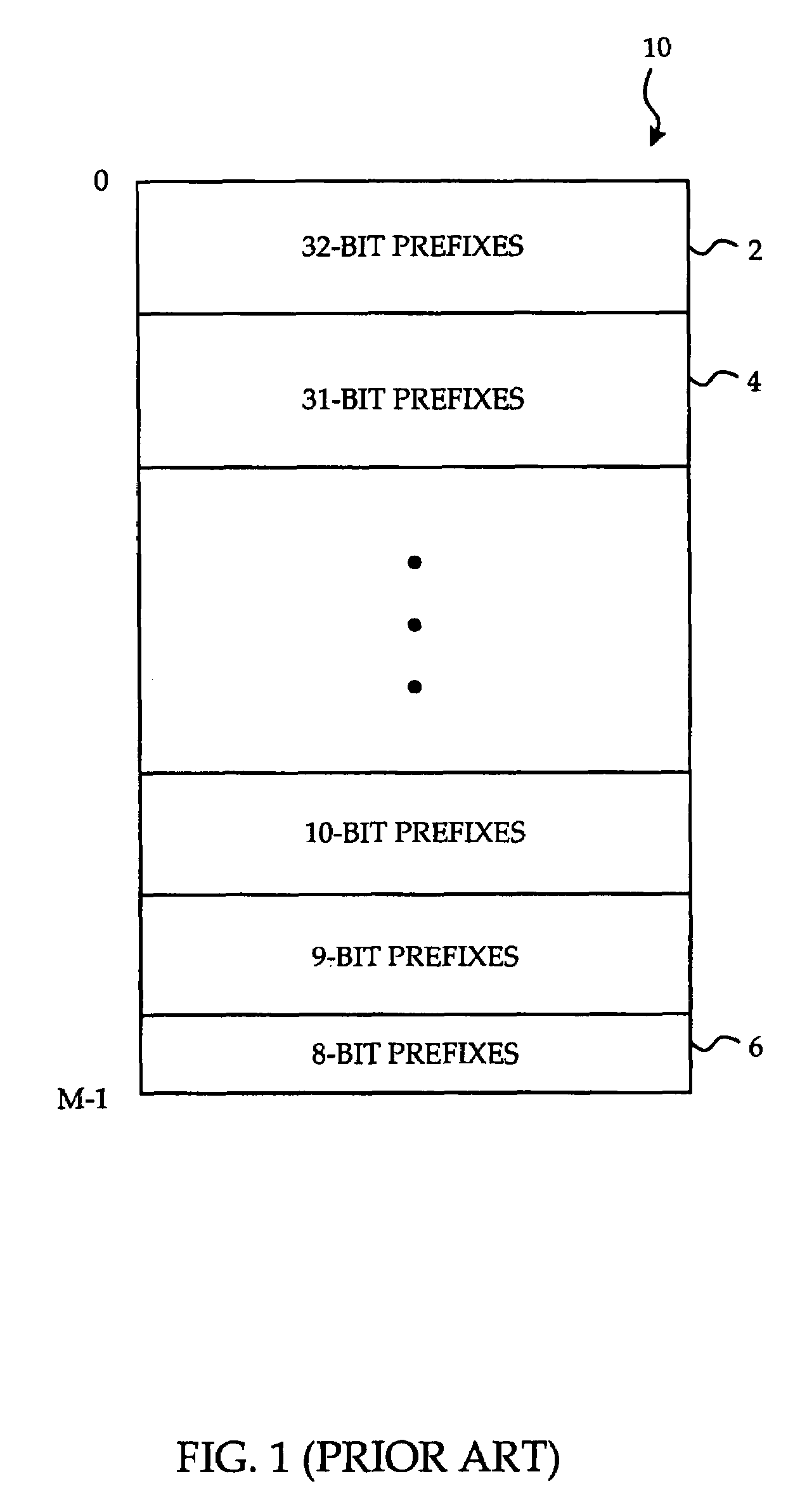
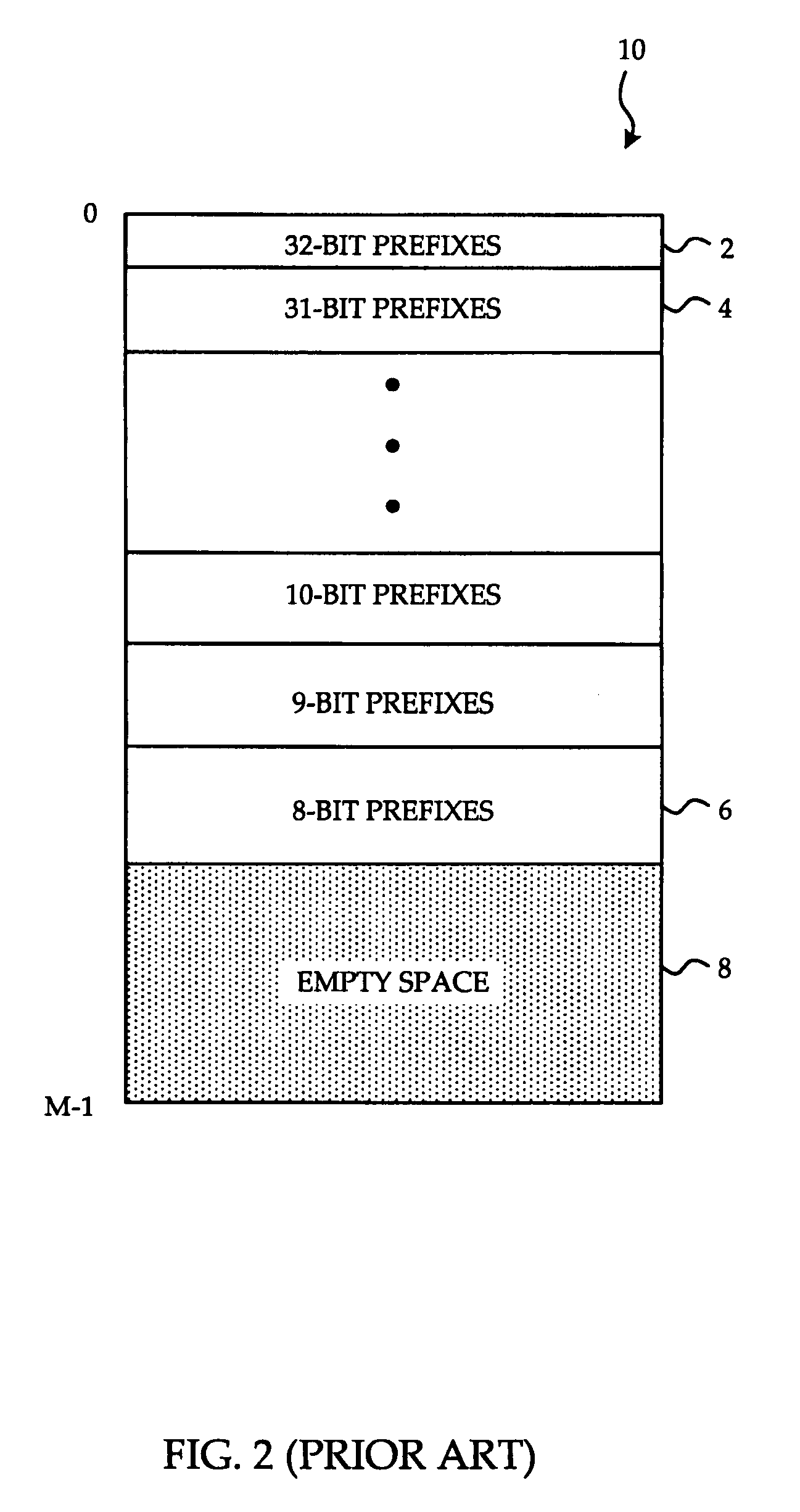
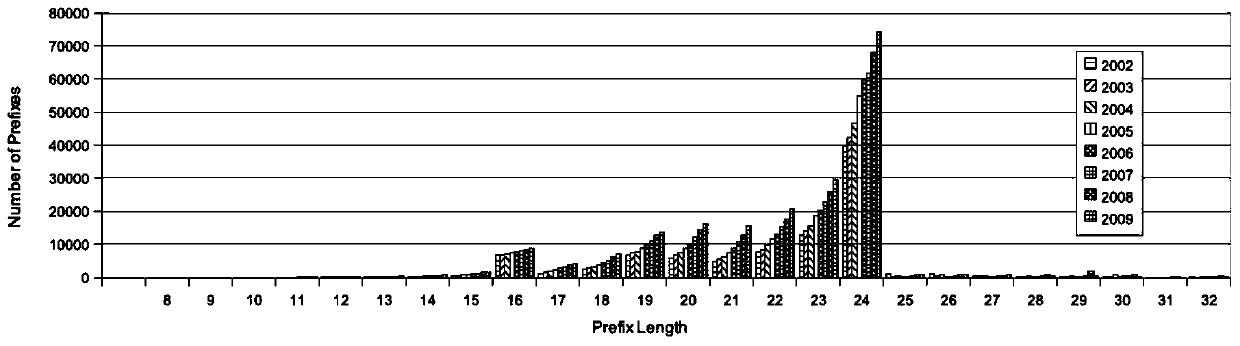
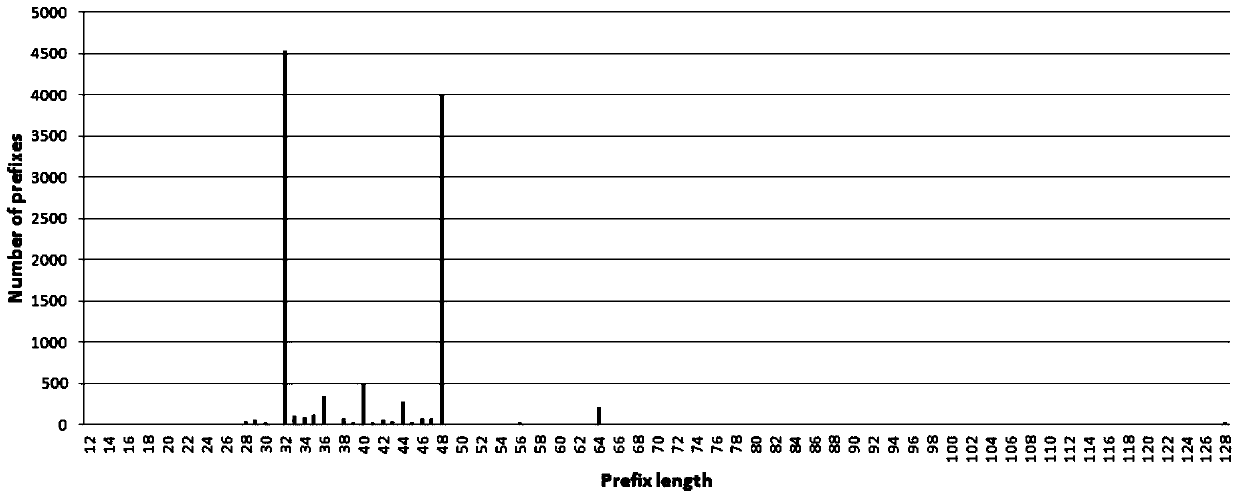
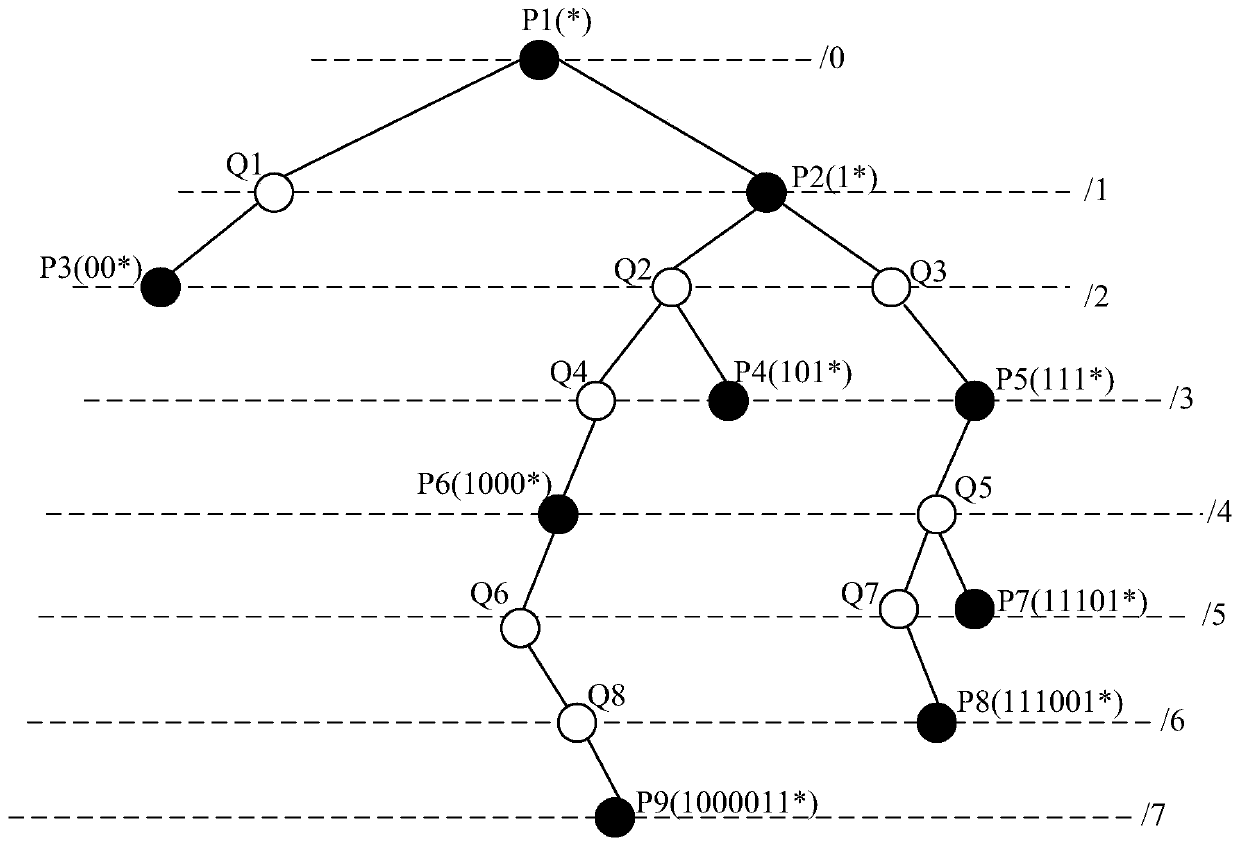
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Ip prefix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
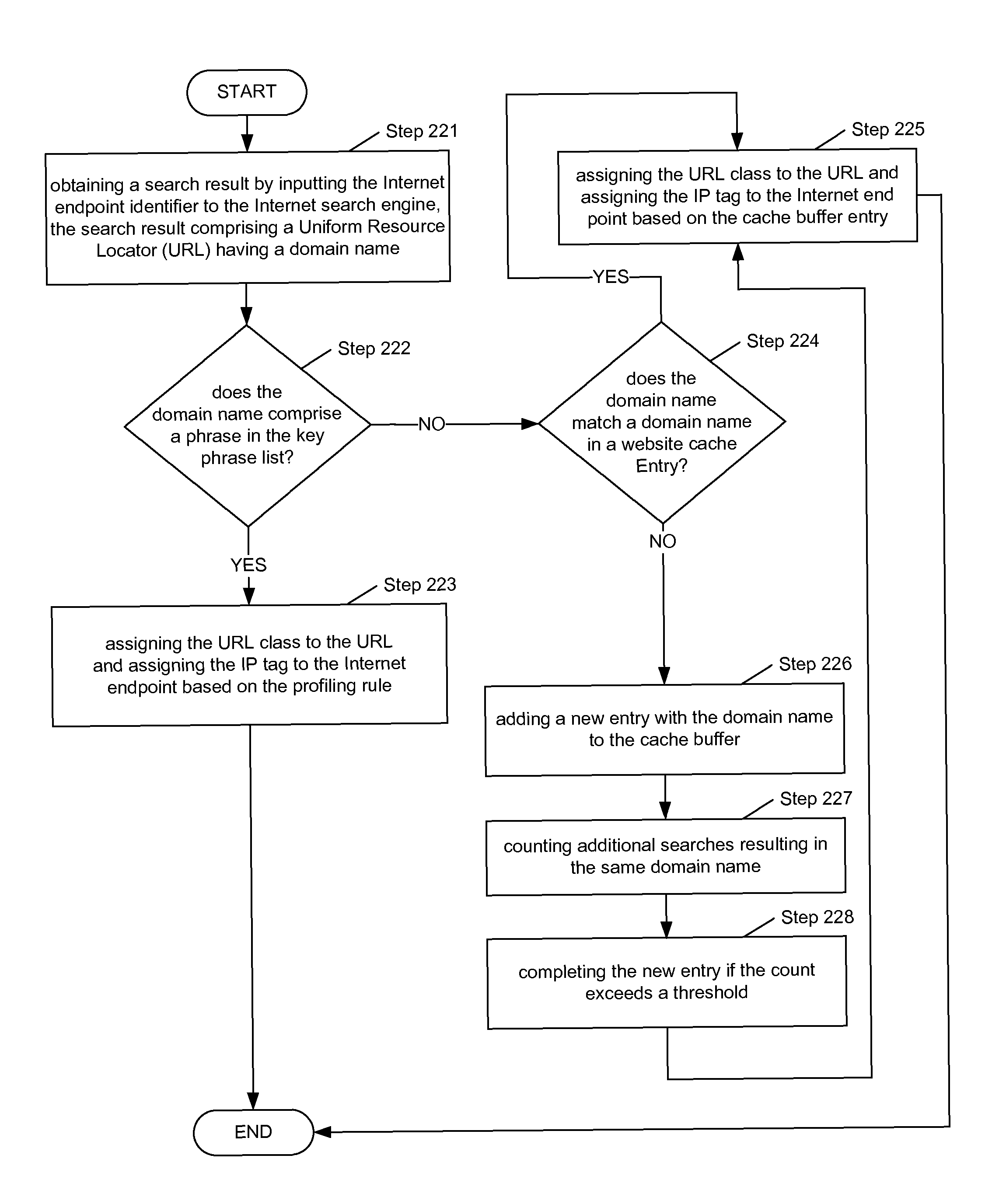
TLDR: an IP address prefix is the fixed part in a contiguous block of IP address, also know as a subnet. Prefixes are useful to refer to the entire subnet for planning, documentation, and routing purposes. Now for the long answer.
Approach for fast IP address lookups
ActiveUS20080056262A1Improve performanceIncrease in sizeData switching by path configurationIp address16-bit
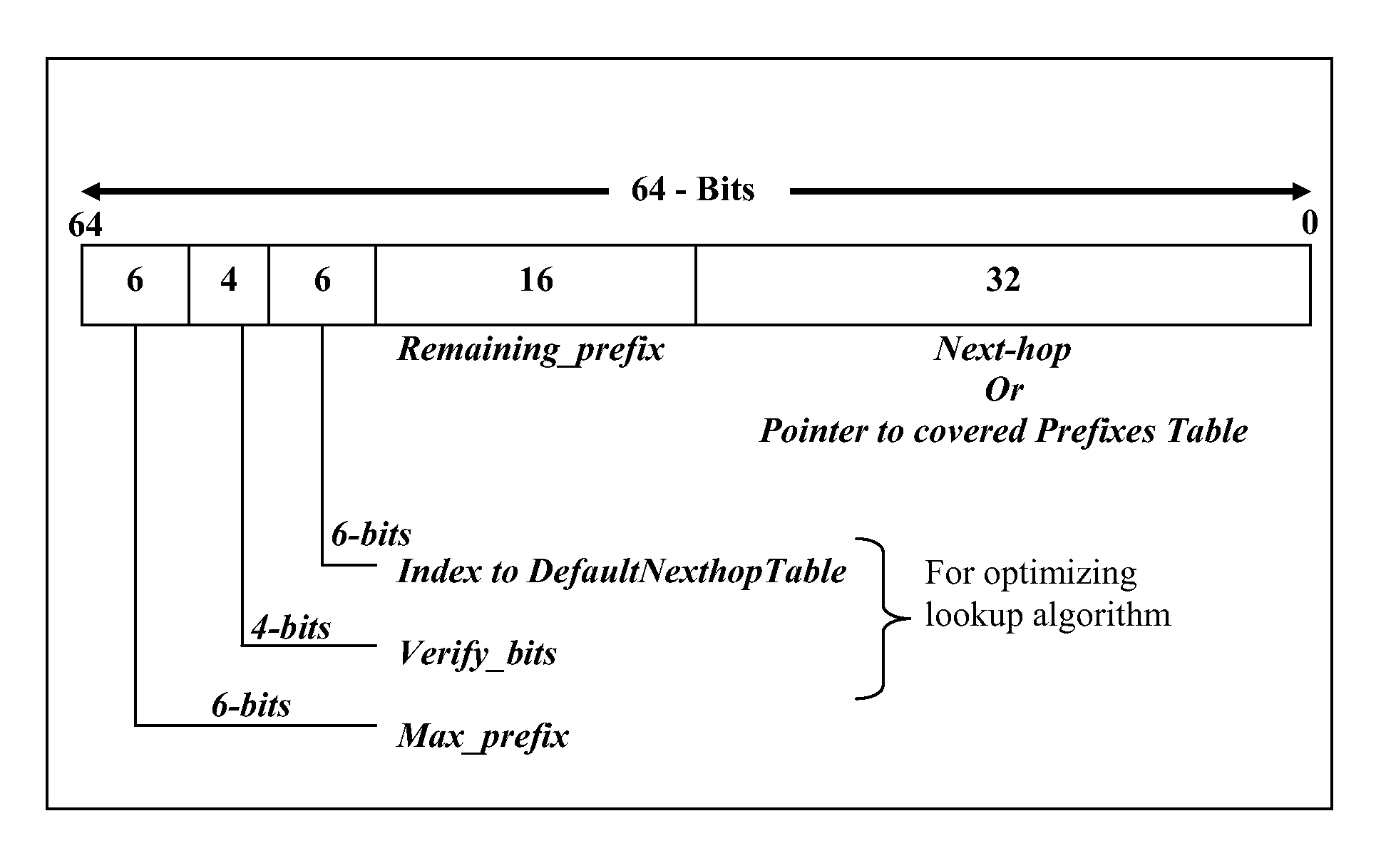
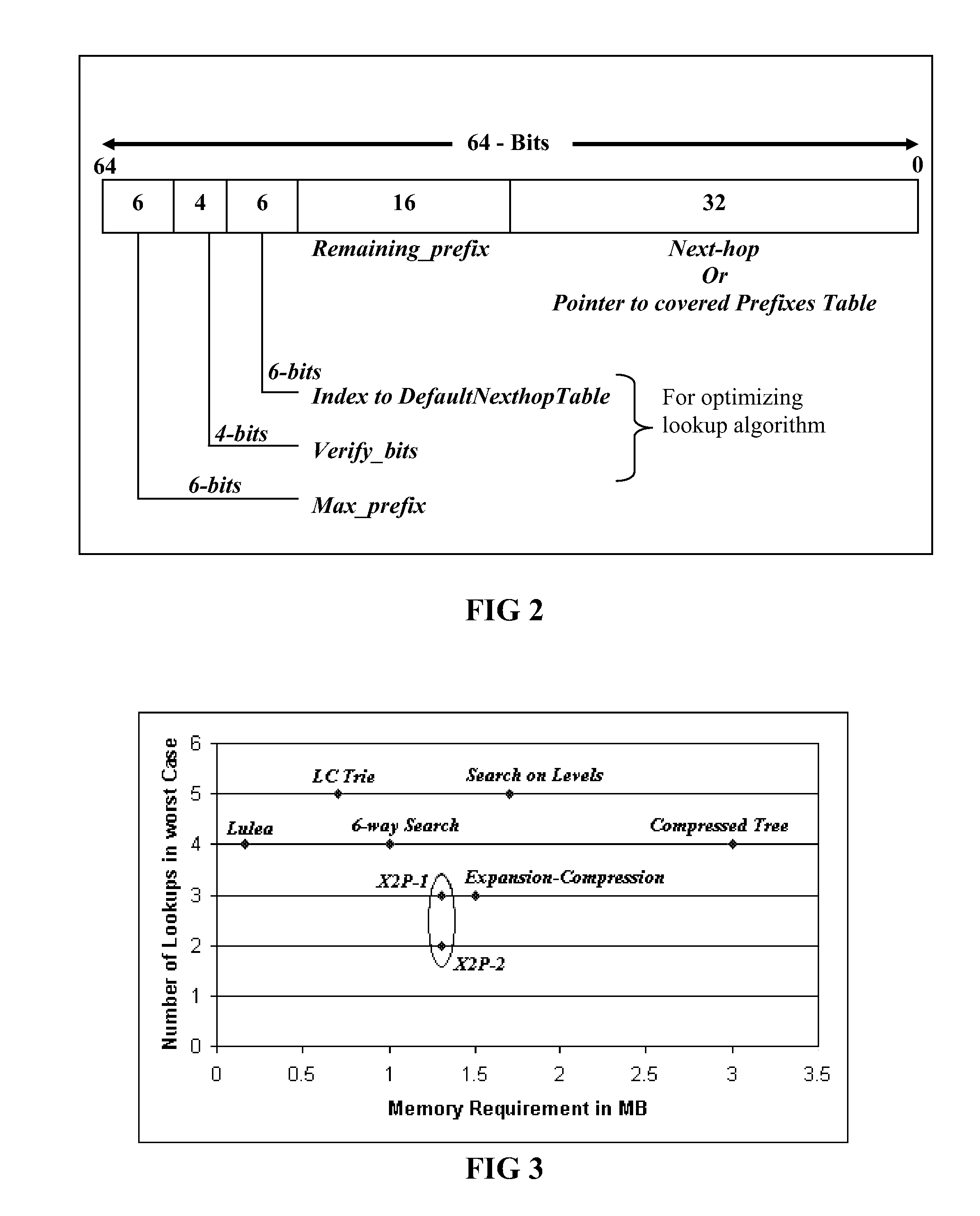
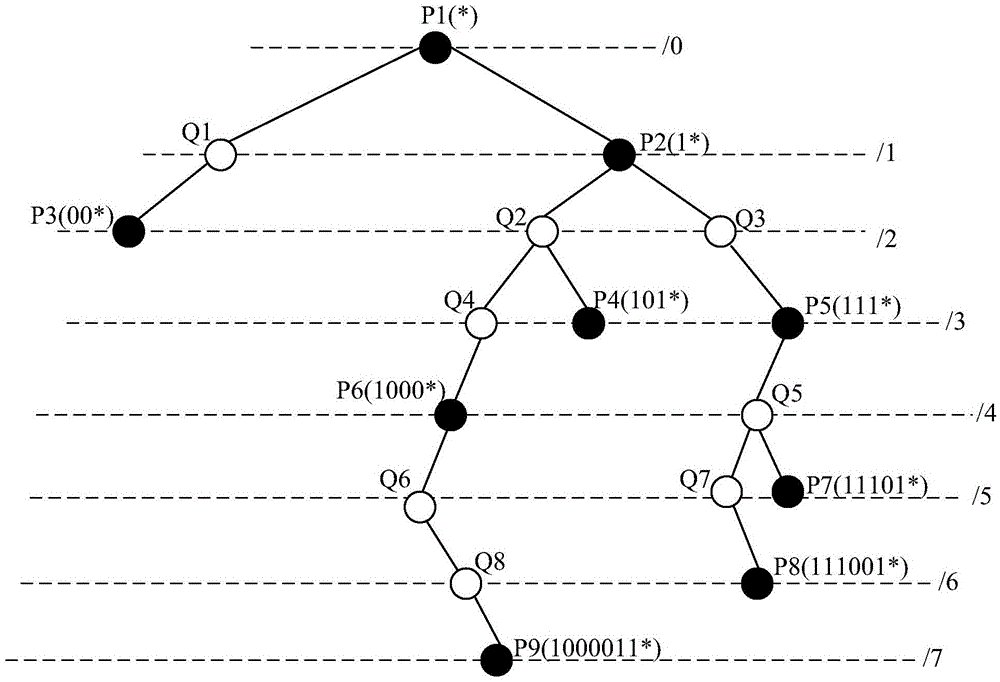
A method and algorithm for IP address lookup for packet forwarding, finds a longest prefix match for a destination address of n bits, using 2n / 2 entries in a lookup table, expanding a given IP address to be matched if its prefix length is more than n / 2, and, completing a lookup operation using the table. The number ‘n” may be 32 or otherwise. An example teaches an IP address lookup table with a maximum address size of 32 bits, using a lookup table with 216 entries. Further, if an IP prefix length is more than 16 bits, then the given address to be matched is expanded to its full prefix length before the lookup operation. The algorithm takes only two memory references for specific hardware, such as IXP1200. For generic hardware, it takes only three memory references. Also taught is a computer readable medium having the method encoded therein.
