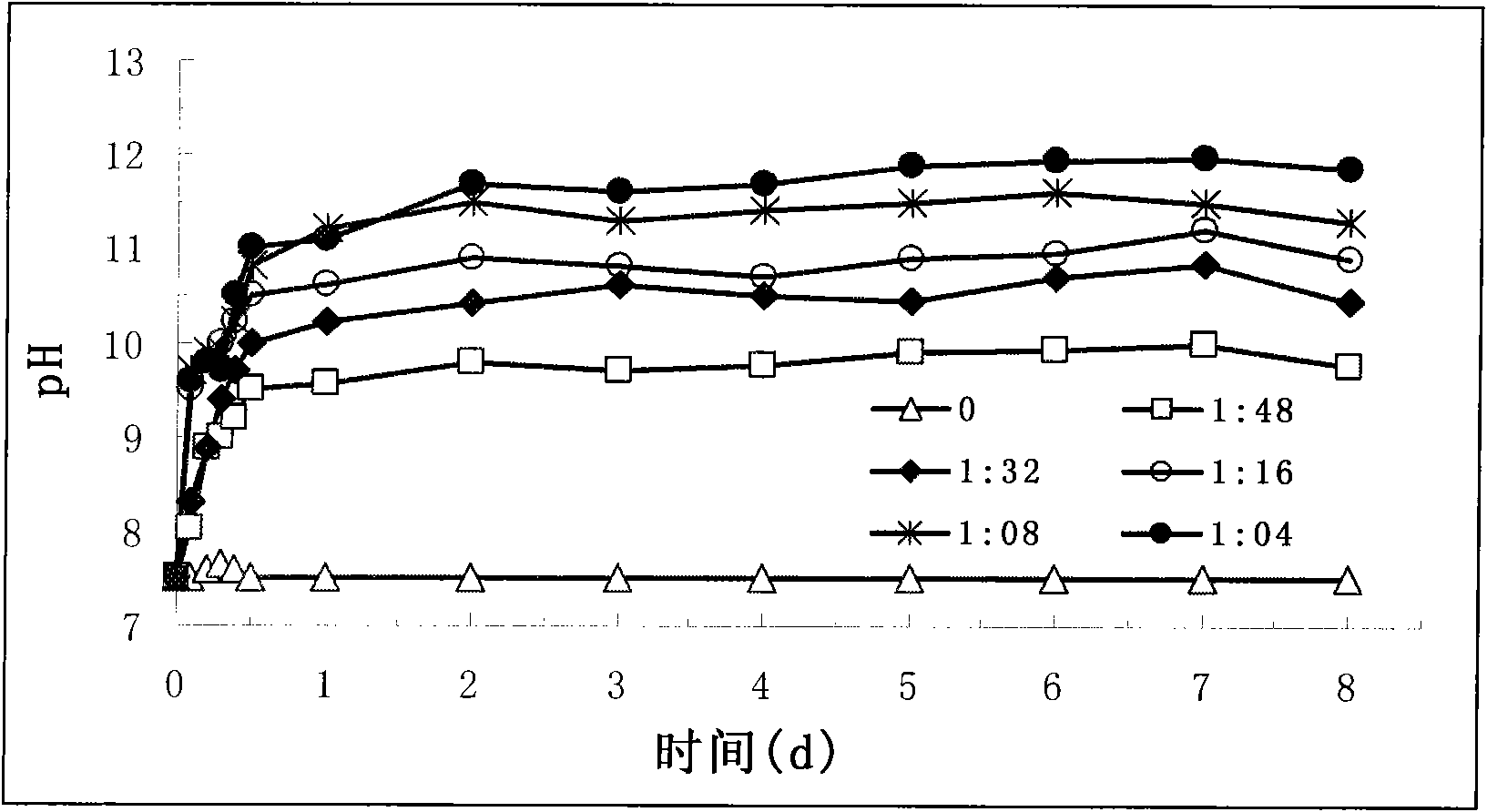
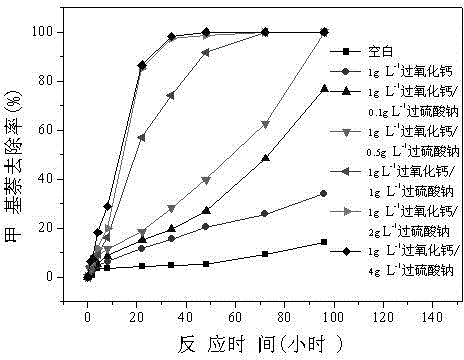
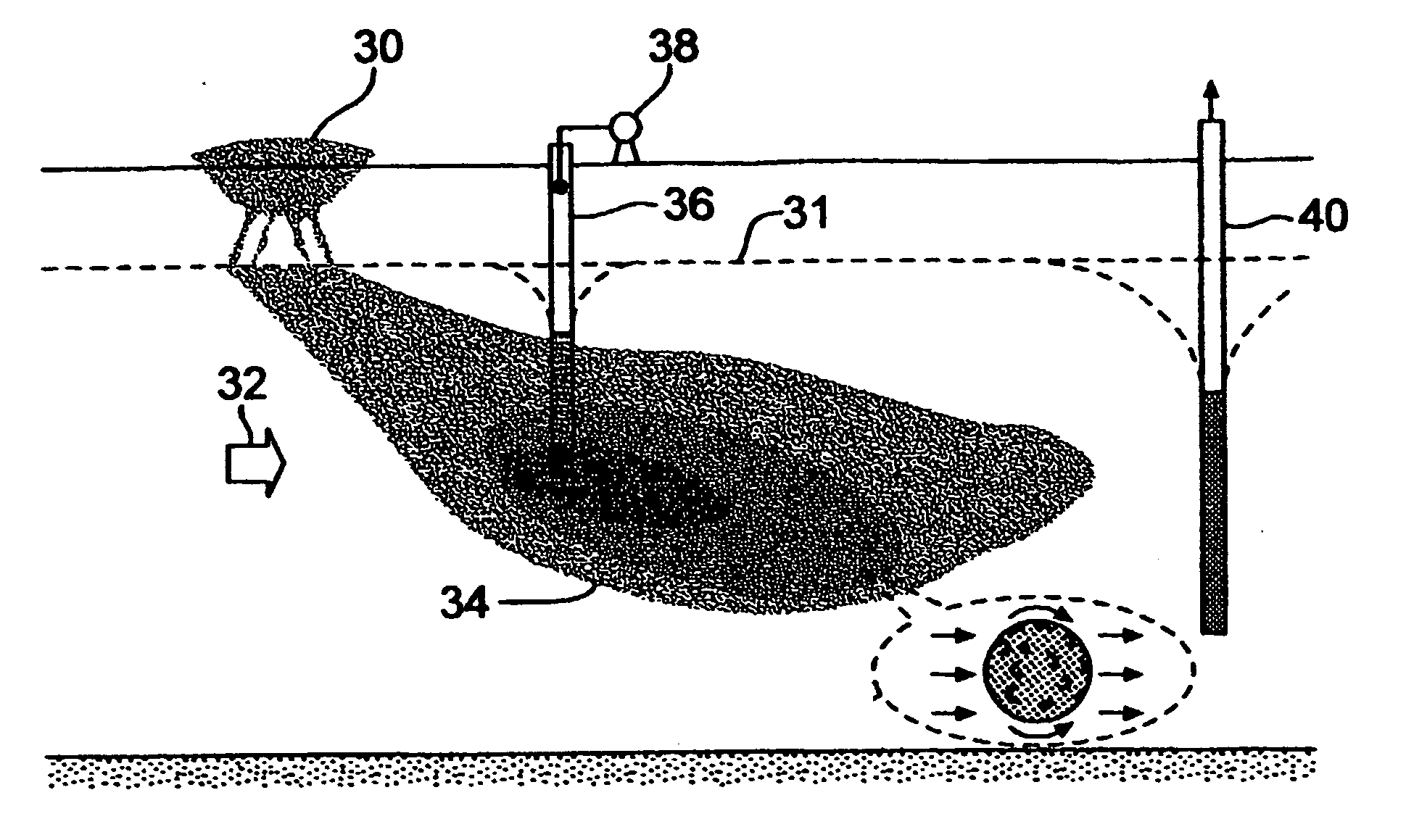
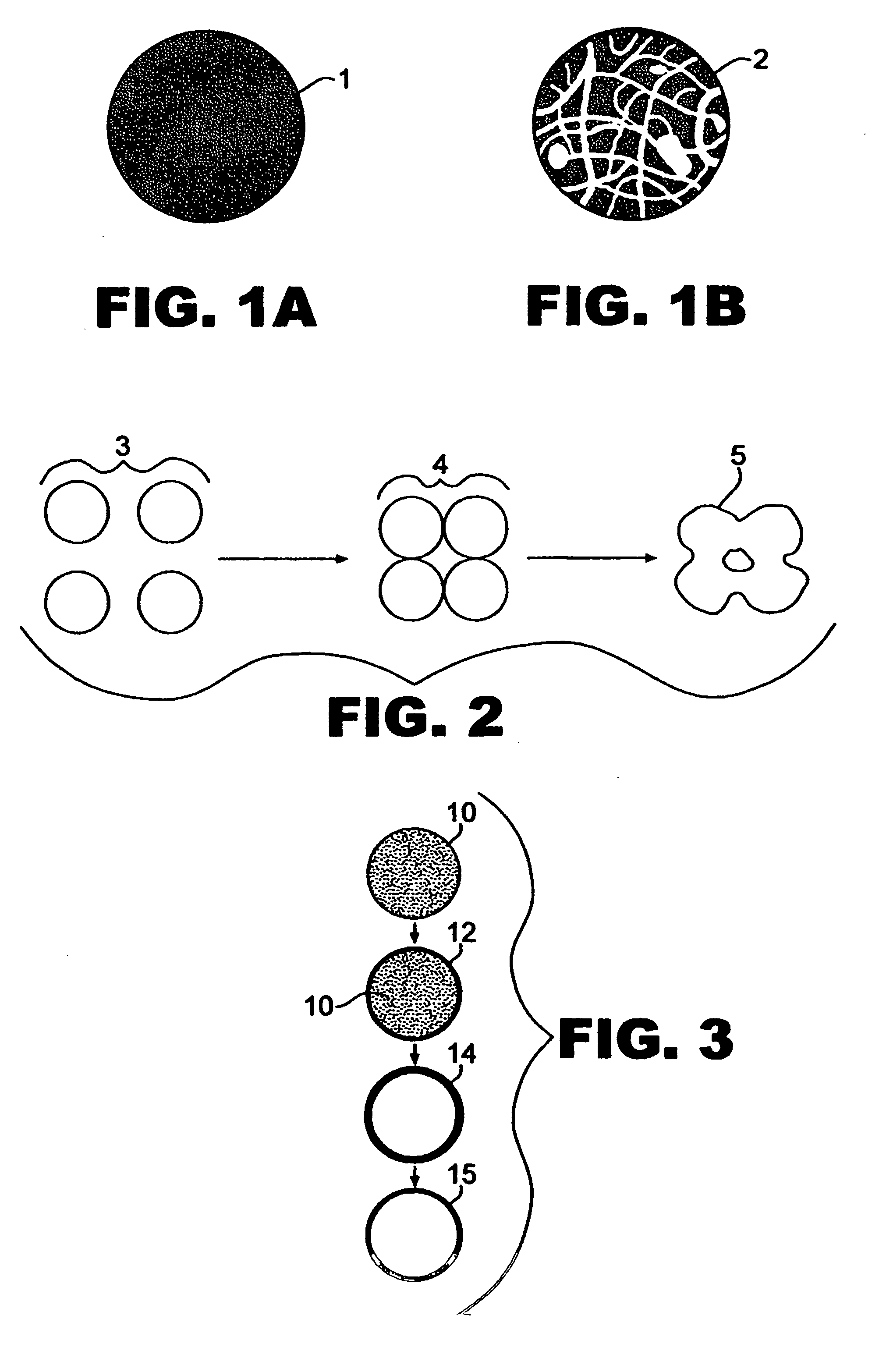
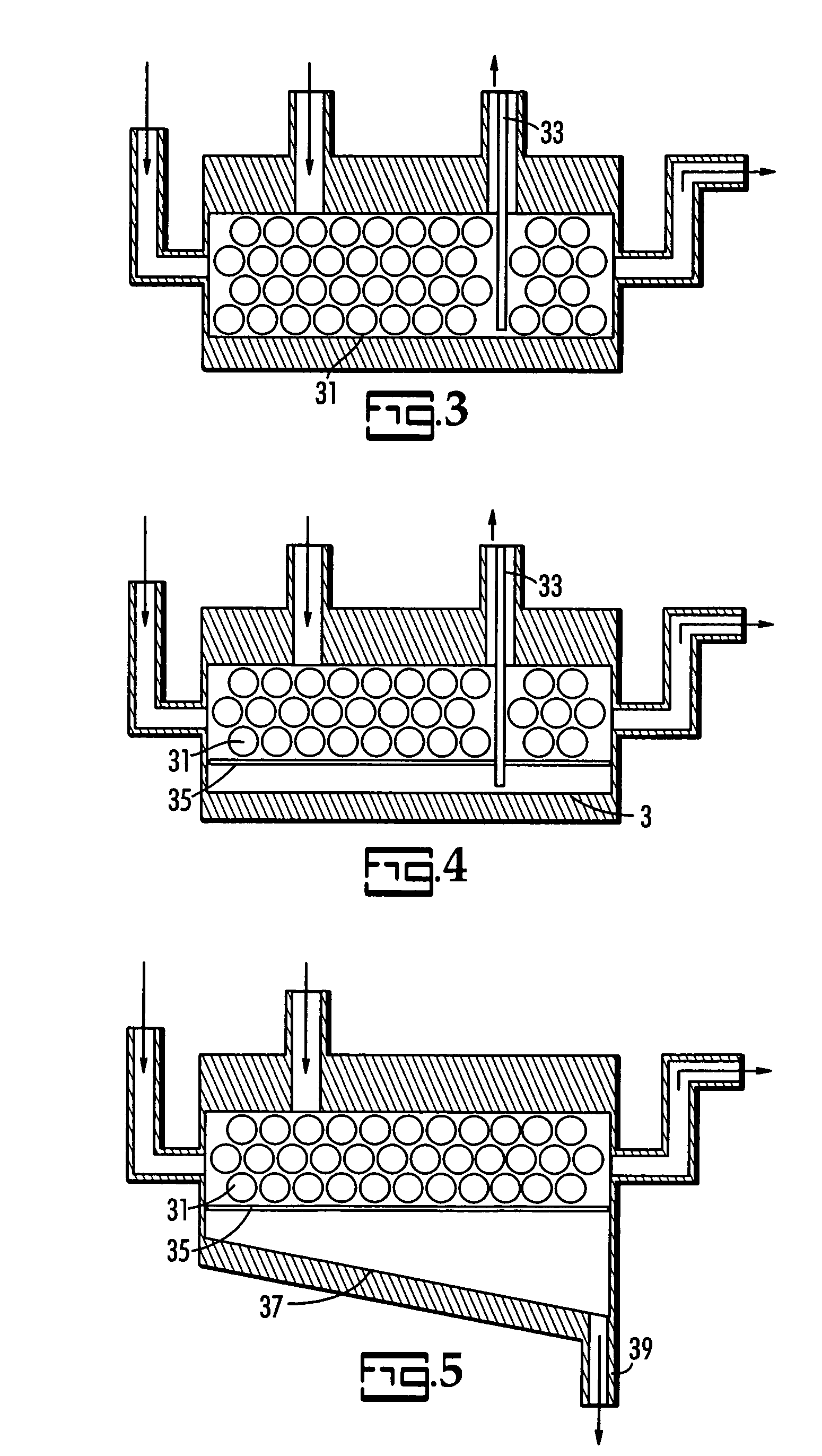
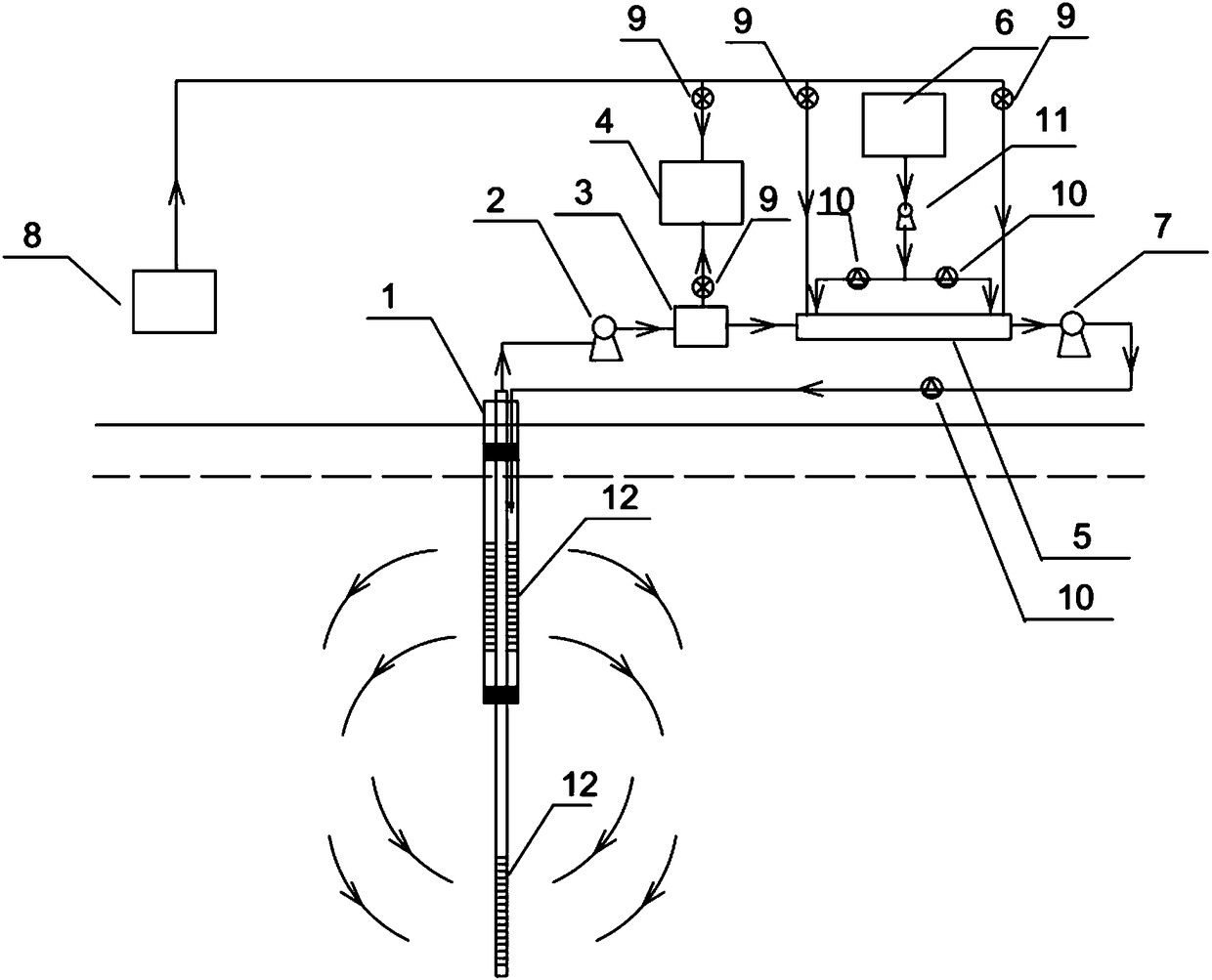
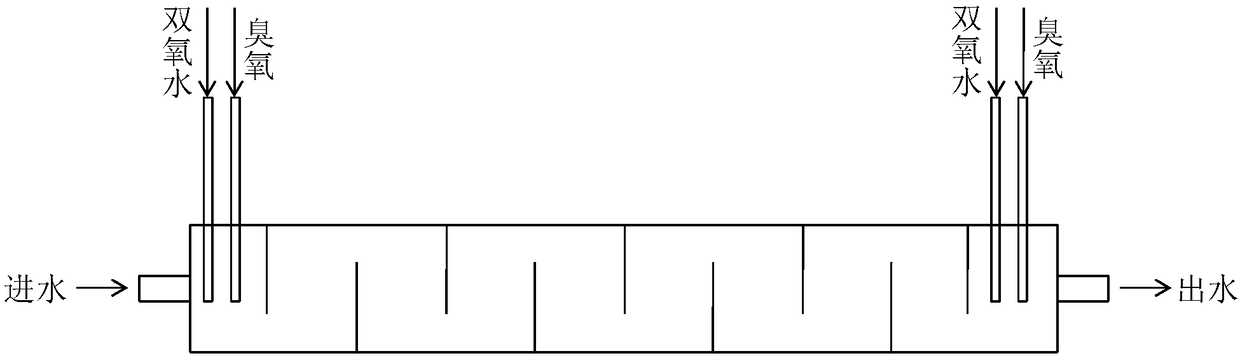
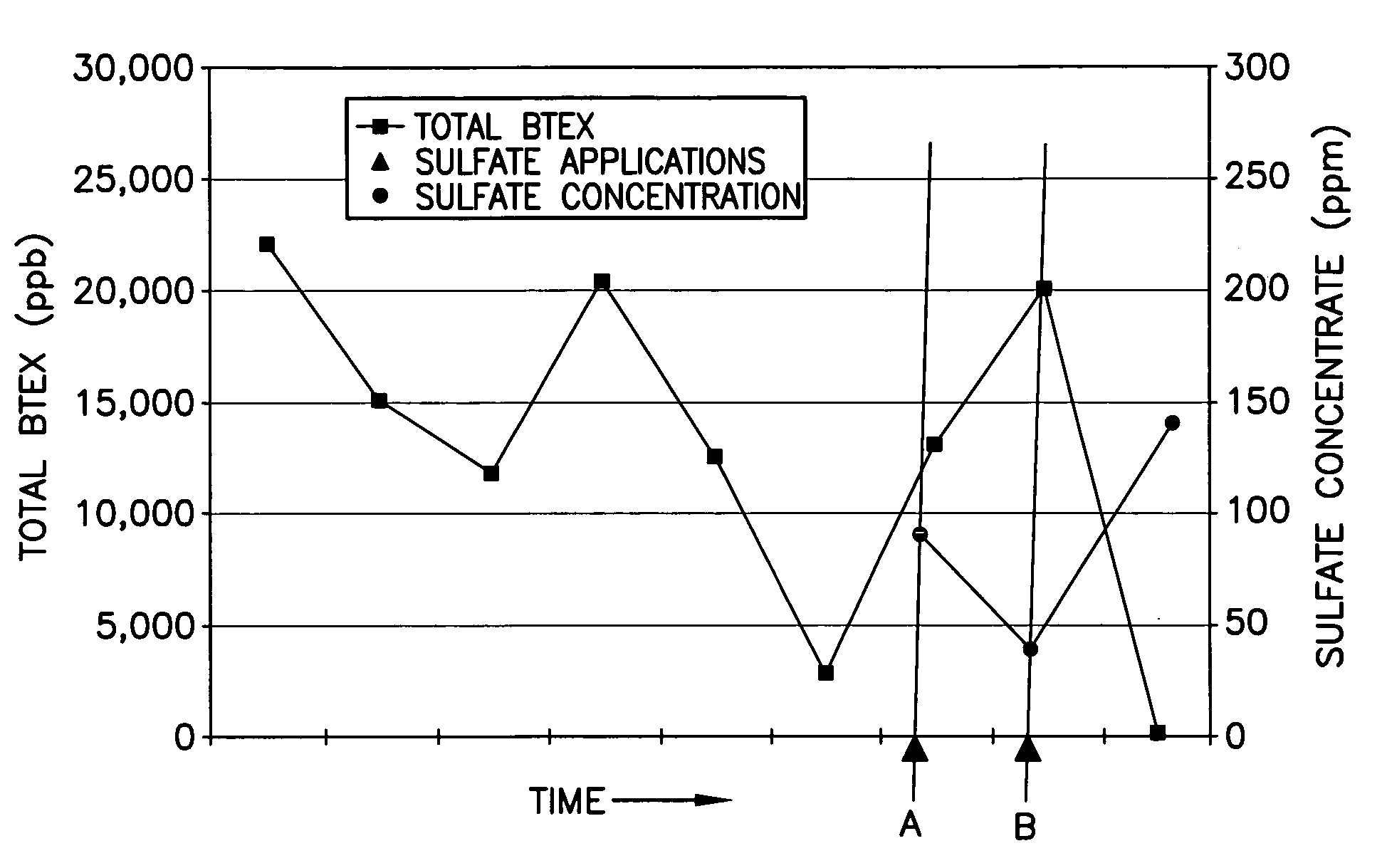
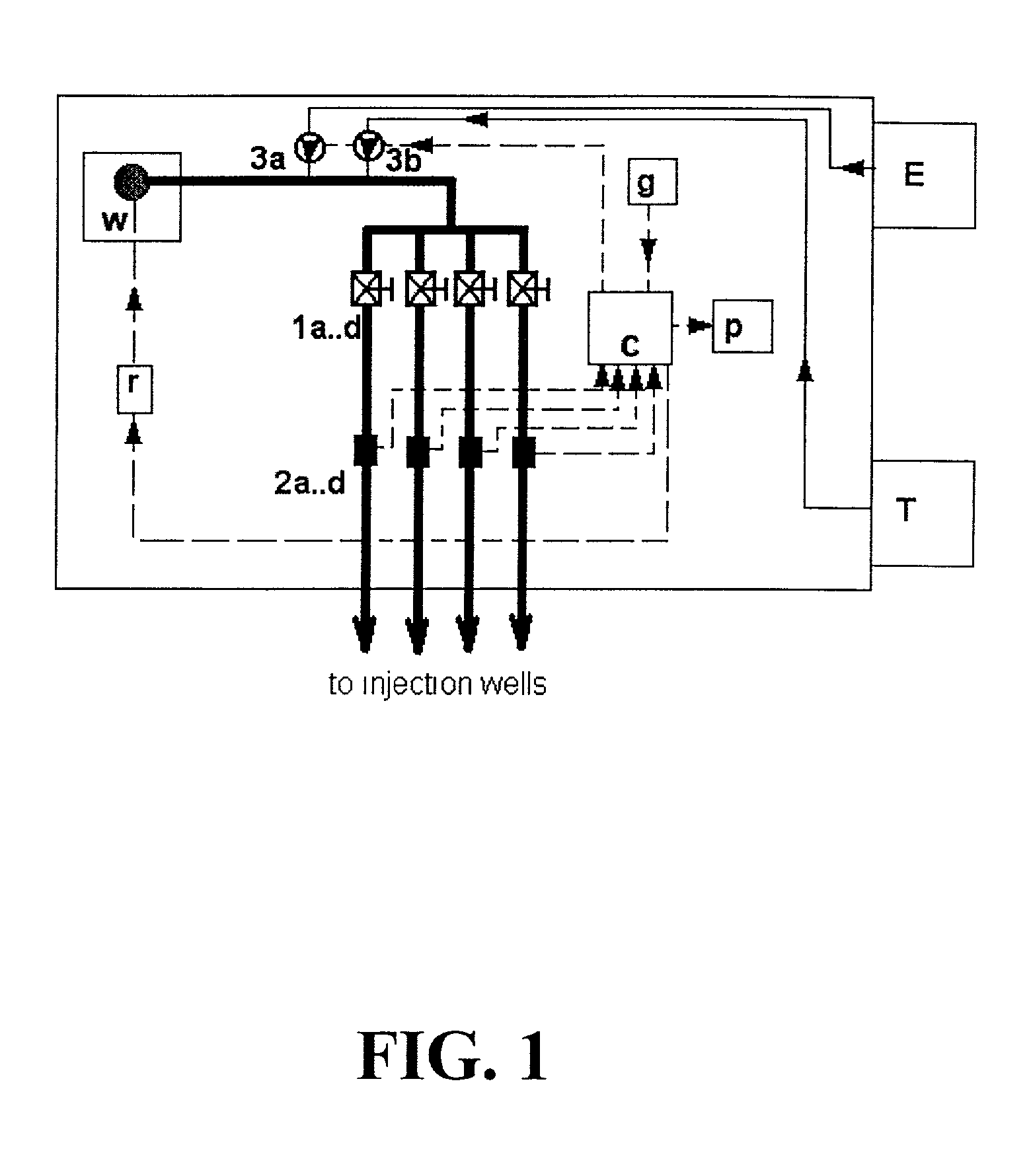
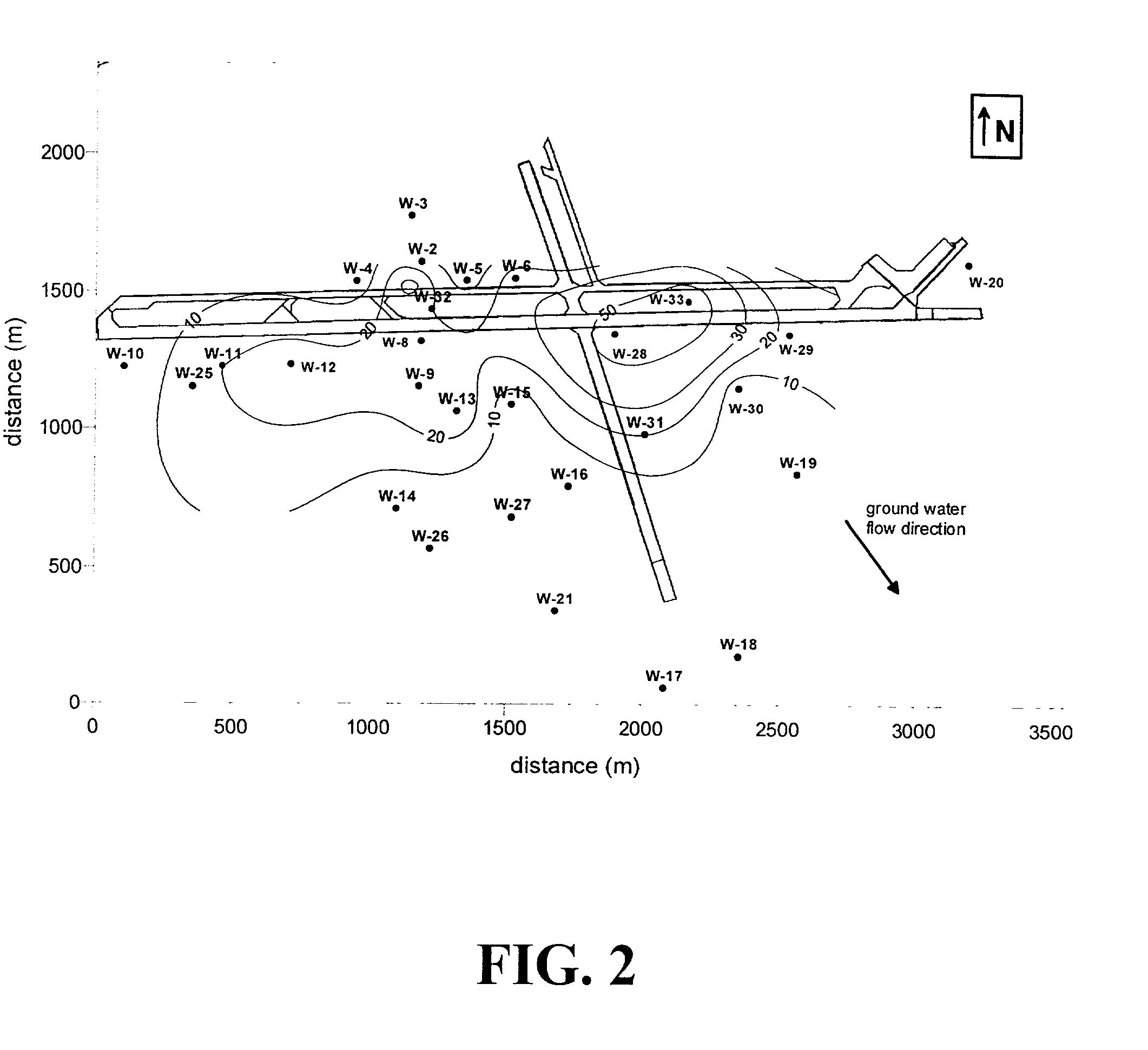
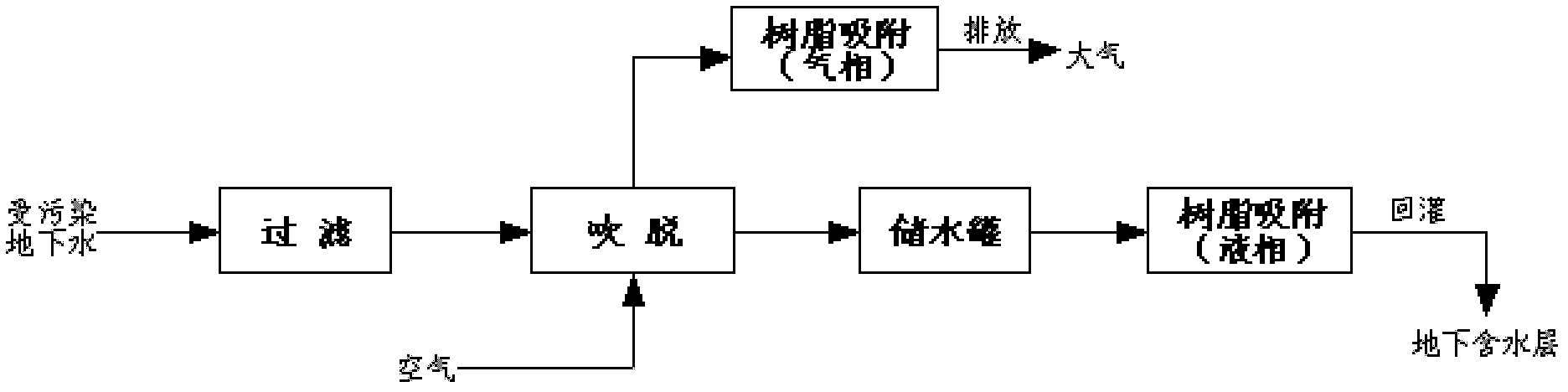
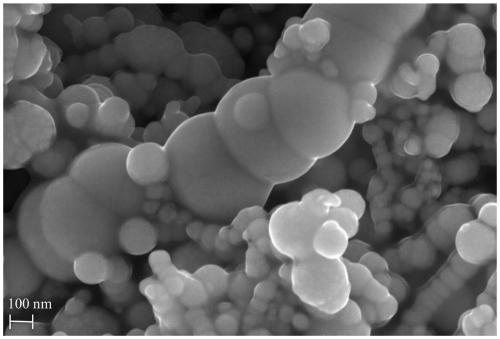
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
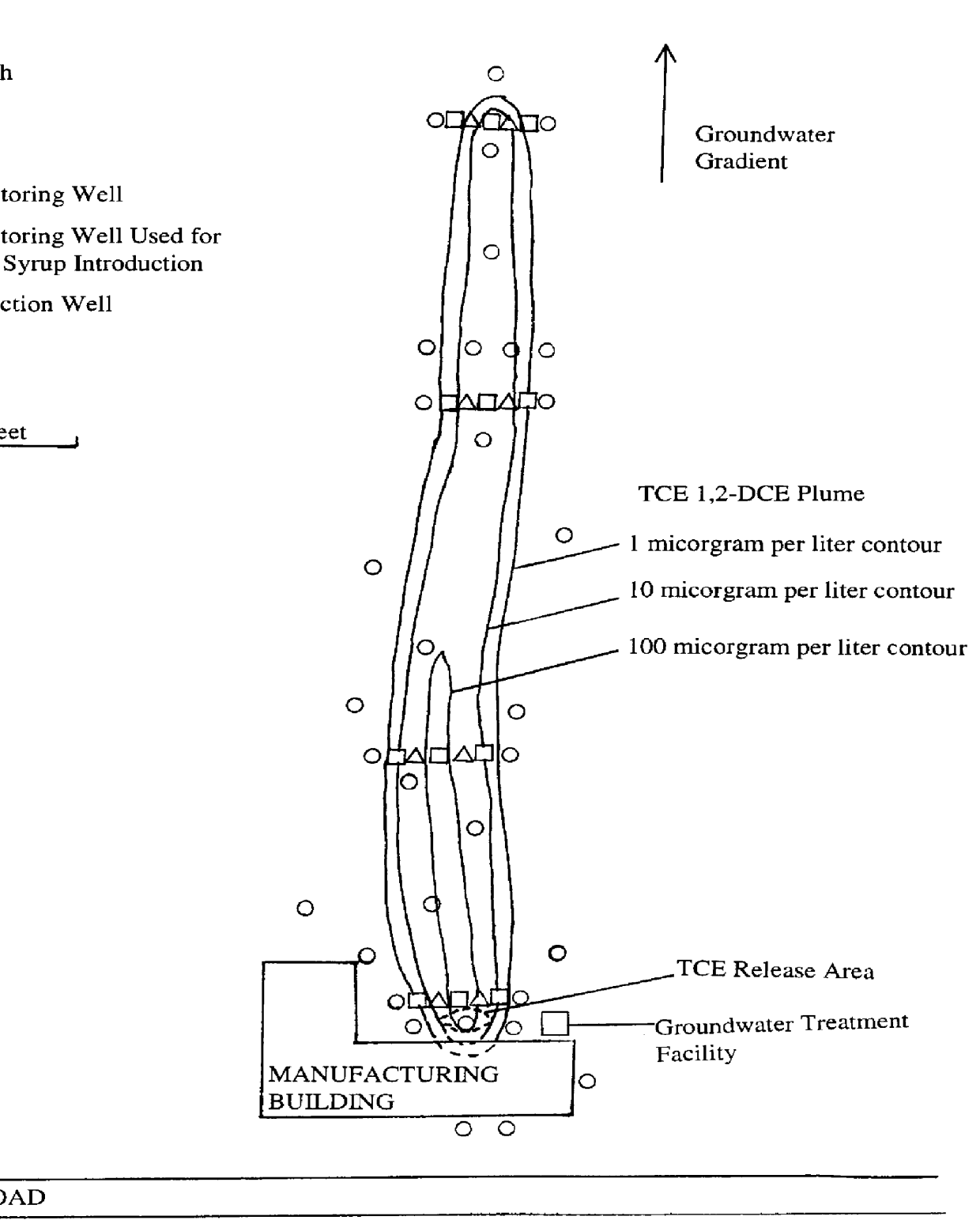
