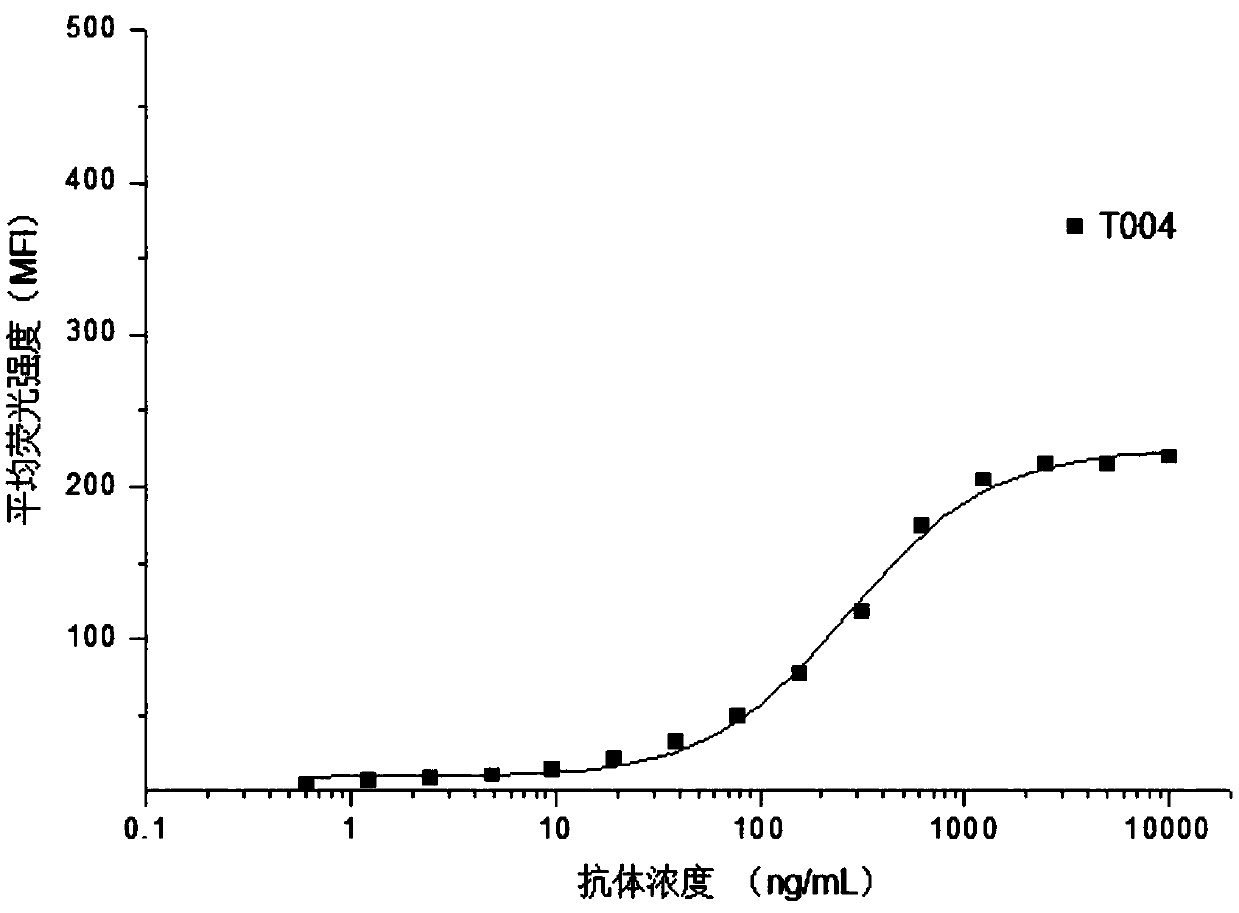
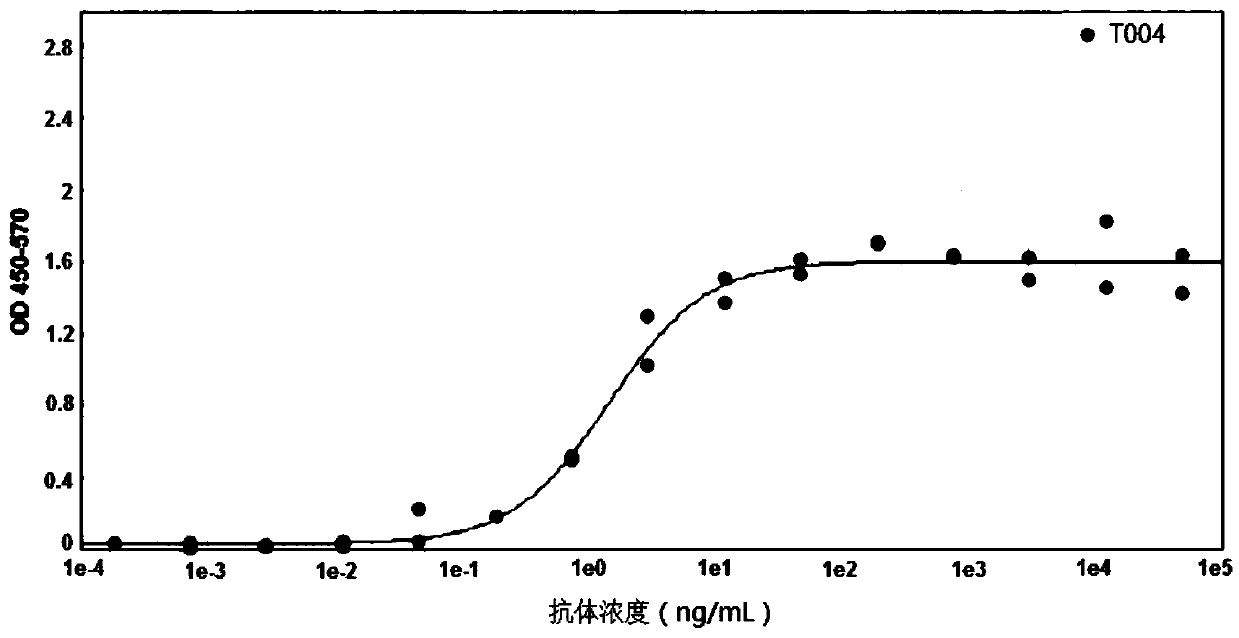
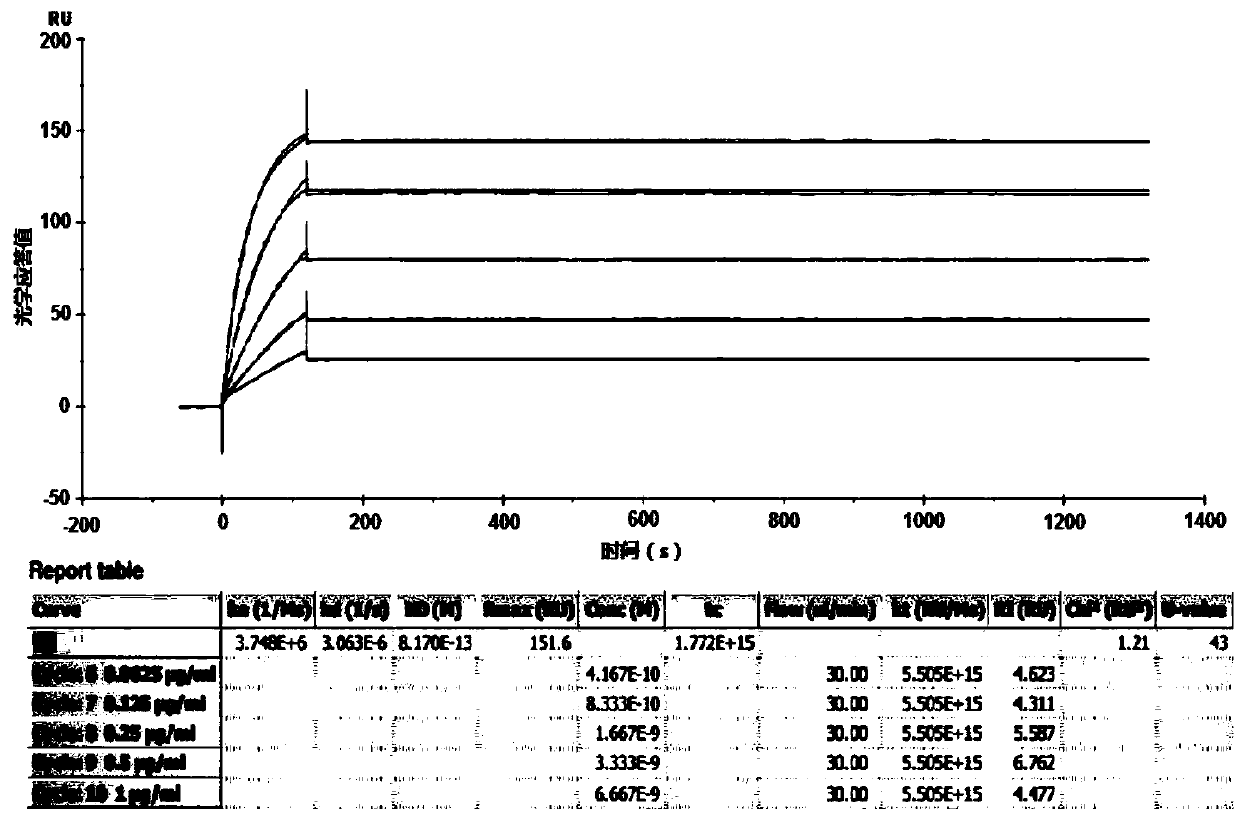
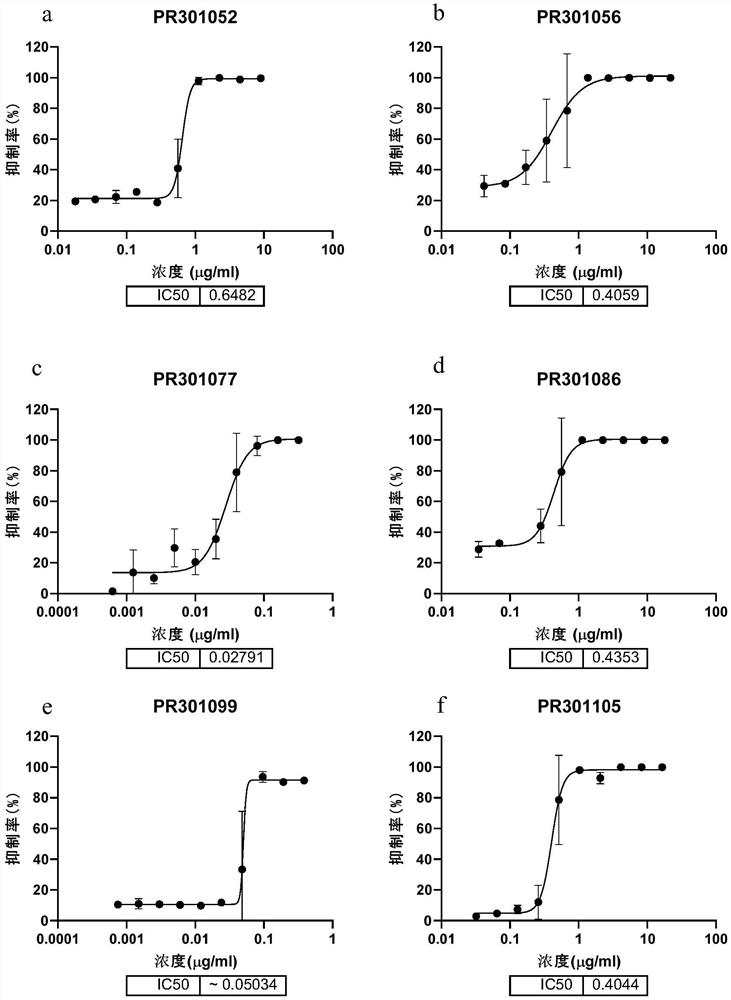
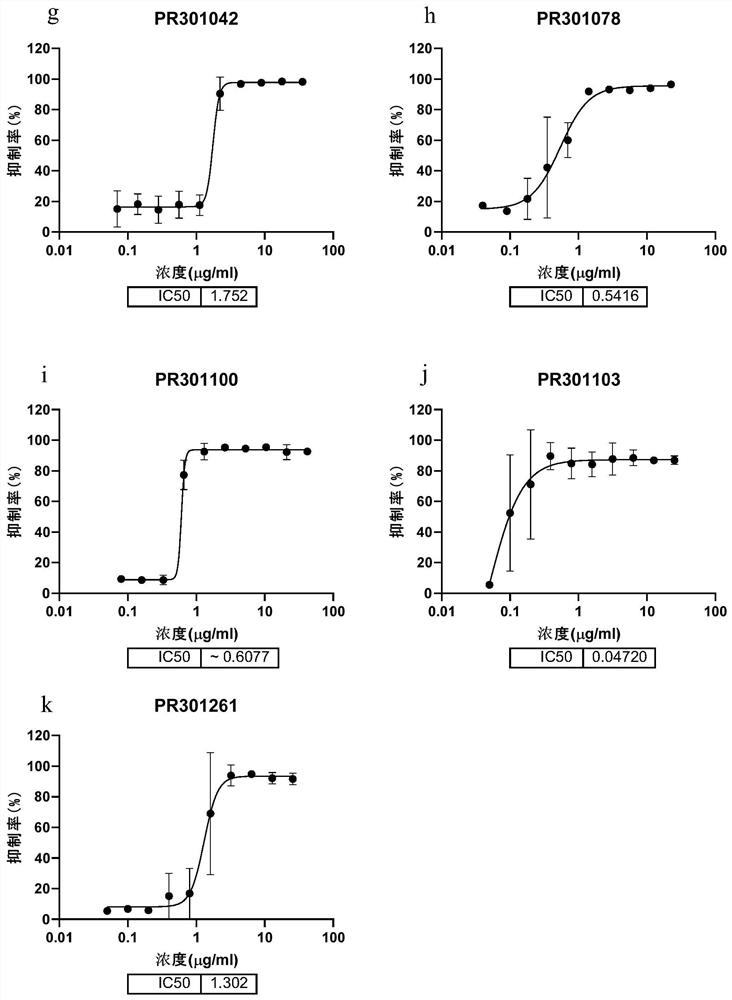
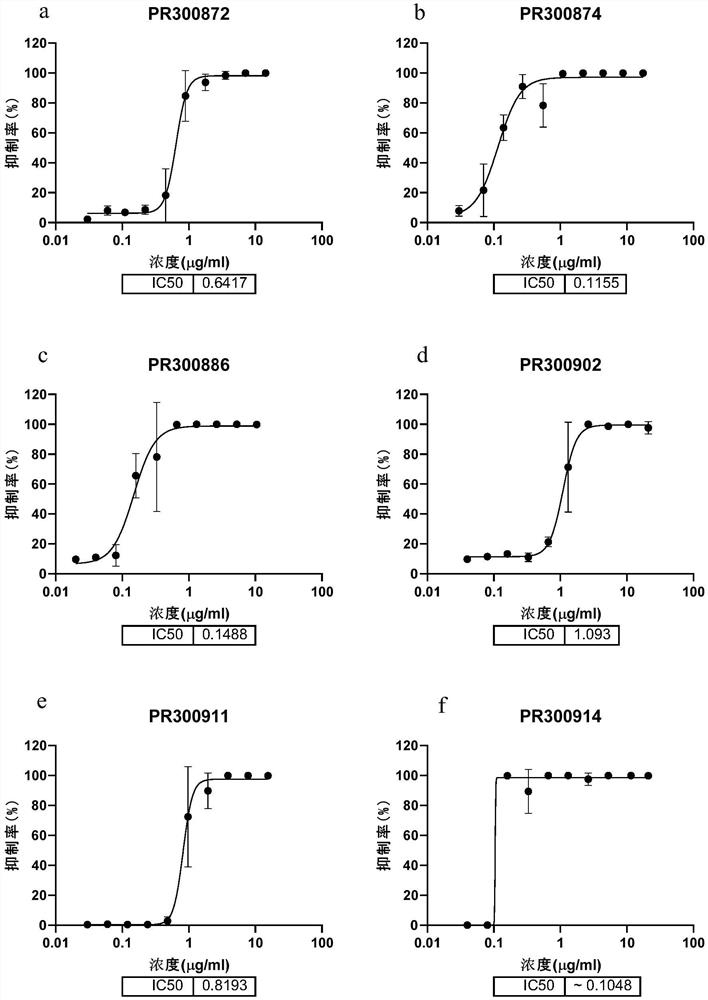
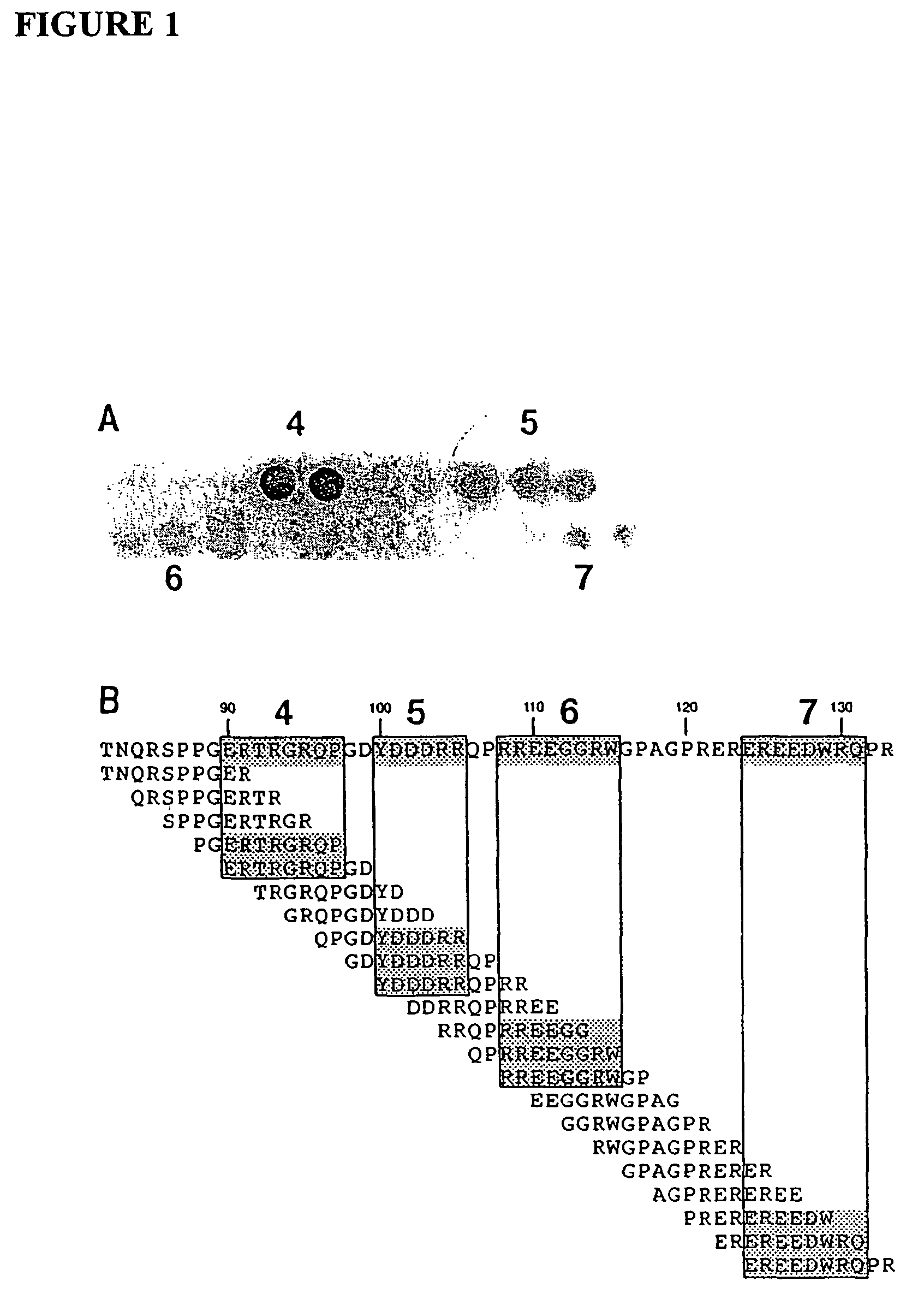
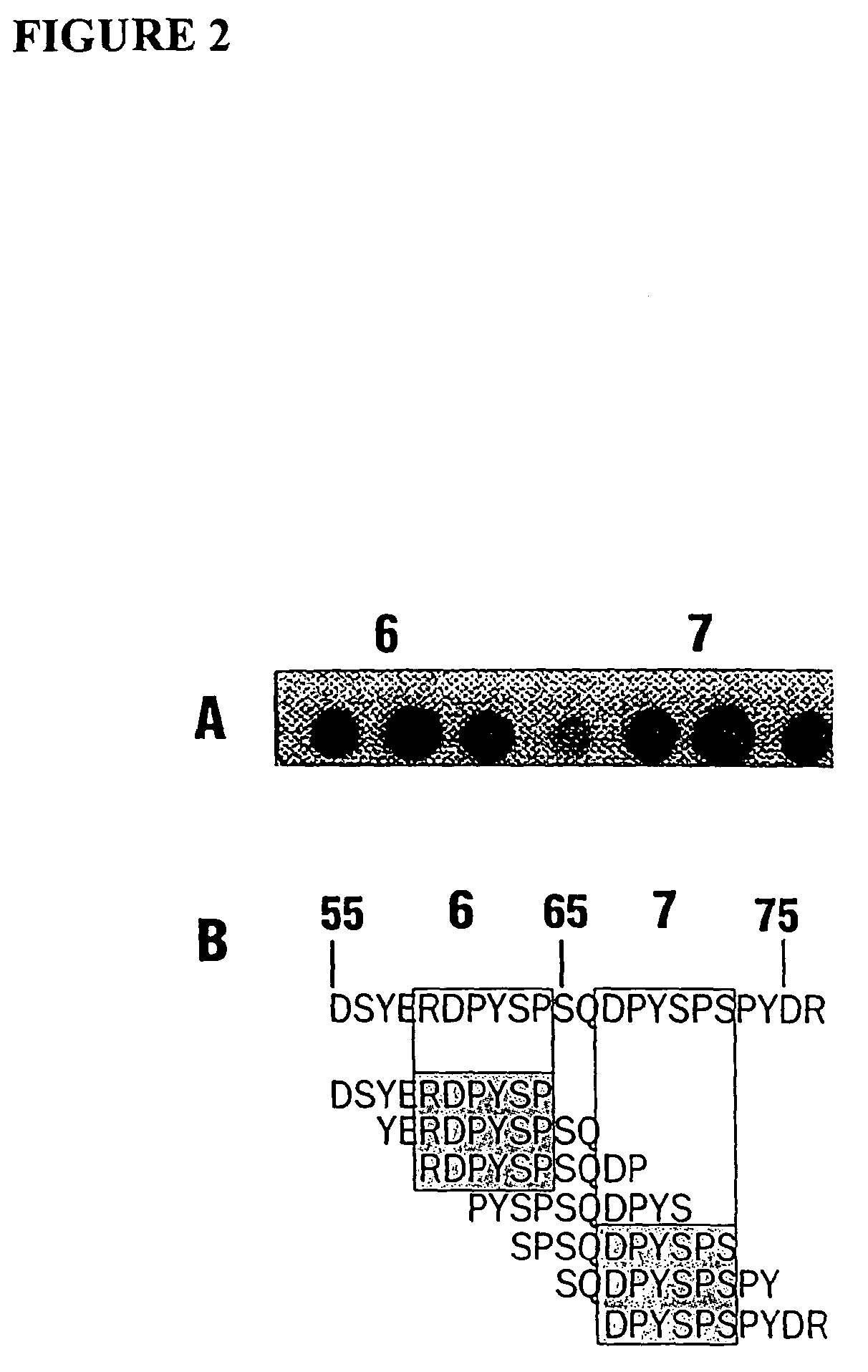
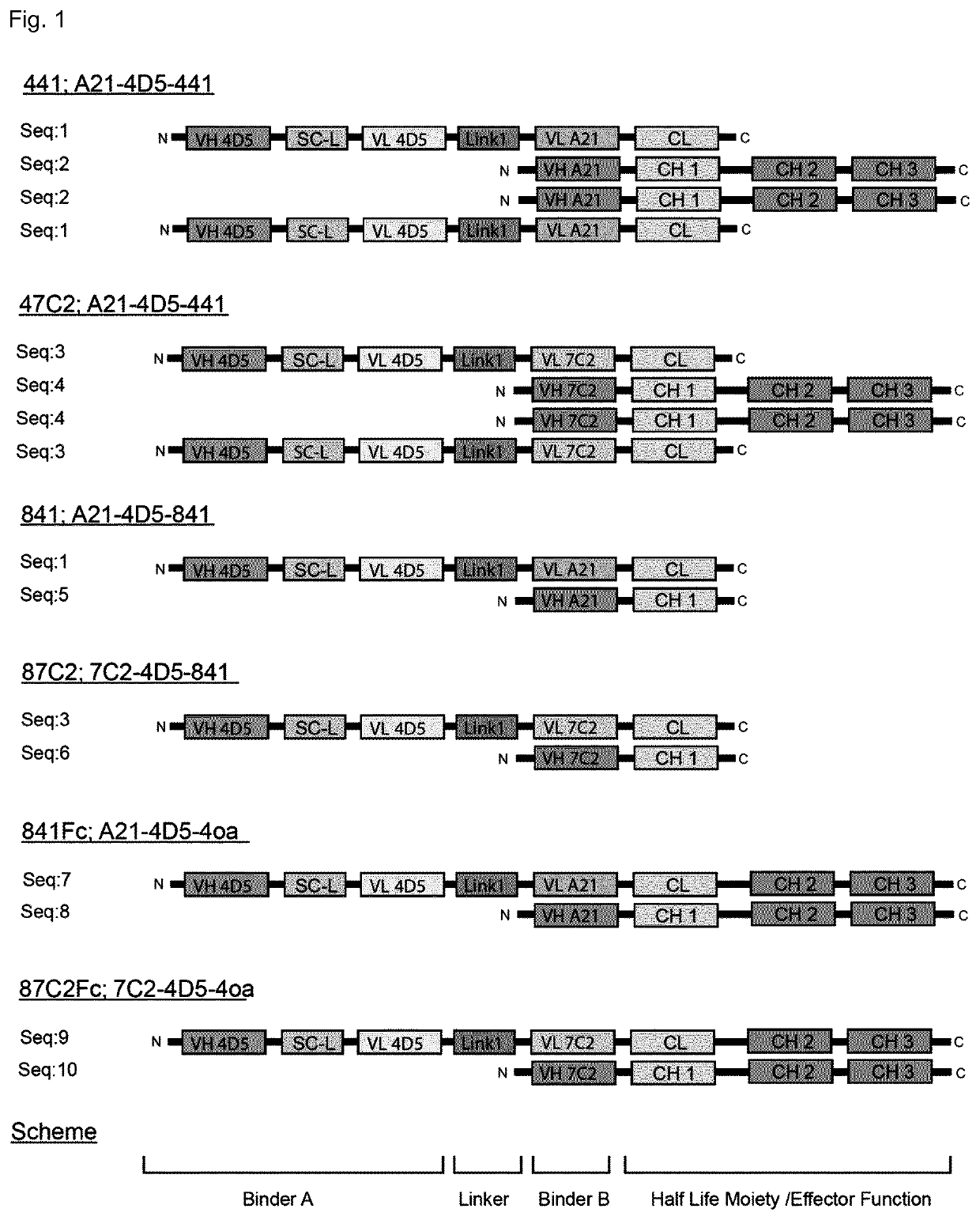
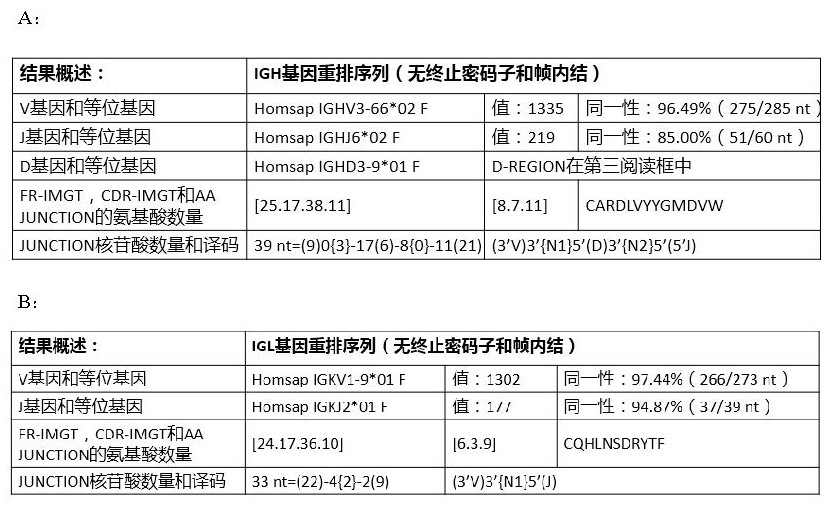
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Ige binding epitopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
EphA2 monoclonal antibodies and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20040028685A1Decrease contactStable interactionOrganic active ingredientsFungiTubular networkLymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management, or prevention of cancer, particularly, metastatic cancer. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of an antibody that binds to EphA2 and agonizes EphA2, thereby increasing EphA2 phosphorylation and decreasing EphA2 levels. In other embodiments, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of an antibody that binds to EphA2 and inhibits cancer cell colony formation in soft agar, inhibits tubular network formation in three-dimensional basement membrane or extracellular matrix preparation, preferentially binds to an EphA2 epitope that is exposed on cancer cells but not non-cancer cells, and / or has a low Koff, thereby, inhibiting tumor cell growth and / or metastasis. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more EphA2 antibodies of the invention either alone or in combination with one or more other agents useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Polypeptide useful in adoptive cell therapy
