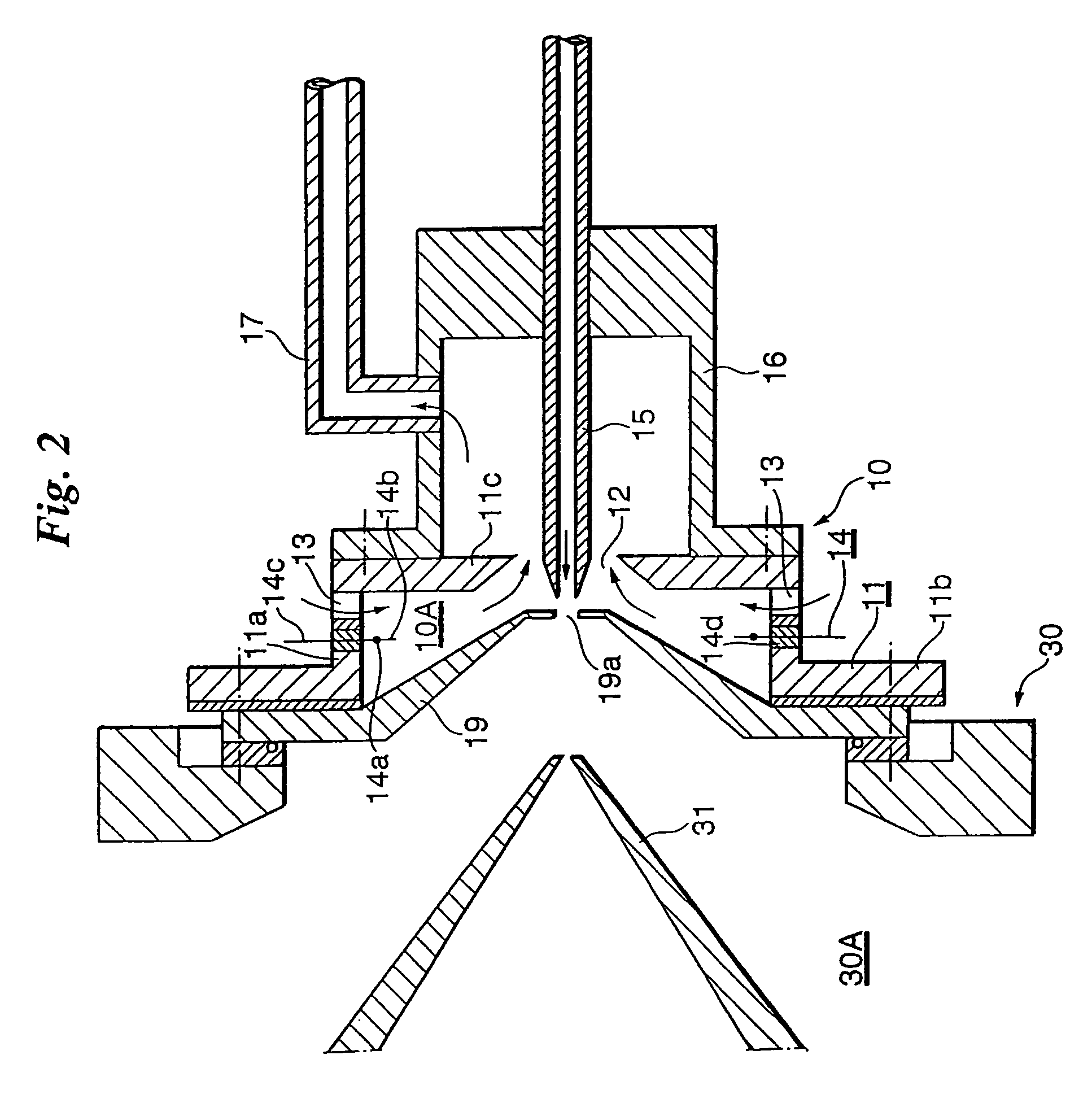
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
183 results about "Electron capture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shell. This process thereby changes a nuclear proton to a neutron and simultaneously causes the emission of an electron neutrino.
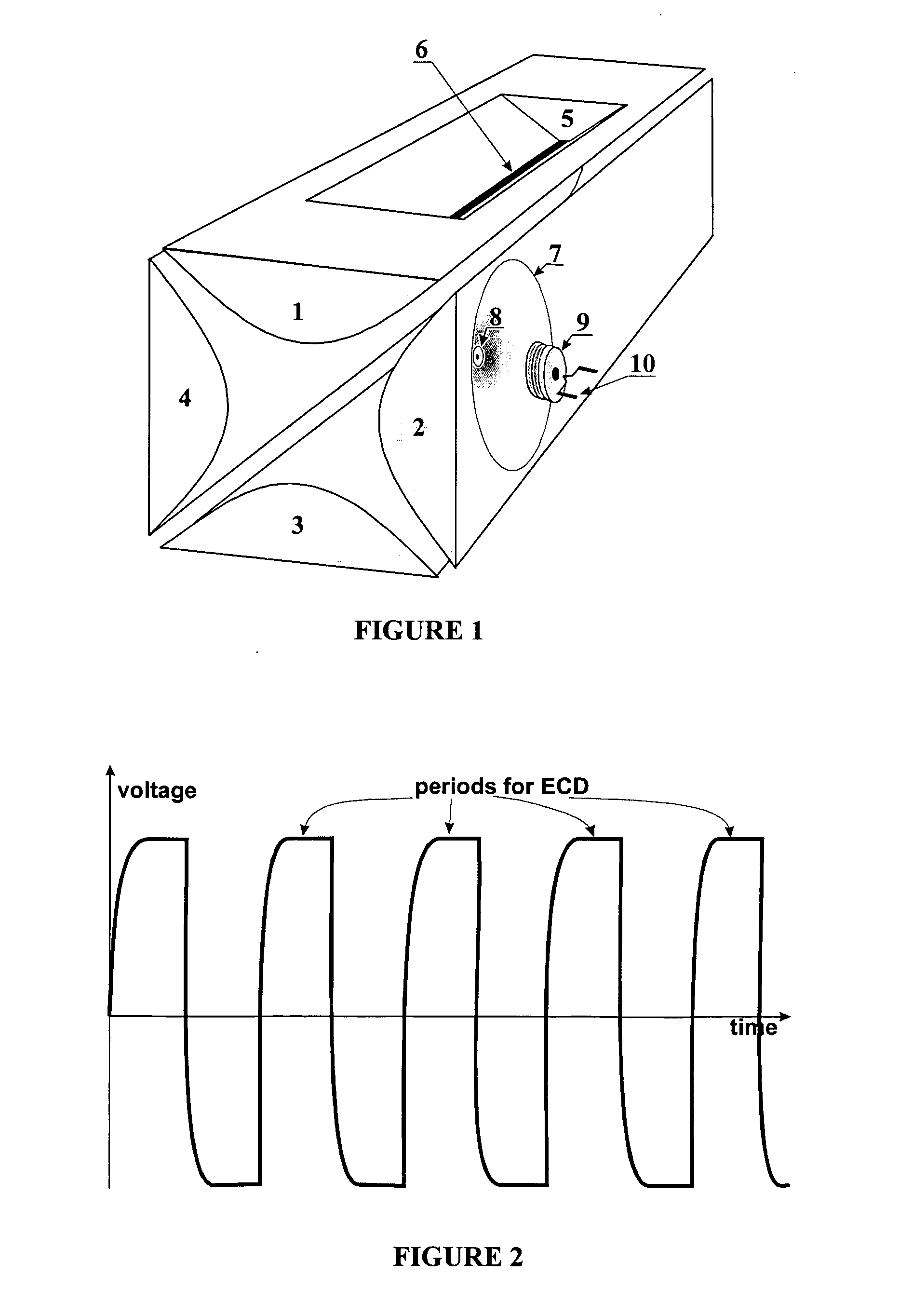
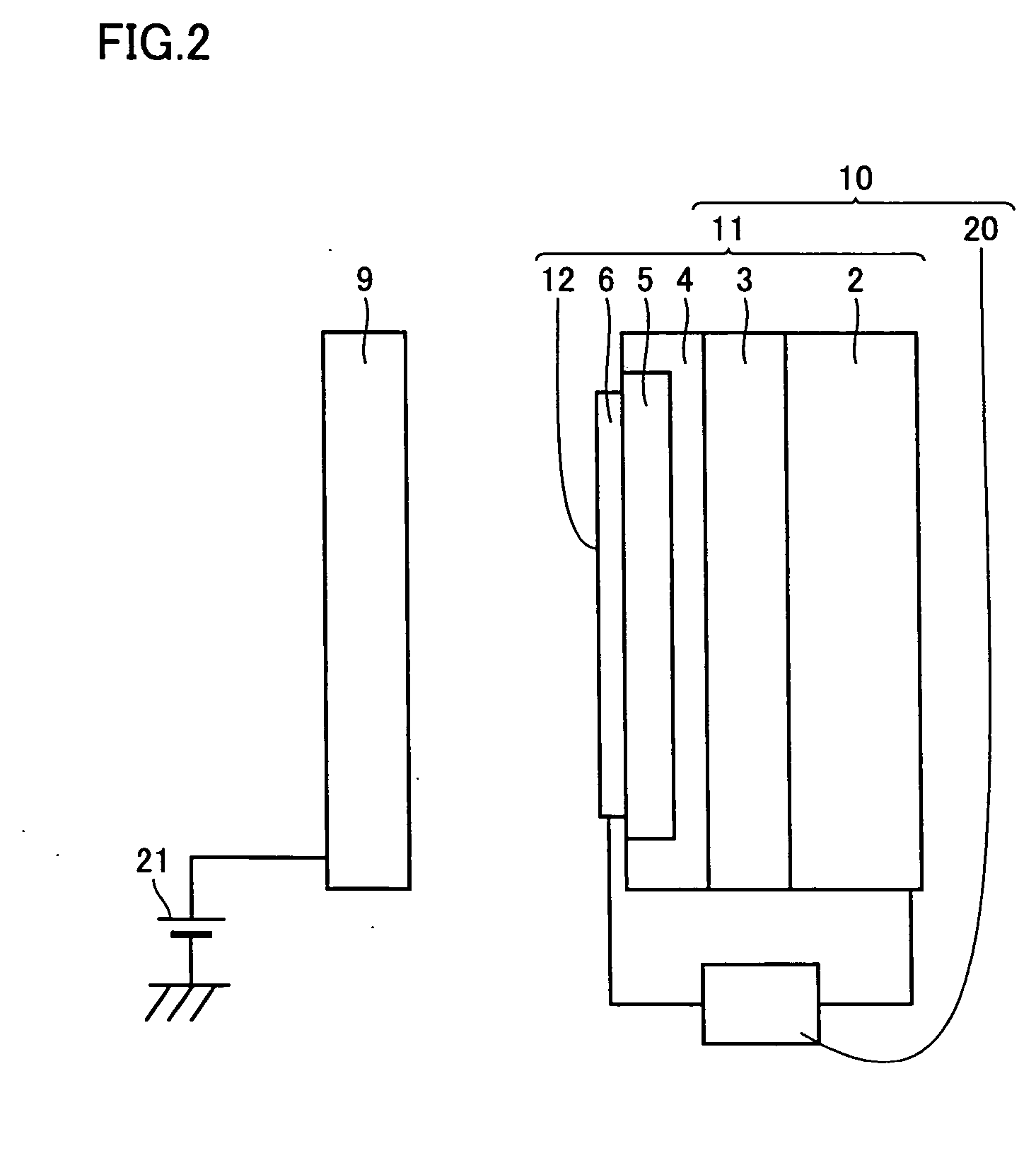
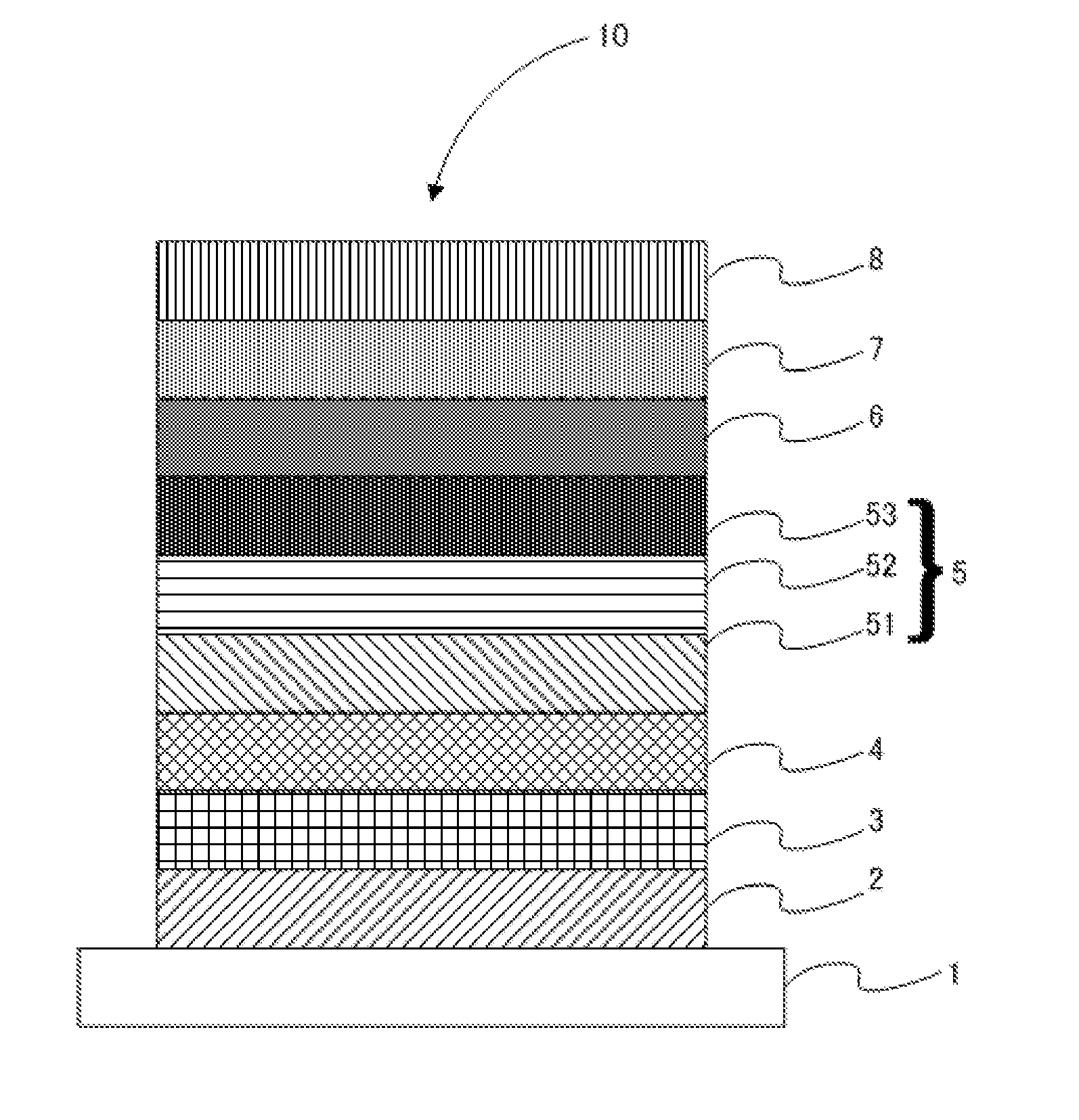
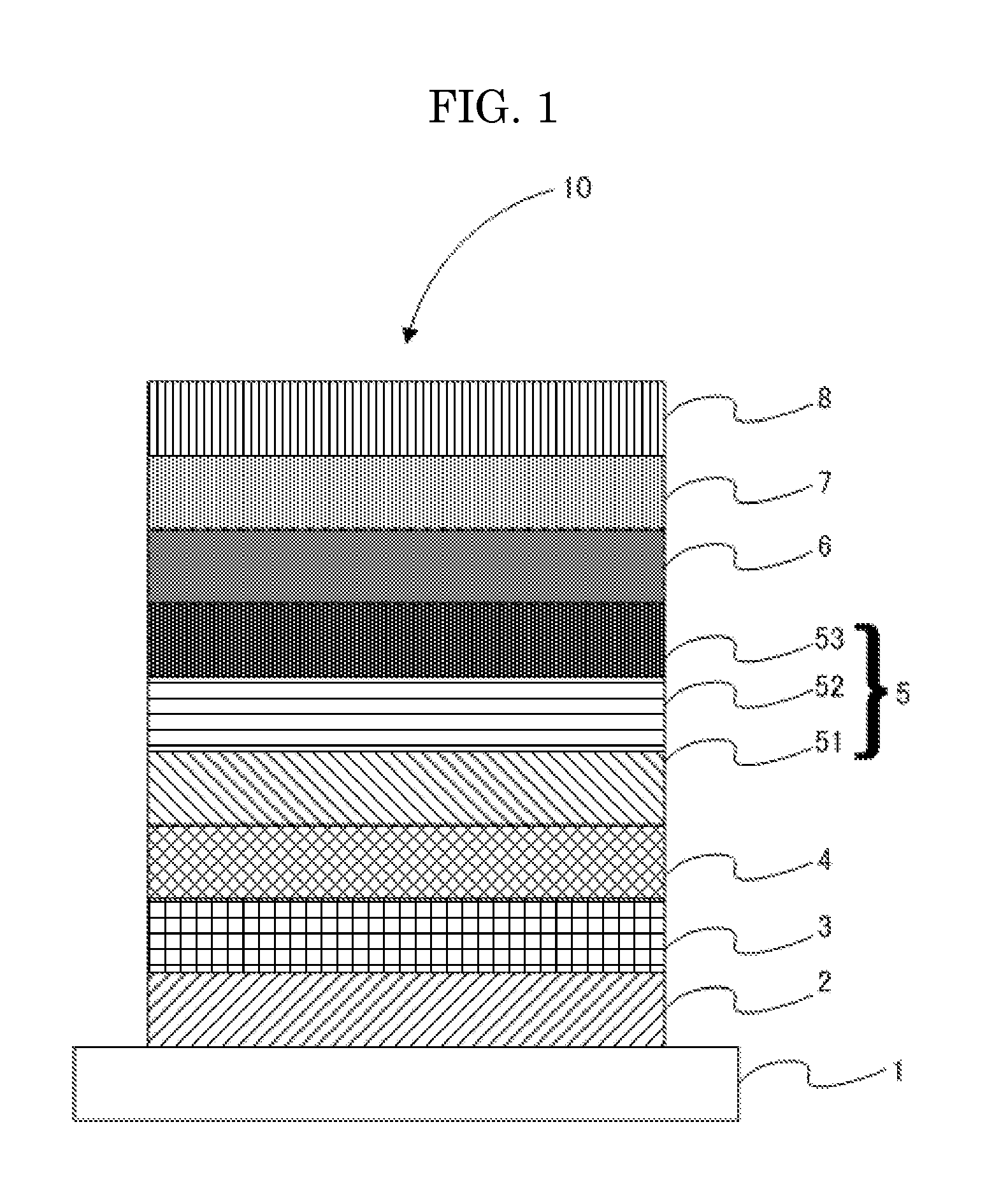
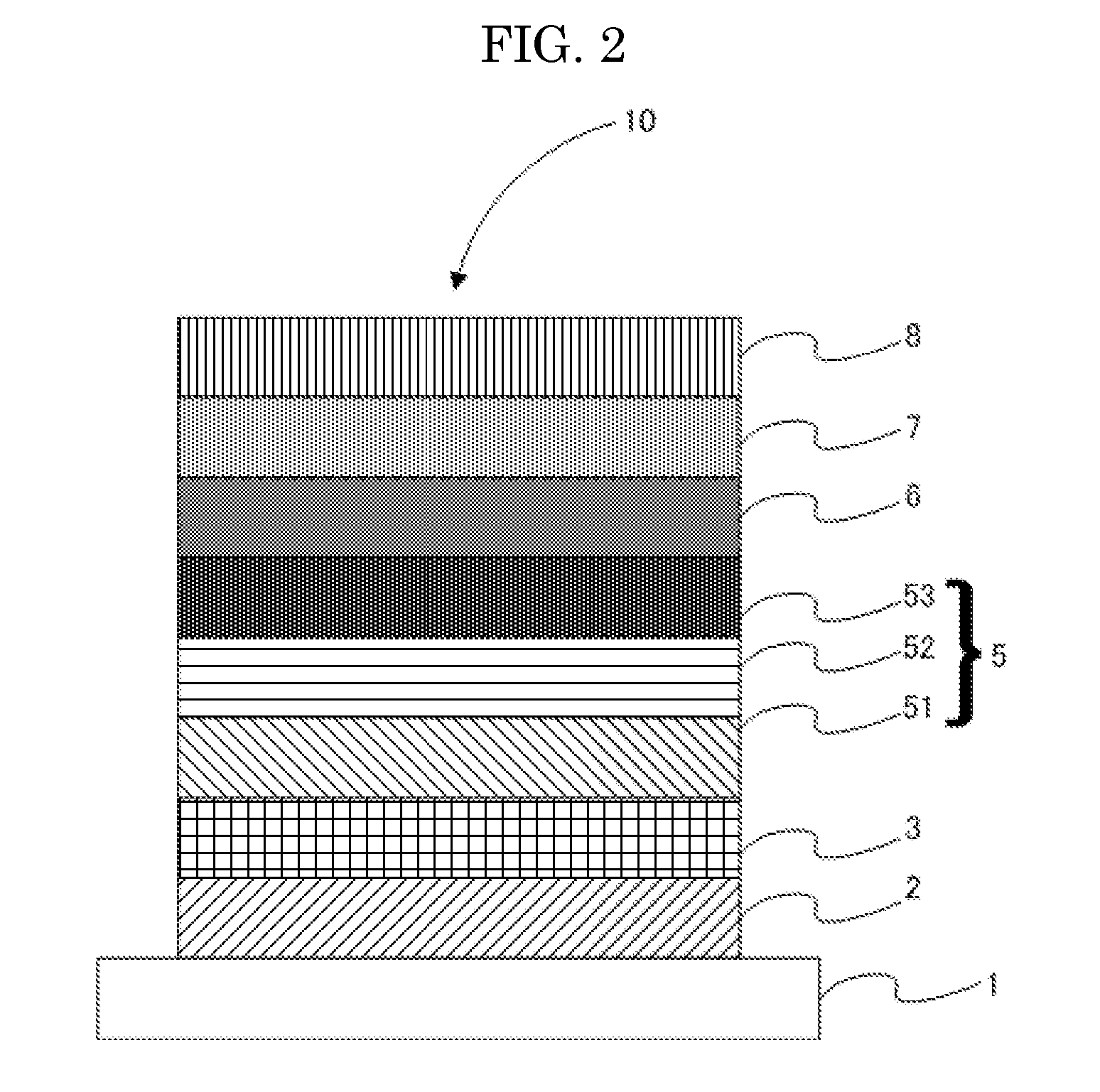
Ligth-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device
ActiveUS20080007164A1Solve low luminous efficiencyReduce power consumptionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsMovement control
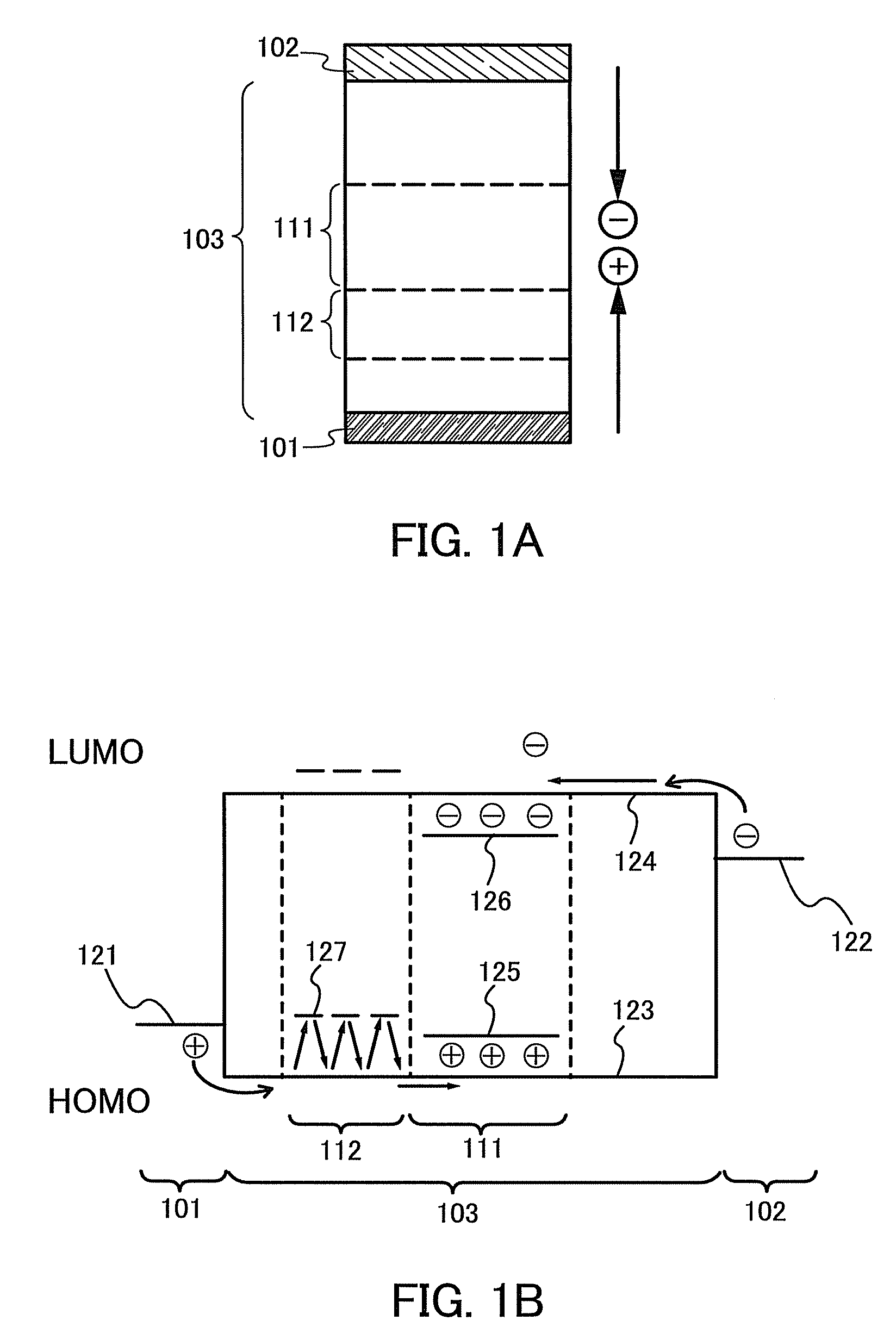
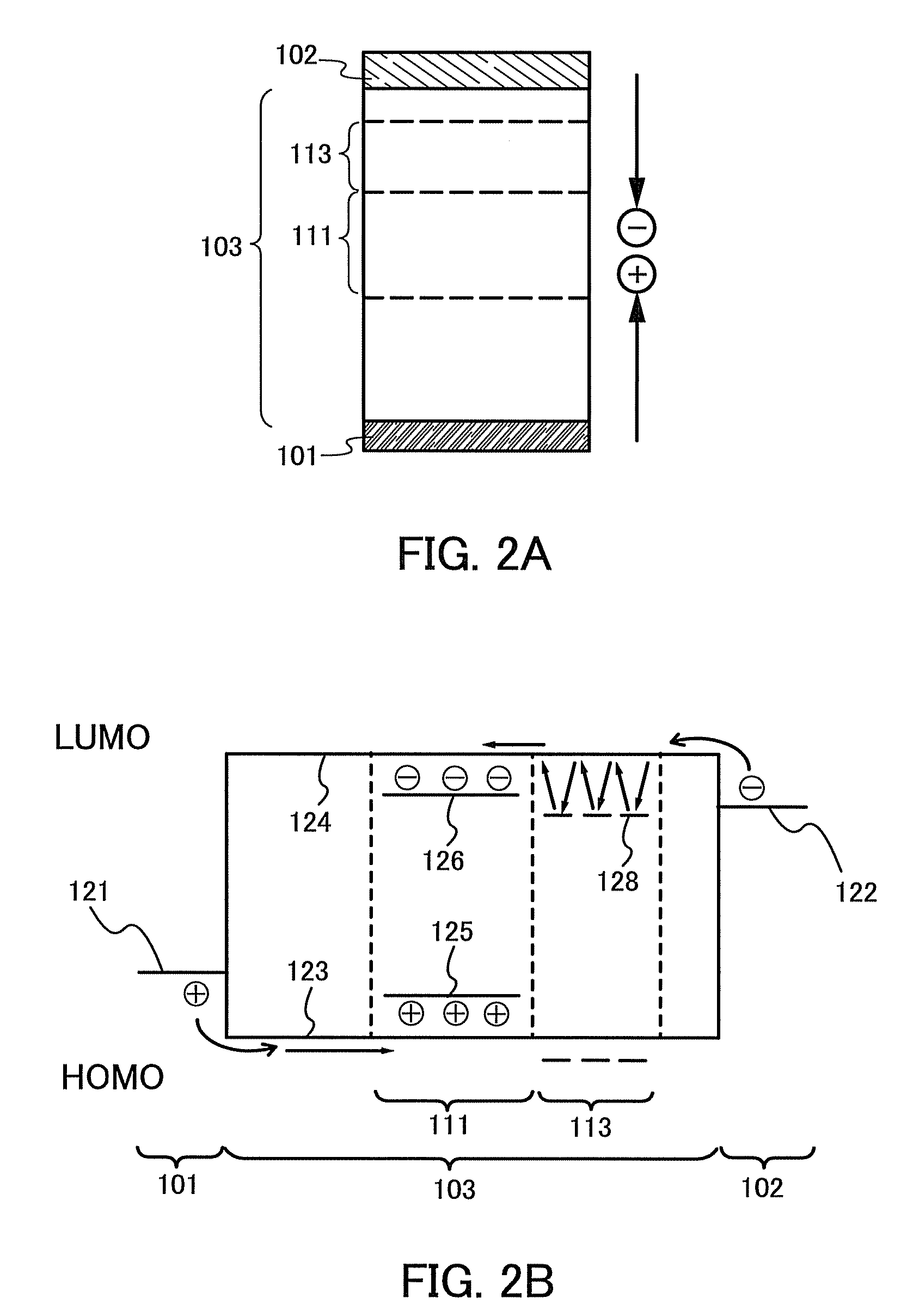
The light-emitting element includes: a light-emitting layer and a layer for controlling the movement of carriers between a first electrode and a second electrode. The layer for controlling the movement of carriers contains a first organic compound and a second organic compound, and is provided between the light-emitting layer and the second electrode. The first organic compound has an electron transporting property, and the second organic compound has an electron trapping property. The weight percent of the first organic compound is higher than that of the second organic compound. The light-emitting layer emits light when a voltage is applied such that the potential of the first electrode is higher than that of the second electrode. The first organic compound having the electron transporting property may be replaced with an organic compound having a hole transporting property, and the second organic compound having the electron trapping property may be replaced with an organic compound having a hole trapping property.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Detectable refrigerant compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050211949A1Easy to detectDetection of fluid at leakage pointHeat-exchange elementsInfraredCorona discharge
Disclosed herein are detectable refrigerant compositions, comprising from about 0.001 to about 5 weight percent tracer compositions, which are useful to identify leaking in a vapor compression refrigeration and / or air conditioning system. The presence of the tracers make the refrigerant compositions detectable by chemo / electro-active array, corona discharge, heated diode, electrochemical, photoionization, infra red, ultrasonic and electron capture detectors.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
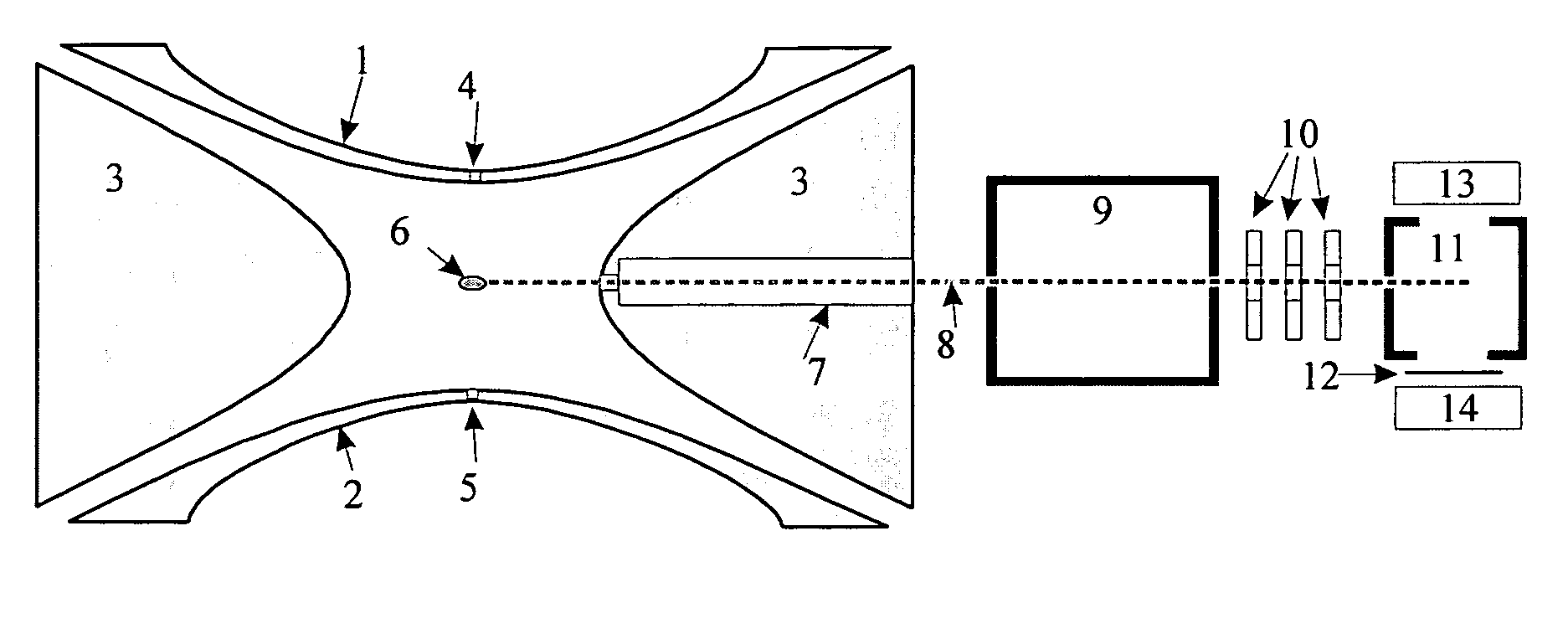
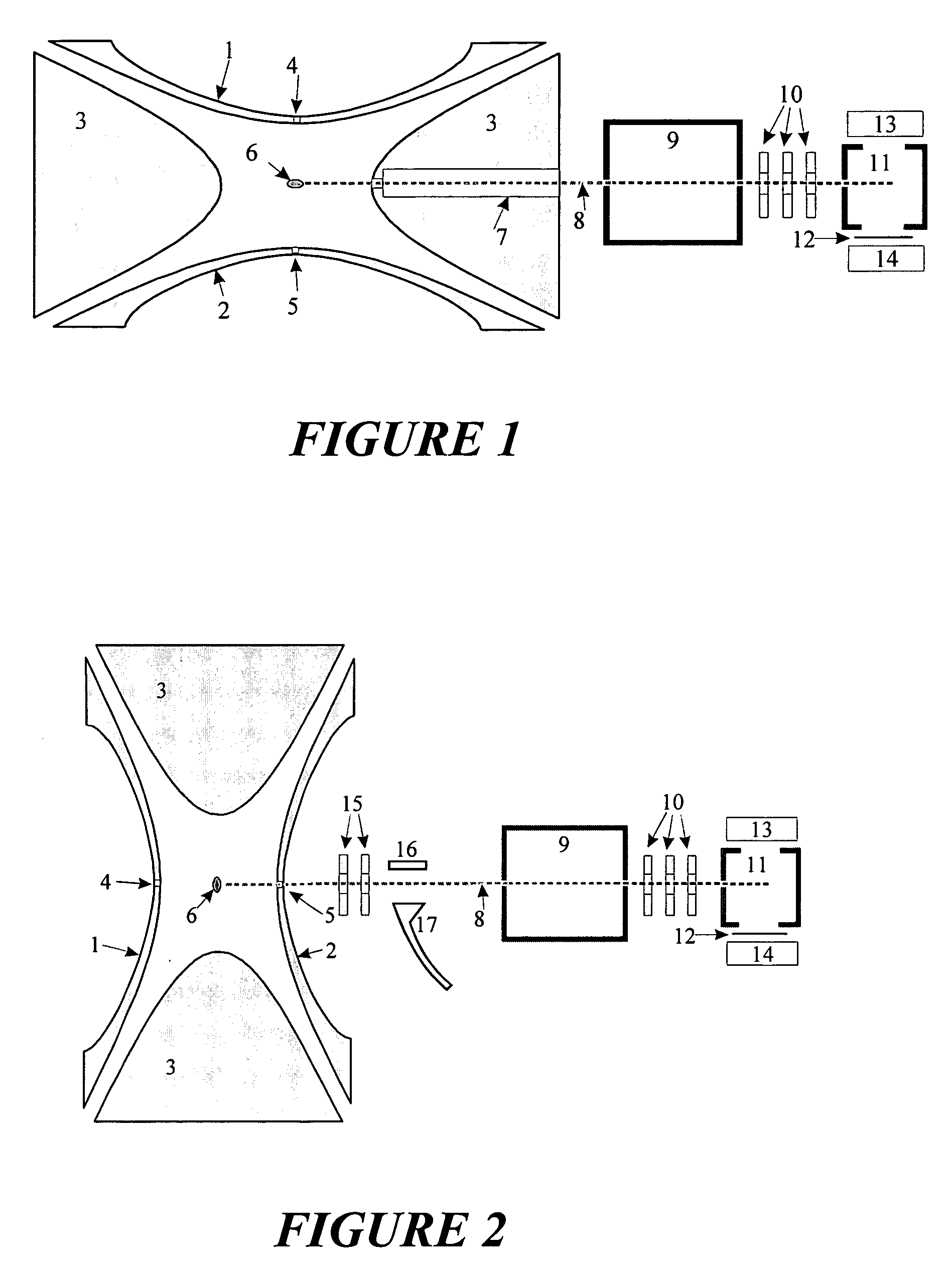
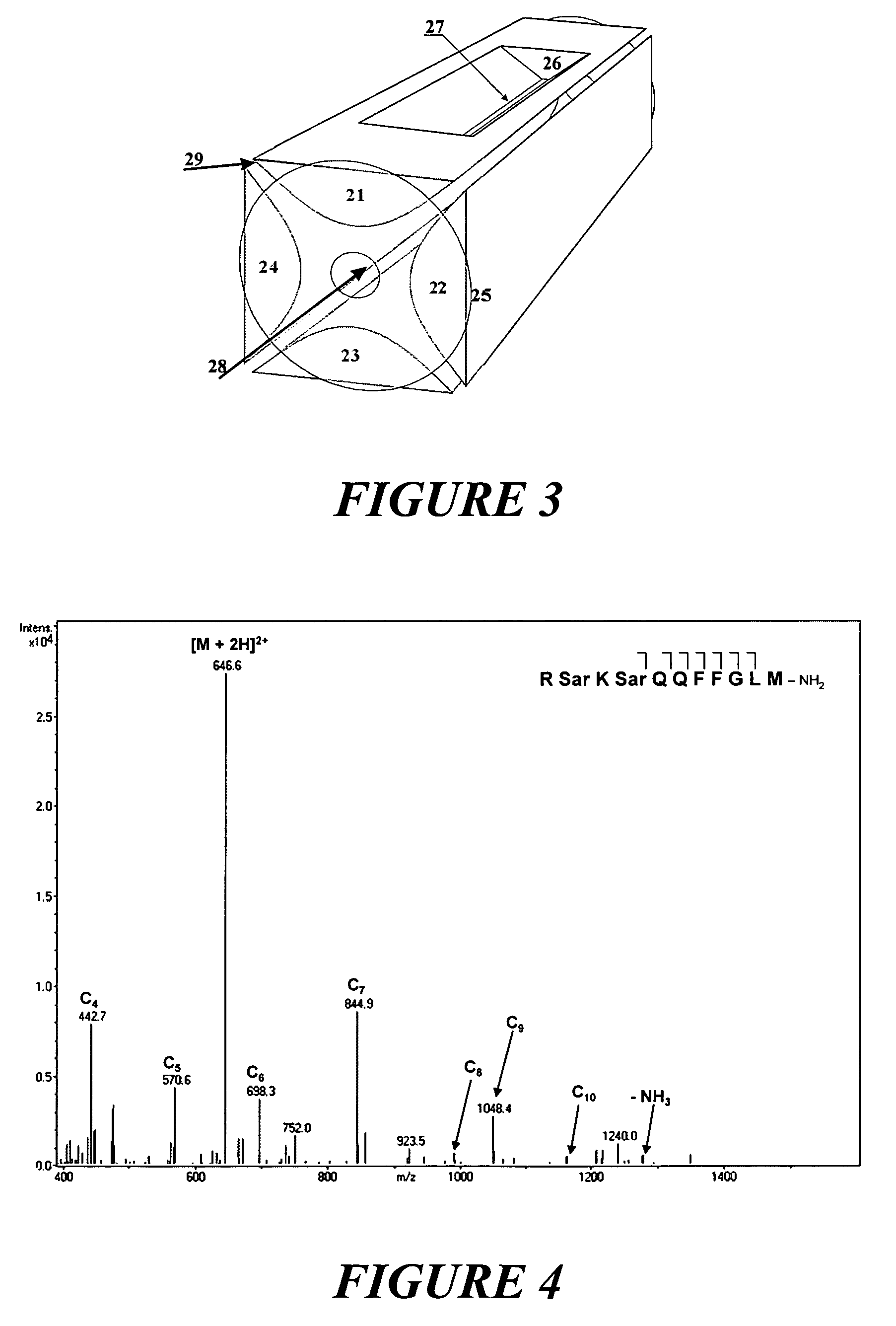
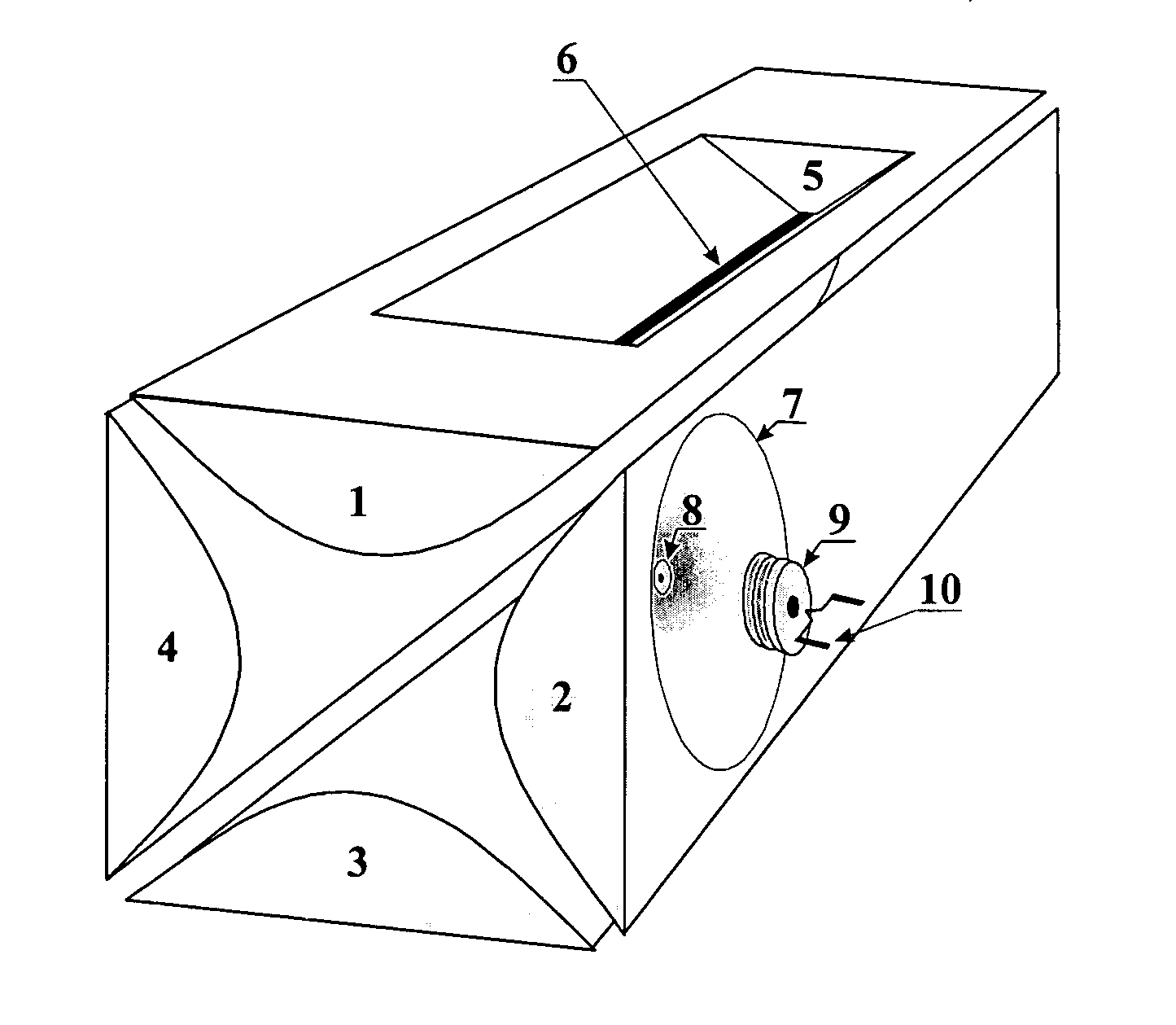
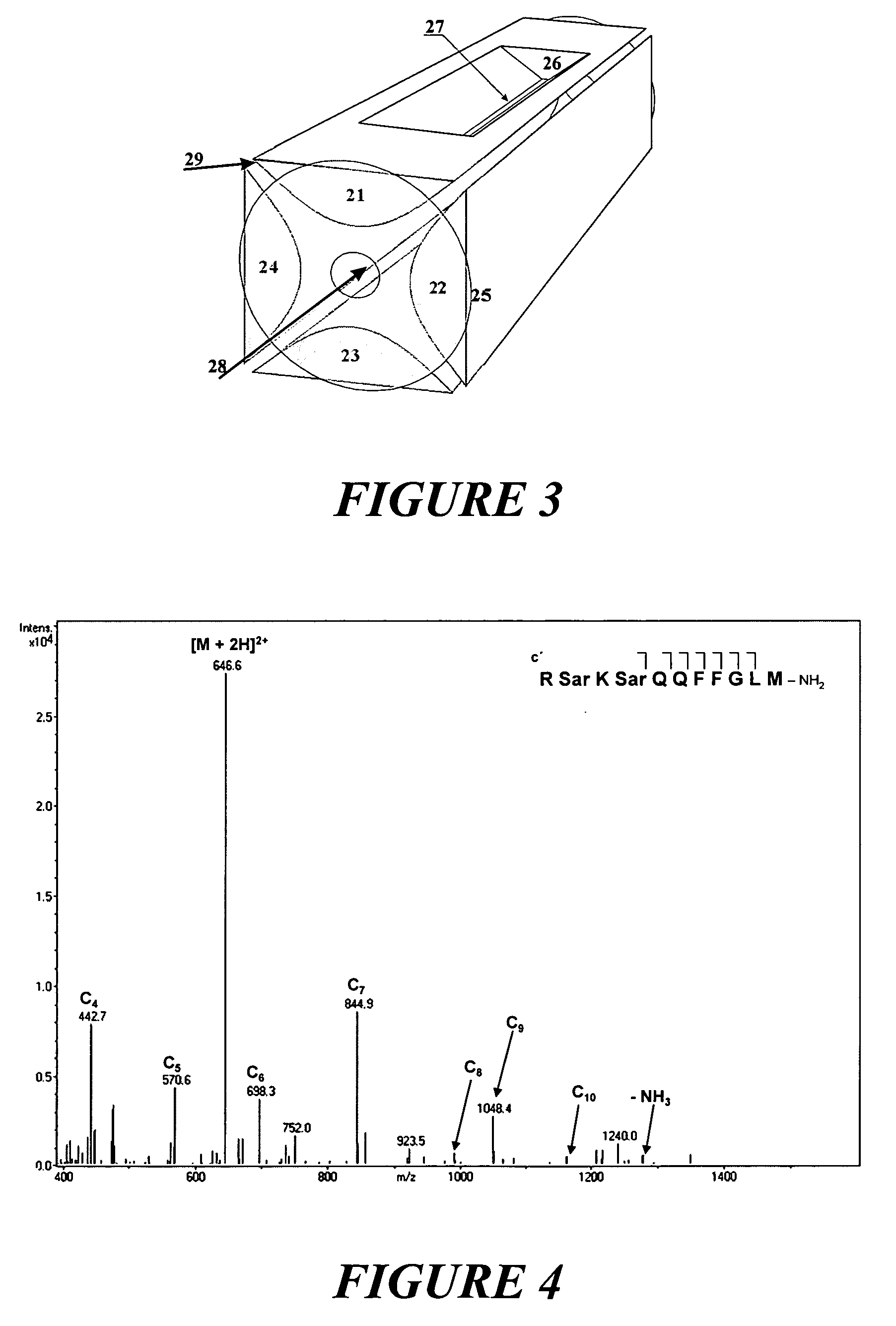
Ion fragmentation by electron capture in linear RF ion traps
ActiveUS6995366B2Extended maintenance periodStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsIon trap mass spectrometryElectron source
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS7528542B2Reduced durabilityExtended service lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantHost material
