Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Ige binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Binding of IgE specific to that allergen is detected by the use of an enzyme linked anti-human IgE antibody in a colorimetric reaction. Results of RAST testing show a very good corelation between the presence of IgE antibody in serum and positive skin and provocation tests, as well as symptoms of allergy.
Method for detecting mite allergen specific antibody in blood serum
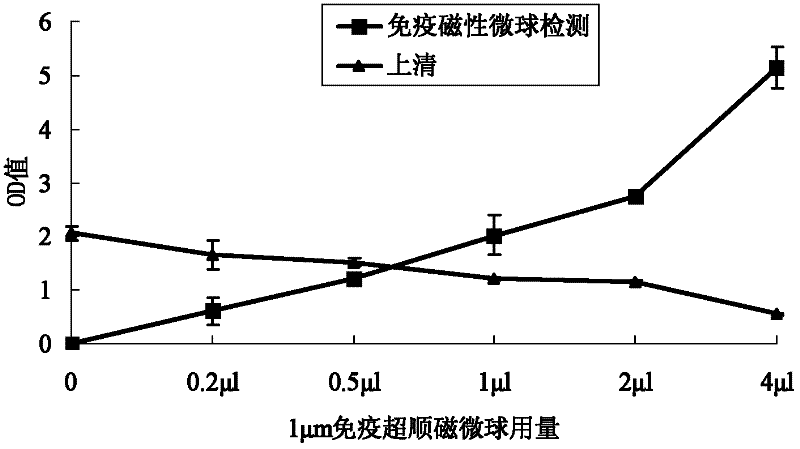
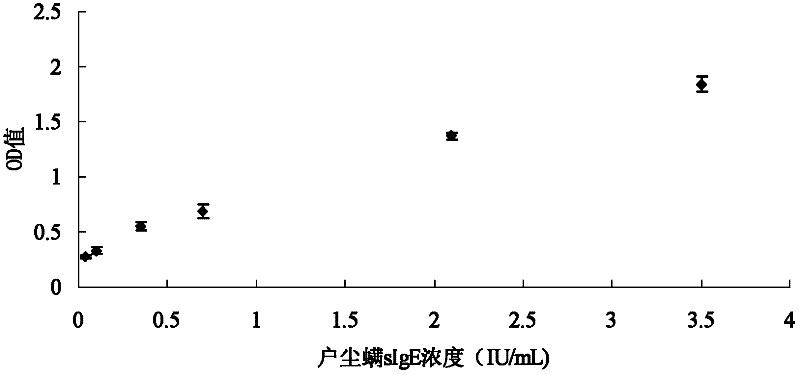
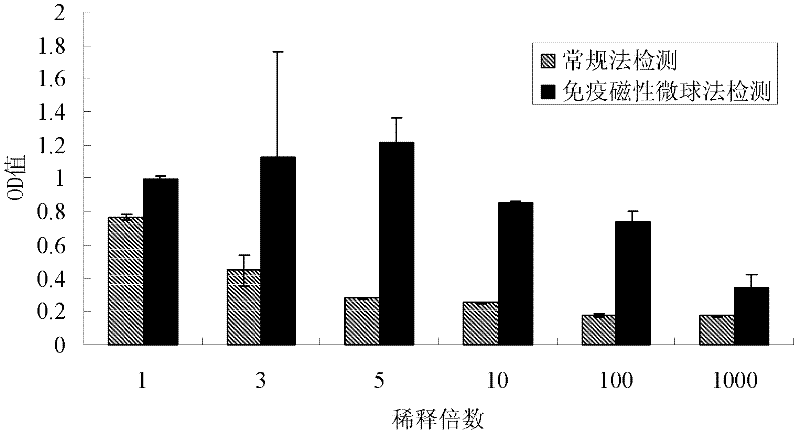
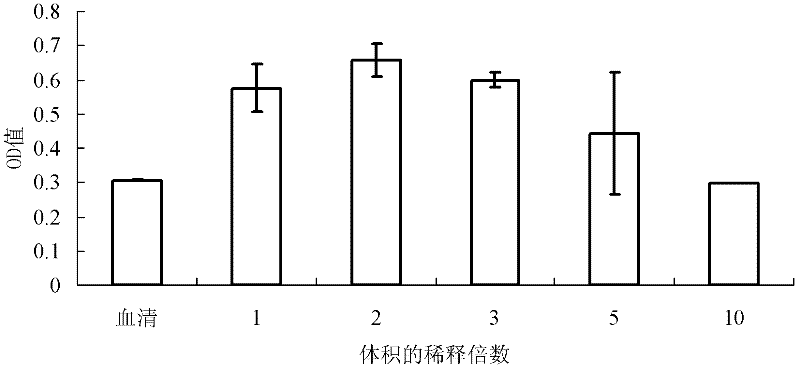
The invention discloses a method for detecting mite allergen specific antibody in blood serum. The method comprises the following steps of: coupling mite allergen with surface carboxyl modified magnetic microspheres to prepare immunomagnetic microspheres; and mixing and incubating the blood serum to be detected and the immunomagnetic microspheres in holes of an elisa (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) plate to combine mite allergen with mite allergen specificity IgE in the blood serum, and detecting by adopting an enzyme-linked immunosorbent method after the elisa plate is washed. In the method disclosed by the invention, a mite allergen is directly coupled onto the surfaces of magnetic microspheres, thus all the impurities except the mite allergen specific antibody in the blood serum can be conveniently removed; and targeted mite allergen specificity antibody detection is carried out, detection time is shortened, and sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of detection are improved. The mite allergen immunomagnetic microspheres prepared by the invention can be used in standard automatic detection to improve detection efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting allergen-specific antibody in serum
The invention discloses a method for detecting allergen-specific antibodies in serum. The method comprises the following steps: coupling anti-human IgE antibodies with carboxyl surface modified magnetic microballoons to obtain immunomagnetic microspheres; incubating the immunomagnetic microspheres with serum to be measured so as to enable the immunomagnetic microspheres to bind to IgE in the serum to be measured; carrying out magnetic separation to obtain immunomagnetic microsphere-IgE conjugates, dissolving deposition of the magnetic separation in a buffer solution, adding the mixed solution into apertures of an enzyme label plate which is coated with allergen, and carrying out detection by the ELISA adsorption method after incubation and plate washing. According to the invention, magnetic microballoons are coupled with anti-human IgE antibodies to prepare immunomagnetic microspheres which are mixed with serum to be measured for incubation and are bond to all the IgE in serum; the immunomagnetic microspheres are enriched and IgE is separated; the ELISA adsorption method is employed to detect whether there is specific IgE bond to allergen in serum. The method provided in the invention enables all the IgE to be separated from serum through immunomagnetic microspheres, impurities to be removed, and sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of ELISA adsorption detection to be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel mutant allergens
