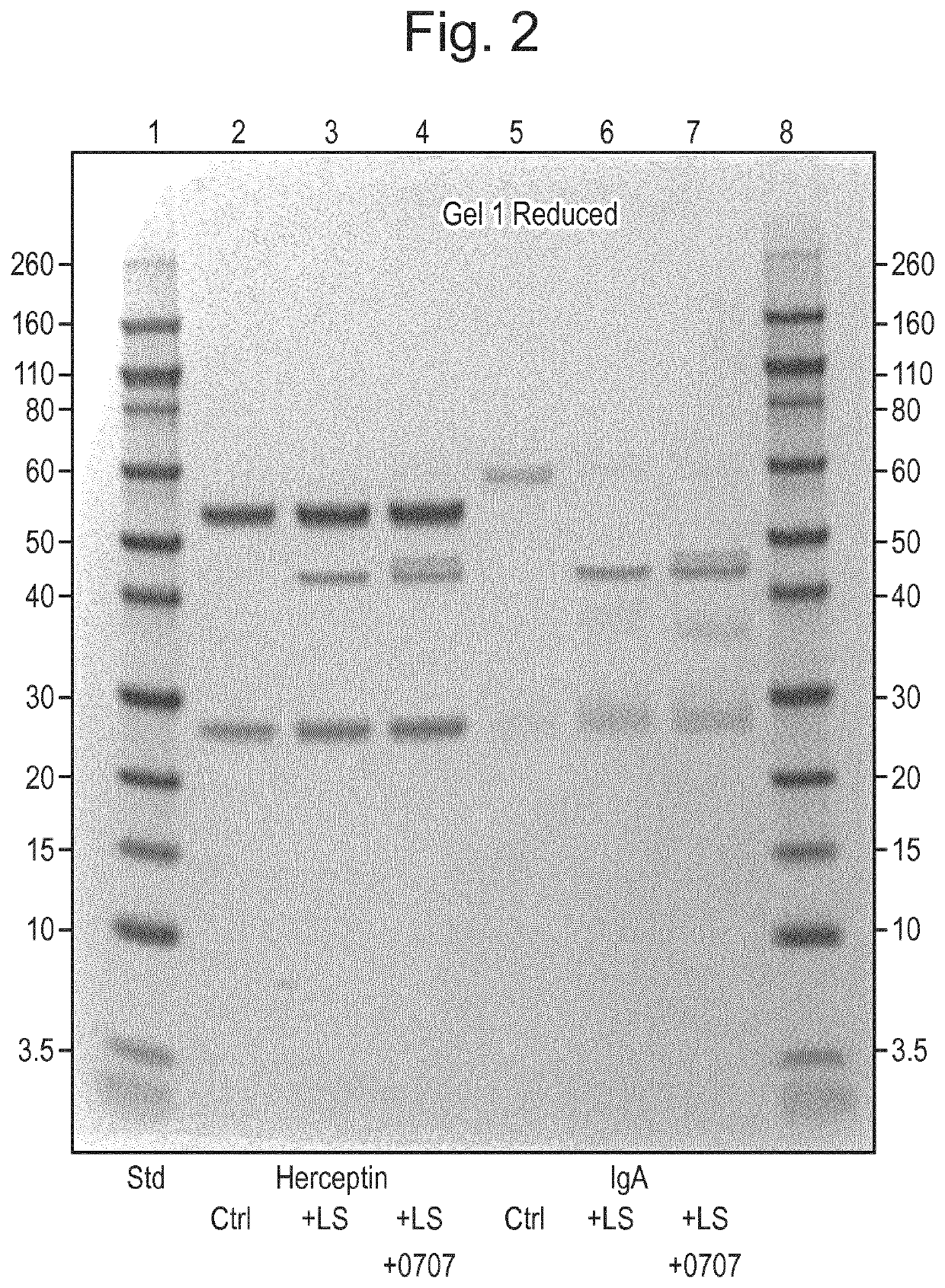
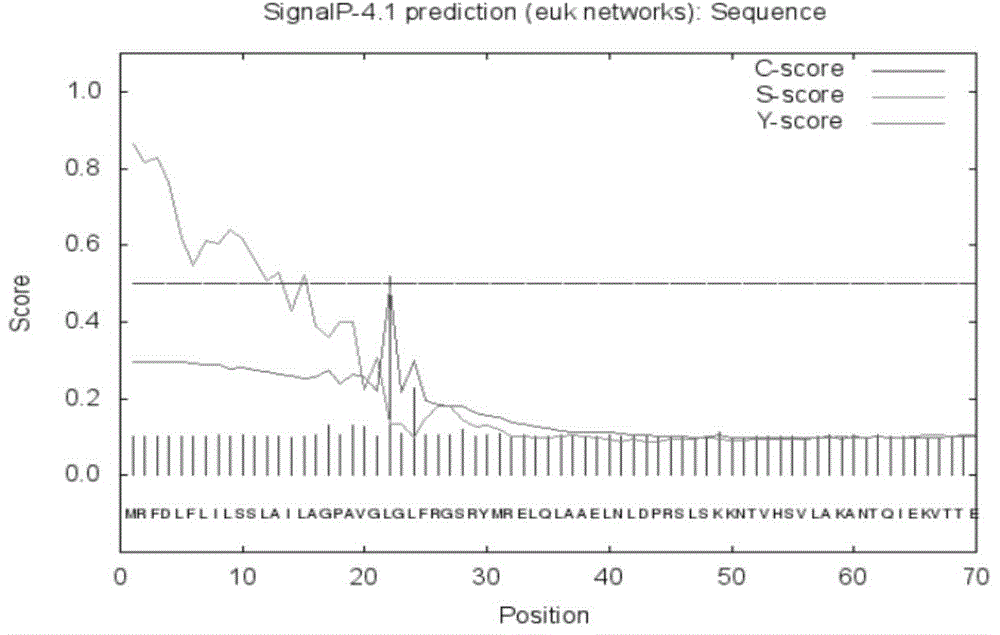
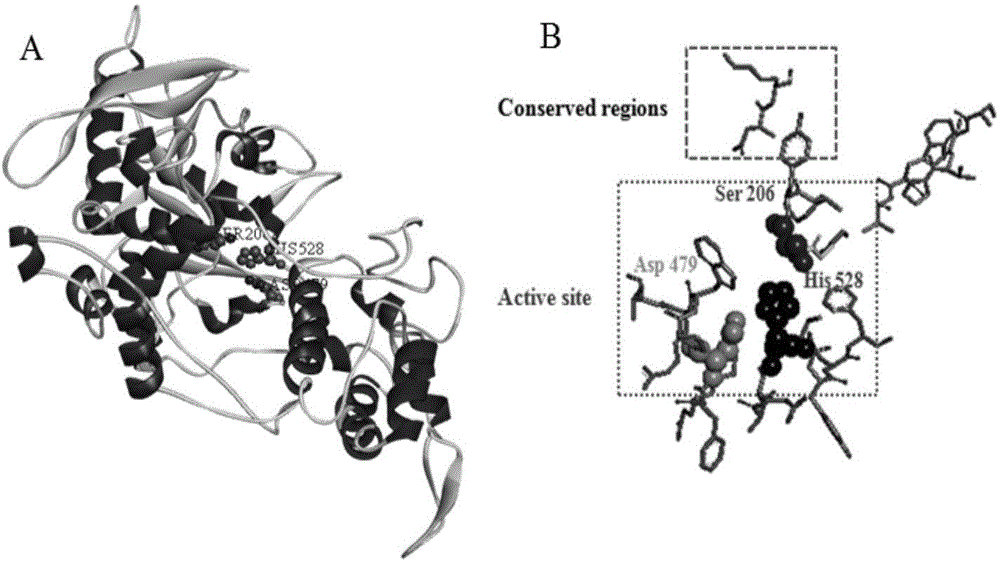
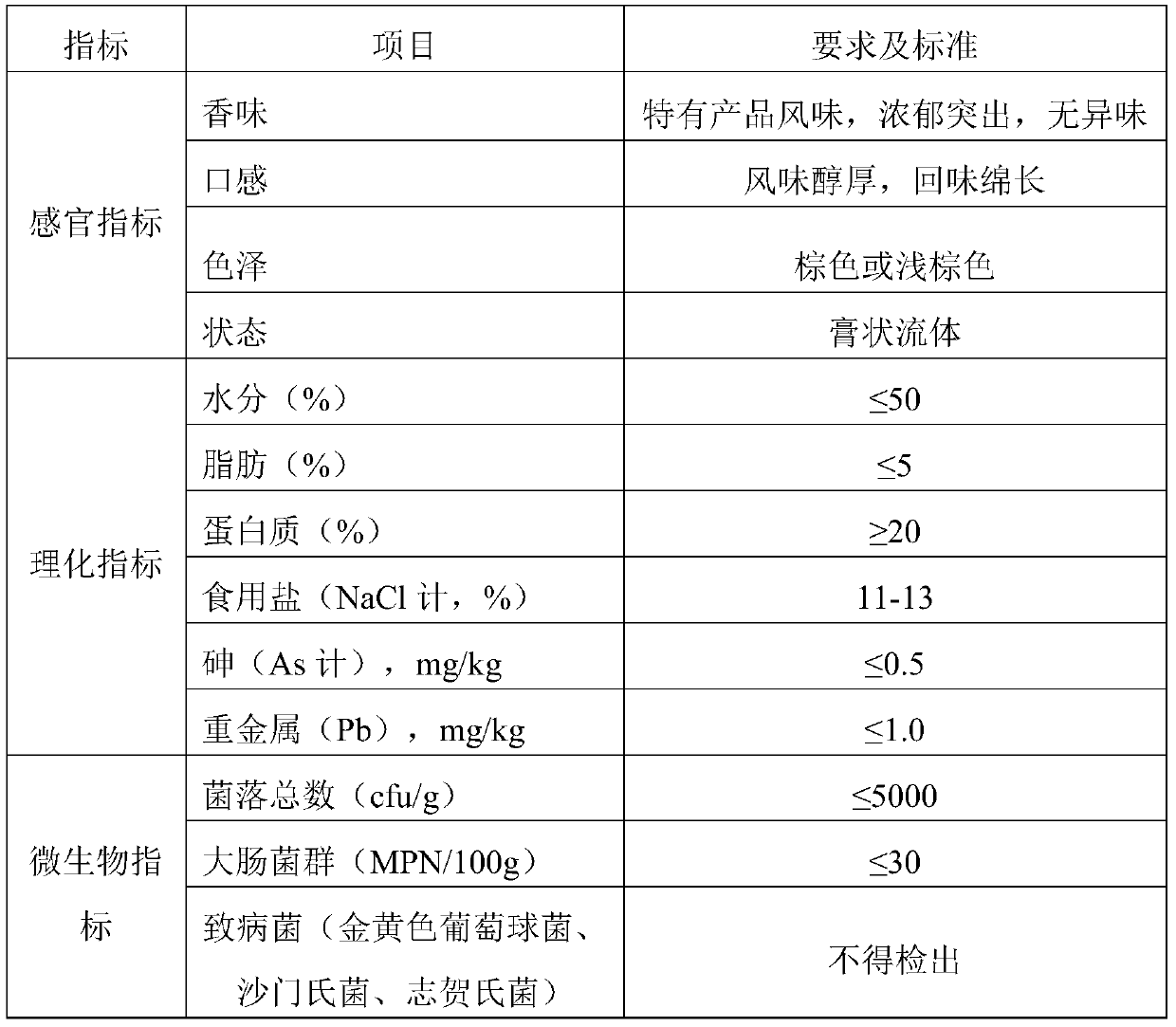
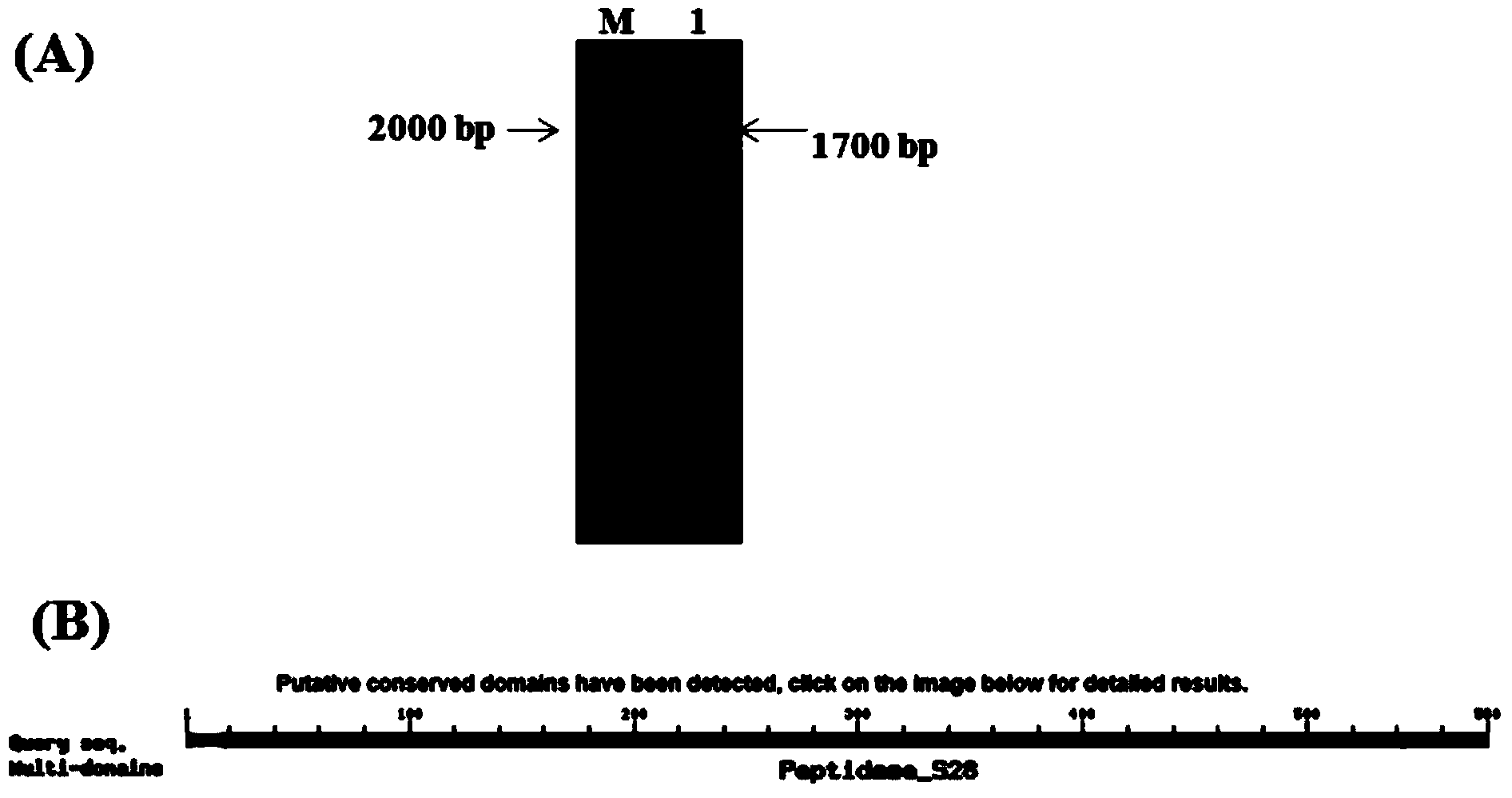
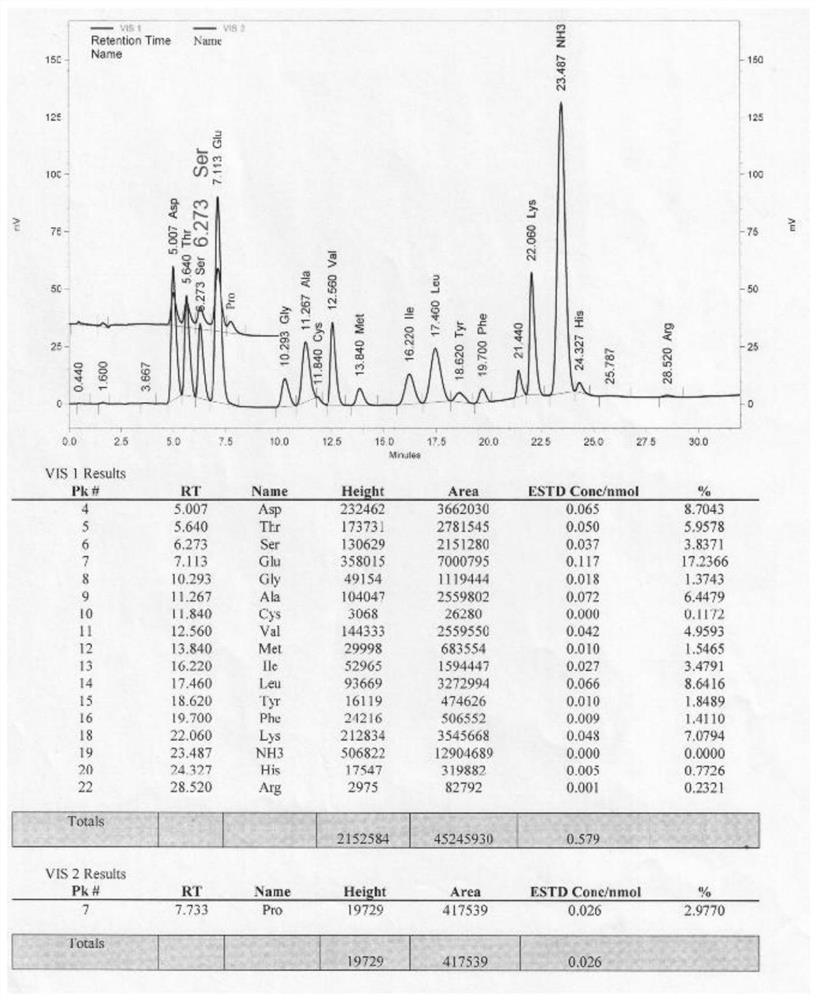
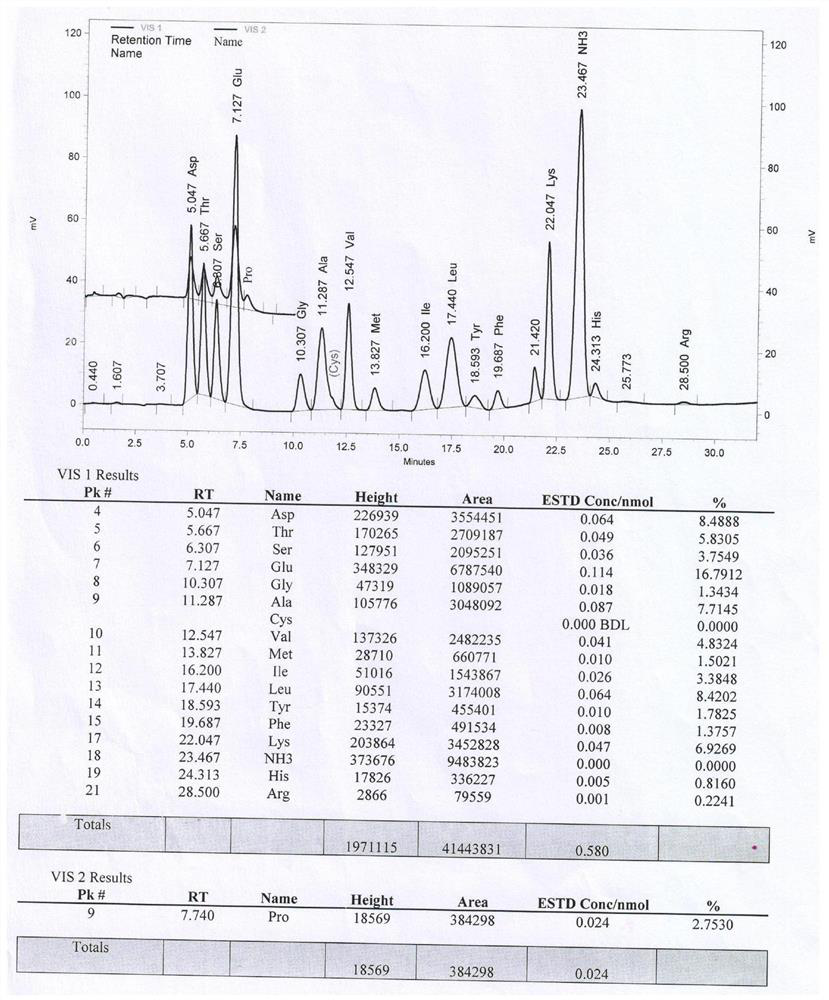
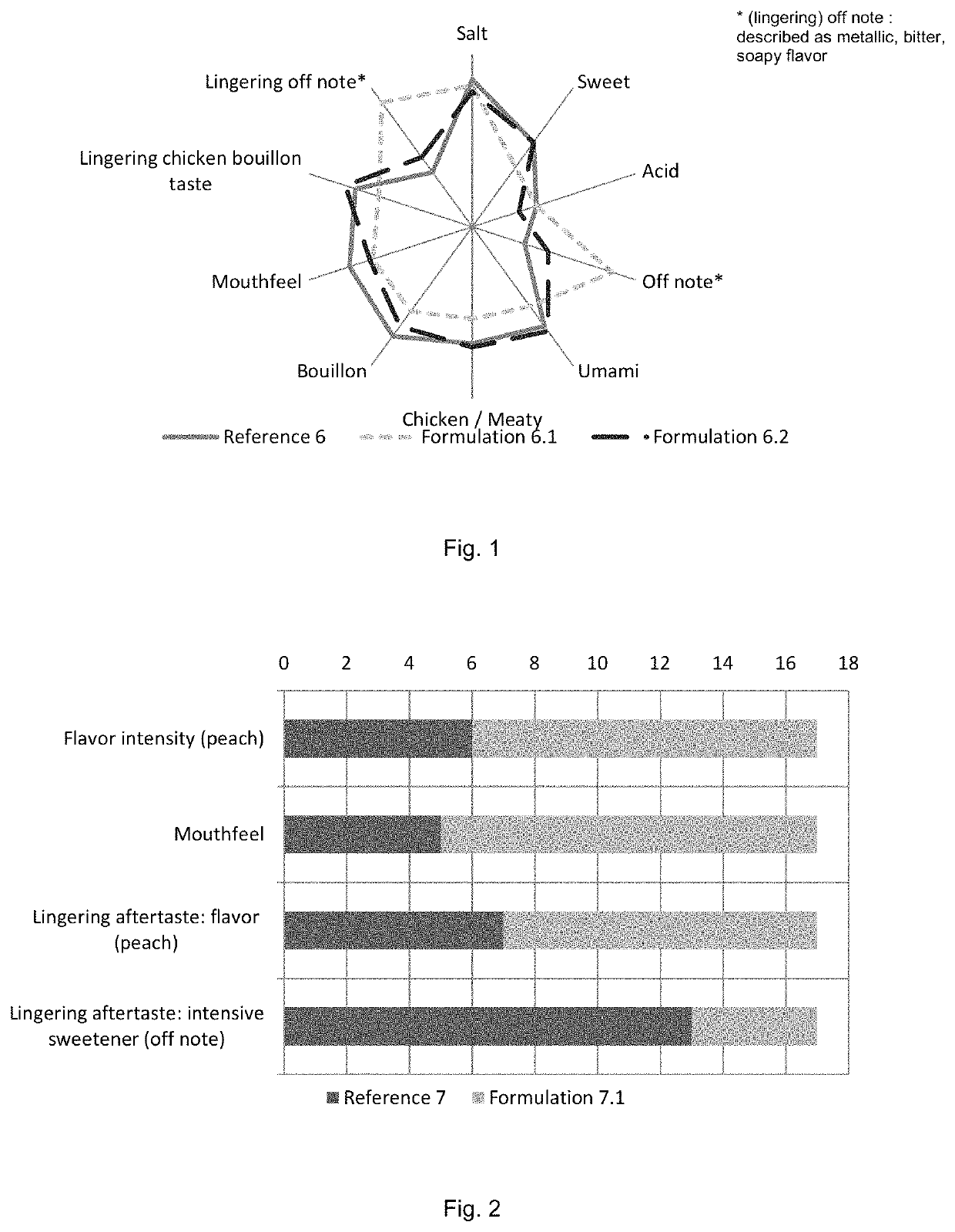
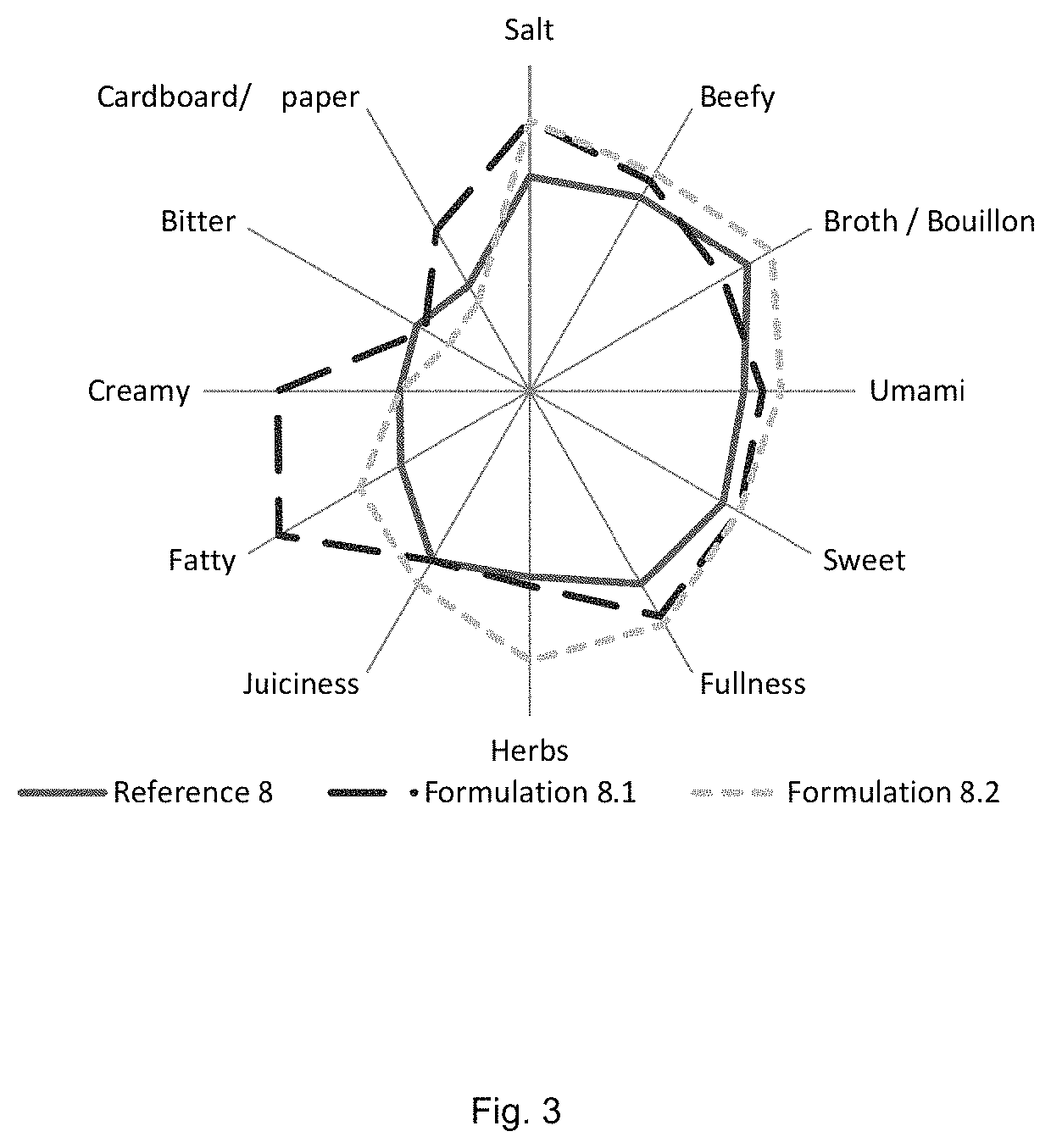
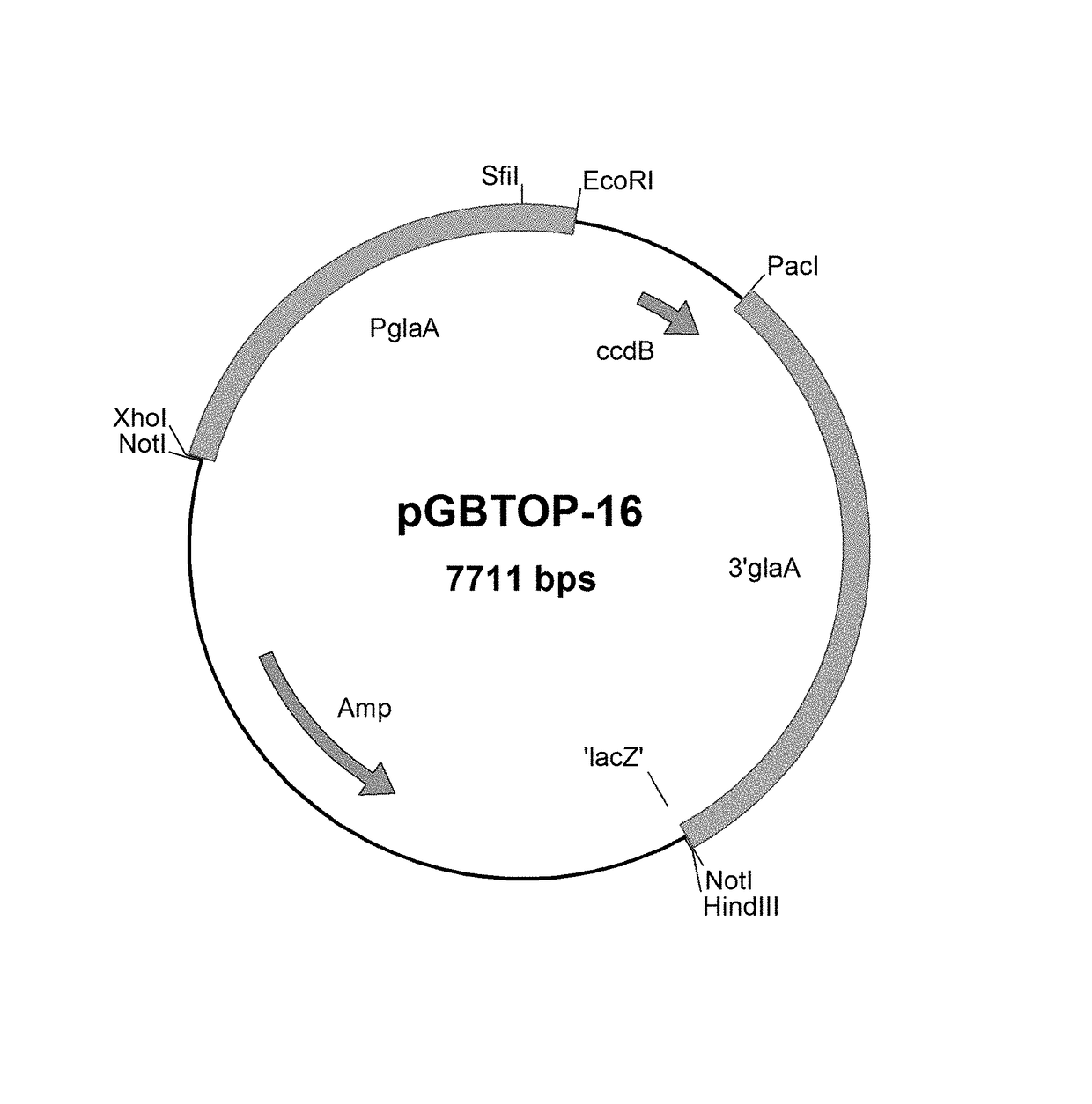
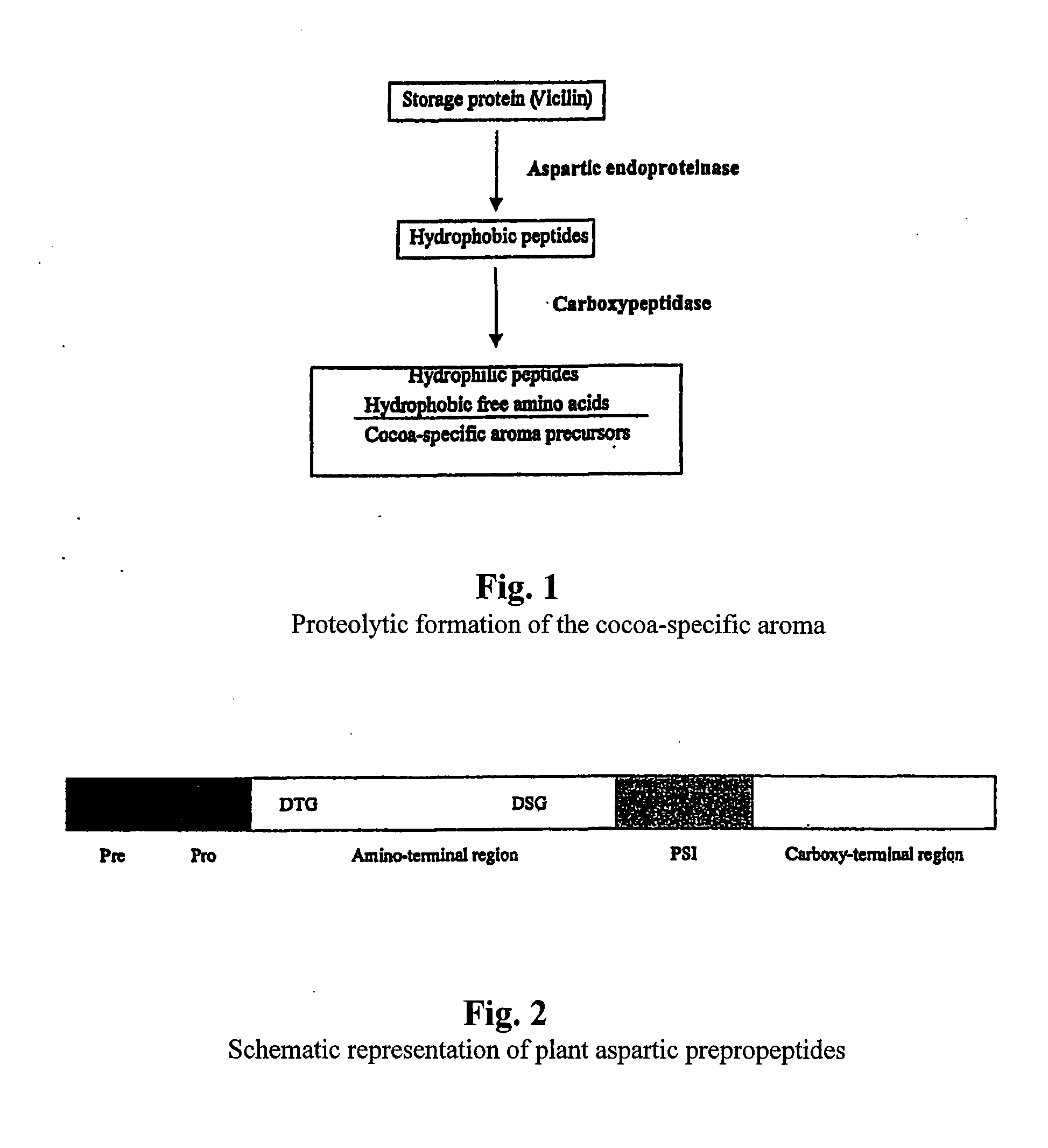
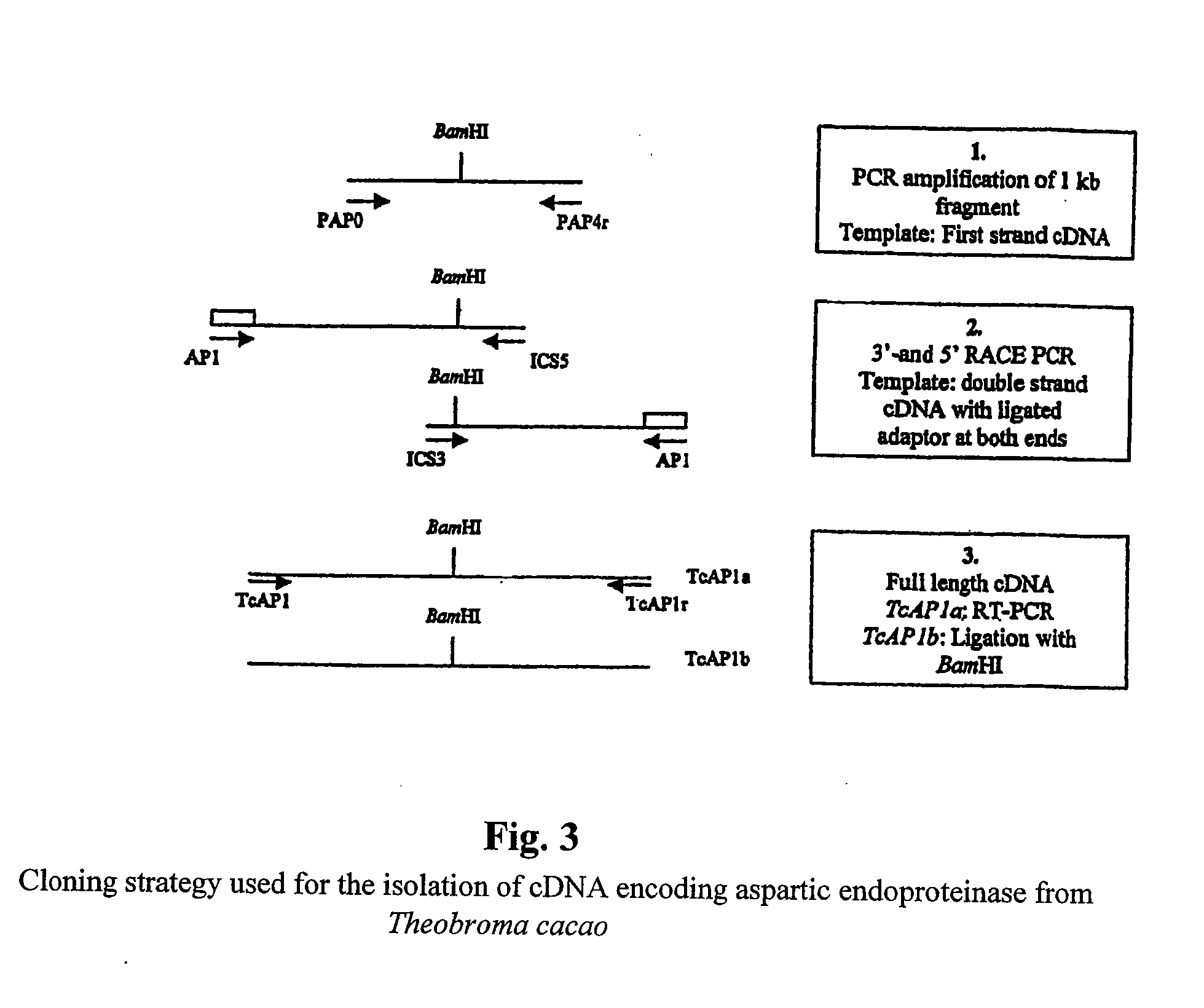
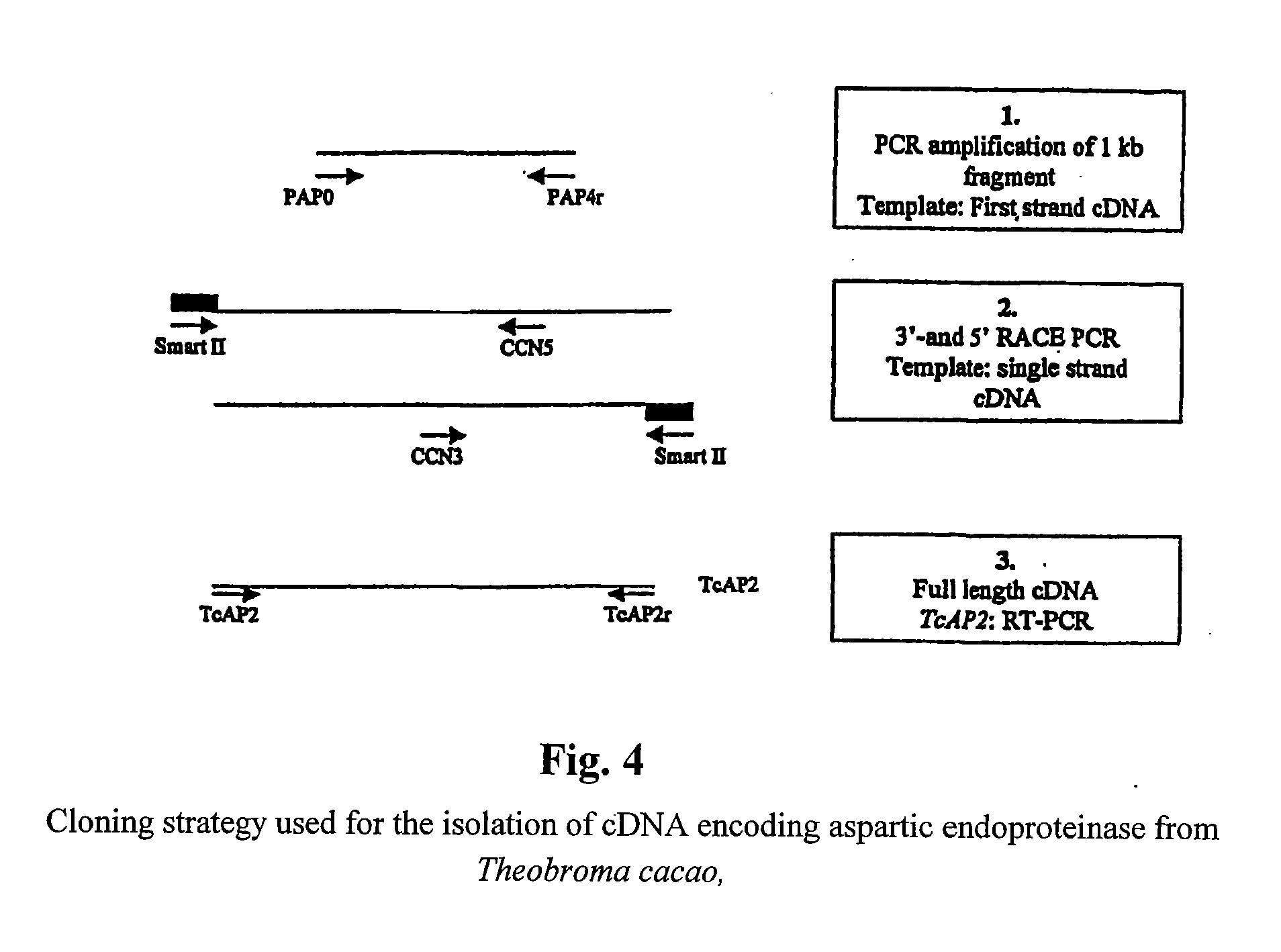
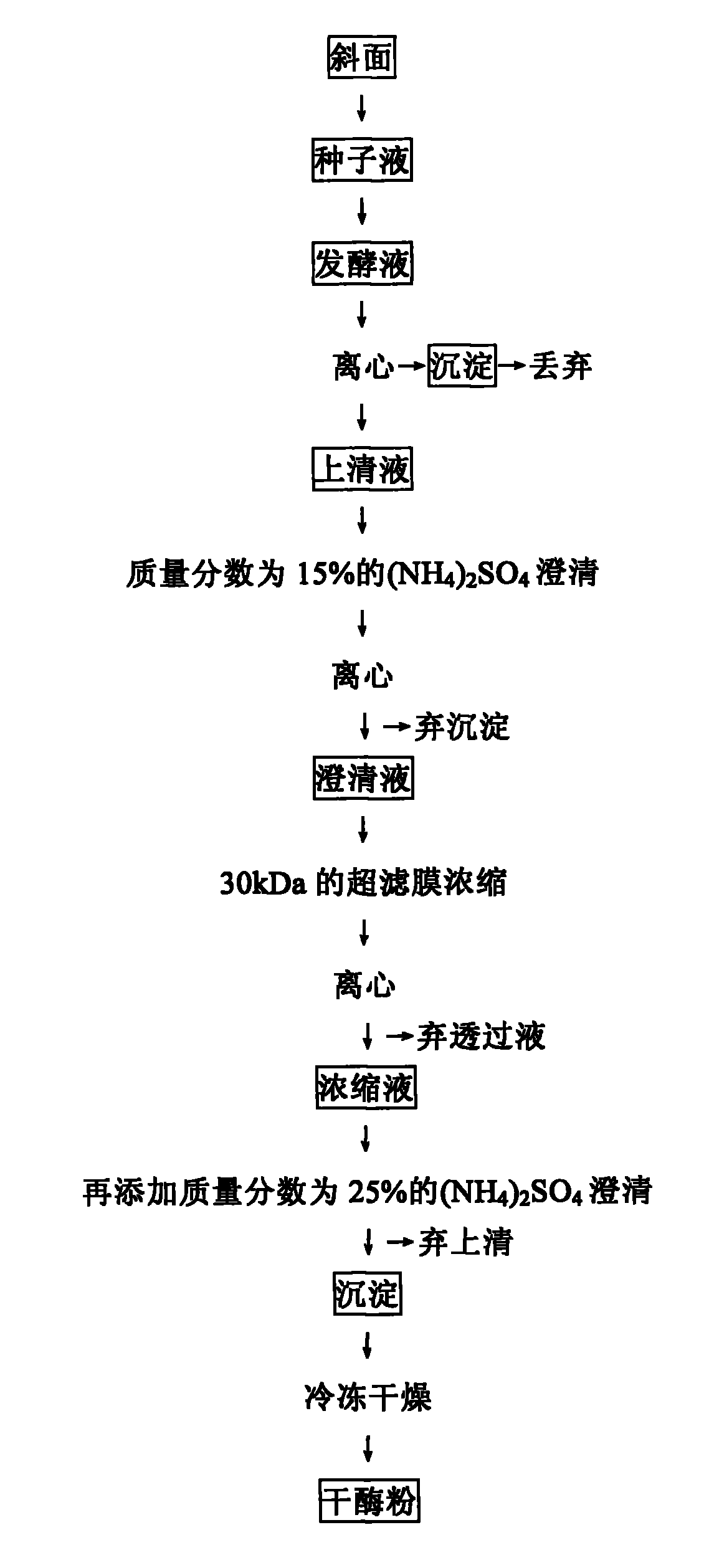
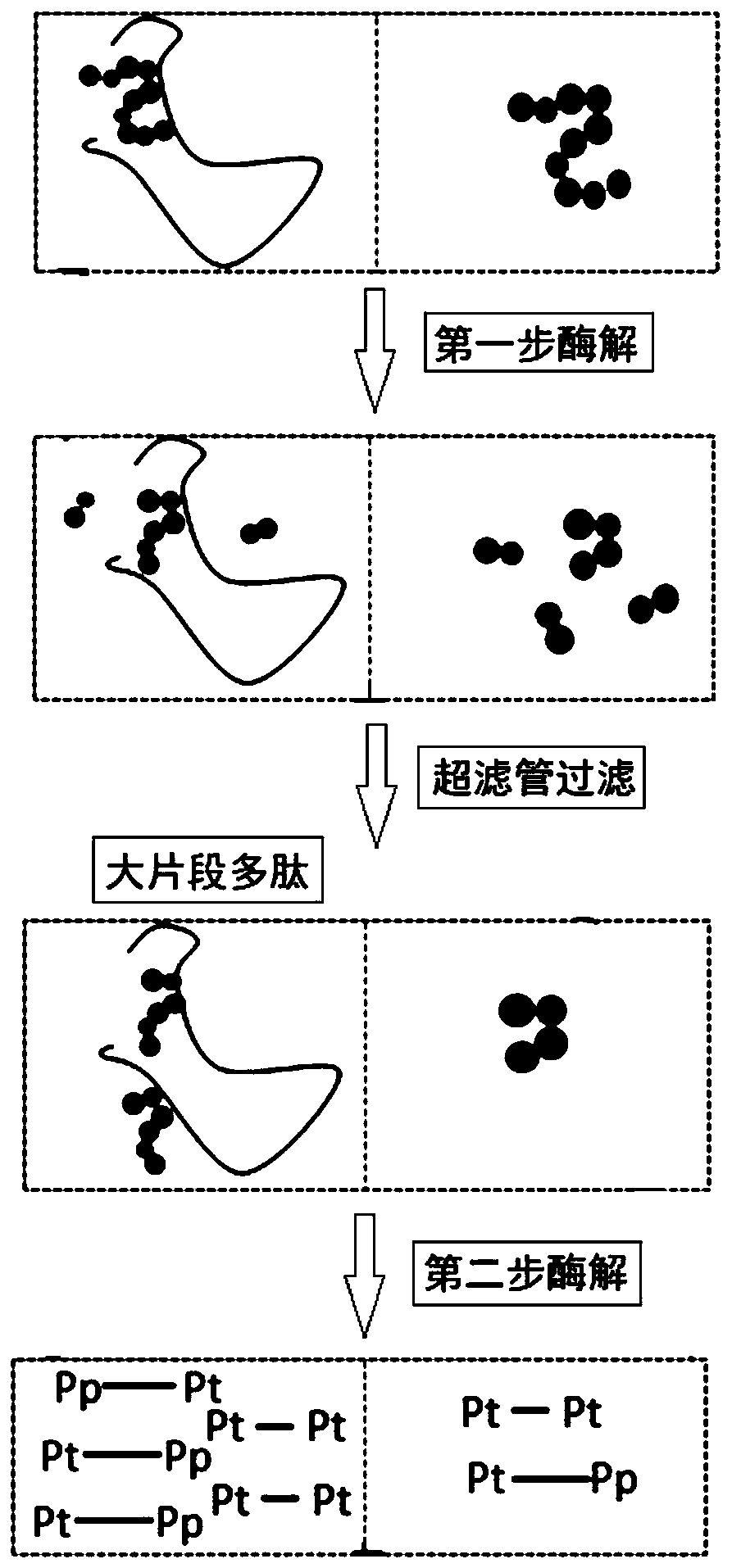
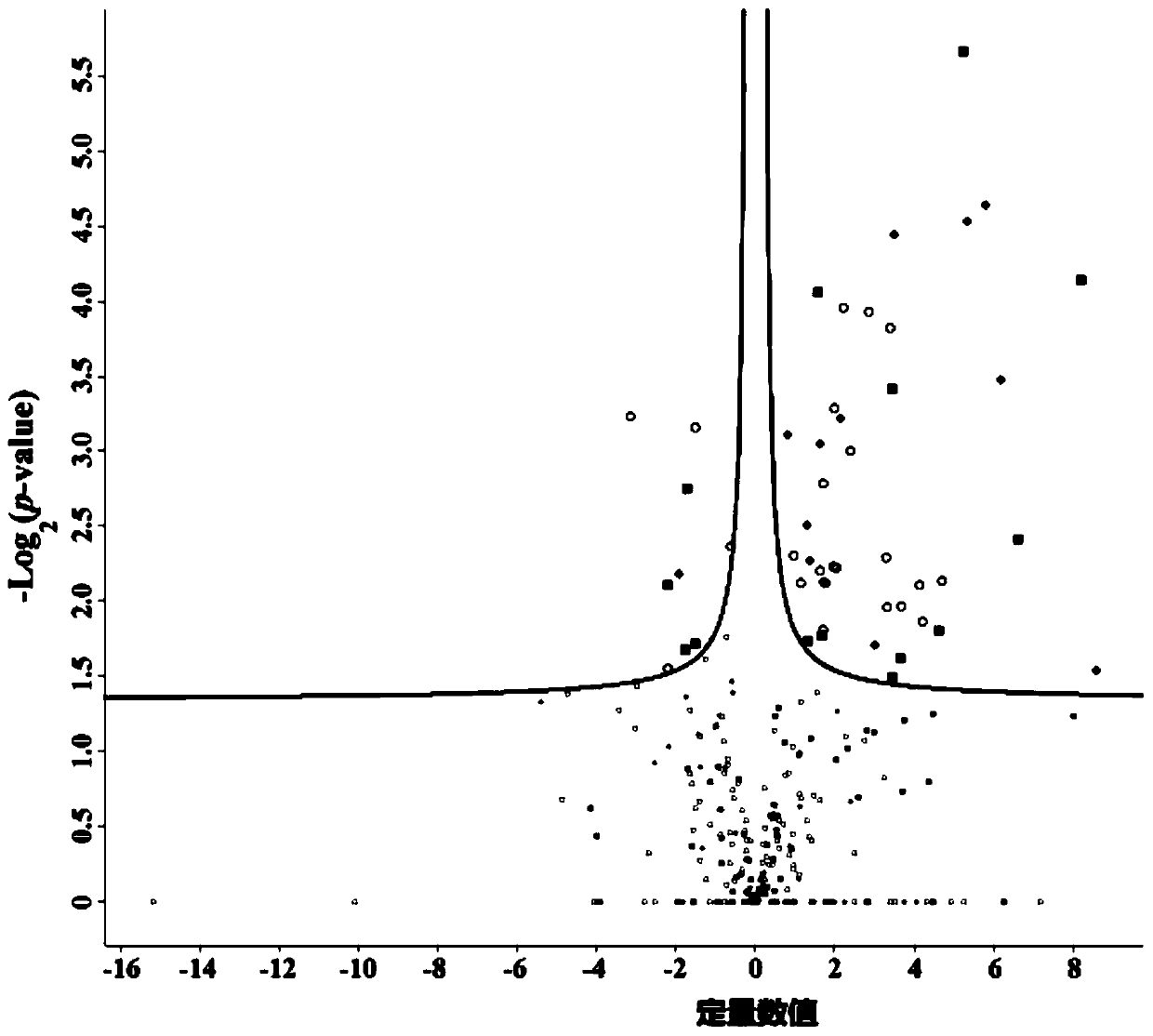
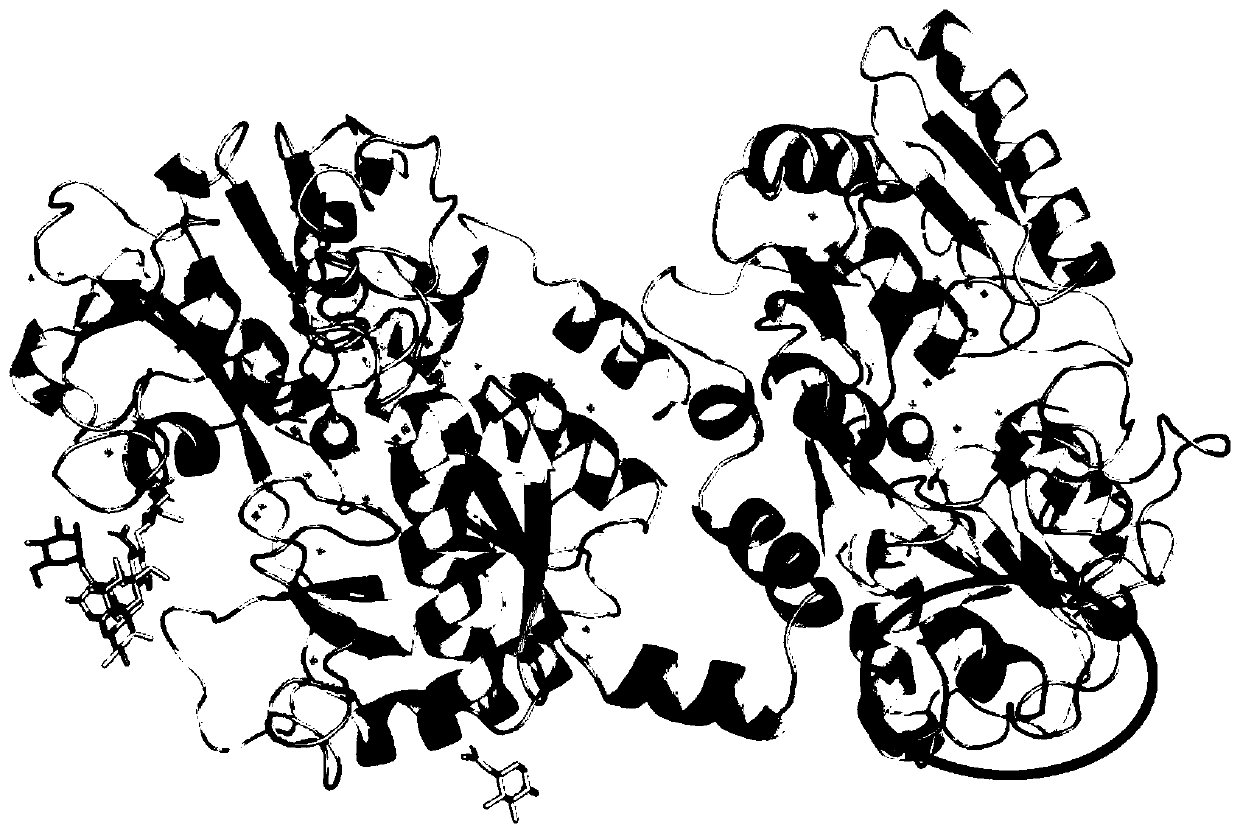
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Endoproteinase Glu-C" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation method and application of drone pupa small-molecular antioxidant peptide
InactiveCN108034683AHigh activityIncrease contentHydrolysed protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsProteinase activityFreeze-drying
The invention provides a preparation method of drone pupa small-molecular antioxidant peptide and belongs to the technical field of functional foods. The method includes the steps of: mixing and homogenizing drone pupa powder with water, regulating pH value of the homogenized liquid, mixing the homogenized liquid with compound enzyme to perform enzymolysis, wherein the compound enzyme includes endo-protease and exo-protease, centrifugally separating and filtering the enzymolytic liquid to prepare a filtrate; perform first ultra-filtering separation to the filtrate to obtain peptide fragments;performing secondary ultra-filtering to remove salts; and performing pressure reduced concentration and freeze drying to obtain