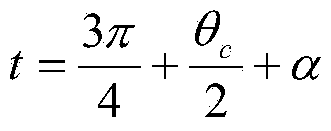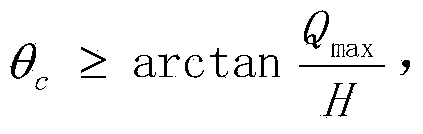Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
180 results about "Half angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The half angle is the angle that is half of original angle. Tha is, the product of two half angles at an edge is equal to the original(full) angle at that same edge.
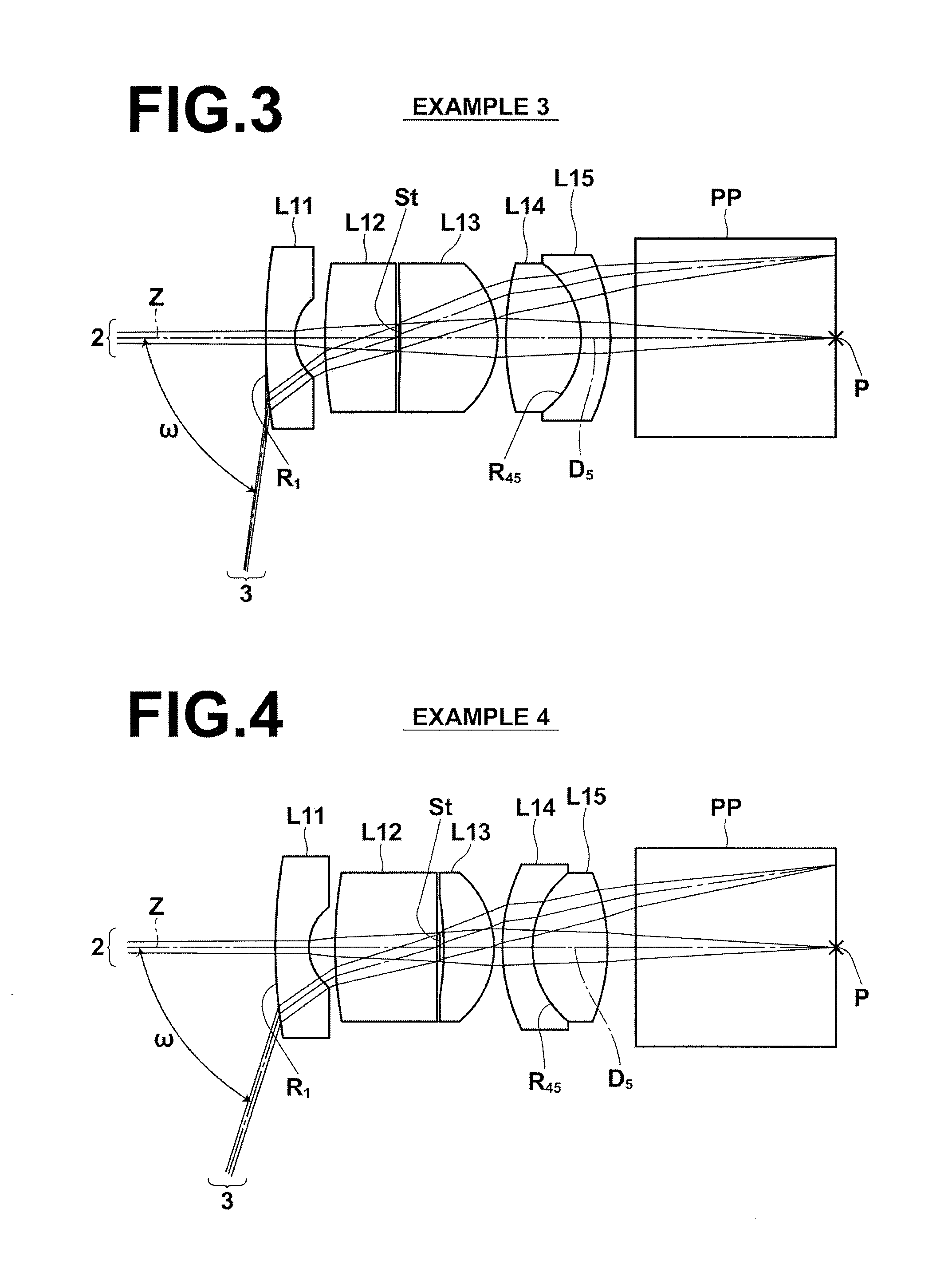
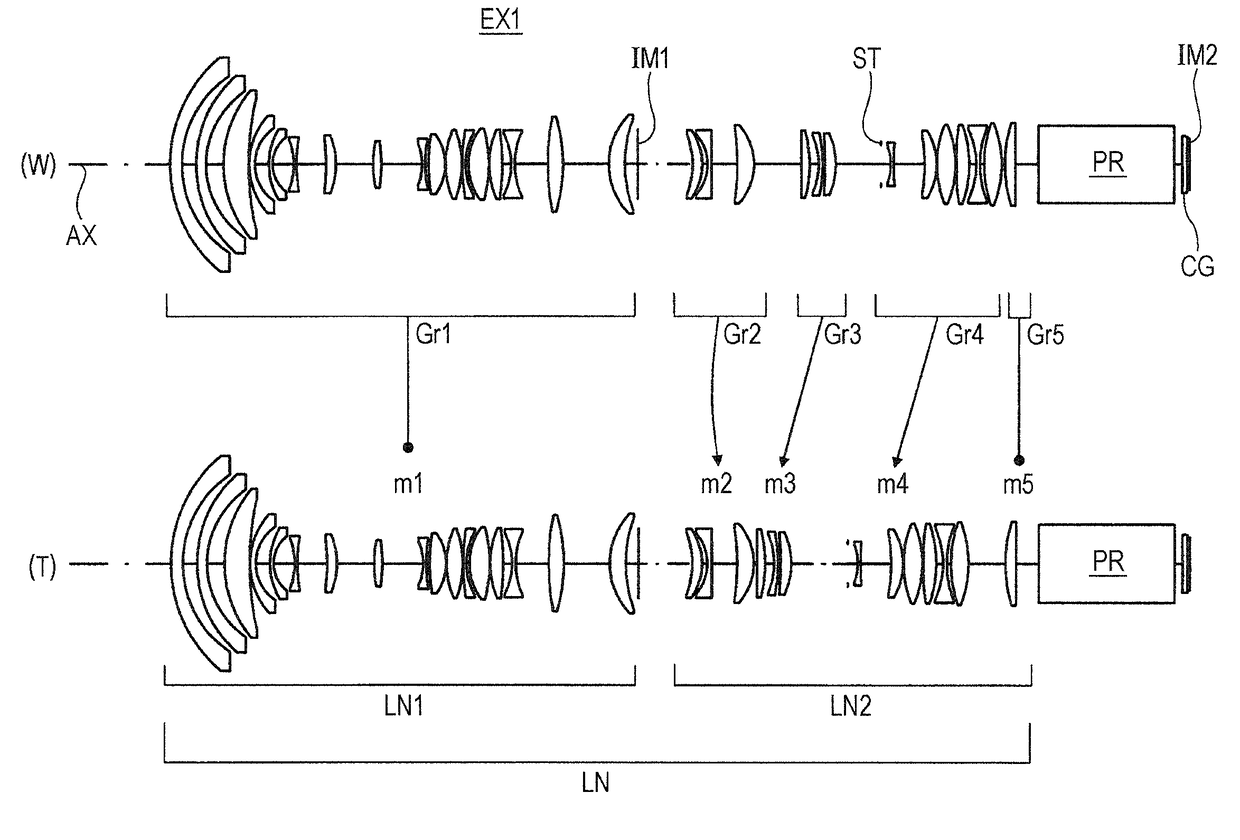
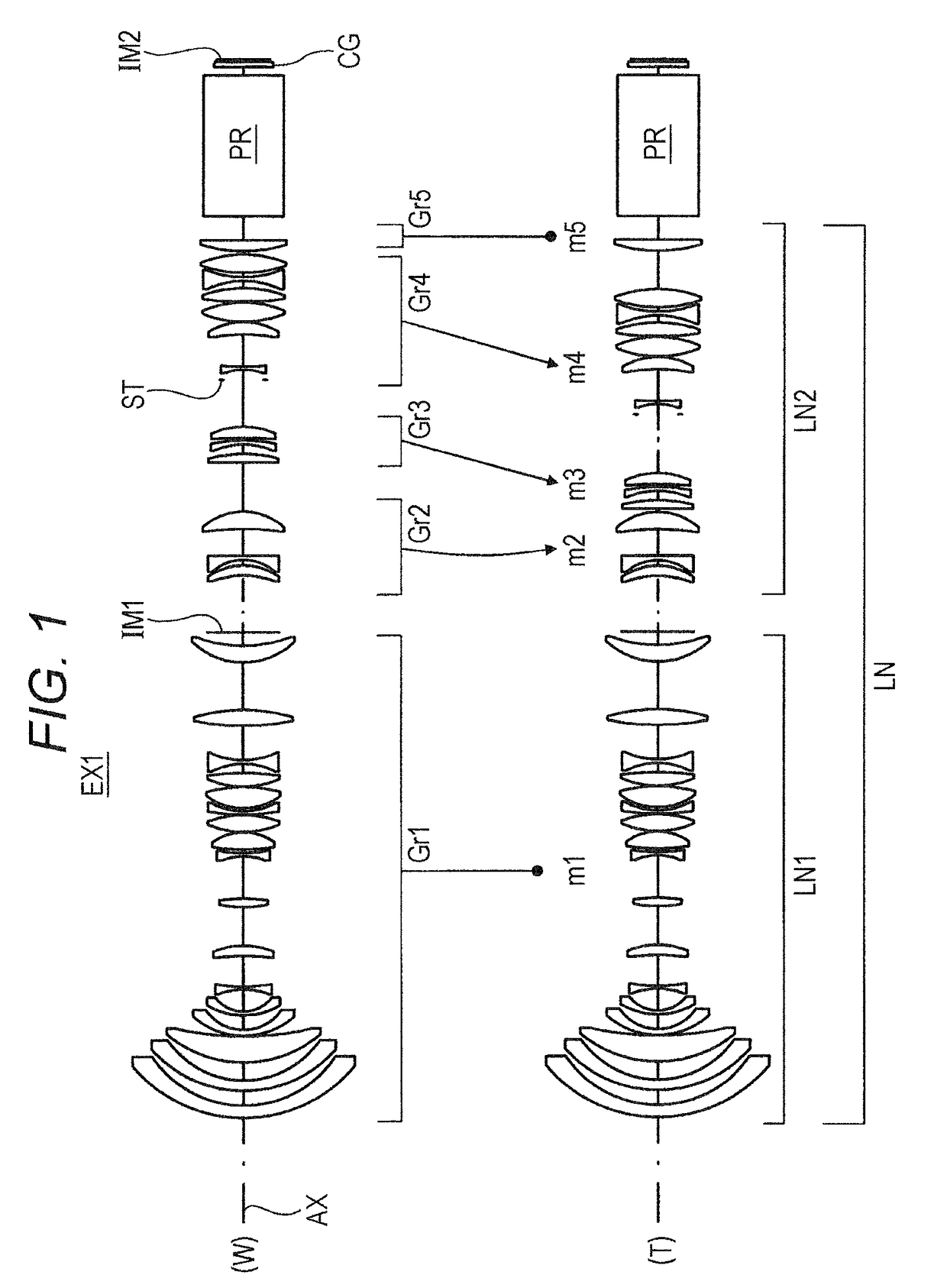
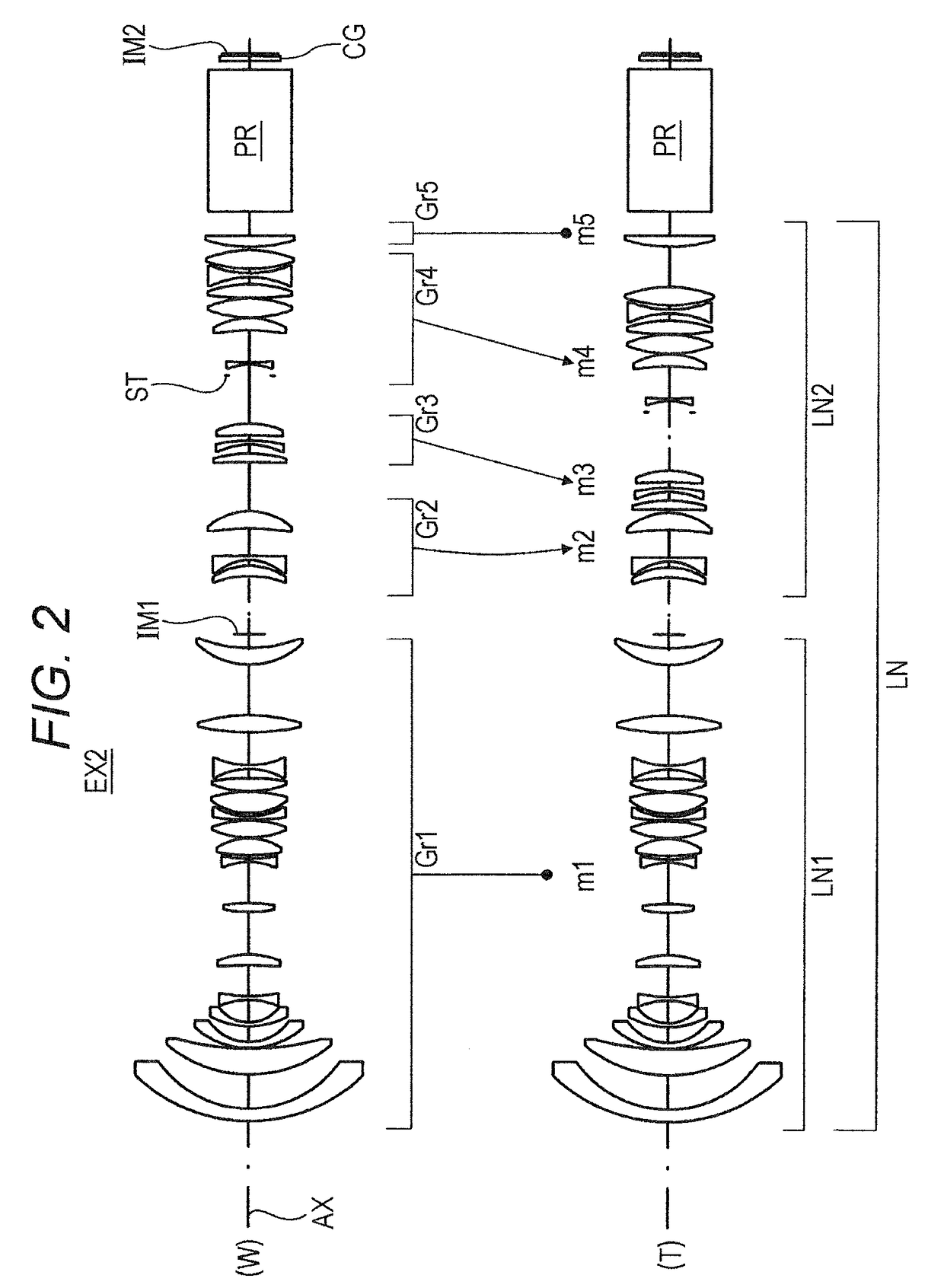
Semicondutor laser device and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20040233950A1Efficient executionLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsTectorial membraneSemiconductor package
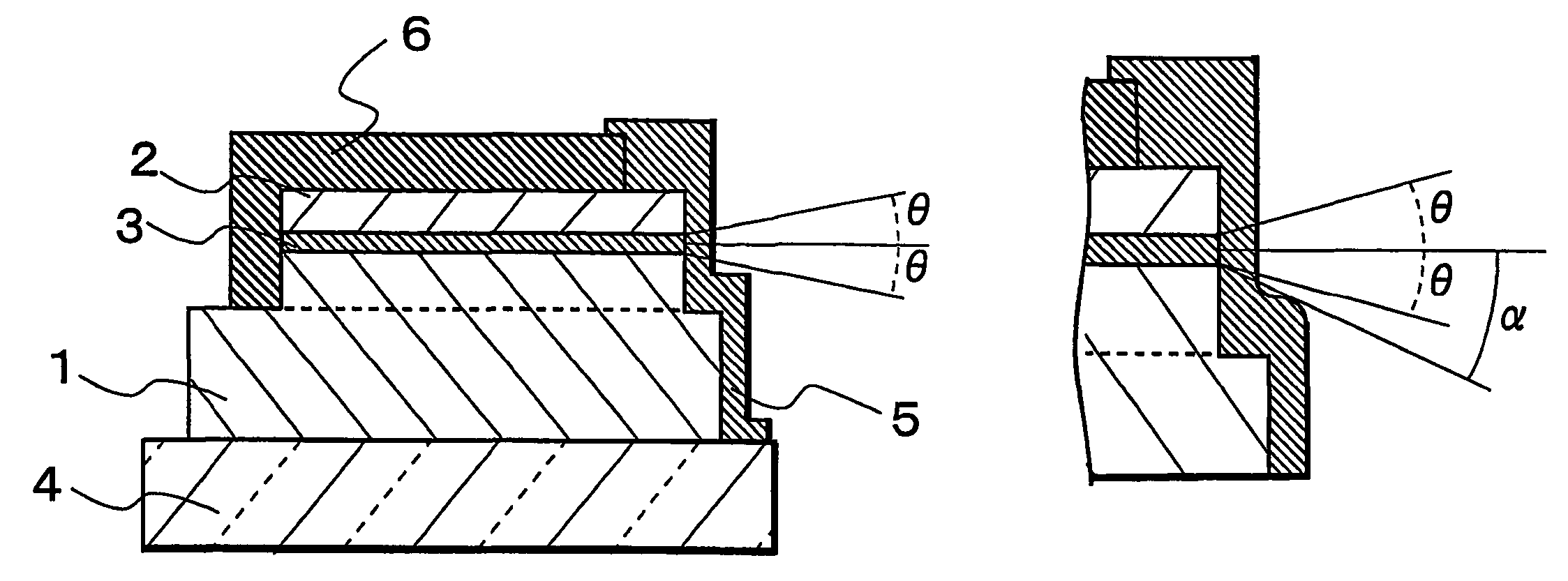
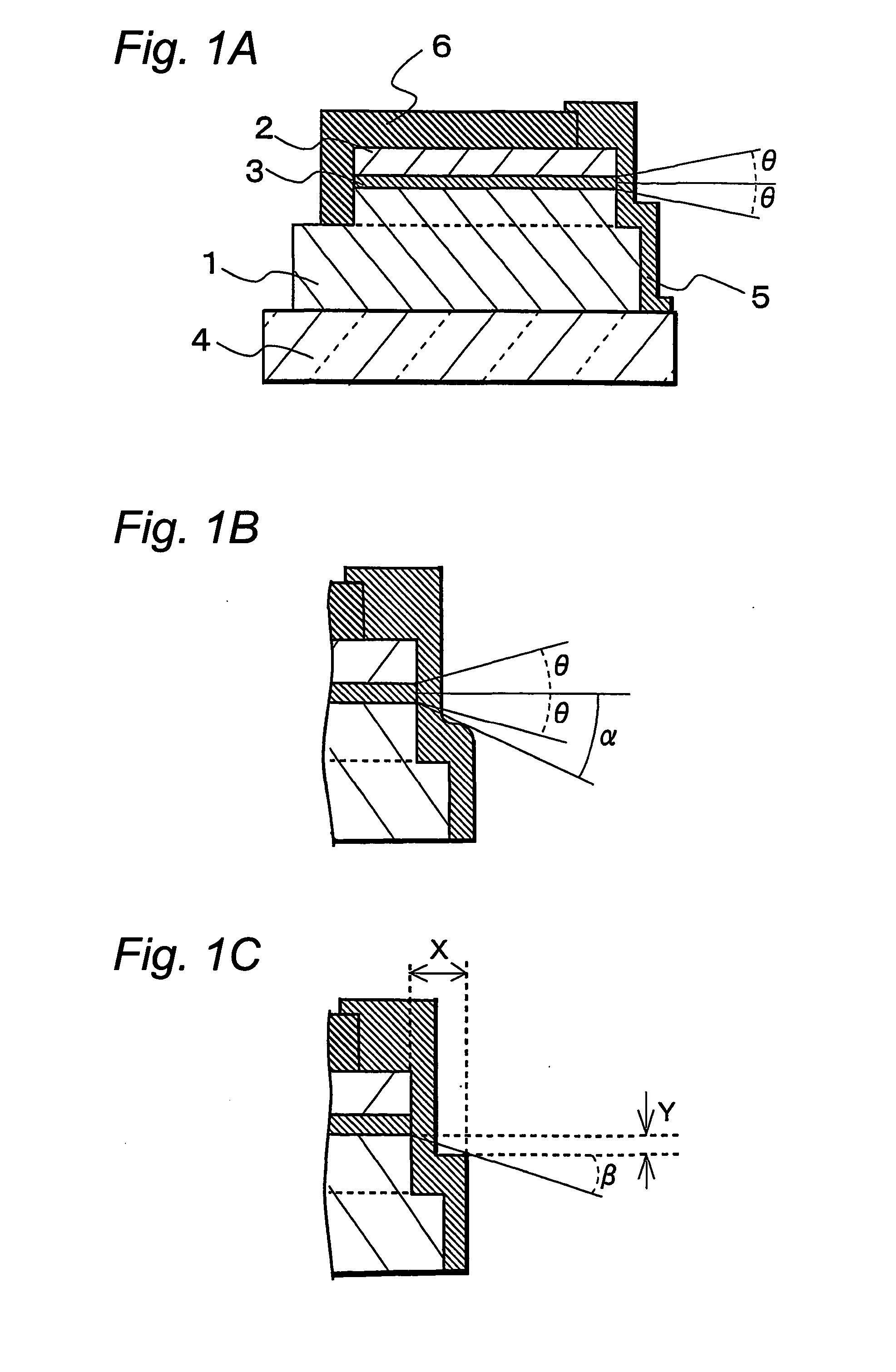
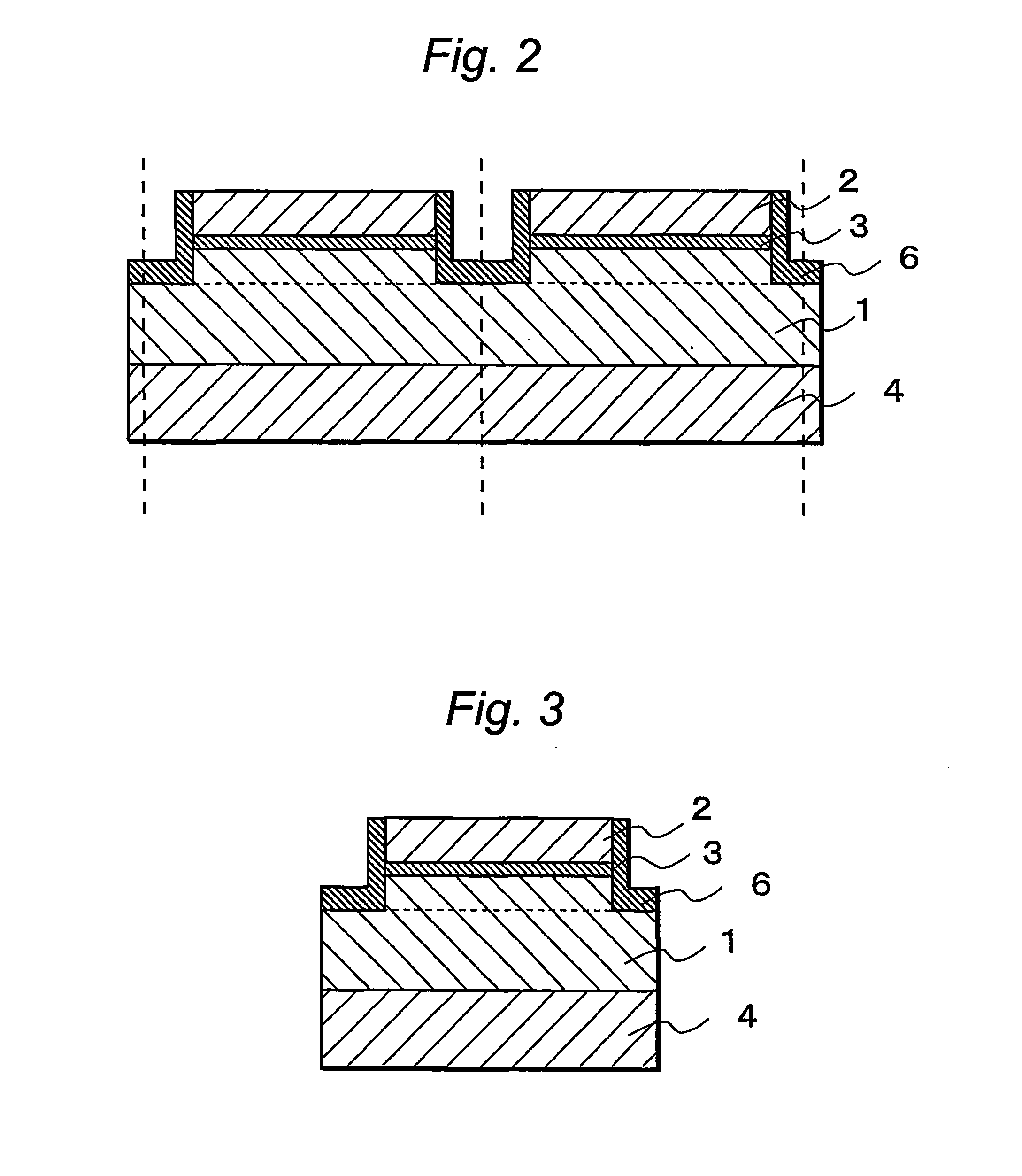
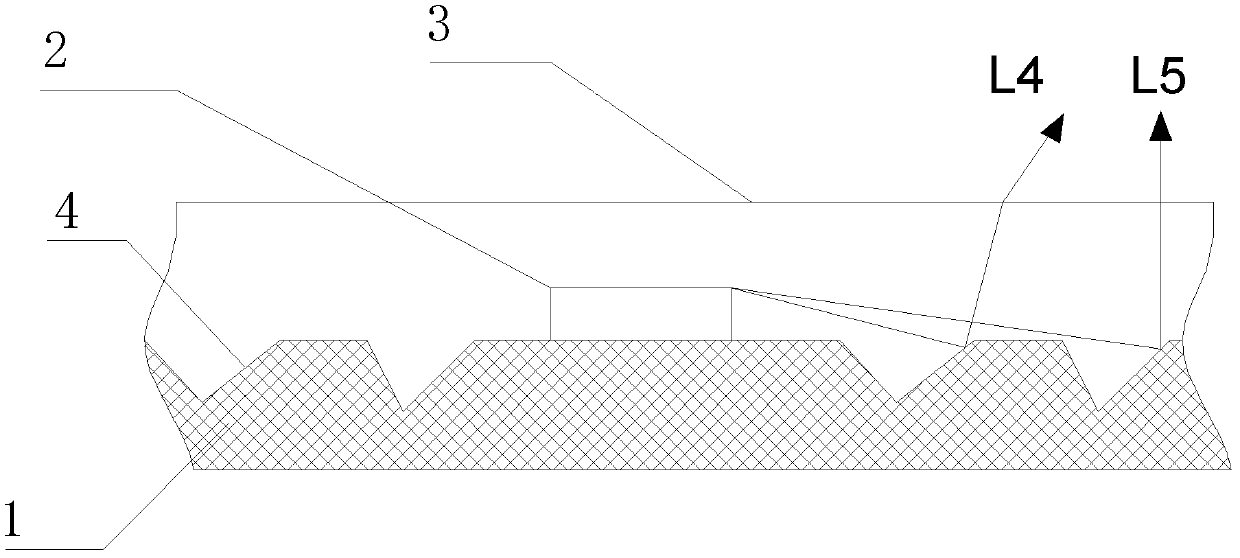
A semiconductor laser device have, on a substrate, a semiconductor layer including an active layer sandwiched between an n-type layer and a p-type layer, the semiconductor layer having a sonator face formed by etching and a projection projecting out in an emission direction relatively to the resonator face, wherein a protective film is formed to extend from the resonator face to an end face of the projection, and, an emission critical angle, which is the largest angle at which light emitted from the resonator face can be radiated without being blocked by the projection and the protective film formed on the projection, is larger than an emission half-angle of an emission distribution in a vertical direction of a laser beam emitted from the resonator face.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Objective lens for endoscopes