InactiveUS20030175312A1Reduce efficacyReducing IgE bindingAllergen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against plantsBiochemistryMutant
Novel recombinant allergens with multiple mutations and reduced IgE binding affinity are disclosed. The allergens are non-naturally occurring mutants of naturally-occurring allergens. The overall alpha-carbon backbone tertiary structure is essentially preserved. Also disclosed is a method for preparing such recombinant allergens as well as uses thereof.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
Nucleic acids encoding ara h 3 polypeptides
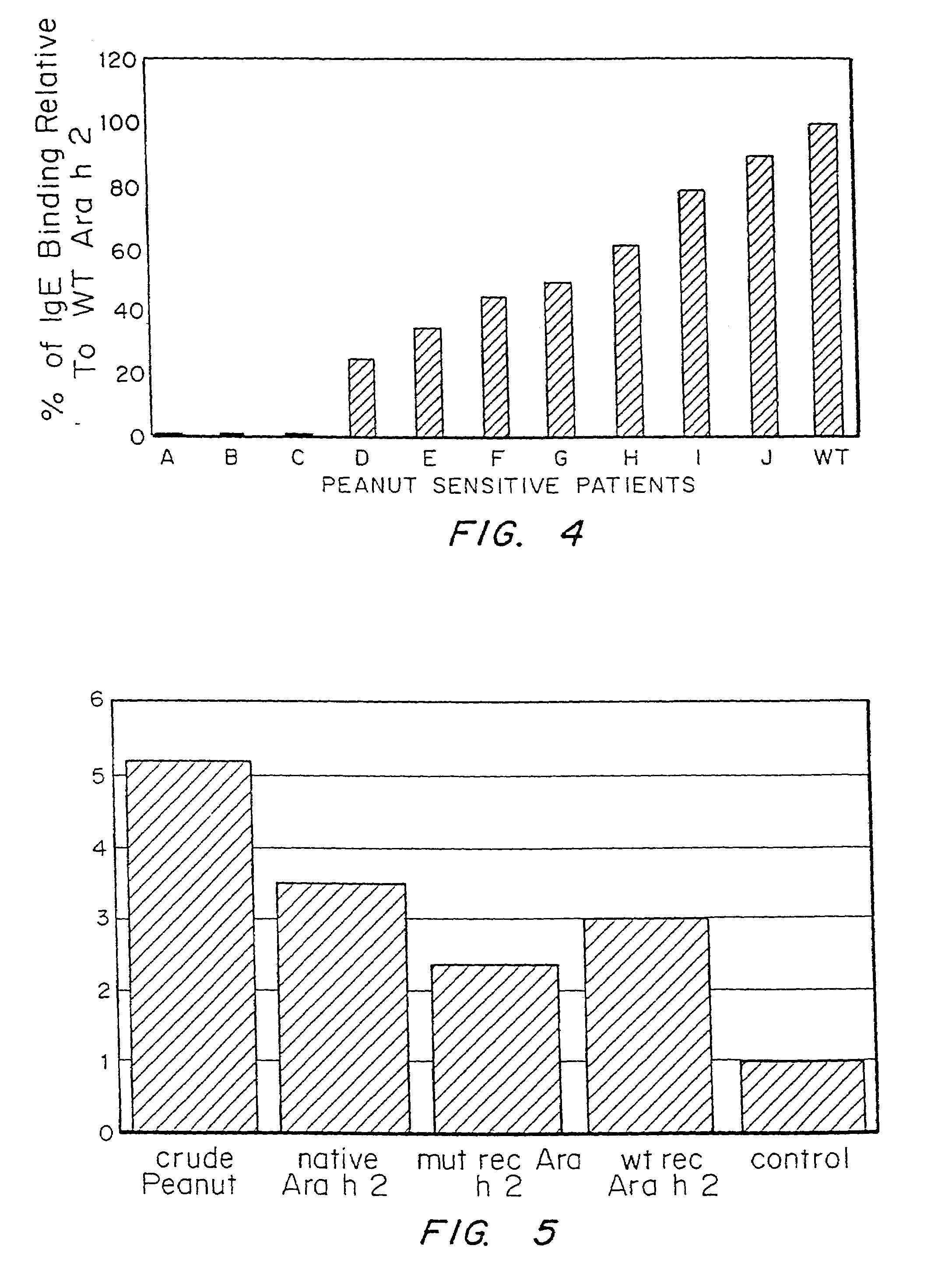
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity. The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Compositions and methods to treat asthma
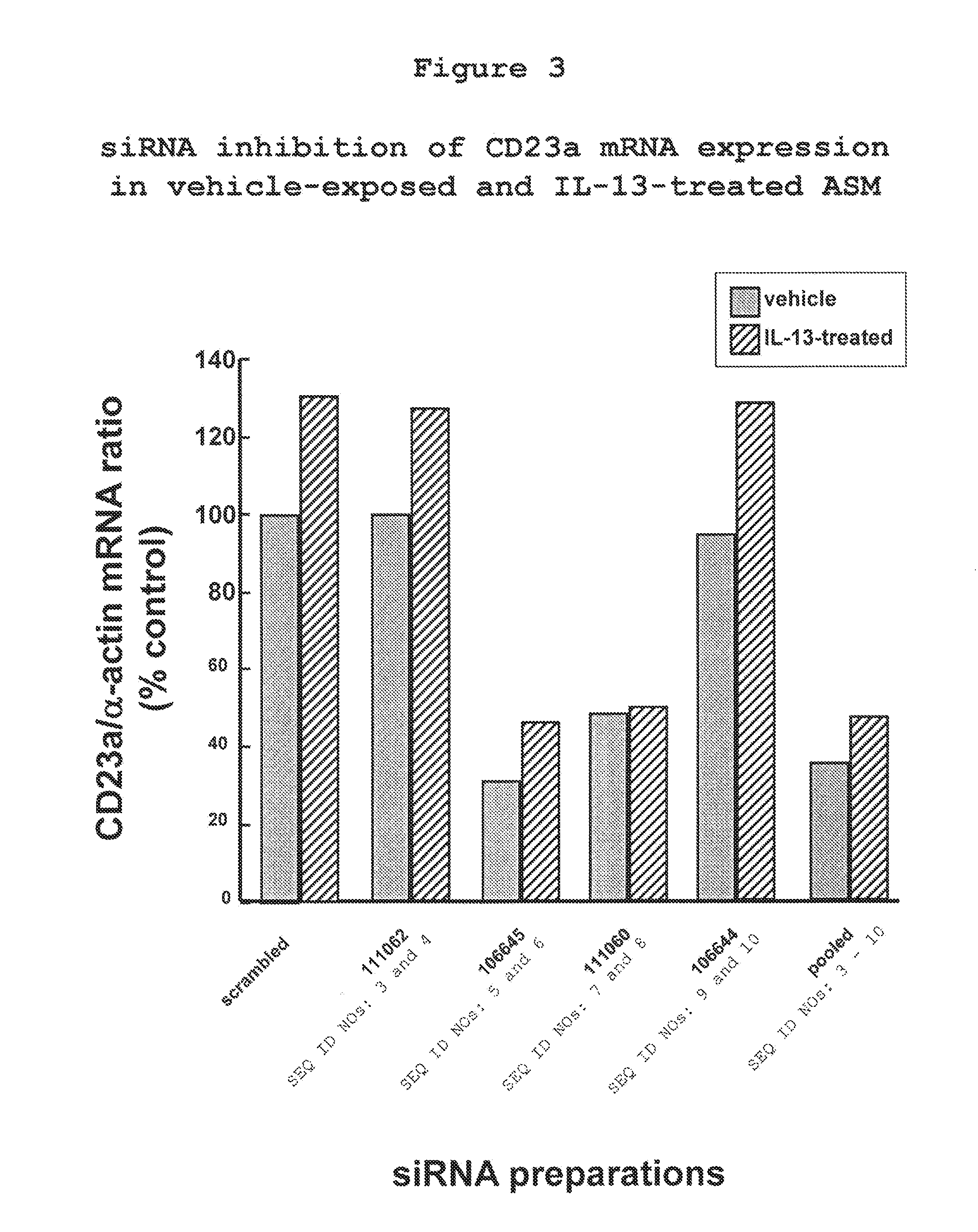
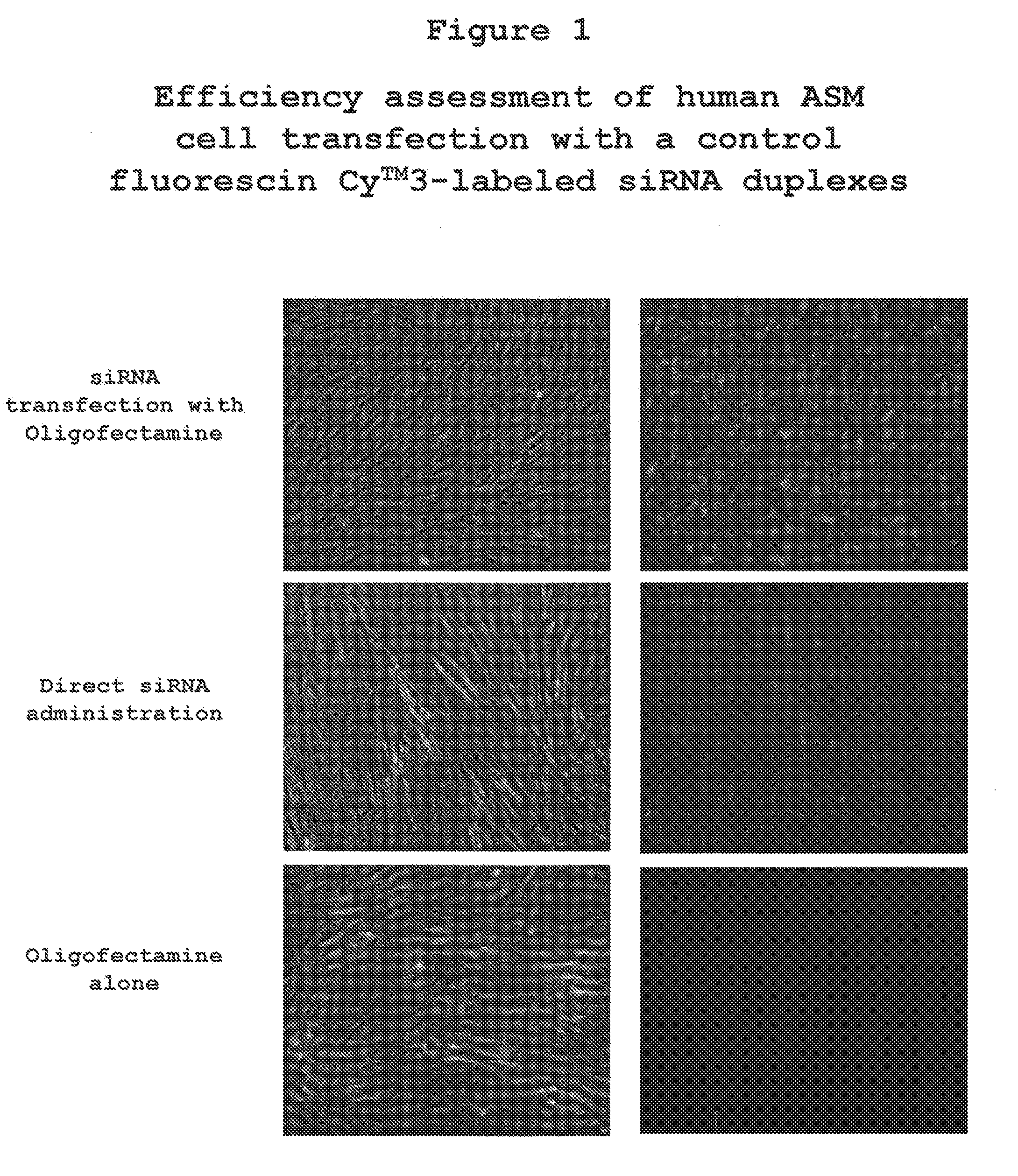
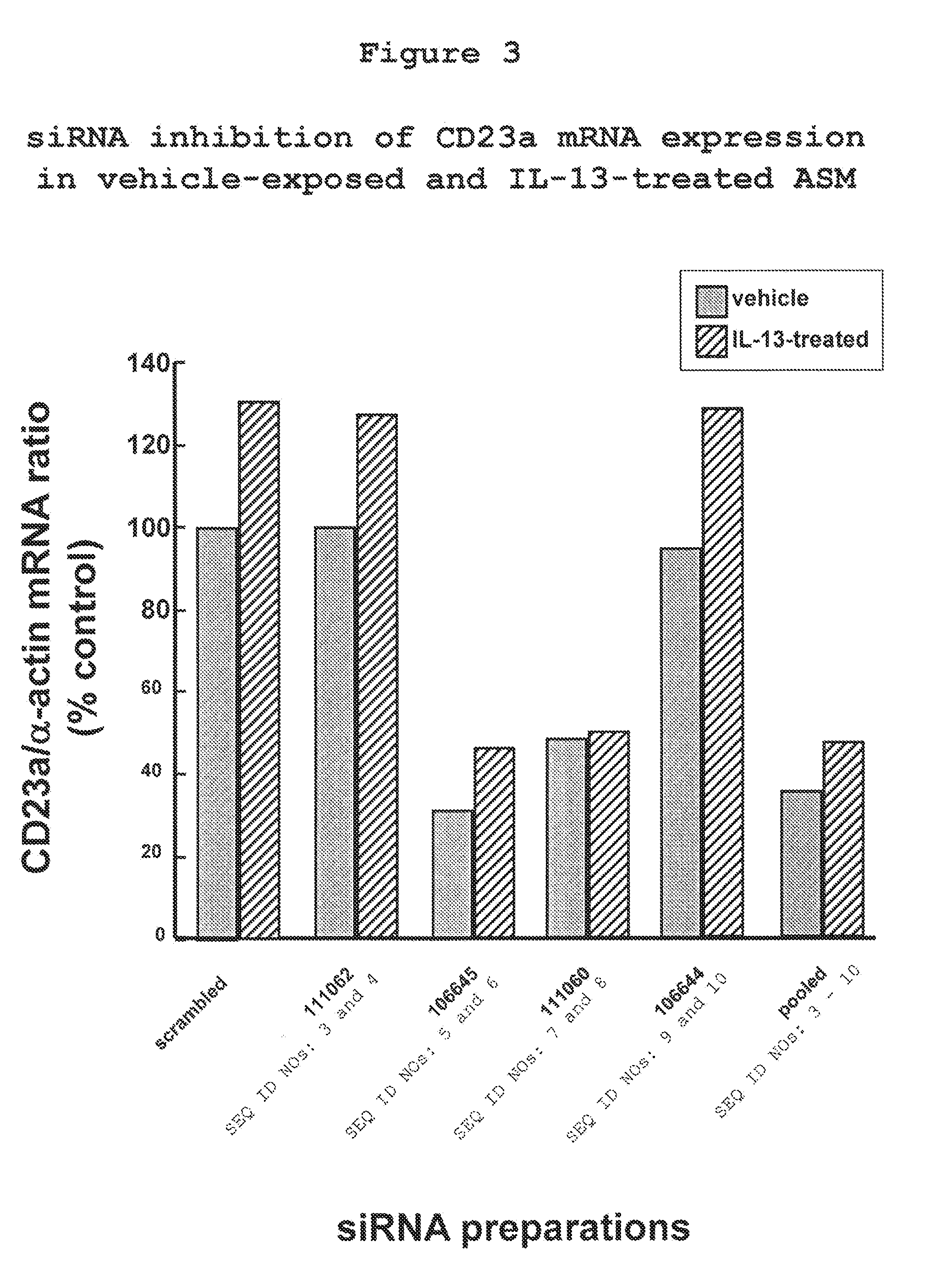
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of asthma. The compositions can be, for example, siRNA directed to CD23. The invention also provides a method of treating asthma with a formulation for in vivo delivery of a CD23 siRNA to inhibit IgE binding in a patient.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS20070213507A1Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsFungi peptidesBinding siteT cell
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Main allergic protein of humulus pollen
ActiveCN101392023AFacilitate quantitative labelingEasy accessImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPlant peptidesSerum igeHumulus pollen
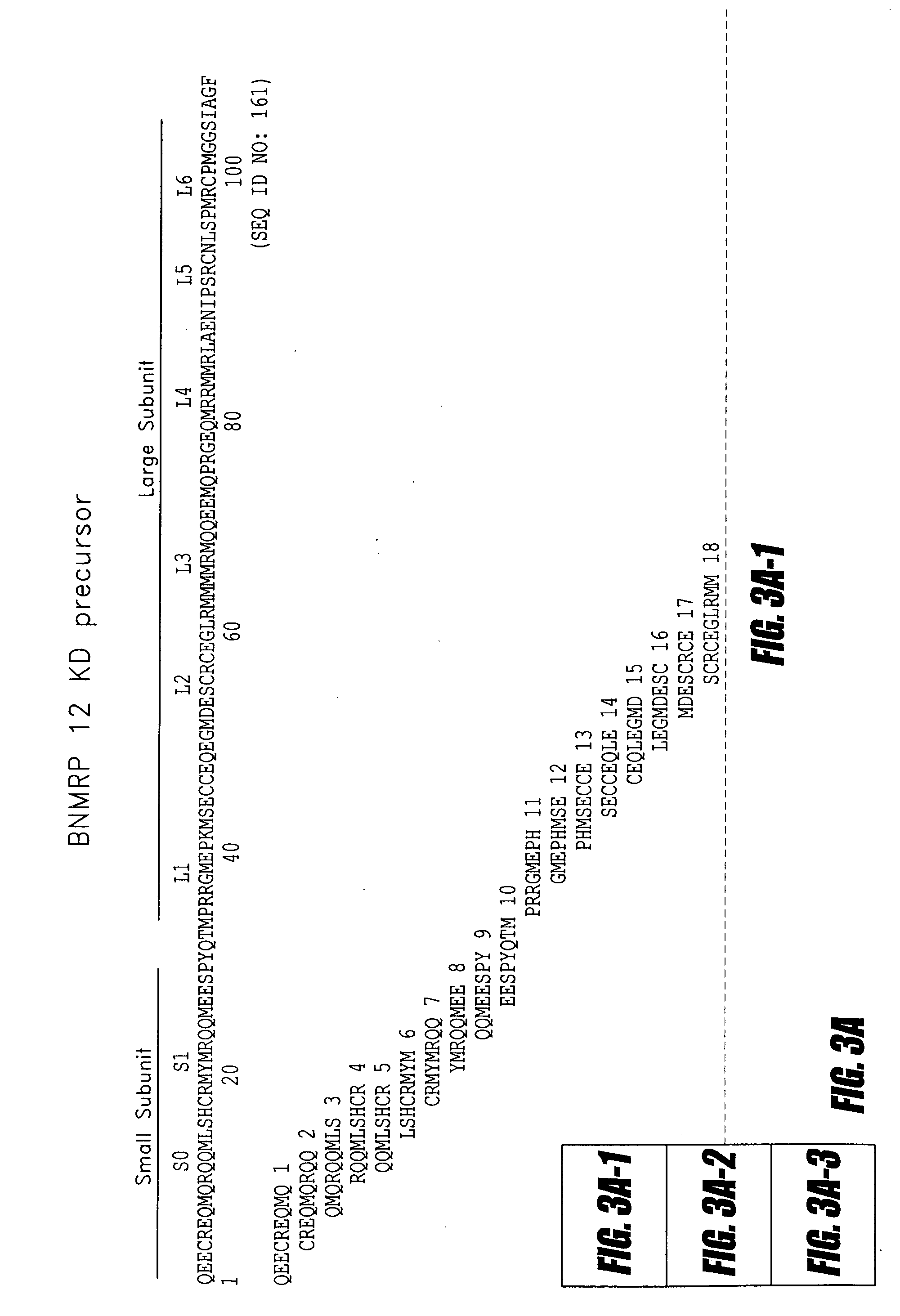
The invention discloses the main sensitization protein of humulus pollen which can be separated and obtained from the humulus pollen and combined with over 89 percent of serological specificity IgE of patients allergic to humulus pollen. The apparent molecular weight of the protein measured by SDS-PAGE is about 12kDa, the isoelectric point is 4.7 and the N-terminal sequence is NH4<+>-MDNPFENGMKA-COO<->. The separation and purification of the protein lay the foundation for realizing the standization of the allergenic preparations of the protein.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Allergen mutants
InactiveUS20040043438A1Increase changeIncrease probabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesBiochemistryMutant
Novel recombinant allergens with multiple mutations and reduced IgE binding affinity are disclosed. The allergens are mutants of naturally occurring allergens. The overall alpha-carbon backbone tertiary structure is essentially preserved. Also disclosed is a method for preparing such recombinant allergens as well as uses thereof.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
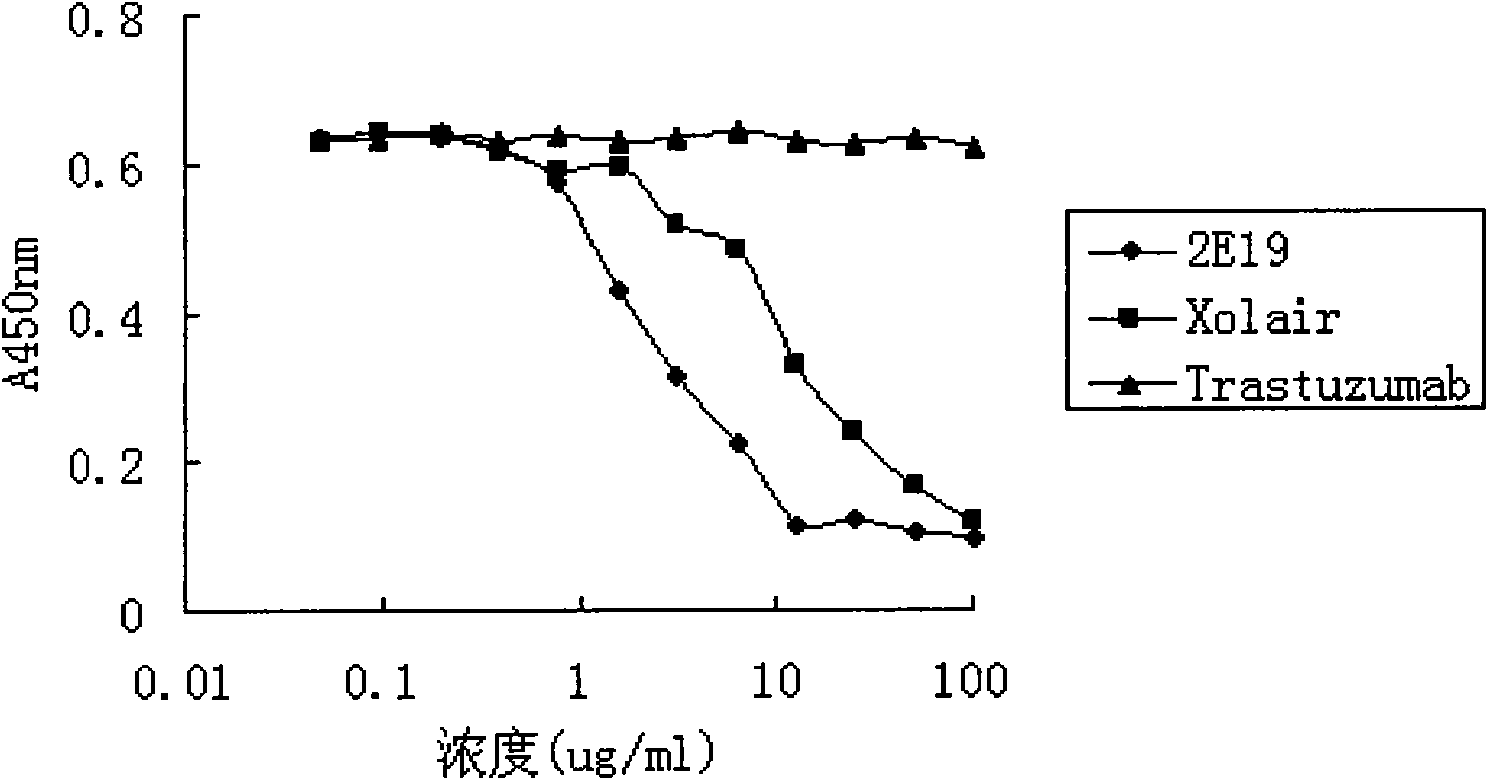
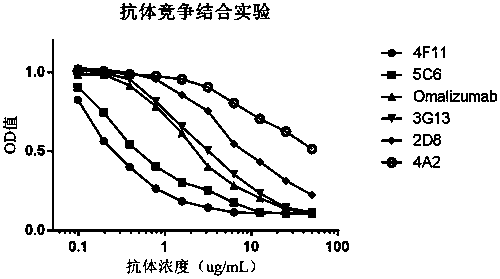
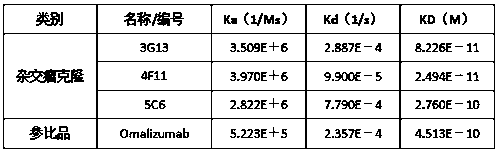
Human monoclonal antibody against IgE, preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN102167745AAntibody affinity is highInhibition of degranulationAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsNucleotideAllergic asthma
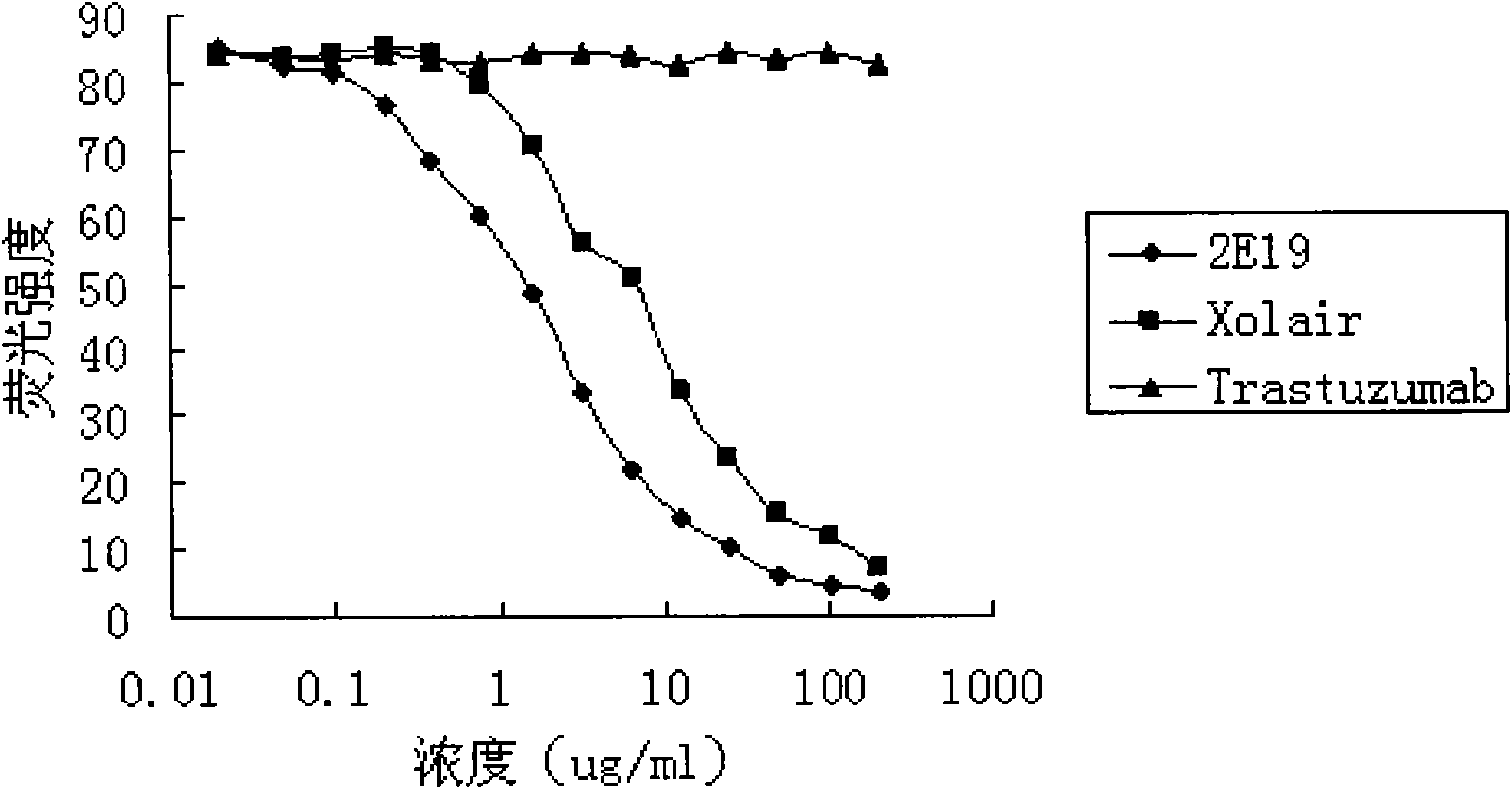