ActiveUS20150093401A1Easy to packAvoids biological effectAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsEpitopeAdoptive cellular therapy
The present invention provides a polypeptide having the formula: St-R1-S1-Q-S2-R2 wherein St is a stalk sequence which, when the polypeptide is expressed at the surface of a target cell, causes the R and Q epitopes to be projected from the cell surface; R1 and R2 are a Rituximab-binding epitopes each having the an amino acid sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID No. 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 and 16 or a variant thereof which retains Rituximab-binding activity; S1 and S2 are optional spacer sequences, which may be the same or different; and Q is a QBEnd1O-binding epitope having the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 2 or a variant thereof which QBEnd1O-binding activity. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence encoding such a polypeptide and uses thereof in adoptive cell transfer.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Therapeutic and Diagnostic Anti-Hsp 70 Antibodies
ActiveUS20070231337A1Modulate immune responseUseful in treatmentAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticDiseaseInfected cell
Methods and compositions for the detection, prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases, including, but not limited to human sarcomas and carcinomas are described. In particular, specific antibodies are provided, which are capable of binding an epitope of Hsp70 that is extracellularly localized on diseased tissue and cells, in particular on tumor cells and infected cells.
Owner:MULTIMMUNE
High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibodies for Botulinum Toxin Type A
Nucleic acids encoding ara h 3 polypeptides
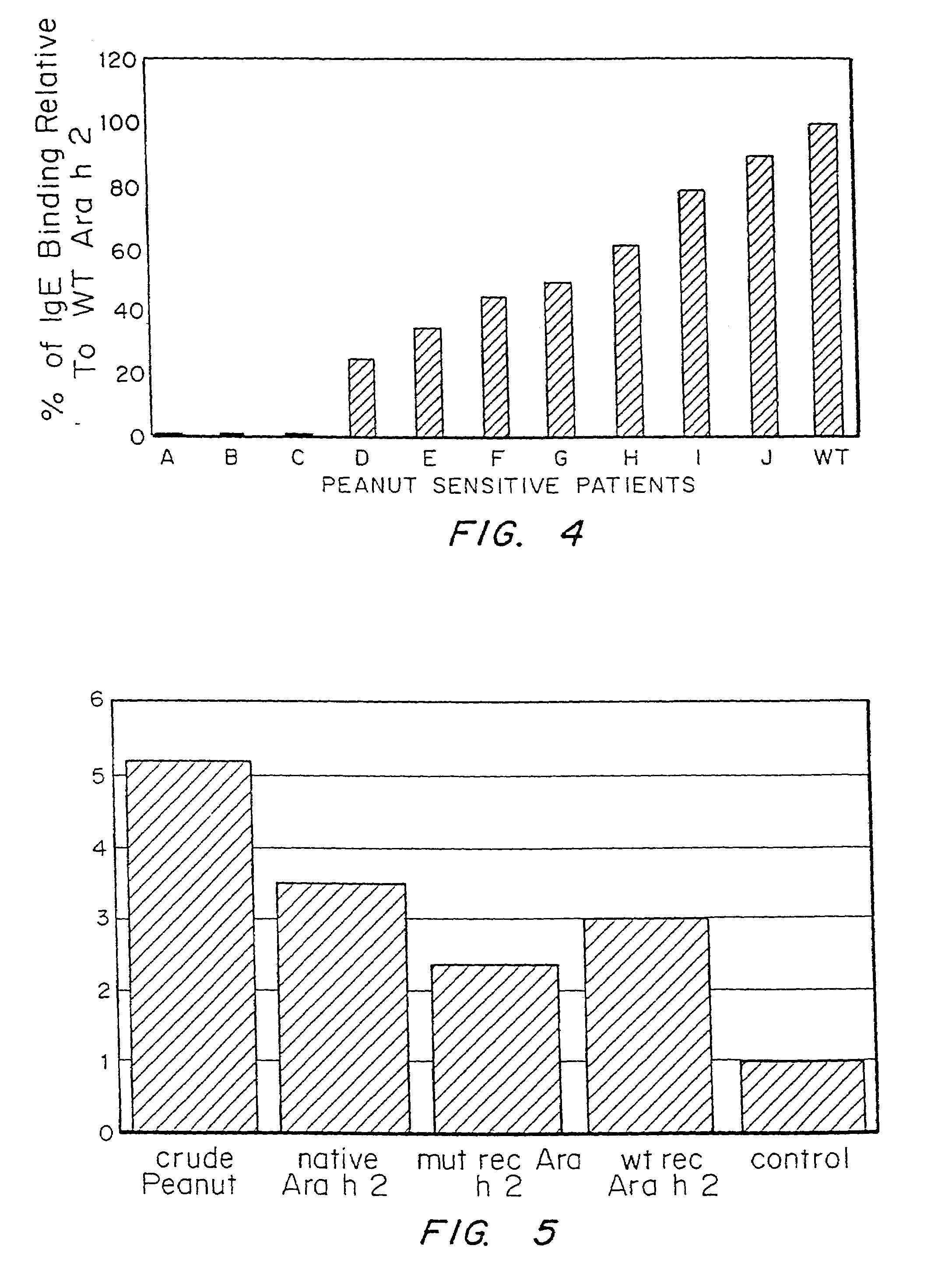
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity. The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody
ActiveCN112794899AAvoid infectionHigh neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsDiagnosis treatmentMutant strain
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, and discloses a fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of the fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody. B-type lymphocytes are screened from blood of a new coronal pneumonia rehabilitation patient, and the affinity constant of the obtained antibody and a virus receptor binding domain (RBD) is 1.19 nM. X-ray crystal diffraction is used for analyzing the three-dimensional structure of the antibody and RBD compound, it is found that the binding epitope of the antibody and the binding epitope of a host cell receptor (ACE2) are highly overlapped, binding of the RBD and the ACE2 can be competitively blocked, and infection of the RBD and the ACE2 is inhibited. The antibody can cope with certain genetic mutations of viruses, the half effective concentration of the antibody for blocking pseudoviruses (accumulated B.1. 1.7 mutant strain genes and D614G) from infecting host cells is 0.57 ng / mL, and the antibody has the advantages of safety, high efficiency and broad spectrum, and is expected to be used as a neutralizing antibody drug for diagnosing, treating and preventing new coronal pneumonia.