ActiveUS20090161234A1Improve image qualityCompact design can be attainedMicroscopesTelescopesConvex sideOptoelectronics
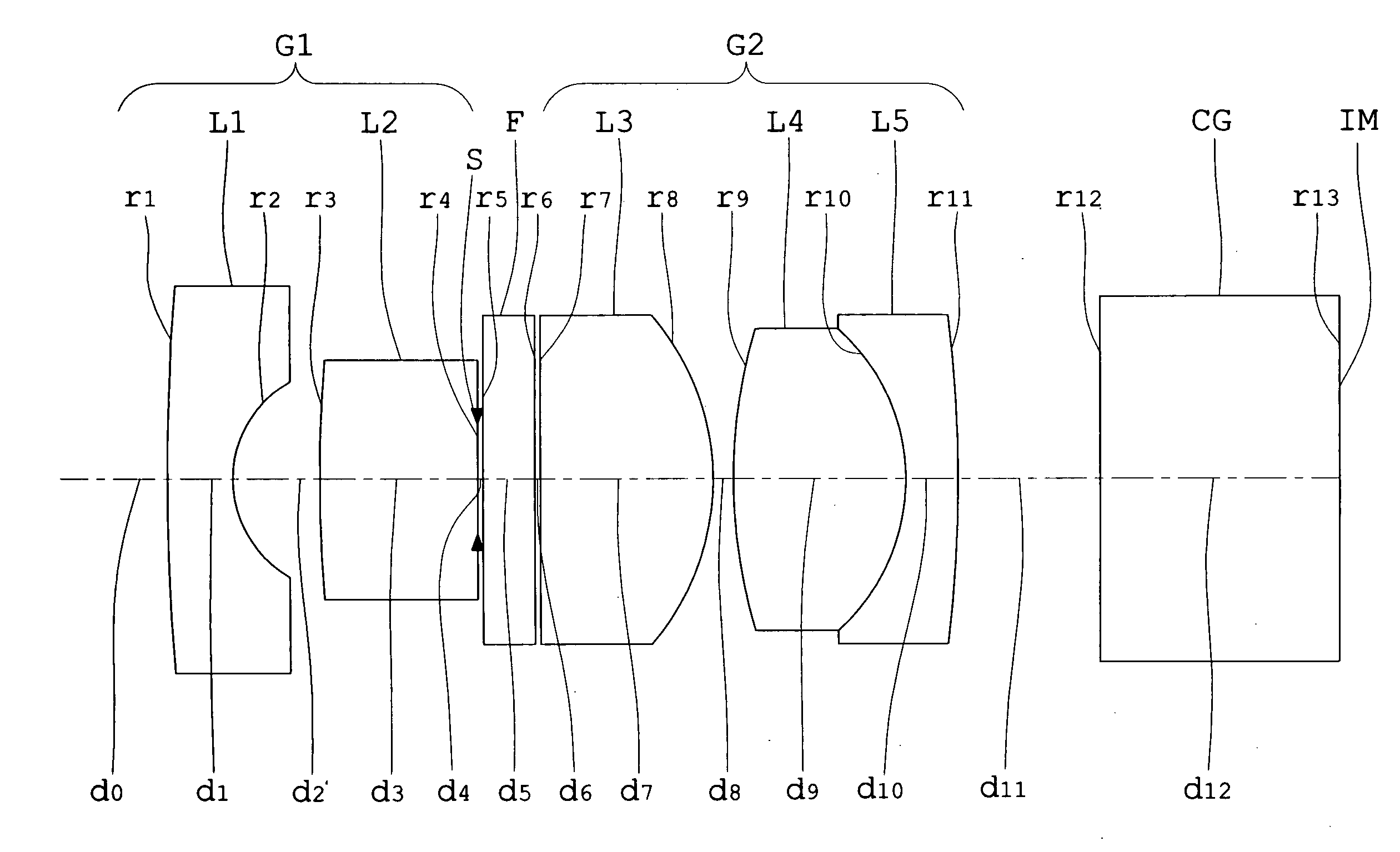
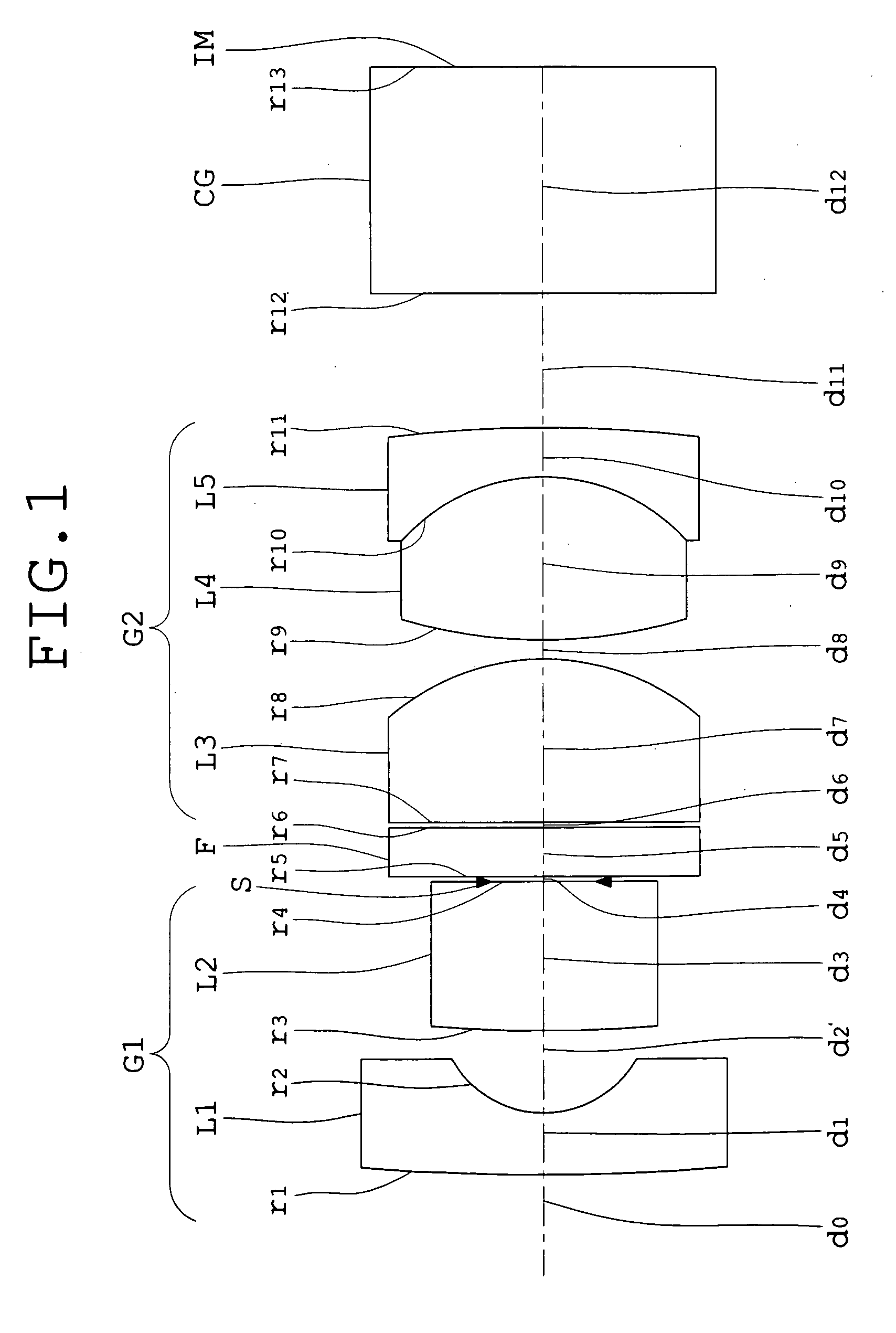
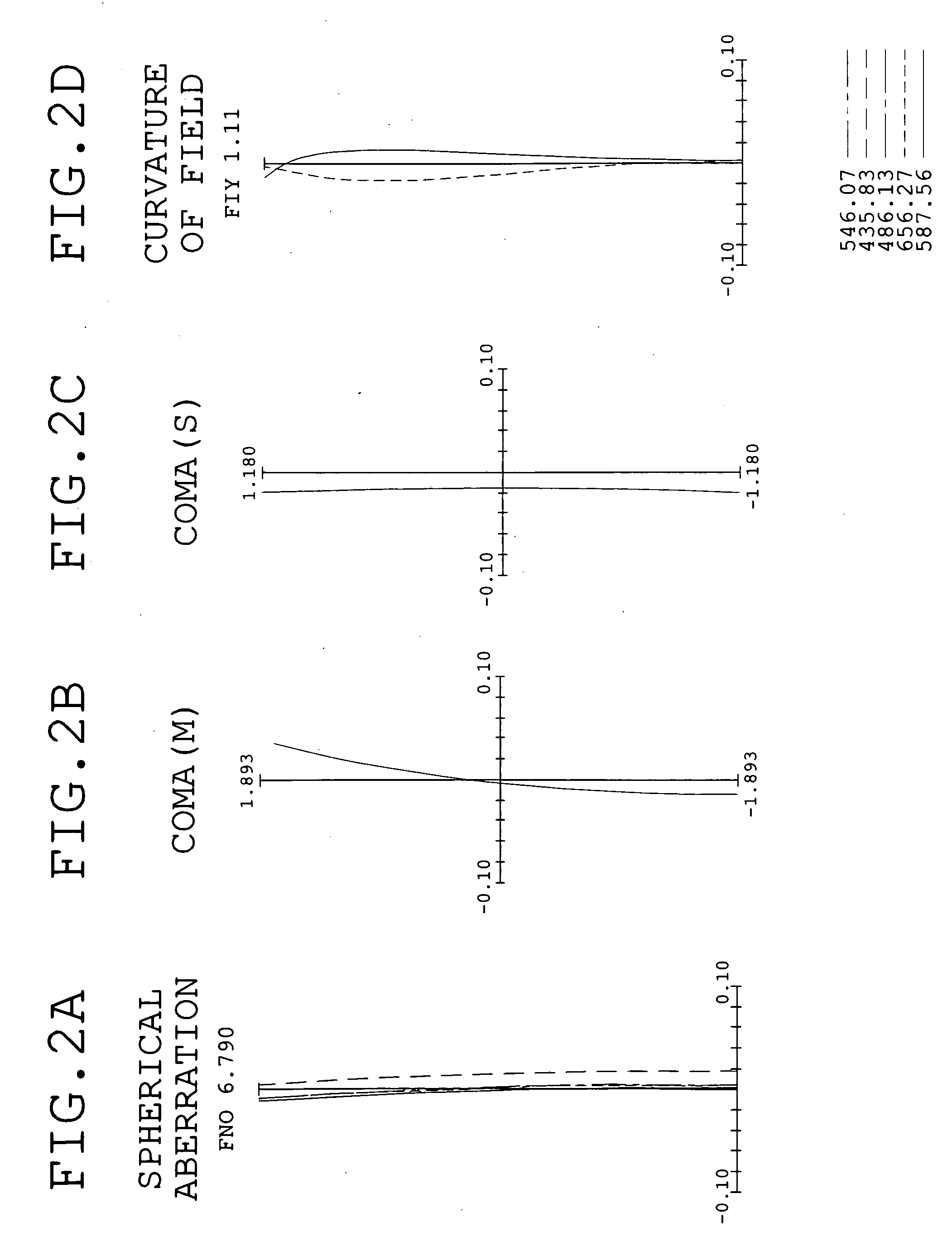
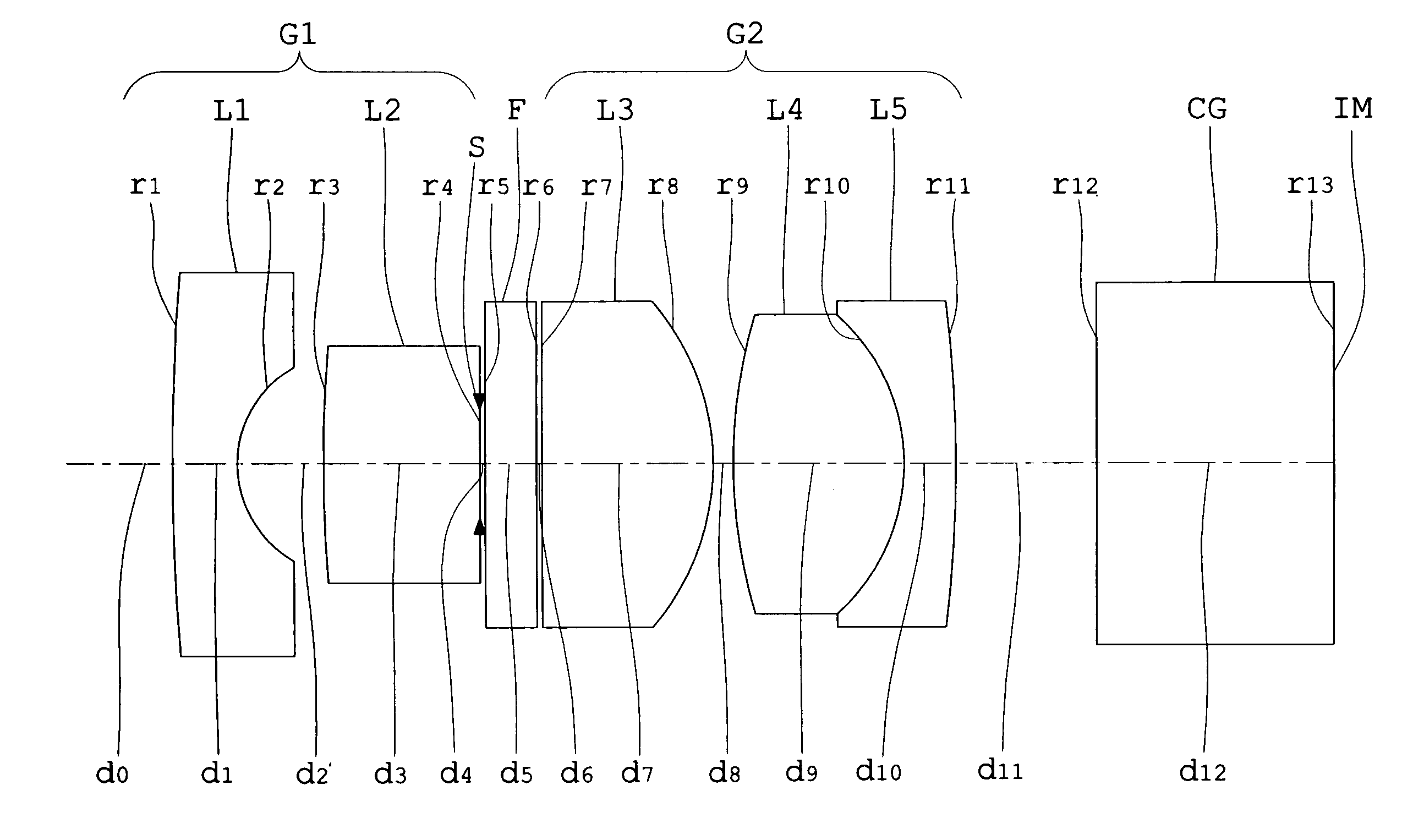
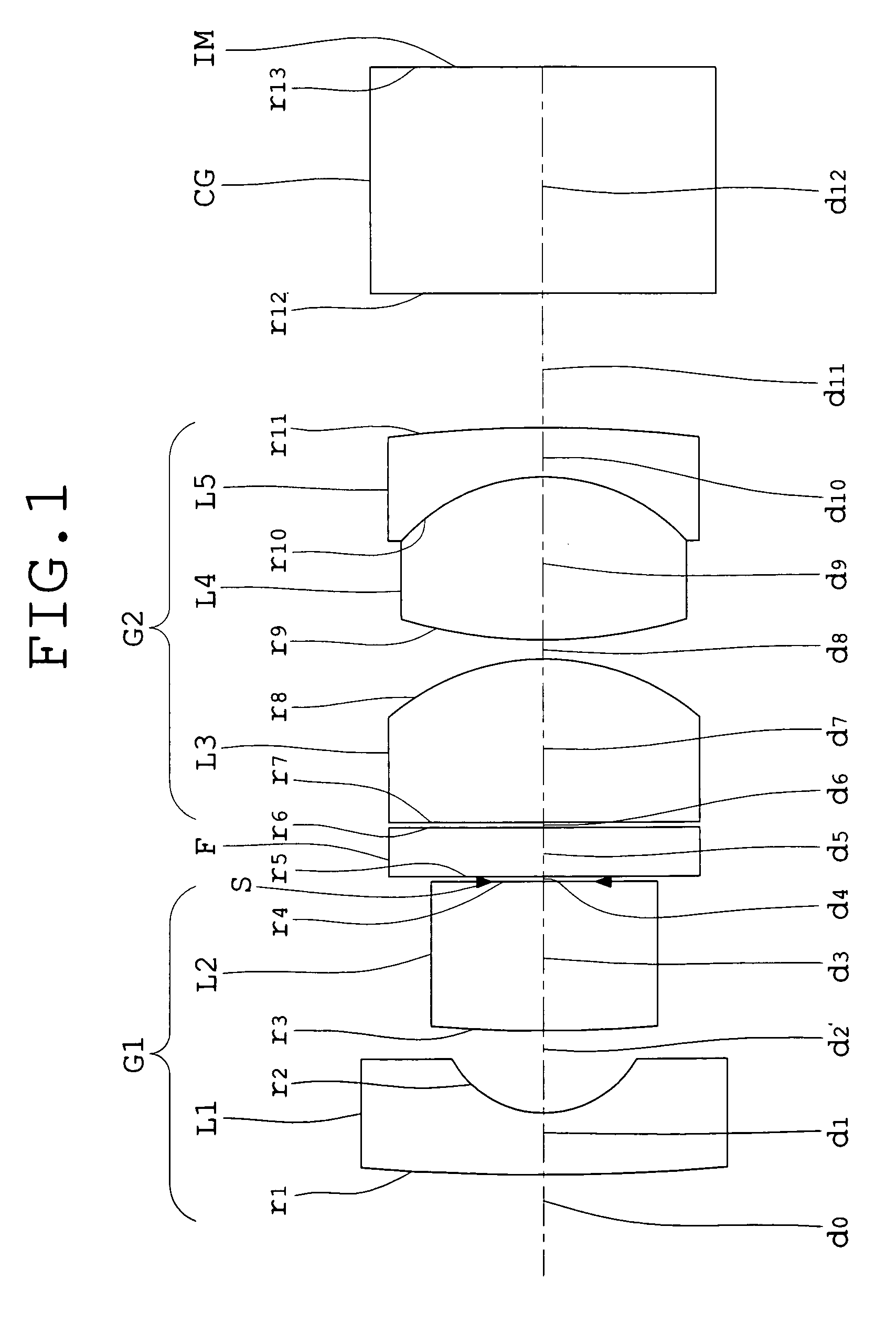
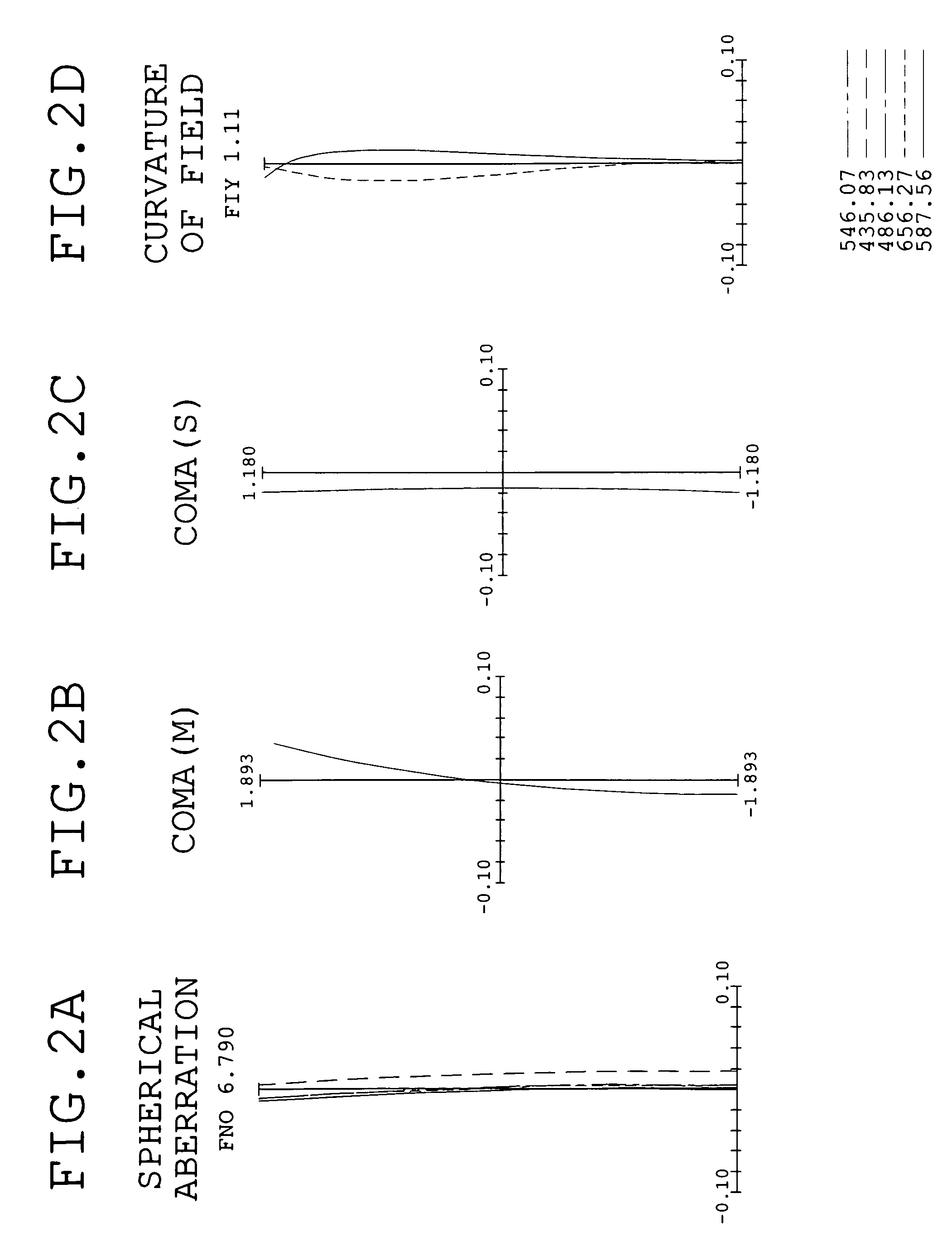
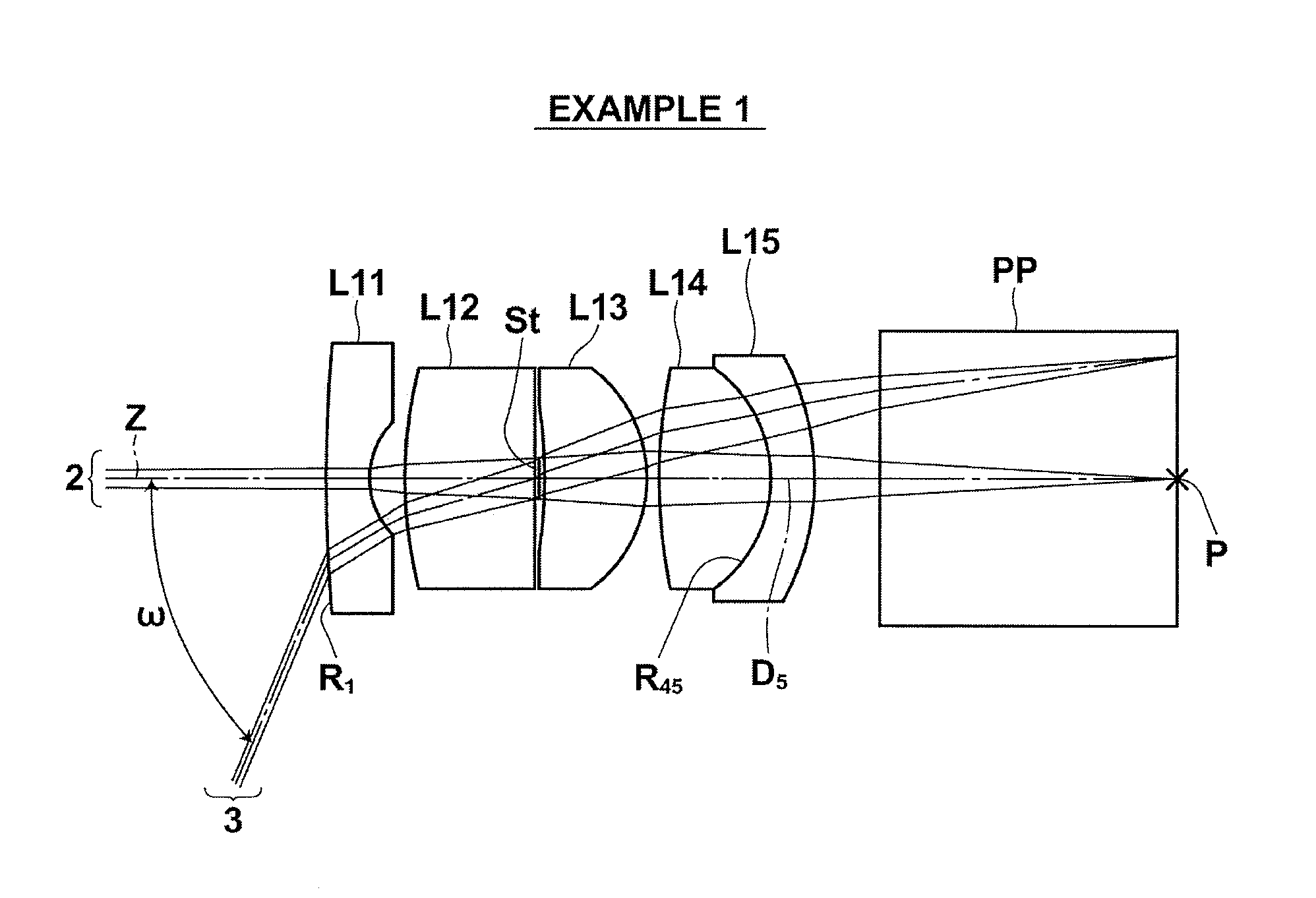
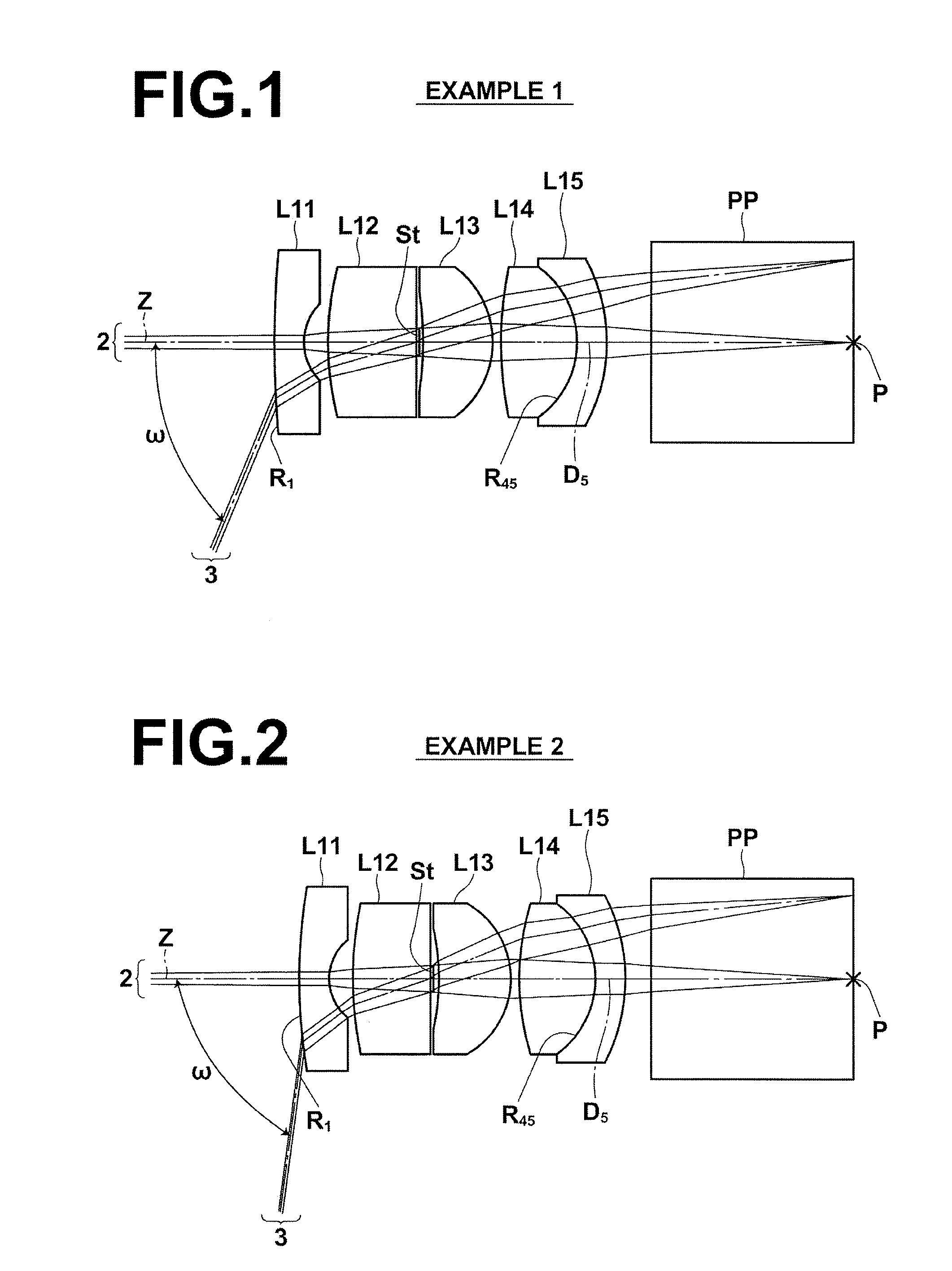
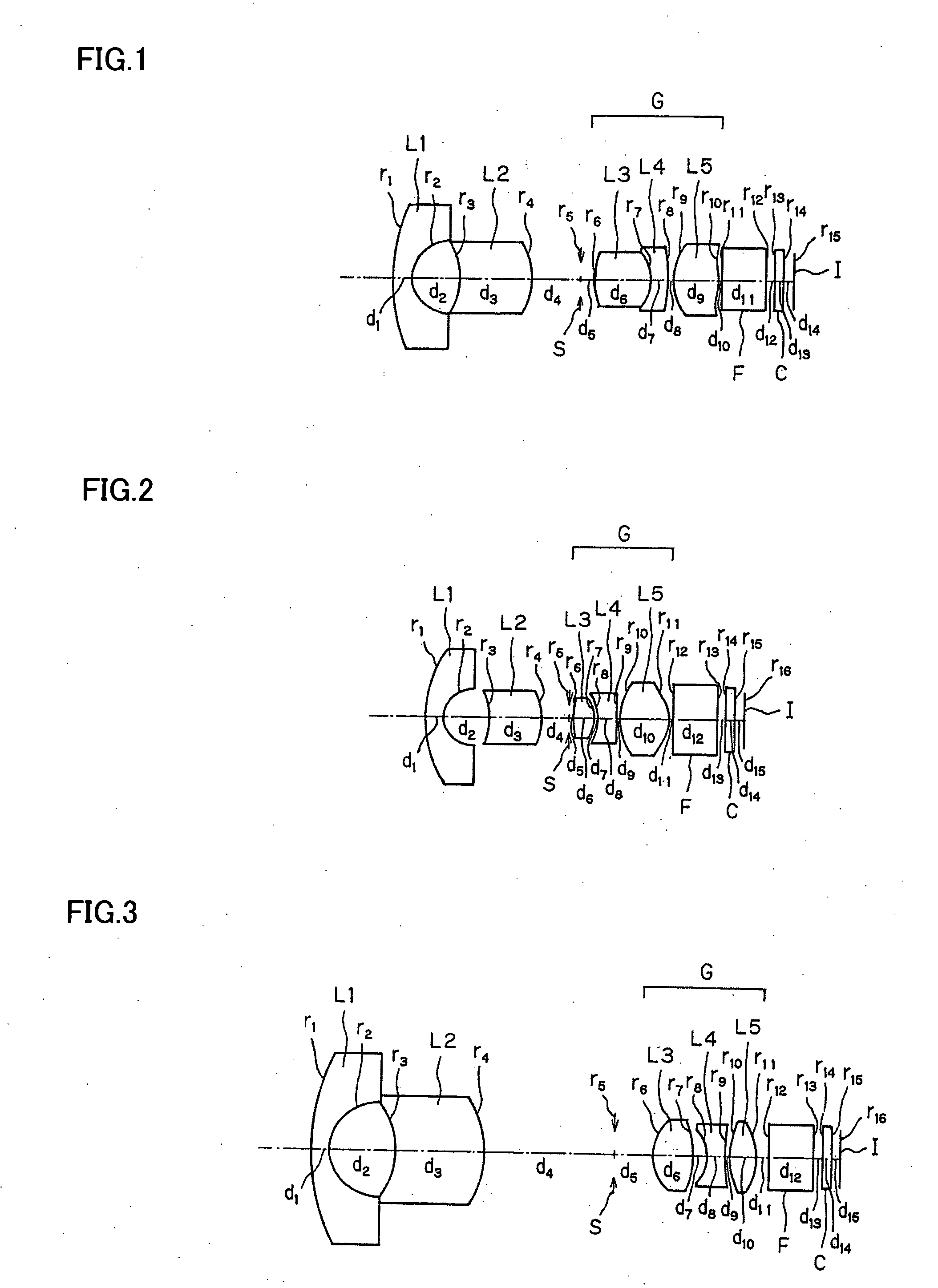
An objective lens for endoscopes has a front lens unit and a rear lens unit with an aperture stop between them. The front lens unit includes a first lens element with negative refracting power of a meniscus shape, with a convex surface facing the object side and a second lens element with positive refracting power, and the rear lens unit includes a third lens element with positive refracting power, with a surface of the minor radius of curvature facing the image side and a cemented lens component of a fourth lens element with positive refracting power and a fifth lens element with negative refracting power. The objective lens satisfies the following conditions:−2<SF<−0.90.94<D / (f×sin θ)<1.70.86<(D1+D2−f1) / (2×f3)<1.13where SF is the shape factor of the first lens element and is a value expressed by SF=(R2+R1) / (R2−R1) when the radius of curvature of the object-side surface is denoted by R1 and the radius of curvature of the image-side surface is denoted by R2; D is a distance (an equivalent-air medium length) from