The invention relates to the biotechnology field, and more specifically, the invention discloses a human monoclonal antibody against IgE, a preparation method and a purpose thereof. According to the invention, a natural human phage antibody library of large capacity is constructed;; a human antibody 2E19 strain against IgE is obtained through screening from the library; an amino acid sequence of a heavy chain variable region is expressed as SEQ ID NO: 6; and the amino acid sequence of a light chain variable region is expressed as SEQ ID NO: 8. Besides, the invention also discloses the preparation method of the antibody 2E19, as well as a nucleotide sequence for encoding the antibody 2E19 and an expression vector and a host cell comprising the nucleotide sequence. The antibody 2E19 of the invention has a higher antibody affinity, so as to be able to obviously inhibit degranulation caused by the combination of IgE and FC epsilon RI on a cell surface, and the antibody 2E19 does not combine with the IgE combined with the FC epsilon RI on the cell surface. The antibody 2E19 of the invention could be used for the preparation of a medicine for treating hypersensitivity diseases, especially for treating allergic asthma.
Owner:越海百奥药业(绍兴)有限公司
Variants of mite group 1 allergens for the treatment of house dust mite allergy
InactiveUS20050053615A1Reduce IgE reactivityAnimal cellsAllergen ingredientsHypersensitive responseInotrope
The present invention provides a method to produce variant recombinant mite Group 1 proteins with properties suitable for accelerated, specific immunotherapy. The variants of the present invention have greatly reduced IgE binding activity, but little or no loss in the ability to stimulate T cells in allergic individuals. The present invention also relates to a variant mite Group 1 protein obtained by such a method, and the use of such a variant mite Group 1 protein to reduce an allergic response to a mite Group 1 protein. The present invention also includes novel mite Group 1 nucleic acid molecules, proteins, recombinant molecules, and recombinant cells, as well as uses thereof.
Owner:HESKA
Compositions and Methods to Treat Asthma
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of asthma. The compositions can be, for example, siRNA directed to CD23. The invention also provides a method of treating asthma with a formulation for in vivo delivery of a CD23 siRNA to inhibit IgE binding in a patient.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Coding gene of scylla paramamosain allergenic protein and application thereof
The invention provides a coding gene of scylla paramamosain allergenic protein and an application thereof. The coding gene of the allergenic protein is composed of a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses an expression vector and a recombinant strain containing the gene, a method for preparing the allergenic protein and the application of the allergenic protein. The coding gene of the scylla paramamosain allergenic protein is cloned into a prokaryotic expression vector, recombinant expression plasmid is constructed, and transferred into host bacteria and inducing expression is carried out; the scylla paramamosain allergenic protein rScy p 9 can be obtained, the IgE binding capacity of the scylla paramamosain allergenic protein rScy p 9 and serum of a crustacean allergic patient is measured, a reference basis can be provided for clinical diagnosis of allergic symptoms and detailed screening of allergens, and prevention, control and treatment of allergicdiseases of the Scy p 9 are timely and accurate.
