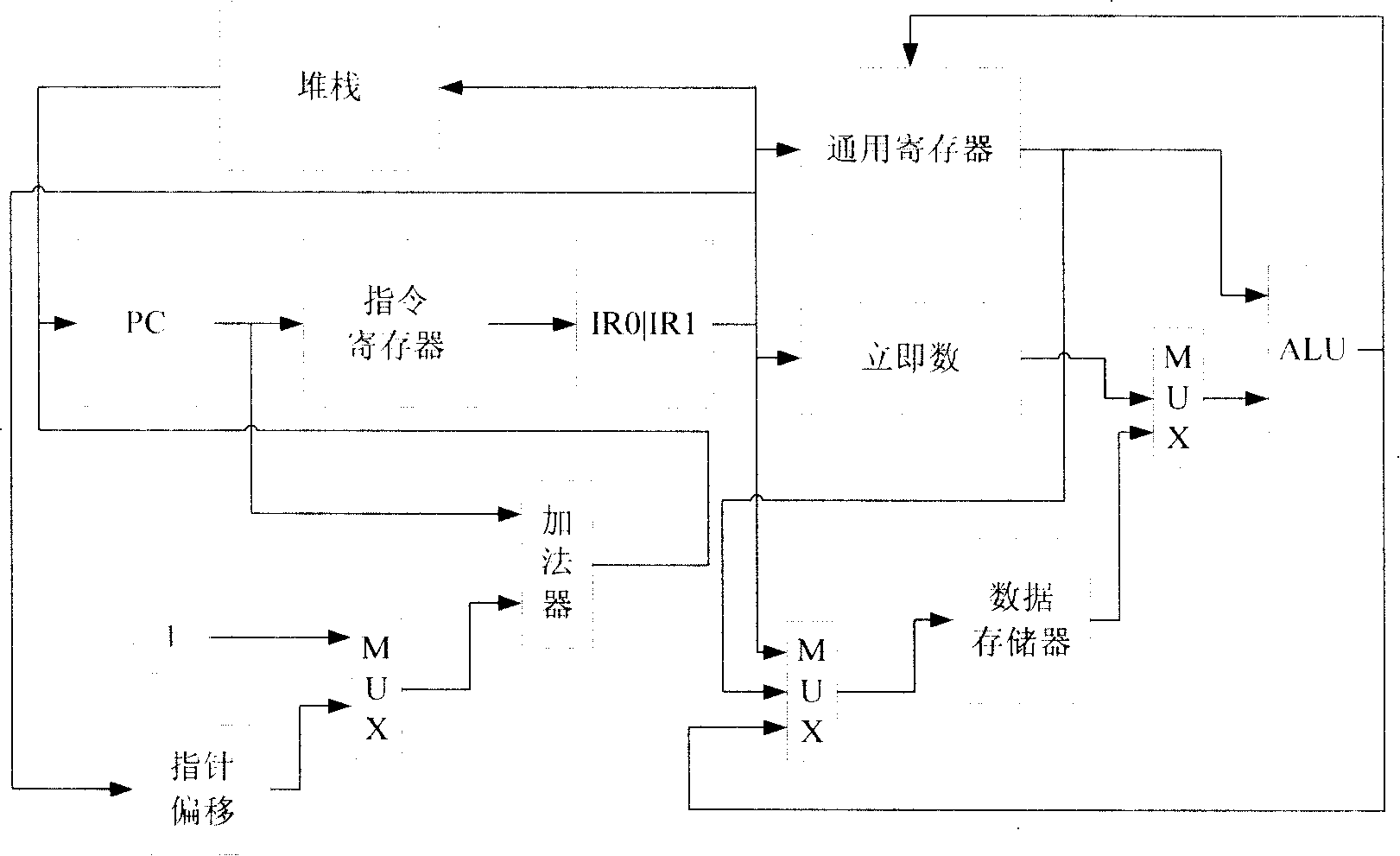
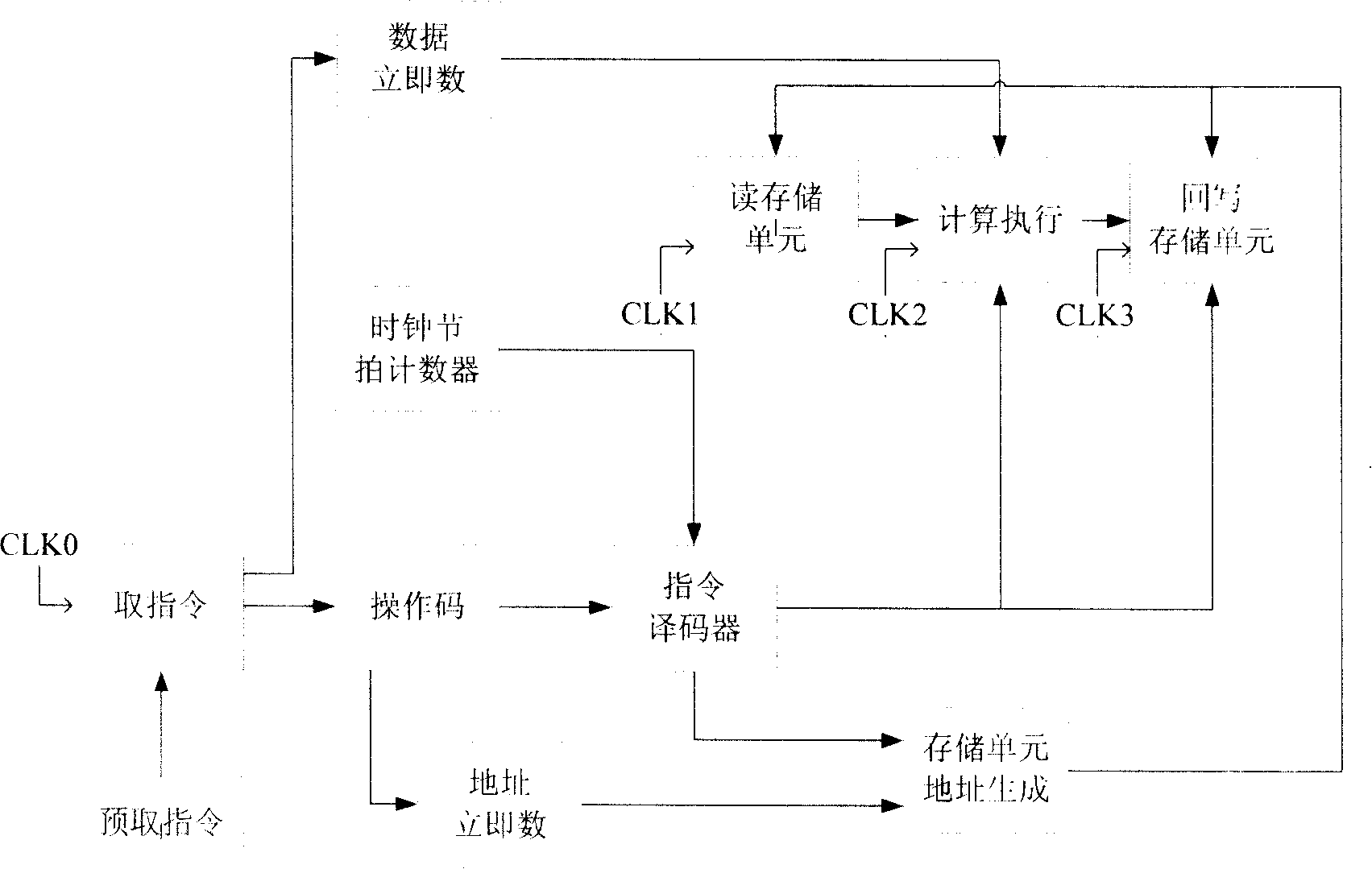
Microprocessor structure based on sophisticated vocabulary computerarchitecture
ActiveCN101178644AProcessing speedRich commandConcurrent instruction executionArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecial function registerMemory interface
The invention relates to a micro-processor architecture based on a complicated instruction set computer structure, comprising a program memory, a random data memory, a particular function register, a data buffer register, a common register, a data bus and an address bus, a memory interface, an operation and control module, an instruction reading and decoder and an instruction array control module. The data bus is divided into a separated eight-byte program data bus and an eight-byte inner random data bus. The invention is applicable to various embedded SOC systems for real time control, and can be widely applied in electric products such as home appliance, civilian use communication and car electronic.
Owner:SHANGHAI EASTSOFT MICROELECTRONICS
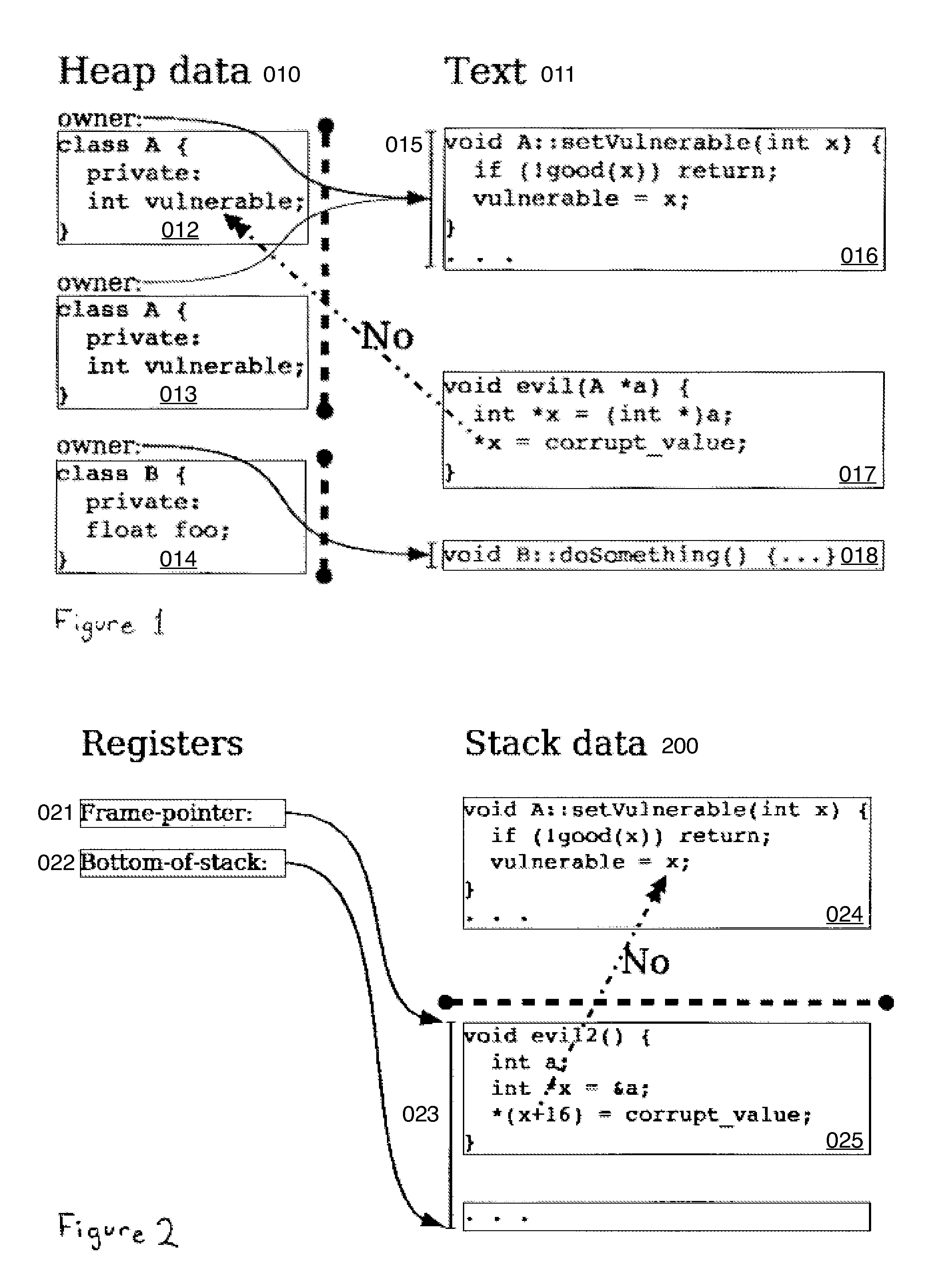
Hard object: hardware protection for software objects
ActiveUS8364910B2Efficiently implement enforceable separation of programDigital computer detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsProcessor registerPhysical address
In accordance with one embodiment, additions to the standard computer microprocessor architecture hardware are disclosed comprising novel page table entry fields 015 062, special registers 021 022, instructions for modifying these fields 120 122 and registers 124 126, and hardware-implemented 038 runtime checks and operations involving these fields and registers. More specifically, in the above embodiment of a Hard Object system, there is additional meta-data 061 in each page table entry beyond what it commonly holds, and each time a data load or store is issued from the CPU, and the virtual address 032 translated to the physical address 034, the Hard Object system uses its additional PTE meta-data 061 to perform memory access checks additional to those done in current systems. Together with changes to software, these access checks can be arranged carefully to provide more fine-grain access control for data than do current systems.
Owner:WILKERSON DANIEL SHAWCROSS +1
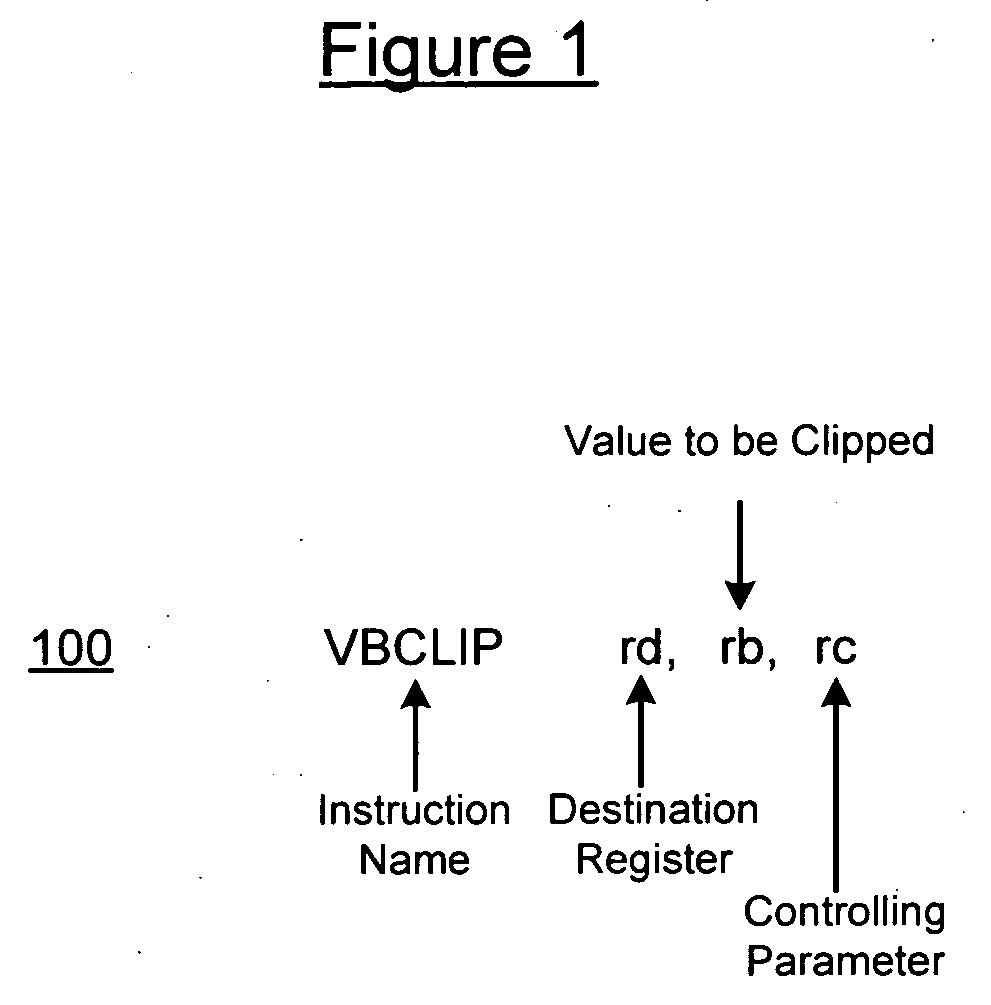
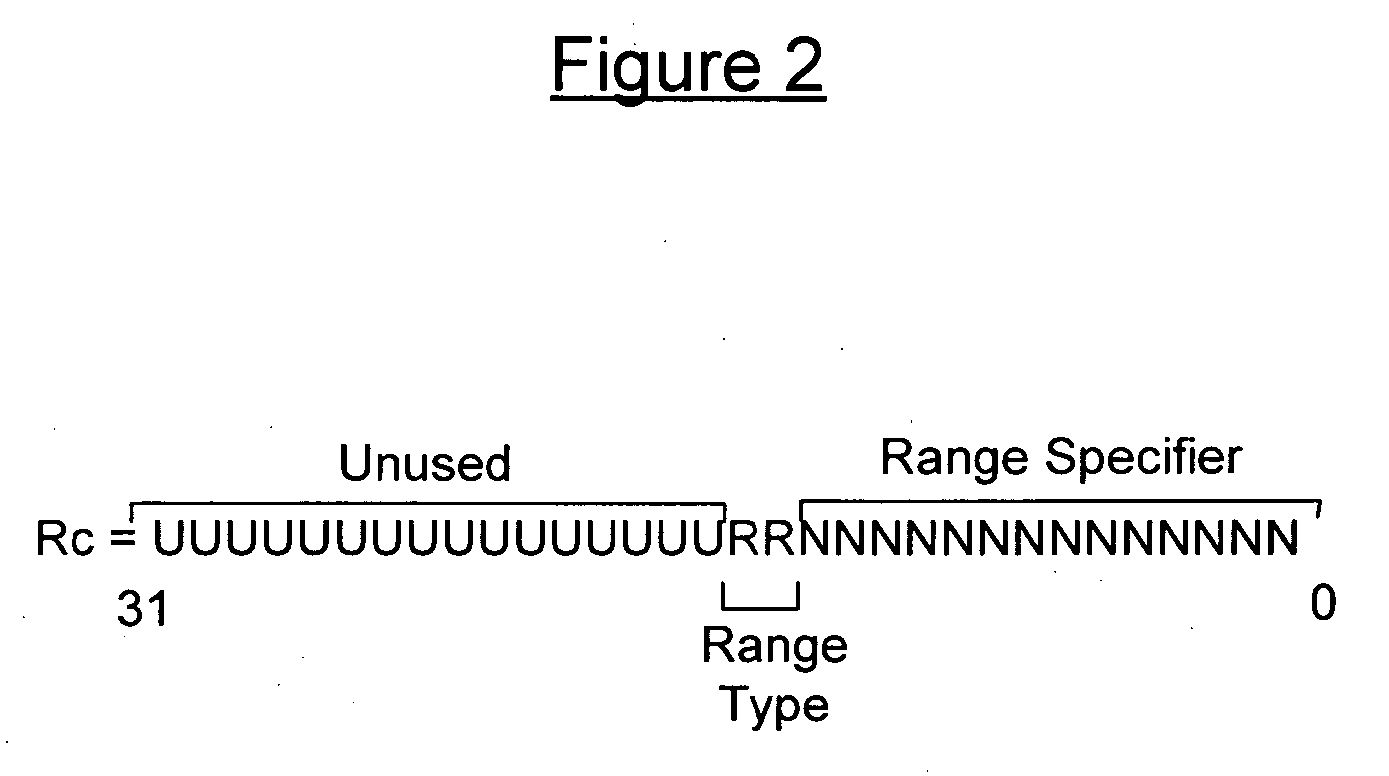
Parameterizable clip instruction and method of performing a clip operation using the same
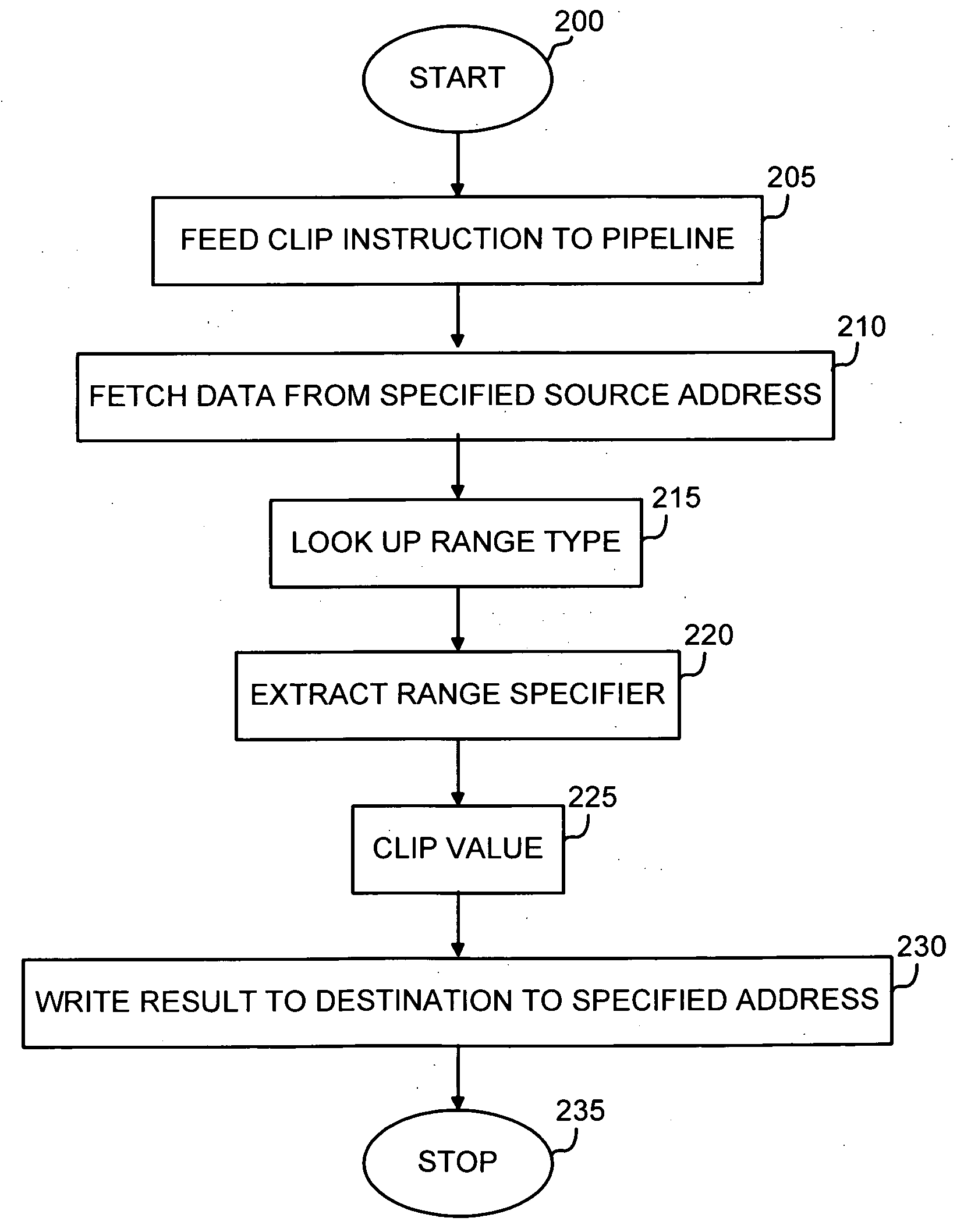
InactiveUS20070074007A1Geometric image transformationDigital computer detailsComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
A parameterizable clip instruction for SIMD microprocessor architecture and method of performing a clip operating the same. A single instruction is provided with three input operands: a destination address, a source address and a controlling parameter. The controlling parameter includes a range type and a range specifier. The range type is a multi-bit integer in the operand that is used to index a table of range types. The range specifier plugs into the range type to define a range. The data input at the source address is clipped according to the controlling parameters. The instruction is particularly suited to video encoding / decoding applications where interpolations or other calculations, lies outside the maximum value and that final result will have to be clipped to saturation value, for example, the maximum pixel value. Signed and unsigned clipping ranges may be used that are not only powers of two.
