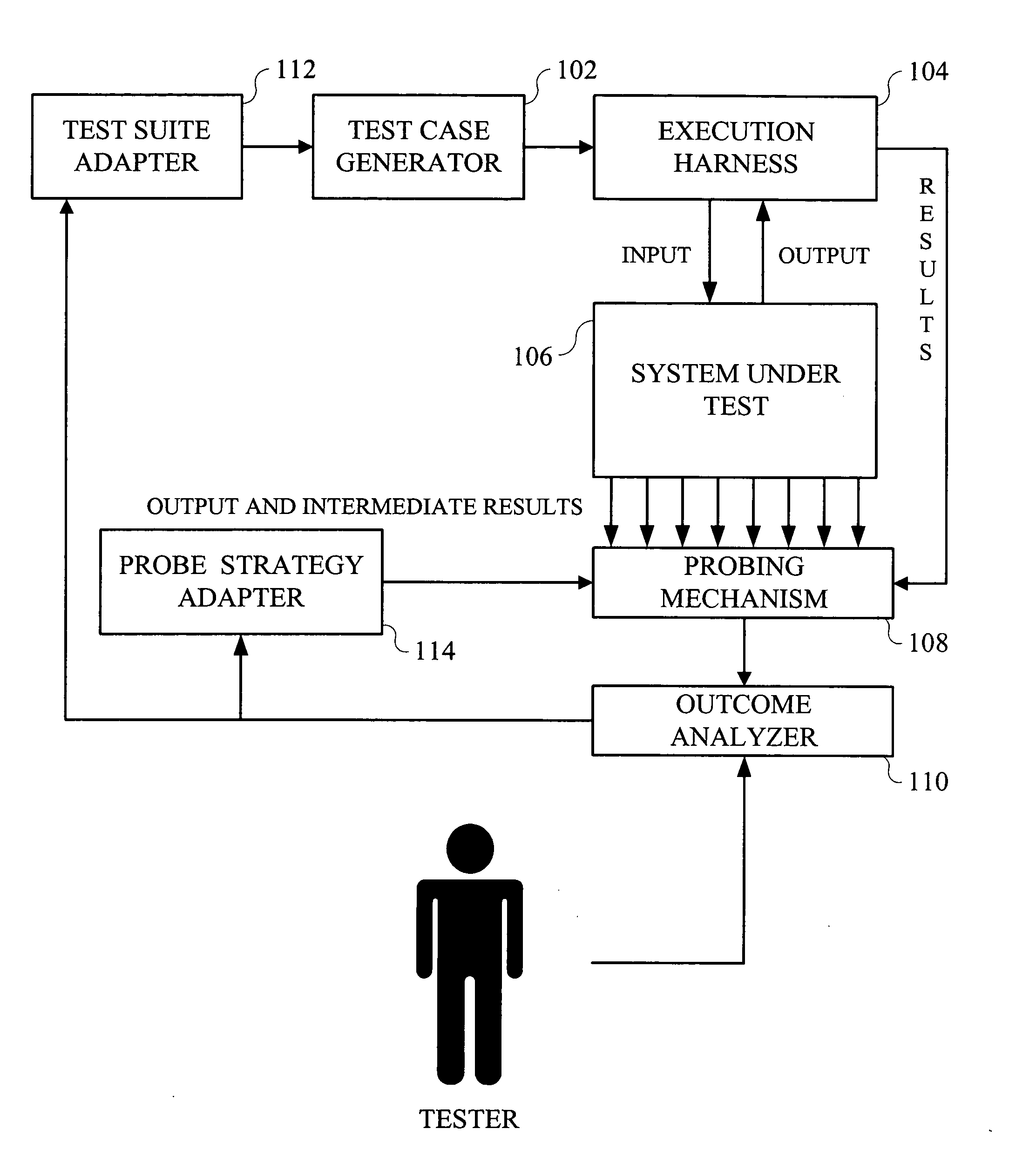
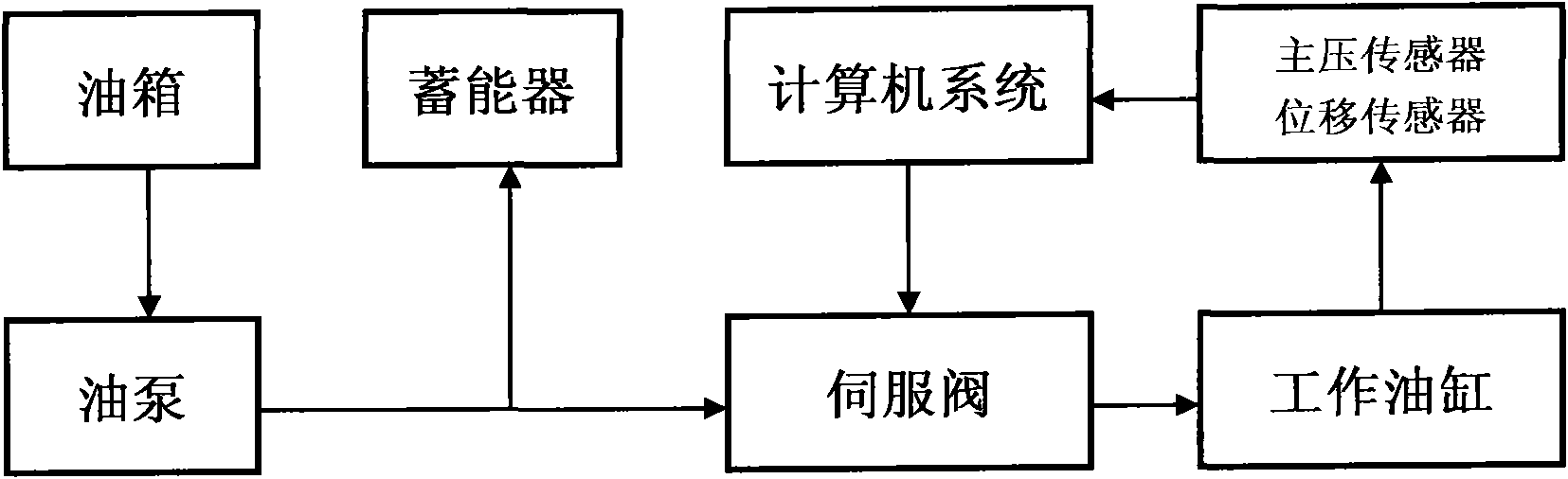
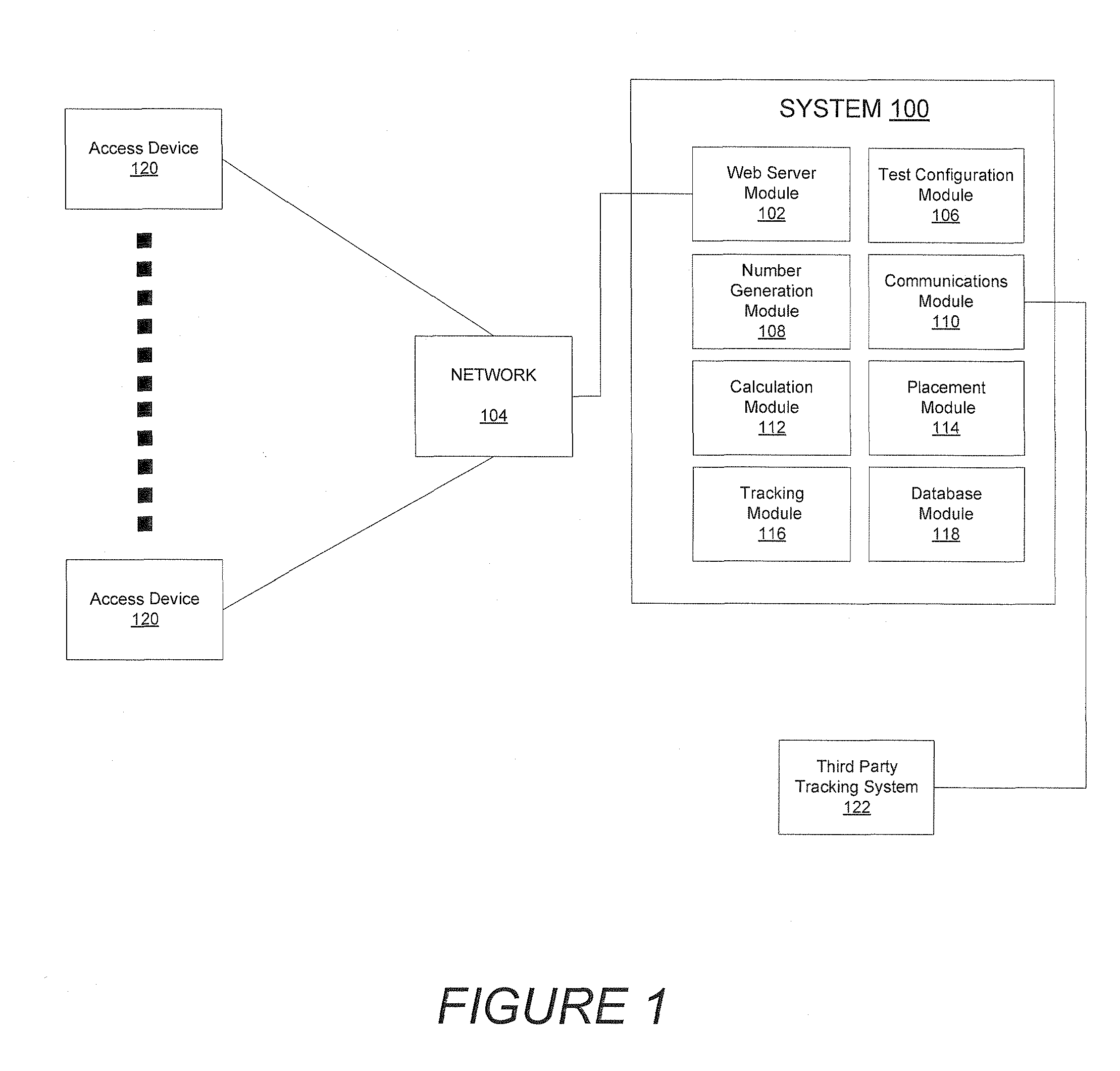
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
726 results about "Test group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
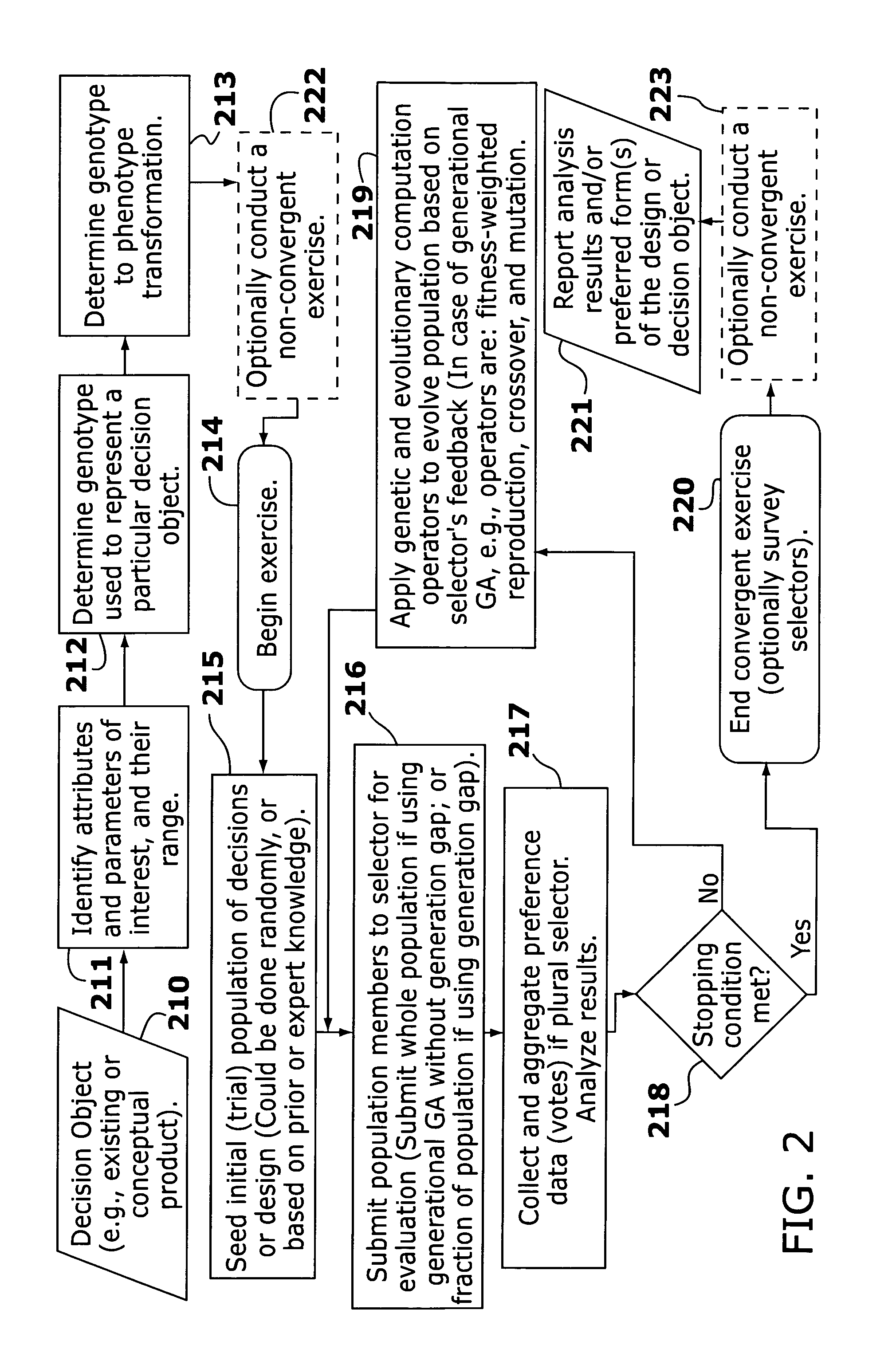
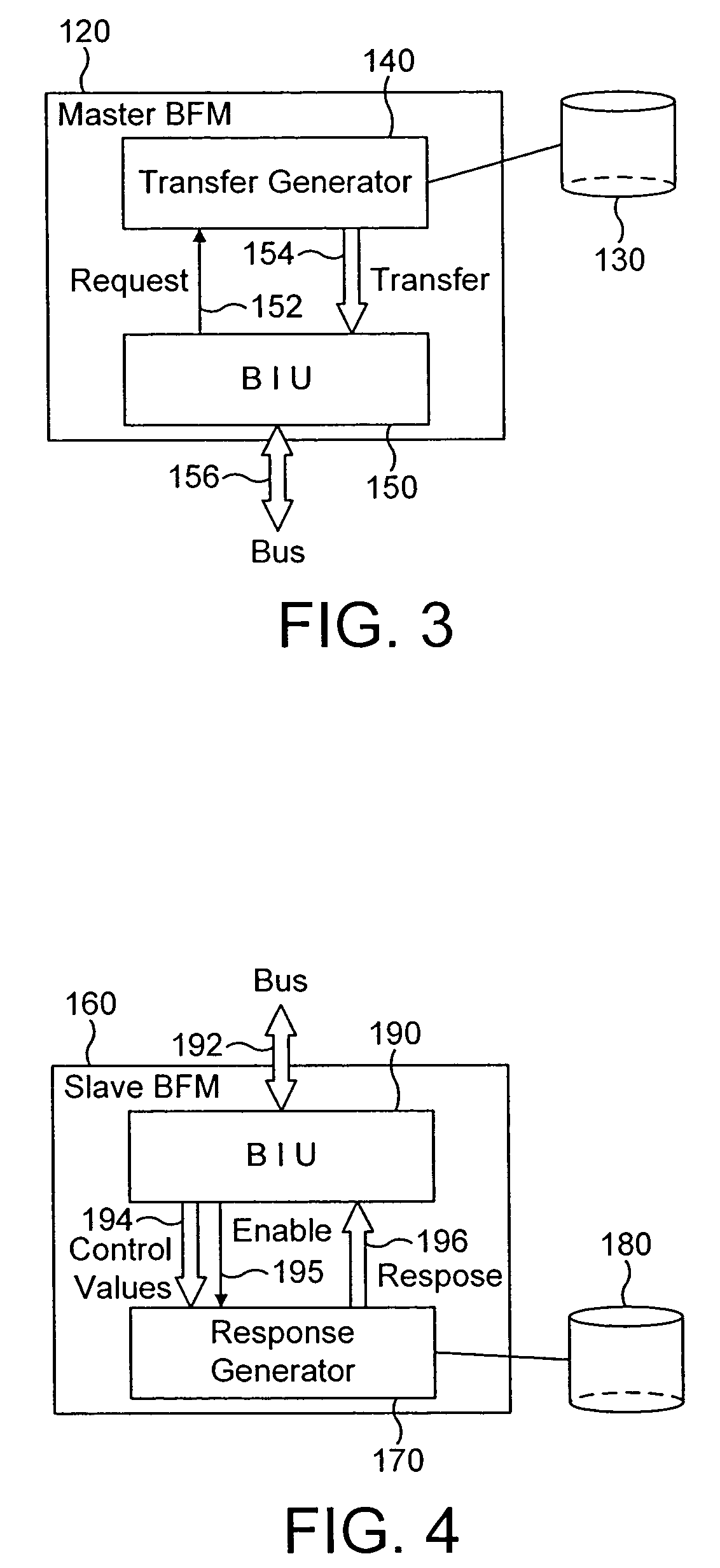
Determining design preferences of a group
ActiveUS20050261953A1Efficient analysisEasy to recruitMarket predictionsDigital computer detailsKnowledge managementTest group
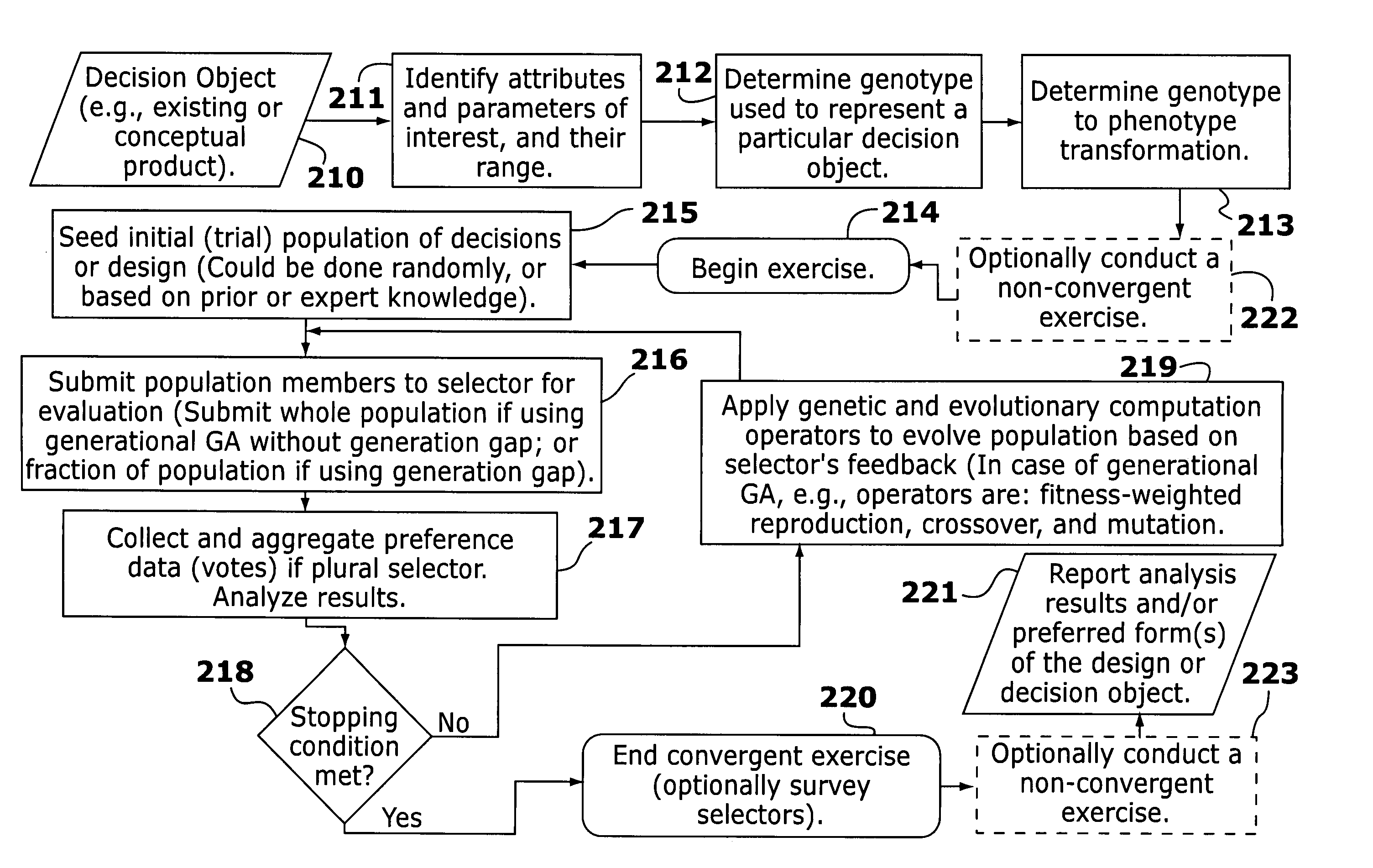
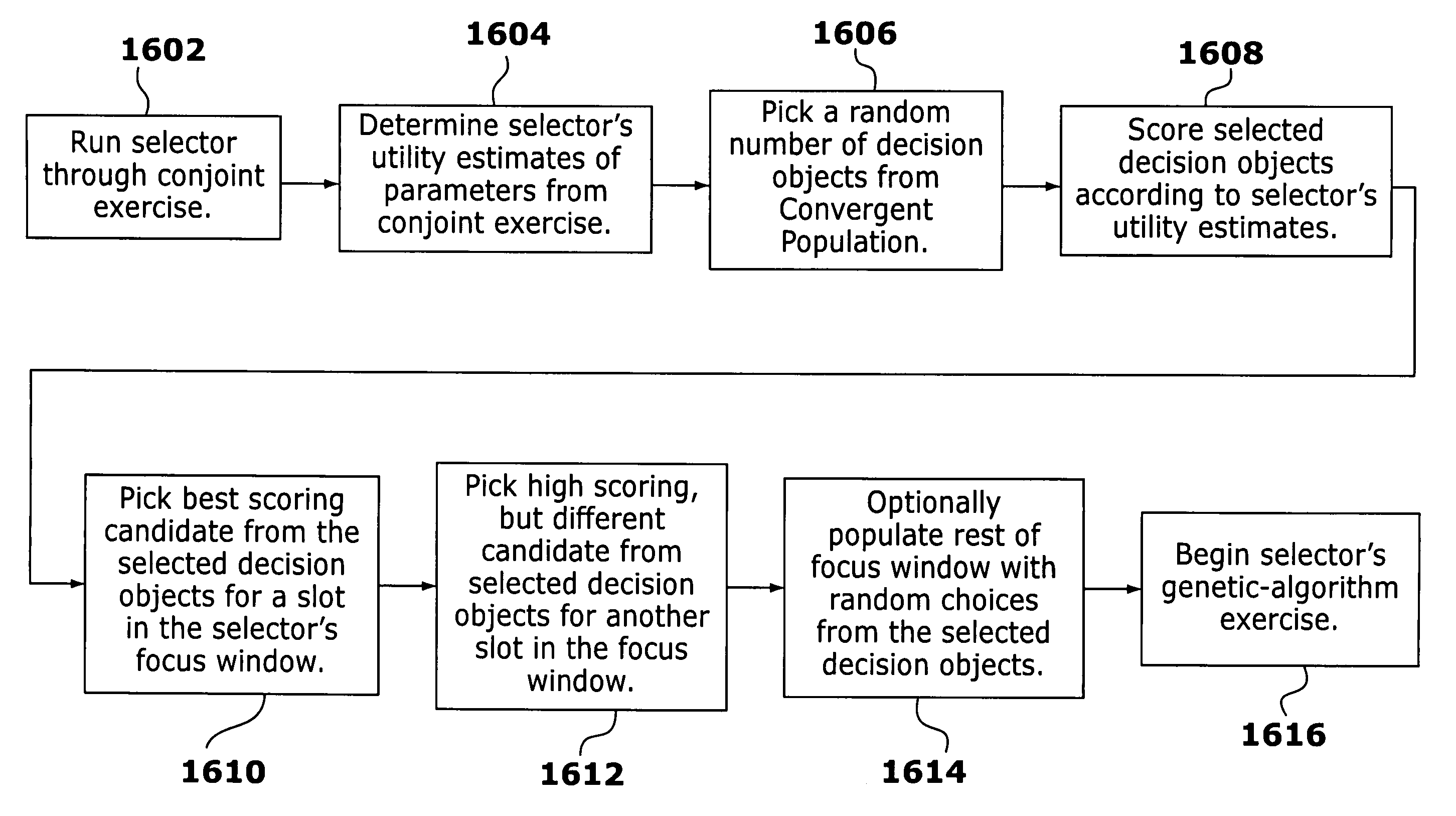
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for conducting market research and developing product designs. The methods involve generating and presenting, typically electronically, generations of design alternatives to persons participating in the design, selection, or market research exercise. The participants transmit data indicative of their preferences among or between the presented design alternatives. Some of the data is used to conduct a conjoint analysis or non-convergent exercise to investigate the drivers of the preferences of the group or its members, and at least a portion are used to derive follow-on generations of design alternatives or proposals. The follow-on designs are preferably generated through the use of an evolutionary or genetic computer program, influenced by the participants' preferences. The process results in the generation of one or more preferred product forms and information permitting a better understanding of what attributes of the product influence the preferences of the test group members.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
Determining design preferences of a group
ActiveUS7308418B2Efficient analysisEasy to recruitMarket predictionsDigital computer detailsMarket placeConjoint analysis
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for conducting market research and developing product designs. The methods involve generating and presenting, typically electronically, generations of design alternatives to persons participating in the design, selection, or market research exercise. The participants transmit data indicative of their preferences among or between the presented design alternatives. Some of the data is used to conduct a conjoint analysis or non-convergent exercise to investigate the drivers of the preferences of the group or its members, and at least a portion are used to derive follow-on generations of design alternatives or proposals. The follow-on designs are preferably generated through the use of an evolutionary or genetic computer program, influenced by the participants' preferences. The process results in the generation of one or more preferred product forms and information permitting a better understanding of what attributes of the product influence the preferences of the test group members.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
System and method of measuring lift in a marketing program
This disclosure concerns methods of measuring lift in a marketing program that resides on a shopping device. The method includes identifying a test group as those shoppers who received a coupon for a unit on a shopping device based on at least one of a historical trait or a real time trait and identifying a control group as shoppers not using the shopping device that would have gotten the coupon for the unit based on at least one of a historical trait or a real time trait had they used the shopping device, wherein the control group and the test group shopped in the same timeframe in the same location of the same store and share the at least one historical trait or real time trait. The net incremental sales of units between the test and control groups is calculated.
