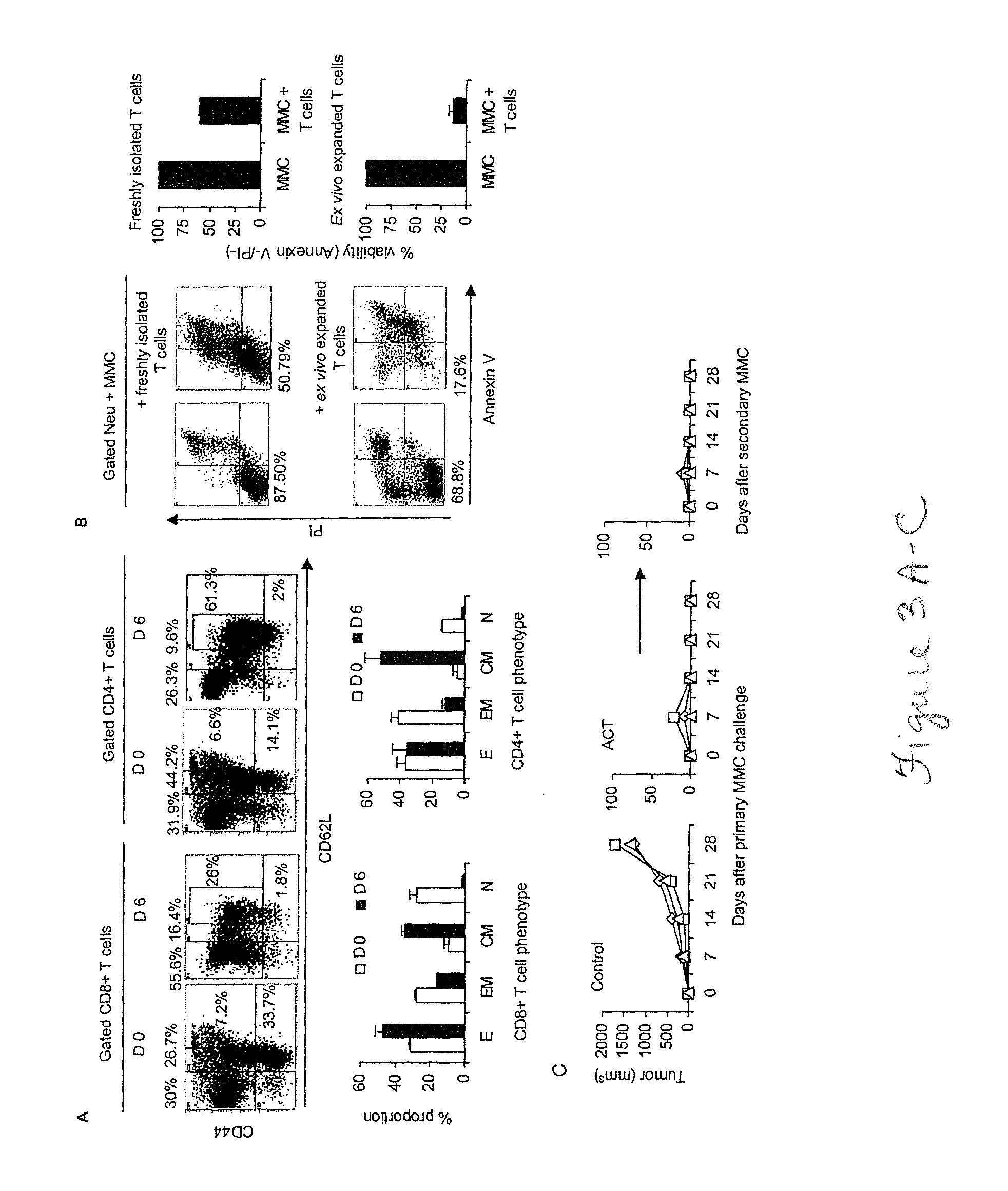
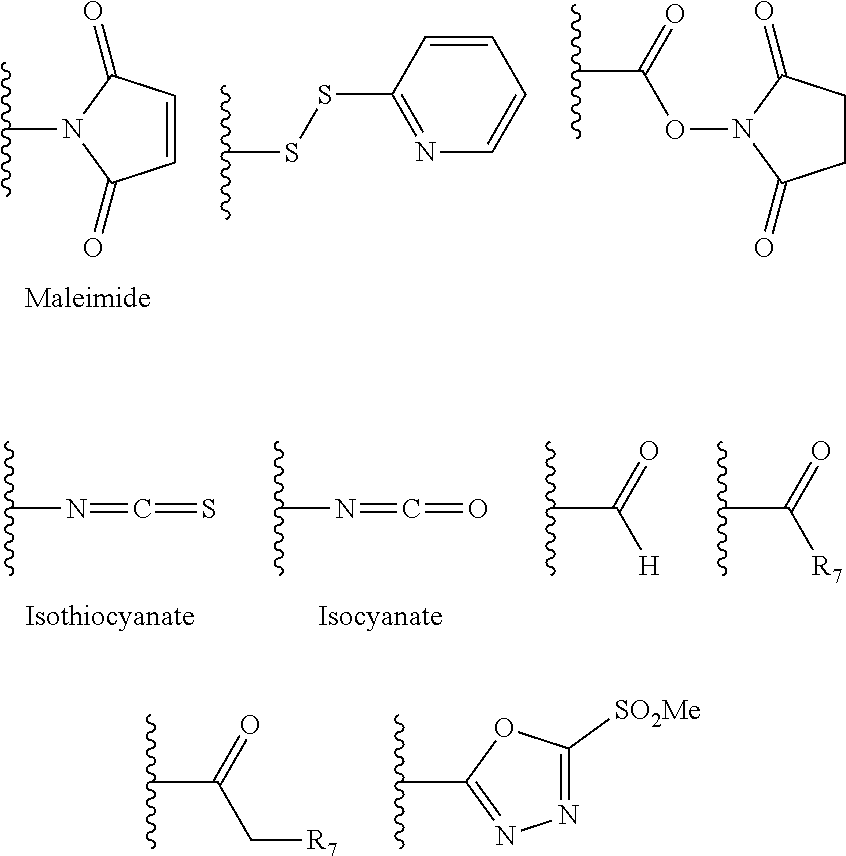
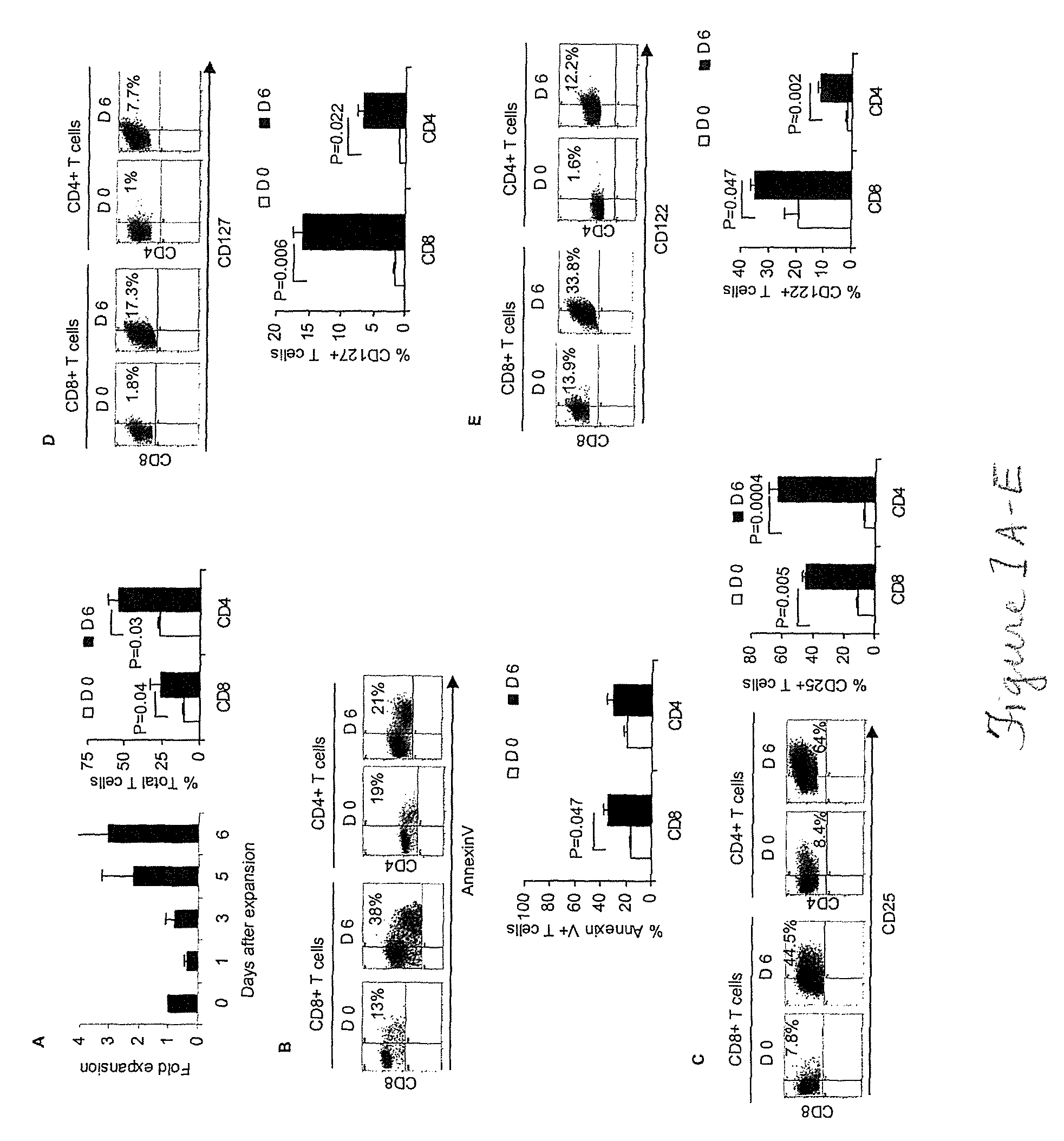
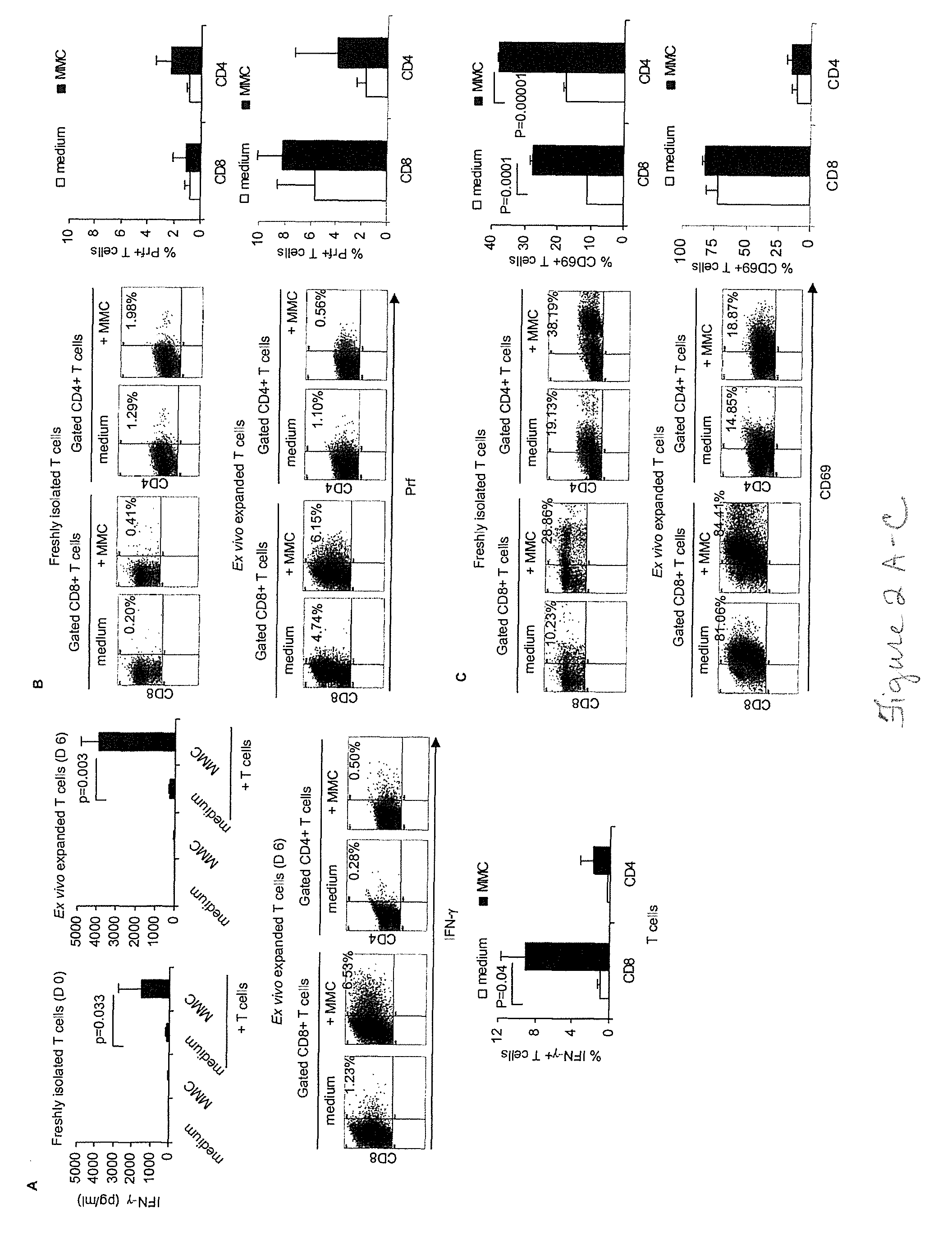
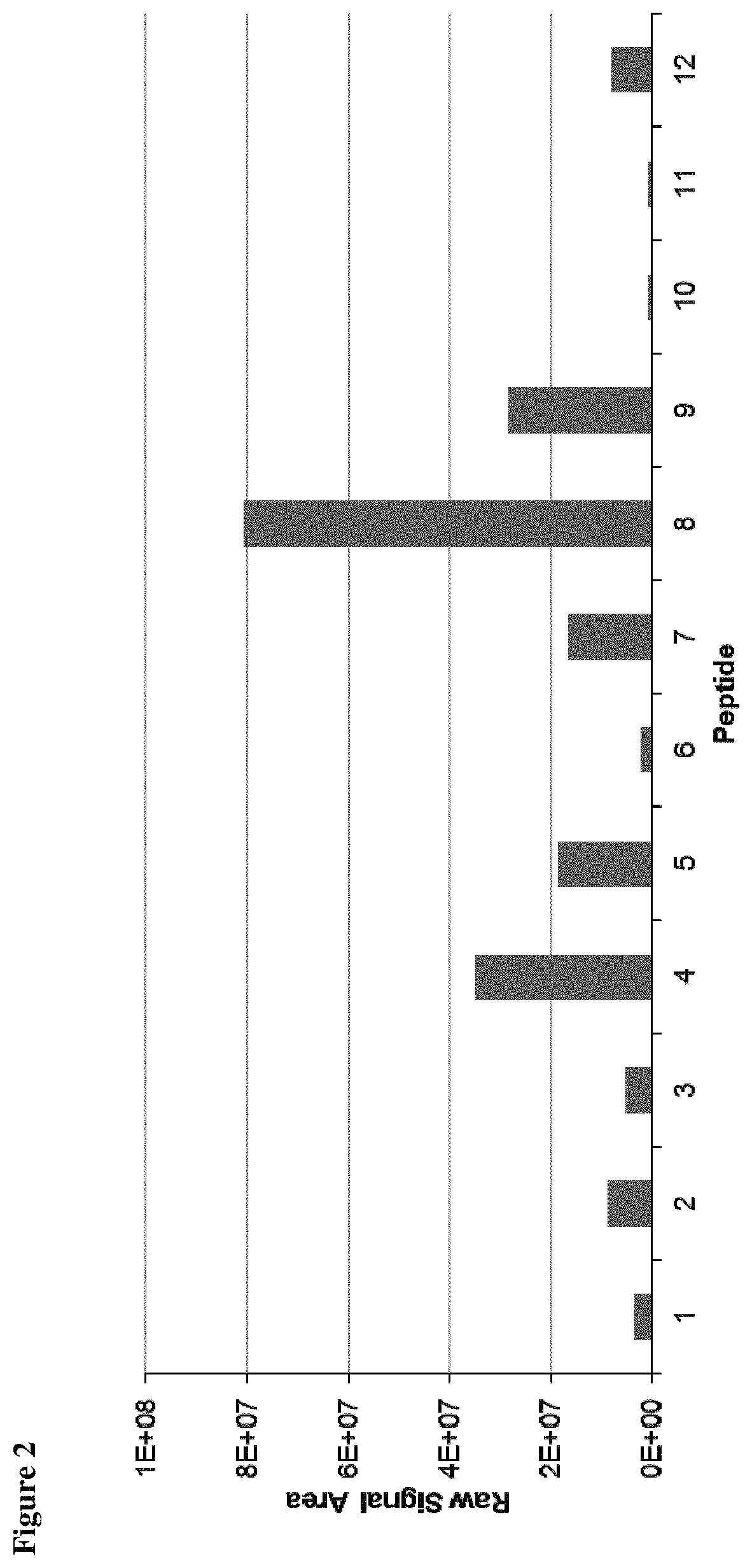
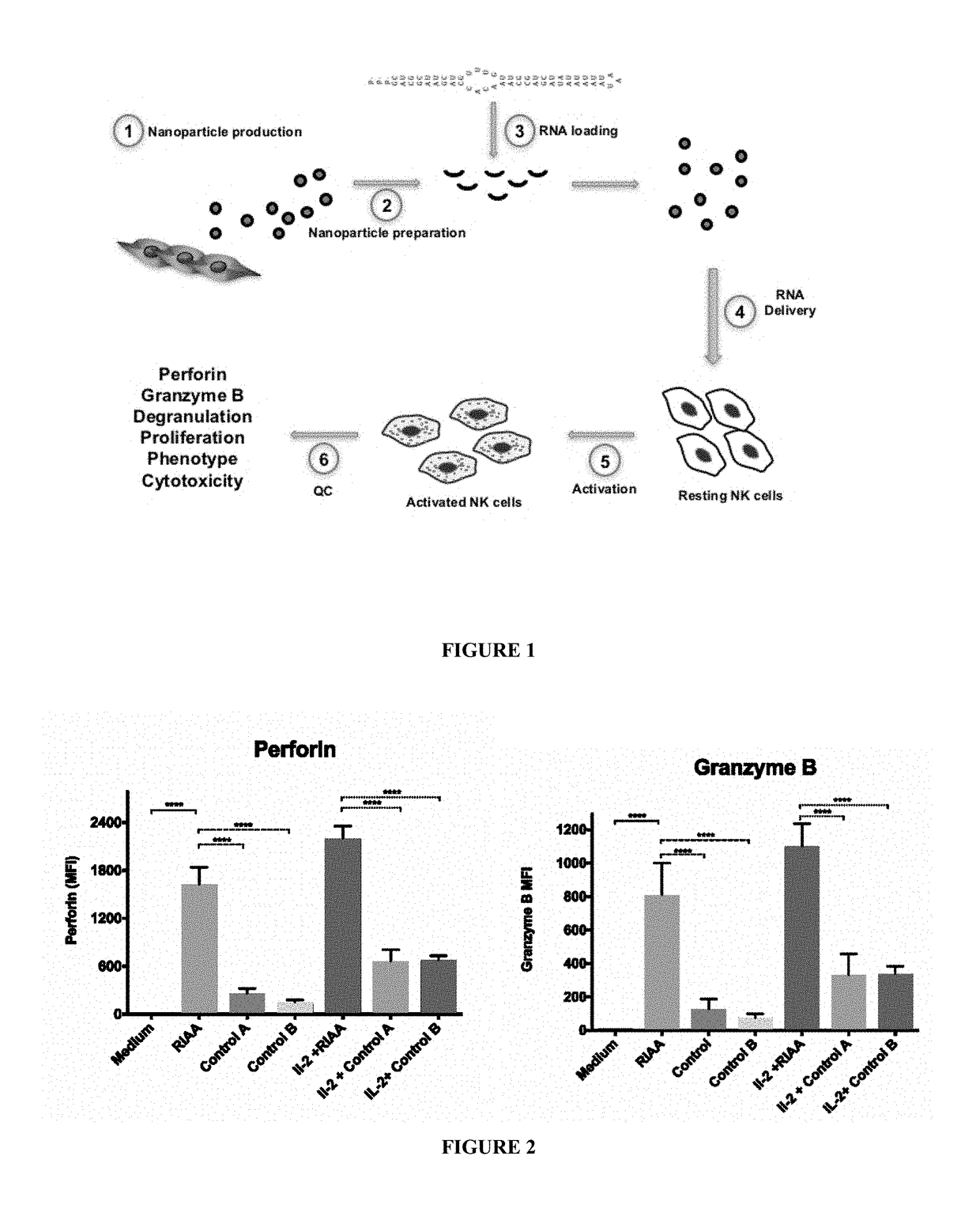
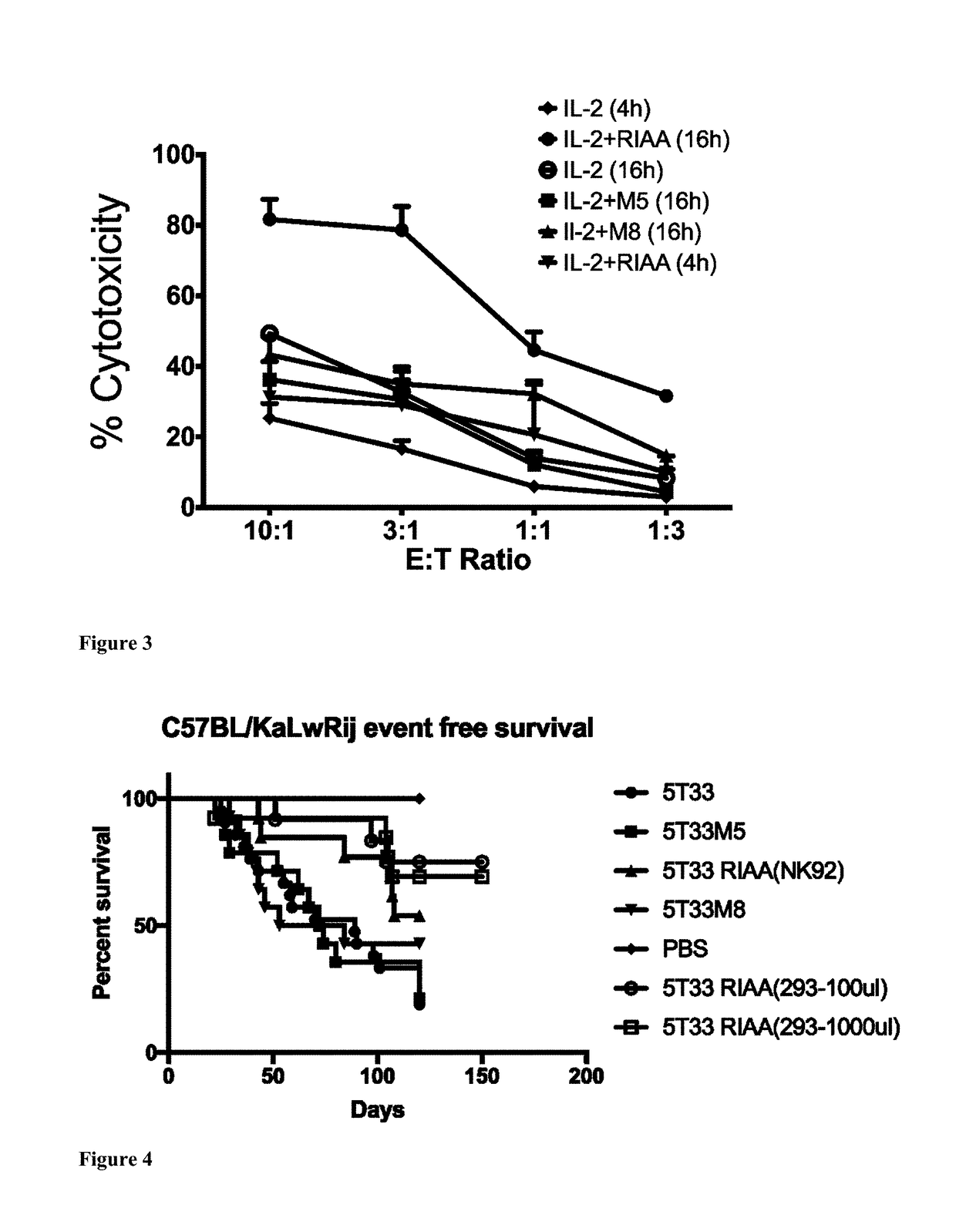
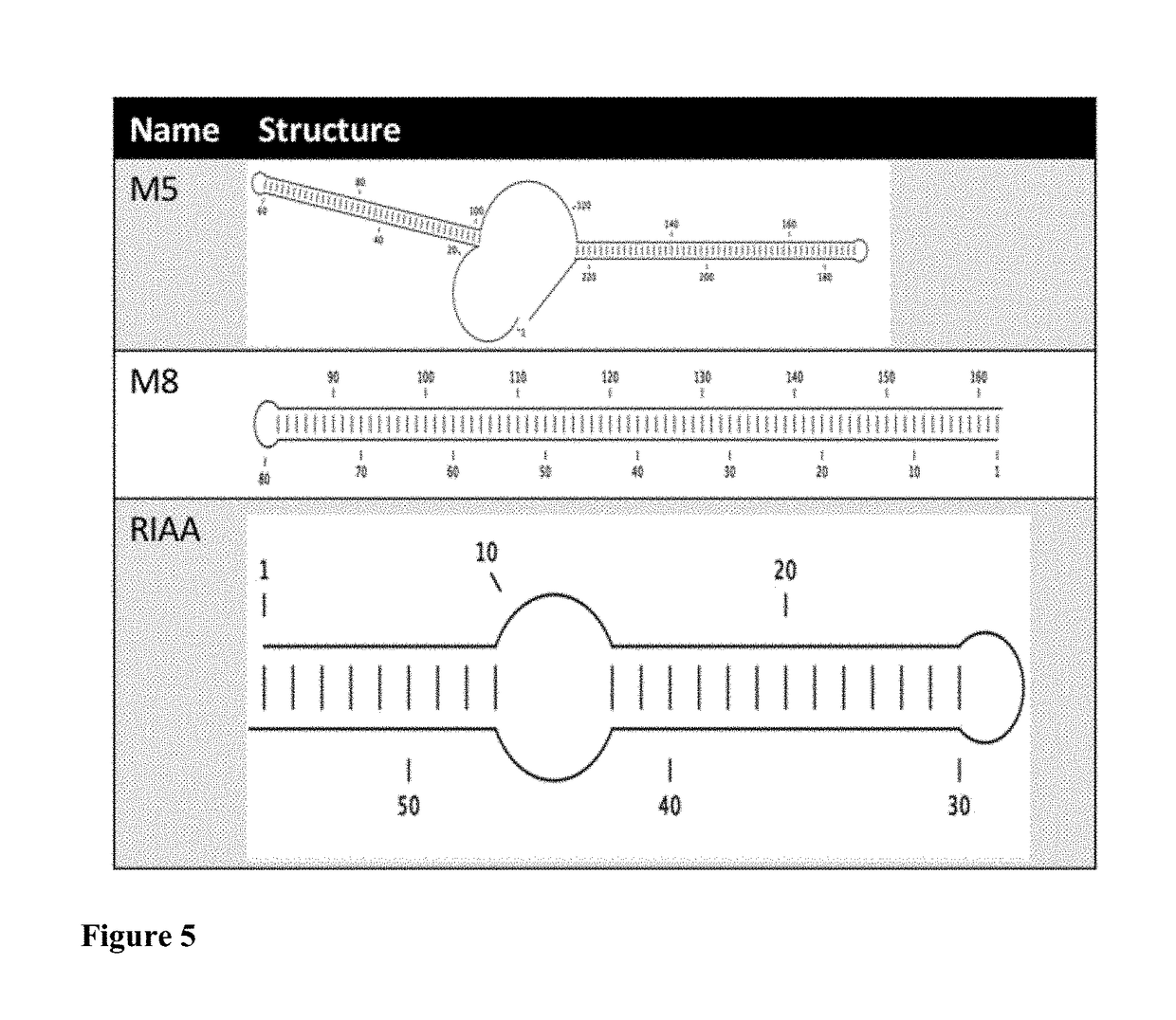
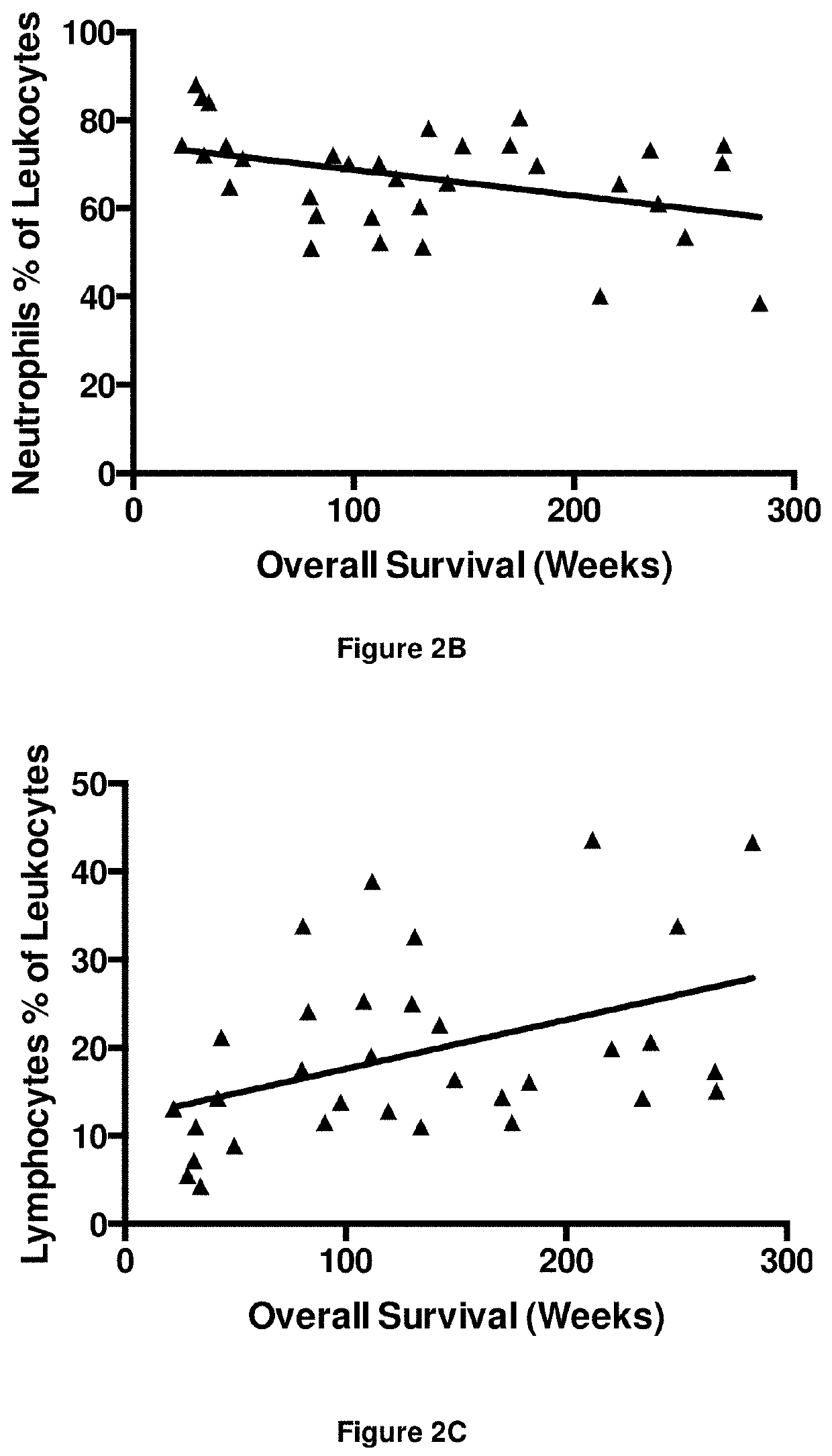
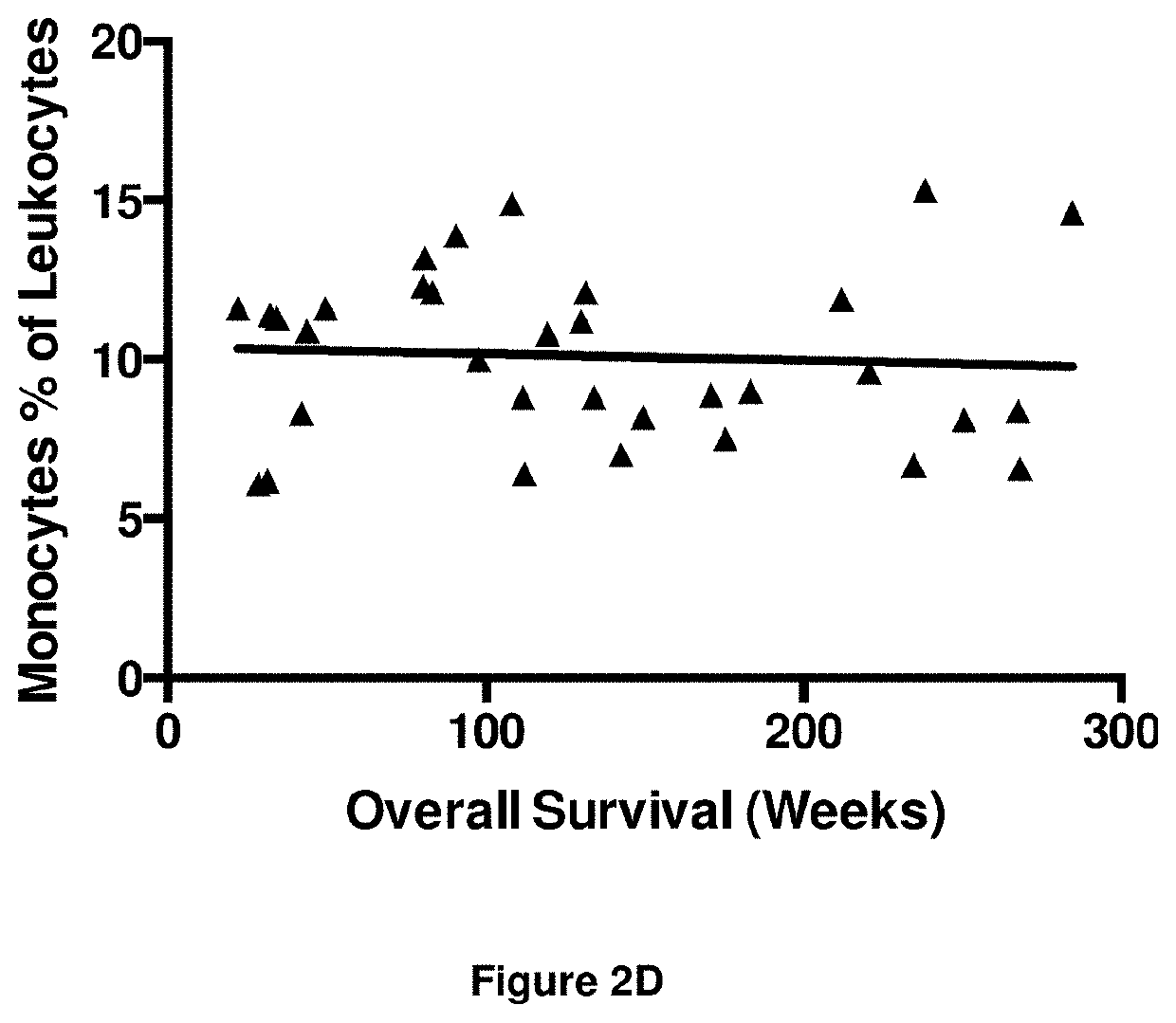