Owner:ARC INT UK
Application program execution enhancing instruction set generation for coprocessor and code conversion with marking for function call translation
InactiveUS7533246B2Long sequenceFast resultsSoftware engineeringRuntime instruction translationCoprocessorAuto-configuration
A method for automatically configuring a microprocessor architecture so that it is able to efficiently exploit instruction level parallelism in a particular application. Executable code for another microprocessor type is translated into the specialized instruction set of the configured microprocessor. The configured microprocessor may then be used as a coprocessor in a system containing another microprocessor running the original executable code.
Owner:CRITICAL BLUE
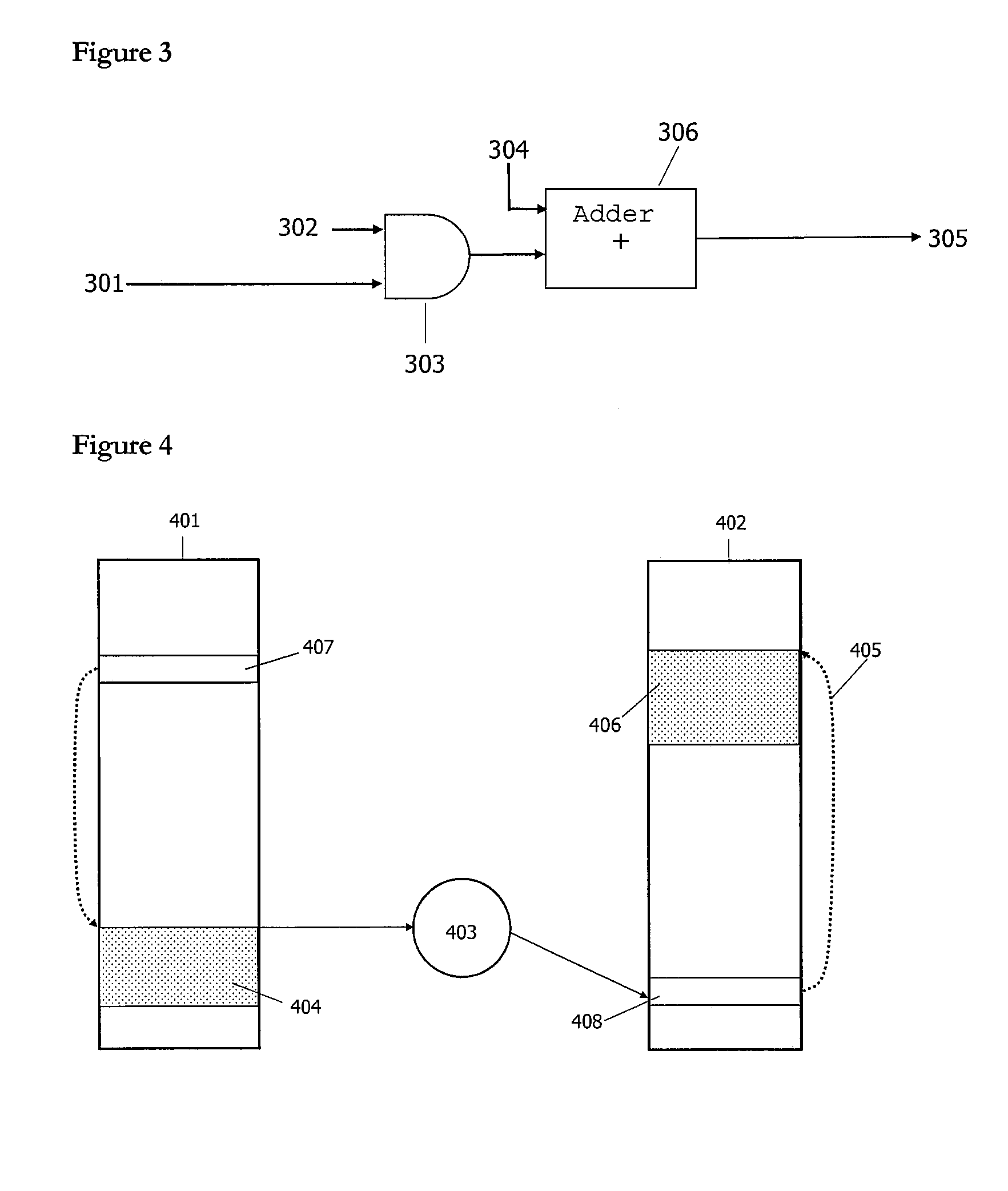
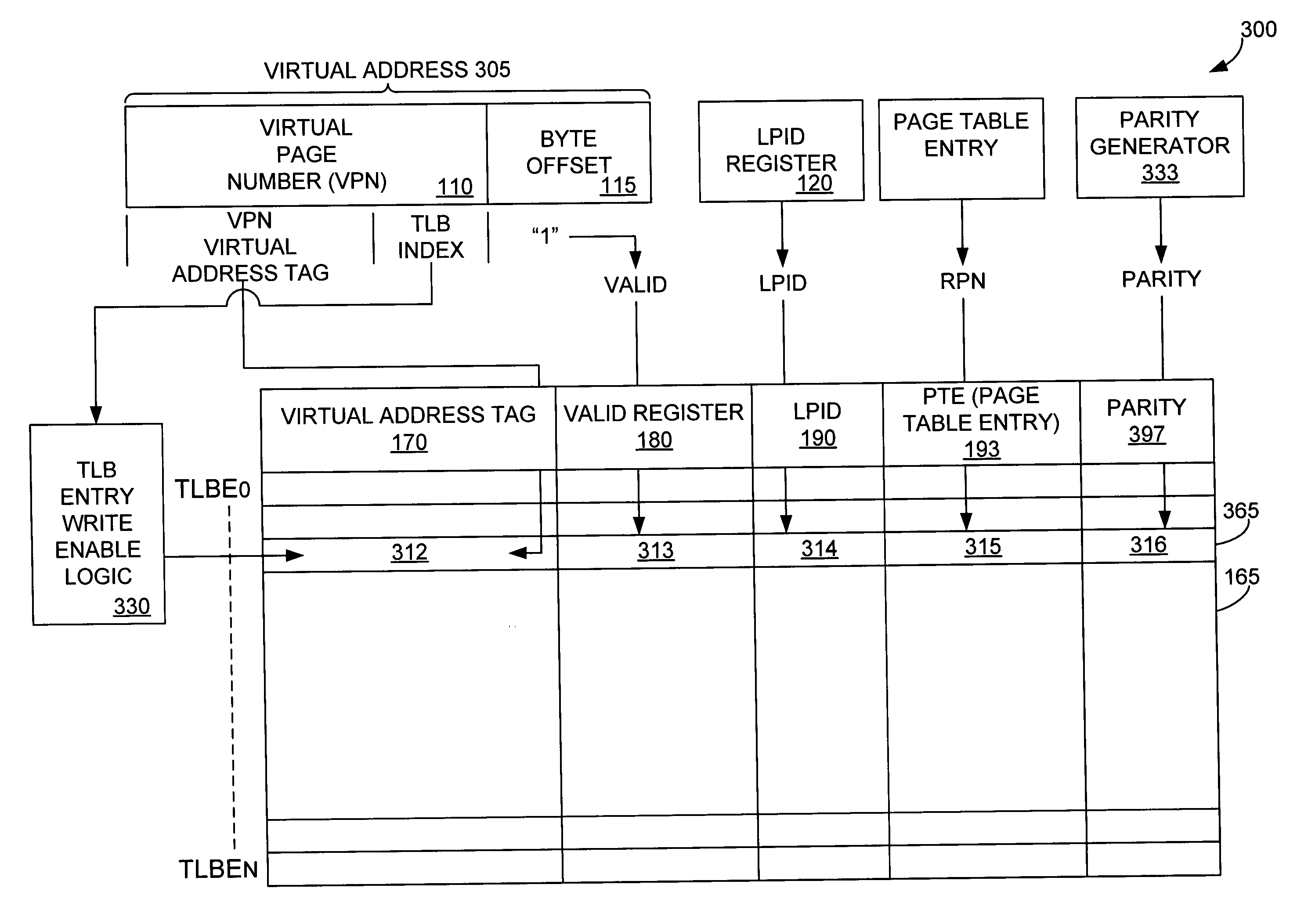
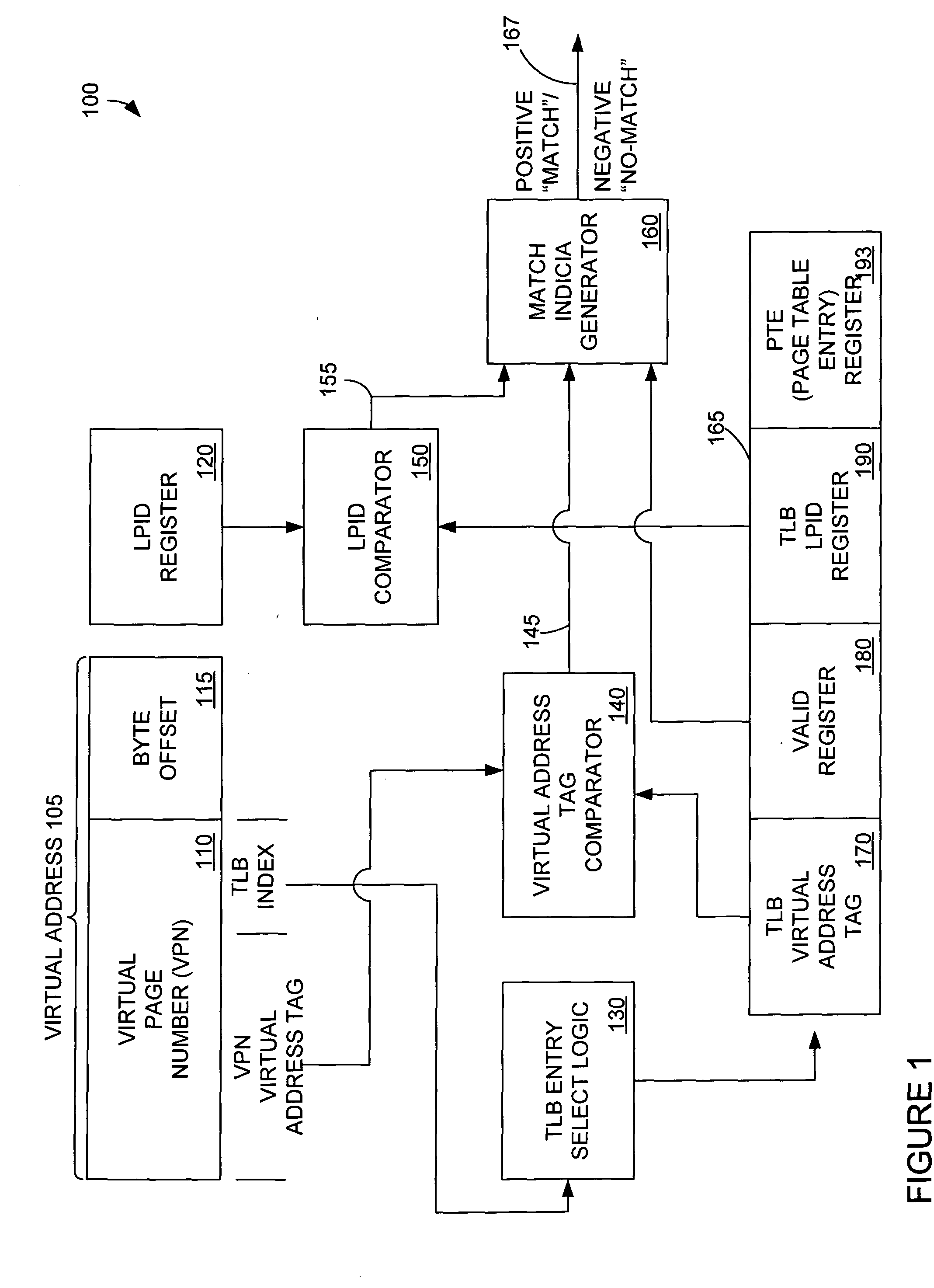
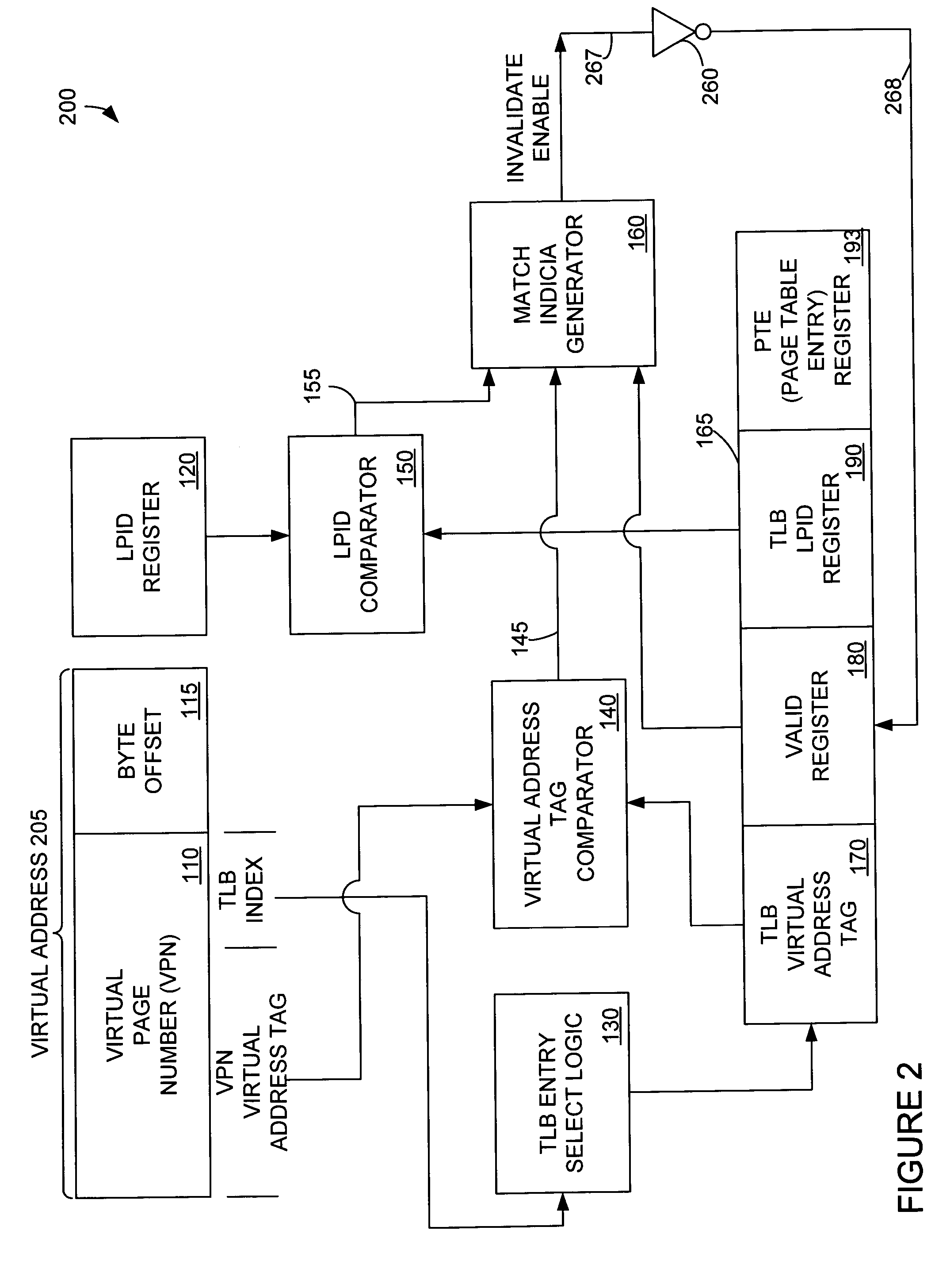
Translation look-aside buffer sharing among logical partitions
InactiveUS20050027960A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPage tableMicroprocessor architecture
The present invention provides for storing and using a stored logical partition indicia in a TLB. A partition in a microprocessor architecture is employed. A virtual page number is selected. A stored LPID indicia corresponding to the selected page number is read from a TLB. The stored logical partition indicia from the TLB is compared to a logical partition indicia associated with the employed partition. If the stored logical partition indicia and the logical partition indicia associated with the employed partition match, a corresponding page table entry stored in the translation look-aside buffer is read. If they do not match, a page table entry from a page table entry source is retrieved and stored in the TLB. If a partition is to invalidate an entry in the TLB, a TLB entry command is generated and used to invalidate a memory entry.