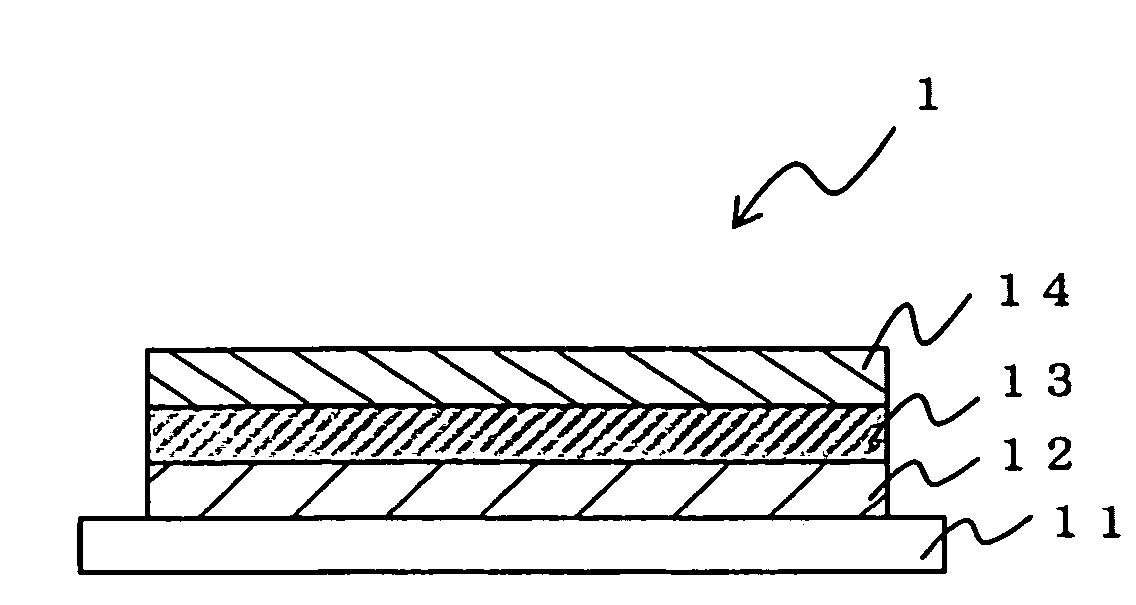
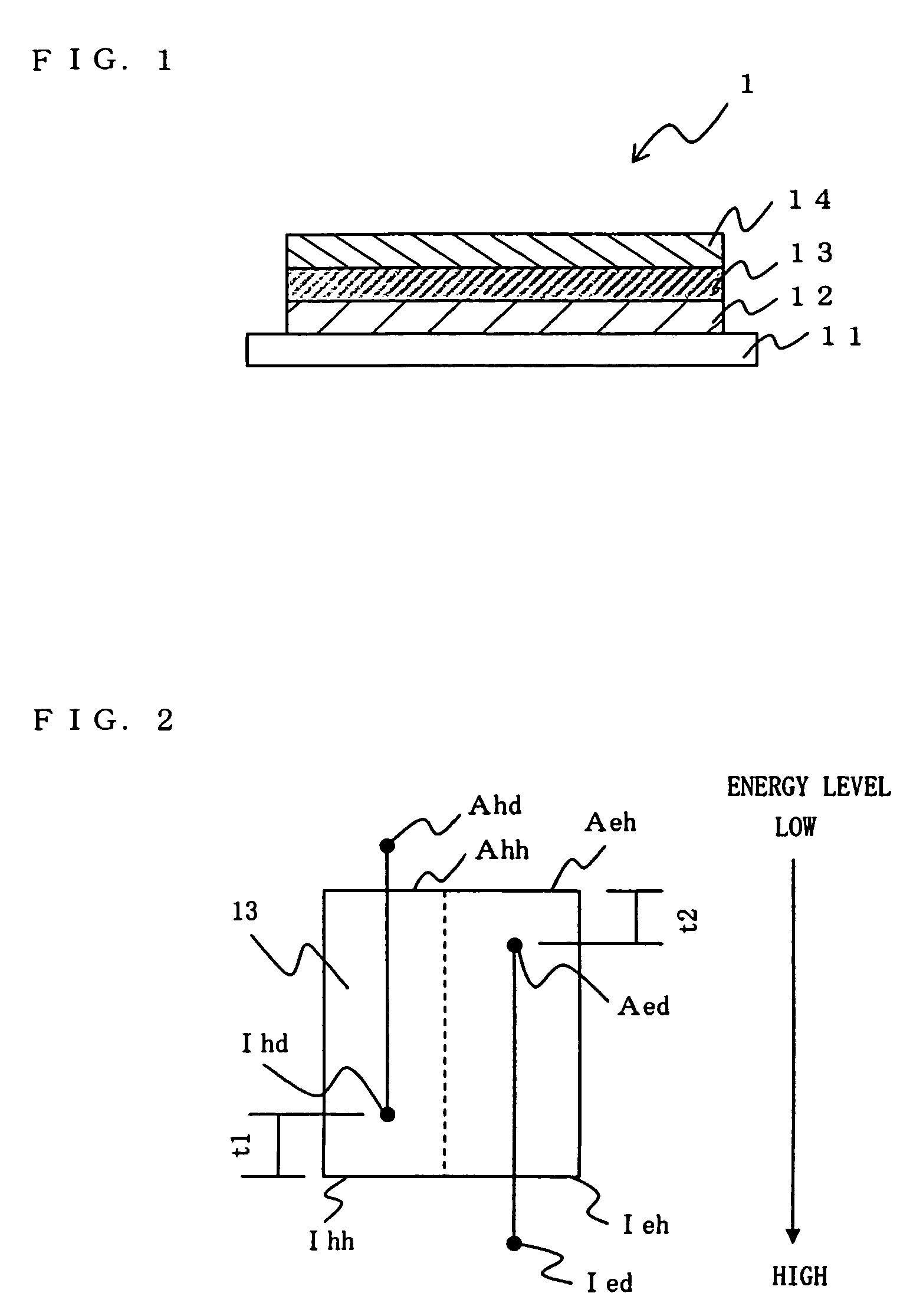
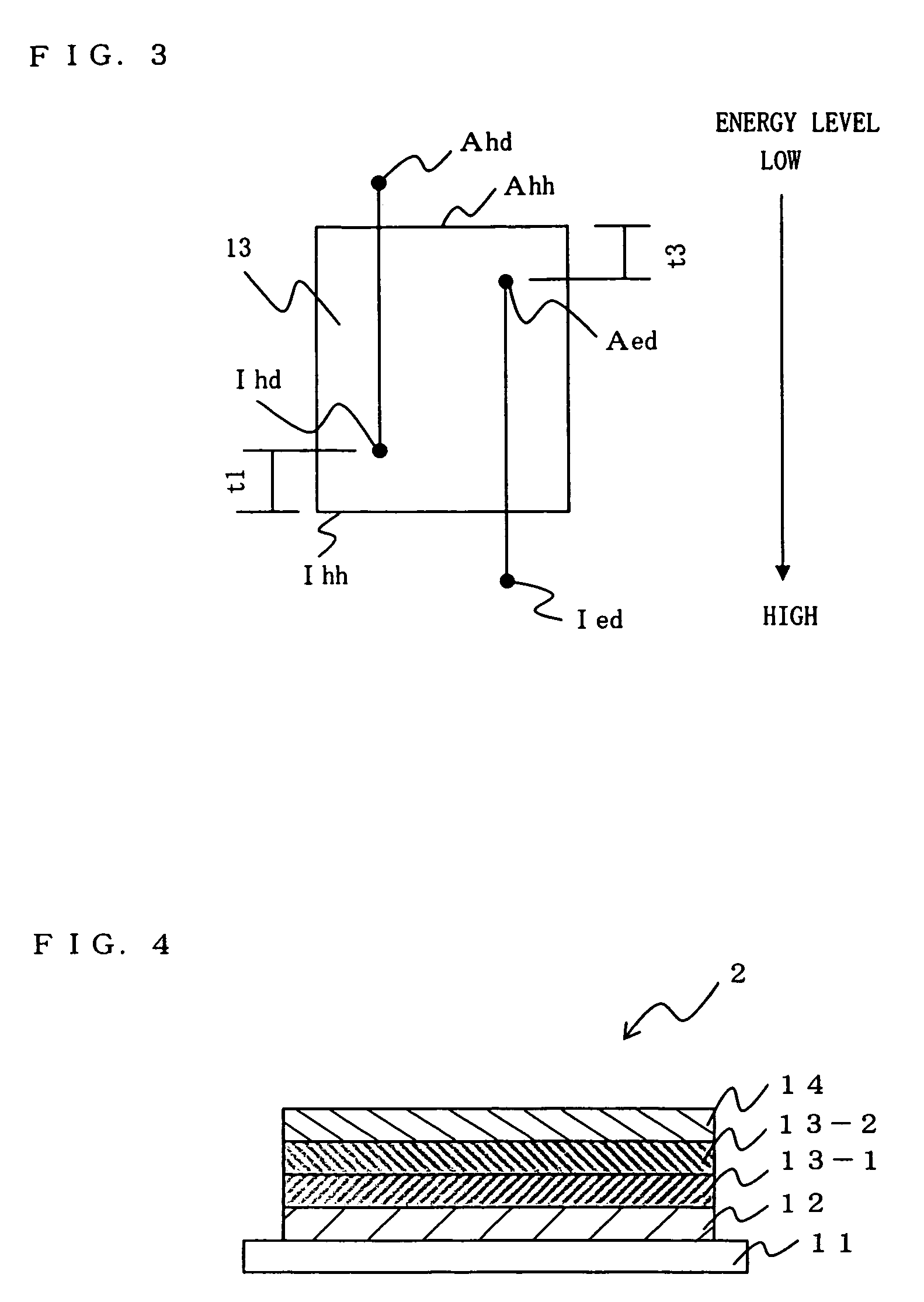
An organic electroluminescent device 1 including: an anode 12, a cathode 14 and an organic emitting layer 13 held therebetween, the organic emitting layer 13 containing one or more host materials, a hole trapping dopant and an electron trapping dopant. The lifetime of an organic EL device 1 can be improved by causing a hole-trapping dopant and an electron-trapping dopant to be together present in its organic emitting layer.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Room temperature solid state gamma or X-ray detectors
InactiveUS6331705B1Reduce in quantityWeaken energySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSolid state detectorX-ray
The invention provides a method for detecting gamma or X-ray radiation with a room temperature solid state detector, which comprises the selection of the detector's electron trapping parameter (muτ)e and / or the detector voltage V so as to tune the electron trapping to optimally compensate for the incomplete charge collection.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION SOREQ NUCLEAR RES CENT THE
Ion fragmentation by reaction with neutral particles
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for the fragmentation of large molecules, especially biopolymers. The invention consists in reacting analyte ions with excited or radical neutral particles, whereby, at least in the case of bombardment of analyte ions with helium atoms from an FAB generator, a new type of fragmentation occurs which strongly resembles fragmentation by electron capture (ECD). The reactions may be performed in magnetic ion traps (ion cyclotron resonance cells, ICR), in RF ion traps according to Wolfgang Paul, in RF ion guides, or in free beams of analyte ions or neutral particles.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Ion fragmentation by electron capture in linear RF ion traps
ActiveUS20050017167A1Weaken energyExtended maintenance periodStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsIon trap mass spectrometryElectron source
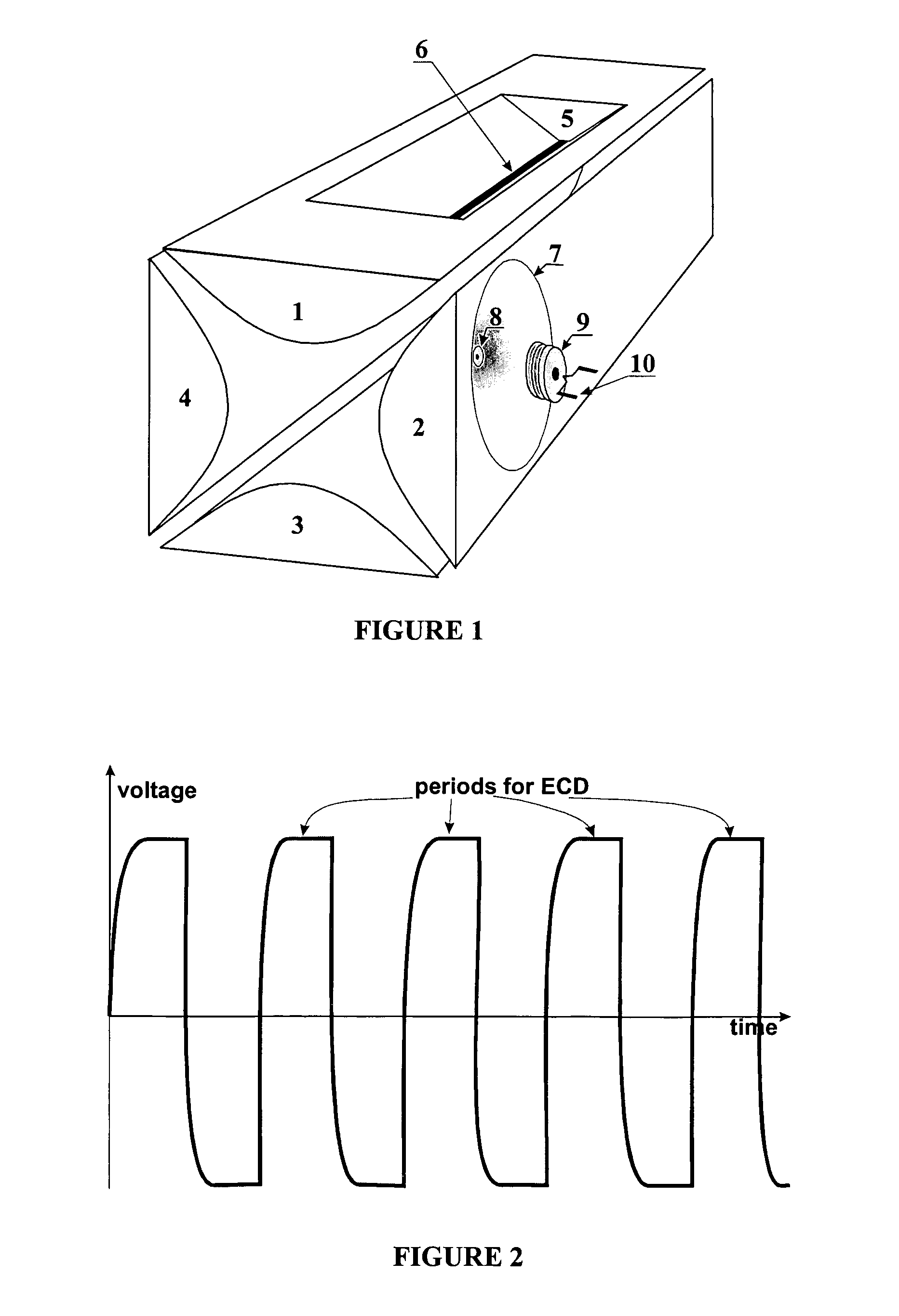
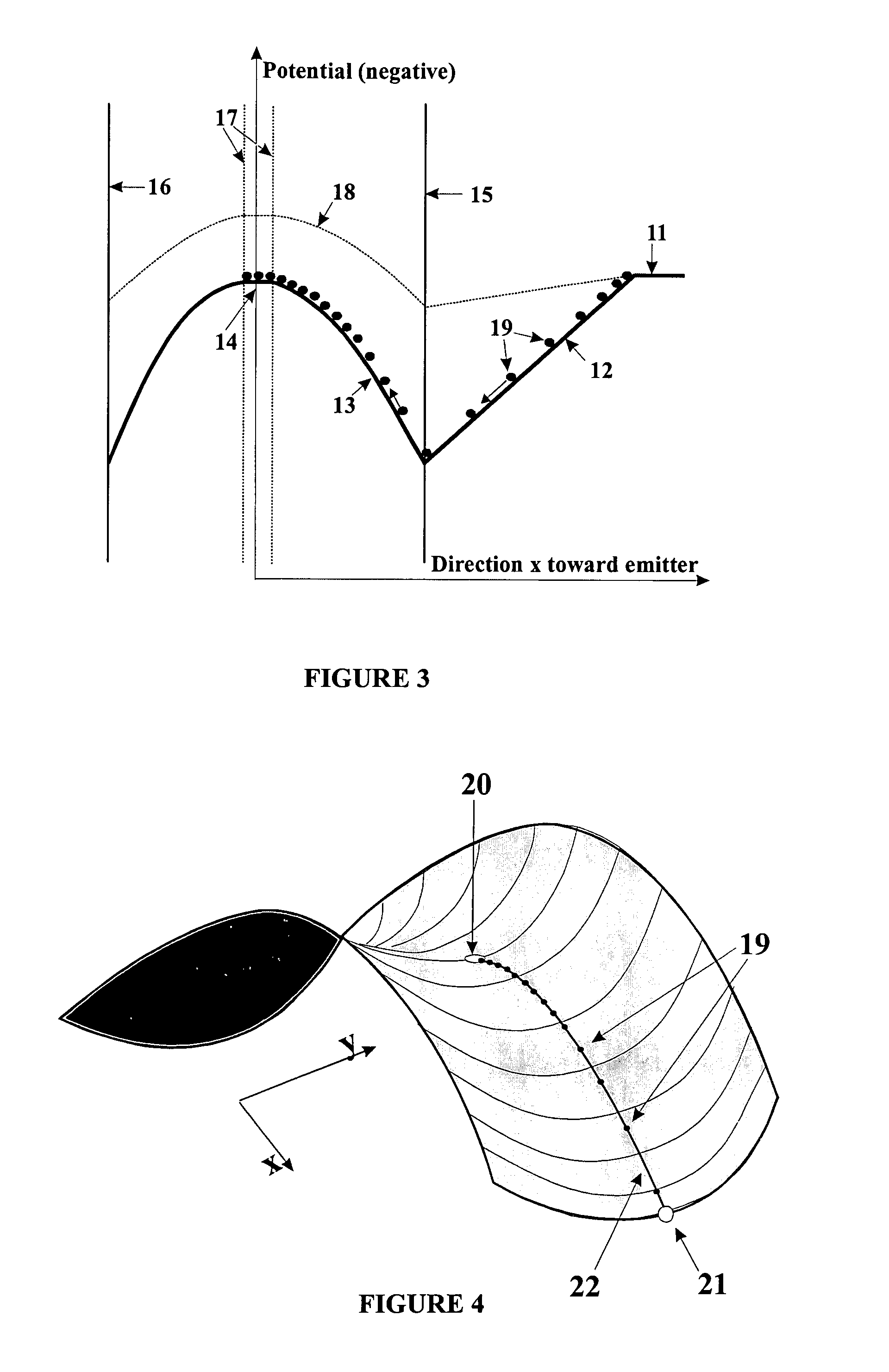
The invention relates to a method and device for the fragmentation of macromolecules in linear quadrupole RF ion traps according to Wolfgang Paul. The invention consists in fragmenting the ions by the capture of low energy electrons (ECD), injected into the linear RF ion trap. One way of doing this is to inject low energy electrons through the gap between the pole rods. Another possibility is to inject the electrons through an opening in one of the pole rods carrying a RF voltage, the electron source being kept at the highest positive potential which is achieved on the center axis of the ion trap during the RF period. Both methods can be improved by pulse-shaped RF voltages, offering longer periods for electron capture. The electron beam can be guided by a magnetic field.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Electron emitter, charger, and charging method