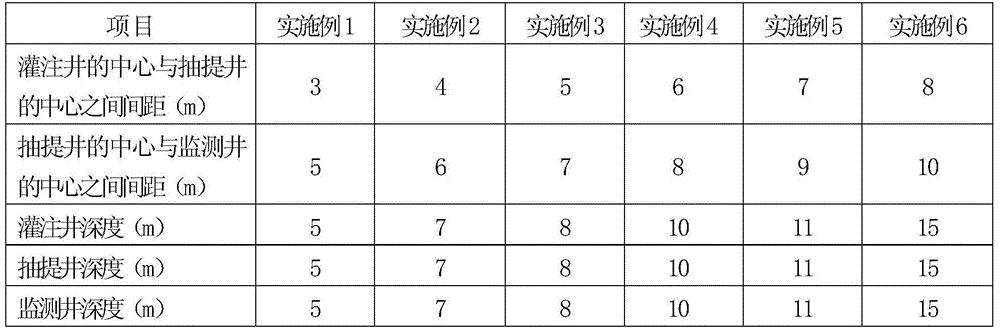
141 results about "Contaminated groundwater" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
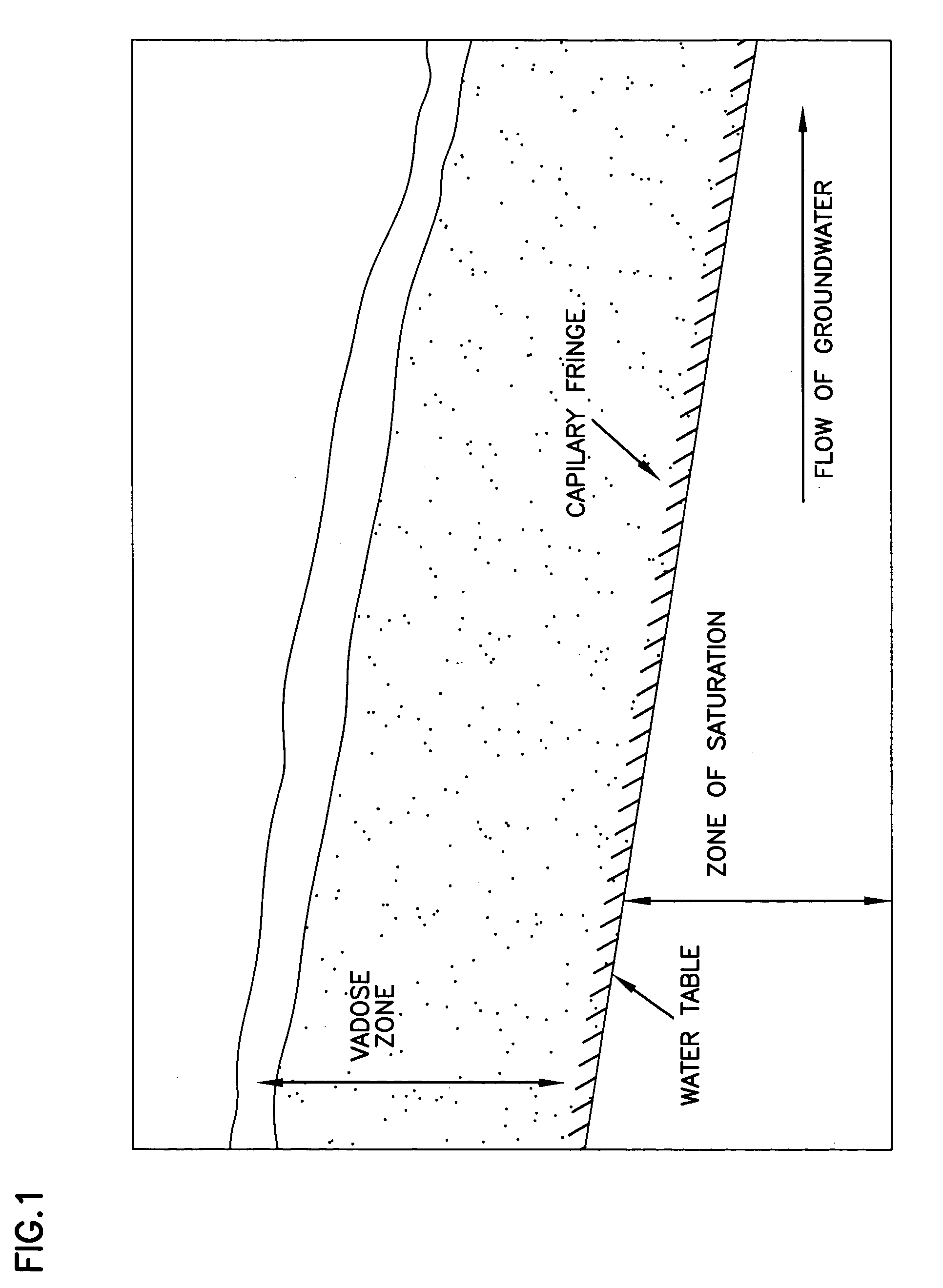
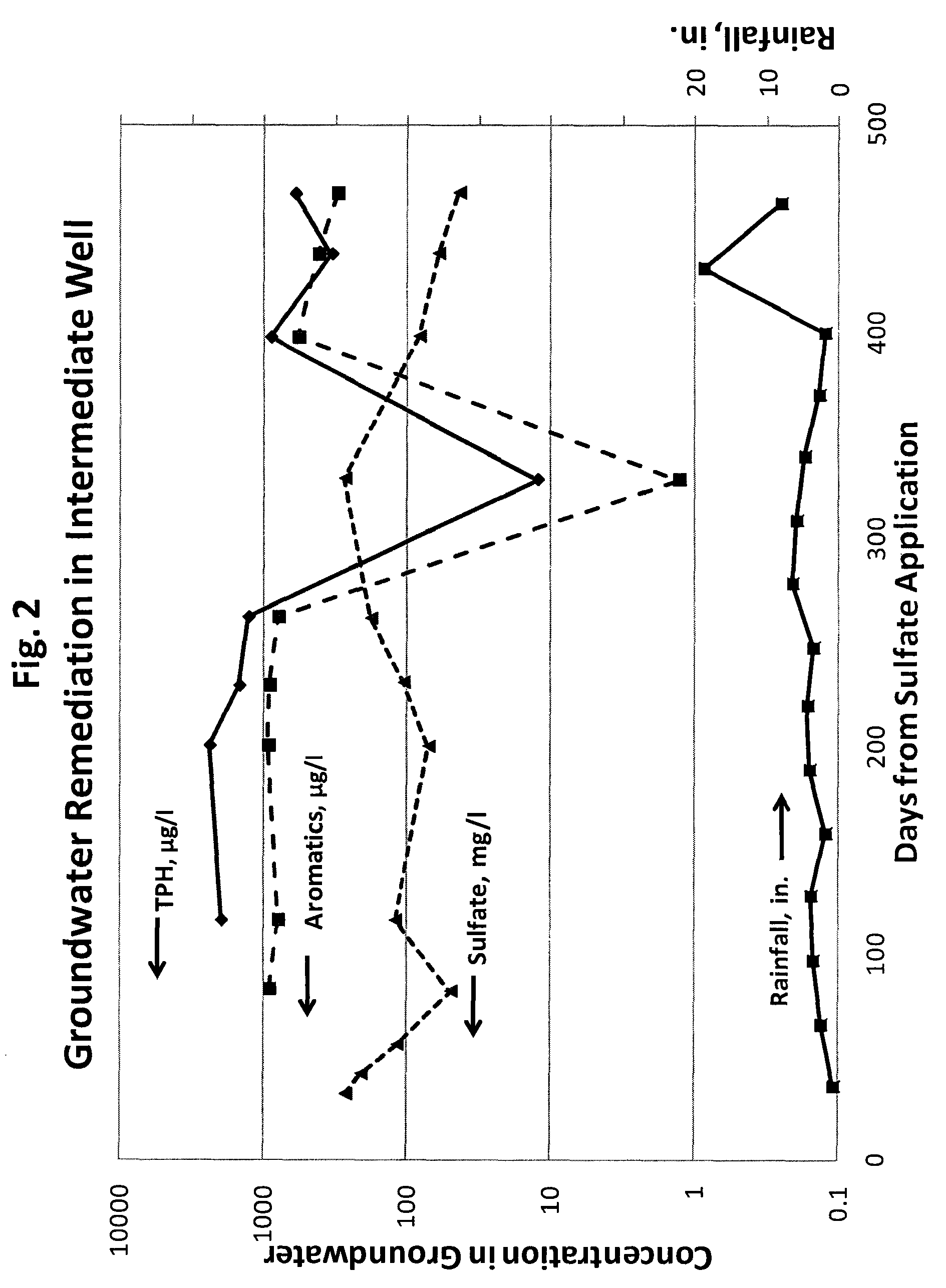
Contamination of Groundwater. The Committee considers groundwater contamination to be the detrimental alteration of the naturally occurring physical, thermal, chemical, or biological quality of groundwater. There are several ways groundwater can be contaminated. The most common avenues for groundwater contamination are: Unplugged abandoned wells.
