Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Multivalent binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
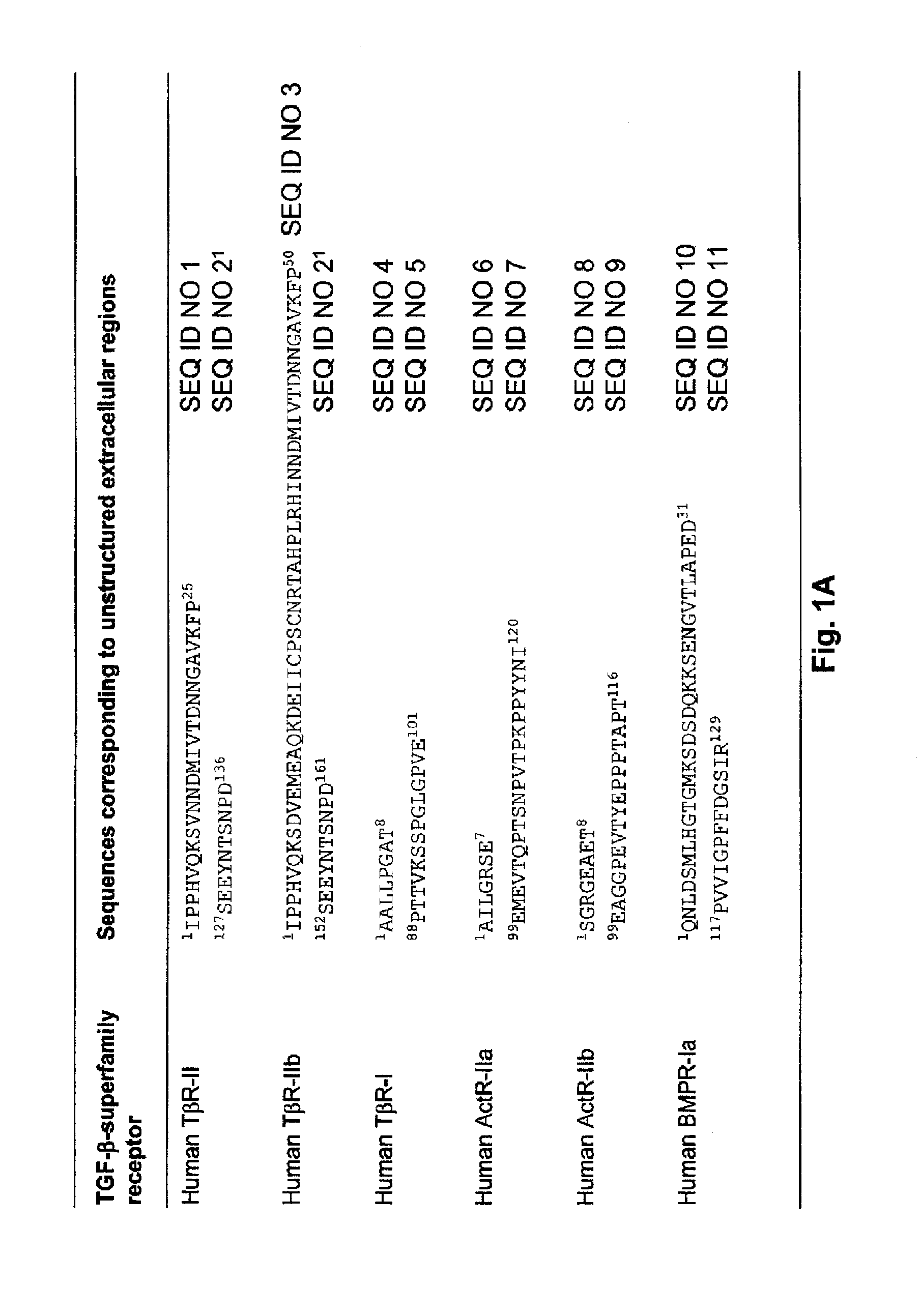
Compositions monovalent for CD40L binding and methods of use
ActiveUS20060062784A1Promote formationAvoid inductionNervous disorderAntipyreticVariable domainMultivalent binding
The invention relates to antibody polypeptides that monovalently bind CD40L. Antibody polypeptides that are monovalent for binding of CD40L can inhibit CD40L activity while avoiding potential undesirable effects that can occur with antibodies capable of divalent or multivalent binding of CD40L. In one aspect, a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide consists of or comprises a single immunoglobulin variable domain that specifically binds and antagonizes the activity of CD40L, preferably without substantially agonizing CD40 activity. In another aspect, the monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide is a human antibody polypeptide. The invention further encompasses methods of antagonizing CD40 / CD40L interactions in an individual and methods of treating diseases or disorders involving CD40 / CD40L interactions, the methods involving administering a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide to the individual.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptides and compositions thereof
ActiveUS7563443B2Improve stabilityIncrease in sizeNervous disorderMetabolism disorderDiseaseVariable domain
The invention relates to antibody polypeptides that monovalently bind CD40L. Antibody polypeptides that are monovalent for binding of CD40L can inhibit CD40L activity while avoiding potential undesirable effects that can occur with antibodies capable of divalent or multivalent binding of CD40L. In one aspect, a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide consists of or comprises a single immunoglobulin variable domain that specifically binds and antagonizes the activity of CD40L, preferably without substantially agonizing CD40 activity. In another aspect, the monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide is a human antibody polypeptide. The invention further encompasses methods of antagonizing CD40 / CD40L interactions in an individual and methods of treating diseases or disorders involving CD40 / CD40L interactions, the methods involving administering a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide to the individual.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
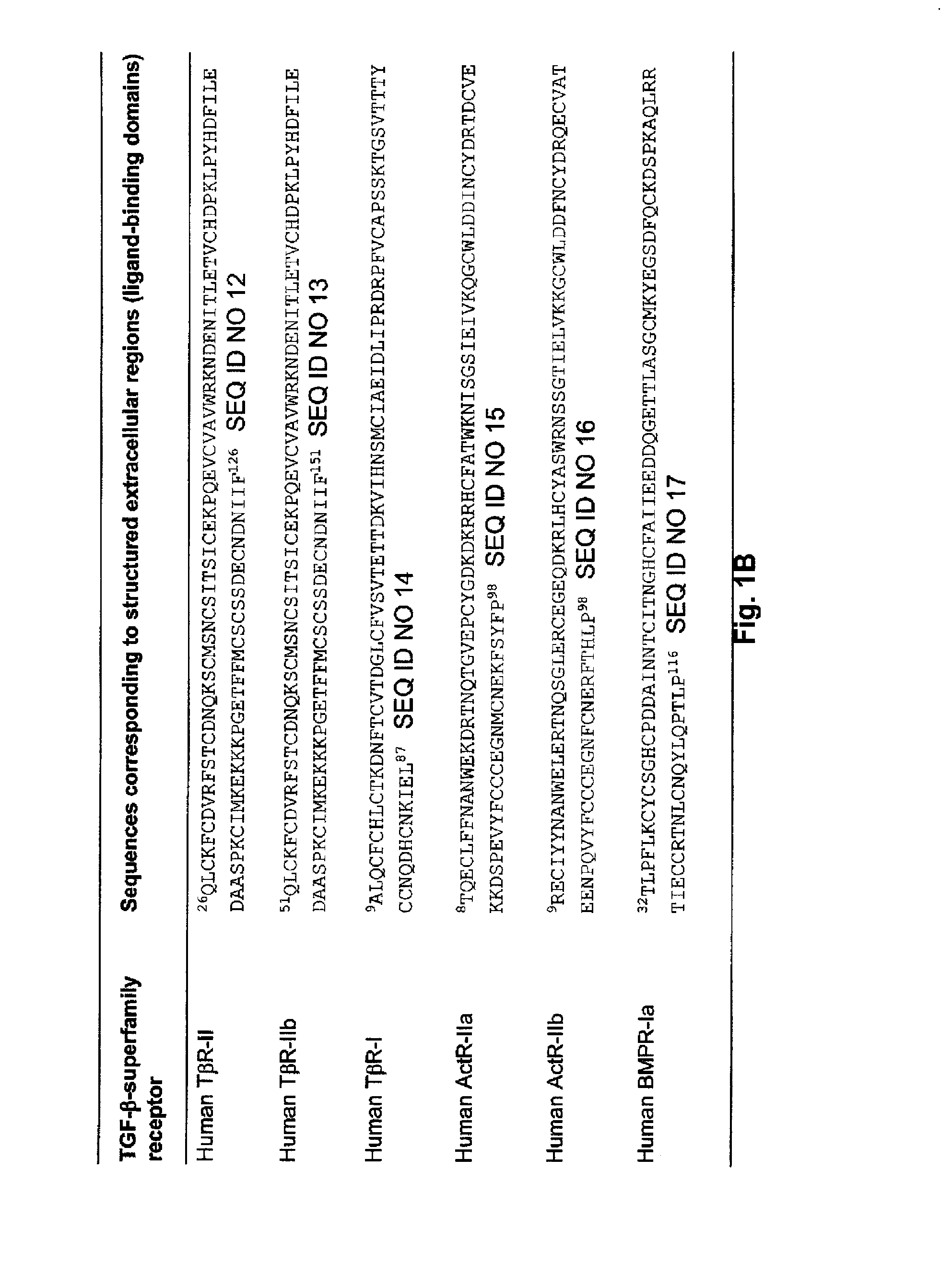
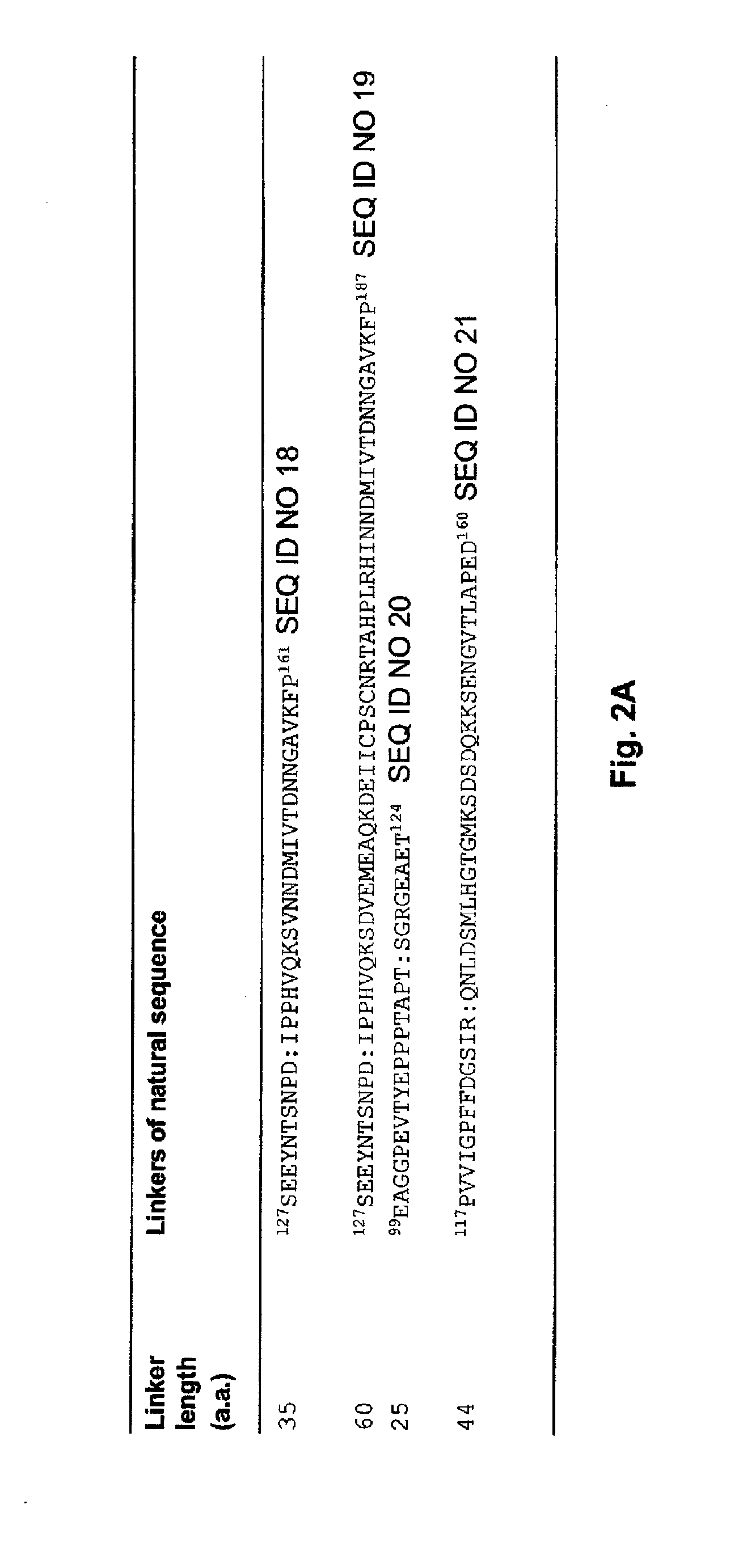
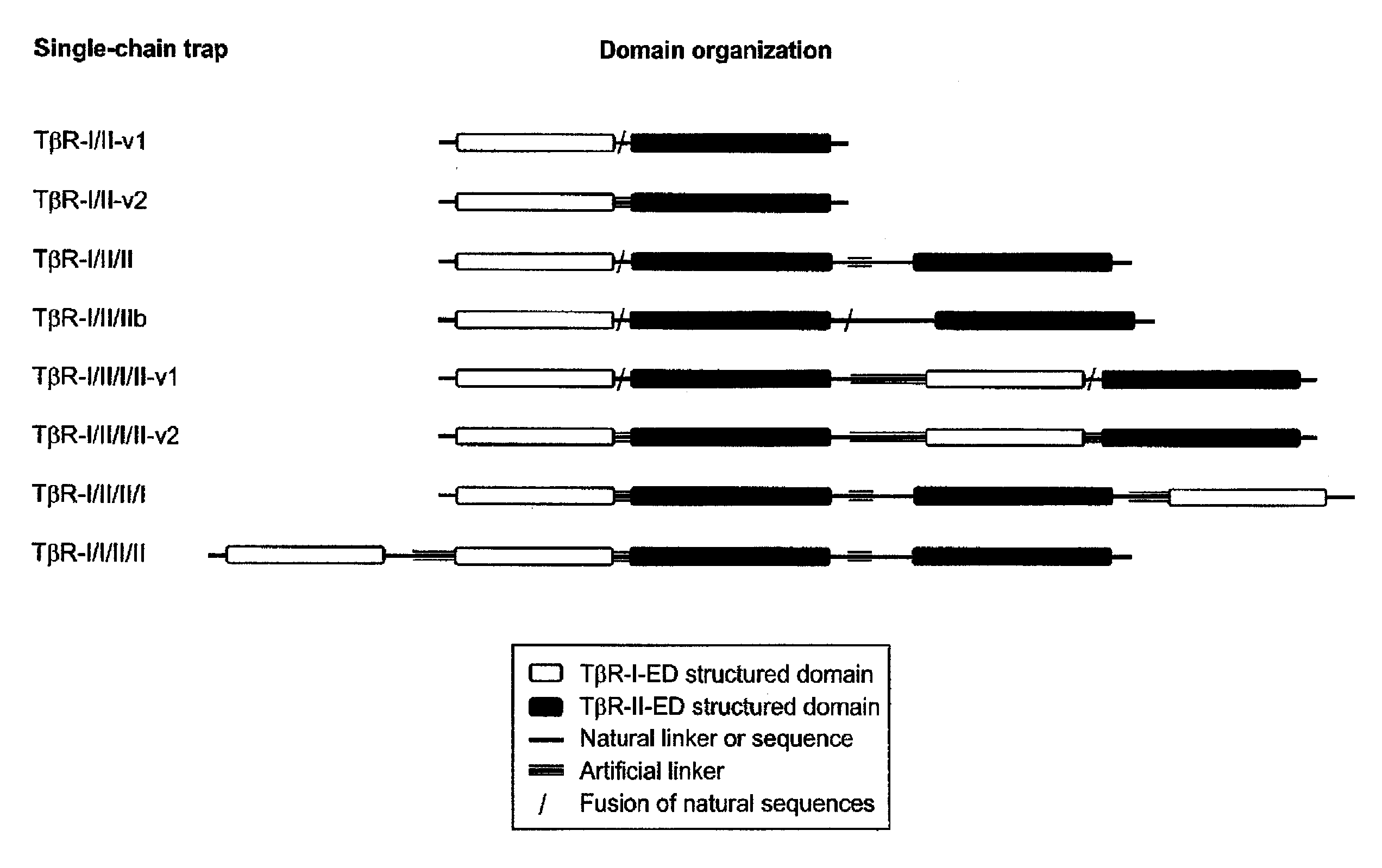
Antagonists of ligands and uses thereof
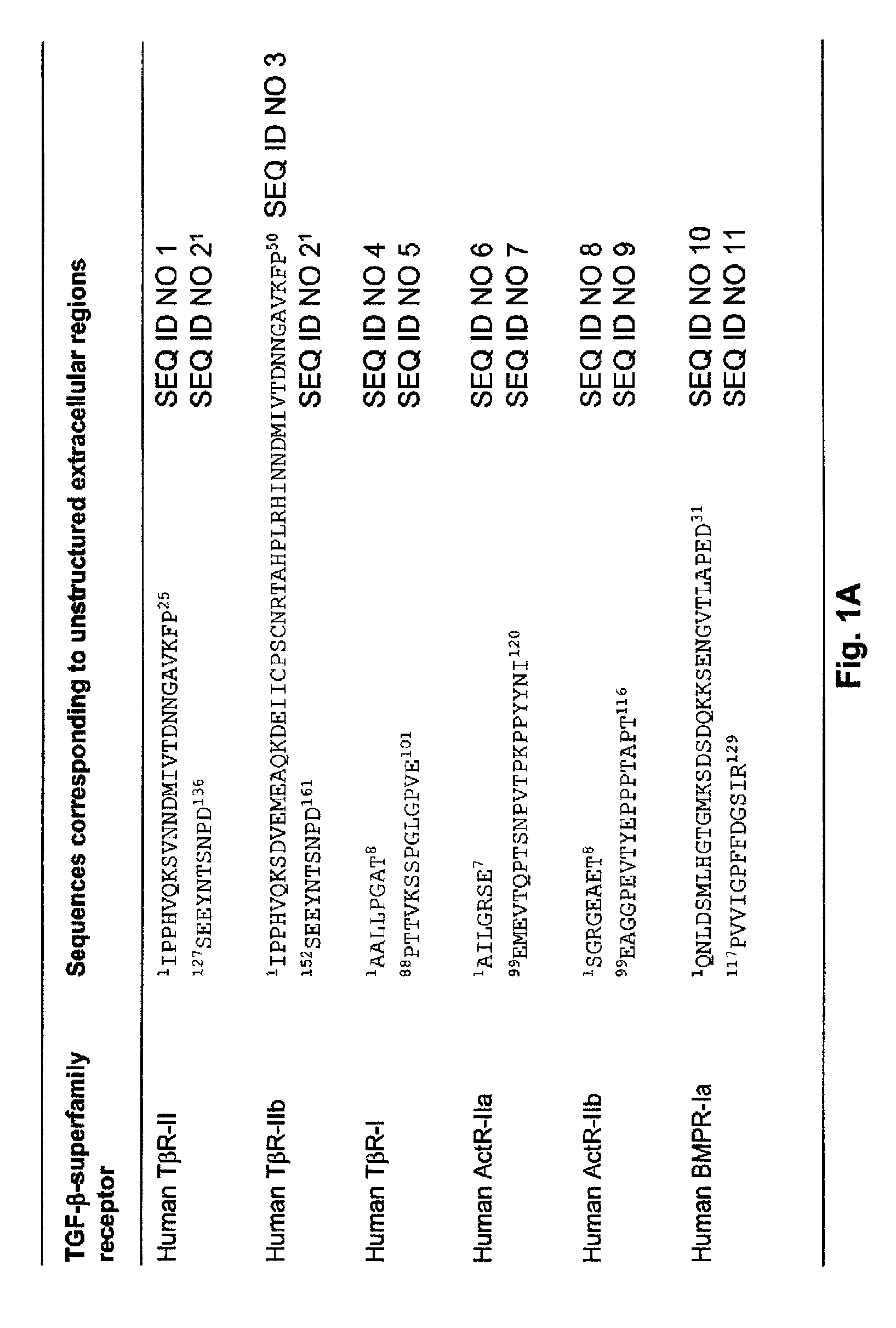
ActiveUS20110236309A1Permitting modulation of cellular responseAvoid interactionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding domainMultivalent binding
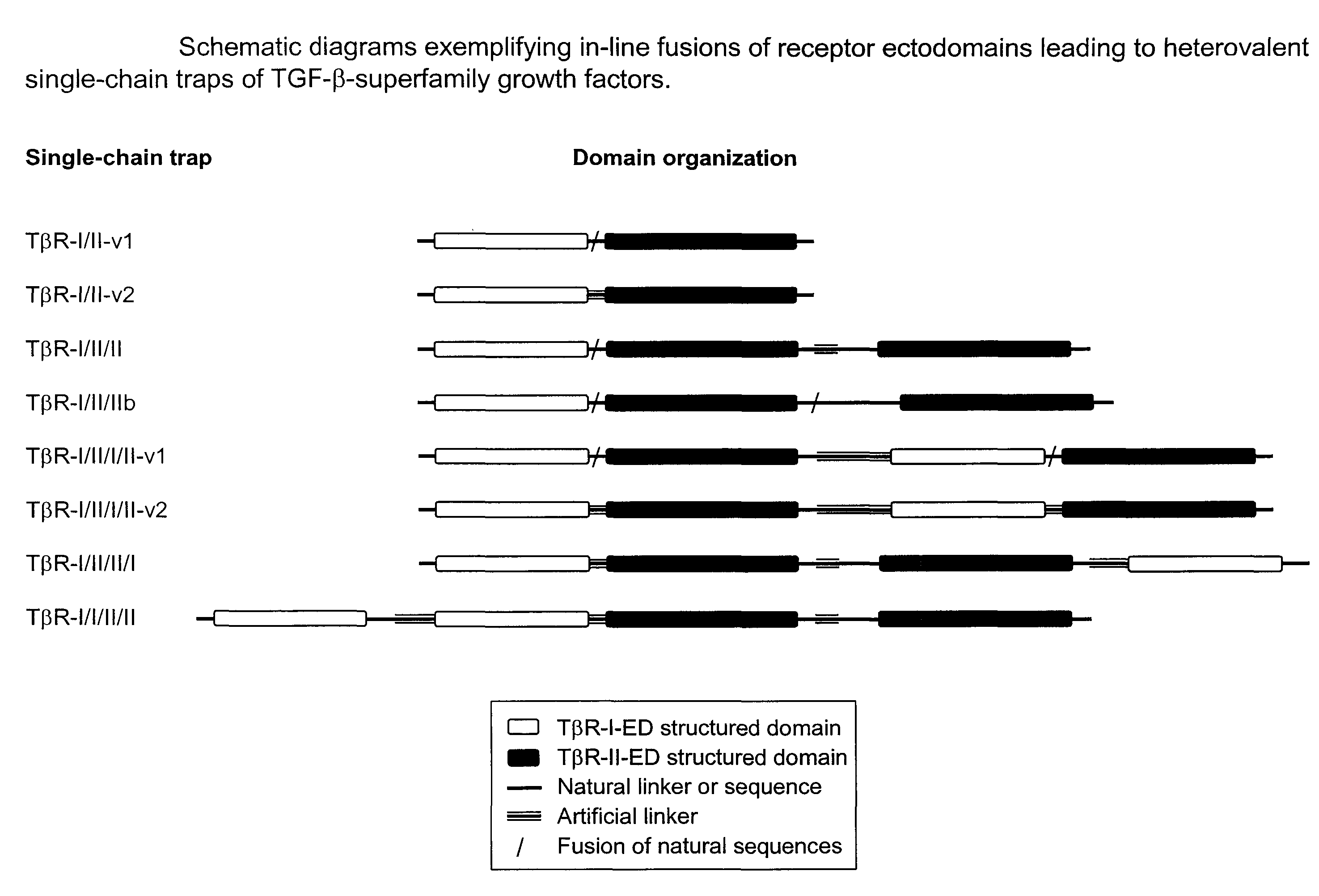
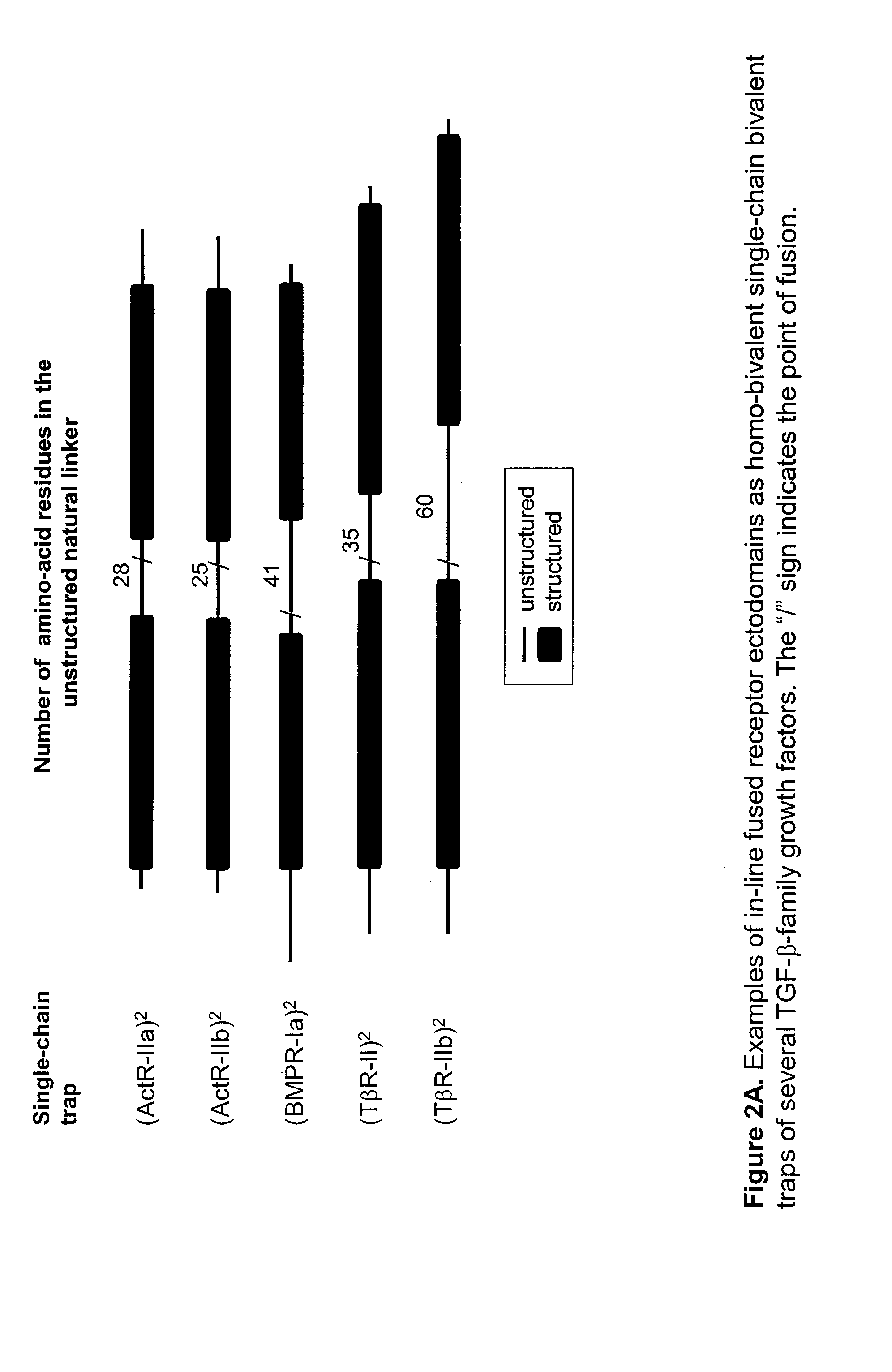