InactiveUS20060291905A1Drive stabilityCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesStatic indicating devicesElectrical polarityPorous semiconductors
Provided are an electron emitter continuously emitting electrons stably even in the atmosphere, a charger using the electron emitter, and a charging method using the charger. The electron emitter includes a electron emitting element consisting of a first electrode, a second electrode, and a semiconductor layer formed therebetween, and a power supply for alternately applying a positive voltage enabling electron emission and a negative voltage having a polarity opposite to the positive voltage. At least a part of the surface on the first electrode side of the semiconductor layer is formed of a porous semiconductor layer. Electrons captured in the porous semiconductor layer in the course of electron emission with application of a positive voltage disturb electron emission from the electron emitting element. Such electrons, however, are removed by application of a negative voltage.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device and Quinoxaline Derivative
ActiveUS20080217608A1Improve visibilityLong life-timeOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesQuinoxalineOrganic compound
The present invention provides light-emitting element having long lifetime, and light-emitting devices and electronic devices having long lifetime. A light-emitting element comprises a first layer and a second layer including a light-emitting substance between a first electrode and a second electrode. The first layer includes a first organic compound and a second organic compound, the first layer is formed between the second layer and the second electrode, the first layer includes the first organic compound more than the second organic compound, the first organic compound is an organic compound having an electron-transporting property, the second organic compound is an organic compound having an electron-trapping property, an energy gap of the second organic compound is larger than that of the light-emitting substance; and a voltage is applied such that a potential of the first electrode is higher than that of the second electrode, so that the light-emitting layer emits light.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
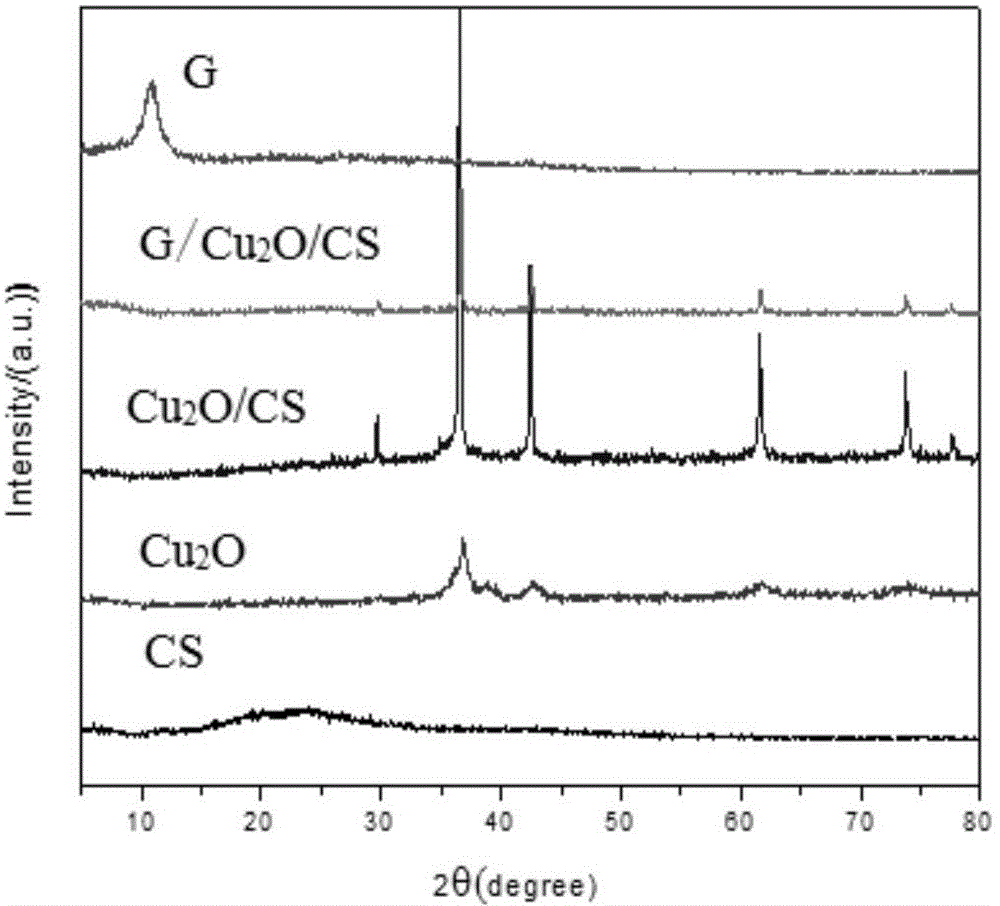
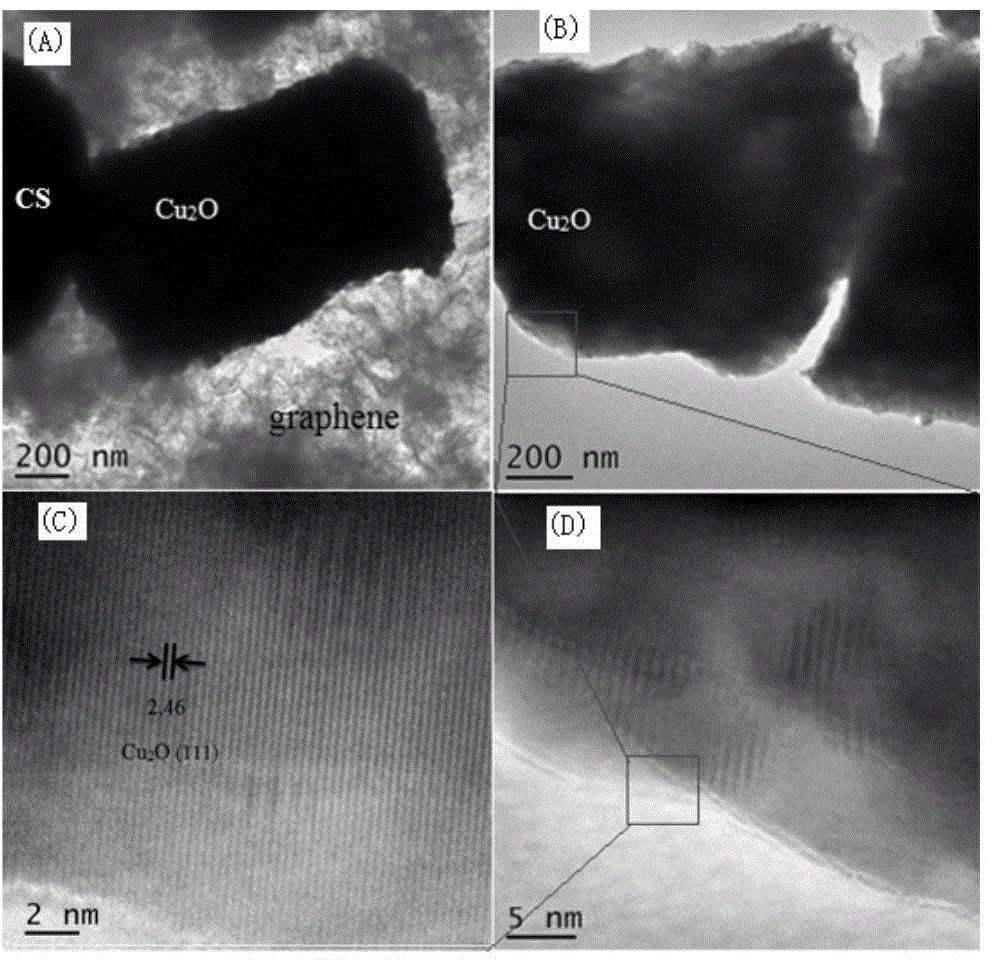
Grapheme/chitosan/cuprous oxide composite material and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN104588110AGuaranteed contentGood biocompatibilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesOxide compositeElectron capture
