Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Yeast display" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Yeast display (or yeast surface display) is a protein engineering technique that uses the expression of recombinant proteins incorporated into the cell wall of yeast for isolating and engineering antibodies.
Yeast Display Systems
InactiveUS20110275535A1Peptide librariesConnective tissue peptidesYeast displayCell surface molecules
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Process for synthesizing ethyl caproate by yeast display lipase synthesis
InactiveCN101285078AImprove operational stabilityHigh biosecurityFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologySurface display
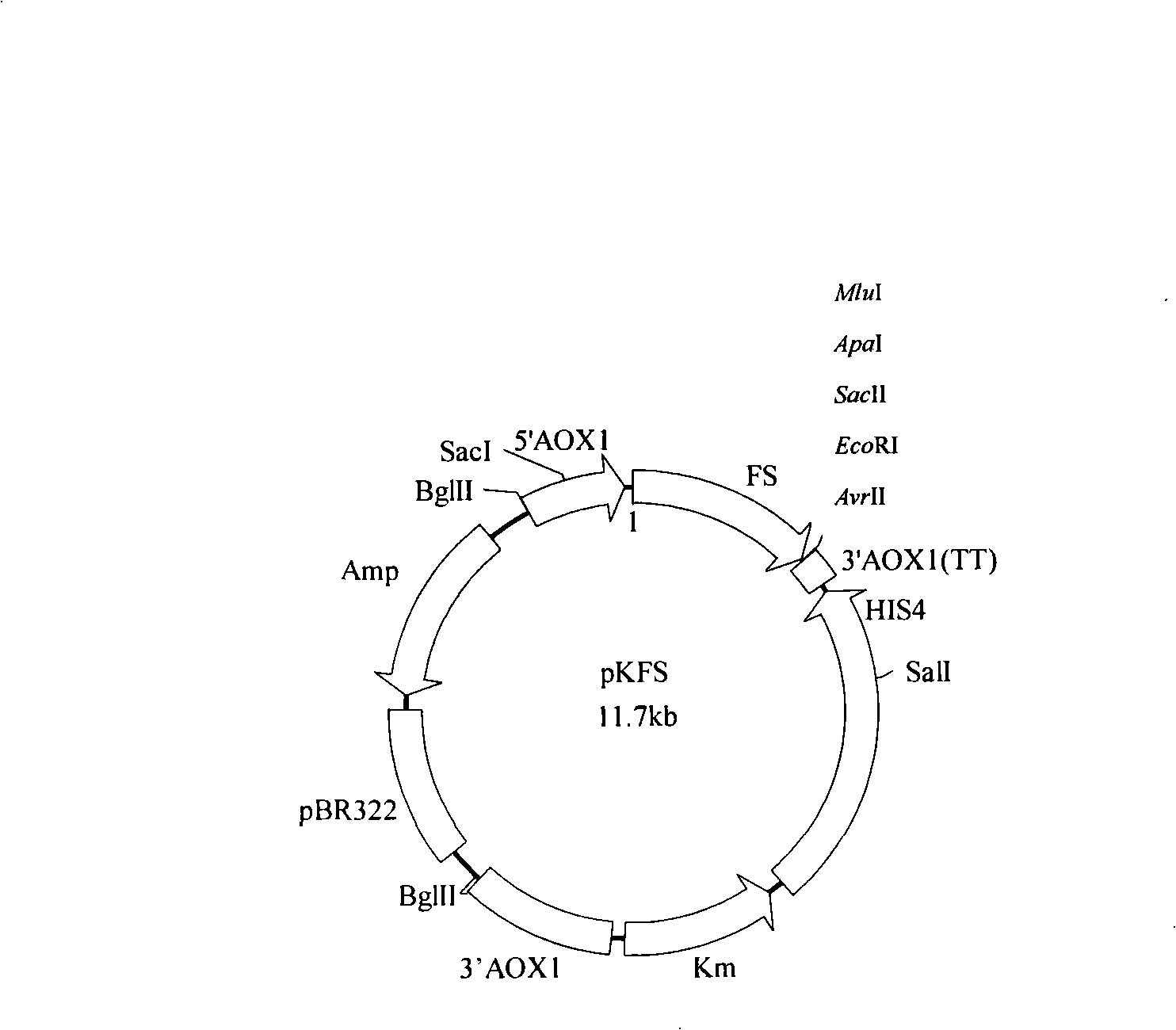
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing ethyl caproate under the catalysis of yeast display lipase. The method comprises two steps, namely the production of full cellular zymin and the synthesis of ethyl caproate. The method comprises the following: a step of cloning the lipase gene into the Pichia yeast surface display vector pKFS to construct the Pichia yeast surface display expression vector pKFS-lipase which is transformed into the host bacteria of Pichia yeast through linearization, a yeast genetic engineering bacteria capable of displaying active pheron on the surface of the Pichia yeast being obtained through screening, and the engineering bacteria being fermented in a rocking bottle to obtain a thallus which is used to make the full cellular zymin after 24 hours of vacuum freeze drying; and then a step of adopting caproic acid and alcohol as raw material which is esterified at the action of the biocatalyst of yeast full cellular zymin with the lipase displayed on the surface to obtain the ethyl caproate product. The method is capable of collecting thalli centrifugally for reuse after the reaction with short reaction time, high yield and good operational stability, thereby greatly reducing production costs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Candida Antarctica lipase B gene and applications thereof in yeast display
ActiveCN101565713AIncrease impressionImprove thermal stabilityFungiBiofuelsPichia pastorisNucleotide
The invention relates to candida Antarctica lipase B gene and applications thereof in yeast display. Coded protein of improved candida Antarctica B and wild type candida Antarctica lipase protein have the same function on the amino acid level; the heat resistance capacity of the enzyme is 50-80 DEG C, and the half-lift is 3-24 hours; a nucleotide sequence is hybridized with SEQ.ID.NO2 from 1st to 978th of nucleotide under the moderate precise condition; and a preservation number of colon bacillus DH5Alpha / Puc57-CALB (Escherichia coliDH5Alpha / pUC57-CALB) which carries the plasmids is CCTCC M 209081. The candida Antarctica lipase B gene is transferred into pichia pastoris host bacteria so as to realize the high-efficient display expression of the candida Antarctica lipase B in pichia pastoris; and the provided pichia pastoris bacteria can effectively display candida Antarctica lipase B, can be widely applied to the synthesis of ethyl caproate, has different melting points and does not contain triglyceride of various fatty acids, a plurality of structured lipids, and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Improved Rhizomucor miehei lipase gene and use thereof in yeast display
ActiveCN101481695AIncrease vitalityImprove catalytic performanceFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to an improved rhizomucor miehei lipase gene and an application to yeast display. The sequence of the improved rhizomucor miehei lipase gene is SEQ.ID.No2, with respect to a recombinant vector pMD18-T-RML containing the gene, RML means lipase gene; and the collection number of a bacterial strain Escherichia coli TOP10 / pMD18-T-RML carrying the plasmid is CCTCC M 208136. In the invention, the gene is transferred into pichia stipitis host strain, so that the rhizomucor miehei lipase is displayed and expressed in the pichia stipitis. The provided pichia stipitis can effectively display the rhizomucor miehei lipase. The lipase can be widely applicable for producing fatty acid methyl ester, ethyl caproate, triglycerides which have different melting points but does not contain various types of fatty acid and a few 'reconstructed esters'.
Owner:DONGGUAN HUAQI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +1
Multivalent binding protein compositions and methods for identifying variants of same
Provided are protein, nucleic acid, and cellular libraries of multivalent binding proteins (e.g., DVD-Fab or DVD-Ig molecules) and the use of these libraries for the screening of multivalent binding proteins using cell surface display technology (e.g., yeast display).