the vertex of the image-side surface of the first lens element to the aperture stop; f is the combined focal length of the entire system; θ is a half angle of view; D1 is an actually measured distance from the vertex of the object-side surface of the first lens element to the aperture stop; D2 is a distance (an equivalent-air medium length) from the aperture stop to the image-side surface of the third lens element; f1 is the focal length of the first lens element; and f3 is the focal length of the third lens element.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
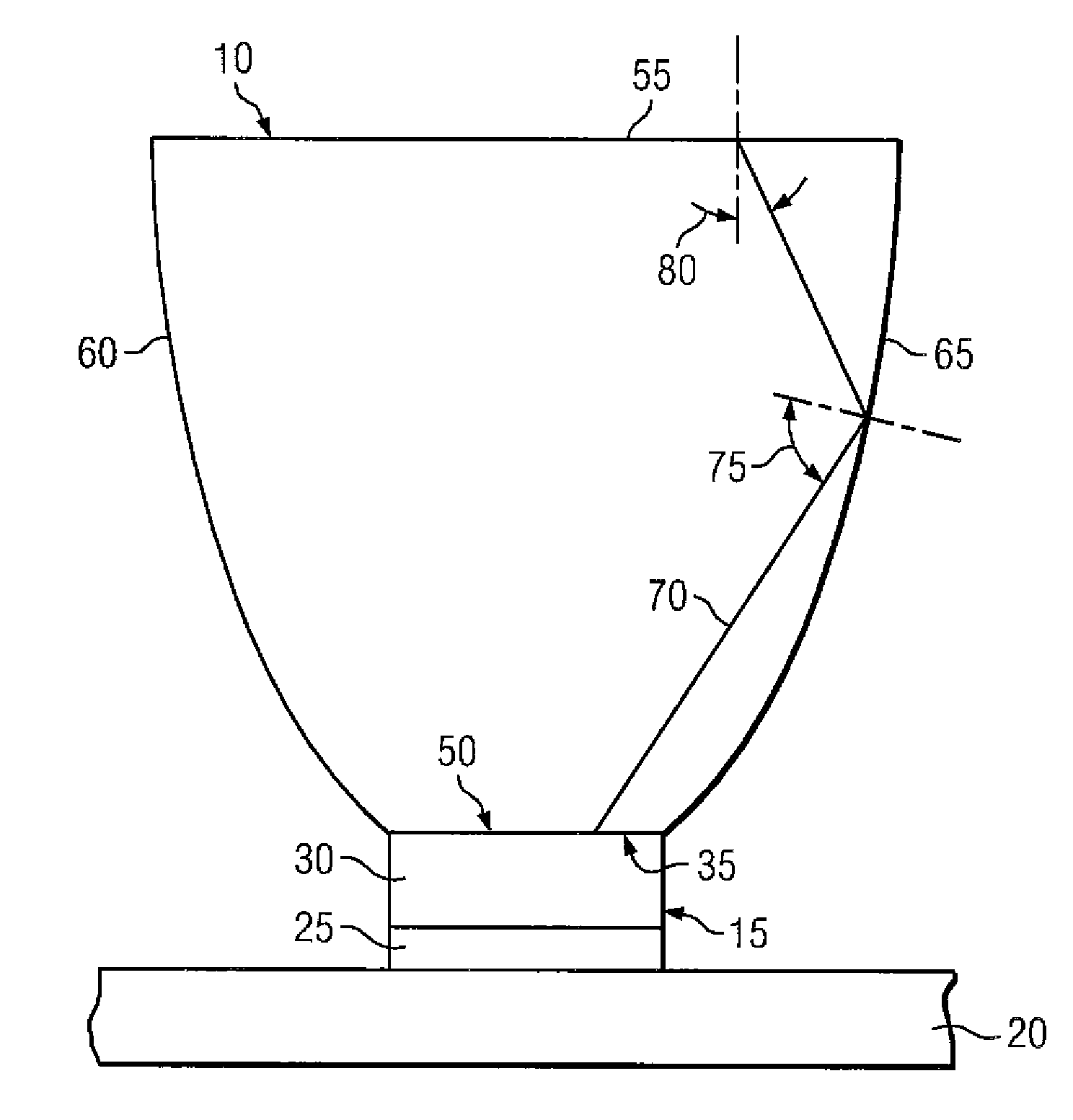
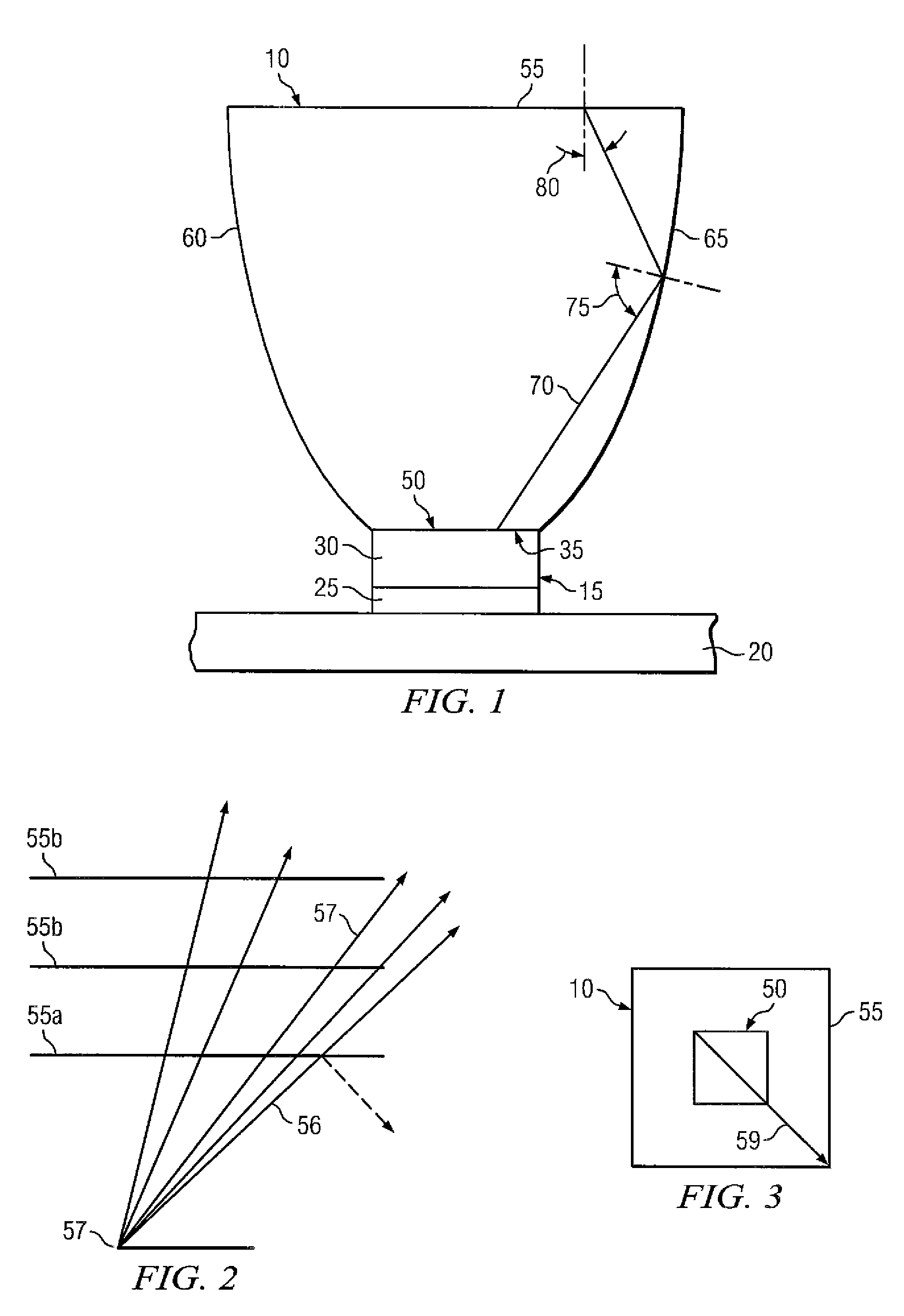
Separate optical device for directing light from an LED
InactiveUS20070152230A1Conserving brightnessSolid-state devicesCondensersAngle of incidenceOptoelectronics
Embodiments of the present invention provide separate optical devices operable to couple to a separate LED, the separate optical device comprising an entrance surface to receive light from a separate LED when the separate optical device is coupled to the separate LED, an exit surface opposite from and a distance from the entrance surface and a set of sidewalls. The exit surface has at least a minimum area necessary to conserve brightness for a desired half-angle of light projected from the separate optical device. Furthermore, each sidewall is positioned and shaped so that at least a majority of rays having a straight transmission path from the entrance surface to that sidewall reflect to the exit surface with an angle of incidence at the exit surface at less than or equal to a critical angle at the exit surface.