The invention discloses a graphene / chitosan / cuprous oxide composite material and a preparation method and applications thereof, which belong to the technical field of visible light catalytic materials. The composite material mainly comprises graphene, chitosan and cuprous oxide, wherein the graphene has extremely good electron capture and transmission performances, and as a carrier of photo-generated electrons, the graphene reduces the recombination rate of photo-generated electrons and holes of the cuprous oxide; by using the excellent adsorption property of the graphene to organic pollutants, the photocatalytic efficiency of a photocatalyst is improved; a good synergistic effect exists among the composited chitosan, the graphene and the cuprous oxide, and while the adsorption effect of the catalyst is improved, the degradation performance of the visible light catalyst to organic pollutants is improved. Under same conditions, compared with cuprous oxide, and cuprous oxide / chitosan, the graphene / chitosan / cuprous oxide composite material shows higher adsorption capacity and photocatalytic properties.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Ion fragmentation by reaction with neutral particles
ActiveUS20060192100A1Optical radiation measurementSugar derivativesIon trap mass spectrometryAnalyte
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for the fragmentation of large molecules, especially biopolymers. The invention consists in reacting analyte ions with excited or radical neutral particles, whereby, at least in the case of bombardment of analyte ions with helium atoms from an FAB generator, a new type of fragmentation occurs which strongly resembles fragmentation by electron capture (ECD). The reactions may be performed in magnetic ion traps (ion cyclotron resonance cells, ICR), in RF ion traps according to Wolfgang Paul, in RF ion guides, or in free beams of analyte ions or neutral particles.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
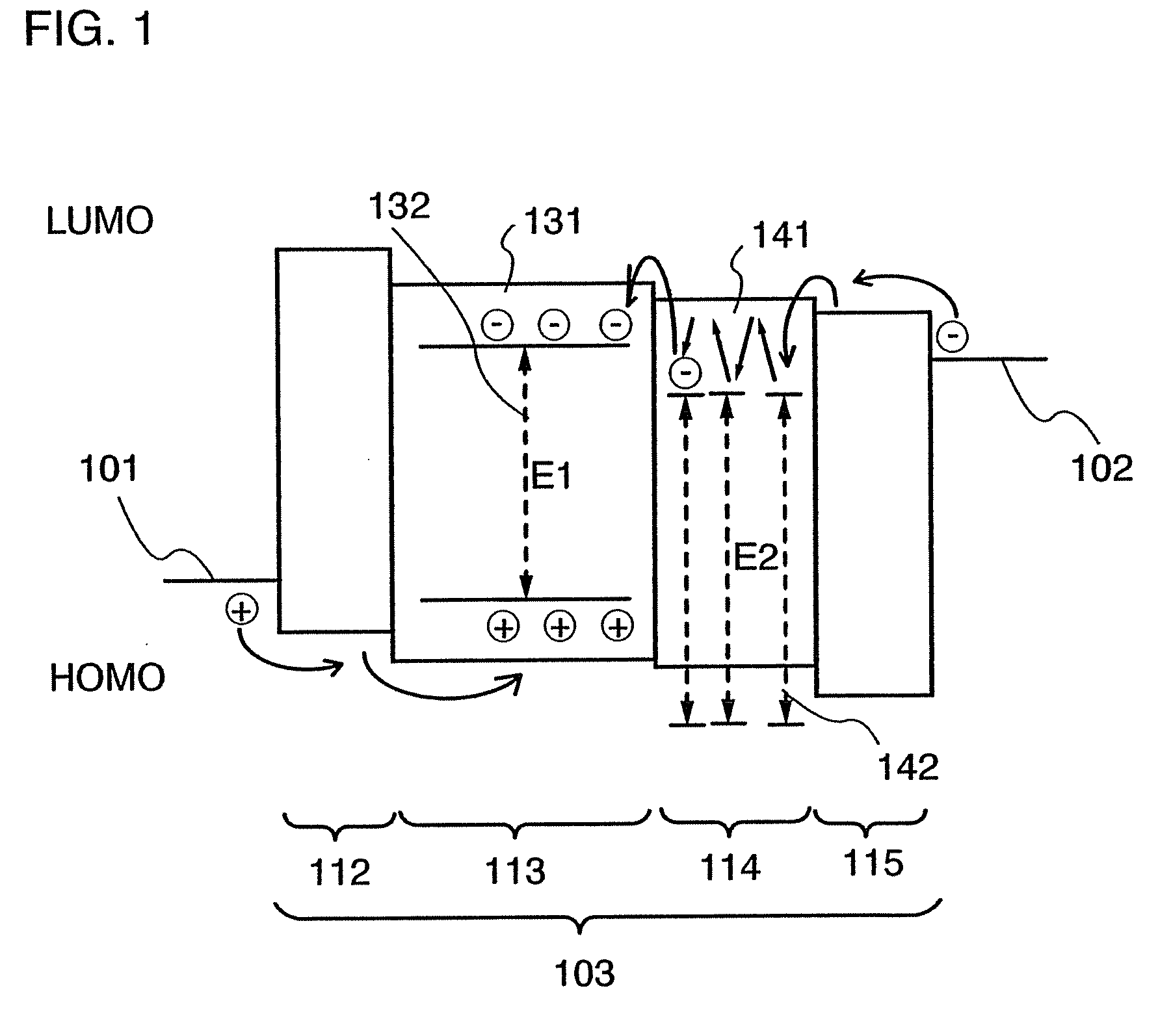
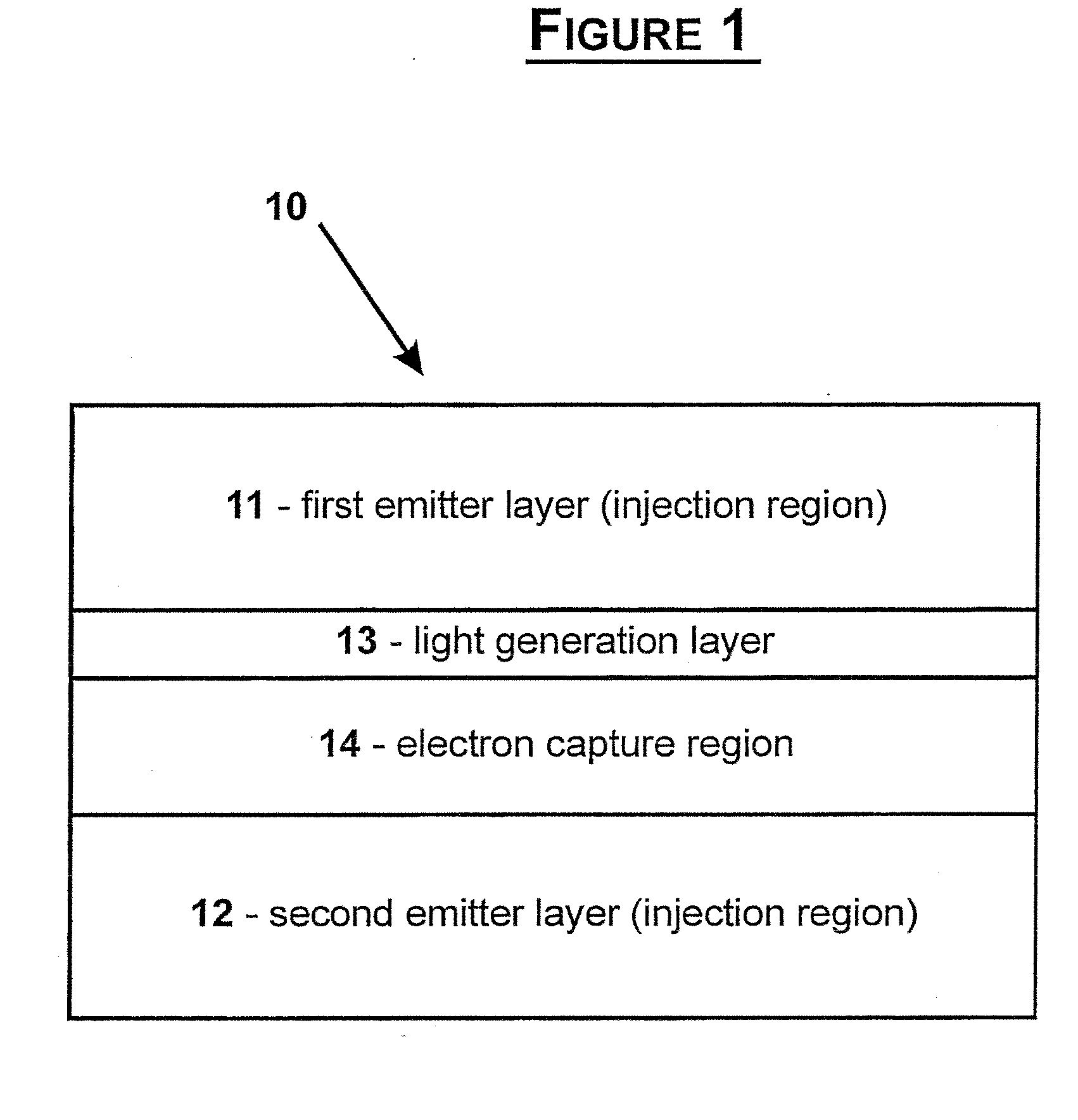
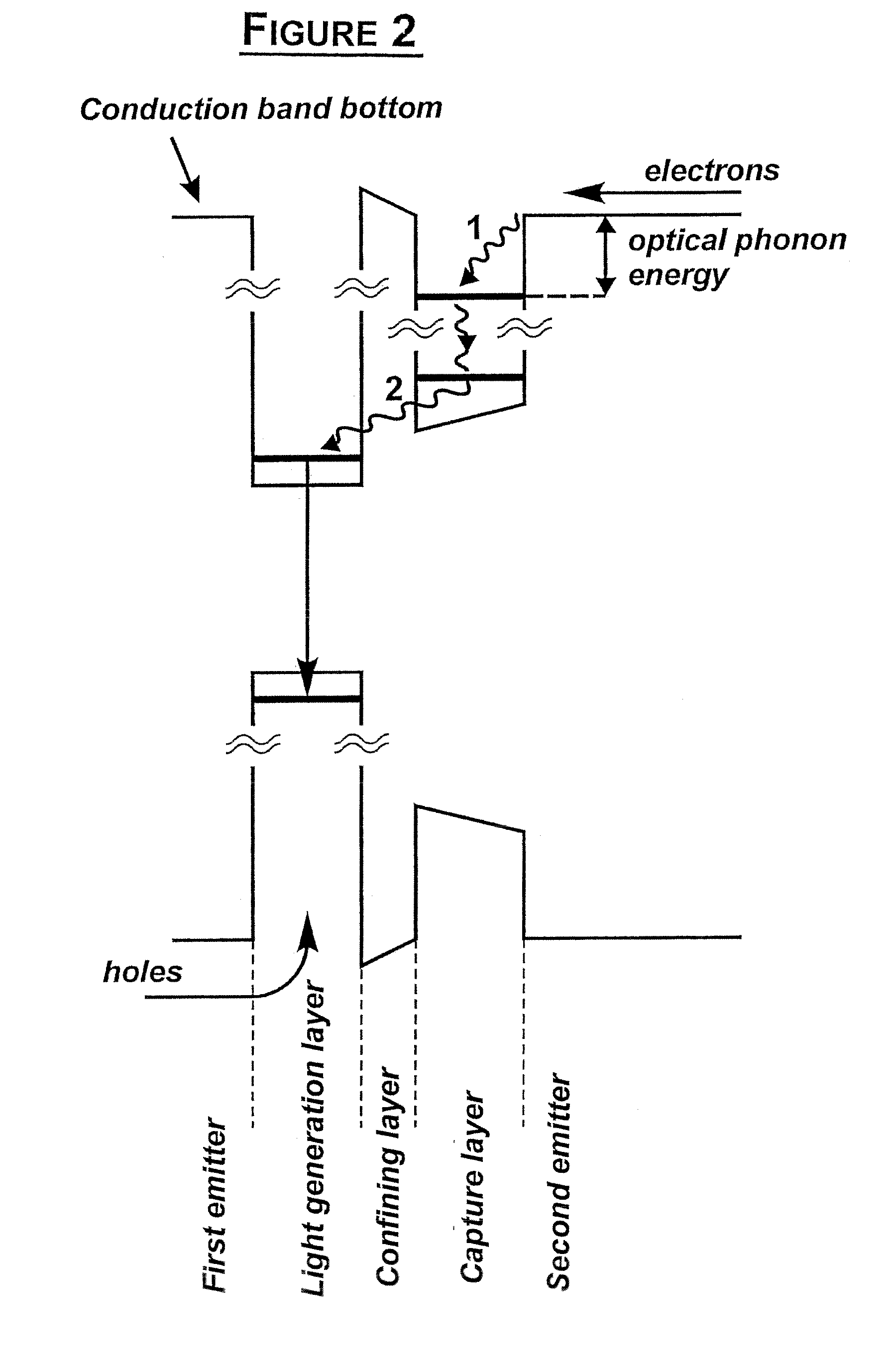
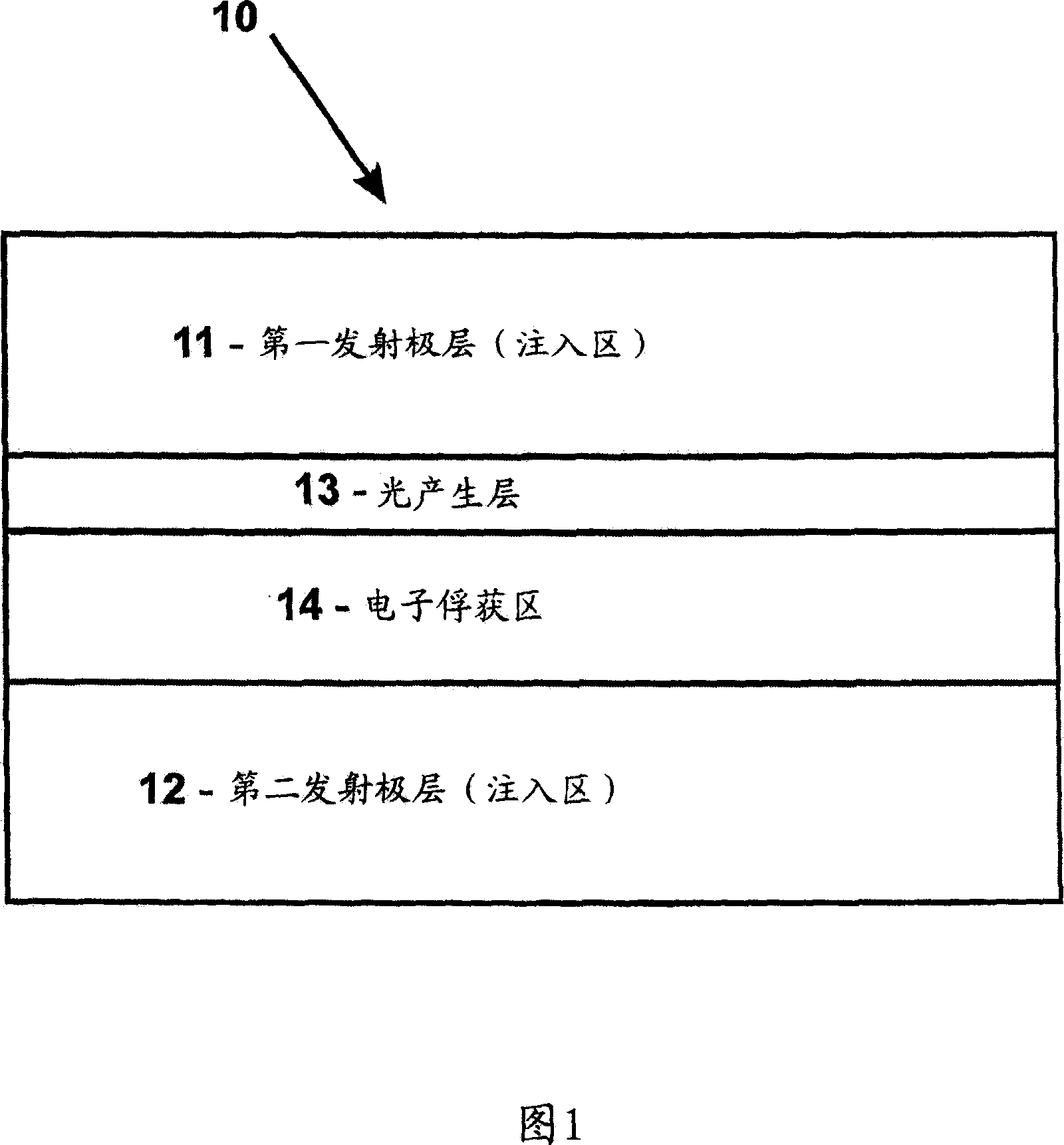
Semiconductor Heterostructure
InactiveUS20080283818A1Enhanced total light generating capabilityEmission rate can be suppressedNanoopticsSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor heterostructuresConduction band
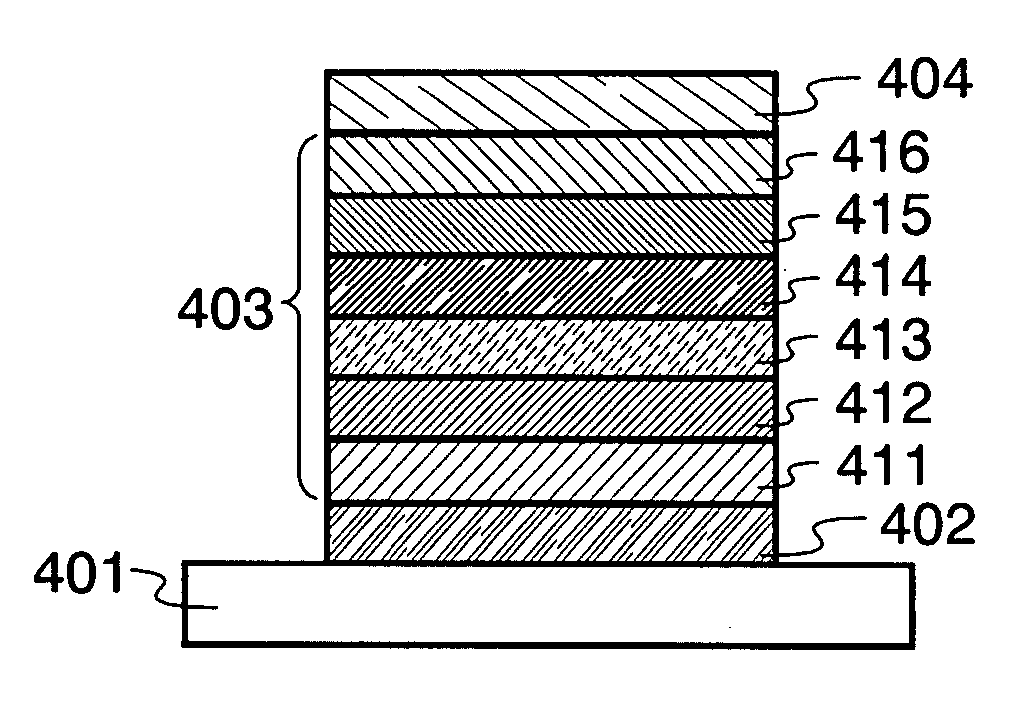
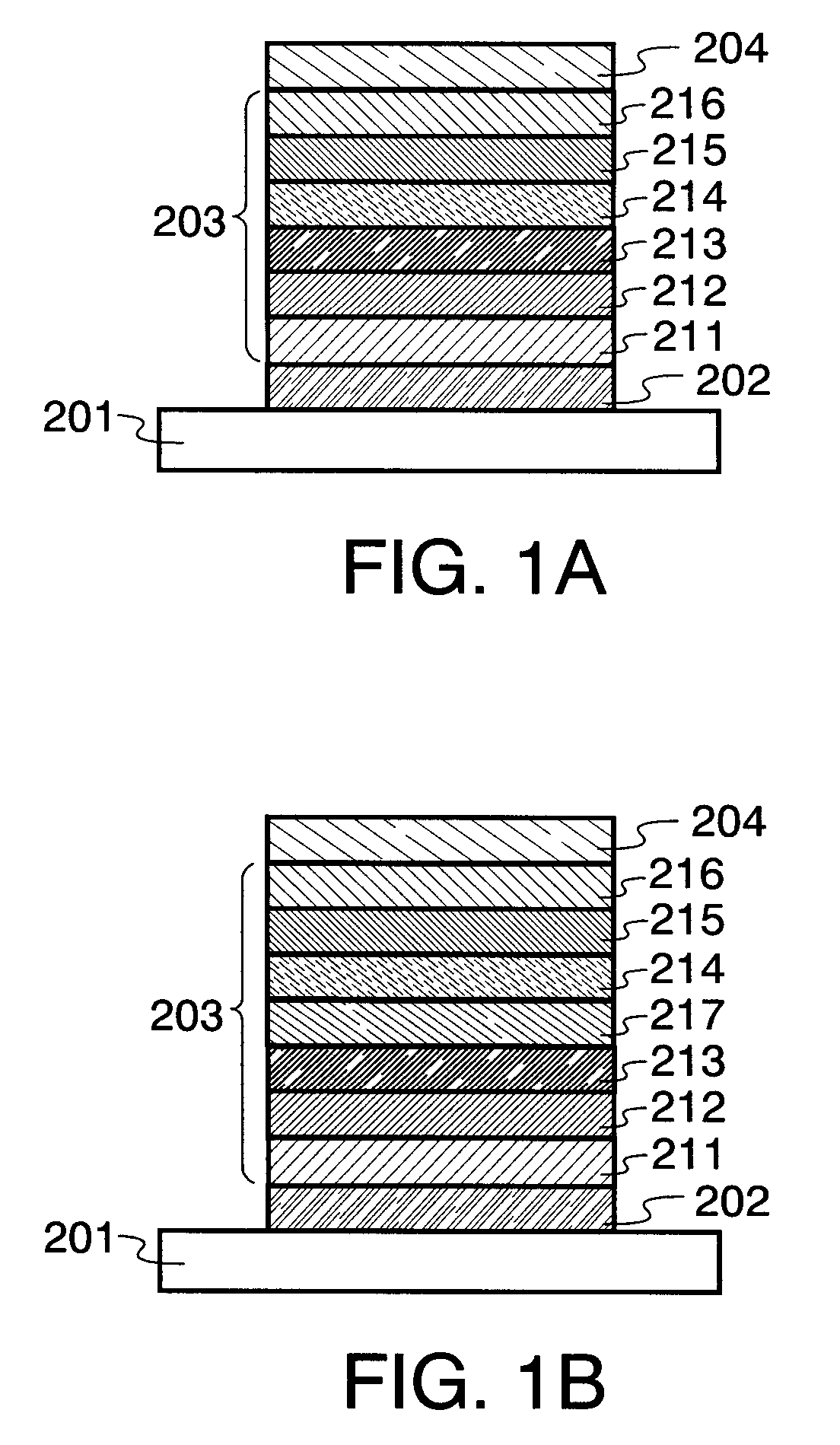
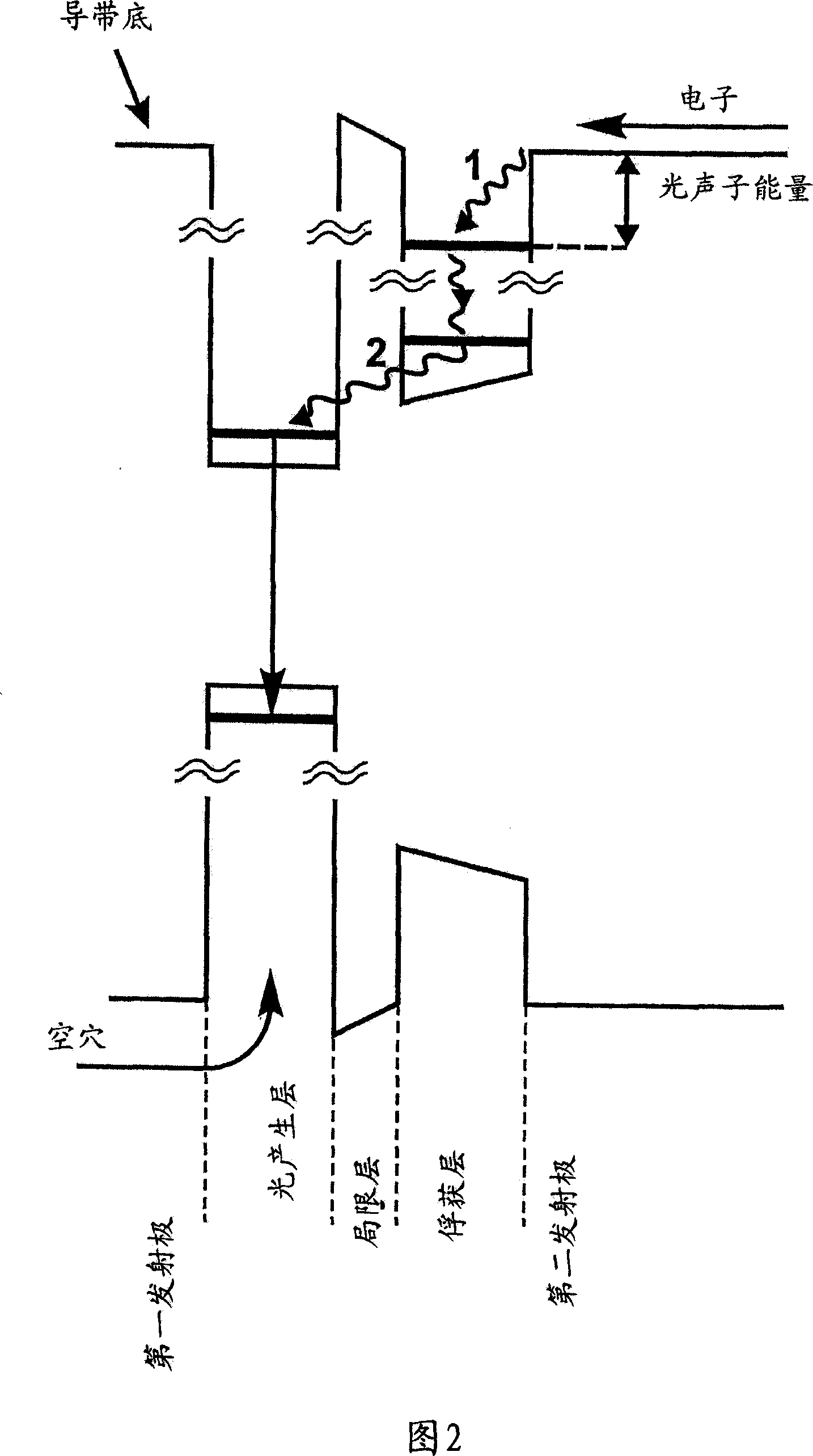
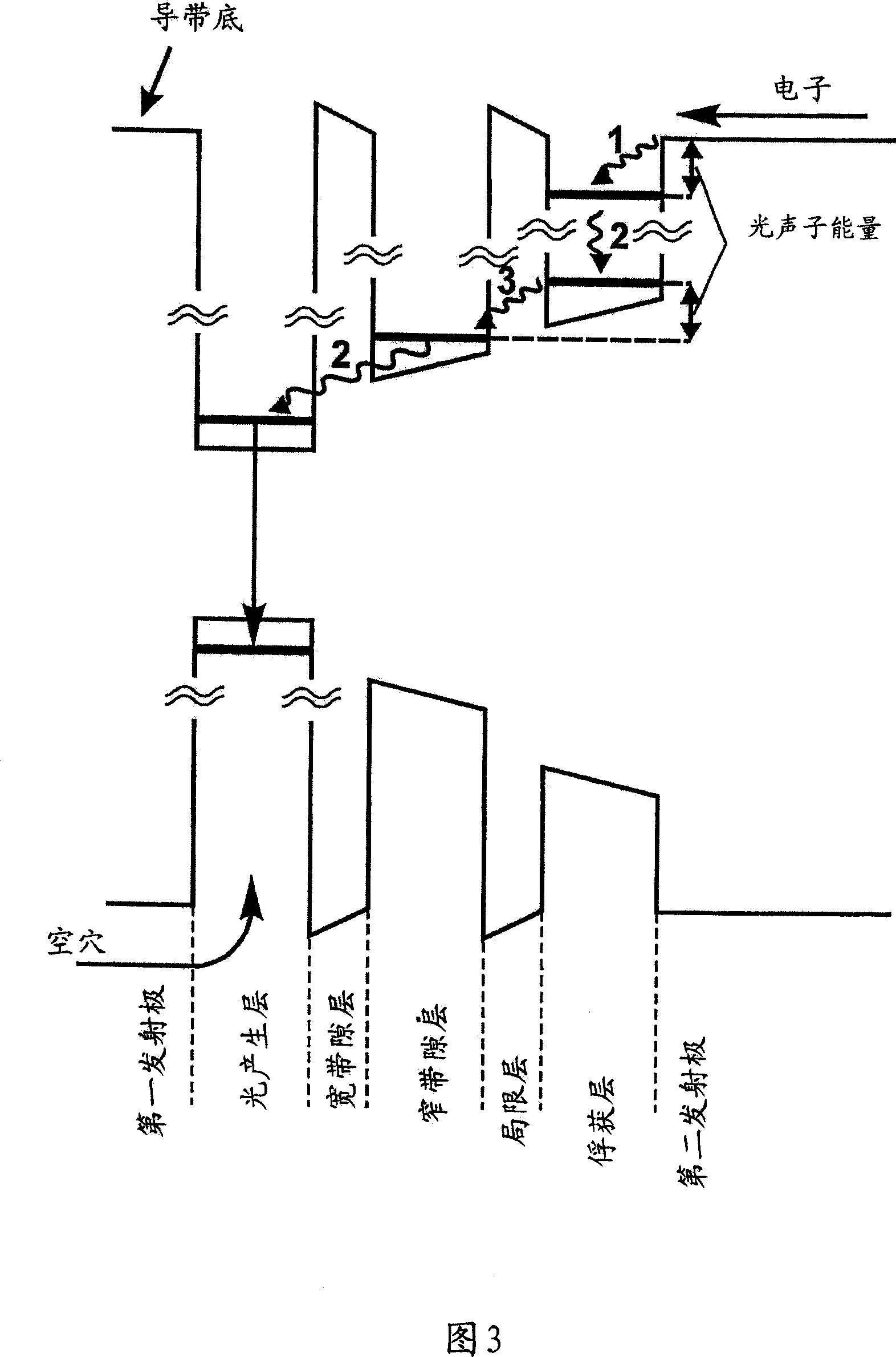
A strained semiconductor heterostructure (10) comprises an injection region comprising a first emitter layer (11) having p-type conductivity and a second emitter layer (12) having n-type conductivity, and a light generation layer (13) positioned between the first emitter layer (11) and the second emitter layer (12). An electron capture region (14) is positioned between the light generation layer (13) and the second emitter layer (12), said electron capture region comprising a capture layer (16) adjacent to the second emitter layer, and a confining layer (15) adjacent to said electron capture layer. According to the present invention, the widths and materials of the confining and capture layers (15, 16) are selected to provide energy difference between one of localized energy levels for electrons in the capture layer (16) and the conduction band bottom of the second emitter layer (12) equal to the energy of the optical phonon.