Owner:厦门市波生生物技术有限公司
Monoclonal antibody of main allergic protein of humulus pollen
ActiveCN101392022AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPlant peptidesSerum igeProtein.monoclonal
The invention provides a monoclonal antibody of the main sensitization protein of humulus pollen, which is obtained by taking the main sensitization protein of the humulus pollen as an immunogen. The main sensitization protein of the humulus pollen can be separated and obtained from the humulus pollen and be combined with over 89 percent of serological specificity IgE of patients allergic to the humulus pollen. The apparent molecular weight of the protein measued by SDS-PAGE is about 12kDa, the isoelectric point is 4.7 and the N-terminal sequence is NH4<+>-MDNPFENGMKA-COO<->. The monoclonal antibody can be used for the quantitative marking of the main sensitization protein in the allergenic preparations of the humulus pollen.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Recombinant allergen with reduced ige binding but undiminished t-cell antigenicity
ActiveUS20050074464A1Reduce the binding forceReduced IgE production-stimulatory activitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsType i allergyImmunomodulations
The present invention relates generally to reagents useful in the immunotherapeutic or immunoprophylactic treatment of allergic diseases. More particularly, the present invention provides modified allergens exhibiting reduced IgE interactivity including reduced IgE production-stimulatory activity, while retaining T-cell antigenicity, which are useful in the immunomodulation of type I allergic disease conditions. The present invention further contemplates a method of immunomodulation of allergic diseases such as type I allergic disease conditions by the administration of modified allergens exhibiting reduced IgE interactivity while retaining T-cell antigenicity.
Owner:MELBOURNE UNIV OF THE
Method for identifying allergenic proteins and peptides
The present invention relates to a method for identifying allergenic proteins and peptides. More specifically, the present invention provides a method for identifying allergenic milk proteins and / or peptides comprising the steps of: providing at least one expression library comprising DNA or cDNA derived from the mammary gland tissue of a lactating mammal, preferably a lactating cow, expressing at least one protein or peptide encoded by said expression library, determining the binding capacity of said at least one protein or peptide to IgE of at least one serum of an individual who is sensitive to mammalian milk,preferably cow's milk, contacting the at least one protein or peptide exhibiting an IgE binding with basophil cells, eosinophil cells or mast cells and identifying the at least one protein or peptide as being allergenic when said basophil cells, eosinophil cells or mast cells release upon contact with at least one protein or peptide at least one mediator.