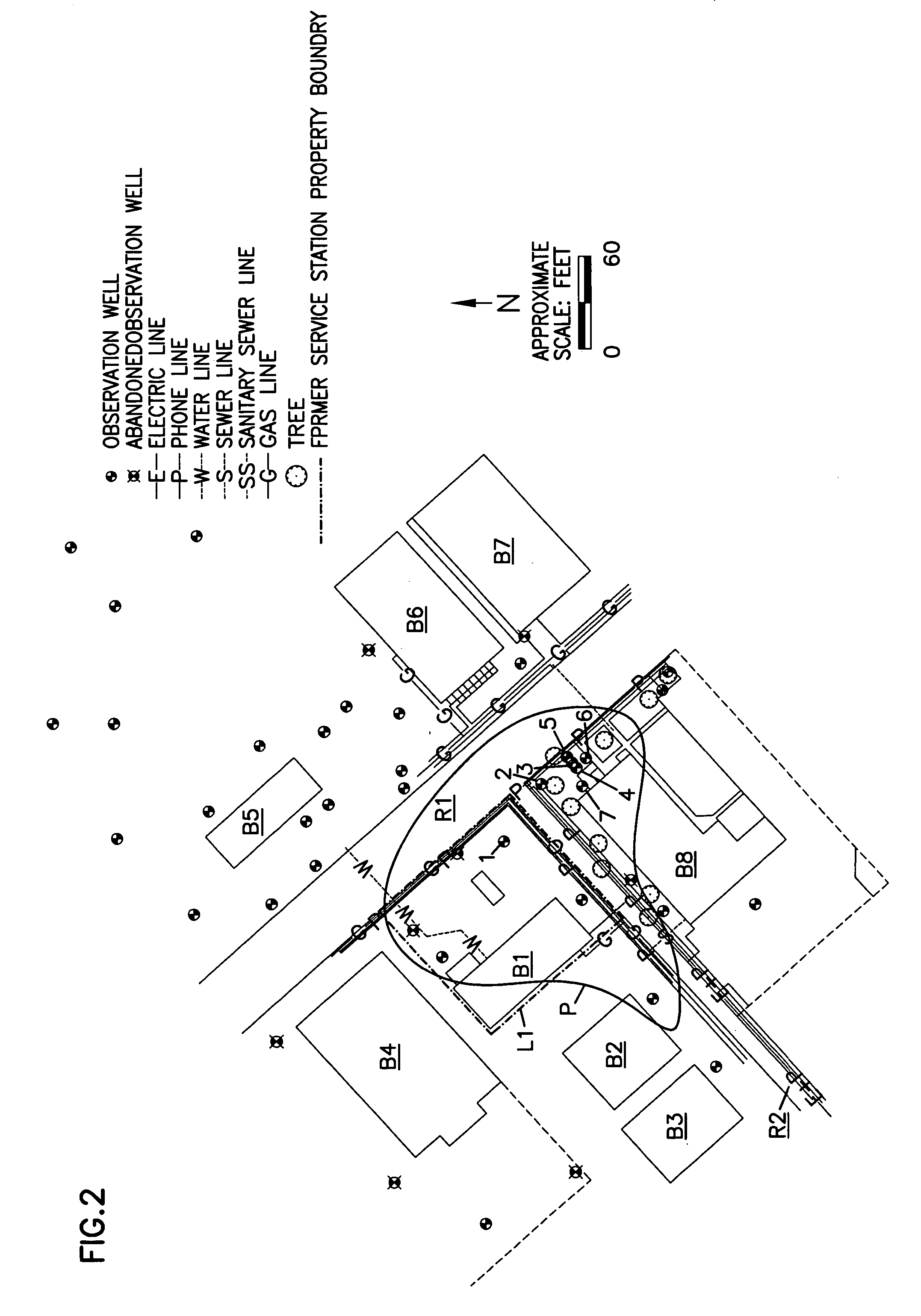
Soil remediation method
The invention relates to a soil remediation method, which comprises the following steps that: 1) a liquid injecting well for injecting chitosan leacheate through a pump is arranged in a soil polluted area, the chitosan leacheate enters the inside of polluted soil through the liquid injecting well, soil percolate seeps through underground water, and heavy metal active ingredients in the soil and the underground water are eluted by the chitosan leacheate to form stable chitosan-metal chelate; and 2) a permeable reactive barrier filled with active substances is constructed in a direction which is vertical to the flow direction of the underground water at the periphery of the liquid injecting well, the soil percolate and the polluted underground water flow through the permeable reactive barrier filled with the active substances, and polluted substances such as the chitosan-metal chelate and the like in the soil and the underground water are removed. Through the soil remediation method, heavy metals in the soil can be effectively removed, a polluted underground water system can be remediated, and most of the heavy metals contained in the soil and the underground water can be gathered in the active substances of the permeable reactive barrier, so that the heavy metals can be recycled. The heavy metal content of the remediated soil and the water quality of the percolate passing through the reactive barrier meet the corresponding national standard.
Owner:JIANGXI JDL ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD
Reductive dehalogenation of organic halides in contaminated groundwater
The invention provides methods and microbial cultures for the bioremediation of organic halide contaminated groundwater contaminated with organic halides, such as di- and trichloroethene. The methods involve adding, in situ to organic halide-contaminated groundwater a carbohydrate and one or more reductive dehalogenation factors, usually in the form of a nutrient extract, both in amounts sufficient to permit in situ reductive dehalogenation of the organic halide by a microbial population. The microbial population may be endogenous to the ground water or added exogenously. The nutrient-enriched ground water is then maintained in situ under reducing conditions to reductively dehalogenate the contaminating organic halide. Enriched bioremediation cultures are produced by adding to organic halide contaminated groundwater which comprises an endogenous microbial population capable of reductive dehalogenation of the organic halide a carbohydrate and frequently, one or more reductive dehalogenation factors. Thereafter, the nutrient-enriched groundwater is incubated under reducing conditions whereby the organic halide is reductively dehalogenated and the microbial population is selectively and numerically expanded to yield a bioremediation culture.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method for recovery of contaminated groundwater through in situ enhanced aeration
InactiveCN101792214AReduce surface tensionIncrease air saturationWater aerationSustainable biological treatmentAeration rateChlorobenzene
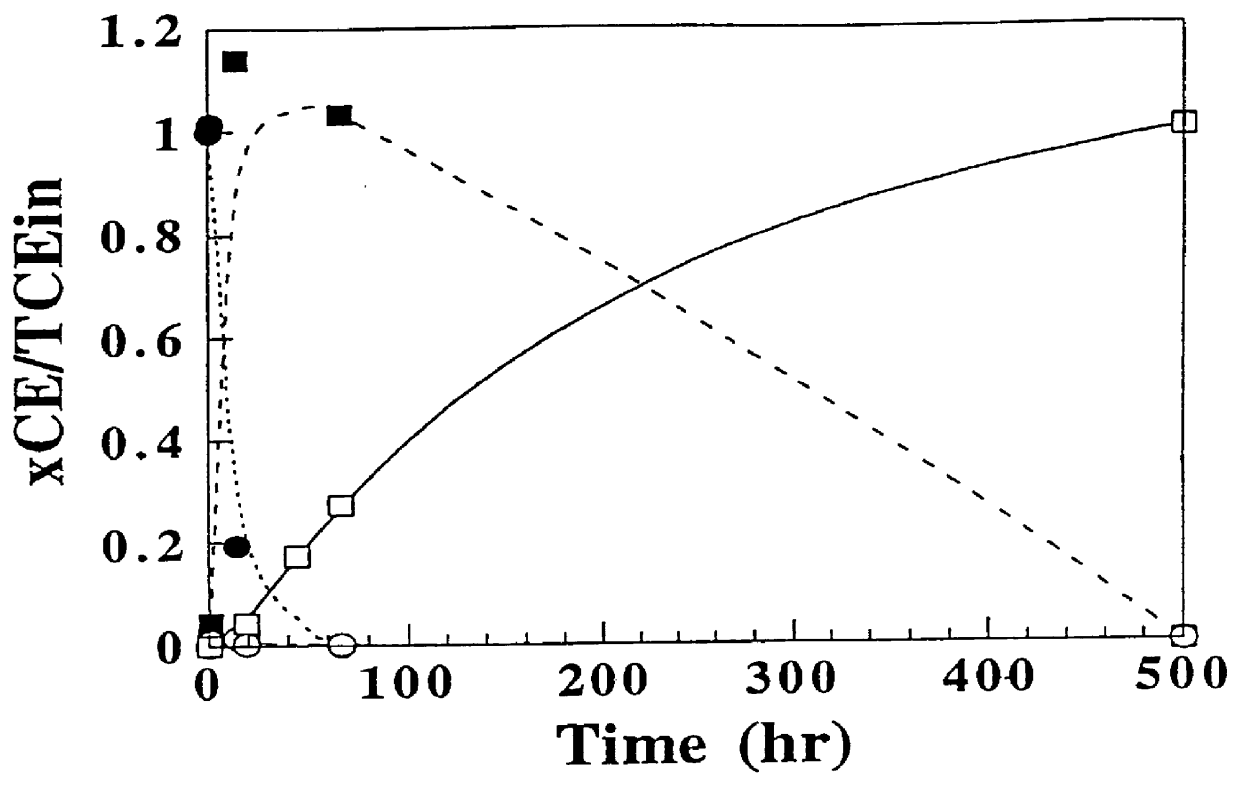
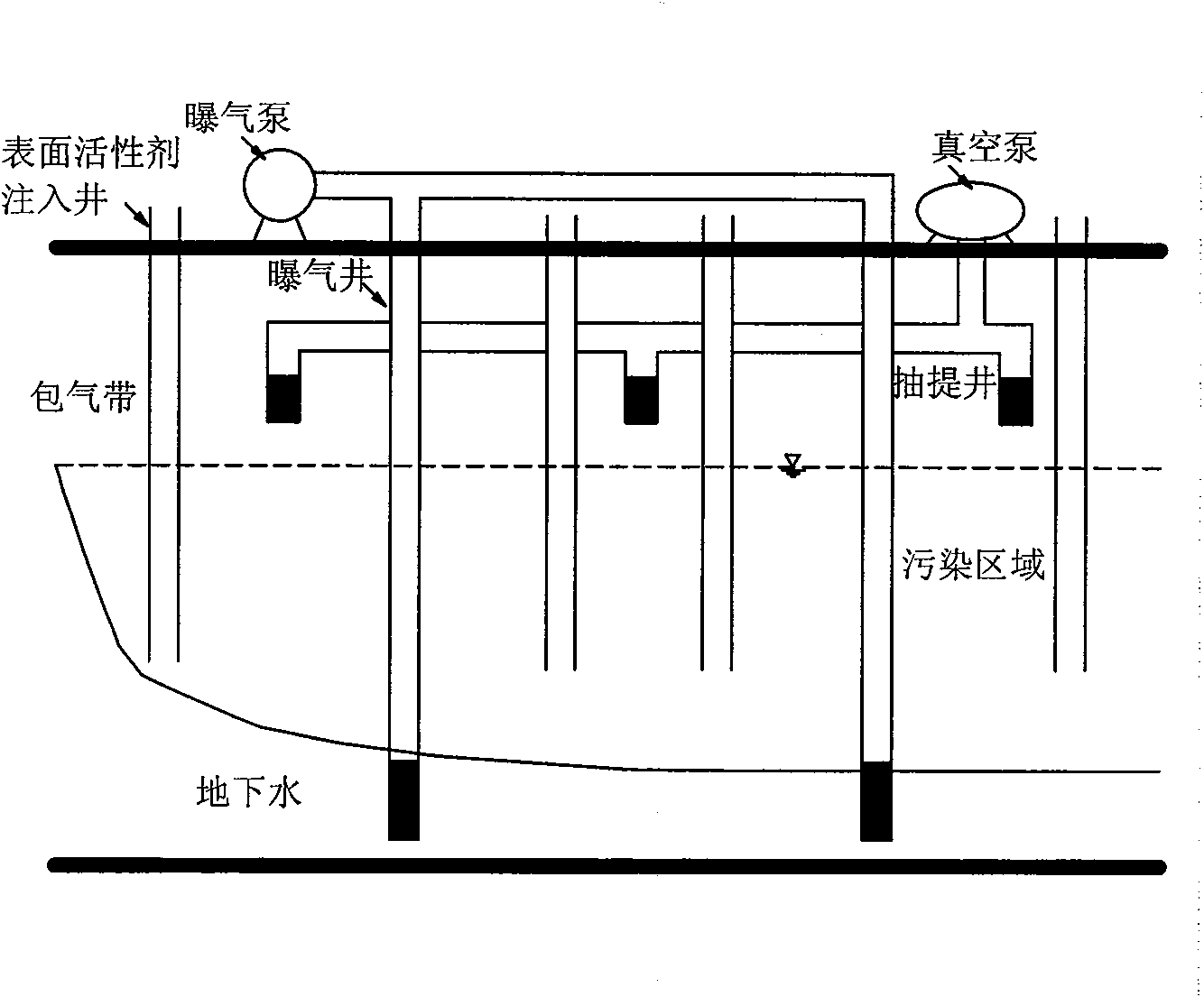
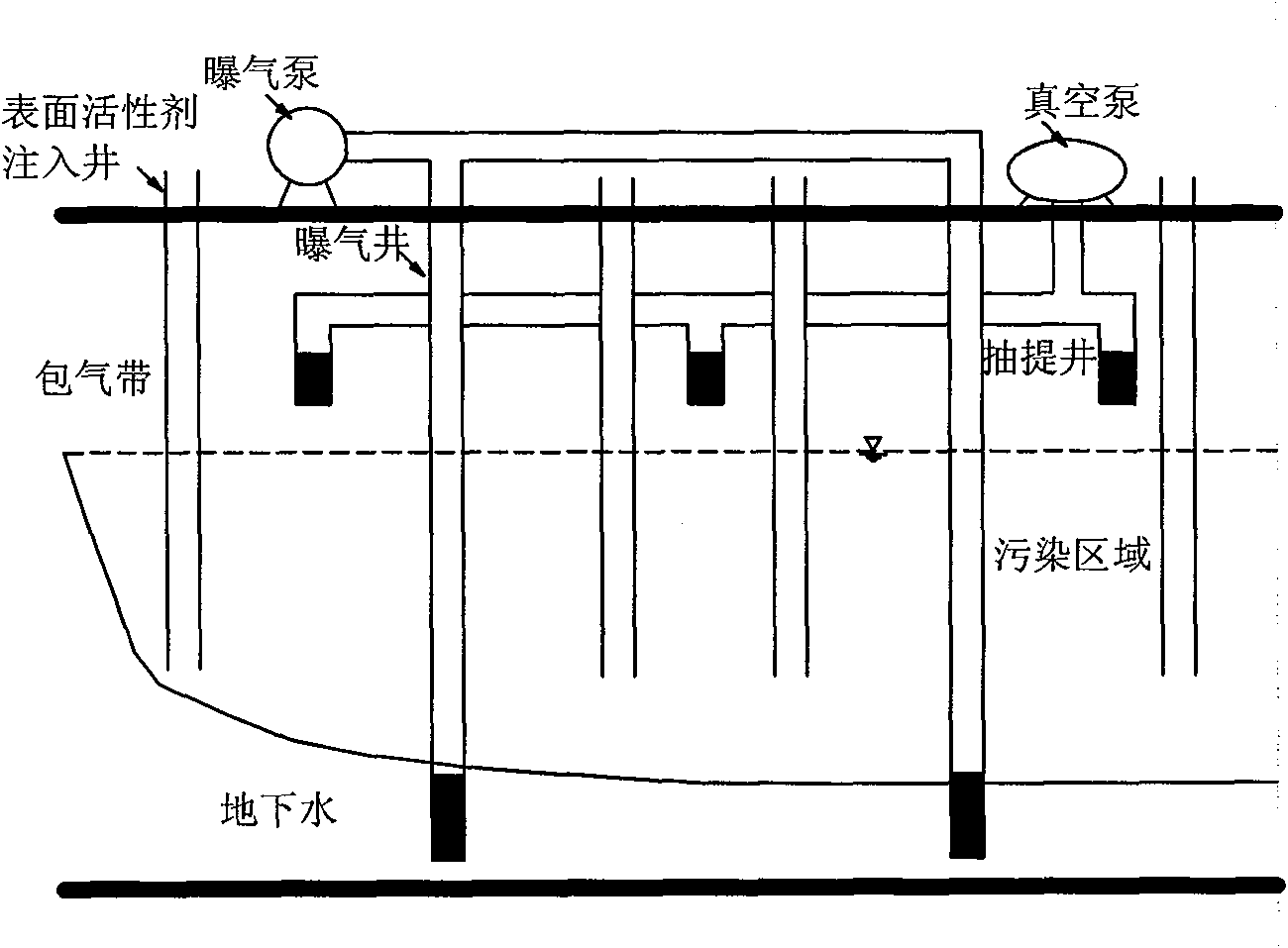
The invention relates to a method for recovery of contaminated groundwater through in situ enhanced aeration, which comprises the following steps: digging more than one surfactant injection well, an aeration well and an extraction well in an area with the groundwater contaminated, injecting surfactant into the area with the groundwater contaminated through the surfactant injection well to dissolve the surfactant into the groundwater so as to form surface tension in the area with the groundwater contaminated, starting the extraction pump to pump an aeration zone into negative pressure, and starting the aeration pump for continuous aeration. The invention effectively solves the problem that the majority of pollutants can be removed only after flowing into the porous channel through diffusion due to the narrow porous channel near the aeration well, and improves the saturation degree of the air in the groundwater, thereby increasing opportunities of exposure the pollutants to the air. Tests show that, when the aeration rate is 100ml / min, the surface tension is reduced to 50.4dyn / cm from 70.5dyn / cm, the half-life for removal of the pollutant chlorobenzene is reduced to 16min from 31min, and simultaneously the trailing concentration is reduce to 5.1mg / L from 22.08mg / L. The removal rate can be increased to 98.5 percent from 89.2 percent after 420 minutes. The invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost, low surfactant injection and less impact on the environment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Metal-treated particles for remediation
The invention relates to metal-treated particles, methods for their preparation and methods for using metal-treated particles for, e.g., remediation of process waste-water, sewage, contaminated groundwater aquifers, and soil containing harmful contaminants. Another aspect of the invention relates to a metal-treated particle comprising a ferrosoferric oxide core and a metal supported on the core, where the average diameter or other largest transverse dimension of the core is from about 75 nm to about 990 nm and the amount of metal supported on the core is from about 8% to about 22% by weight, based on the weight of the metal-treated particle.