Owner:SUZHOU YUZHIBO BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS20070213507A1Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsFungi peptidesBinding siteT cell
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
EpA2 monoclonal antibodies and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070166314A1Lower Level RequirementsIncreased phosphorylationOrganic active ingredientsFungiNon cancerCancer prevention
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management, or prevention of cancer, particularly, metastatic cancer. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of an antibody that binds to EphA2 and agonizes EphA2, thereby increasing EphA2 phosphorylation and decreasing EphA2 levels. In other embodiments, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of an antibody that binds to EphA2 and inhibits cancer cell colony formation in soft agar, inhibits tubular network formation in three-dimensional basement membrane or extracellular matrix preparation, preferentially binds to an EphA2 epitope that is exposed on cancer cells but not non-cancer cells, and / or has a low Koff, thereby, inhibiting tumor cell growth and / or metastasis. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more EphA2 antibodies of the invention either alone or in combination with one or more other agents useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Colon and pancreas cancer peptidomimetics
ActiveUS20130247232A1Slow tumor growthExcellent tumor regressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopePancreas Cancers
The invention relates to a peptidomimetic of an NPC-1 epitope on the MUC5AC protein which is differentially expressed in pancreatic and colorectal cancer, and diagnostic and therapeutic usages. Further, antibodies that selectively bind the NPC-1 epitope peptidomimetics and may be used in diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
Owner:PRECISION BIOLOGICS INC
Epha2 monoclonal antibodies and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20100278838A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce proliferationOrganic active ingredientsFungiCancer preventionAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management, or prevention of cancer, particularly, metastatic cancer. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of an antibody that binds to EphA2 and agonizes EphA2, thereby increasing EphA2 phosphorylation and decreasing EphA2 levels. In other embodiments, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of an antibody that binds to EphA2 and inhibits cancer cell colony formation in soft agar, inhibits tubular network formation in three-dimensional basement membrane or extracellular matrix preparation, preferentially binds to an EphA2 epitope that is exposed on cancer cells but not non-cancer cells, and / or has a low Koff, thereby, inhibiting tumor cell growth and / or metastasis. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more EphA2 antibodies of the invention either alone or in combination with one or more other agents useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Recombinant anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody
PendingCN110878122AHigh affinityGood antitumor effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsComplementarity determining regionAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a recombinant anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody, relates to the technical field of biological medicines, and is used for providing an effective treatment medicine for patients with advanced or metastatic cancers, in particular to the patients with ineffective or drug-resistant treatment by an existing anti-PD-L1 medicine. The complementarity determining region of the antibodyhas sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 to SEQ ID NO: 6. Compared with an existing anti-PD-L1 drug, the antibody has a unique binding epitope, and is better in affinity to human PD-L1 and better in tumorinhibition effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHANGJIANG BIOTECH
Anti-coronavirus antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN113480644AImprove blockageImprove bindingImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHeavy chainAntigen Binding Fragment
The invention discloses an anti-coronavirus antibody and application thereof. The coronavirus is a novel coronavirus, and particularly relates to an antibody specifically combined with a novel coronavirus S-RBD protein and an antigen binding fragment of the antibody. The antibody or the antigen binding fragment thereof comprises a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region, the heavy chain variable region comprises HCDR1, HCDR2 and HCDR3, and the light chain variable region comprises LCDR1, LCDR2 and LCDR3. Sequences of all the CDRs and variable regions are shown in the invention. The antibody or the antigen binding fragment thereof provided by the invention has relatively high binding capacity with a new coronavirus, and also has relatively excellent neutralizing activity ( IC50 values of the neutralizing activity are all lower than a [mu]g / mL level), a relatively good mutant virus coverage spectrum and various binding epitopes.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS7879977B2Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from yeastsBinding siteADAMTS Proteins
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
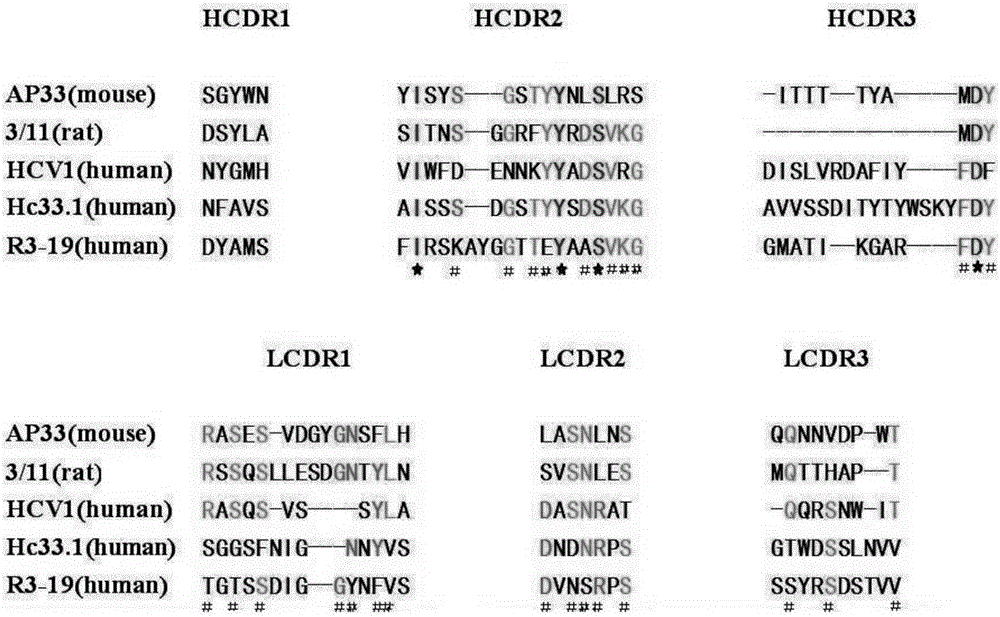
Multi sub-gene resistant type HCV (Hepatitis C Virus) antibody gene R3-19 and application thereof
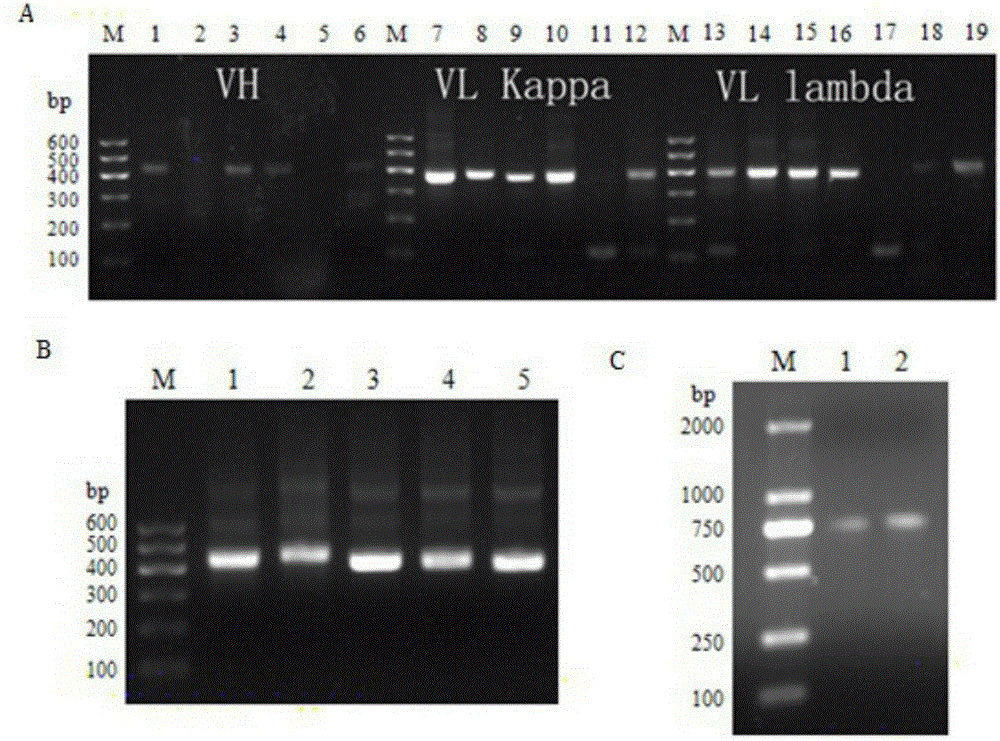
InactiveCN105219780AExtensive featuresBroad neutralization capacityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsLinear epitopeScFv Antibodies
The invention discloses a multi sub-gene resistant type HCV (Hepatitis C Virus) antibody gene R3-19, wherein the heavy chain amino acid sequence thereof is shown by SEQ ID NO.38, and the light chain amino acid sequence is shown by SEQ ID NO.39, the antibody gene is obtained by vanning in an independently-constructed anti-HCV scFv antibody library through E2 region aa412-423 linear epitope (an HCV CD81 receptor binding epitope) synthetic peptide which is highly conservative in various subtype HCVs; the antibody library is formed by 39 parts of anti-HCV antibody positive peripheral blood samples of Chinese patients, the HCVs infected by the patients cover the main HCV popular subtypes in China, therefore, the R3-19 is an anti-HCV antibody which is typical in China and has wide binding characteristic, and has excellent application value in the fields of HCV diagnosis, HCV treatment, vaccine research and development and the like in China.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Chicken infectious bursal disease virus ibdv VP2 protein ligand-binding epitope polypeptide and application thereof
InactiveCN102268077AAvoid infectionReduce infection ratePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementInfectious bursal disease virus IBDVCell
The present invention relates to the linear ligand epitope of Bursal bursal virus and its specific application. The polypeptide P22 on the IBDVVP2 protein is synthesized, and the CEF is used as the target cell. Through the infection and harvest of IBDV, the virulence and half tissue culture of IBDV are measured. Infection dose and infection ratio, the combination test of synthetic polypeptides and target cells, the virus blocking test and the test of polypeptide blocking IBDV infection target cells, the screened specific binding target cells can inhibit virus infection ligand epitope polypeptides, and The ligand epitope of IBDV was precisely mapped. The polypeptide P22 of the present invention can inhibit IBDV from infecting CEF, and with the increase of polypeptide concentration, the infection rate of CEF decreases in a dose-dependent manner. When the polypeptide concentration is 0.2 mmol / L, it can completely inhibit IBDV from infecting CEF target cells. The invention provides a theoretical basis for further research on the virus ligand epitope from the aspect of the interaction between the virus ligand and the virus receptor.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Marker-suicide gene useful in adoptive cell therapy