Owner:OPTOGAN OY
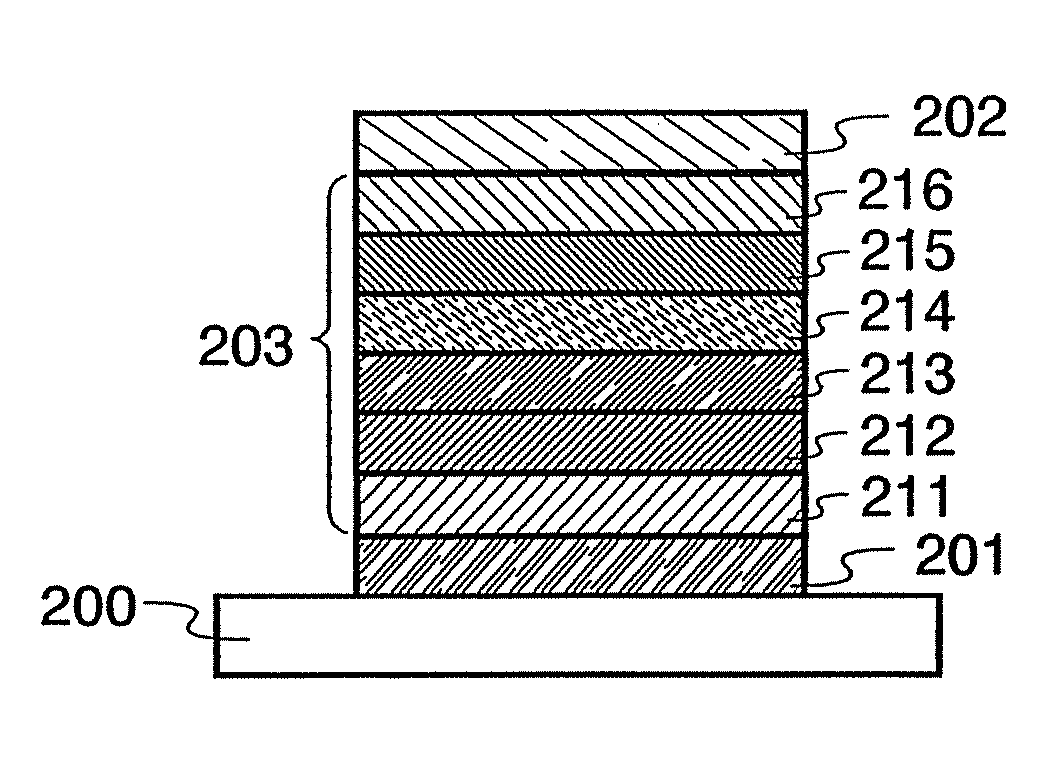
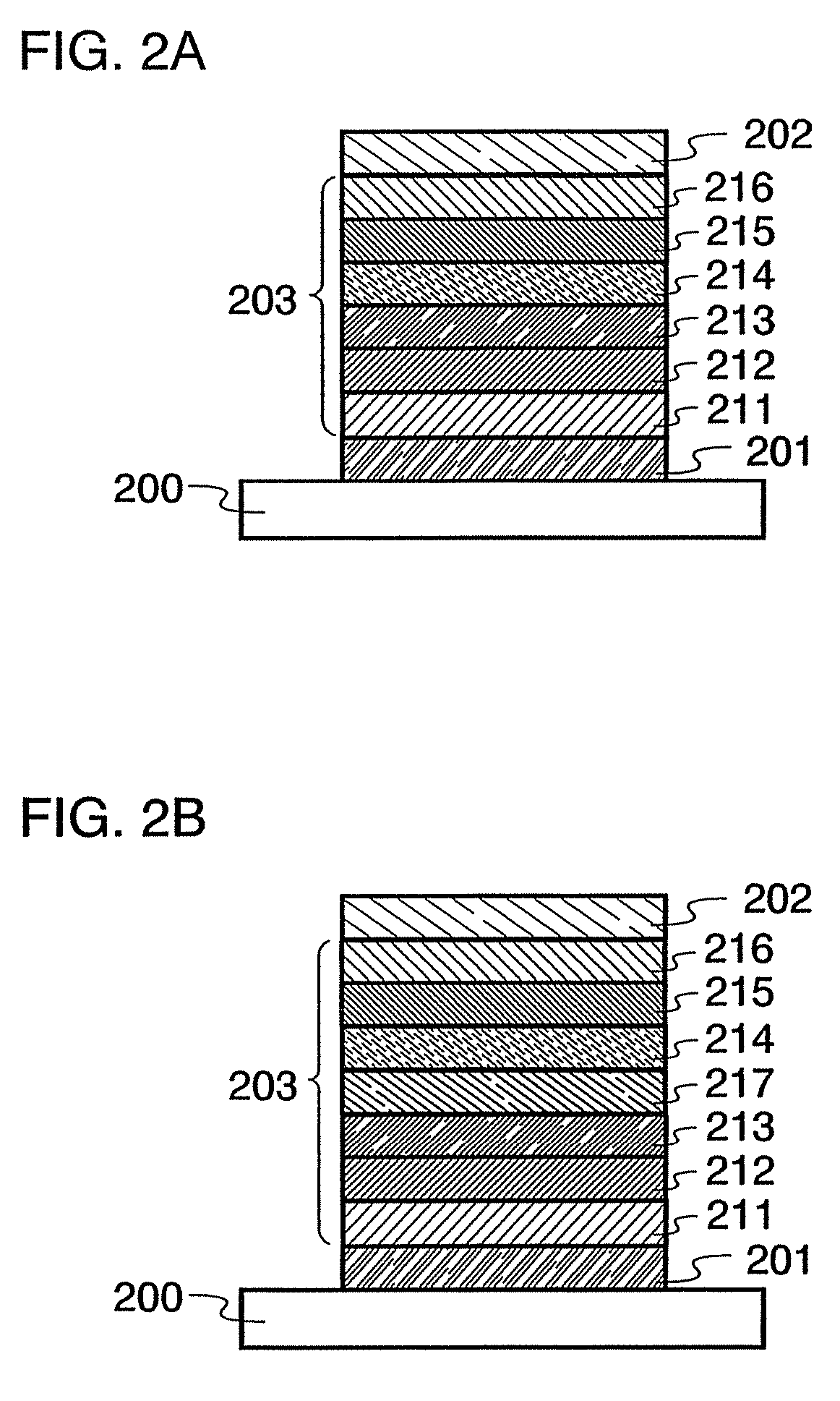
Organic electric field light-emitting element
ActiveUS20110175071A1Improve emission efficiencyImprove permanenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHost materialOrganic layer
An organic electric field light-emitting element, containing an anode; a cathode; and an organic layer provided therebetween and containing a first organic layer, a second organic layer and a third organic layer laminated in this order from the anode side, wherein the first organic layer contains a first host material in an amount of 10 to 90 mass % and a first hole-transporting phosphorescent material in an amount of 10 to 90 mass %; the second organic layer contains a second host material in an amount of 65 to 96.9 mass %, a second hole-transporting phosphorescent material in an amount of 3 to 30 mass %, and an electron-trapping material in an amount of 0.1 to 5 mass %; the third organic layer contain a hole-blocking material whose T1 is higher than that of the second hole-transporting phosphorescent material by at least 0.1 eV, wherein the second host material, the second hole-transporting phosphorescent material, and the electron-trapping material satisfy the following relationship:|HOMOt2|>|HOMOh2||HOMOt2|>|HOMOp2||LUMOh2|+0.25 eV<|LUMOt2||LUMOp2|+0.25 eV<|LUMOt2|and wherein the total average thickness of the first and second organic layers is at least 40 nm.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Semiconductor light emitting device
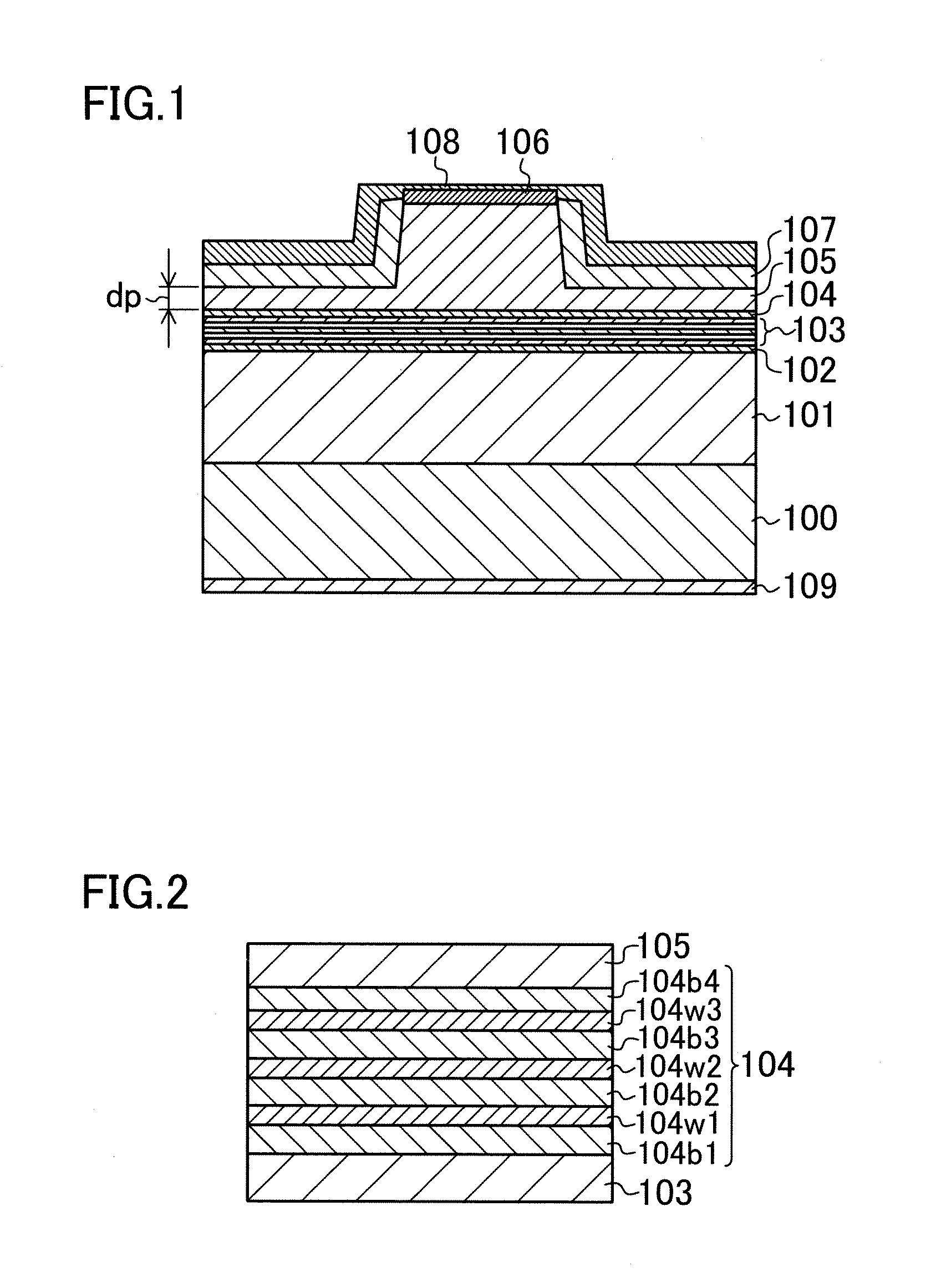
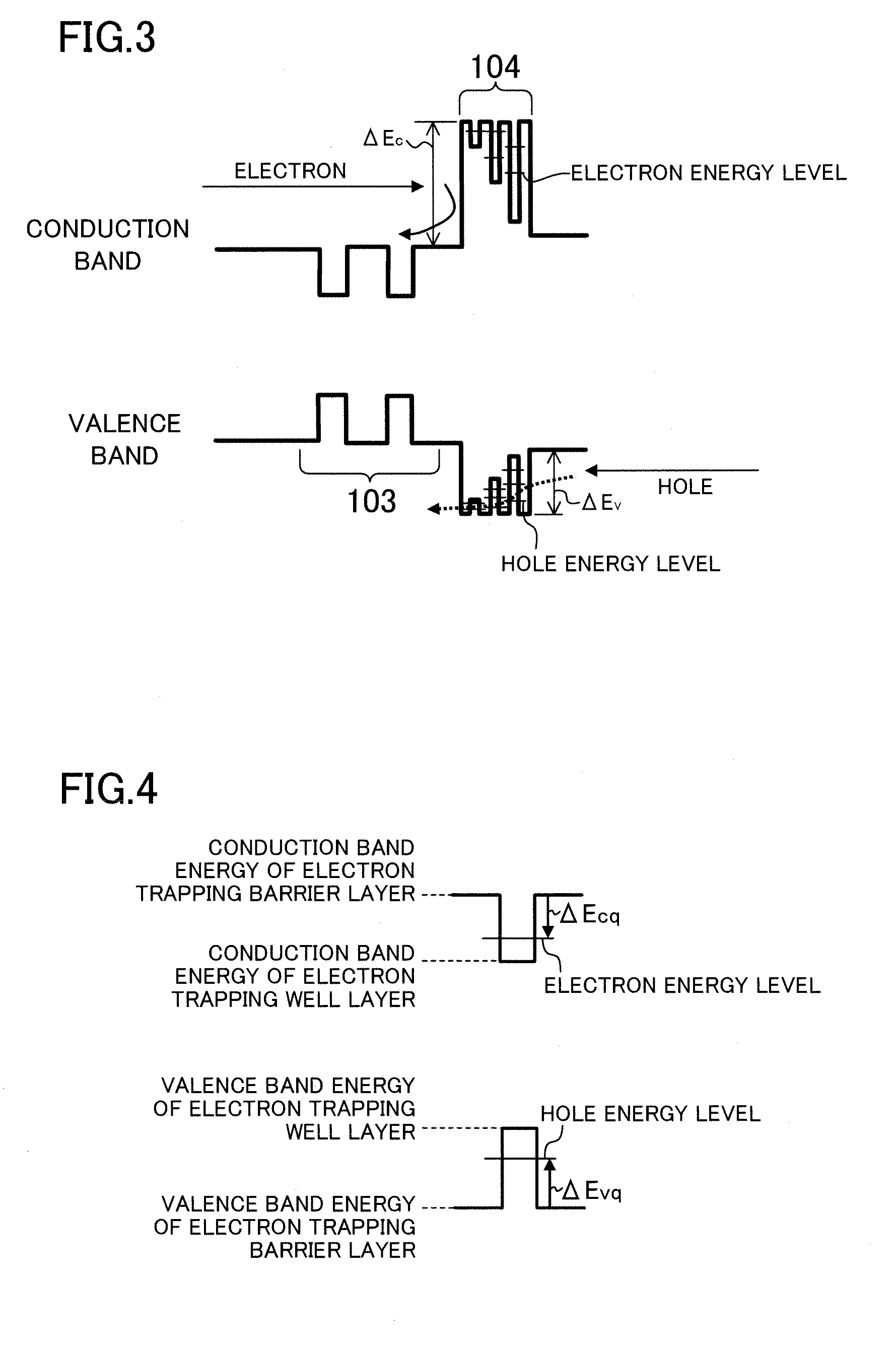
InactiveUS20110272667A1Reduce overflowOverflow of the electrons can be reducedOptical wave guidanceNanoopticsQuantum wellElectron capture
A semiconductor light emitting device includes: a first cladding layer made of a first conductivity type group III nitride semiconductor; an active layer formed on the first cladding layer; a quantum well electron barrier layer which is formed on the active layer, and includes electron trapping barrier layers made of AlxbGaybIn1-xb-ybN (0≦xb<1, 0<yb≦1, 0≦1-xb-yb<1), and two or more electron trapping well layers made of AlxwGaywIn1-xw-ywN (0≦xw<1, 0<yw≦1, 0≦1-xw-yw<1); and a second cladding layer which is formed on the quantum well electron barrier layer, and is made of a second conductive type group III nitride semiconductor. Each of the electron trapping well layers is formed between the electron trapping barrier layers, and band gap energies of the electron trapping well layers increase with decreasing distance from the active layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20060051563A1Excellent in light emitting life propertyImprove propertiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron holeElectron injection
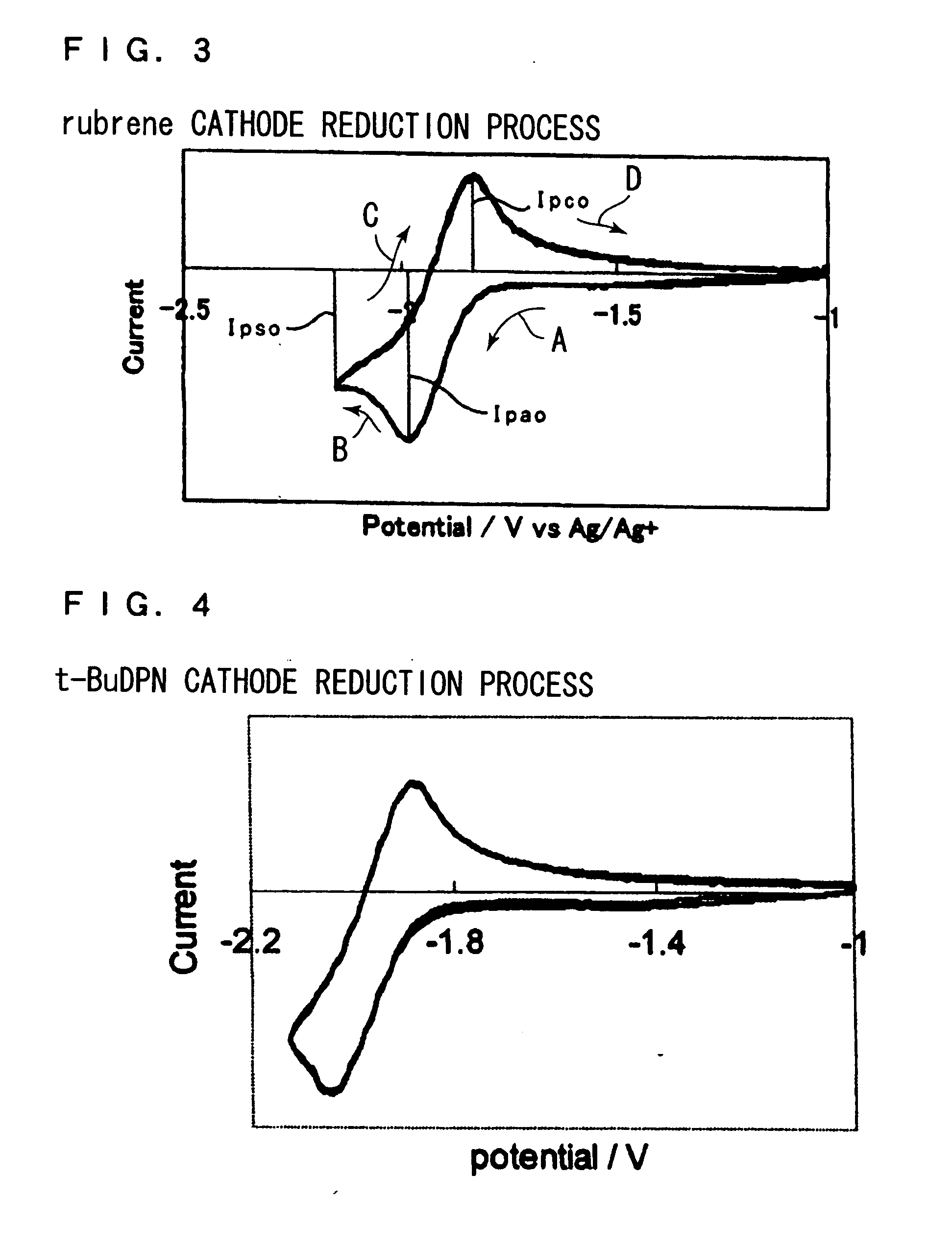
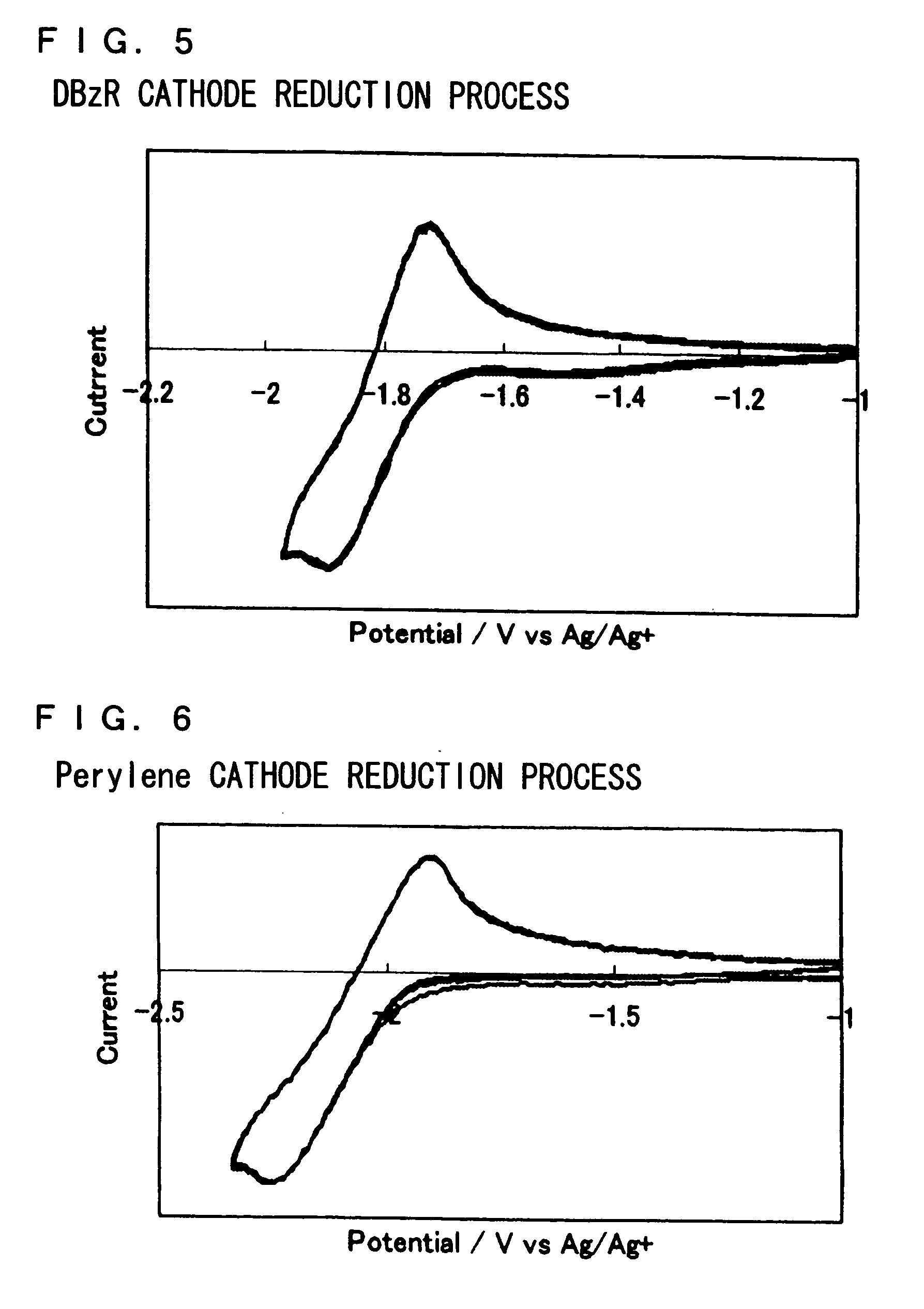
An organic electroluminescent device in which a light emitting layer is disposed between a hole injection electrode and an electron injection electrode, and a hole transporting layer is disposed between a hole injection electrode and a light emitting layer, wherein the hole transporting layer contains an electron trapping material exhibiting a reversible cathode reduction process in cyclic voltammetry measurement and having a reduction potential smaller than that of a hole transporting material contained in the hole transporting layer, or wherein the electron transporting layer contains a hole trapping material exhibiting a reversible anode reduction process in cyclic voltammetry measurement and having an oxidation potential smaller than that of an electron transporting material contained in the electron transporting layer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method of manufacturing SONOS flash memory device
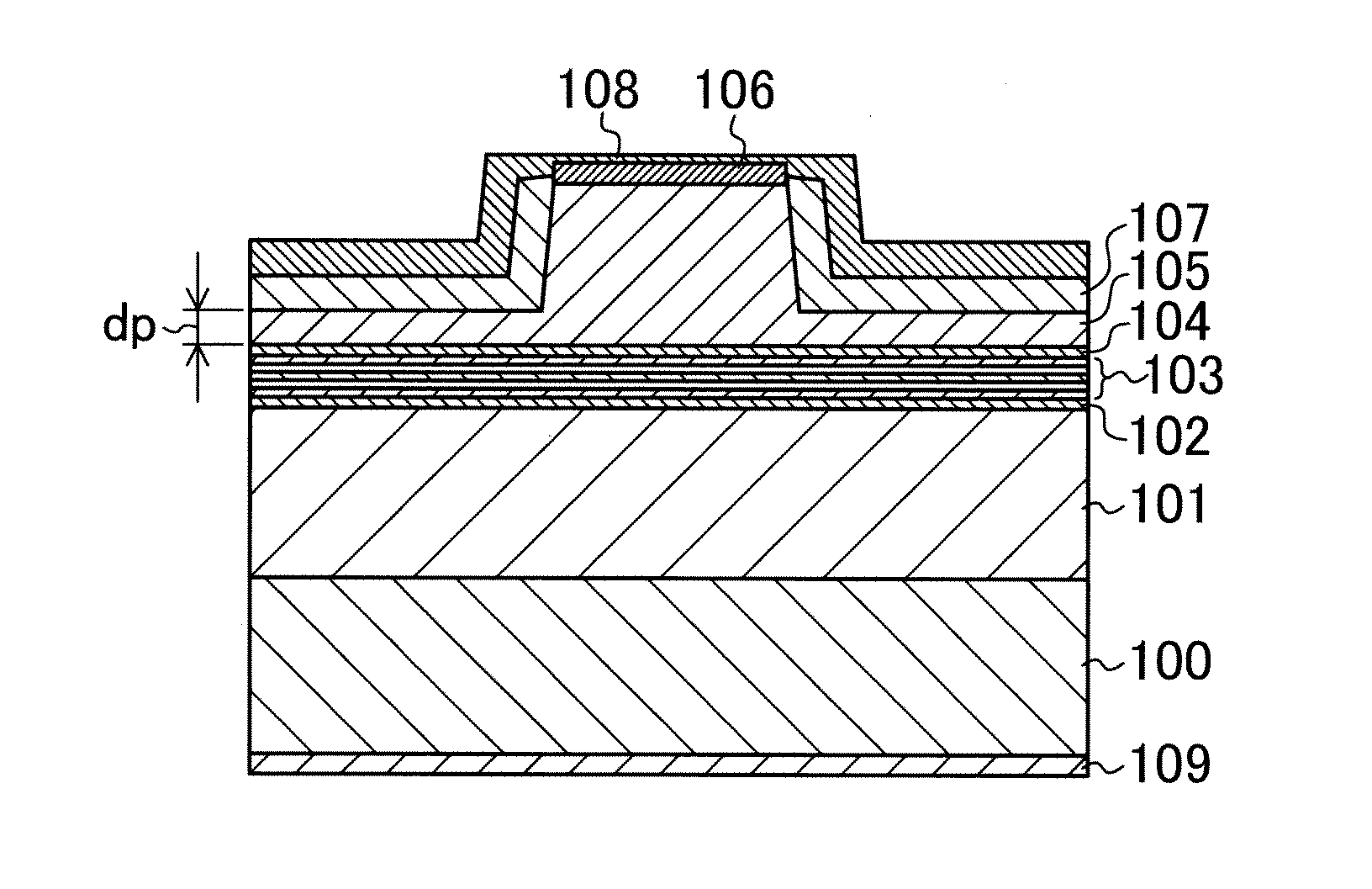
InactiveUS6849514B2Prevent travelEnsure device characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectron captureNitride
A method of manufacturing a SONOS flash memory device is disclosed. The disclosed method comprises the steps of forming a lower oxide layer, a tunnel nitride layer, a sacrificial oxide layer, and an insulating layer for a hard mask in sequence on a semiconductor substrate; removing a portion of the insulating layer by an etching process; forming spacers on sidewalls of the insulating layer etched; removing some part of the sacrificial oxide layer and the tunnel nitride layer by an etching process using the insulating layer and the spacers as a mask; removing the insulating layer, the spacers, and the sacrificial oxide layer; removing a portion of the lower oxide layer by an etching process using the tunnel nitride layer etched as a mask; depositing an upper oxide layer and a polysilicon layer in sequence over the resulting structure; and forming a gate having two separate tunnel nitride layer parts by removing some parts of the polysilicon layer, the upper oxide layer, and the tunnel nitride layer in sequence by an etching process. By separating the tunnel nitride layer into two parts, movement of electrons captured in the tunnel nitride layer can be completely prevented. Therefore, the present invention can obviate device malfunction, thereby ensuring device characteristics and reliability.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sulphide electron capture luminous material