Owner:CATALINA MARKETING CORP
System and method for paper independent copy detection pattern
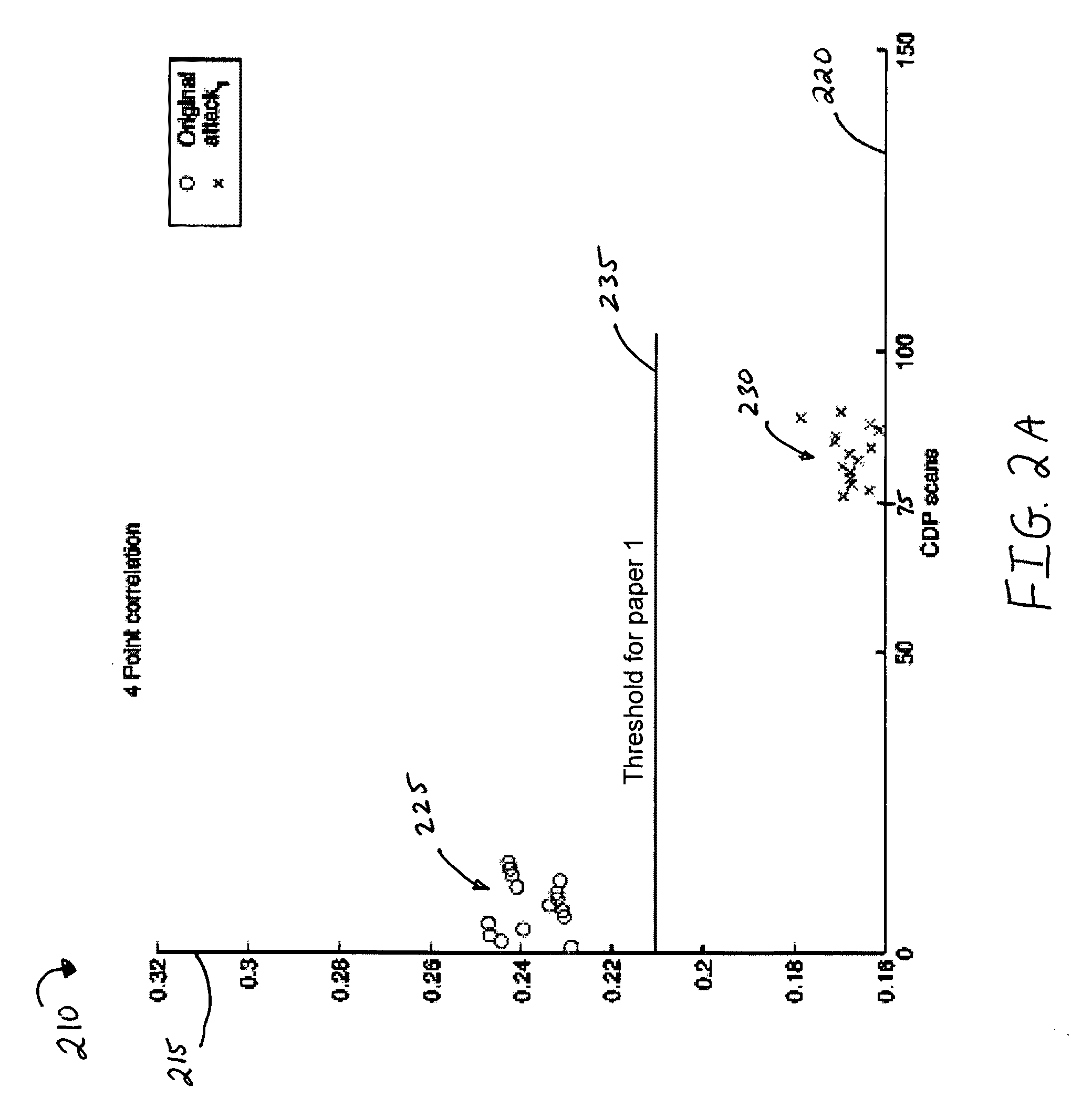
InactiveUS20100080471A1Efficient and robust verification thresholdDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionCopy detectionDocument preparation
Systems and methods for detecting copies of documents are described. In one example, a system and method for detecting copies of documents utilizes multiple authentication tests performed using original and scanned copy detection patterns. The system captures a CDP that may be skewed or improperly sized. The system also retrieves or reconstitutes the expected CDP. Then the system performs a first correlation to determine if the captured CDP indicates the correct document identification and then if necessary, one or more authentication tests are applied wherein the authentication test may be grouped into distinct orthogonal test groups. The authentication tests applied may be selected according to usefulness, system throughput or target document valuation parameters.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
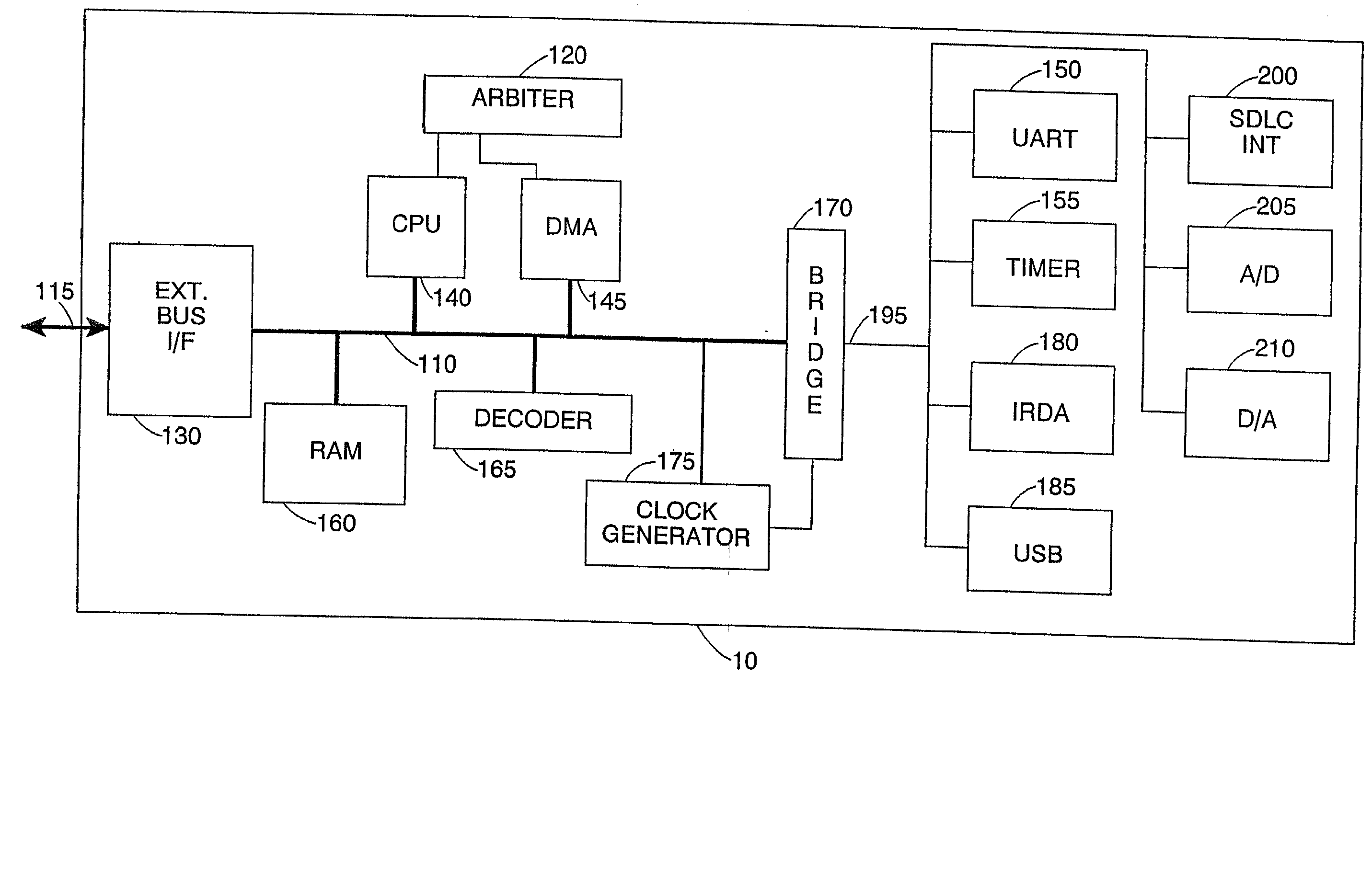
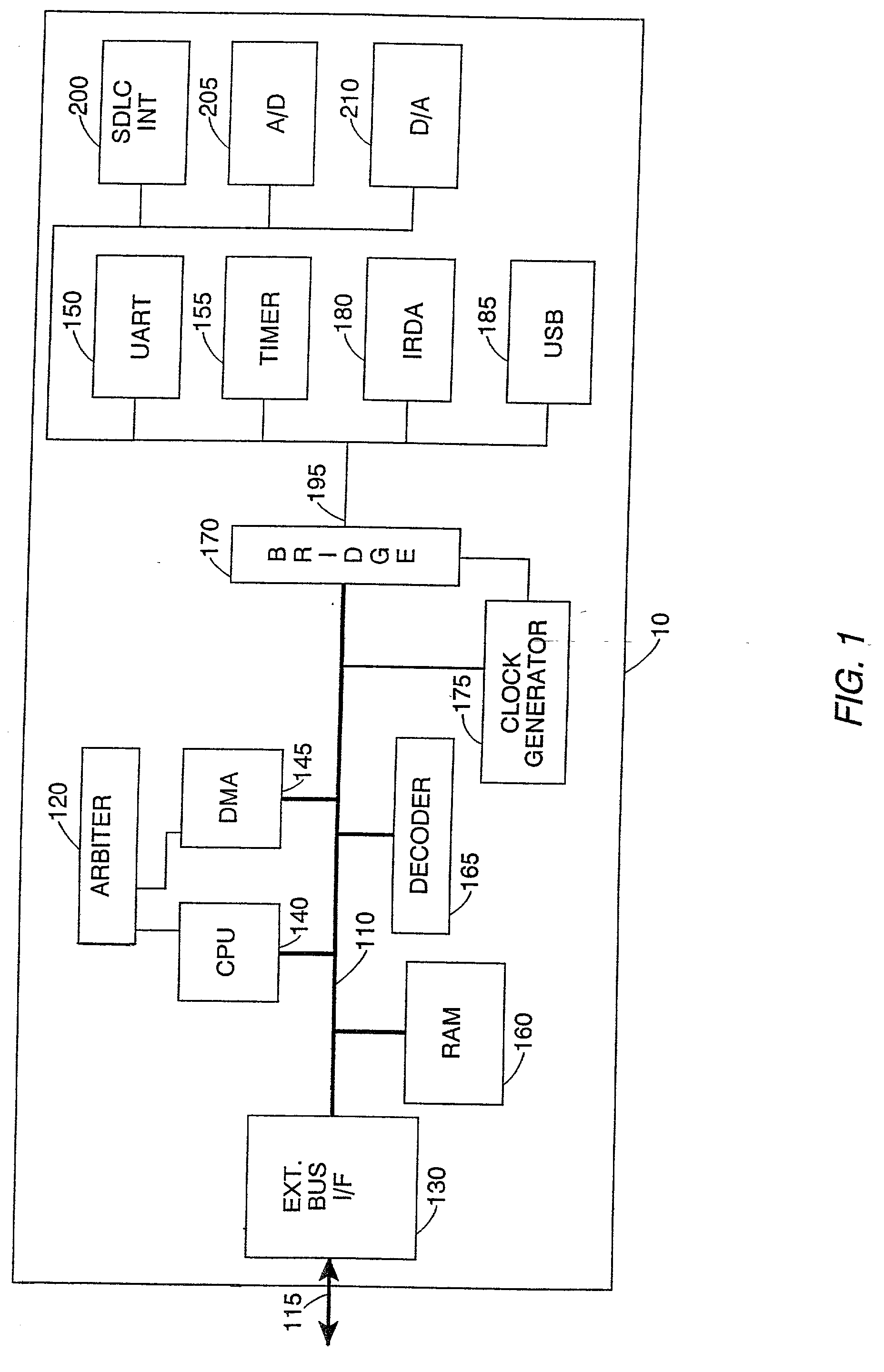
Testing compliance of a device with a bus protocol
InactiveUS20020183956A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceSpecial data processing applicationsDevice typeTest sequence
The present invention provides a system and method for testing compliance of a device with a bus protocol. The method comprises the steps of reading a configuration file containing predetermined parameters identifying the type of device and capabilities of the device, and then employing a configuration engine to dynamically generate a test environment for the device by creating selected test components which are coupled via the bus with a representation of the device to form the test environment, the test components being selected dependent on the configuration file. A test sequence is then executed, during which signals passed between the representation of the device and one or more of the test components are monitored to generate result data indicating compliance with the bus protocol. This approach has been found to provide a particularly user friendly and efficient approach for testing compliance of devices with a bus protocol.