Owner:ABBVIE INC
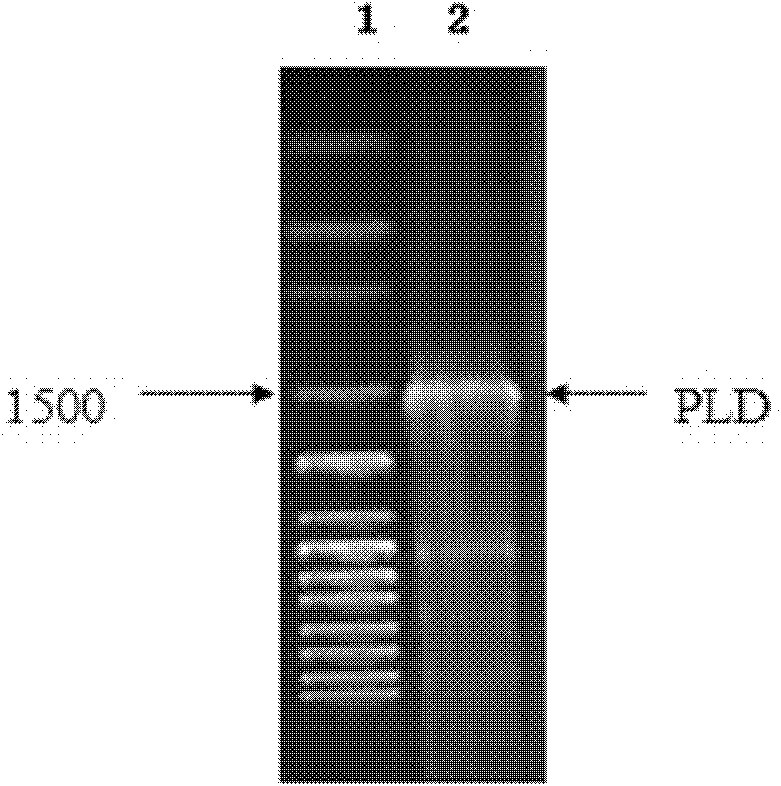
Preparation of highly active phospholipase d and yeast whole cell catalyst displaying phospholipase d on the cell surface
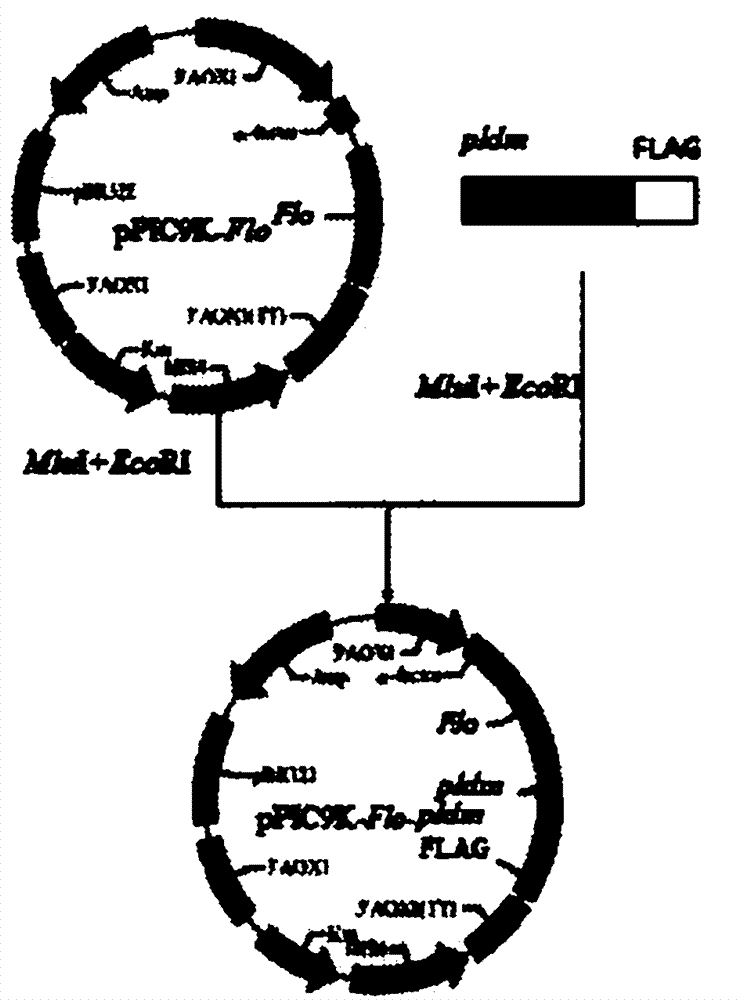
The invention relates to preparation of high-activity phospholipids enzyme D and cell surface display phospholipids enzyme D yeast whole cell catalysts, which belongs to a method for carrying out site directed mutagenesis wild phospholipids enzyme D by recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) for improving the activity, connecting the mutated gene with yeast show carriers pPIC9K-Flo and efficiently displaying the mutated gene on the surface of pichia pastoris cells, and relates to a preparation method of the high-activity phospholipids enzyme D and cell surface display phospholipids enzyme D yeast whole cell catalysts. The method has the advantages that the activity of the wild phospholipids enzyme D is improved and is shown on the surfaces of the pastoris cells, the stability is improved,and the advantages of immobilized enzymes are realized. The method has the technical scheme that wild phospholipids enzyme D genes are separated from microbes, particularly streptomyces aureofuscus, the mutation is carried out on the amino acid residue of Glu69 and Ser285, through the efficient expression on the surfaces of the pichia pastoris cells, the enzyme activity of the high-activity phospholipids enzyme is improved by 11 percent than the wild type phospholipids enzyme D, and the enzyme activity of the recombination strains GS115 / pPIC9K-Flo-pldm prepared through high-density fermentation is 120U / (g. stem cells).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
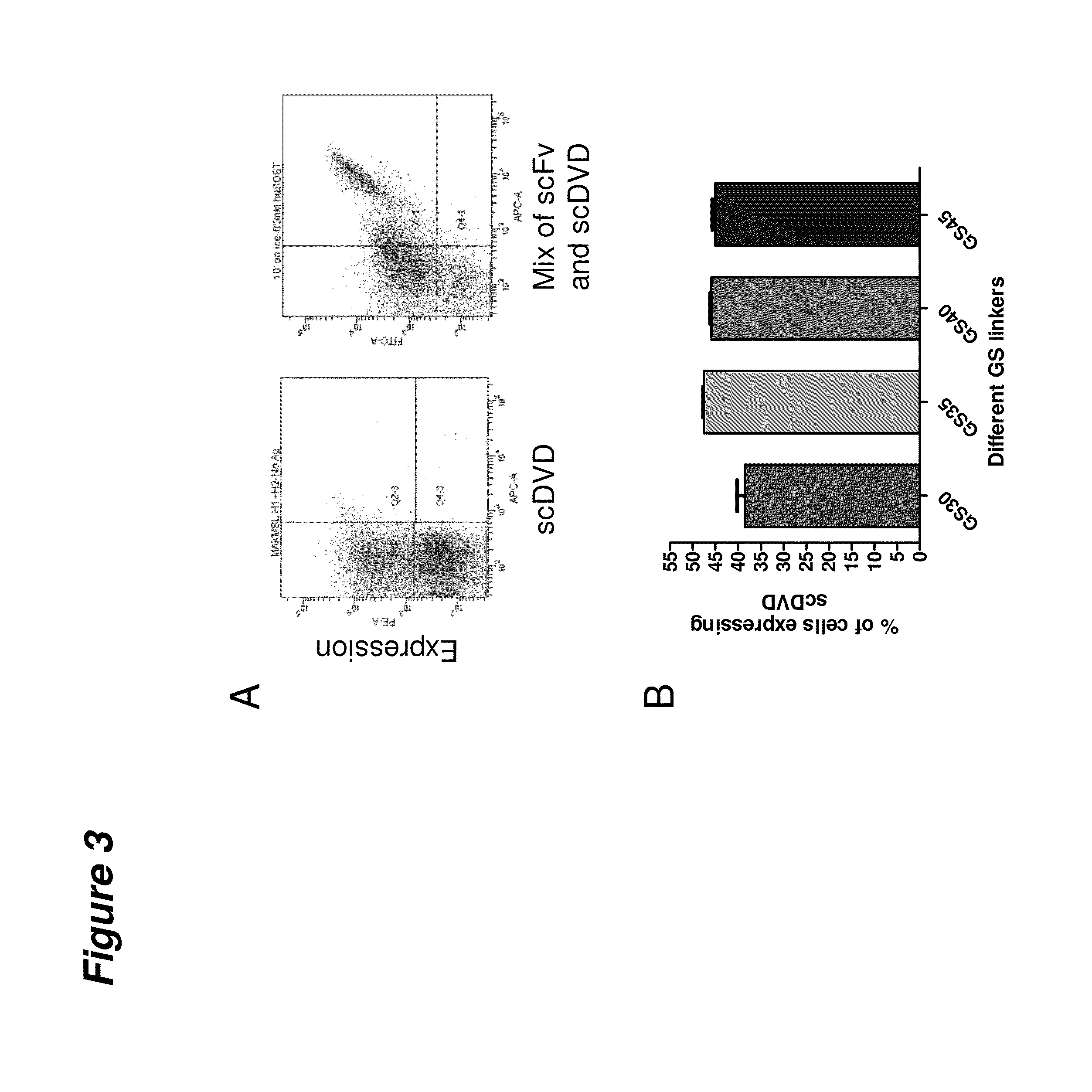
Single-chain multivalent binding protein compositions and methods
InactiveUS20140221621A1High affinityPeptide librariesHybrid immunoglobulinsYeast displayMultivalent binding
Provided are protein, nucleic acid, and cellular libraries of single chain multivalent binding proteins (e.g., scDVD and scDVDFab molecules) and methods of using these of these libraries for the screening of single chain multivalent binding proteins using cell surface display technology (e.g., yeast display).
