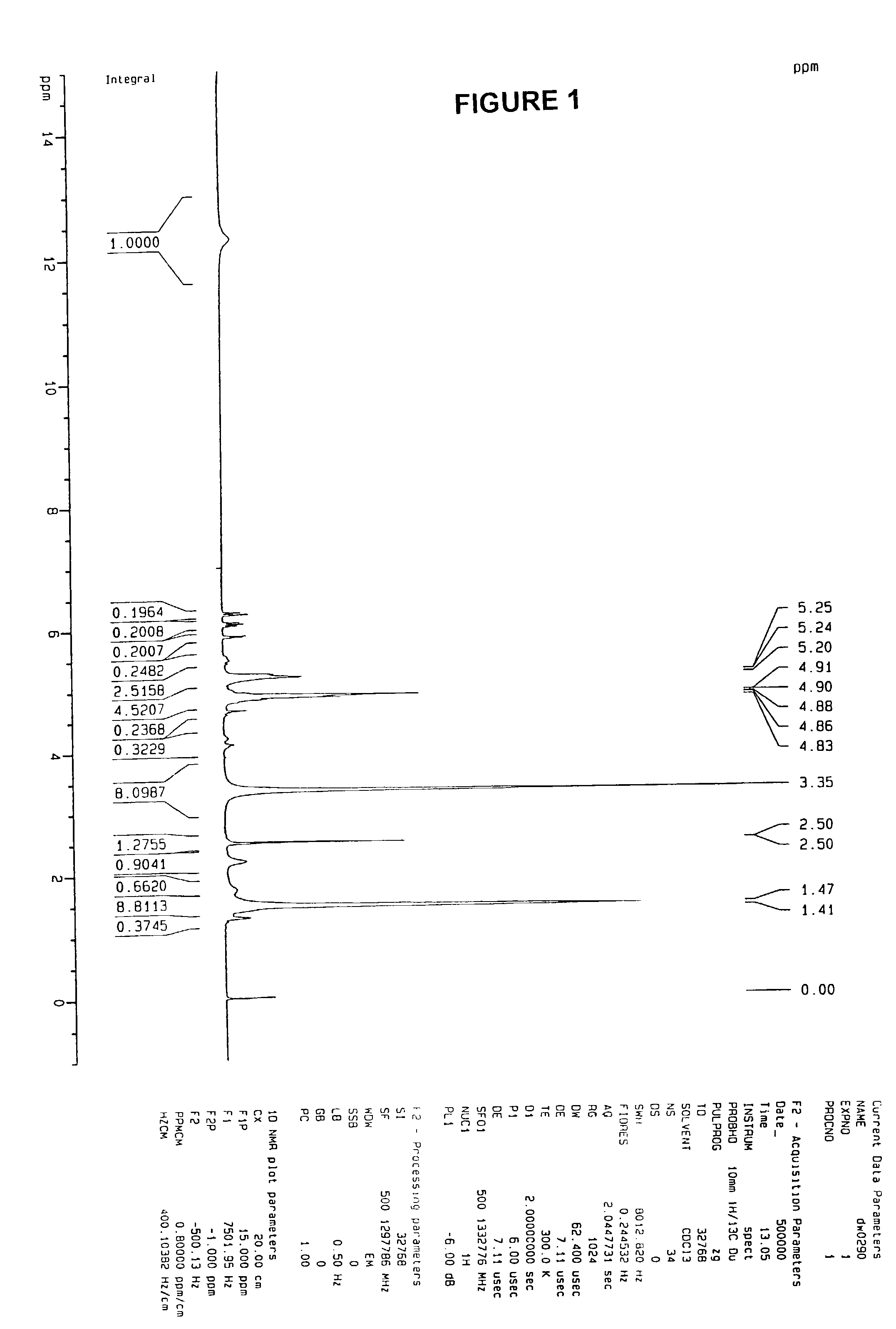
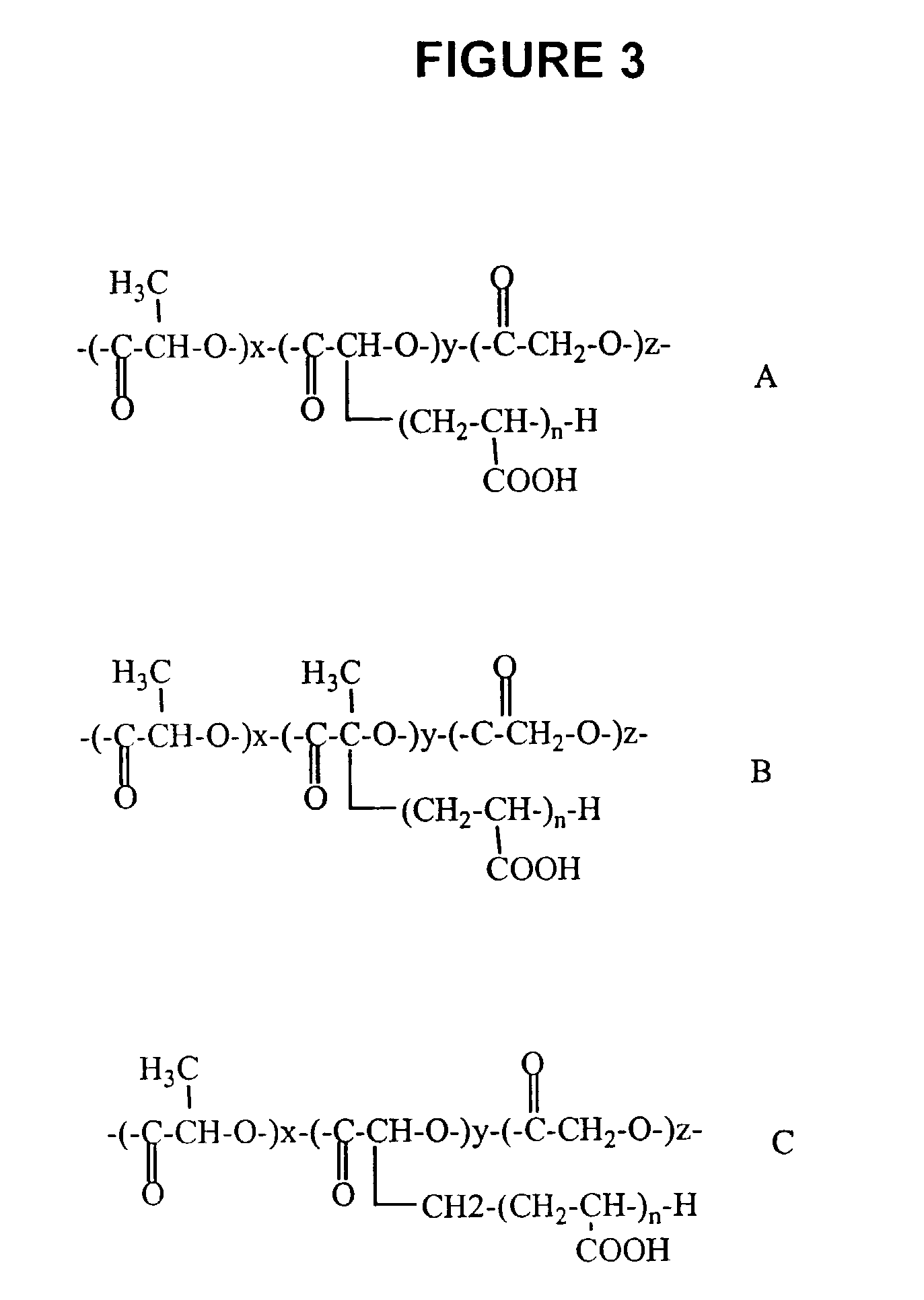Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Ionizing irradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Food irradiation (the application of ionizing radiation to food) is a technology that improves the safety and extends the shelf life of foods by reducing or eliminating microorganisms and insects. Like pasteurizing milk and canning fruits and vegetables, irradiation can make food safer for the consumer.