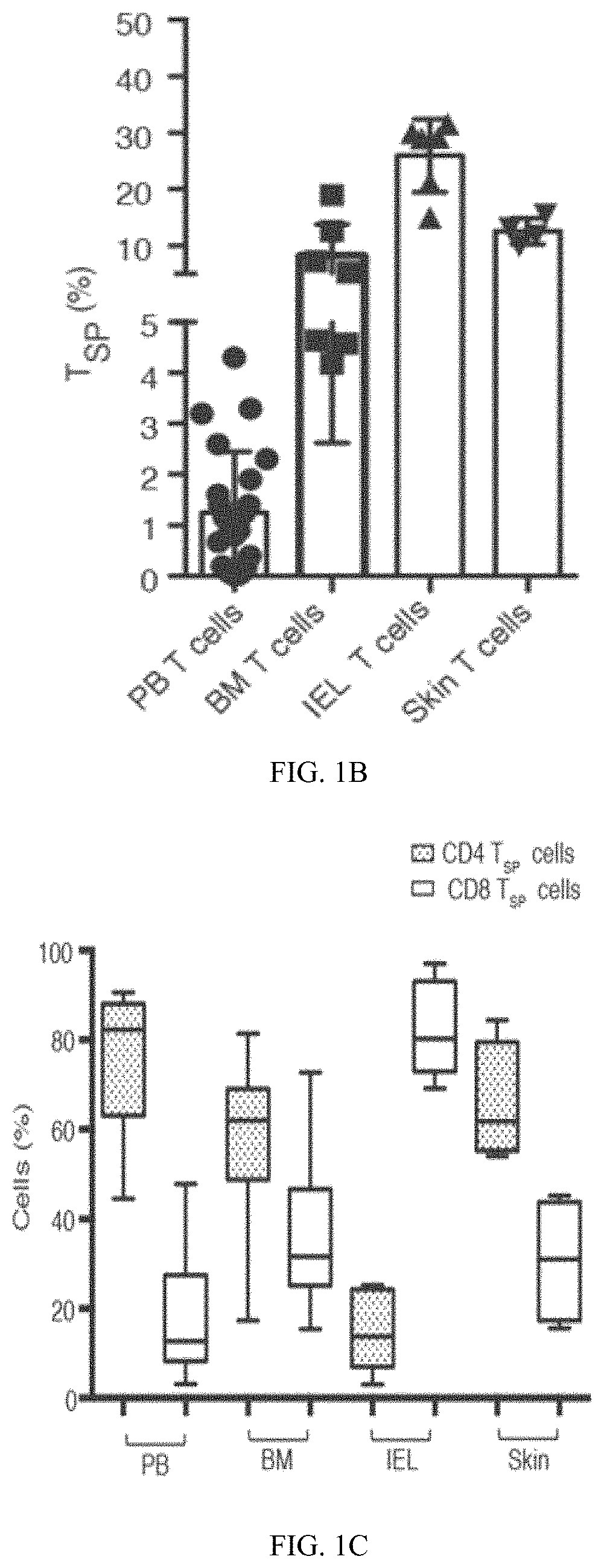
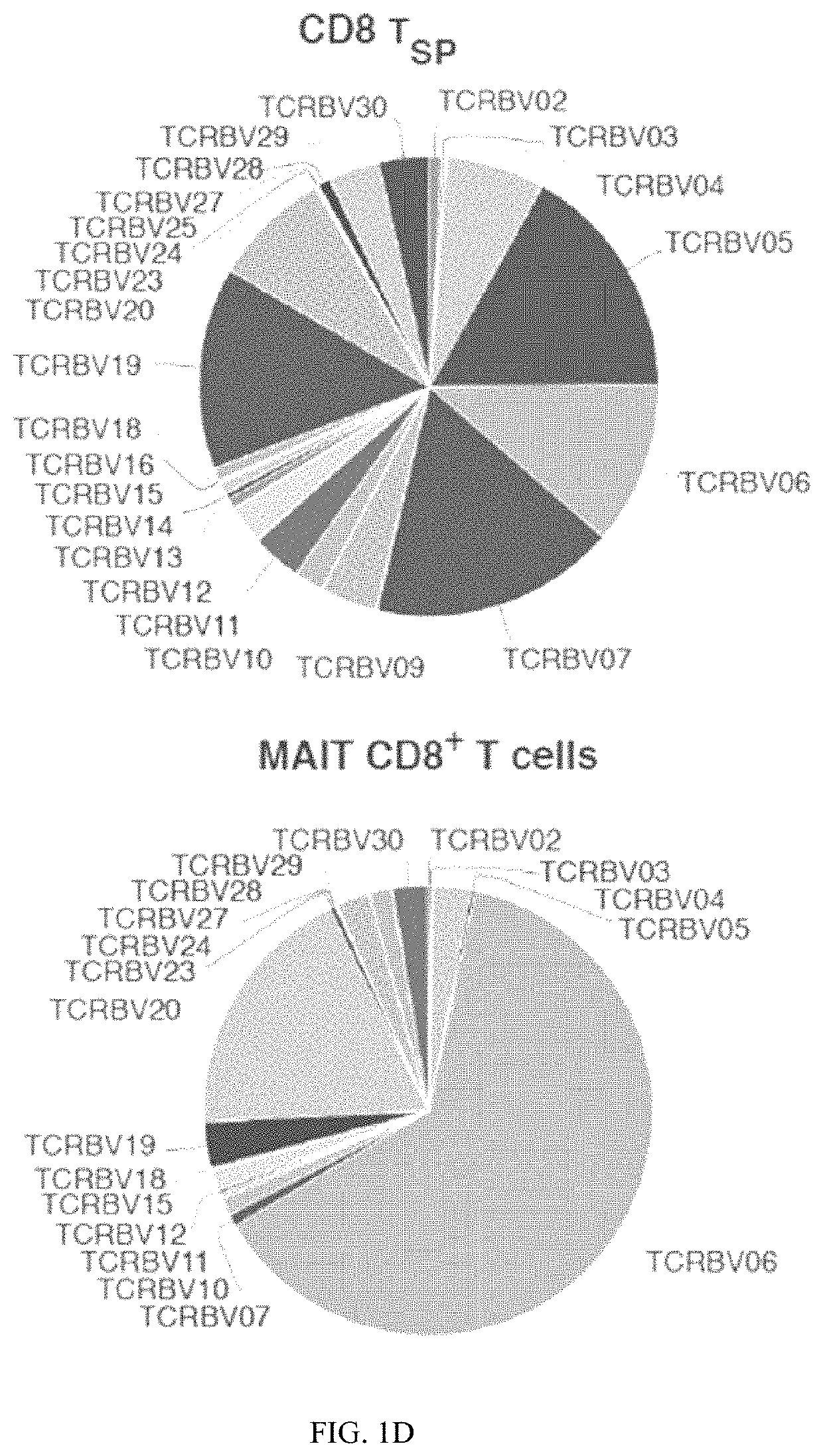
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Adoptive cell transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
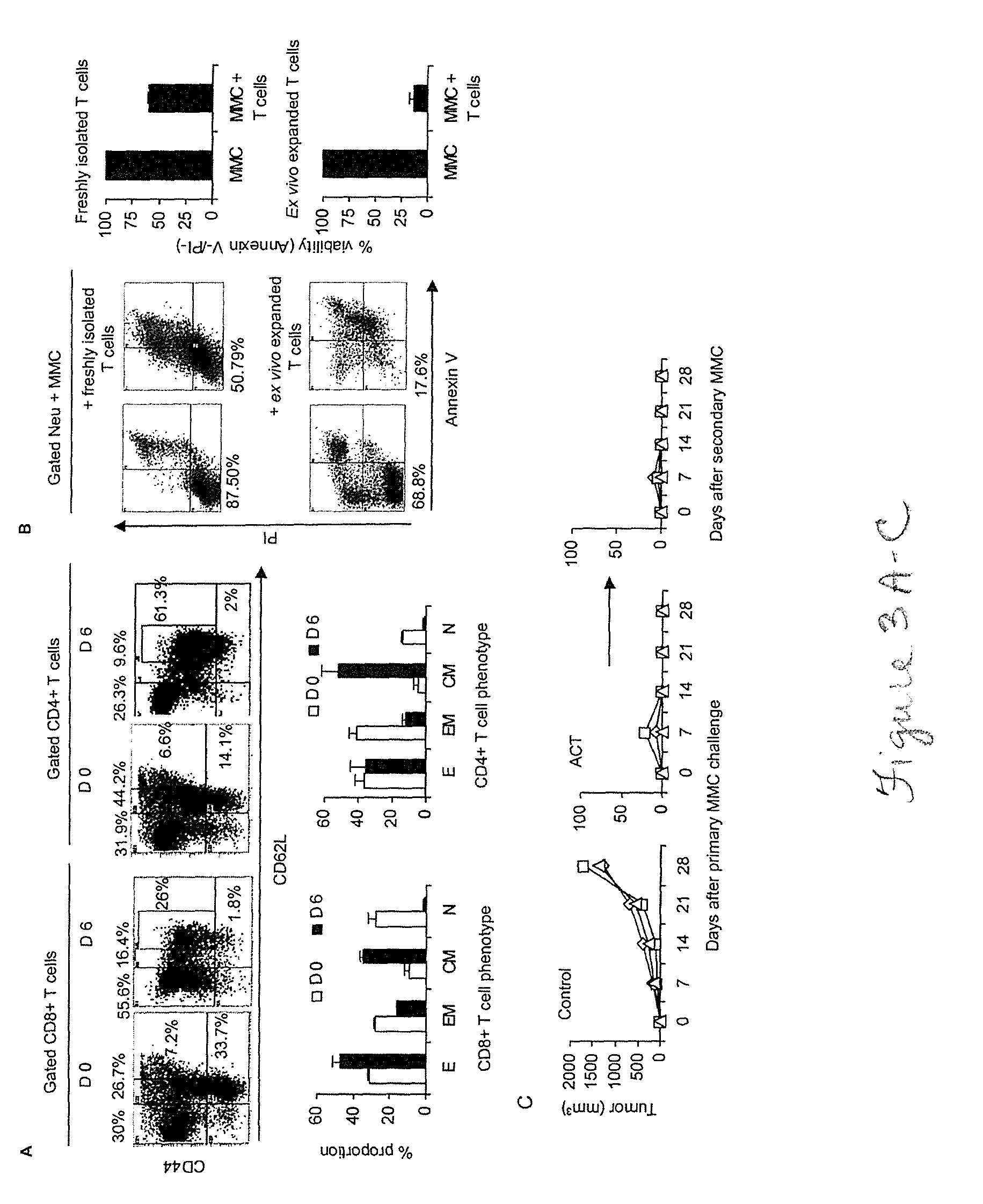
Adoptive cell transfer (ACT) is the transfer of cells into a patient. The cells may have originated from the patient or from another individual. The cells are most commonly derived from the immune system with the goal of improving immune functionality and characteristics. In autologous cancer immunotherapy, T cells are extracted from the patient, genetically modified and cultured in vitro and returned to the same patient. Comparatively, allogeneic therapies involve cells isolated and expanded from a donor separate from the patient receiving the cells.