Owner:CRANE CO
Method for controlling pollution of ground water of sulfate polluted site and remediating soil
ActiveCN104671385AReduce volumeEfficient removalContaminated soil reclamationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSulfate radicalsGround water pollution
The invention discloses a method for controlling pollution of ground water of a sulfate polluted site and remediating soil. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) building an isolating wall between the site and a pollutant source; (2) performing pollution control by adopting a hydraulic capture technology; and (3) pumping water, injecting water and stopping pumping and injecting in a reciprocating manner for 3 times, and performing water quality monitoring to achieve the aim of controlling the pollution of the ground water and remediating soil. The method disclosed by the invention is used for comprehensively controlling ground water sulfate pollution by combining an anti-seepage dirt isolating wall, the hydraulic capture technology and a coagulation-sedimentation method, and can be used for effectively removing sulfate ions from polluted ground water. The hydraulic capture technology in the method disclosed by the invention adopts a hydraulic control method to gradually eliminate polluted ground water bodies, and the ground water pumped out by using an inner circular layer by the system is relatively small in volume, thereby reducing the treatment cost while ensuring that pollution plumes cannot exceed an isolation belt.
Owner:上海骄阳环境工程有限公司
Using noble gas geochemistry to evaluate fluid migration in hydrocarbon bearing black shales
InactiveUS20120134749A1Well formedHigh organic contentHydraulic engineering apparatusMarine site engineeringFluid migrationNoble gas
American energy costs steadily increase leading to increased unconventional energy use. However, scientific barriers prevent widespread and economic development of these resources. In gas shale plays, resource utilization is limited by the understanding of how hydrocarbons and other fluids migrate in fractured rock. This limits industry's ability to extract hydrocarbons with enhanced recovery methods; prevents exploration in areas where hydrocarbons do not collect in traditional traps; and could unfortunately lead to dangerous environmental consequences such as contaminated groundwater. To address these concerns, the present invention integrates geochemical and geostructural techniques in a novel method for evaluating and optimizing the placement and drilling strategies of extraction wells in hydrocarbon rich black shales. By correctly choosing hydrocarbon “sweet spots” companies can reduce the number of unprofitable wells, choose directional drilling and completion strategies to accurately reflect the subsurface, and better select prime small- and full-field reservoirs.
Owner:DARRAH THOMAS
Permeable-reactive barrier monitoring method and system
InactiveUS20030035691A1Reduced responseRapid responseWater treatment parameter controlWater cleaningBarrier treatmentEnvironmental engineering
A method comprises conducting a permeable-reactive barrier (PRB) treatment of a contaminated aqueous medium and in-well monitoring effectiveness of the permeable-barrier treatment. A system comprises a PRB zone to treat a contaminated groundwater and an in-well sensor located within a gradient of the contaminated groundwater or within the PRB zone to sense a characteristic of the groundwater.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sustained-release potassium permanganate oxidant for in-situ chemical remediation of groundwater
InactiveCN102491425AGood dispersionTo achieve the purpose of in situ chemical repairManganates/permanganatesWater/sewage treatment by oxidationParaffin waxMedicine
The invention relates to a sustained-release potassium permanganate oxidant for in-situ chemical remediation of groundwater. The sustained release of the sustained-release KMnO4 oxidant is achieved by dispersing KMnO4 into molten paraffin wax, and then cooling and solidifying in a die to prepare the sustained-release KMnO4 oxidant in different shapes. KMnO4 particles are uniformly wrapped in the paraffin wax, and when the sustained-release KMnO4 oxidant is in contact with the groundwater, the KMnO4 in the paraffin wax can be released to the groundwater at a certain rate, then organic pollutants in the groundwater are oxidized, and the residual paraffin wax is taken out of the groundwater after the release is completed. According to the invention, the paraffin wax is selected as a carrier of the KMnO4, and the KMnO4 is easy to disperse in the paraffin wax, so that the price is low and the sustained-release KMnO4 oxidant is convenient to recover. The sustained-release KMnO4 oxidant can be used for not only achieving the in-situ chemical remediation purpose of the polluted groundwater, but also avoiding the loss due to excessive one-time dosing of the KMnO4 or poor effects due to insufficient dosing and influence of a byproduct, namely MnO2 on an underground environment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
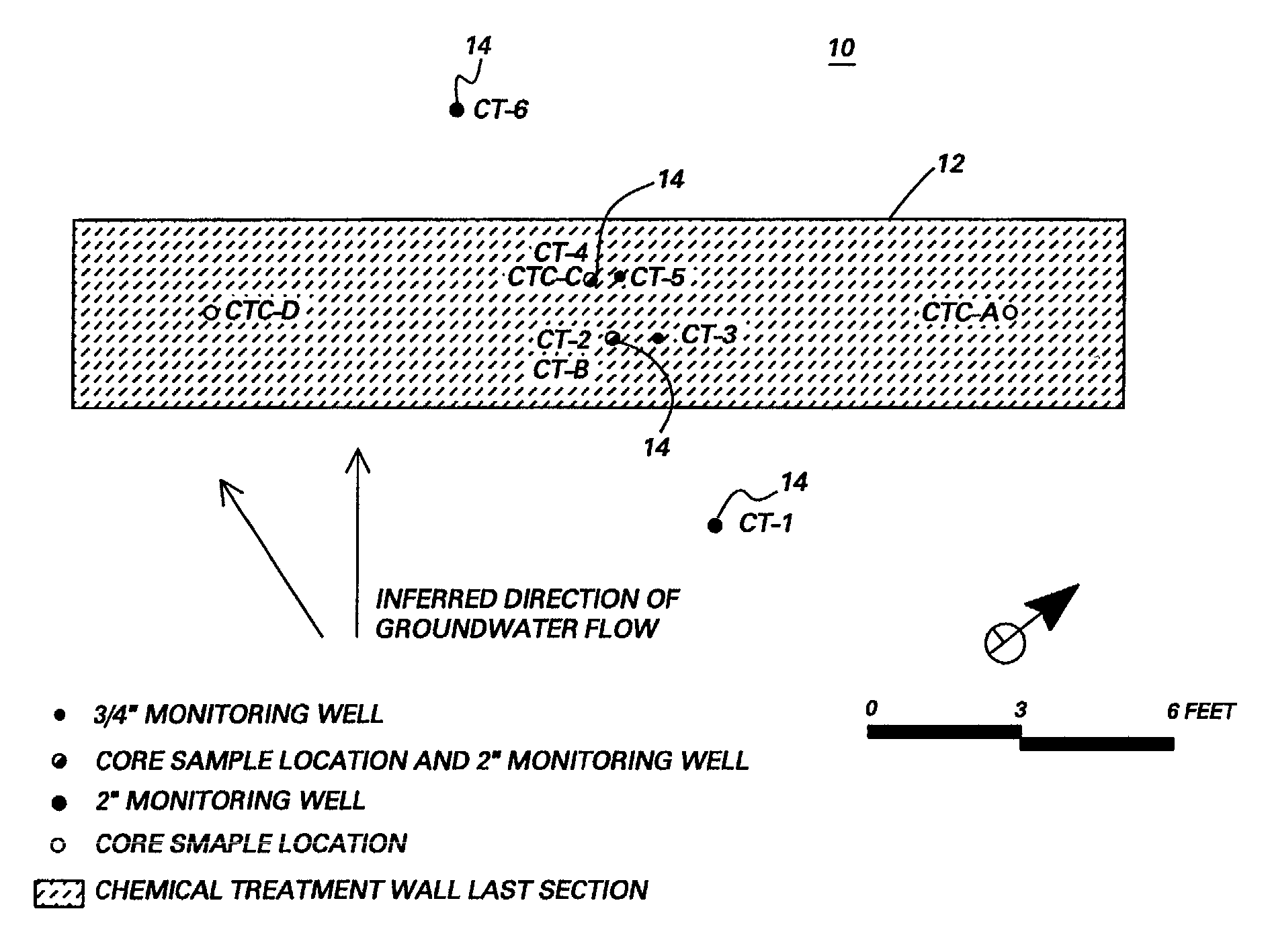
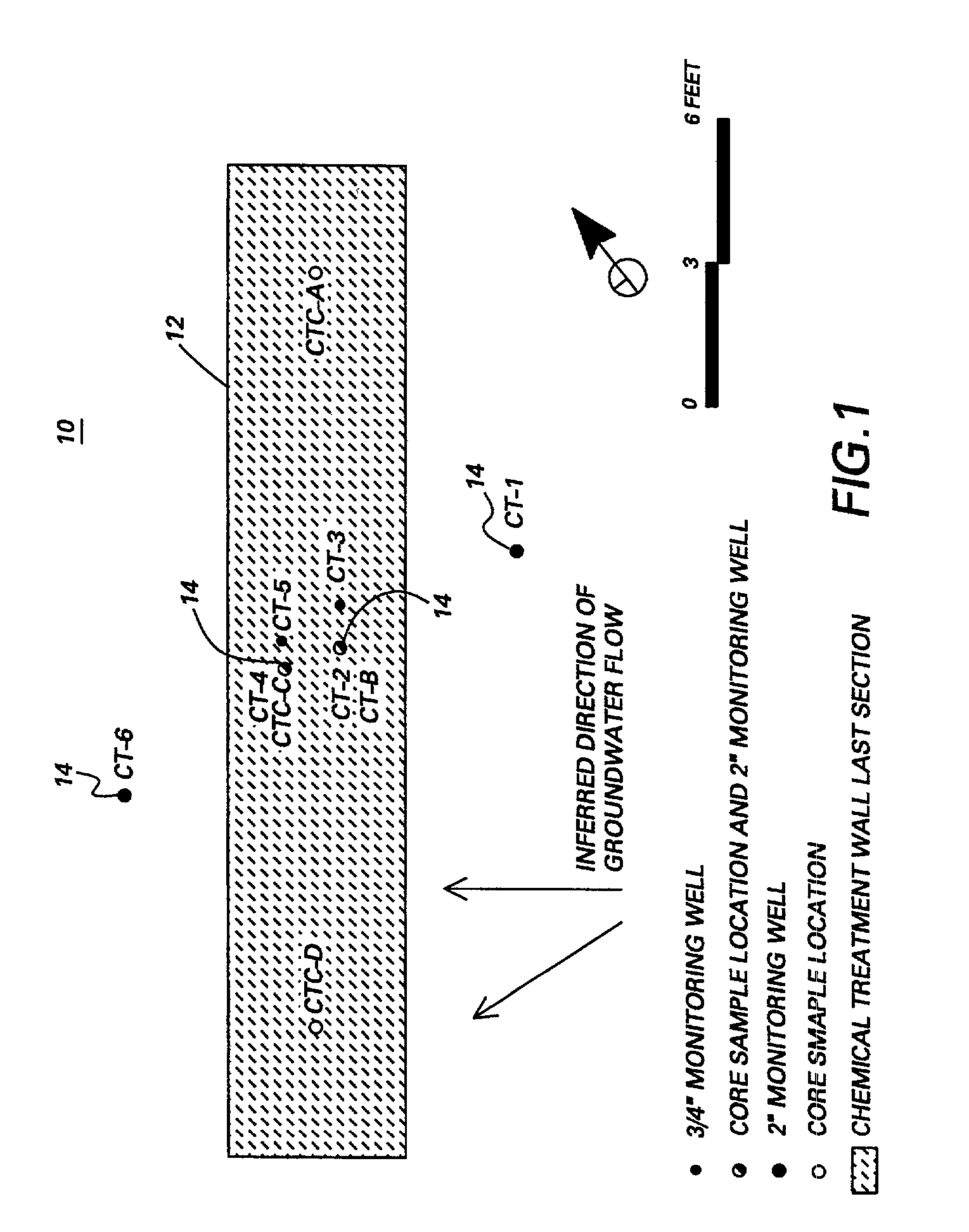
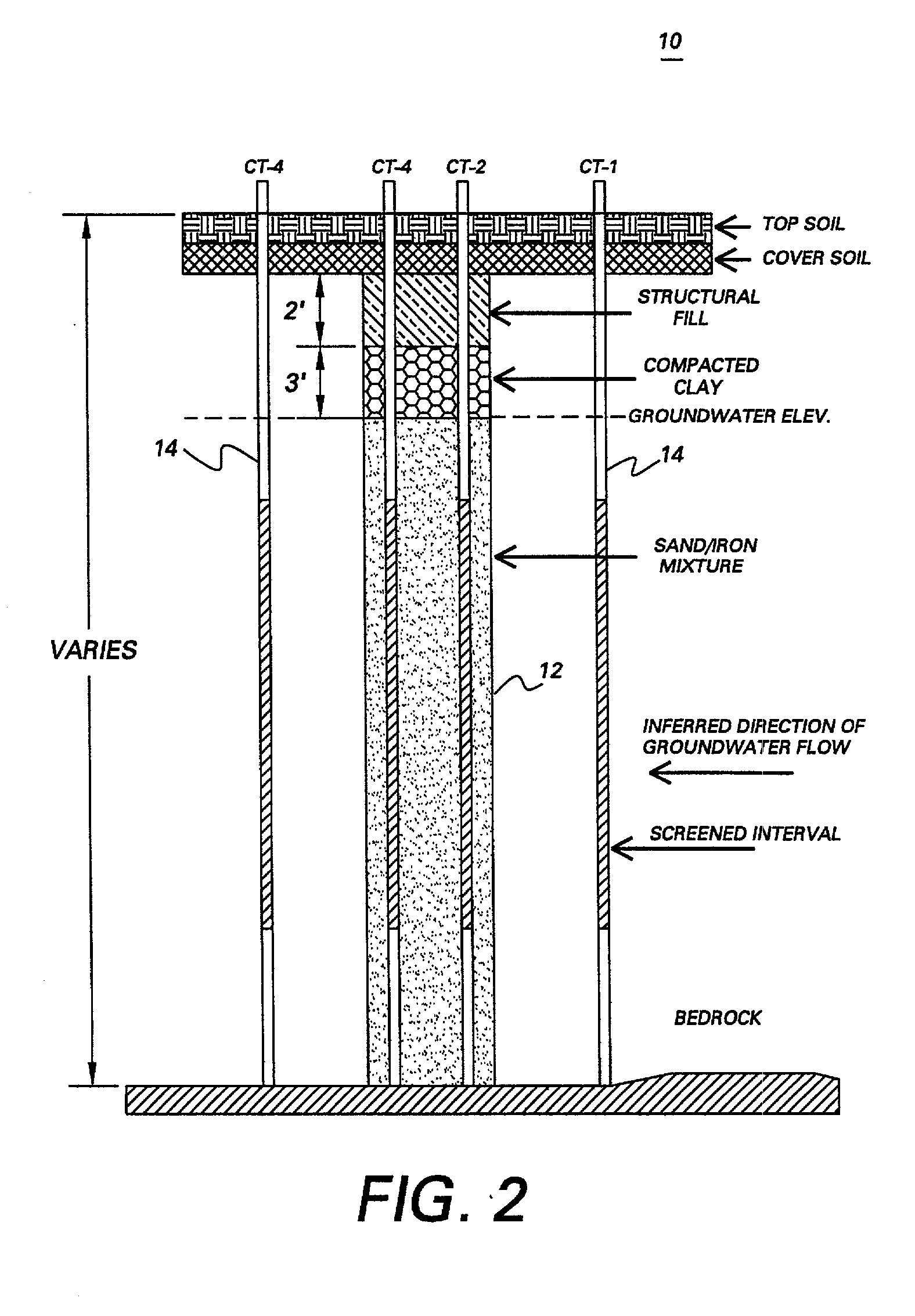
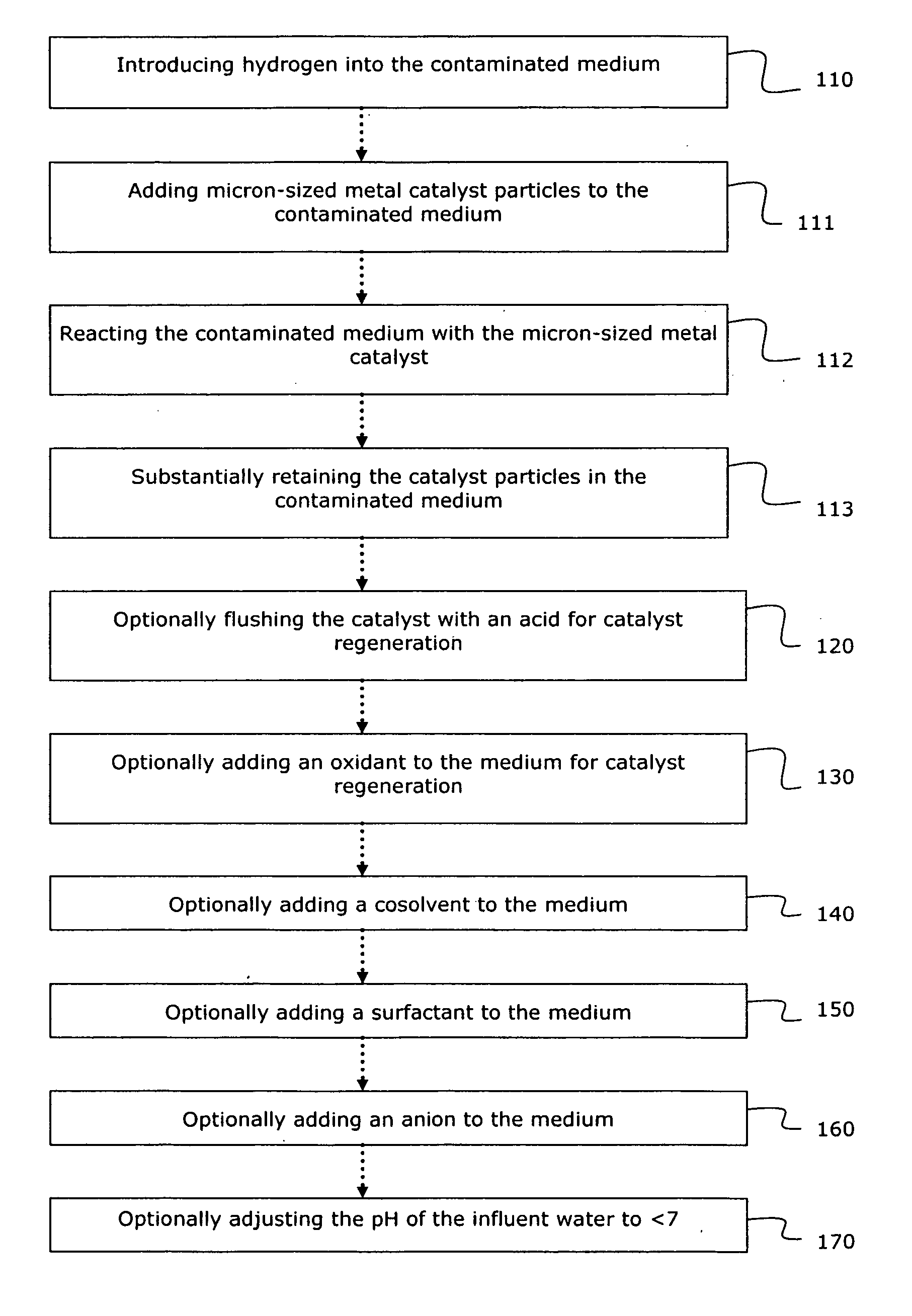
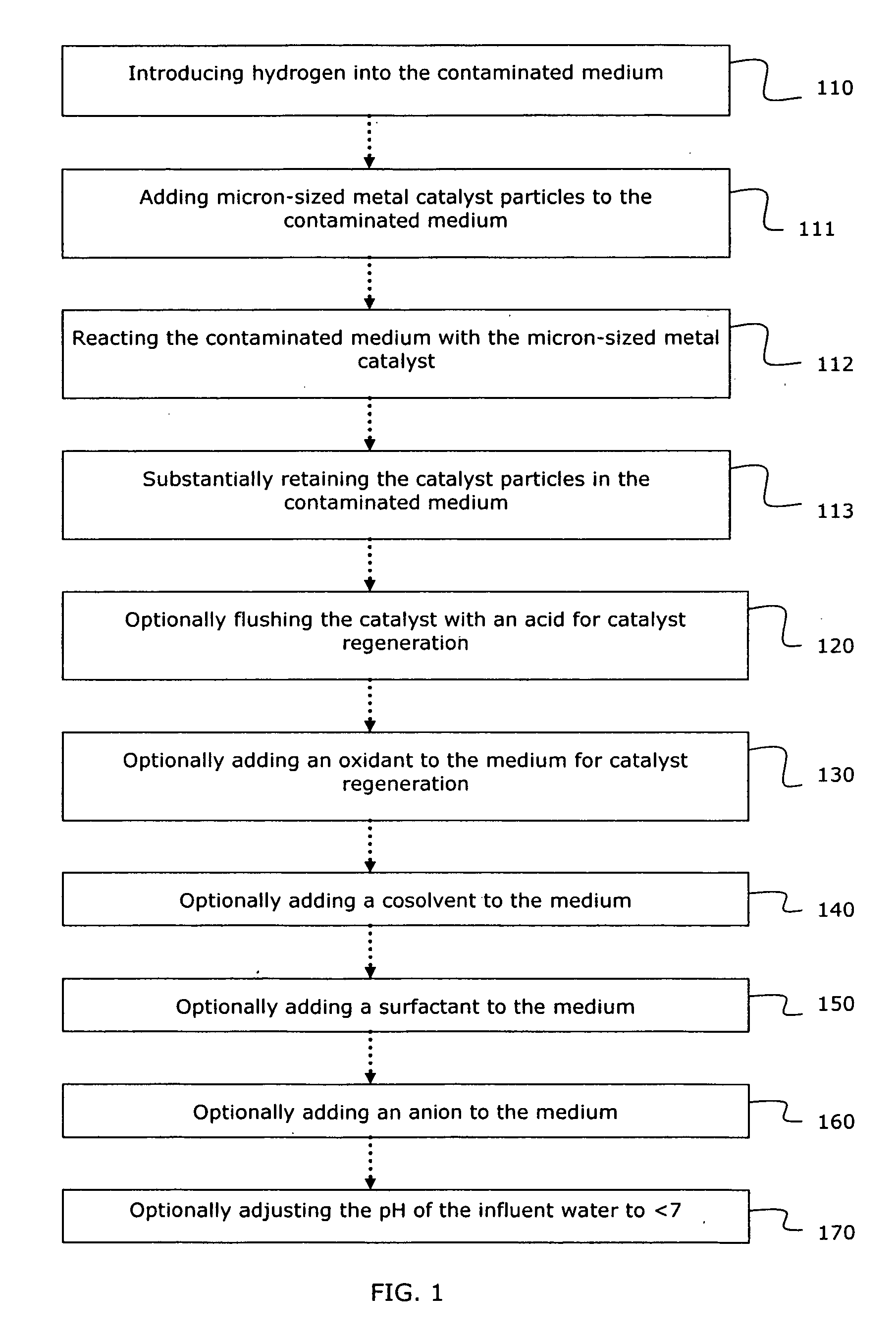
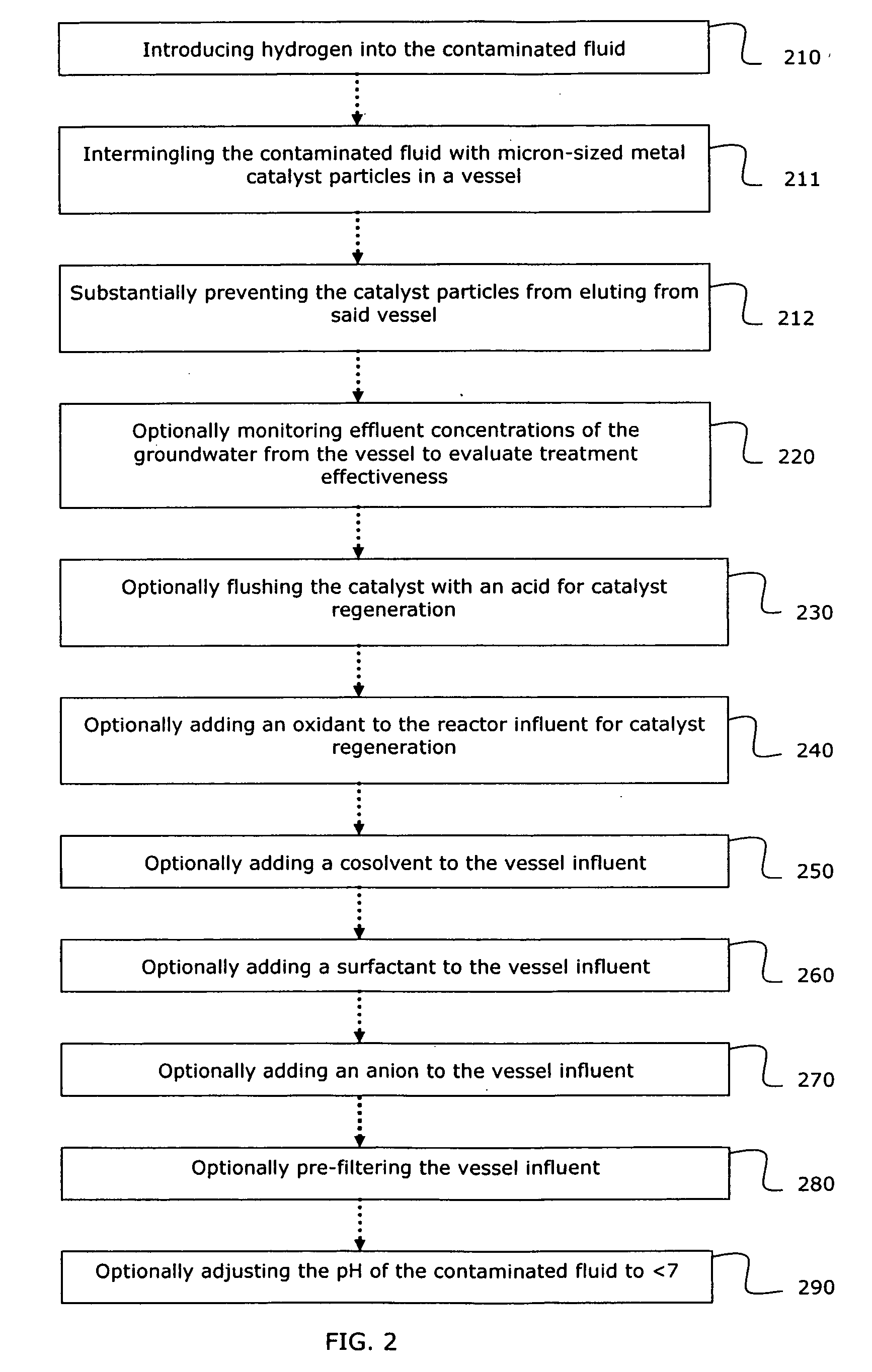
System and method for catalytic treatment of contaminated groundwater or soil
ActiveUS20070119786A1Preventing the catalyst particles from elutingSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsHydrogenMetal catalyst
Owner:SHAW ENVIRONMENTAL & INFRASTRUCTURE
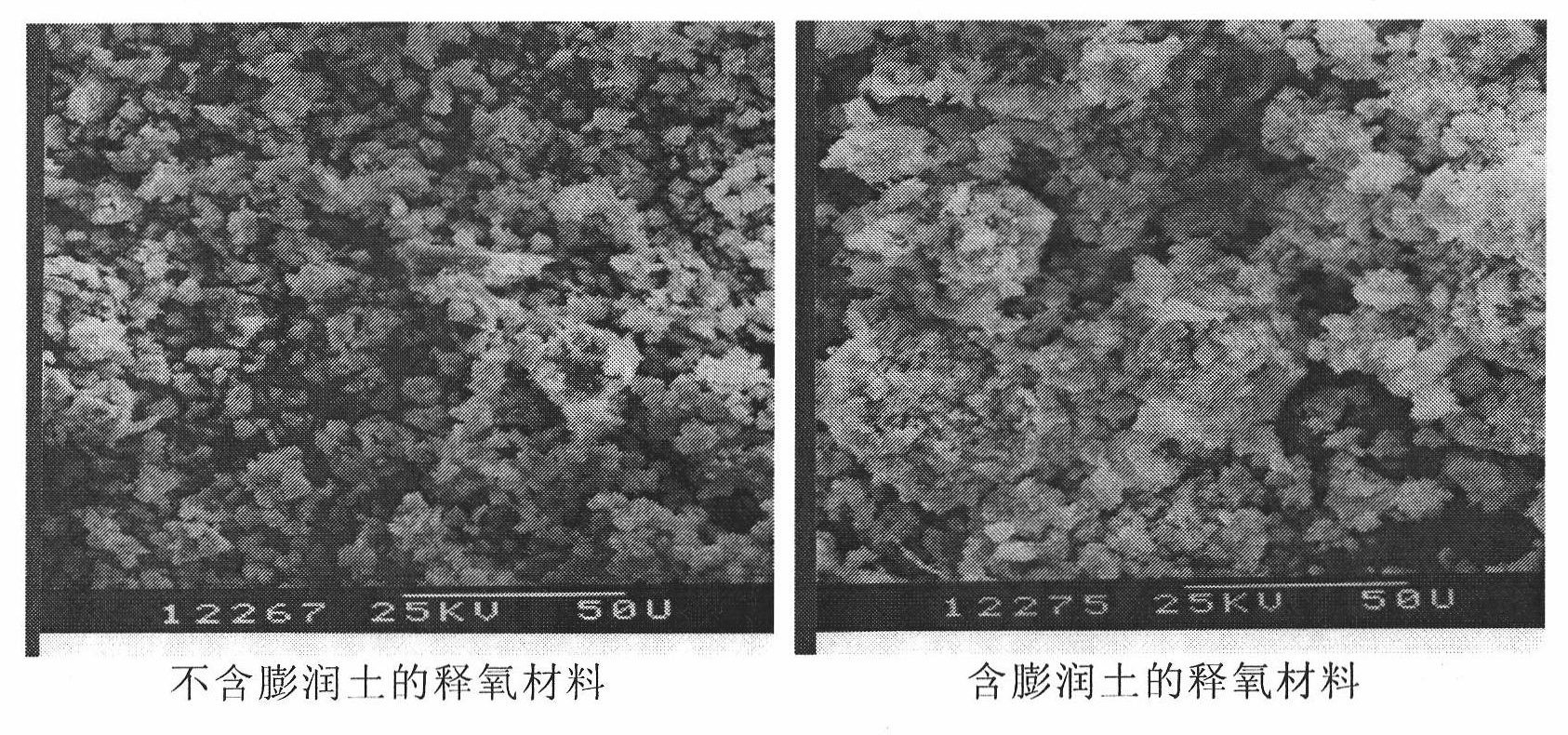
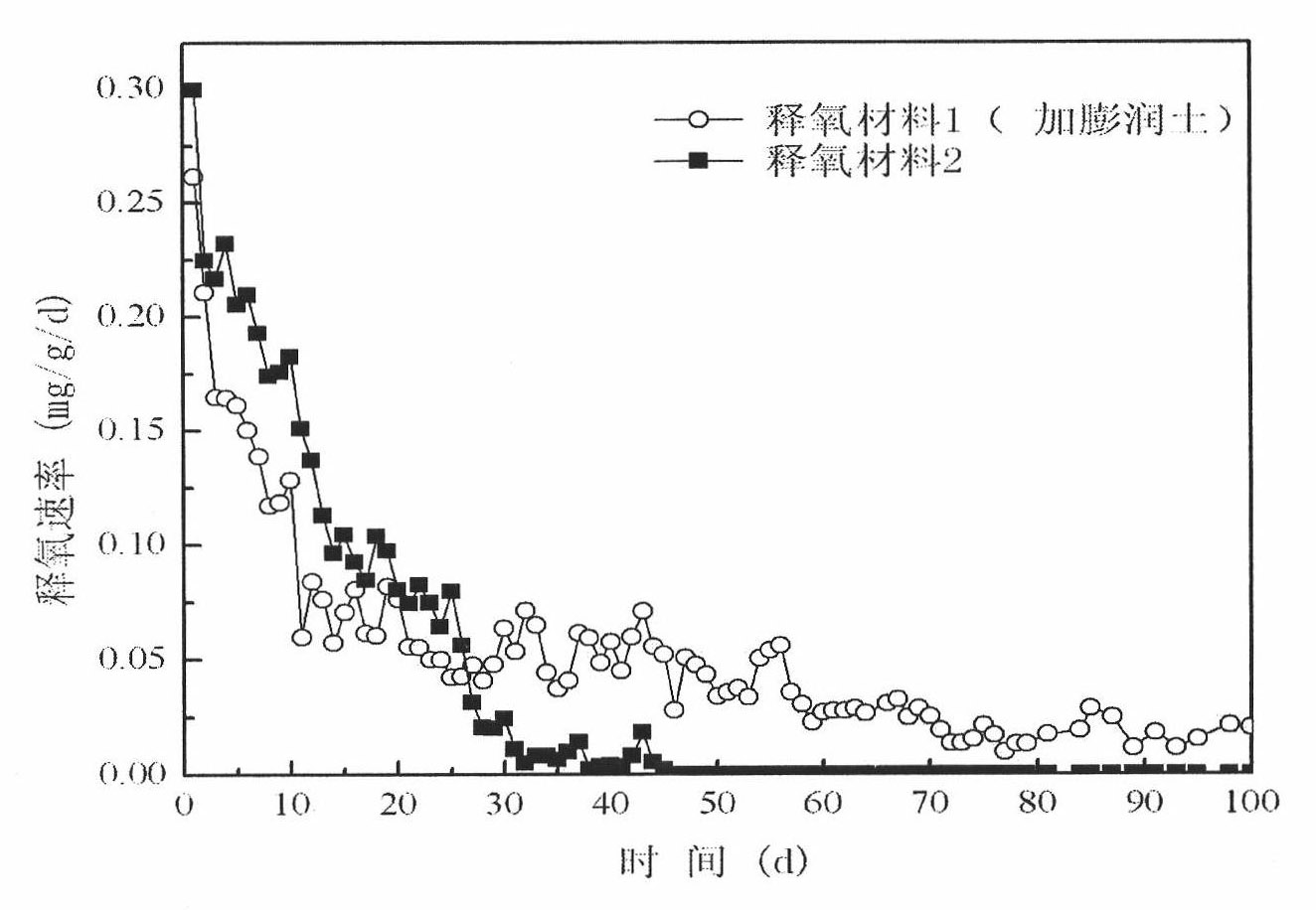
Oxygen releasing material for permeable reactive barrier aerobic biodegradation of groundwater
InactiveCN101921018AInitial oxygen contentSlow oxygen release rateSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentIn situ bioremediationEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to an oxygen releasing material for permeable reactive barrier aerobic biodegradation of groundwater, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5-20% of oxygen releasing compound, 5-20% of bentonite and the balance of coagulant. The oxygen releasing material added with the bentonite has the advantages of large oxygen releasing amount, long oxygen releasing time, low cost and easy preparation; and moreover, the used materials are all natural and easy to obtain and do not cause secondary pollution to the groundwater environment, thereby remarkably improving the in situ bioremediation technology of the contaminated groundwater.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF WATER +1
Method for removing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon methylnaphthalene substance by adopting double oxidants including persulfate and calcium peroxide
ActiveCN104445570ALow costEasy to transportWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a method for removing a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon methylnaphthalene substance by adopting double oxidants including persulfate and calcium peroxide. The method comprises the steps of adding persulfate and calcium peroxide into a water body containing methylnaphthalene, stirring uniformly, and reacting for 4-5 days under the condition that the pH of the system is neutral and weakly acidic, thus removing the pollutant by oxidization. The double oxidants are added into the water, and free hydroxy and sulfate radicals are generated to attack the pollutant, so that the pollutant is effectively degraded. The double oxidants including persulfate and calcium peroxide can simultaneously generate free hydroxy and sulfate radicals with extremely strong oxidation, so that the acting pollutant range is wider than that of a traditional method, and the pollutant sensitive to the free hydroxy and sulfate radicals can be simultaneously removed. The acting time is long, the applicable pH range is wide, a promotion effect on microbes in the environment is achieved, the bioremediation efficiency of microbes in environmental media can be improved, and then the repair efficiency of a polluted area is improved. The method is applicable in the field of polluted underground water repair.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for treating contaminated water