The invention provides hetero-multivalent ligand binging agents (traps) for members of the TGF-β superfamily, as well as methods for making and using such constructs. In an embodiment of the invention there is provided a hetero-multivalent binding agent with affinity for a member of the TGF-β superfamily, said agent comprising the general structure (I): (<bd1>-linker1)k-[{<bd1>-linker2-<bd2>-linker3r-}n-(<bd3>)m-(linker4-<bd4>)d]h, where bd1, bd2, bd3 and bd4 are polypeptide binding domains having an affinity for different sites on the same member or for different members of the TGF-β superfamily, wherein at least two of bd1, bd2, bd3, and bd4 are different from each other.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Antagonists of ligands and uses thereof
ActiveUS8658135B2Minimizing energyReduce incompatibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding domainMultivalent binding
The invention provides hetero-multivalent ligand binging agents (traps) for members of the TGF-beta superfamily, as well as methods for making and using such constructs. In an embodiment of the invention there is provided a hetero-multivalent binding agent with affinity for a member of the TGF-beta superfamily. The agent comprises the general structure I: (<bd1>-linker1)k-[{<bd1>-linker2-<bd2>-linker3f-}n-(<bd3>)m-(linker4-<bd4>)d]h, where bd1, bd2, bd3 and bd4 are polypeptide binding domains having an affinity for different sites on the same member or for different members of the TGF-beta superfamily; at least two of bd1, bd2, bd3, and bd4 are different from each other.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Peptide linkers for effective multivalent peptide binding
InactiveUS20100158823A1High binding affinityPromotes and enhances multivalent bindingCosmetic preparationsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTarget surfaceBinding peptide
Short single chain peptides having affinity for a target surface often lack the binding durability required for certain commercial applications. One way to improve durability is to promote multivalent binding by linking together binding sequences using peptide linkers. However, the resulting single chain binding peptides often suffer from linker entropy. It has been discovered that the use of rigid peptide linkers when linking together multiple binding sequences enhances the binding affinity of the resulting single chain peptide.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Compositions monovalent for CD40L binding and methods of use
ActiveCN101061140AImprove stabilityAvoid approachingImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseVariable domain
The invention relates to antibody polypeptides that monovalently bind CD40L. Antibody polypeptides that are monovalent for binding of CD40L can inhibit CD40L activity while avoiding potential undesirable effects that can occur with antibodies capable of divalent or multivalent binding of CD40L. In one aspect, a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide consists of or comprises a single immunoglobulin variable domain that specifically binds and antagonizes