ActiveUS10925943B2Valid choiceEasy to packAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingAdoptive cell transfer
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Monoclonal antibody for identifying EB virus gH glycoprotein, and application of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN113372440AHigh binding activityHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsViral glycoproteinAntigen Binding Fragment
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibodies, and discloses a monoclonal antibody for recognizing EB (Epstein-Barr) virus gH glycoprotein, and application of the monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody or the antigen binding fragment thereof is subjected to specific binding with the 573th, 625th, 627th and 655th amino acids of the gH protein, wherein the amino acid sequence of the gH protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 11. The binding activity of the monoclonal antibody or the antigen binding fragment thereof is superior to the binding activity of other monoclonal antibodies (AMMO1, M3 and 1D8); affinity to the gLgH protein is high; strong neutralizing activity is realized in all epithelial cell infection models; an obvious inhibition effect for cell membrane fusion is achieved; and a way that the monoclonal antibody or the antigen binding fragment thereof is subjected to the specific binding with the 573th, 625th, 627th and 655th amino acids of the gH protein is different from other reported gLgH neutralizing antibody recognition and binding epitopes.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT +1
Immunological entity clustering software
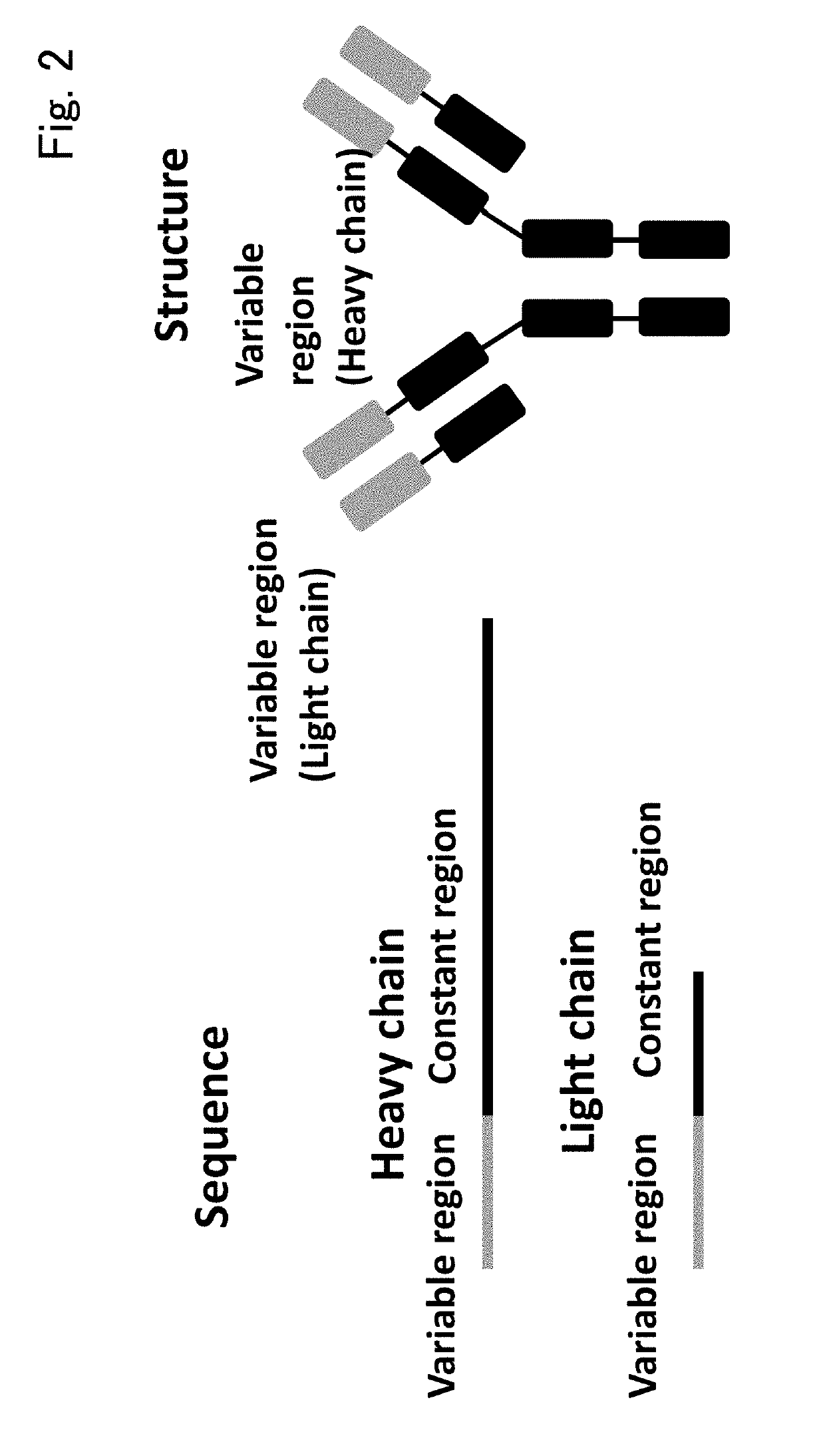
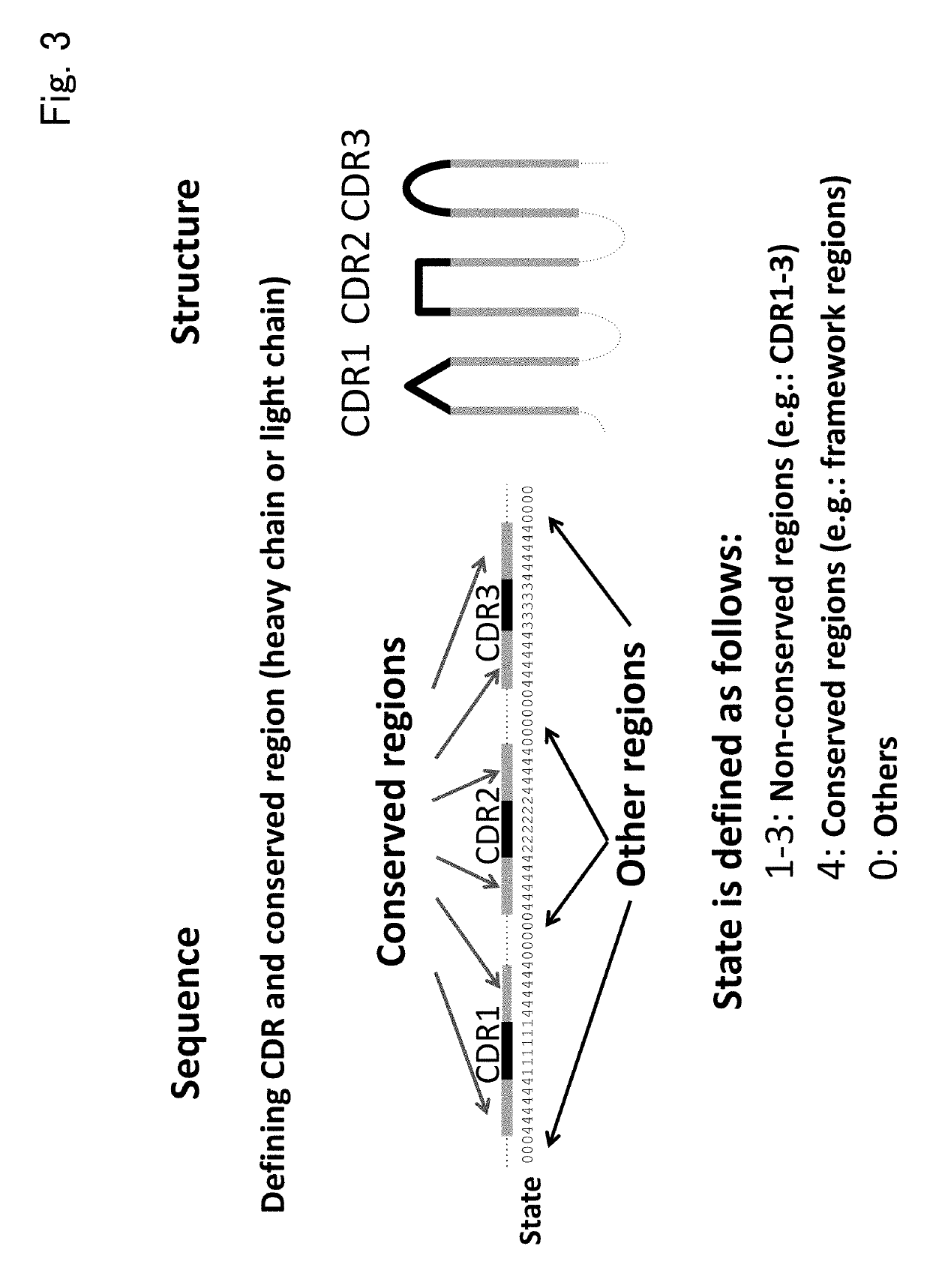
The present invention provides a novel method for classifying antibodies. Specifically, the present invention provides, for a first immunological entity and a second immunological entity, a method for classifying whether a binding epitope is the same or different, and a method for performing clustering based on the classification, the methods including: identifying an array of immunological entities such as antibodies as several portions (for example, a framework region and three CDRs); in order to define a storage region, using the array as a three-dimensional structure model; introducing an index of similarity such as structure and / or array characteristic amounts into an evaluation function for evaluating the similarity or dissimilarity of two immunological entities; and analogizing the similarity of an epitope on the basis of the similarity of an antibody.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
IgG epitope peptide of whey allergen beta-lactoglobulin
PendingCN114874310AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisCow milkingMilk Serum
Owner:AUSNUTRIA DAIRY CHINA
Fully human monoclonal antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of fully human monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN112794898AHigh affinityHigh neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsMutationIge binding epitopes
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, and discloses a fully human monoclonal antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of the fully human monoclonal antibody. An SARS-CoV2 receptor binding domain (RBD) is used as a probe, flow cytometry is used for screening B lymphocytes of a new coronary pneumonia rehabilitation patient, and the affinity constant of the prepared monoclonal antibody and the RBD is 4.03 nM. X-ray crystal diffraction is used for analyzing the three-dimensional structure of the antibody and RBD compound to find that binding epitopes of the antibody and a host cell receptor (ACE2) are overlapped, binding of the RBD and the ACE2 can be competitively blocked, the virus is prevented from infecting host cells, some genetic mutations of the new coronavirus can be coped with. The median effective concentration (IC50) for blocking pseudoviruses (accumulated B.1. 1.7 mutant strain genes and D614G) from infecting host cells is 0.12 ng / mL, and the application prospect of diagnosing, treating and preventing the new coronal pneumonia is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU YUZHIBO BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Her2-binding tetrameric polypeptides
PendingUS20210395396A1Superior HER inactivationCut surfaceHybrid immunoglobulinsFusion with DNA-binding domainDiseaseMalignant Neoplastic Disease
The invention relates to a tetrameric polypeptide comprising a first polypeptide chain comprising a first VL antigen binding domain and a first CL constant domain, a second polypeptide chain comprising a first VH antigen binding domain, a first CH1 constant domain, a first CH2 constant domain and a first CH3 constant domain, a first ligand binding to a HER2 D4 epitope linked to the N-terminus of said first VL antigen binding domain or said first VH antigen binding domain by a first interdomain amino acid linker, a third polypeptide chain comprising a second VL antigen binding domain and a second CL constant domain, a fourth polypeptide chain comprising a second VH antigen binding domain, a second CH1 constant domain, a second CH2 constant domain and a second CH3 constant domain and a third ligand binding to a HER2 D4 epitope linked to the N-terminus of said second VL antigen binding domain or said second VH antigen binding domain by a second interdomain amino acid linker, wherein the VL antigen binding domains and the VH antigen binding domains together constitute a second ligand and a fourth ligand binding to a HER2 D1 epitope. The invention further relates to the tetrameric polypeptide for use in a method for the prevention or treatment of a malignant neoplastic disease, an isolated nucleic acid and a host cell for expression of the polypeptide and a method for obtaining the polypeptide.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
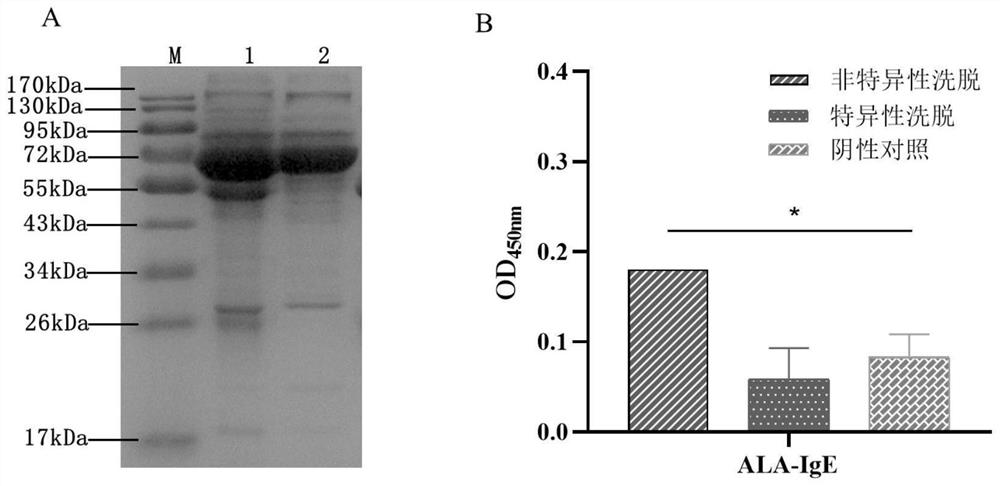
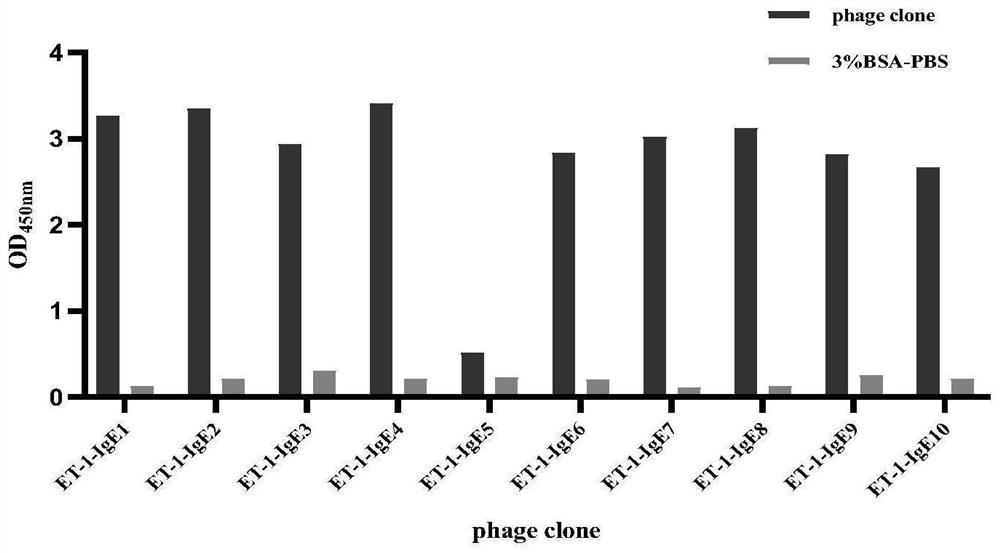
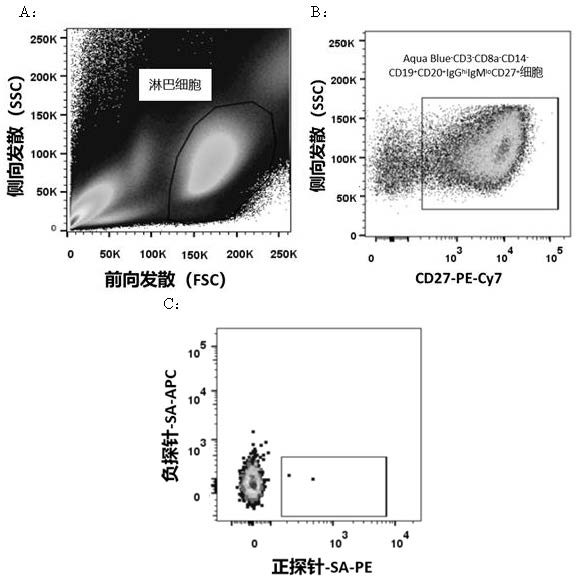
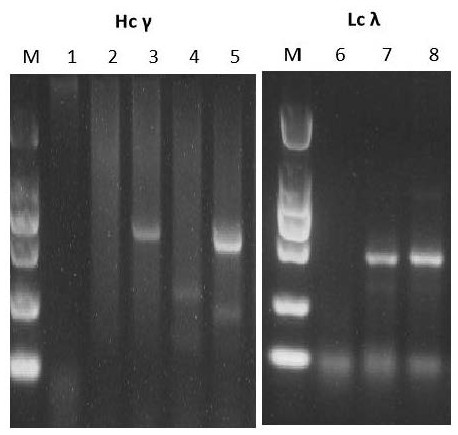
IgE binding epitope of main allergen alpha-lactalbumin of cow milk whey
The invention relates to an IgE (Immunoglobulin E) binding epitope of a whey allergen alpha-lactalbumin. The amino acid sequence of the IgE binding epitope is 11Glu-Leu-Lys-Asp-Leu-Lys-Gly-Tyr-Gly-Gly-Val-Ser-Leu-Pro-Glu-Trp-Val 27. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the IgE binding epitope. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, 16 parts of serum are screened by adopting an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and finally 12 parts of serum of a child patient with cow milk allergy are obtained. High-purity cow milk specific IgE purified by a Hitrap Protein G HP affinity chromatography column is used as a target molecule, and affinity panning is carried out on a phage dodecapeptide library. And predicting the linear epitope by using bioinformatics software, and finally obtaining the IgE epitope information of the whey allergen alpha-lactalbumin. The invention has great significance for ascertaining the immunological mechanism of cow milk allergy, researching the effect of the epitope in food anaphylaxis and guiding the development of hypoallergenic dairy products for directionally breaking the epitope.