Owner:ILLUMITEX INC
Objective lens for endoscopes
ActiveUS8098441B2Improve image qualityCompact design can be attainedMicroscopesTelescopesOptoelectronicsEndoscope
An objective lens for endoscopes has a front lens unit and a rear lens unit with an aperture stop between them. The front lens unit includes a first lens element with negative refracting power and a second lens element with positive refracting power, and the rear lens unit includes a third lens element with positive refracting power, a cemented lens component of a fourth lens element with positive refracting power and a fifth lens element with negative refracting power. The objective lens satisfies the following conditions:−2<SF<−0.90.94<D / (f×sin θ)<1.70.86<(D1+D2−f1) / (2×f3)<1.13where SF is the shape factor of the first lens element; D is a distance from the vertex of the image-side surface of the first lens element to the aperture stop; f is the combined focal length of the entire system; θ is a half angle of view; D1 is an actually measured distance from the vertex of the object-side surface of the first lens element to the aperture stop; D2 is a distance from the aperture stop to a vertex of the image-side surface of the third lens element; f1 is the focal length of the first lens element; and f3 is the focal length of the third lens element.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
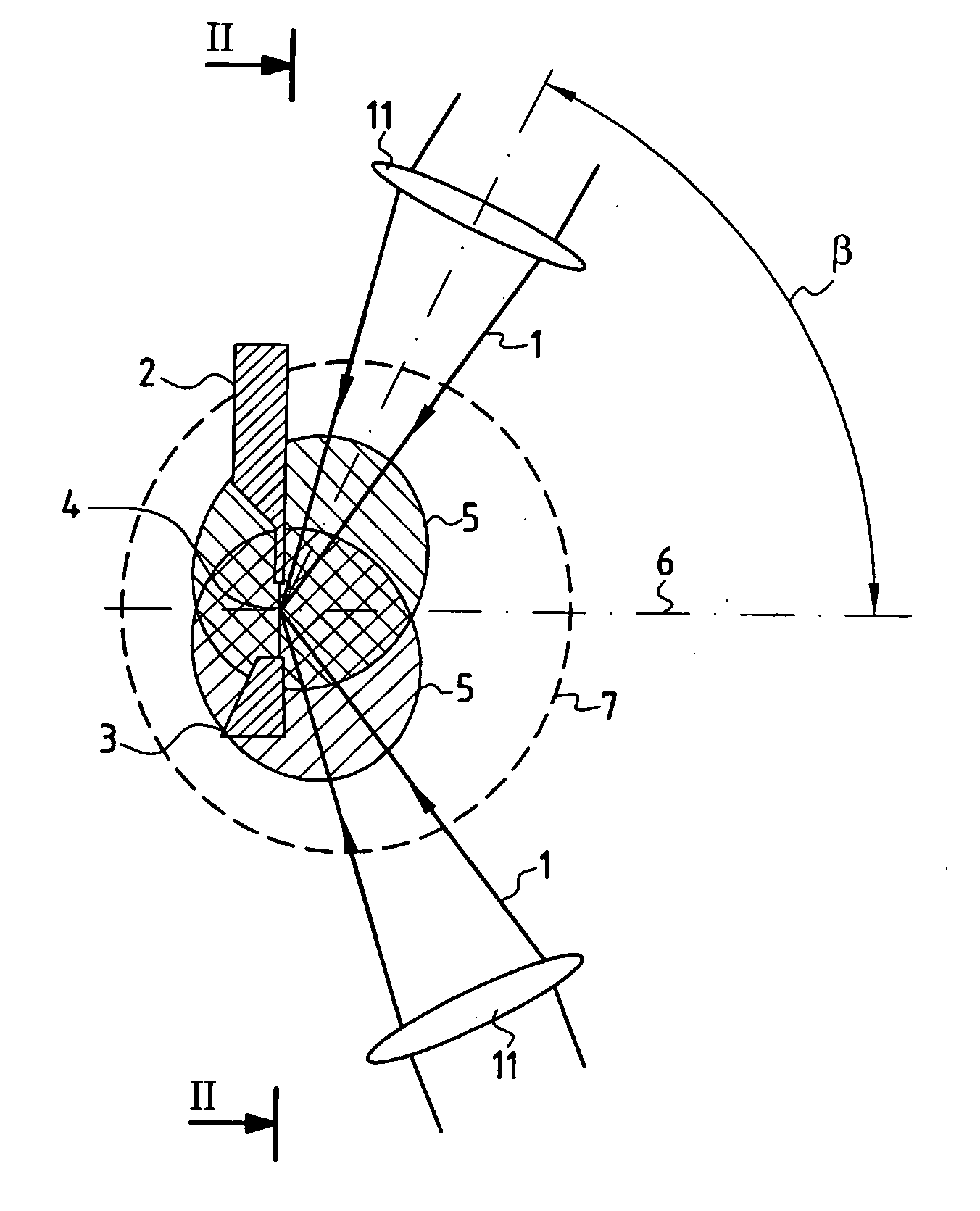
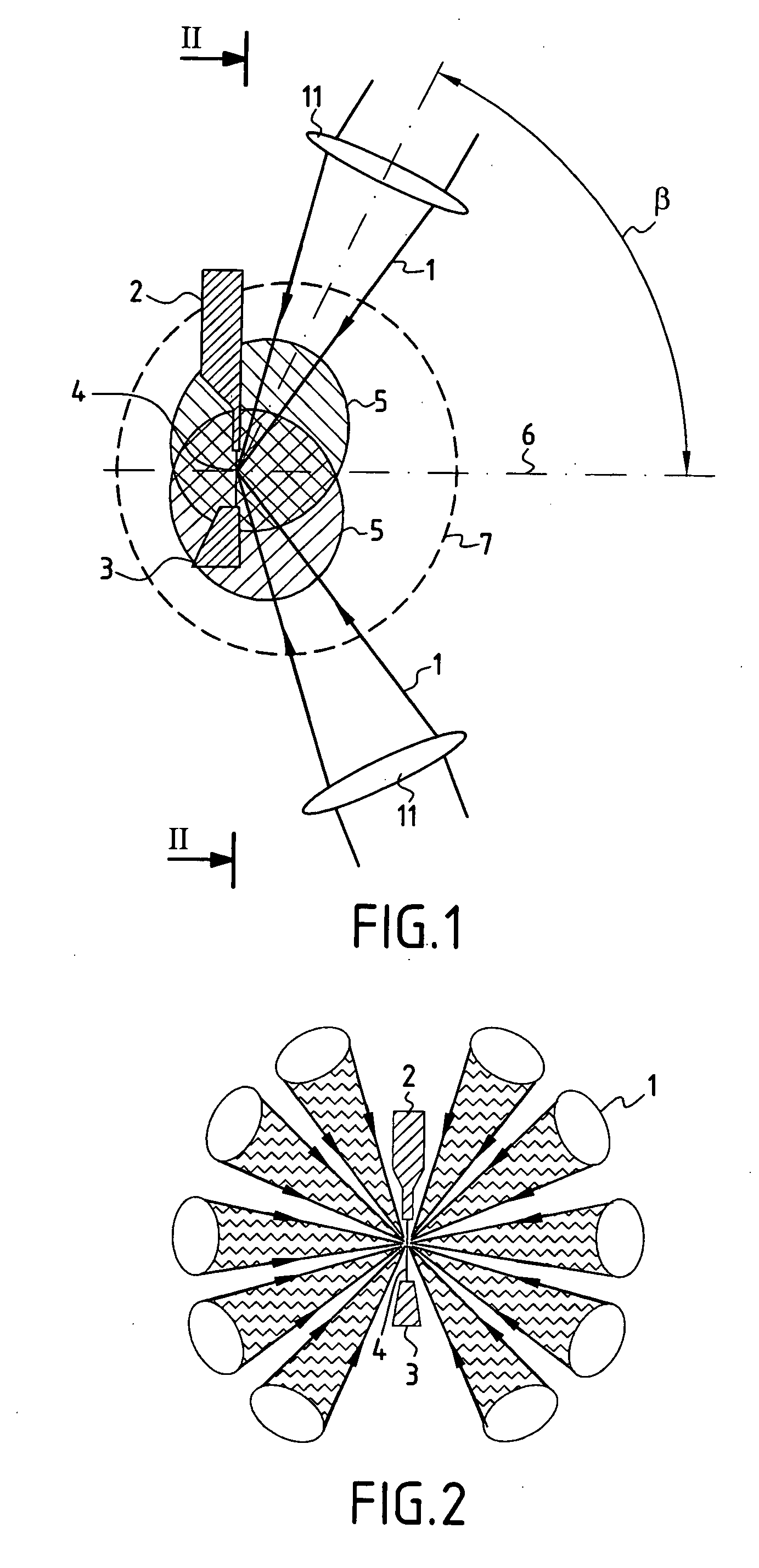
Apparatus for generating light in the extreme ultraviolet and use in a light source for extreme ultraviolet lithography
InactiveUS20060039435A1Increase powerIncrease laser powerNanoinformaticsPhotometryLithographic artistUltraviolet
The device comprises a device (2) for creating an essentially linear target (4) in an evacuated space where laser beams (1) are focused, the target being suitable for interacting with the focused laser beams (1) to emit a plasma emitting radiation in the extreme ultraviolet. A receiver device (3) receives the target (4) after it has interacted with the focused laser beams (1), and a collector device (110) collects the EUV radiation emitted by the target (4). The focusing elements (11) for focusing the laser beams on the target (4) are arranged in such a manner that the laser beams (1) are focused on the target (4) laterally, being situated in a common half-space relative to the target (4) and being inclined at a determined angle lying in the range about 60° to about 90° relative to a mean collection axis (6) perpendicular to the target (4). The collector device (110) is disposed symmetrically about the mean collection axis (6) in the half-space containing the laser beams (1) focused on the target (4) and inside a conical space (8) centered on the mean collection axis (6) with a vertex situated at the target (4) and a half-angle at the vertex that is less than the angle of inclination of the focused laser beams (1) relative to the mean collection axis (6). The device is suitable for use as a source for EUV radiation in lithography for fabricating integrated circuits.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
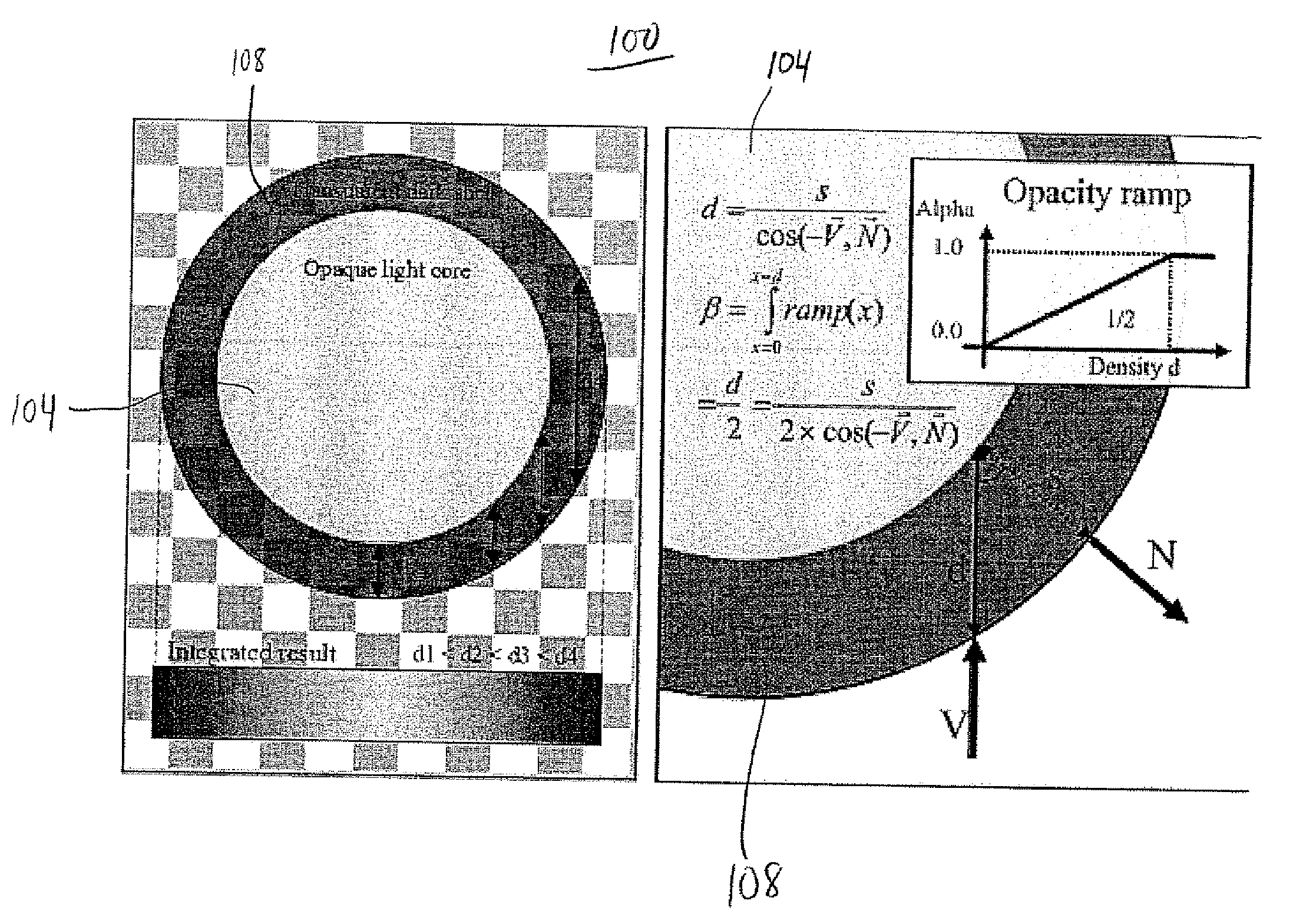
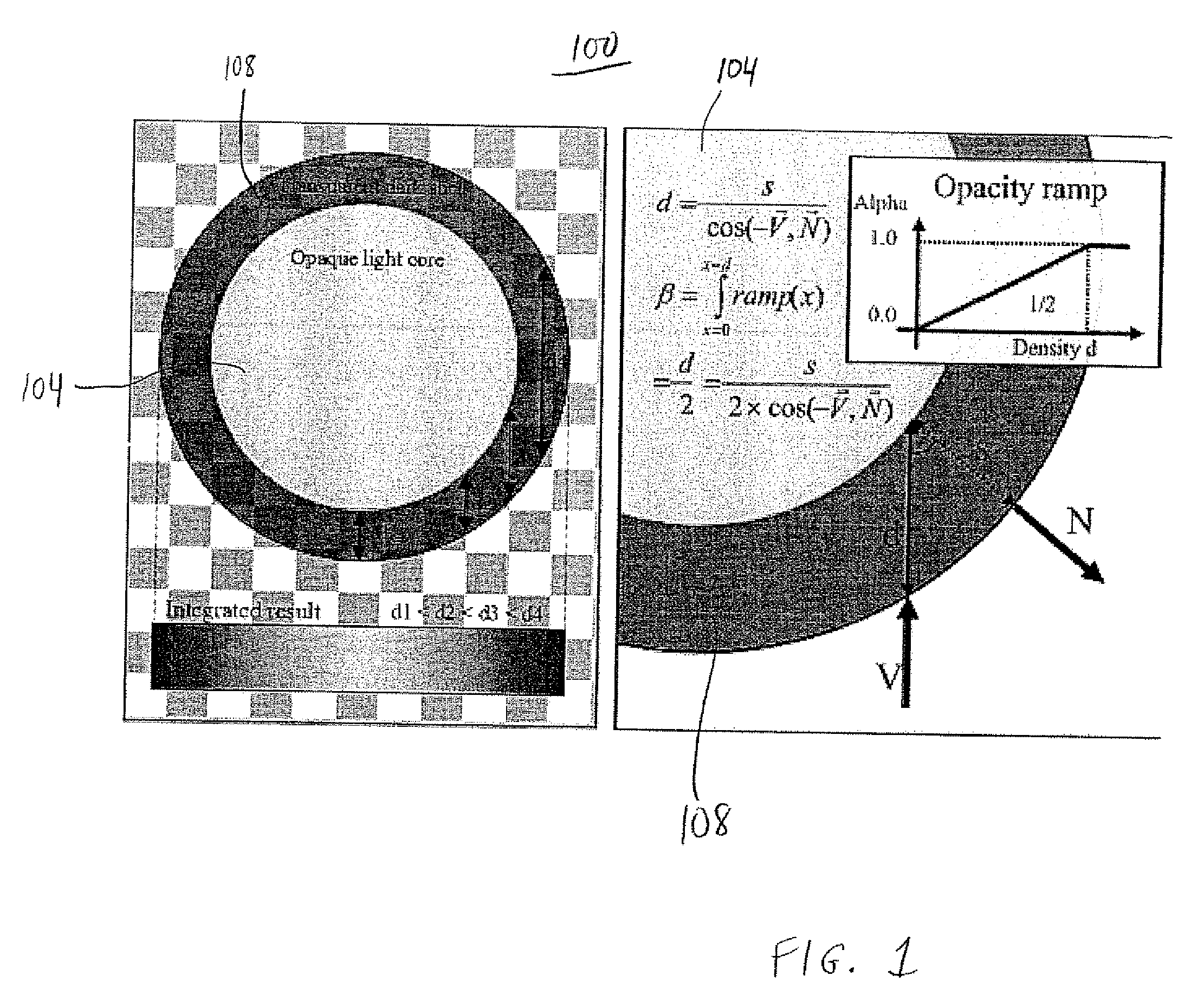
Gradient free shading for volume rendering using shadow information
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Objective lens for endoscope and endoscope
ActiveUS20100305405A1Enhance the imageBack focal lengthSurgeryEndoscopesOphthalmologyMicroscope objective
In an objective lens for an endoscope, the full angle of view exceeds 120 degrees, and a most-object-side surface of the objective lens is spherical. Further, the following condition formulas (1) and (2) are satisfied:0.7<θ8 / θ10<0.8 (1); and5<R1 / f<15 (2),where θ10: half angle of view corresponding to a maximum image height;θ8: half angle of view corresponding to an image height that is 80% of the maximum image height;R1: curvature radius of the most-object-side surface; andf: focal length of the entire system of the objective lens.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Separate optical device for directing light from an LED
InactiveUS7772604B2Conserving brightnessSolid-state devicesCondensersAngle of incidenceOptoelectronics
Embodiments of the present invention provide separate optical devices operable to couple to a separate LED, the separate optical device comprising an entrance surface to receive light from a separate LED when the separate optical device is coupled to the separate LED, an exit surface opposite from and a distance from the entrance surface and a set of sidewalls. The exit surface has at least a minimum area necessary to conserve brightness for a desired half-angle of light projected from the separate optical device. Furthermore, each sidewall is positioned and shaped so that at least a majority of rays having a straight transmission path from the entrance surface to that sidewall reflect to the exit surface with an angle of incidence at the exit surface at less than or equal to a critical angle at the exit surface.
Owner:ILLUMITEX INC
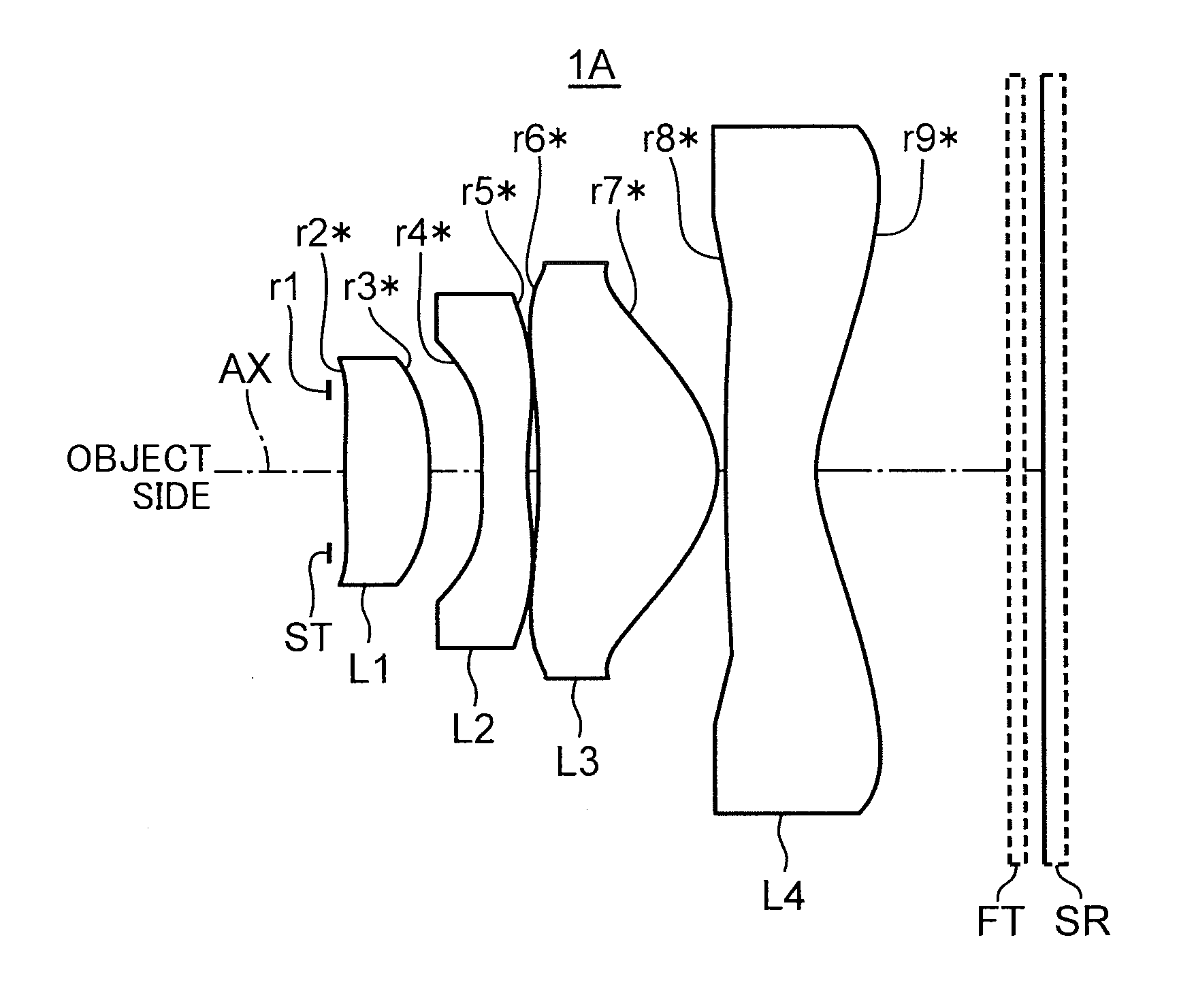
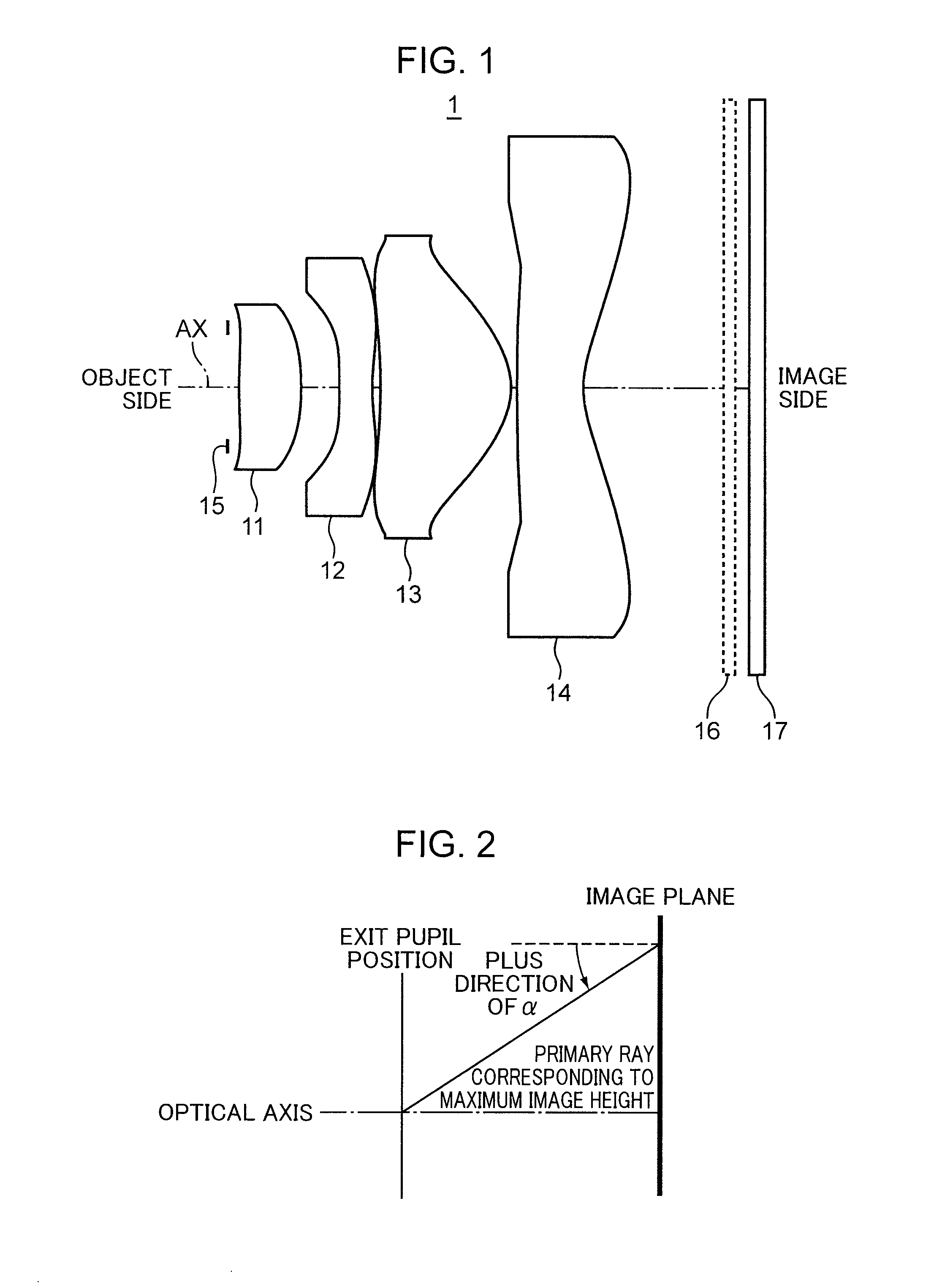
Imaging Optical System, Imaging Device, and Digital Apparatus
An imaging optical system, an imaging device, and a digital apparatus have a four lens construction with positive, negative, positive, and negative refractive powers. A surface position at the maximum effective diameter of the second lens element is located on the object side than a surface vertex thereof. The fourth lens element has an inflection point at a position other than the intersection of the optical axis and the fourth lens element. The optical system satisfies the following conditions.0.7<f1 / f<5−0.8<(RS1+RS2) / (RS1−RS2)<3−3<(RS3+RS4) / (RS3−RS4)<20.03<d2 / TL<0.22W>72ν4>50,and0.55<Y / TL<0.8where f1 is a focal length of the first lens element, f is a focal length of the entire optical system, RS1, RS3, RS2, RS4 are curvature radii of the object-side surface and the image-side surface of the first and second lens elements, d2 is an optical axis distance between the first and second lens elements, TL is a total length of the entire optical system, W is a maximum half angle of view, ν4 is an Abbe number of the fourth lens element, and Y is a maximum image height.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTICS
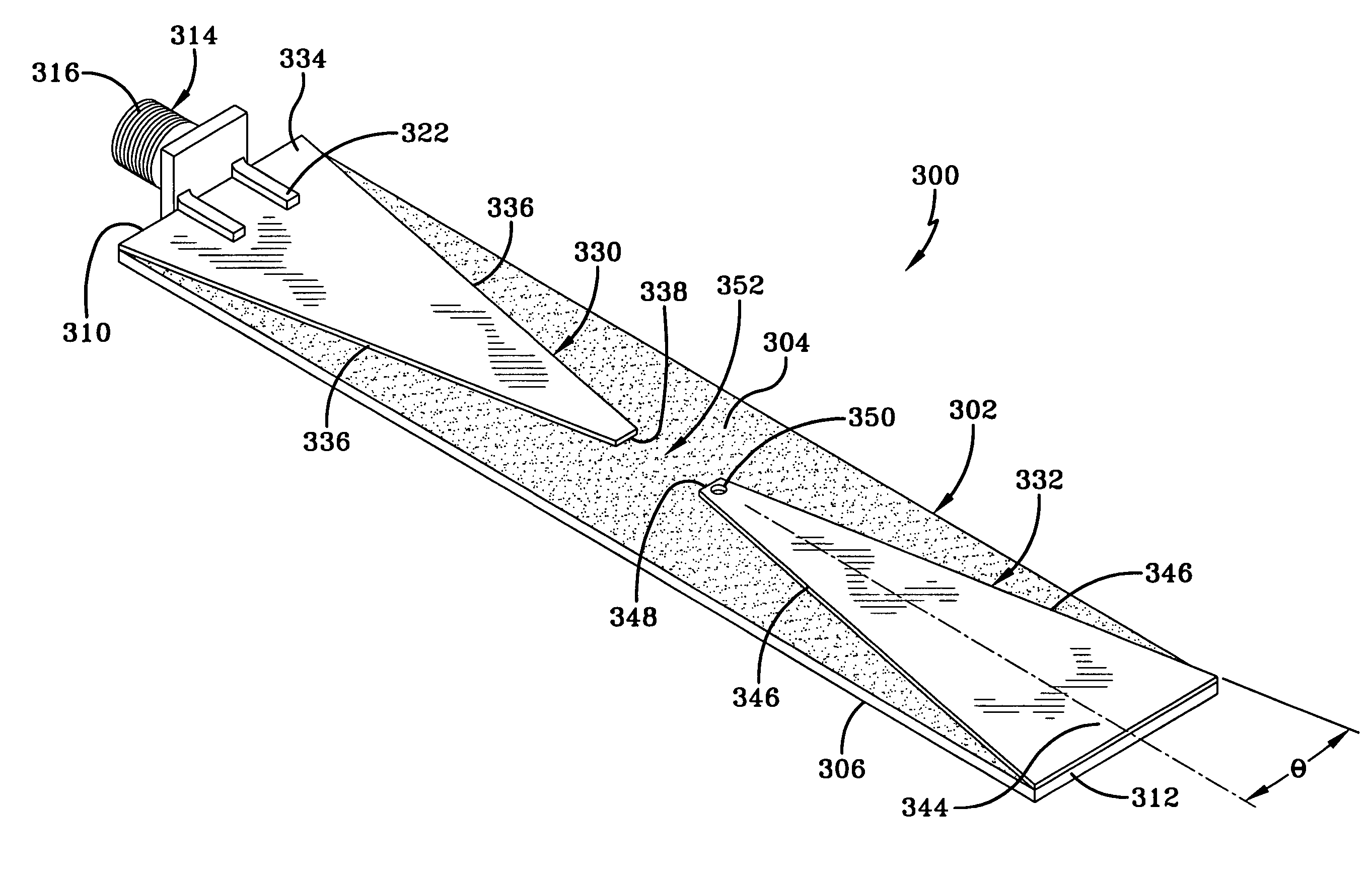
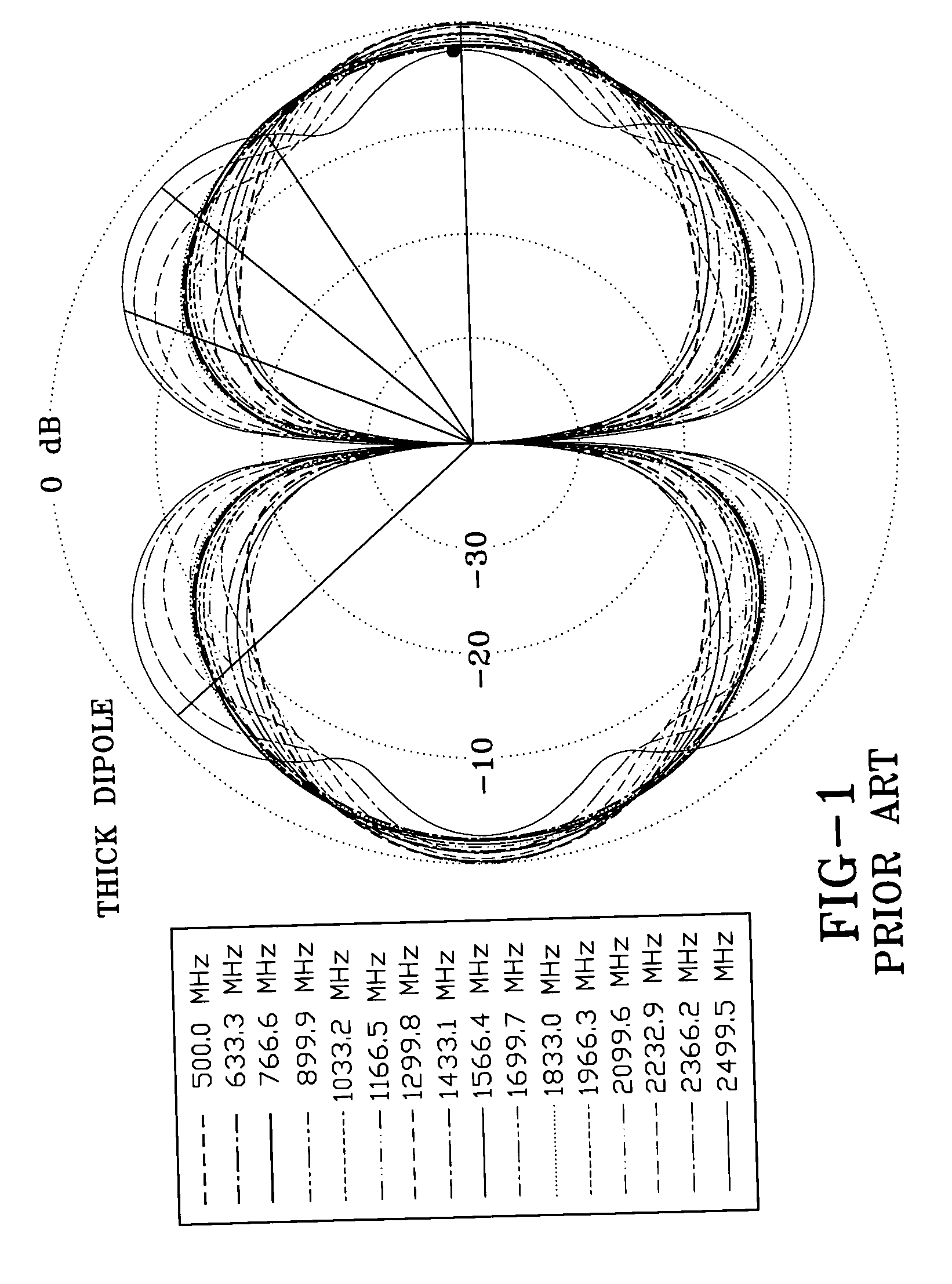
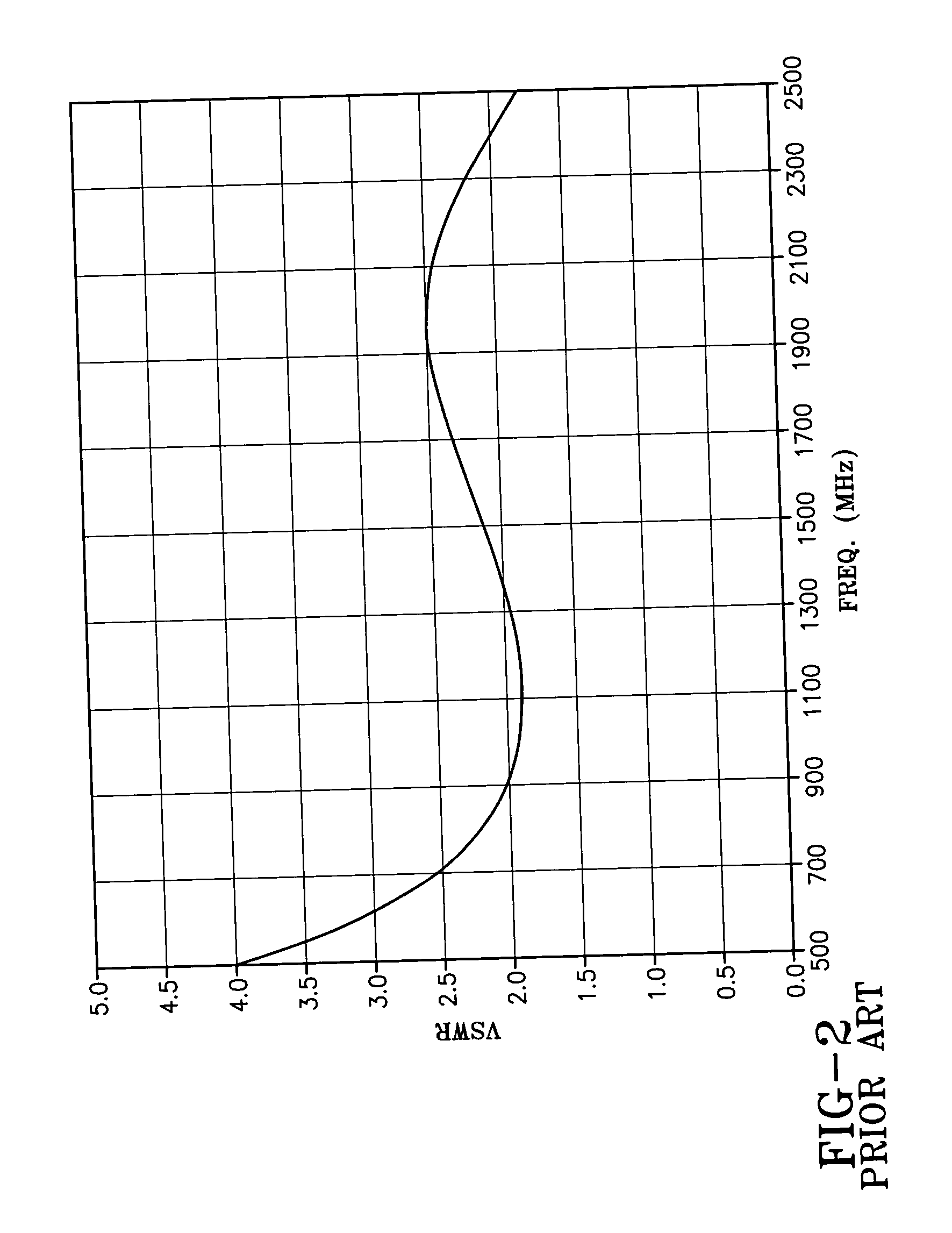
Wide band biconical antennas with an integrated matching system
A biconical antenna includes an entry conic having an entry base opposite an entry vertex and a termination conic having a termination base opposite a termination vertex. The entry and termination conics share substantially the same axis and the entry vertex is adjacent the termination vertex. The transmission line is received by the entry conic and terminated in the termination conic. Together, the entry conic and the termination conic phase correct energy emanating from the transmission line. Another embodiment of the antenna comprises an entry conic having at least two sub-conics and a termination conic having at least two sub-conics. Each of the sub-conics having an integer multiple of a half-angle. The biconical antenna may also include a multi-conductor transmission line, wherein the biconical antennas are arranged in a co-linear relationship. Each of the multi-conductors is coupled to at least one of the plurality of biconical antennas. The biconical antennas may also be constructed on a circuit board substrate.
Owner:SHAKESPEARE CO
Frequency-converted light source
ActiveUS20150177593A1Improve efficiencyIncrease powerPoint-like light sourceLight demodulationFrequency conversionHarmonic
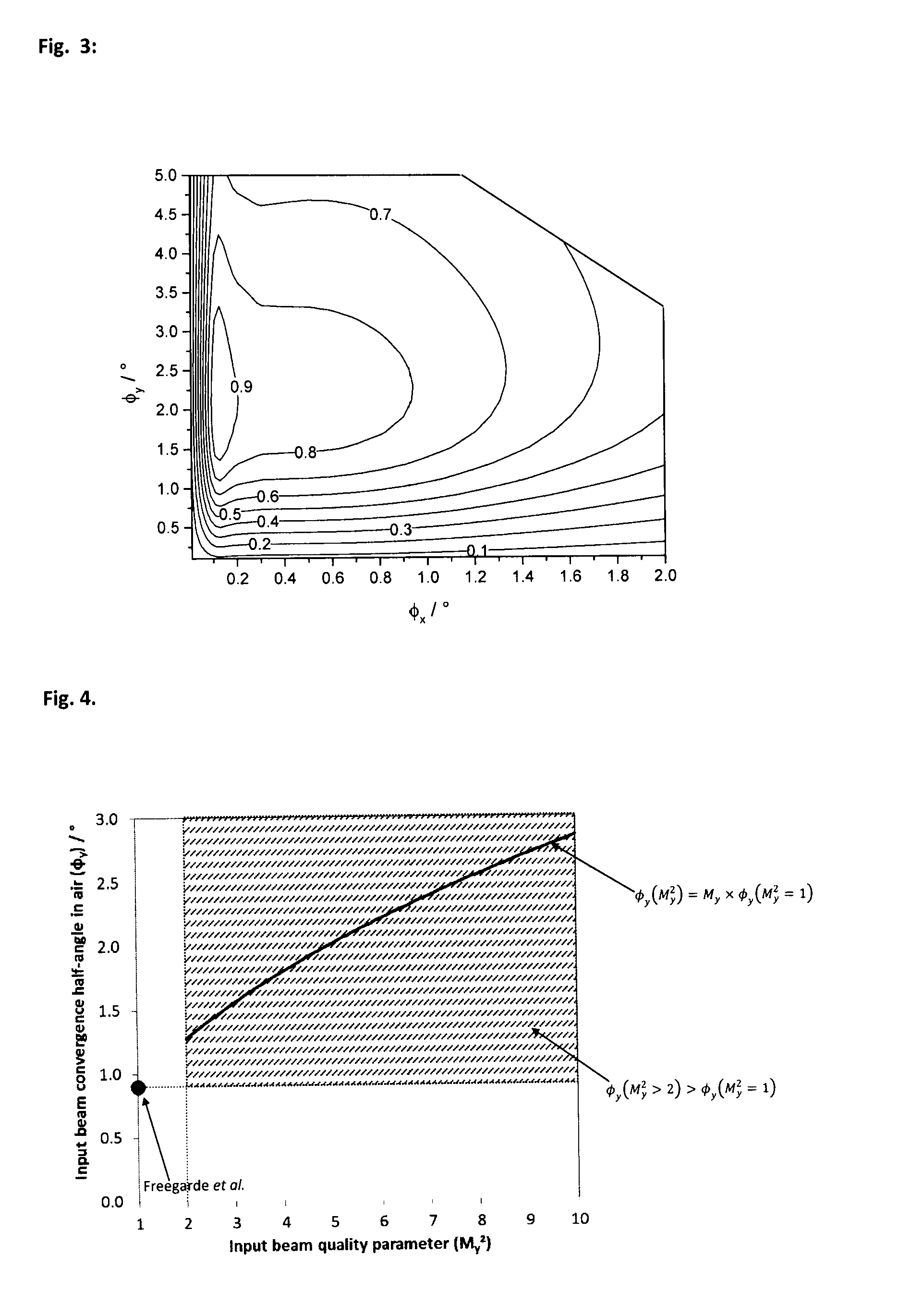
A nonlinear frequency conversion (NLFC) component is incorporated into a light source. The light source includes a light emitting element that emits a non-diffraction limited input light beam, and the NLFC component that exhibits walkoff and performs an NLFC process, such as second harmonic generation. An optical component is configured to converge the non-diffraction limited input beam into the NLFC component with a determined convergence half-angle. The convergence half-angle in air in a non-walkoff plane of the NLFC component is larger than a convergence half-angle angle for diffraction-limited light. Said convergence half-angle may be a multiple, ε×M, multiplied by the convergence half-angle value for diffraction-limited light, wherein ε has a value between a lower value equal to the larger of 0.4 and1Mand an upper value of 5.0, where M is the square root of the beam quality factor for the non-diffraction limited light.
Owner:SHARP KK
Projection Optical System and Projector
ActiveUS20170153427A1Improve performanceLow costProjectorsOptical elementsIntermediate imageAngle of view
A projection optical system capable of performing magnification projection of an image displayed on an image display surface, with a 40° half angle of view, or more includes, in an order from a magnification side: a first optical system; and a second optical system, wherein the second optical system forms an intermediate image of the image, the first optical system performs magnification projection of the intermediate image, and the following conditional expressions (1) and (2) are satisfied: 1<Ff / |Fw|<2 . . . (1), 0.4<Lf / Lw<0.6 . . . (2), where, Ff: a focal length of the first optical system, Fw: a focal length of an entire system, Lf: a distance on optical axis, from a most-magnification-side surface vertex to the intermediate image, in the first optical system, Lw: an entire length of a lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
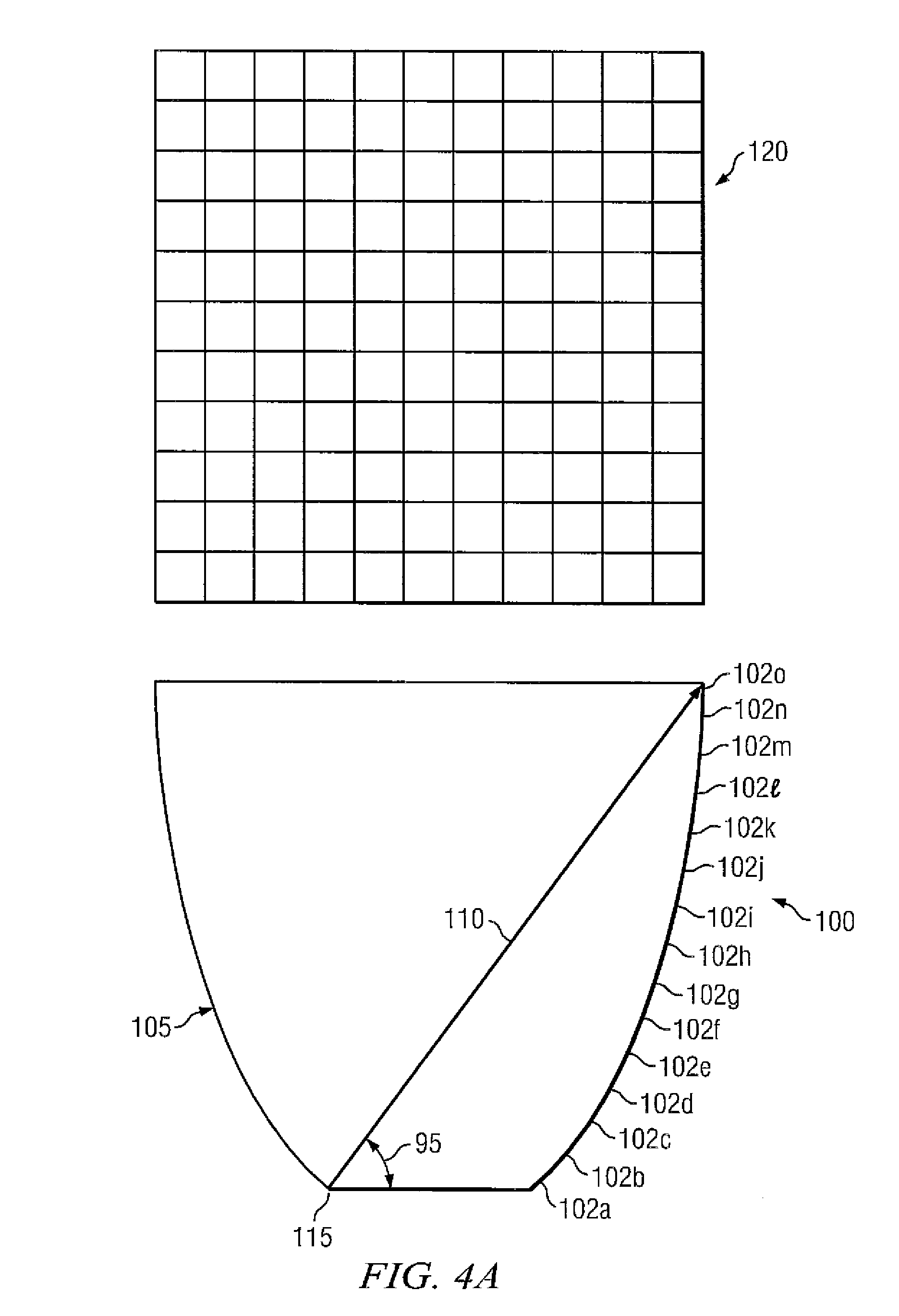
Compound paraboloid condenser
InactiveCN101697032AOvercome efficiencyOvercoming adjustmentSolar heat devicesPhotovoltaicsEngineeringParaboloid
The invention relates to a compound paraboloid condenser which belongs to the field of solar energy utilization. An ordinary CPC curve is rotated by 2-5 degrees towards the central line of the condenser around an upper edge point of the CPC curve to form a new CPC curve, wherein the best rotating angle is 3 degrees; and dielectric media are filled between the new curve and the original curve to form a novel CPC condenser. The outer surface of the condenser can achieve sunlight reflection by adopting a metal reflecting plane or a reflecting coating. The novel CPC condenser can achieve the CPC optical efficiency of the same concentrating ratio and increase the receiving half-angle of the compound paraboloid condenser to solar rays.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Modeling method for compound parabolic concentrator for linear Fresnel light condensing and heat collecting system on basis of matlab
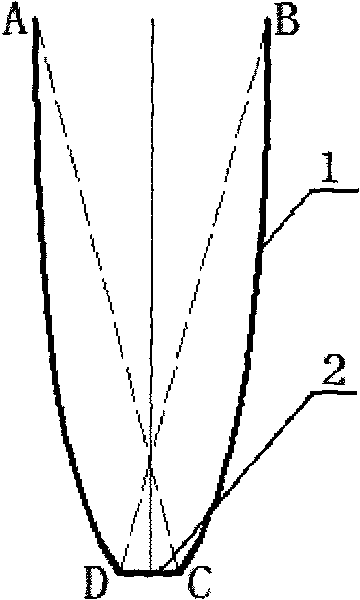
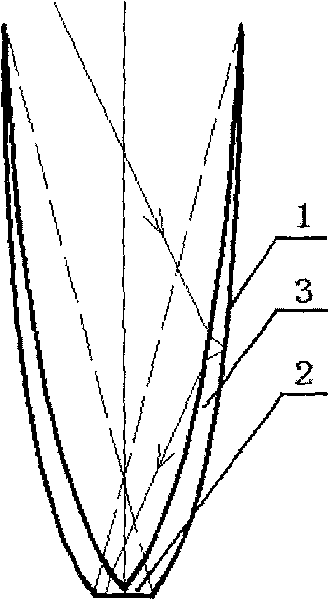
ActiveCN103810352AAccurate calculation of convergence rateSimple modeling methodSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodInvolute
The invention relates to a modeling method for a compound parabolic concentrator (CPC) for a linear Fresnel light condensing and heat collecting system on the basis of matlab. The modeling method comprises the following steps: 1, determining the maximum receiving half angle theta c of the CPC; 2, using an outer diameter circle of a metal inner pipe of a vacuum heat collecting tube as a base circle of an involute; 3, rotating the involute by an angle alpha by using a circle center O as the center, so that a point C on the involute, which meets the condition that t=t0, is positioned on a center shaft of the CPC and the distance between the point C and the metal inner tube of the heat collecting tube is the sum of the distance between the point and a glass outer tube of the heat collecting tube and the distance between the glass outer tube and the metal inner tube of the heat collecting tube; 4, using a point on the involute, which meets the condition (refer to the specification), as a junction point of an involute CFB and a parabola A; 5, rotating the parabola by an angle theta c around the vertex of the parabola to enable the parabola to pass through a left junction point FB and using a right junction point FA as a focus to obtain a parabolic equation; 6, carrying out simulating calculation on a relation of a convergence rate and an intercepting ratio of the CPC by utilizing a ray tracing method, and selecting the suitable intercepting ratio.