Owner:ABBVIE INC
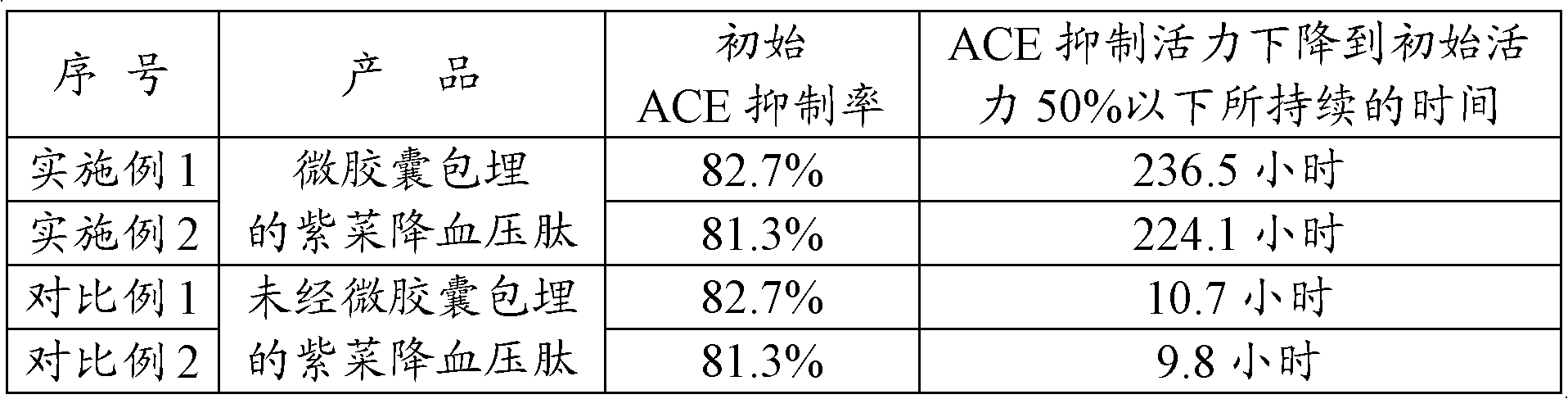
A kind of preparation method of microcapsule-embedded laver blood pressure lowering peptide
InactiveCN102296101AHigh activityHigh dissolution rateMicroorganism based processesCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesClaviceps purpureaPentagalacturonic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing micro capsulate embedded antihypertensive peptide derived from laver, which comprises: adding laver dry powder and yeast display type polygalacturonase into water, uniformly mixing, reacting at 35 to 37 DEG C for 30 to 45 minutes with stirring, crushing at 28 to 35 DEG C for 1 to 2 hour by ultrasonic waves with power of 730 to 750W, separating and purifying to obtain laver protein; adding laver protein and yeast display type polygalacturonase into water, uniformly mixing, reacting at 35 to 40 DEG C for 2 to 2.5 hours with stirring, separating andpurifying to obtain antihypertensive peptide derived from laver; and embedding the antihypertensive peptide derived from laver by using beta-cyclodextrin. In the invention, yeast display type polygalacturonase and ultrasonic waves are used in combination to make laver protein dissolve out, then the micro capsules of embedded antihypertensive peptide derived from laver are prepared by enzymolysis in presence of yeast display type protease and micro capsule embedding technology, and the obtained antihypertensive peptide derived from laver has high yield and high activity continuity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
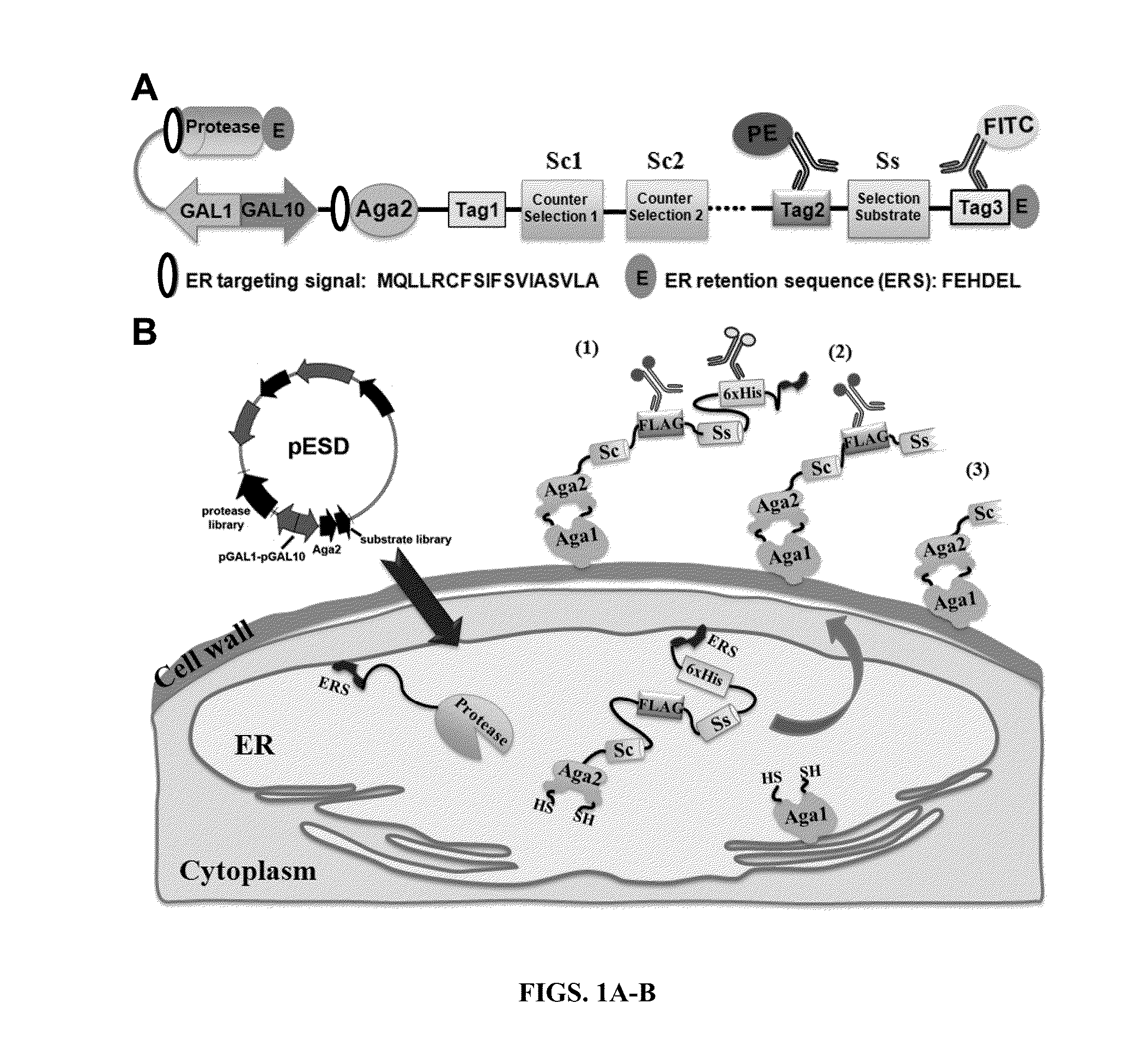
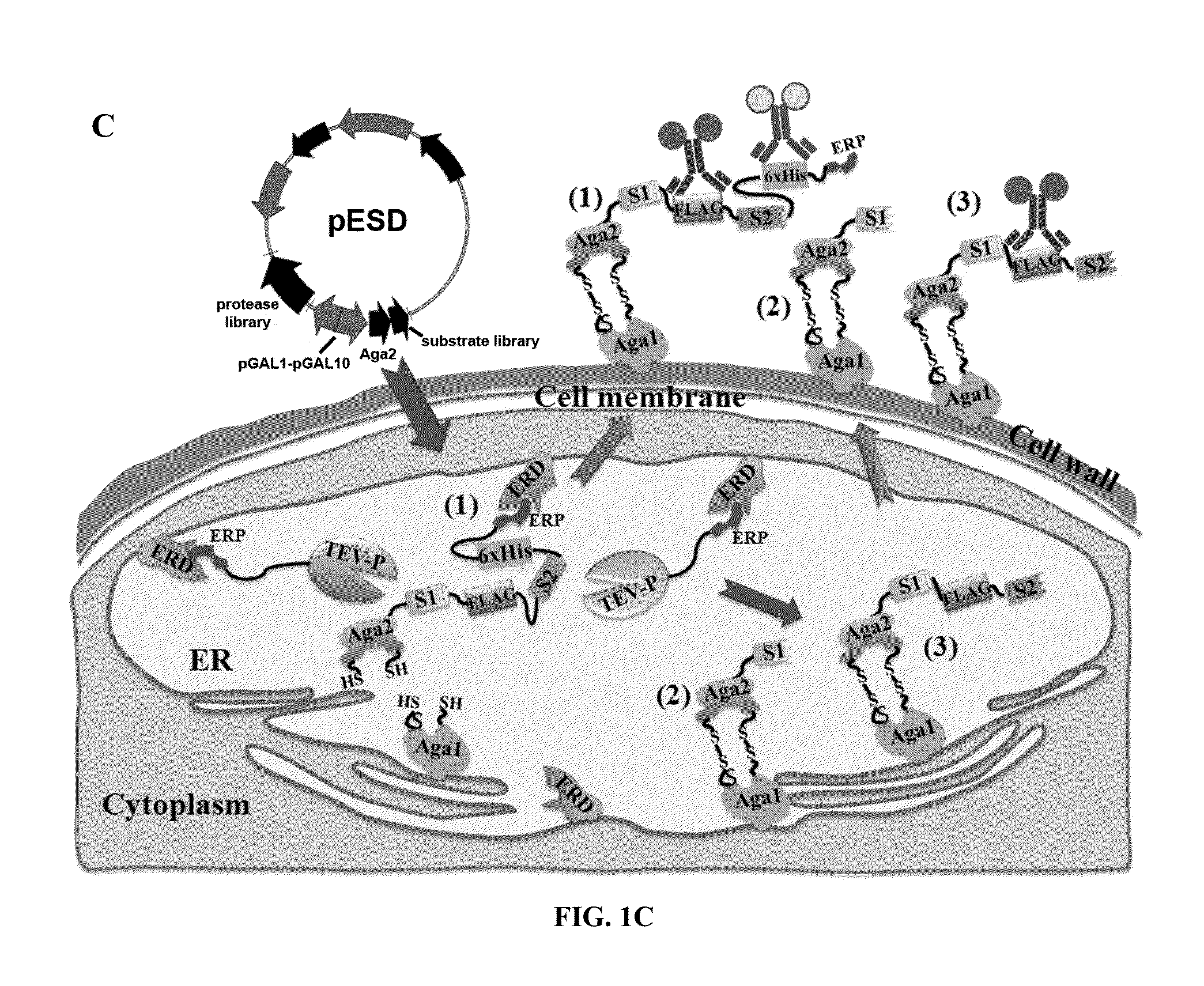
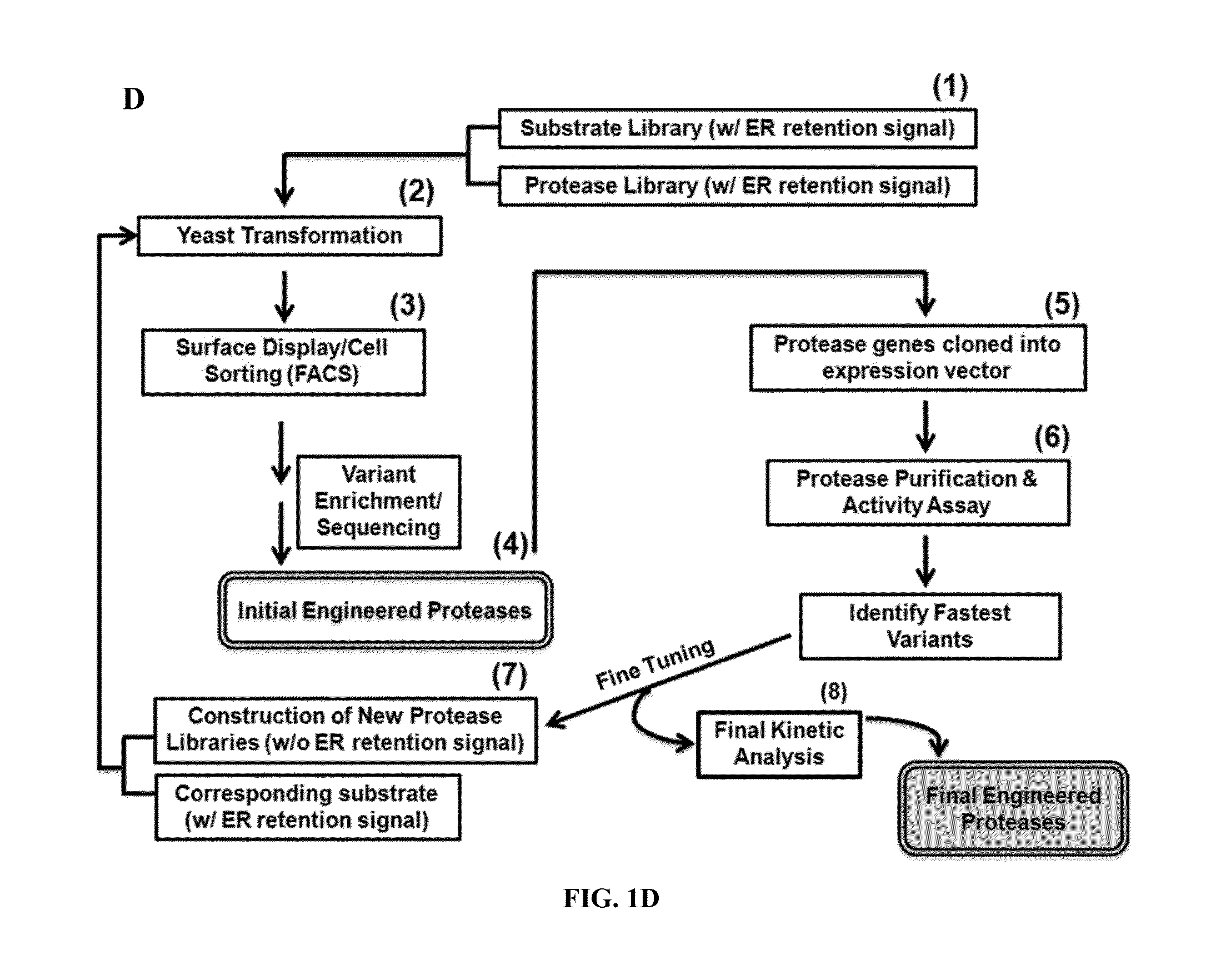
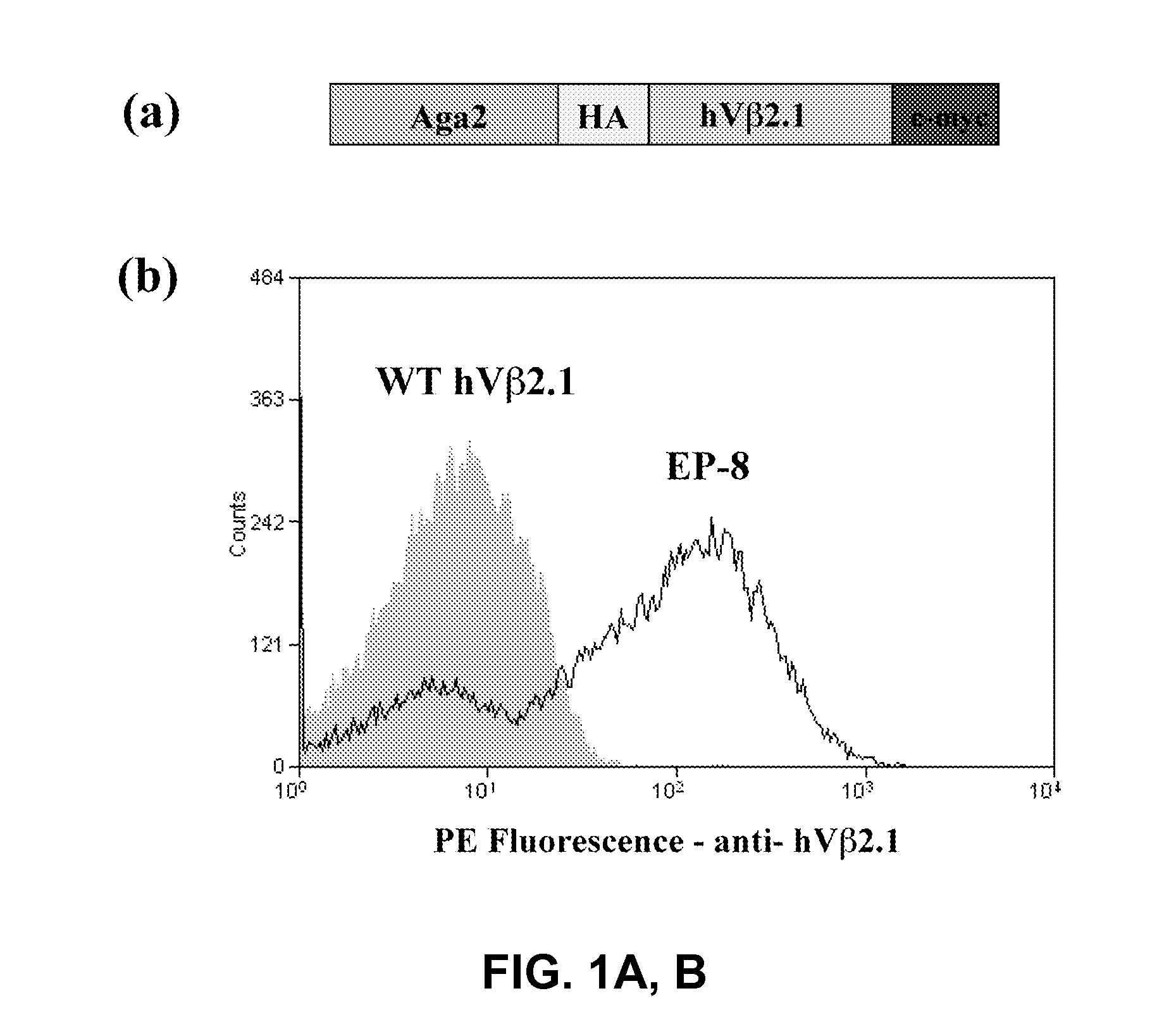
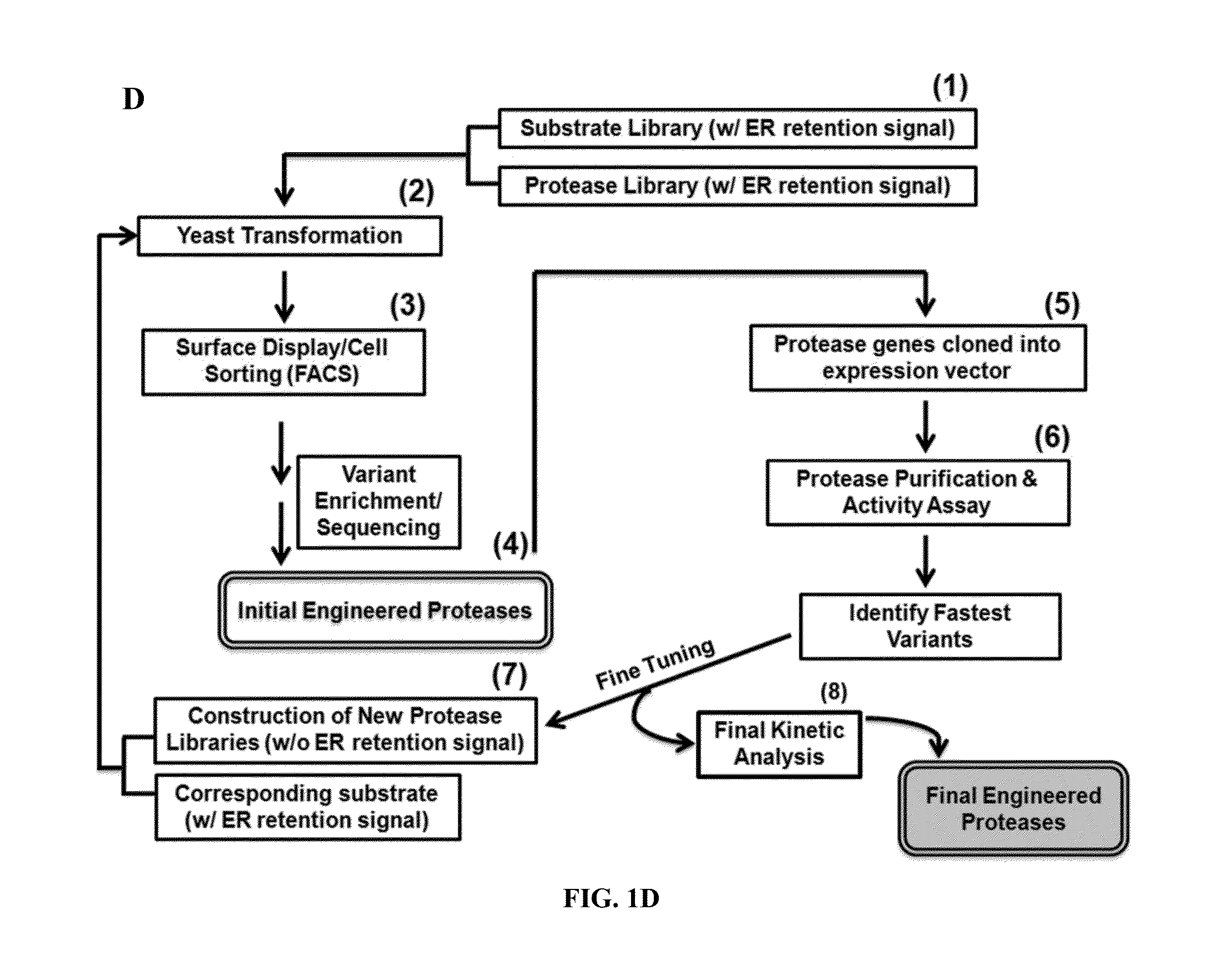
Method for engineering proteases and protein kinases
ActiveUS8945855B2High activityEfficient identificationHydrolasesMicroorganismsEngineering proteinYeast display
Provided are methods for protein engineering, such as engineering proteases or kinases. The methods may utilize yeast display and / or ER sequestration of proteins or substrates. In some aspects, TEV proteases with altered substrate specificity, potency, and / or efficiency are provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Grass carp hemorrhage vaccine prepared through yeast display and preparation method of grass carp hemorrhage vaccine
InactiveCN105879022AAvoid efficiencyAvoid attenuationFungiViral antigen ingredientsSurface displayYeast display
The invention discloses a grass carp hemorrhage vaccine prepared by adopting a yeast surface display technology, relating to the preparation of genetic engineering vaccines. The grass carp hemorrhage vaccine is prepared in a manner that GCRV-VP7 protein is displayed on the surface of brewer's yeast cells EBY100 delta Mnn9 with glycosylated genes knocked out. The brewer's yeast is an expression system of eukaryon, the galactosylated modification is carried out on the virus coat protein expressed by the brewer's yeast, and then an immune system of the grass carp is induced to generate virus-neutralizing antibodies. The grass carp hemorrhage vaccine has the advantages that a used yeast strain EBY100 delta Mnn9 with glycosylation deficiency can effectively remove the super glycosylation of the protein on the surface of the yeast, and thus the problem that the GCRV-VP7 antigen is covered, consequently, the vaccine efficiency loss and decrease are caused, is solved; the yeast cells are easy to culture and low in preparation cost, and thus the grass carp hemorrhage vaccines can be prepared in large scale at low cost.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA +1
Method for catalytic synthesis of vitamin E succinate by utilizing yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212577BImprove operational stabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisOrganic solvent
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Neutralizing Agents for Bacterial Toxins
InactiveUS20110245153A1Prevents and reduces bindingPreventing and reducing toxic effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideYeast displayBacterial Toxin Neutralization
Stabilized variable regions of the T cell receptor and methods of making the same using directed evolution through yeast display are provided. In one embodiment, the variable region is variable beta. In one embodiment, the stabilized T cell receptor variable regions have high affinity for a superantigen, such as TSST-1 or SEB. These T cell receptor variable regions are useful as therapeutics.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH NIH U S DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN RESOURCES DHHS U S GOVT