Owner:MJN U S HLDG LLC
Mutant of scylla paramamosain allergic protein Scy p 4 and application of mutant
ActiveCN110627890ALittle side effectsImprove safety indexPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunological disordersSafety indexWild type
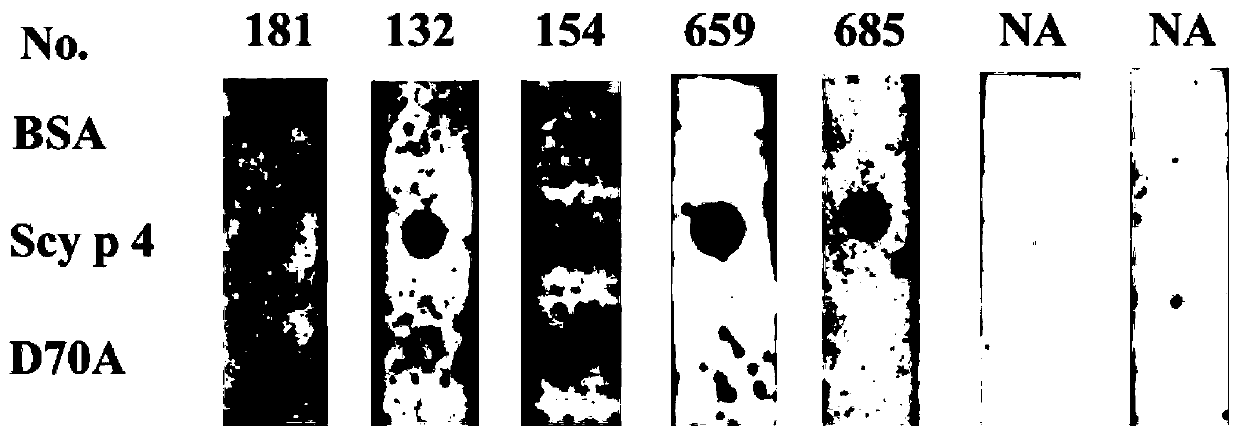
The invention provides a mutant of scylla paramamosain allergic protein Scy p 4 and application thereof, wherein the mutant is obtained by mutating the 70th site of an amino acid sequence of the scylla paramamosain allergic protein Scy p 4 into alanine, and the amino acid sequence of scylla paramamosain allergic protein Scy p 4 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the mutant of the scylla paramamosain allergic protein Scy p 4, a wild type Scy p 4 gene is subjected to site-directed mutagenesis by means of overlap extension PCR, the mutated gene is recombined with an expression vector and thentransferred into host cells, and the mutant of the Scy p 4 gene with low allergenicity is successfully constructed; and compared with the wild type allergen, the mutant has reduced IgE binding activity, and the mutant can be used for immunotherapy or immunoprophylaxis, and can reduce side effects in immunotherapy and improve safety index of treatment.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN107686521AImprove thermal stabilityLong storage timeAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsDiseaseMonoclonal antibody
The invention provides a novel humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody, which can be combined with IgE and can inhibit the anaphylactic reaction caused by combination of IgE with a receptor Fc EpsilonRI; higher stability is realized. The novel humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody provided by the invention can be used for treating allergic diseases, and is used for treating allergic asthma or urticaria.
Owner:越海百奥药业(绍兴)有限公司
Novel mutant allergens
Novel recombinant allergens with multiple mutations and reduced IgE binding affinity are disclosed. The allergens are non-naturally occurring mutants of naturally-occurring allergens. The overall PROPORTIONAL -carbon backbone tertiary structure is essentially preserved. Also disclosed is a method for preparing such recombinant allergens as well as uses thereof.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
Method for expressing and purifying soluble dermatophagoides pteronyssinus major allergen Der p 2 protein
InactiveCN106282213AGood effectHigh expressionPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesEscherichia coliSolubility
The invention relates to a method for performing high-solubility expression and purification on dermatophagoides pteronyssinus major allergen Der p 2 protein in Escherichia coli. According to the method, the Escherichia coli chaperonin trigger factor (TF) is used as a fusion tag to implement high-solubility expression of Der p 2 and obtain the optimized high-efficiency purification technique; and the purity of the sample obtained by the method is higher than 98%. The verification proves that the purified recombinant Der p 2 protein has a consistent secondary structure folding state with the naturally extracted Der p 2 protein and has the identical combination activity with specific IgE in the serum of the dermatophagoides-pteronyssinus-allergic patient. The fusion expression method used in the invention can implement soluble expression of the Der p 2 protein, has the advantages of cuttable fusion tag, high recombinant protein expression level and simple purification technique, is suitable for large-scale industrial production, and can maintain the natural activity of the product.
Owner:SHENZHEN PKU HKUST MEDICAL CENT
Epitope identification and modification for reduced allergenic activity in proteins targeted for transgenic expression
InactiveUS20060112453A1Reduced and allergenic activityIncrease contentBiocideImmunoglobulinsProtein targetA-DNA