the activity of CD40L, preferably without substantially agonizing CD40 activity. In another aspect, the monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide is a human antibody polypeptide. The invention further encompasses methods of antagonizing CD40 / CD40L interactions in an individual and methods of treating diseases or disorders involving CD40 / CD40L interactions, the methods involving administering a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide to the individual.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Antagonist of ligands and uses thereof
ActiveUS8318135B2Minimizing energyReduce incompatibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBinding domain
The invention provides multivalent ligand binding agents (traps) for members of the TGF-β superfamily and polypeptide linkers and methods for making and using such constructs. The traps may be used as therapeutic or diagnostic (imaging or non-imaging) agents for diseases / disorders caused by over-production / activity of the target ligand. In an embodiment of the invention there is provided a multivalent binding agent with affinity for a member of the TGF-β superfamily, the agent having the general structure I:(<bd1>-linker1)k-[{<bd1>-linker2-<bd2>linker3f-}n-(<bd3>)m-(linker4-<bd4>)d]h,where:n and h are independently greater than or equal to 1;d, f, m and k are independently equal to or greater than zero;bd1, bd2, bd3 and bd4 are polypeptide binding domains having an affinity for the same member of the TGF-β superfamily, with bd1, bd2, bd3, and bd4 being independently the same or different from each other; and,linker1, linker2, linker3 and linker4 are unstructured polypeptide sequences;wherein the number of amino acids in each linker is determined independently and is greater than or equal to X / 2.5; where,X equals the shortest linear distance between:(a) the C-terminus of an isolated form of the binding domain that is located at the N-terminus of the linker and that is specifically bound to its ligand; and,(b) the N-terminus of an isolated form of the binding domain that is located at the C-terminus of the linker and that is specifically bound to its ligand.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Anti-cd40 antibodies, uses and methods
ActiveUS20140348836A1Strong binding specificityMinimizing systemic exposureHybrid immunoglobulinsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiseaseDendritic cell
The present invention relates to antibodies (and fragments, variants, fusions and derivatives thereof) with multivalent binding specificity for CD40, which have a potency for dendritic cell activation which is higher than, or is equal to, the potency for B cell activation and wherein the antibody, antigen-binding fragment, or fusion, variant or derivative thereof has an affinity (KD) for CD40 of less than 1×10−10 M, which have utility in the treatment of diseases such as cancer. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions, uses, methods and kits comprising such antibodies.