Owner:兰州大成科技股份有限公司 +2
Non-imaging optical corner turner
InactiveUS20050084212A1Effectively turningEasy to handleLaser using scattering effectsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberLight beam
The present invention provides a device and method to efficiently turn light from an optical fiber around a corner while avoiding the frustrated-TIR loss that would occur if the fiber were bent. The invention uses non-imaging optics which efficiently deal with beam divergence half-angles less than 90°. By recognizing that most light from a fiber optic source will have a divergence half-angle of less than 90 degrees, a practical solution is achieved using non-imaging optics.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
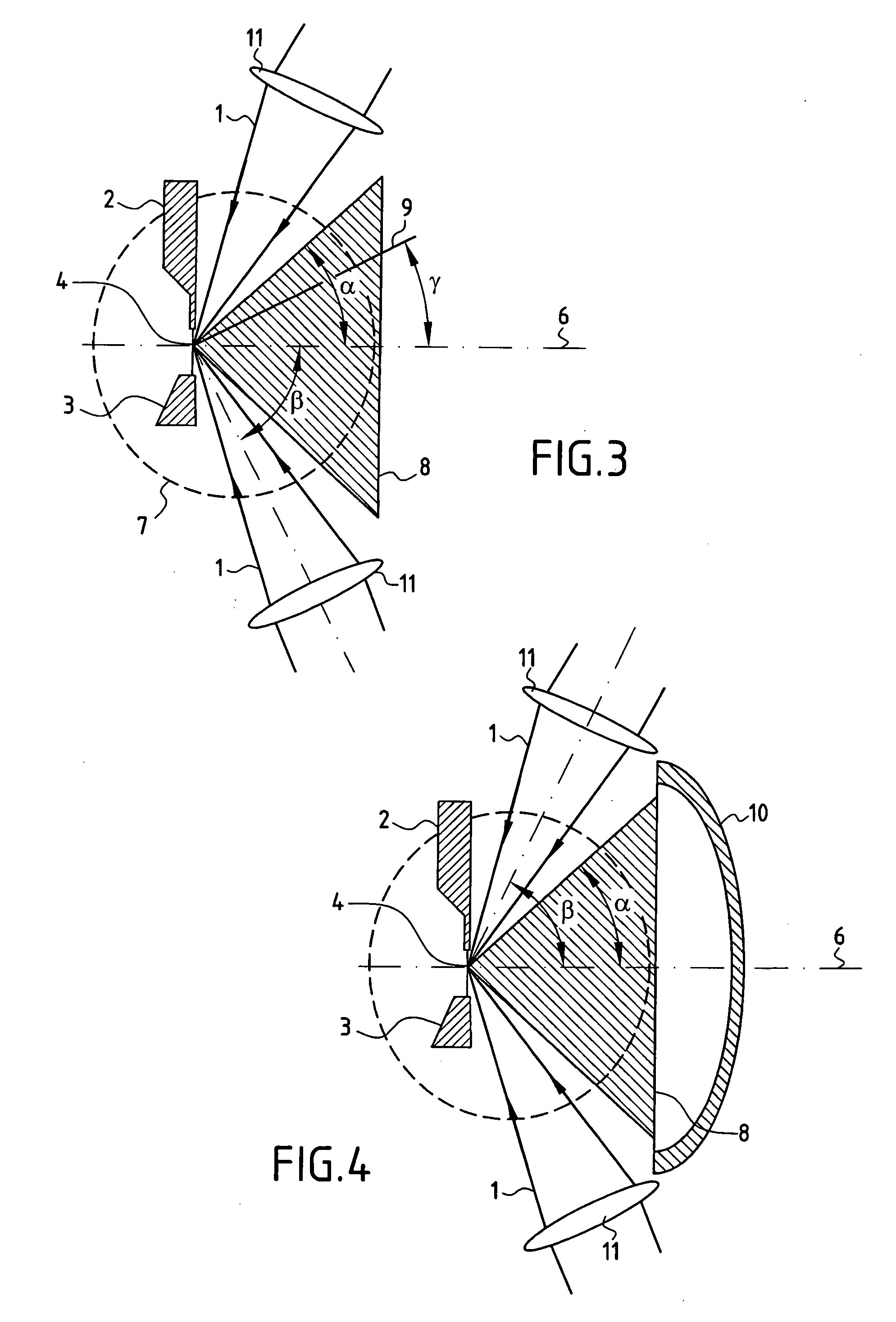
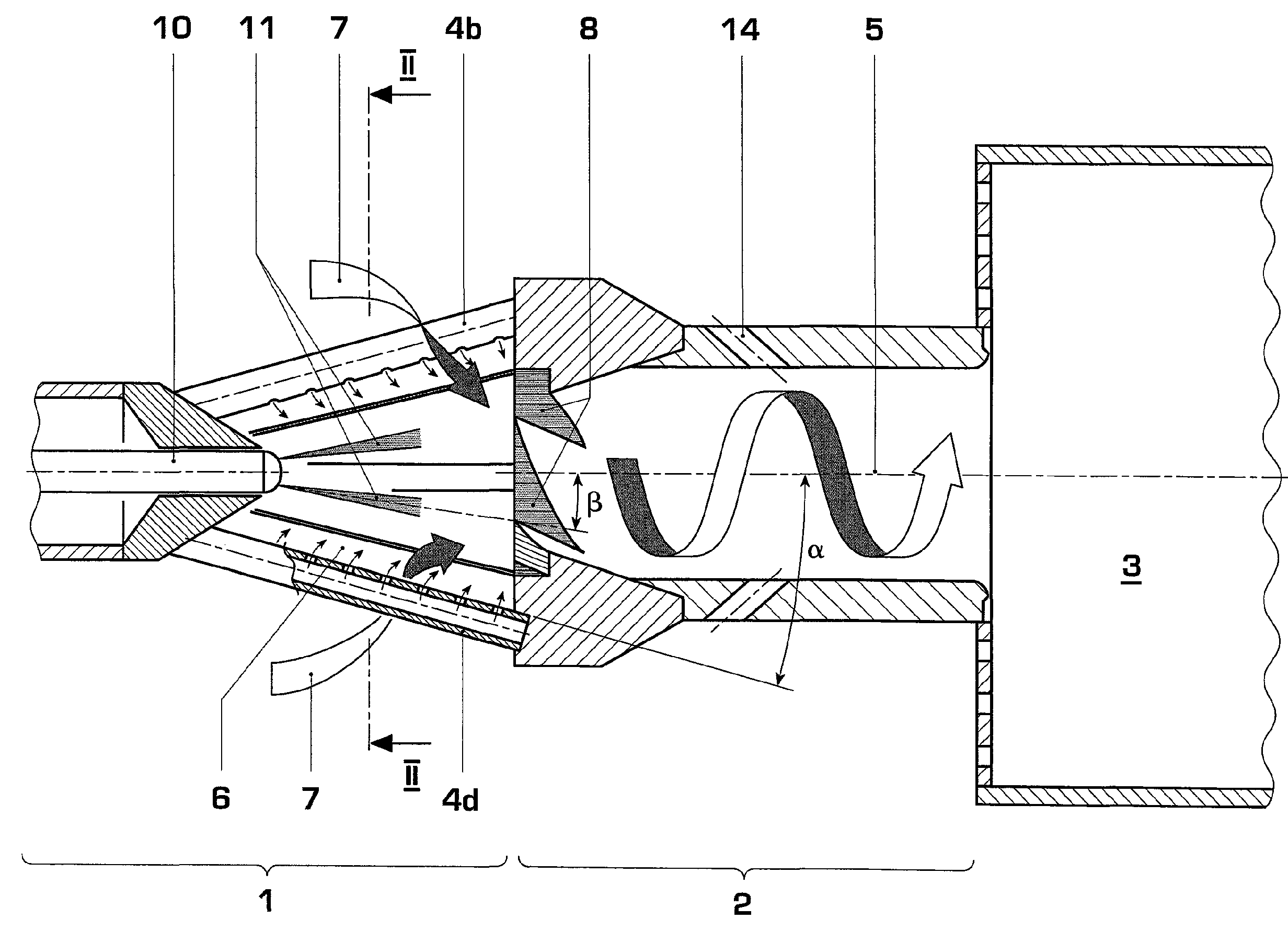
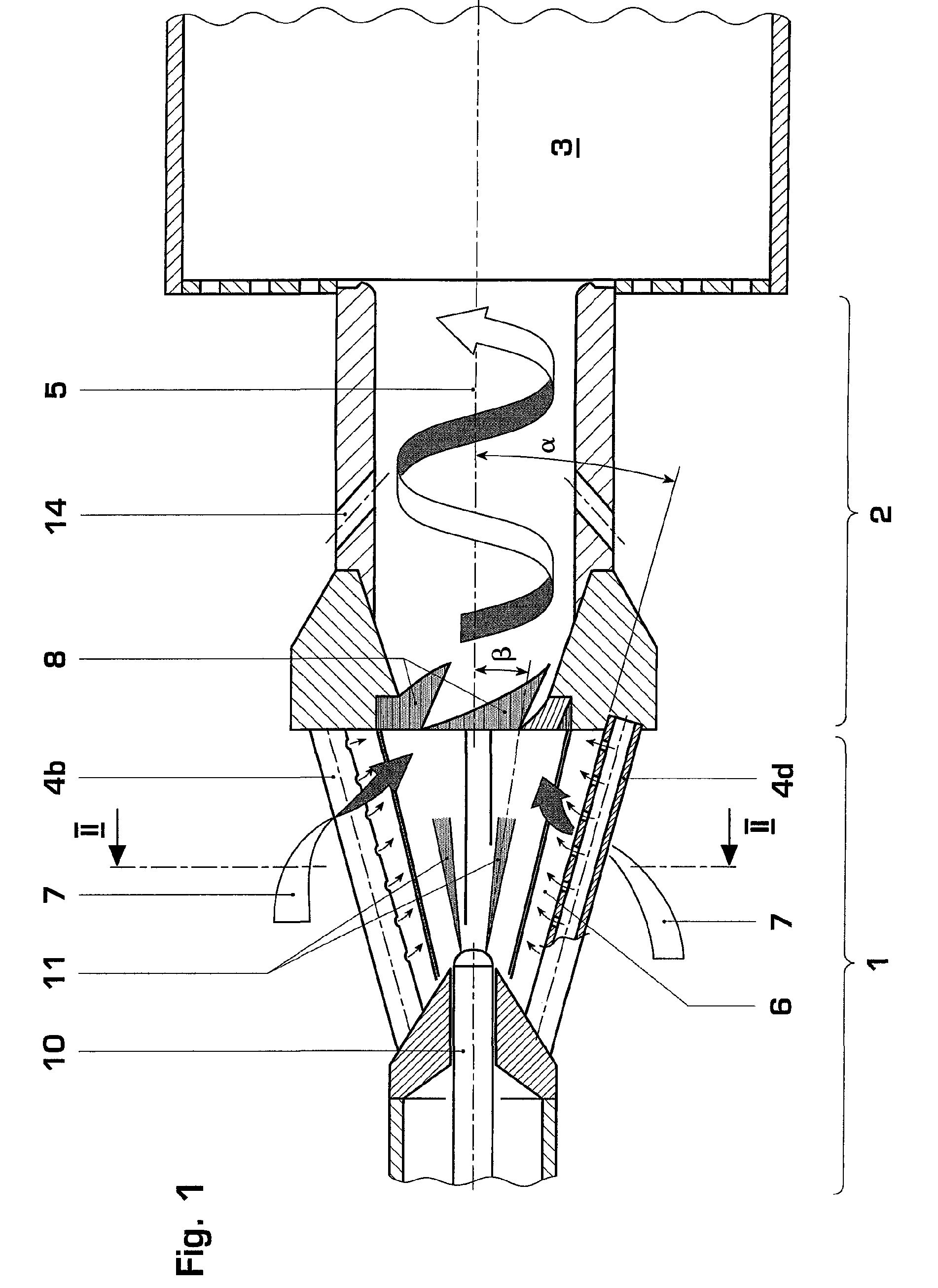
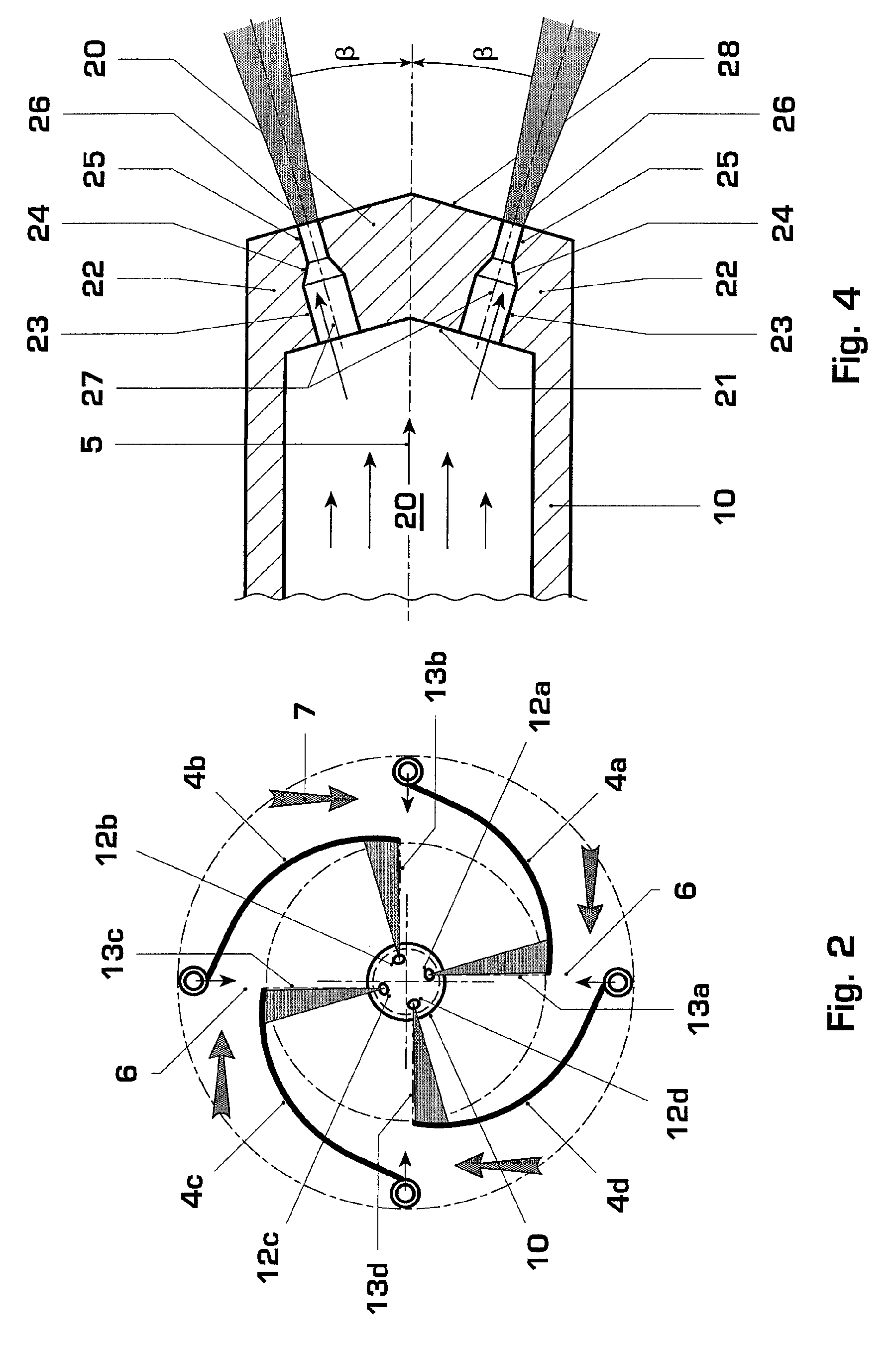
Burner for a gas turbine
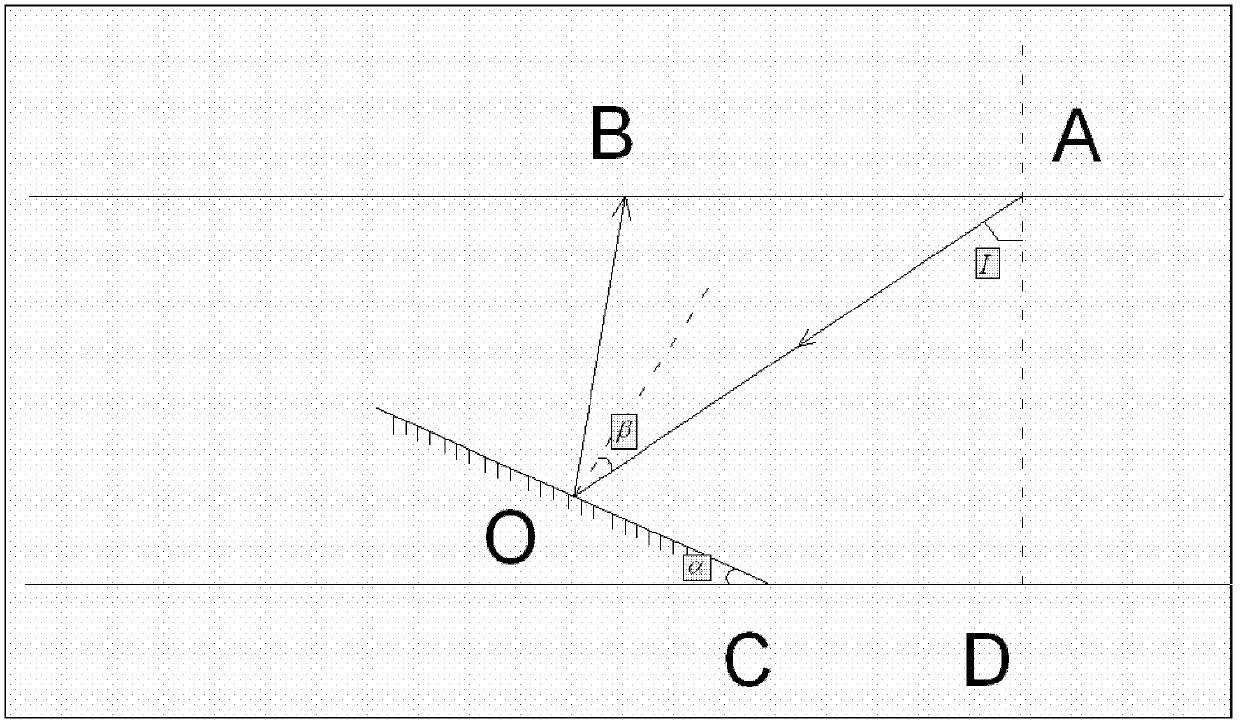
A premix burner, for example for a gas turbine, having a conical swirl generator (1) and a cylindrical mixing section (2) which follows it in the direction of flow, includes a high-pressure atomizer nozzle (10) with one or more fuel feed passages. The high-pressure atomizer nozzle (10) includes at least two outlet passages, through which liquid fuel enters the swirl generator (1), these passages being arranged off-center with respect to the longitudinal axis of the nozzle and being configured in such a way that the spray cone (11) of the fuel is oriented at an angle (β) with respect to the longitudinal axis of the swirl generator (1) which is smaller than the cone half-angle (α) of the swirl generator (1). The outlet passages in particular have an internal geometry with a conically narrowed section.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
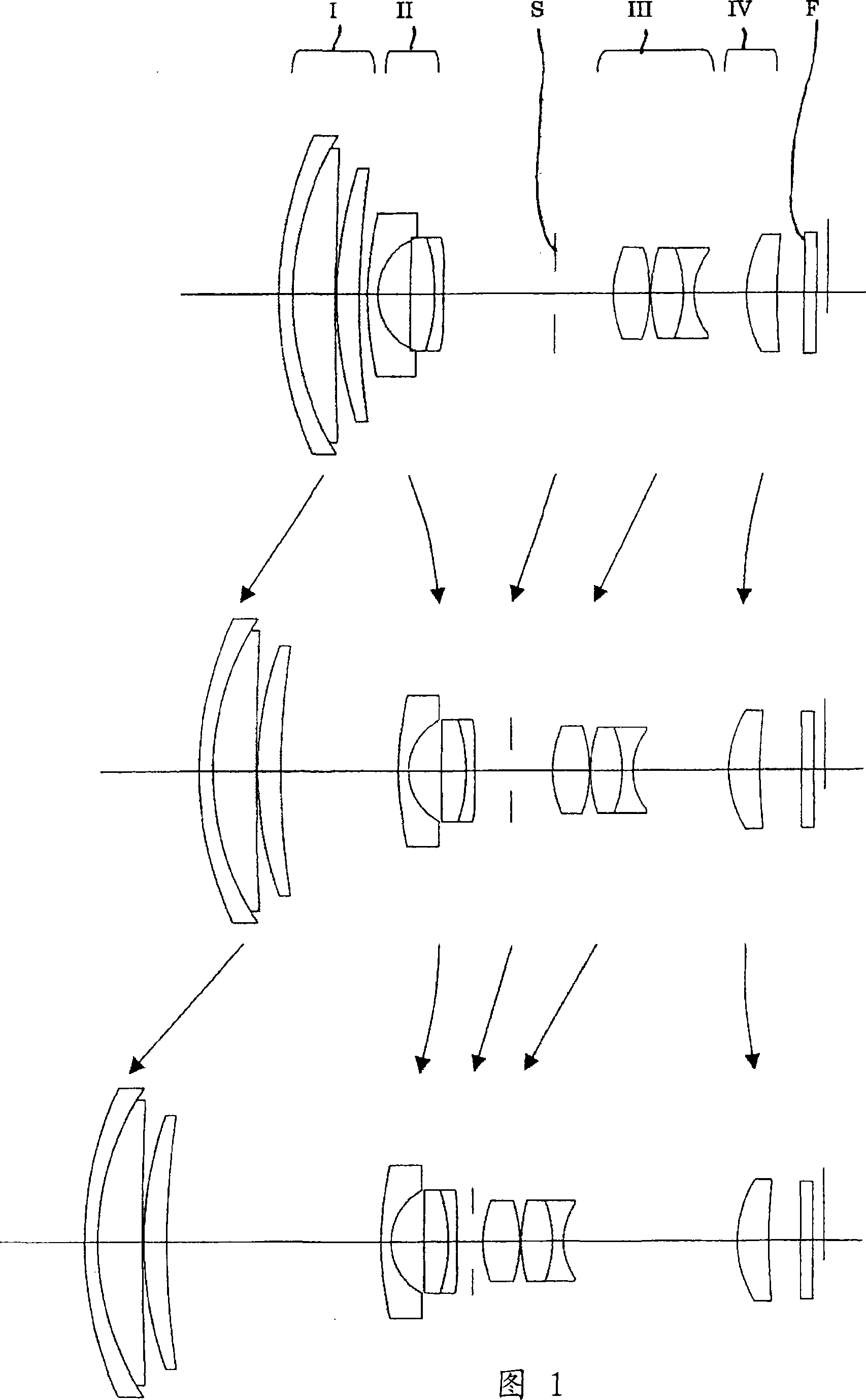
Zoom lens, imaging device, and personal digital assistant
InactiveCN101101368ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionRefractive index
The invention provides a zoom lens capable of achieving a half angle of view over 38 degrees at the wide-angle end, a magnification ratio 6.5 to 10 or more, and a resolving power corresponding to an imaging element of 5 to 8 million pixels, with a configuration of as few as 10 to 11 pieces of lenses. The zoom lens of the invention includes a first lens group through a third lens group I to III of positive / negative / positive in order from the object side, or further includes a fourth lens group of positive IV. In the zoom lens, when changing magnification from a wide-angle end toward a telephoto end, a spacing between the first lens group and the second lens group increases and a spacing between the second lens group and the third lens group decreases.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical imaging lens
The present application discloses an optical imaging lens. The optical imaging lens includes, in an order from an object side to an image side along an optical axis: a first lens having optical power;a second lens having optical power; a third lens having negative optical power; a fourth lens having optical power and whose object side is convex; a fifth lens having optical power and whose objectside is concave; a sixth lens having optical power; a seventh lens having optical power; and an eighth lens having optical power. The total effective focal length f of the optical imaging lens and themaximum half angle of view of the optical imaging lens Semi-FOV meet: fxtan(Semi-FOV)>5.5mm, and the total effective focal length f of the optical imaging lens and the effective focal length f1 of the first lens meet: 0.5<f / f1<1.5.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Polycrystalline diamond elements having convex surfaces
ActiveUS20100064538A1Easy to polishReduce wearLayered productsRecord information storagePolycrystalline diamondRms roughness
A diamond element (10) having a convex surface is disclosed, the convex surface including a spherical segment for which the maximum peak to valley deviation from a perfect spherical surface is less than about 5 μm. The diamond element (10) may be a solid polycrystalline diamond material and / or may comprise base material which is coated with diamond. Alternatively or in addition, the RMS deviation from a perfect spherical surface may be less than about 500 nm, or the RMS roughness less than about 30 nm. A diamond element (10) with a radius of curvature less than about 20 mm is also disclosed. In one aspect a diamond element (10) having a conical half-angle greater than about 10° is described. Diamond elements (10) of this type are intended for use as metrology tips. Key to this invention is the realization that a diamond surface, particularly a diamond surface with low Ra (roughness) and which is free of defects such as pits, digs and scratches, accumulates less material from the surface being measured, and thus provides a longer life.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
LED lamps
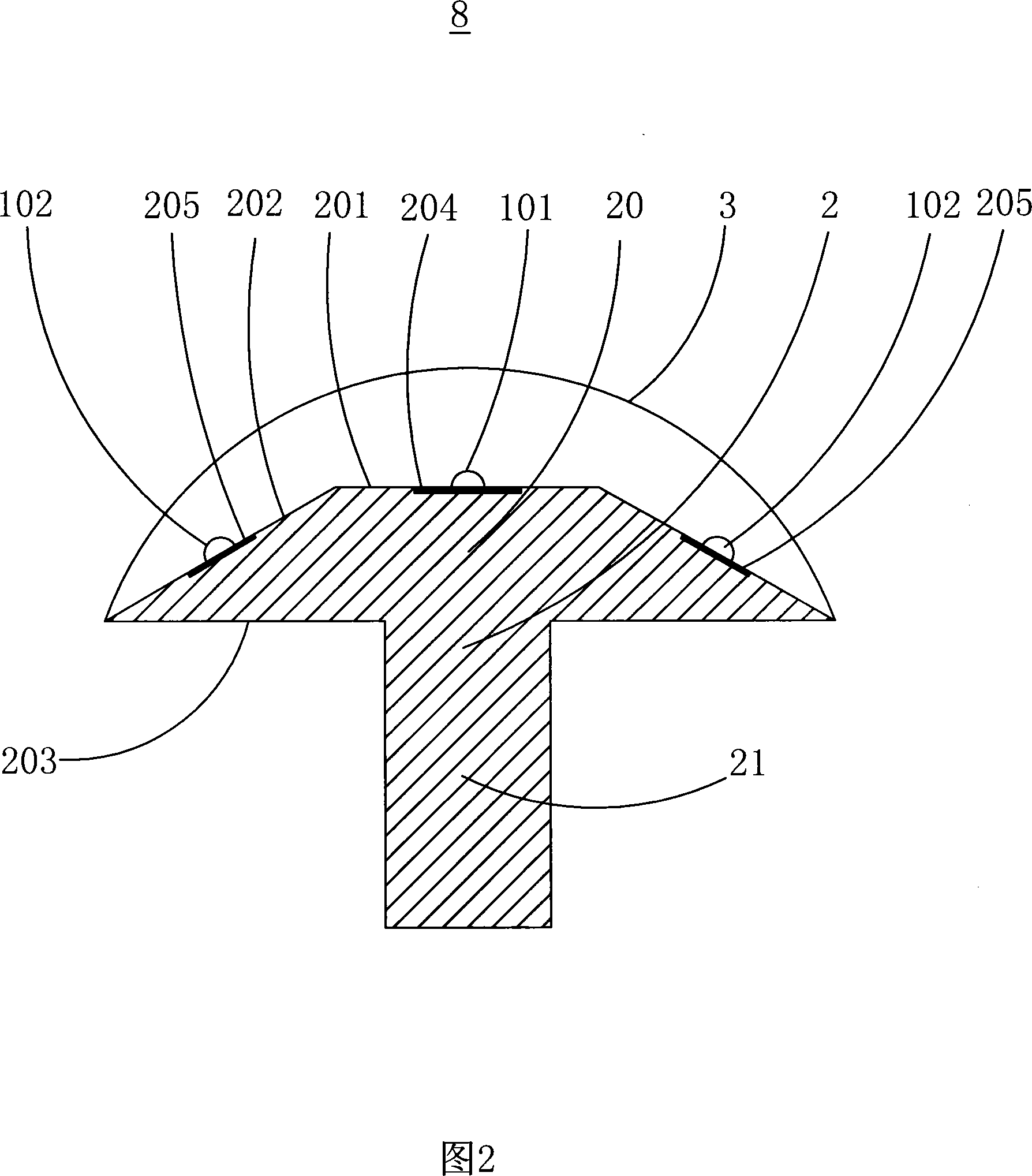
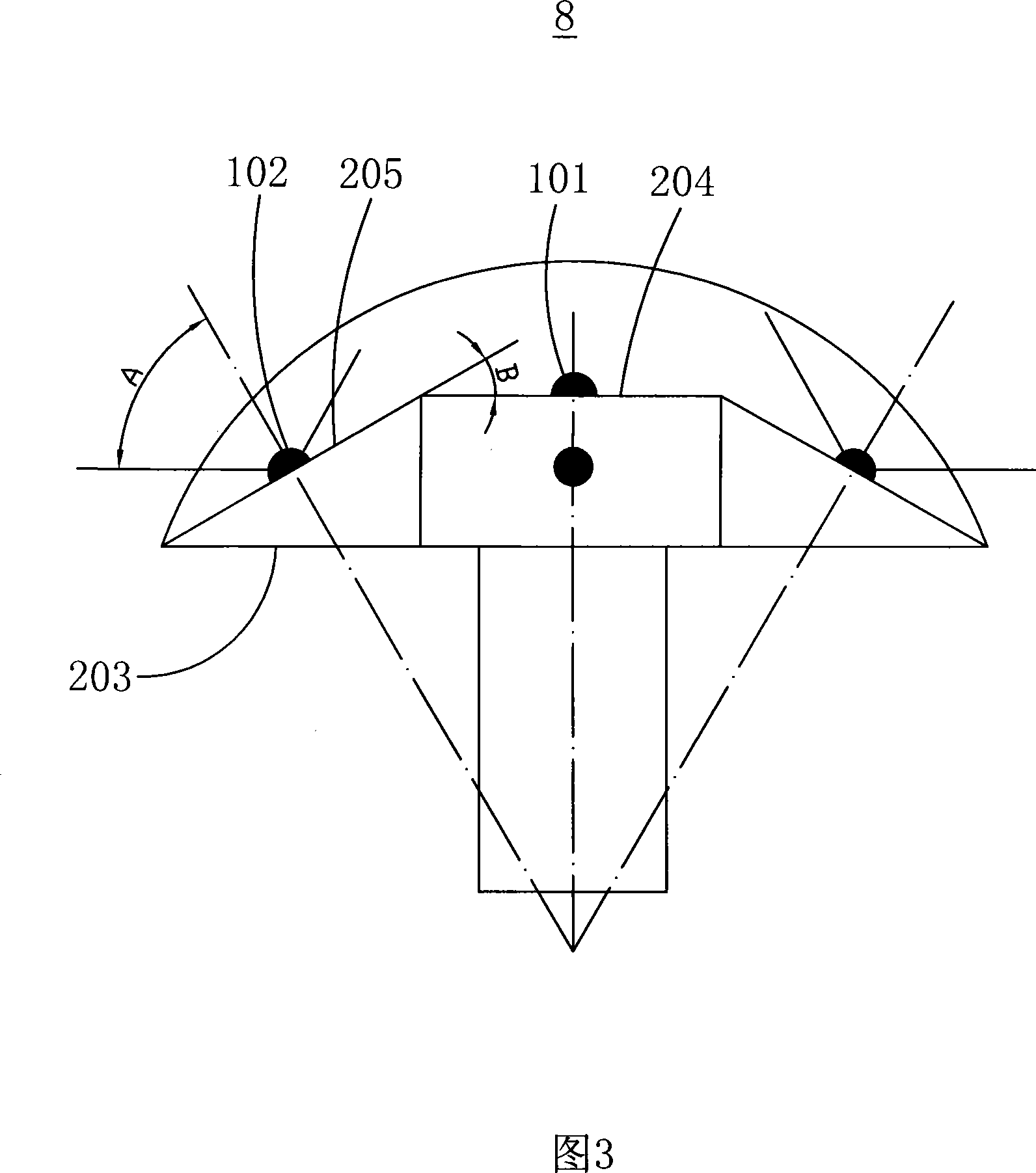