Methods of making functional biodegradable polymers
There is provided a method to modify biodegradable polymers using the direct reaction of a biodegradable polymer in a vinyl monomer and may take place in the presence of initiators. The initiator may be free radical initiators, heat, ionic initiators, UV irradiation, ionizing irradiation and other high energy irradiation. Suitable biodegradable polymer include polycaprolactone, poly(lactic acid), poly(glycolic acid) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). Suitable vinyl monomers include acrylates, methacrylates and the like.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method for removing antibiotic resistance genes through ionizing irradiation
The invention discloses a method for removing antibiotic resistance genes through ionizing irradiation. Antibiotic mushroom dregs are treated with an ionizing irradiation technology (including gamma-rays and high-power electron beams generated by an electronic accelerator) to damage DNA of microbial cells, so that the resistance genes are effectively removed, and residual antibiotics can be decomposed simultaneously. The method is efficient and wide in application range; radiation can be performed at the normal temperature, no chemical reagents or only a few chemical reagents are required to be added, and no secondary pollution can be caused. The method can be applied to removal of the resistance genes in the antibiotic mushroom dregs, can be applied to removal of the resistance genes in water, soil and sludge and has wide application prospects in the environmental field.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
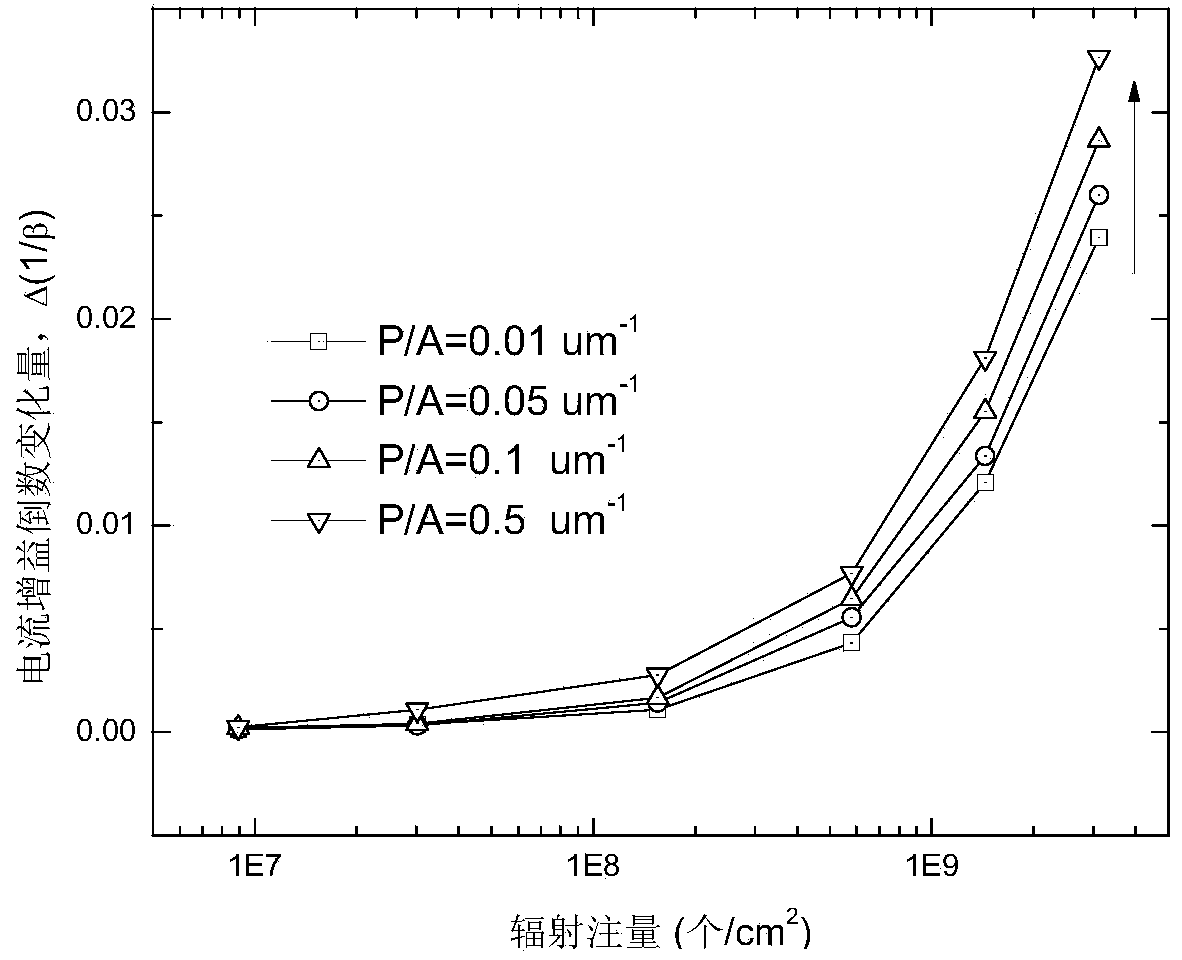
Radiation-proof strengthening method for bipolar device based on geometric structure of emitter region
ActiveCN103871873AImprove radiation resistanceThe preparation process steps are simpleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowIonizing irradiation
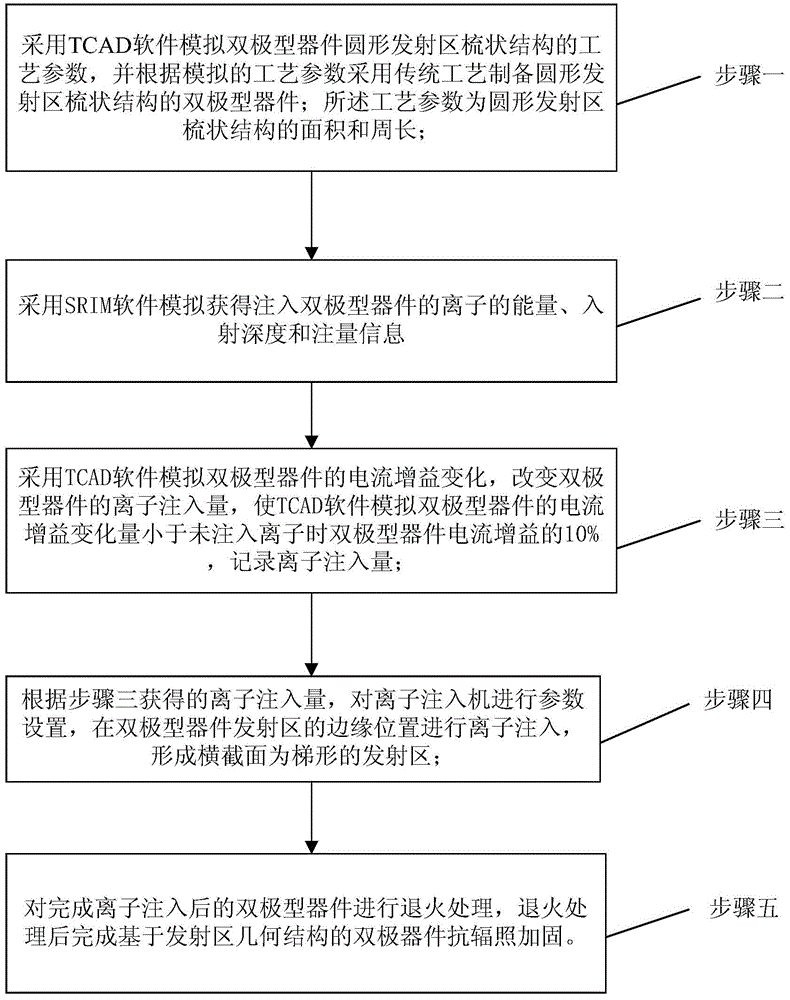
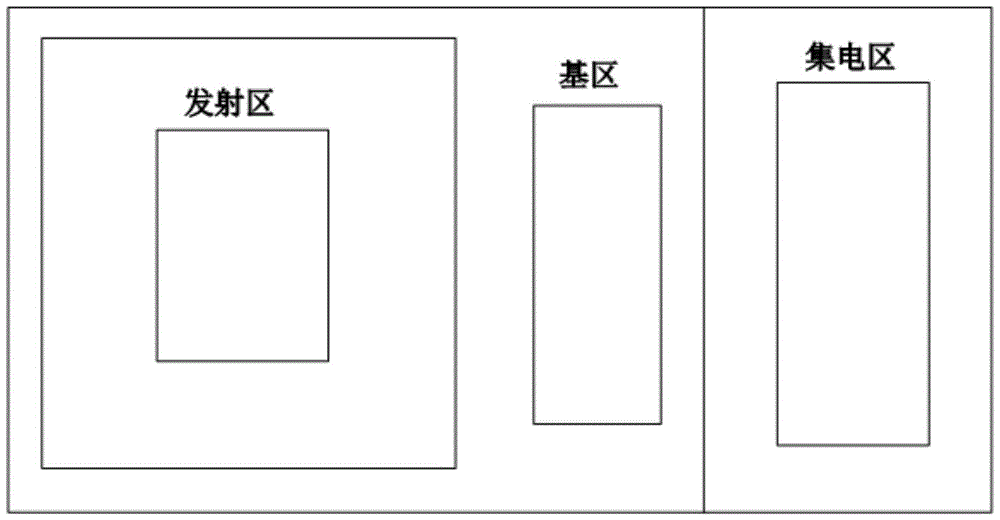
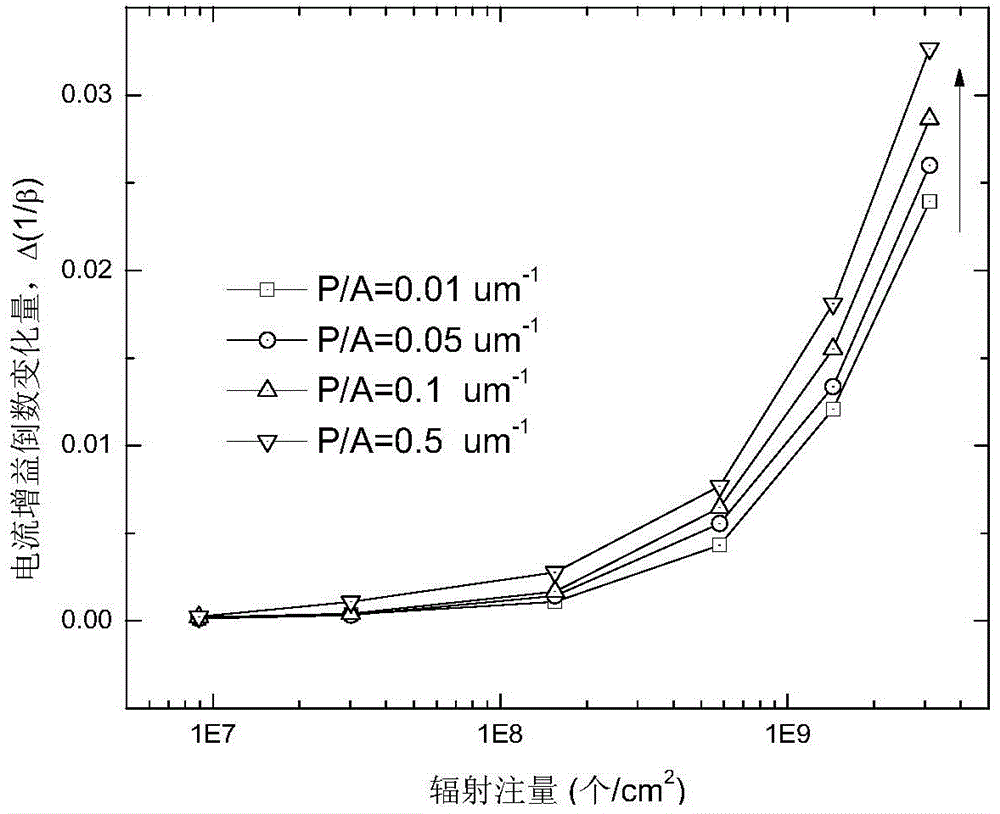
The invention relates to and is applicable to the technical field of electronics, in particular to a radiation-proof strengthening method for a bipolar device based on the geometric structure of an emitter region. The radiation-proof strengthening method aims to solve the problems that an existing bipolar junction transistor and a circuit are high in damage degree of current gain in a space radiation environment, and an existing bipolar device is low in radiation resistance ability. According to the radiation-proof strengthening method for the bipolar device, the traditional bipolar device process is reserved, and manufacturing process steps are very simple. By means of the radiation-proof