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
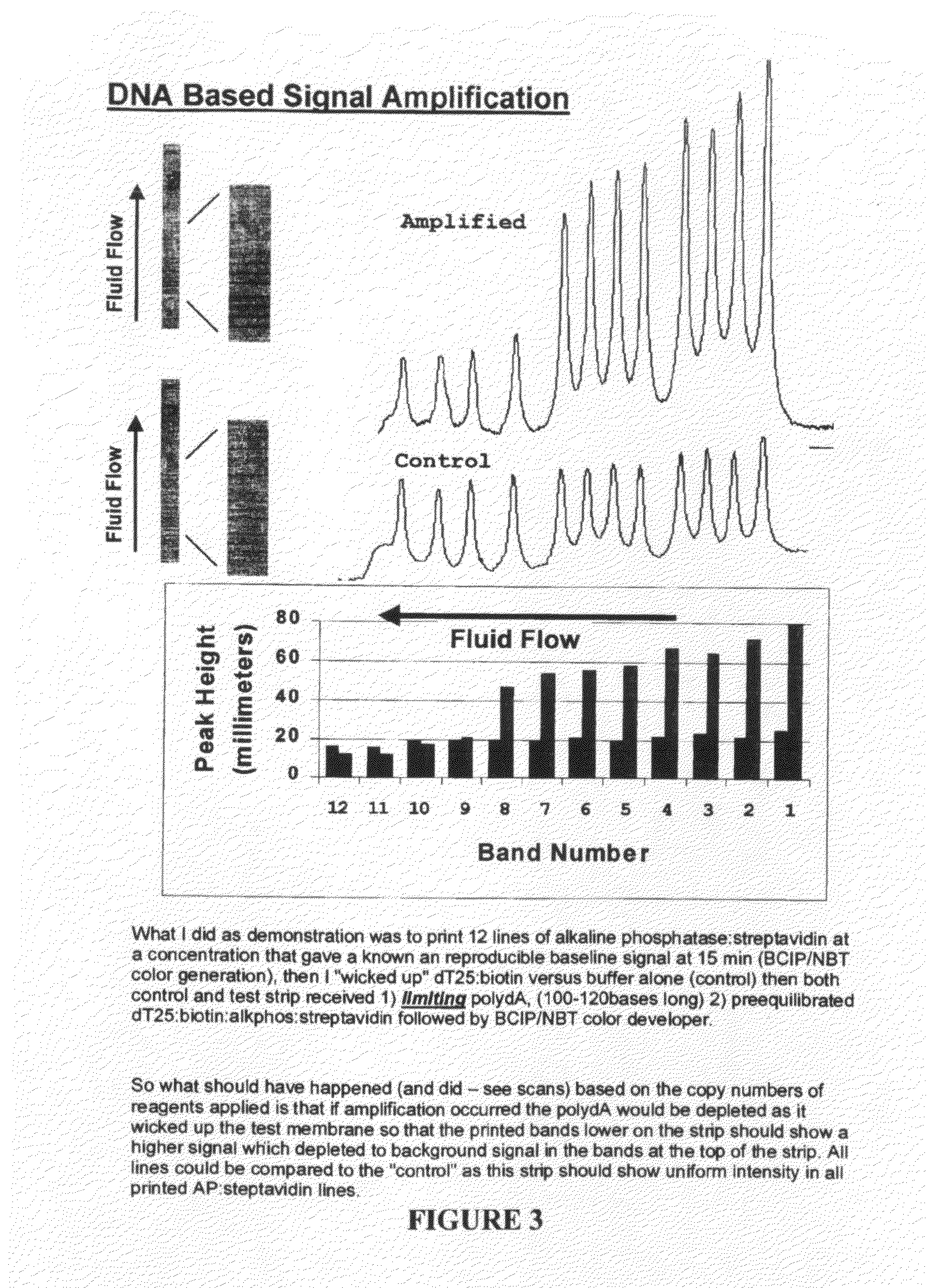
Methods and compositions for multivalent binding and methods for manufacture of rapid diagnostic tests
InactiveUS20100143905A1High affinityConstant gainMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresRapid screening testMultivalent binding
The invention provides reagents and methods for multivalent binding and quantitative capture of components in a sample. In one aspect, reagents and methods for diagnostic assay for antigen, ligand, binding agent, or antibody are provided. Compositions of a non-natural or deliberately constructed nucleic acid-like polymeric scaffold are provided, to which multiple antibodies, peptides or other binding agents can be affixed by hybridization of a oligonucleotide: binding agent complex such that the nucleic acid: binding agent construction displays multivalent behavior when interacting with a multivalent analyte. Methods for constructing and using the scaffolds are described. Such compositions may include assembly of mixed specificity binding agents such that the composition displays multivalent binding behavior against a target containing mixed analytes which can be bound by the construct to effect a binding affinity increase such as is observed in avidity reagents against single analytes expressed multiply on the target analyte. A manufacturing method for producing rapid diagnostic assays in a decentralized manner is also described. The method generates net economic advantages over conventional diagnostic manufacturing practices.
Owner:LANE MICHAEL J +2
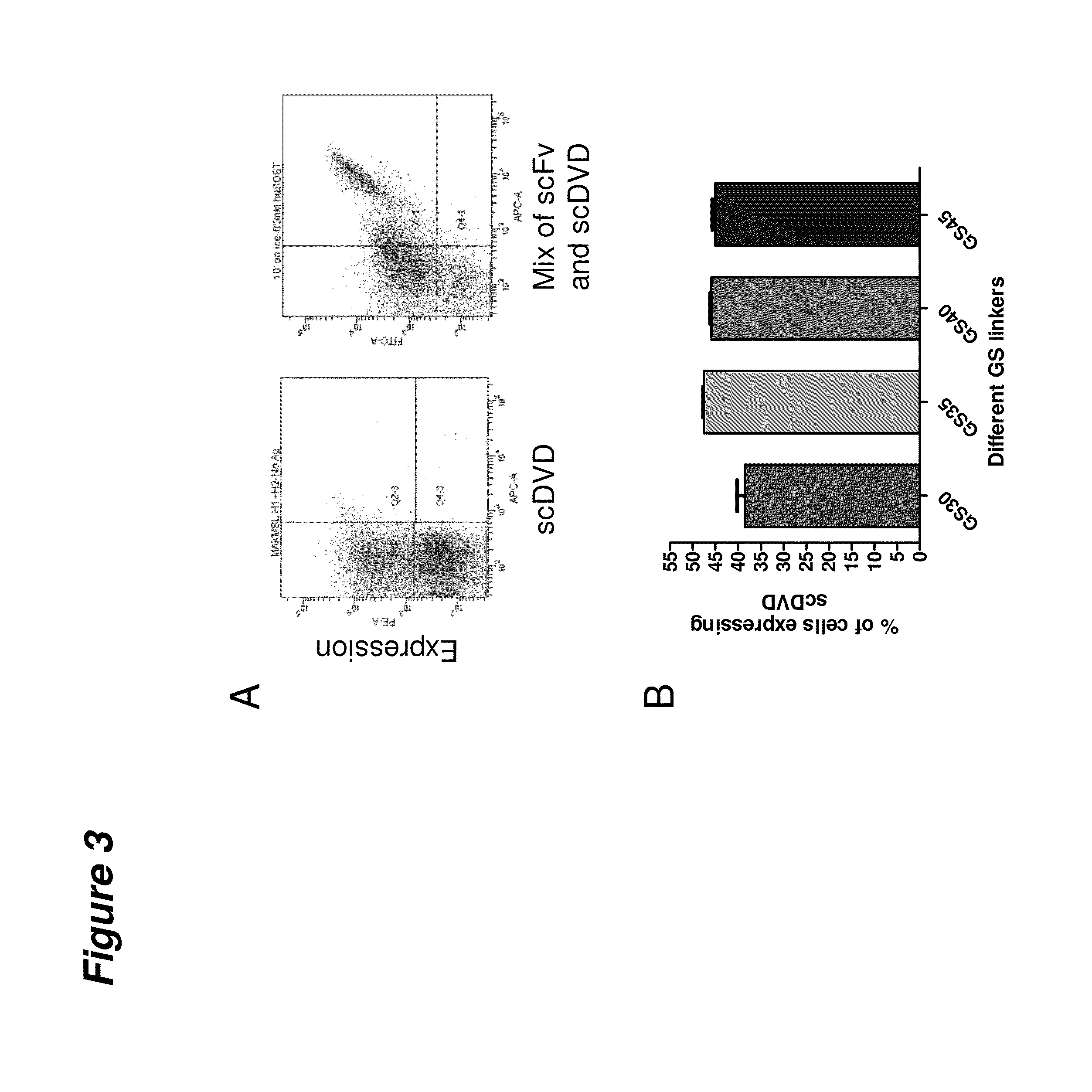
Multivalent binding protein compositions and methods for identifying variants of same
Provided are protein, nucleic acid, and cellular libraries of multivalent binding proteins (e.g., DVD-Fab or DVD-Ig molecules) and the use of these libraries for the screening of multivalent binding proteins using cell surface display technology (e.g., yeast display).
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Single-chain multivalent binding protein compositions and methods
InactiveUS20140221621A1High affinityPeptide librariesHybrid immunoglobulinsYeast displayMultivalent binding
Provided are protein, nucleic acid, and cellular libraries of single chain multivalent binding proteins (e.g., scDVD and scDVDFab molecules) and methods of using these of these libraries for the screening of single chain multivalent binding proteins using cell surface display technology (e.g., yeast display).
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Anti-CD40 antibodies and methods of treating cancer
ActiveUS9676862B2Good effectHybrid immunoglobulinsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiseaseDendritic cell
The present invention relates to antibodies (and fragments, variants, fusions and derivatives thereof) with multivalent binding specificity for CD40, which have a potency for dendritic cell activation which is higher than, or is equal to, the potency for B cell activation and wherein the antibody, antigen-binding fragment, or fusion, variant or derivative thereof has an affinity (KD) for CD40 of less than 1×10−10 M, which have utility in the treatment of diseases such as cancer. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions, uses, methods and kits comprising such antibodies.