Owner:WIPRO LTD
Method for defending border gateway protocol prefix hijacking attack
InactiveCN102158469AAllocation is accurateFree from hijackingPublic key for secure communicationBorder Gateway ProtocolAccreditation
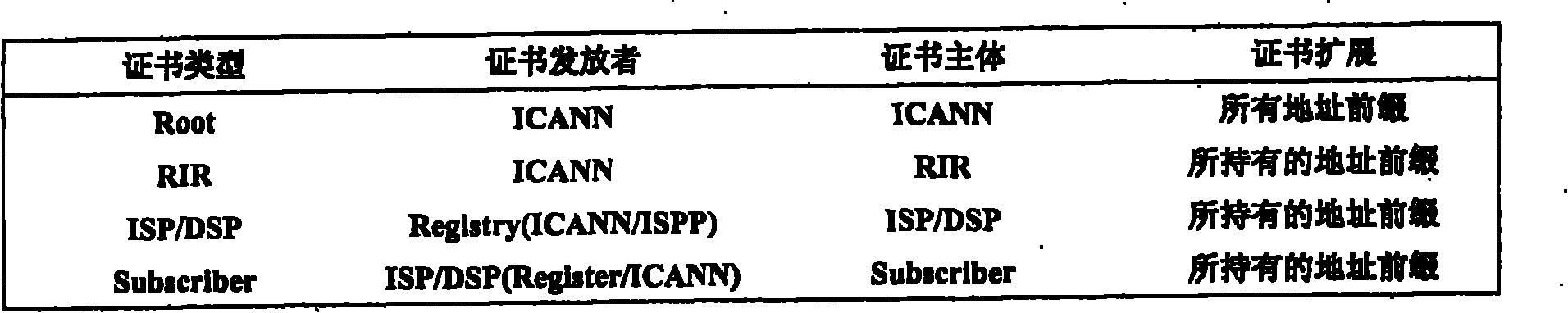
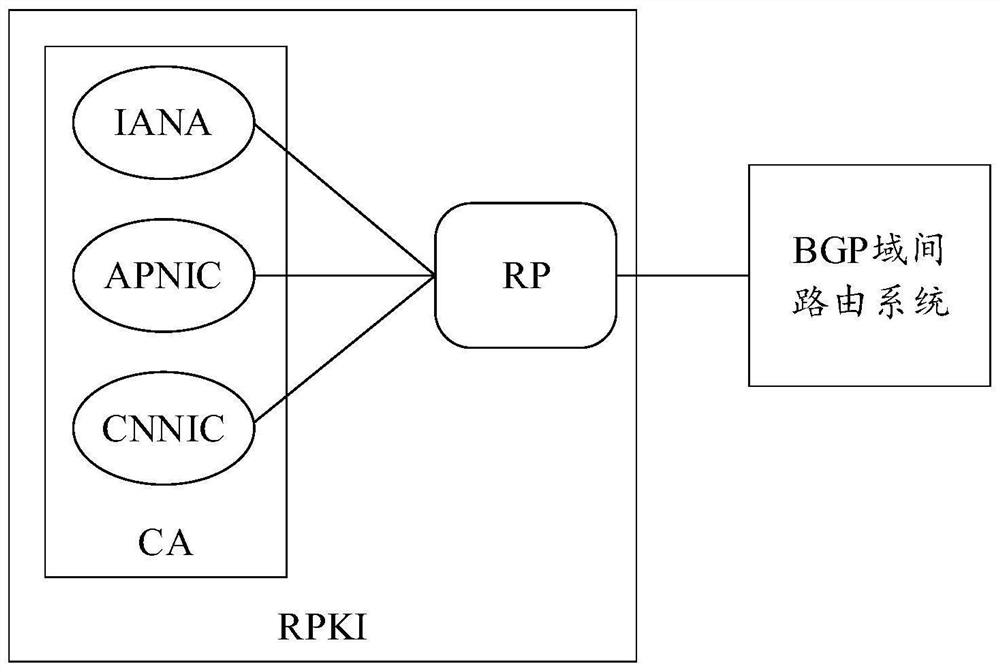
The invention discloses a method for defending border gateway protocol prefix hijacking attack. Firstly, a layered dispatching system is structured according to IP (Internet Protocol) prefix and AS numbers to assign PKIs (Public Key Infrastructures), and two types of the PKIs based on the IP prefix and the AS number are assigned; the two types of PKIs respectively comprise IP prefix assignment certification and AS number assignment certification; the PKI is updated according to the assignment and revocation of the IP prefix and the AS number; the assignment of the PKI adopts the method that an ISP (Internet Service Provider) builds a assignment library; and when the IP prefix and announce messages of AS reach a router, verification is performed, a public key is validated firstly, then an assignment certificate and connectivity are validated, and the accreditation of the IP prefix or the AS number is validated. The method can protect an inter-domain routing system from the attacking of prefix hijacking, IP subnetwork prefix hijacking and particularly upper layer ISP prefix hijacking, and simultaneously can effectively prevent IP prefix AS path hijacking and IP subnetwork prefix AS path hijacking.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
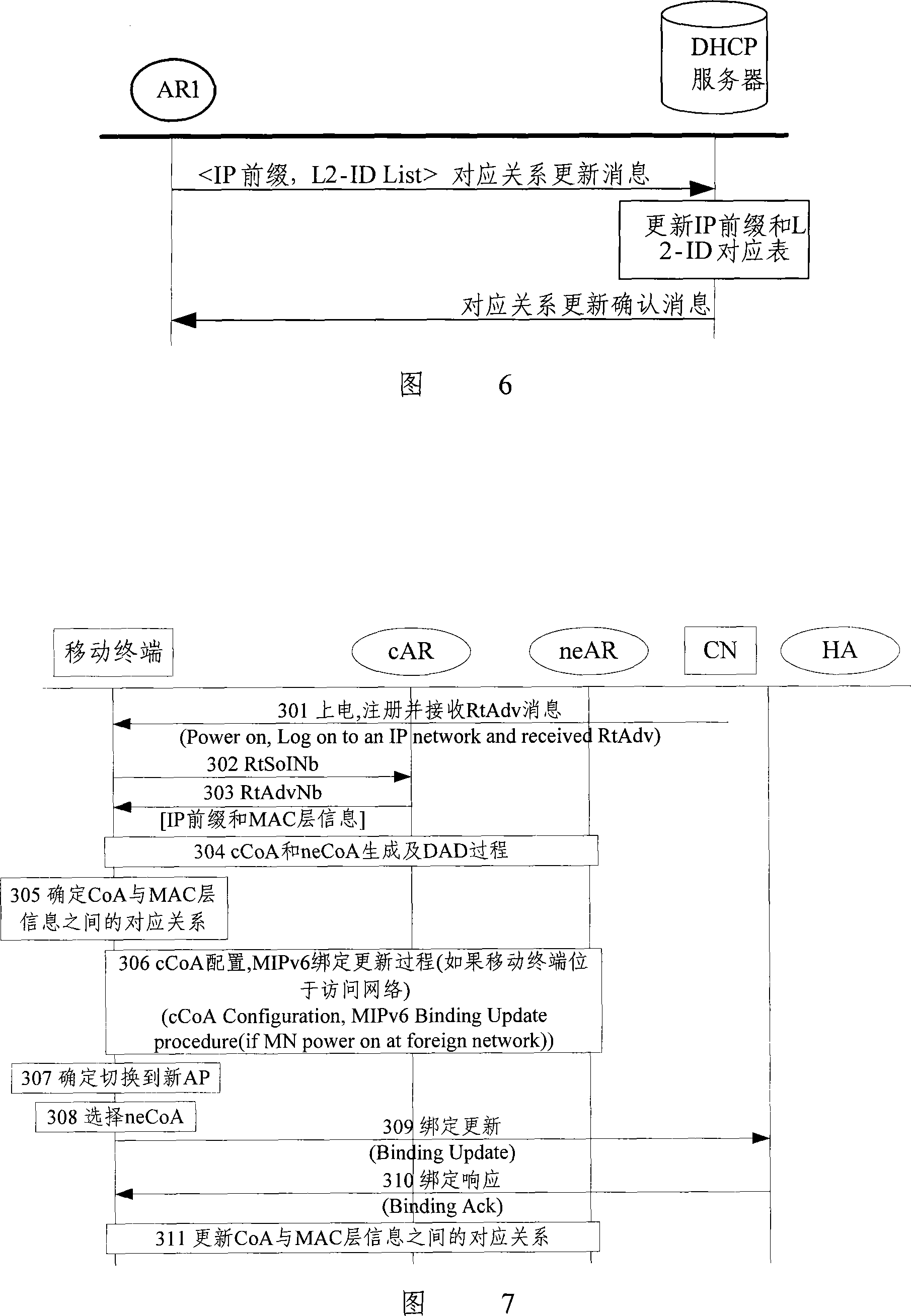
IP address configuration and mobile detection method for mobile IP
ActiveCN101127727ALatency for Simplified ConfigurationResolve address conflictsData switching by path configurationNetwork data managementIp addressIp prefix
The utility model discloses an IP address configuring and mobile detecting method for the mobile IP, comprising the following steps, a piece of access equipment gets an IP prefix and a corresponding access area identification list; a terminal gets the IP prefix of each access device and the corresponding access area identification list, the terminal gets an IP address which can be used according to the IP prefix and the access area identification list; regarding to each IP prefix, terminal gets the IP address which can be used according to the IP prefixes, tests the IP address repeatedly and sets up and stores the corresponding relationship between the IP address which are repeatedly inspected and the access area identification list. The terminal is state or stateless.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
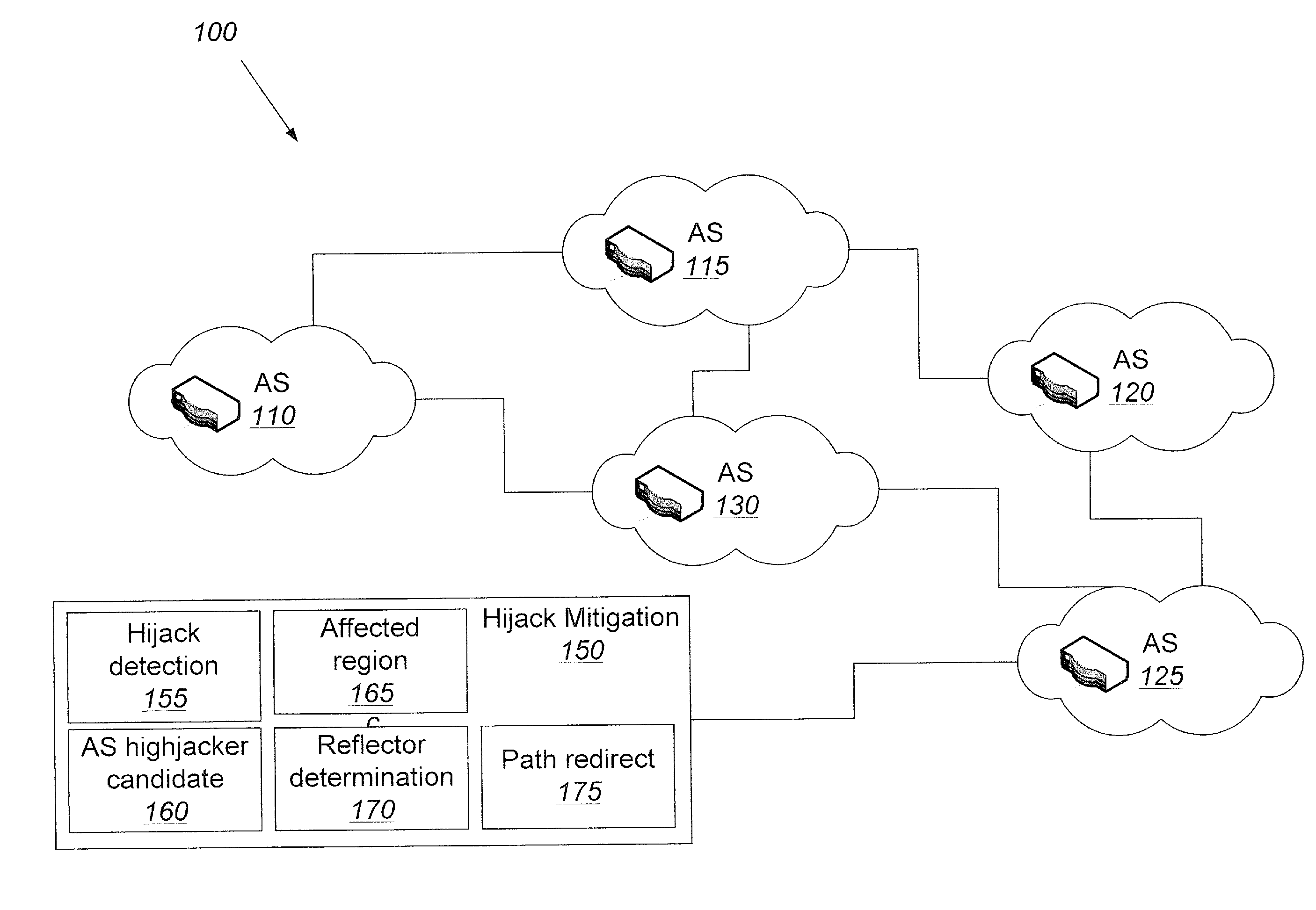
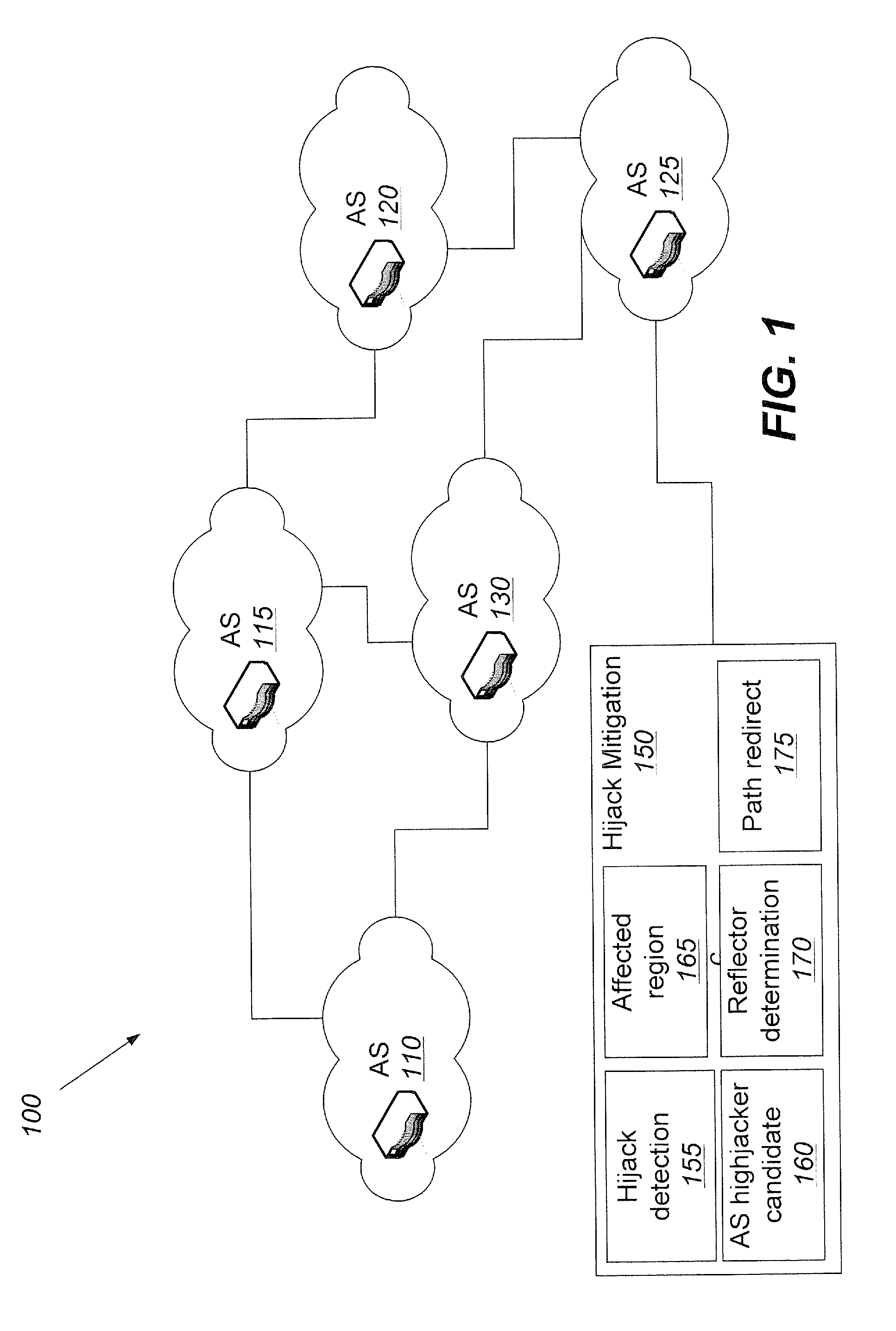
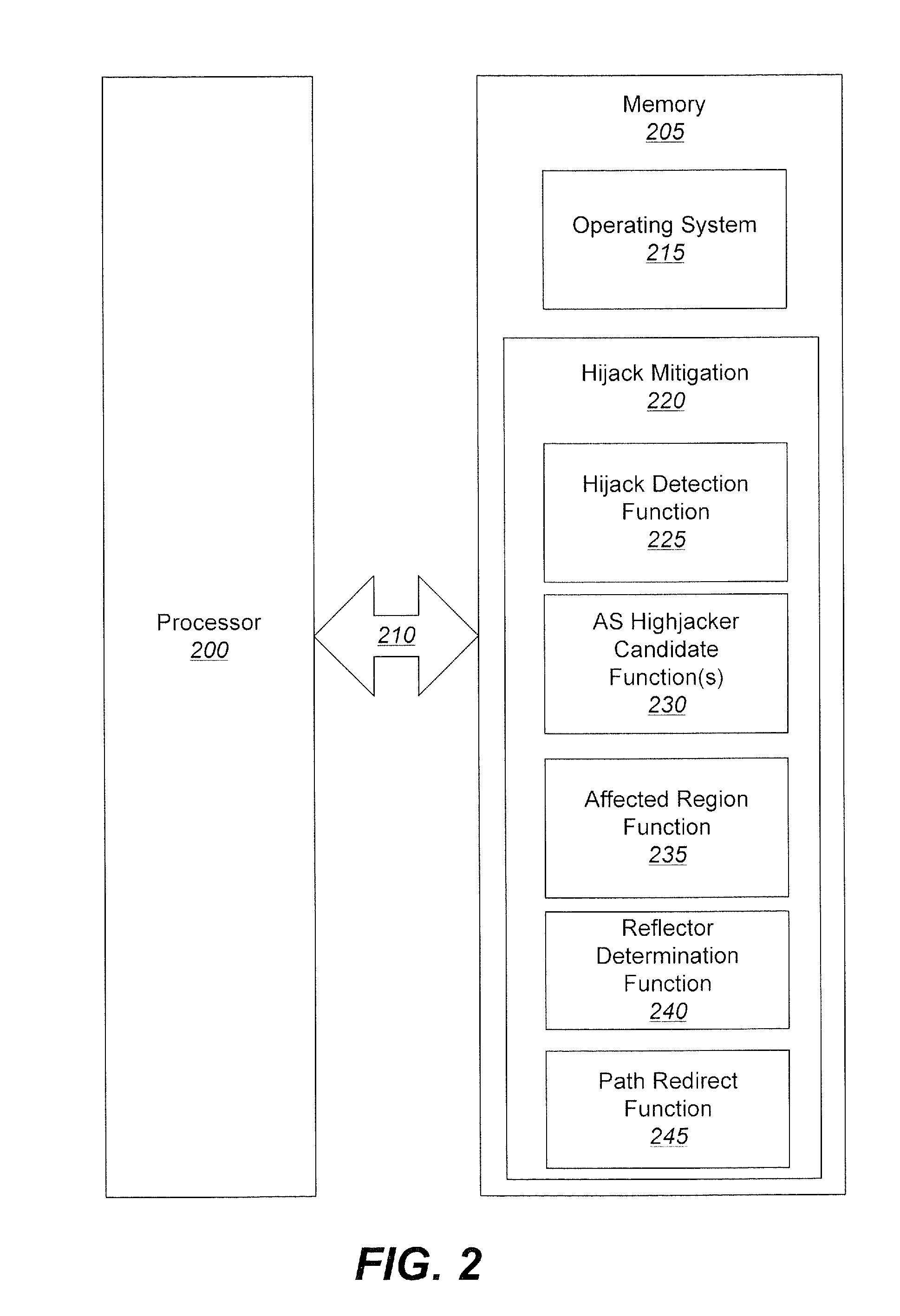
Methods, systems, and computer program products for protecting against IP prefix hijacking
InactiveUS20110138466A1Limit scopeWell formedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionIp prefixDistributed computing
A communication network is operated by identifying at least one potential hijack autonomous system (AS) that can be used to generate a corrupt routing path from a source AS to a destination AS. For each of the at least one potential hijack AS the following operations are performed: identifying at least one regional AS that is configured to adopt the corrupt routing path from the source AS to the destination AS and determining a reflector AS set such that, for each reflector AS in the set, a source AS to reflector AS routing path and a reflector AS to destination AS routing path do not comprise any of the at least one regional AS. A reflector AS is then identified that is common among the at least one reflector AS set responsive to performing the identifying and determining operations for each of the at least one potential hijack AS.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