InactiveUS20070158275A1Reduce decreaseIncrease surface areaWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationAbove groundSewage
Zero valent iron particles (14) having enhanced surface area are used to treat contaminated groundwater in-situ or above ground. Hollow and / or porous zero valent iron particles (14) having a generally spherical shape and porous surface are produced using a sacrificial substrate (10) and thermal treatment.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
Method for treating contaminated water
InactiveUS7611637B2Increase surface areaWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationAbove groundSewage
Zero valent iron particles (14) having enhanced surface area are used to treat contaminated groundwater in-situ or above ground. Hollow and / or porous zero valent iron particles (14) having a generally spherical shape and porous surface are produced using a sacrificial substrate (10) and thermal treatment.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
Heavy metal dangerous waste in-situ storage and underground water pollution prevention method
ActiveCN104923544AEasy to refine and recycleSolid waste disposalContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentWater flowEnvironmental engineering
The invention belongs to the field of heavy metal pollution prevention and discloses a heavy metal dangerous waste in-situ storage and underground water pollution prevention method. According to the method, firstly, closure cover is carried out on original heavy metal dangerous waste piles in a valley; then, a vertical seepage prevention curtain is arranged at a valley mouth in the downstream position of the valley for primarily blocking underground water polluted after closure; finally, a permeable reactive barrier is arranged below water flow of the vertical seepage prevention curtain for polluted underground water remediation. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages as follows: an in-situ storage technology is adopted for heavy metal dangerous waste left over by history and polluted underground water remediation is carried out, so that environment is protected, and resources are provided for conveniently refining and recycling heavy metals after the condition is mature in the future.
Owner:HUNAN AIRBLUER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Process for restoration of ground water used in in-situ uranium mining
ActiveUS7294271B1Increase contactEasy to cleanContaminated soil reclamationWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWater useWater cycling
A process for biological restoration of ground water in a mineralized sandstone formation using a nutrient source. The process is used in conjunction with mining uranium using in-situ pump and treat technology. The restoration of the ground water is designed to meet federal and state regulations. The process includes pumping the contaminated ground water from the mineralized sandstone formation using production wells to the ground surface. The ground water is then circulated through at least one ion exchange column. The ion exchange column is used to capture any residual uranium remaining in solution. The treated ground water then flows from the ion exchange column through at least one reverse osmosus unit. The reverse osmosus unit is designed to help decrease any remaining dissolved solids in solution, such as sodium and chloride. From the reverse osmosus unit, the ground water is circulated through at least one de-carbonation column. The de-carbonation column is used to remove residual carbon dioxide in the ground water. Upon exiting the de-carbonation column, a nutrient source is introduced into the ground water for stimulating the indigenous bacteria in the mineralized sandstone formation. The ground water is now pumped back into the ground where it is reintroduced into the sandstone formation.
Owner:POWER RESOURCES
Passive treatment of wastewater and contaminated groundwater
InactiveUS7147779B1High puritySteady nutritional sourceWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment compoundsWastewaterPassive Treatment
A bioremediation system using inorganic oxide-reducing microbial consortia for the treatment of, inter alia coal mine and coal yard runoff uses a containment vessel for contaminated water and a second, floating phase for nutrients. Biodegradable oils are preferred nutrients.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS
Method for remediating contaminated underground water in situ on basis of persulfate thermal activation technique
InactiveCN102241454AStrong oxidationImprove mineralization abilityMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationPersulfateSulfate
The invention discloses a method for remediating contaminated underground water in situ on basis of a persulfate thermal activation technique, which relates to a method for remediating contaminated underground water. The method is used to solve the problems of large investment and low efficiency of the conventional underground water remediation technique. The method comprises: adding persulfate or persulfate compound oxidizer into water, and pumping the solution by an anticorrosion pump into underground water to be remediated; and 2, after the persulfate or persulfate compound oxidizer is mixed with the underground water for 10 to 24 hours, pumping high-pressure vapor into the underground water to be remediated, and remediating the contaminated underground water after 1 to 2 days. When the method disclosed by the invention is used, the work amount is small, the technical investment is small, new toxic matters are not introduced into water, the implementation is easy, and the removal rate of the contaminants reaches 85 to 95 percent. The method is used in the field of underground contaminated water treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
In-situ soil and underground water integrated remediation system and remediation method
PendingCN108435765AEasy to operateImprove repair effectContaminated soil reclamationUnderwaterTreated water
The invention relates to the field of environmental protection, in particular to an in-situ soil and underground water integrated remediation system and remediation method. The system comprises an extraction-injection system, an ozone generation system, a wastewater treatment system, a waste gas treatment system and a hydrogen peroxide configuration system. The extraction-injection system, the ozone generation system, the wastewater treatment system, the waste gas treatment system and the hydrogen peroxide configuration system are connected through corresponding pipelines and are equipped withcorresponding liquid flow meters and gas flow meters. According to the method, through combination with the advantages of extraction-treatment, extraction-injection integration, an underwater circulating well, gas-liquid pollutant treatment, ozone-hydrogen peroxide combined oxidation and in-situ oxidation, polluted underground water is extracted and then is subjected to oxidation treatment through ozone and hydrogen peroxide; and then the treated water containing the ozone and hydrogen peroxide is injected underground to conduct in-situ oxidation remediation. By means of the method, organic polluted soil and underwater can be restored simultaneously. Moreover, the remediation range is wide, the remediation period is short, the cost is low, and operation is convenient.