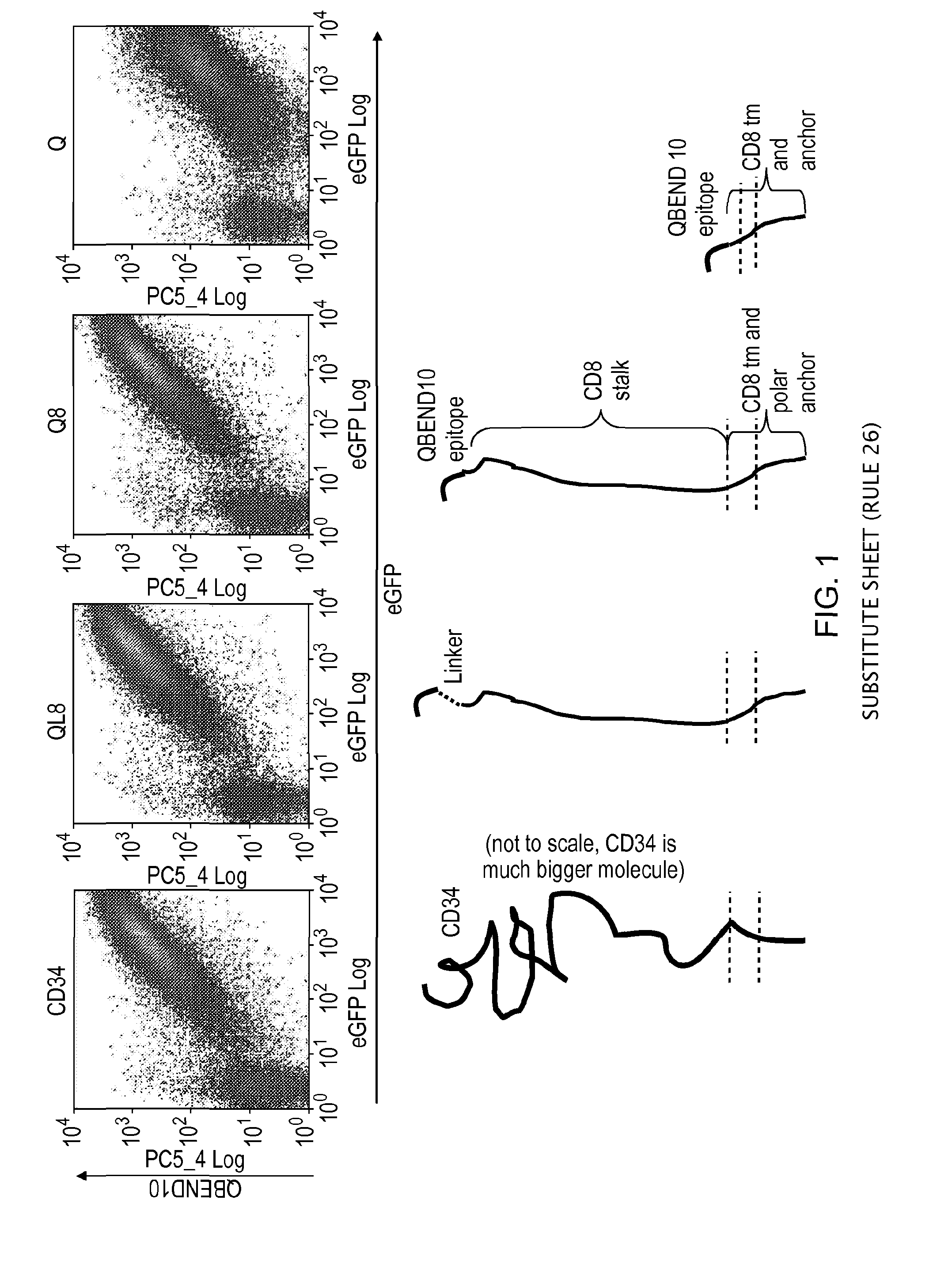
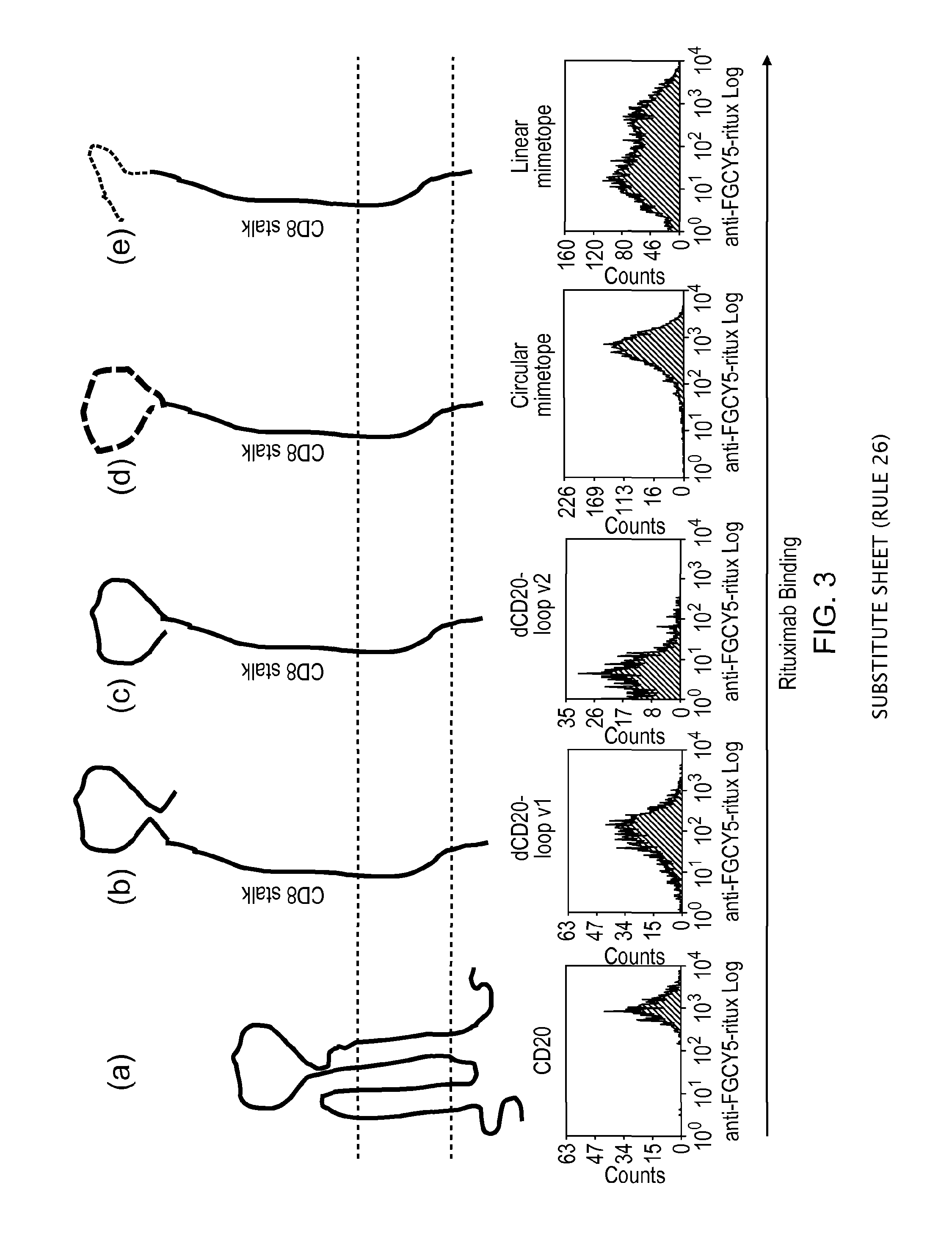
Polypeptide useful in adoptive cell therapy
ActiveUS20150093401A1Easy to packAvoids biological effectAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsEpitopeAdoptive cellular therapy
The present invention provides a polypeptide having the formula: St-R1-S1-Q-S2-R2 wherein St is a stalk sequence which, when the polypeptide is expressed at the surface of a target cell, causes the R and Q epitopes to be projected from the cell surface; R1 and R2 are a Rituximab-binding epitopes each having the an amino acid sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID No. 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 and 16 or a variant thereof which retains Rituximab-binding activity; S1 and S2 are optional spacer sequences, which may be the same or different; and Q is a QBEnd1O-binding epitope having the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 2 or a variant thereof which QBEnd1O-binding activity. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence encoding such a polypeptide and uses thereof in adoptive cell transfer.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
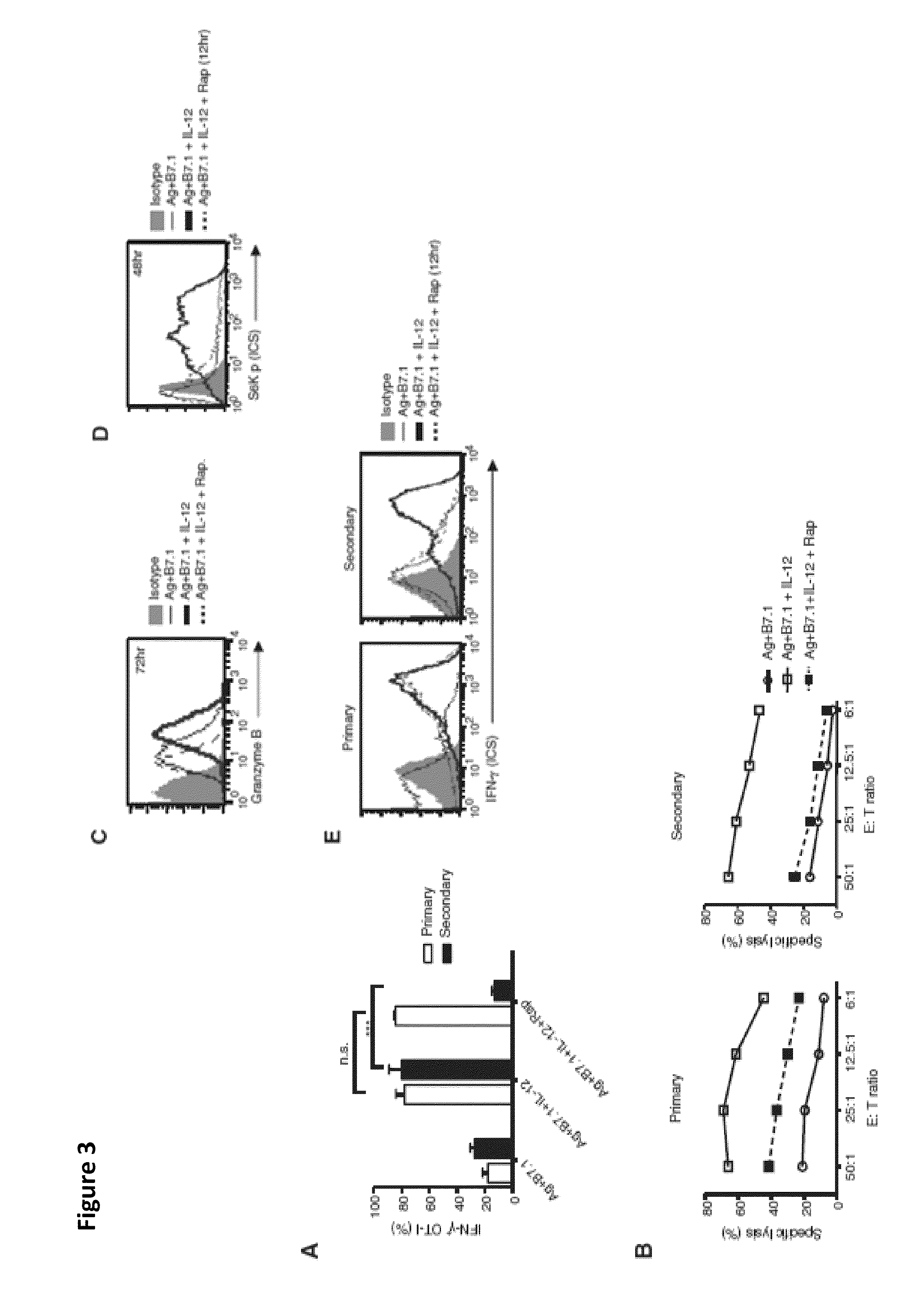
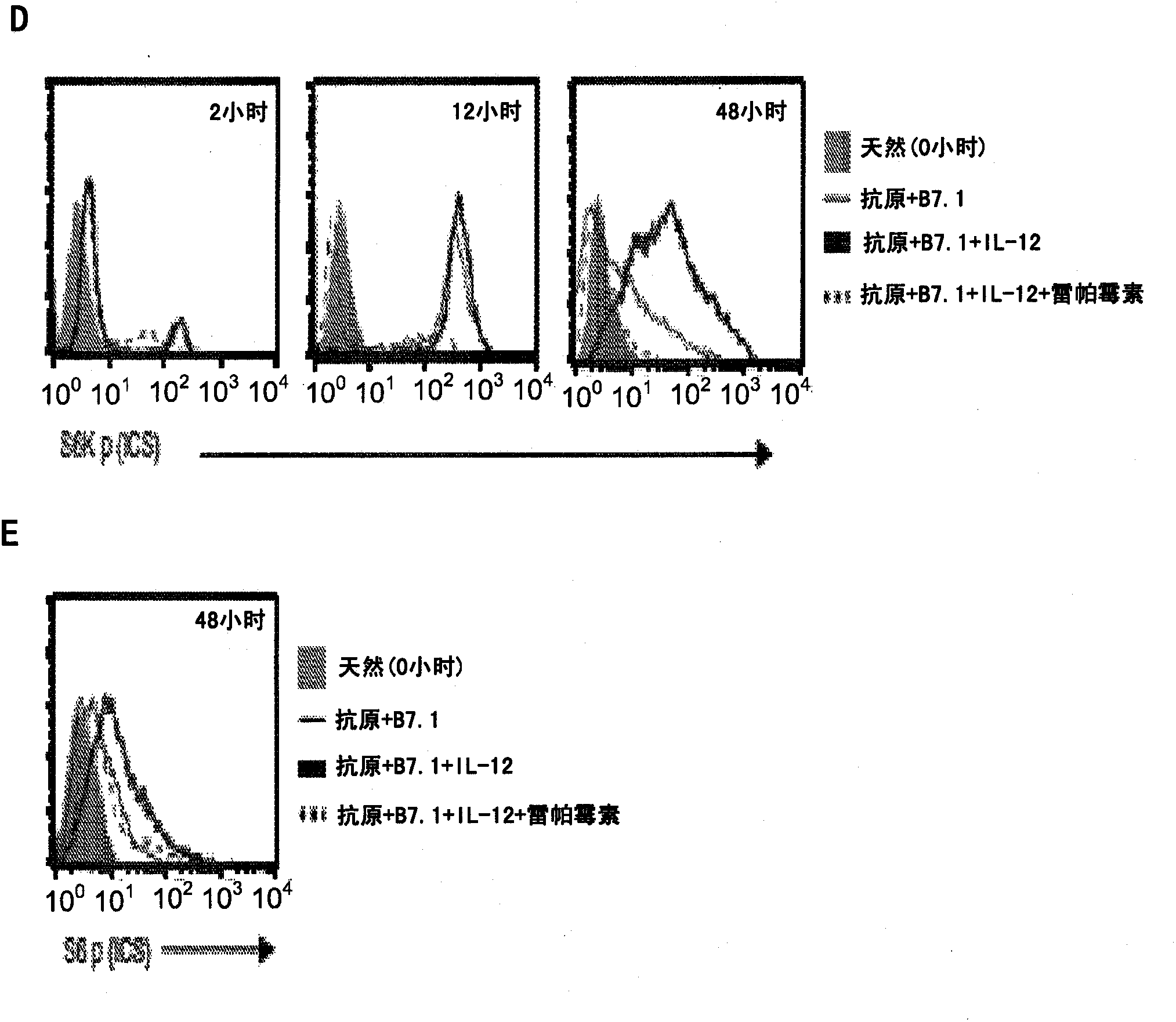
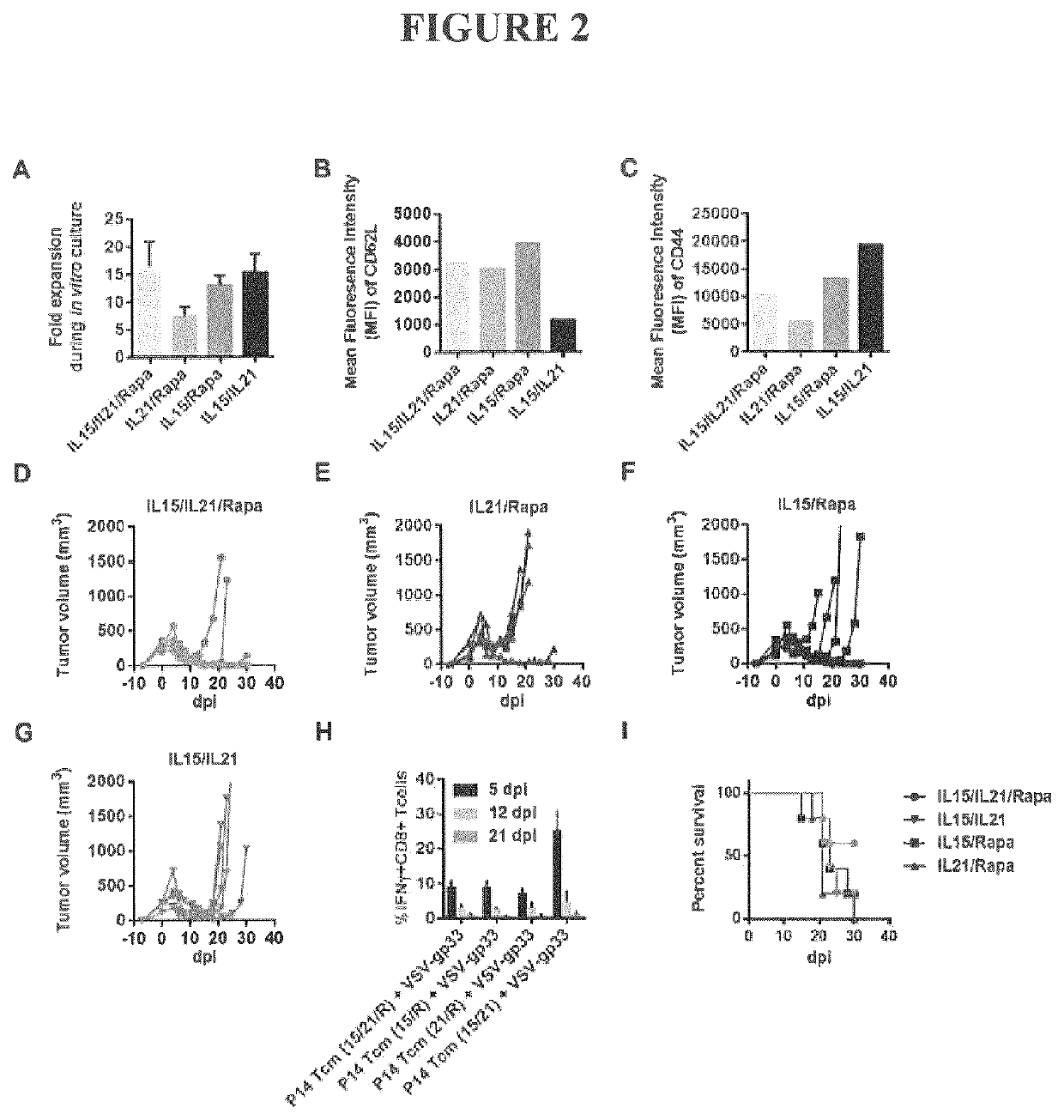
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING mTOR INHIBITORS FOR ENHANCING IMMUNE RESPONSES
InactiveUS20100196311A1Enhance immune responseSuitable for useBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAntigenCD8
Provided are compositions and methods for enhancing immune responses to an antigen. The compositions contain an isolated population of CD8+T cells and an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). The method for obtaining an enhanced immune response to an antigen in an individual entails administering to the individual the antigen and an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). CD8+T cells may also be used for adoptive cell transfer (ACT) therapy.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Method of enhancing persistence of adoptively infused t cells
InactiveUS20190292520A1Improving efficacy and viabilityEfficacyImmunoglobulin superfamilyGenetically modified cellsCytokineAdoptive cell transfer
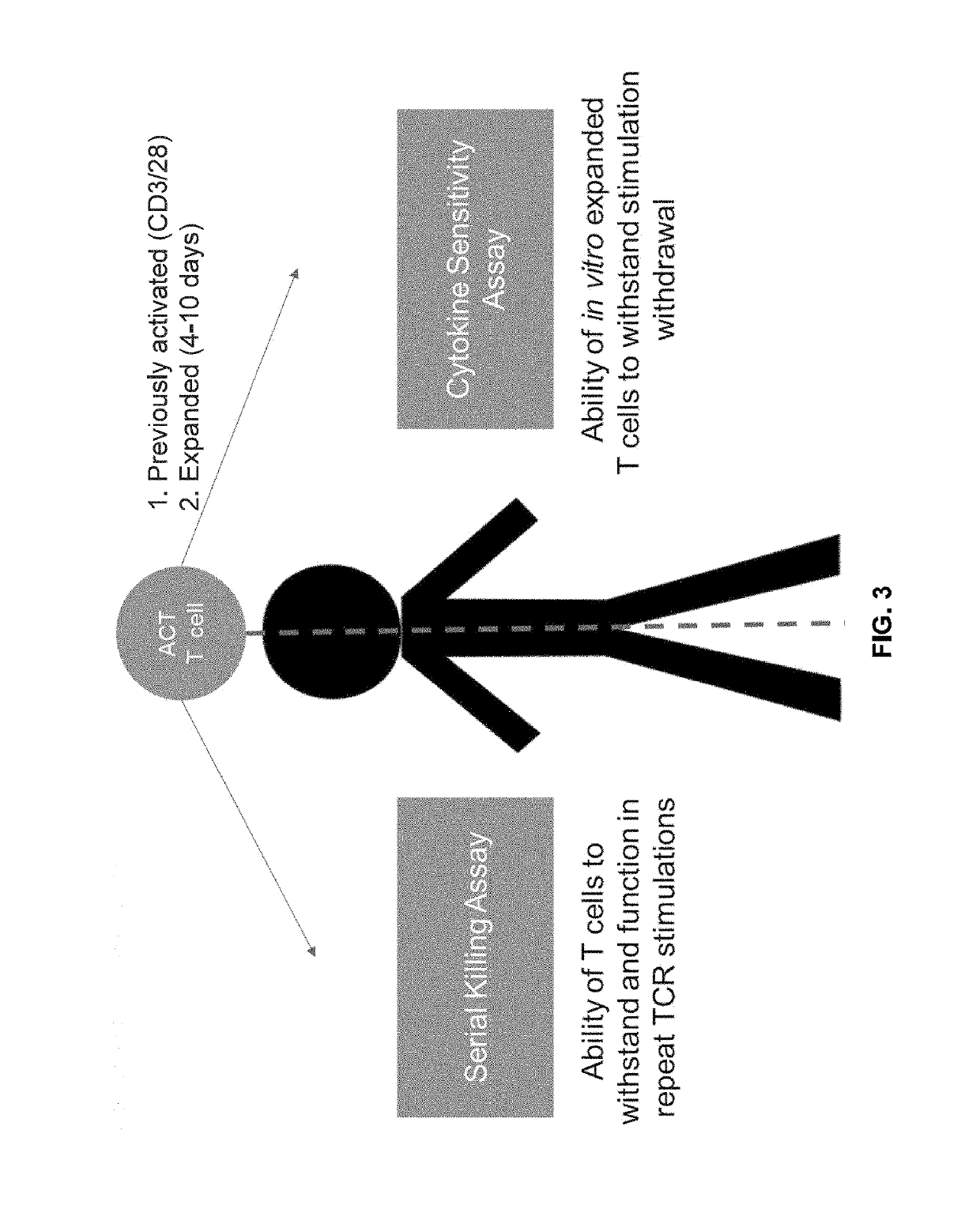
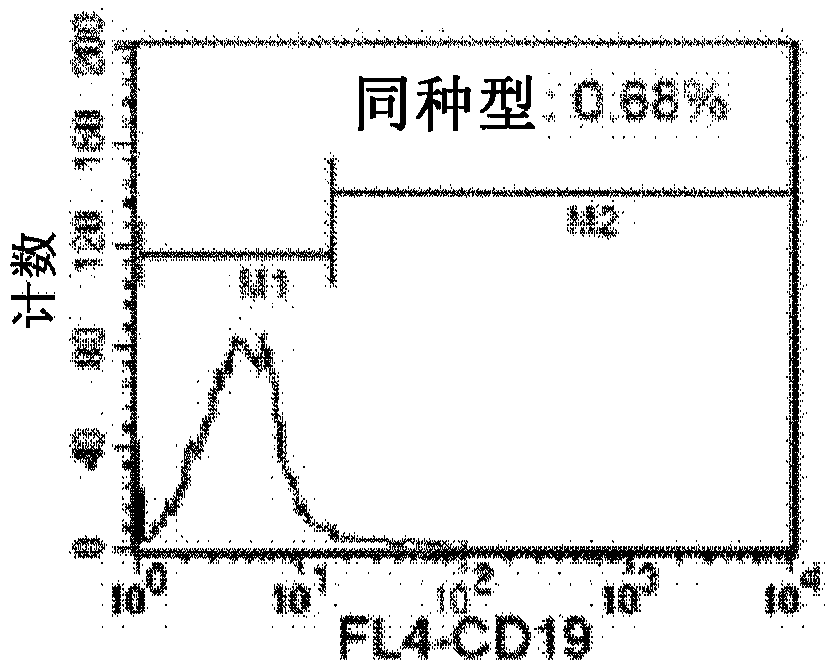
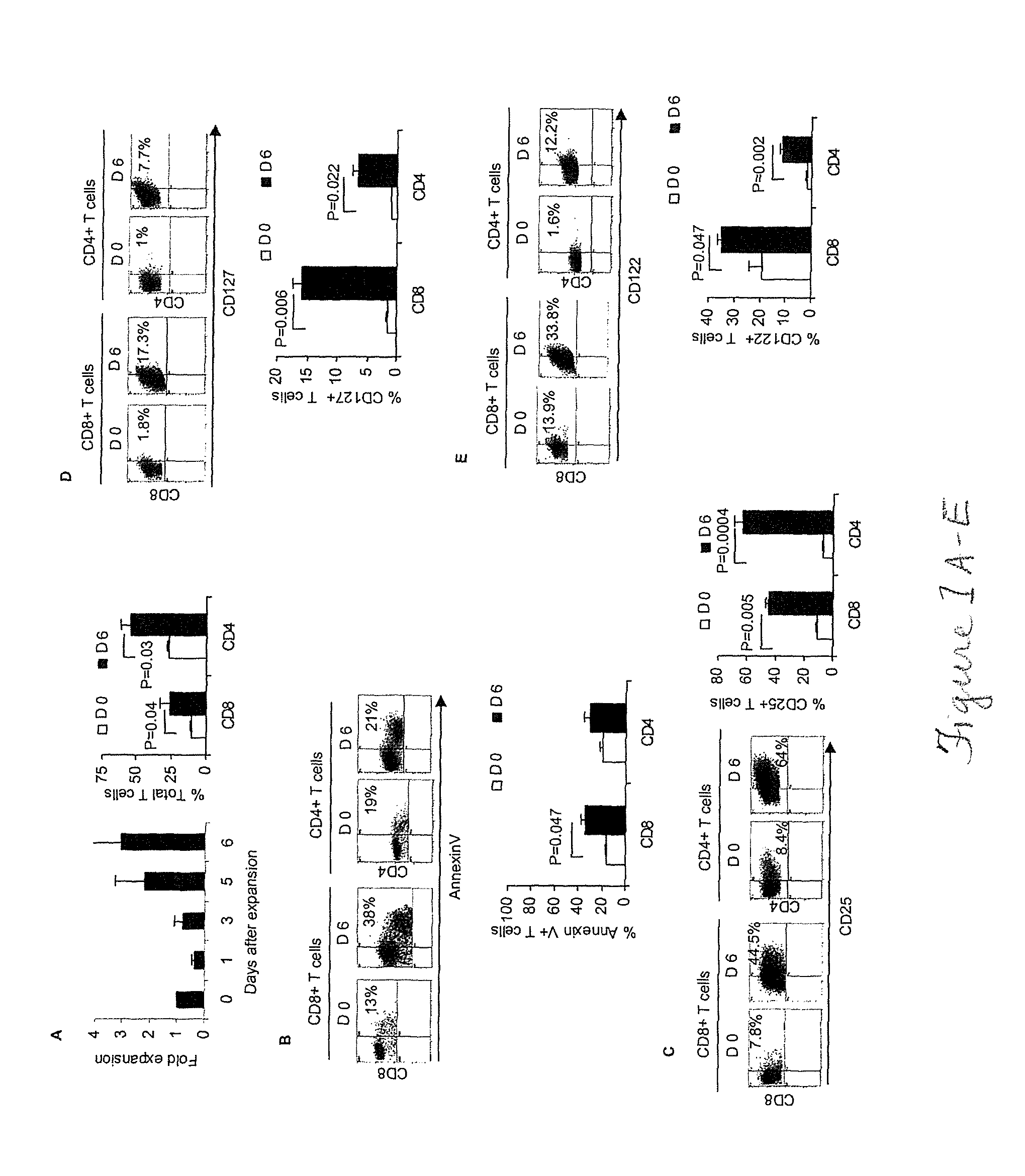
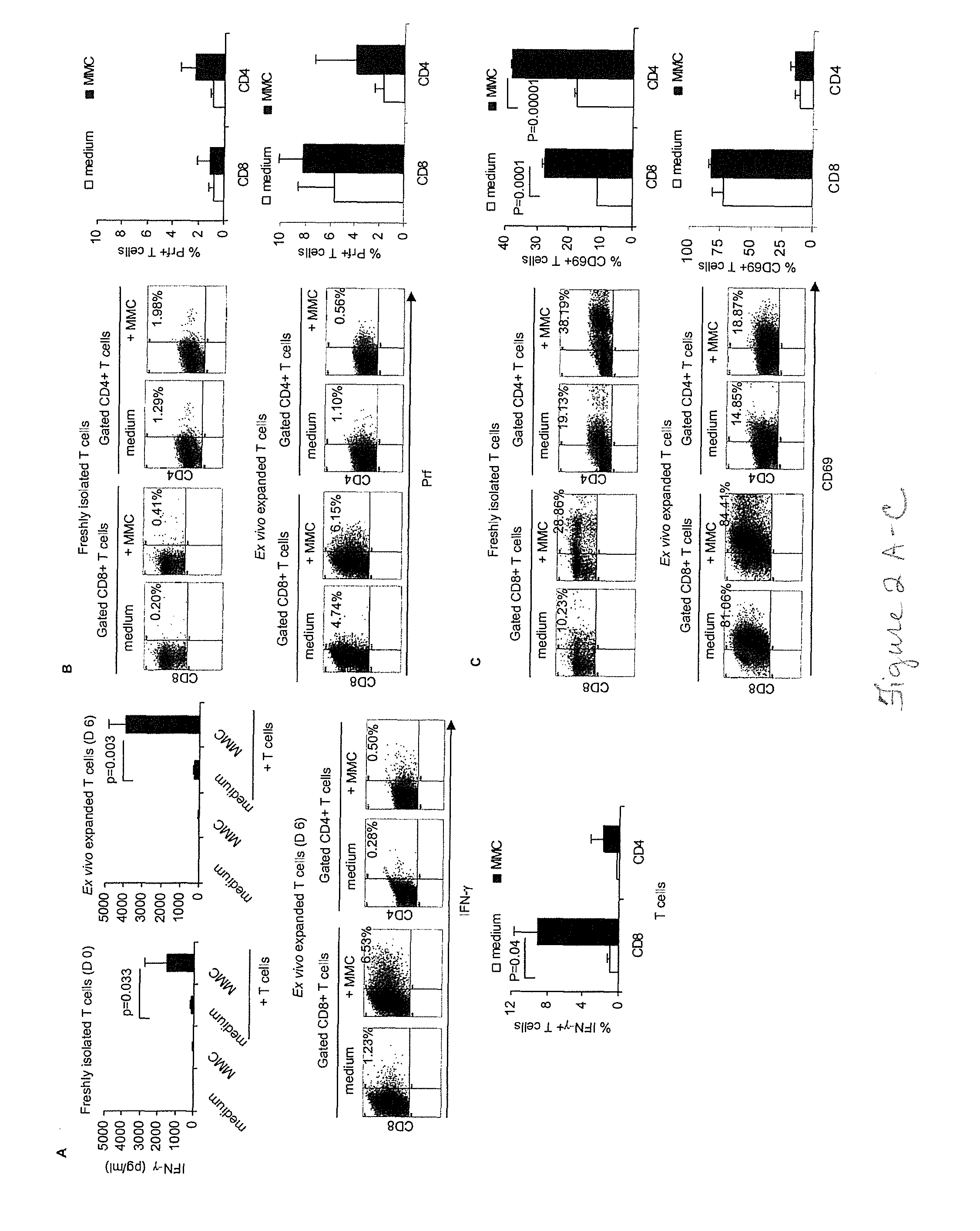