Owner:IBM CORP
Generating code for a configurable microprocessor
InactiveUS20050257200A1Reduce in quantityEasy to codeSoftware engineeringCAD circuit designParallel computingExecution unit
A process for generating executable code for a configurable microprocessor architecture. The architecture contains registers distributed between execution units under direct software control. A internal representation allows explicit allocation of both register and connectivity resources in the architecture.
Owner:CRITICAL BLUE
Microprocessor architecture capable of supporting multiple heterogeneous processors
InactiveUS20060064569A1Excessive latencyReduce latencyProgram synchronisationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationExchange networkMicroprocessor architecture
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
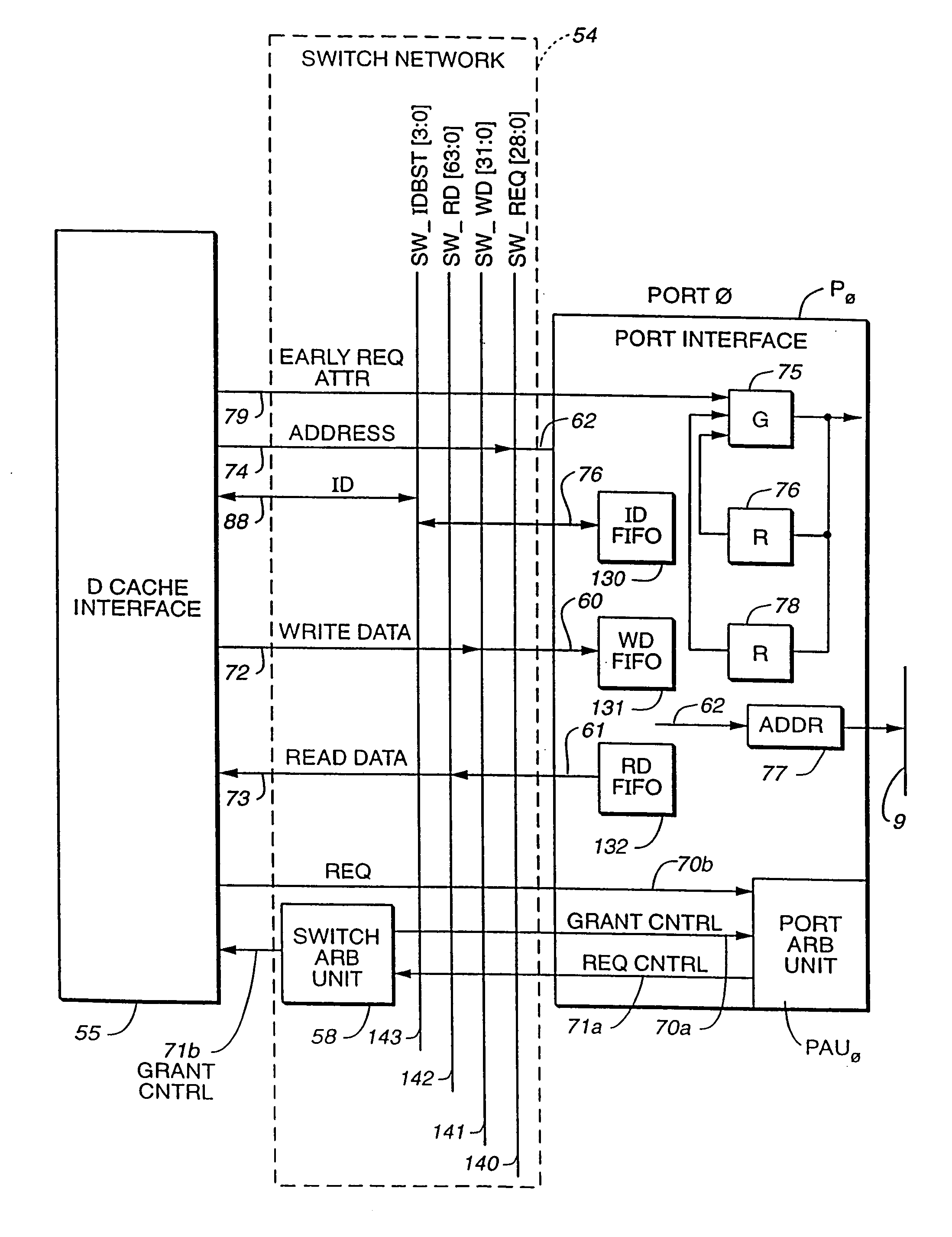
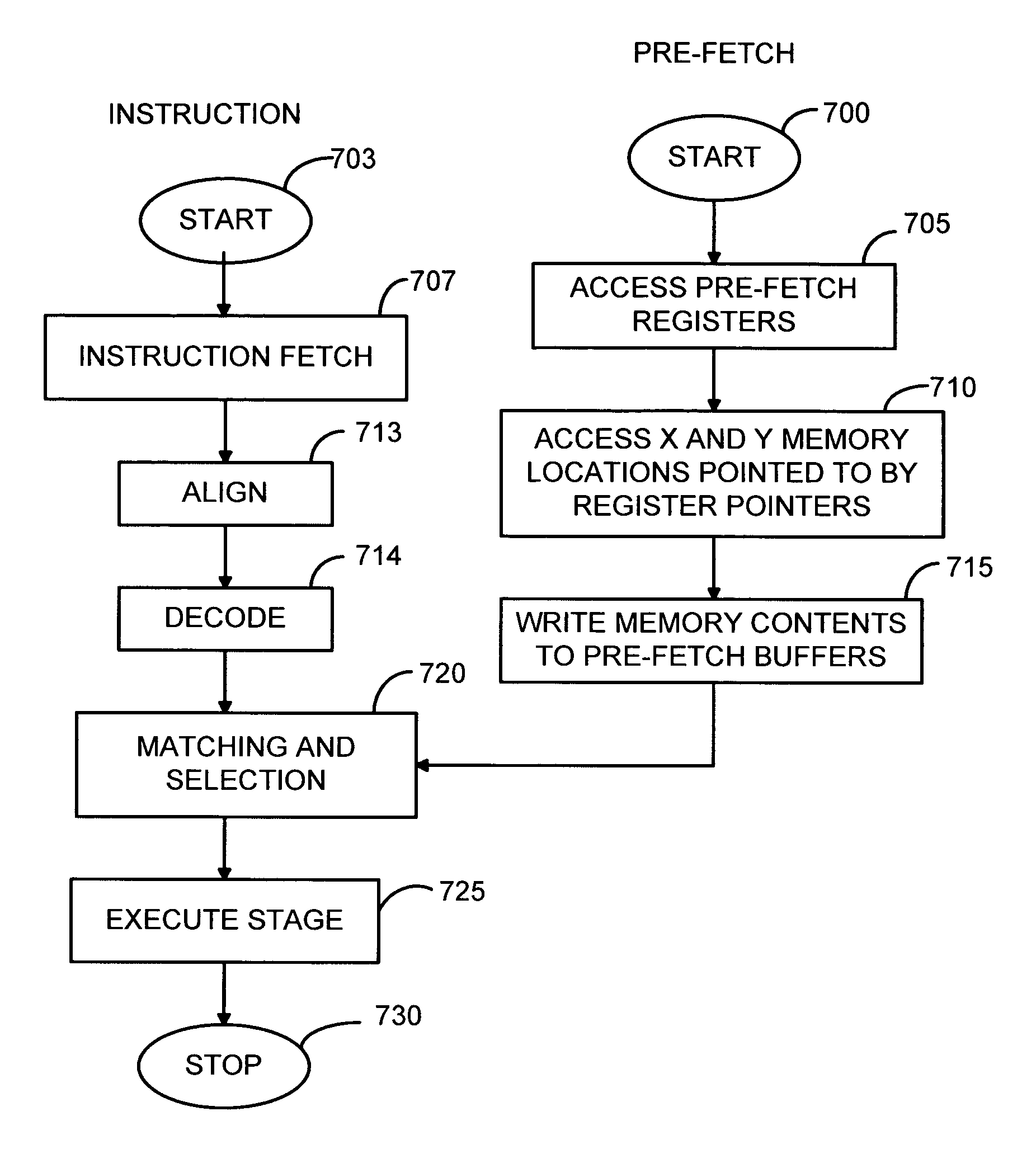
Microprocessor architecture including zero impact predictive data pre-fetch mechanism for pipeline data memory
InactiveUS20050278505A1Impact speedIncrease clock speedEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionOperandExecution unit
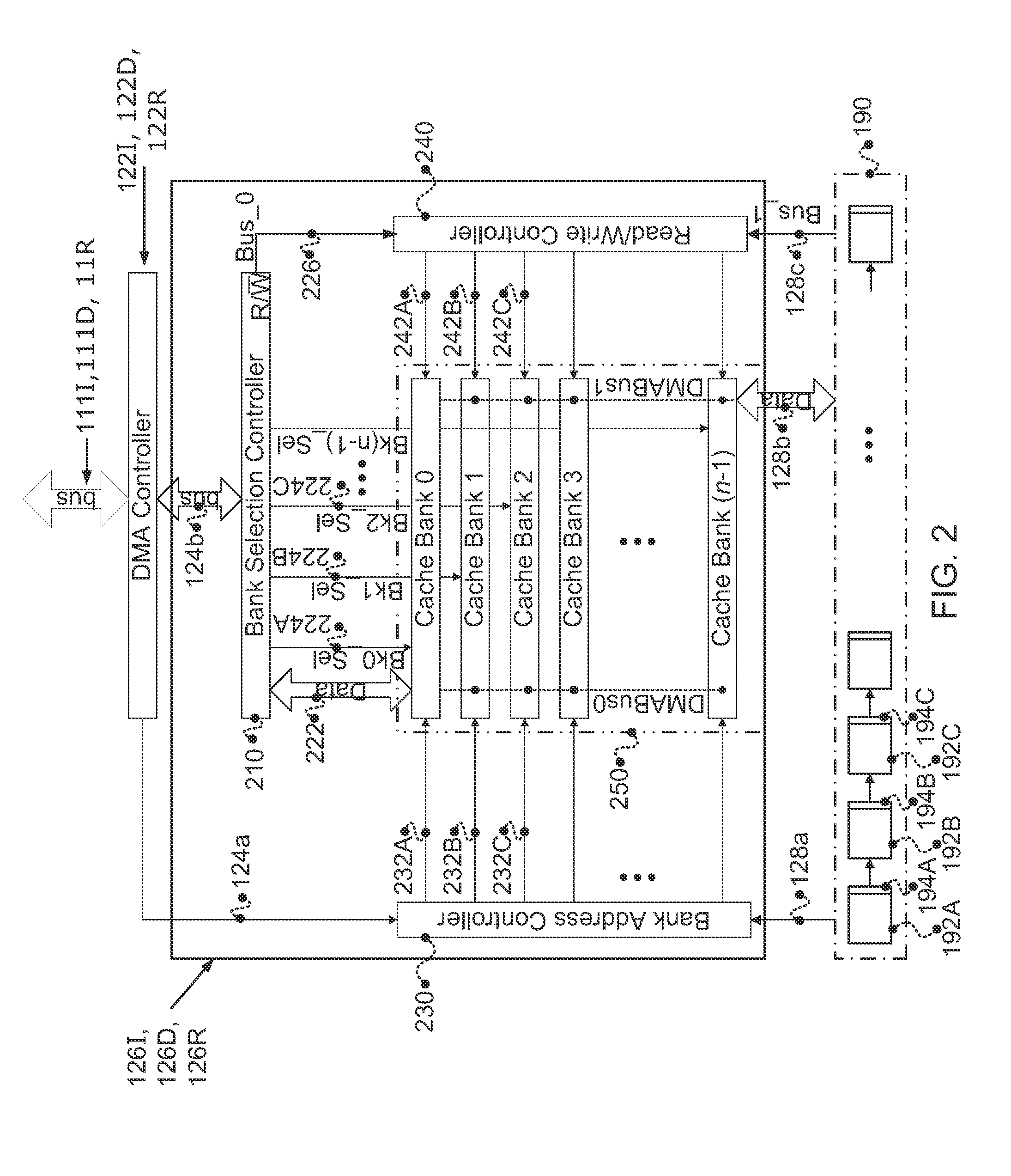
A microprocessor architecture including a predictive pre-fetch XY memory pipeline in parallel to the processor's pipeline for processing compound instructions with enhanced processor performance through predictive prefetch techniques. Instruction operands are predictively prefetched from X and Y based on the historical use of operands in instructions that target X and Y memory. After the compound instruction is decoded in the pipeline, the pre-fetched operand pointer, address and data is reconciled with the operands contained in the actual instruction. If the actual data has been pre-fetched, it is passed to the appropriate execute unit in the execute stage of the processor pipeline. As a result, if the prediction is correct, the data to use for access can be selected and the data selected fed to the execution stage without any addition processor overhead. This pre-fetch mechanism avoids the need to slow down the clock speed of the processor or insert stalls for each compound instruction when using XY memory.