strengthening method for the bipolar device, the influence of positive charges captured by oxide induced through ionizing irradiation and the interface state on performance parameters of the device can be lowered substantially by improving the geometric structure of the emitter region, and the radiation resistance ability of the bipolar device is enhanced remarkably by 2-5 times compared with that of the existing bipolar device.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +2
Method for preparing middle size or oligo-glucomannan using radiation method for degrading plump konnjaku fine powder
The invention discloses a making method of middle and low glucomannan polysaccharide liquid through irradiating, decomposing and bulking konjak powder, which comprises the following steps: bulking konjaku flour through water completely; ionizing and irradiating to degrade glucomannan; stewing; sedimenting; filtering to remove non-degraded slag to obtain the product; sealing the food through flexible bag or hard glass container; sterilizing; setting the molar rate of konjaku flour and water at 15-60 with pH value at 3-9; obtaining the adsorbent of ionizing irradiation at 3-6; irradiating under normal temperature through Co-60 gamma ray or X-ray or electronic ray.
Owner:FARM PROD PROCESSING & NUCLEAR AGRI TECH INST HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
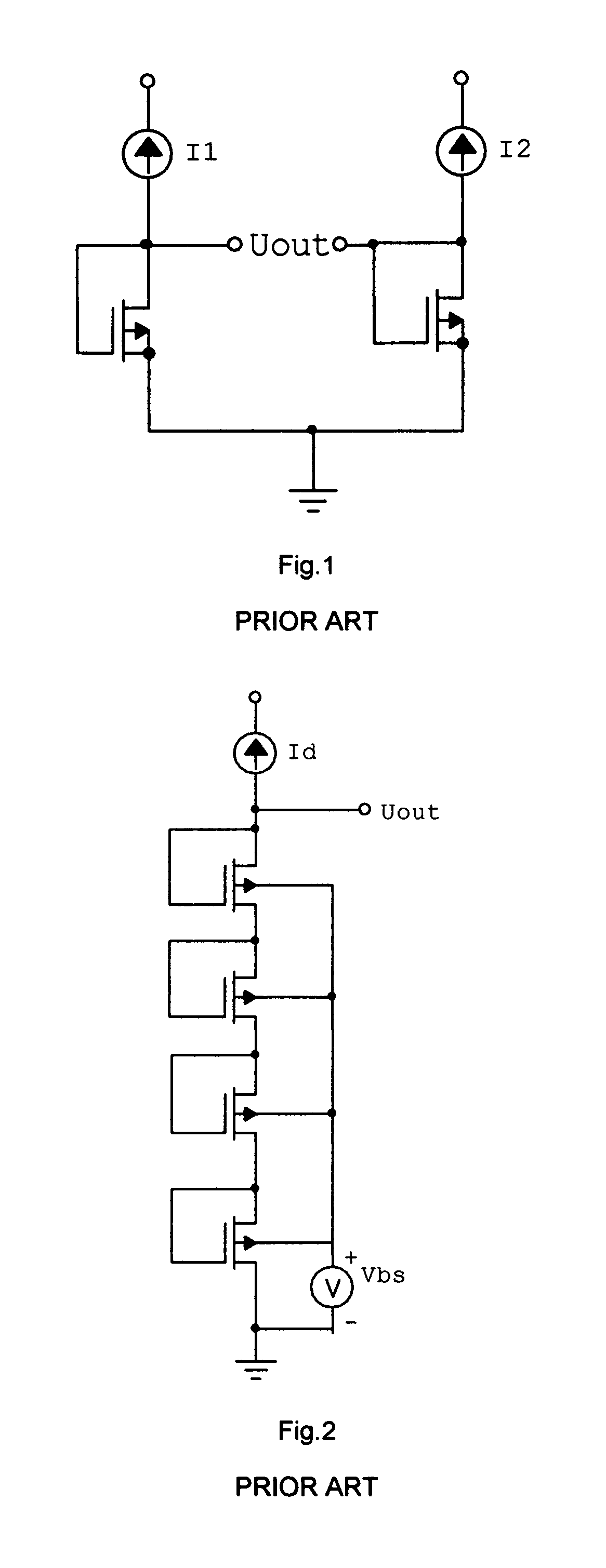
Personal dosimeter on the base of radiation integrated circuit
InactiveUS8198595B2Minimum temperature effectInsensitive to temperature changesDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansMOSFETDosimeter
This invention provides a radiation dosimeter and new method of operation which comprise two types of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) circuits allowing to amplify the threshold voltage changes due to radiation and provide temperature compensation. The first type dosimeter is a radiation integrated circuit (RADIC) which includes two radiation field-effect transistors (RADFET) and two MOSFETs, integrated into the same substrate. The second type of radiation circuit includes two RADFETs, integrated into the same substrate, and two resistors. The amplification of the threshold voltage change is achieved by using amplification principles of an MOSFET inverter. In both cases, under the ionizing irradiation, the gate of first RADFET is forward biased and the gate of second RADFET is biased off. In the reading mode the amplified differential threshold voltage change is measured. The increased radiation sensitivity allows to measure of the milli-rad doses. The temperature effect and drift is substantially eliminated. These radiation integrated circuits can be used as a personal dosimeter in the nuclear, industrial and medical fields.