Disclosed is a method for identification of key amino acids in plant proteins critical in generating allergenic activity through mapping the epitope(s) harboring human IgE binding activity. The identified epitope (s) are then modified by amino acid substitution preferably by alanine substitution, for reduced or negative IgE-binding activity. A plant gene expression system comprising a DNA construct placed operably under the control of a promoter sequence that confers seed-specific expression is also disclosed for the expression of the modified proteins. The Brazil nut 2S sulfur-rich protein was exemplified. The method disclosed herein is particularly useful for the production of dietary proteins with improved nutritional quality and reduced or negative allergenicity for human and animal consumption through genetic engineering.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
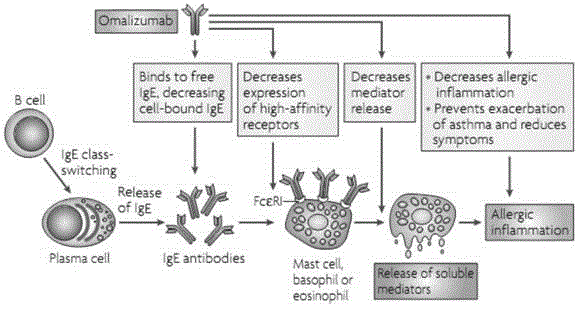
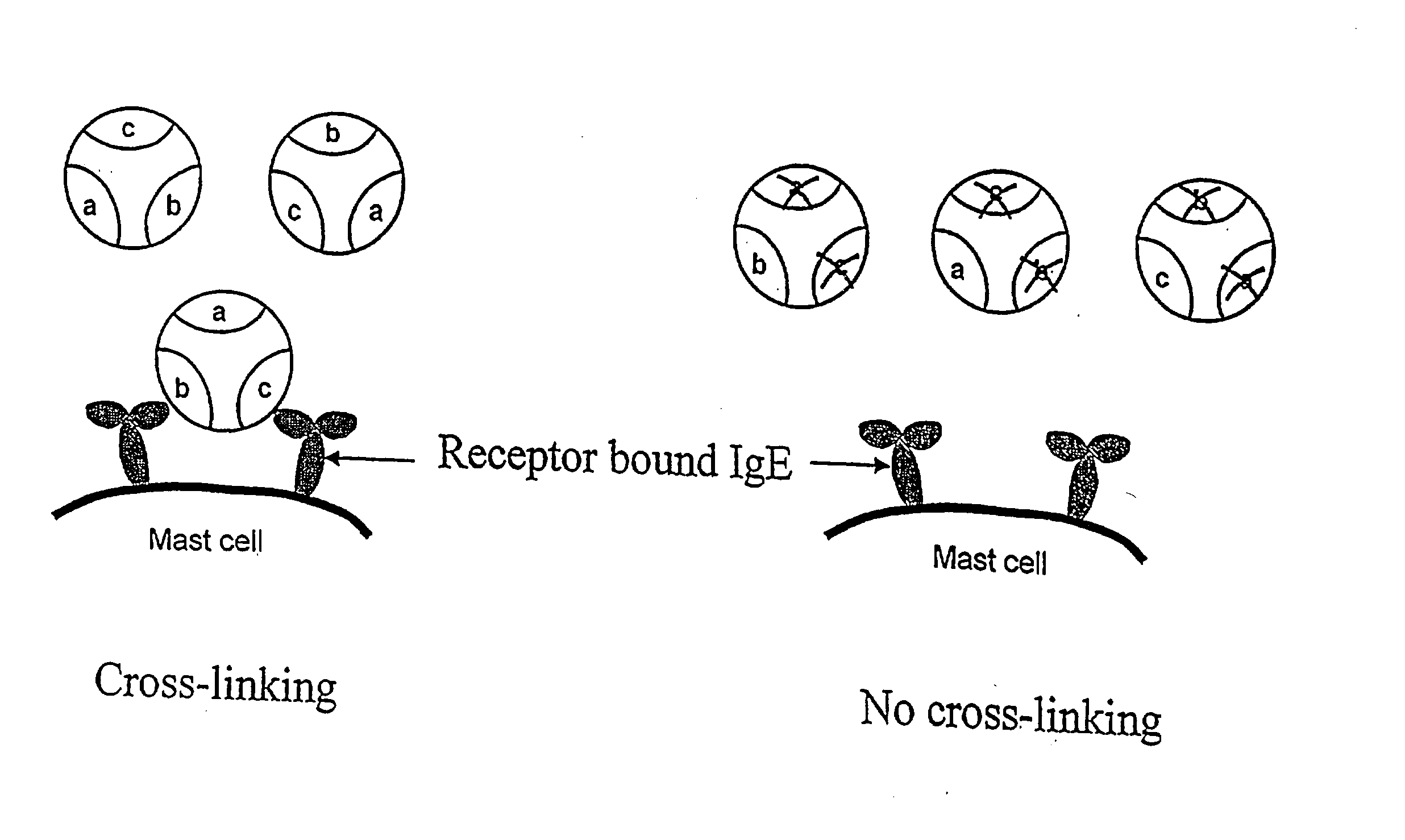
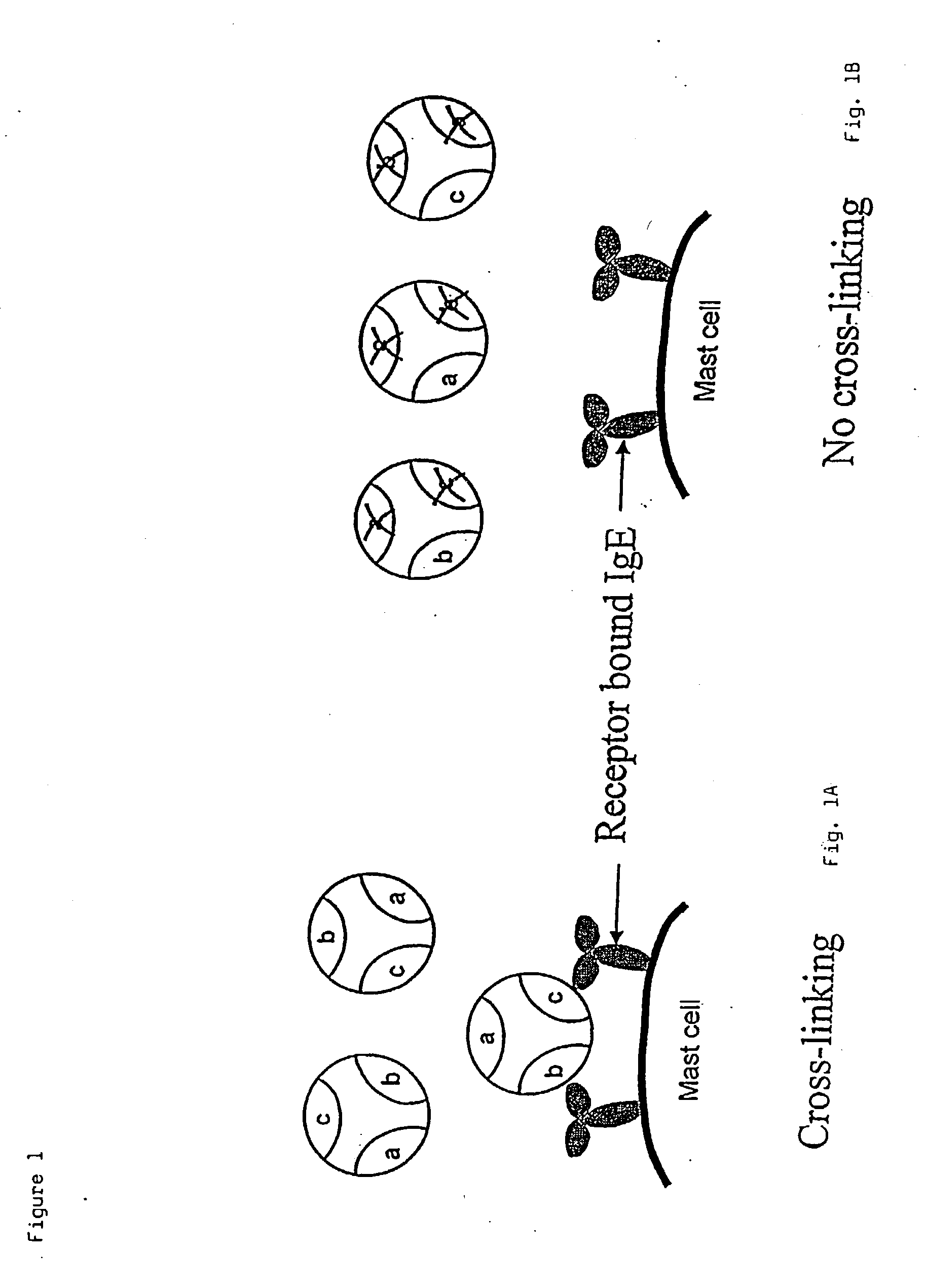
Administering IgE antagonists during pregnancy to ameliorate allergic diseases in the offspring
InactiveUS20020006402A1Less immunogenicLow immunogenicityAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAllergyIge binding
The invention relates to IgE antagonists, including monoclonal antibodies, and their use in ameliorating asthma and allergic diseases in offspring of mothers treated during pregnancy with such antagonists. The preferred IgE antagonists do not induce release of the mediators of allergy. One example of such IgE antagonists are anti-IgE antibodies which bind to secreted IgE, to membrane IgE on the surface of IgE-producing B cells, but not to IgE bound to the Fc∈RI on the surface of basophils or mast cells. Preferably, these antibodies also do not bind to IgE bound to Fc∈RII receptors. It is also preferable if these antibodies have human IgG1 or IgG3 constant regions, as well as further human portions, if desired.
Owner:TANOX
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS7879977B2Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from yeastsBinding siteADAMTS Proteins
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
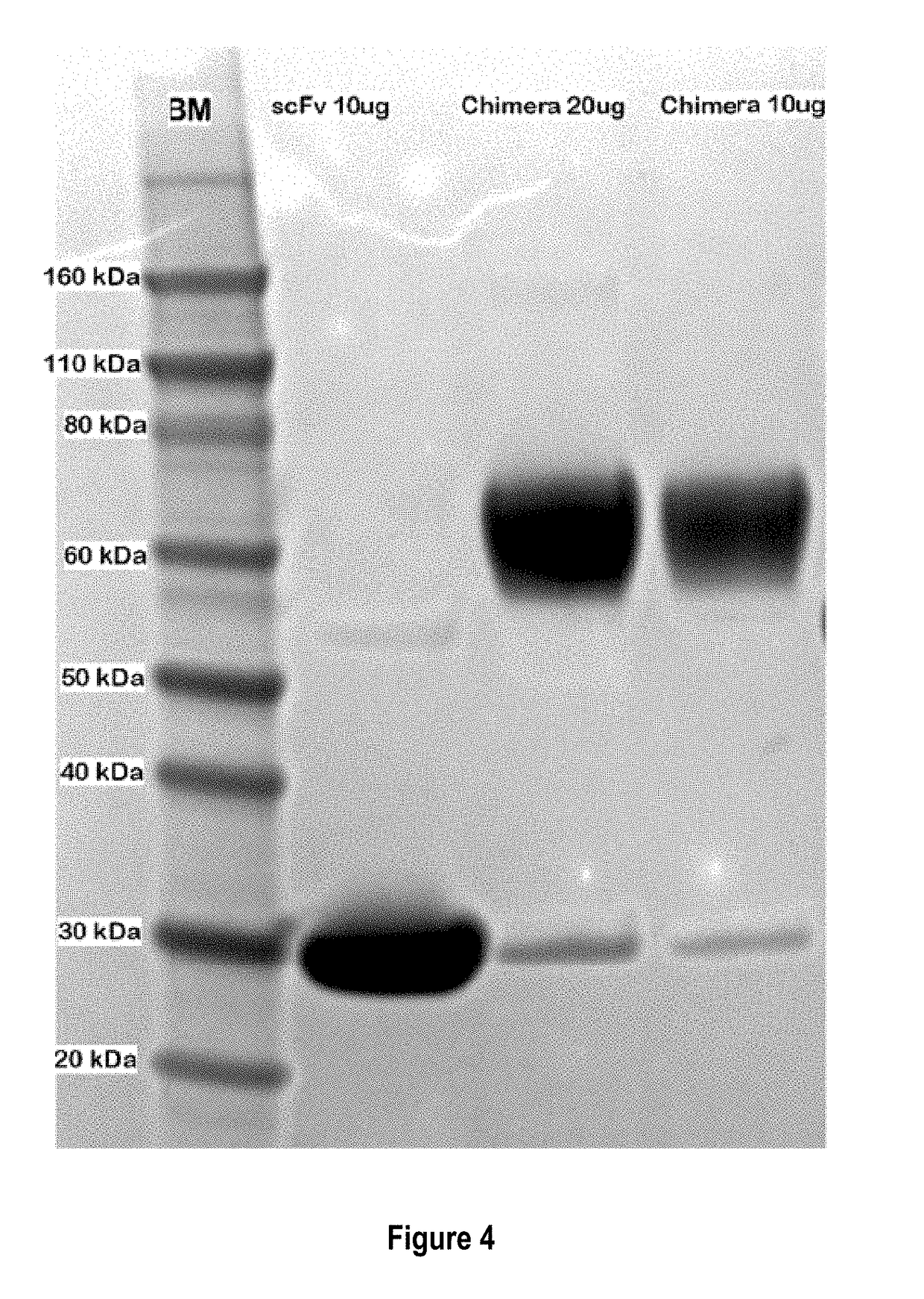
Treatment of allergic diseases with chimeric protein
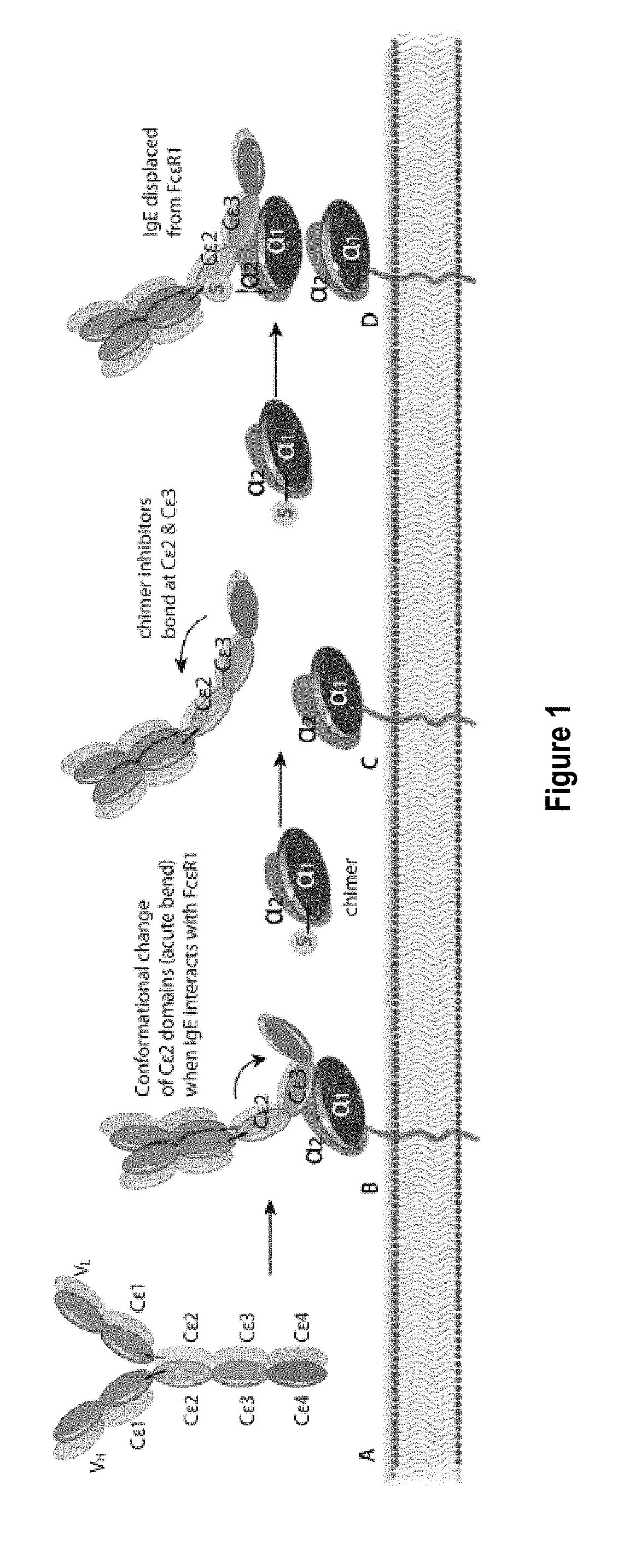
ActiveUS20180230236A1Reduce free serum IgE levelDecreasing IgE levelSenses disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLinker peptideDisease cause
The present invention provides a chimeric protein comprising: a) a single chain variable fragment (scFv) that binds to a mammalian IgE at an epitope within the amino acid sequence VDGQKATNIFPYTAPGTK (SEQ ID NO:1) of canine IgE or at an epitope within the corresponding amino acid sequence of a different mammalian species; b) a linker peptide; and c) an amino acid sequence comprising an IgE high affinity receptor alpha chain, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Novel mutant allergens
Novel recombinant allergens with multiple mutations and reduced IgE binding affinity are disclosed. The allergens are non-naturally occurring mutants of naturally-occurring allergens. The overall PROPORTIONAL -carbon backbone tertiary structure is essentially preserved. Also disclosed is a method for preparing such recombinant allergens as well as uses thereof.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
Treating atopic dermatitis with lgE antagonists
InactiveCN1289253AFacilitated releaseRelease noPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid cell preparationMast cellAtopic dermatitis
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of atopic dermatitis comprising a suitable IgE antagonist which does not induce release of the mediators of allergy; for example, anti-IgE antibodies which bind to secreted IgE, to membrane IgE on the surface of IgE-producing B cells, but not to IgE bound to the Fc epsilon RI on the surface of basophils or mast cells. Preferably, these antibodies also do not bind to IgE bound to Fc epsilon RII receptors. It is also preferable if these antibodies have human IgG1 or IgG3 constant regions, as well as further human portions, if desired. The pharmaceutical composition can be administered systemically or topically.