the drone pupa small-molecular antioxidant peptide. The method can reduce generation of bitter peptides in the enzymolytic liquid and increase content of the small-molecular peptides in the enzymolytic liquid. The molecular weight of the drone pupa small-molecular antioxidant peptide is less than 1 kU, and the peptide has high-active anti-oxidizing performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
TGF-beta activation and use
InactiveUS20050065089A1Improve biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPlasminChemistry
Proteases are added to Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) along with calcium and thrombin to activate latent TGF-β. The proteases include plasmin, calpin, MMP-9, thrombospondin, transglutaminase, the mannose 6-phosphate receptor (M6PR), furin, substilisin-like endoproteases, and integrins. Dermatopontin can also be added to the PRP to enhance its biologic activity.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Method for extracting low molecular weight active collagen peptide from pigskin
InactiveCN102911991AHigh activityHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsFermentationCollagenanOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of deep processing of pigskin, particularly relates to a method for extracting pigskin collagen peptide. The method uses fresh pigskin to serve as a raw material, and a pure biology method is used for obtaining the pigskin collagen peptide. The method for extracting low molecular weight active collagen peptide from the pigskin comprises the following steps of: taking the fresh pigskin to serve as the raw material, firstly conducting outer cutting on collagen in the pigskin by adopting aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase; separating