Owner:URYUPIN FR OLEG +1
Method for curing an overcoat in a photoconductor used in an electrophotographic imaging device
A method of curing a protective overcoat layer on the outermost portion of an organic photoconductor drum using dual curing process is provided. The first curing step applies either ionizing irradiation, such as with an electron beam or by gamma rays or applies non-ionizing irradiation such as ultraviolet light to the overcoated photoconductor drum. A mask or shield is sized to be placed over the print area of the initially cured photoconductor drum, thereby exposing the outermost edges of the photoconductor drum. The outer edges of the masked photoconductor drum is then exposed to a second curing step using non-ionizing irradiation such as ultraviolet light.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Use of peptides for the control of radiation injury
ActiveCN101443080AConvenience to workPeptide/protein ingredientsMedical devicesWhole bodyGamma irradiation
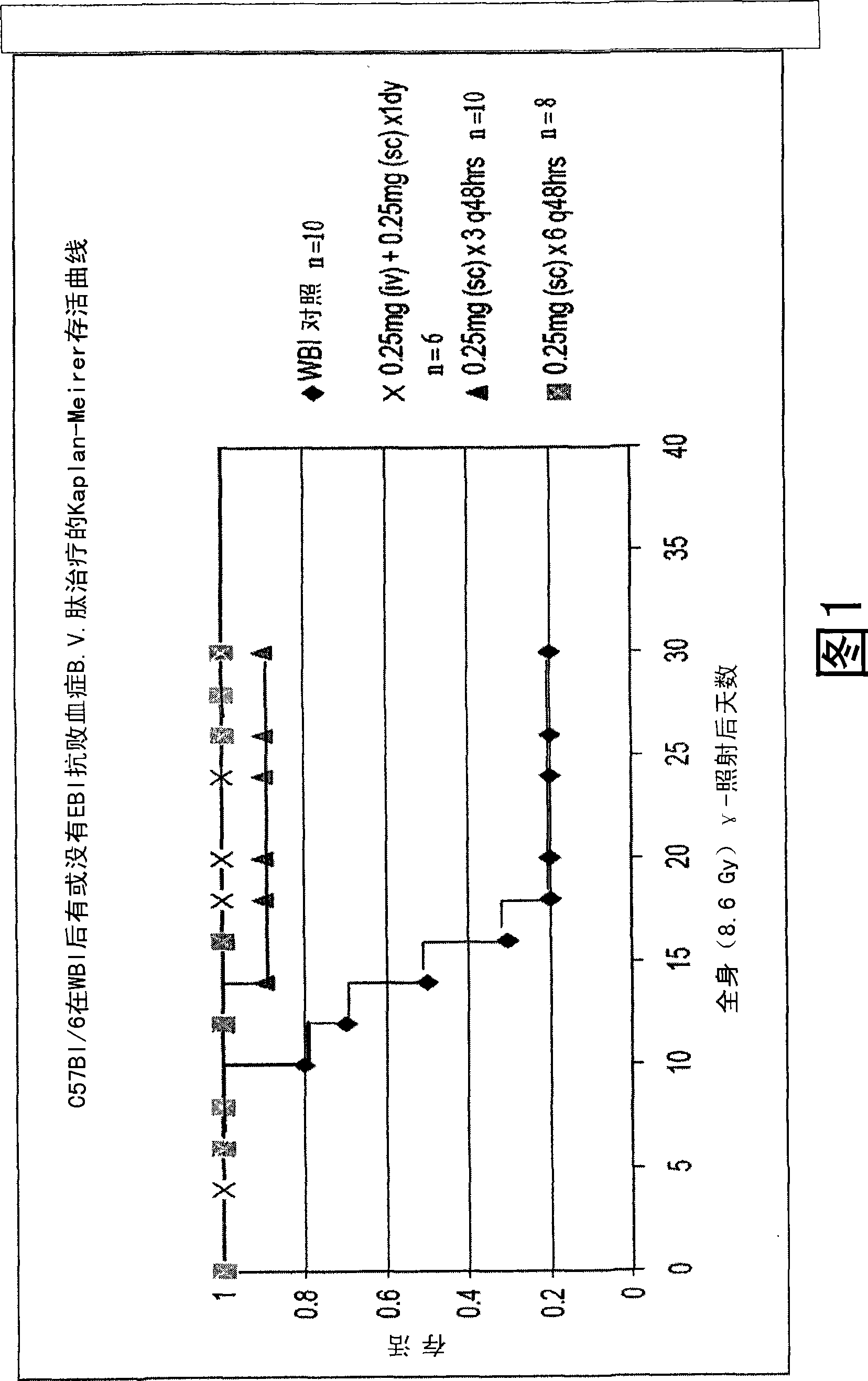
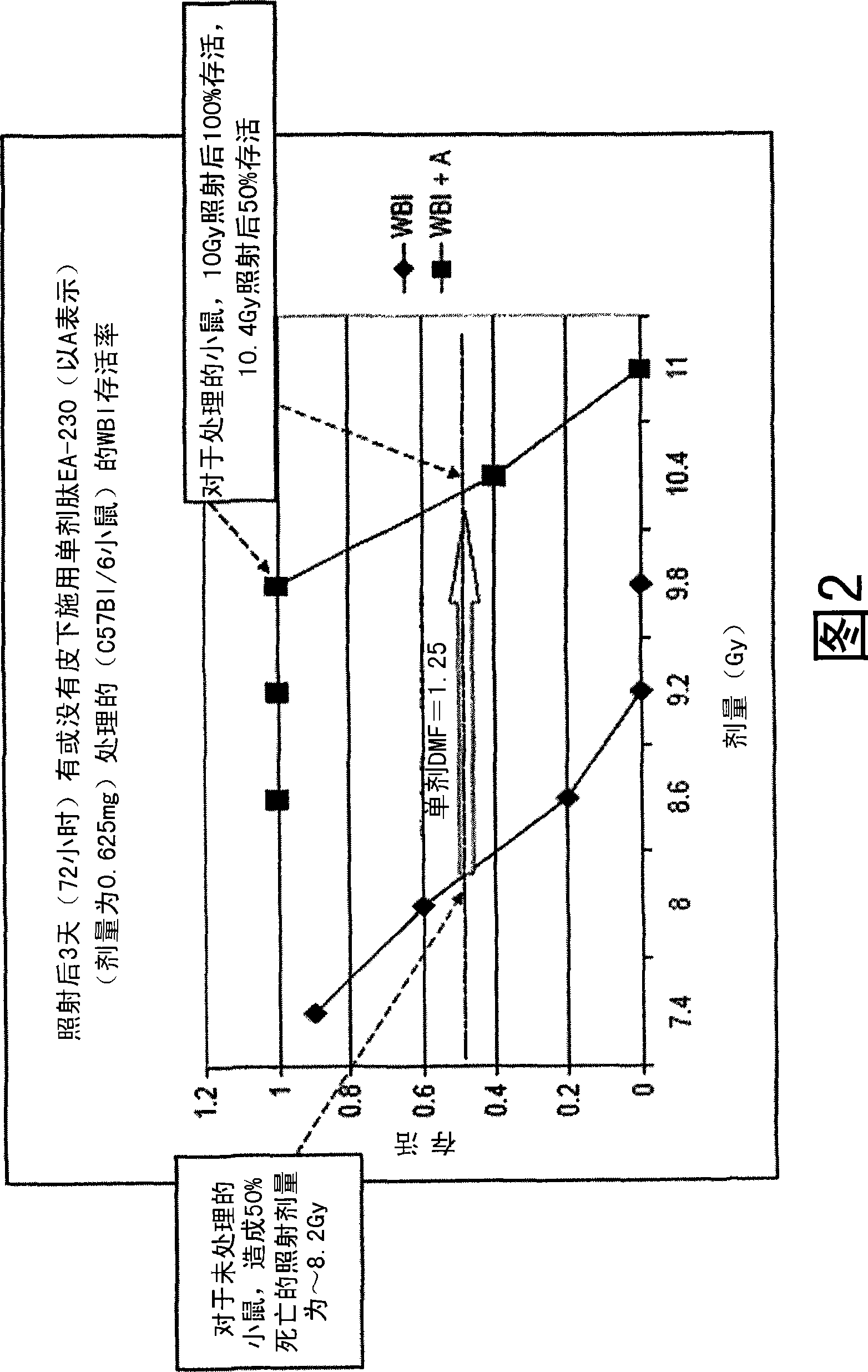
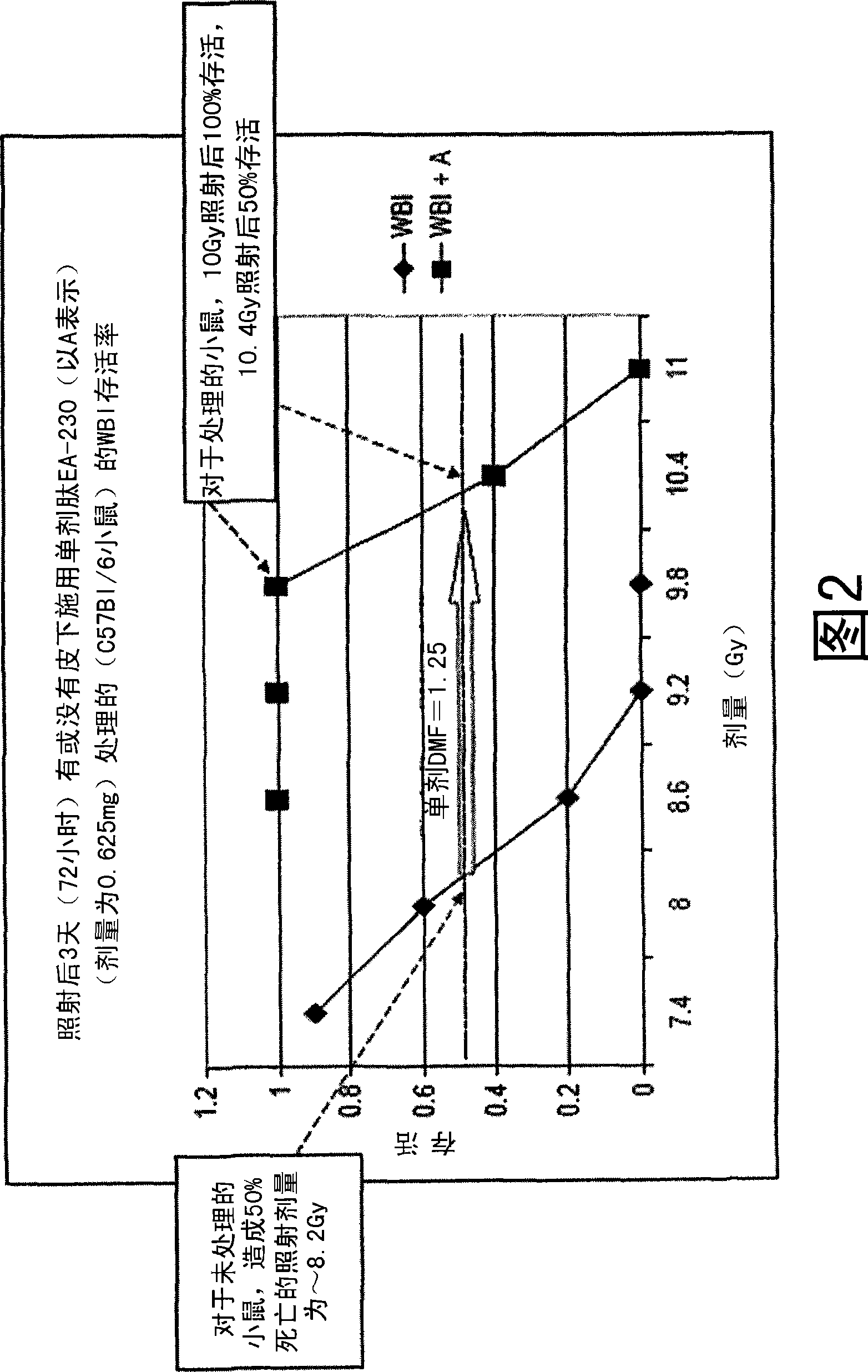
The invention relates to the field of drug development against acute radiation injury caused by exposure to high-energy electromagnetic waves (X-rays, gamma rays) or particles (alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons). To date, there is no effective drug to ameliorate radiation injury after accidental exposure to ionizing irradiation. The invention provides a method of treating radiation injury of a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids. Furthermore, the invention provides use of a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids for the production of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of a subject suffering from or believed to be suffering from radiation injury. In particular, the invention provides anti-radiation peptides having a dose reduction factor (DRF) against acute gamma irradiation of at least 1.10, said DRF determinable by testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a test group of mice treated with said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and, testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a control group of mice treated only with the vehicle of said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and wherein the DRF is calculated by dividing the LD5O / 3O of the peptide-treated animals by the LD50 / 30 of the vehicle-treated animals.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