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
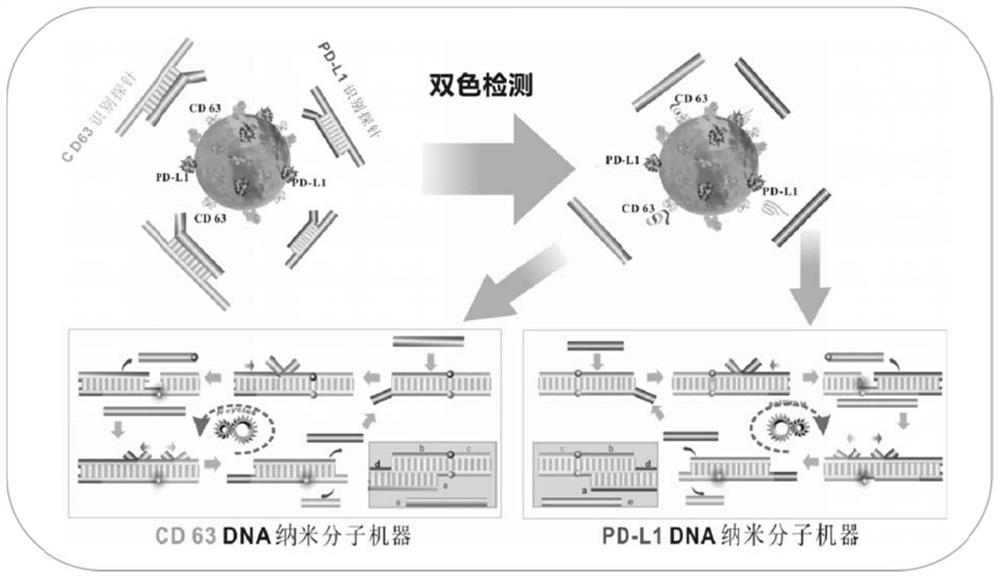
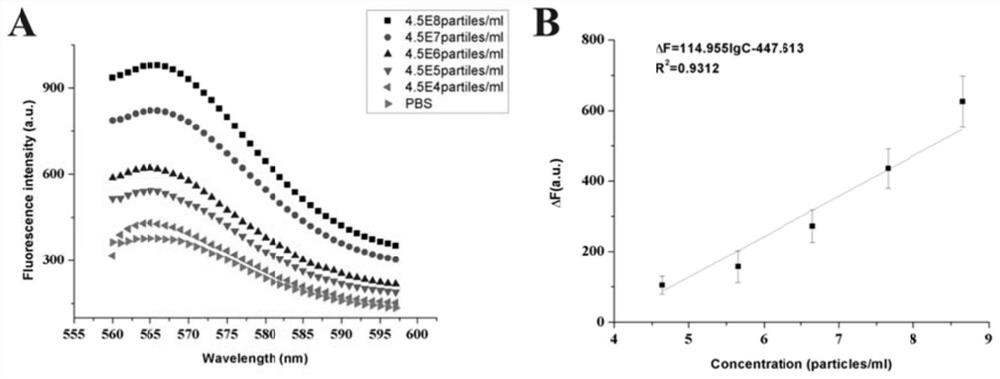
DNA nano-molecule machine for exosome and surface protein analysis and application
ActiveCN112391448AMeet the needs of analysisAchieve ultra-sensitive quantitative detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAptamerProtein markers
The invention relates to a DNA nano-molecule machine for exosome and surface protein analysis and application. The DNA nano-molecule machine comprises an identification probe generating response to asurface marker of an exosome, a signal probe containing two Toehold regions and a fuel probe capable of driving cycling of a strand displacement reaction. The exosome is subjected to polyvalent conjugation with a specific aptamer in the identification probe through the surface marker of the exosome, so as to release an initiating strand in the identification probe; the initiating strand invades the signal probe and drives branches of the strand to migrate and release a quenching strand through being conjugated with a Toehold region I, a fluorescence reporter group is liberated, and a concealedToehold region II is exposed; and the fuel probe starts up a Toehold-mediated strand displacement cyclic reaction through being conjugated with the Toehold region II, and continuous branch migrationand polyvalent recovery occur. Supersensitive quantitative detection on the exosome can be achieved; bi-color or multicolor analysis on two or more kinds of protein markers on the surface of the exosome can be achieved; and the operation is simple, the consumed time is short, the sample consumption is low, the sensitivity is high, and the specificity is good.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Methods of producing target molecule in transgenic animal and purification of target molecule
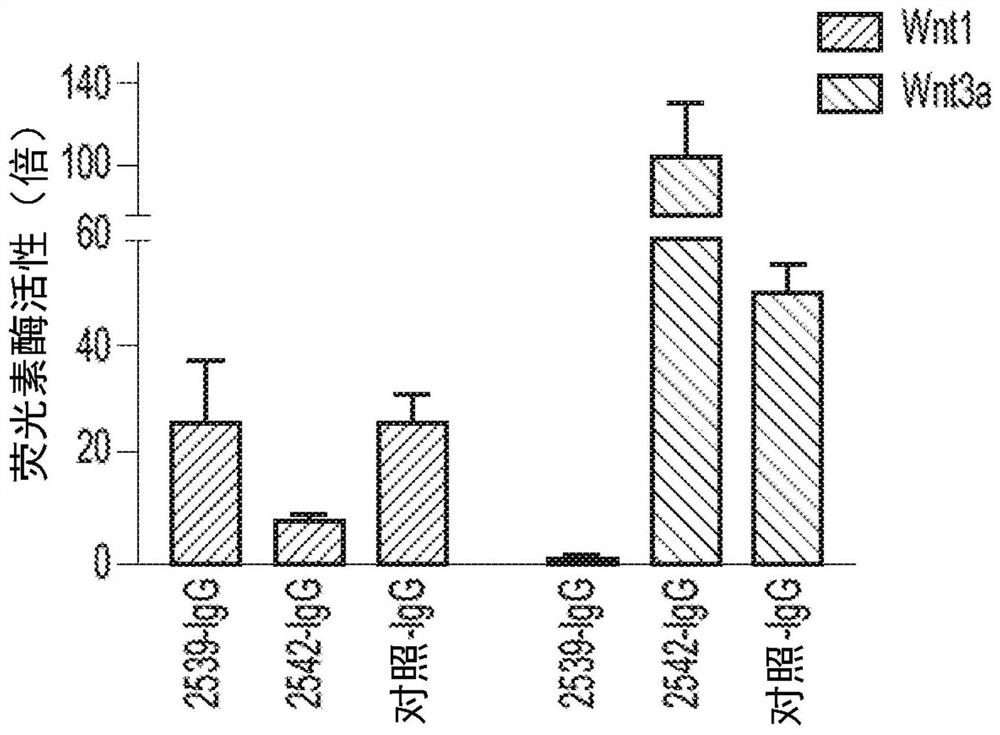
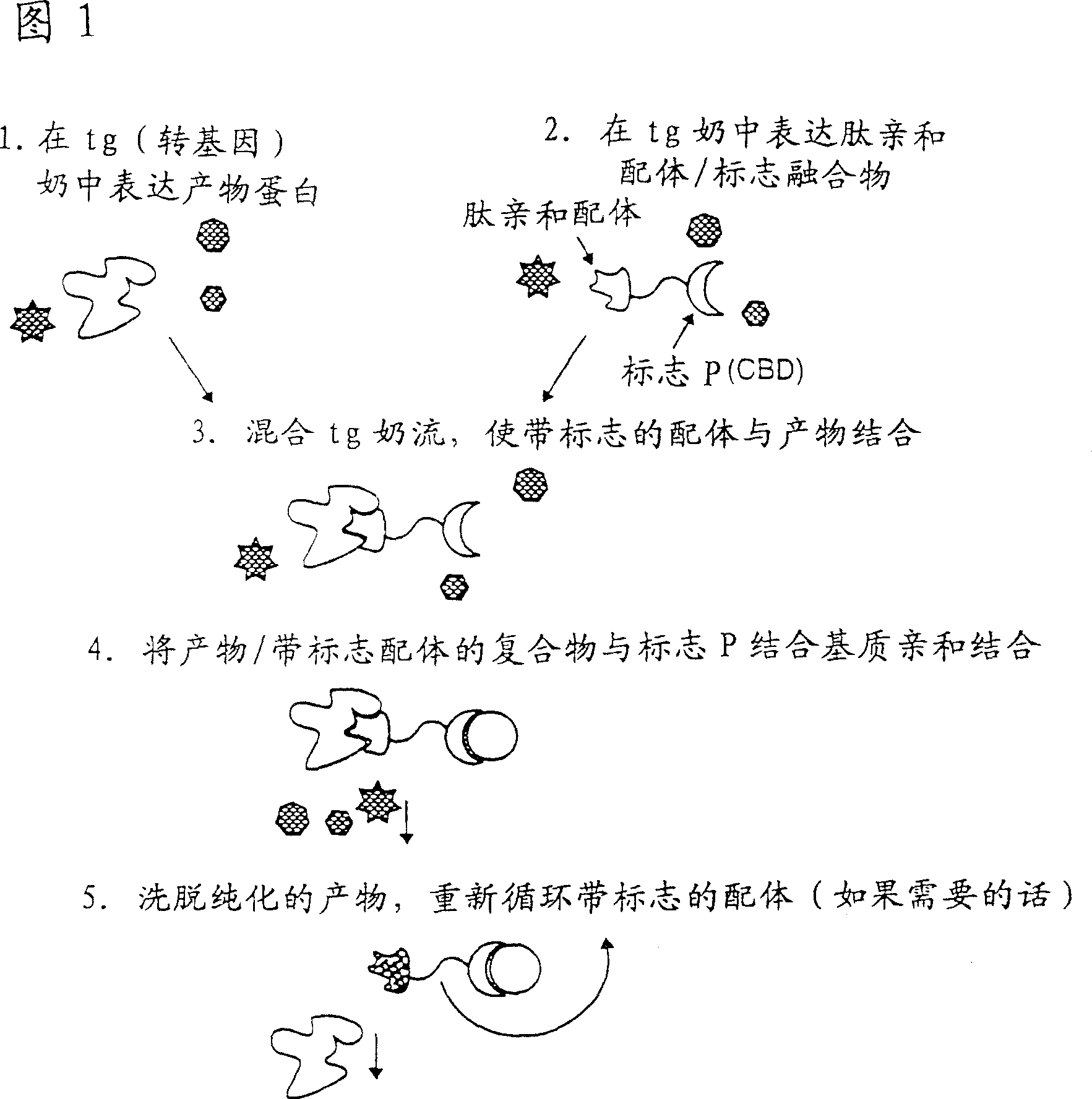
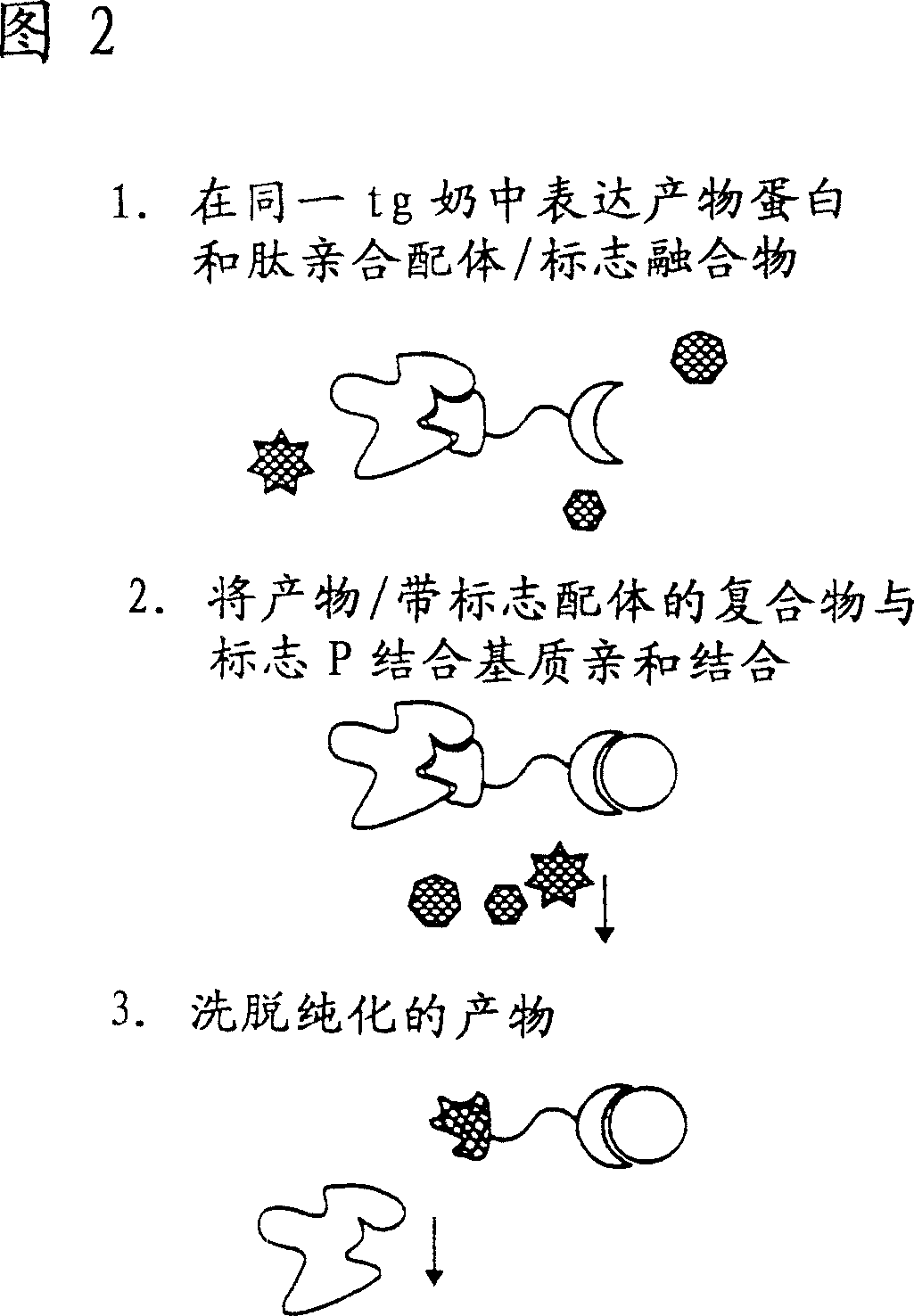
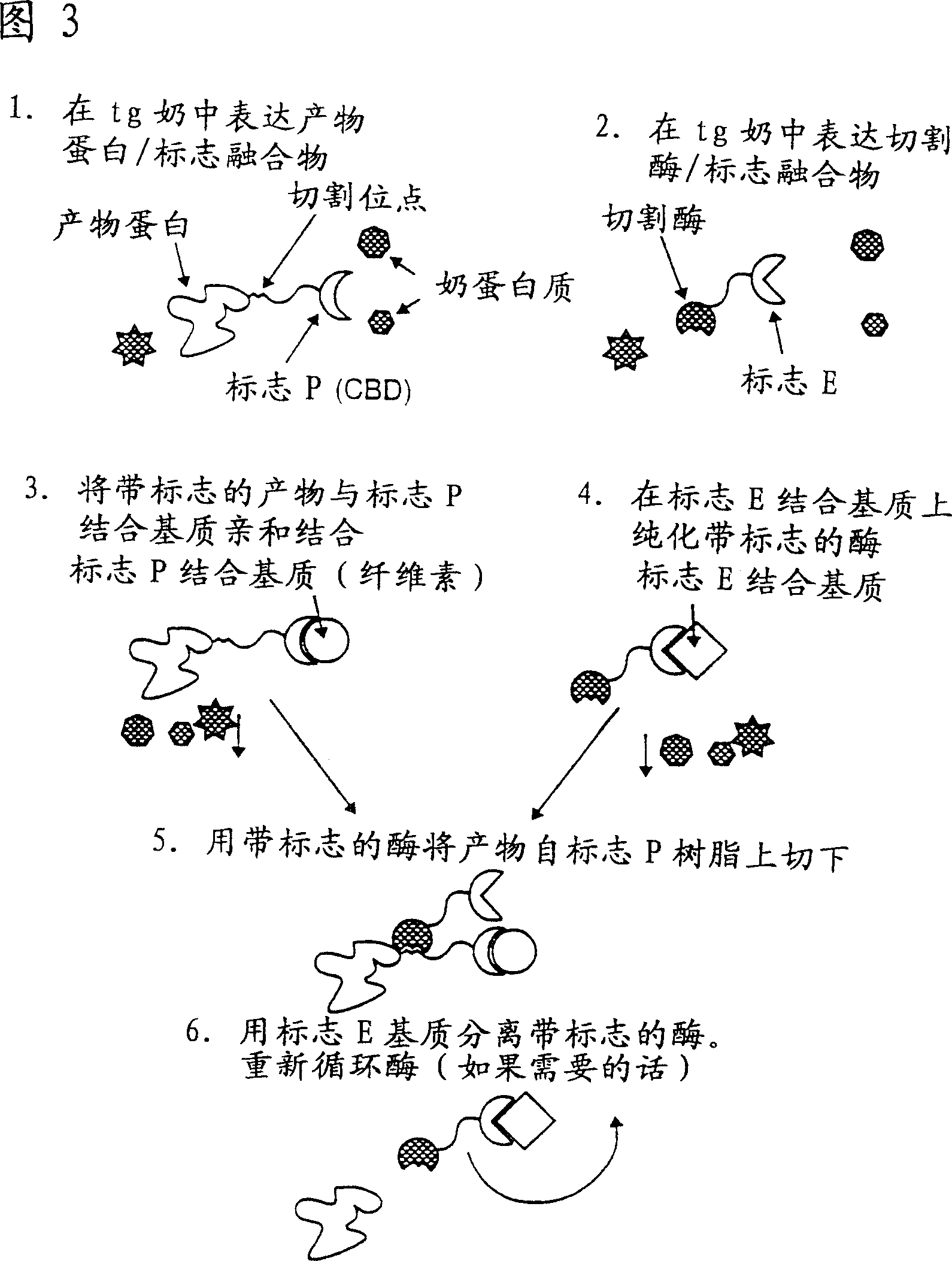
InactiveCN1387399AShorten the timeLow costVectorsPeptide preparation methodsEpitopeMultivalent binding
The present invention provides systems and methods for preparing and purifying target molecules present in biological systems. The systems and methods according to the present invention utilize a transgenically expressed multivalent binding polypeptide as an affinity medium for purifying the target molecule to purify the target molecule. The transgene multivalent binding polypeptide not only binds to the target molecule (for example, the bindable epitope of the target molecule), but also binds to the substrate.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Multi-analyte assay
InactiveUS20160011185A1High sensitivityEnhanced signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPopulationMultivalent binding