InactiveCN101870867AImprove stabilityMoisture decomposition does not occurLuminescent compositionsInfraredUltraviolet
The invention discloses a sulphide electron capture luminous material, which comprises a ZnS substrate material, wherein main activating agents containing Pb and Cu acid compounds are added into the ZnS substrate material, at least one kind of co-activating agents containing Sm, Eu, Er, Yb and Mn acid compounds is added into the ZnS substrate material, the mixture is dried after being uniformly mixed, and high-temperature sintering is carried out in protective atmosphere. After ultraviolet ray absorption, the materials have momentary sunset glow, and can generate green light under the stimulation of infrared rays between 800 and 2000 nm. The electron capture luminous material of the invention can be used for detecting, tracking, checking and identifying invisible near infrared light. The invention can be widely applied to the multi-disciplinary technical fields such as near infrared laser detection, laser light spot display, optical fiber communication indication, optical information storage, X-ray image processing, infrared imaging and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI KEYAN PHOSPHOR TECH
Method of and apparatus for ionizing sample gas
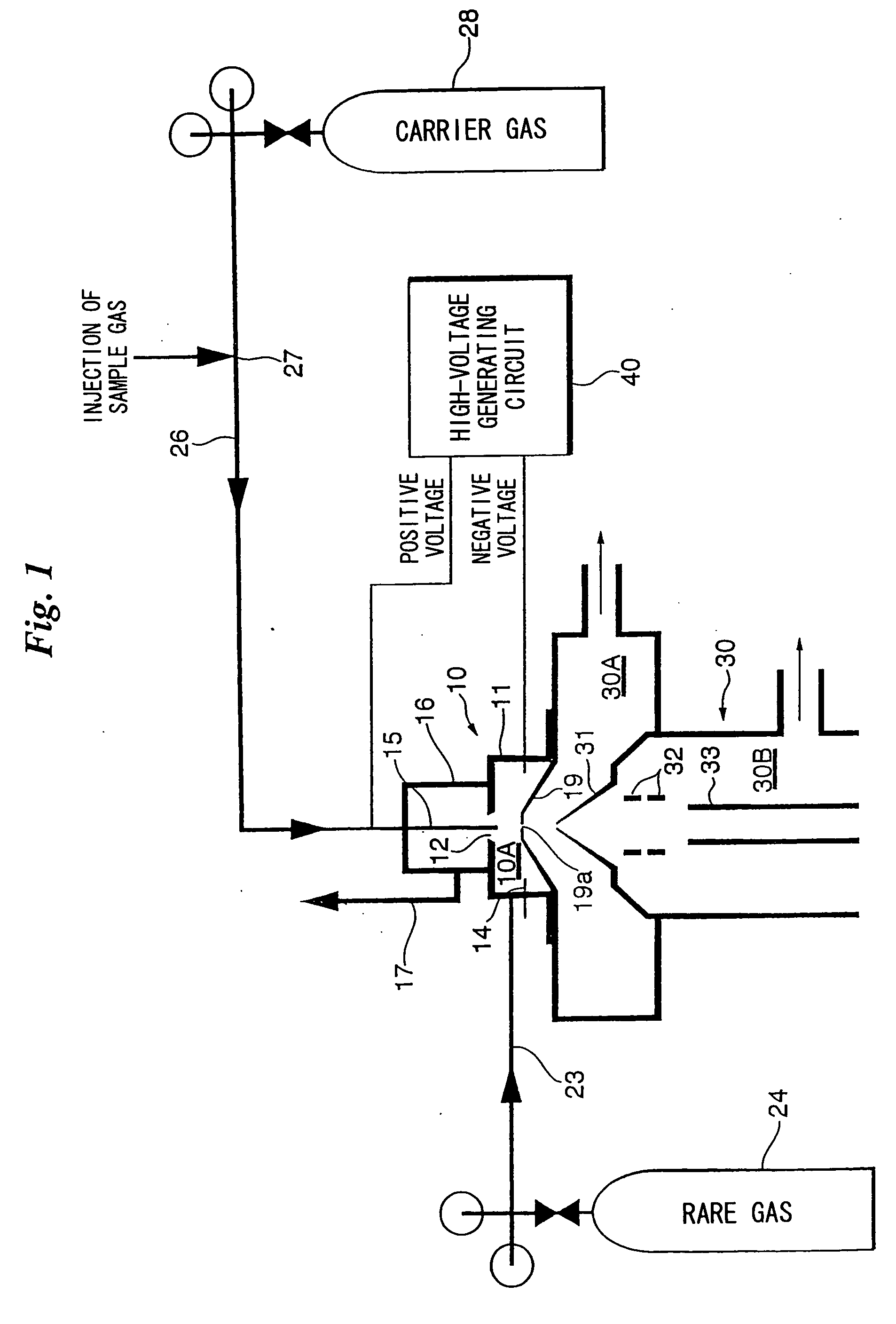
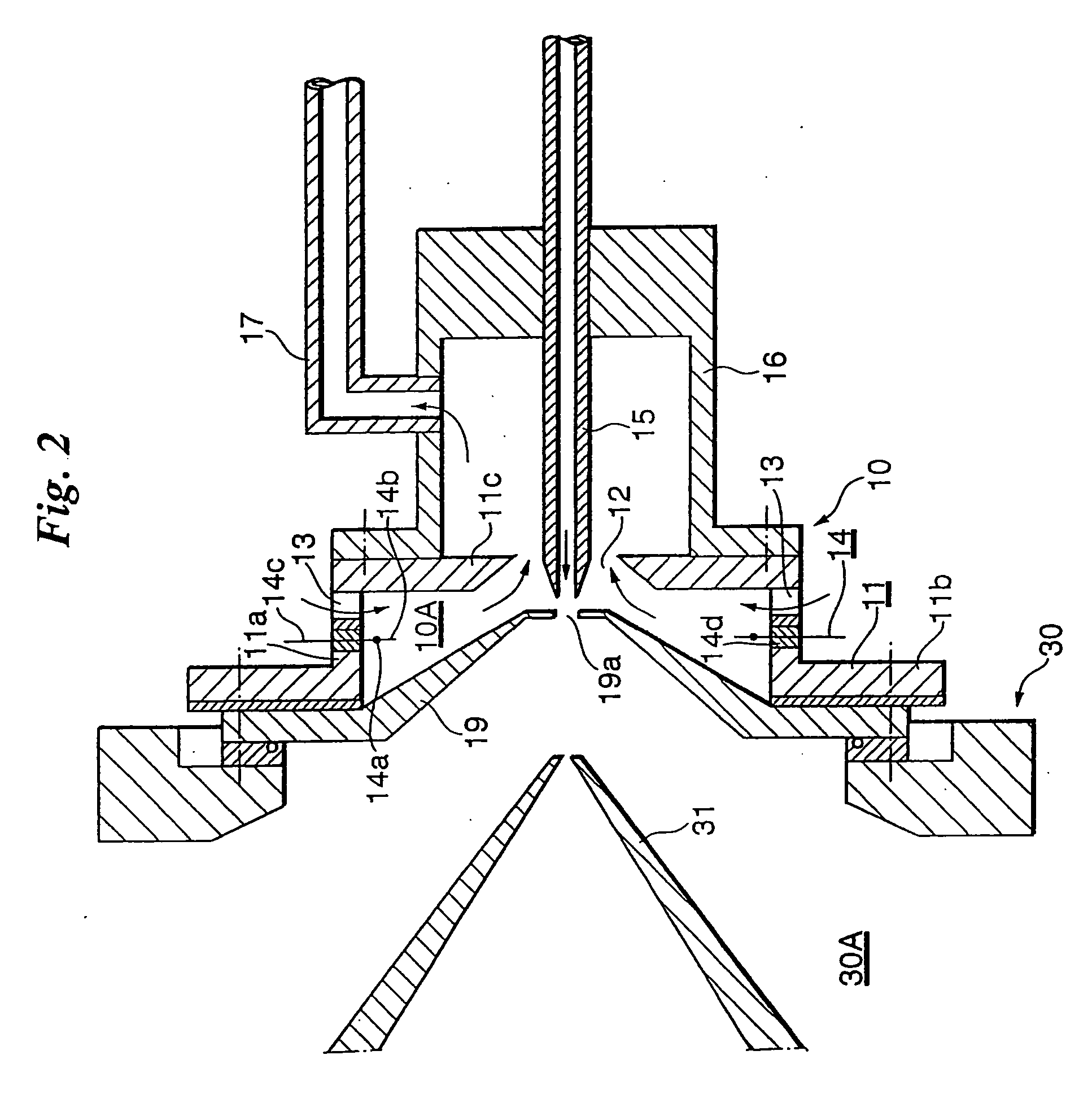
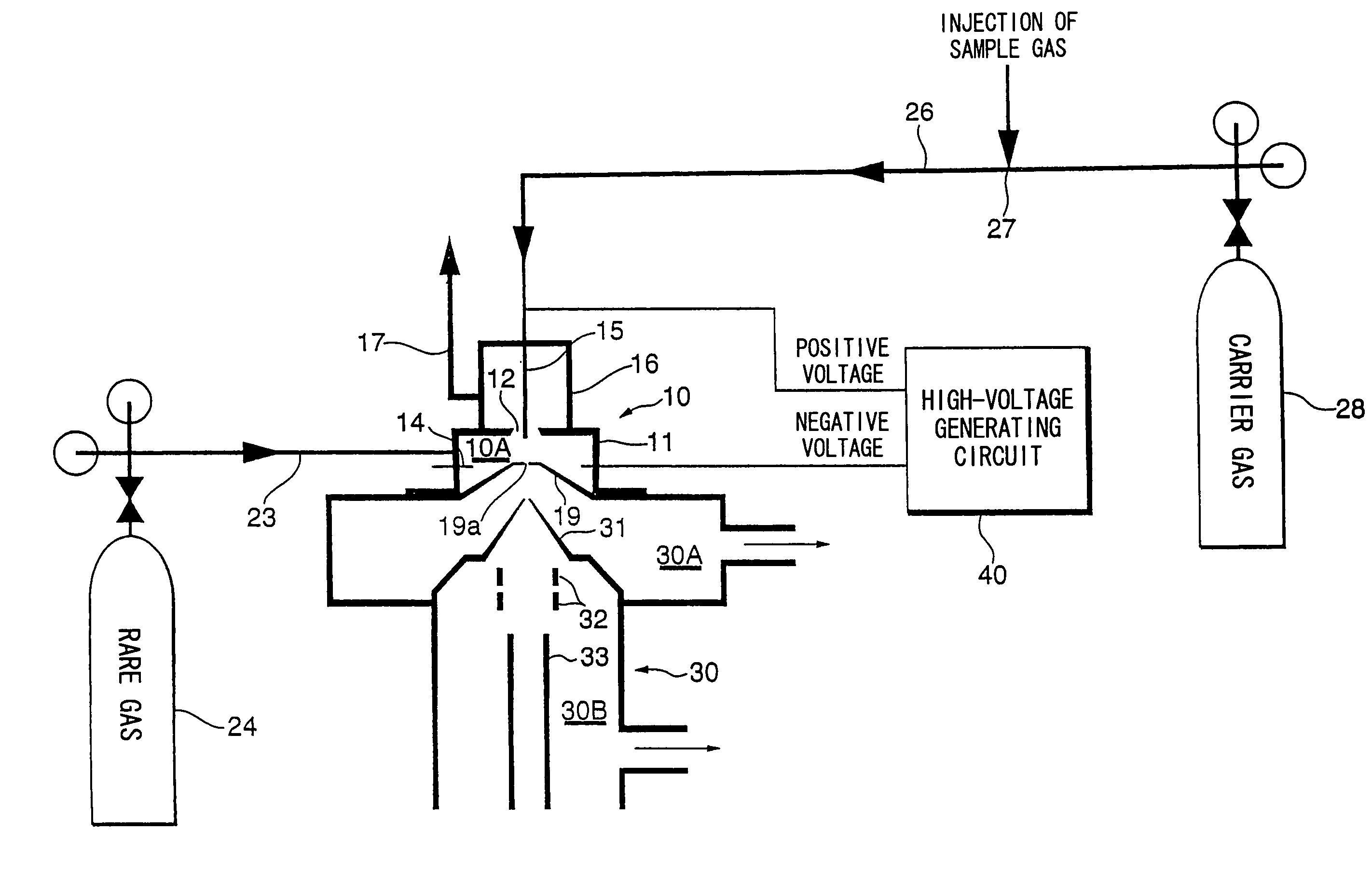
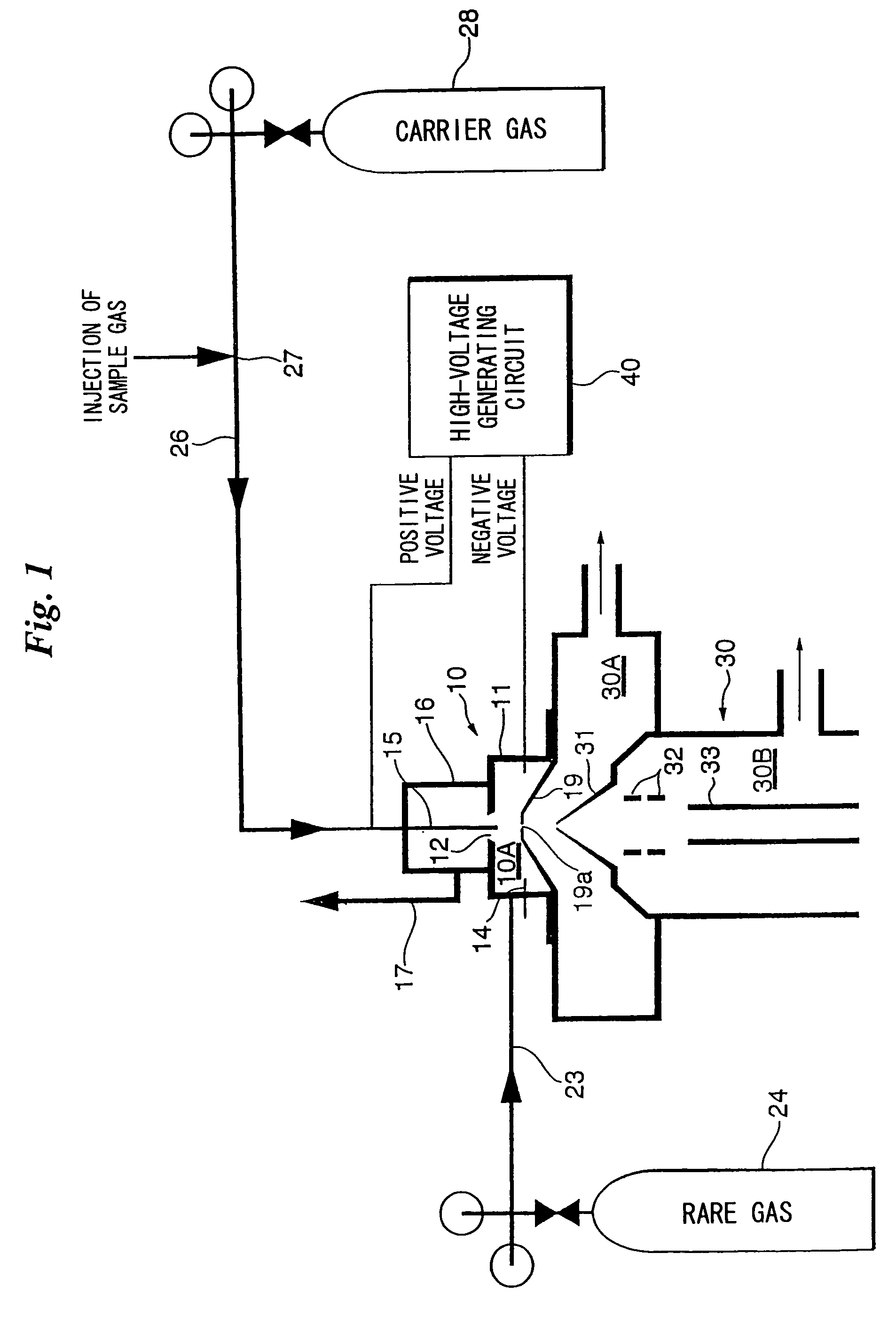
ActiveUS20050001161A1Improve ionization efficiencyAvoid reorganizationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansNoble gasPenning ionization
Ionization efficiency is improved in Penning ionization capable of selective ionization. A metastable excited species of a rare gas is produced by introducing the rare gas into an ionization space and inducing an electrical discharge, a sample gas is introduced into the ionization space and Penning ionization is produced owing to collision between the sample gas and the metastable excited species of the rare gas. Electrons released from atoms or molecules positively ionized by Penning ionization are captured by applying a positive potential to an electron-capture electrode placed in the ionization space, and the atoms or molecules positively ionized are guided to a mass analyzer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF YAMANASHI
Method of and apparatus for ionizing sample gas
ActiveUS7091493B2Improve ionization efficiencyAvoid reorganizationScattering properties measurementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNoble gasPenning ionization
Ionization efficiency is improved in Penning ionization capable of selective ionization. A metastable excited species of a rare gas is produced by introducing the rare gas into an ionization space and inducing an electrical discharge, a sample gas is introduced into the ionization space and Penning ionization is produced owing to collision between the sample gas and the metastable excited species of the rare gas. Electrons released from atoms or molecules positively ionized by Penning ionization are captured by applying a positive potential to an electron-capture electrode placed in the ionization space, and the atoms or molecules positively ionized are guided to a mass analyzer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF YAMANASHI
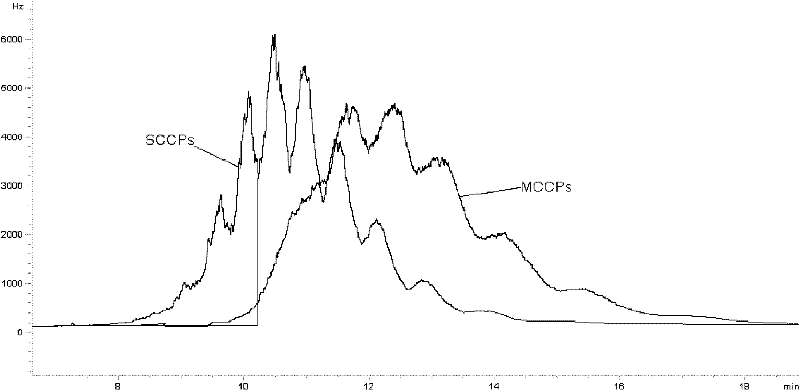
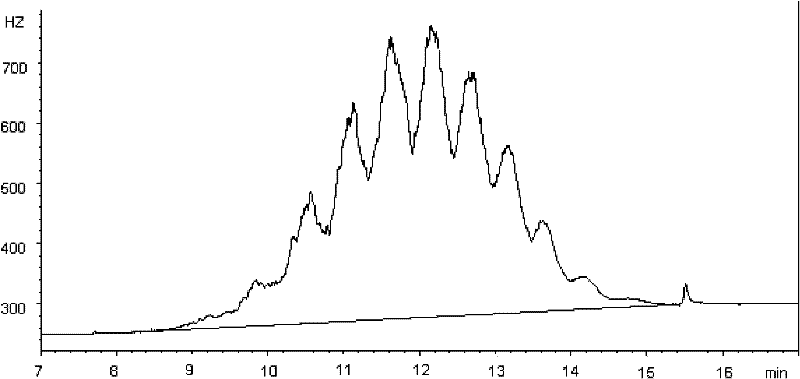
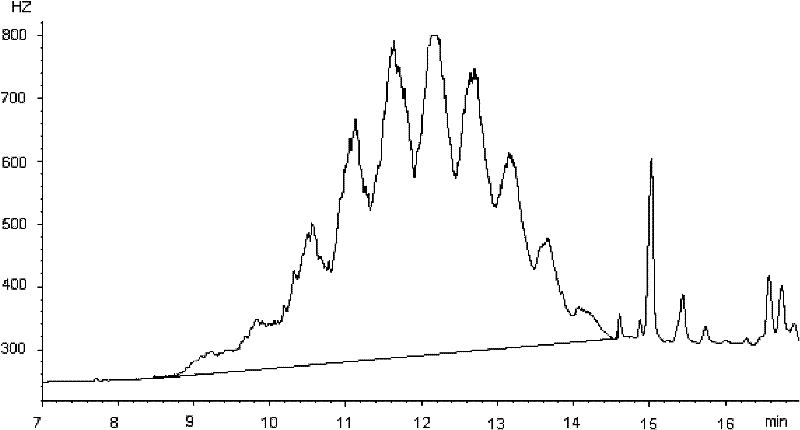
Method for determination of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in plastic, rubber and textile materials
InactiveCN102288691AEffective interferenceEffectively remove interferenceComponent separationPurification methodsGas phase
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, and specifically relates to a method for determining short-chain chlorinated paraffins in plastics, rubber, and textile materials. (2) purification by sulfonation with concentrated sulfuric acid; and (3) detection step (2) using gas chromatography-electron capture detector or gas chromatography-negative chemical ionization (NCI) mass spectrometry detector The content of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in the obtained purified samples. Beneficial effects of the present invention: Utilize concentrated sulfuric acid sulfonation purification method, can effectively remove interference, use gas chromatography-electron capture detector and NCI mass spectrometry detector to detect medium and short-chain chlorinated paraffins in plastics, rubber, textile materials, can realize Accurate quantification; according to the specific mass spectrum of short-chain chlorinated paraffins, the interference of medium and long-chain chlorinated paraffins can be effectively eliminated, making the qualitative more accurate, the selectivity stronger, and the sensitivity higher.