RVA-APC combined method for discrimination of ionizing irradiation wheat and flour
InactiveCN104535459AEasy to measureRapid determinationFlow propertiesCombined methodIonizing irradiation
The invention discloses a RVA-APC combined method for discrimination of ionizing irradiation wheat and flour. The method includes: taking test wheat raw grain or flour sample and a wheat raw grain or flour product (unirradiated) of the same variety and producing area to do contrast; conducting sample pretreatment, grinding the sample into flour and performing sieving by a 80-mesh sieve; conducting RVA test on the sample, weighing 2.0-3.5g of the sample, adding 20.0-30.0g of distilled water, and then putting the mixture into a RVA tester to carry out heating determination to obtain 6 main characteristic spectrum values in the RVA tester; performing APC determination on the sample; conducting comparison with the contrast group, if five RVA characteristic indexes, i.e. peak viscosity, through viscosity, final viscosity, breakdown and setback decrease, the pasting temperature rises and the aerobic plate count is less than 10<6> cfu / g, determining that ionizing irradiation occurs yet and the greater the difference is, the higher the received irradiation dose is. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of small detection sample amount, simple operation, fast determination process, and low cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
Integrated treatment method of heavy metal passivation and nutrient nitrogen and phosphorus recovery for domestic animal sewage
ActiveCN107298512APassivation fastEfficient passivationWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryElectrolysisReverse osmosis
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Laminate and process for producing the laminate
InactiveUS20110198117A1Improve adhesionImprove electrical performanceSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorIonizing irradiation
A laminate including a resin layer and a metal layer, the resin layer being obtained by modifying at least part of the surface of a resin film including a thermoplastic cyclic olefin resin by ionizing irradiation, and the metal layer being formed on the modified area of the surface of the resin film by plating, a method of producing the same, and an electronic circuit board including a circuit formed by etching the metal layer of the laminate by photolithography, are disclosed. The laminate ensures that the insulating resin layer (flat surface) exhibits high adhesion to the conductor layer.