Preparation method of non-fusion anti-desmoglein DSG3 rabbit-derived monoclonal antibody
PendingCN111606994AHigh affinityImprove featuresFungiSerum immunoglobulinsPichia pastorisPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a preparation method of a non-fusion anti-desmoglein DSG3 rabbit-derived monoclonal antibody. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) selecting a suitable immune animal, and carrying out DSG3 immunization on the animal; 2) extracting successfully immunized animal blood, collecting peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and separating out a B lymphocyte population capable of secreting a DSG3 antibody; 3) establishing a rabbit-derived single-chain antibody yeast display library; 4) constructing a DSG3 rabbit-derived monoclonal antibody expression vector library; 5) constructing a DSG3 rabbit-derived monoclonal antibody yeast expression library: namely converting a pichia pastoris expression vector PZ recombinant plasmid into yeast expression bacteria X33, and screening X33 recombinant transformation monoclonal bacteria capable of secreting a DSG3 antibody; 6) obtaining a X33 recombinant conversion monoclonal strain that can stably secrete a DSG3 antibody; and 7) purifying the obtained DSG3 rabbit-derived monoclonal antibody. The provided preparation method can prepare a stable DSG3 antibody, has industrial repeatability and is suitable for industrial popularization and application.
Owner:湖南远泰生物技术有限公司
Method for engineering proteases and protein kinases
ActiveUS20140017764A1High activityEfficient identificationHydrolasesMicroorganismsEngineering proteinYeast display
Provided are methods for protein engineering, such as engineering proteases or kinases. The methods may utilize yeast display and / or ER sequestration of proteins or substrates. In some aspects, TEV proteases with altered substrate specificity, potency, and / or efficiency are provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Method for synthesizing L-ascorbyl palmitate by catalysis of yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212575AImprove operational stabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-ascorbyl palmitate by catalysis of yeast display lipase. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving L-ascorbic acid and palmitic acid into an organic solvent, adding the yeast display lipase, reacting for 4 to 8 hours in the absence of oxygen at the temperature of between 50 and 60 DEG C, and performing separation and purification to obtain the L-ascorbyl palmitate, wherein the yeast display lipase is prepared by the following steps of: transferring linearly treated recombinant plasmids to pichia pastoris GS115, inoculating the obtained transformant to a buffered methanol complex (BMMY) medium, performing induced culture for 72 to 144 hours, performing centrifugal collection on bacteria, and performing flushing, biological imprinting and freeze drying on the bacteria to obtain the yeast display lipase. The lipase is displayed outside cells, and the L-ascorbyl palmitate is synthesized by catalysis of the enzyme preparation, so that the transformation efficiency is improved, the reaction time is shortened and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for catalytic synthesis of glucose laurate by utilizing yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212580AImprove operational stabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for catalytic synthesis of glucose laurate by utilizing yeast display lipase, and the method comprises the following steps: dissolving glucose and laurate in an organic solvent, adding the yeast display lipase, reacting at 50-60 DEG C for 10-14 hours, and separating and purifying, thus obtaining glucose laurate. The preparation method of the yeast display lipase comprises the following steps: transforming the recombinant plasmid subjected to linear treatment into a Pichia Pastoris yeast GS115, inoculating the obtained transformants into a BMMY (buffered methanol-complex medium), inducing and culturing for 72-144 hours, carrying out centrifugal collection on thallus, washing, and carrying out organism printing and frozen drying on the washed thallus, thus obtaining the yeast display lipase. Through displaying lipase outside cells, and utilizing the lipase to conduct catalytic synthesis of the glucose laurate, the conversion efficiency can be improved, the reaction time is shortened, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