the collagen from other tissue elements in the pigskin, then the pigskin is in a scattered state, and using endo protease to conduct enzymolysis on protein to enable the protein to form micromolecular protein peptides. Different protein peptides are scientifically selected in different stages, processing steps are optimized, production efficiency is improved, yield of the collagen peptide is promoted, and activity of the collagen peptide is improved.
Owner:HUZHOU JIAMEI BIOCHEM PRODS
Gene engineering bacterium for efficiently expressing Aspergillus oryzae prolyl endopeptidase and application thereof
ActiveCN103602605ACannot meet the requirements of industrial applicationIncrease productionFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyAcid-fast
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacterium for efficiently expressing Aspergillus oryzae prolyl endopeptidase and application thereof. A gene S2 is introduced into Pichia pastoris to perform efficient expression. The gene S2 codes a new proline-specific endoprotease, and the nucleotide sequences are disclosed as 1) or 2): 1) nucleotide sequences disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2; and 2) nucleotide sequences of proline-specific endoprotease with coding activity obtained by performing base deletion, substitution, insertion or mutation on the defined nucleotide sequence. The obtained recombinase has the advantages of proline-specific endoprotease activity, acid environment resistance and the like, has obvious effects on enhancing the stability of beer, wine, fruit juice beverages and other non-living things, and has huge application potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing health-care concentrated chicken soup by utilizing enzymolysis process