The present invention is directed to devices and methods using pan-generic antibodies to detect bacteria in a sample. The invention relates to binding assays, especially immunoassays, utilizing a multivalent binding agent immobilized on a particle. The invention also relates to the surprising discovery that increasing the size of the particles improves the sensitivity of the screen. The invention provides, inter alia, a lateral flow device for detecting bacteria in a sample, the device comprising a flow path for the sample and further comprising a pan-generic binding agent specific for other or more bacterial antigens, wherein the pan-generic binding agent is immobilized via a linker on a population of particularly-sized detectable particles; and a capture binding agent that captures the population of particles bound to bacterial antigens, wherein the capture binding agent is immobilized on the flow path, and wherein the population of detectable particles are disposed along the flow path such that the sample contacts the population of detectable particles before contacting the capture binding agent.
Owner:VERAX BIOMEDICAL
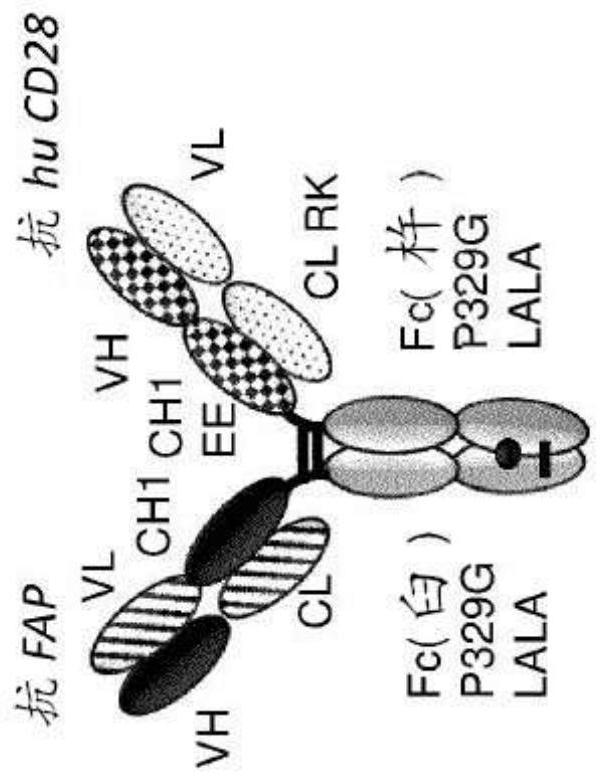
Tumor-targeted superagonistic cd28 antigen binding molecules
InactiveUS20200223925A1Promising resultHigh ratePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTumor targetTumor targeting
The present invention relates to tumor targeted superagonistic antigen binding molecules capable of multivalent binding to CD28, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing these antibodies, and methods of using the same.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Peptide linkers for effective multivalent peptide binding
InactiveUS8697654B2High binding affinityEnhancement and promotionCosmetic preparationsImpression capsTarget surfaceBinding peptide
Short single chain peptides having affinity for a target surface often lack the binding durability required for certain commercial applications. One way to improve durability is to promote multivalent binding by linking together binding sequences using peptide linkers. However, the resulting single chain binding peptides often suffer from linker entropy. It has been discovered that the use of rigid peptide linkers when linking together multiple binding sequences enhances the binding affinity of the resulting single chain peptide.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
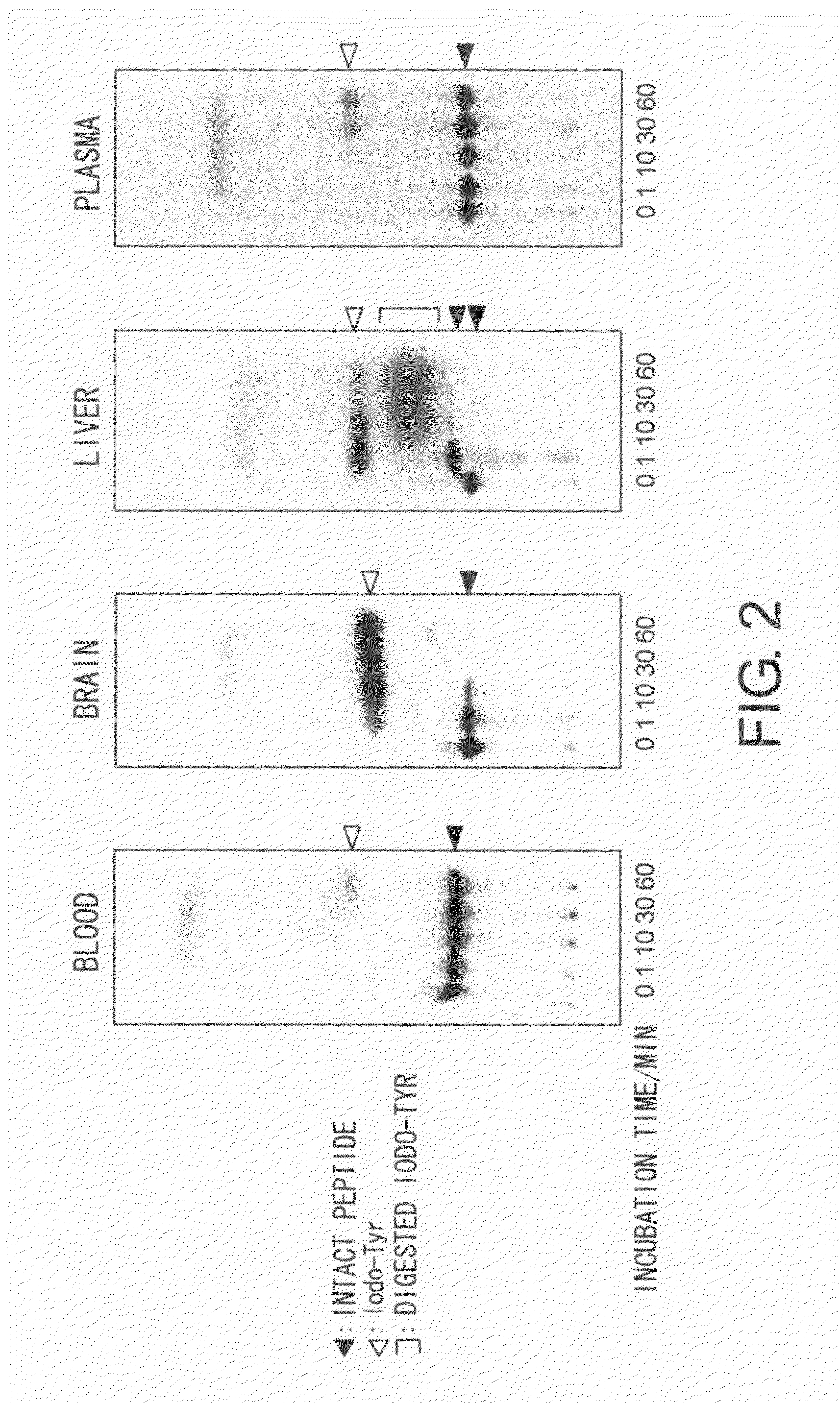
Brain-localizing polypeptides comprising a multivalent binding moiety and improved metabolic stability
InactiveUS20100111838A1Good metabolic stabilityProblem in their useNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMetabolic stabilityMultivalent binding
Brain-localizing polypeptides carrying a reactive group for linking to a molecule that does not have brain-localizing activity were successfully produced by introducing at least two lysine residues into cyclized polypeptides having a brain-localizing motif sequence. These polypeptides have improved metabolic stability compared to conventional brain-localizing polypeptides, and can efficiently translocate desired molecules into the brain.