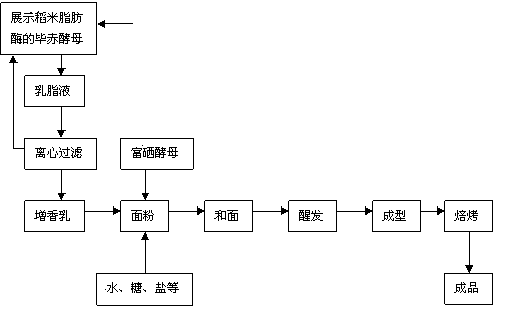
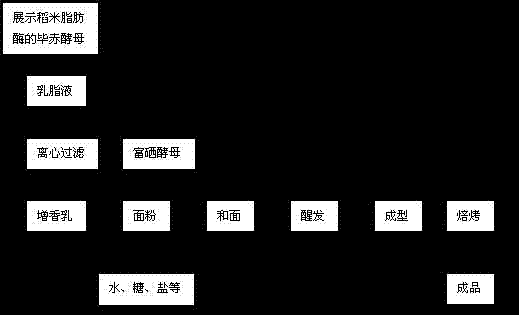
Method for producing cream-aroma selenium-enriched bread from yeast display lipase
InactiveCN103734221AGreat tasteRich frankincenseFungiPre-baking dough treatmentPichia pastorisYeast display
The invention discloses a method for producing cream-aroma selenium-enriched bread from yeast display lipase. The method includes displaying rice lipase on the surface of pichia pastoris, performing multiplication culture for 48-96 hours, enabling yield of the rice lipase to sharply increase with yield of yeast, adding 1-4 parts of saccharomycetes displayed with the rice lipase into 200-300 parts of cream liquid for esterlysis reaction at the temperature of 35-55 DEG C for 2-6 hours, subjecting the mixture to filtering separation, washing the yeast to allow the same to be reusable, adding filtrate into 1000 parts, by weight, of flour, then adding 1-4 parts of selenium-enriched yeast and other raw materials, and performing dough kneading, fermentation, forming and baking to obtain the delicious healthcare bread with rich cream aroma and rich organic selenium.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for disrupting seaweed cells by using yeast display pectinase cooperated with ultrasonic waves
InactiveCN102321598AImprove hydrolysis activitySignificant blood pressure lowering activityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesPectinaseYeast display
The invention discloses a method for disrupting seaweed cells by using yeast display pectinase cooperated with ultrasonic waves, which comprises the following steps that: dry seaweed powder and yeast display pectinase are added into water, are uniformly mixed, are subjected to enzymatic reaction for 30 to 45min at the temperature of 35 to 37 DEG C, and are disrupted for 65 to 70min by utilizing ultrasonic waves with the power of 730 to 750W at the temperature of 30 to 32 DEG C. The invention also discloses a method for extracting seaweed proteins and porphyra polysaccharides, which is characterized in that: cell disruption liquid obtained after the seaweed cells are disrupted is separated. The invention also discloses a method for preparing seaweed antihypertensive peptides, which is characterized in that: the separated seaweed proteins are subjected to enzymatic reaction for 130 to 133min at the temperature of 36 to 37 DEG C by using protease. In the method, the seaweed cell walls are degraded by yeast display pectinase, and ultrasonic wave treatment is synergically carried out, so that the seaweed cells are efficiently disrupted, thereby the disruption rate of the seaweed cells is improved, and the yields of seaweed polysaccharides, seaweed proteins and seaweed antihypertensive peptides are increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation of high-activity phospholipids enzyme D and cell surface display phospholipids enzyme D yeast whole cell catalysts
The invention relates to preparation of high-activity phospholipids enzyme D and cell surface display phospholipids enzyme D yeast whole cell catalysts, which belongs to a method for carrying out site directed mutagenesis wild phospholipids enzyme D by recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) for improving the activity, connecting the mutated gene with yeast show carriers pPIC9K-Flo and efficiently displaying the mutated gene on the surface of pichia pastoris cells, and relates to a preparation method of the high-activity phospholipids enzyme D and cell surface display phospholipids enzyme D yeast whole cell catalysts. The method has the advantages that the activity of the wild phospholipids enzyme D is improved and is shown on the surfaces of the pastoris cells, the stability is improved,and the advantages of immobilized enzymes are realized. The method has the technical scheme that wild phospholipids enzyme D genes are separated from microbes, particularly streptomyces aureofuscus, the mutation is carried out on the amino acid residue of Glu69 and Ser285, through the efficient expression on the surfaces of the pichia pastoris cells, the enzyme activity of the high-activity phospholipids enzyme is improved by 11 percent than the wild type phospholipids enzyme D, and the enzyme activity of the recombination strains GS115 / pPIC9K-Flo-pldm prepared through high-density fermentation is 120U / (g. stem cells).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for catalytic synthesis of starch phosphate by utilizing yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212585AHigh Catalytic Synthesis Conversion EfficiencyReduce manufacturing costFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisYeast display