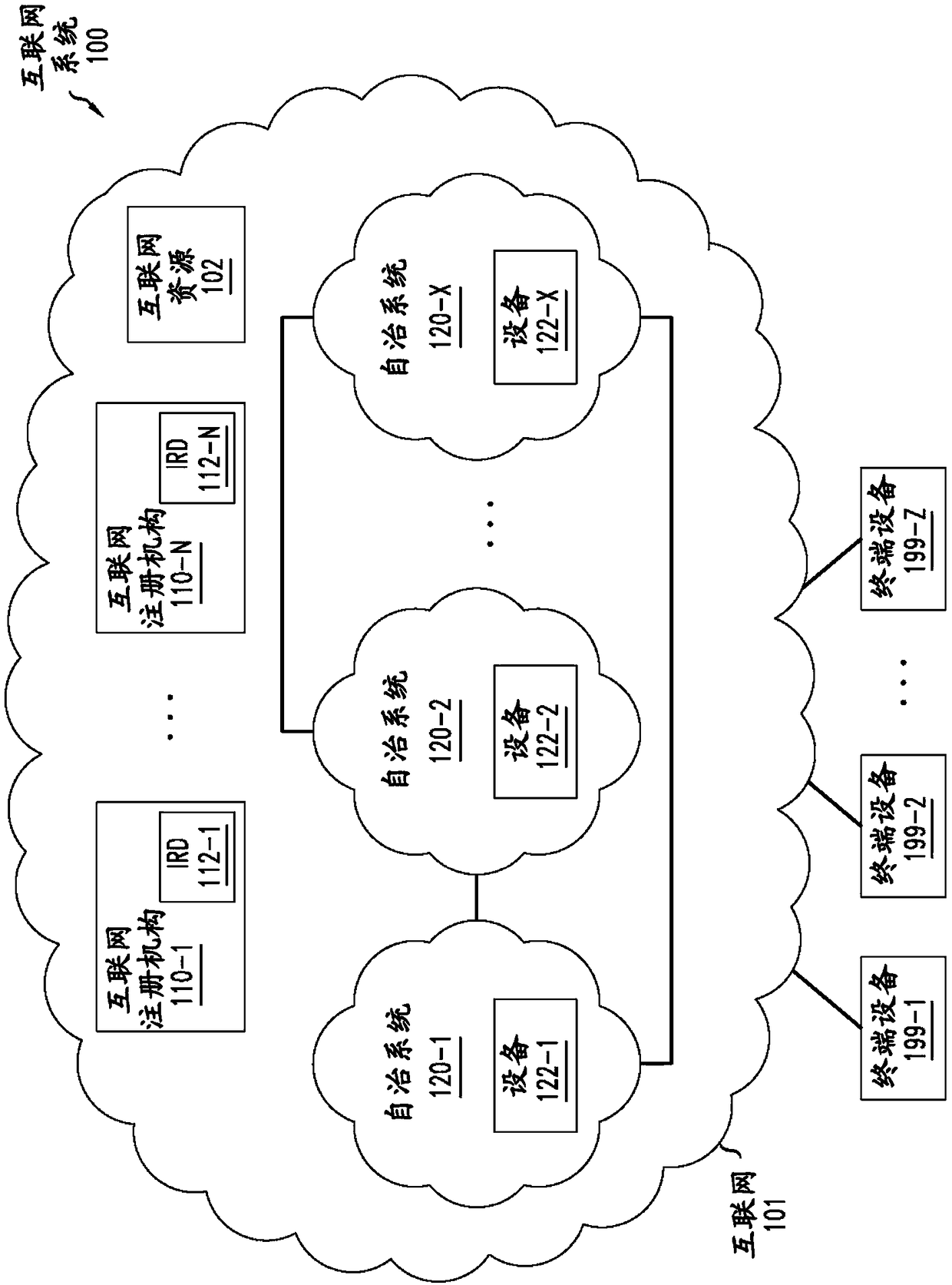
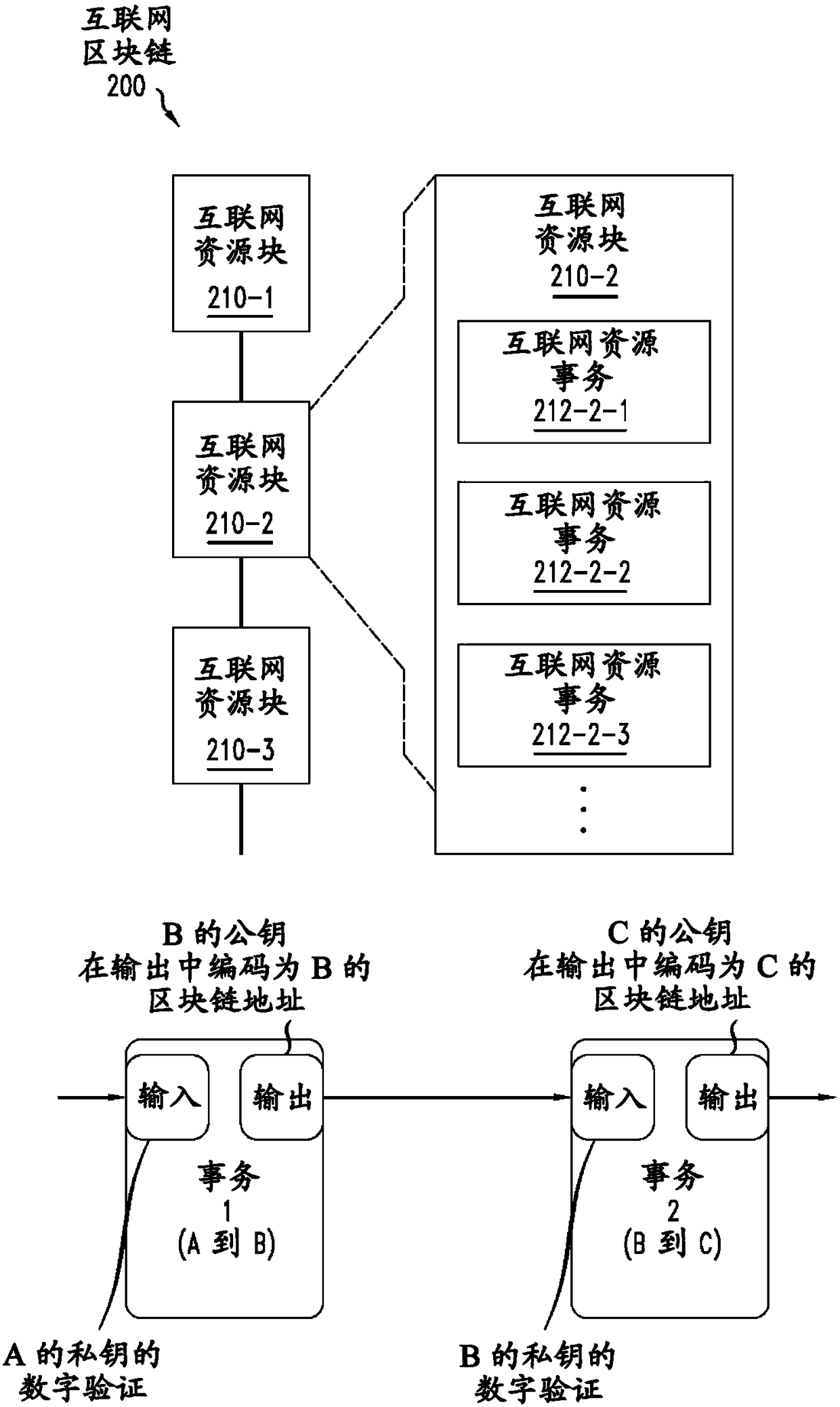
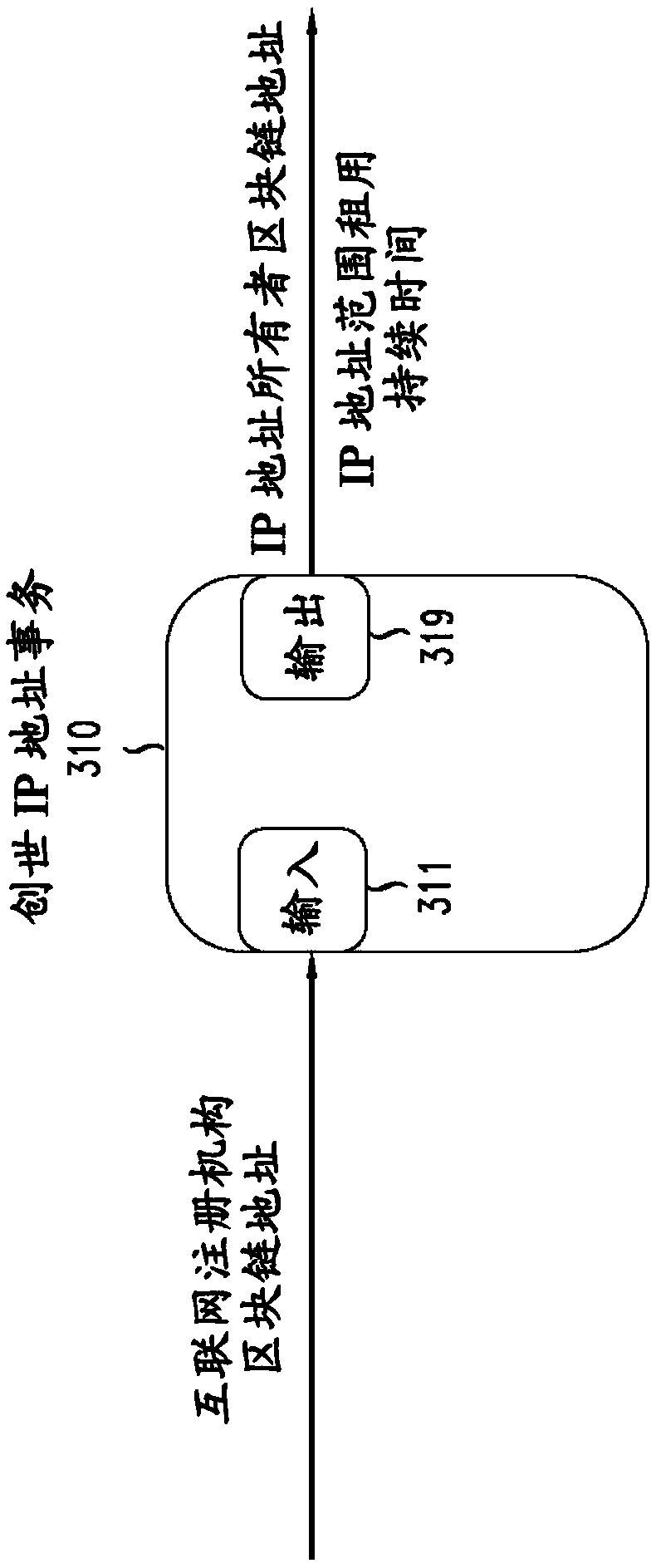
Securing transactions for allocation of internet resources with blockchain
Owner:NOKIA OF AMERICA CORP
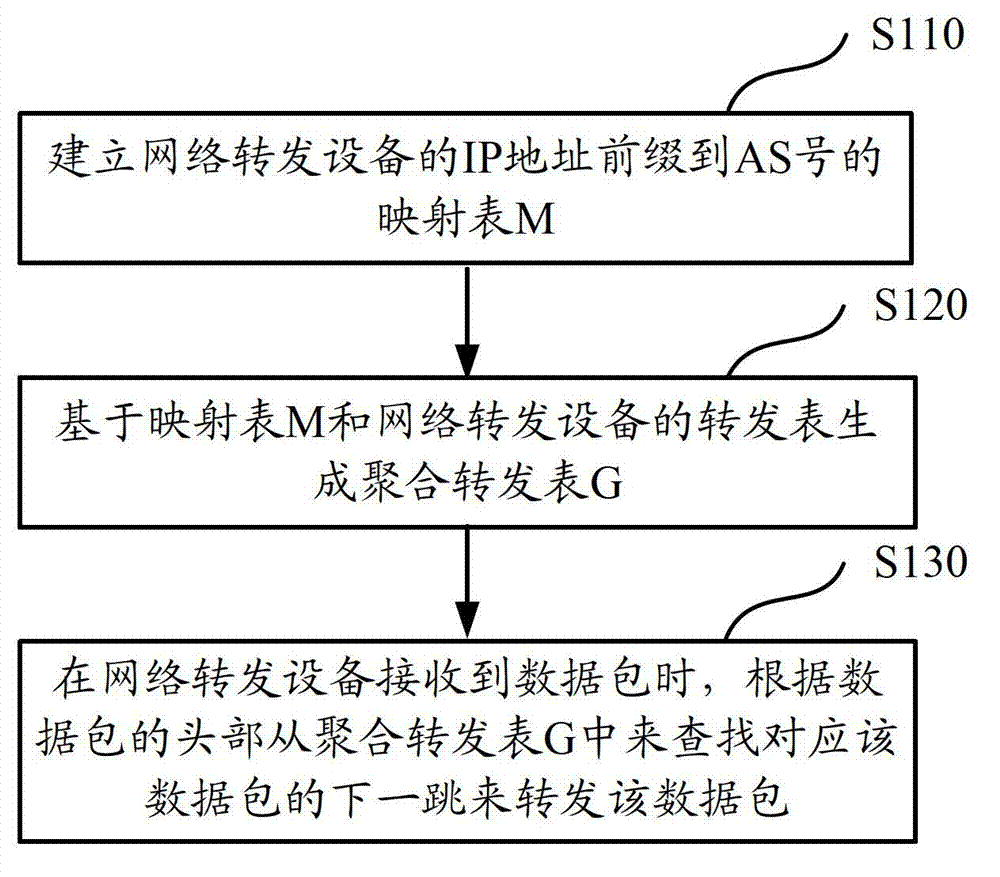
Internetwork routing method and network forwarding equipment
ActiveCN103179038AEnhance aggregation abilityMeet actual needsData switching networksTraffic capacityTTEthernet
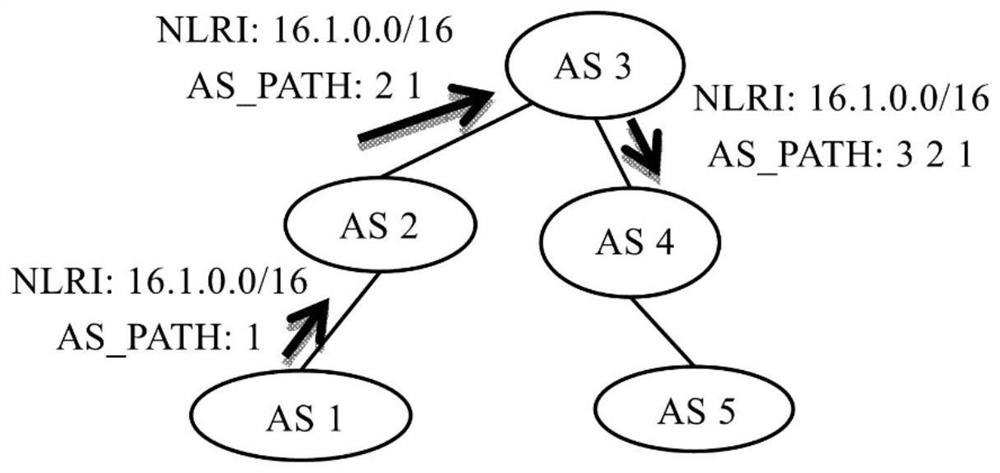
The invention discloses an internetwork routing method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a mapping table from an internet protocol (IP) address prefixes of network forwarding equipment to AS numbers; generating an aggregation forwarding table based on the mapping table and a forwarding table of the network forwarding equipment, wherein the aggregation forwarding table comprises table entries of the IP address prefixes and the AS numbers; and when the network forwarding equipment receives the data packet, searching the next hop which corresponds to a data packet from the aggregation forwarding table according to the head of the data packet, so as to forward the data packet. According to the method, because the AS numbers are introduced into the forwarding table, the IP address prefix table entries from the same AS declaration in the forwarding table are aggregated into the AS number table entry. The aggregation property of the IP address prefix entries is enhanced, and one part of IP prefixes are kept due to the requirements of traffic engineering, so that the IP aggregation property is improved and the requirements of traffic engineering are met, and therefore the AS number routing of the traffic engineering is not influenced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
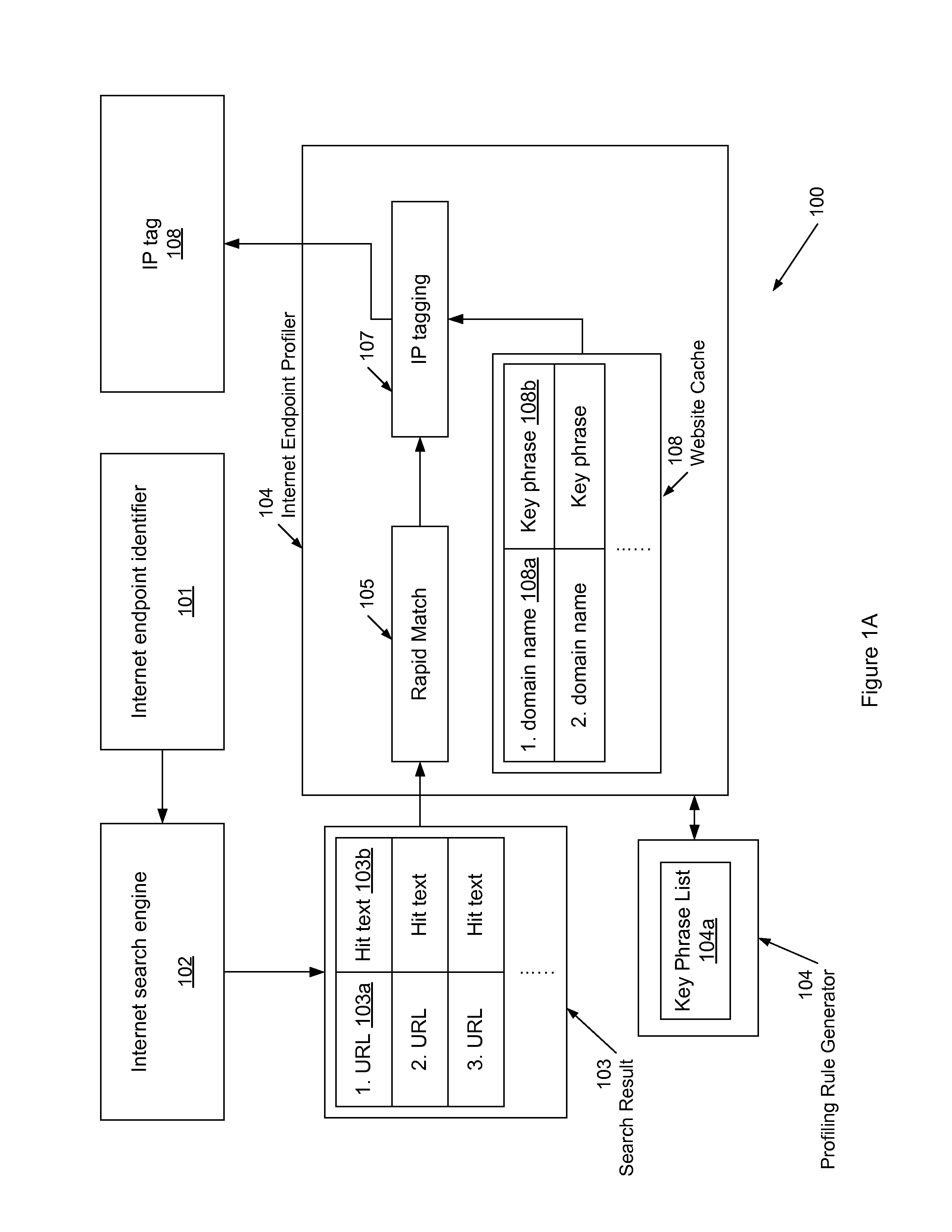
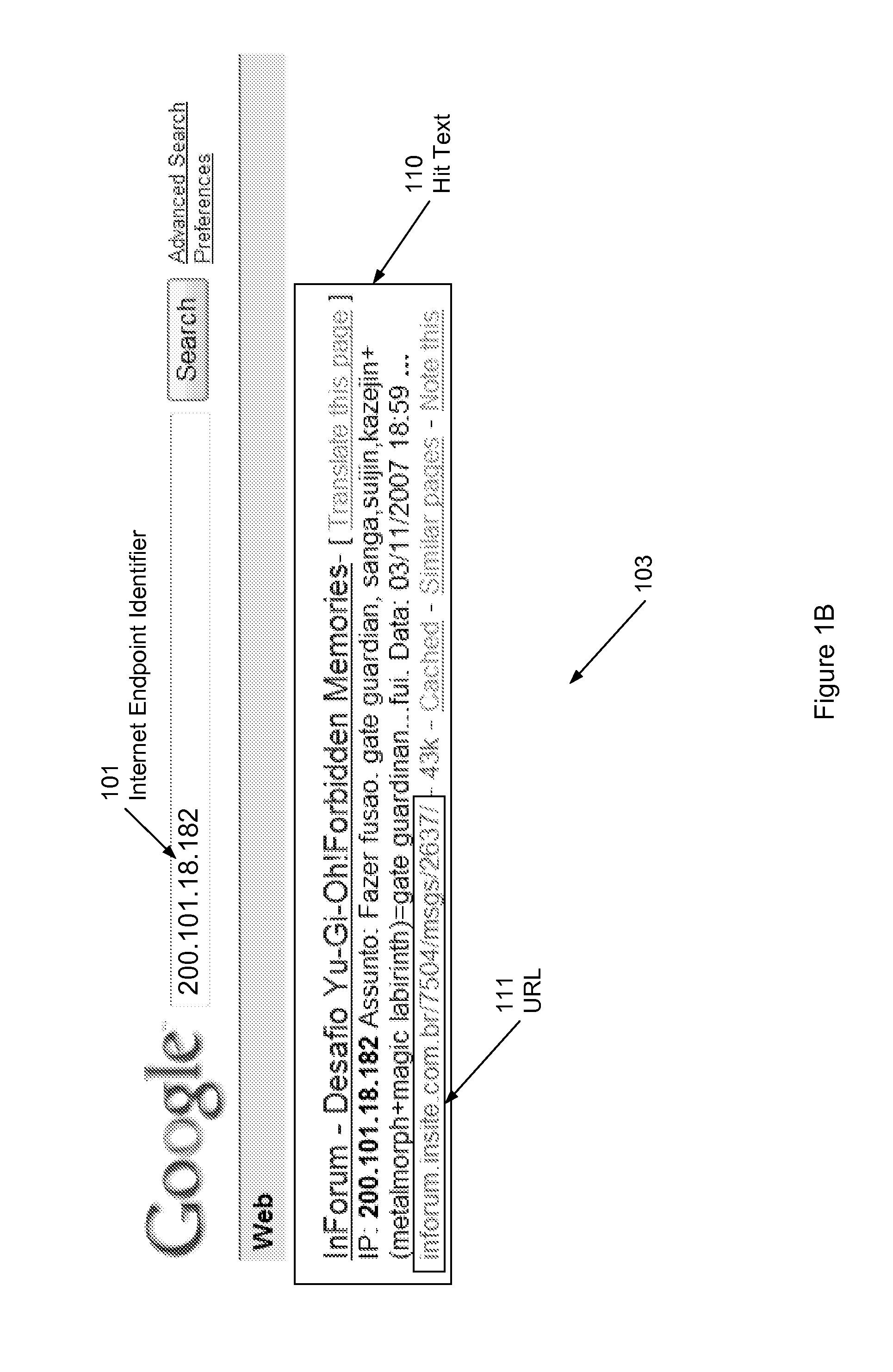
System and method for internet endpoint profiling
Owner:THE BOEING CO
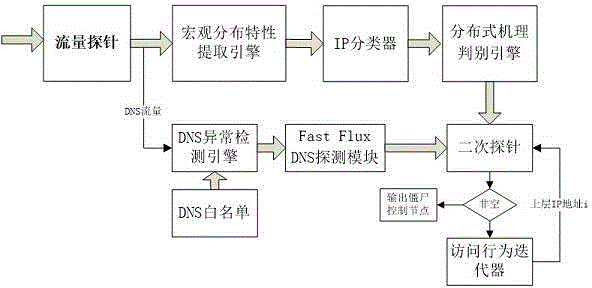
A method for tracking a backbone network botnet based on a distributed space-time mechanism
InactiveCN104135400AAvoid passivationEffective Iteration TrackingData switching networksDomain nameFeature extraction
There is provided a method for tracking a backbone network botnet based on a distributed space-time mechanism. According to the method, a traffic probe sends DNS data in traffic to a DNS abnormity traffic detection engine, which executes filtering by using a white list and sends DNS access data to a Fast Flux DNS detection module to detect a domain name with Fast Flux DNS characteristic. The traffic probe sends a TCP handshake message and an end message that are in the traffic to a macro distribution characteristic extraction engine to obtain IP address data represented by macro distribution characteristic, and an IP cluster executes clustering to obtain an IP prefix for abnormal behavior, and sends the IP prefix to a distributed mechanism determination engine to execute abnormity IP behavior feature extraction. Filter processing of a secondary probe is executed on the domain name with Fast Flux DNS characteristic and the abnormity IP behavior feature, and the filtered result is inputted to an iterator and iterated to output intermediate node information; the iteration is executed repeatedly by the secondary probe and the iterator until there is no output from the secondary probe, and at the moment, the intermediate node information is a trackable botnet node with the highest hierarchy.