Owner:ARM LTD
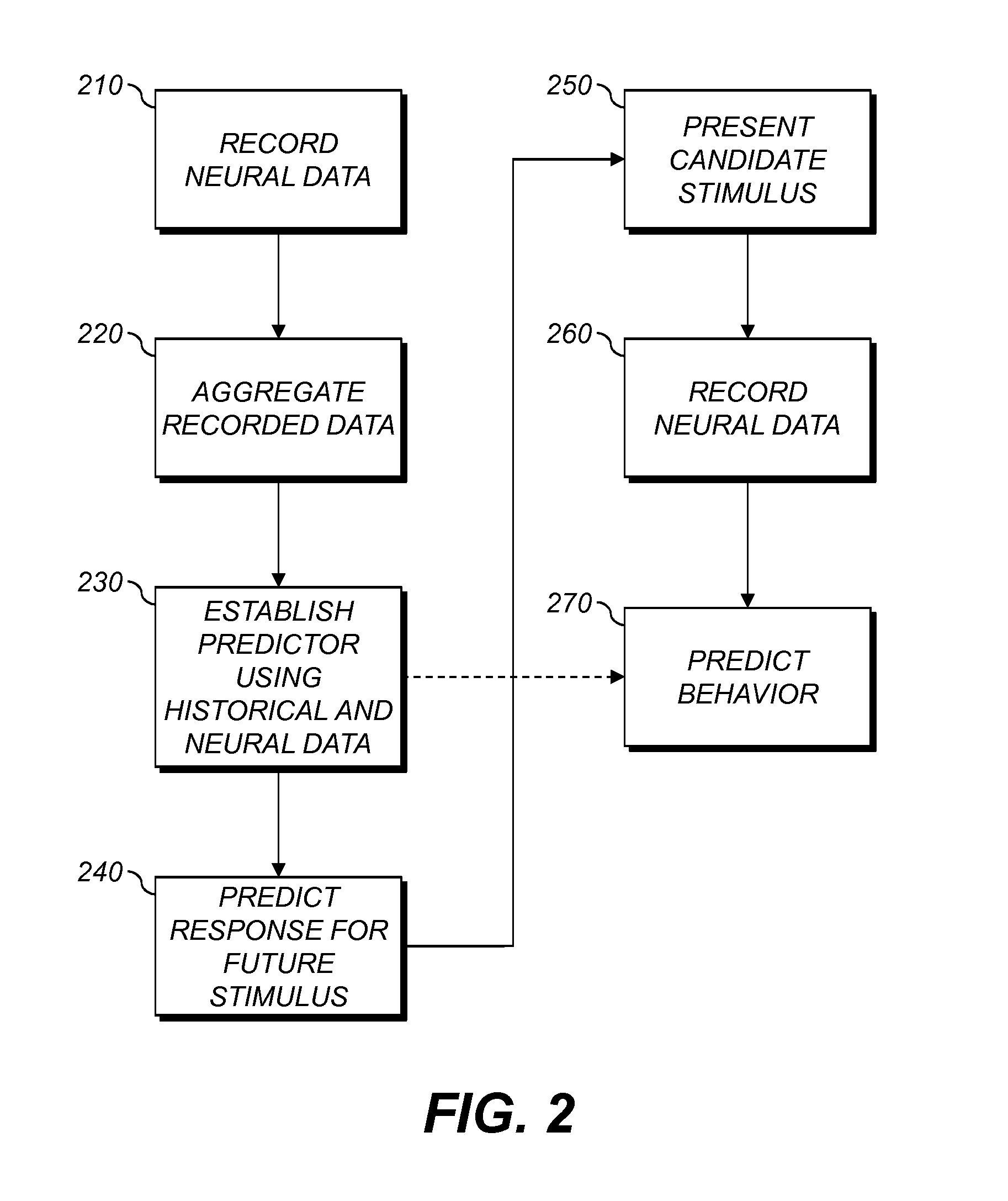
Predicting Response to Stimulus
InactiveUS20150248615A1Not effectiveMedical data miningDigital computer detailsTest groupMachine learning
A method of predicting response to a sensory stimulus includes, with a processor, automatically receiving behavioral data representing the response of a first population of subjects to a reference stimulus. Data representing the neurological responses of a second, different population of subjects to the reference sensory stimulus are received and processed to provide group-representative data indicating commonality between the neurological responses of at least two members of the second population. A mapping from the group-representative data to the received behavioral data is produced. Test data representing the neurological responses of a third population of subjects to a test sensory stimulus are received and processed to provide test group-representative data indicating commonality between the neurological responses to the test sensory stimulus of at least two members of the third population. The mapping is applied to the test group-representative data to provide predicted behavioral data.
Owner:OPTIOS INC
Method and apparatus for scheduling a use of test resources of a test arrangement for the execution of test groups
InactiveUS20130006567A1Effective applicationEliminate resource conflictElectrical testingTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTest flowTest group
A method for scheduling a use of test resources comprises obtaining an assignment of a test resource to each test group of a test flow. The test flow comprises an initial execution order. The method comprises checking for a resource conflict between an assignment of a test resource to a given test group in a test flow and an assignment of other test resources to other test groups and test flows. The other test groups are scheduled for a temporally overlapping execution with the given test group. The method comprises manipulating the test flow execution order of the test groups. The resource conflict is eliminated by performing a swap between a test group associated with the resource conflict in a test flow with a higher priority compared to a time-interval-insertion in combination with a movement, and moving the test group associated with the resource conflict to an inserted time interval.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
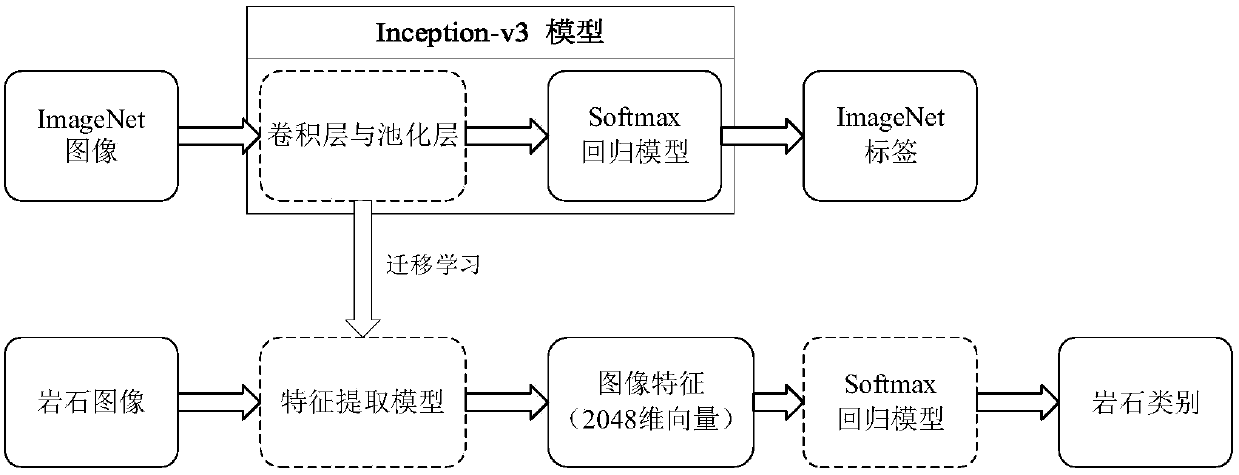
Method for automatically identifying and classifying rock lithology in deep learning mode
ActiveCN107633255ATo achieve the purpose of automatic identificationReduce the influence of subjective factorsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesLithologyFeature extraction
The invention discloses a method for automatically identifying and classifying rock lithology in a deep learning mode, aiming at analyzing rock lithology in geological engineering. The method includesthe following steps: A. based on the kinds of rocks, acquiring rock images of different types, and grouping the rock images into a training group and a test group; B. taking a convolutional neural network Inception-v3 model as a pre-training model, acquiring image features by using a feature extraction model of the pre-training model; C. establishing a Softmax regression model; D. training a model for automatically identifying and classifying rock images; and E. testing the model for automatically identifying and classifying rock images. According to the invention, the method herein, by establishing the model for automatically identifying and classifying rock images, can analyze the geological conditions in an automatic and intelligent manner, greatly save labor and materials, and reducescost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
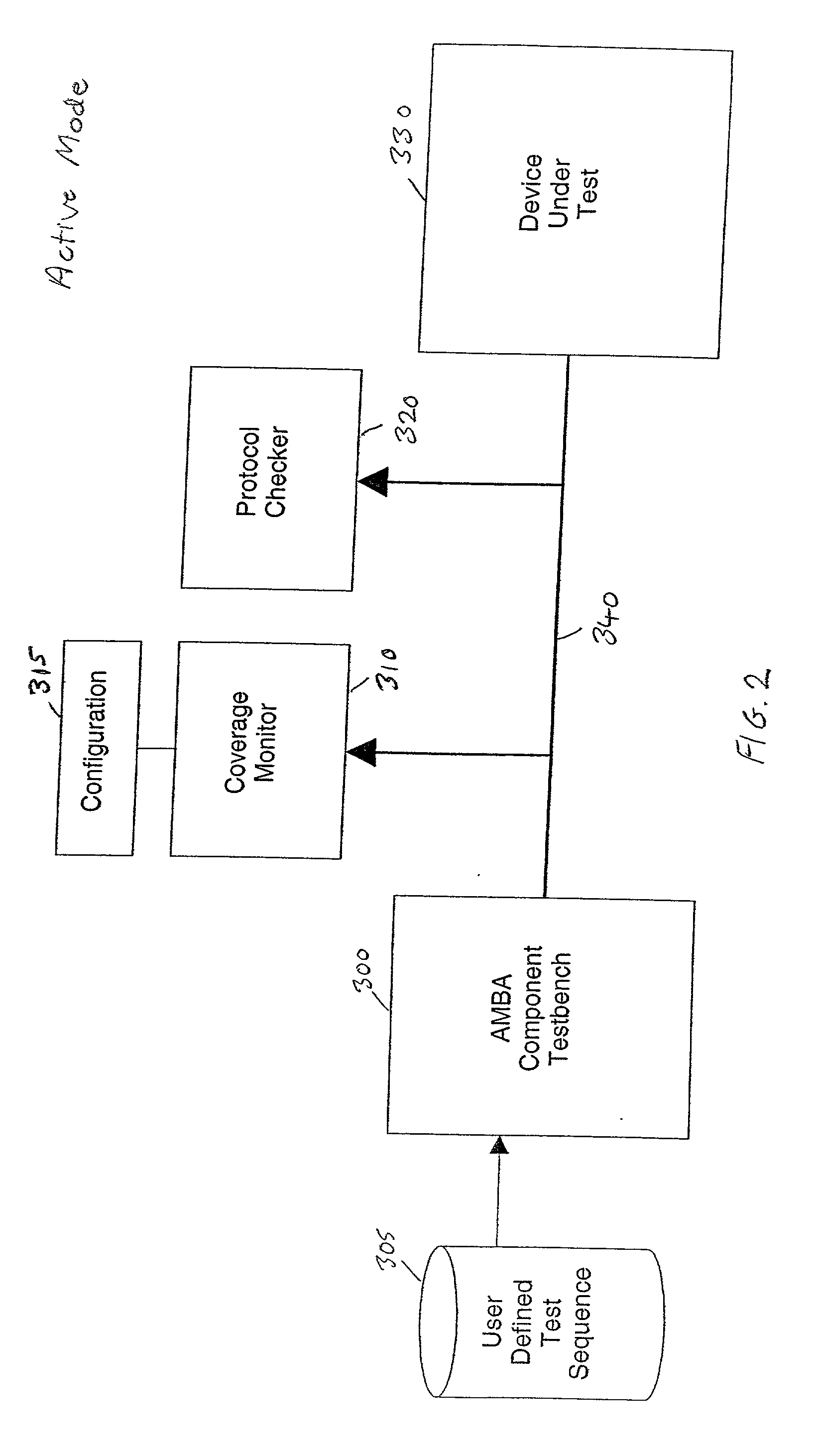
Test component and method of operation thereof
ActiveUS20040243334A1Many timesShorten the timeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionReal systemsEquipment under test
A test component and method of operation thereof are provided, the test component being arranged in a test environment to issue a test sequence over a bus to a device under test. A configuration file is provided to specify the behaviour of the test component, the configuration file comprising a plurality of regions with each region specifying attributes for use in determining the test sequence. A number of the regions specify constraint attributes defining allowable test sequences. The method of the present invention comprises the steps of: (a) when a test sequence is required to be issued, causing the test component to select, based on predetermined criteria, one of a number of regions provided by the configuration file; and (b) using the constraint attributes for that selected region to generate the test sequence to be issued on to the bus. It has been found that such an approach provides an efficient technique for enabling the test component to be configured to emulate the actual component which in the real system will interact with the device being tested. It has also been found that the time taken to write the tests required for the device under test is significantly reduced compared to prior art techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method, device and system for monitoring subsea components
A system, device and method of monitoring components of a BOP of a subsea well. The method includes grouping, by the control device, two or more of a plurality of BOP components into a test group; receiving, by the control device, one or more actual BOP component profiles from the grouped BOP components in the test group; and analyzing, by the control device, the received one or more actual BOP component profiles. The two or more BOP components may be solenoid valves, flow meters, transducers, other devices, or a combination therein. The method includes grouping, by the control device, two or more of a plurality of BOP components into a test group; receiving, by the control device, one or more actual BOP component profiles from the grouped BOP components in the test group; and analyzing, by the control device software for the testing Pods, the received one or more actual BOP component profiles.