The present disclosure provides for methods of improving the efficacy of T cells. In an aspect, the disclosure further provides for methods of enhancing the persistence of T cells for adoptive cell transfer or therapy (ACT). Cytokine sensitivity assays (CSA) and associated methodology capable of predicting the persistence of adoptively infused T Cells are further provided for by way of the instant disclosure. The disclosure also provides for methods of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof as well as T cells populations produced by methods described herein.
Owner:IMMATICS US INC
Methods for enhancing in vivo persistence and efficacy of exogenously administered t cells, genetically modified t cells and method and method of use
ActiveCN108473956APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyNucleotideReverse transcriptase
A method for enhancing the in vitro and in vivo lifespan of T cells is provided. A method for enhancing the life span of a T cell is provided. The method includes engineering the T cell to express exogenous ribonucleic acid (RNA), where the RNA includes a nucleic acid encoding telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT). T cells genetically engineered to transiently express exogenous RNA which includes the coding sequence for TERT (TERT T cells) are provided. TERT T cells have one or more of the following characteristics when compared to a T cells not expressing TERT from an exogenously introducednucleotide: enhanced in vitro and in vivo proliferation, decreased number of senescent cells, and enhanced in vivo anti-cancer activity. The modified TERT T cells can be used in adoptive cell transfer to treat a subject in need thereof.
Owner:BEIHAO STEM CELL & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST CO LTD +1
Composition and method for immunological treatment of cancer, prevention of cancer recurrence and metastasis, and overcoming immune suppresor cells
InactiveUS20130309213A1Suitable for useLong-term protectionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsCancer preventionDisease
Methods for the ex vivo generation of cells of the innate (NKT cells and NK cells) and adaptive (T cells) immune systems for use in adoptive cell transfer (ACT) are provided. The NKT cells render T cells resistant to immune suppression (e.g. they are resistant to the effects of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs)). The method involves culturing disease-primed immune cells (obtained from a cancer patient or from a patient with an infectious disease) with i) byrostatin and ionomycin (B / I) to activate and differentiate the cells; followed by sequentially culturing the cells with a) a combination of IL-7 and IL-15 and then b) IL-2, to further differentiate the cells and to render them immune resistant. The resistant immune cells are used to treat and prevent cancer and infectious diseases.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Compositions and methods for immunomodulation