The invention discloses a method for catalytic synthesis of starch phosphate by utilizing yeast display lipase, and the method comprises the steps: dissolving grain starch in water, adding NaH2PO4 and the yeast display lipase after imbibition, reacting at 55-65 DEG C for 1-1.5 hours, and separating and purifying, thus obtaining the starch phosphate. The preparation method of the yeast display lipase comprises the following steps: transforming the recombinant plasmid subjected to linear treatment into a Pichia Pastoris yeast GS115, inoculating the obtained transformants into a BMMY (buffered methanol-complex medium), inducing and culturing for 72-144 hours, carrying out centrifugal collection on thallus, washing, and carrying out organism printing and frozen drying on the thallus, thus obtaining the yeast display lipase. Through displaying lipase outside cells, and utilizing the lipase to conduct catalytic synthesis of the starch phosphate, the conversion efficiency can be improved, the reaction time is shortened, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing frankincense selenium-rich blueberry vinegar by means of yeast display of lipase
The invention discloses a method for producing frankincense selenium-rich blueberry vinegar by means of yeast display of lipase. The method comprises the following steps: displaying rice lipase on the surface of pichia pastoris, performing multiplication culture for 48-96 hours to increase the yield of the rice lipase greatly along with the yield of the pichia pastoris, adding 1-4 parts by weight (wet weight) of the yeast on which the rice lipase is displayed into 200-300 parts of cream, carrying out an esterlysis reaction at 35-55 DEG C for 2-6 hours, and filtering to obtain aroma-enhanced emulsion; producing blueberry vinegar rich in organic selenium from selenium-rich blueberry and selenium-rich yeast serving as basic raw materials by adopting a semi-solid method, and mixing the aroma-enhanced emulsion and the selenium-rich blueberry vinegar in the ratio of 1:9-3:7 (w / w) to obtain the a frankincense selenium-rich blueberry vinegar health-care beverage which is deeply loved by customers. By using the frankincense selenium-rich blueberry vinegar, trace element necessary for human bodies, namely, selenium can be replenished safely and efficiently for customers, and the health-care functions of eyesight improving, skin moistening and ageing resisting of the blueberry vinegar are brought into play.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for catalytic synthesis of L-ascorbic acid linoleate by utilizing yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212574BImprove operational stabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisOrganosolv
The invention discloses a method for catalytic synthesis of L-ascorbic acid linoleate by utilizing yeast display lipase, and the method comprises the following steps: dissolving L-ascorbic acid and linoleic acid in an organic solvent, adding the yeast display lipase, reacting at 50-60 DEG C for 4-8 hours under an anaerobic condition, and separating and purifying, thus obtaining the L-ascorbic acid linoleate. The preparation method of the yeast display lipase comprises the following steps: transforming the recombinant plasmid subjected to linear treatment in a Pichia Pastoris yeast GS115, inoculating the obtained transformants into a BMMY (buffered methanol-complex medium), inducing and culturing for 72-144 hours, carrying out centrifugal collection on thallus, washing, and carrying out organism printing and frozen drying on the thallus, thus obtaining the yeast display lipase. Through displaying lipase outside cells, and utilizing the lipase to conduct catalytic synthesis of the L-ascorbic acid L-ascorbic acid linoleate, the conversion efficiency can be improved, the reaction time is shortened, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing cream-aroma selenium-enriched bread from yeast display lipase
InactiveCN103734221BGreat tasteRich frankincenseFungiPre-baking dough treatmentPichia pastorisYeast display