Owner:谭宏凯
Fully human monoclonal antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of fully human monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN114656556AHigh affinityHigh neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsMemory B-LymphocyteFlow cytometry
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, and discloses a fully human monoclonal antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of the fully human monoclonal antibody. A receptor binding domain (RBD) of virus S protein is used as a probe, flow cytometry is used for screening memory B lymphocytes of a novel coronavirus pneumonia rehabilitation patient, and the affinity constant of the prepared monoclonal antibody and the RBD is 4.48 nM. X-ray crystal diffraction is used for analyzing the three-dimensional structure of an antibody and RBD compound, it is found that binding epitopes of the antibody and a host cell receptor (ACE2) are partially overlapped, binding of the RBD and the ACE2 can be competitively blocked, the virus is prevented from infecting host cells, some genetic mutations of the novel coronavirus can be effectively coped with, and the novel coronavirus can be effectively prevented from being infected. The lowest half effective inhibition concentration of the compound for blocking the infection of the novel coronavirus on host cells can reach 20.93 ng / mL, and the compound has the advantages of safety, high efficiency and broad spectrum, and is expected to be used for diagnosing, treating and preventing novel coronavirus pneumonia.
Owner:SUZHOU YUZHIBO BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
High-affinity monoclonal antibodies for botulinum toxin type B
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
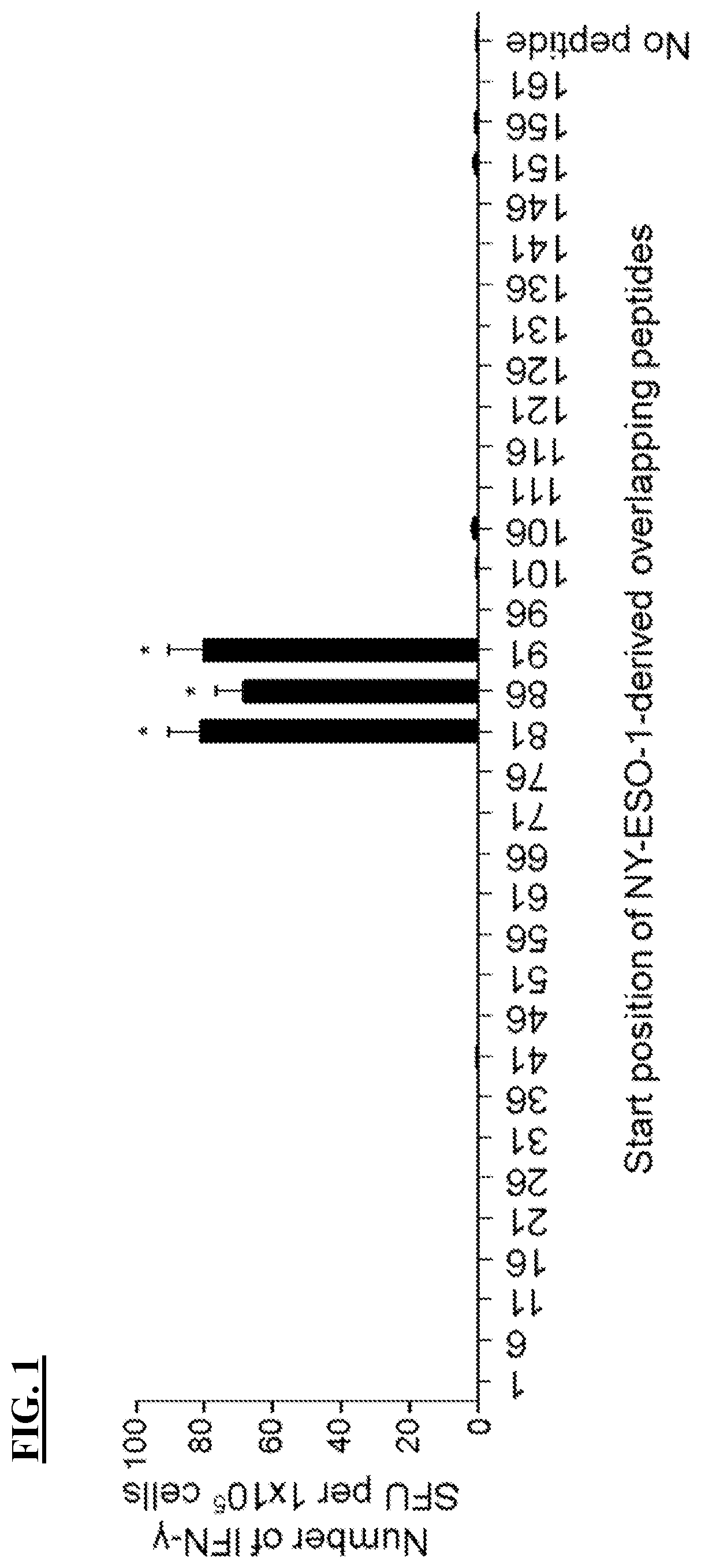
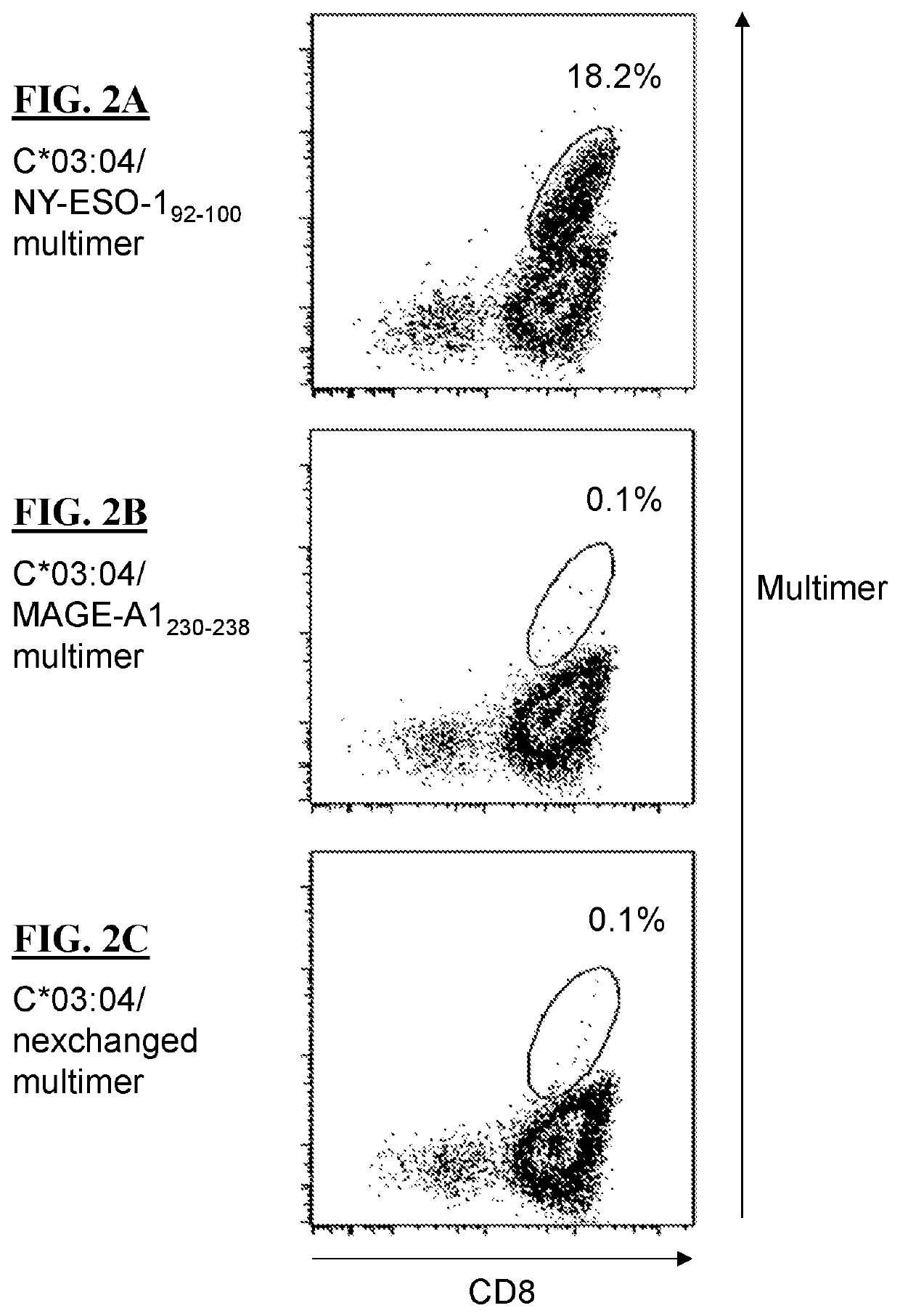
T cell receptors and methods of use thereof
The present disclosure is directed recombinant T cell receptors capable of binding an NY-ESO-1 epitope and nucleic acid molecules encoding the same. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecules further comprise a second nucleotide sequence, wherein the second nucleotide sequence or the polypeptide encoded by the second nucleotide sequence inhibits the expression of an endogenous TCR. Other aspects of the disclosure are directed to vectors comprising the nucleic acid molecule and cells comprising the recombinant TCR, the nucleic acid molecule, or the vector. Still other aspects of the disclosure are directed to methods of using the same. In some embodiments, the methods comprise treating a cancer in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Monoclonal antibody 8F9 specifically bound to GP1 subunit of EBOV and application thereof