Owner:南京烽火星空通信发展有限公司
Method of three-layer conversion information down transmitting hardware LPM table
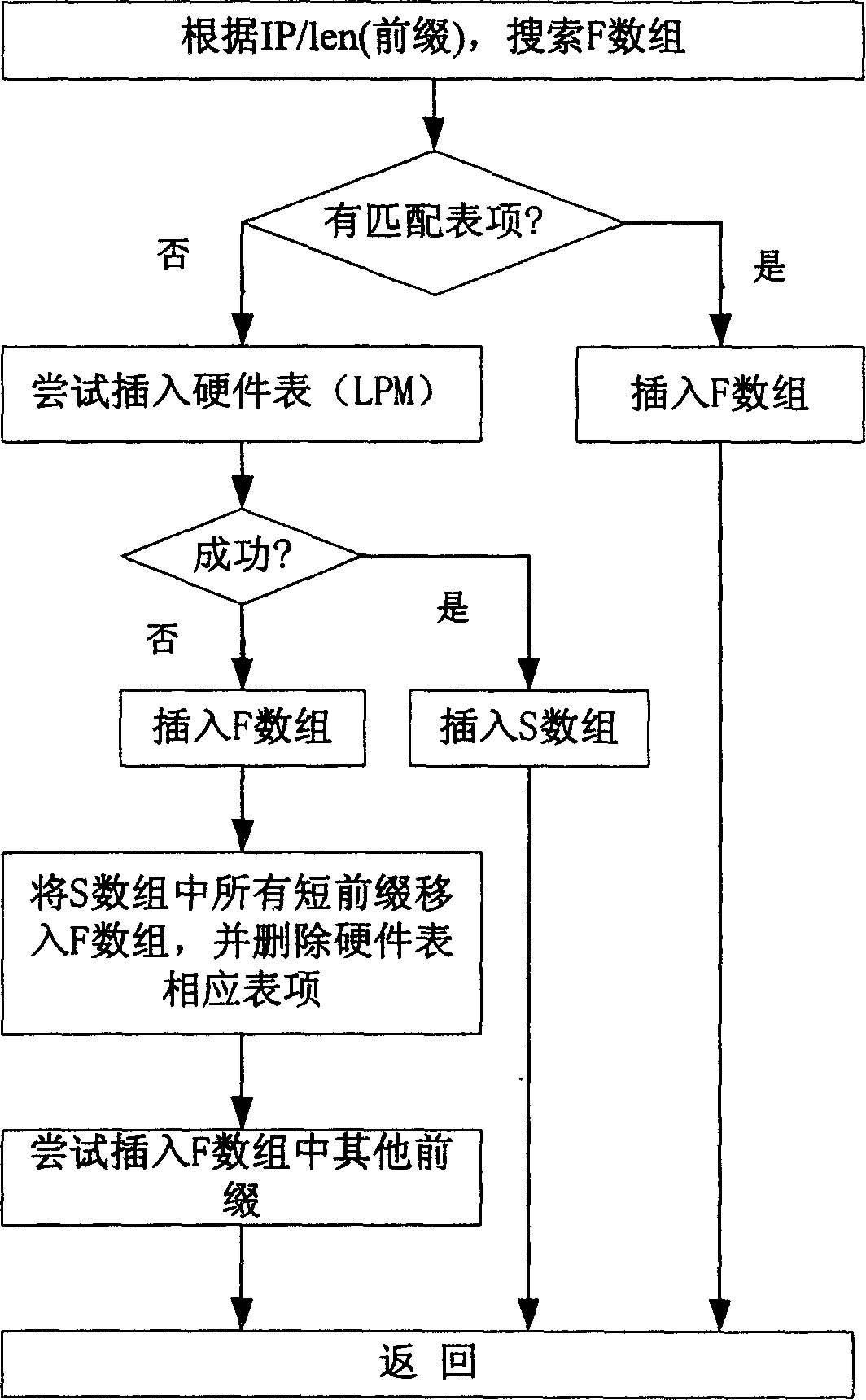
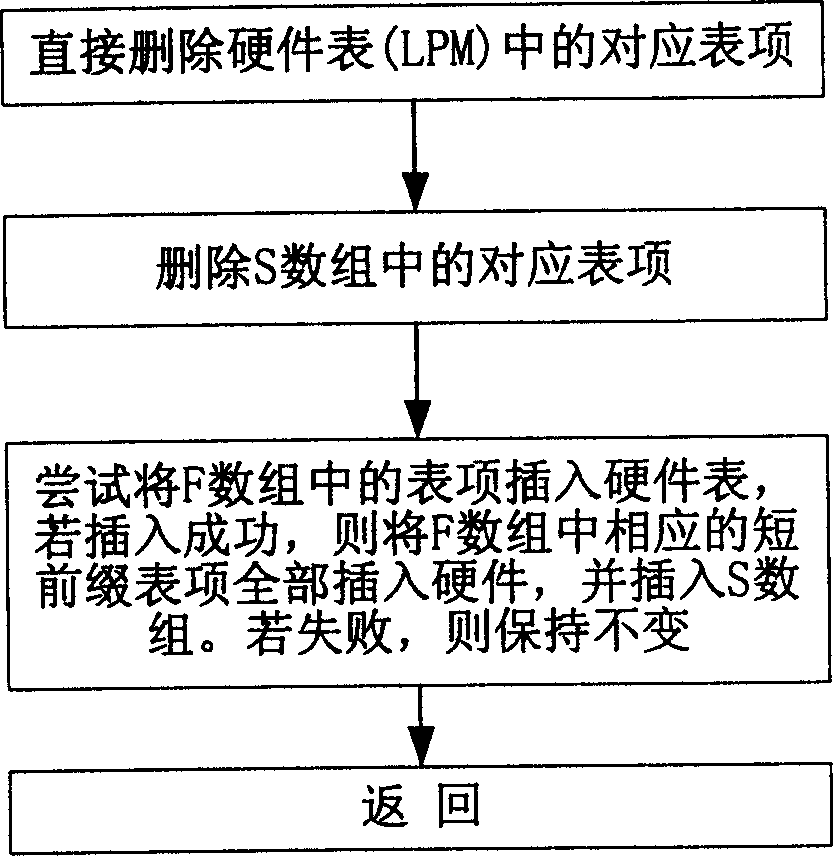
InactiveCN1561050AReduce invalid timesImprove forwarding efficiencyData switching networksArray data structureNetwork packet
This invention discloses a method for delivering a three-layer forward information to hardware LPM list, among which, the top layer FIB is delivered to said hardware LPM list and tuple S and F of IP prefix value are designed for storing FIB successful or failed delivery. When FIB is delivered, tuple F is searched first to see if there is item matched to said IP prefix, if so, the route item list is inserted into tuple F, otherwise, the IP prefix value is inserted into LPM list. If the insertion is done, it is stored in tuple S, if its failed, it's inserted into tuple F and all short prefix lists of the IP prefix values in LPM are cancelled. After that, other prefix values in F are tried to insert into LPM, if it's done, all short prefixes related to IP are inserted into LPM and S.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Loop detection and prevention
Various systems and methods for preventing loops. For example, one method involves receiving a multicast data packet at a node. The node is coupled to a local area network (LAN). An internet protocol (IP) prefix is assigned to the LAN. The method involves determining whether a source address included in the packet is covered by the IP prefix. Depending on the direction of travel of the multicast data packet and whether or not the source address is covered by the IP prefix, the node determines whether a loop exists.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
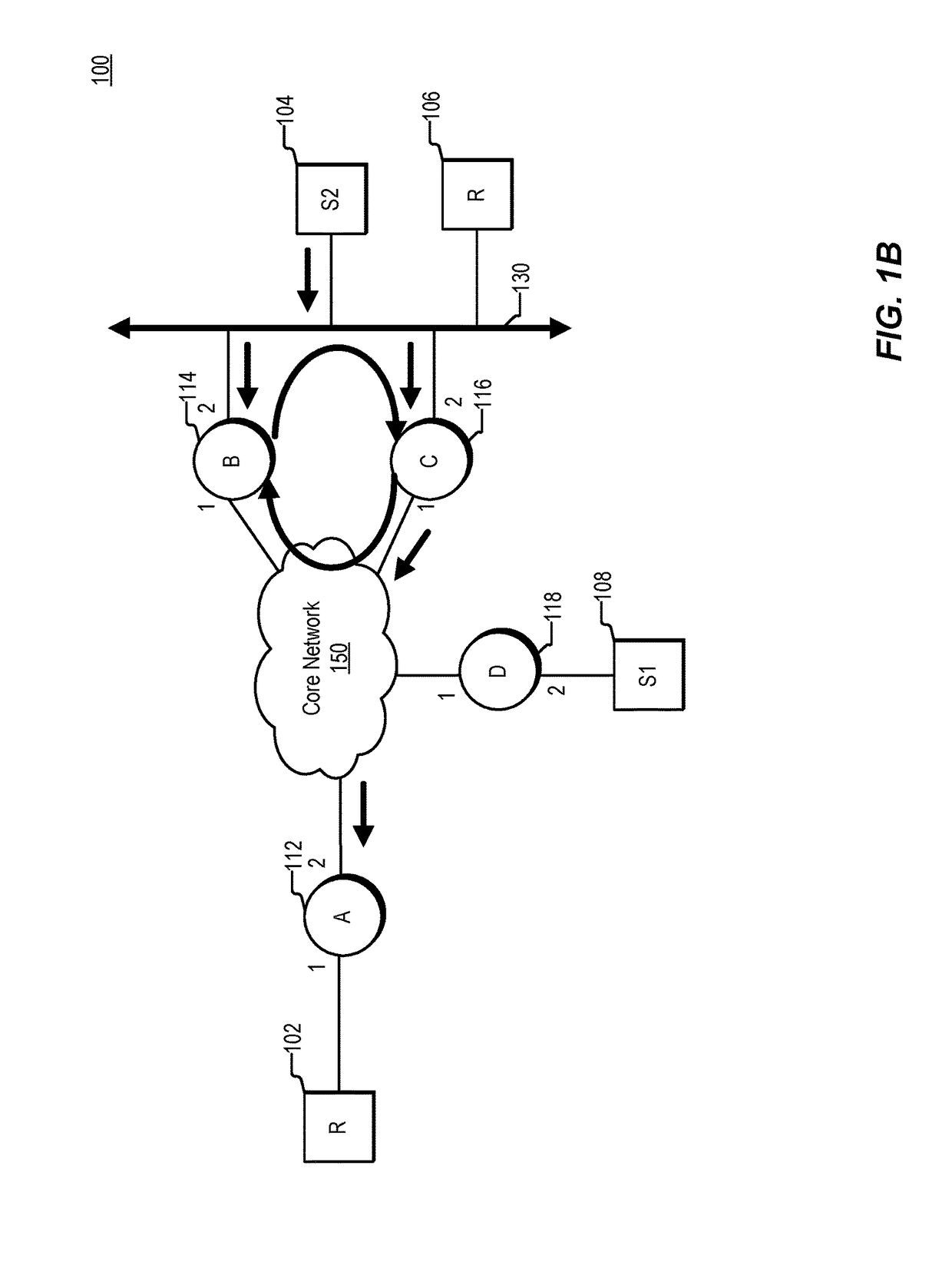
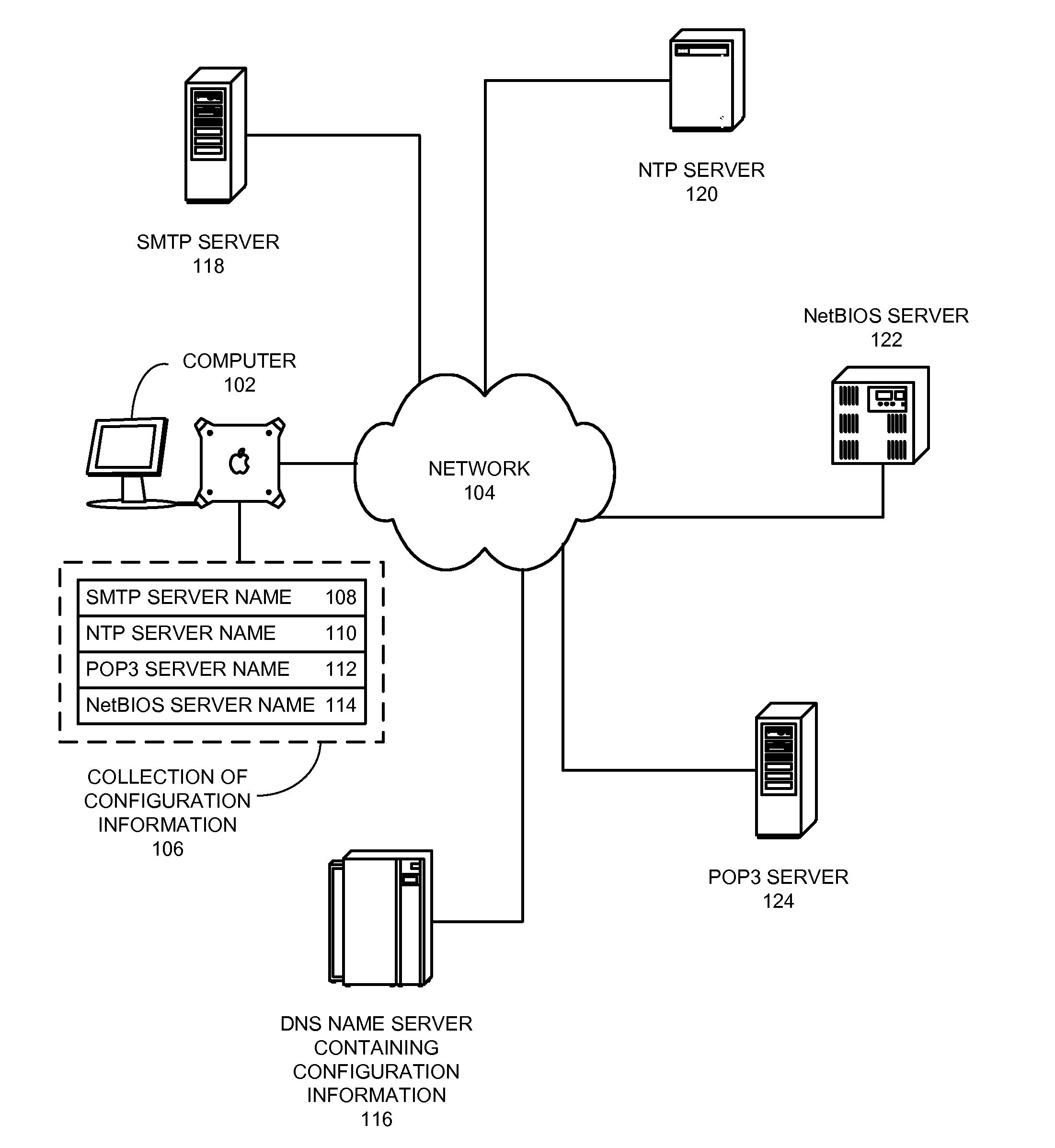
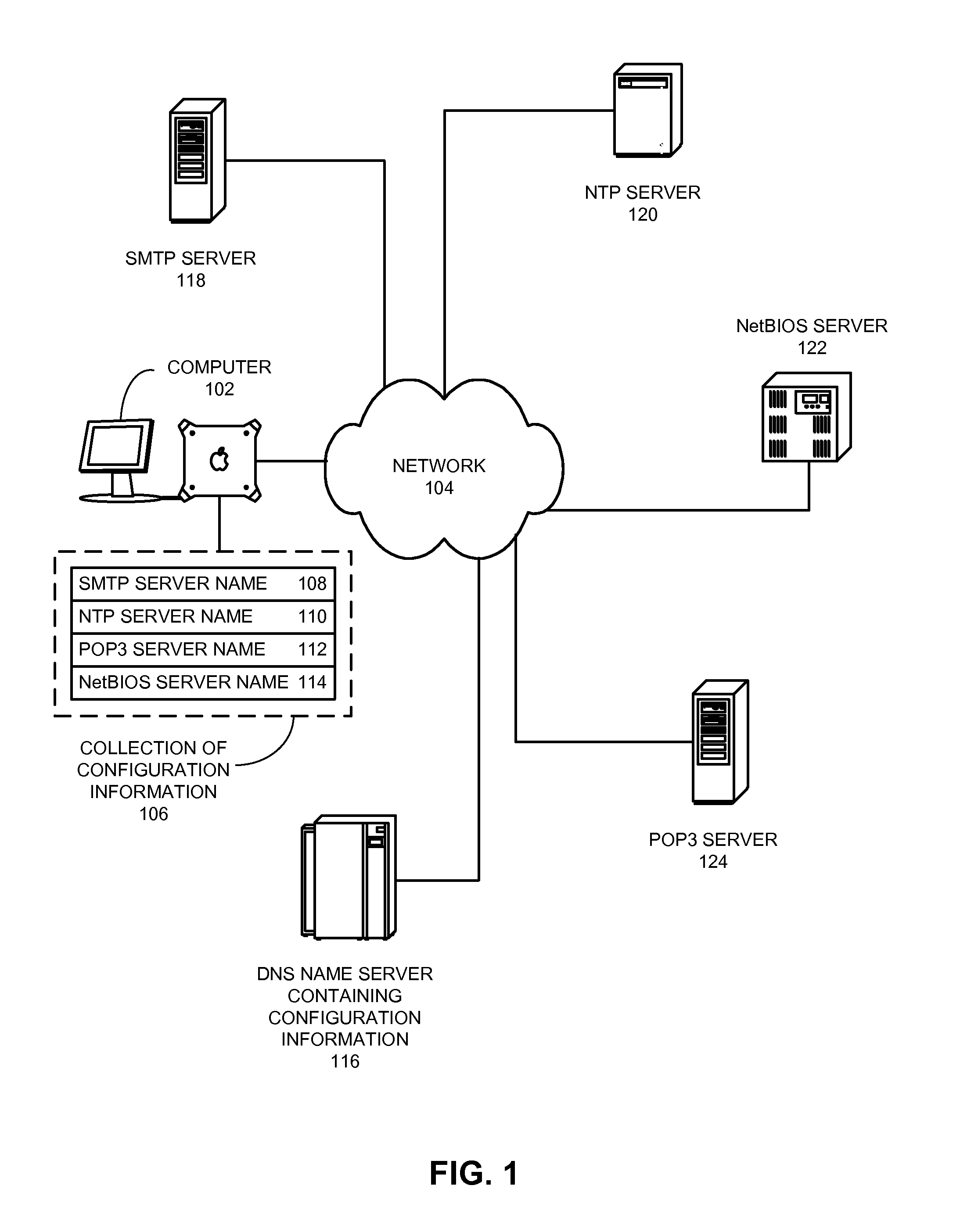
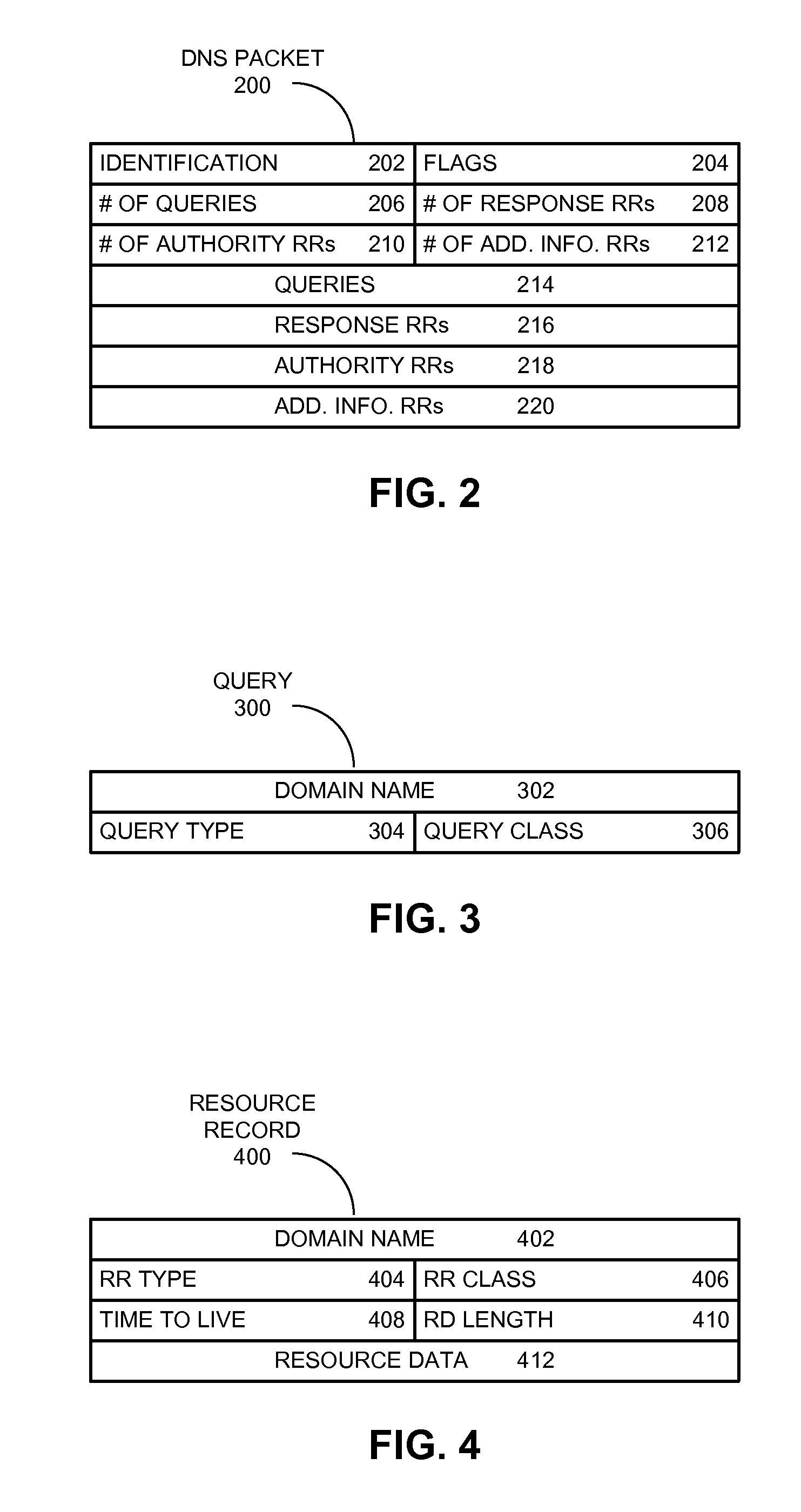
Method and apparatus for looking up configuration information for a network node
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for looking up location-specific configuration information for a network node or a subnet. During system operation, a network node creates a query message containing a key that comprises an Internet Protocol (IP) prefix and a string, wherein the IP prefix identifies the network node or the subnet, and the string specifies the type of configuration information. The network node then sends the query message to a name server, which is part of a distributed system that provides a global naming service, wherein the name server additionally stores configuration information. Finally, the network node receives a response message from the name server, wherein the response message contains the requested configuration information.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method for IP longest prefix match using prefix length sorting
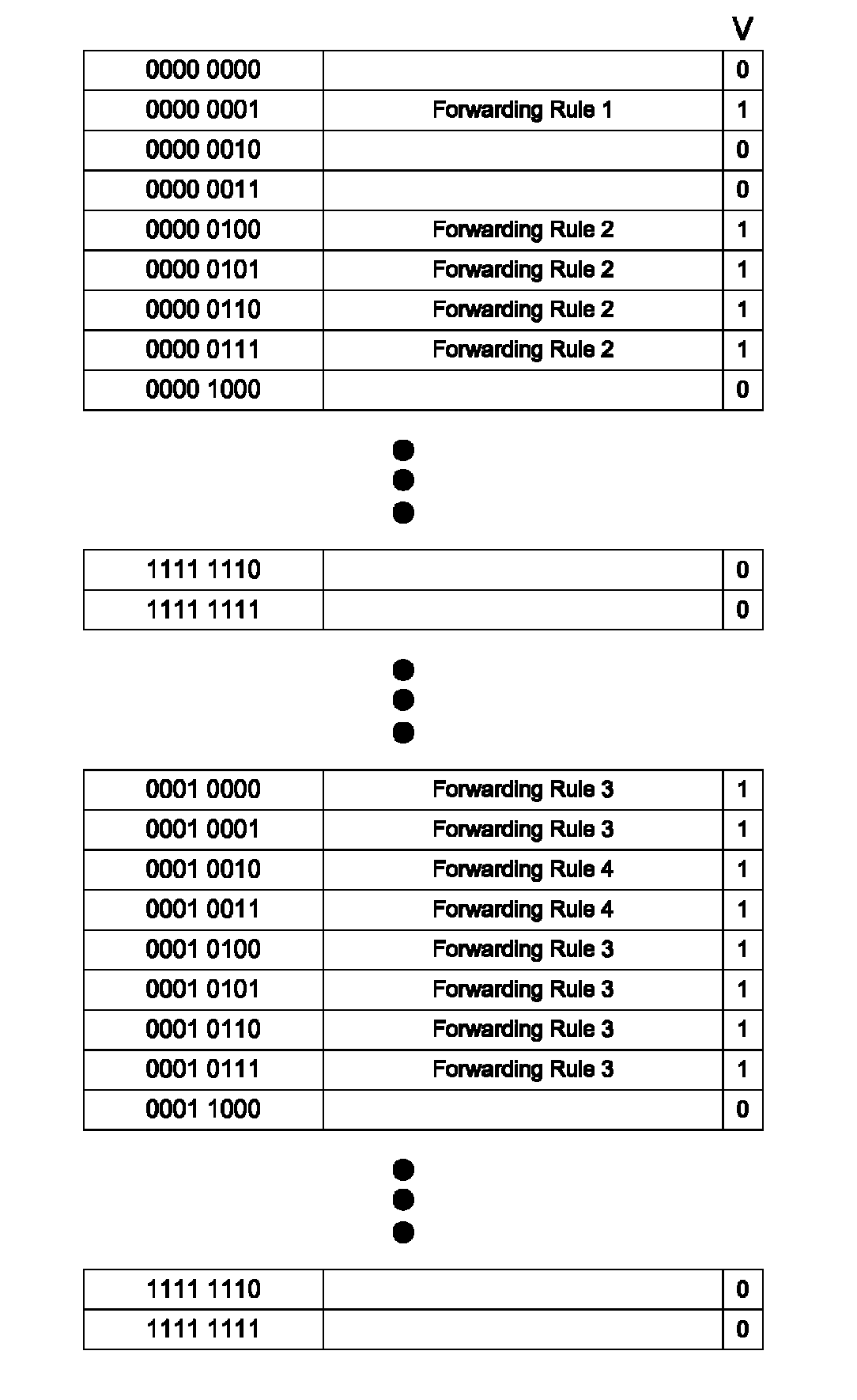
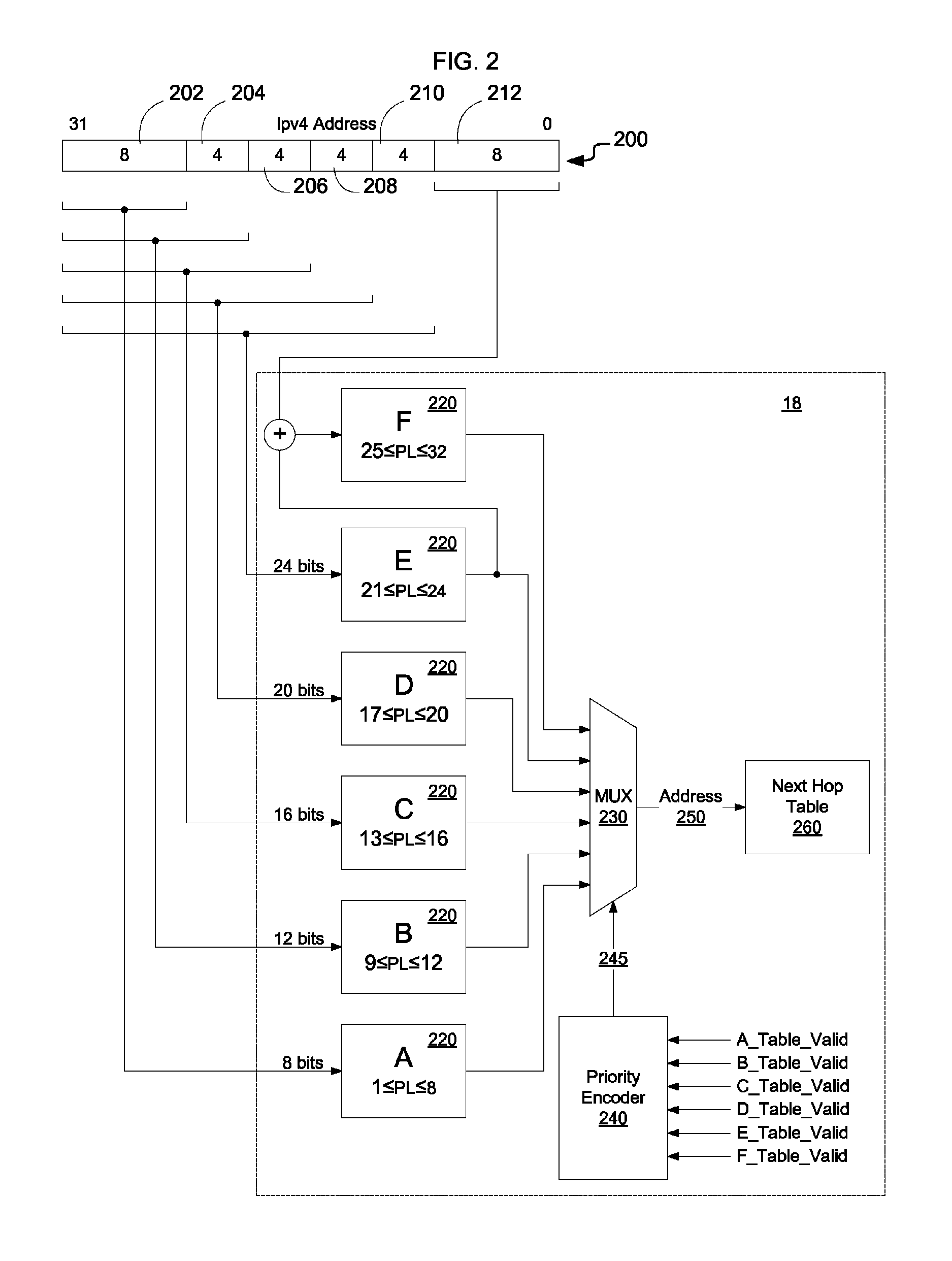
ActiveUS8848707B2Low costReduce overheadData switching by path configurationLongest prefix matchTerm memory
Prefix length memory tables are used to enable fast IPv4 LPM lookups using a single memory access for a first range of IP prefixes, and using two memory accesses for larger IP prefixes. Each of the prefix length memory tables is used to hold a set of forwarding rules associated with a different prefix length range. IP LPM operations are then performed in parallel in each of the prefix length memory tables of the set, and the forwarding rule matching the longest prefix is returned from each of the memory tables. A priority encoder is used to select between positive results from the multiple prefix length memory tables to enable the forwarding rule with the largest matching prefix to be used to key into the next hop forwarding table. The method utilizes low cost DDR SDRAM rather than TCAM, and also exhibits low overhead.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
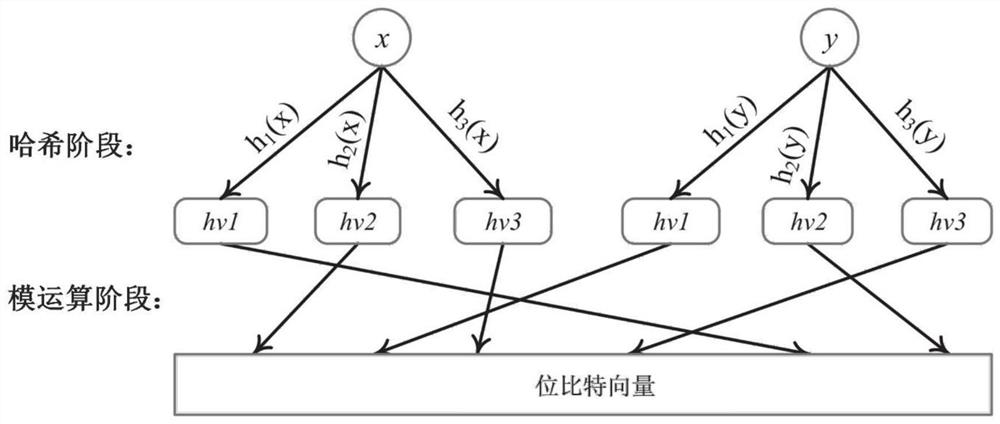
Flexible IP addressing method and device based on single Hash Bloom filter
ActiveCN113315705ASmall amount of calculationReduce computing costData switching networksRouting tableIp address
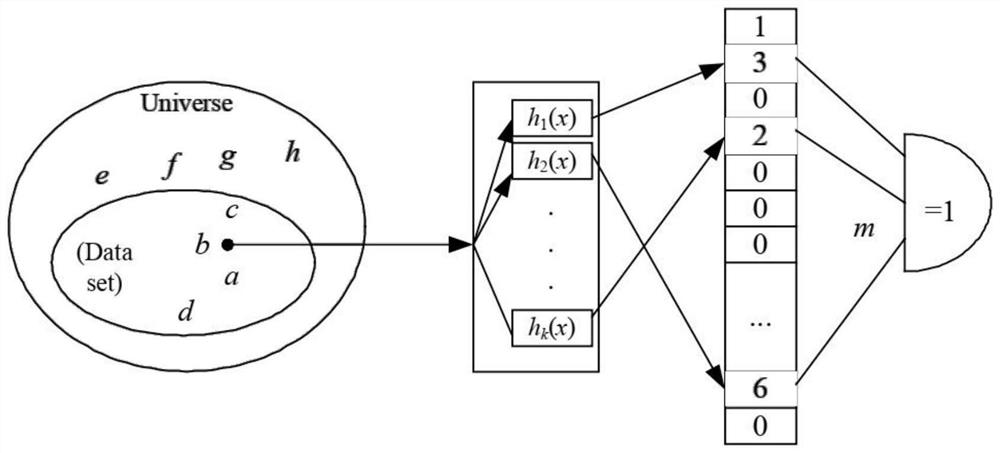
The invention discloses a Flexible IP addressing method and device based on a single Hash Bloom filter, and the method comprises the steps: dividing the prefixes of all IP addresses in a routing table into N types according to the length, correspondingly setting one Bloom filter for each prefix length, and dividing the bit vector of each Bloom filter into k partitions; mapping each prefix length to each partition of the corresponding Bloom filter, and storing IP prefix information in a hash table; when addressing operation is carried out, W prefixes being taken out from a destination address, the intercepted prefixes being sent into the corresponding Bloom filters, and a matching vector being returned; and addressing according to a hash table and the matching vector to obtain a storage space of the destination address. According to the method, the calculation amount of the Bloom Filter is effectively reduced to the original calculation amount, the addressing calculation cost is greatly reduced, the addressing efficiency of mass communication subjects is improved, and the expandability of Flexible IP under multiple semantics is supported.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
IP routing search method and device