Owner:HYDRIL USA MANUFACTURING LLC
Systems and methods for conducting internet content usage experiments
ActiveUS7343390B2Efficient executionDisturbing flow of offeredMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram loading/initiatingInternet contentTest group
A system and method for efficiently executing a plurality of live parallel Internet content usage experiments using a large pool of randomly selected participating users (separated into control and test groups) while minimally disturbing offered content is provided. In an illustrative implementation, a content provider communicates the parameters for a content usage experiment to a content server. A complimentary test subject verification script operates on the content server that determines which client computing devices are to be included in the experiment group. In operation, a participating client computing device requests content from the content provider's server. The content provider's server executes the test subject verification script to determine if the client computing device is to be considered as a test subject. The content usage of the experiment content and non-experiment content is tracked and compared to each other to determine if the experiment content impacted content usage.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for assigning computer users to test groups
A system and method to efficiently and randomly place users into a test group associated with a test running on a website being hosted on a server is disclosed. When a user first accesses the website, a random value is transmitted to the user in such a manner that the random value is stored in a computer-readable memory local to the user. Each subsequent time the user accesses the website, the random value is returned to the server from the user. The server may then place the user into a test group for a test to which the user will be exposed on the website based upon the result of an operation that includes the random value received from the user and a unique test value previously associated with the test.
Owner:OVERSTOCK COM
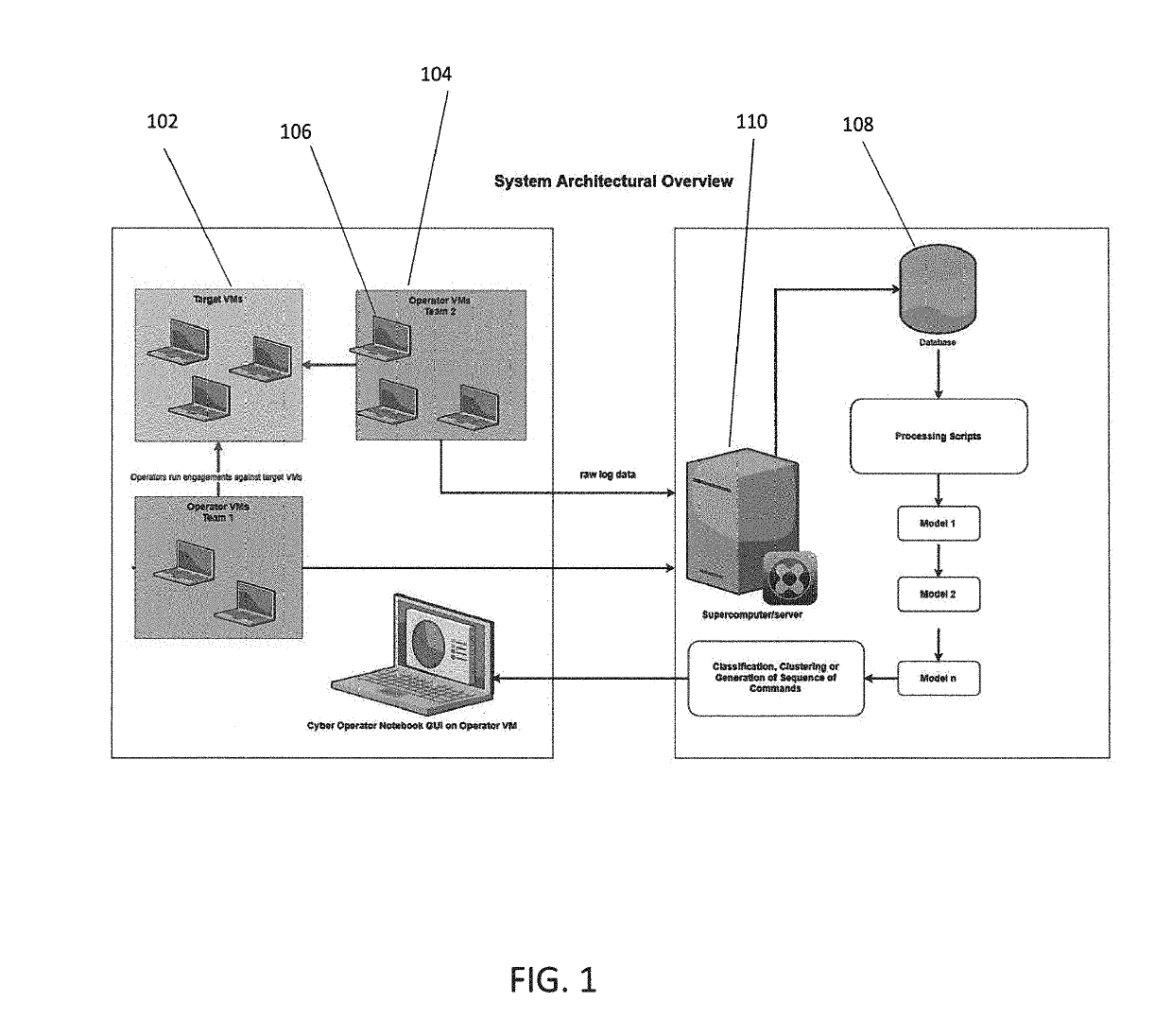
Method and system for penetration testing classification based on captured log data
Aspects of the invention comprise methods and systems for collecting penetration tester data, i.e. data from one or more simulated hacker attacks on an organization's digital infrastructure in order to test the organization's defenses, and utilizing the data to train machine learning models which aid in documenting tester training session work by automatically logging, classifying or clustering engagements or parts of engagements and suggesting commands or hints for an tester to run during certain types of engagement training exercises, based on what the system has learned from previous tester activities, or alternatively classifying the tools used by the tester into a testing tool type category.
Owner:CIRCADENCE
Methods and apparatus for adaptive problem determination in distributed service-based applications
InactiveUS20050154939A1Easy to findError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsDistributed servicesComputer science
A technique for problem determination in a distributed application is provided. Testing results of the application are first obtained through execution of test cases of a test group in the application. The testing of the application is then adaptively refined when the testing results have one or more failures, to expose problems that caused the one or more failures.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Manifold rock mass simulation test detection equipment
InactiveCN101813587AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesComputerized systemTested time
The invention relates to manifold rock mass simulation test detection equipment which is provided with more than 3 test groups, each test group comprises an axial loading system, a pressure chamber, a confining pressure loading system and a detection data recording system, and all test groups can carry out different simulation test detections. By adopting the structure, test time can be saved. All test groups are connected with a computer system and are controlled by the computer system, the computer system receives data output by the axial loading system and the pressure chamber and compares the data with preset simulation data, sends a regulation command to the axial loading system and the confining pressure loading system according to the comparison result to enable main pressure and confining pressure of the pressure chamber to be kept stable, and automatically records a detection result. The data sampling speed and the response speed of the computer system are high, therefore, the success rate and the accuracy of the test are high.
Owner:CHANGCHUNSHI HUAYU TESTING MACHINERIES INSTR
Sleep apnea syndrome assessment method based on electrocardiogram signals
InactiveCN106361277AStrong recognition abilitySolve the waste of manpower and material resources,Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalMedicine
The invention discloses a sleep apnea syndrome assessment method based on electrocardiogram signals. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the night electrocardiogram signals; pre-processing the electrocardiogram signals so as to obtain clean electrocardiogram signals; finding out the position of a peak value of R wave by virtue of R wave detecting algorithm, and conducting calculation so as to obtain RR sequences; interpolating the RR sequences, so that the RR sequences are identical in length; and dividing the interpolated RR sequences into three groups in accordance with a sample: a pre-training group, a fine-adjusting group and a test group, wherein by virtue of the pre-training group and the fine-adjusting group, an OSAS (obstructive sleep apnea syndrome) recognition model is constructed and optimized, and by virtue of the test group, an assessment result of the model on the OSAS is obtained. The method provided by the invention, by collecting the human electrocardiogram signals in a noninvasive mode, can be used for assessing the sleep apnea syndrome, and for the RR sequences extracted from original electrocardiogram signals, characteristic learning and OSAS recognition model construction can be conducted by virtue of a sparse self-coding network; meanwhile, network parameters are optimized through micro-adjusting, so that the model is more excellent in recognition capacity and good assessment is conducted; and the method provided by the invention is available by collecting the electrocardiogram signals within 8h at night.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
System and method for assigning computer users to test groups
A system and method to efficiently and randomly place users into a test group associated with a test running on a website being hosted on a server is disclosed. When a user first accesses the website, a random value is transmitted to the user in such a manner that the random value is stored in a computer-readable memory local to the user. Each subsequent time the user accesses the website, the random value is returned to the server from the user. The server may then place the user into a test group for a test to which the user will be exposed on the website based upon the result of an operation that includes the random value received from the user and a unique test value previously associated with the test.