Owner:内蒙古睿达鑫科技有限责任公司
In situ remediation of contaminated groundwater
Owner:ANTEA USA
In situ perfusion method for remediation of organic contaminated groundwater
ActiveCN105712412AIncrease the speed of diffusionReduce dependenceWater resource protectionContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
The invention relates to an in situ perfusion method for remediation of organic contaminated groundwater. The method includes: opening an extraction valve and a by-pass valve, starting an extraction pump, and conveying contaminated groundwater in an extraction well into a reagent preparation tank through an extraction pipeline; starting a stirrer in the medicament preparation tank, adding a reagent into the reagent preparation tank and stirring the reagent with groundwater evenly to obtain a remediation reagent; opening a reagent perfusion valve and a reagent perfusion pump, injecting the remediation reagent into perfusion wells through a circulating water pipeline and perfusion pipelines; closing the reagent perfusion valve and the reagent perfusion pump, starting the extraction pump and injecting the groundwater in the extraction well into respective perfusion wells through the circulating water pipeline and the perfusion pipelines, and circulating the water power between the extraction well and the perfusion wells; starting a self-priming jet pump on a sampling pipeline, collecting the groundwater in a monitoring well, detecting the redox potential of groundwater and organic pollutant removal rate, and ending remediation until the groundwater is detected to be qualified. The method provided by the invention saves remediation time and cost, and improves the remediation effect.
Owner:WELLE ENVIRONMENTAL GRP CO LTD
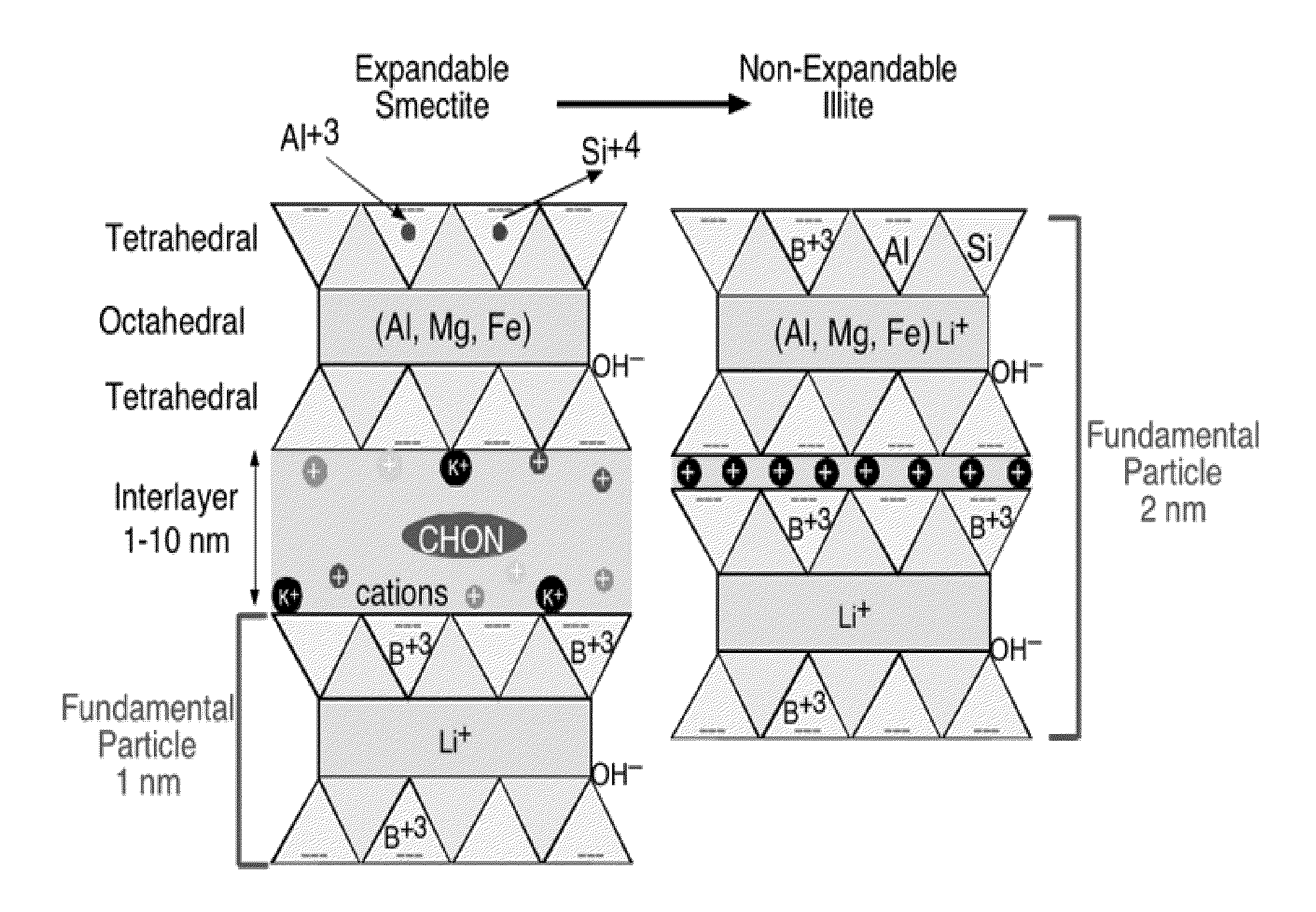
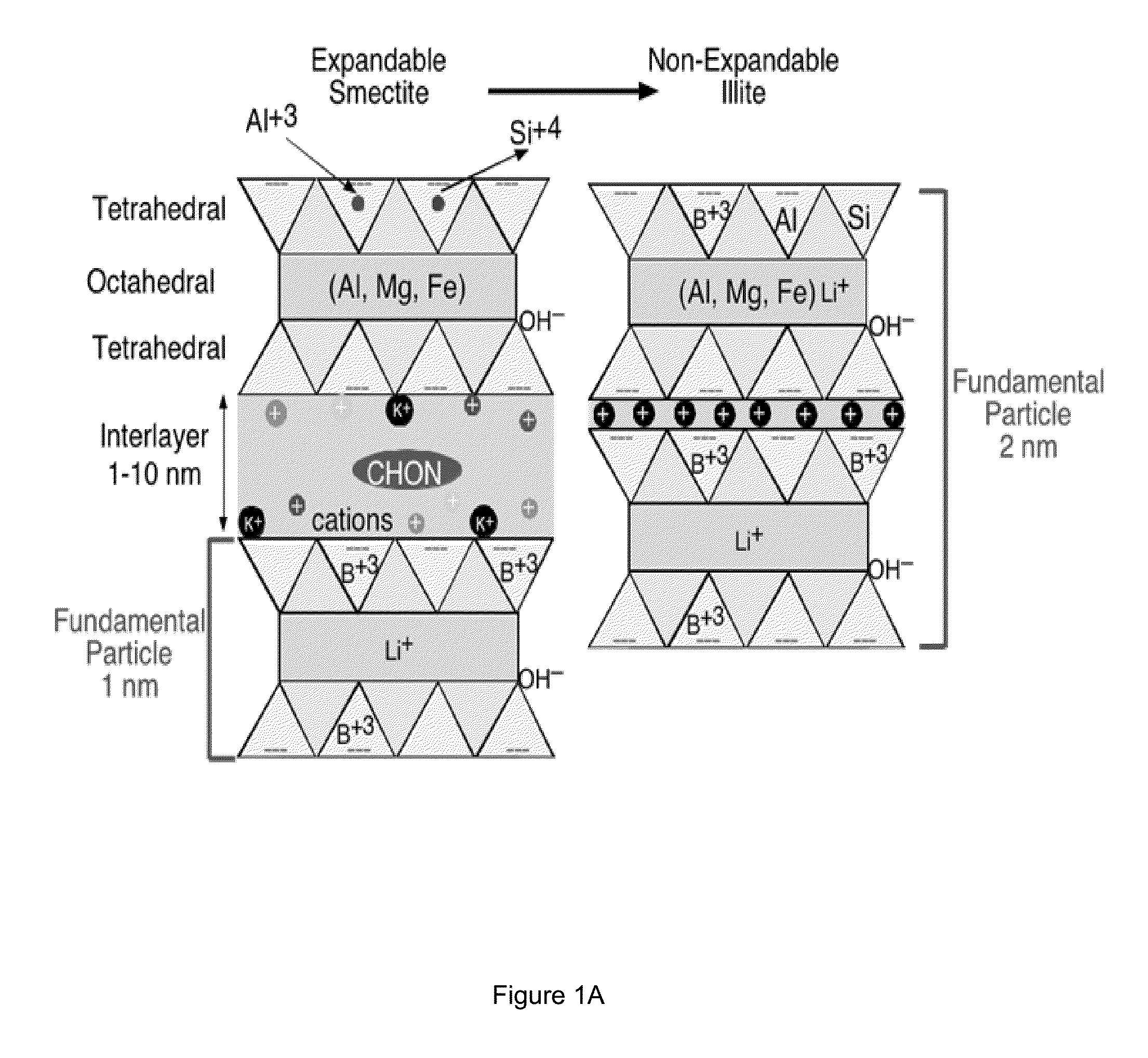
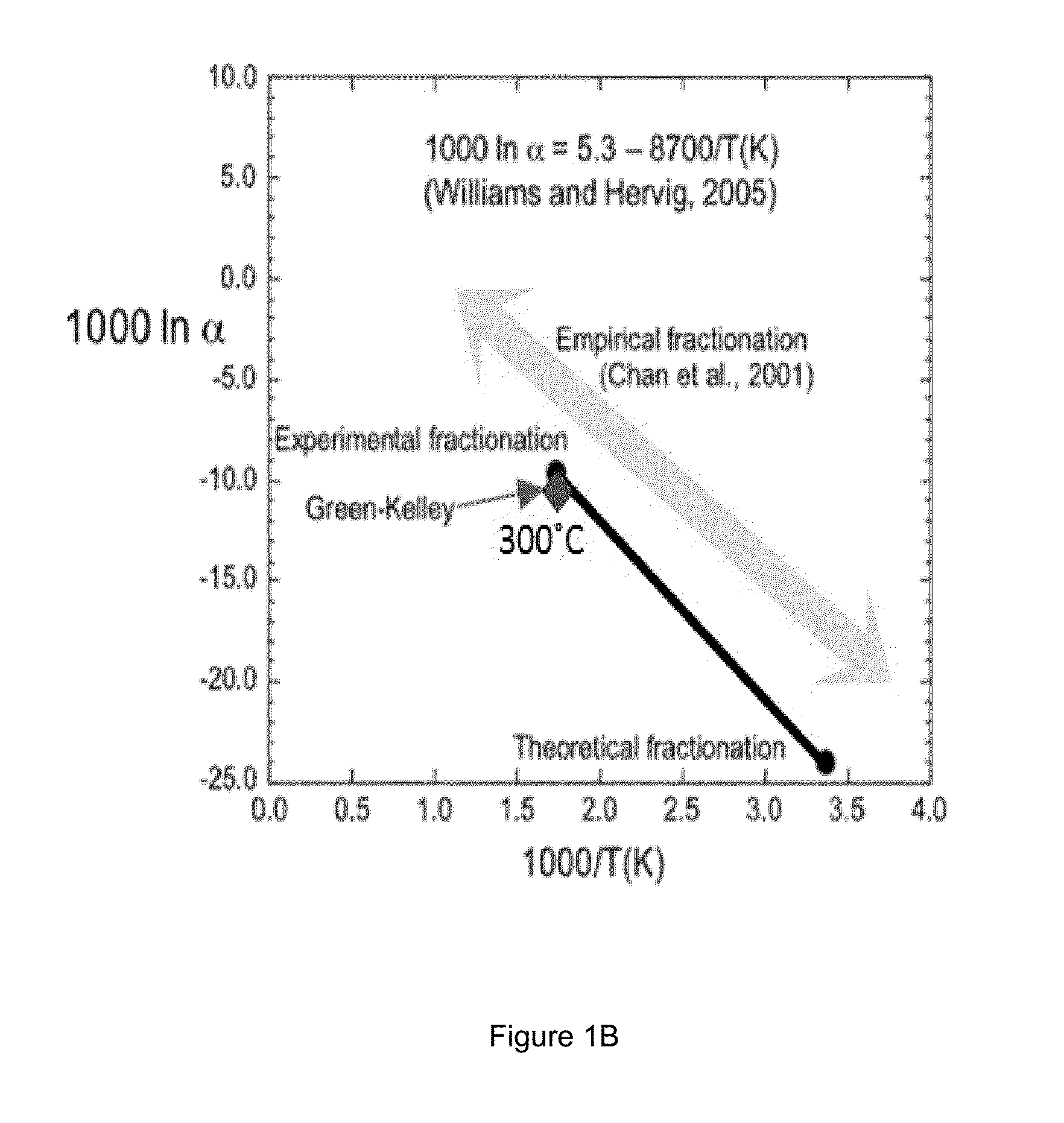
Boron And Lithium Isotopic Method For Tracing Hydrocarbons And Their By-Products
ActiveUS20150198577A1Enhanced overall recoveryEasy to explainEarth material testingIsotope separationGroundwater contaminationRock sample
The invention relates to methods for determining the source of hydrocarbons presented in the pores of a host rock or found in contaminated groundwater. The method includes the steps of (a) determining a first isotopic composition of boron and / or lithium in one or more components within a potential source rock sample, such as kerogen, clay, or water; (b) determining a second isotopic composition of boron and / or lithium in the hydrocarbons found within the pores of a host rock sample or in contaminated groundwater; and (c) comparing the first and second isotopic compositions to determine whether the potential source rock is the source of the hydrocarbons within the pores of the host rock or in contaminated groundwater. The comparison is facilitated by using the isotope fractionation between the kerogen, clay, or water components and the bitumen component of the potential source rock, which allows one to predict the isotope composition of any hydrocarbons originating in the bitumen component of the source rock, based on the isotope composition of one of the other three phases. The method can be used to select host rock for extracting oil and other hydrocarbons, as well as in remediating groundwater contamination.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
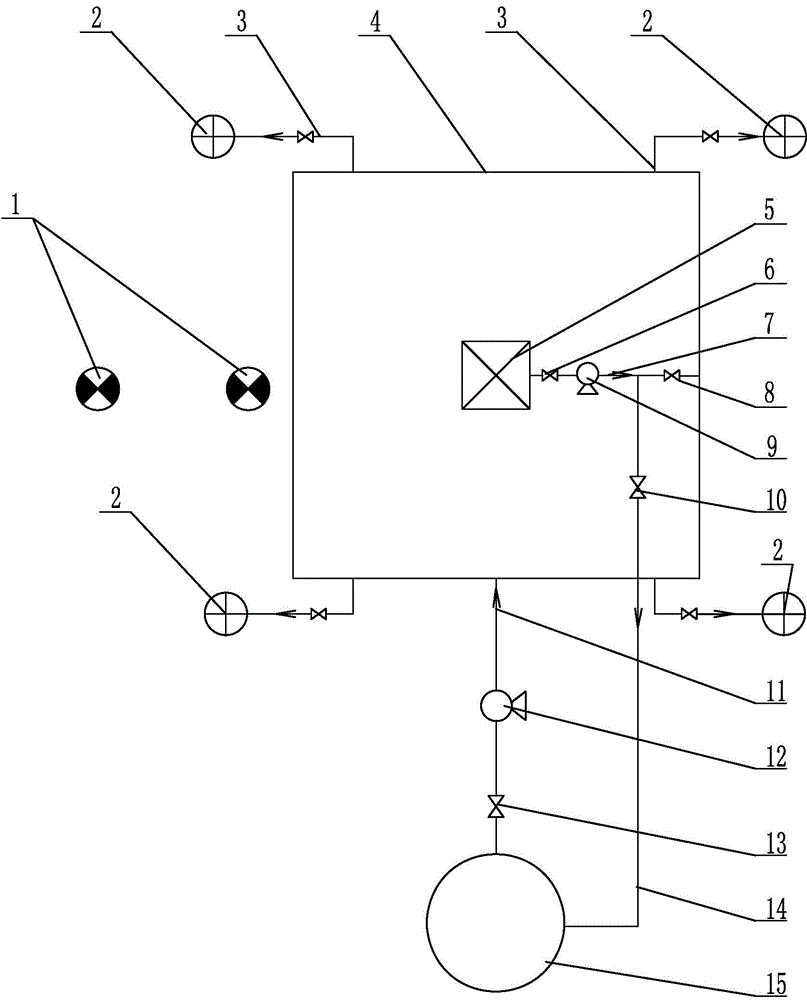
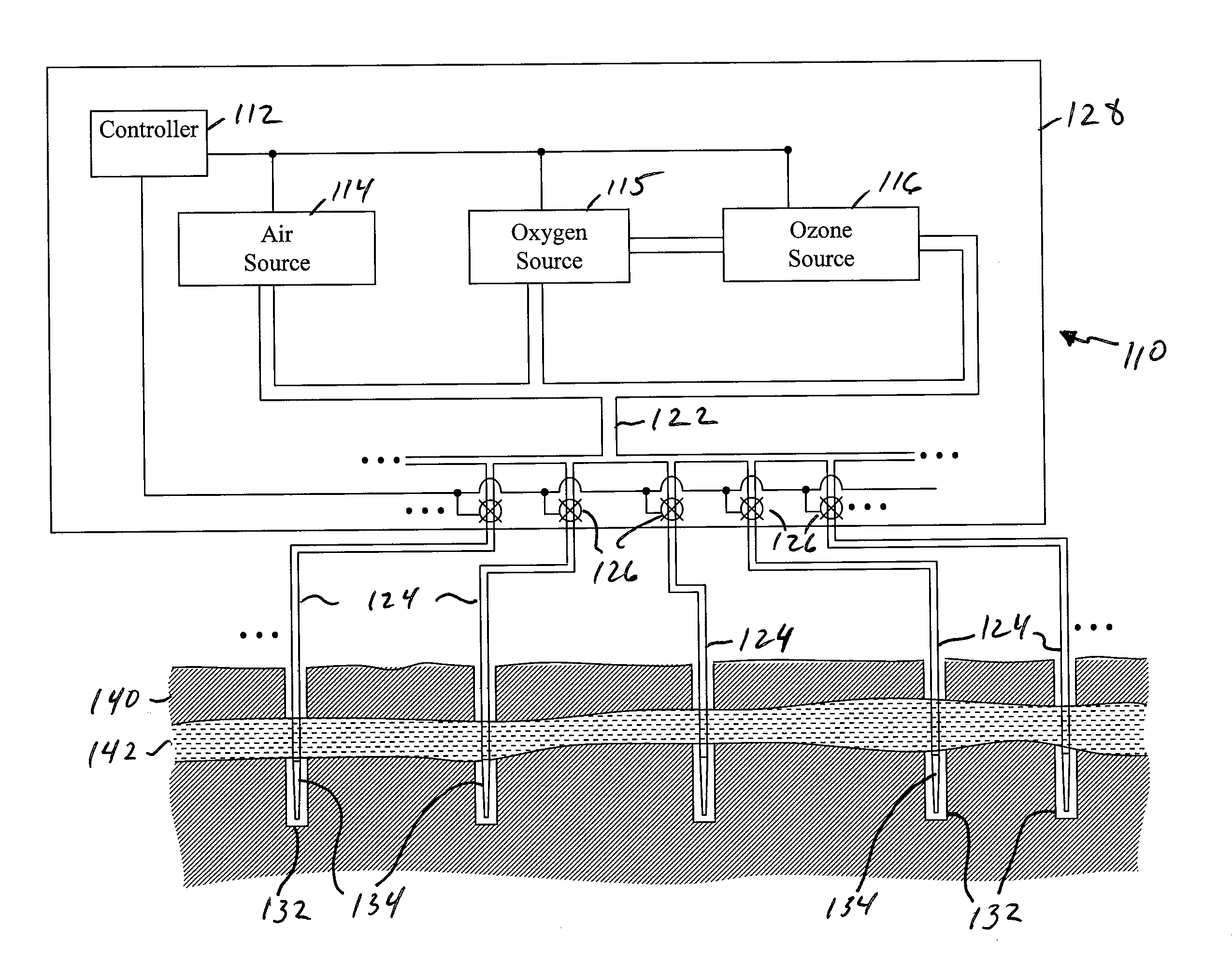
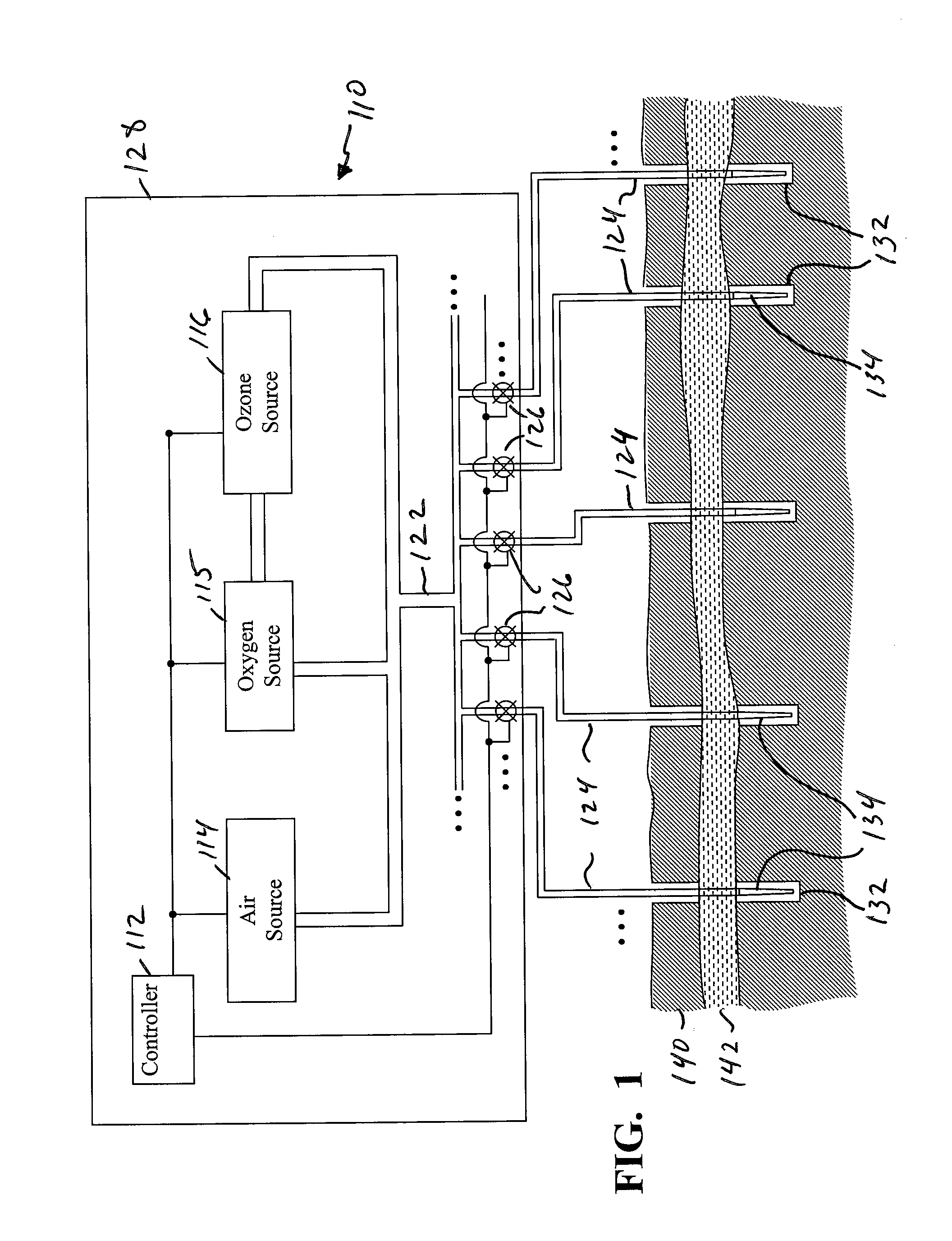
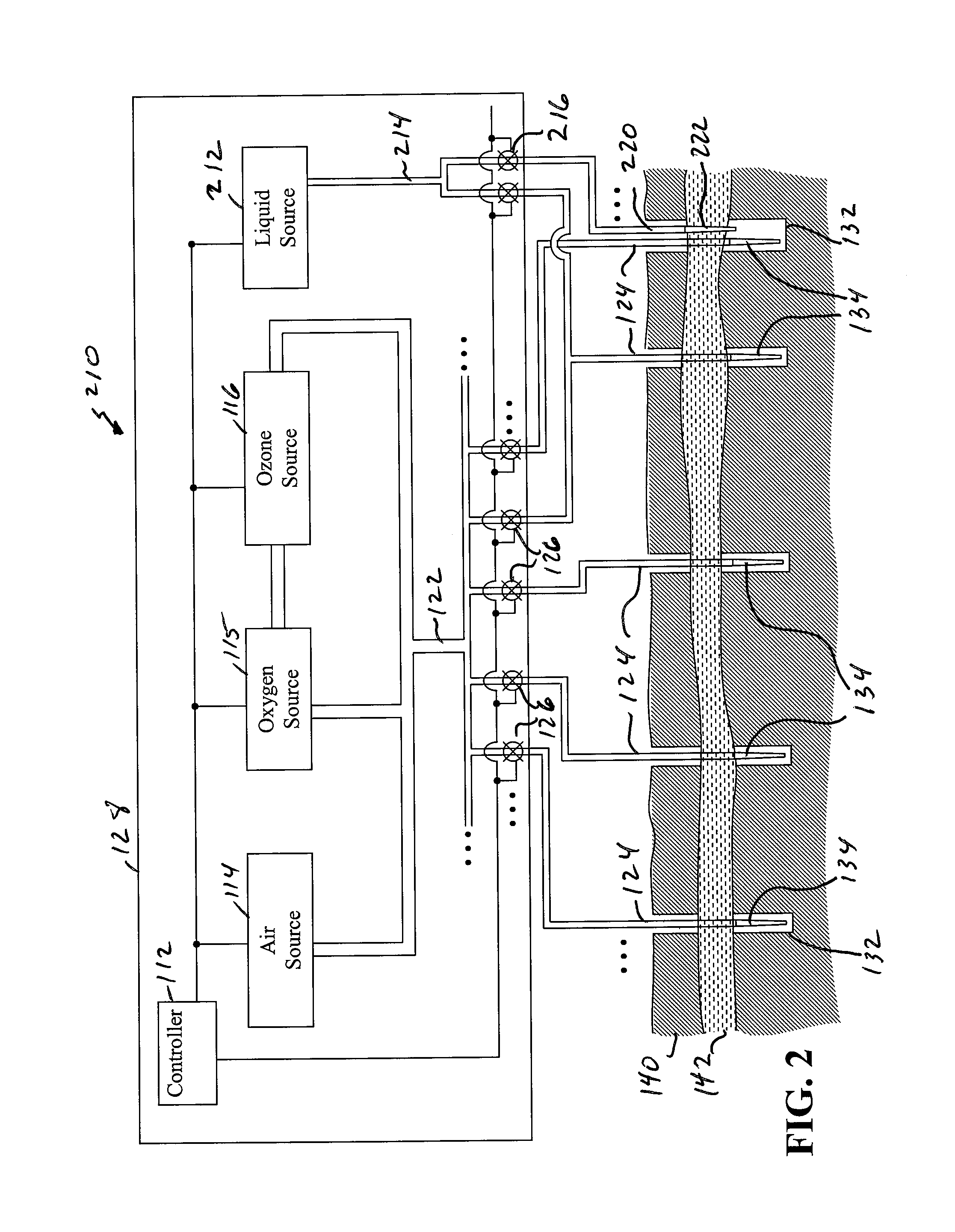
Systems, methods and processes for use in providing remediation of contaminated groundwater and/or soil
The present embodiments provide methods, systems and processes for use in treating soil and / or ground water. Some of these embodiments provide systems for use in remediating contaminants, where the system comprises: a plurality of gas product sources positioned at a geographic location to be treated; a distribution manifold coupled with the plurality of product sources; a plurality of diffuser coupled with the distribution manifold and is positioned within separate wells within the soil; and a controller coupled with the plurality of product sources and the distribution manifold. The controller: activates one or more of the product sources to generate, locally at the geographic location, one of five different gas products in accordance with a first step of a treatment schedule; and communicates with the distribution manifold to direct the generated one of the five gas products to a predefined one of the diffuser.