PendingCN111567776APreserve health benefitsPreserve the delicious effectNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsBiotechnologyRadix Astragali seu Hedysari
The invention provides a method for preparing health-care concentrated chicken soup by utilizing an enzymolysis process. The method comprises the following steps of S1, cleaning a chicken skeleton, sanhuang chicken dices, folium cortex eucommiae, radix astragali, fresh gingers and green Chinese onion; S2, soaking the chicken skeleton and a sanhuang chicken in hot water, filtering out the hot water, adding cold water, adding cooking wine, the fresh gingers, the green Chinese onion, the folium cortex eucommiae and the radix astragali, and performing boiling so as to obtain crude chicken soup; S3, separating the crude chicken soup through a filter screen to obtain soup and a chicken bone and chicken meat mixture, and centrifuging the soup to obtain a grease layer and a clear soup layer; S4, adding water into the chicken bone and chicken mixture, heating the mixture to 55+ / -5 DEG C, adding endoprotease for primary enzymolysis to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate 1, and continuing to add flavourzyme into the enzymatic hydrolysate 1 for secondary enzymolysis to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate 2; S5, after the enzymatic hydrolysate 2 is subjected to enzyme deactivation, performing filtering and separating to obtain a liquid material; S6, mixing the clear soup layer and the liquid material, and performing vacuum concentration to obtain semi-finished health-care concentrated chicken soup; and S7, adding seasoning substances into the semi-finished health-care concentrated chicken soup to obtain the health-care concentrated chicken soup.