Owner:ARC INT LTD
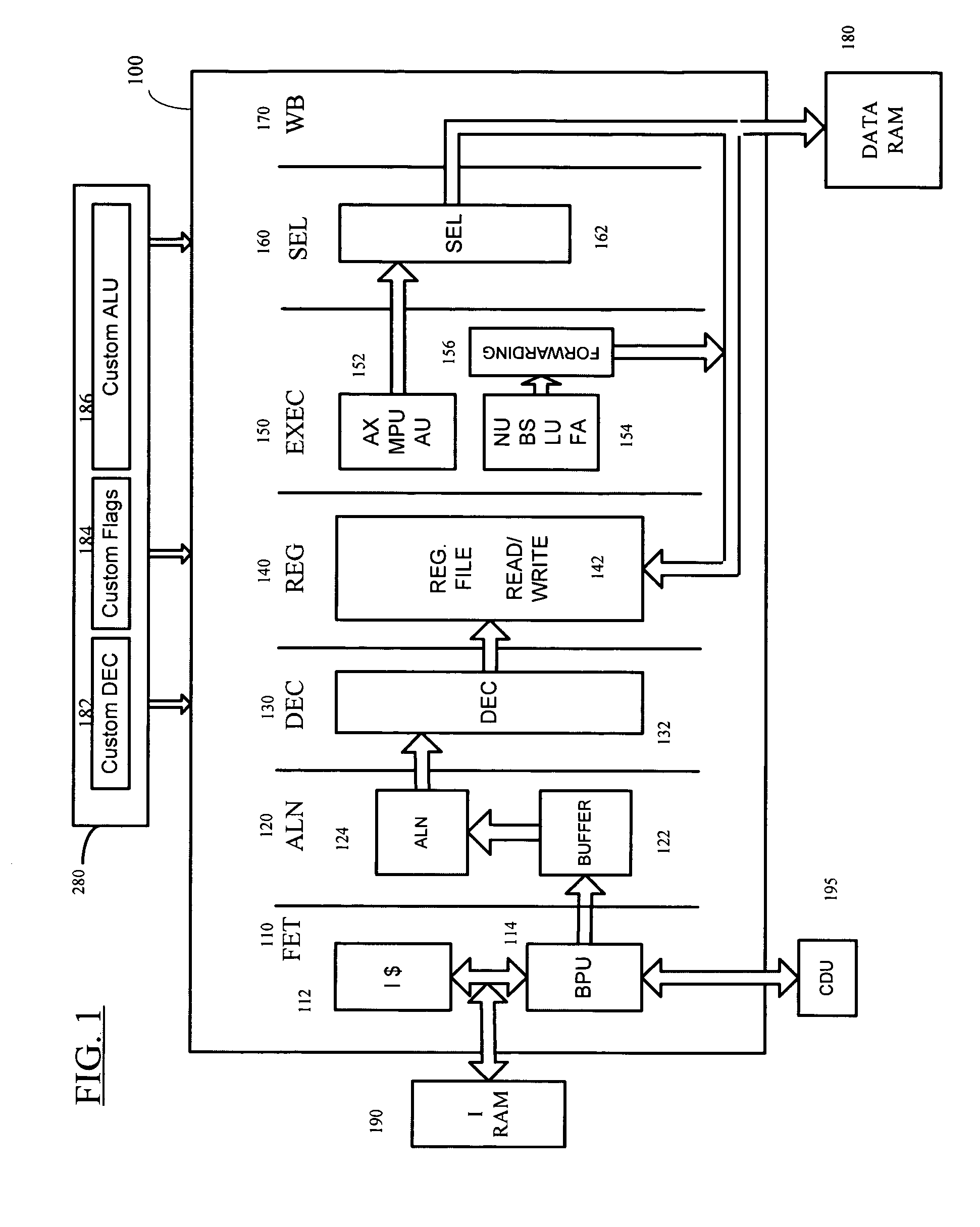
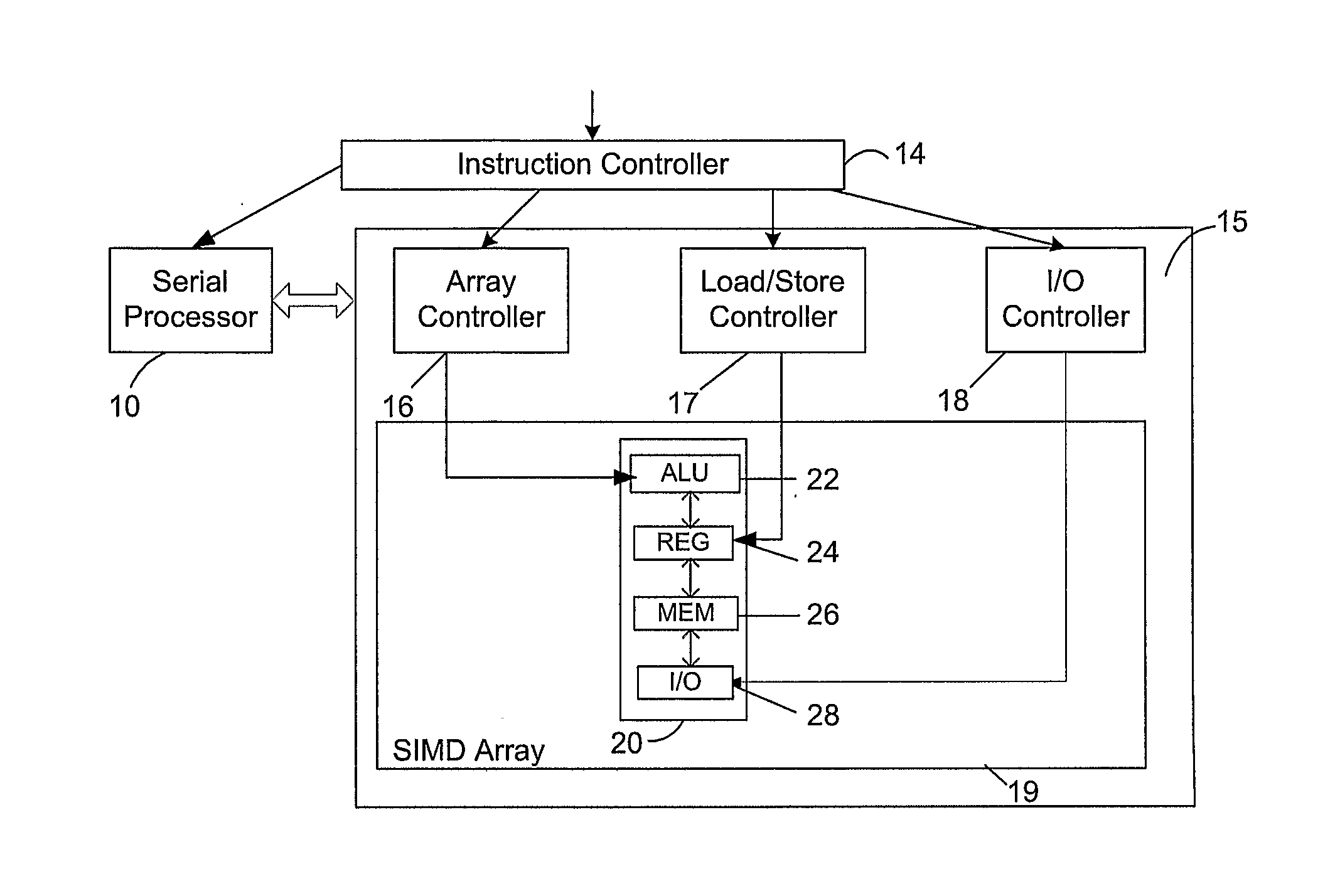
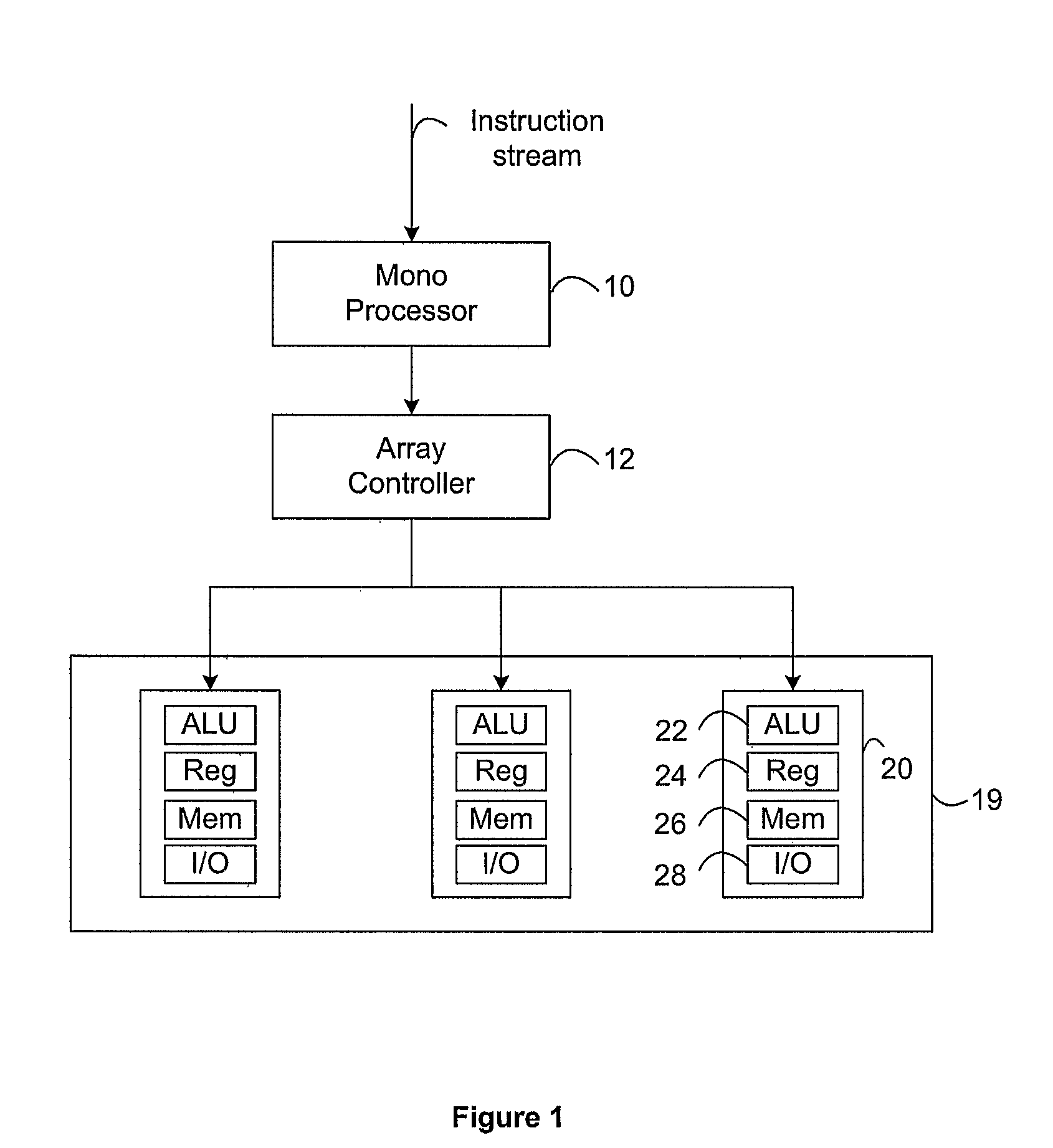
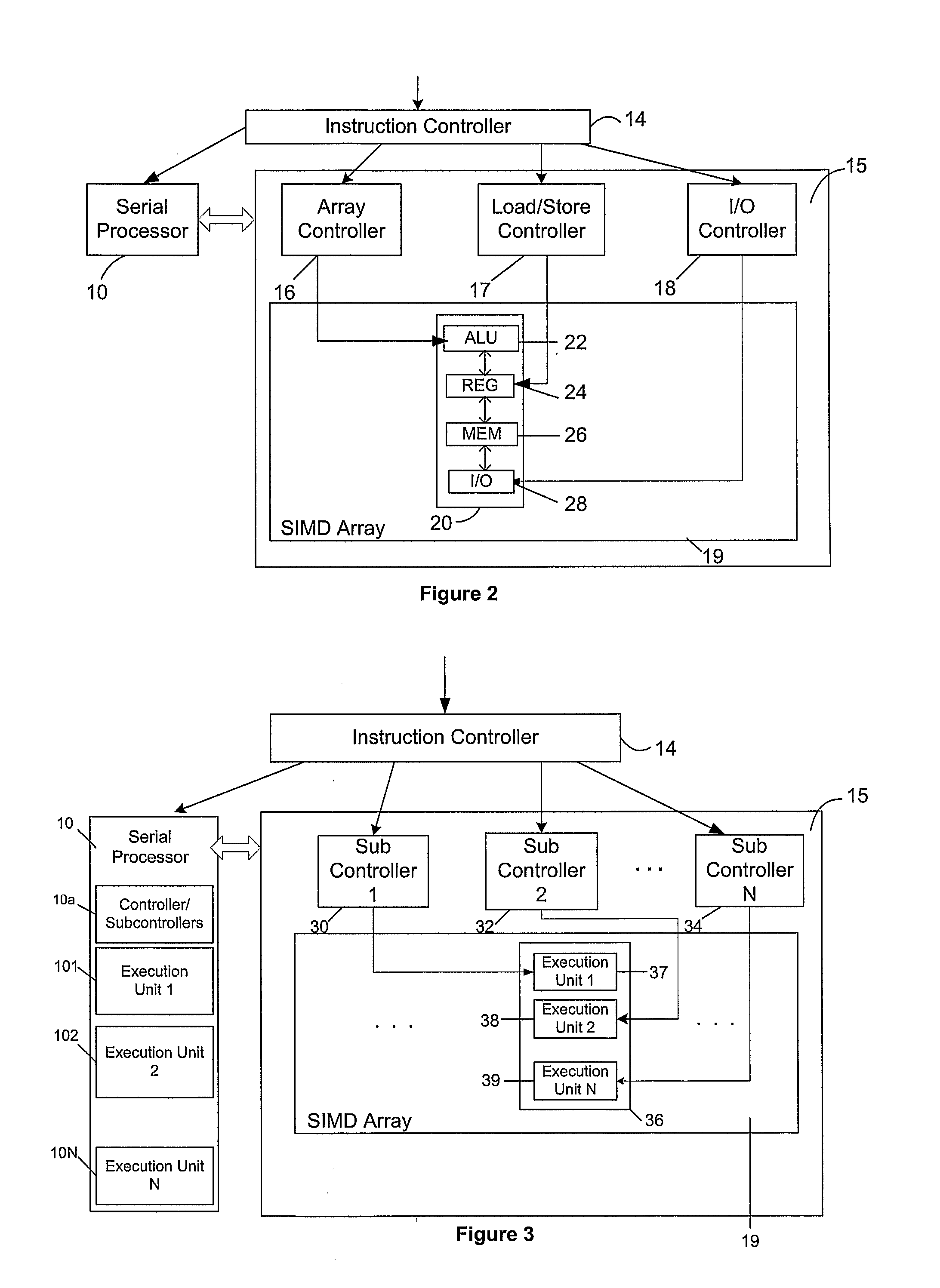
Microprocessor Architectures
InactiveUS20080209164A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsProgram control using wired connectionsExecution unitProcessing element
A microprocessor architecture comprises a plurality of processing elements arranged in a single instruction multiple data SIMD array, wherein each processing element includes a plurality of execution units, each of which is operable to process an instruction of a particular instruction type, a serial processor which includes a plurality of execution units, each of which is operable to process an instruction of a particular instruction type, and an instruction controller operable to receive a plurality of instructions, and to distribute received instructions to the execution units in dependence upon the instruction types of the received instruction. The execution units of the serial processor are operable to process respective instructions in parallel.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
High-performance superscalar-based computer system with out-of order instruction execution and concurrent results distribution
InactiveUS20070101103A1Easy to modifyRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsInstruction memoryFloating point
The high-performance, RISC core based microprocessor architecture includes an instruction fetch unit for fetching instruction sets from an instruction store and an execution unit that implements the concurrent execution of a plurality of instructions through a parallel array of functional units. The fetch unit generally maintains a predetermined number of instructions in an instruction buffer. The execution unit includes an instruction selection unit, coupled to the instruction buffer, for selecting instructions for execution, and a plurality of functional units for performing instruction specified functional operations. A unified instruction scheduler, within the instruction selection unit, initiates the processing of instructions through the functional units when instructions are determined to be available for execution and for which at least one of the functional units implementing a necessary computational function is available. Unified scheduling is performed across multiple execution data paths, where each execution data path, and corresponding functional units, is generally optimized for the type of computational function that is to be performed on the data: integer, floating point, and boolean. The number, type and computational specifics of the functional units provided in each data path, and as between data paths, are mutually independent.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
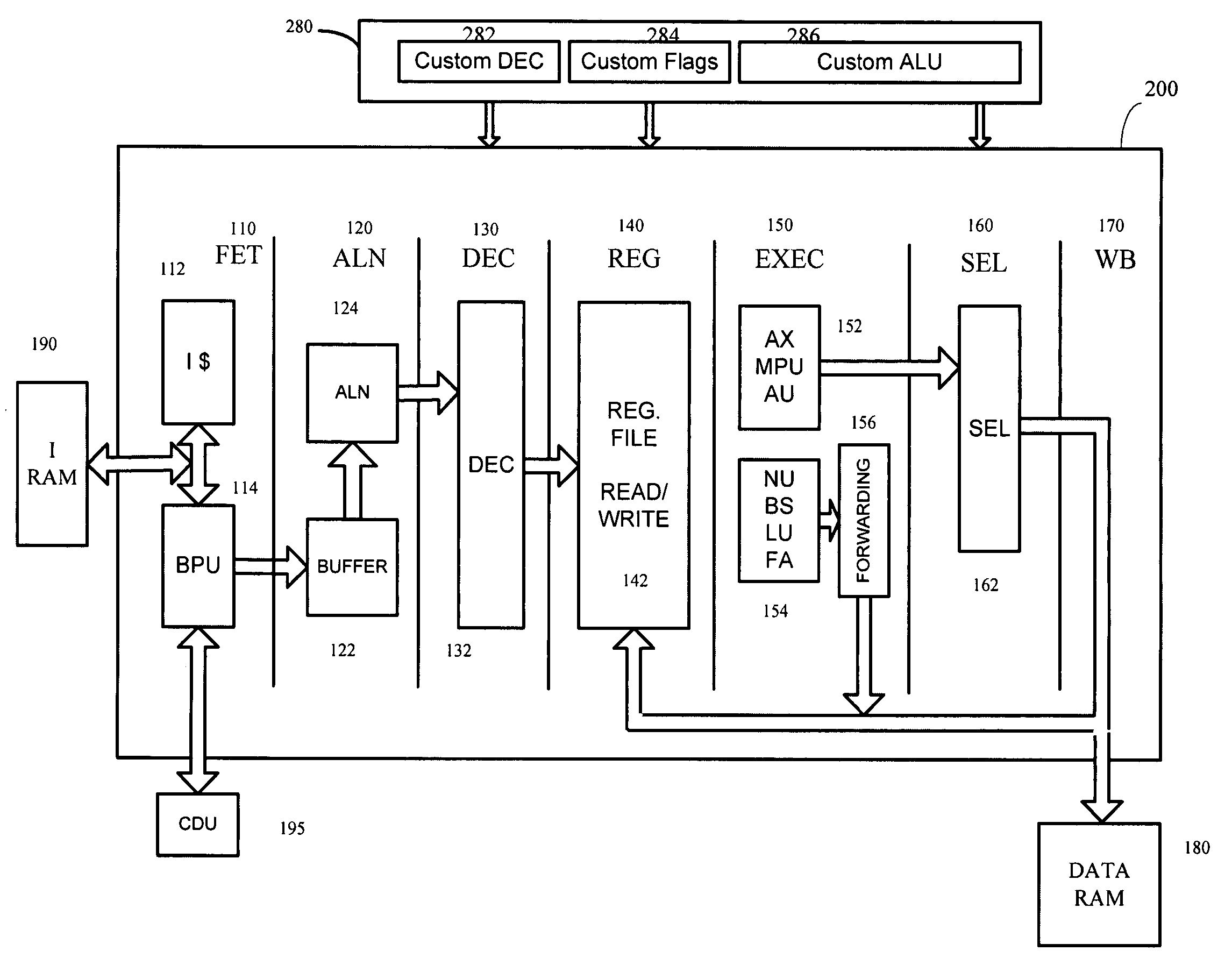
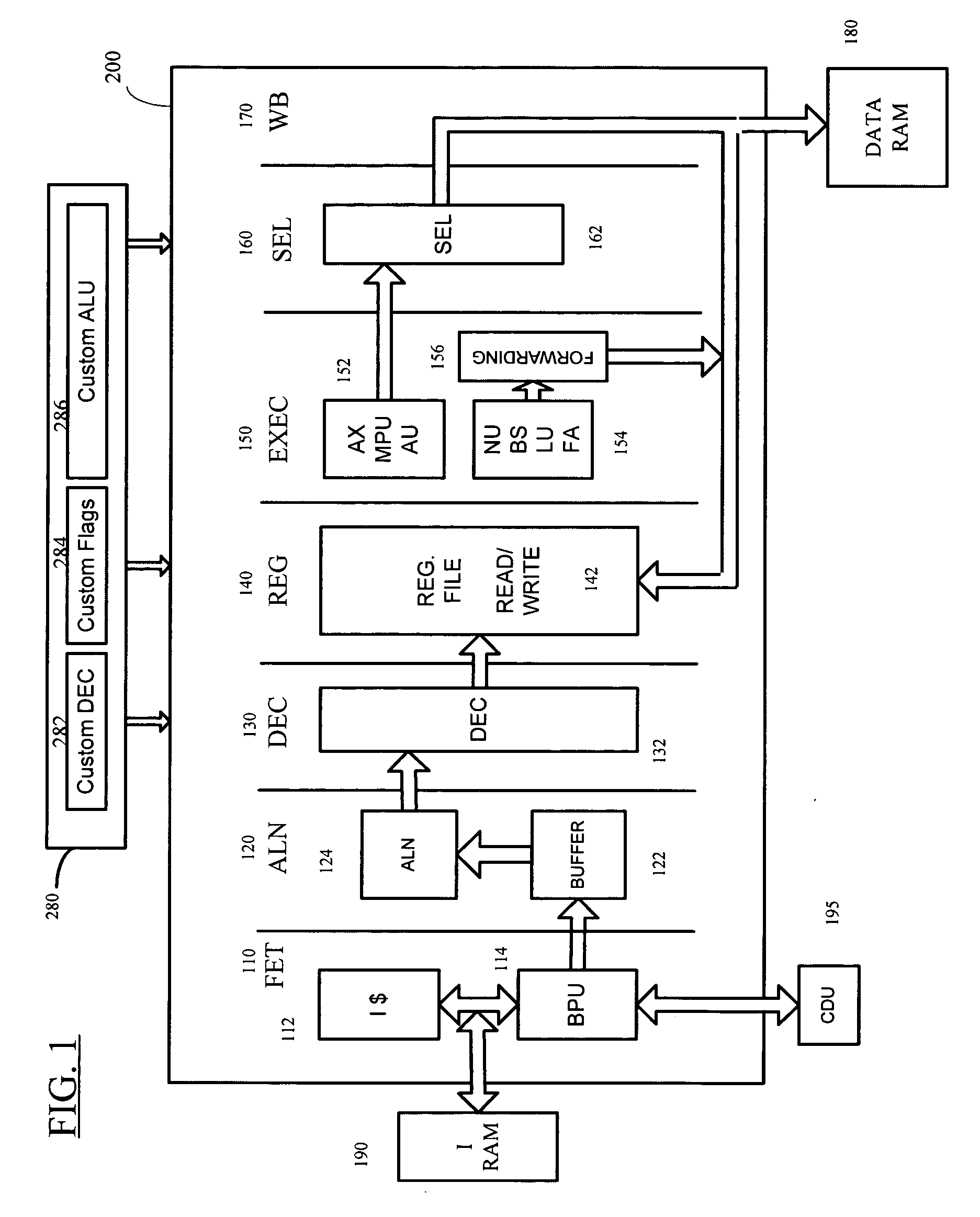
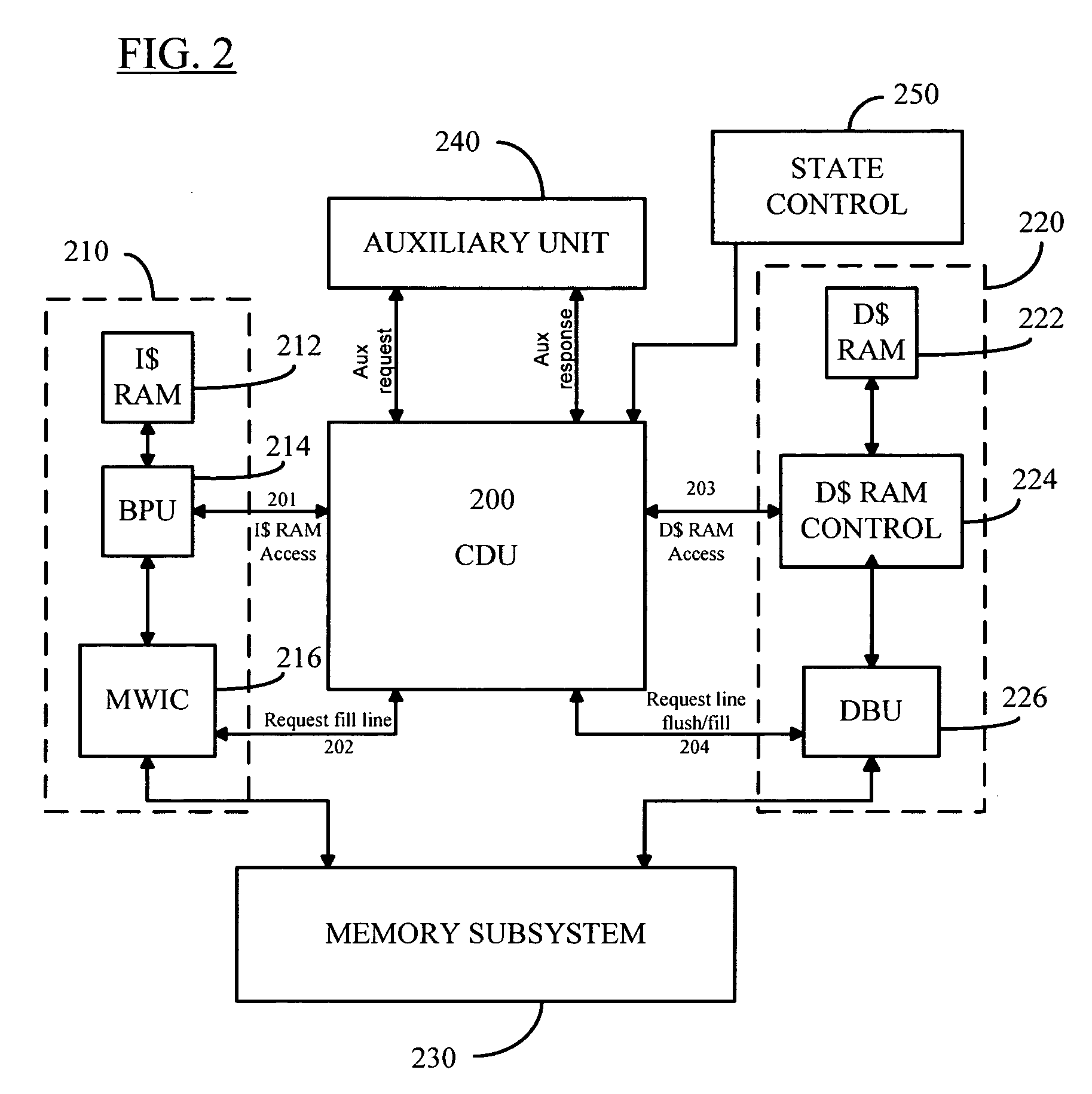
Microprocessor architecture including unified cache debug unit
InactiveUS20050273559A1Overcomes shortcomingError detection/correctionInstruction analysisInstruction pipelineMicroprocessor architecture
A microprocessor architecture including a unified cache debug unit. A debug unit on the processor chip receives data / command signals from a unit of the execute stage of the multi-stage instruction pipeline of the processor and returns information to the execute stage unit. The cache debug unit is operatively connected to both instruction and data cache units of the microprocessor. The memory subsystem of the processor may be accessed by the cache debug unit through either of the instruction or data cache units. By unifying the cache debug in a separate structure, the need for redundant debug structure in both cache units is obviated. Also, the unified cache debug unit can be powered down when not accessed by the instruction pipeline, thereby saving power.
Owner:ARC INT LTD
Automatic configuration of a microprocessor influenced by an input program
InactiveUS7415689B2Improve performanceConcurrent instruction executionCAD circuit designControl flowComputer architecture