Owner:ACTGEN +1
High affinity antibodies to pd-1 and lag-3 and bispecific binding proteins made therefrom
PendingCN112074541AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBinding siteIntravenous gammaglobulin
High-affinity antibodies recognizing Programmed Death Ligand-1 (PD-1) and Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 protein (LAG-3) are disclosed. Binding sites from humanized anti-PD-1 and anti-LAG-3 antibodies are incorporated into a Fabs-in-Tandem Immunoglobulin format without significant loss of binding affinity, and the resultant bispecific, multivalent binding proteins are able to bind to both PD-1 and LAG-3 simultaneously. Such bispecific FIT-Ig binding proteins are useful for treatment of cancer.
Owner:EPIMAB BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Antagonist of ligands and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100120147A1Minimize molecular mechanic energyReduce incompatibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding domainMultivalent binding
The invention provides multivalent ligand binging agents (traps) for members of the TGF-β superfamily and polypeptide linkers and methods for making and using such constructs. In an embodiment of the invention there is provided a multivalent binding agent with affinity for a member of the TGF-β superfamily, said agent comprising the general structure I: (<bd1>-linker1)k-[{bd1>-linker2-<bd2>-linker3f-}n-(<bd3>)m-(linker4-<bd4>)d]h, where: -n and h are independently greater than or equal to 1; -d, f, m and k arc independently equal to or greater than zero; -bd1, bd2, bd3 and bd4 are polypeptide binding domains having an affinity for the same member of the TGF-β superfamily, with bd1, bd2, bd3, and bd4 being independently the same or different from each other; and, -linkeri, linker2, linker3 and linker4 are unstructured polypeptide sequences; wherein the number of amino acids in each linker is determined independently and is greater than or equal to X / 2.5; where, X equals the shortest linear distance between: (a) the C-terminus of an isolated form of the binding domain that is located at the N-terminus of the linker and that is specifically bound to its ligand; and, (b) the N-terminus of an isolated form of the binding domain that is located at the C-terminus of the linker and that is specifically bound to its ligand.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
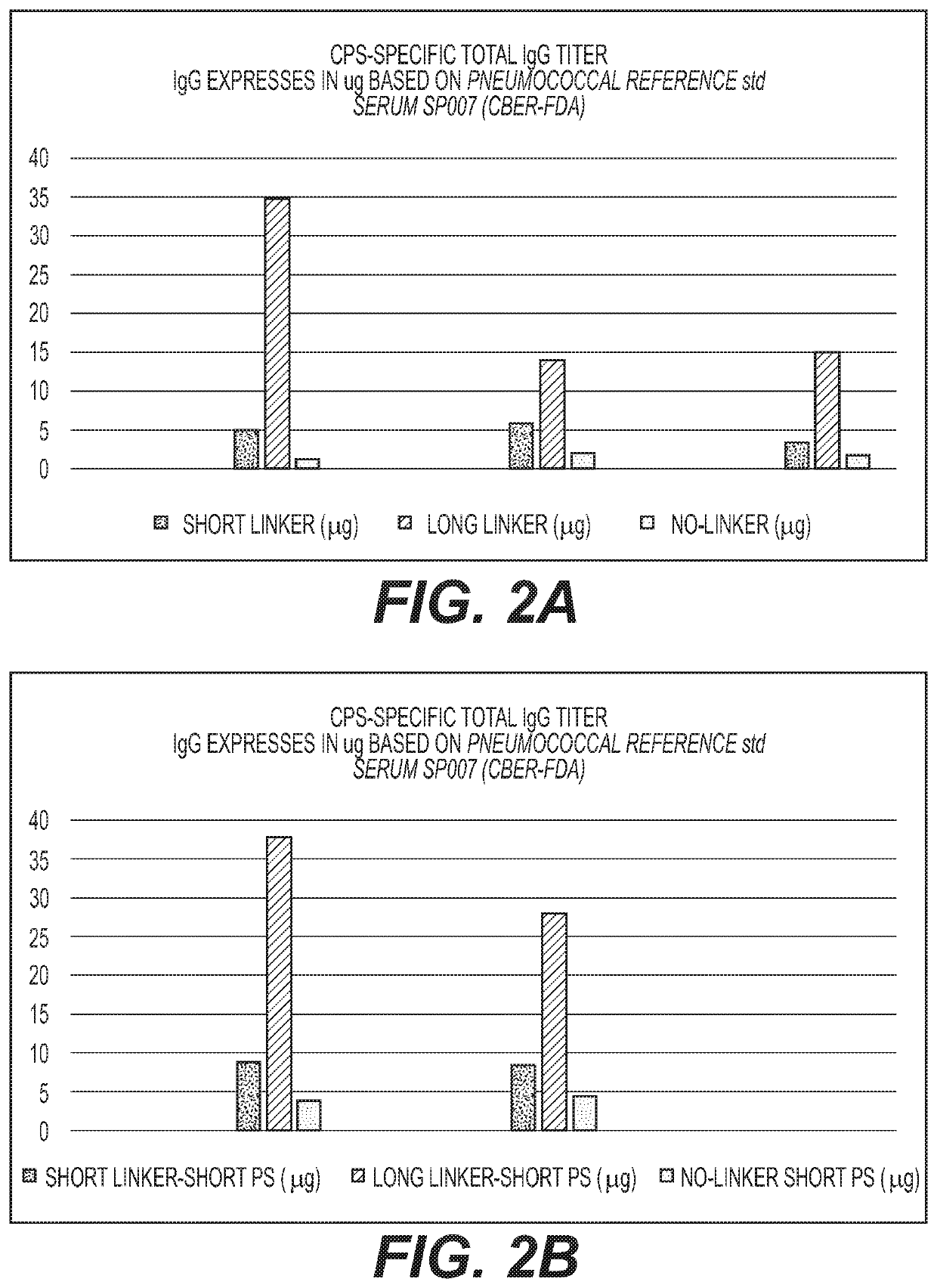
Multivalent conjugate vaccines with bivalent or multivalent conjugate polysaccharides that provide improved immunogenicity and avidity
ActiveUS10688170B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCarrier proteinMultivalent binding
The disclosure describes compositions containing conjugates using novel linkers, bivalent polysaccharide conjugates, and methods of bivalent polysaccharide conjugation in the development of multivalent conjugate vaccines. Conjugation of capsular polysaccharides to carrier proteins is carried out using homo-bifunctional and / or hetero-bifunctional linkers of specific lengths. Incorporation of the linkers and their use in bifunctional linkers induces higher titers of functional antibodies with high avidity, eliciting higher immunologic memory, and reduced carrier protein effect. This provides immunochemically cross-reactive capsular polysaccharides wherein one or more cross-reactive capsular polysaccharides are conjugated sequentially or concurrently to carrier protein using bifunctional linkers bearing the same or different functional groups. Such a linker and the size of the capsular polysaccharides provides an effective multivalent conjugate vaccine with high antibody titers and a reduced carrier effect and results in reduction in the content of the capsular polysaccharide and protein per dose of vaccine which reduces reactogenicity.