InactiveUS20180221508A1Increases delivery and biodistributionPowder deliveryDrug photocleavageAntitumor immunityAdjuvant
The present invention relates to modulation of the tumor microenvironment to increase cancer specific immune responses. Conjugates, nanoparticles and formulations of the present invention relieve the inhibitory effect induced by tumor cells, and enhance antitumor immunity. The compostions provided herein can be used as immunotherapies, or as adjuvants used in conjunction with other immunotherapies such as peptide vaccines, cell vaccines and / or adoptive T cell transfer.
Owner:TVA (ABC) LLC
Methods for producing autologous immune cells resistant to myeloid-derived suppressor cells effects
InactiveUS8741642B2Suitable for useLong-term protectionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseIonomycin
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Methods and compositions containing mTOR inhibitors for enhancing immune response
Provided are compositions and methods for enhancing immune responses to an antigen. The compositions contain an isolated population of CD8+T cells and an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). The method for obtaining an enhanced immune response to an antigen in an individual entails administering to the individual the antigen and an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). CD8+T cells may also be used for adoptive cell transfer (ACT) therapy.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
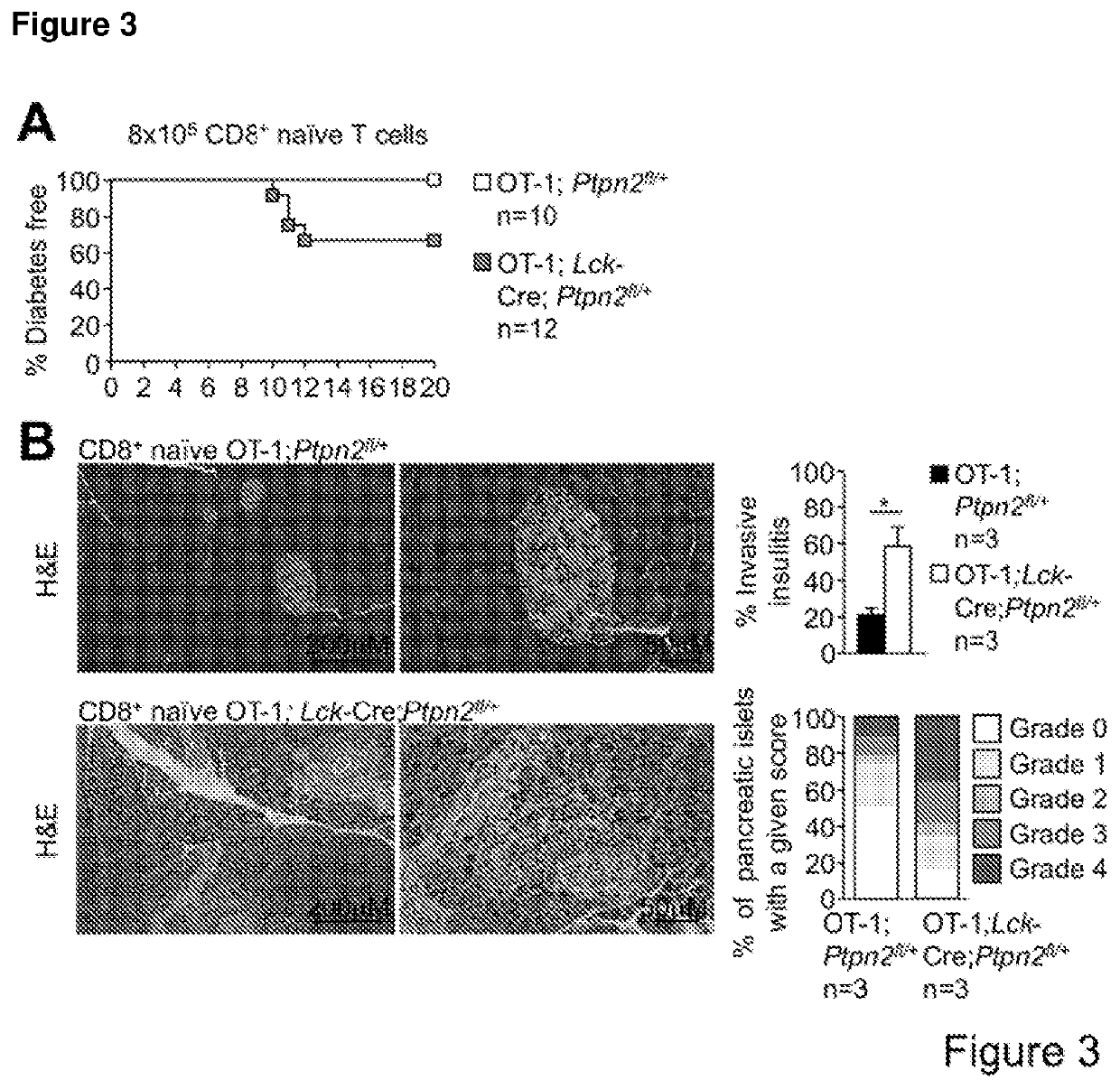
Method of producing leukocytes using ptpn2 inhibition for adoptive cell transfer
InactiveUS20170224731A1Enhance immune responsePromote differentiationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyWhite blood cellCytotoxicity
The present invention generally relates to methods of preparing leukocytes, particularly T cells, ex vivo for use in immunotherapy, particularly cancer immunotherapy. More specifically, the invention relates to methods for the preparation of leukocytes exhibiting cytotoxic properties for use in adoptive cell transfer. The invention also relates to cells and compositions including them for cancer immunotherapy. The invention also relates to methods of immunotherapy, particularly cancer immunotherapy. The present invention relates to a method for producing a leukocyte that has an enhanced capacity for killing a target cell, the method including contacting the leukocyte with a PTPN2 inhibitor in conditions for enabling the inhibitor to inactivate PTPN2 in the leukocyte, thereby producing a leukocyte that has an enhanced capacity for killing a target cell. Preferably, the leukocyte is contacted with the PTPN2 inhibitor in the absence of a T helper cell.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