Owner:OVERSTOCK COM
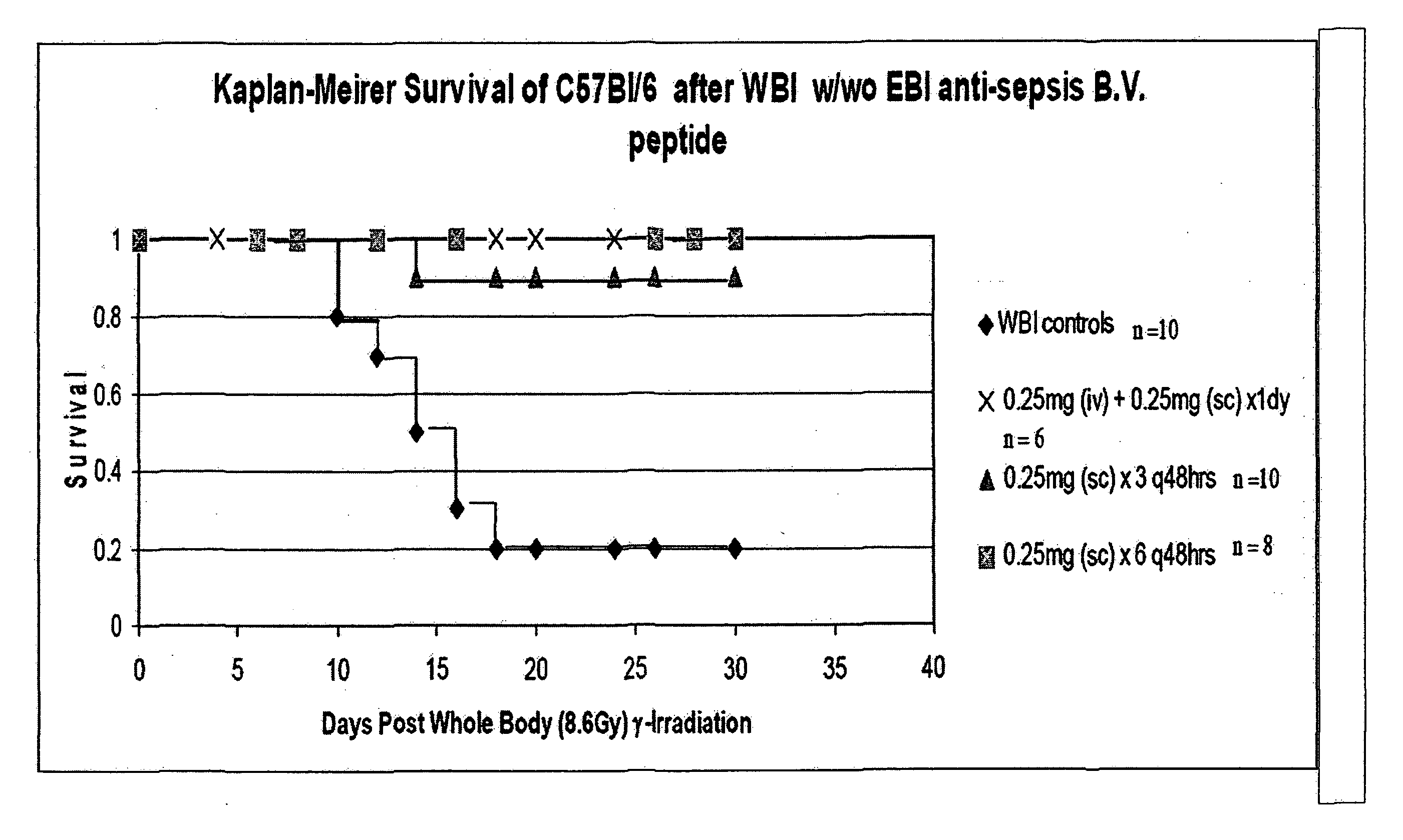
Control of radiation injury
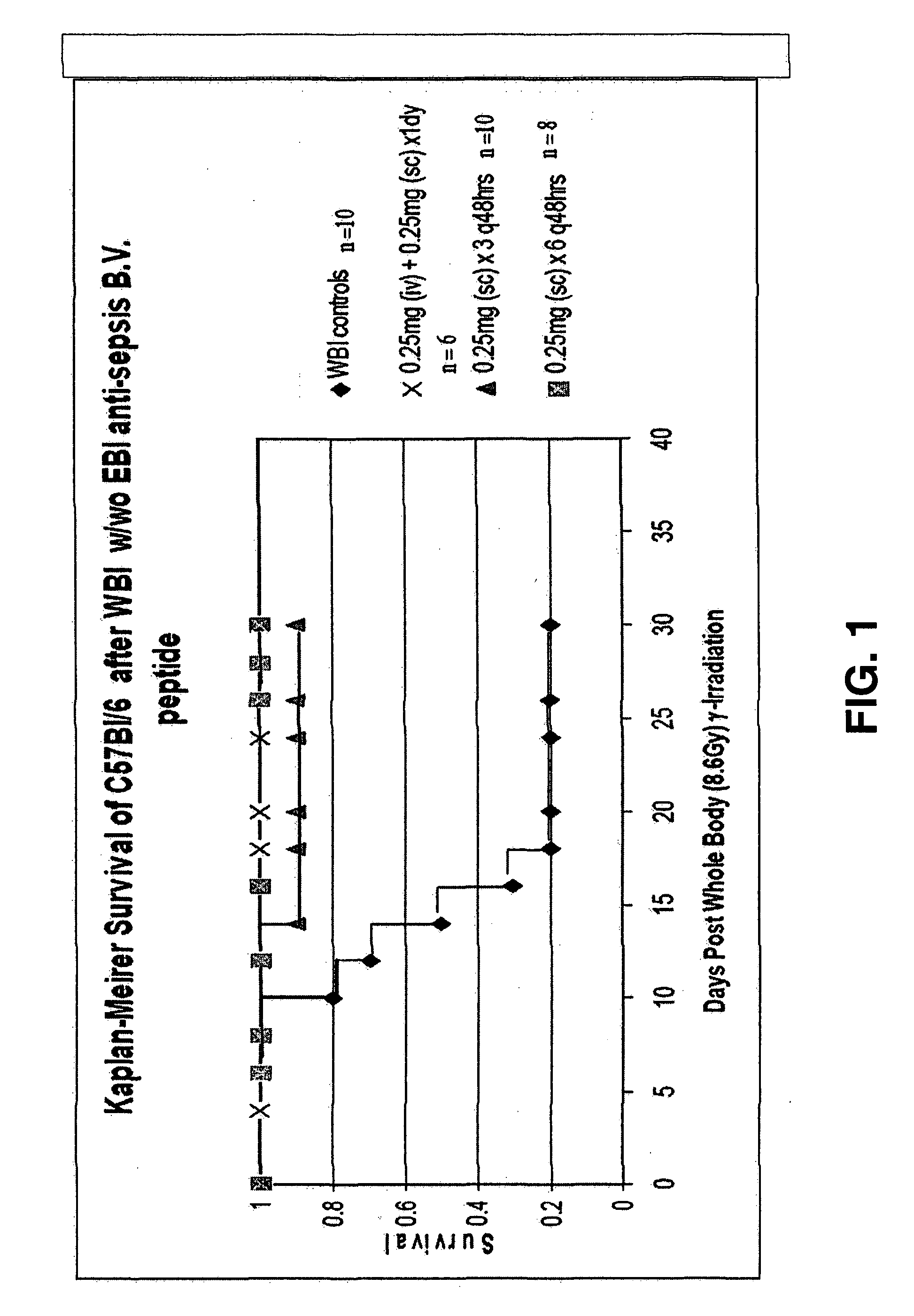
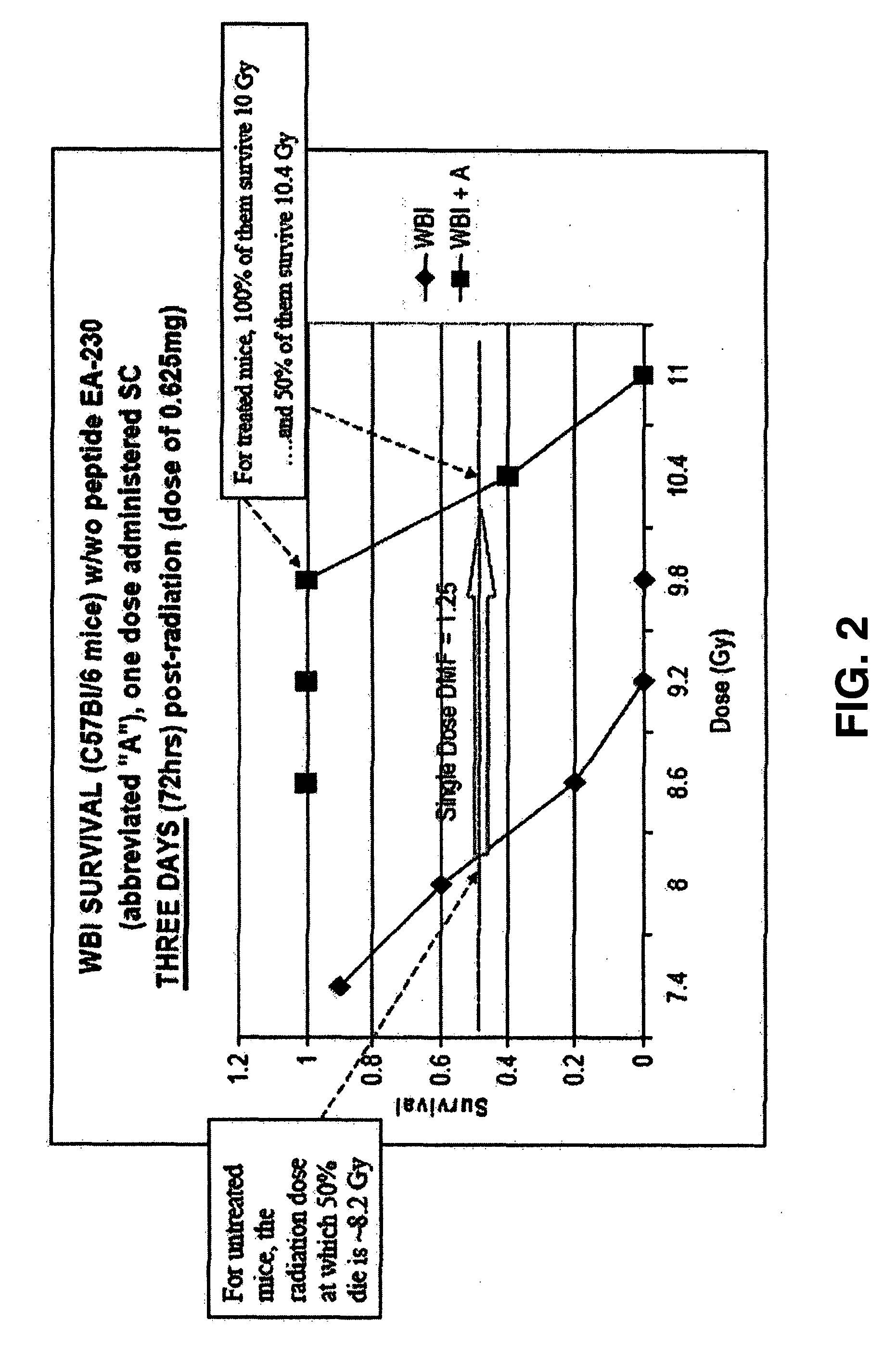
ActiveUS20080027007A1Shorten the counting processBad radiation exposureDigestive systemTetrapeptide ingredientsWhole bodyGamma irradiation
The invention relates to the field of drug development against acute radiation injury caused by exposure to high-energy electromagnetic waves (X-rays, gamma rays) or particles (alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons). To date, there is no effective drug to ameliorate radiation injury after accidental exposure to ionizing irradiation. The invention provides a method of treating radiation injury of a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids. Furthermore, the invention provides use of a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids for the production of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of a subject suffering from or believed to be suffering from radiation injury. In particular, the invention provides anti-radiation peptides having a dose reduction factor (DRF) against acute gamma irradiation of at least 1.10, said DRF determinable by testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a test group of mice treated with said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and, testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a control group of mice treated only with the vehicle of said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and wherein the DRF is calculated by dividing the LD50 / 30 of the peptide-treated animals by the LD50 / 30 of the vehicle-treated animals.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
Parameter testing method and device
The invention discloses a parameter testing method and device. The parameter testing method comprises confirming a testing target and a testing parameter which is corresponding to the testing target and dividing clients into a plurality of testing groups according to client identifications; configuring a parameter value of the testing parameter for every testing group and enabling the configured parameter values of testing groups to be different; testing the clients which are corresponding to the parameter value and of the testing group according to the parameter value of the testing parameter and obtaining testing effects of a plurality of testing groups; and confirming a parameter which is utilized in a testing group with the optimal effect among the testing effects of the plurality of testing groups. The parameter testing method and device has the advantages of being capable of supporting tests of a plurality of parameter values, finding out the testing group with the optimal testing effect to rapidly obtain the parameter value of the testing parameter with the optimal testing effect, saving time and achieving the target of a maximum advertising effect.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
A false comment detection method based on comment external information
InactiveCN109670542AImplement false detectionImprove versatilityDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionData set
The invention provides a false comment detection method based on comment external information. According to the method, the comment content and the external attribute in the comment document are extracted and labeled; comments and label data sets thereof are formed; comments and tag data sets thereof are divided into a training group and a testing group according to a proportion of 4: 1, and thenperforming the text preprocessing on the training group and the test group, establishing a false comment detection model, extracting an external attribute vector by utilizing a convolutional neural network, extracting a comment content vector by utilizing a long-short-term memory network added with an attention mechanism, and performing linear combination on the extracted features in a linear combination layer after feature extraction. According to the method, the false detection of all international e-commerce English comments can be achieved, good universality is achieved, the precision of the detection method reaches 81.4%, and the detection method can be qualified for most detection tasks.