The invention provides an LED light, which comprises a plurality of LEDs, an LED supporting body and lenses. The LEDs are arranged on the LED supporting body. The LED supporting body comprises a supporting basal body with lateral surfaces. The supporting basal body comprises a first LED supporting face in planar shape and a plurality of first LEDs arranged and supported on the supporting face, at least three planar second LED supporting faces to support a plurality of second LEDs arranged on the second LED supporting faces. The second LEDs are distributed on a circle at an equivalent angle. The circle is tangent to all of the lateral surfaces of the supporting basal body. The second LEDs are arranged at the tangent points of the lateral surfaces of the supporting basal body and the circle. The radiant half-angle of the second LEDs is A; the included angle between the first supporting face and the second supporting faces is B, and the sum of A and B is more than or equal to 70 degrees, and is less than or equal to 100 degrees.
Owner:NINGBO YAMAO OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Single crystal diamond elements having convex surfaces and methods of its fabrication
ActiveUS20090022951A1Quality improvementLow radius of curvatureLayered productsRecord information storageCircular coneConvex side
A single crystal diamond element having a convex surface is disclosed, the convex surface including a spherical segment for which the maximum peak to valley deviation from a perfect spherical surface is less than about 5 μm. Alternatively or in addition, the RMS deviation from a perfect spherical surface may be less than about 500 nm, or the RMS roughness less than about 30 nm. A single crystal diamond element with a radius of curvature less than about 20 mm is also disclosed. In one aspect a single crystal diamond element having a conical half-angle greater than about 10° is described. The invention also provides a method for forming a rotationally symmetrical surface on a single crystal diamond element, comprising rotating the element about a first axis, applying a laser beam to the element in a direction perpendicular to the first axis, and translating the laser beam in two dimensions in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the beam. If the two-dimensional path follows the arc of a circle a spherical surface may be formed. The invention also provides improving a spherical surface on a single crystal diamond element by pressing a rapidly rotating cup onto a slowly rotating element. The element may be a lens, in particular a solid immersion lens.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus including the same
A zoom lens includes, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens unit having a positive refractive power that does not move for zooming; a second lens unit having a negative refractive power that moves during zooming; a third lens unit having a positive refractive power that moves during zooming; and at least one lens unit having a positive refractive power, and focal lengths of the zoom lens at a wide angle end and a telephoto end, a maximum value of a half angle of field at the wide angle end, and products of lateral magnifications of lens units arranged on the image side of the third lens unit in a state in which focus is at infinity at the telephoto end and the wide angle end are appropriately set.
Owner:CANON KK
Imaging lens system and capsule endoscope
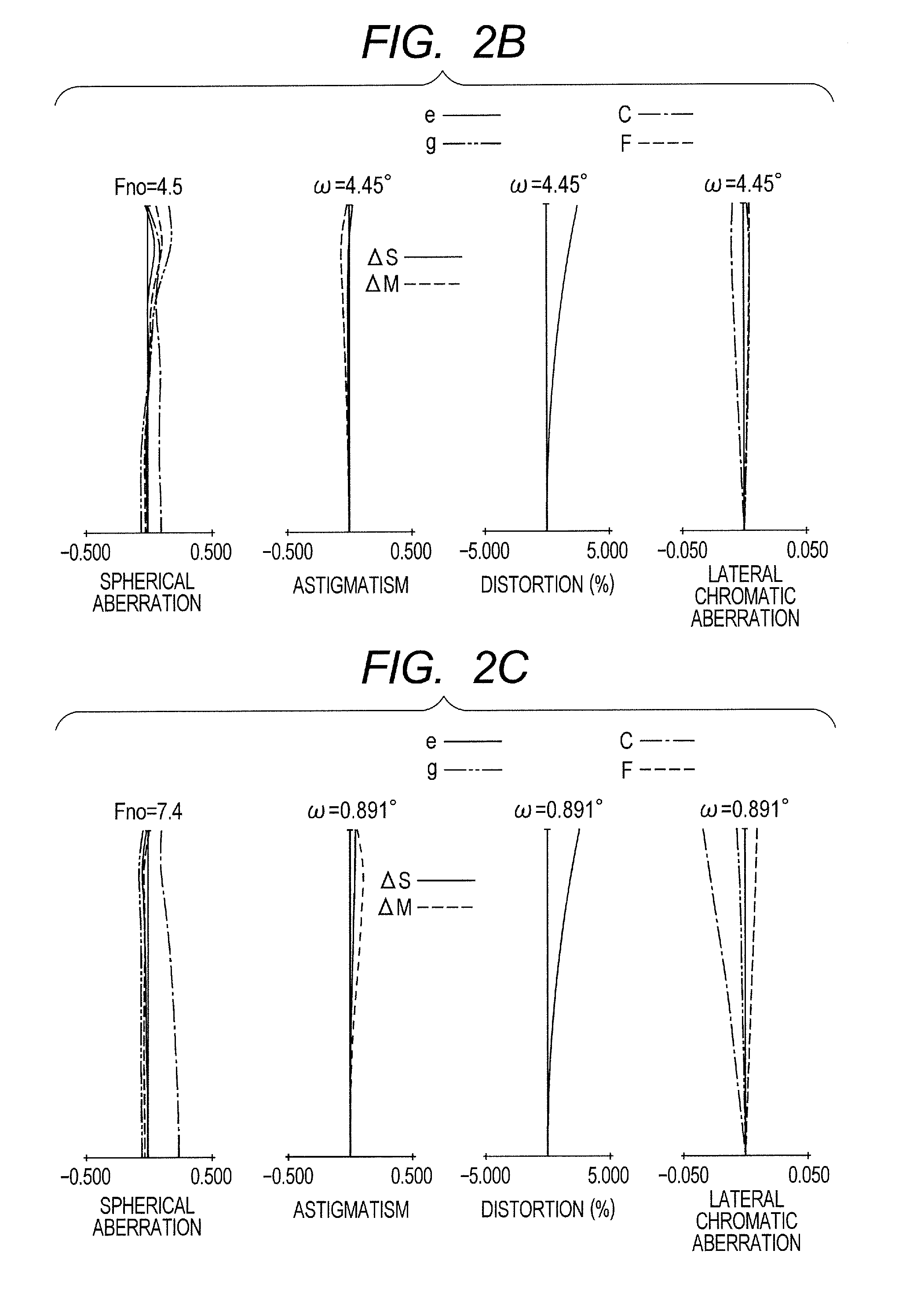
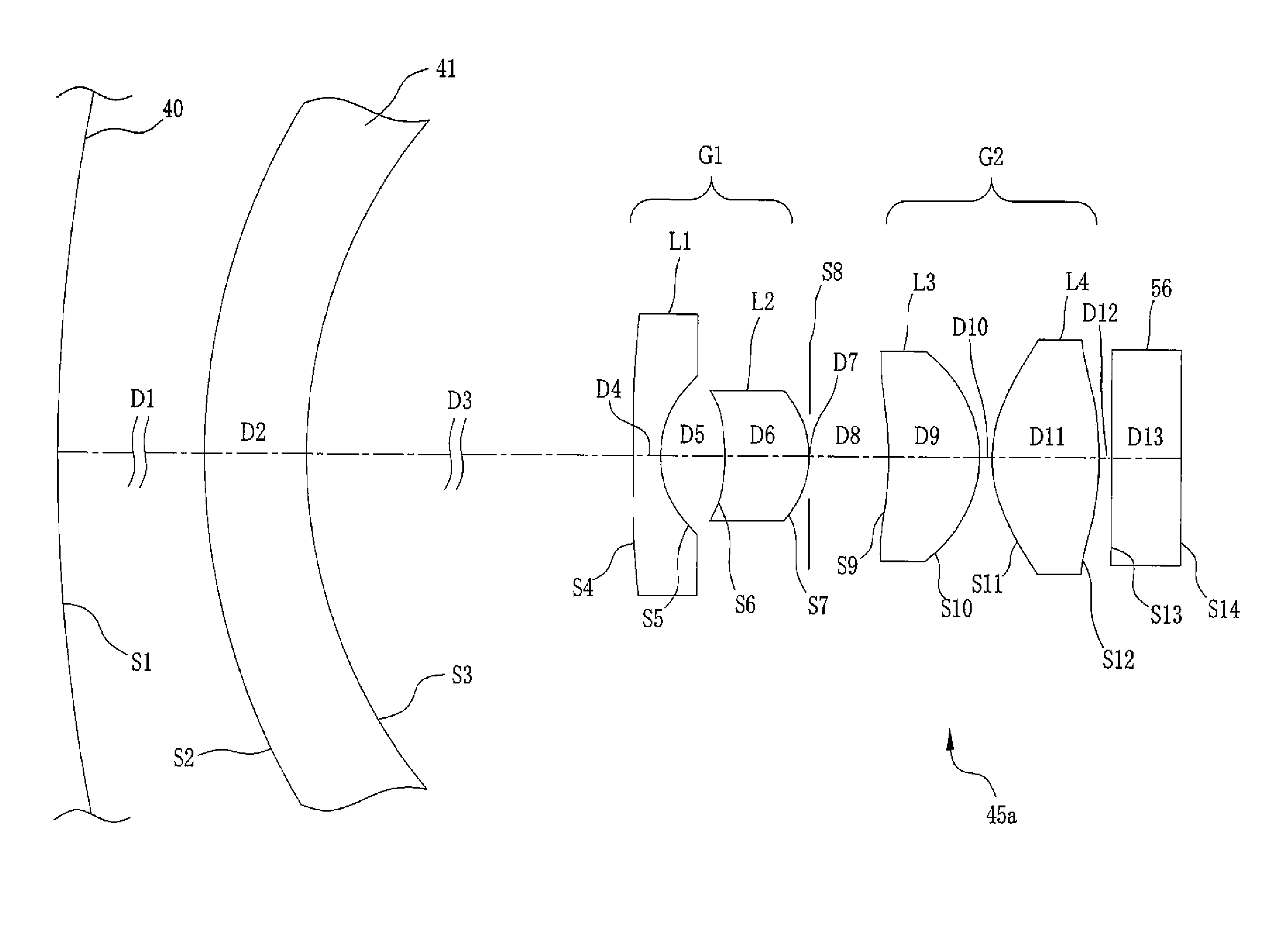
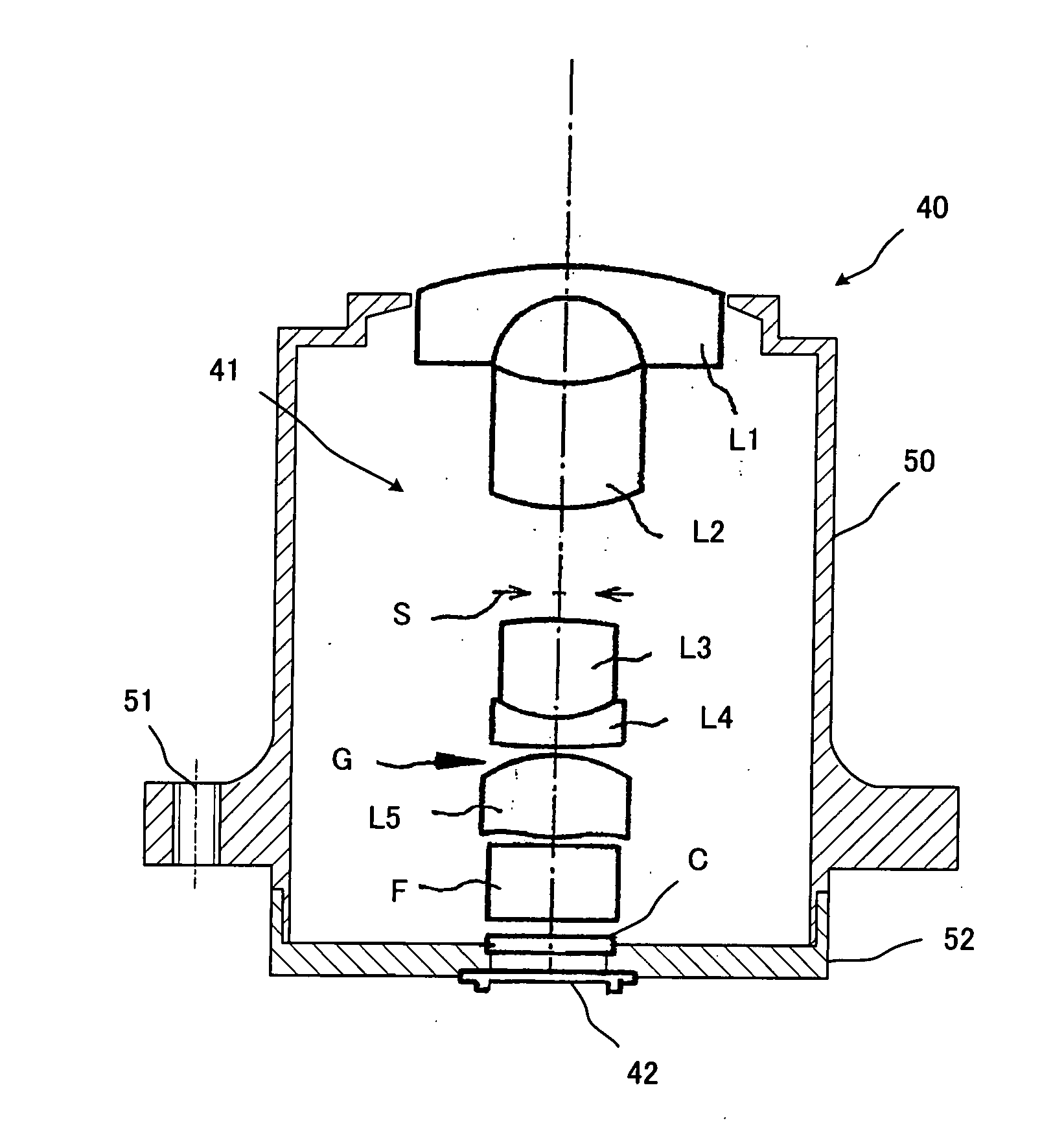
InactiveUS20090141364A1Easy-to-swallow sizeImprove distortionSurgeryEndoscopesCamera lensConditional expression
A capsule endoscope has an imaging lens system 45a that forms an image of a substantially spherical object 40 in a plane shape on the imaging surface. The imaging lens system 45a includes first to fourth lenses L1 to L4 and an aperture diaphragm S7. The surface shapes and arrangement thereof are set in consideration of a front cover 41 of the capsule endoscope and a cover glass 56 of an imaging device. Further, the imaging lens system is configured so that the following conditional expression is satisfied with respect to an arbitrary half angle of view ω:0.7<(Y(ω+Δω)−Y(ω)) / Y(Δω)where Y(ω) denotes an image height for the half angle of view ω of the imaging lens system, andΔω denotes an amount of minute change of the half angle of view (ω).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Two-stage asymmetrical composite parabolic reflector condenser in smooth transition connection
InactiveCN102213825AImprove spotlight effectEffective workMirrorsCondensersOptical radiationNon symmetric
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
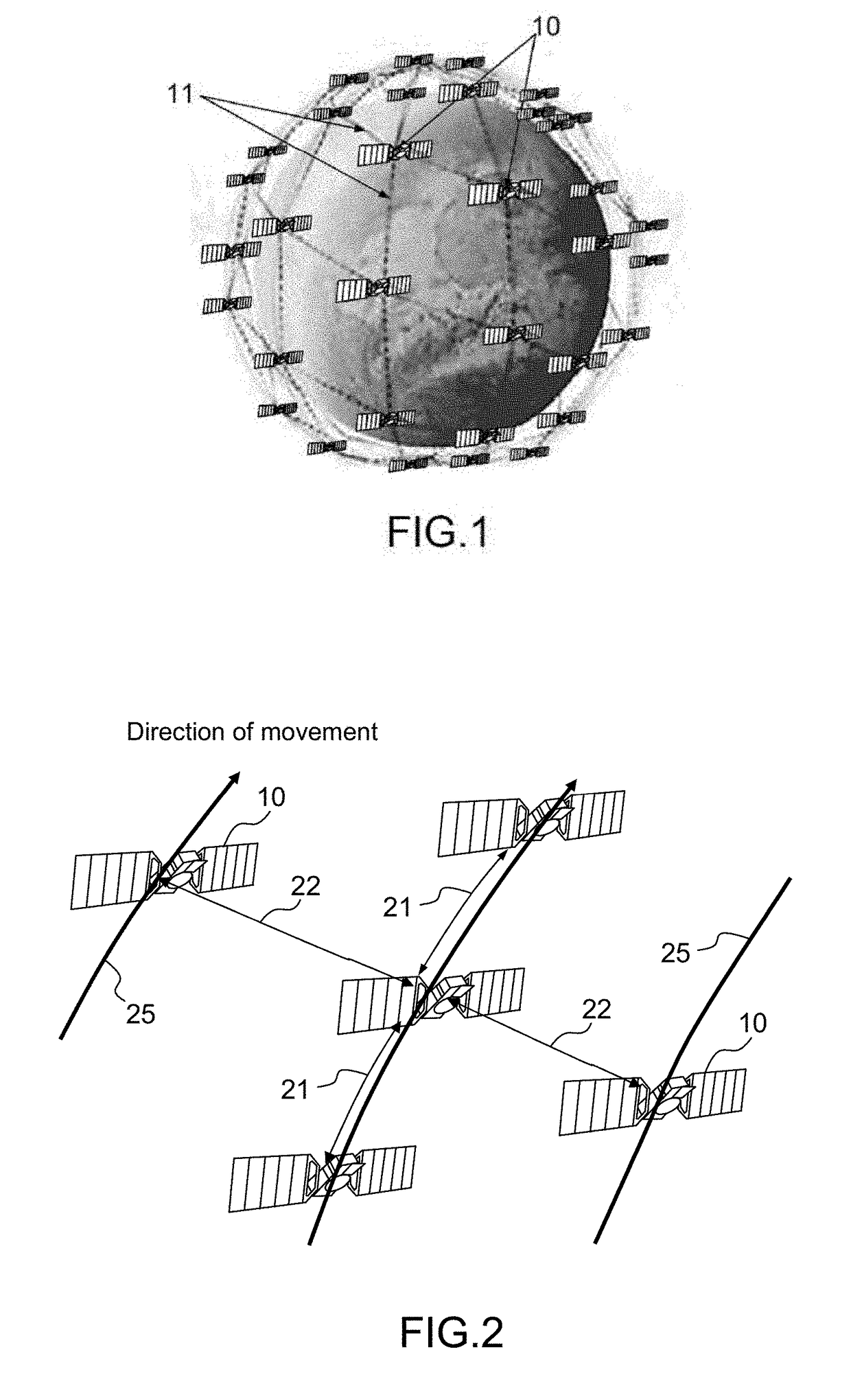
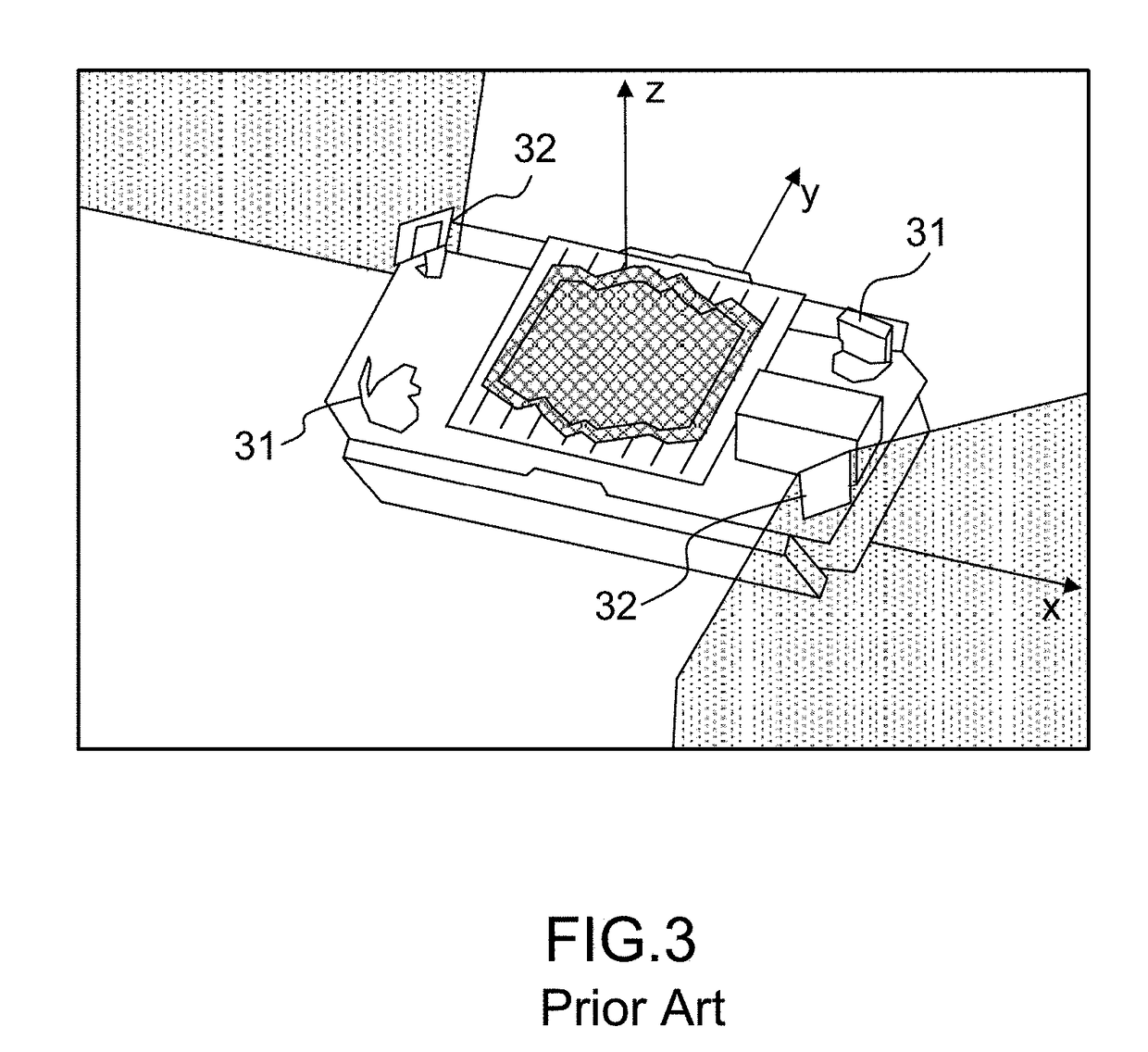
Inter-satellite communication device, associated satellite and associated constellation of satellites
ActiveUS20170324465A1Avoid the inter-orbital plane links being brokenSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionCommunication linkSatellite orbit
An inter-satellite communication device for satellites orbiting within a constellation of satellites comprises at least one optical terminal dedicated to intra-orbital plane communication links and at least one optical terminal dedicated to inter-orbital plane communication links, each optical terminal dedicated to intra-orbital plane communications configured to transmit and receive optical signals with an optical terminal of an identical satellite orbiting in the same orbital plane, each optical terminal dedicated to inter-orbital plane communications configured to transmit and receive optical signals with an optical terminal of an identical satellite in an orbital plane adjacent over the entirety of its orbit in its orbital plane and each optical terminal dedicated to inter-orbital plane communications having a field of regard such that the half-angle at the vertex of the latter is larger than the maximum value of the azimuthal angle over a revolution around the Earth.