Owner:JAPAN SURFACE TREATMENT INST +2
Method to make a photoconductor drum having an overcoat using a dual curing process
ActiveUS10289014B1Pretreated surfacesElectrography/magnetographyNon-ionizing radiationElectrical conductor
A method of preparing an organic photoconductor drum having a protective overcoat on its outermost surface is provided. In an example embodiment, a photoconductor drum having an electrically conductive substrate, a charge generation layer, a charge transport layer and an outermost protective overcoat layer is provided. The photoconductor drum is cured using a two-step process. The first curing step applies either ionizing irradiation, such as with an electron beam or by gamma rays or applies non-ionizing irradiation such as ultraviolet light to the photoconductor drum. A mask is sized and placed over the print area of the initially cured photoconductor drum, thereby exposing the outermost edges of the photoconductor drum. The outer edges of the masked photoconductor drum is then exposed to a second curing step using ultraviolet light irradiation.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
Methods for treating combined radiation and thermal injury
InactiveUS9272013B2Improve survivalAccelerated burn healingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsThermal injuryMedicine
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Ionizing irradiation sterilization of bacterial minicell-based biopharmaceuticals and methods of use
Disclosed herein are methods of terminally sterilizing bacterial minicells or compositions comprising bacterial minicells by exposure to ionizing irradiation. Also disclosed are terminally sterilized bacterial minicells, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the bacterial minicells, and methods of use the bacterial minicells and pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:VAXIION THERAPEUTICS
VOC waste gas microwave combustion furnace
InactiveCN101293172AFast and effective decompositionReduce pollutionGas treatmentDispersed particle separationHigh energyMicrowave effect
The present invention provides a VOC exhaust microwave combustion furnace. Nanometer titanium dioxide is adopted as accelerant and coated on active carbon and other supporters; the supporters are filled in a high-temperature ceramic pipe arranged the carrier of a reaction tank in the combustion furnace; after the high-temperature ceramic pipe is irradiated by the microwave energy generated by a microwave generator of a magnetic control pipe, the specific inductive capacity of the original filled single supporter can be increased so as to enhance the microwave effect and the titanium dioxide can be excited to generate high-energy free radical, electron and hole; the microwave generator of the magnetic control pipe provided by the present invention can generate non-ionizing irradiation microwave energy and then form ionic conduction and dipole rotation to ensure the movement of target molecules, thus destroying and decomposing the target pollutants (organic gas in the industrial exhaust). Therefore, the combustion furnace provided by the present invention has the advantages of energy saving, low energy loss, time saving, no addition of any chemical oxide, no secondary pollution, etc., thus being consistent with safety and suitability.
Owner:曾川连
Production technology for treating traditional Chinese medicine material powder through ionizing radiation
InactiveCN107836705AAvoid the problem that the grafting rate can only be increased by 10%Reduce the degree of polymerizationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFood shapingMonomerΓ ray irradiation
The invention discloses a production process for ionizing radiation treatment of Chinese herbal medicine powder. The present invention comprises the following steps: (1) Grinding Chinese herbal medicines into powdery particles, steaming them with water, pouring out the liquid, heating and concentrating to obtain concentrated liquid, soaking the cooked powdery particles in ethanol solution, filtering, and The liquid is heated to volatilize ethanol and mixed with the concentrated solution, and the filtered powdery particles are dried; (2) Weigh the dried powdery particles and add citric acid, irradiate with gamma rays after stirring, and spin dry after irradiation to obtain The solid matter is then repeatedly washed with ethanol solution, and dried to obtain powdery pretreatment particles; (3) adding the powdery pretreatment particles into the redox system with vinyl monomers, and grafting the vinyl monomers into the powdery Modified cellulose is obtained by pretreating the particles. The invention has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, excellent medicinal effect in the produced finished product and the like.
Owner:袁士林
Personal dosimeter on the base of radiation integrated circuit.
InactiveUS20110260070A1Minimum temperature effectInsensitive to temperature changesDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansMOSFETRadiation sensitivity