Owner:江苏特味浓食品股份有限公司
Novel proline specific endoprotease gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103589741AImprove toleranceCannot meet the requirements of industrial applicationFungiHydrolasesEndoprotease activityProteinase activity
The invention discloses a novel proline specific endoprotease gene and an application thereof. The gene is characterized in that a nucleotide sequence of the gene is represented by 1) or 2): 1) the nucleotide sequence of the gene is a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1; and 2) on the basis of the nucleotide sequence limited by 1), the nucleotide sequence of coded and activated proline specific endoprotease is formed through absence, substitution, insertion or mutation of a basic group. A recombinant enzyme obtained through the gene has the advantages of proline specific endoprotease activity, resistance to acid environment and the like, has an obvious effect on the improvement of the non-biological stability of beer, wine, juice and the like and has the huge utilization potentiality.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Blood Pressure Lowering Peptides in a Single Enzymatic Step
ActiveUS20080113896A1High yieldEfficient and convenient recoveryAngiotensinsMetabolism disorderProteasePeptide
A process to produce IPP and VPP from a protein source that comprises the -I-P-P- and -V-P-P- sequence in its protein sequence and whereby at least 40% of -I-P-P- sequence present in the protein source is converted into the peptide IPP and at least 40% of the -V-P-P- sequence present in the protein source is converted into the peptide VPP, which comprises the use of a proline specific endoprotease and an amino-peptidase preferably in a single enzymatic step.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Preparation method for debitterizing antioxidant oyster peptide
ActiveCN110819677ASolve the problem of heavy bitter tasteHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsFermentationBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a preparation method for debitterizing antioxidant oyster peptide. The method includes endoproteolysis and exoprotease enzymolysis; a debitterizing promoter is added during enzymolysis; and the debitterizing promoter includes trehalose, and can also include carboxymethyl cellulose. Through the addition of the trehalose as the debitterizing agent during the enzymolysis, exonuclease debitterizing methods can be improved, the problem of strong bitter taste in antioxidant oyster peptide can be effectively solved, the yield of debitterizing oyster peptide can be increased, and debitterizing reaction time can be shortened; the effect of inhibiting Maillard reaction inhibitors can be achieved by adding the trehalose, so that the product with light color and pure taste canbe obtained; and the method is low in cost, simple in operation and suitable for the industrial production of the antioxidant oyster peptide without adding new equipment on the basis of the prior art.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Method for the manufacturing of recombinant proteins harbouring an n-terminal lysine
InactiveUS20150232828A1The method is accurate and reliableNeed for goodNervous disorderSugar derivativesMicrobiologyNucleic acid sequencing
This invention relates to a novel method for manufacturing and obtaining recombinant proteins, such as clostridial neurotoxins, harbouring an N-terminal lysine from precursor proteins. The method comprises the step of expressing a nucleic acid sequence encoding a precursor protein comprising an N-terminal motif, which can be recognised by an endoprotease specific for a lysine in P′1 position, and the step of cleaving the precursor protein with the endoprotease. The invention further relates to novel precursor proteins used in such methods, nucleic acid sequences encoding such precursor proteins and novel recombinant proteins, such as clostridial neurotoxins, harbouring an N-terminal lysine.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology-based protein-polysaccharide complex digestibility analyzing method