ActiveCN111138531AEffective neutralizationUnique CDR regionViral antigen ingredientsGenetically modified cellsCombination therapyAmino acid
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody 8F9 capable of resisting Ebola virus glycoprotein GP1 subunit. The antibody has a unique CDR region and has good binding activity with EBOV GP, and the EC50 value is 0.015 [mu]g / mL. 8F9 effectively neutralizes EBOV pseudotype viruses in vitro compared to a control antibody. The neutralizing activity of 8F9 is enhanced along with the increase of the concentration of antibody, and 90% protection can be realized on EBOV pseudotype viruses infected cells at the concentration of 1 [mu]g / mL. 8F9 also has good in-vitro neutralization activity on EBOV andcan be used as a candidate treatment drug for Ebola virus diseases, and the binding epitope of 8F9 is located at 227th-295th amino acids of a GP antigen; and 8F9 is different from a neutralization antibody in the prior art, and has the potential of forming cocktail combination therapy with other neutralization antibody.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
T cell receptors and methods of use thereof
PendingUS20220169695A1Inhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsVirusesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The present disclosure is directed recombinant T cell receptors capable of binding an NY-ESO-1 epitope and nucleic acid molecules encoding the same. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecules further comprise a second nucleotide sequence, wherein the second nucleotide sequence or the polypeptide encoded by the second nucleotide sequence inhibits the expression of an endogenous TCR. Other aspects of the disclosure are directed to vectors comprising the nucleic acid molecule and cells comprising the recombinant TCR, the nucleic acid molecule, or the vector. Still other aspects of the disclosure are directed to methods of using the same. In some embodiments, the methods comprise treating a cancer in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
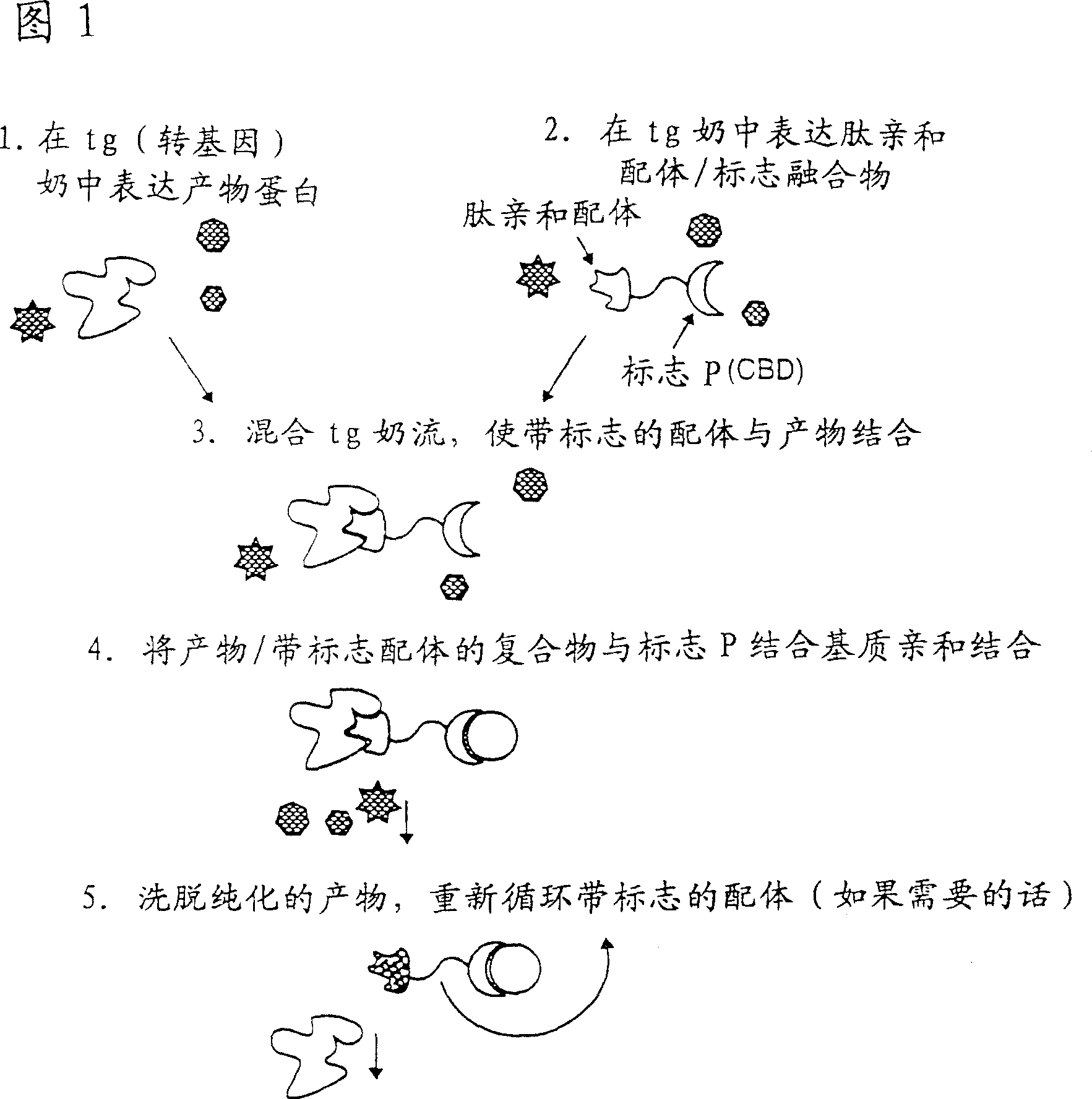
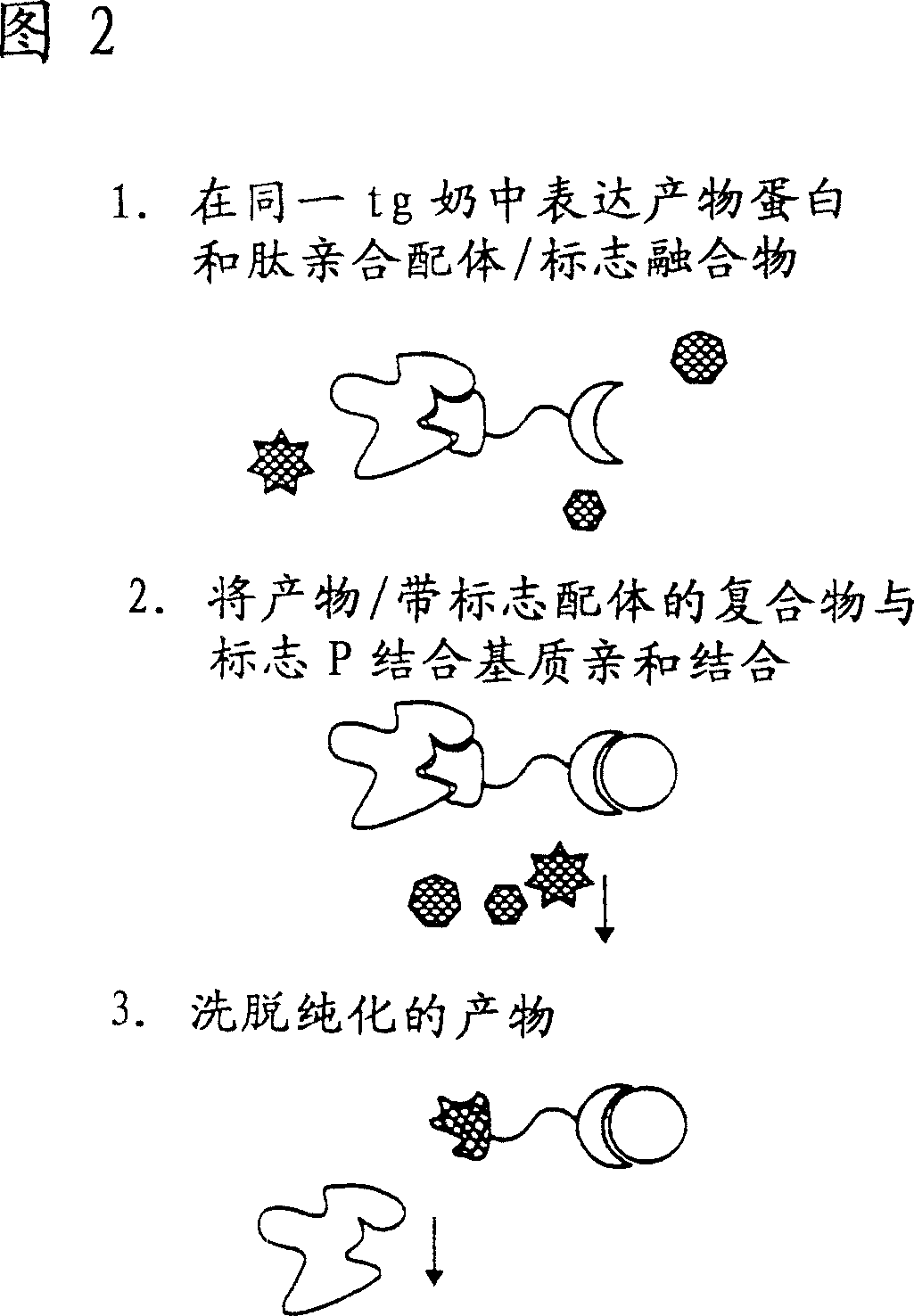
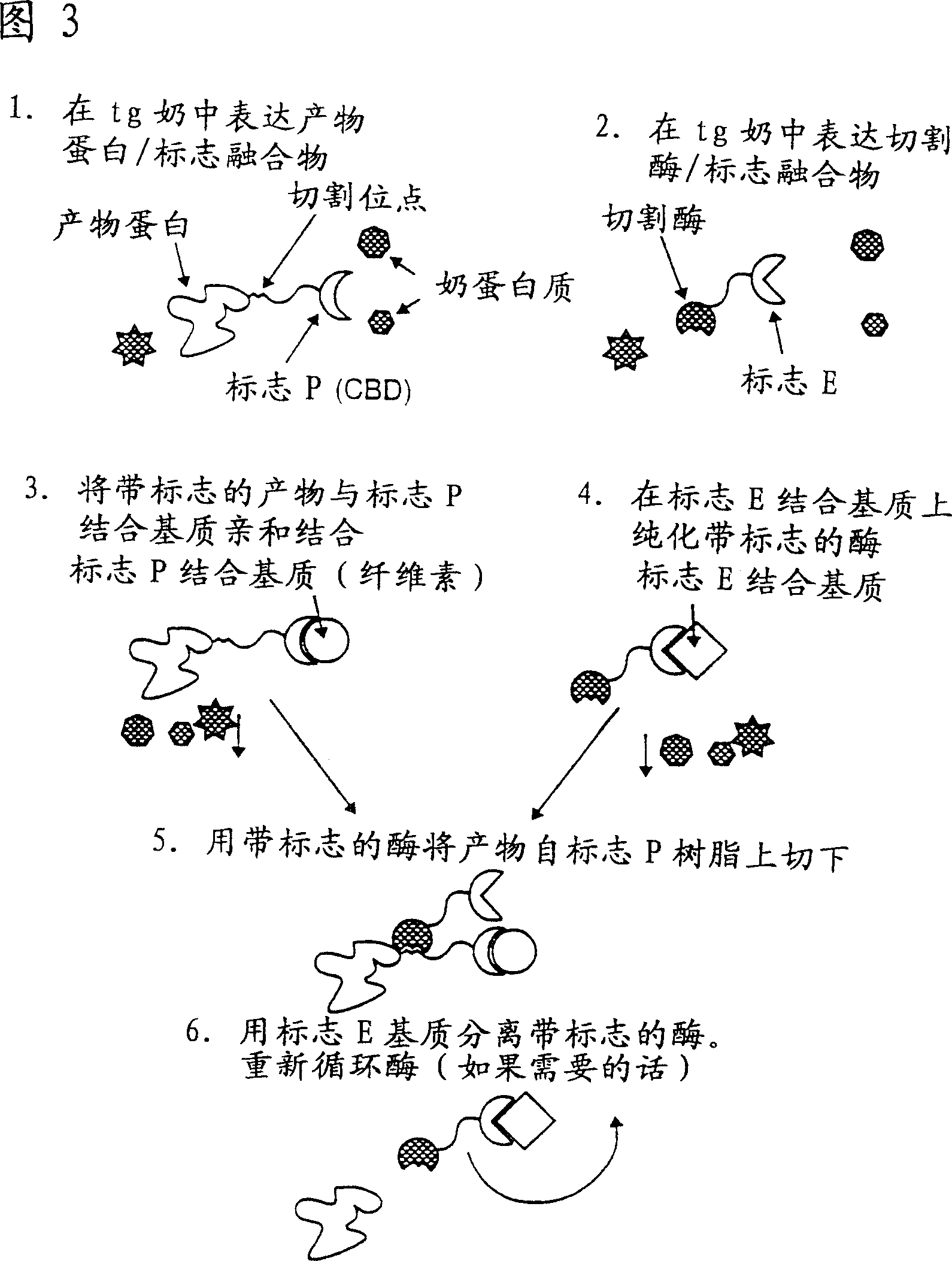
Methods of producing target molecule in transgenic animal and purification of target molecule
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
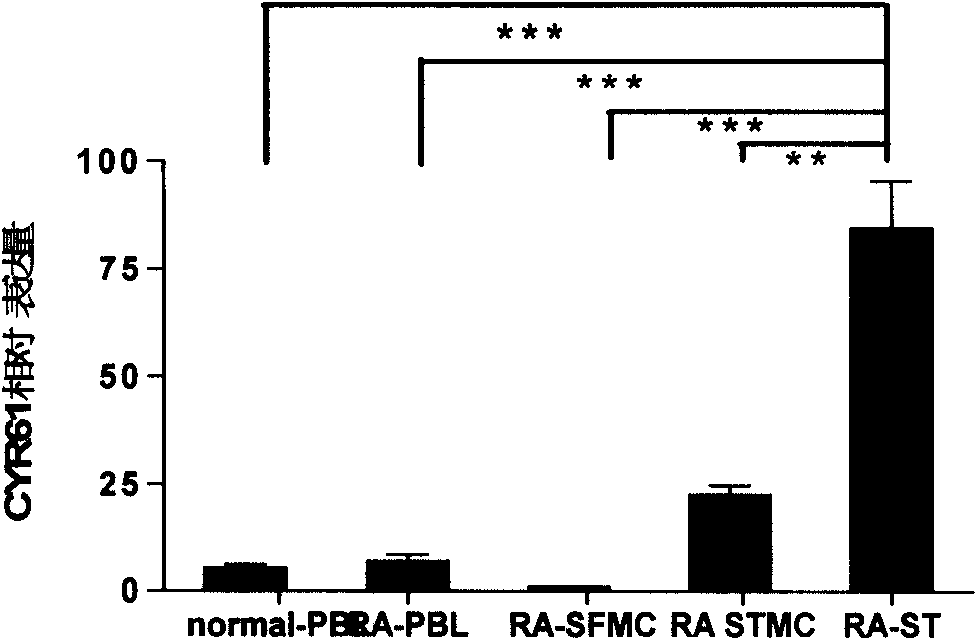