Owner:THALES SA
Wide band biconical antennas with an integrated matching system
ActiveUS20050093756A1Waveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorLinear relationship
A biconical antenna; an entry conic having an entry base opposite an entry vertex and a termination conic having a termination base opposite a termination vertex. The entry and termination conics share substantially the same axis and the entry vertex is adjacent the termination vertex. The transmission line is received by the entry conic and terminated in the termination conic. Together, the entry conic and the termination conic phase correct energy emanating from the transmission line. Another embodiment of the antenna comprises an entry conic having at least two sub-conics and a termination conic having at least two sub-conics. Each of the sub-conics having an integer multiple of a half-angle. The biconical antenna may also include a multi-conductor transmission line, wherein the biconical antennas are arranged in a co-linear relationship. Each of the multi-conductors is coupled to at least one of the plurality of biconical antennas.
Owner:SHAKESPEARE CO
Method for fast measurement and judgment of central line of equipment like rotary kiln
InactiveCN101718539AEasy to manage systematicallyEasy to measureMeasurement devicesRotary drum furnacesFast measurementEngineering
The invention relates to a method for fast measurement and judgment of a central line of equipment like a rotary kiln, which comprises the following steps: firstly measuring the actual horizontal projection distance A1 of the central line of a wheel belt and a support wheel, further calculating the horizontal movement adjustment quantity X of the support wheel and the support half-angle theta of the support wheel after adjustment according to a formula, judging whether the horizontal movement adjustment quantity X of the support wheel can lead the support half-angle theta of the support wheel after the adjustment to be not less than 28.5, and finally determining a group of X values which are in line with the requirements for fast adjustment of the central line of a cylinder body of the rotary kiln. The measurement method has the advantages of simpleness, easy operation, small system error, high adjustment accuracy and fast speed.
Owner:TIANJI COAL CHEM IND GROUP
Pellicle inspection apparatus
ActiveUS20150293460A1High precisionAvoid it happening againPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusForeign matterLithographic artist
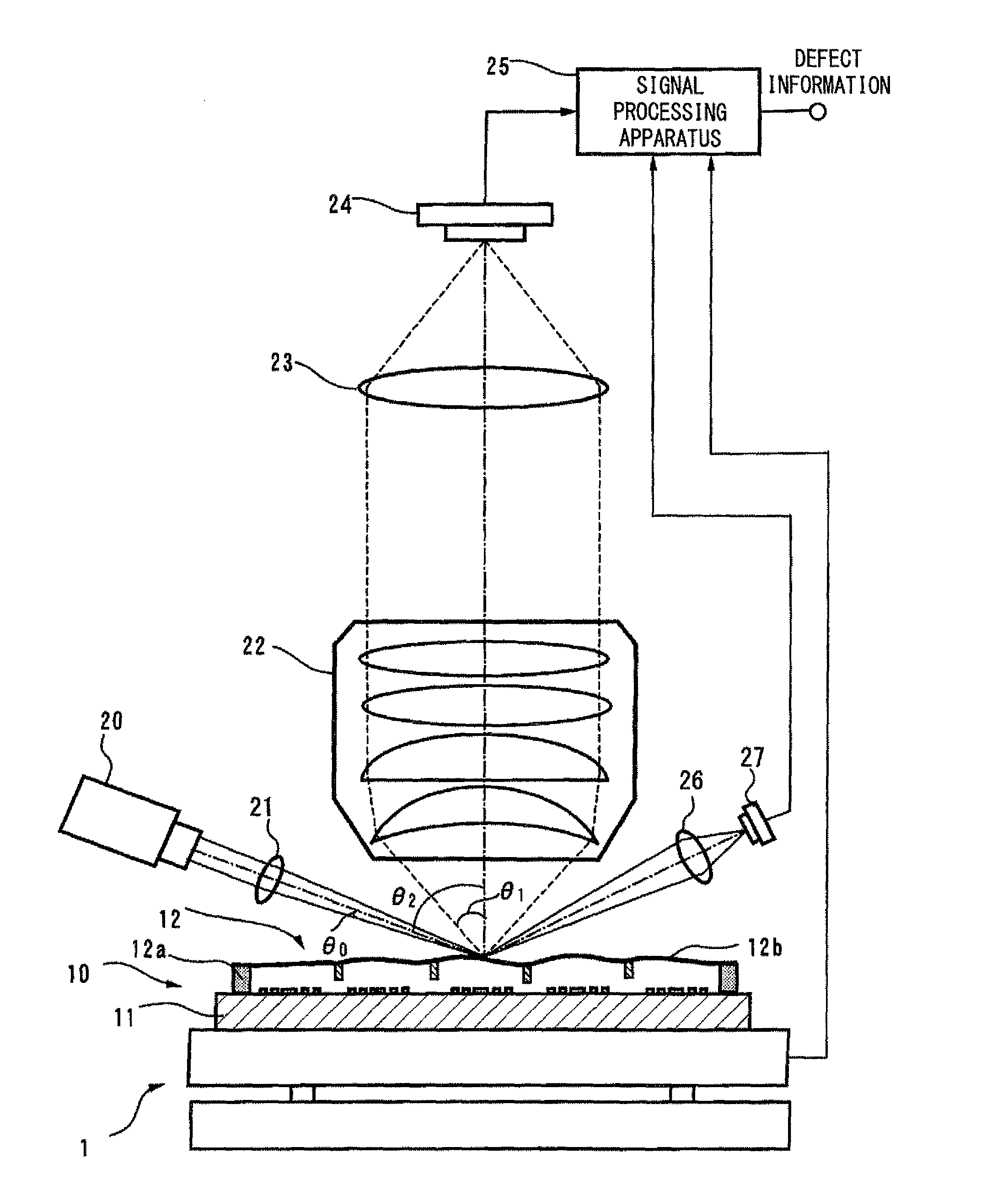
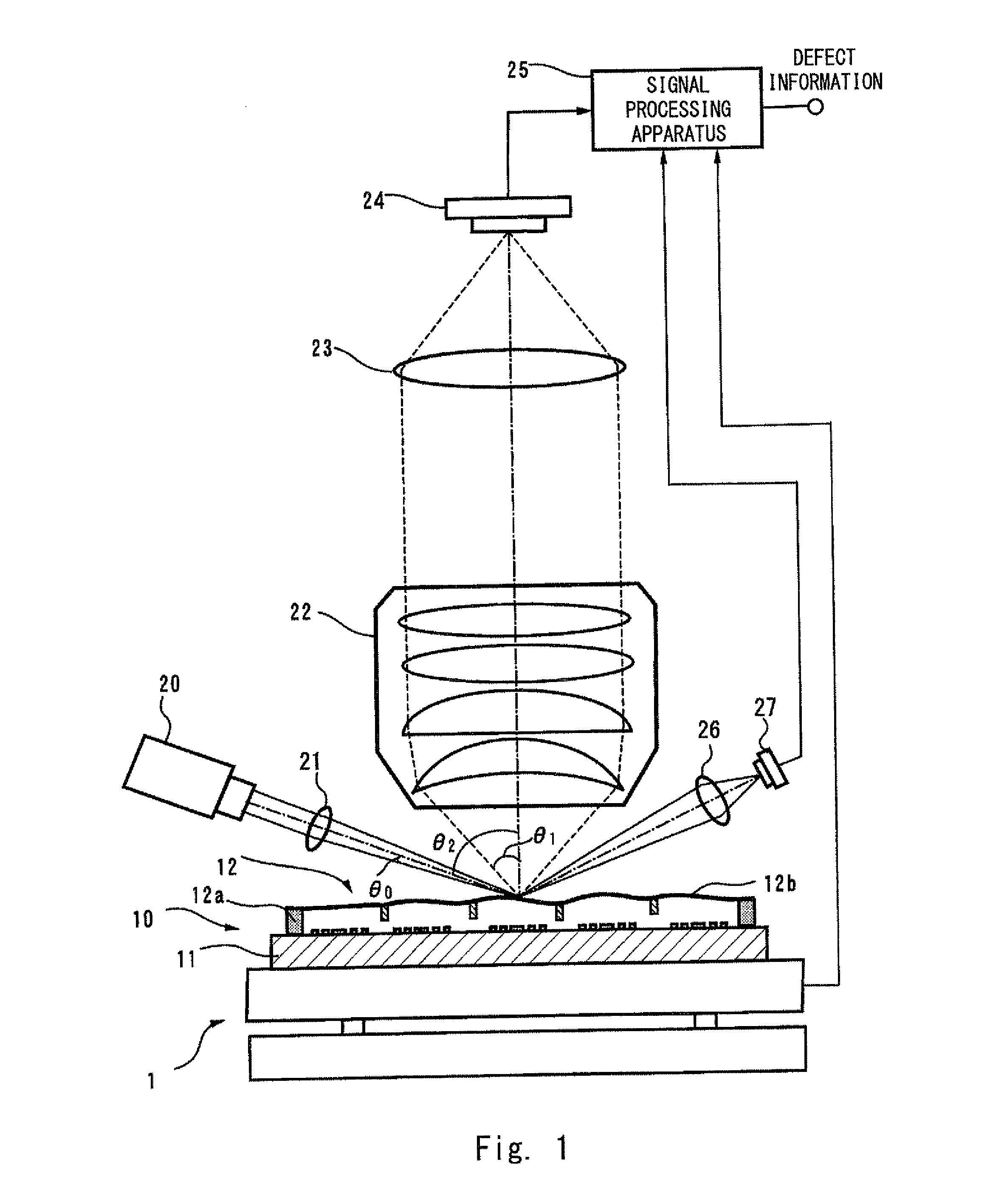
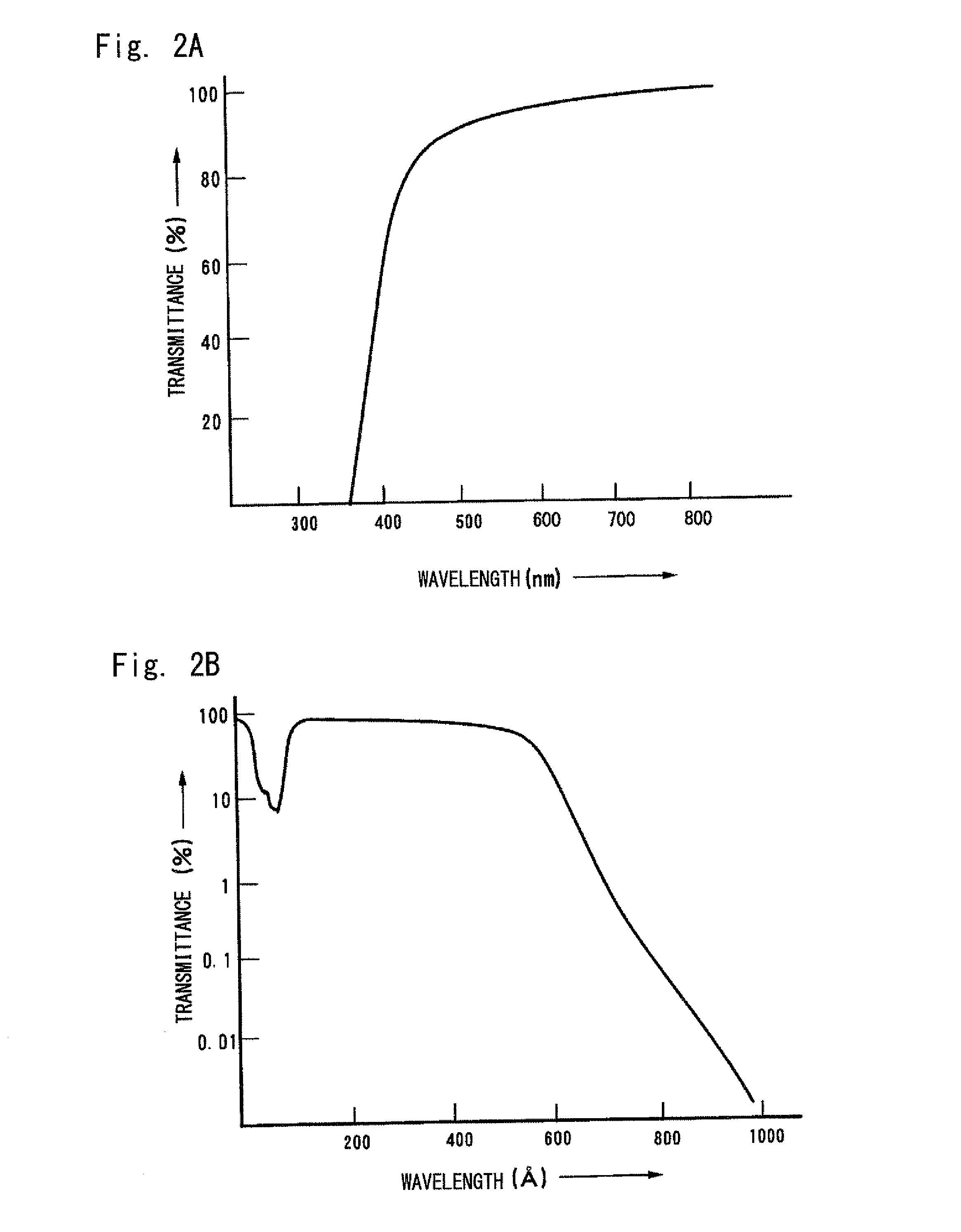
Provided with a pellicle inspection apparatus that inspects a pellicle film of a mask provided with a pellicle and used in EUV lithography. The pellicle inspection apparatus includes: an illumination optical system that projects a converging illuminating beam toward the pellicle film;a light collection optical system including an object lens having an optical axis substantially orthogonal to the pellicle film and that collects scattering light outgoing from a foreign substance present on the pellicle film; and a detection system that detects the scattering light collected by the light collection optical system, wherein an incident angle θ2 of the illuminating beam with respect to the pellicle film satisfies Expression θ2−θ0>θ1+23°, where θ0 is a collecting angle (half angle) of the illuminating beam, and θ1 is a maximum light-receiving angle (half angle) of the object lens.
Owner:LASERTEC CORP
LED (Light Emitting Diode) packaging device based on graphical packaging substrate
InactiveCN102324460AImprove light extraction efficiencyHigh light efficiencySemiconductor devicesRefractive indexEngineering
The invention discloses an LED (Light Emitting Diode) packaging device based on a graphical packaging substrate. The LED packaging device based on the graphical packaging substrate comprises a graphical substrate, at least one LED chip and a packaging adhesive body, wherein the LED chip is arranged on the graphical substrate; the packaging adhesive body covers the LED chip; the surface of the graphical substrate is provided with a projection or a recess; a line plane angle alpha between the side edge of a longitudinal cross section of the projection or the recess and the horizontal plane of the graphical substrate and the refractive index n of the packaging adhesive body satisfy the following relation: according to the invention, the light efficiency can be increased by about 35%, the light producing efficiency of the LED packaging device is largely enhanced and simple structure is also obtained; in addition, the half angle width of the LED packaging device is 45 degrees smaller than the half angle width of a traditional LED device based on a mirror face substrate; and relatively concentrated lights and convenience in secondary light distribution are obtained. Finally, because the line plane angle alpha can be freely set according to needs without need of arranging a complicated curved-plane lens, the LED packaging device based on the graphical packaging substrate is beneficial for realizing the thinning of the packaging and also favorable for being mounted downstream.
Owner:FOSHAN NATIONSTAR OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image-formation optical system and imaging system using the same
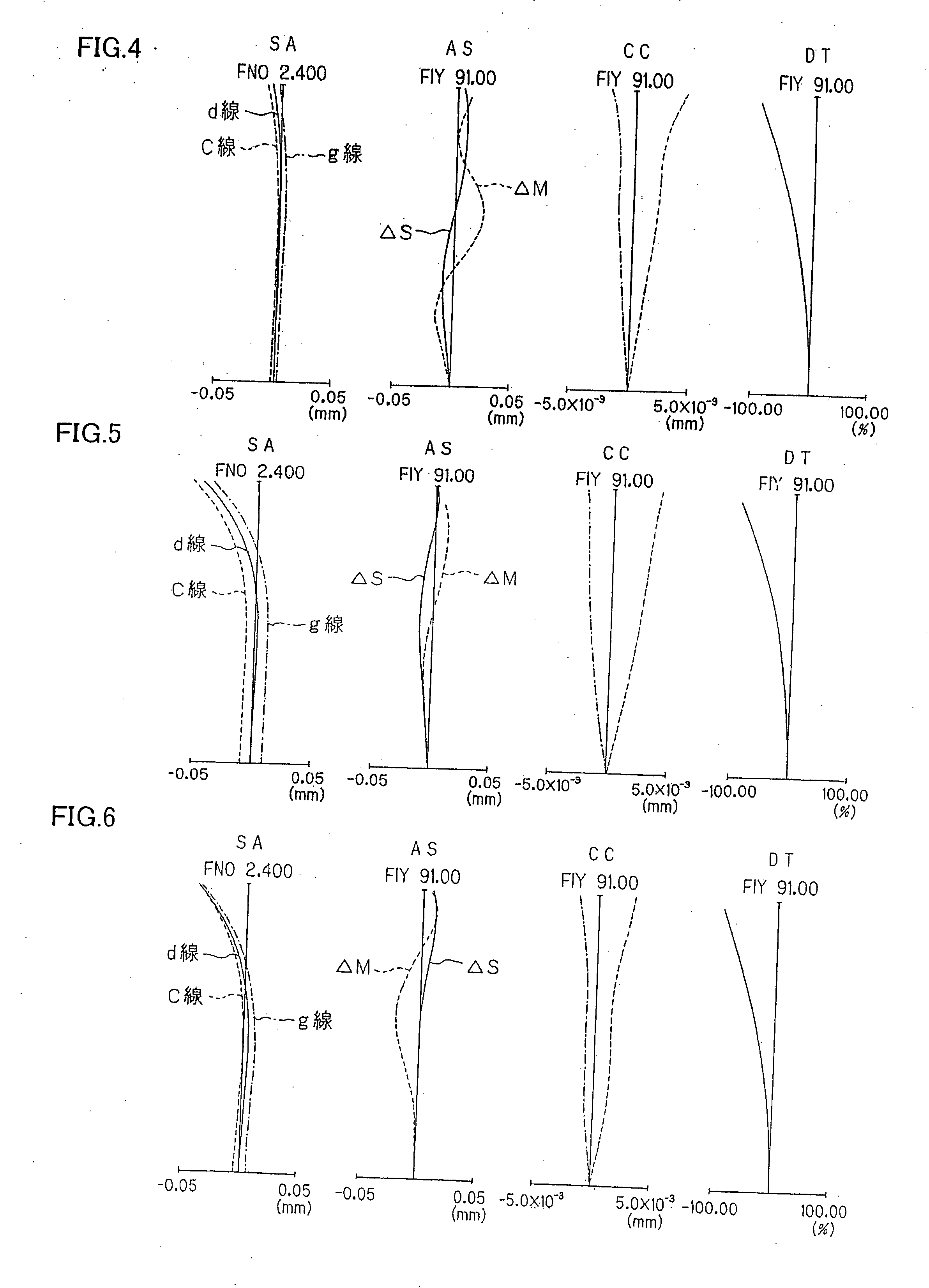
The invention relates to a compact image-formation optical system that is diminished in a diametrical direction with as few lenses as possible while well adapting to an wide-angle arrangement having a half angle of 90° or greater, and an imaging system incorporating the same. The image-formation optical system comprises, in order from its object side, a first lens L1 that is a negative lens, a second lens L2 that is a meniscus lens concave on its object side, an apertures stop S, and a lens group G having positive refracting power.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com