Owner:SGS STANDARD TECHNICAL SERVICES SHANGHAI CO LTD
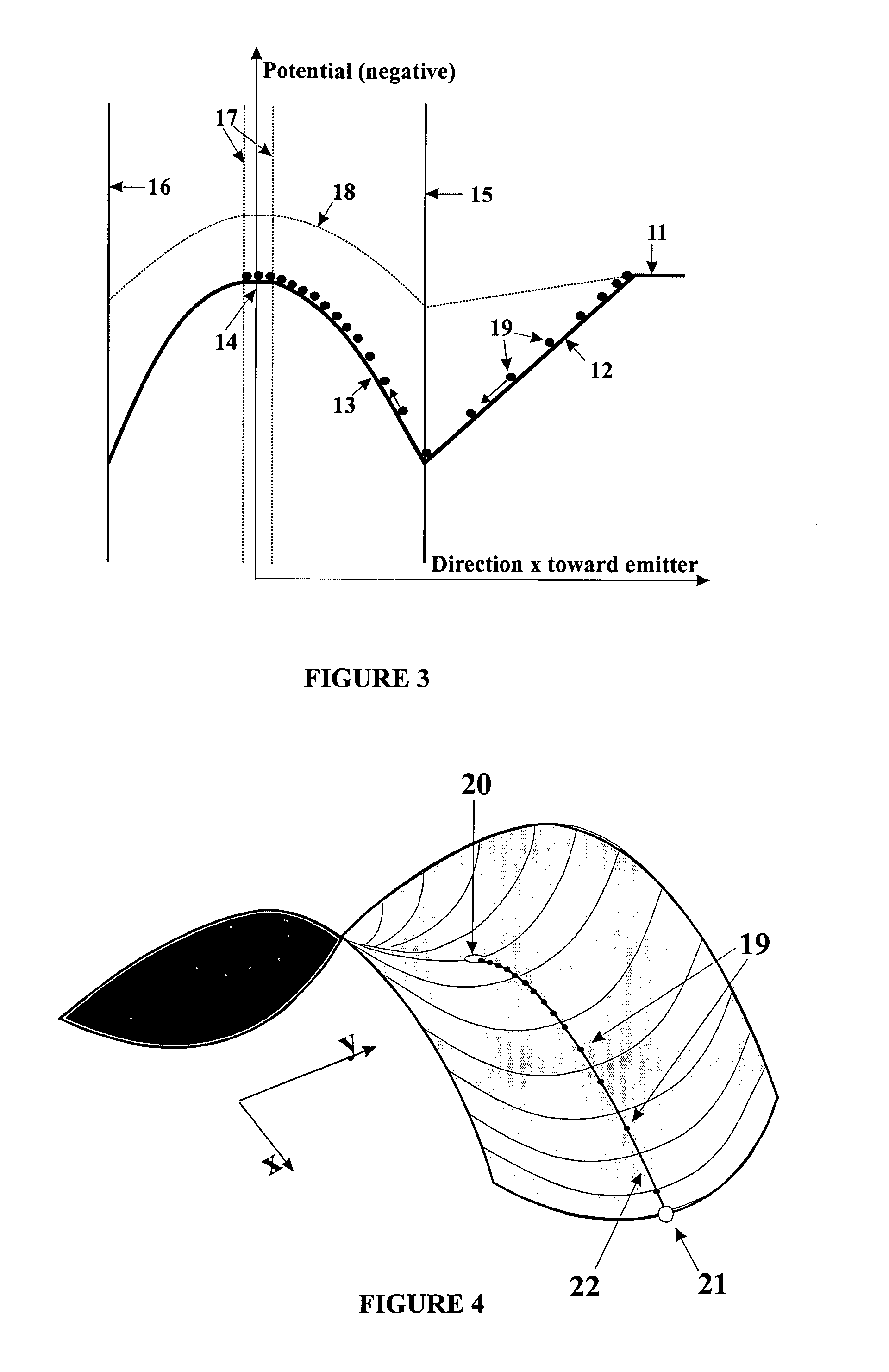
Ion fragmentation in RF ion traps by electron capture with magnetic field
InactiveUS20050017165A1Prevent ionizationStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryElectron capture
The invention relates to a method and device for the fragmentation of macromolecules, preferably biomolecules, by electron capture in RF quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometers according to Wolfgang Paul. The invention comprises steering a beam of low energy electrons through a magnetic guide field exactly into an ion cloud in the center of the ion trap.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
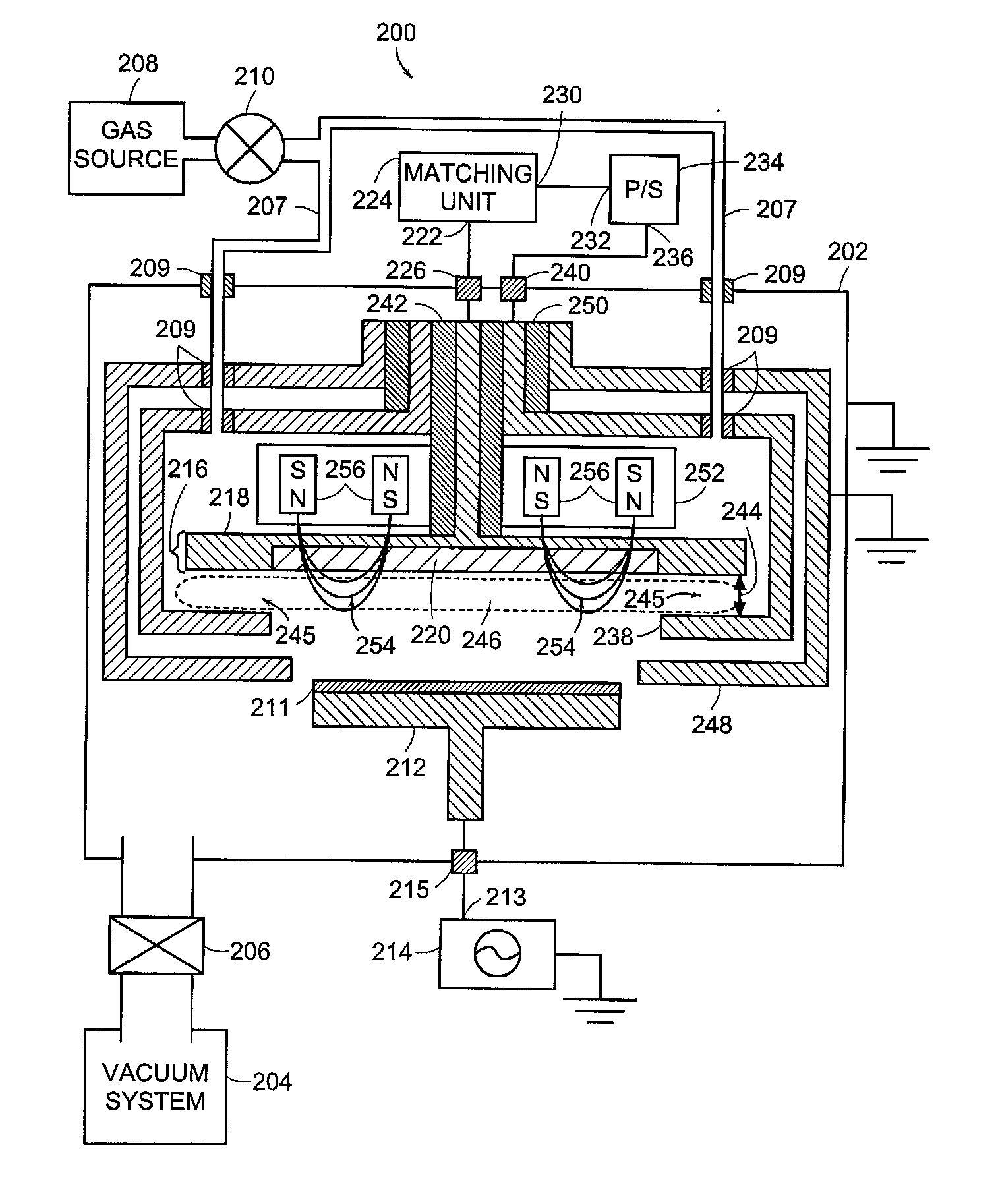
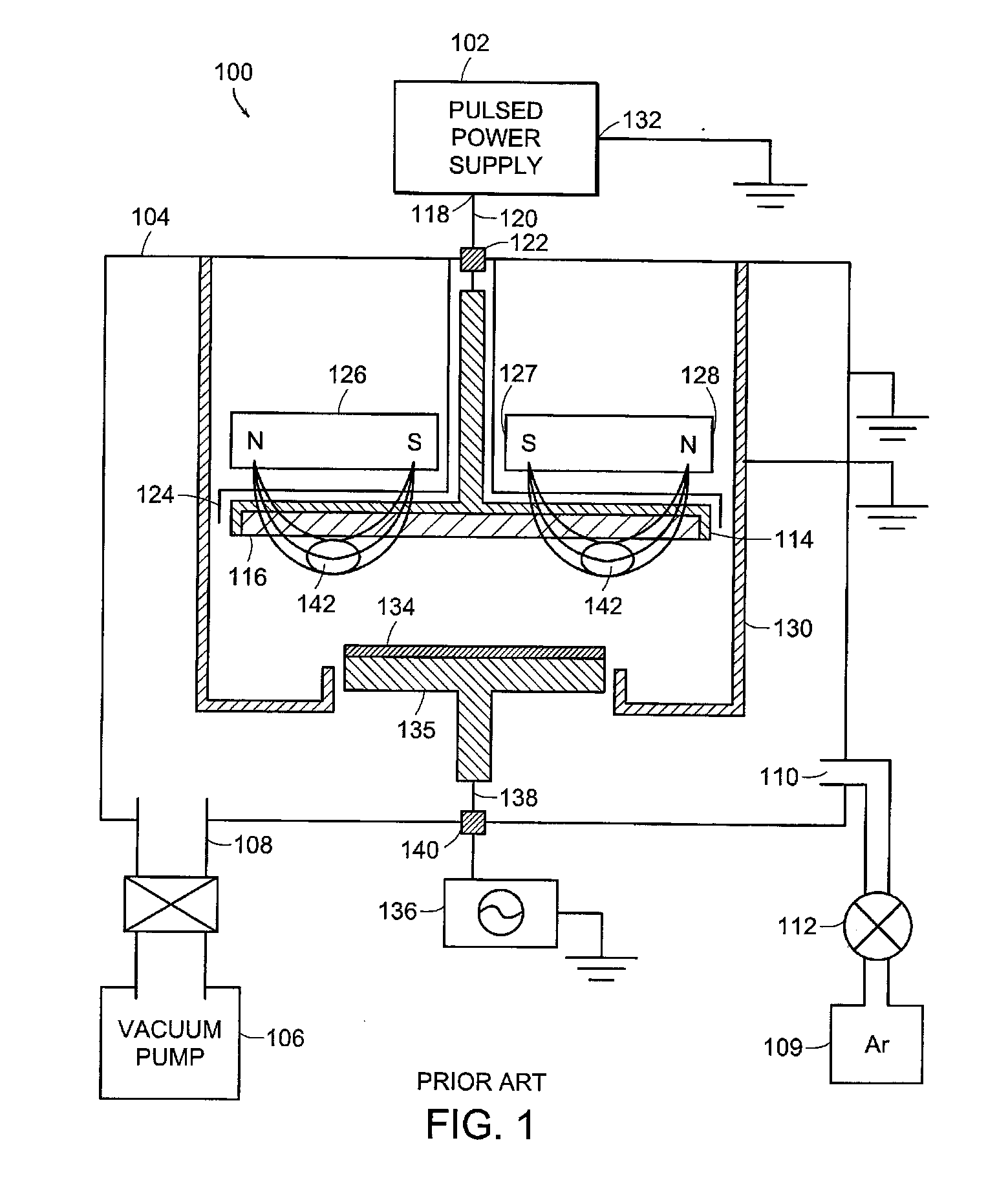
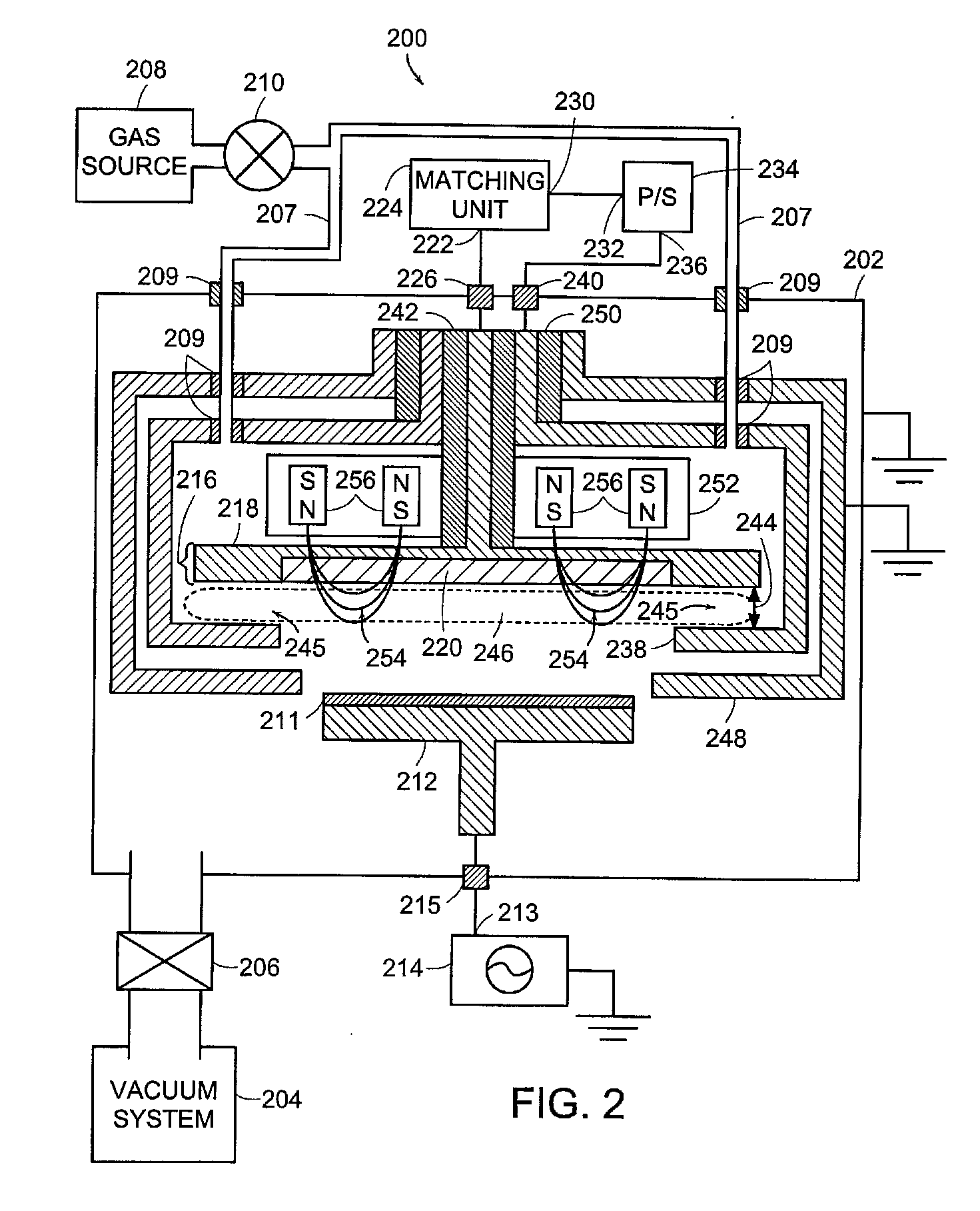
High-Power Pulsed Magnetron Sputtering
Magnetically enhanced sputtering methods and apparatus are described. A magnetically enhanced sputtering source according to the present invention includes an anode and a cathode assembly having a target that is positioned adjacent to the anode. An ionization source generates a weakly-ionized plasma proximate to the anode and the cathode assembly. A magnet is positioned to generate a magnetic field proximate to the weakly-ionized plasma. The magnetic field substantially traps electrons in the weakly-ionized plasma proximate to the sputtering target. A power supply produces an electric field in a gap between the anode and the cathode assembly. The electric field generates excited atoms in the weakly ionized plasma and generates secondary electrons from the sputtering target. The secondary electrons ionize the excited atoms, thereby creating a strongly-ionized plasma having ions that impact a surface of the sputtering target to generate sputtering flux.
Owner:ZOND
Method capable of simultaneously measuring organochlorine pesticide concentration and synthetic musk concentration in human serum
The invention relates to a method capable of simultaneously measuring organochlorine pesticide concentration and synthetic musk concentration in human serum. According to the method, the aim of measuring organochlorine pesticide and synthetic musk in the serum is realized through a chemical pretreatment method of liquid-liquid extraction, gel permeation chromatography and silica gel alumina column, in combination with a detection technology of gas chromatography-electron capture detection (GC-ECD) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The method provided by the invention belongs to the technical field of physico-chemical analysis measurement of organic chemicals. In the method provided by the invention, the serum pretreatment process comprises organic solvent liquid-liquid extraction, gel permeation chromatographic column degreasing, silica gel alumina column purification, separation and concentrating to constant volume, finally, GC-ECD and GC-MS are used for detection, detection spectrograms of organochlorine pesticide and synthetic musk in serum sample are respectively obtained, and concentration values of organochlorine pesticide and synthetic musk in the serum are calculated through a special formula. The method provided by the invention is a steady, relatively high-sensitivity and high-precision effective measurement method.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Semiconductor heterostructure
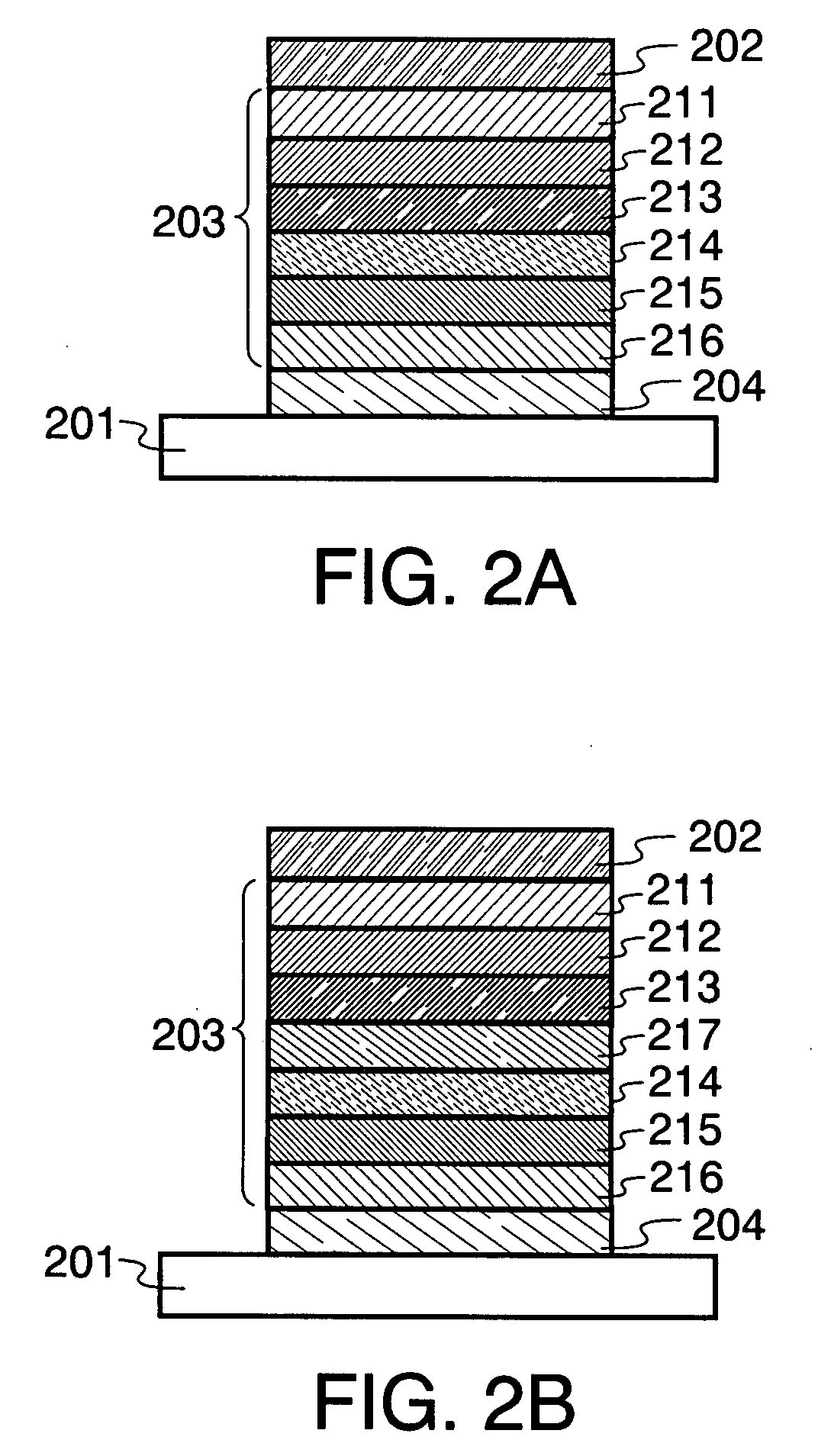
InactiveCN101057343ASame lattice constantPrevent escapeNanoopticsSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor heterostructuresConduction band
A strained semiconductor heterostructure (10) comprises an injection region comprising a first emitter layer (11) having p-type conductivity and a second emitter layer (12) having n-type conductivity, and a light generation layer (13) positioned between the first emitter layer (11) and the second emitter layer (12). An electron capture region (14) is positioned between the light generation layer (13) and the second emitter layer (12), said electron capture region comprising a capture layer (16) adjacent to the second emitter layer, and a confining layer (15) adjacent to said electron capture layer. According to the present invention, the widths and materials of the confining and capture layers (15, 16) are selected to provide energy difference between one of localized energy levels for electrons in the capture layer (16) and the conduction band bottom of the second emitter layer (12) equal to the energy of the optical phonon.