The invention provides an IP routing search method and device. The method comprises the steps of establishing a multibit trie for routing distribution of an IP prefix in each VPN (Virtual Private Network), and dividing each multibit trie into multiple levels; establishing an input key for each level according to a VPN identifier and all bits of an IP address before each level when routing search is carried out on an IP address in one VPN, calculating the input key for each level by employing a Hash function of each level, and carrying out routing search by employing a data structure information pointer of a sub _Trie node corresponding to the longest Hash hit result. According to the method and the device, the IP routing search efficiency is improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
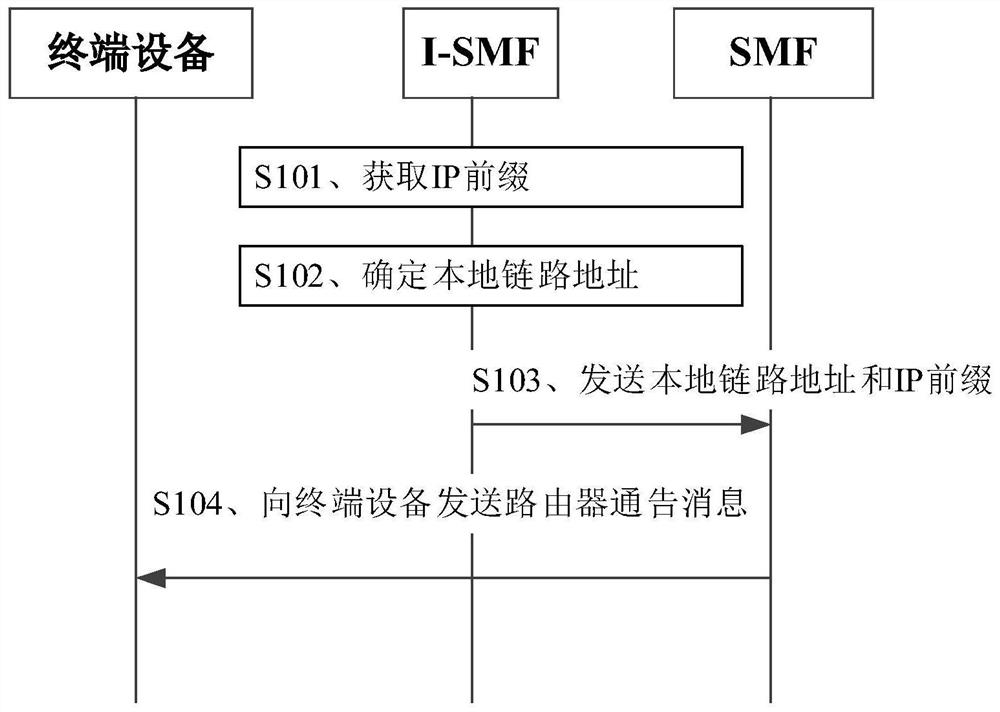
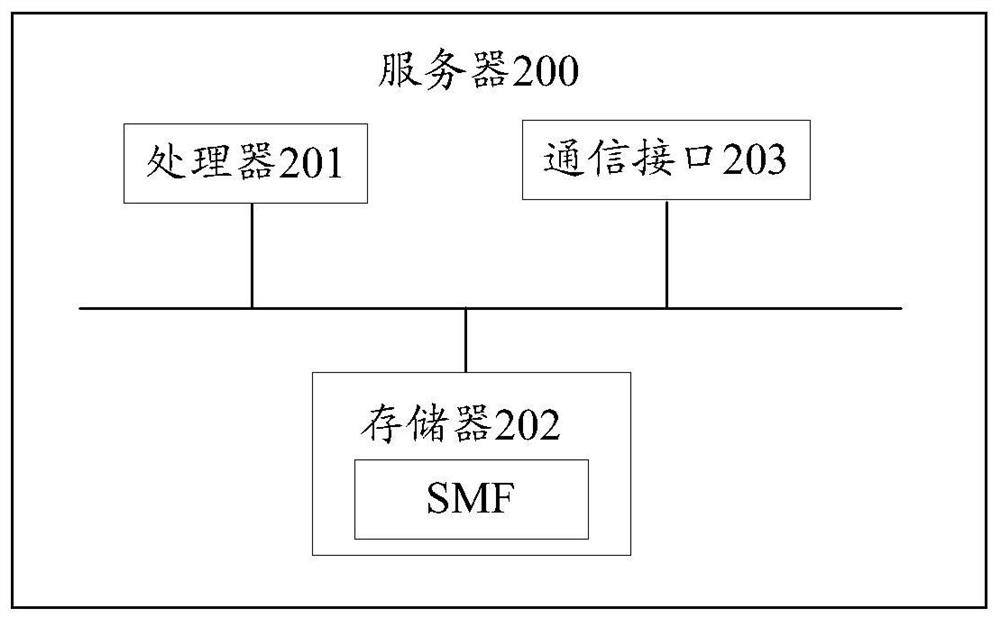
Router notification message sending method and device
The invention provides a router notification message sending method and device. The method comprises the following steps: a session management function network element receives a local link address and an IP prefix from an intermediate session management function network element, wherein the local link address and the IP prefix correspond to a local session anchor function network element managedby the intermediate session management function network element; and the session management function network element sends a router notification message to terminal equipment, wherein the router notification message comprises the local link address and the IP prefix. Therefore, the problem of how to construct or generate the router notification message and send the router notification message to the terminal equipment in a scene of realizing shunting through multiple hosts when the terminal equipment is served by multiple SMFs is solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Automatic signing and issuing method and device for routing origin authorization
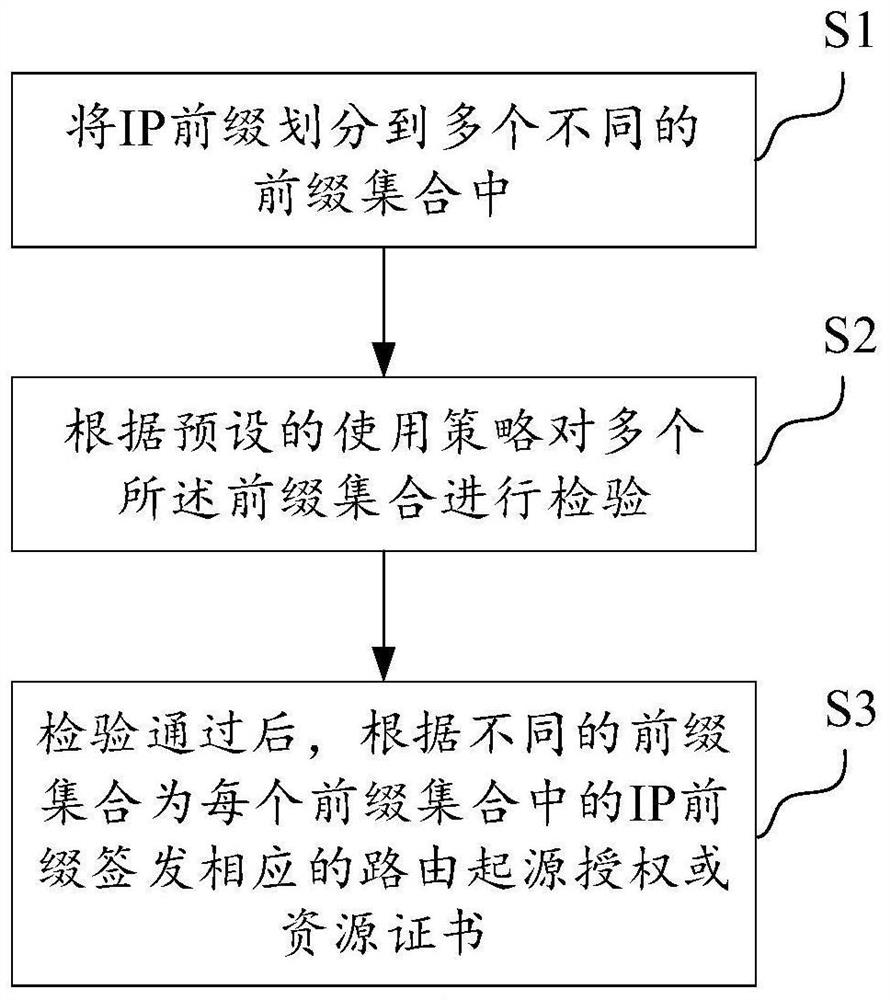
ActiveCN112003959AAvoid duplicationPrevent duplicate authorizationUser identity/authority verificationData switching networksEngineeringIp prefix
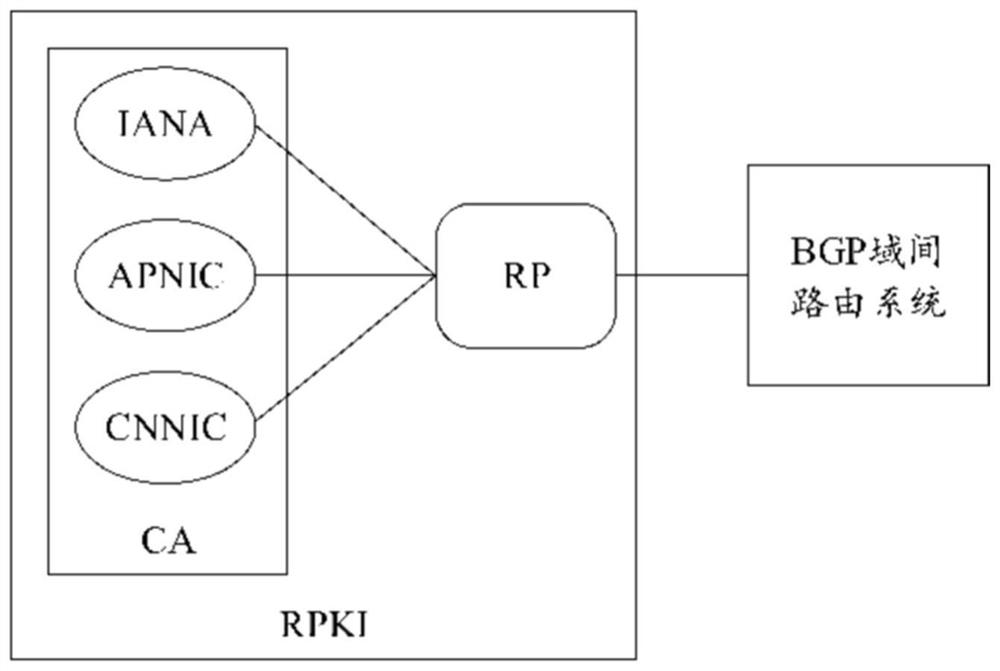
The invention relates to an automatic signing and issuing method and device for routing origin authorization. The method comprises the steps of dividing IP prefixes into a plurality of different prefix sets; checking the plurality of prefix sets according to a preset use strategy; and after the verification is passed, signing and issuing corresponding routing origin authorization or resource certificates for the IP prefixes in each prefix set according to different prefix sets. According to the scheme, based on an INR use strategy, whether an IP prefix meets the INR use strategy or not and whether INR distribution and authorization conflicts exist or not are checked; and after the check is passed, a corresponding resource certificate and routing origin authorization are automatically signed and issued according to the willingness of the INR holder so as to prevent repeated INR allocation and repeated INR authorization caused by manual operation from being unable to be detected by an RPKI relying party.
Owner:深圳网基科技有限公司
IP route search method and device
ActiveCN106330721ASimplify the search processImprove search efficiencyData switching networksIp addressTheoretical computer science
The present invention proposes an IP route search method and device. The method includes the following steps that: a Multibit Trie tree is constructed for the distribution of IP prefixes in each VPN; routes on high 1-to-m-level IP prefixes of the Multibit Trie tree are expanded onto (m+1)-level IP prefixes through adopting a prefix expansion method, wherein m is an integer larger than 1; each branch of the (m+1)-level IP prefixes of the Multibit Trie tree is adopted as one Branch_Tree, and the data structure information of each Branch_Tree is stored; and when route search is carried out for one IP address in one VPN, a corresponding Branch_Tree is searched out in a Multibit Trie tree corresponding to the VPN according to the high m+1 bit of the IP address, and a corresponding route is searched out in the Branch_Tree. With the IP route search method and device adopted, IP route search efficiency can be improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
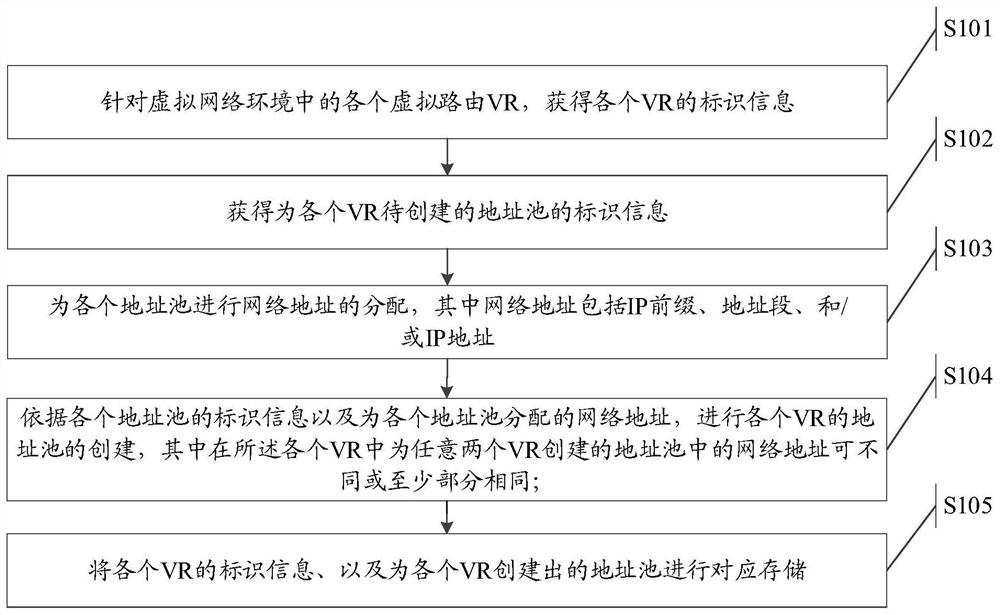
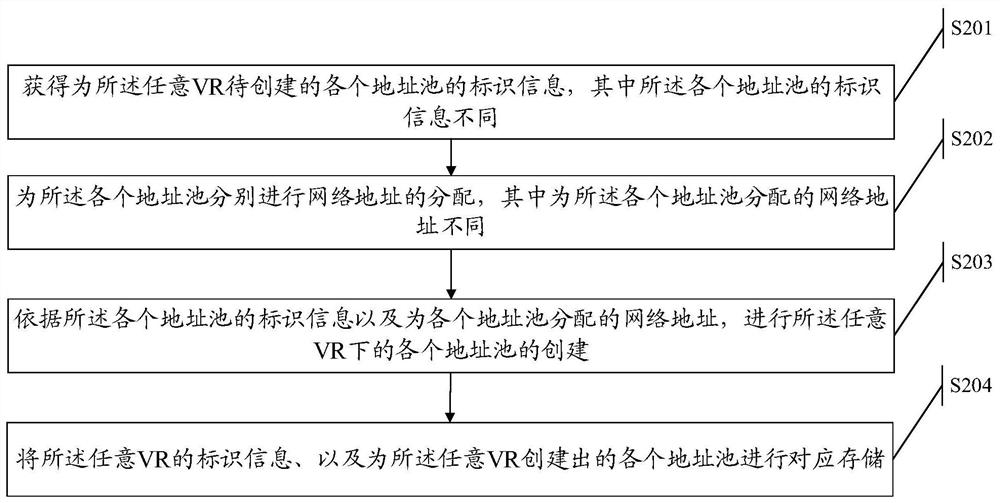
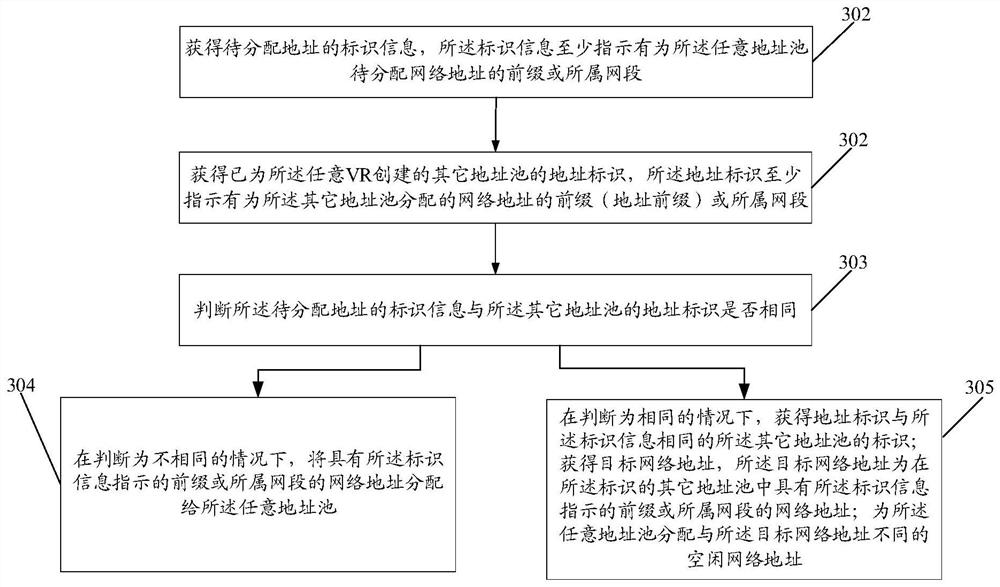
Creation method and device and storage medium
The embodiment of the invention provides a creation method and device, and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the identification information of each VR for each virtual routing VR in a virtual network environment; obtaining identification information of an address pool to be created for each VR; allocating a network address to each address pool, wherein the network address is at least one of an IP prefix, an address field and an IP address; according to the identification information of the address pools and the network addresses allocated to the address pools, creating the address pools of the VR, wherein the network addresses in the address pools created for any two VR in the VR can be different or at least partially the same; and correspondingly storing theidentification information of each VR and the address pool created for each VR.