This invention provides a radiation dosimeter and new method of operation which comprise two types of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) circuits allowing to amplify the threshold voltage changes due to radiation and provide temperature compensation. The first type dosimeter is a radiation integrated circuit (RADIC) which includes two radiation field-effect transistors (RADFET) and two MOSFETs, integrated into the same substrate. The second type of radiation circuit includes two RADFETs, integrated into the same substrate, and two resistors. The amplification of the threshold voltage change is achieved by using amplification principles of an MOSFET inverter. In both cases, under the ionizing irradiation, the gate of first RADFET is forward biased and the gate of second RADFET is biased off. In the reading mode the amplified differential threshold voltage change is measured. The increased radiation sensitivity allows to measure of the milli-rad doses. The temperature effect and drift is substantially eliminated. These radiation integrated circuits can be used as a personal dosimeter in the nuclear, industrial and medical fields.
Owner:URYUPIN FR OLEG +1
Device for measuring size of steel bar in structure and method thereof
InactiveUS20080198962A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityBuilding reinforcementsUsing wave/particle radiation meansReinforced concreteMetallurgy
A gamma ray, an X-ray or an ionizing irradiation penetrates through a steel bar in a reinforced concrete structure. An image of the steel bar is thus projected on a film. Through geometric relationships between the image and the steel bar itself, the size of the steel bar is calculated. The size of the steel bar obtained according to the present invention is reliable and accurate. And the data obtained can be used for structure safety.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
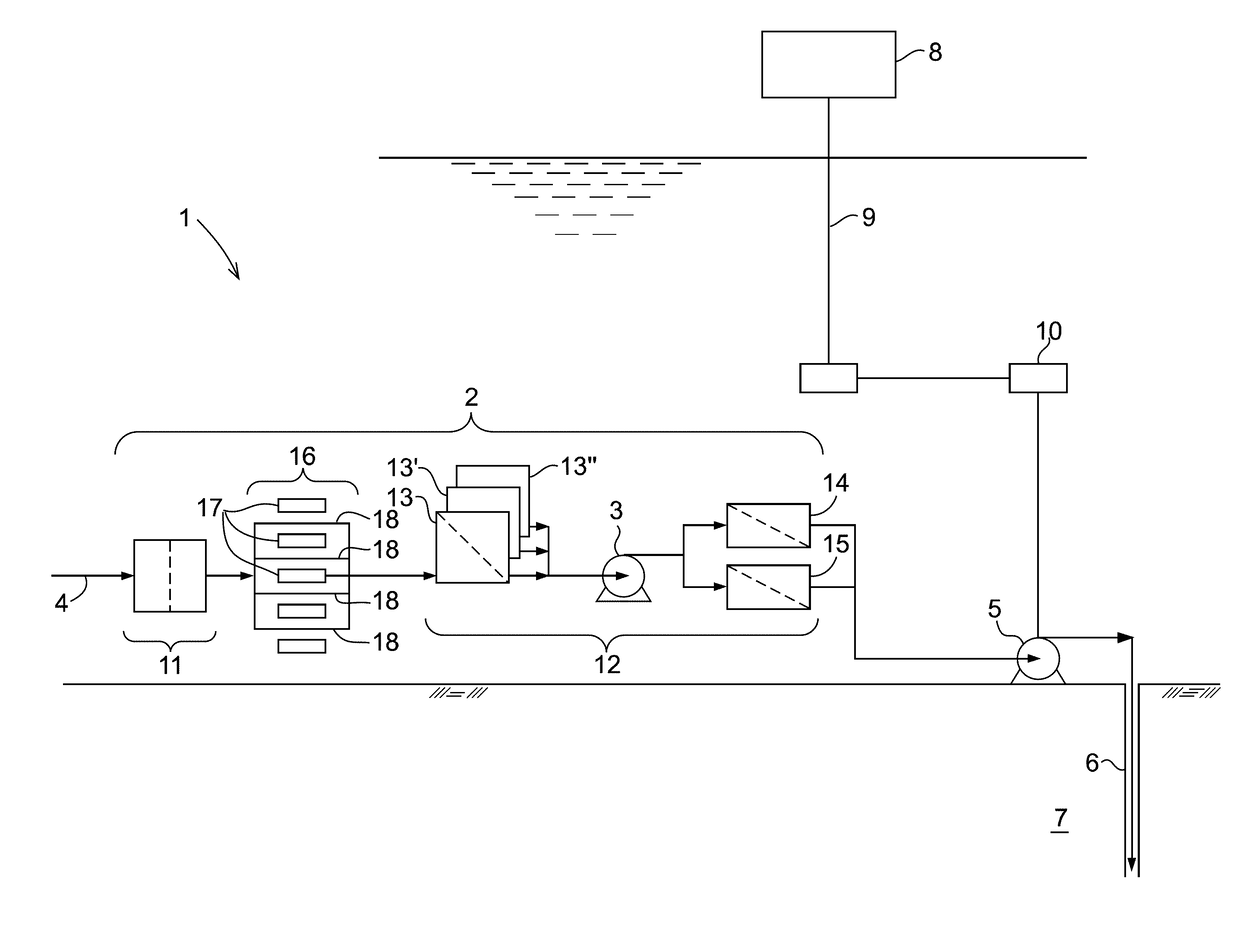
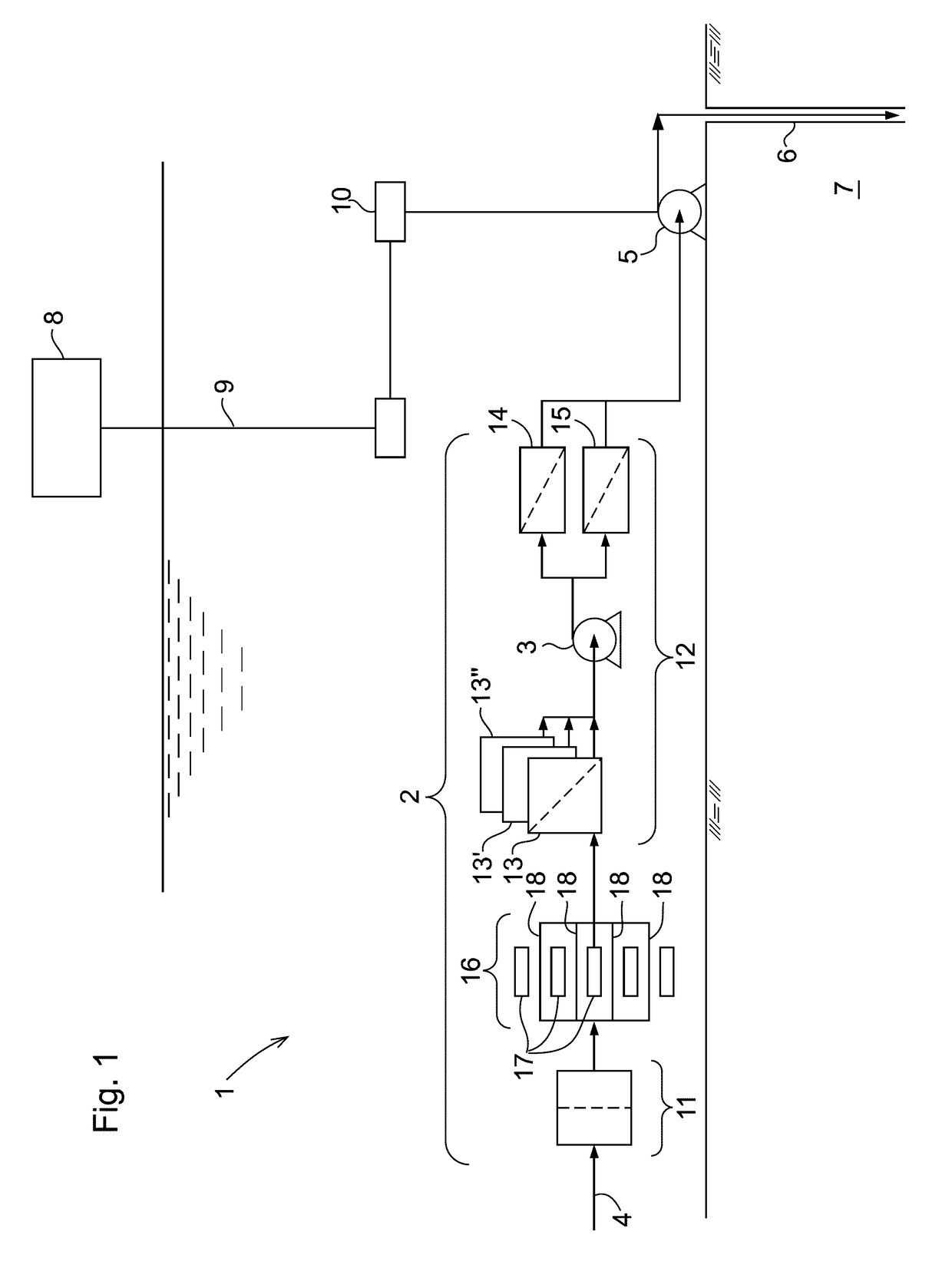
Method and system for water injection into an oil and/or gas containing subterranean formation
PendingUS20180194658A1Easy to disinfectReduce demandMembranesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFiltrationIonizing irradiation
A method and system for water injection into an oil and / or gas containing subterranean formation is shown, the method comprising: arranging a submerged water filtration station with a pump feeding inlet seawater through at least one filtering membrane to a water injection pump, subjecting the water to ionizing irradiation at a location between the seawater inlet and the water injection pump, whereby at said location the water is guided past a submerged radiation source which is distributed for penetration of the body of injection water.
Owner:VETCO GRAY SCANDINAVIA
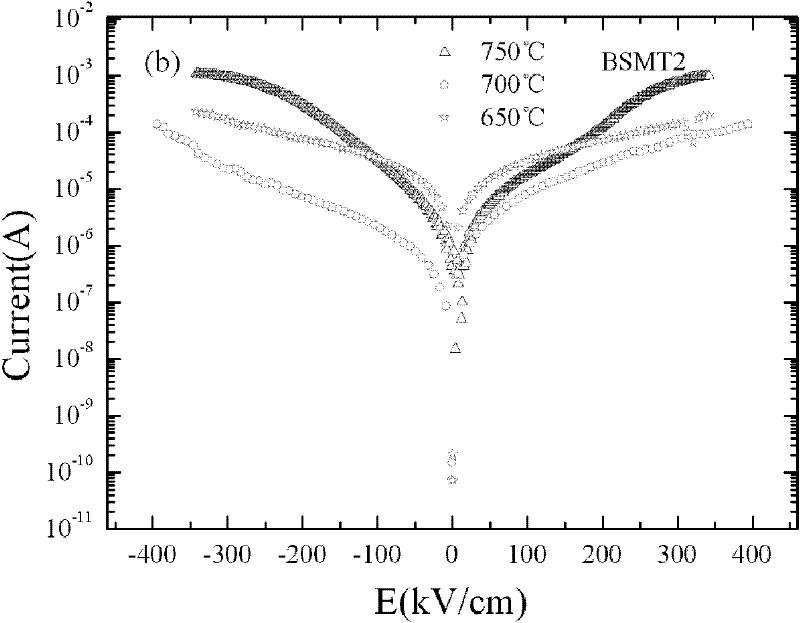
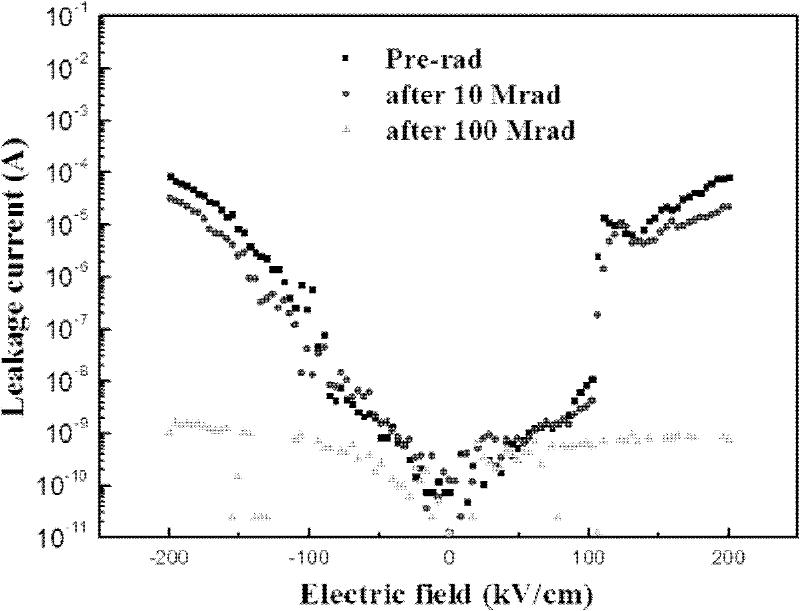
Method for improving performance of lead-free ferroelectric film and lead-free ferroelectric film prepared by same
The invention discloses a method for improving the performance of a lead-free ferroelectric film and the lead-free ferroelectric film prepared by the same, in particular to a method for reducing the drain current of a lead-free ferroelectric film by utilizing the ionizing irradiation effect and the lead-free ferroelectric film obtained by the same, belonging to the field of lead-free ferroelectric films. Energy carrying particle beams such as charged particles or gamma rays and the like are used for irradiating the lead-free ferroelectric film at room temperature, the total irradiation dose is 10Mrad-100Mrad, and the ferroelectric film with the reduced drain current can be obtained after irradiation. The invention has significance of improving the working stability and the service life of a ferroelectric memory and reducing the heating productivity.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method for degrading moxifloxacin hydrochloride in waste water
ActiveCN105417622AReduce dosageReduce radiation doseWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsIonizing irradiationWastewater
The invention discloses a method for degrading moxifloxacin hydrochloride in waste water. Hydroxyl radicals.OH which is high in oxidizing ability and generated through ionizing irradiation are used for promoting degrading of moxifloxacin hydrochloride in the waste water, and Cu2+ and Zn2+ are added into the waste water to catalyze degrading of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, reduce the absorption dose required by waste water irradiation treatment and reduce cost. According to the specific scheme, a certain amount of Cu2+ and Zn2+ are added into the moxifloxacin hydrochloride waste water with the concentration being 10 mg / L-100 mg / L, the concentration range of Cu2+ is 0.2-0.6 mg / L, the concentration range of Zn2+ is 0.4-0.8 mg / L, irradiation treatment is carried out through gamma rays or high-power electron beams, the dose ranges from 1kGy to 3kGy, and therefore moxifloxacin hydrochloride has an irradiation degrading reaction. Cu2+ and Zn2+ are used at the same time for joint irradiation treatment, the use amount of Cu2+ and Zn2+ is reduced, and secondary pollution is reduced. Meanwhile, the irradiation dose is greatly reduced, the treatment effect is good, secondary pollution is little, and energy is saved.