An automatic process for configuring a microprocessor architecture that consists of a number of execution units with configurable connectivity between them. The data and control flows within an input program are used to influence the process so that the resulting microprocessor is able to efficiently exploit parallelism available within the input program.
Owner:CRITICAL BLUE
Scaleable microprocessor architecture
InactiveUS20030212878A1Executed quickly and reliablyGeneral purpose stored program computerNext instruction address formationArray data structureCode density
A scaleable microprocessor architecture has an efficient and orthogonal instruction set of 20 basic instructions, and a scaleable program word size from 15 bits up, including but not limited to 16, 24, 32, and 64 bits. As many instructions are packed into a single program word as allowed by the size of a program word. An integral return stack is used for nested subroutine calls and returns. An integral data stack is also used to pass parameters among nested subroutines. The simplified instruction set and the dual stack architecture make it possible to execute all instructions in a single clock cycle from a single phase master clock. Additional instructions can be added to facilitate accessing arrays in memory, for multiplication and division of integers, for real time interrupts, and to support an UART I / O device. This scaleable microprocessor architecture greatly increases code density and processing speed while decreasing significantly silicon area and power consumption. It is most suitable to serve as microprocessor cores in System-on-a-Chip (SOC) integrated circuits.
Owner:TING CHEN HANSON
Radar level meter and method for processing signals thereof
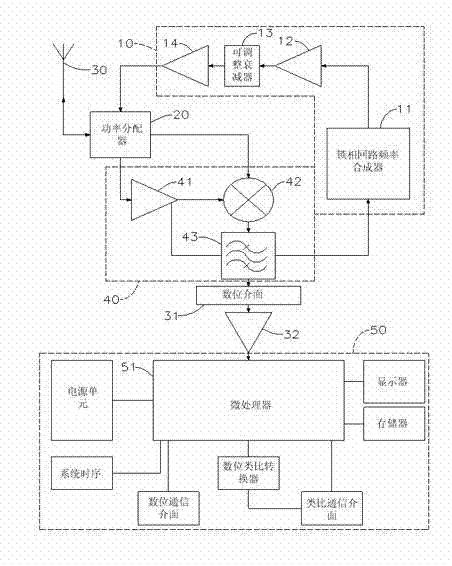
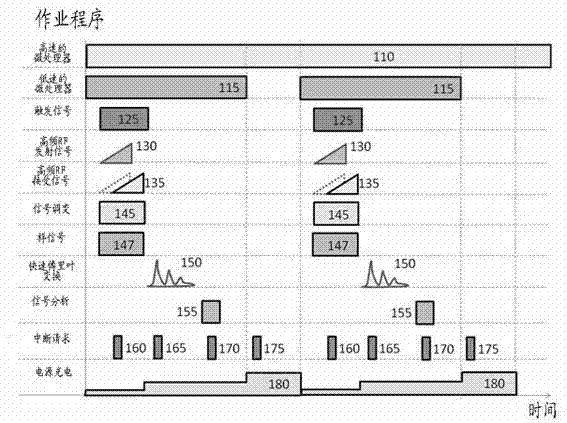
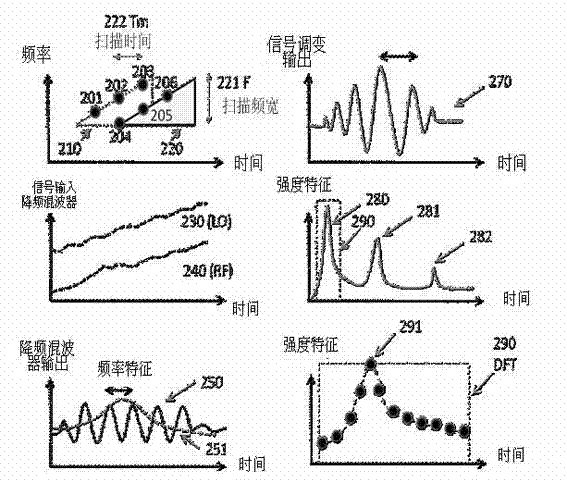
InactiveCN103090930AOvercome the shortcomings of the two-wire control update rate being too slowReduce power consumptionMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsLow speedFrequency spectrum
Disclosed are a radar level meter and a method for processing signals thereof. The radar level meter is provided with a micro control unit architecture, the architecture comprises a high-speed microprocessor, a low-speed microprocessor and a power charging and discharging circuit, and requirements on low power consumption and high update rate can be met. The method for processing the signals is a method for modulating the signals of the frequency-modulated continuous-wave radar level meter, and includes generating a high-frequency beat signal and feeding the high-frequency beat signal into a down-conversion mixer; converting the high-frequency signal into an intermediate-frequency periodic signal; converting the intermediate-frequency periodic signals into spectrum characteristics via fast Fourier transfer to obtain an FFT (fast Fourier transfer) signal; performing digital filtering transfer for the FFT signal for at least once to obtain final frequency characteristics; and finally acquiring the level distance by a physical value conversion program to obtain a high-precision distance relation.
Owner:上海凡宜科技电子有限公司 +1
Configurable microprocessor architecture incorporating direct execution unit connectivity
InactiveUS20050216707A1Reduce in quantityOptimization mechanismRegister arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingExecution unit
An architecture for a highly configurable and scalable microprocessor architecture designed for exploiting instruction level parallelism in specific application code. It consists of a number of execution units with configurable connectivity between them and a means to copy data through execution units under software control.
Owner:CRITICAL BLUE
Microprocessor and method for register addressing therein
ActiveUS20090204754A1Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerData operationsOperand
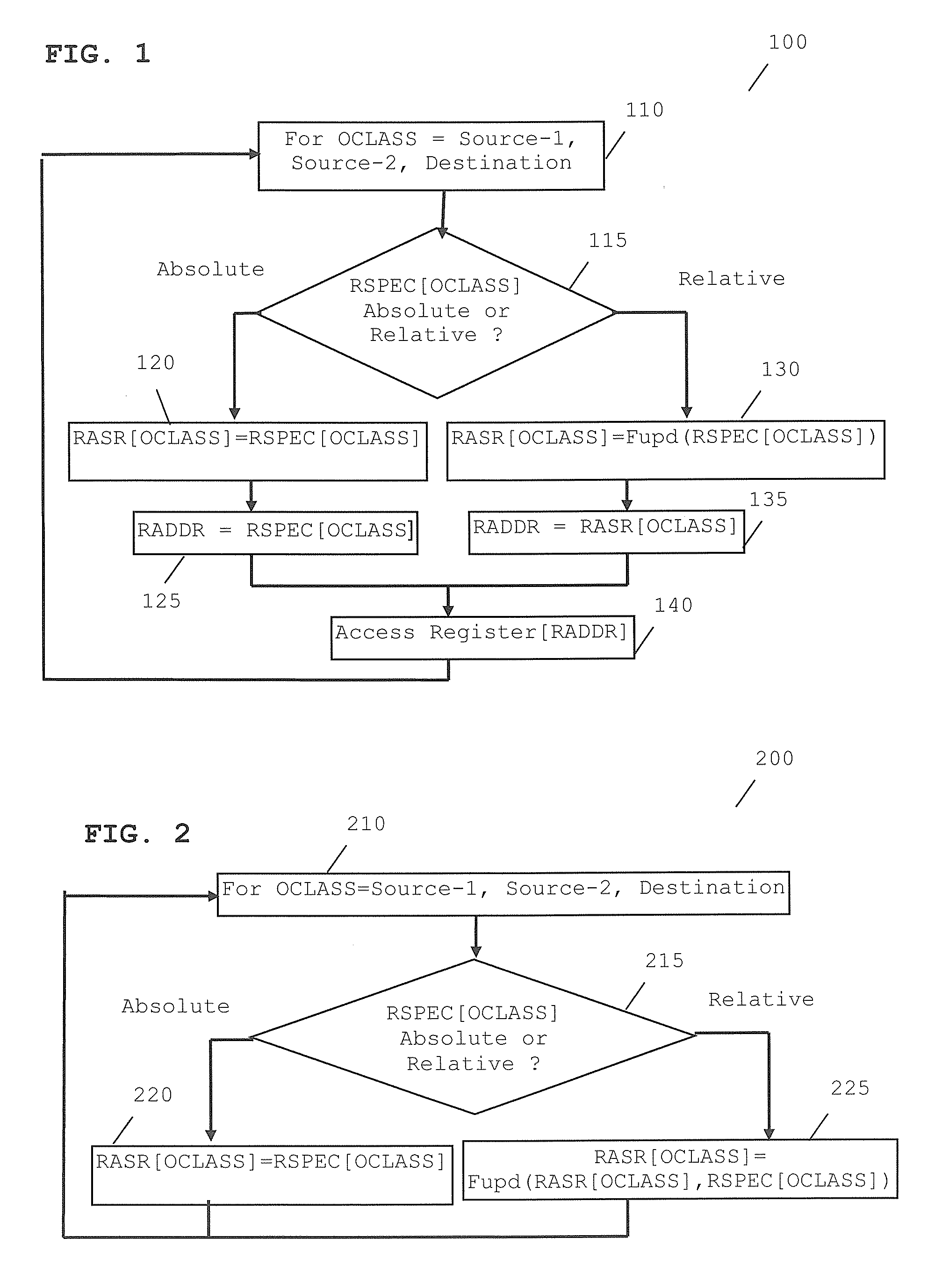
A microprocessor architecture comprising a microprocessor operably coupled to a plurality of registers and arranged to execute at least one instruction. The microprocessor is arranged to determine a class of data operand. The at least one instruction comprises one or more codes in a register specifier that indicates whether relative addressing or absolute addressing is used in accessing a register. In this manner, absolute and relative register addressing is supported within a single instruction word.