Owner:田刚
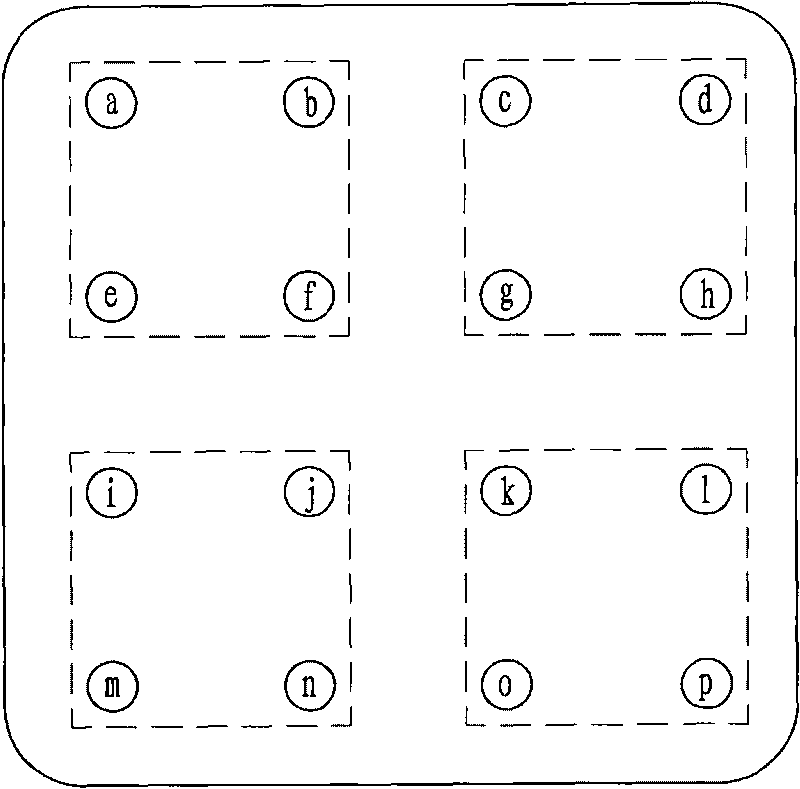
Comprehensive insulation and voltage resistance testing device of electric connector
The invention relates to a comprehensive insulation and voltage resistance testing device of an electric connector. Contact couples of electric conversion connector interfaces, which are connected with the electric connector to be tested, are divided into four test groups in a staggered row and staggered column mode; in the four test groups, a testing cable switches a common output interface connected with a testing power supply; a sequential control circuit controls the transverse short circuiting of the four test groups to test the transverse voltage of the contact couples, the longitudinal short circuiting of the four test groups to test the longitudinal voltage of the contact couples and the short circuiting of the four test groups to test voltage between the contact couples and a casing; and the comprehensive results of the testing voltage in the transverse direction and the longitudinal direction and between the contact couples and the casing are compared with insulation parameters and dielectric withstand voltage parameters which are set in a control system to complete the performance testing of an electric connector product to be tested. The invention has the advantages of few testing steps, short fixed conduction time, large testing quantity within unit time, high testing efficiency and testing degree of automation, accurate control of testing time, ensured voltage increase time of insulation and dielectric withstand voltage and accurate testing result.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND GRP HANGLIAN TECH CO LTD
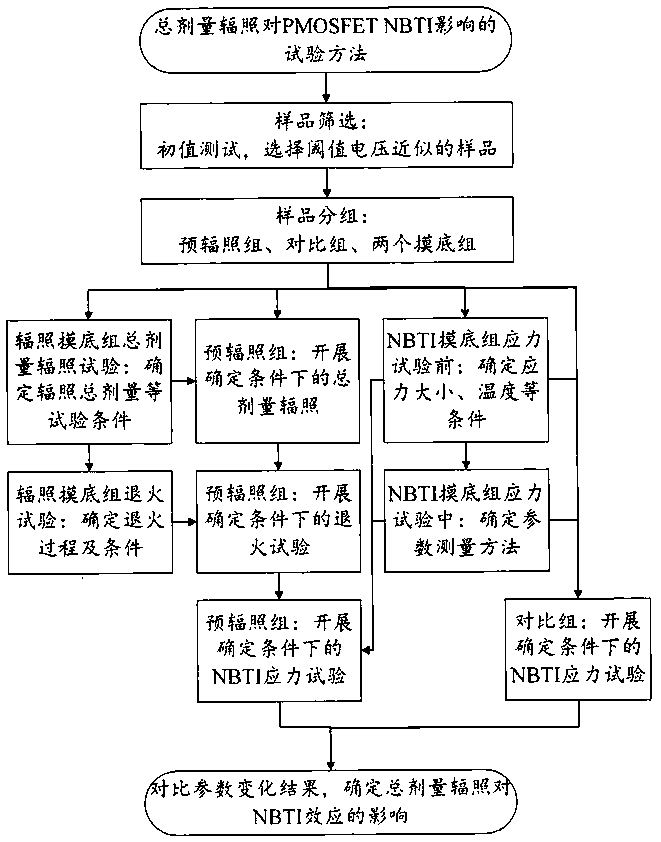
Test method for influence of total dose irradiation on PMOSFET negative bias temperature instability
ActiveCN108037438AEnsure consistencySemiconductor operation lifetime testingPre irradiationTest sample
The invention relates to a method for testing the influence of total dose irradiation on the PMOSFET negative bias temperature instability. The method includes test sample grouping and test parameterselection; the total dose irradiation and annealing tests of the test sample; and the negative bias temperature instability measurement of the test sample. In order to ensure the consistency and accuracy of the test result, the sample is divided into a pre-irradiation group, a comparison group and two pre-test groups, and on the basis of the pre-test, the total dose irradiation and annealing testsare carried out on the pre-irradiation group under the determination condition, the comparison group and the pre-irradiation group are subjected to a negative bias temperature instability test underthe same condition, and the test result is compared, the influence of the total dose irradiation on the negative bias temperature instability of the sample is obtained. The method provided by the invention can represent the influence of the total dose irradiation on the negative bias temperature instability of a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
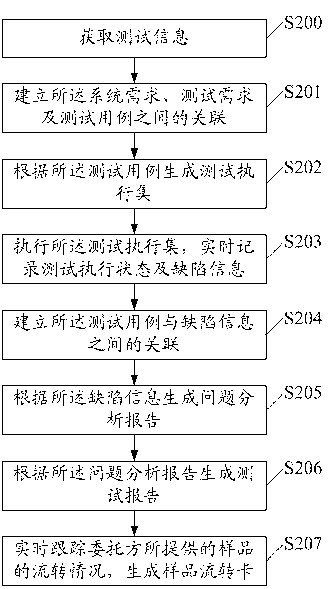
Project test procedure management method based on software testing and evaluation platform
InactiveCN103257918AEnsure comprehensive statistical analysisComprehensive statistical analysis guaranteeSoftware testing/debuggingSystem requirementsTest execution
The invention discloses a project test procedure management method based on a software testing and evaluation platform. The management method comprises the steps of acquiring test information, wherein the test information comprises system requirements submitted by a client, a test schedule submitted by a project leader, test requirements submitted by project members and test cases submitted by test group members; establishing an association among the system requirements, the test requirements and the test cases; generating a test execution set according to the test cases; and executing the test execution set and recording test execution states and defect information in real time; and establishing an association between the test cases and the defect information. By means of the management method, each link of plans, requirements, cases, defects, reports and the like can be tracked through the whole process, and one-stop test project control can be achieved.
Owner:广州博纳信息技术有限公司
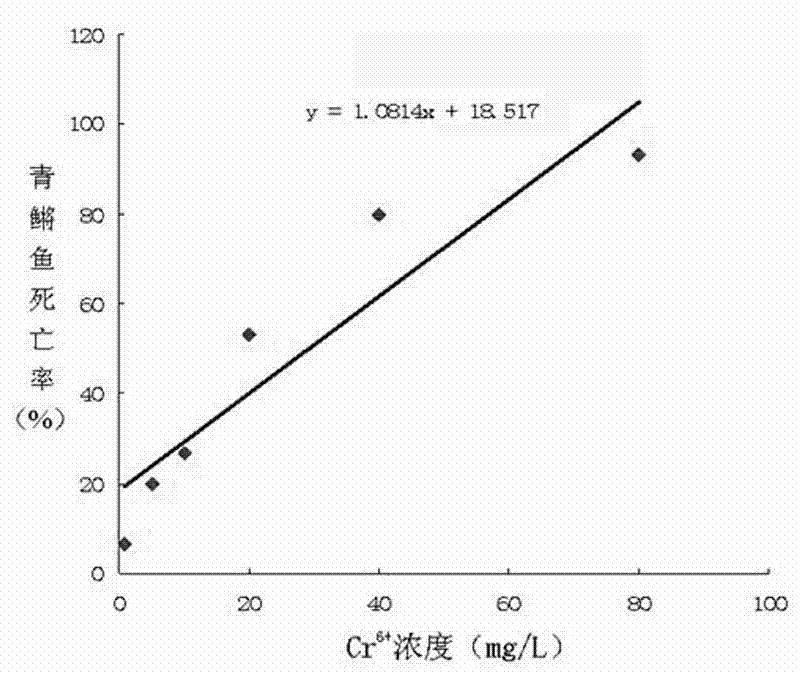
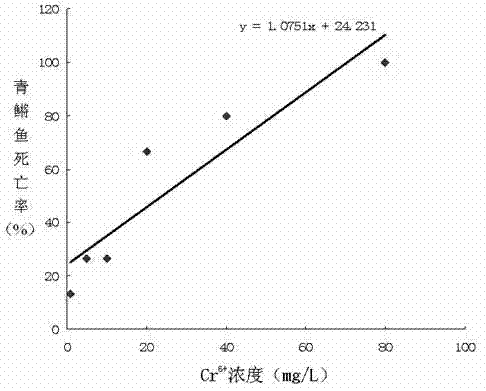
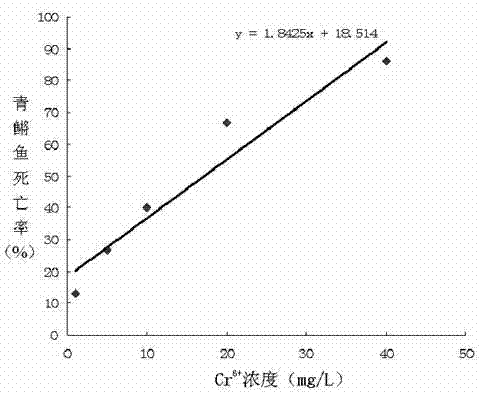
Method for detecting water toxicity by using biologic fish toxicity test
InactiveCN102175829ARealize quantitative evaluationReduce cancer riskClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMortality rateWater quality
The invention discloses a method for detecting water toxicity by using a biologic fish toxicity test. The method comprises the steps of: breeding medakas; preparing Cr6+ solutions at different concentrations; performing the biologic fish toxicity test by taking standard water as a control group and Cr6+ solutions at different concentrations as test groups; detecting death rates of medakas after 24 hours, 48 hours, 78 hours and 96 hours; drawing a standard curve of Cr6+ to the death rate; performing the biologic fish toxicity test by using a water sample to be detected and setting up a standard water control group; detecting the death rates of medakas after 24 hours, 48 hours, 78 hours and 96 hours; substituting the corresponding standard curve; and representing the water toxicity of the water sample with Cr6+ concentration. Through the standard curve of Cr6+ to the death rate, the water toxicity is quantitatively evaluated and the water pollution condition can be judged; the method provides technical supports for sudden water pollution and a water treatment technology of a water plant; and the risk of causing human cancers by exposure of drinking water is reduced.