Owner:SANGFOR TECH INC
System and method of fast adaptive TCAM sorting for IP longest prefix matching
InactiveUS7706375B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationRouting tableIp address
A system and method are provided for sorting IP routing table entries in a TCAM for longest IP prefix matching LPM of destination IP addresses. The IP routing table is divided into logical blocks, for each block an associated routing entry IP prefix length. Each block is of a respective size whose proportion of the total size of the routing table is determined by the associated IP prefix length. The blocks are ordered so that the TCAM returns an LPM when queried. Starting block sizes can be initialized to proportions which reflect actual expected numbers by proportion of routing entries by IP prefix length. The blocks also grow and shrink as entries are added and deleted so as to more closely mirror real-world populations of expected entries having the IP prefix length in question.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and device for processing link state information
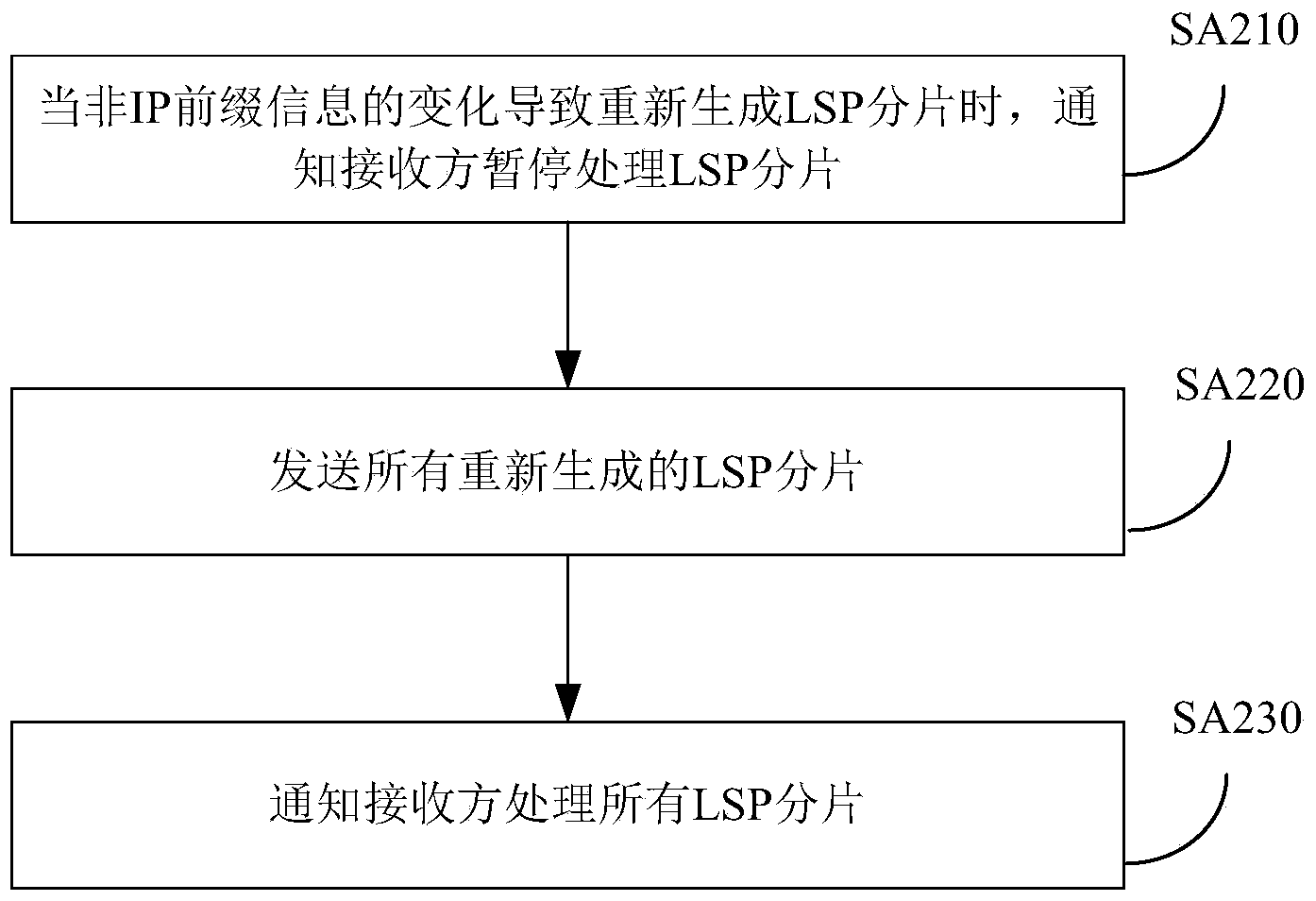
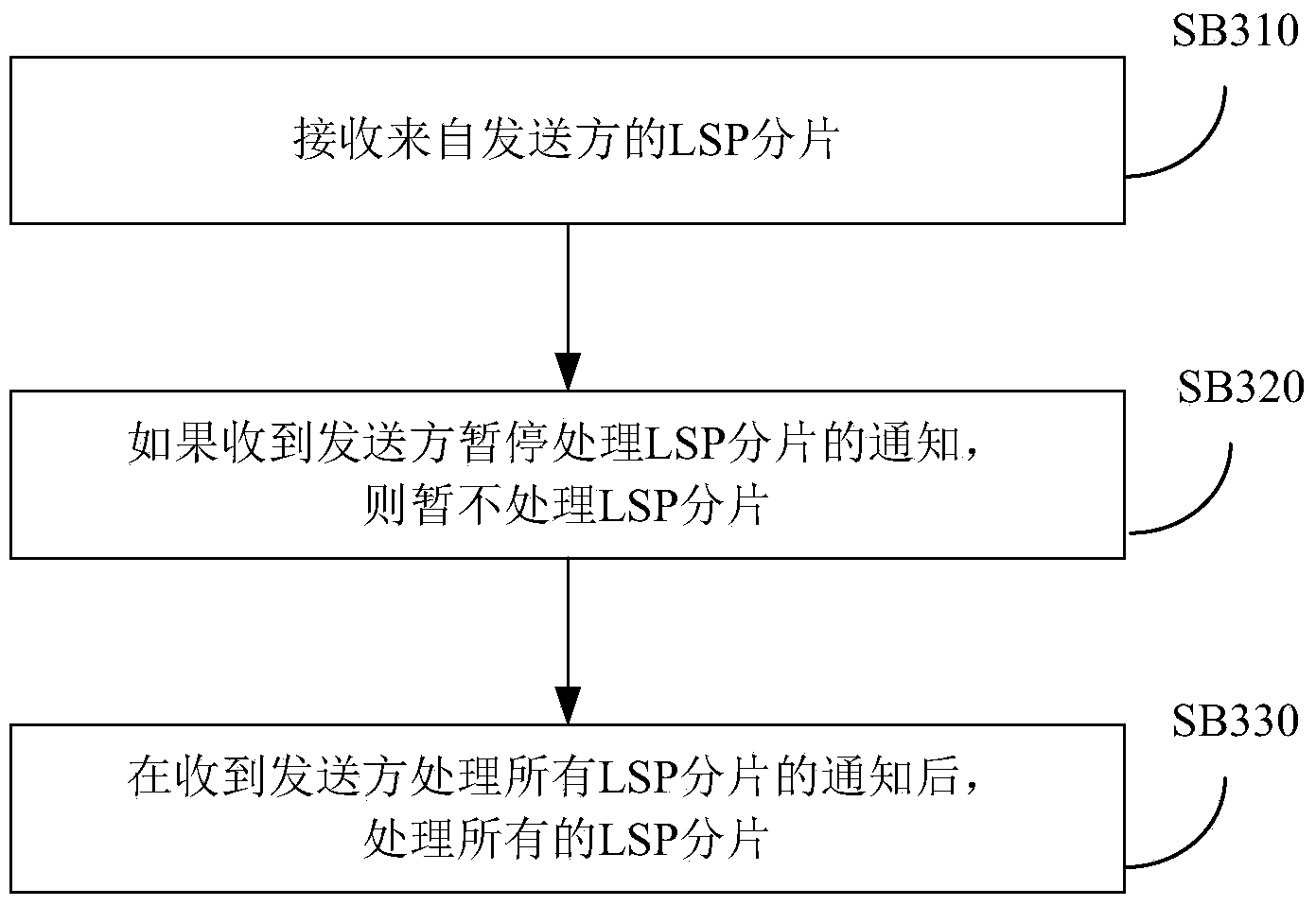
ActiveCN103763199AAvoid short interruptionsImprove accuracyData switching networksRouting tableIp prefix
The invention provides a method for processing link state information, and the method is applied to an intermediate system. The method comprises the steps that when LSP fragmentations are generated again due to the change of non-IP prefix information, a receiver is informed not to process the LSP fragmentations temporarily; all the LSP fragmentations generated again are sent; the receiver is informed to process all the LSP fragmentations. By means of the technical scheme, the occurrence that due to the regeneration of the LSP fragmentations, an IS-IS router of the receiver is deleted from a routing table, and the dataflow is temporarily interrupted during the process of adding the IS-IS router back to the routing table is avoided.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
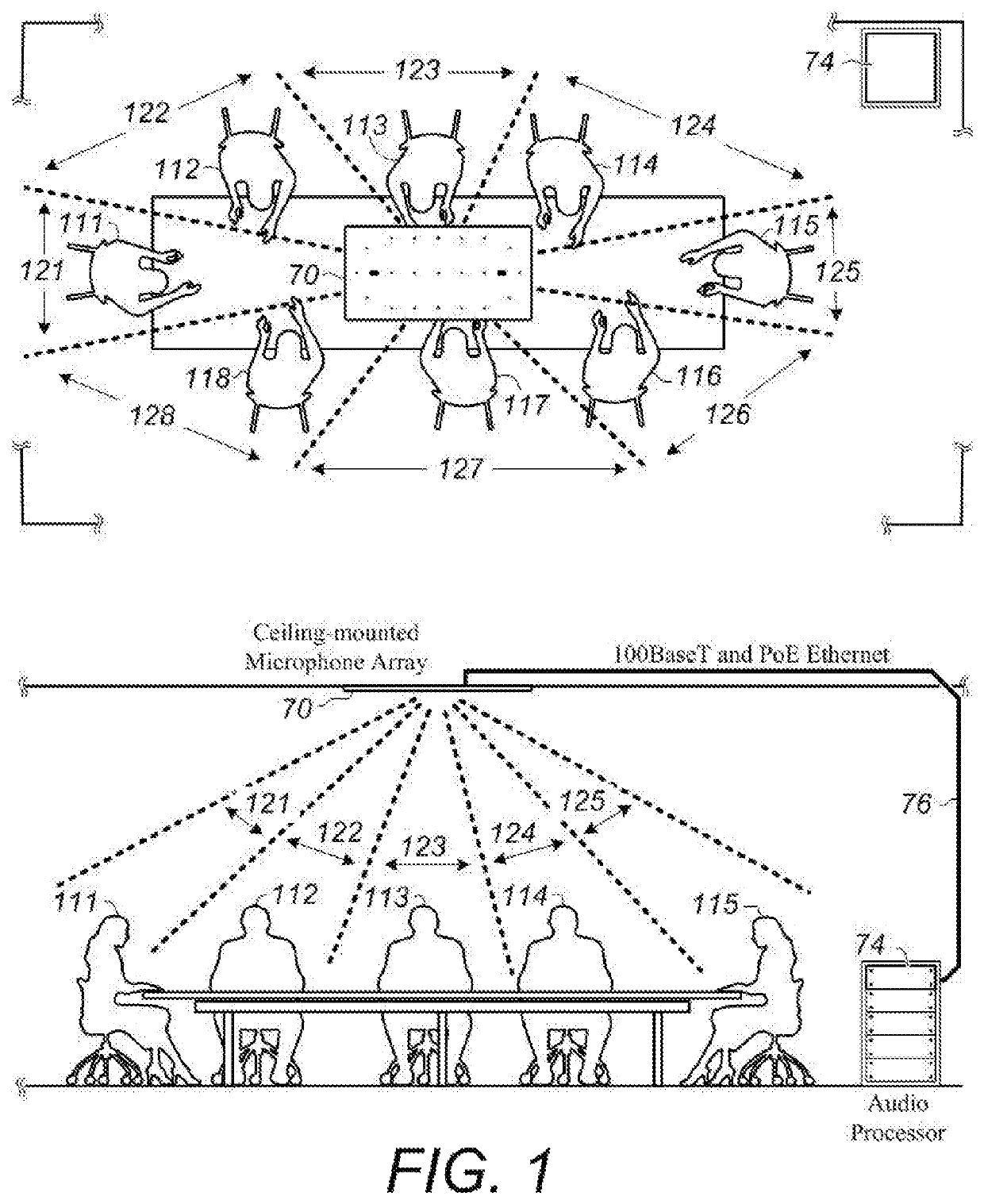
Microphone array system with Ethernet connection
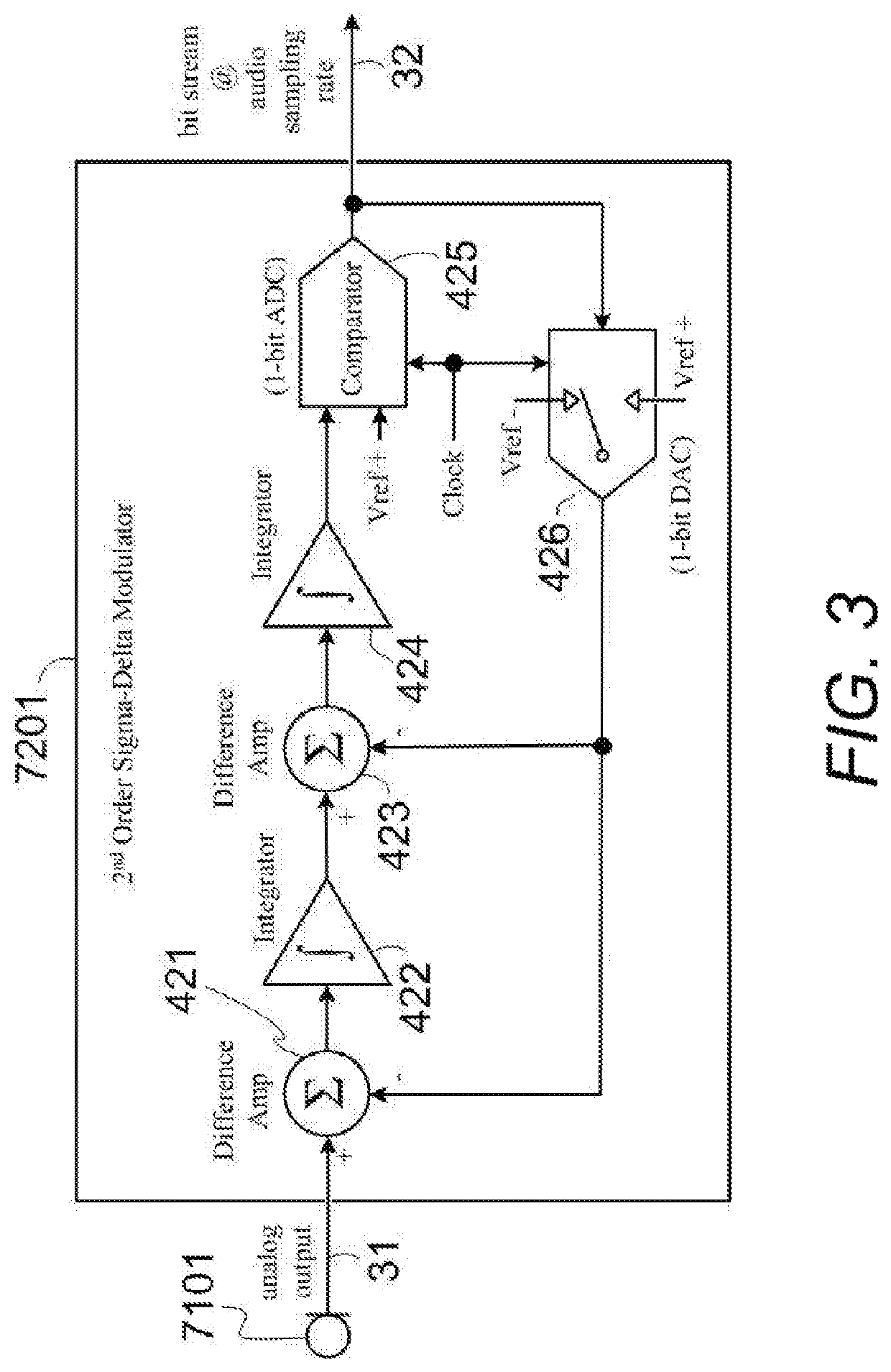
A microphone array configurable to connect via an Ethernet connection with an audio processor includes a plurality of MEMS microphones (7101-7121), a plurality of sigma-delta modulators (7201-7221), a processor and storage (90), and an Ethernet physical interface (80) operating at a network data transmission rate. Each sigma-delta modulator converts the analog output of a corresponding microphone into a bit stream at an audio sampling rate. The processor and storage performs a data-interleaving operation (92) to combine the bit streams from the sigma-delta modulators into a microphone audio frame serial bit stream (34), and loads the microphone audio frame serial bit stream into a FIFO memory (94) at a FIFO serial data load rate. The processor and storage computes an Ethernet FCS checksum on the microphone audio frame serial bit stream, concatenates, an FCS delay gap, the Ethernet FCS checksum, a timing gap, a frame prefix, a UDP / IP prefix, a payload, and the microphone audio frame serial bit stream to form an Ethernet frame packet serial bit stream, unloads this Ethernet packet serial bit stream from the FIFO memory at the network data transmission rate and transmits the Ethernet frame packet serial bit stream from the Ethernet physical interface.