Owner:INVENTPRISE INC
Tumor-targeted superagonistic cd28 antigen binding molecules
PendingCN113286822AGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTumor targetPharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to tumor targeted superagonistic antigen binding molecules capable of multivalent binding to CD28, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing these antibodies, and methods of using the same.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
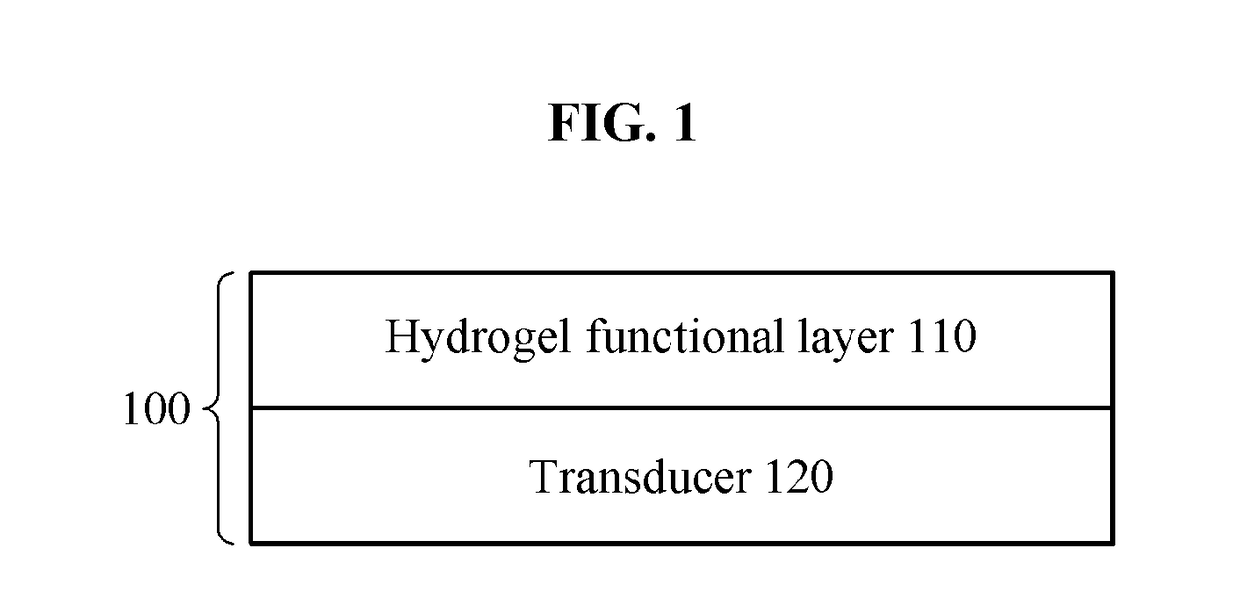
Biochip and method for manufacturing biochip
ActiveUS20180149641A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetTransducer
Disclosed are a biochip capable of detecting and analyzing multivalent bindings between target protein and binding mediator from monovalent bindings and a method for manufacturing the same. A biochip according to an embodiment comprises: a hydrogel functional layer on which a binding mediator is formed and of which physical properties are changed by a reaction between target protein to be introduced and the binding mediator; and a transducer configured to deliver a displacement signal corresponding to a change in the physical properties of the hydrogel functional layer to an analysis instrument, wherein the reaction is multivalent bindings between the target protein and the binding mediator, and de-swelling occurs in at least a portion of the hydrogel functional layer by the multivalent bindings.
Owner:SCHOLAR FOXTROT CO LTD
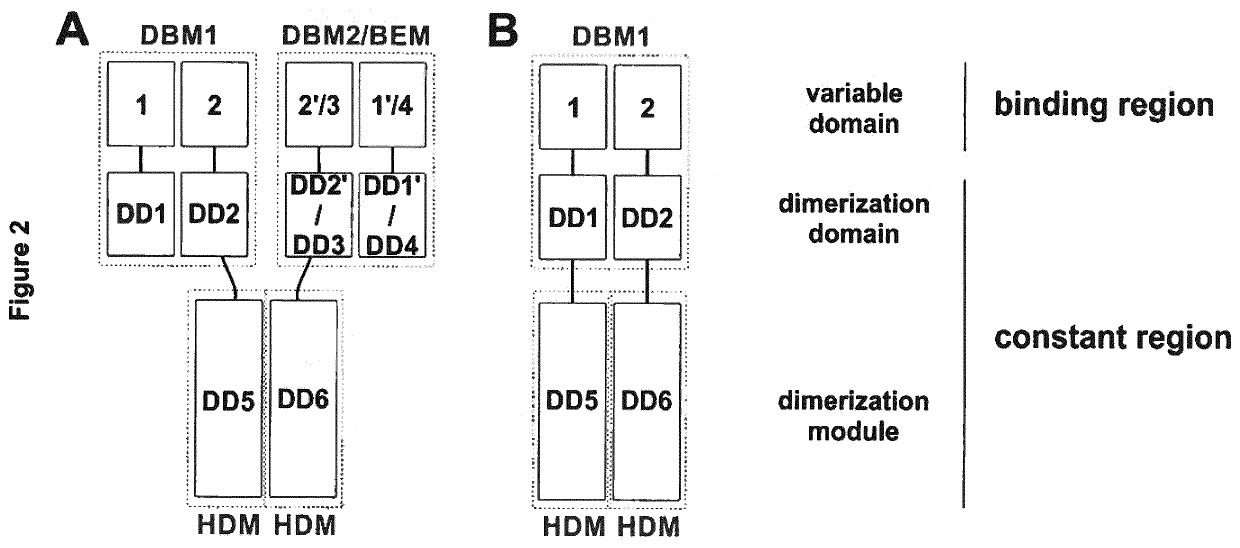
Multivalent binding molecules
ActiveUS20210002376A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseAntigen binding
The present invention relates to a modular multivalent antigen-binding protein complex, use of the antigen-binding protein complex in medicine and use of the antigen-binding protein complex in the prophylaxis, treatment or diagnosis of a disorder or disease.
Owner:UNIV STUTTGART
Compositions monovalent for CD40L binding and methods of use
ActiveCN101061140BImprove stabilityAvoid approachingImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseIntravenous gammaglobulin
The invention relates to antibody polypeptides that monovalently bind CD40L. Antibody polypeptides that are monovalent for binding of CD40L can inhibit CD40L activity while avoiding potential undesirable effects that can occur with antibodies capable of divalent or multivalent binding of CD40L. In one aspect, a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide consists of or comprises a single immunoglobulin variable domain that specifically binds and antagonizes the activity of CD40L, preferably without substantially agonizing CD40 activity. In another aspect, the monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide is a human antibody polypeptide. The invention further encompasses methods of antagonizing CD40 / CD40L interactions in an individual and methods of treating diseases or disorders involving CD40 / CD40L interactions, the methods involving administering a monovalent anti-CD40L antibody polypeptide to the individual.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
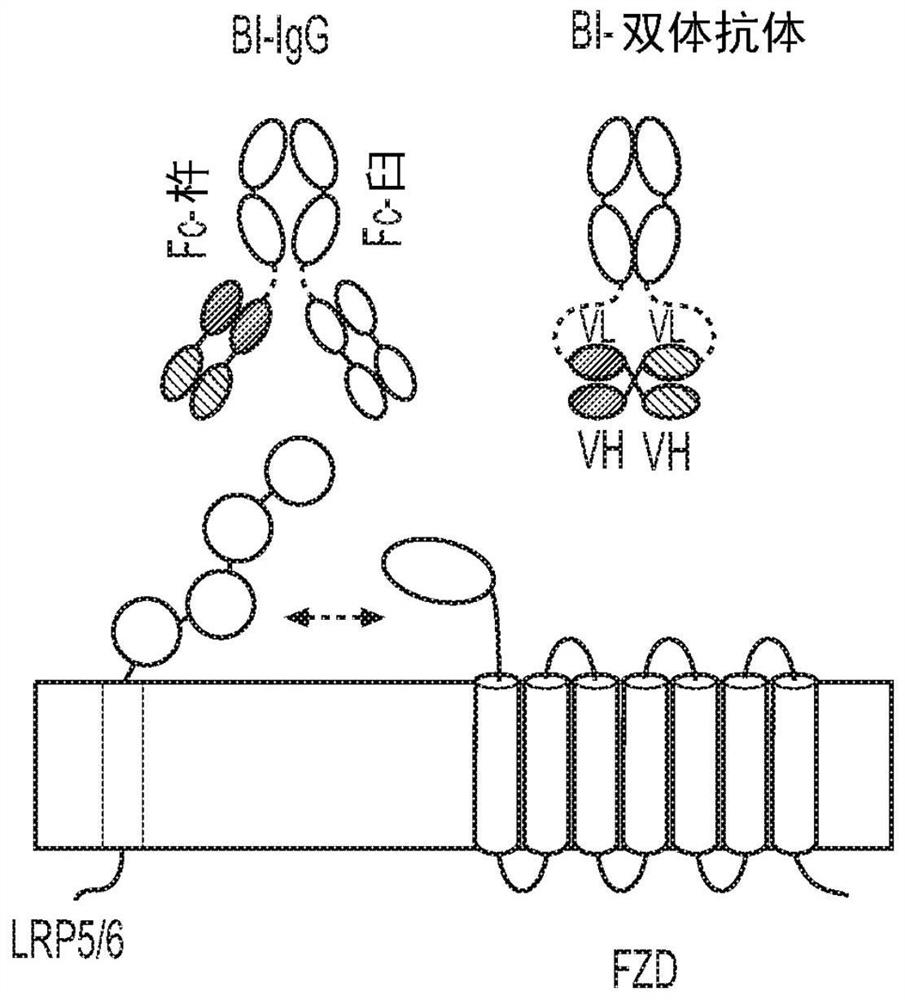
Multivalent FZD and WNT binding molecules and uses thereof
PendingCN114423784AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsArtificial cell constructsFc domainSignalling pathways
Described herein are methods of affecting binding of a multivalent binding molecule to a FZD receptor and a Wnt co-receptor on a cell, wherein binding of the multivalent binding molecule to both the FZD receptor and the co-receptor on the cell activates the Wnt signaling pathway. Also described herein are multivalent binding molecules that activate the Wnt signaling pathway, comprising an FZD receptor binding domain and a Wnt co-receptor binding domain on either end of the Fc domain, and methods of using the same.
Owner:ANTLERA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods of producing target molecule in transgenic animal and purification of target molecule
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Biochip and method for manufacturing biochip
ActiveUS10359422B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetTransducer
Disclosed are a biochip capable of detecting and analyzing multivalent bindings between target protein and binding mediator from monovalent bindings and a method for manufacturing the same. A biochip according to an embodiment comprises: a hydrogel functional layer on which a binding mediator is formed and of which physical properties are changed by a reaction between target protein to be introduced and the binding mediator; and a transducer configured to deliver a displacement signal corresponding to a change in the physical properties of the hydrogel functional layer to an analysis instrument, wherein the reaction is multivalent bindings between the target protein and the binding mediator, and de-swelling occurs in at least a portion of the hydrogel functional layer by the multivalent bindings.
Owner:SCHOLAR FOXTROT CO LTD
Multivalent binding molecules activating wnt signaling and uses thereof
Described herein are methods to affect binding by a multivalent binding molecule to a FZD receptor and a Wnt co-receptor on a cell wherein binding by the multivalent binding molecule to both FZD receptor and co-receptor on the cell activates a Wnt signaling pathway. Also described herein are multivalent binding molecules comprising a FZD receptor binding domain and a Wnt co-receptor biding domainon either end of an Fc domain that activate a Wnt signaling pathway and methods for their use.
Owner:ANTLERA THERAPEUTICS INC
Immunostimulatory multimer binding molecules
PendingCN114269785AImmunoglobulin superfamilyHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunostimulantMultivalent binding
The present disclosure provides multivalent binding molecules comprising a modified J chain comprising an immunostimulatory agent. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding the binding molecules or subunits thereof, as well as vectors and host cells comprising the polynucleotides. The present disclosure also provides methods for producing and / or using multivalent binding molecules comprising a modified J chain comprising an immunostimulatory agent.
Owner:IGM BIOSCI INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com