Owner:永兴惠友新材料技术有限公司
Hydrophilic polymer compositon and method of forming a hydrophilic polycaprolactone
A hydrophilic polymer and method which forms a low contact angle, non-turbulent laminar flow boundary layer on a material surface such as the surface of a vessel's hull. The method comprises exposing polycaprolactone (PCL) to ionizing irradiation, such as; Electron Acceleration (E-Beam), Gamma II, Cobalt and X-ray to form a cross linked polymer composition having a soluble component and an insoluble component with the concentration of the soluble component being above at least 63% of the polymer composition such that the “XL-PCL” polymer is hydrophilic. A hydrophilic coating is then formed by adding a solvent to the “XL-PCL” polymer composition, filtering out as much of the insoluble PCL component from the remaining solvent solution and volatilizing the solvent leaving a hydrophilic “XL-PCL polymer, comprised of the XL-PCL” insoluble component. A coating which includes up to 37% of insoluble “XL-PCL” and a soluble component of 63% of the “XL-PCL” may be rolled milled or otherwise homogenized into the solution. The coating when in contact with water forms a boundary layer with no water contact angle or minimal contact angle.
Owner:LUSTGARTEN STEWART J
A method for degrading organic pollutants in water by ionizing radiation
ActiveCN111115745BEfficient degradation abilityEfficient mineralizationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationRadiation applicationsIndustrial waste waterIonizing irradiation
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment, and in particular relates to a method for removing refractory organic pollutants in water by intensified ionizing radiation, comprising: uniformly mixing waste water containing organic pollutants with a certain amount of MOF or its derivative materials, and performing ionization Irradiation treatment. The method has high irradiation efficiency and can be carried out at normal temperature. The MOF material can be reused, and can be applied to the treatment of refractory industrial wastewater such as effluent from urban sewage plants, pharmaceutical wastewater, and dye wastewater.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Use of peptides for the control of radiation injury
The invention relates to the field of drug development against acute radiation injury caused by exposure to high-energy electromagnetic waves (X-rays, gamma rays) or particles (alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons). To date, there is no effective drug to ameliorate radiation injury after accidental exposure to ionizing irradiation. The invention provides a method of treating radiation injury of a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids. Furthermore, the invention provides use of a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids for the production of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of a subject suffering from or believed to be suffering from radiation injury. In particular, the invention provides anti-radiation peptides having a dose reduction factor (DRF) against acute gamma irradiation of at least 1.10, said DRF determinable by testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a test group of mice treated with said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and, testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a control group of mice treated only with the vehicle of said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and wherein the DRF is calculated by dividing the LD5O / 3O of the peptide-treated animals by the LD50 / 30 of the vehicle-treated animals.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
Radiation Hardening Method for Bipolar Devices Based on the Geometric Structure of Emitter Region
ActiveCN103871873BImprove radiation resistanceThe preparation process steps are simpleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowIonizing irradiation
The invention relates to and is applicable to the technical field of electronics, in particular to a radiation-proof strengthening method for a bipolar device based on the geometric structure of an emitter region. The radiation-proof strengthening method aims to solve the problems that an existing bipolar junction transistor and a circuit are high in damage degree of current gain in a space radiation environment, and an existing bipolar device is low in radiation resistance ability. According to the radiation-proof strengthening method for the bipolar device, the traditional bipolar device process is reserved, and manufacturing process steps are very simple. By means of the radiation-proof strengthening method for the bipolar device, the influence of positive charges captured by oxide induced through ionizing irradiation and the interface state on performance parameters of the device can be lowered substantially by improving the geometric structure of the emitter region, and the radiation resistance ability of the bipolar device is enhanced remarkably by 2-5 times compared with that of the existing bipolar device.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +2
A method for degrading moxifloxacin hydrochloride in waste water
ActiveCN105417622BReduce dosageReduce radiation doseWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsTherapeutic effectGamma ray
The invention discloses a method for degrading moxifloxacin hydrochloride in waste water. Hydroxyl radicals.OH which is high in oxidizing ability and generated through ionizing irradiation are used for promoting degrading of moxifloxacin hydrochloride in the waste water, and Cu2+ and Zn2+ are added into the waste water to catalyze degrading of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, reduce the absorption dose required by waste water irradiation treatment and reduce cost. According to the specific scheme, a certain amount of Cu2+ and Zn2+ are added into the moxifloxacin hydrochloride waste water with the concentration being 10 mg / L-100 mg / L, the concentration range of Cu2+ is 0.2-0.6 mg / L, the concentration range of Zn2+ is 0.4-0.8 mg / L, irradiation treatment is carried out through gamma rays or high-power electron beams, the dose ranges from 1kGy to 3kGy, and therefore moxifloxacin hydrochloride has an irradiation degrading reaction. Cu2+ and Zn2+ are used at the same time for joint irradiation treatment, the use amount of Cu2+ and Zn2+ is reduced, and secondary pollution is reduced. Meanwhile, the irradiation dose is greatly reduced, the treatment effect is good, secondary pollution is little, and energy is saved.
Owner:永兴惠友新材料技术有限公司
Locally injectable dosimetric organ spacer
The present invention relates to a system, a method and a filler for measuring a dose of ionizing radiation received by a pre-determined part of the body during radiotherapy while creating a space between the organ to be irradiated and organs to be protected. The invention also relates to uses of such filler. The system comprises an injectable dosimetric filler, which under the influence of ionizing irradiation undergoes measurable physical and / or chemical changes, while preserving its spatial integrity; a detector system for measuring the physical and / or chemical changes within the radiation sensitive filler by sending an energy wave to the radiation sensitive filler and capturing the signal emitted therefrom; and a control unit for processing the signal captured by the detector system and calculating a dose of ionizing radiation previously or simultaneously received by each part of the volume of the radiation sensitive filler on the basis of said signal.
Owner:DOSEVUE NV
Ionizing irradiation sterilization of bacterial minicell-based biopharmaceuticals and methods of use
Disclosed herein are methods of terminally sterilizing bacterial minicells or compositions comprising bacterial minicells by exposure to ionizing irradiation. Also disclosed are terminally sterilized bacterial minicells, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the bacterial minicells, and methods of use the bacterial minicells and pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:VAXIION THERAPEUTICS
Method for improving performance of lead-free ferroelectric film and lead-free ferroelectric film prepared by same
ActiveCN101798239BEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesParticle beamRoom temperature
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
A Method for Annealing Displaced Defects Based on Ionizing Radiation Induction
ActiveCN108346565BLow costSimple stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIonizing irradiationParticle physics
The invention relates to a method for inducing the defect annealing based on ionization irradiation, and aims at solving a problem that the particle radiation will cause the displacement damage to a device. The method comprises the steps: calculating the ionization / displacement absorbed dose and range of unit fluence incident particles based on a Monte Carlo computing method; determining the typeof incident particles according to the proportional relation between the ionization and the displacement absorbed dose and the features of a sample, thereby guaranteeing that the incident particles can promote the annealing of existing defect in the sample in a conveying process of the sample. The method is simple in steps, and is easy for operation. The method is used for the technical field of spatial environment effects, nuclear science and application technologies.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com