ActiveCN109444313AAccurate identificationDetermine the binding siteComponent separationProtein solutionUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology-based protein-polysaccharide complex digestibility analyzing method. The liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology-based protein-polysaccharide complex digestibility analyzing method comprises in vitro digesting protein solution and protein-polysaccharide complex solution in simulative gastric juice; performing denaturation treatment on digested proteins and digested protein-polysaccharide complexes, removing low-molecular-weight peptide fragments through an ultrafiltration pipe, and further completely hydrolyzing large-fragment polypeptides retained inside the ultrafiltration pipe through a second endo protease with clear enzyme-digesting points except pepsase to obtain a number of polypeptide fragments;detecting the composition and abundance of the polypeptide fragments through the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology; according to the abundance of the polypeptides digested by the second endo protease and the pepsase, determining the digestibility of the pepsase; further, according to the high-abundance polypeptides in the two types of peptide fragments in the protein-polysaccharide complex group, deducting the binding sites of proteins and polysaccharides.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing shellfish high fischer ratio oligopeptides through cooperation of subcritical water and enzyme method
ActiveCN111235206AMeets requirementsQuality improvementPeptide preparation methodsFermentationActivated carbonHydrolysate
The invention discloses a method for preparing shellfish high fischer ratio oligopeptides through cooperation of subcritical water and an enzyme method. The method comprises the following steps of (1)performing treatment with subcritical water: performing homogenization on shellfish processing by-products, performing mixing with water, performing extraction with the subcritical water and performing filtering to obtain extraction liquid; (2) performing enzymolysis: performing enzymolysis on the extraction liquid obtained in the step (1) with endoprotease, and then performing enzymolysis with exoprotease to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate ; (3) performing clarification: removing solid granules in the enzymatic hydrolysate obtained in the step (2), to obtain clear enzymatic hydrolysate ; (4) performing decoloring: decoloring the clear enzymatic hydrolysate obtained in the step (3) with activated carbon to obtain decolored enzymatic hydrolysate ; and (5) performing refining: performing ultrafiltration on the decolored enzymatic hydrolysate obtained in the step (4), then performing nanofiltration to obtain high fischer ratio oligopeptides filtrate, and drying the high fischer ratio oligopeptides filtrate. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the fischer ratio of the products is effectively increased, the production time is greatly shortened, the energy consumption is reduced, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Inhibiting material for inverting enzyme for angiotensin I
InactiveCN1351174ABlood pressure lowering activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAlgae medical ingredientsProteinase activityBlood pressure