Owner:泰诺士公司
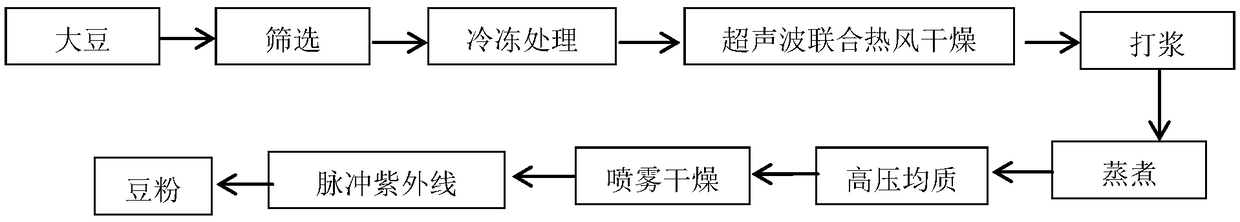
Processing method for low-allergenic soybean powder
InactiveCN109105519AReduce sensitizationAllergenicity reductionMilk substitutesFood scienceSoybean productUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a processing method for a low-allergenic soybean powder, belonging to a traditional soybean product processing technology. The processing method comprises the following steps:(1) soaking selected soybeans, then wiping moisture from soaked soybeans with a gauze, and placing wiped soybeans into a vacuum refrigerator; (2) laying frozen soybeans onto the gauze, and placing thegauze into an ultrasonic hot-air dryer; (3) directly pulping dried soybeans, carrying out filtering with a filter screen, stewing obtained raw soybean milk in a stewing pot, carrying out continuous boiling, and adding alkaline protease; (4) conveying the soybean milk into a homogenizer for homogenization, and carrying out spray-drying; and (5) irradiating obtained soybean powder with a pulsed ultraviolet light for sterilization so as to obtain the low-allergenic soybean powder. According to the invention, by combination of soybean vacuum freezing with an ultrasonic hot-air drying technology and an ultraviolet pulse technology, various microorganisms in food and packaging are killed through instantaneous and high-intensity pulse light energy; immunoreactivity is reduced, and changing of aprotein structure and reduction of an IgE binding ability are promoted, so allergenicity of the soybeans is reduced; compared with traditional hot-air drying, ultrasonic hot-air drying needs shorter heating time, so allergenic substances in the soybeans are rapidly destroyed; and bacteria in the soybean powder grow more slowly than the bacteria in traditional soybean powder, so the shelf life of the soybean powder is prolonged.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
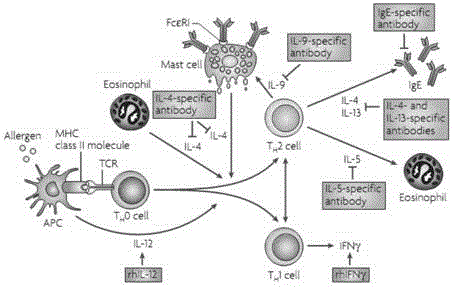
Composition for inducing th2 cells, therapeutic composition for th2 type disease, and use of the composition
The present invention provides a complex of an antigen and IgE binding to the antigen, a composition including an antigen and IgE binding to the antigen, and a method of using the complex or the composition. With the present invention, it is possible to induce naive T cells to develop into Th2 cells. Moreover, the present invention clarified a working mechanism of a Th2-type immune response, particularly a production mechanism of early IL-4. With use of the present invention, it is possible to provide a technique of treating and preventing Th2-type diseases.
Owner:HYOGO COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof
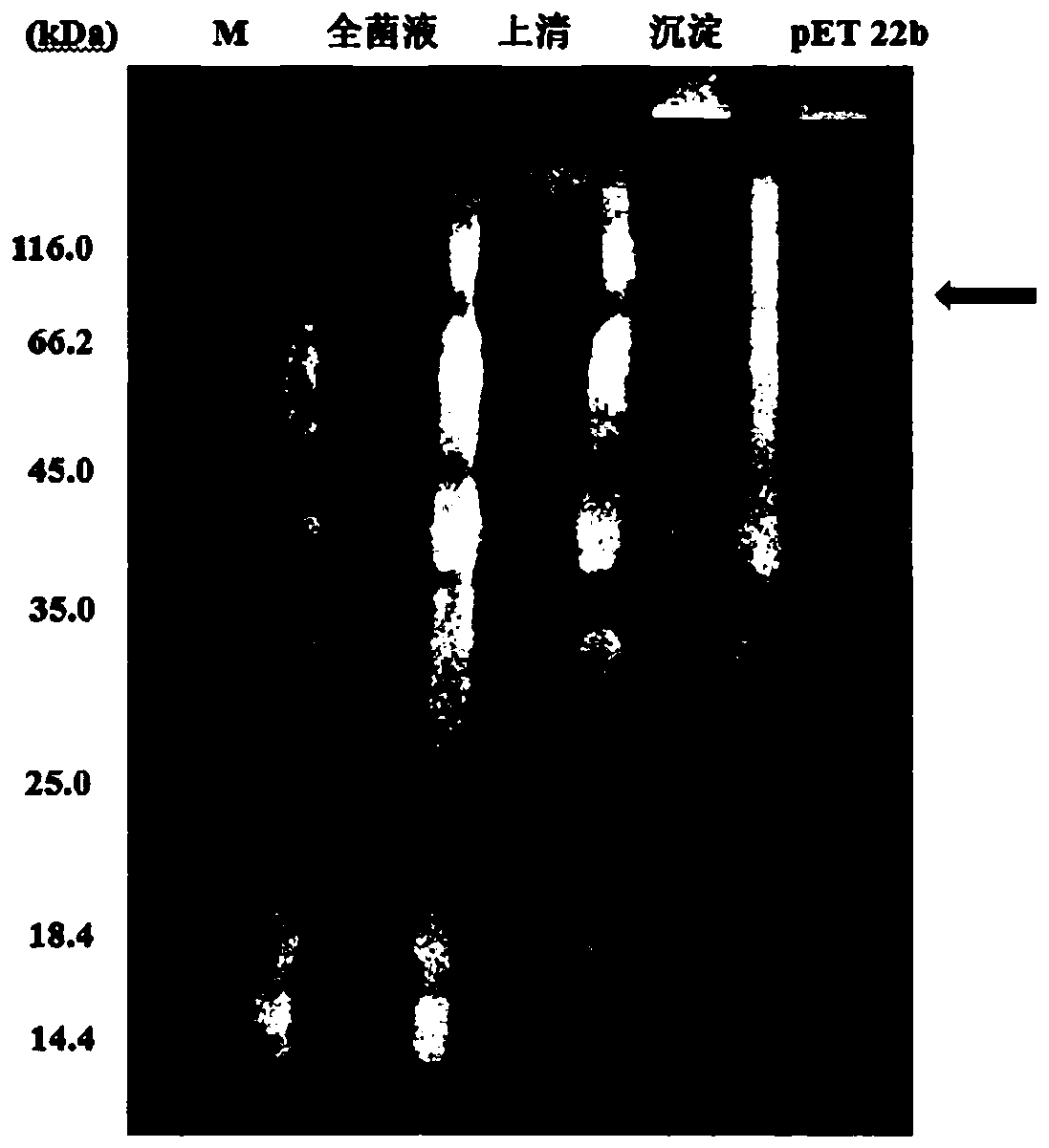
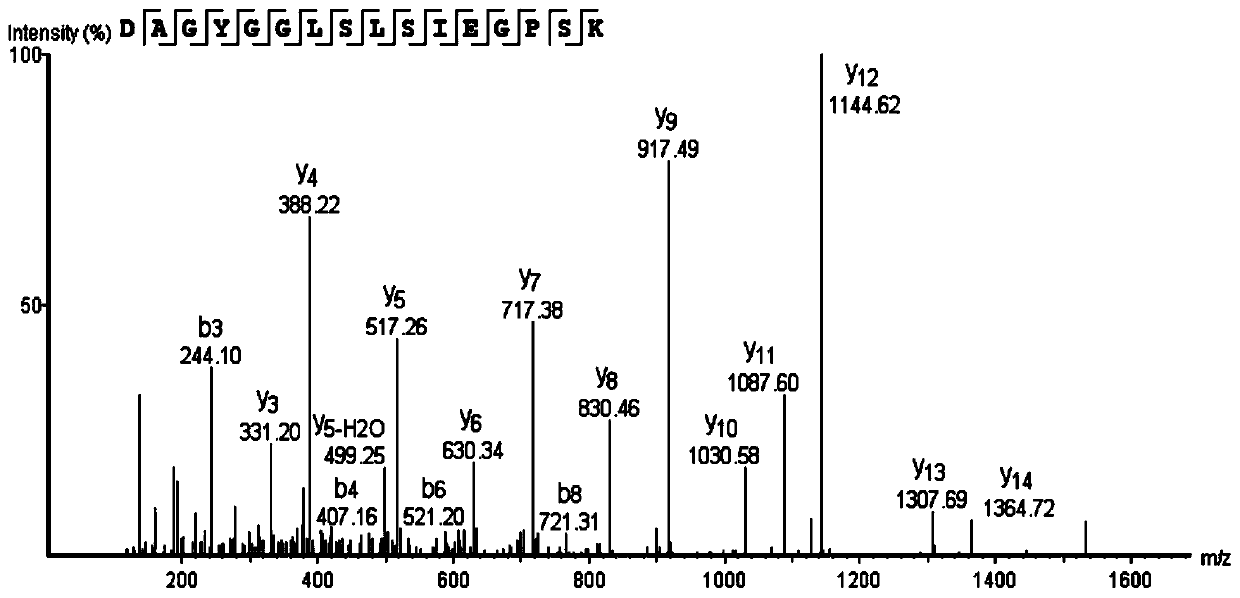
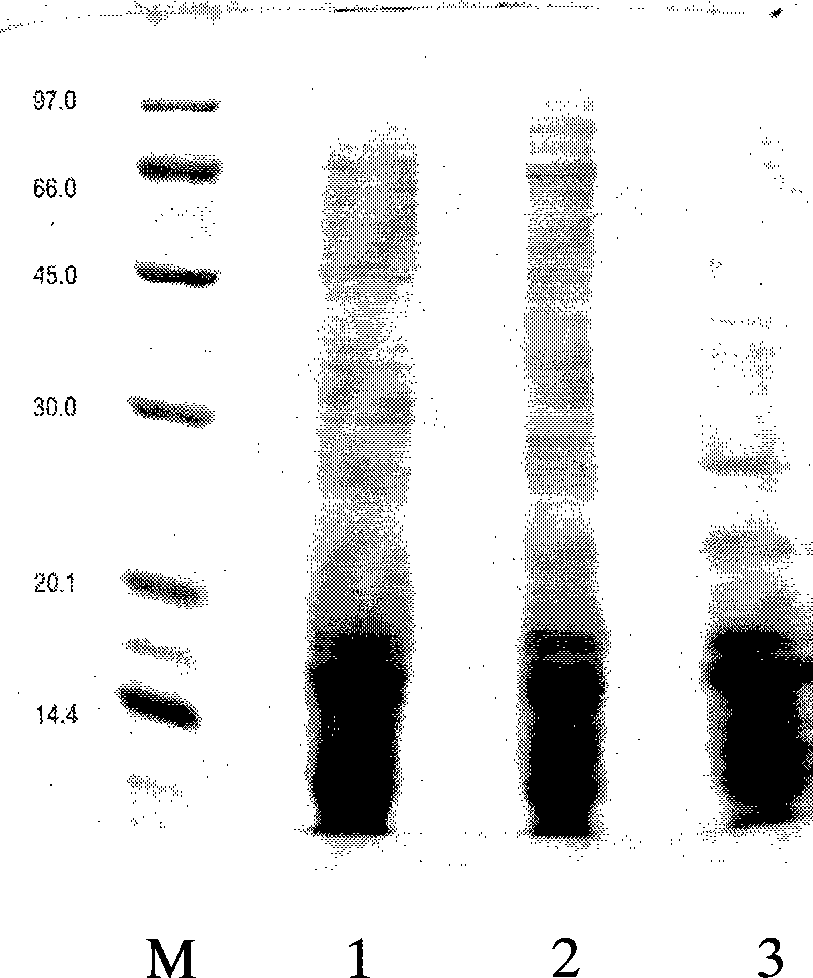
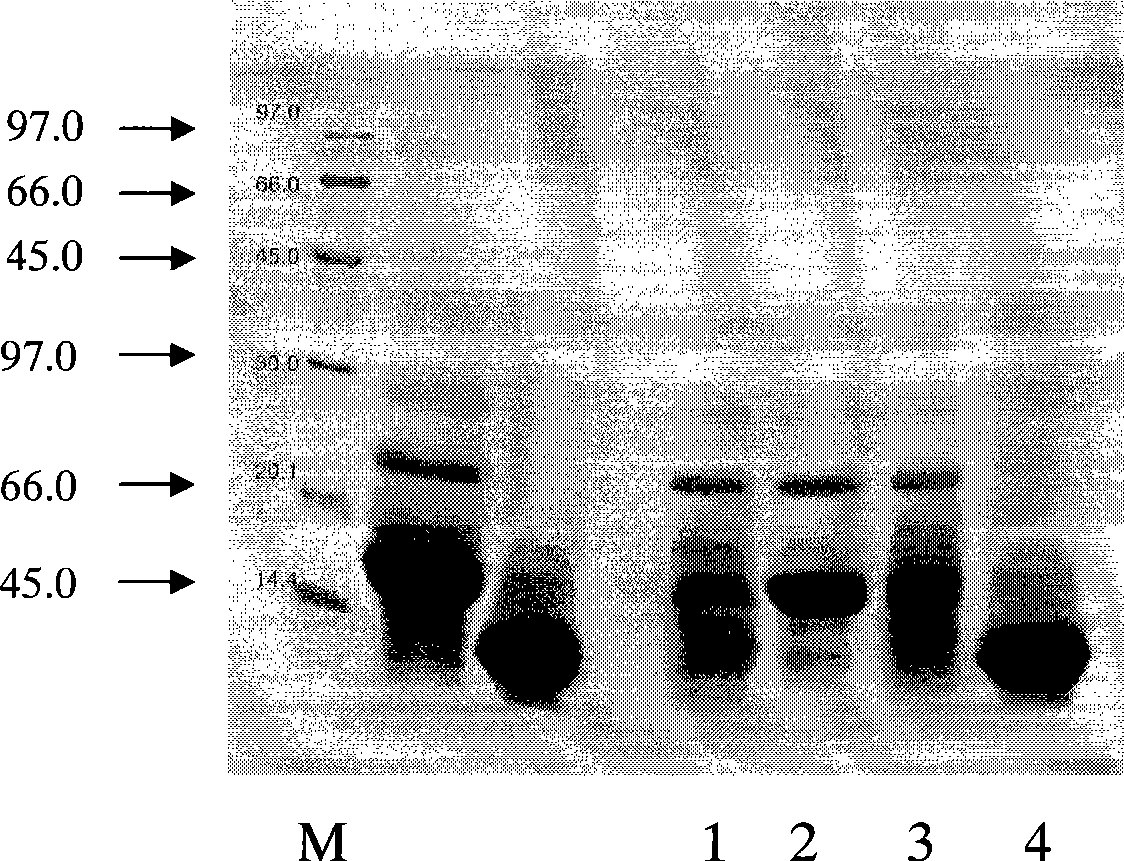
ActiveCN110577598AHigh resolutionHigh sensitivityMicroorganismsBiological material analysisDiseaseAntigen