Chimeric antigen receptors with mutated cd28 costimulatory domains
Disclosed herein are chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) polypeptides, which can be used with adoptive cell transfer to target and kill cancers, that comprise a co-stimulatory signaling region having a mutated form of a cytoplasmic domain of CD28 that enhances CAR-T cell function, e.g. by reducing CAR-T cell exhaustion. Also disclosed are immune effector cells, such as T cells or Natural Killer (NK) cells, which are engineered to express these CARs. Therefore, also disclosed are methods of providing an anti-tumor immunity in a subject with a tumor associated antigen-expressing cancer that involvesadoptive transfer of the disclosed immune effector cells engineered to express the disclosed CARs.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Method for treating epstein-barr virus—positive cancer with immunotherapy
InactiveUS10342865B2Reduce the amount requiredReduced activityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiviralsDiseasePrognosis biomarker
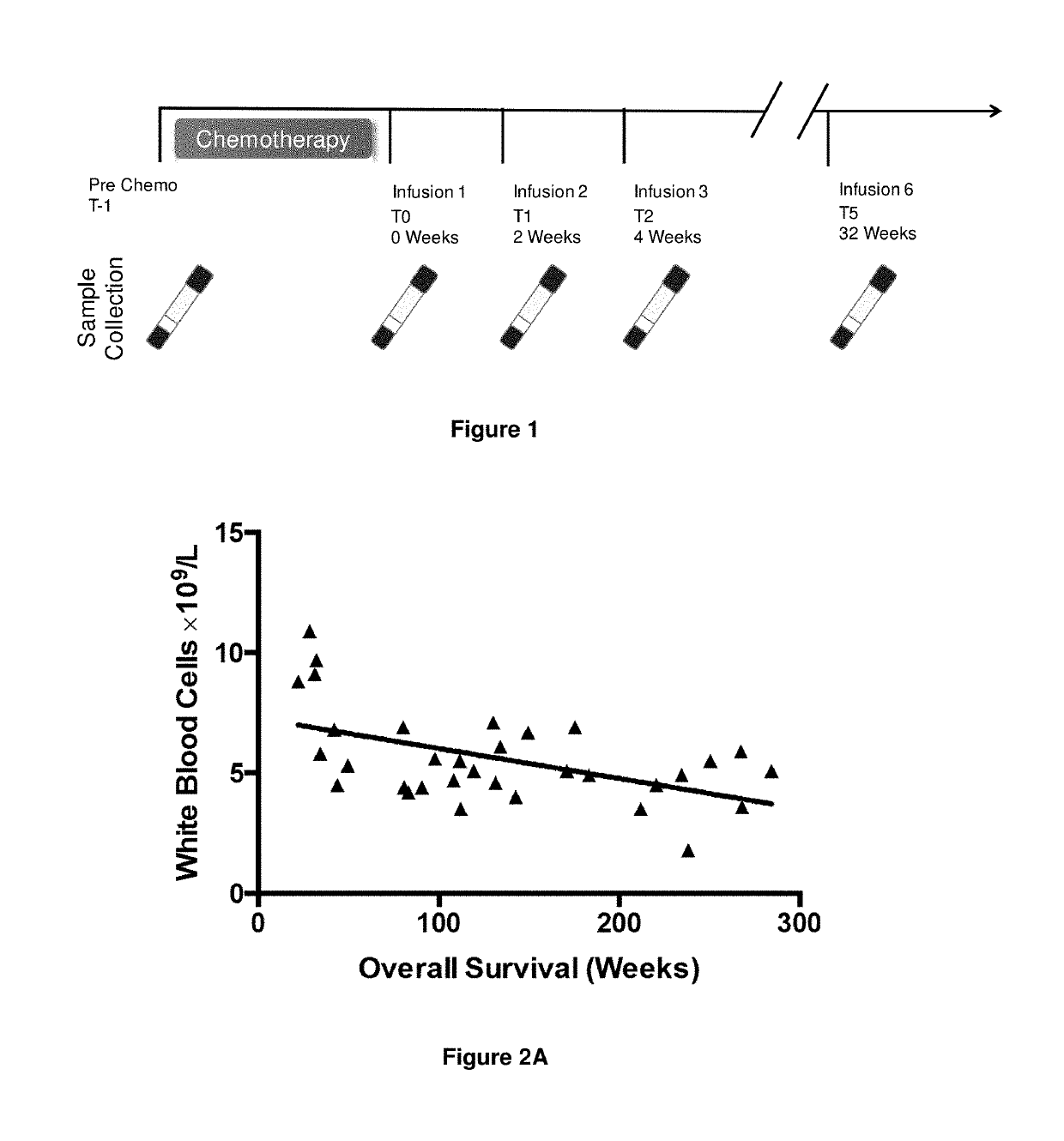
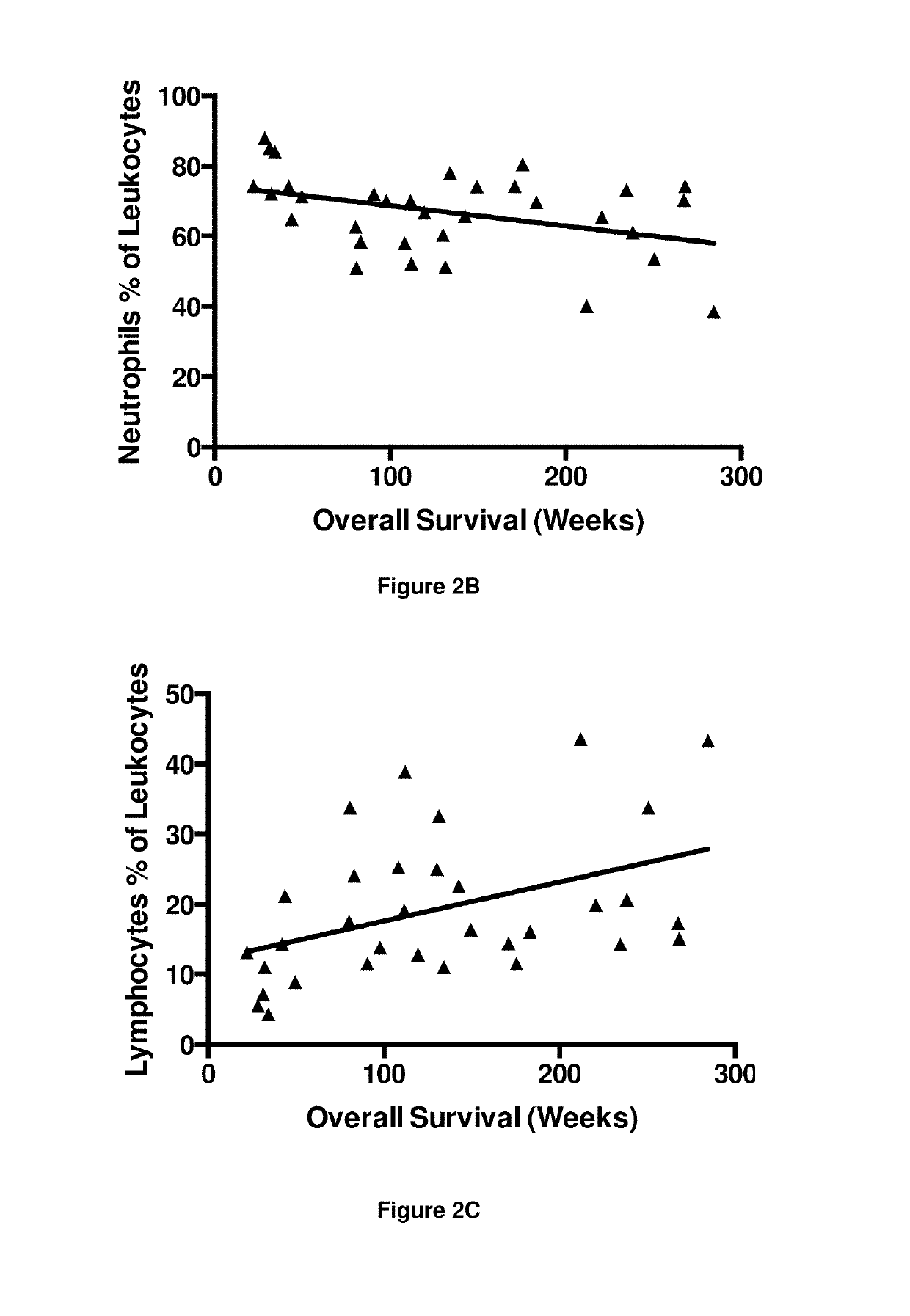
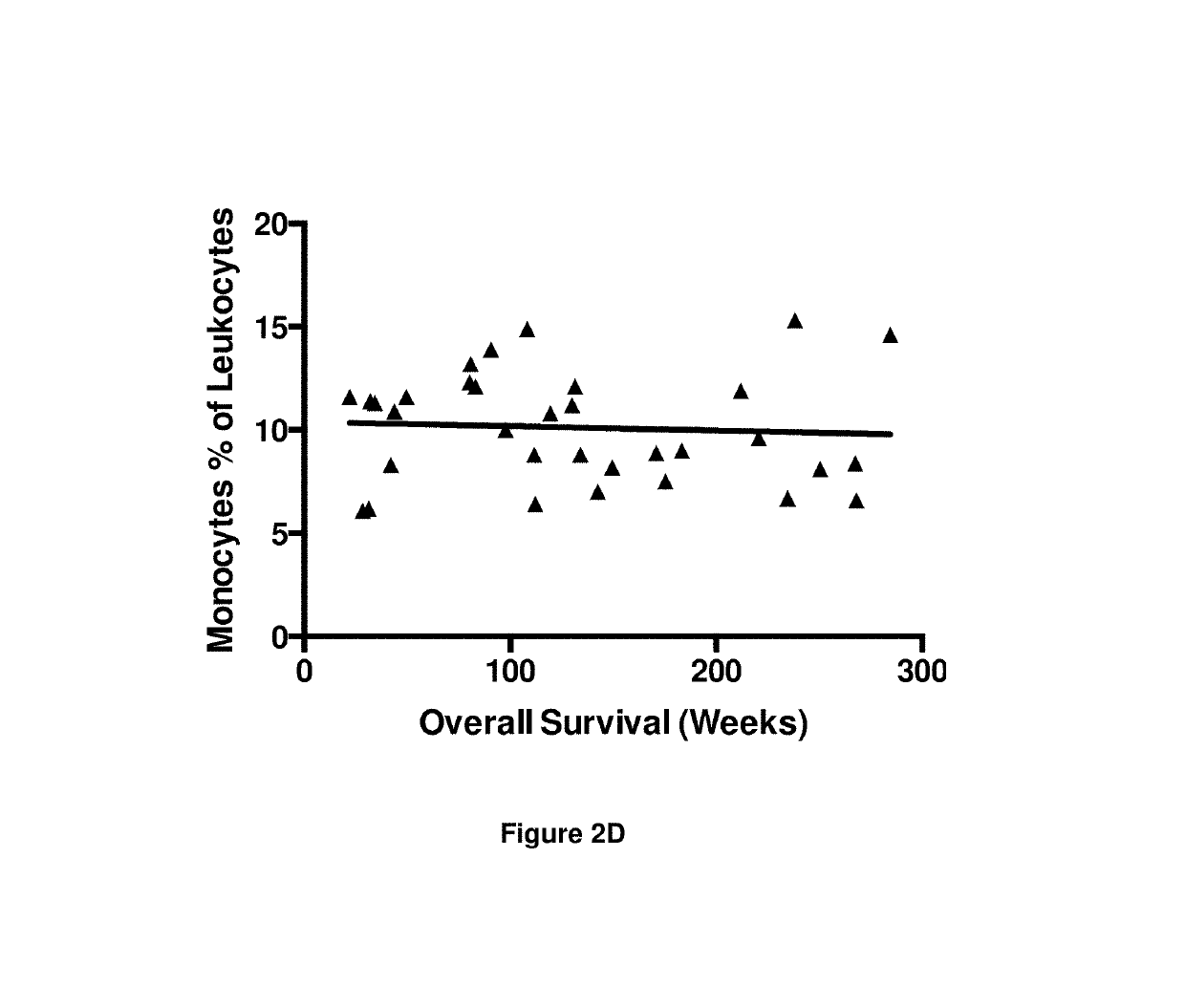
A method for predicting whether a patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of a disease by adoptive cell transfer (ACT), is disclosed comprising: (i) analyzing a blood-derived sample obtained from the patient for one or more prognostic markers of long-term survival on treatment of a disease by ACT, and; (ii) based on the analysis of step (i), predicting whether the patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of the disease by ACT. Also disclosed are methods for treating a patient by ACT, methods for selecting a patient for treatment by ACT, and methods for selecting a patient for treatment of a disease by ACT.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE LTD +2
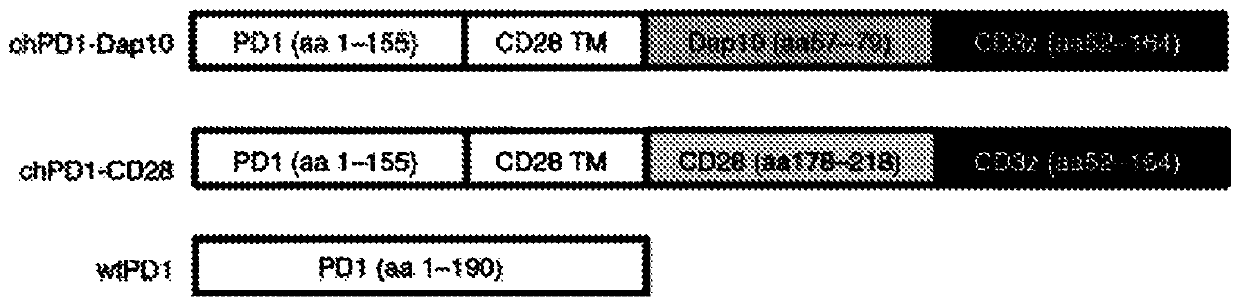
Pd1-specific chimeric antigen receptor as an immunotherapy
ActiveUS20200281974A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorEngineered genetic
Provided herein are methods and compositions useful for treating PDL1 and / or PDL2 positive cancers through adoptive cell transfer of T cells genetically engineered to express a PD1-specific chimeric antigen receptor. Co-stimulatory domains such as Dap 10 may be included to enhance efficacy.