The invention discloses a method for producing cream-aroma selenium-enriched bread from yeast display lipase. The method includes displaying rice lipase on the surface of pichia pastoris, performing multiplication culture for 48-96 hours, enabling yield of the rice lipase to sharply increase with yield of yeast, adding 1-4 parts of saccharomycetes displayed with the rice lipase into 200-300 parts of cream liquid for esterlysis reaction at the temperature of 35-55 DEG C for 2-6 hours, subjecting the mixture to filtering separation, washing the yeast to allow the same to be reusable, adding filtrate into 1000 parts, by weight, of flour, then adding 1-4 parts of selenium-enriched yeast and other raw materials, and performing dough kneading, fermentation, forming and baking to obtain the delicious healthcare bread with rich cream aroma and rich organic selenium.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for catalytically synthesizing L-ascorbyl oleate with yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212572BImprove operational stabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for catalytically synthesizing L-ascorbyl oleate with yeast display lipase. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving L-ascorbic acid and oleic acid in an organic solvent; adding yeast display lipase to react at 50-60 DEG C for 4-8 hours under anaerobic conditions; and carrying out separation and purification to prepare L-ascorbyl oleate, wherein the yeast display lipase is prepared by transforming recombinant plasmid which is subjected to linearization into Pichia pastoris GS115, inoculating the obtained transformant in a BMMY culture medium, carrying out inducing culture for 72-144 hours, centrifuging to collect a thallus, and carrying out washing, bio-imprinting and freeze-drying on the thallus. By displaying the lipase outside the cell and utilizing the lipase preparation to catalytically synthesize the L-ascorbyl oleate, the invention improves the transformation efficiency, shortens the reaction time and lowers the production cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Selenium-enriched yeast gene engineering bacteria and surface display system thereof and construction method of surface display system
PendingCN113322223AEnabling Yeast Surface DisplayFacilitates antiviral activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySurface display
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to selenium-enriched yeast gene engineering bacteria and a surface display system thereof and a construction method of the surface display system. Yeast gene engineering bacteria are cultured by using a culture medium, and then sodium selenite is added for continuous culture to obtain the selenium-enriched yeast gene engineering bacteria. Goat gamma-interferon is inserted into a His tag, and pYD1-CapIFN-gamma is constructed by taking a pYD1 shuttle plasmid as a skeleton; and then the pYD1-CapIFN-gamma is introduced into the selenium-enriched yeast gene engineering bacteria to obtain a goat gamma-interferon selenium-enriched yeast display system. The system carries out selenium-enriched transformation on the yeast in the system, so that the application range of a goat gamma-interferon yeast expression system is widened; the yeast surface display of the goat gamma-interferon is implemented, which is more beneficial for exerting the antiviral activity of the goat gamma-interferon; and a foundation is laid for research and development of a safer, more effective and cheaper novel yeast feed additive capable of resisting to viruses and enhancing the immunity of organisms.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI
Yeast-displayed polygalacturonase combined with ultrasonic treatment to extract laver polysaccharides
InactiveCN102286110AHigh activityPromote fragmentationHydrolasesFermentationPichia pastorisPentagalacturonic acid
The invention discloses a method for extracting porphyra polysaccharide through ultrasonic treatment with cooperation of yeast display type polygalacturonase. The method comprises the following steps of: adding dry porphyra powder and yeast display type polygalacturonase to water, mixing uniformly, stirring to react at 35-37 DEG C for 30-45min, crushing at 28-35 DEG C for 1-2 hours by utilizing ultrasonic with power of 730-750W to obtain a cell disruption liquid, separating and purifying to obtain the porphyra polysaccharide. According to the method disclosed by the invention, and the polygalacturonase is displayed outside pichia pastoris cells and is cooperated with the ultrasonic to crush porphyra cells, thus the process is simple and convenient, the condition is gentle, the process is easy to be controlled and is safe and reliable, and higher-yield and higher-purity porphyra polysaccharide can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Construction of fully human antibody yeast display technique