Monoclonal antibody (hybrid tumor) for neutralizing CYR61 and applications thereof
InactiveCN101747435BPrecise positioningAntipyreticAnalgesicsAntiendomysial antibodiesHumanized antibody
The invention relates to a monoclonal antibody capable of neutralizing CYR61 and applications thereof and a hybrid tumor capable of generating the monoclonal antibody. The technical scheme adopted by the invention relates to the monoclonal antibody secreted by the mouse anti-human CYR61 monoclonal antibody hybrid tumor CGMCC No.2766 or CGMCC No.2767, and the applications of the monoclonal antibody to preparation of a medicament for treating rheumatic disease, wherein the rheumatic disease is the chronic infectious arthritis. The invention has the advantages that: (1) the self-prepared monoclonal antibody can research pathogenesis of CYR61 in rheumatoid arthritis and can accurately position the expression of CYR61 and detect the CYR61 level of the blood serum and the lesion sites (such as joints); (2) the monoclonal antibody can be used for preparing a detection kit so as to distinguish clinical diagnostics of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis; and (3) the monoclonal antibody also can search the combination epitope where the CYR61 on the surface of the synovium and in the synovial of the rheumatoid arthritis patient can be neutralized, and provides the screening basis for preparing a humanized antibody which can neutralize the CYR61 in the next step.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF IMMUNOLOGY
T cell receptors and methods of use thereof
PendingCN114364806APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
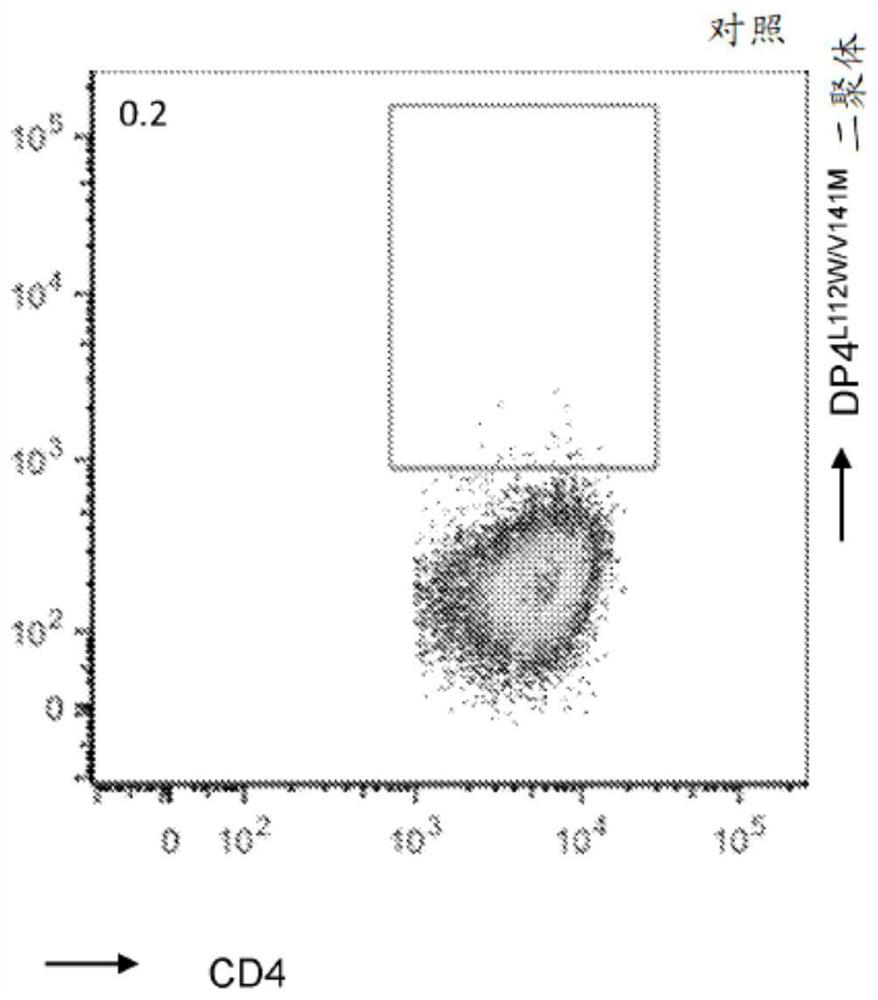
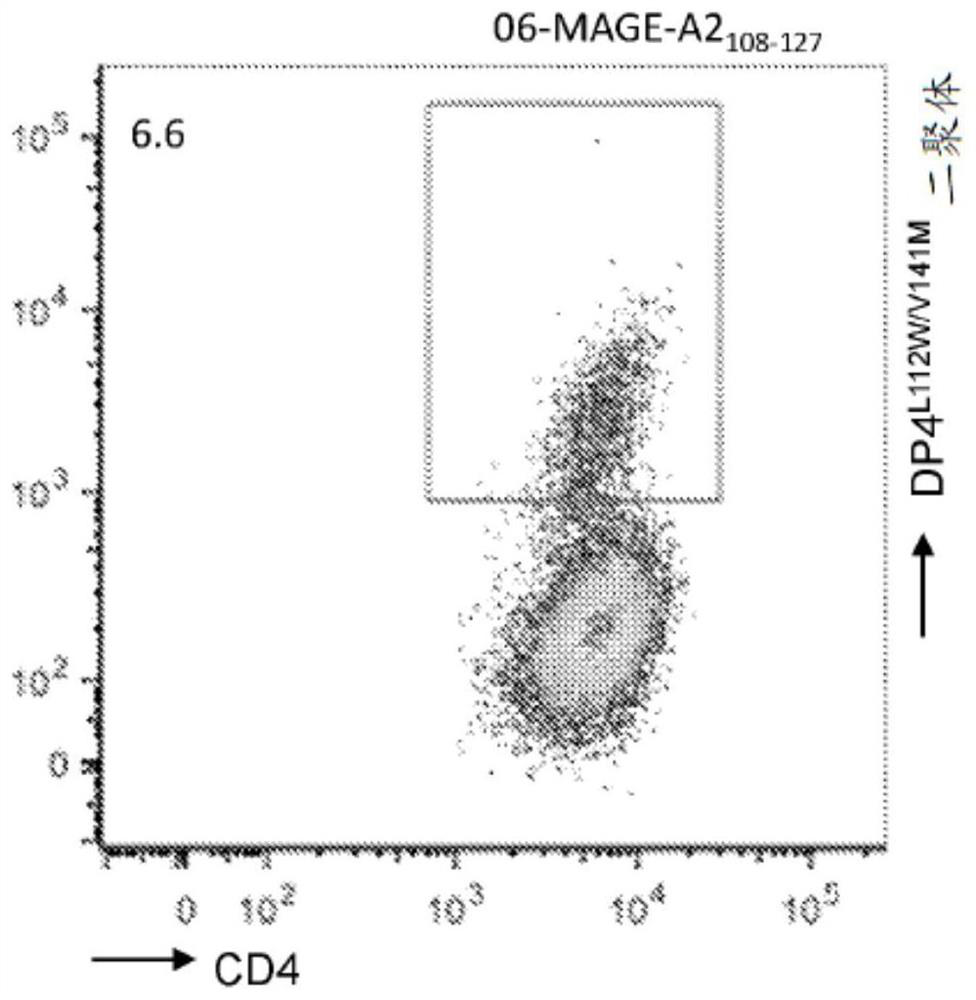
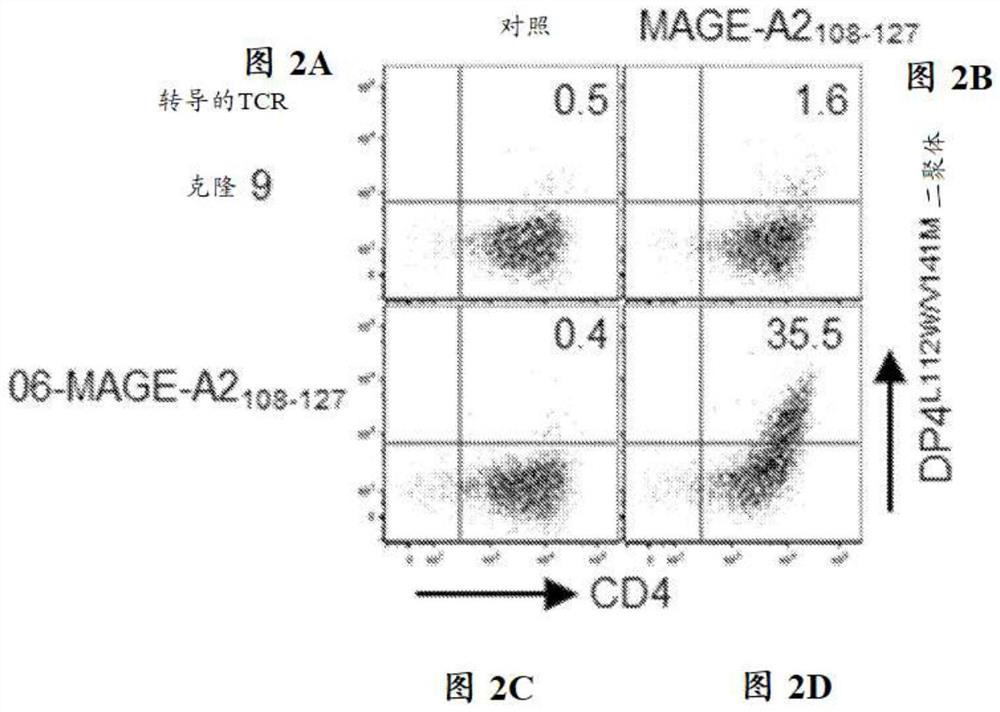
The present disclosure relates to recombinant T cell receptors capable of binding to MAGE-A2 epitopes and nucleic acid molecules encoding the recombinant T cell receptors. In some aspects, the nucleic acid molecule further comprises a second nucleotide sequence, where the second nucleotide sequence or a polypeptide encoded by the second nucleotide sequence inhibits expression of an endogenous TCR. Other aspects of the disclosure relate to a vector comprising the nucleic acid molecule and a cell comprising the recombinant TCR, the nucleic acid molecule, or the vector. Other aspects of the disclosure relate to methods of using the recombinant TCRs, the nucleic acid molecules, the vectors, and the cells. In some aspects, the methods include treating cancer in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com