Owner:NXP USA INC
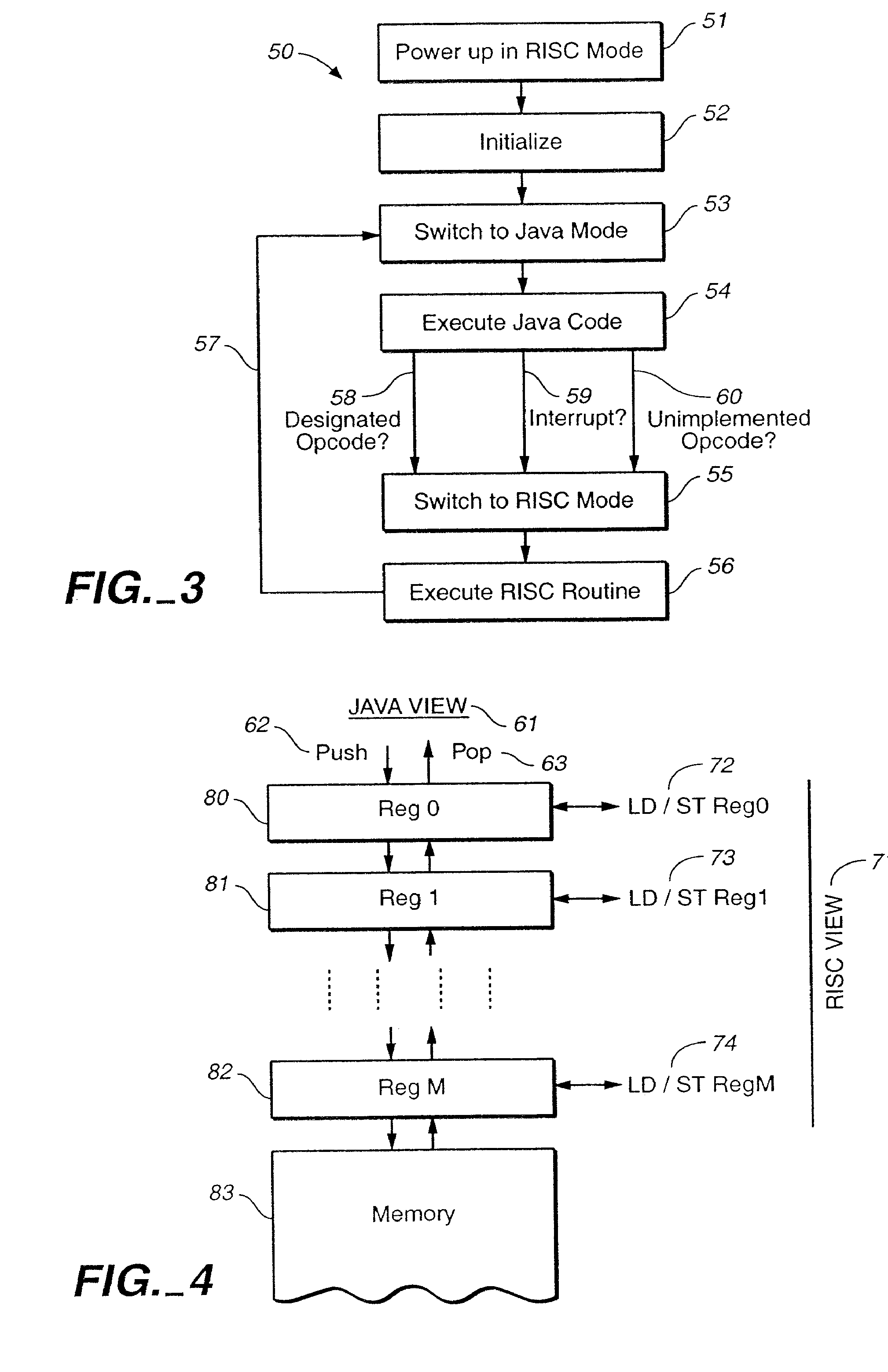
Microprocessor for executing byte compiled JAVA code
InactiveUS20070168954A1Small and power efficientEasy to integrateRuntime instruction translationDigital computer detailsOperandDatapath
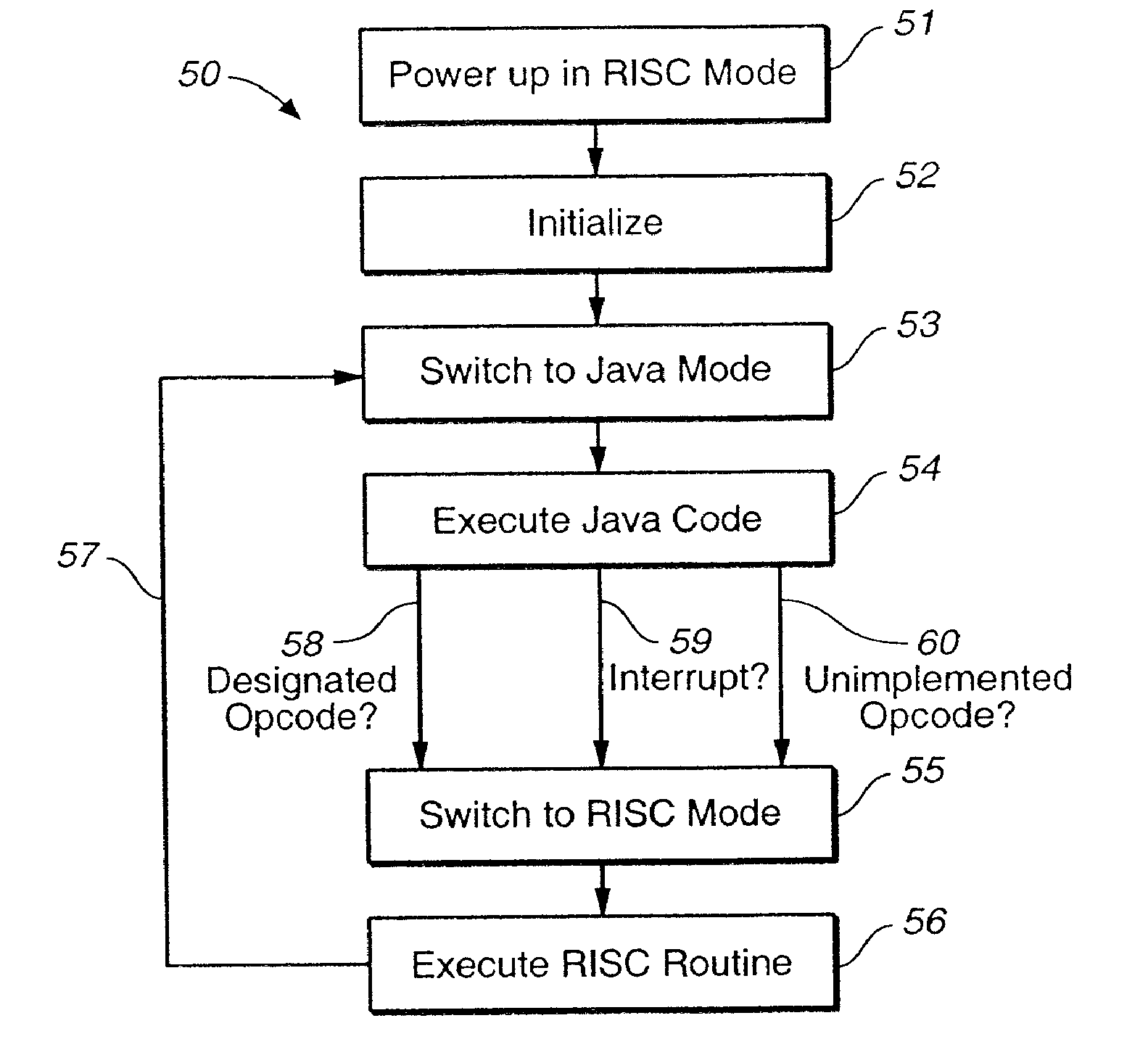
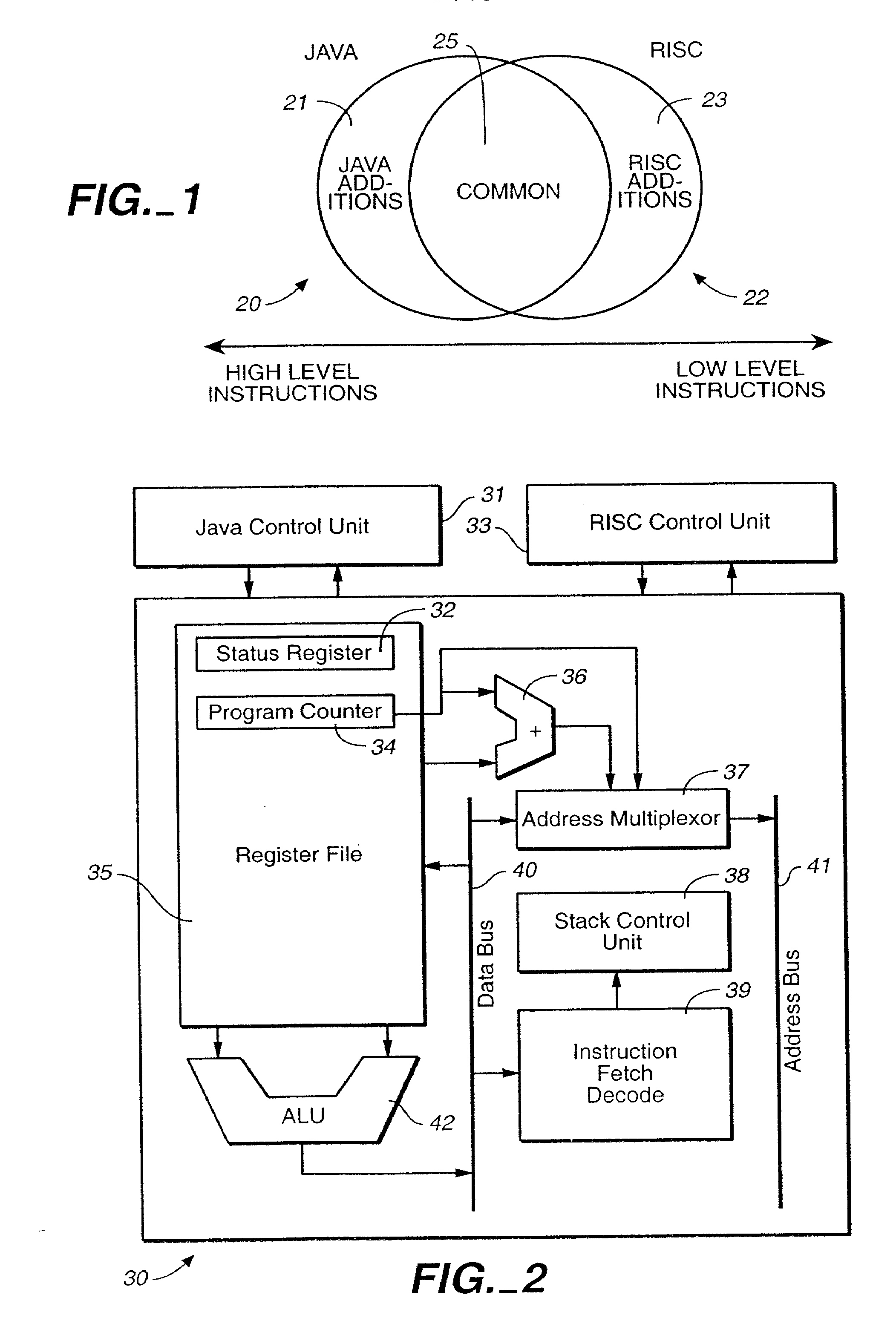
A microprocessor architecture for executing byte compiled Java programs directly in hardware. The microprocessor targets the lower end of the embedded systems domain and features two orthogonal programming models, a Java model and a RISC model. The entities share a common data path and operate independently, although not in parallel. The microprocessor includes a combined register file in which the Java module sees the elements in the register file as a circular operand stack and the RISC module sees the elements as a conventional register file. The integrated microprocessor architecture facilitates access to hardware-near instructions and provides powerful interrupt and instruction trapping capabilities.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
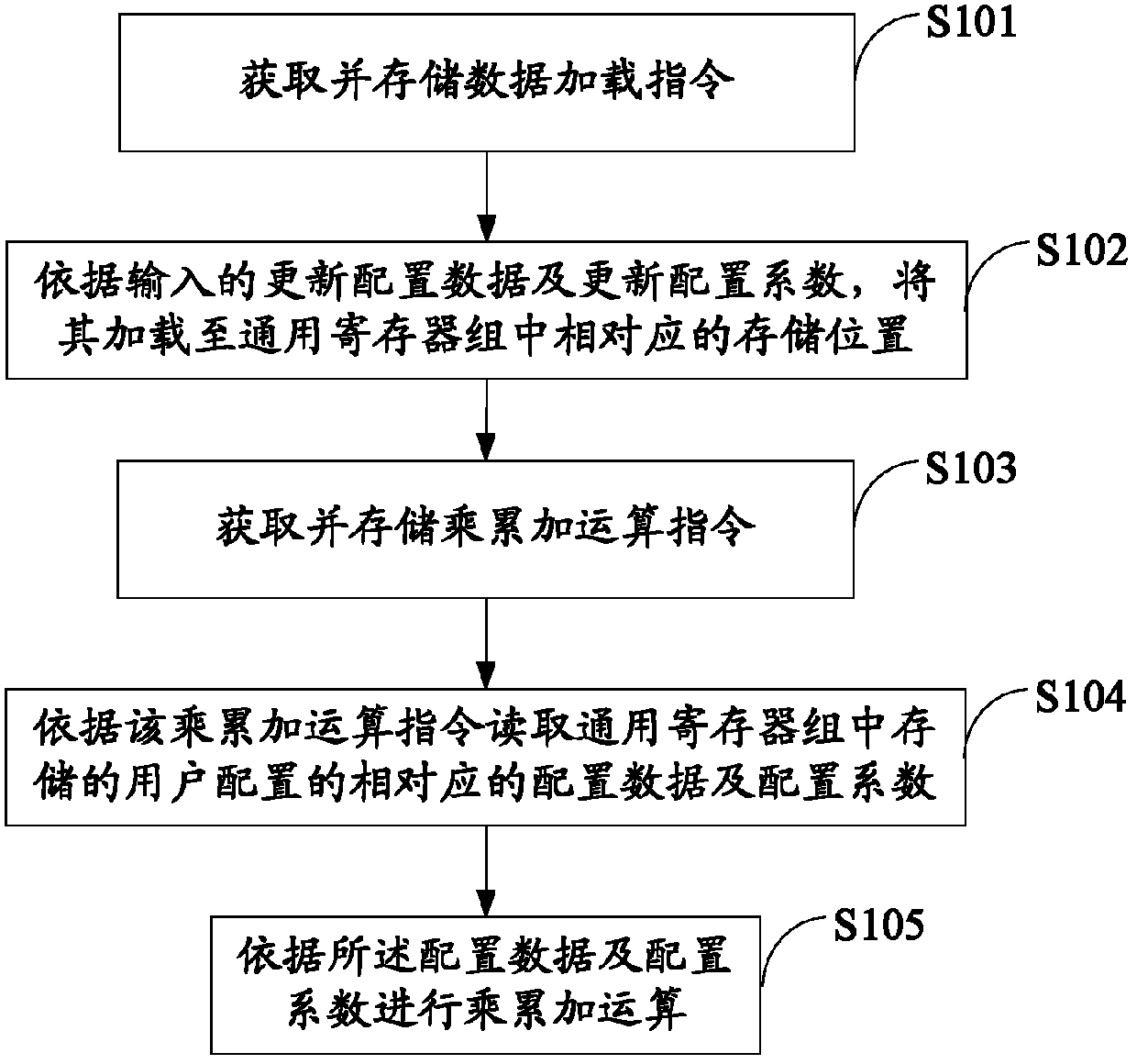
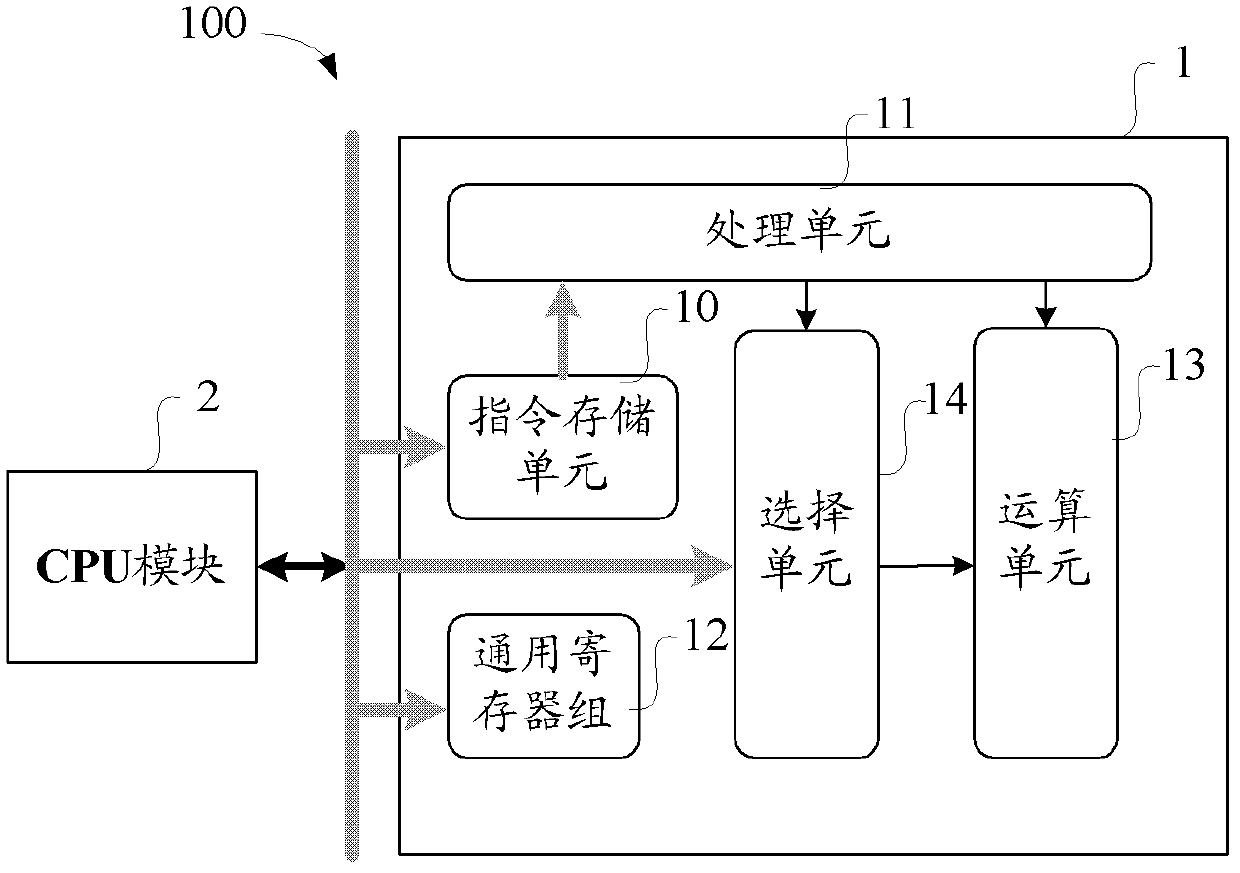
Programmable digital filtering implementation method, apparatus, baseband chip and terminal thereof
InactiveCN103378820AFlexible programmingAny multiply-accumulate operationDigital technique networkGeneral purposeMultiply–accumulate operation
The invention discloses a programmable digital filtering implementation method, an apparatus, a baseband chip and a terminal thereof. The method comprises the steps of acquiring and storing a multiply-accumulate operation instruction; reading corresponding configuration data and a configuration coefficient that are stored in a general-purpose register block to user configuration according to the multiply-accumulate operation instruction; and carrying out a multiply-accumulate operation based on the configuration data and the configuration coefficient. The digital filtering device with microprocessor architecture can be used for achieving any multiply-accumulate operation. Especially in the multi-mode mobile terminal baseband processing, a set of filter resources is used for replacing different filter resources in multiple modes, so that the area of the device is greatly reduced. Different types of filter can be programmed flexibly, and through the processing of software radio, system resources can be saved and energy consumption can be reduced to some extent.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
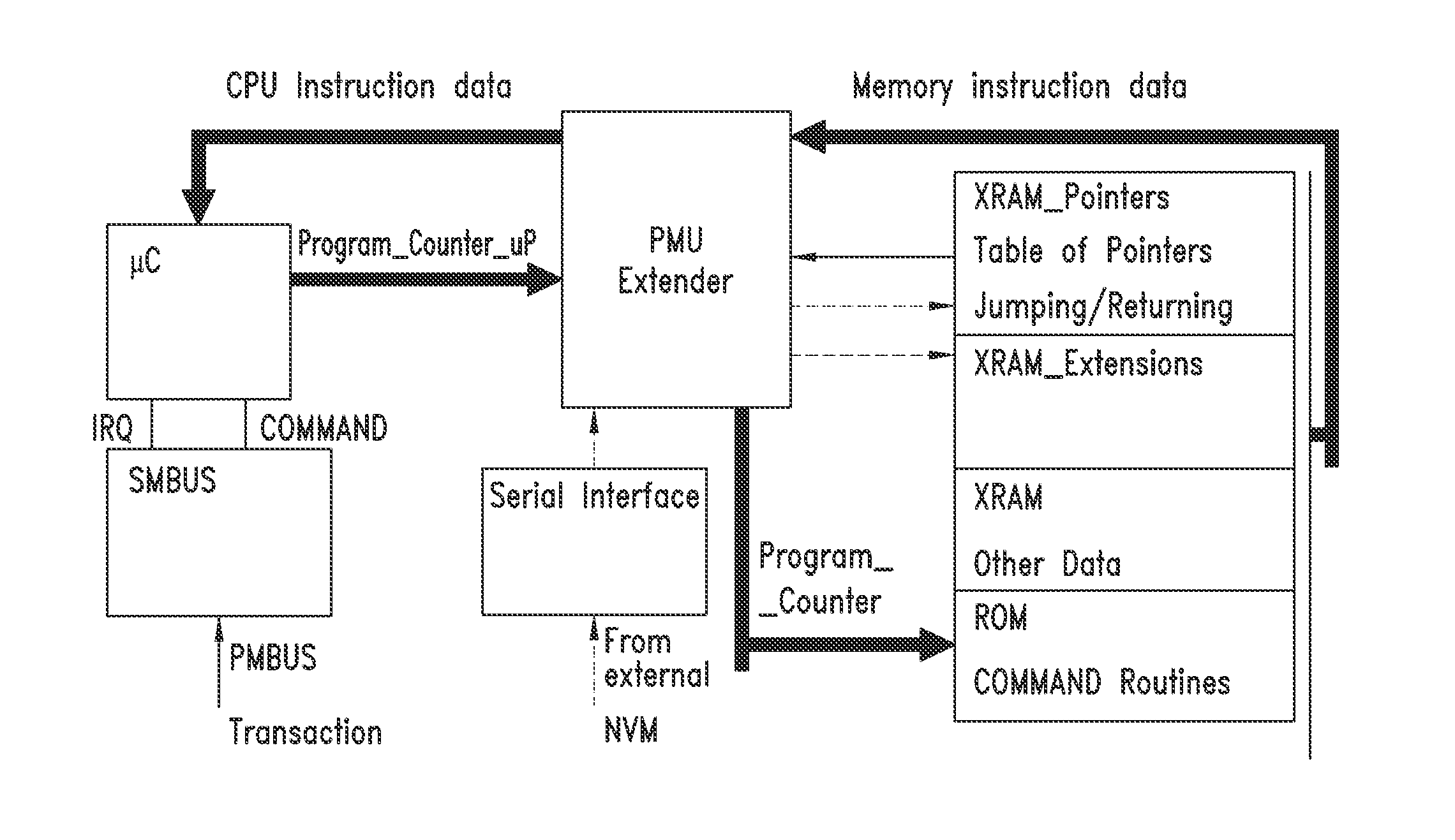
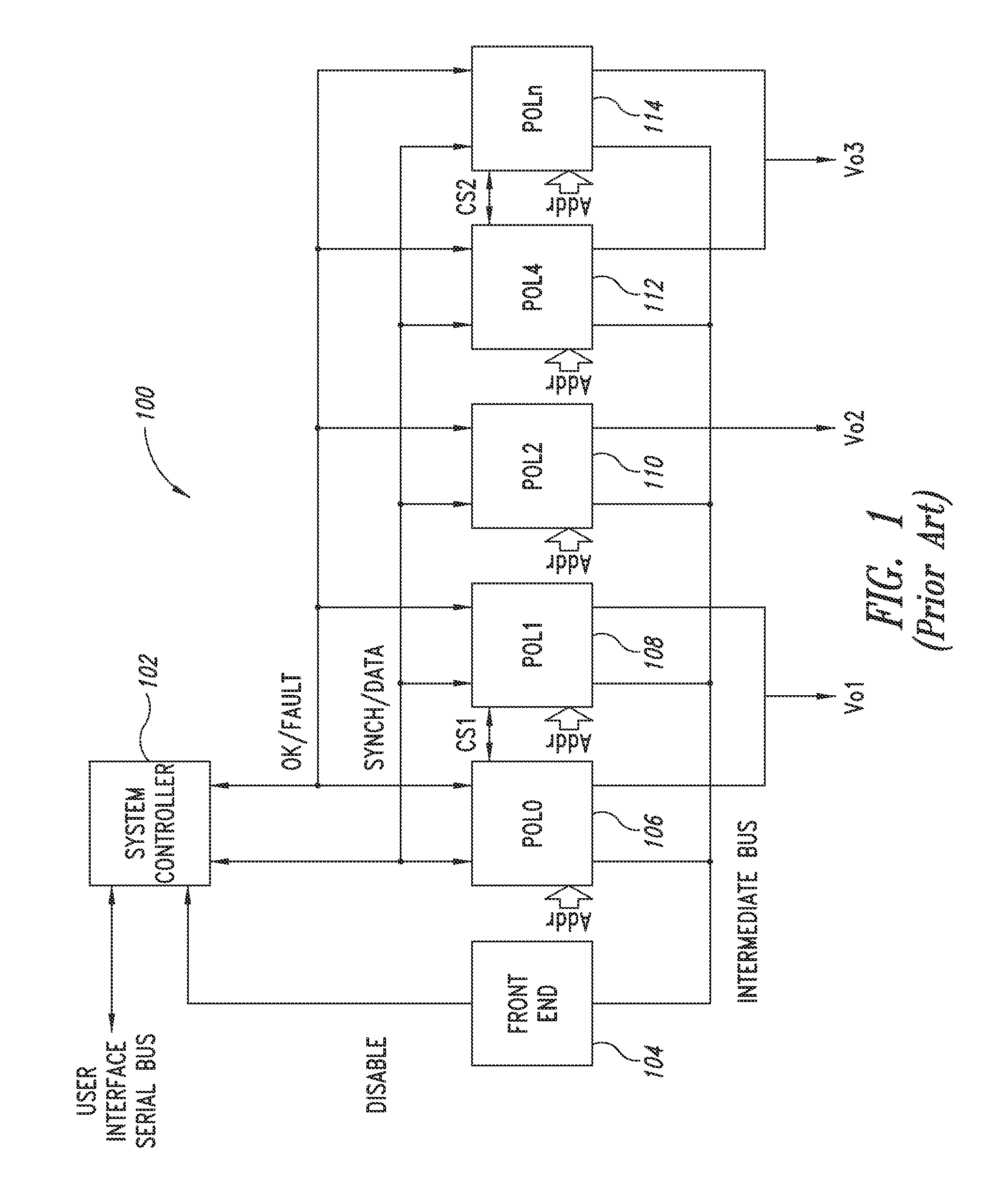
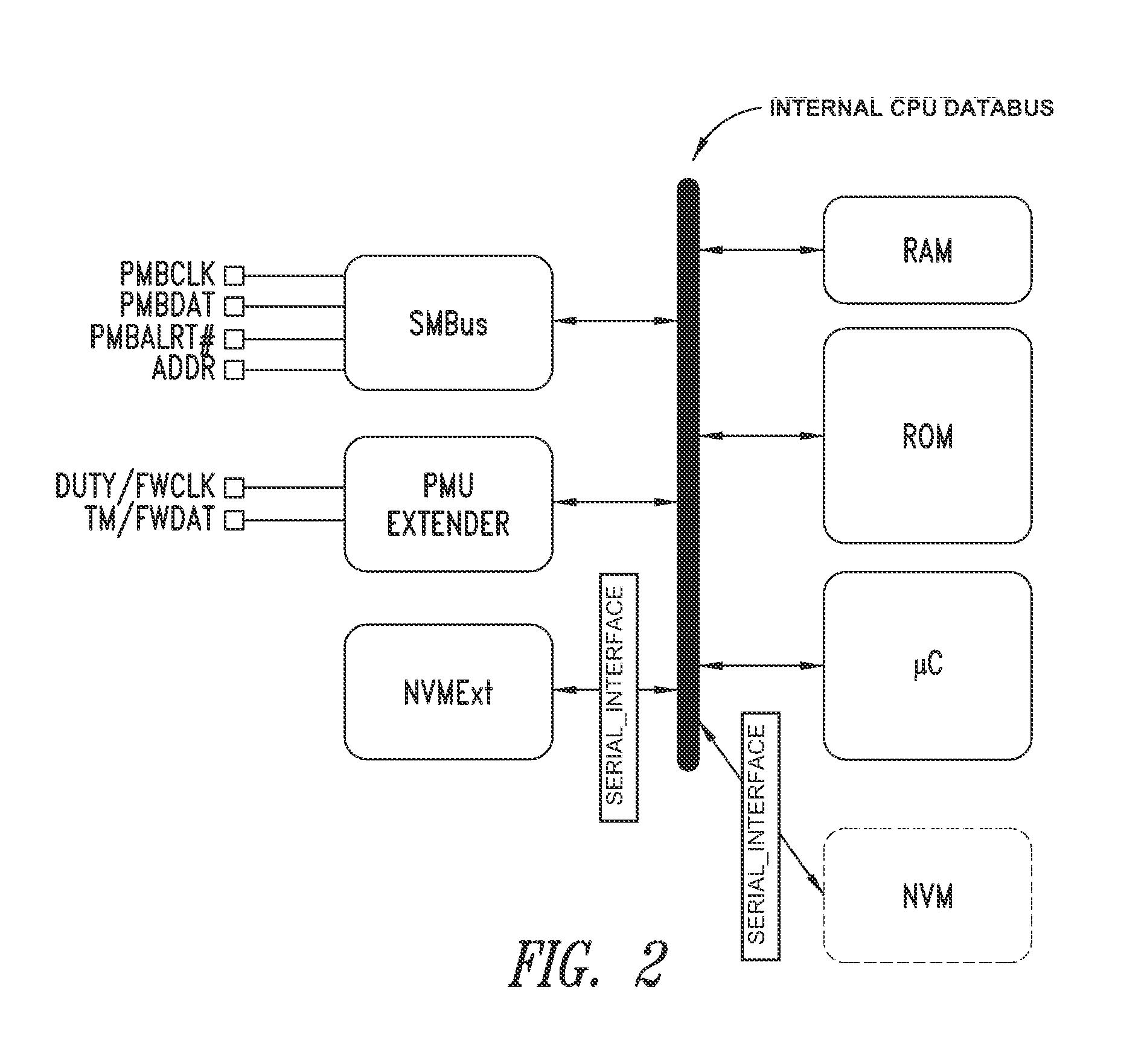
Power management architecture based on micro/processor architecture with embedded and external nvm
ActiveUS20130326124A1Remarkable advantage of flexibilityReduce riskMemory adressing/allocation/relocationThree-or-more-wire dc circuitsStructure of Management InformationProgram counter
A control unit for power supply circuits of points of load (POL) of an electronic system includes a means for autonomous customization by the customer-user of the original control program residing in the ROM of the device, as well as configuration of control parameters of the POL. Microprocessor architecture of the device includes a dedicated logic block and a rewritable non-volatile memory coupled to the data bus of the device or to an auxiliary bus thereof, thus providing a means for software extension of the power supply circuits. RAM is loaded at start-up with data of modified or added routines for implementing new commands and values of configuration and control data of the POL. The RAM may optionally be subjected to encryption / decryption for protection. During operation, program execution jumps from ROM address space to RAM address space and vice versa when certain values of a program counter are reached.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Plasma system with integrated power supply, motion control, gas control and torch