Owner:CRESTRON ELECTRONICS
Encoding method and system as well as decoding method and system for routing origin authorization compression
ActiveCN113794724ASecure Compression EncodingScalable Compression CodingChannel coding adaptationData switching networksTree rootPathPing
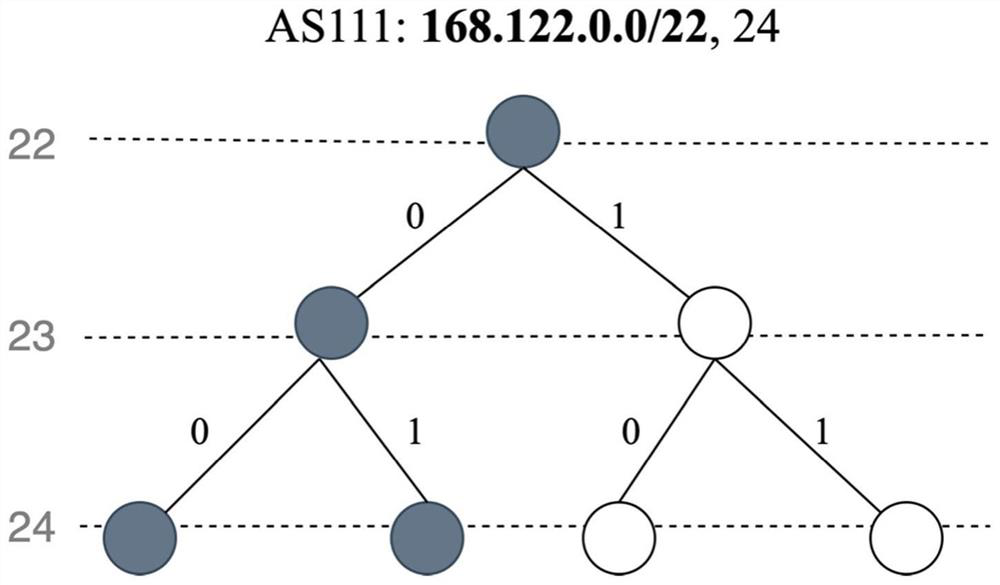
The invention relates to an encoding method and system as well as a decoding method and system for routing origin authorization compression. The encoding method comprises the following steps of: giving an authorization IP prefix set of an AS, and maintaining IP prefixes through using an IP prefix tree; splitting the IP prefix tree into a plurality of mutually disjoint independent sub-tree blocks, wherein each sub-tree block is uniquely determined by the position of a root node of the sub-tree block in the original prefix tree; encoding a path from a root node of an original prefix tree to the root node of the sub-tree block into an integer which is used as a unique identifier of the sub-tree block; encoding all nodes contained in the whole sub-tree blocks into a bitmap (bitmap); and encoding routing origin authorization information of a given AS into a plurality of eitimers and bitmap tuples. According to the encoding method and system as well as the decoding method and system, not only can high security like a mini ROA be realized, but also the expansibility bottleneck can be broken through, and safe and extensible compressed coding of the routing origin authorization information is realized.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
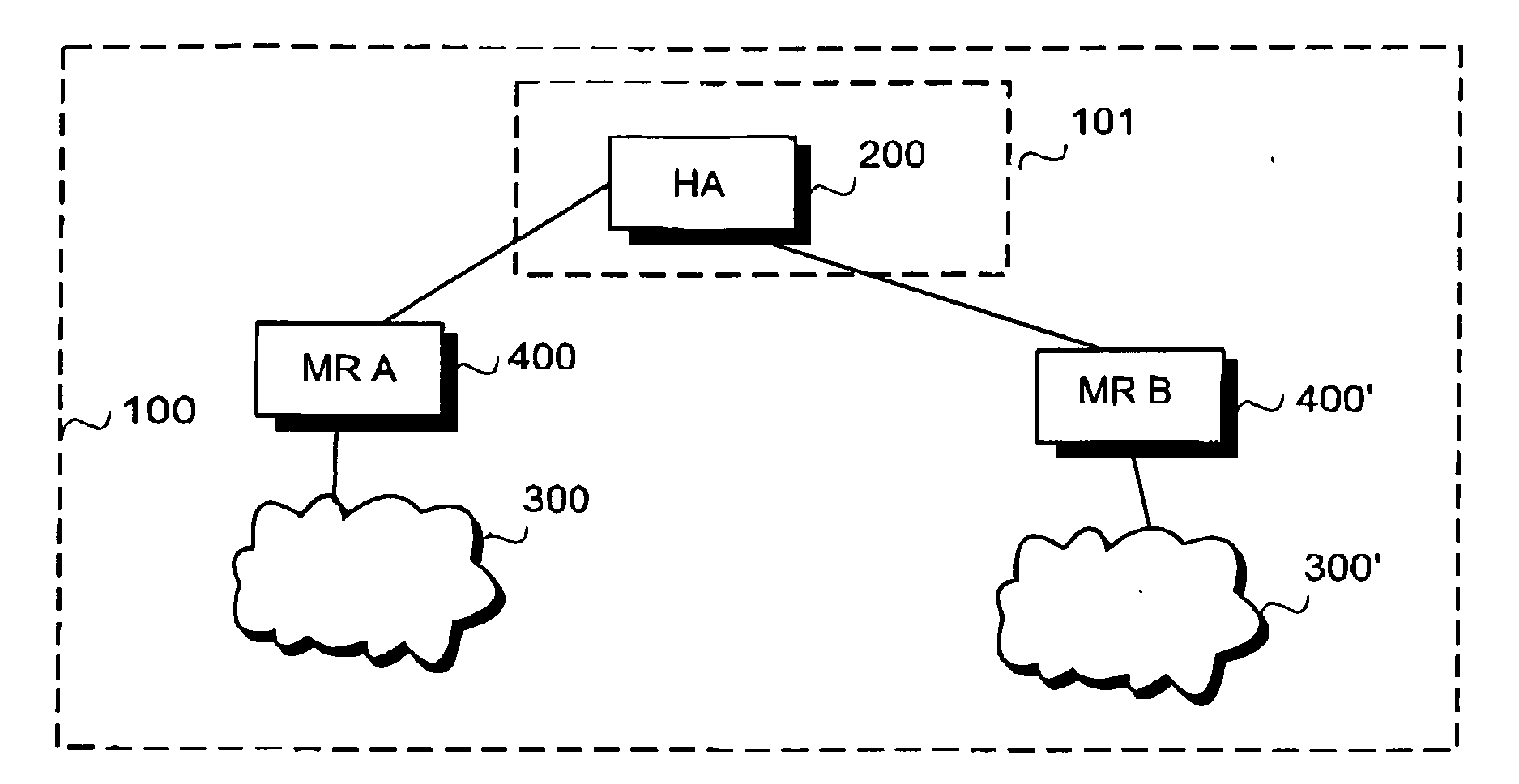
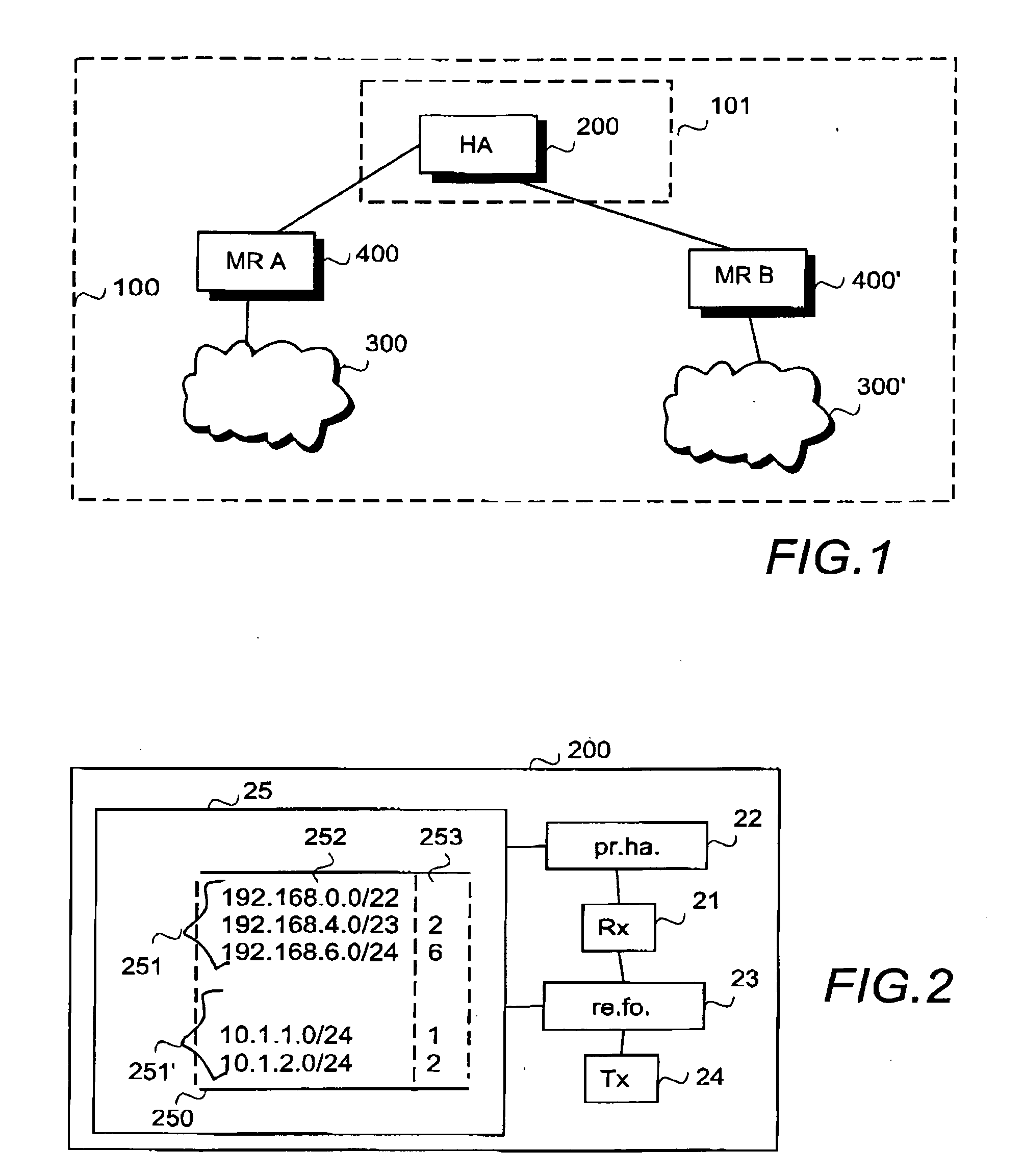
Delivery of IP prefixes
ActiveUS20090207856A1Small sizeReduce message sizeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareIp prefix
In order to reduce the size of a signaling message advertising prefixes, a super block prefix is determined amongst two or more prefixes having a common pattern. Information on the super block prefix and delta information on each non-super-block prefix is used in the messages instead of the prefixes as such, the delta information indicating how the prefix differs from the super block prefix.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Flexible IP addressing method and device based on single hash bloom filter
ActiveCN113315705BSmall amount of calculationReduce computing costTransmissionIp addressParallel computing
The invention discloses a flexible IP addressing method and device based on a single hash bloom filter. filter, in which the bit vector of each bloom filter is divided into k partitions; each prefix length is mapped to each partition of the corresponding bloom filter, and the IP prefix information is stored in the hash table; the addressing operation is performed When , W kinds of prefixes are intercepted to the destination address, and the intercepted prefixes are sent to the corresponding Bloom filter, and a matching vector is returned; according to the hash table and the matching vector, the storage space of the destination address is obtained. The invention effectively reduces the calculation amount of Bloom Filter to the original calculation amount, greatly reduces the calculation cost of addressing, improves the addressing efficiency of massive communication subjects, and supports the scalability of Flexible IP under multiple semantics.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
IP routing lookup method and device
ActiveCN106330721BSimplify the search processImprove search efficiencyData switching networksIp addressPrivate network
This application proposes an IP route lookup method and device. The method includes: constructing a Multibit Trie for the route distribution of IP prefixes in each VPN; using the method of prefix expansion to extend the routes on the IP prefixes of the Multibit Trie higher than 1~m to the m+1 IP prefixes , m is an integer greater than 1; each branch of the m+1 level IP prefix of the Multibit Trie is used as a Branch_Tree, and the data structure information of each Branch_Tree is preserved; when a routing search is performed to an IP address in a VPN According to the upper m+1 bits of the IP address, the corresponding Branch_Tree is found in the Multibit Trie corresponding to the VPN, and the corresponding route is found in the Branch_Tree. The application improves the efficiency of IP routing lookup.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
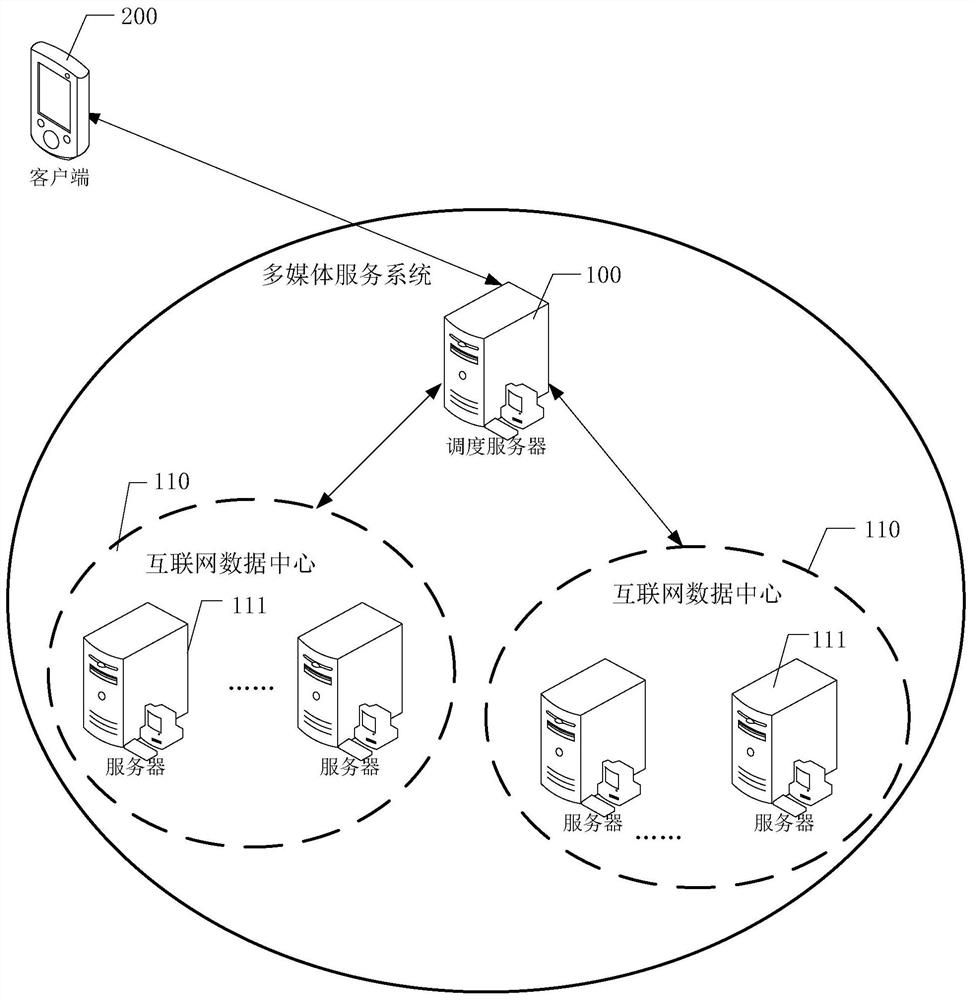
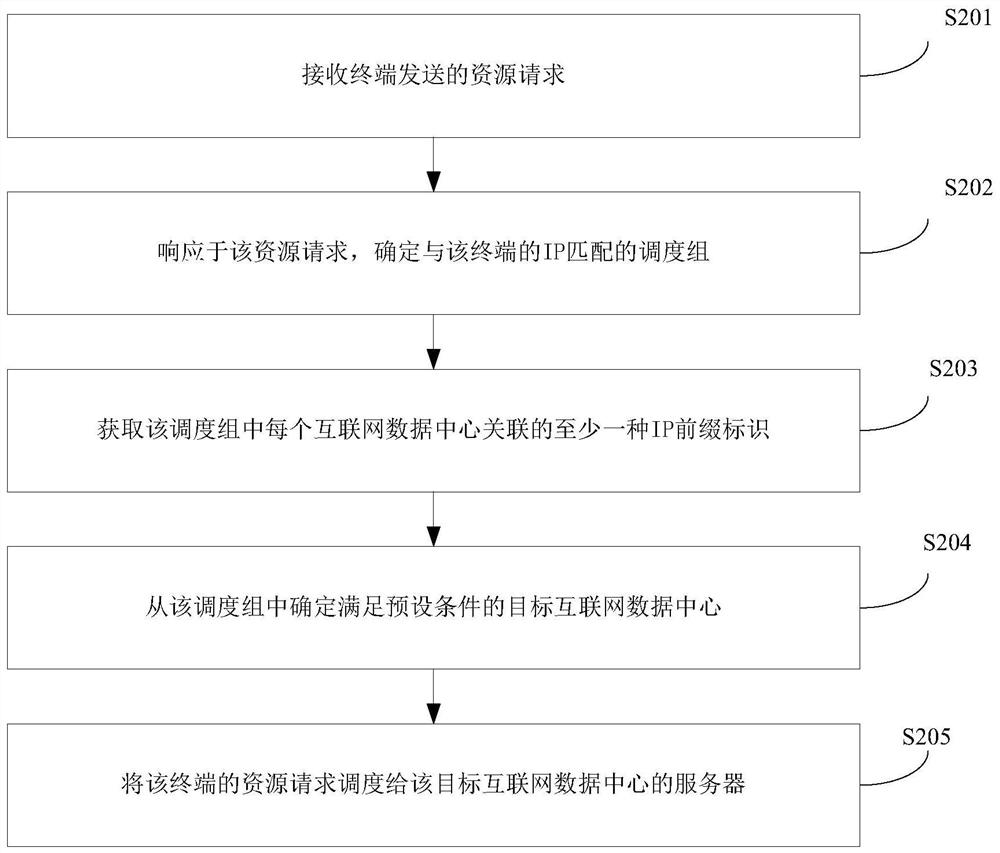
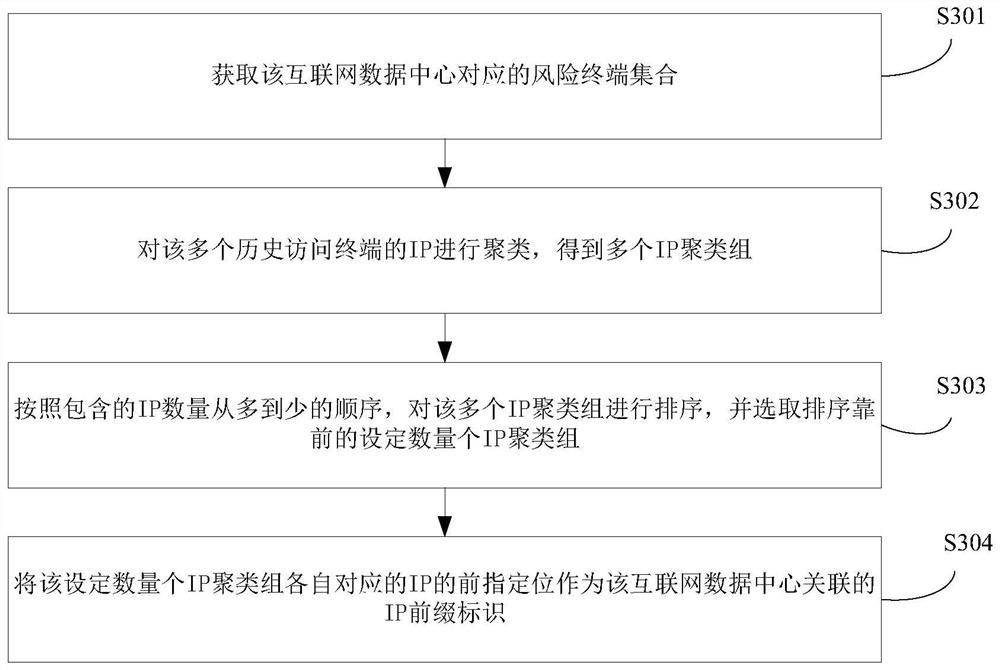
Resource request scheduling method and device