Owner:LONGWOOD UNIVERSITY
Marker-suicide gene useful in adoptive cell therapy
ActiveUS10925943B2Valid choiceEasy to packAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingAdoptive cell transfer
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
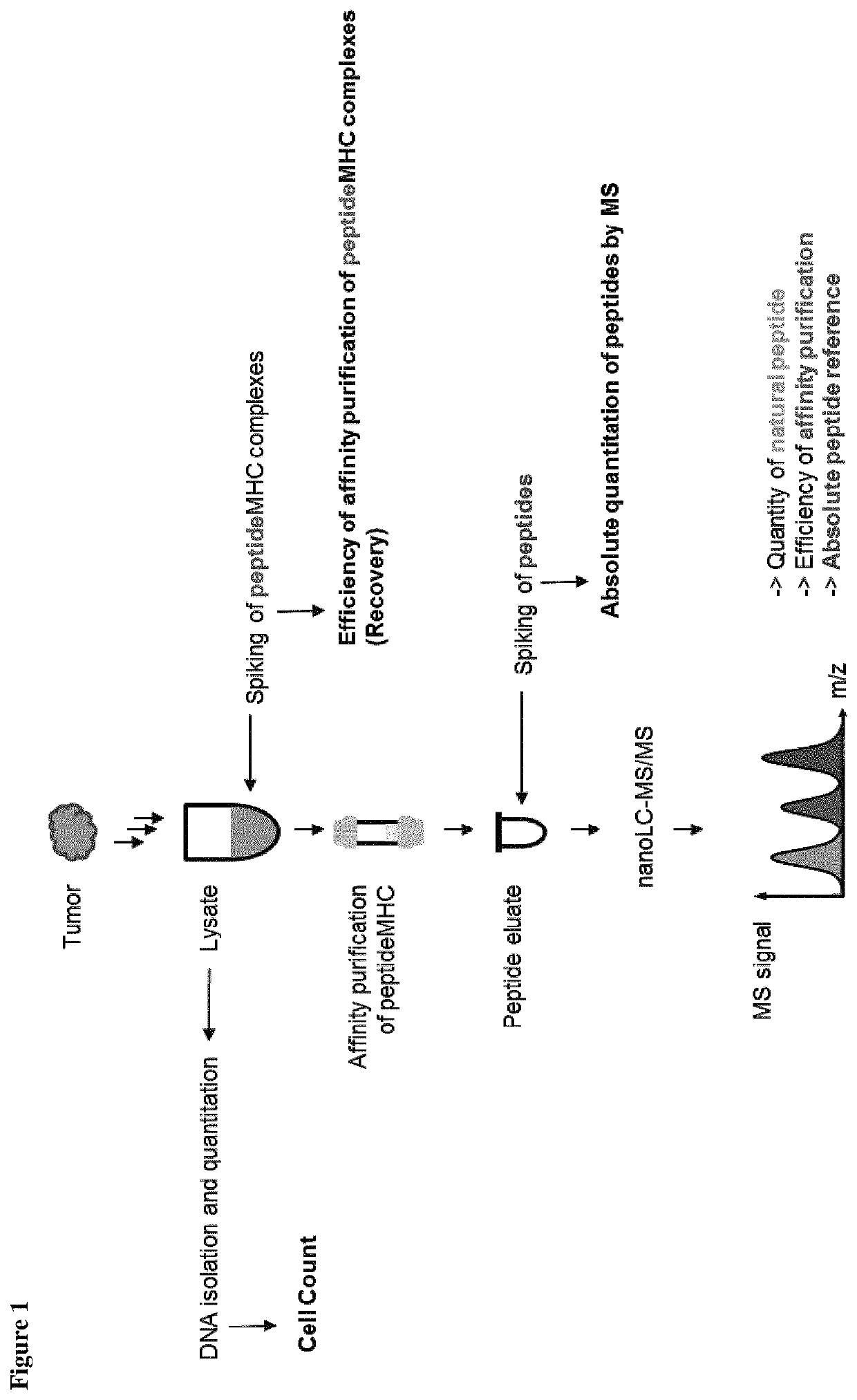
Method for the absolute quantification of naturally processed HLA-restricted cancer peptides
ActiveUS10545154B2Efficiency and precisionEasy to handleMass spectrometric analysisOmicsPeptide antigenAutoimmune condition
The present invention relates to a method for the absolute quantification of naturally processed HLA-restricted cancer peptides, i.e. the determination of the copy number of peptide(s) as presented per cell. The present invention can not only be used for the development of antibody therapies or peptide vaccines, but is also highly valuable for a molecularly defined immuno-monitoring, and useful in the processes of identifying of new peptide antigens for immunotherapeutic strategies, such as respective vaccines, antibody-based therapies or adoptive T-cell transfer approaches in cancer, infectious and / or autoimmune diseases.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Novel RNA construct and methods of use thereof for enhancing the therapeutic effects of cytotoxic cells and stem cells
The present invention comprises Rig I agonists for enhancing the effects of cytotoxic cells and stem Cells. The Rig I agonists can be used in vivo as small molecule therapeutics or in vitro to enhance cells for adoptive cell transfer. Applications include cancer therapy, immune system enhancement, chronic viral infection and treatment of viral induced inflammation and enhancement of virus based therapies.
Owner:VYCELLIX INC
Methods and compositions for treating cancer
ActiveUS20190076385A1Easy to useEnhance immune functionOrganic active ingredientsGenetically modified cellsAntigenCo administration
Methods for treating cancer are disclosed which comprise administering to a subject T cells which have been pretreated ex vivo or in vitro with a fatty acid catabolism promoter to condition the T cell to use fatty acids rather than glucose for energy production. Still other methods comprise co-administering to a subject having a cancer characterized by a solid tumor (a) an immunotherapeutic composition targeting an antigen or ligand on the tumor cell; and (b) a compound or reagent that promotes the use of fatty acid catabolism by tumor antigen-specific T cells in the tumor microenvironment and / or T cells pretreated ex vivo with the fatty acid catabolism promoter to condition the T cell to use fatty acids rather than glucose for energy production for adoptive cell transfer. Both methods may also employ co-administration of a checkpoint inhibitor.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY
Method for the absolute quantification of naturally processed hla-restricted cancer peptides
PendingUS20200103408A1Efficiency and precisionEasy to handleMass spectrometric analysisOmicsPeptide antigenAutoimmune condition
The present invention relates to a method for the absolute quantification of naturally processed HLA-restricted cancer peptides, i.e. the determination of the copy number of peptide(s) as presented per cell. The present invention can not only be used for the development of antibody therapies or peptide vaccines, but is also highly valuable for a molecularly defined immuno-monitoring, and useful in the processes of identifying of new peptide antigens for immunotherapeutic strategies, such as respective vaccines, antibody-based therapies or adoptive T-cell transfer approaches in cancer, infectious and / or autoimmune diseases.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Auto/allo-immune defense receptors for the selective targeting of activated pathogenic t cells and nk cells
PendingUS20210077530A1Easy to usePrevent rejectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsReceptor
Embodiments of the disclosure concern engineered auto / allo-immune defense receptor (ADR)-expressing T cells that selectively target activated T cells, including pathogenic T cells, to incapacitate them. The chimeric receptors comprise moieties for targeting 4-1BB, 0X40, and CD40L, for example, whose expression is indicative of activated T cells. In particular embodiments, there are methods of preventing or treating conditions associated with activated T cells using adoptive T-cell transfer of cells encoding the ADRs.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Method of producing leukocytes using ptpn2 inhibition for adoptive cell transfer
PendingUS20210052648A1Efficient preparationIncrease capacityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyWhite blood cellAdoptive cell transfer
The present invention generally relates to methods of preparing leukocytes, particularly T cells, ex vivo for use in immunotherapy, particularly cancer immunotherapy. More specifically, the invention relates to methods for the preparation of leukocytes exhibiting cytotoxic properties for use in adoptive cell transfer. The invention also relates to cells and compositions including them for cancer immunotherapy. The invention also relates to methods of immunotherapy, particularly cancer immunotherapy. The present invention relates to a method for producing a leukocyte that has an enhanced capacity for killing a target cell, the method including contacting the leukocyte with a PTPN2 inhibitor in conditions for enabling the inhibitor to inactivate PTPN2 in the leukocyte, thereby producing a leukocyte that has an enhanced capacity for killing a target cell. Preferably, the leukocyte is contacted with the PTPN2 inhibitor in the absence of a T helper cell.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
Clinical correlates of immunotherapy efficacy
InactiveUS20170312355A1Accurate identificationAccurate powerMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiviralsDiseasePrognosis biomarker
A method for predicting whether a patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of a disease by adoptive cell transfer (ACT), is disclosed comprising: (i) analysing a blood-derived sample obtained from the patient for one or more prognostic markers of long-term survival on treatment of a disease by ACT, and; (ii) based on the analysis of step (i), predicting whether the patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of the disease by ACT. Also disclosed are methods for treating a patient by ACT, methods for selecting a patient for treatment by ACT, and methods for selecting a patient for treatment of a disease by ACT.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE +2
Auto/allo-immune defense receptors for the selective targeting of activated pathogenic t cells and nk cells
PendingUS20220000920A1Easy to usePrevent rejectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsReceptor
Embodiments of the disclosure concern engineered auto / allo-immune defense receptor (ADR)-expressing T cells that selectively target activated T cells, including pathogenic T cells, to incapacitate them. The chimeric receptors comprise moieties for targeting 4-1BB, OX40, and CD40L, for example, whose expression is indicative of activated T cells. In particular embodiments, there are methods of preventing or treating conditions associated with activated T cells using adoptive T-cell transfer of cells encoding the ADRs.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Cells, compositions and methods for enhancing immune function
PendingCN113905747AImprove retentionImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsCD8Oncology
The present disclosure relates generally to polypeptides, cells, compositions and methods for enhancing immune function, and in particular the immune function of T cells, such as CD8+ T cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to modified DNAM-1 polypeptides, T cells expressing recombinant and / or modified DNAM-1, and methods of using these cells in adoptive T cell transfer, such as for the treatment of cancer or infection. The disclosure also relates to methods for preparing T cells with enhanced immune function; methods for preparing T cells for adoptive cell therapy; methods for assessing the immune function of T cells in a subject or cell population; methods for predicting the responsiveness of a subject with cancer to cancer therapy; and methods for predicting the survival or survival time of a subject with cancer.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
Method for treating epstein-barr virus - positive cancer with immunotherapy
InactiveUS20190381167A1Reduce the amount requiredReduced activityMicrobiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsDiseasePrognosis biomarker
A method for predicting whether a patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of a disease by adoptive cell transfer (ACT), is disclosed comprising: (i) analysing a blood-derived sample obtained from the patient for one or more prognostic markers of long-term survival on treatment of a disease by ACT, and; (ii) based on the analysis of step (i), predicting whether the patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of the disease by ACT. Also disclosed are methods for treating a patient by ACT, methods for selecting a patient for treatment by ACT, and methods for selecting a patient for treatment of a disease by ACT.
Owner:TESSA THERAPEUTICS PTE LTD +2
Cells, compositions and methods for enhancing immune function
PendingUS20220135642A1Increased cell surface expressionImprove retentionImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsAdoptive cellular therapyCD8
The present disclosure relates generally to polypeptides, cells, compositions and methods for enhancing immune function, and in particular the immune function of T cells, such as CD8+ T cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to modified DNAM-1 polypeptides, T cells expressing recombinant and / or modified DNAM-1, and methods of using these cells in adoptive T cell transfer, such as for the treatment of cancer or infection. The disclosure also relates to methods for preparing T cells with enhanced immune function; methods for preparing T cells for adoptive cell therapy; methods for assessing the immune function of T cells in a subject or cell population; methods for predicting the responsiveness of a subject with cancer to cancer therapy; and methods for predicting the survival or survival time of a subject with cancer.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
Methods to mobilize tissue resident cells for adoptive t cell therapy
ActiveUS11213546B2Organic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAdoptive cell transferCell subpopulations
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
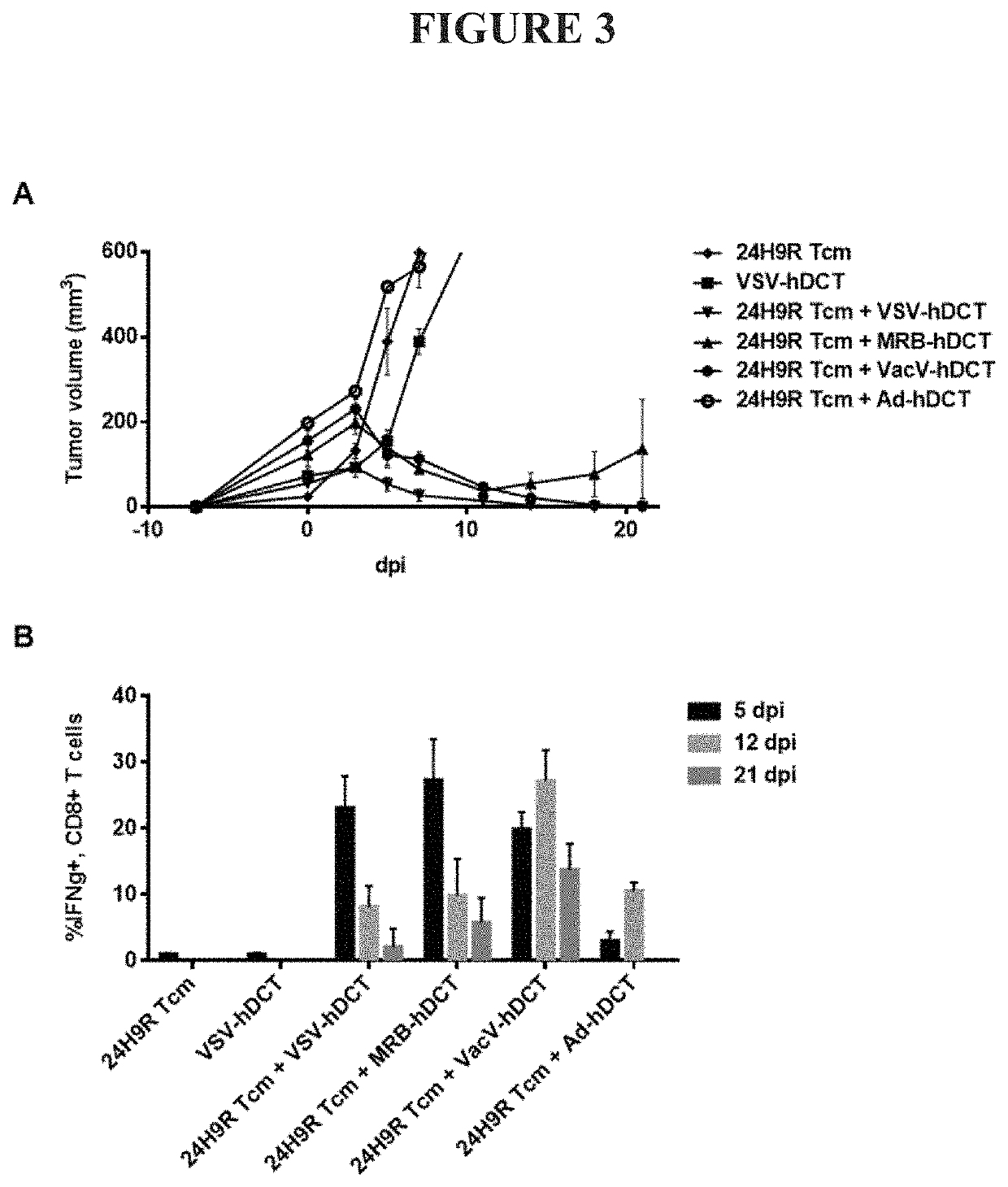
Adoptive cell transfer and oncolytic virus combination therapy
InactiveUS20210338732A1High selectivitySsRNA viruses negative-senseMammal material medical ingredientsCD8Tumor antigen
The present invention describes a method for treating cancer comprising adoptive transfer of tumor antigen specific CD8+ T cells and an oncolytic virus vaccine targeting the same antigen.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Chimeric antigen receptor tumor infiltrating lymphocytes
Disclosed are compositions and methods for targeted treatment of infections and cancers expressing cancers. In particular, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are genetically engineered to express chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) polypeptides to produce CAR-TILs that can be used with adoptive cell transfer to target, penetrate, and kill solid tumor masses. Therefore, also disclosed are methods of providing an immunotherapy in a subject with an infection or cancer that involves adoptive transfer of the disclosed CAR-TILs.
Owner:H 李 莫菲特癌症中心和研究所公司
Pd1-specific chimeric antigen receptor as immunotherapy
InactiveCN111433354APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorEngineered genetic
Provided herein are methods and compositions useful for treating PDL1 and / or PDL2 positive cancers through adoptive cell transfer of T cells genetically engineered to express a PD1-specific chimeric antigen receptor. Co-stimulatory domains such as Dap 10 may be included to enhance efficacy.
Owner:朗沃德大学
Method of enhancing persistence of adoptively infused t cells
PendingUS20210017493A1Improving efficacy and viabilityGood curative effectImmunoglobulin superfamilyGenetically modified cellsAdoptive cell transferCytokine
The present disclosure provides for methods of improving the efficacy of T cells. In an aspect, the disclosure further provides for methods of enhancing the persistence of T cells for adoptive cell transfer or therapy (ACT). Cytokine sensitivity assays (CSA) and associated methodology capable of predicting the persistence of adoptively infused T Cells are further provided for by way of the instant disclosure. The disclosure also provides for methods of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof as well as T cells populations produced by methods described herein.
Owner:IMMATICS US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com