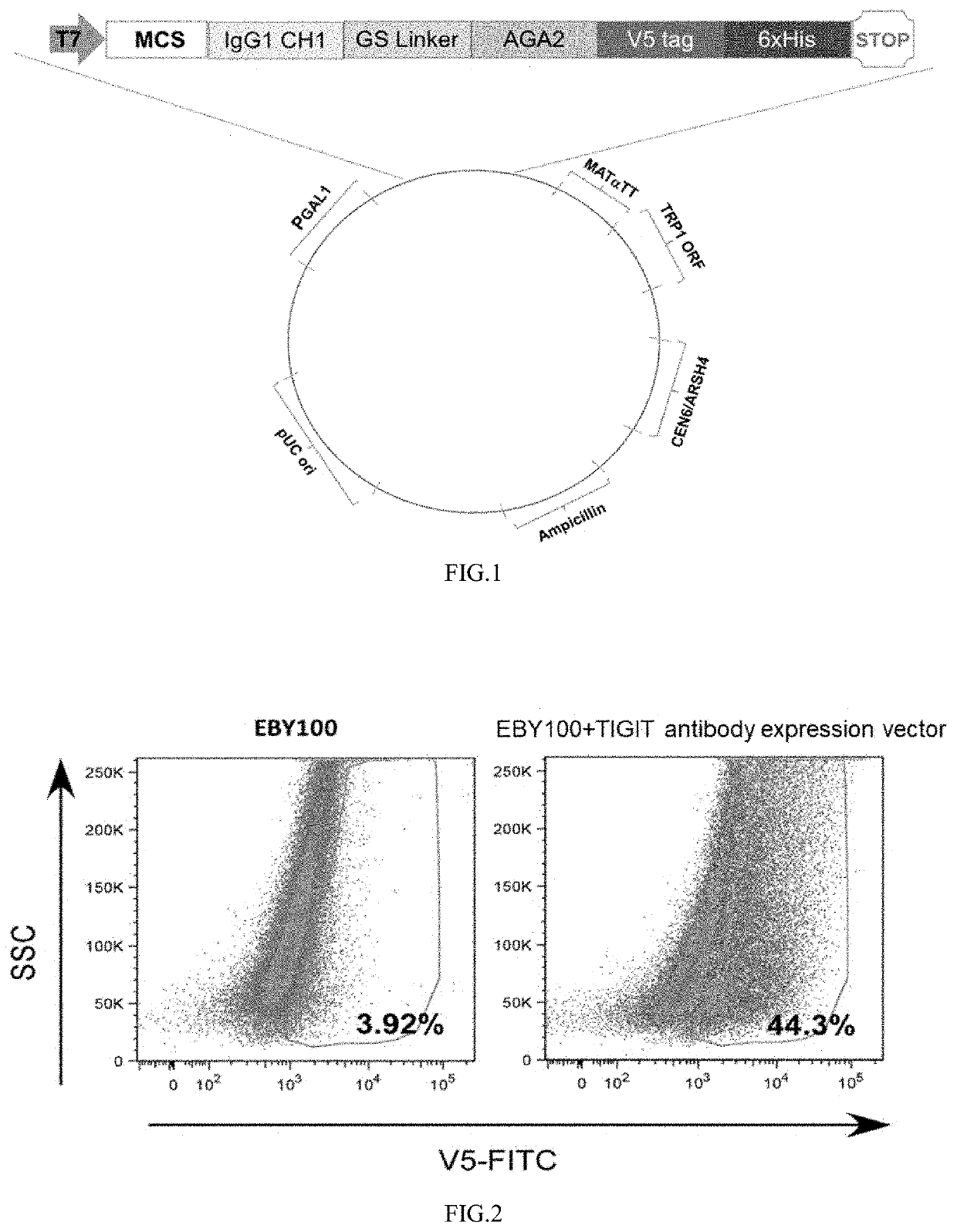
ActiveUS20220135988A1Improve transformation efficiencyRich diversityMicroorganism librariesNucleic acid vectorYeast displayTransformation efficiency
The present disclosure application relates to a construction method of a yeast display library (YSD), specifically to a construct for a yeast display library, an expression vector, a host cell and a construction method and use thereof. The yeast display library provided by the present application has high transformation efficiency and rich diversity.
Owner:ADLAI NORTYE BIOPHARMA CO LTD
Method for establishing HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) virus antibody yeast display library, method for screening virus broad-spectrum neutral antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN104725501AQuality improvementImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsYeast AntibodyYeast display
The invention provides a method for screening a virus broad-spectrum neutral antibody and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: preparing or providing a virus antigen protein; marking the virus antigen protein by using a fluorescence marker; preparing a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) template of a virus positive patient, designing primers, and amplifying the antibody gene; establishing a yeast antibody display library by using the obtained antibody gene; carrying out antigen protein mixed incubation on yeast cells in the obtained antibody display library and the obtained virus with the fluorescence marker, setting a cell separation door, and separating fluorescence positive yeast cells by a flow cytometry; and carrying out sequencing identification on the fluorescence positive yeast cells to obtain the virus broad-spectrum neutral antibody. The invention also provides a method for establishing an HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) virus antibody yeast display library and application thereof.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for synthesizing fructose palmitate by catalysis of yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212578AImprove operational stabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing fructose palmitate by catalysis of yeast display lipase. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving fructose and palmitic acid into an organic solvent, adding the yeast display lipase, reacting for 10 to 14 hours at the temperature of between 50 and 60 DEG C, and performing separation and purification to obtain the fructose palmitate, wherein the yeast display lipase is prepared by the following steps of: transferring linearly treated recombinant plasmids to pichia pastoris GS115, inoculating the obtained transformant to a buffered methanol complex (BMMY) medium, performing induced culture for 72 to 144 hours, performing centrifugal collection on bacteria, and performing flushing, biological imprinting and freeze drying on the bacteria to obtain the yeast display lipase. The lipase is displayed outside cells, and the fructose palmitate is synthesized by catalysis of the enzyme preparation, so that the transformation efficiency is improved, the reaction time is shortened and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for synthesizing L-ascorbyl palmitate by catalysis of yeast display lipase
InactiveCN102212575BImprove operational stabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-ascorbyl palmitate by catalysis of yeast display lipase. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving L-ascorbic acid and palmitic acid into an organic solvent, adding the yeast display lipase, reacting for 4 to 8 hours in the absence of oxygen at the temperature of between 50 and 60 DEG C, and performing separation and purification to obtain the L-ascorbyl palmitate, wherein the yeast display lipase is prepared by the following steps of: transferring linearly treated recombinant plasmids to pichia pastoris GS115, inoculating the obtained transformant to a buffered methanol complex (BMMY) medium, performing induced culture for 72 to 144 hours, performing centrifugal collection on bacteria, and performing flushing, biological imprinting and freeze drying on the bacteria to obtain the yeast display lipase. The lipase is displayed outside cells, and the L-ascorbyl palmitate is synthesized by catalysis of the enzyme preparation, so that the transformation efficiency is improved, the reaction time is shortened and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com