Owner:H2O ENG LLC
Bioremediation of nitrate contaminated groundwater
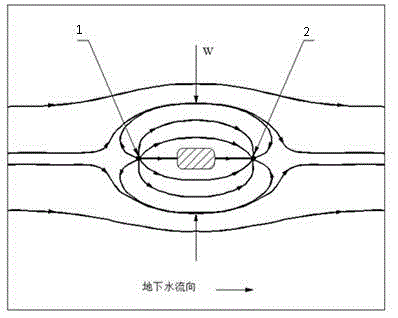
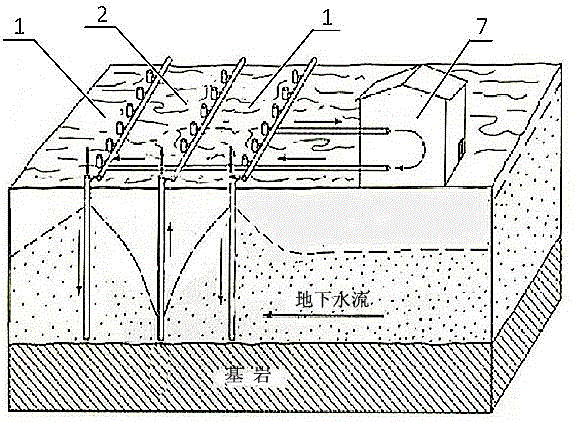
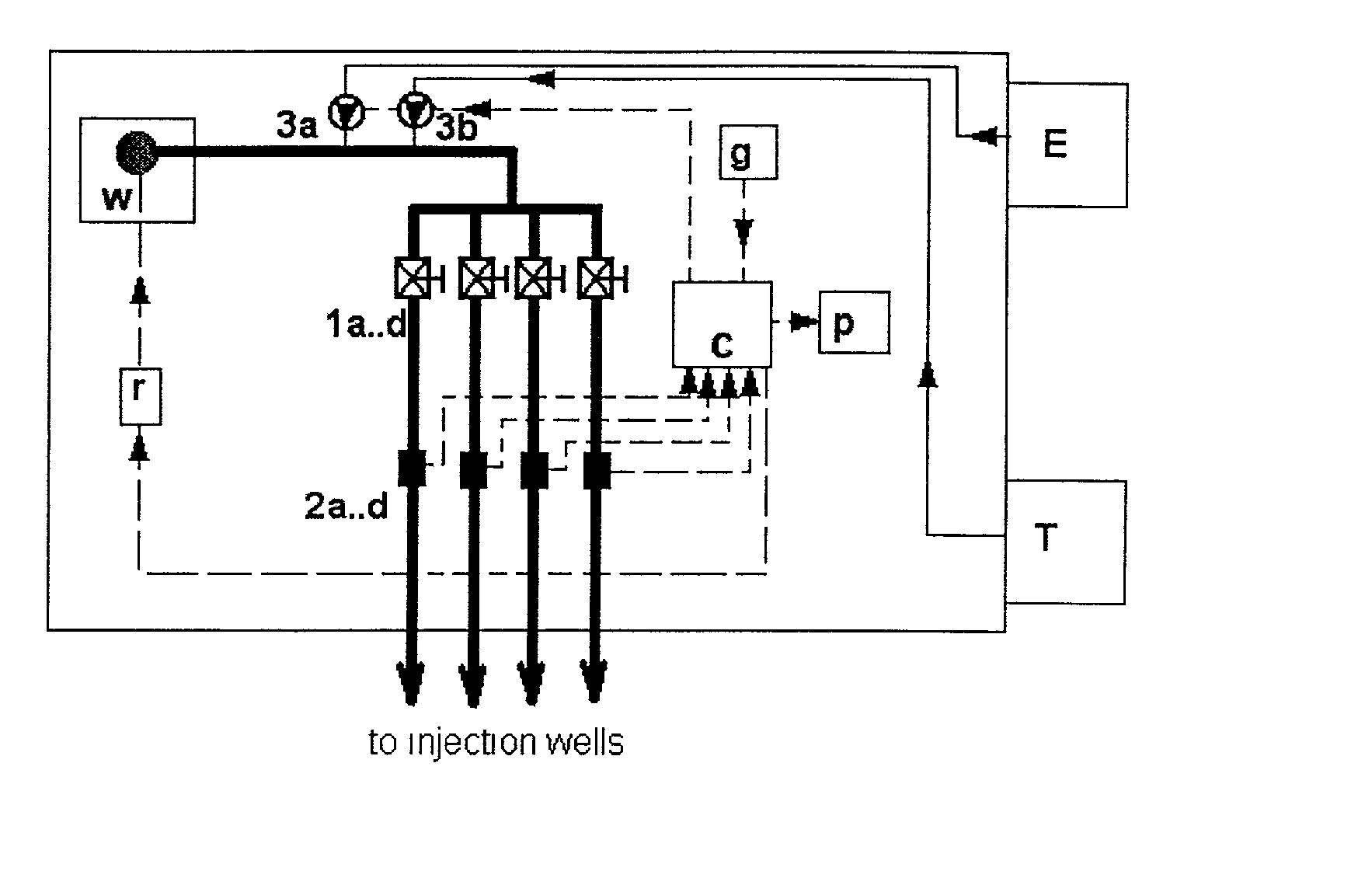
The invention disclosed relates to a method and apparatus for the denitrification of groundwater in situ in an aquifer under substantially anaerobic conditions, the method comprising (a) providing a network, including an extraction well for removal of groundwater from the aquifer and a plurality of injection wells for returning groundwater to the aquifer, the injection wells being arranged in a line substantially perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow, the extraction well being located downstream or upstream of the line of injection wells, and the spacing of the wells and the number of injection wells being determined by the mathematical relationship <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00001"> <number>1< / number> J = C p + nC 1 W → min ( 1 ) <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00001" file="US20020020664A1-20020221-M00001.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00001" wi="216.027" he="18.00225" file="US20020020664A1-20020221-M00001.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> where J is the cost of treatment, Cp and C1 are the costs of extraction and injection wells, respectively; n is the number of injection wells, and W is the distance across the protected area, and wherein the water stream is evenly distributed between injection wells, according to the relationship: <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>Fl=Fe / n=const (2) < / in-line-formula>where F is the water flow rate (e-extraction well, i-injection well) and n is the number of injection wells, (b) removing groundwater from the aquifer by the extraction well, (c) adding a carbon source to the groundwater in a controlled manner, (d) returning the carbon source amended groundwater to the aquifer by the injection wells in even distribution, the water flow rate being controlled, and (e) monitoring the nitrate concentration of the groundwater removed from the extraction well, a decrease in nitrate concentration being indicative of denitrification.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Volatile organic compound contaminated groundwater restoration method
InactiveCN102992508AGood removal effectSolve pollutionWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeMultistage water/sewage treatmentDesorptionGas phase
The present invention discloses a volatile organic compound contaminated groundwater restoration method, wherein a stripping-resin adsorption combination process is adopted to remove volatile organic compounds in groundwater. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) contaminated groundwater is extracted and filtered, and then enters a stripping tower from the top, such that the volatile organic compounds in the groundwater enter a gas phase; (2) stripping gas discharged from the top of the tower is collected through a top gas collector, and then is introduced into a gas phase adsorption column filled with an adsorption resin to carry out an adsorption treatment; (3) at a room temperature, the stripped groundwater in the step (1) is introduced in a liquid phase adsorption column filled with an adsorption resin to carry out a treatment; (4) recharging the treated groundwater in the step (3) to the groundwater layer; and (5) regenerating the adsorption resins in the step (2) and the step (3) by using a desorption agent, wherein the adsorption resins are subjected to adsorption penetrating. According to the present invention, the stripping-resin adsorption combination process is adopted to remove volatile organic compounds in groundwater, a new groundwater ectopy restoration technology is provided, and the restoration method provides high removal effects for various volatile organic compounds in the extracted groundwater.
Owner:江苏常环环境科技有限公司
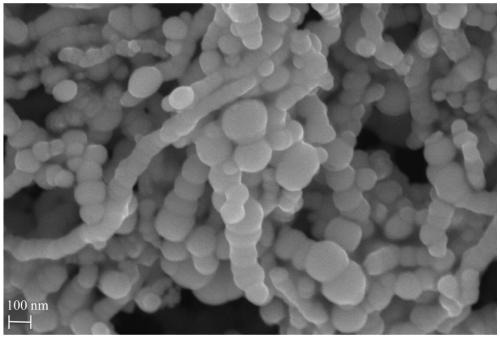
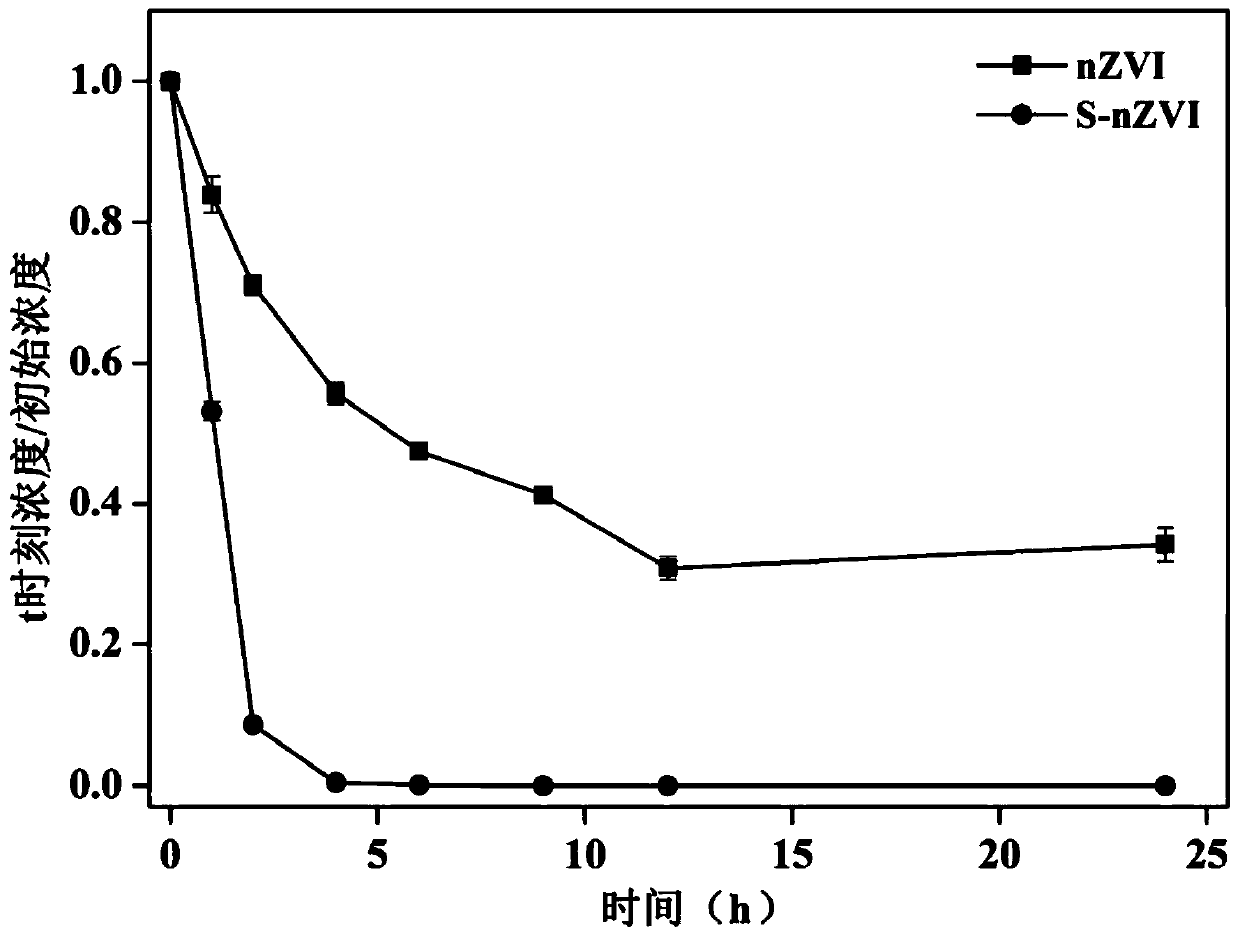
Sulfide nanometer zero-valent iron particle as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110156133AHigh selectivityImprove reduction conversion efficiencyTransportation and packagingWater contaminantsFerrousNanometre