The object of the invention is to produce a peptide with potent the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity by decomposing the protein contained in wakame with protease, using wakame being a food material ingested daily as a raw material, and to provide a safe food composition with hypotensive activity, using the treatment product thereof as a raw material. The inventors have found that, when performing the decomposing treatment of wakame with various proteases, a group of endo-type enzymes produced by Bacillus produce peptides with particularly strong ACE inhibitory activity, leading to the completion of the invention.
Owner:RIKEN VITAMIN COMPANY
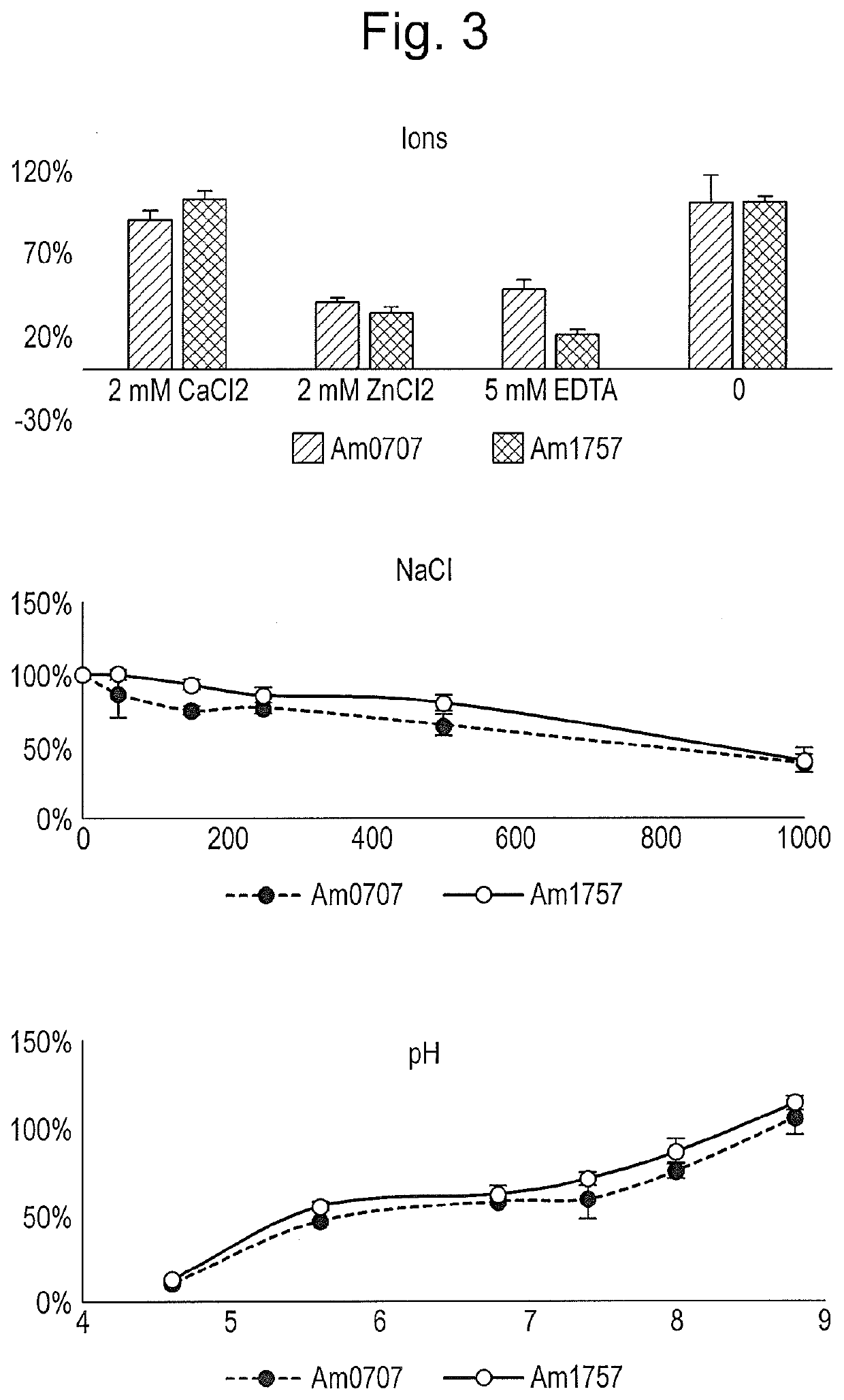
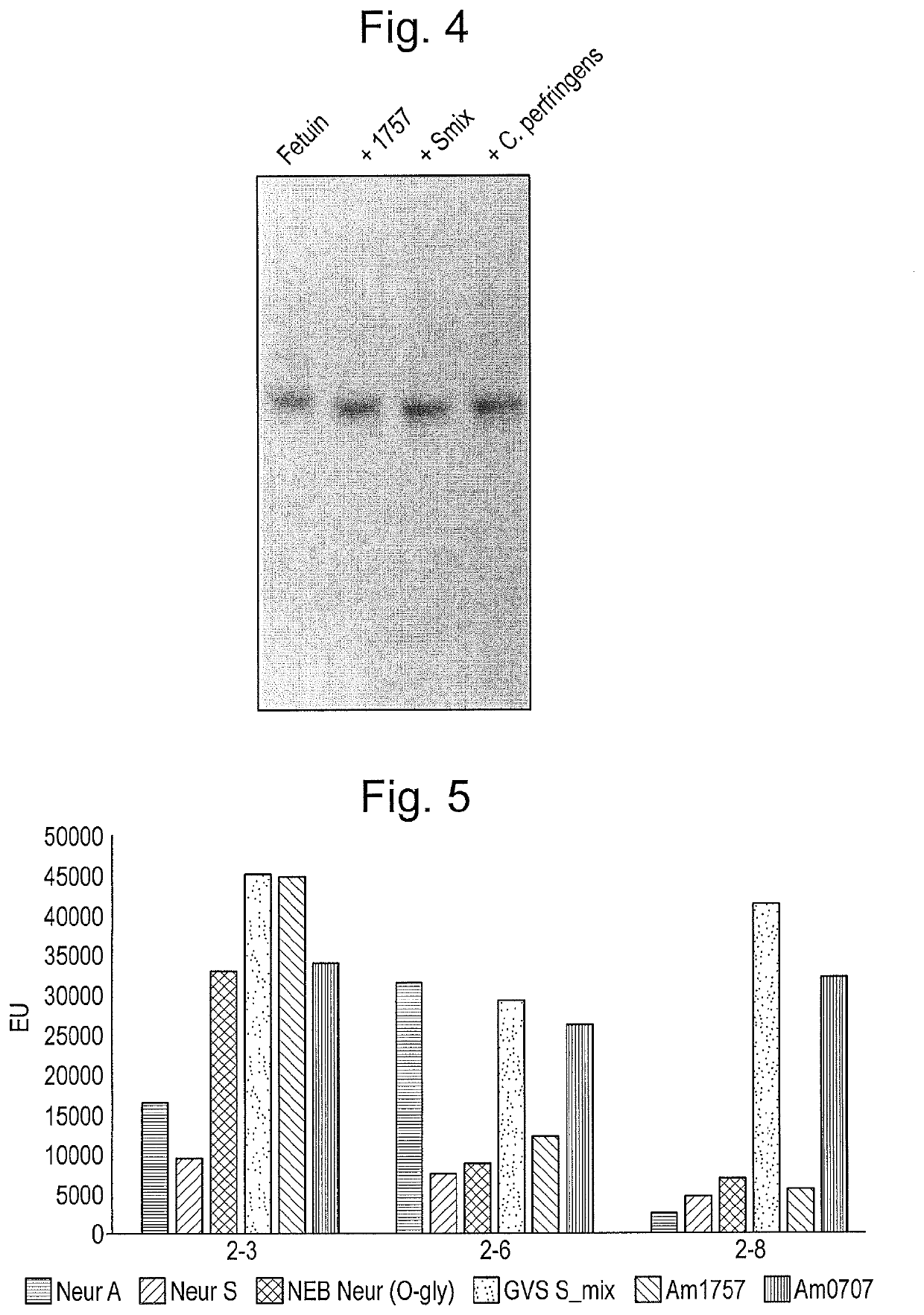
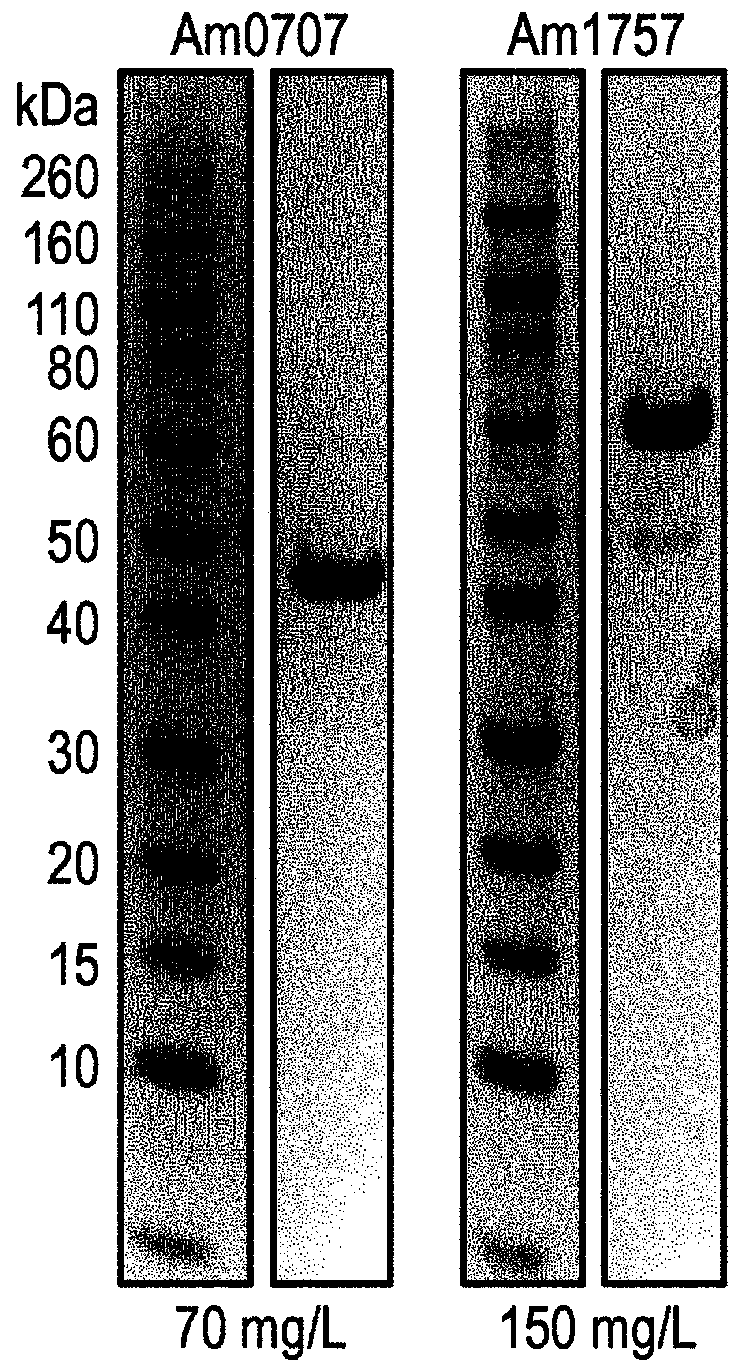
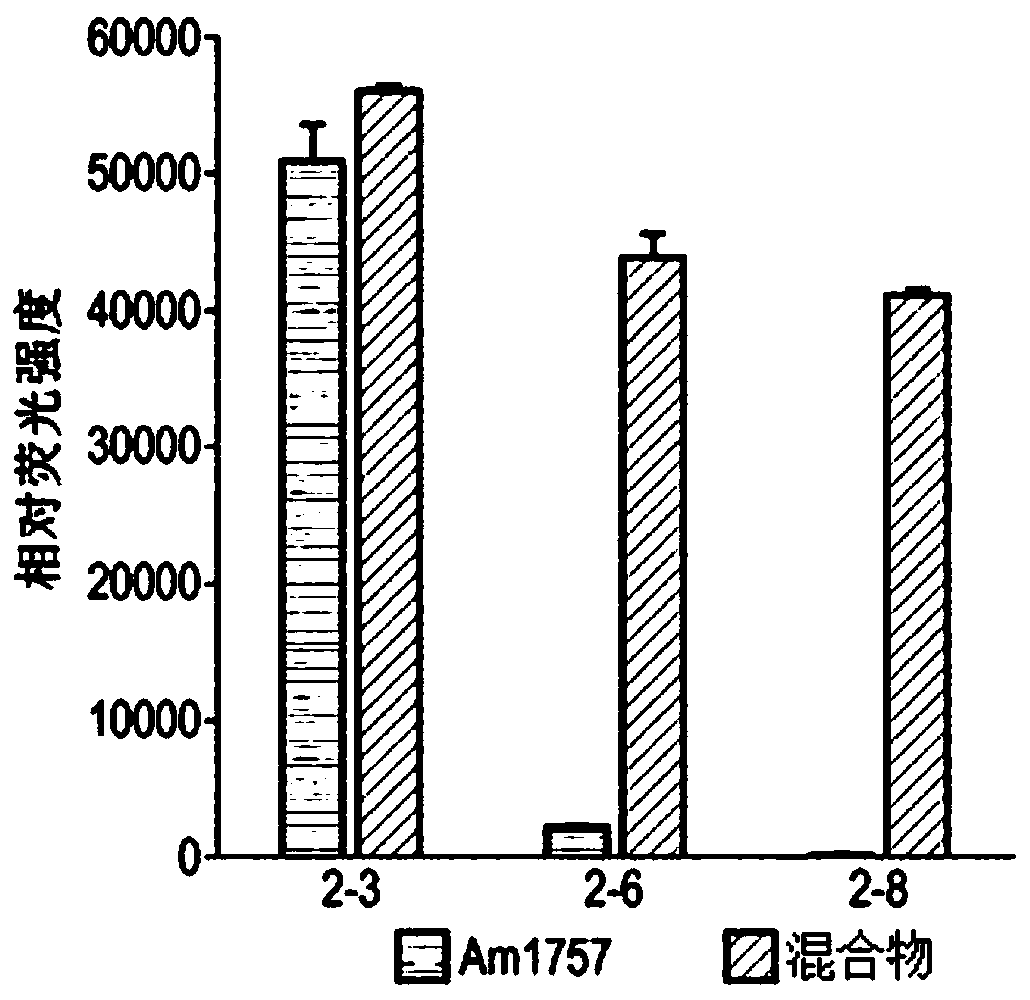
Protease and Binding Polypeptide for O-Glycoproteins
Owner:GENOVIS AB
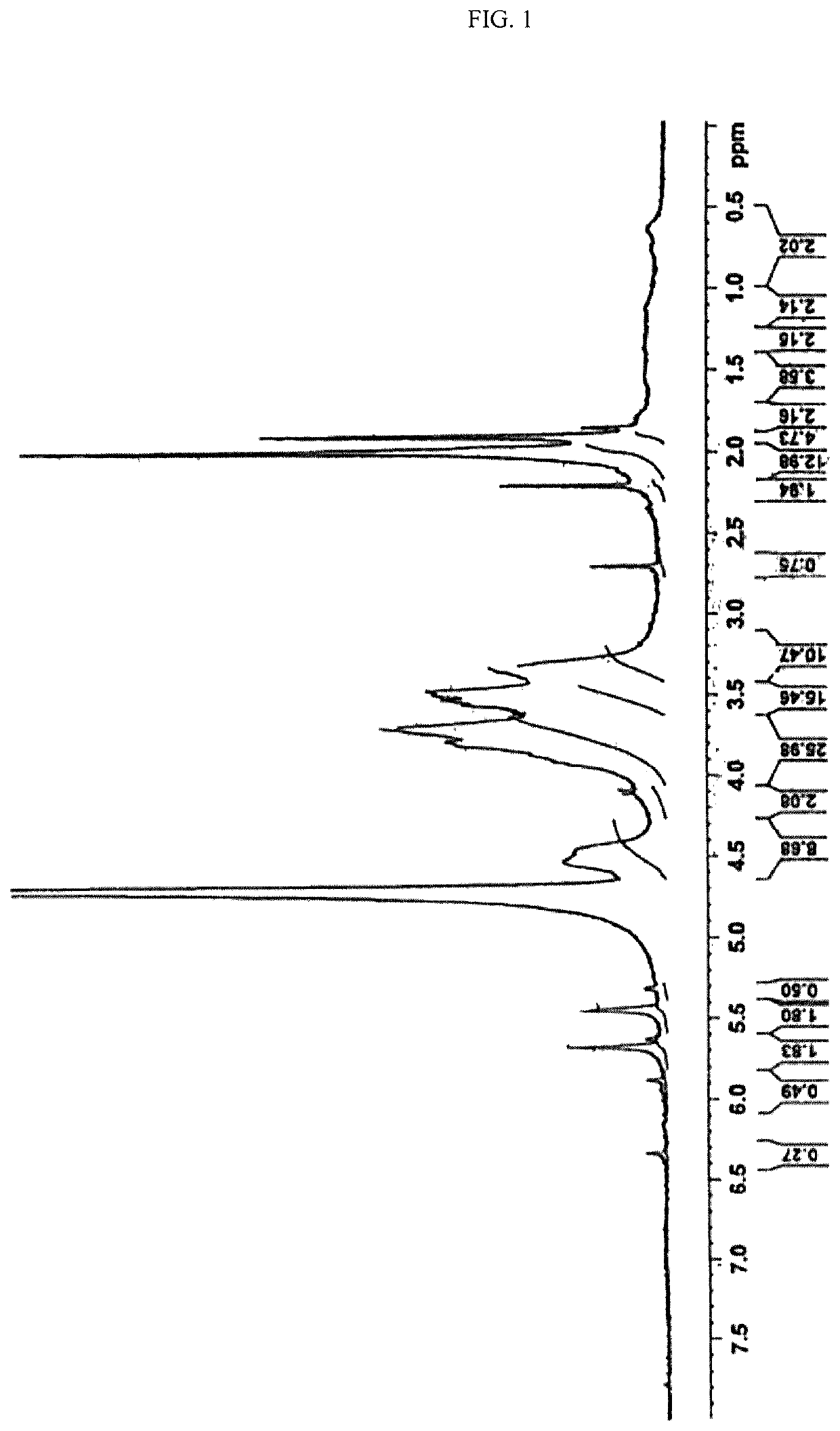
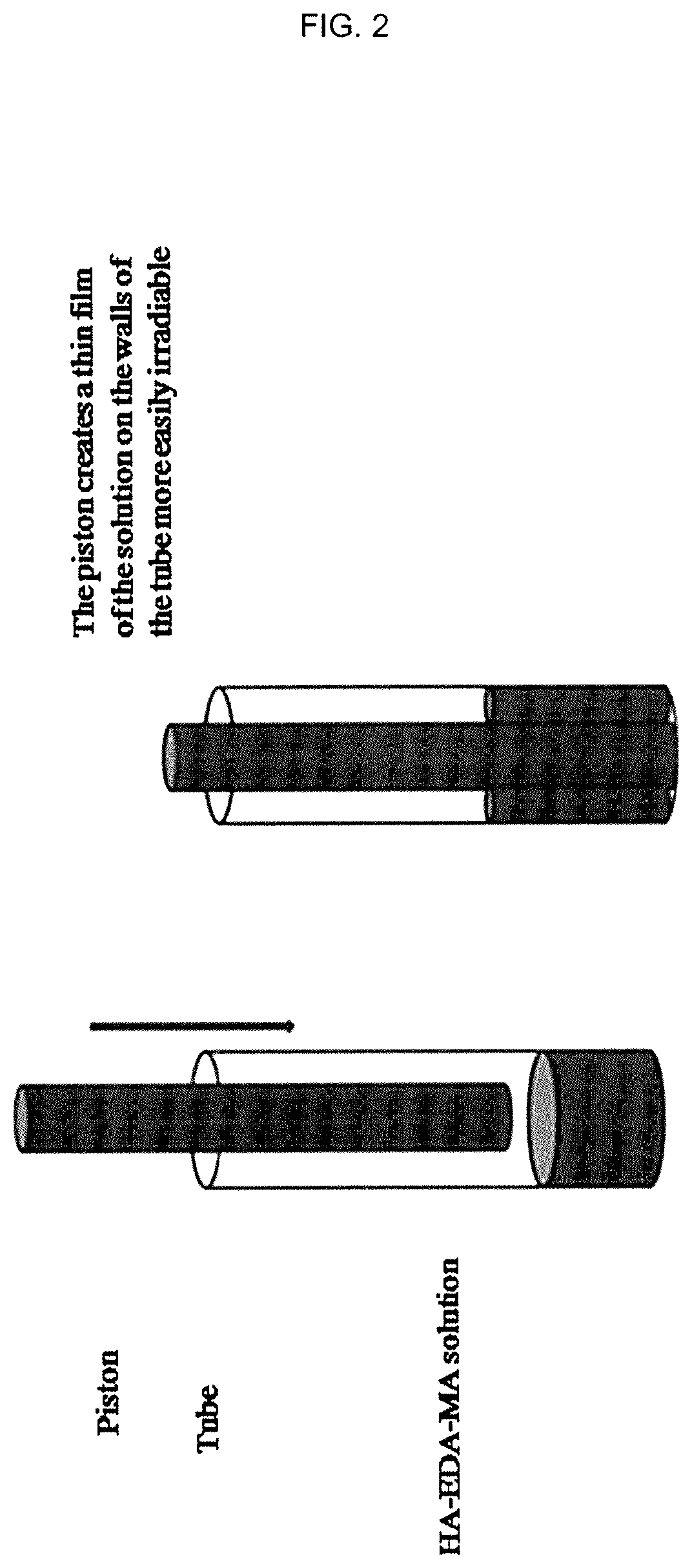
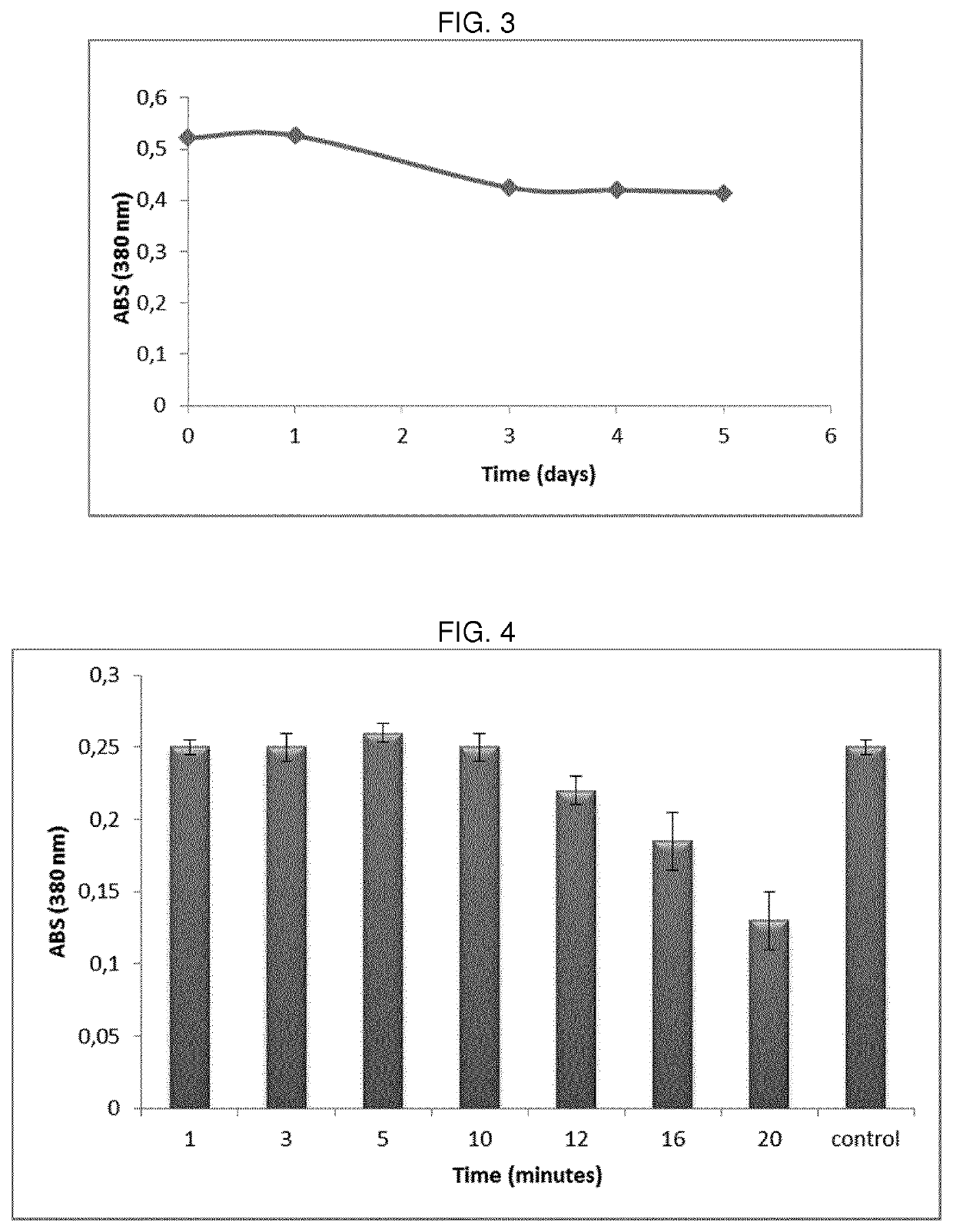
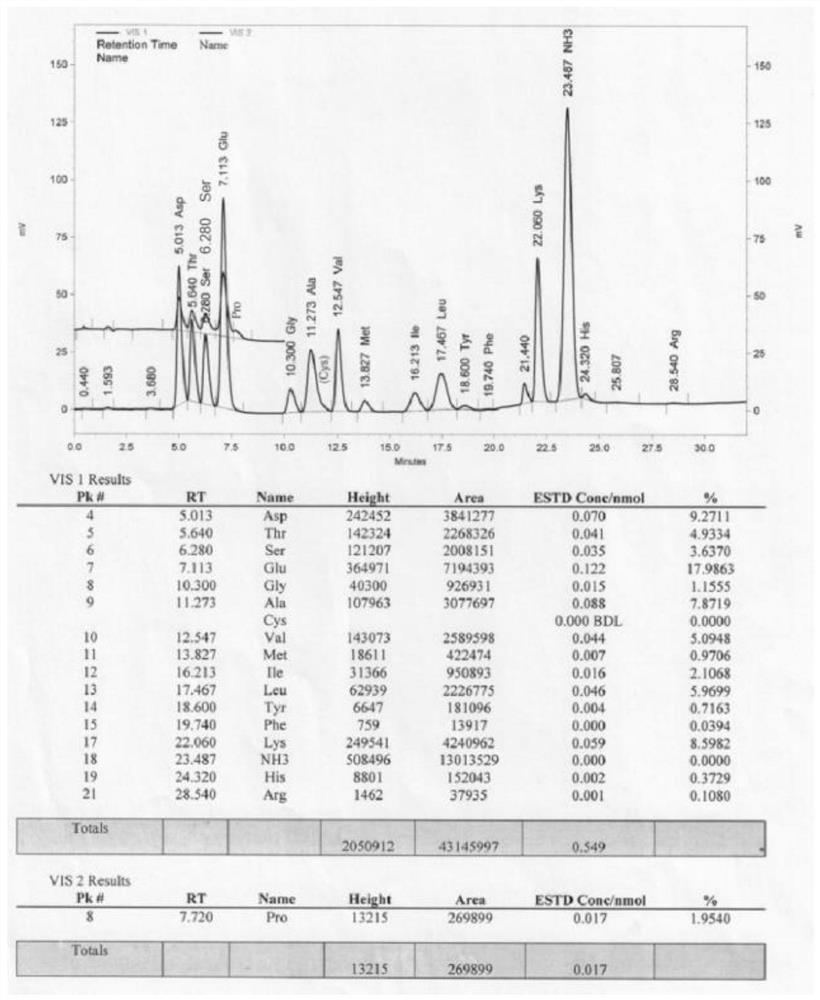
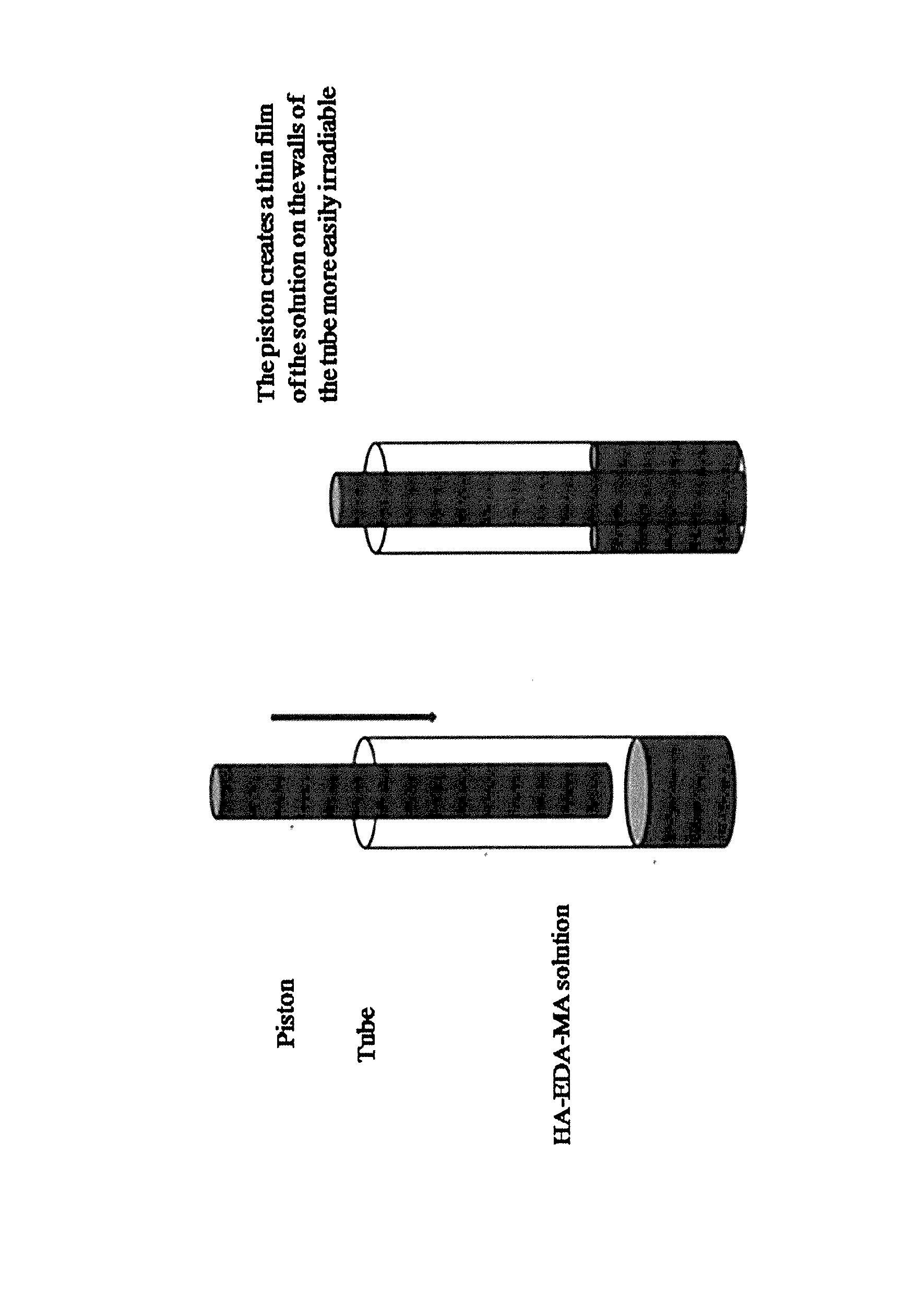
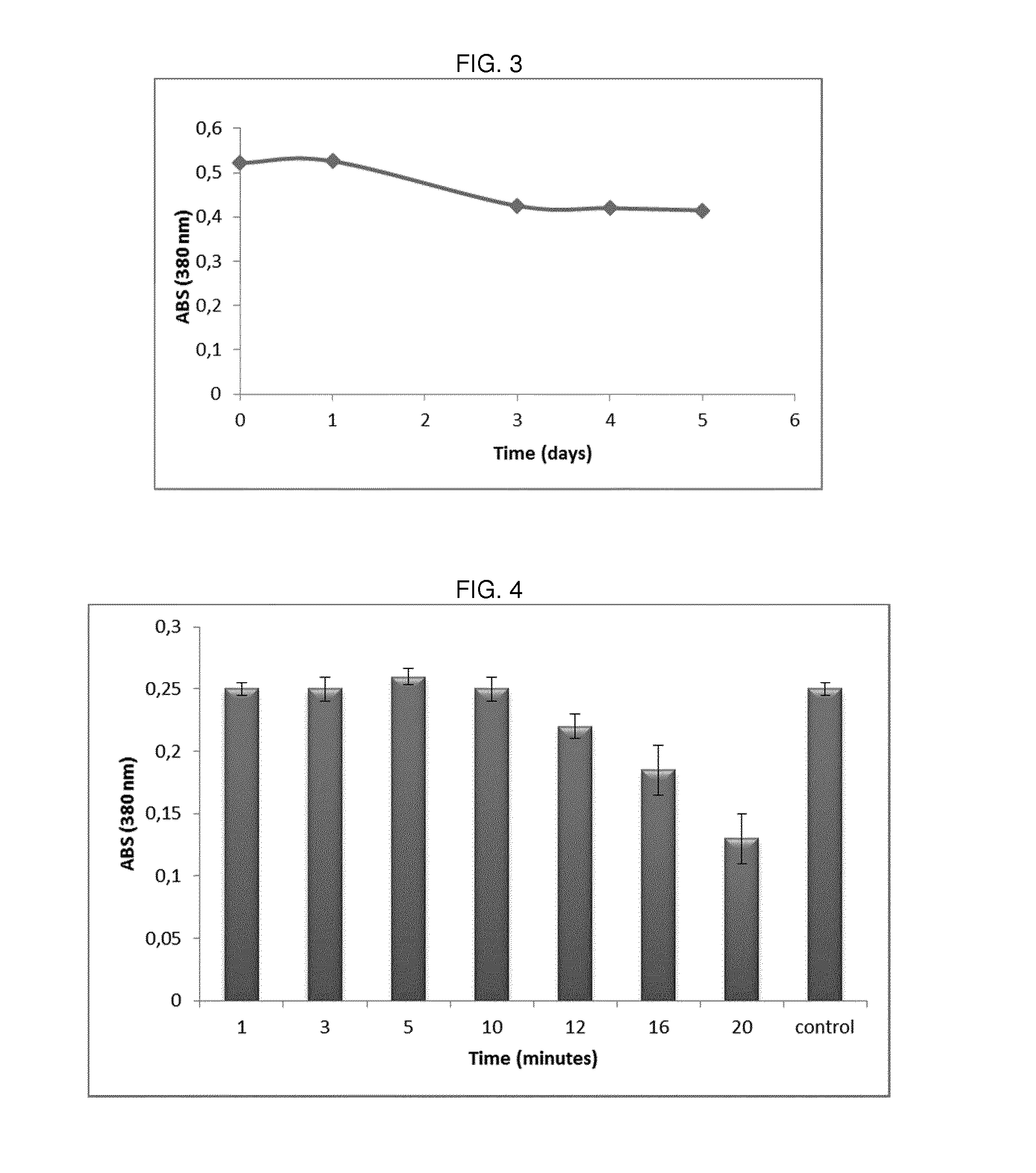
Hydrogels of methacrylic hyaluronic acid derivatives for oral enzyme therapy in celiac disease
ActiveUS10709787B2Extended shelf lifeKeep for a long timePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsOral treatmentEthylenediamines
The present invention relates to a composition comprising hydrogels from functionalized hyaluronic acid derivatives, said hydrogels loaded with exogenous enzymes selected in the group consisting of prolyl endopeptidase (PEP) and endoprotease (EP) intended for the oral treatment of celiac disease. Specifically, this invention concerns a one-pot methodology useful to prepare methacrylic derivatives of hyaluronic acid, through the formation of a specific active group on hydroxyl groups of hyaluronic acid, the subsequent substitution of the inserted active group with ethylenediamine and finally, the reaction with methacrylic anhydride. The obtained methacrylic hyaluronic acid derivatives are used to prepare hydrogels through irradiation and loaded with exogenous enzymes selected in the group consisting of prolyl endopeptidase (PEP) and endoprotease (EP). The ability of prepared hydrogels to allow the enzyme release, as active form in simulated gastrointestinal fluids is proved.
Owner:NEMYSIS
Whey protein peptide and high-F-value oligopeptide with liver injury protection effect as well as preparation method and application of whey protein peptide and high-F-value oligopeptide
ActiveCN114836503AReduce contentIncrease contentHydrolysed protein ingredientsDigestive systemHydrolysateOligopeptide
The invention provides a group of whey protein peptides and high-F-value oligopeptides with a liver injury protection effect as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of active peptides. According to the method, the high-F-value oligopeptide is prepared by hydrolyzing whey protein through three enzymes, firstly, a small amount of alkaline protease is used for pretreating the high-F-value oligopeptide, the solubility of the high-F-value oligopeptide is improved, the peptide chain of the high-F-value oligopeptide is damaged, the subsequent enzymolysis efficiency is improved, then endonuclease treatment and exonuclease treatment are sequentially adopted, and finally the high-F-value oligopeptide exists in enzymatic hydrolysate in a free state, so that the high-F-value oligopeptide is obtained. And finally adsorbing the aromatic amino acid by using specific resin to obtain whey protein peptide with F value greater than 20, and finally separating and screening to obtain two oligopeptides with high F value. The whey protein peptide and the high-F-value oligopeptide can reduce the content of malondialdehyde and triglyceride in the liver and increase the content of reduced glutathione, and have an auxiliary protection effect on chemical liver injury.