The present application discloses a resource request scheduling method and device. The method includes: receiving a resource request sent by a terminal, the resource request carrying the terminal's Internet Protocol address IP; in response to the resource request, determining that the resource request matches the terminal's IP The dispatching group; obtain at least one IP prefix identifier associated with each Internet data center in the dispatching group, and the IP prefix identifier associated with the Internet data center belongs to the IP prefix corresponding to the historical access terminal with communication connection failure in the Internet data center Designate a position; determine a target Internet data center that meets a preset condition from the scheduling group, and the preset condition includes: at least one associated IP prefix identifier does not include a previous position of the terminal's IP; the terminal's resource request Dispatched to the server of the target Internet data center. The solution of the present application can realize resource request scheduling in a more reasonable manner, and reduce jamming on the user terminal side.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
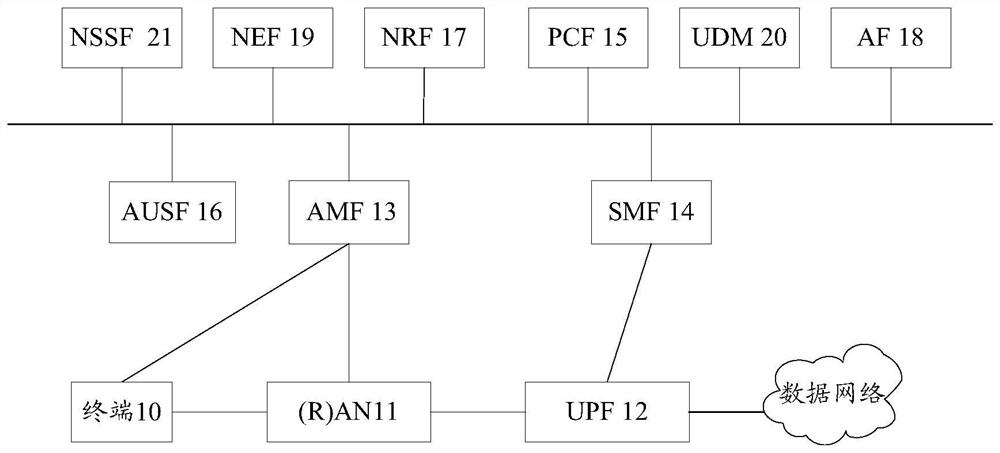
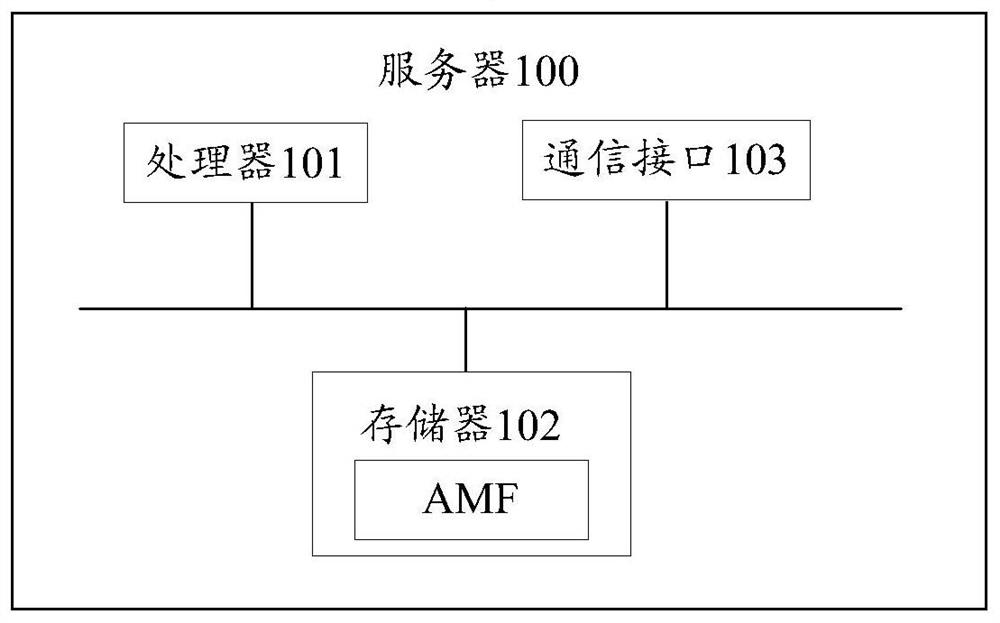
A method, device and system for determining PCF
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, device, and system for determining PCF, which relate to the field of communication technologies and can reduce signaling overhead required for determining PCF to a certain extent. The method includes: when the first AMF receives the PCF identification information sent by the second AMF, and there is a target PCF in the PCF corresponding to the PCF identification information, the first AMF acquires policy information from the target PCF, wherein the PCF identification information includes at least Identification information of a first PCF, where the identification information of the first PCF includes at least one of the IP address of the first PCF, the IP prefix of the first PCF, and the FQDN of the first PCF, and the first AMF is the The AMF that provides services for the secondary access network, and the second AMF is the AMF that provides services for the terminal's last access to the network. The method is applied in the process of the terminal accessing the network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
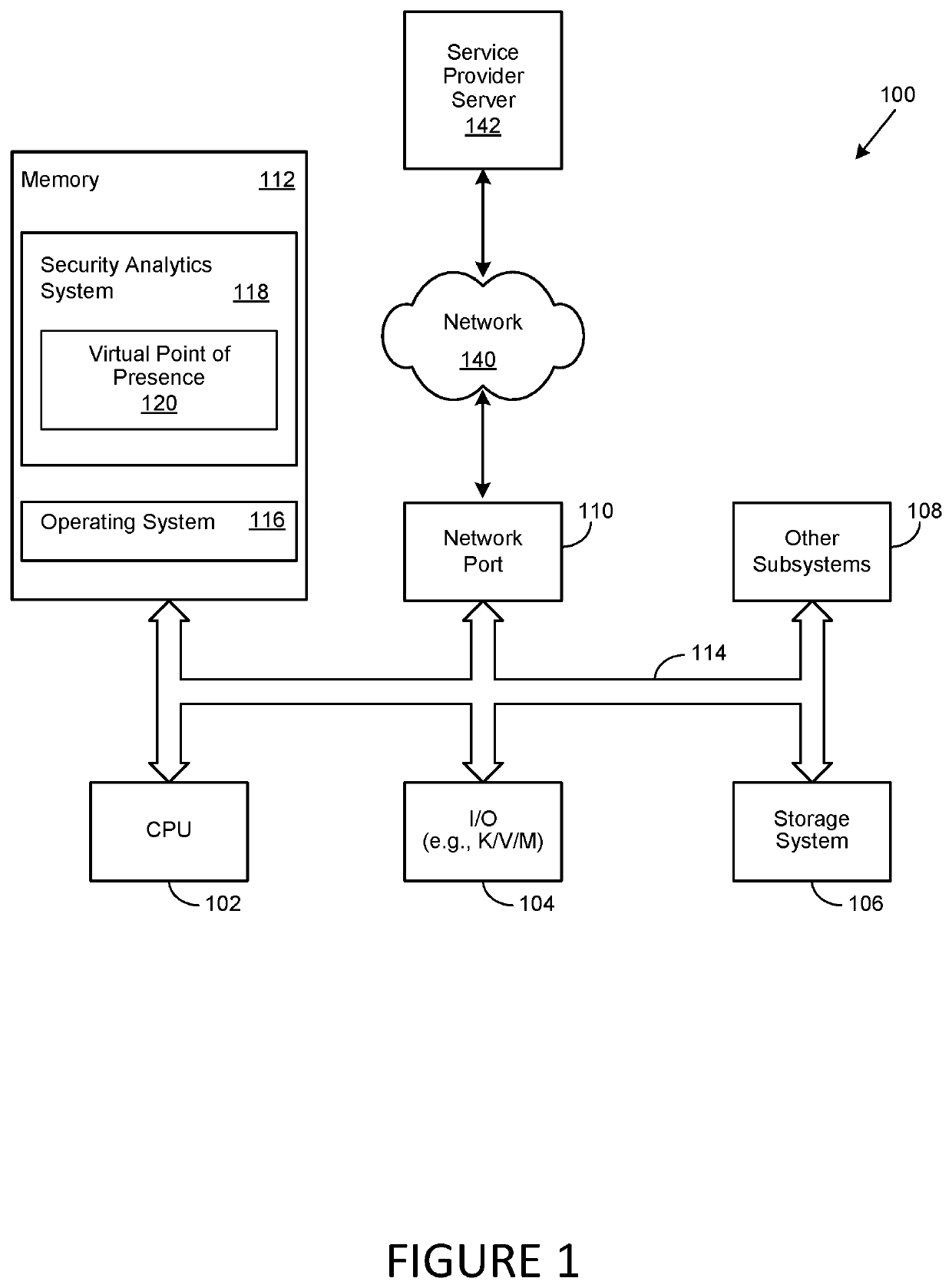
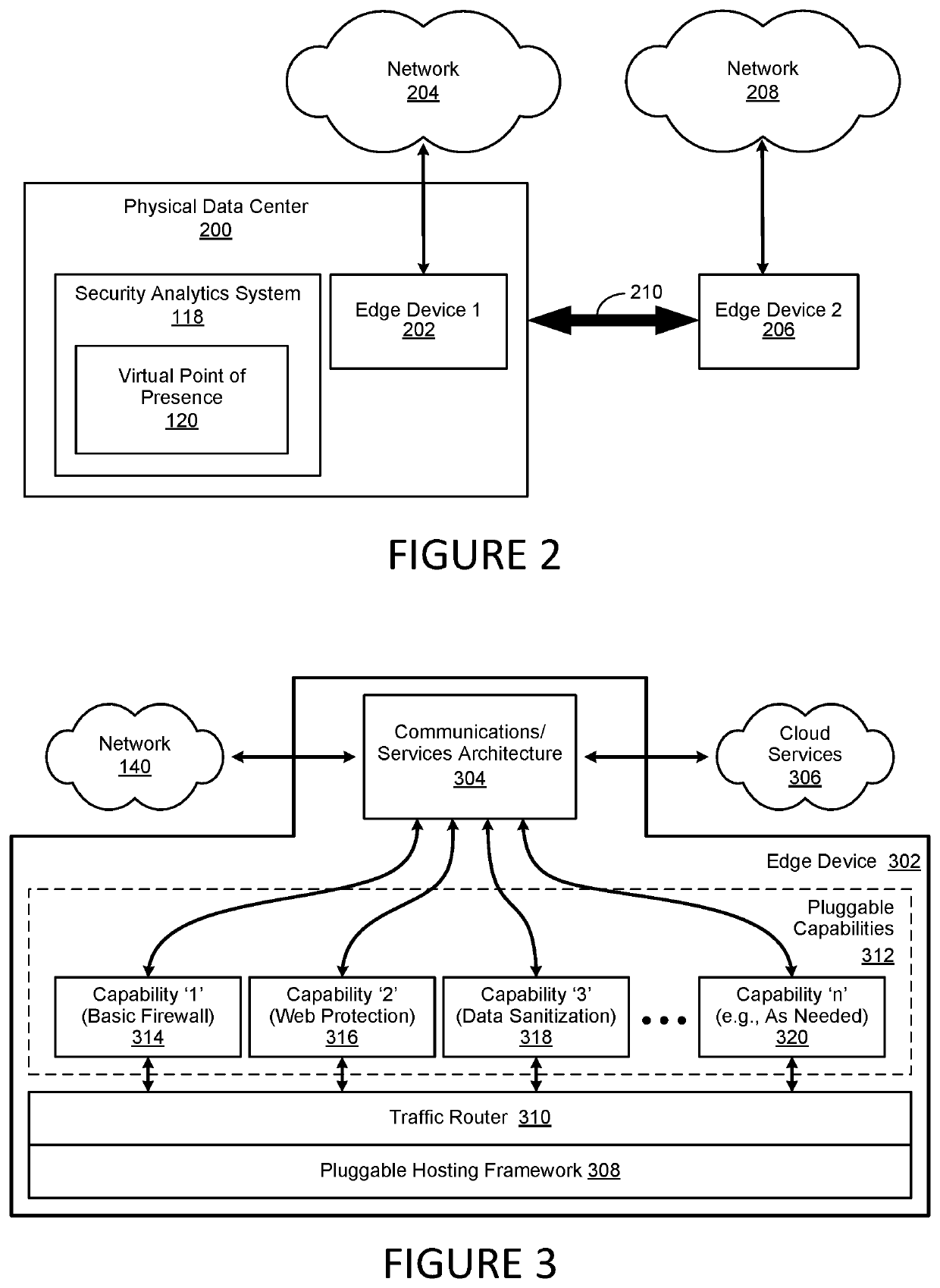
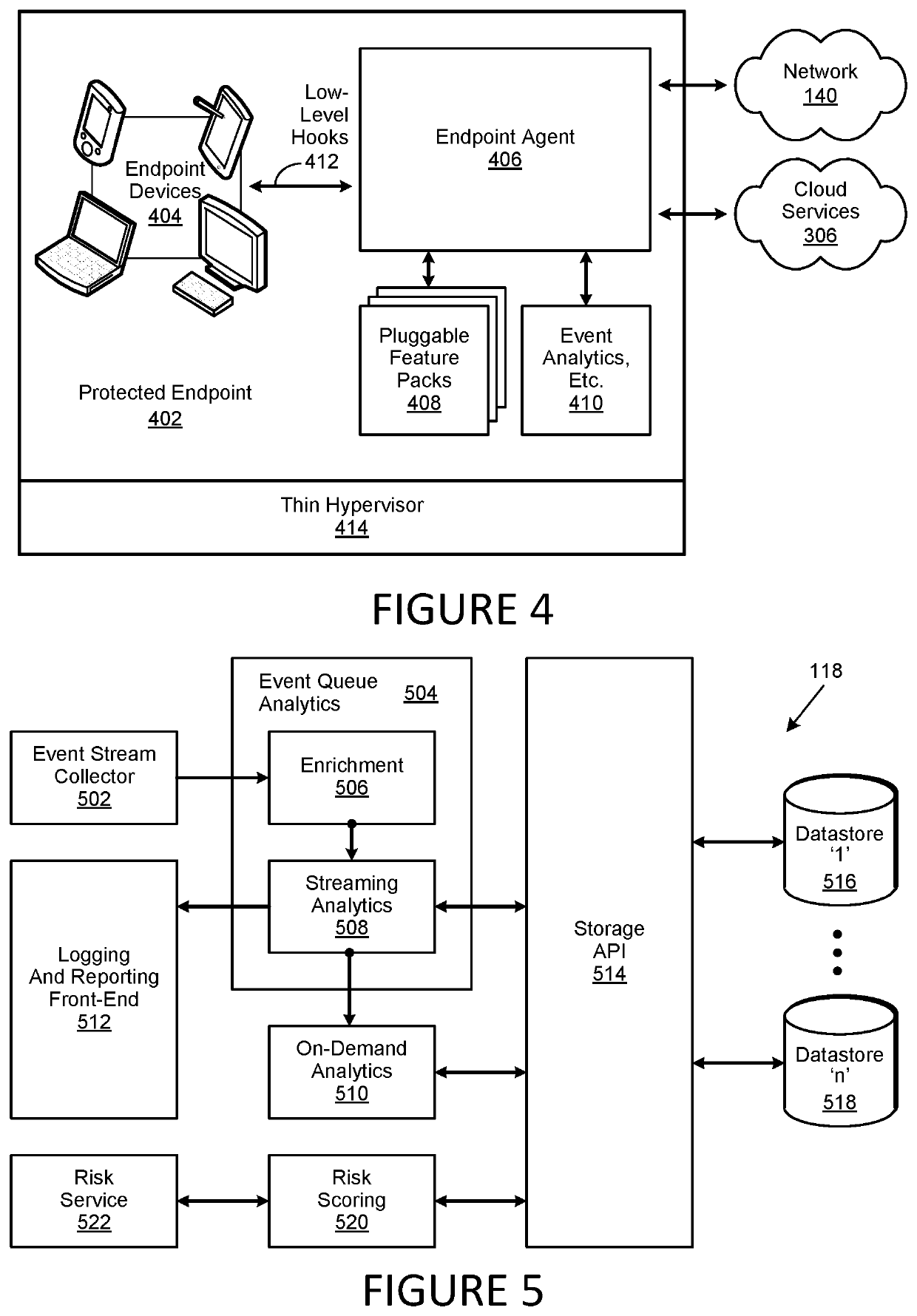
Virtual Point of Presence in a Country to Allow for Local Web Content
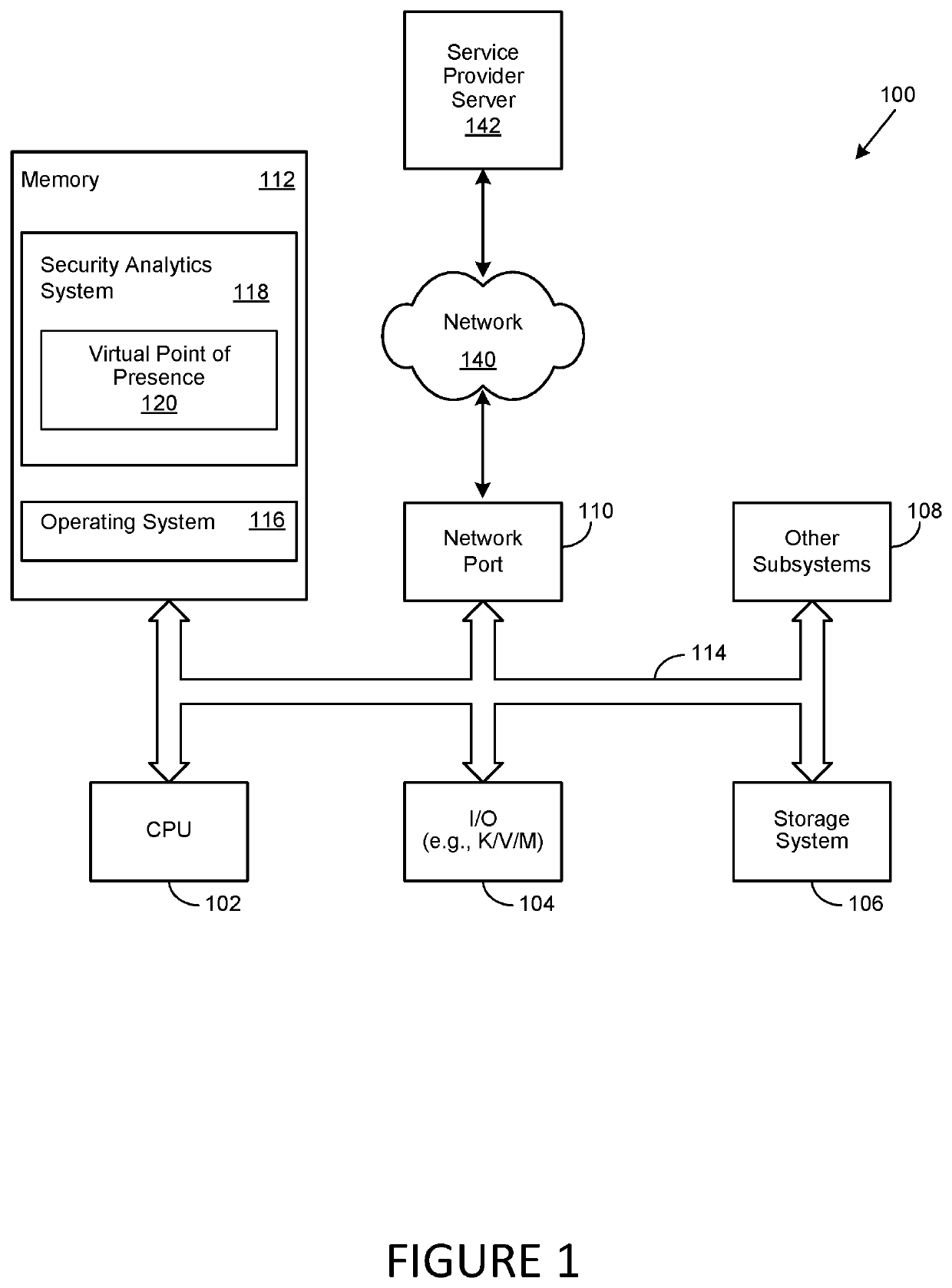
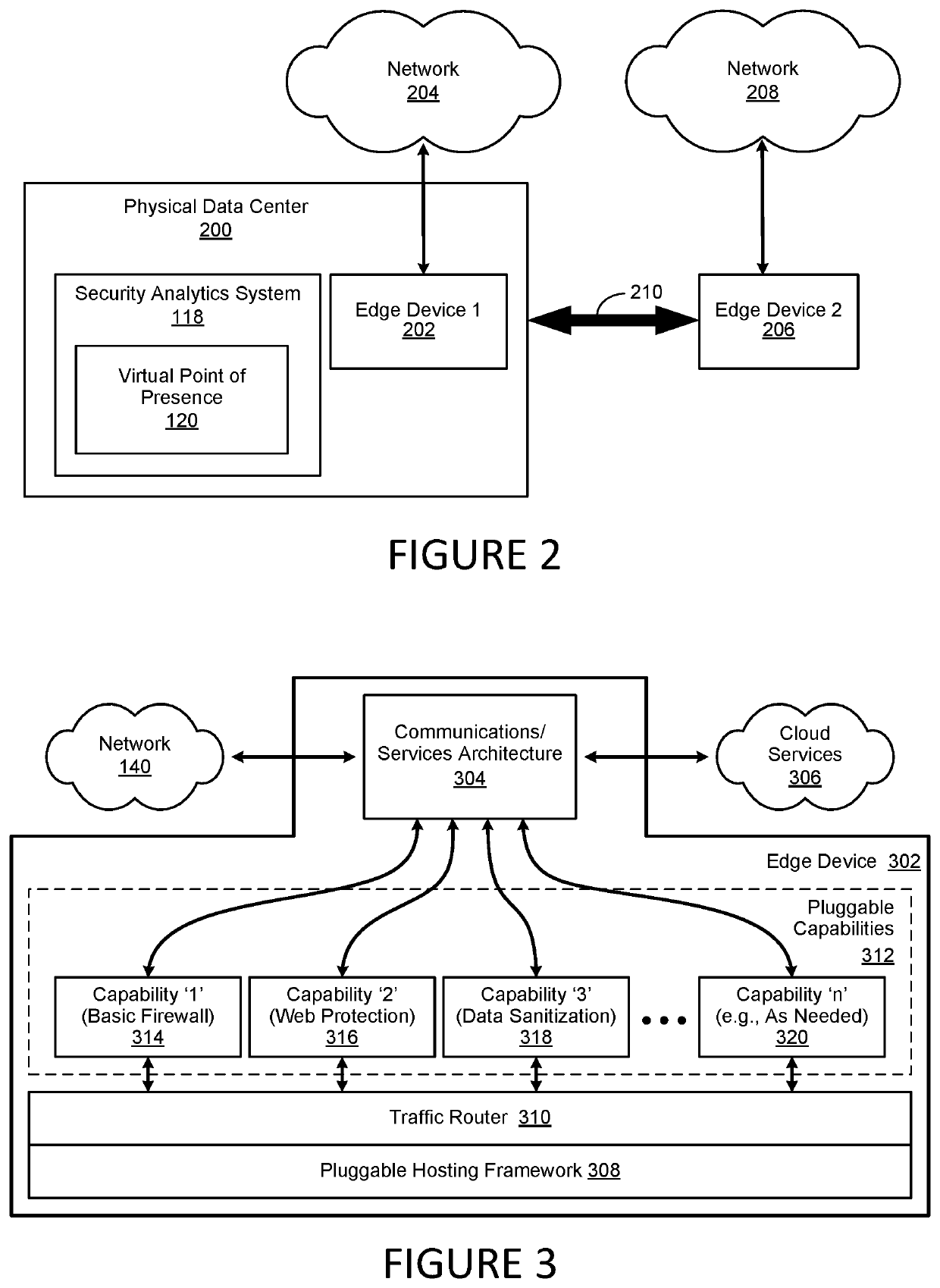
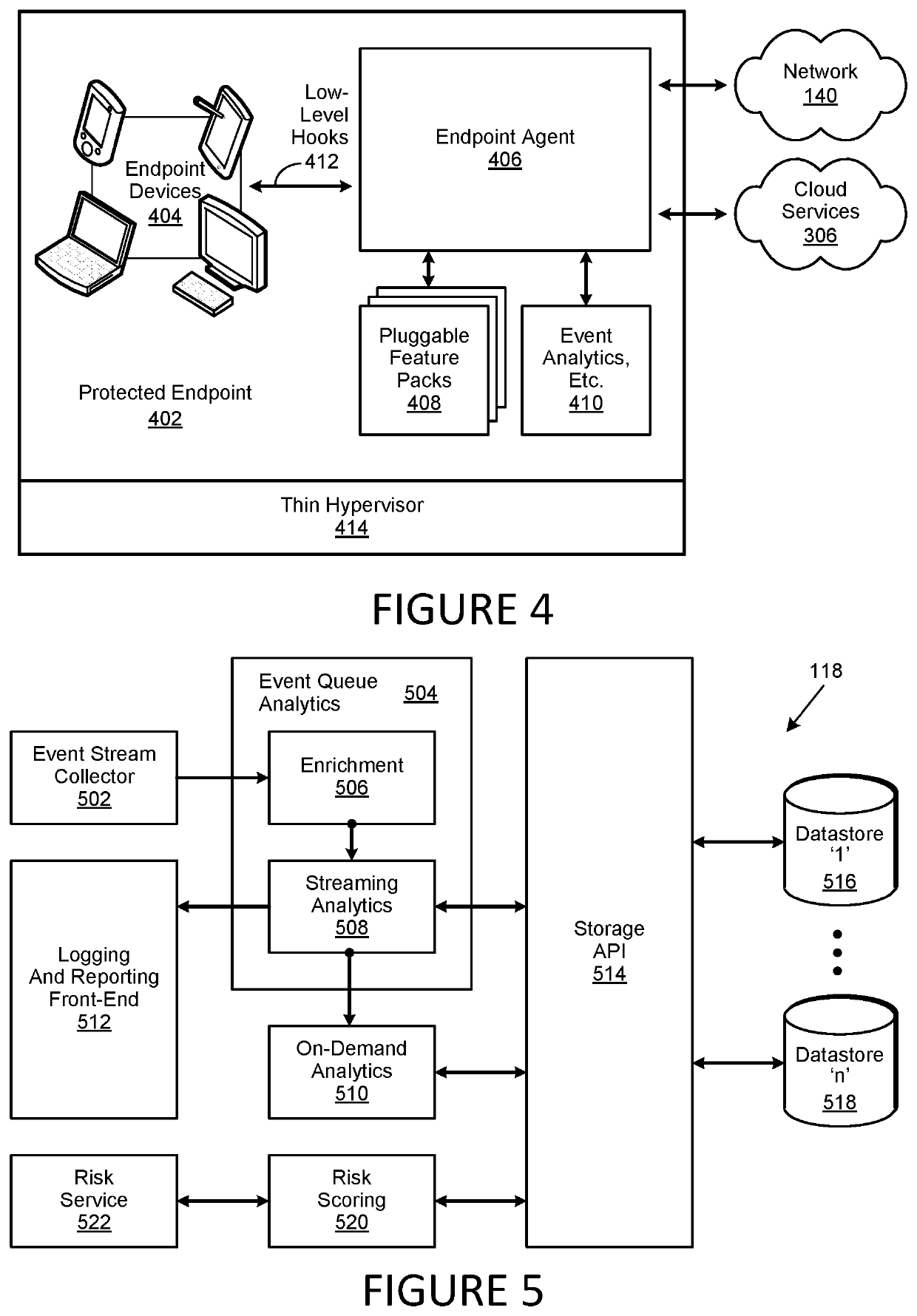
A method, system and computer-usable medium are disclosed for establishing a virtual point of presence or VPoP in a country or locale by registering an internet protocol (IP) prefix range for communication specific to the locale in a physical data center; implementing proxy servers on the data center that support the IP prefix range; geolocating users in the locale to the IP prefix range; network address translating inbound connections to the IP prefix range with IP addresses on the proxy servers to provide extended IP network addresses; and providing content to the users by the proxy servers on using the extended IP network addresses.
Owner:FORCEPOINT LLC
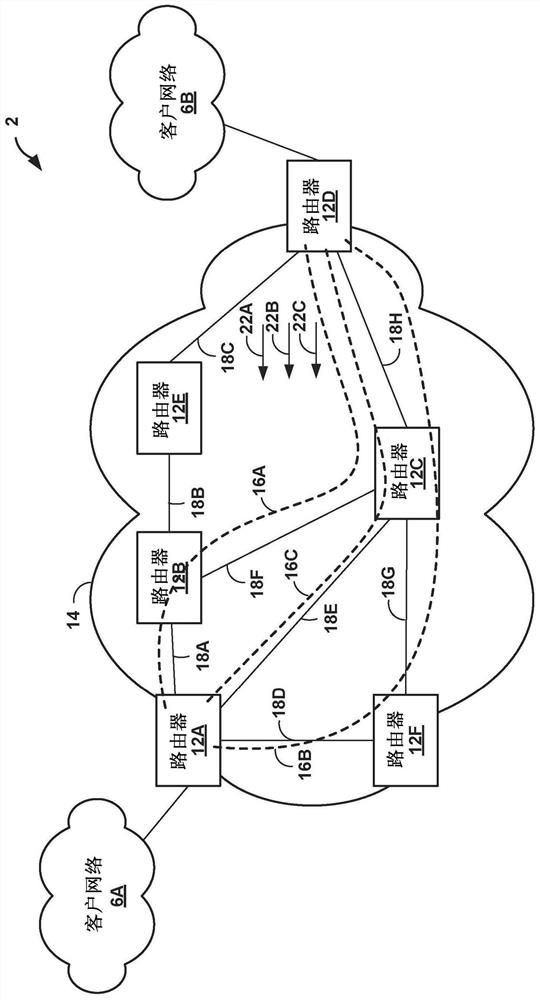
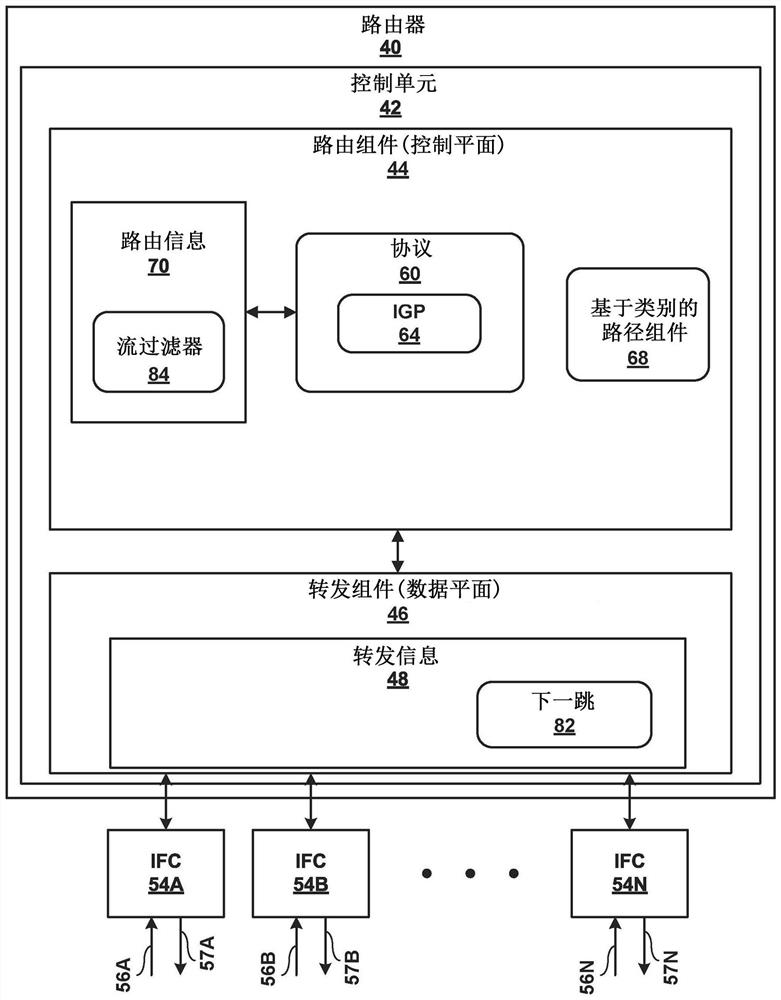
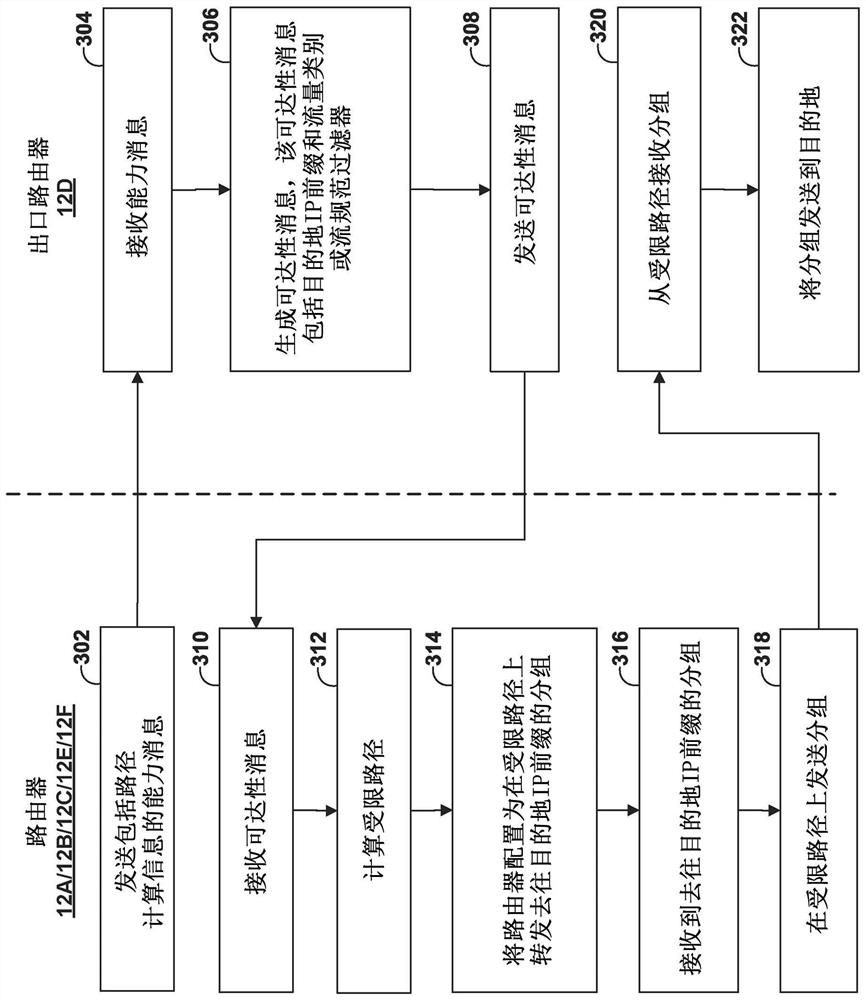
Class-based traffic engineering in IP network
The invention relates to class-based traffic engineering in IP network. Techniques are described for class-based traffic engineering in an IP network. For example, routers of an IP network may establish one or more constrained traffic engineered paths using a link-state protocol (e.g., IGP) without using signaling protocols, such as RSVP or SPRING, or encapsulating packets over MPLS. For example,an egress router of the IP network may receive a capability message specifying the capability of routers to compute a constrained path to the egress router, wherein the capability message comprises path computation information including an identifier of a path computation algorithm to be used by the one or more of the plurality of network devices to reach the egress network device. The egress router may advertise a reachability message including a destination IP prefix and the identifier of the path computation algorithm to cause routers in the IP network to compute the constrained path to reach the egress router.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Virtual point of presence in a country to allow for local web content
A method, system and computer-usable medium are disclosed for establishing a virtual point of presence or VPoP in a country or locale by registering an internet protocol (IP) prefix range for communication specific to the locale in a physical data center; implementing proxy servers on the data center that support the IP prefix range; geolocating users in the locale to the IP prefix range; network address translating inbound connections to the IP prefix range with IP addresses on the proxy servers to provide extended IP network addresses; and providing content to the users by the proxy servers on using the extended IP network addresses.
Owner:FORCEPOINT LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com