Owner:济南市供排水监测中心
Device and method for generating test case
InactiveCN101377758AImprove completenessReduce human subjective judgmentSoftware testing/debuggingSystem under testTest group
The invention discloses a method for generating test cases and a device thereof, which is to solve the problem that the test cases can not be tested comprehensively. The method comprises the following steps: a mapping table is generated according to the relevance of key operations between the functional modules of a system to be tested; furthermore, discretionary two key operations which are relevant are connected to generate test groups according to the execution order in the mapping table, and then an arbitrary test group as an initial test group is connected with the test group having the same key operations with the initial unit to form service stream; finally, test cases in service stream are output according to the service stream in combination with the connections of the key operations in the mapping table. According to the proposal provided by the invention, analysis is conducted from the angle of interaction between a plurality of modules, thus improving the completeness of test cases.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Management system and method for cache replacement strategy
The invention discloses a management system and a management method for a cache replacement strategy, and overcomes the disadvantage in the prior art that the adoption of a single replacement strategy cannot effectively meet the access demand of an application program with a plurality of different local access characteristics of the cache. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing a cache into a first part and a second part; dividing the first part into a first test group and a second test group, wherein a first replacement strategy is adopted by the first test group and a second replacement strategy is adopted by the second test group; setting a strategy selection register and recording failure frequencies of the first test group and the second test group; and when the access of the second part is failed, selecting the replacement strategy for the second part from the first and the second replacement strategies according to the value of the strategy selection register. Compared with the prior art, the invention improves the application performance of the cache.
Owner:BEIJING PKUNITY MICROSYST TECH
Methods for adaptive problem determination in distributed service-based applications
InactiveUS7360120B2Easy to findError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsDistributed servicesTest group
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Regression test method, device and system
ActiveCN105718371AEasy maintenanceSolve efficiency problemsSoftware testing/debuggingRegression testingTest efficiency
The invention provides a regression test method, a regression test device and a regression test system. The regression test method comprises the following steps: generating a test task according to a regression test plan; checking test item files corresponding to the test task from a test case library, wherein the test item files comprise test group files which need to be operated to achieve the test task, and the test group files comprise test specification files corresponding to test cases; calling the test cases corresponding to the test specification files in the test group files, configuring corresponding test cases according to the test specification files so as to perform regression tests; managing test results of the regression tests. By adopting the regression test method, equipment is automatically operated to achieve convenient test case maintenance and large-scale test case implementation, meanwhile the purposes of test flexibility, convenience, instantaneity and maintenance convenience can be also achieved, the development and test efficiency can be improved, and the problems that a conventional regression test is low in efficiency, high in time price and high in labor cost can be solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN PANGO MICROSYST CO LTD
Reagents and test methods with the test group before a transfusion
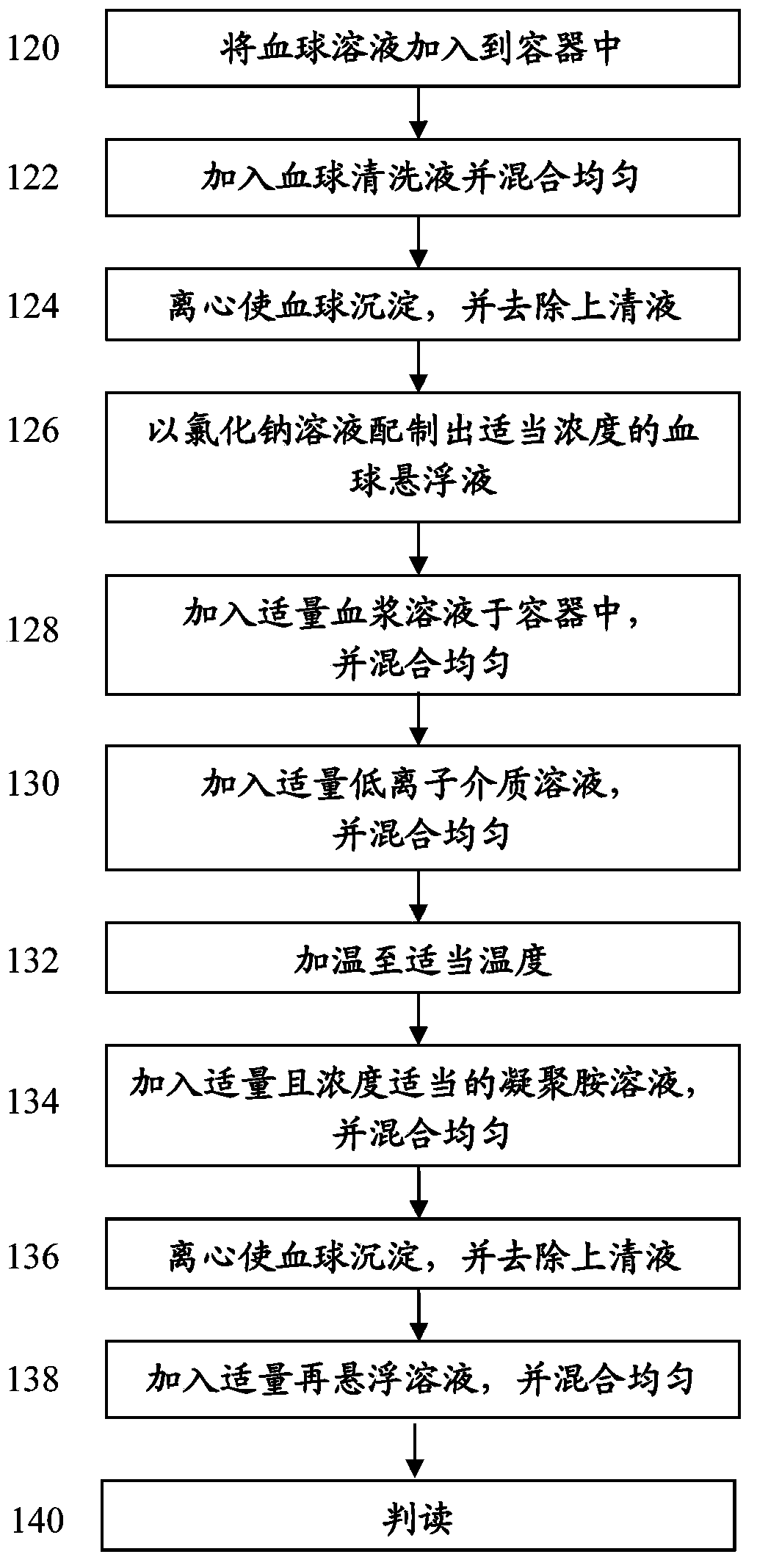
InactiveCN103424555AReduce distractionsImprove inspection accuracyBiological testingWorkloadTest group
The present invention provides a reagent set with the test method and test before a blood transfusion, is a method to improve the traditional manual polybrene method and the detection sensitivity of the detection reagent set, the cleaning liquid reagent set comprising blood, a solution of low ionic medium, polybrene solution and resuspension solution. The method and reagent set of the present invention made without clinical significance of antibodies has a lower detection sensitivity, but the clinical significance of the antibody has a high detection sensitivity, thus reducing the workload for the subsequent identification of the antibody, reducing testing costs, giving patients more secure rapid transfusion quality.
Owner:林妈利 +1
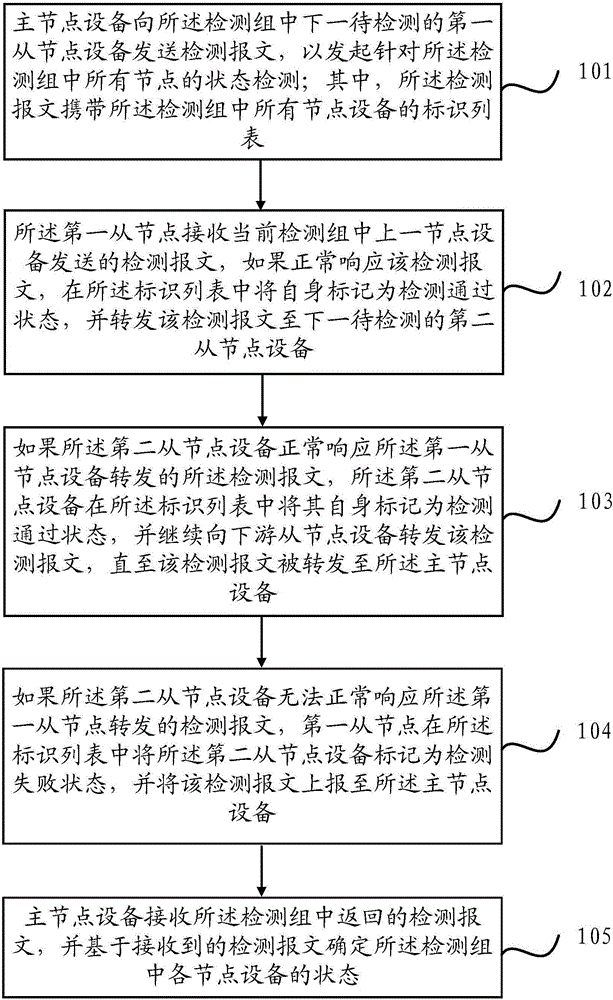
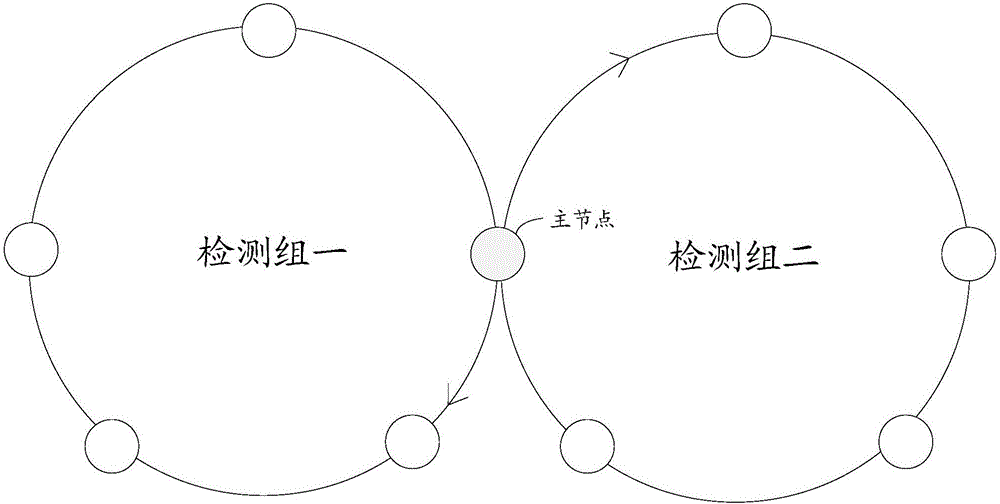
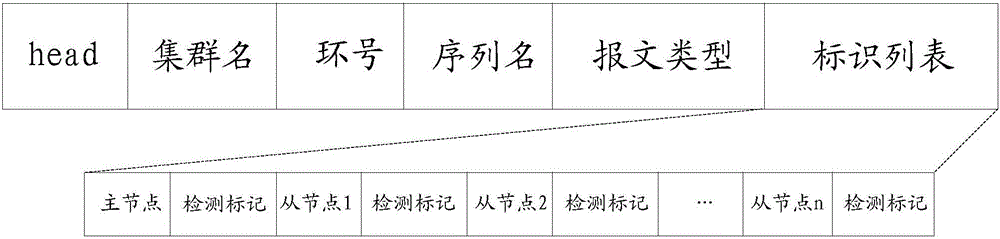
Node equipment state detection method and node equipment state detection device
ActiveCN105897507ARelieve dealing with stressReduce the numberData switching networksComputer networkTest group
The invention provides a node equipment state detection method and a node equipment state detection device. The method and the device are applied to an equipment cluster which is pre-divided into one or more circular test groups with the same master node. The method comprises the following steps: a master node sends a test message carrying an identity list of all nodes to first slave node equipment; if the first slave node responds to the message normally, the first slave node is self-marked as 'test passed' in the identity list and forwards the message to a second slave node; if the second slave node responds to the message normally, the second slave node is self-marked as 'test passed' in the identity list and continues to forward the message until the message is forwarded to the master node; if the second slave node cannot respond to the message normally, the first slave node marks the second slave node as 'test failed' in the identity list and reports the message to the master node; and the master node determines the state of each node in a test group based on the received test message. Through the method and the device, the processing pressure on the master node equipment can be alleviated.
Owner:HANGZHOU DT DREAM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com