Owner:JIANGSU QIRUI MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Yeast cell wall derived flavour
ActiveUS11297860B2Low in fatEnhancement of a fatty and creamy mouthfeelMilk preparationGlycosylasesGlucanaseCell wall
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Proline-specific endoprotease and use thereof
The present invention relates to a polypeptide having proline-specific endoprotease activity, wherein the polypeptide has less than 70% residual activity when the polypeptide has been kept at a temperature of 65° C. for 15 min.The invention further relates to a polypeptide having proline-specific endoprotease activity comprising an amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein SEQ ID NO: 1 comprises at least one combination of amino acid substitutions selected from the group consisting of a combination selected from the group consisting of (K238E, I204V, V460A), (F279S, A242V, N507I), (T145A, K424M), (T359A, F379S), (M170I, A421T), (N441S, G484S), (L470H, Q288R), (L470H, E387G), (T281S, L373I), (P304A, P469A), and (P466T, P469Q), a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide having proline-specific endoprotease activity, a method of making a variant polypeptide having proline-specific endoprotease activity, a recombinant host cell and a method of producing the polypeptide and a process for the preparation of a food or feed product wherein the polypeptide is used.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pure draft beer film cleaning and regenerating enzyme preparation and cleaning method using same
InactiveCN102492663BImprove regenerative recoveryExtended service lifeHydrolasesCleaning using liquidsBiotechnologyNeutral proteinase
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV +1
A method for preparing shellfish high f-value oligopeptides by subcritical water-assisted enzymatic method
ActiveCN111235206BIncrease profitReduce pollutionPeptide preparation methodsFermentationActivated carbonEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing shellfish high F-value oligopeptides by a subcritical water-assisted enzymatic method, comprising the following steps: 1) subcritical water treatment: homogenate shellfish processing by-products and mix them with water, use subcritical water Extract with critical water and filter to obtain the extract; 2) Enzymolysis: Use endoprotease to enzymolyze the extract obtained in step 1), and then use exoprotease to enzymolyze to obtain enzymolysis; 3) Clarification: Remove the solid particles in the enzymatic hydrolysis solution obtained in step 2) to obtain a clarified enzymatic hydrolysis solution; 4) Decolorization: use activated carbon to decolorize the clarified enzymatic hydrolysis solution obtained in step 3) to obtain a decolorized enzymatic hydrolysis solution; 5) Refining: The decolorized enzymatic hydrolyzate obtained in step 4) is first subjected to ultrafiltration and then nanofiltration to obtain a high F value oligopeptide filtrate; and the high F value oligopeptide filtrate is dried. The invention effectively improves the F value of the product, greatly shortens the production time, reduces energy consumption, and reduces production costs.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Native protein purification technology
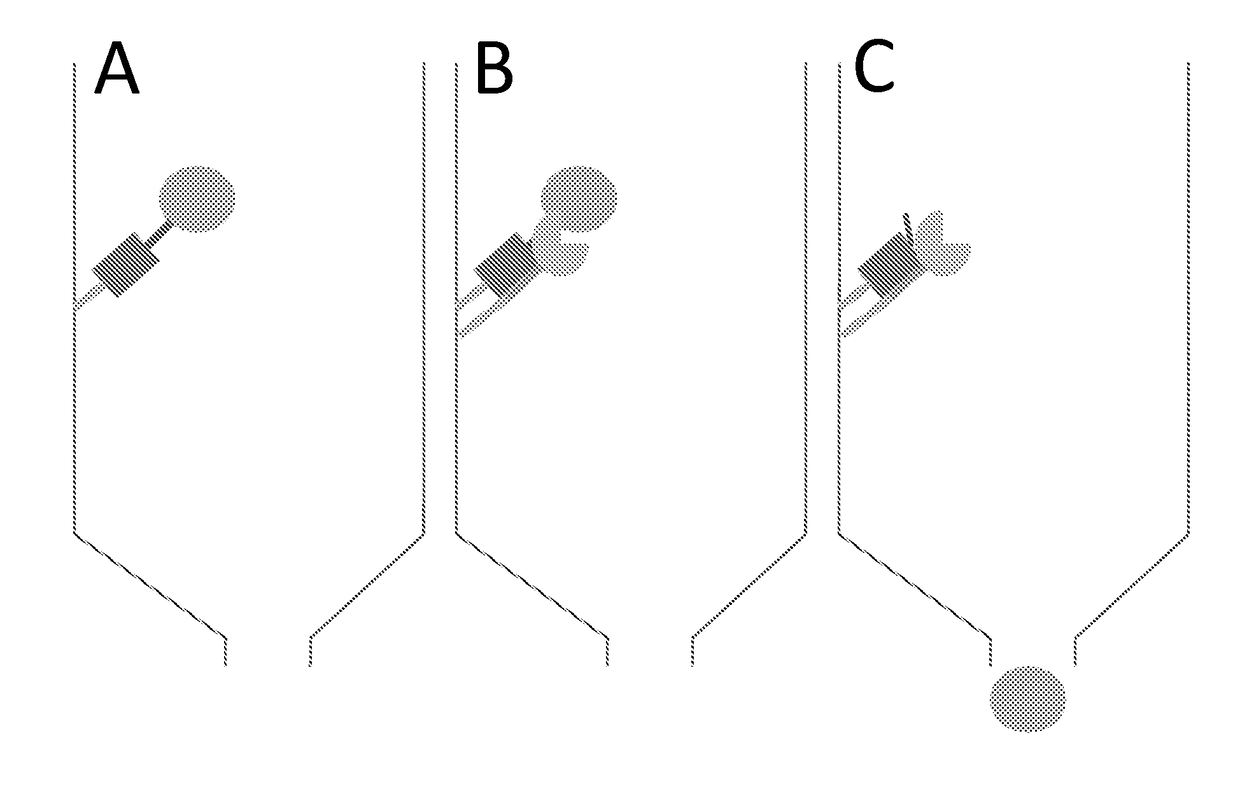
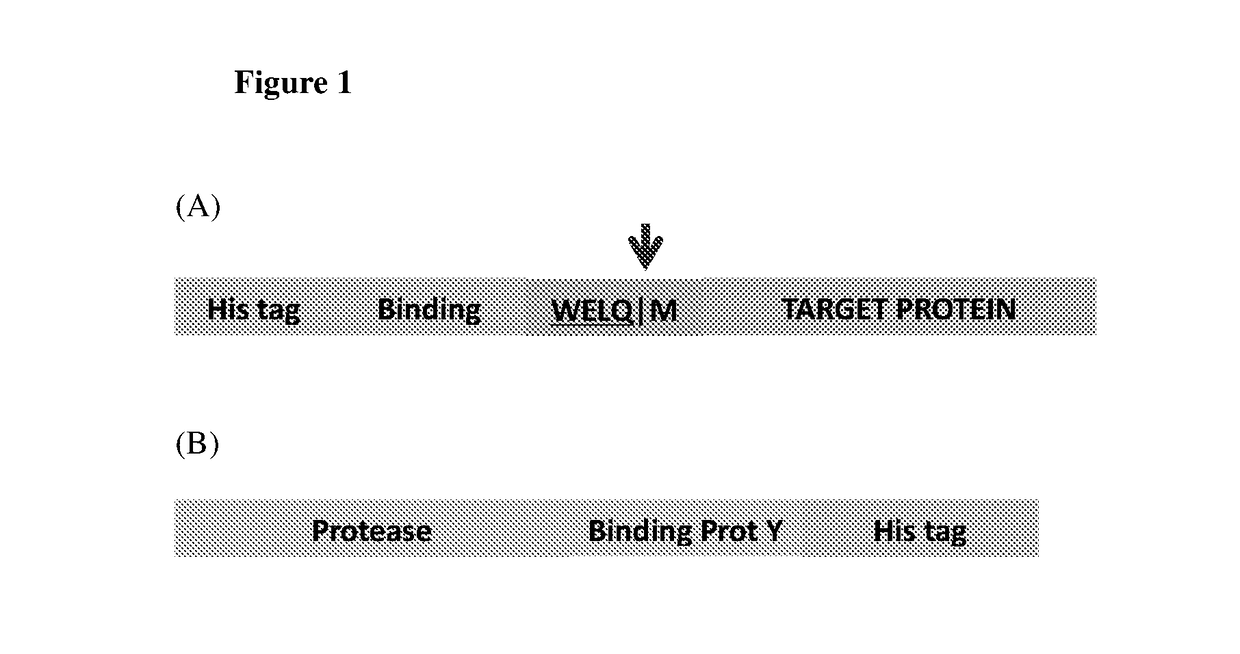
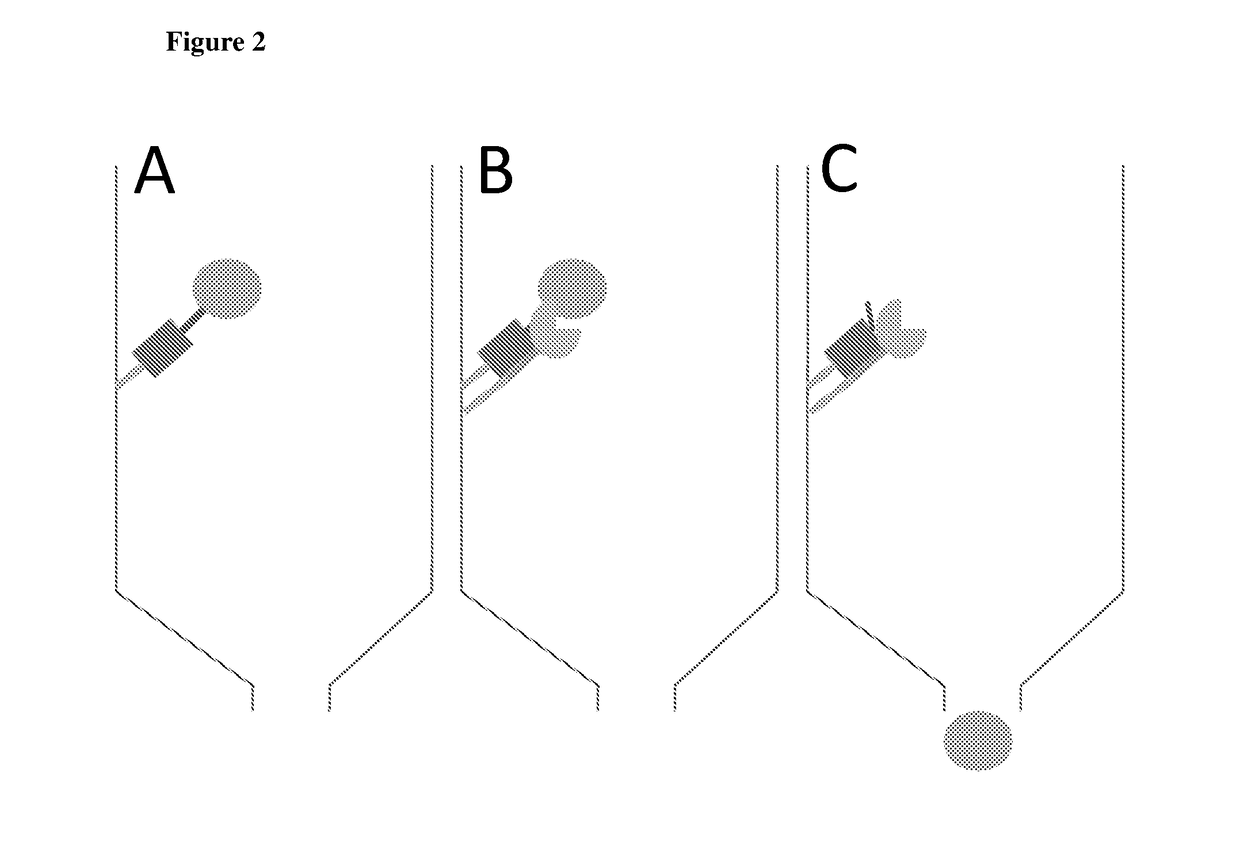
InactiveUS20180141972A1Allow purificationIneffective bindingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsProtein targetAmino acid
The present invention relates to an isolated polypeptide comprising (a) a protein of interest; (b) a first member of a pair of binding partners; (c) an affinity tag for immobilizing the polypeptide on a solid support; and (d) a modified endoprotease recognition site, wherein the modified endoprotease recognition site is located directly adjacent to the N-terminal amino acid of the protein of interest and comprises or only consists of the amino acid sequence N-terminal of the cleavage site of the native endoprotease recognition site. The present invention also relates to a nucleic acid encoding the above polypeptide and a host cell thereof, a method for isolating a protein of interest using the above polypeptide as a fusion partner and a protease fusion protein with the second member of the pair of binding partners and kits thereof. In addition, a method of degrading a target protein, a method of treatment and use of a fusion protease protein comprising a protease and a target protein binding element are also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
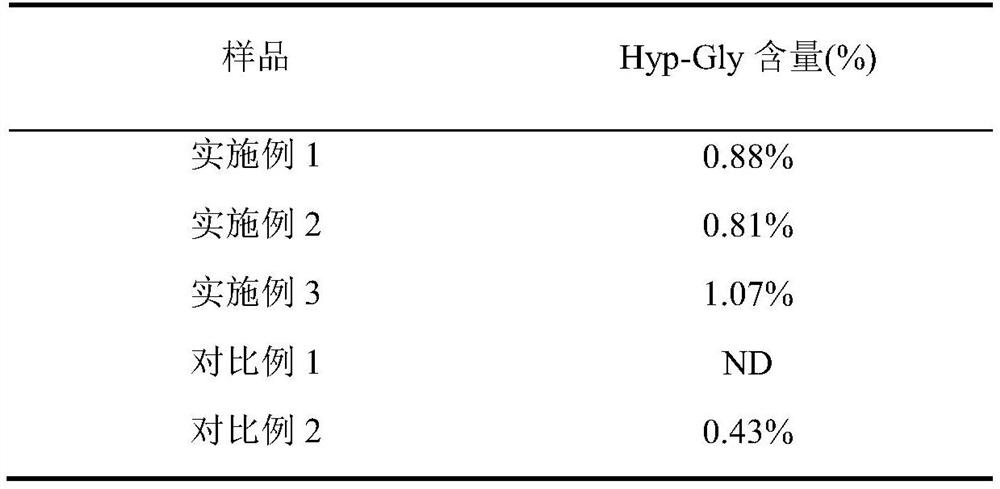
Collagen small molecule peptide rich in dipeptide Hyp-Gly, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114032269AHigh content of Hyp-GlyIncrease moisturePeptide preparation methodsFermentationDipeptideCollagenan
The invention discloses a collagen small molecule peptide rich in dipeptide Hyp-Gly, a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the content of the dipeptide Hyp-Gly in the collagen small molecule peptide is 0.8% or above, and the peptide with the molecular weight smaller than 1000 Da accounts for 85% or above. According to the invention, specific endoprotease and exopeptidase are adopted for step-by-step hydrolysis, and directional release of Hyp-Gly is controlled, so that damage of excessive enzymolysis to peptide bonds on Hyp-Gly dipeptide is avoided so as to improve the content of dipeptide Hyp-Gly in a collagen peptide product and increase the content of small molecule peptide components smaller than 1000 Da; and the collagen small molecule peptide rich in dipeptide Hyp-Gly can be used for preparing functional food with beautifying and skin care effects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Hydrogels of methacrylic hyaluronic acid derivatives for oral enzyme therapy in celiac disease
ActiveUS20170049896A1Stable long shelf-lifeLong shelf lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticEthylenediamineOral treatment
The present invention relates to a composition comprising hydrogels from functionalized hyaluronic acid derivatives, said hydrogels loaded with exogenous enzymes selected in the group consisting of prolyl endopeptidase (PEP) and endoprotease (EP) intended for the oral treatment of celiac disease. Specifically, this invention concerns a one-pot methodology useful to prepare methacrylic derivatives of hyaluronic acid, through the formation of a specific active group on hydroxyl groups of hyaluronic acid, the subsequent substitution of the inserted active group with ethylenediamine and finally, the reaction with methacrylic anhydride. The obtained methacrylic hyaluronic acid derivatives are used to prepare hydrogels through irradiation and loaded with exogenous enzymes selected in the group consisting of prolyl endopeptidase (PEP) and endoprotease (EP). The ability of prepared hydrogels to allow the enzyme release, as active form in simulated gastrointestinal fluids is proved.
Owner:NEMYSIS
Fermentation preparation and extraction method for bacillus subtilis debitterized aminopeptidase
ActiveCN101492663BNo bitternessReduce or eliminate bitternessMicroorganism based processesEnzymesUltrafiltrationOligopeptide
The invention discloses a method for preparing and extracting Bacillus subtilis debittering aminopeptidase by fermentation, which belongs to the technical field of enzyme preparation and food additive. The invention uses the fermentation cylinder production condition of Bacillus subtilis Zj016 to collect fermentation liquor and obtain the product of debittering aminopeptidase by carrying out clarifying, ultrafiltration concentration and salting out on the fermentation liquor. The aminopeptidase produced by the selected Bacillus subtilis Zj016 is exopeptidase which can dissociate amino acid from a polypeptide chain amino terminal. Researched by the laboratory, the aminopeptidase cooperates with alkali protease to hydrolyze soybean protein isolate; the prepared soybean peptide does not havebitterness, and the contents of oligopeptide like dipeptide and tripeptide are higher. Besides, researches on the enzyme lines produced by the Bacillus subtilis show that the Bacillus subtilis only produces circumscribed prolease and does not have the activity of endo protease; moreover, the circumscribed prolease has a stronger hydrolysis capacity to the terminal amino acid with strong hydrophobicity. The research further explains that the invention can reduce or eliminate the bitterness generated during hydrolysis of the soybean protein.
Owner:江苏博立生物制品有限公司
A method for analyzing the digestibility of protein-polysaccharide complex based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
ActiveCN109444313BAccurate identificationDetermine the binding siteComponent separationProtein solutionIn vitro digestion
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Yeast cell wall derived flavour
ActiveUS20220183332A1Low in fatEnhancement of a fatty and creamy mouthfeelMilk preparationGlycosylasesGlucanaseCell wall
The present invention relates to a method for producing a flavour composition comprising providing a slurry of yeast cell walls and contacting the slurry of yeast cell walls with a glucanase and with an endoprotease, followed by separating a liquid fraction by solid / liquid separation to provide the liquid flavour composition.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
A kind of preparation method of debittering and antioxidant oyster peptide
ActiveCN110819677BSolve the problem of heavy bitter tasteHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsFermentationMaillard reactionCellulose
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Enzymes for Glycan Analysis
The present invention relates to enzymes and combinations thereof useful for studying glycoproteins, and corresponding methods of use. In particular, the invention relates to a sialidase composition comprising an additional protease and / or glycosidase, preferably an O-glycoprotein-specific endoprotease and / or an O-glycosidase.
Owner:GENOVIS AB
Enzymes for glycan analysis
The present invention relates to enzymes and combinations thereof useful for studying glycoproteins, and corresponding methods of use. In particular, the invention relates to a sialidase composition comprising an additional protease and / or glycosidase, preferably an O-glycoprotein-specific endoprotease and / or an O-glycosidase.
Owner:GENOVESE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com