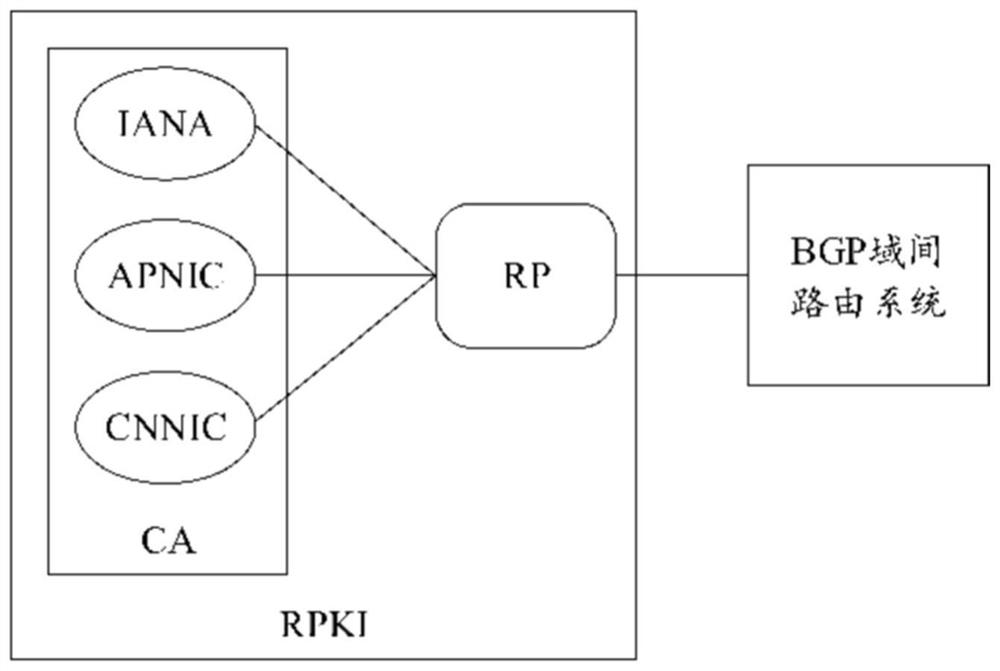
Encoding method and system as well as decoding method and system for routing origin authorization compression
An encoding method and technology of origin, applied in the field of information processing, can solve the problems of ROA data object issuance and size increase, high transmission, verification and use overhead, reduce the scalability of RPKI system, etc. Extended compression coding, high security effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
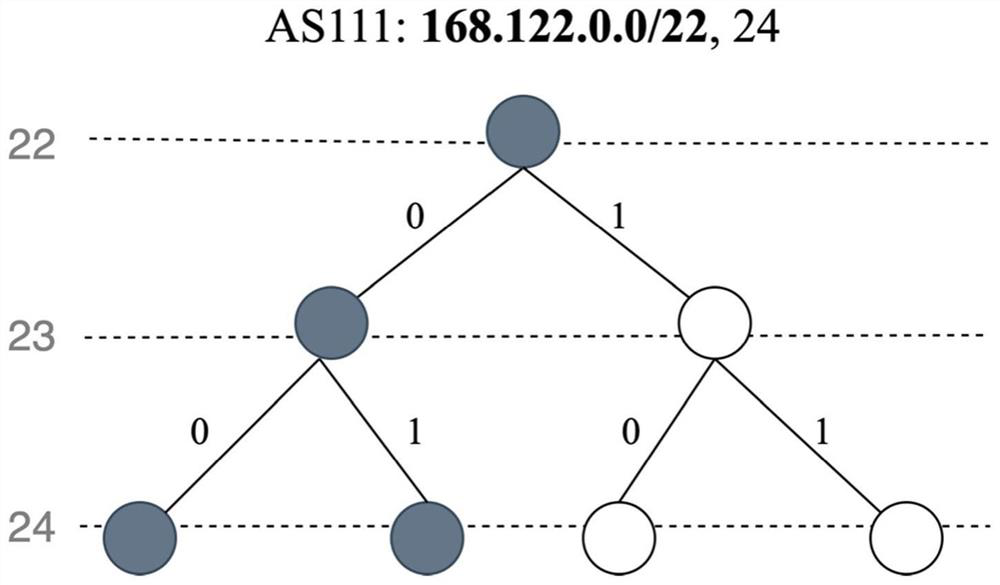
[0048] Assume that the CA plan will Figure 8 When the three IPv4 prefixes in are authorized to AS 111, then the AS obtains an authorized IP prefix set P={34.0.0.0 / 7,32.0.0.0 / 8,38.128.0.0 / 9} in the announced state. For AS 111, the CA first initializes a STMa (assuming the data structure is a hash table) for it to store one or more subtree blocks (identifier, bitmap), where the key is the identifier and the value is the bitmap. The encoding process of CA is actually operated one by one based on the IP prefix.
[0049] In the IPv4 prefix tree, the 5th and 10th layers are both the mounting layer. According to the specific operation content of mounting the IP prefix, the prefix lengths of the above three IPv4 prefixes are 7, 8 and 9 respectively, and the CA will determine the Layer 5 is their mounting layer. Take the authorized IPv4 prefix 34.0.0.0 / 7 as an example. Since 34.0.0.0 is a 32-bit IPv4 prefix in dot-ten notation, its binary form is: 00100010 0000000000000000 00000000....
Embodiment 2
[0051] Assume that the CA plan will Figure 9 When one of the IPv4 prefixes is authorized to AS 222, the AS obtains an authorized IP prefix set P={10.1.0.0 / 16}. For AS 222, the CA first initializes a STMa for it. In the IPv4 prefix tree, the 15th and 20th layers are both the mounting layer. According to the specific operation content of mounting the IP prefix, the prefix length of the above IPv4 prefixes is 16, and the CA will determine the 15th layer as its mounting layer. carrier layer.
[0052]For the IPv4 prefix 10.1.0.0 / 16, the first 16 bits jointly determined by the CA according to its IP address and prefix length are: 0000101000000000, therefore, the identifier of the root of the subtree it mounts is: 1000010100000000 (000010100000000 is the prefix of 0000101000000000 15 bits). Therefore, the bit string determined by the 16th bit is: 1, and by adding 1 in front of it, the node number of the IP prefix in the subtree is 3 (the binary bit code of 3 is: 11). Therefore, t...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Assume that the CA plan will Figure 10 When the two IPv4 prefixes in are deauthorized to AS 111, the CA first initializes an STMw for AS 111. The encoding operation of the subtree blocks determined for the above two IPv4 prefixes is basically the same as the encoding operation in Embodiment 1, except that the revocation flag of the bitmap is set to "1", indicating that the above two authorized IPv4 prefixes are in the revoked state. Therefore, the CA can get an STMw containing one entry (id=100100, bm=00000000000000000000000100100001). Finally, the CA encapsulates the content in the STMw in the SubTreeBlock field of the ROA data object in units of tuples (identifier, bitmap), and sets the asID field to an integer 111, and sends it to the RP through the rysnc protocol / RRDP protocol.
[0055] 2. Maintenance operation of routing origin authorization information based on subtree mapping
[0056] Embodiment one:
[0057] Suppose the RP receives the ROA data object sent f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com