Owner:OPTOGAN OY
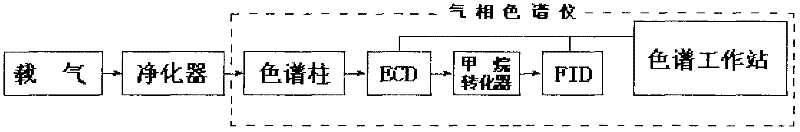
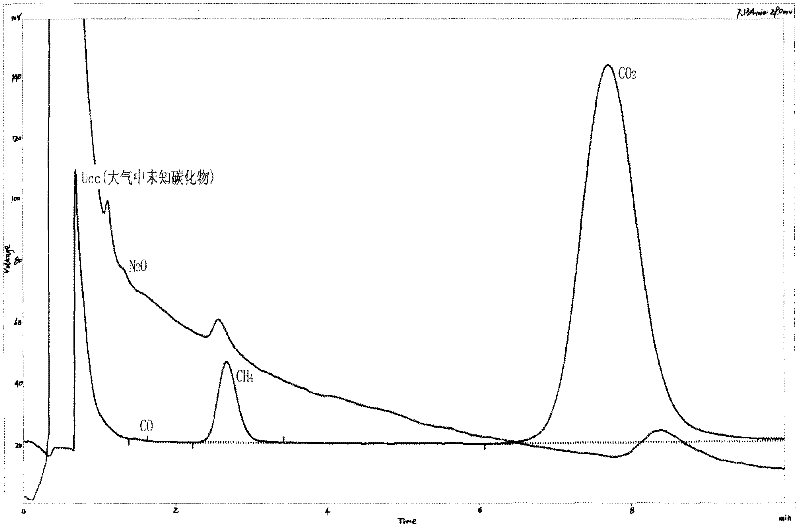
Method for analyzing N2O, CO, CH4 and CO2 in atmosphere with one injection by gas chromatography
InactiveCN102495158AReduce precision errorShort measuring cycleComponent separationHydrogenElectron capture detector
The present invention relates to a method for analyzing N2O, CO, CH4 and CO2 in atmosphere with one injection by gas chromatography. According to the method, a carrier gas with the purity less than 10-5% passes through a purifier under the output pressure of 0.20-0.60 Mpa, such that the purity of the purified carrier gas is less than 10-6% or 10-7%; the purified carrier gas is introduced into a chromatographic column loaded with a sample requiring detection in a gas chromatograph, after an adsorption effect and a desorption effect, N2O, CO, CH4 and CO2 in the sample requiring detection sequentially enter an electron capture detector, a methane converter and a hydrogen flame ionization detector perform detections at the temperature of 90-350 DEG C; finally the data from the electron capture detector and the hydrogen flame ionization detector are concurrently input to a chromatographic work station in the gas chromatograph to obtain the analysis result chromatogram. The method of the present invention is simple, and is easy to operate. With the method of the present invention, the data accuracy error can be effectively reduced, and the sample measurement period can be shortened.
Owner:LANZHOU CENT FOR OIL & GAS RESOURCES INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CAS
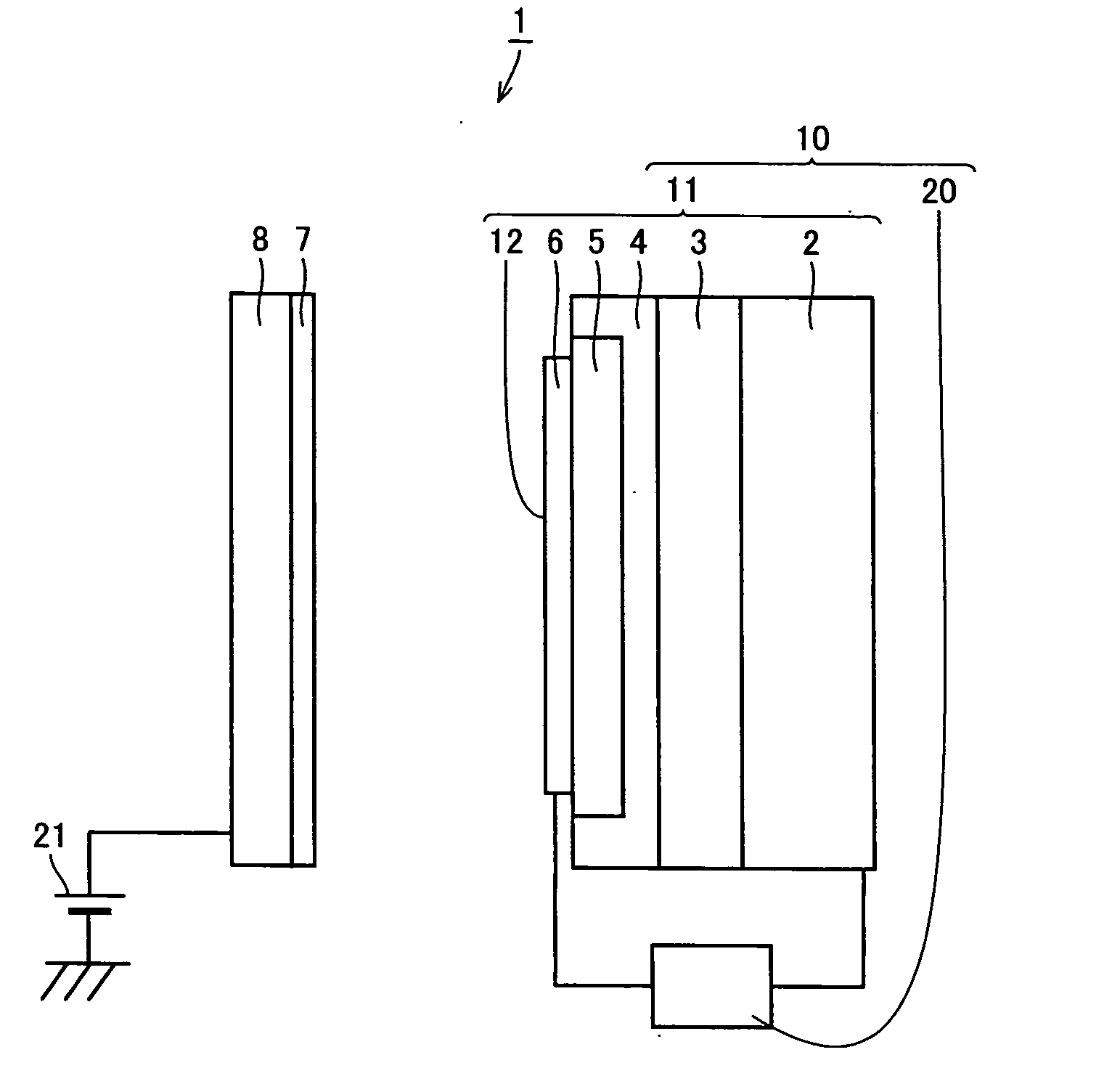
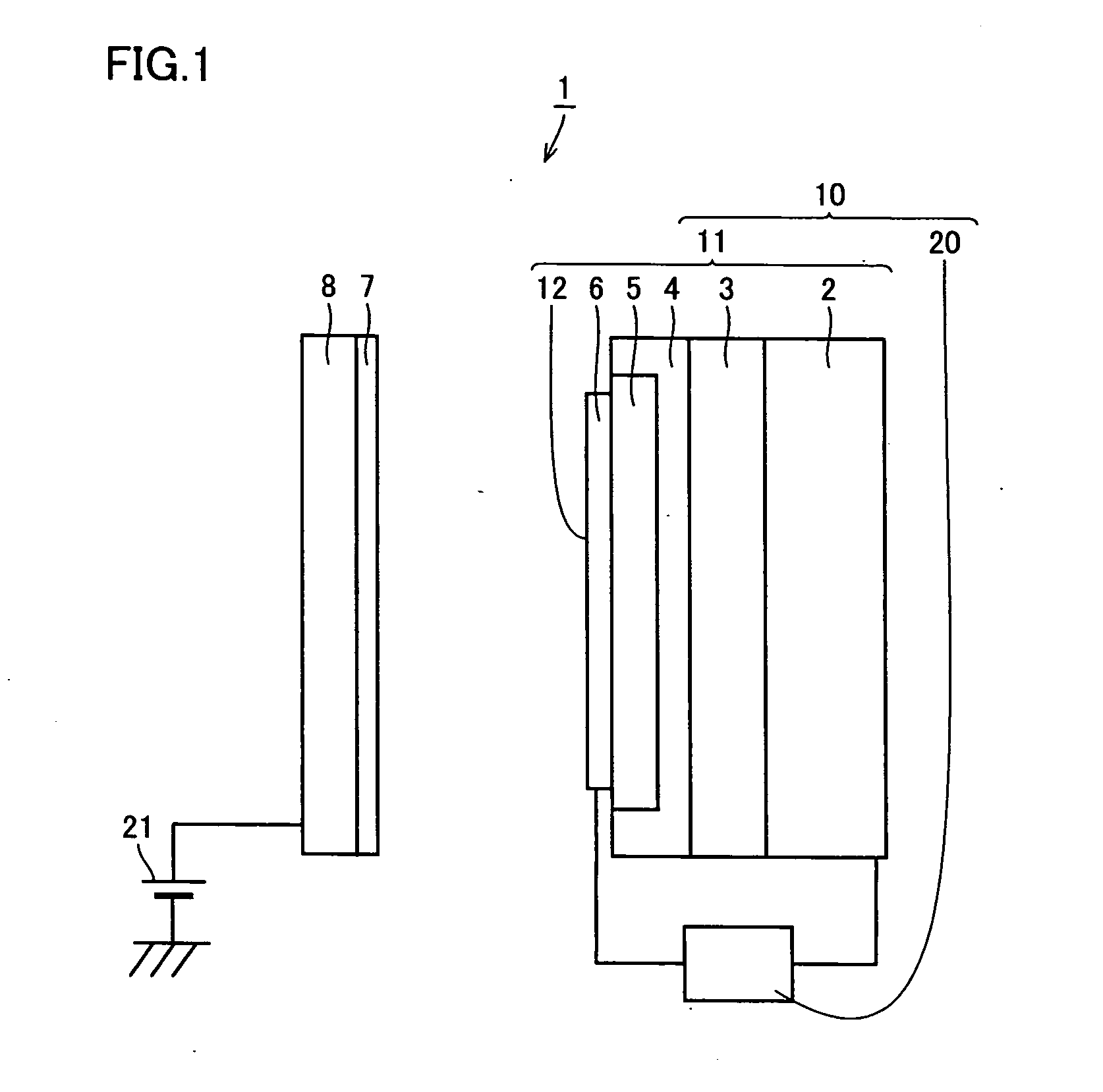
Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device
ActiveUS8247804B2Improve carrier balanceEmit light moreSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionElectron capture
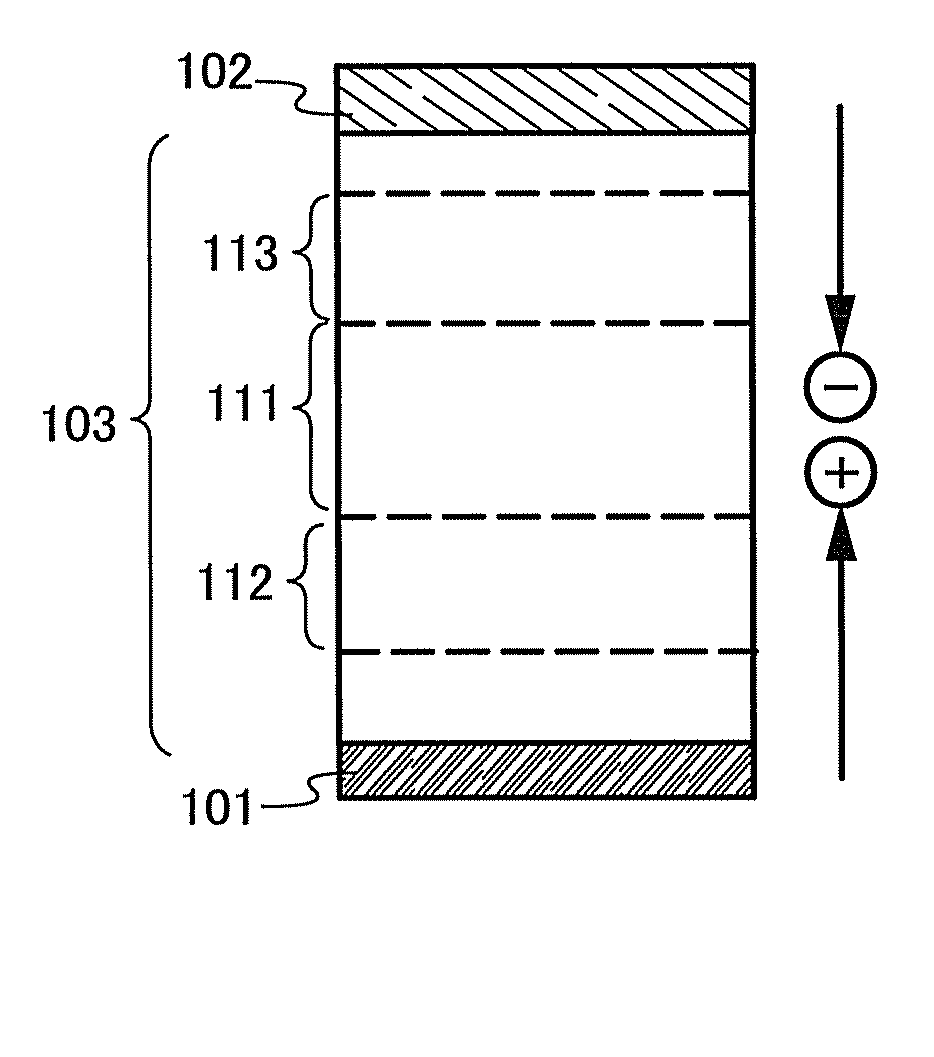
Disclosed is a light-emitting element with a good carrier balance and manufacturing method thereof which does not require the formation of the heterostructure. The light-emitting element includes an organic compound film containing a first organic compound as the main component (base material) between an anode and a cathode, wherein the organic compound film is provided in contact with the anode and with the cathode. The first organic compound further includes a light-emitting region to which a light-emitting substance is added and includes a hole-transport region to which a hole-trapping substance is added and / or an electron-transport region to which an electron-trapping substance is added. The hole-transport region is located between the light-emitting region and the anode, and the electron-transport region is located between the light-emitting region and the cathode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method to monitor process charging effect
InactiveUS6958249B1The process is simple and effectiveSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectron captureOxide
A new method is provided for monitoring the effect of electron charging during the creation of a semiconductor device. The method of the invention makes use of electron trapping that occurs as a result of FN tunneling in a layer of interlayer oxide of an EEPROM device. The electron trapping is monitored under conditions of processing. After the electron trapping has occurred, the rate of discharge of the trapped electron charge is measured during Wafer Acceptance Testing (WAT).
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Quantum trap structure of semiconductor light-emitting diode for increasing internal quantum efficiency
ActiveCN1937267AImprove leakage currentImprove efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum efficiencyQuantum well
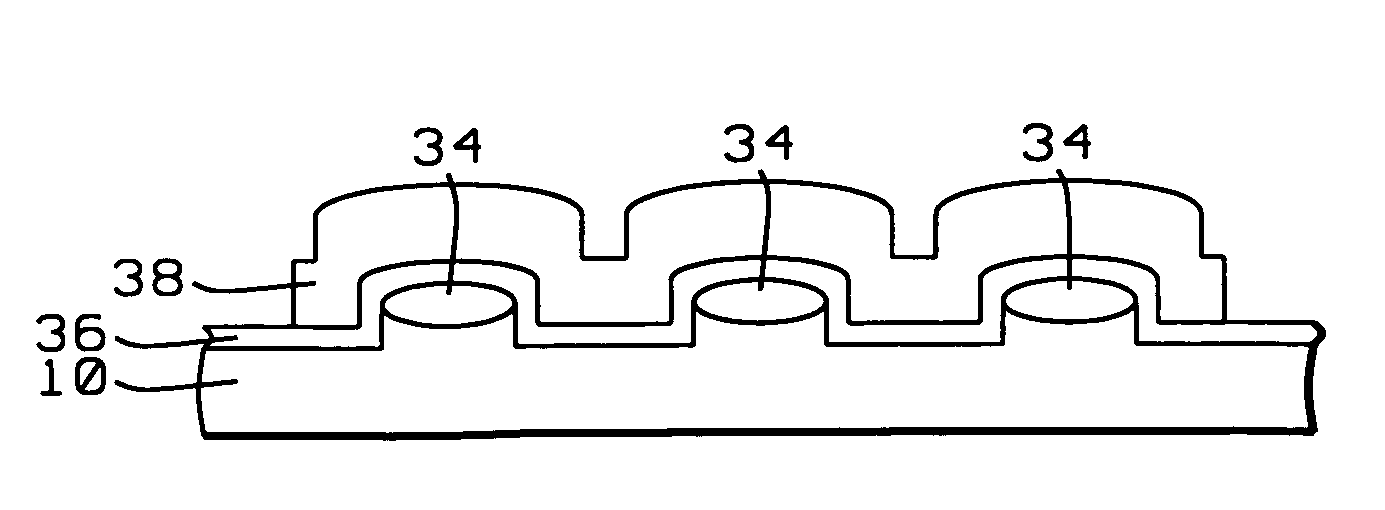
Characters of the disclosed structure of quanta trap are that through tunneling barrier layer 5 with high tunneling probability, home position electron capture layer 3 or home position hole capture layer 4 are connected to quanta trap layer 2; layres 1, 3 or 4, 5 and 2 constitute a cycle to carry out activity repeatedly. Number of cycles can be selected from 1 to 10; both of upmost and undermost layers are barrier layers 1; thickness of home position electron capture layer 3 or home position hole capture layer 4 is between 1nm to 3nm. Being as active layer, the structure can increase probability of capturing electrons or holes so as to raise internal quantum efficiency of gallium nitride based light emitting diode of blue green light.
Owner:HC SEMITEK SUZHOU
Detectable Refrigerant Compositions and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090189077A1Easy to detectDetection of fluid at leakage pointAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectron capture detectorCorona discharge
Disclosed herein are detectable refrigerant compositions, comprising from about 0.001 to about 5 weight percent tracer compositions, which are useful to identify leaking in a vapor compression refrigeration and / or air conditioning system. The presence of the tracers make the refrigerant compositions detectable by chemo / electro-active array, corona discharge, heated diode, electrochemical, photoionization, infrared, ultrasonic and electron capture detectors.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Manipulation of conductive and magnetic phases in an electron trapping semiconducting
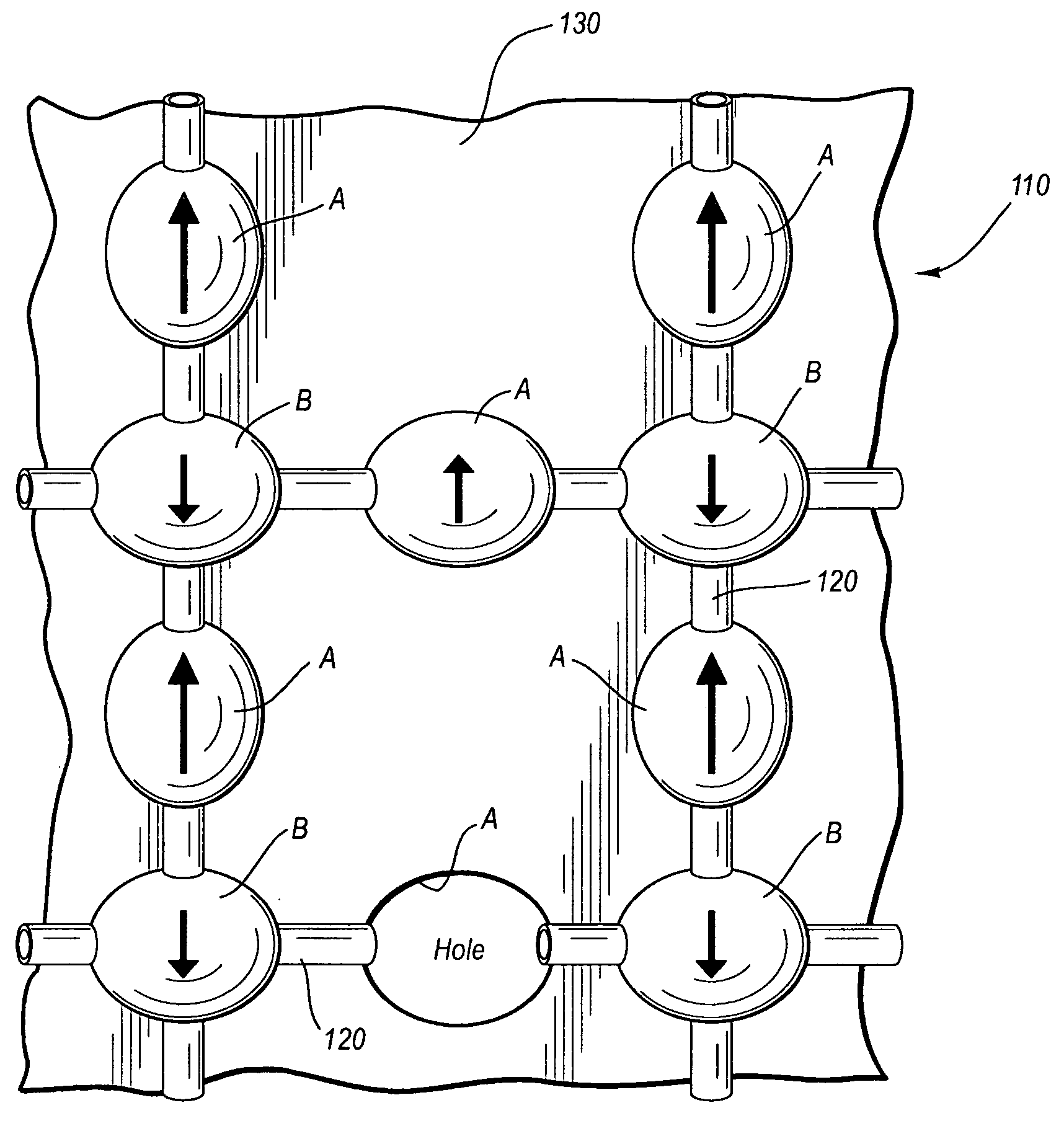
InactiveUS20060138397A1Increase electron densitySolid-state devicesSuperconductor devicesMOSFETMagnetic phase
A semiconductor strip array that can be configured to exhibit distinct electrical and / or magnetic phase characteristics according to the many-body effects phenomenon in electron gases is disclosed. The strip array can be incorporated into a MOSFET architecture and utilized in amplifier and memory cell applications. Significantly, the strip array can exhibit superconductive characteristics under relatively high temperature conditions. In one embodiment, the strip array comprises a grounded substrate, a plurality of strips deposited on the substrate in an intersecting pattern to define the strip array, an insulating layer atop the array, a source, and a drain. The intersecting strip array defines primary electron trapping sites at the strip intersections and secondary electron trapping sites on the strips between the intersections. The strip array is further configured to exhibit distinct electrical and / or magnetic properties according to a selective concentration of electrons injected into the primary and secondary electron trapping sites.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com