ActiveUS20150273618A1Added user flexibilityImproved system level process controlWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusTorchEngineering
An integrated plasma cutting system includes a plasma cutting power supply and a motion control device to move a torch along a desired cut path relative to a workpiece. The system also includes a torch height control device to adjust a gap between a tip of the torch and the workpiece and a gas control device to regulate a gas used in the integrated plasma cutting system. The system further includes a centralized controller that includes an integrated microprocessor architecture that controls a sequence of the plasma arc, controls the regulation of the gas used in the integrated plasma cutting system gases, and controls coordination of the movement of the torch along the cut path with adjusting the gap without aid of an intervening microprocessor architecture in any one of the plasma cutting power supply, the motion control device, the torch height control device and the gas control device.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Automatic configuration of a microprocessor influenced by an input program
InactiveUS20050251647A1Improve performanceConcurrent instruction executionCAD circuit designControl flowComputer architecture
An automatic process for configuring a microprocessor architecture that consists of a number of execution units with configurable connectivity between them. The data and control flows within an input program are used to influence the process so that the resulting microprocessor is able to efficiently exploit parallelism available within the input program.
Owner:CRITICAL BLUE
OS Friendly Microprocessor Architecture
InactiveUS20140082298A1Improve business performanceImprove performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConcurrent instruction executionOperational systemEngineering
The present invention is a microprocessor architecture for efficiently running an operating system. The improved architecture provides higher performance, improved operating system efficiency, enhanced security, and reduced power consumption.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
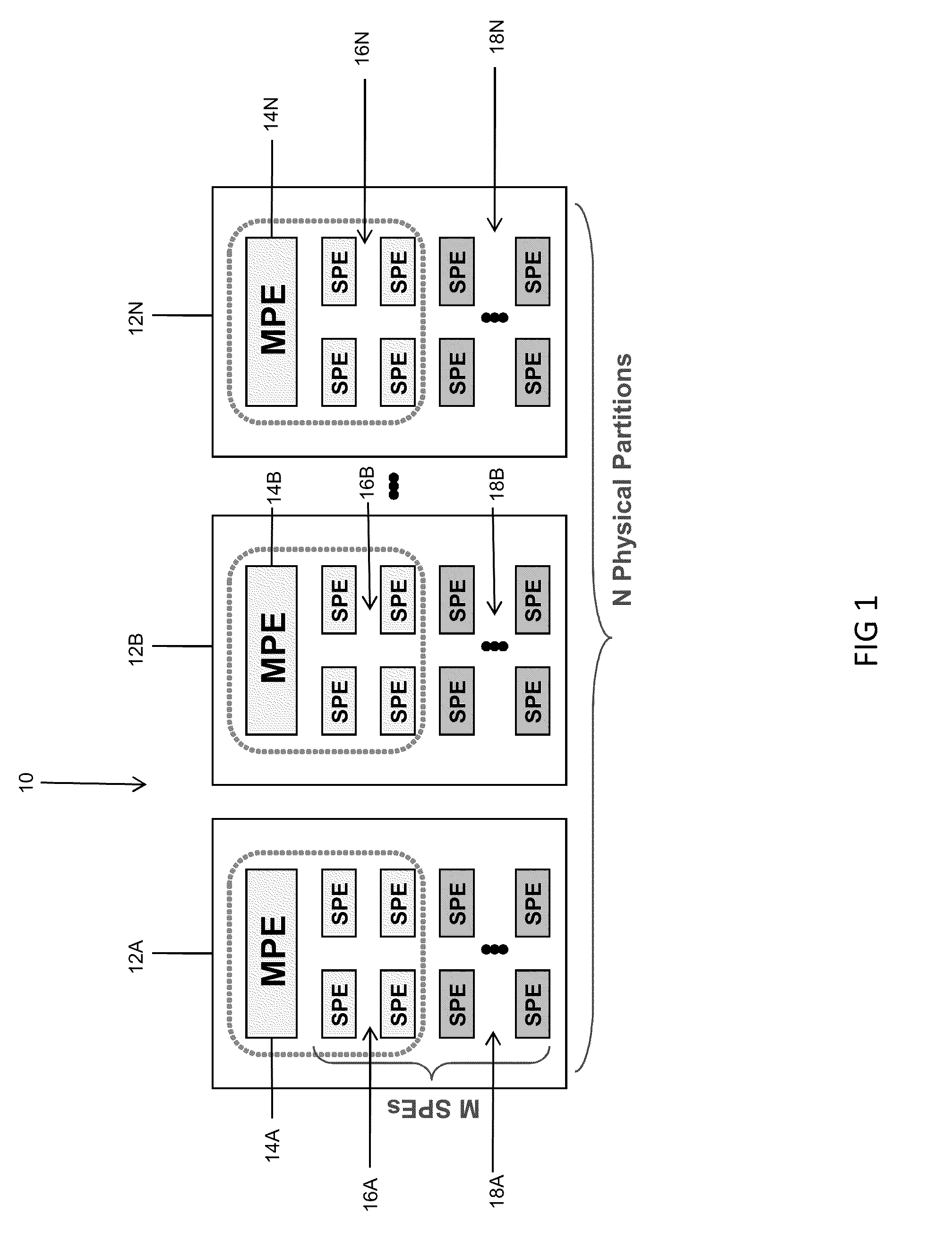
Virtualization across physical partitions of a multi-core processor (MCP)
ActiveUS20100082942A1Reduce hardwareReduce compiler design complexityEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerVirtualizationProcessing element
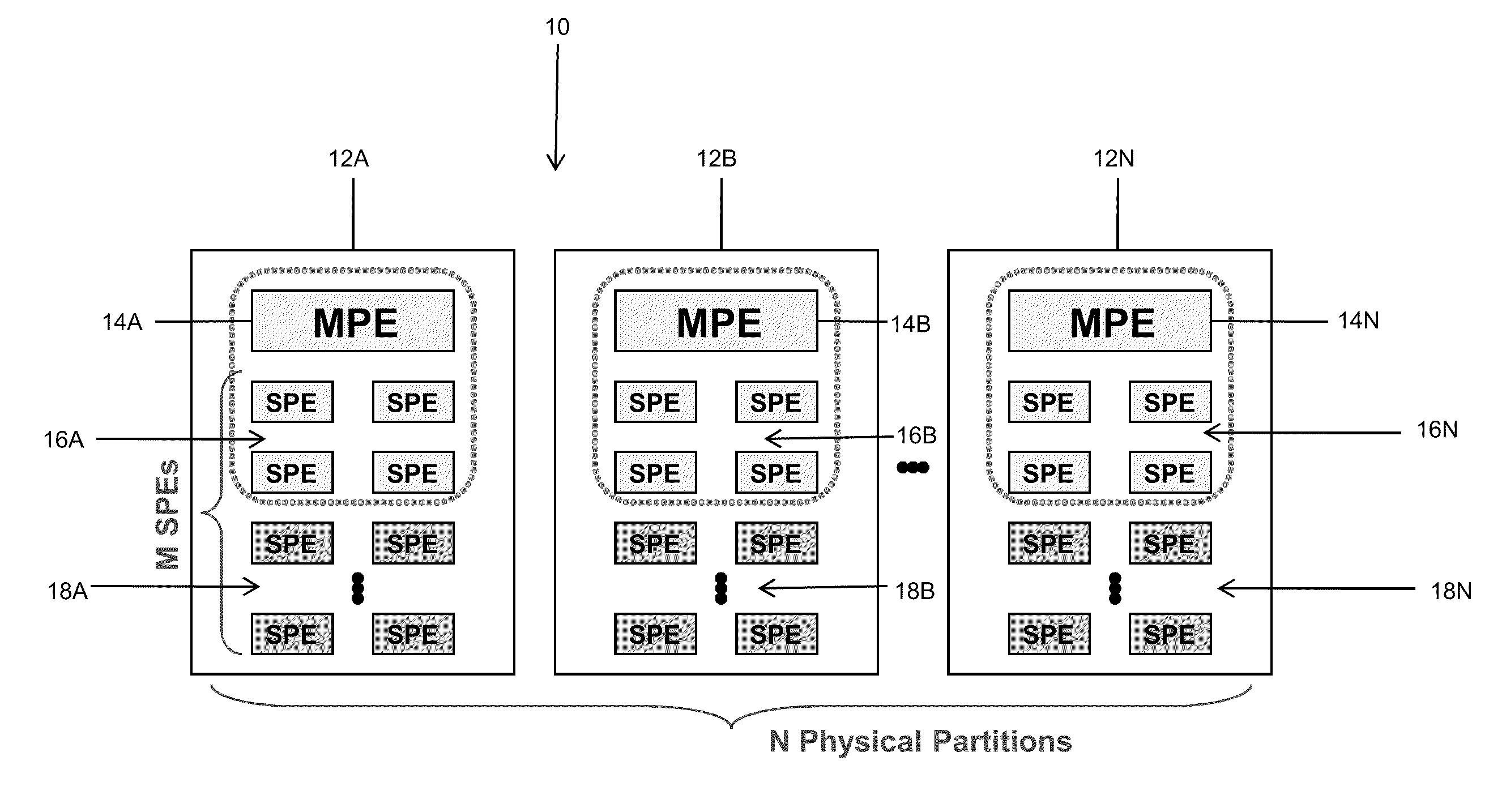
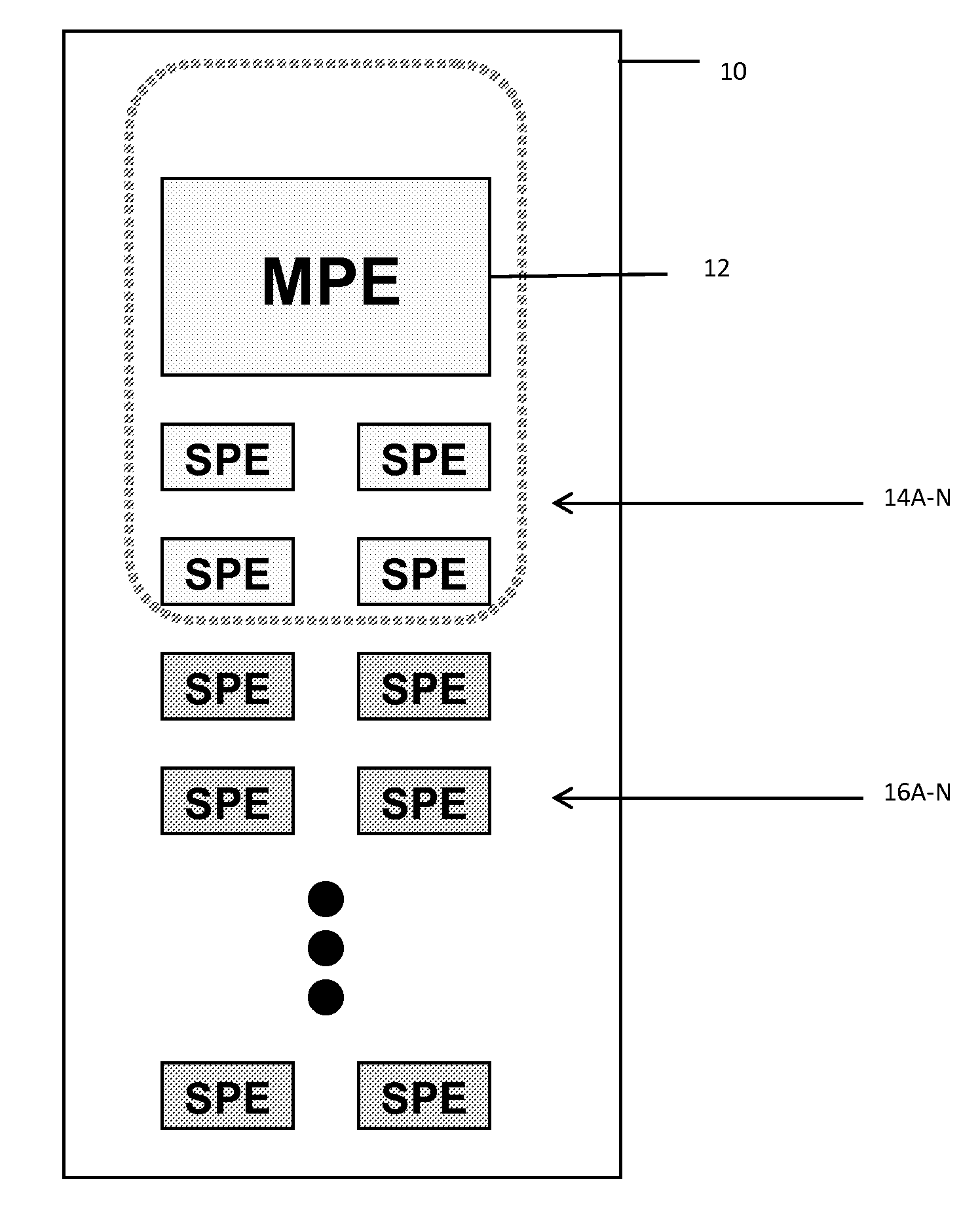
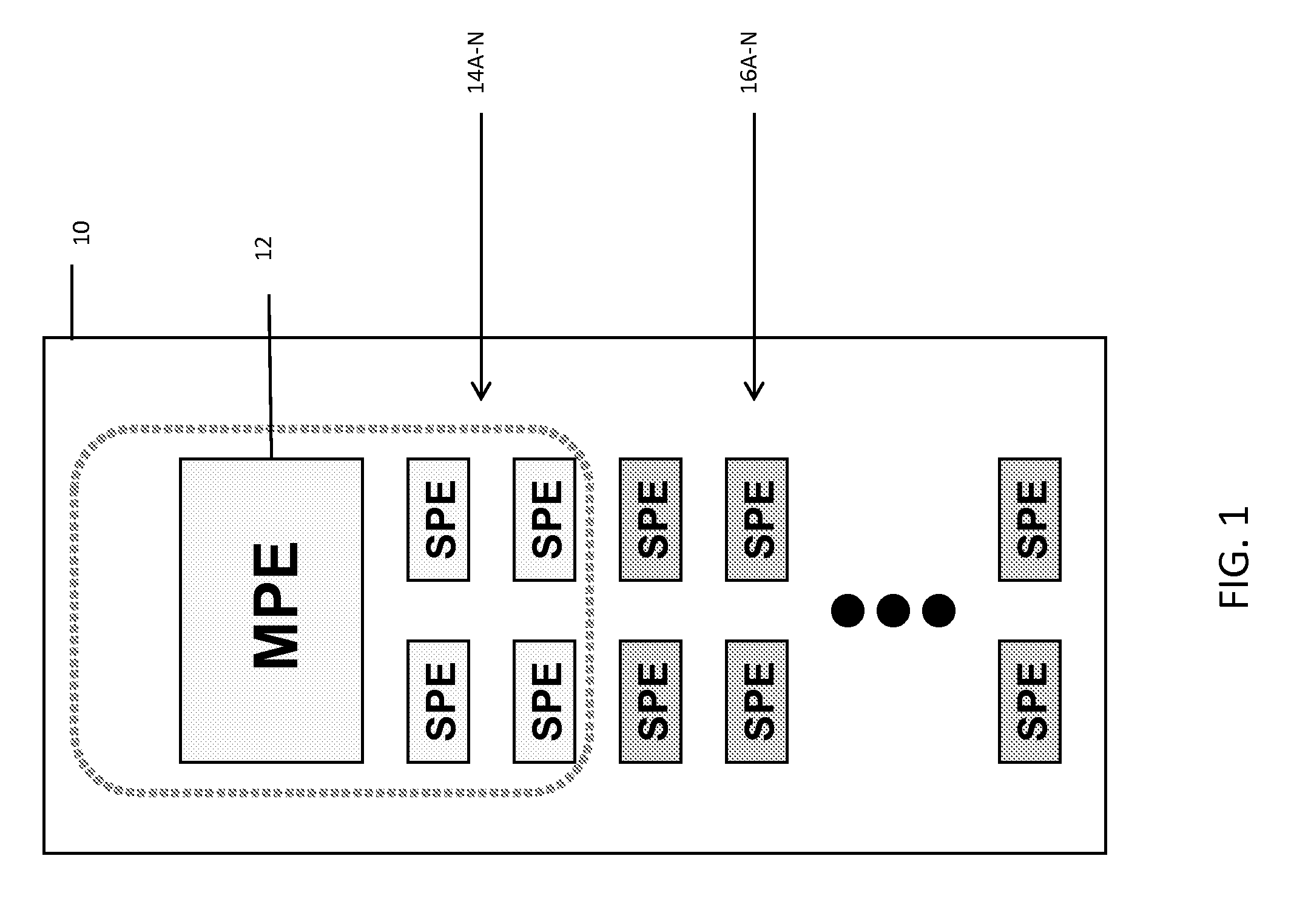
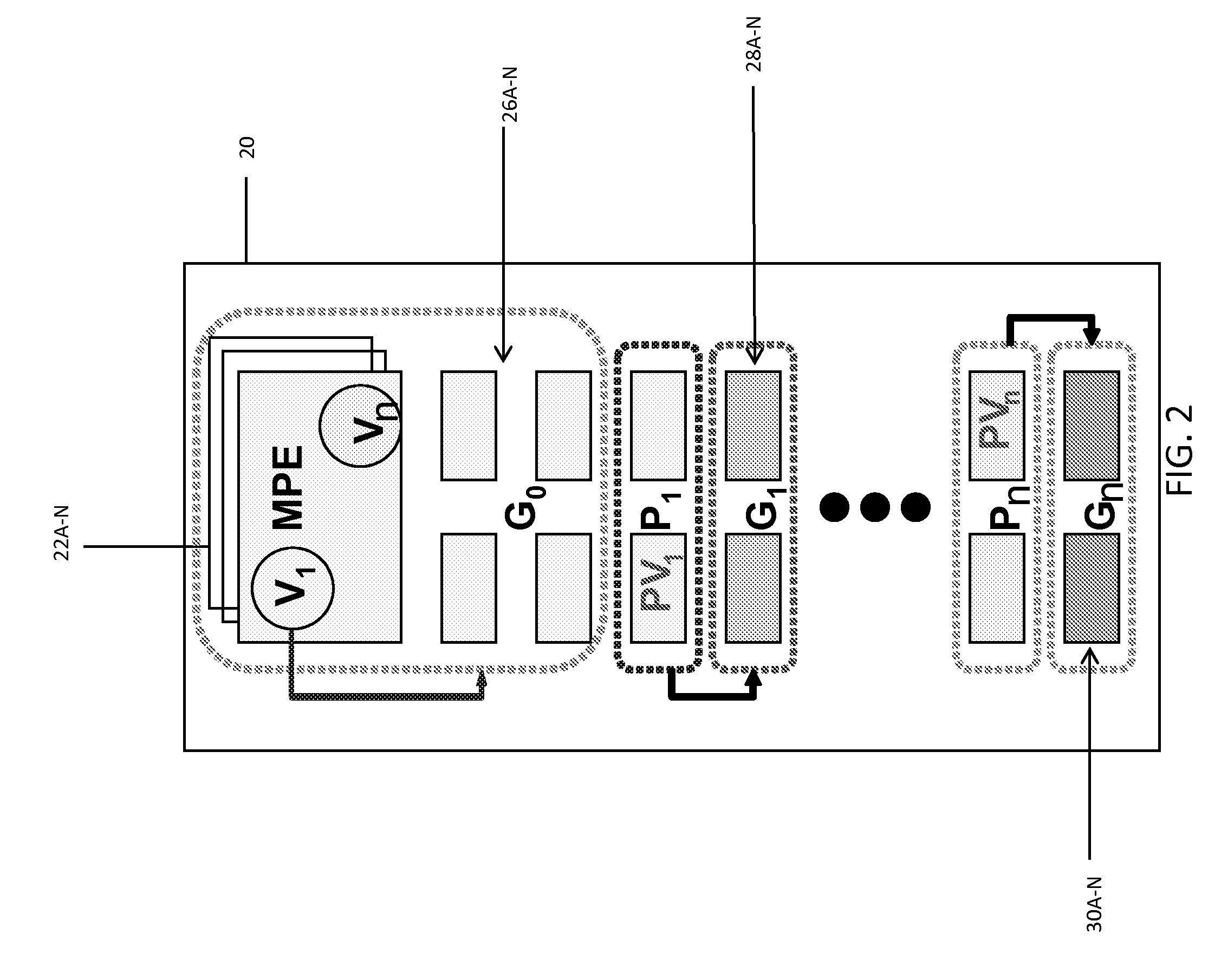