The invention provides an anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides preparation and application of a hybridoma cell strain for generating an anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody. The anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody aims at a non-IgE binding site of sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha], and the combination of the anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and the non-IgE binding site does not influence the combination of sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] and IgE. The antibody can be combined with a sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] antigen with high specificity, and has high affinity, good specificity and high antibody titer (the combination rate of the antibody diluted by 1: 50 times and sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha]reaches 96.7%). The antibody can simply, conveniently, quickly and specifically carry out accurate analysis and detection on trace sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha], and lays a good foundation for researchingthe effect of the protein on various diseases.
Owner:李莉 +1
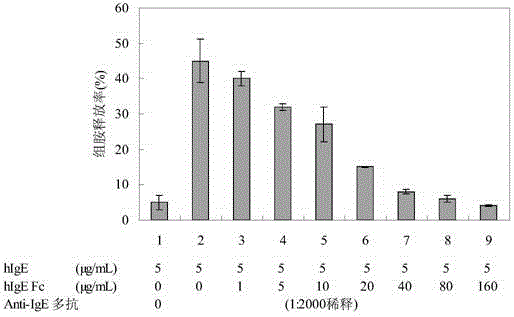
Human immune globulin epsilon heavy chain constant region (hIgE Fc) fragment protein and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104403000AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseBinding site
The invention relates to a human immune globulin epsilon heavy chain constant region (hIgE Fc) fragment protein and a preparation method and an application thereof. The human immune globulin epsilon heavy chain constant region (hIgE Fc) fragment protein is capable of combining an IgE binding site on Fc epsilon RI molecule. The human immune globulin epsilon heavy chain constant region (hIgE Fc) fragment protein can be used for allergy diseases, such as allergy asthma and rhinitis.
Owner:SHANGHAI KEXIN BIOTECH
Recombinant fish roes and preparation method thereof
The invention provides recombinant fish roes and a preparation method thereof. The recombinant fish roes are prepared by the following steps: (1), preparing a reaction product stock solution; (2), preparing mixed paste of fresh fish roes and egg liquid; (3), carrying out deodorization by using ozone of which the concentration is 1.8mg / L; (4), preparing a starch solution; (5), preparing an edible gum solution; (6), adding water, and carrying out uniform mixing; (7), carrying out soaking in a calcium chloride solution for 10 minutes; and (8), carrying out soaking in gallotannic acid for 20 minutes, fishing the soaked fish roes out, and carrying out thorough draining so as to obtain the recombinant fish roes. The recombinant fish roes provided by the invention have the following advantages: (1), the recombinant fish roes are low in allergen IgE binding activity; (2), the recombinant fish roes are uniform in granules, small in fishy smell, rich in nutrition, and unique in flavor; and (3), the preparation method of the recombinant fish roes is simple in processes, and relatively low in cost.
Owner:FUQING BRANCH OF FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



























![Anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof Anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/4461c338-d194-40e3-8692-ff17536c8178/HDA0001692109080000011.png)
![Anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof Anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/4461c338-d194-40e3-8692-ff17536c8178/HDA0001692109080000012.png)
![Anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof Anti-sFc [epsilon] RI [alpha] monoclonal antibody and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/4461c338-d194-40e3-8692-ff17536c8178/HDA0001692109080000013.png)