Among other things, the disclosure is applied to a generic microprocessor architecture with a set (e.g., one or more) of controlling / main processing elements (e.g., MPEs) and a set of groups of sub-processing elements (e.g., SPEs). Under this arrangement, MPEs and SPEs are organized in a way that a smaller number MPEs control the behavior of a group of SPEs using program code embodied as a set of virtualized control threads. The apparatus includes a MCP coupled to a power supply coupled with cores to provide a supply voltage to each core (or core group) and controlling-digital elements and multiple instances of sub-processing elements. In accordance with these features, virtualized control threads can traverse the physical boundaries of the MCP to control SPE(s) (e.g., logical partitions having one or more SPEs) in a different physical partition (e.g., different from the physical partition from which the virtualized control threads originated.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
High-performance superscalar-based computer system with out-of-order instruction execution and concurrent results distribution
InactiveUS7555632B2Easy to modifyRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerInstruction memoryFloating point
The high-performance, RISC core based microprocessor architecture includes an instruction fetch unit for fetching instruction sets from an instruction store and an execution unit that implements the concurrent execution of a plurality of instructions through a parallel array of functional units. The fetch unit generally maintains a predetermined number of instructions in an instruction buffer. The execution unit includes an instruction selection unit, coupled to the instruction buffer, for selecting instructions for execution, and a plurality of functional units for performing instruction specified functional operations. A unified instruction scheduler, within the instruction selection unit, initiates the processing of instructions through the functional units when instructions are determined to be available for execution and for which at least one of the functional units implementing a necessary computational function is available. Unified scheduling is performed across multiple execution data paths, where each execution data path, and corresponding functional units, is generally optimized for the type of computational function that is to be performed on the data: integer, floating point, and boolean. The number, type and computational specifics of the functional units provided in each data path, and as between data paths, are mutually independent.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
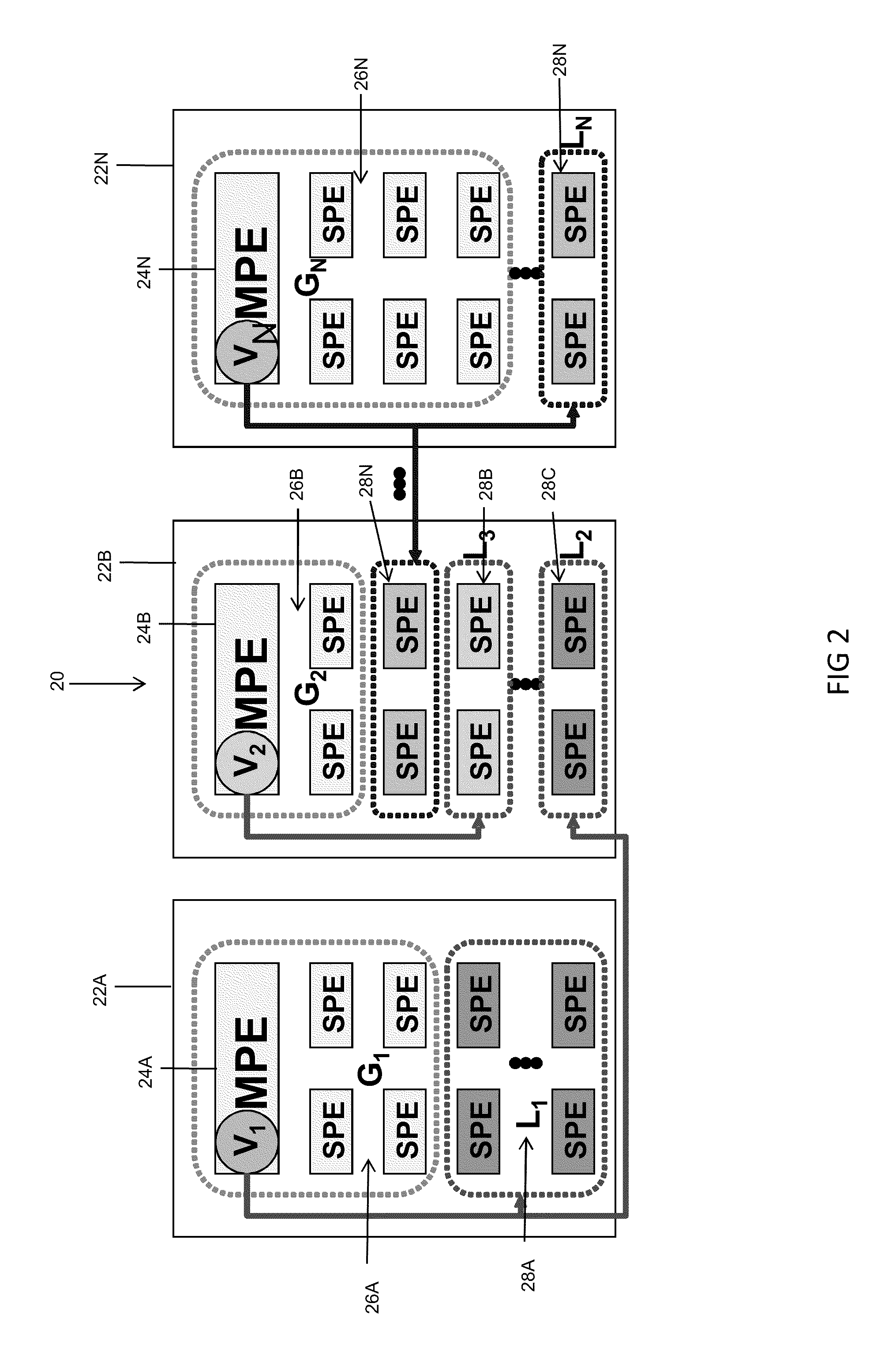
Delegated virtualization in a multi-core processor (MCP)
ActiveUS20100082941A1Energy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsData virtualizationProcessing element
The disclosure is applied to a generic microprocessor architecture with a set (e.g., one or more) of controlling elements (e.g., MPEs) and a set of groups of sub-processing elements (e.g., SPEs). Under this arrangement, MPEs and SPEs are organized in a way that a smaller number MPEs control the behavior of a group of SPEs using program code embodied as a set of virtualized control threads. The arrangement also enables MPEs delegate functionality to one or more groups of SPEs such that those group(s) of SPEs will act as pseudo MPEs. The pseudo MPEs will utilize pseudo virtualized control threads to control the behavior of other groups of SPEs. In a typical embodiment, the apparatus includes a MCP coupled to a power supply coupled with cores to provide a supply voltage to each core (or core group) and controlling-digital elements and multiple instances of sub-processing elements.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com