The invention discloses a sulfide nanometer zero-valent iron particle as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the sulfide nanometer zero-valent iron particlecomprises the following steps: 1) reacting ferrite and NaBH4, and preparing nanometer zero-valent iron particles; and 2) coating the nanometer zero-valent iron particles with elemental sulfur powder,and preparing elemental sulfur coated nanometer zero-valent iron particles. The nanometer zero-valent iron particles are subjected to coating modification by taking the elemental sulfur powder as a sulfur source, the preparation method is mild in reaction conditions, simple in operation and low in production cost, and large-scale production is conveniently performed. Moreover, the prepared sulfide nanometer zero-valent iron particle has high selectivity on targeted pollutants and high reductive transformation efficiency, and can be applied to repair treatment of contaminated underground wateror soil on a large scale.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
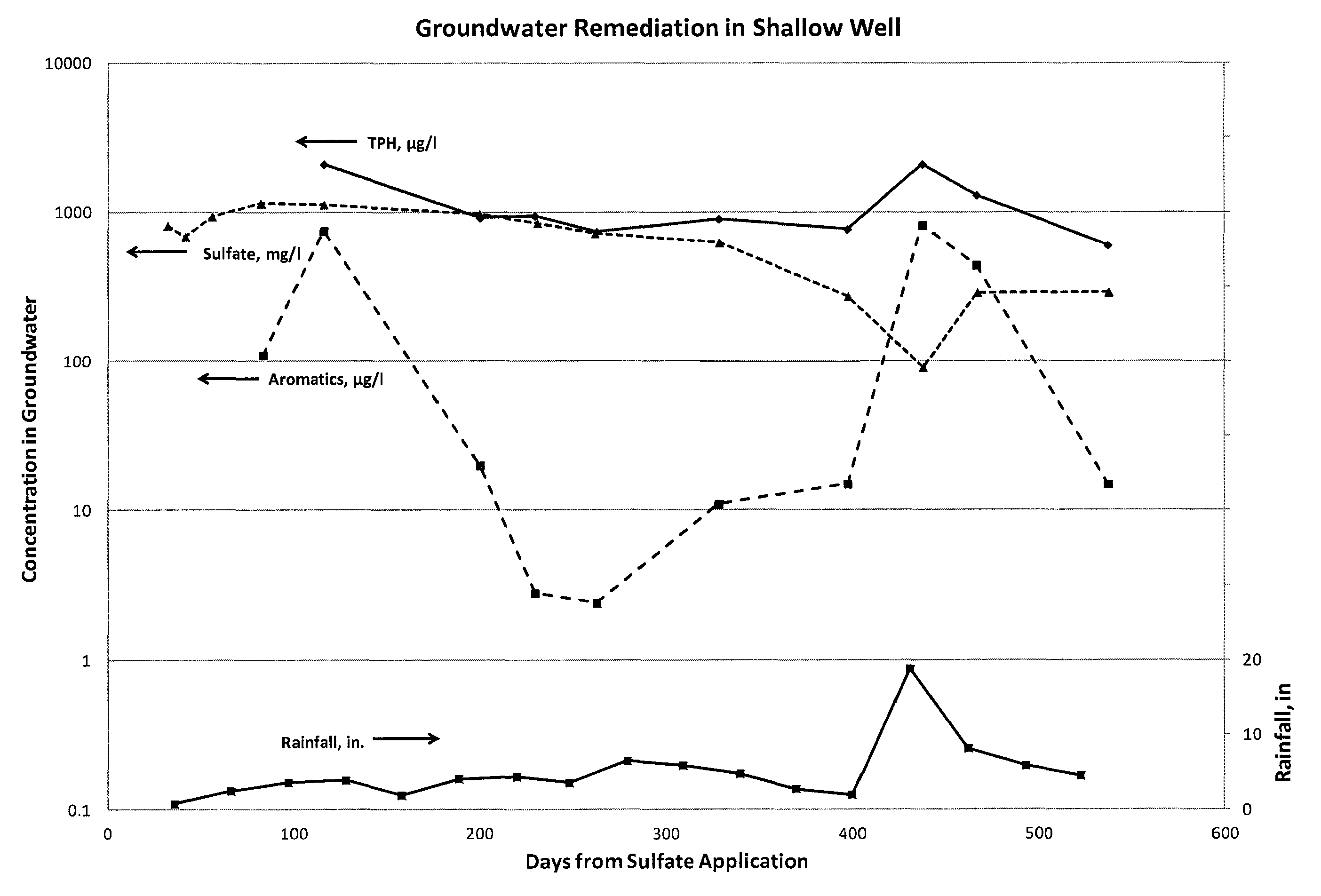
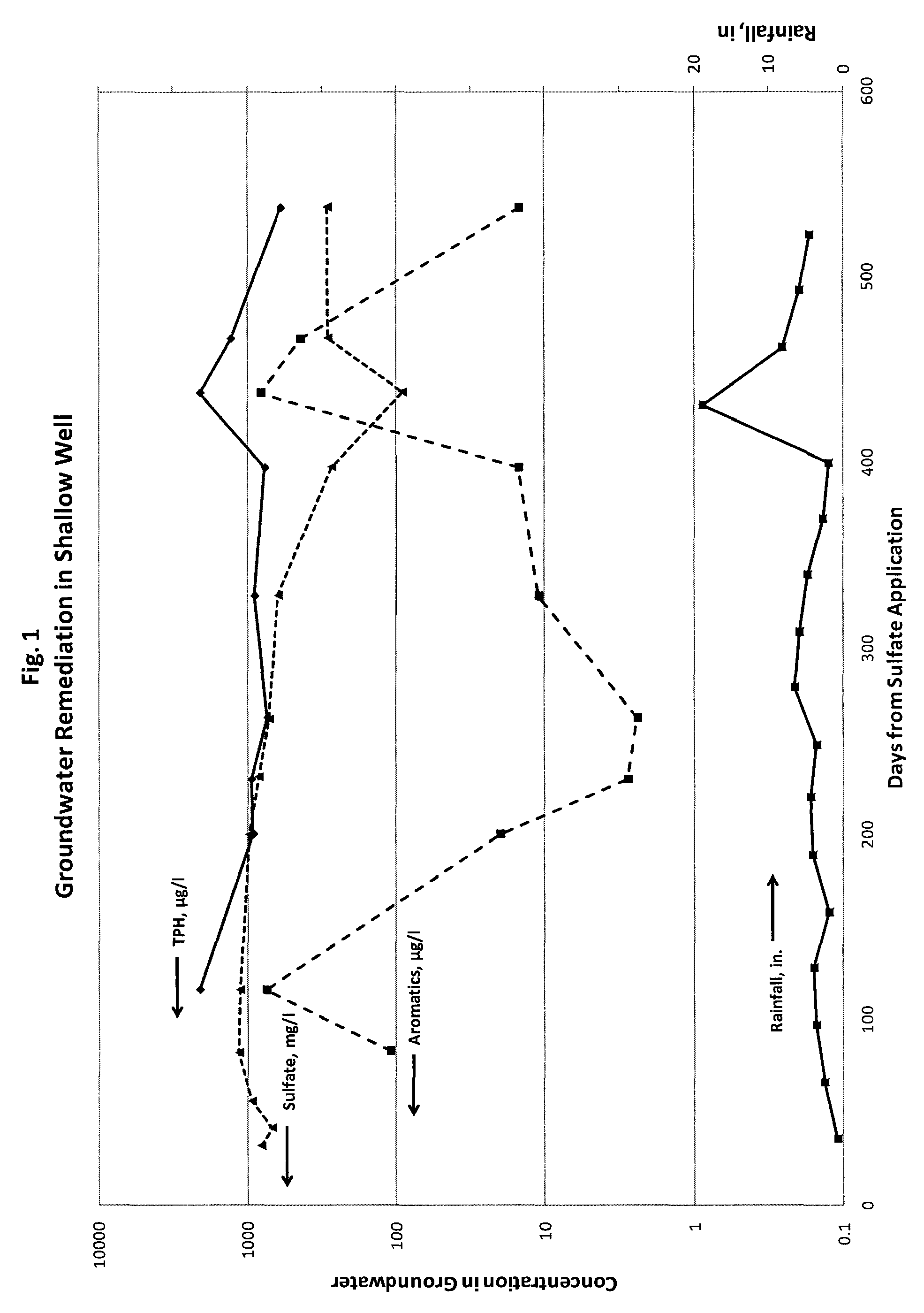
In situ bioremediation of contaminated groundwater using electron acceptor salts
ActiveUS8986545B2Water treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsIn situ bioremediationEarth surface
A process is provided for bioremediating petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater by applying at least one electron acceptor salt to a ground surface overlying the contaminated groundwater. The process includes identifying characteristics of the aquifer, in which the contaminated groundwater is found, to enable treatment of aquifers at a range of depths below the ground surface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
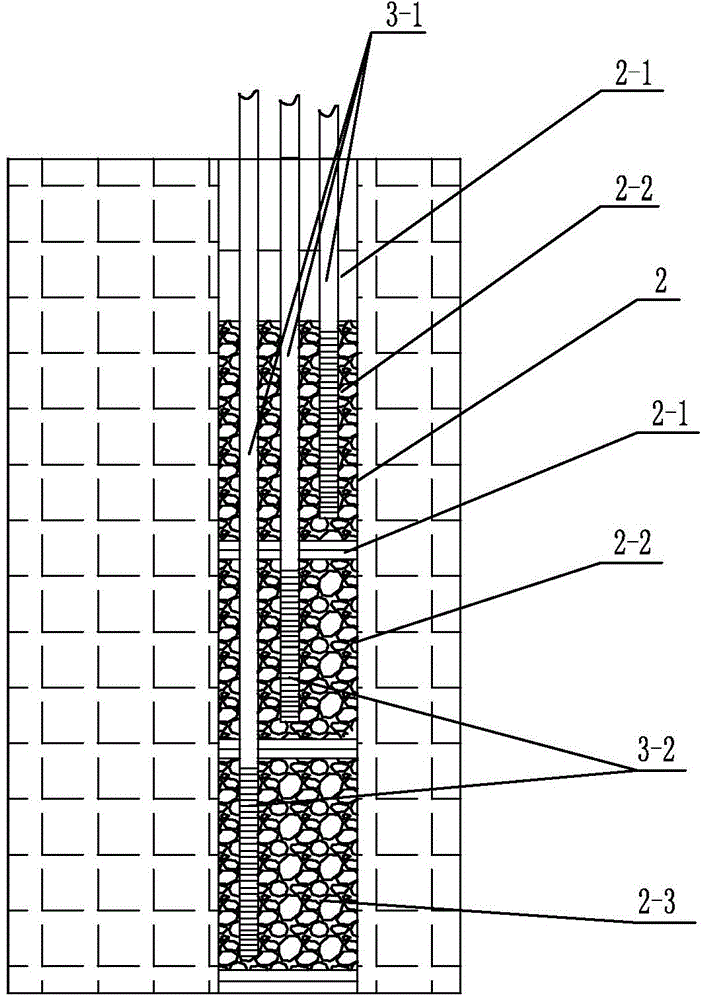
Method and system for remediation of contaminated groundwater by adopting horizontal transverse pipes arranged in radiation type
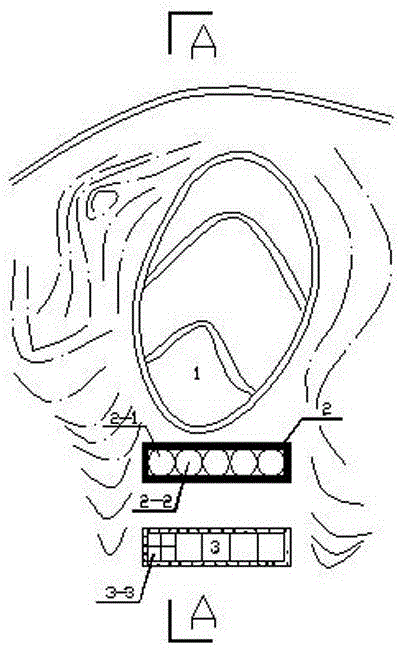
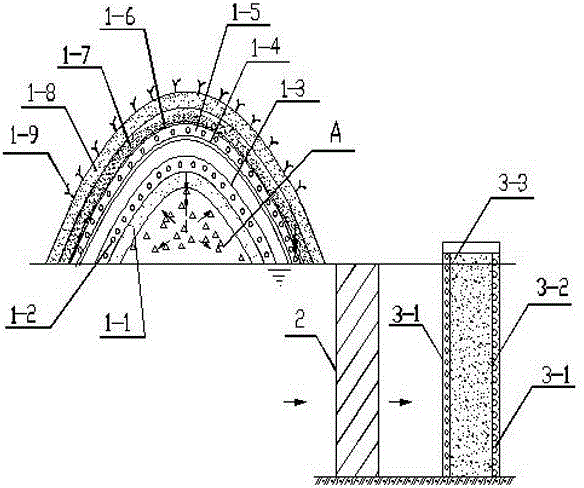
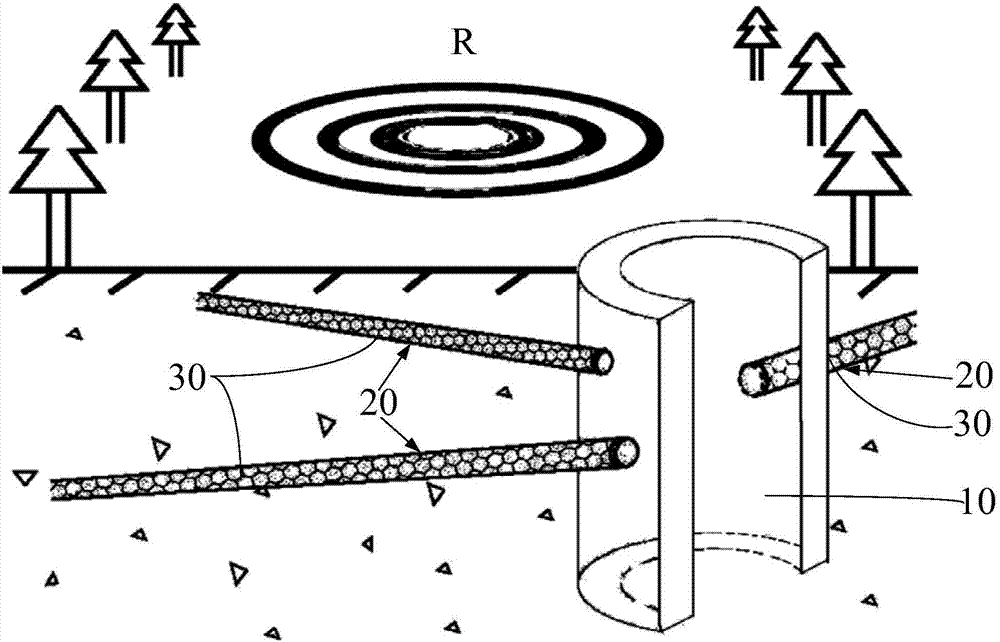
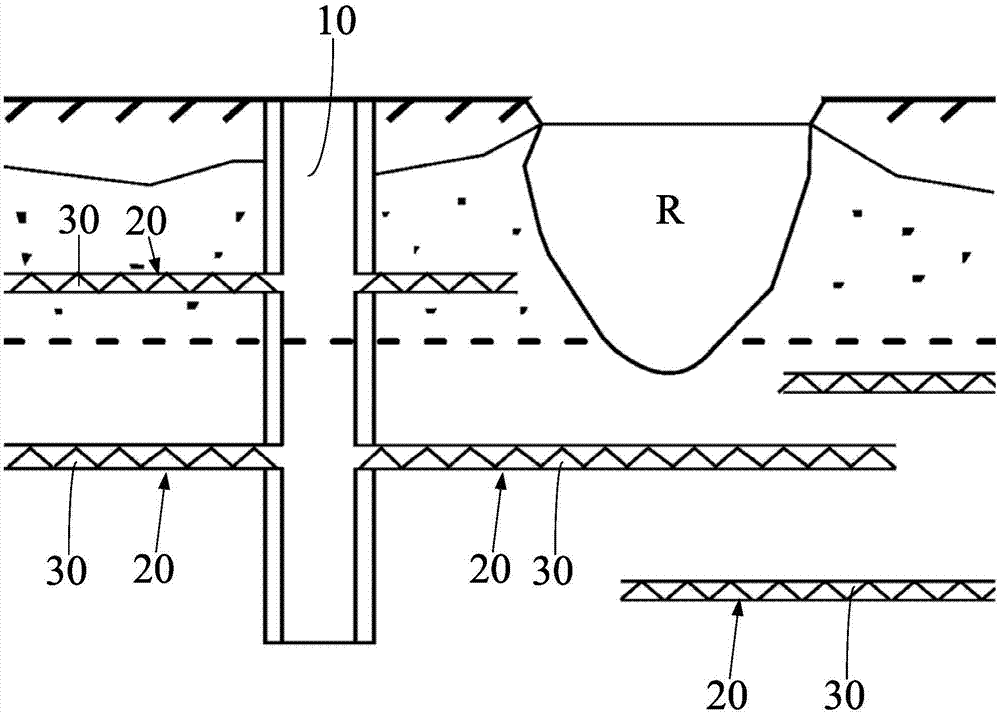
PendingCN108002468AIncrease the collection areaImprove collection and processing efficiencySewerage structuresTreatment involving filtrationIn situ remediationGroundwater remediation
The invention belongs to the technical field of contaminated groundwater treatment, and more specifically relates to a method and system for remediation of contaminated groundwater by adopting horizontal transverse pipes arranged in a radiation type. According to the method provided by the invention, channel groups are arranged in the remediation areas of groundwater to place the transverse pipe groups, and the transverse pipe groups and a water collecting vertical shaft work together, so that the collection area of the groundwater can be greatly increased, the efficiency of collection and treatment of the groundwater can be effectively improved, the in-situ remediation treatment of deep groundwater can be realized, and the elevation range of groundwater treatment can be accurately controlled; the number of water supply vertical shafts can be greatly reduced, the construction costs can be reduced, and the construction difficulties and safety risks can be reduced; the problem that the elevation range of groundwater treatment is difficult to accurately control through a method of discharging the groundwater by adopting pipe well groups is overcome, and the difficulty that a permeablereactive barrier cannot repair the deep groundwater is overcome; and according to the method and system for remediation of the contaminated groundwater by adopting the horizontal transverse pipes arranged in the radiation type, the technical project quantity is small, the construction cost is low, the horizontal transverse pipes can collect and treat the groundwater for a long time after being driven under the ground, and the operation and maintenance costs in the later period are low.
Owner:POWERCHINA WATER ENVIRONMENT GOVERANCE
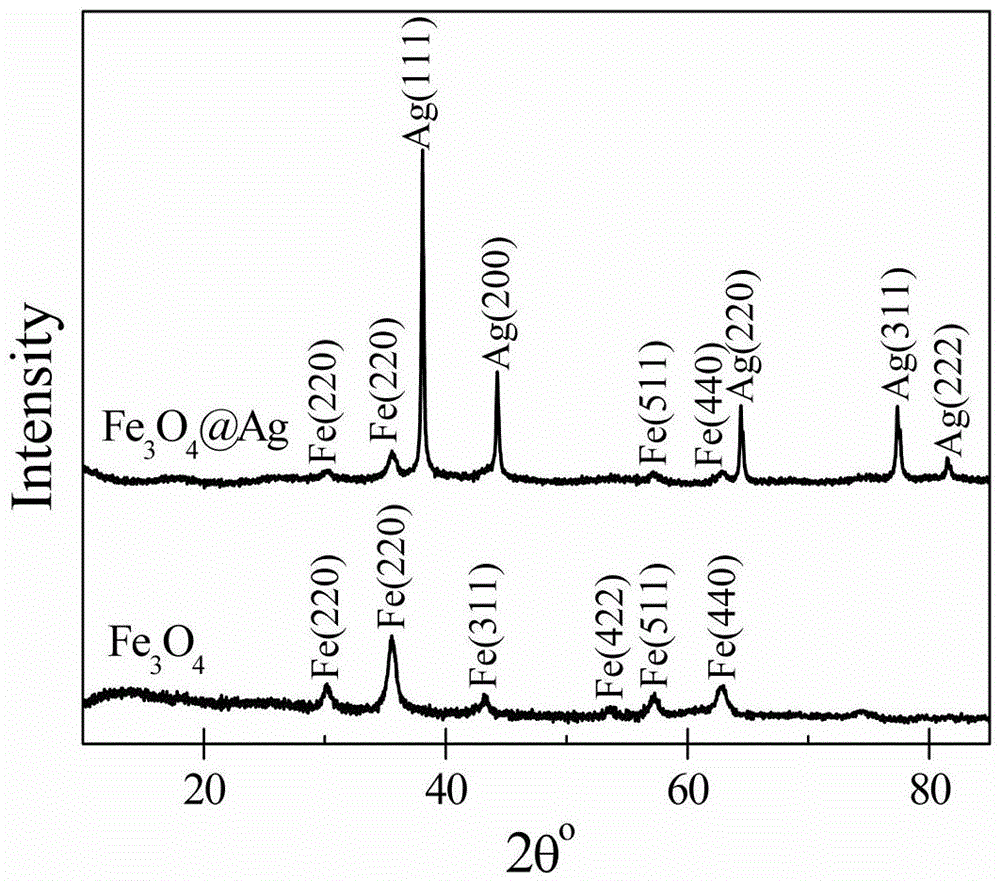
Method for detection of arsenic in underground water
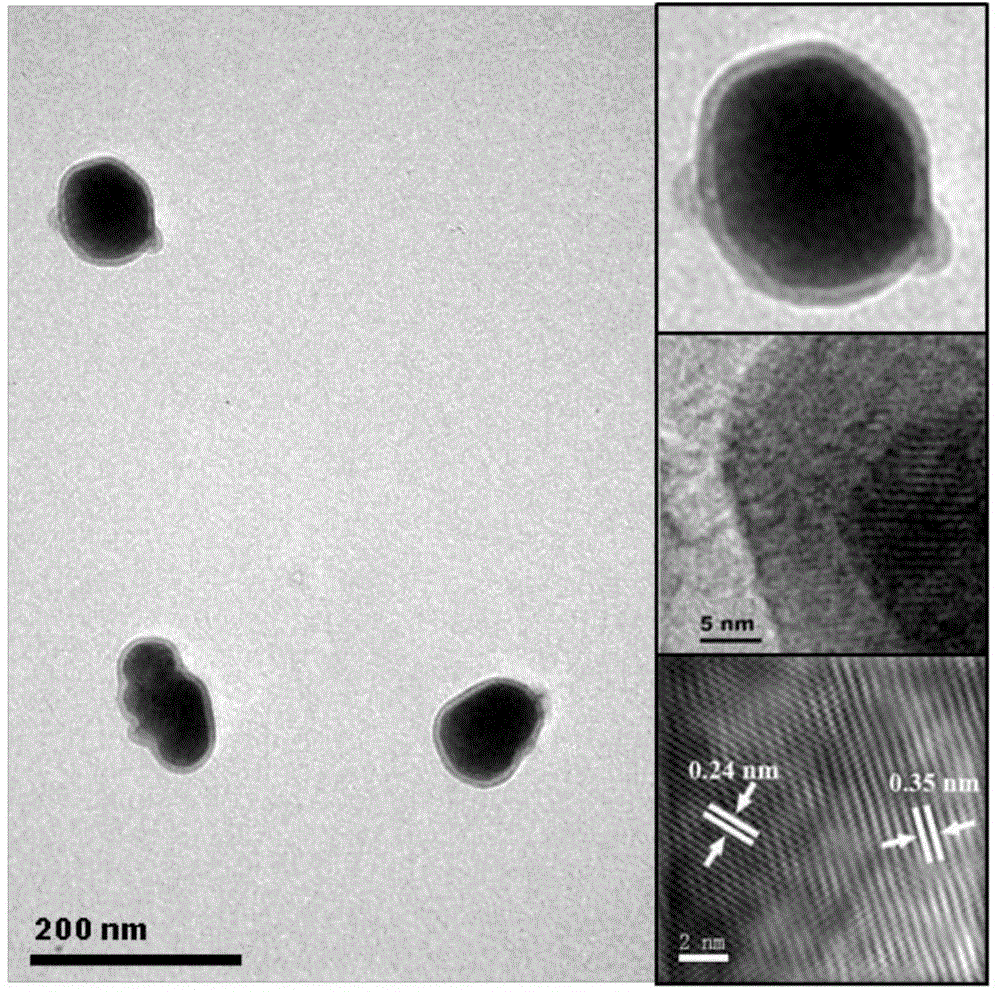
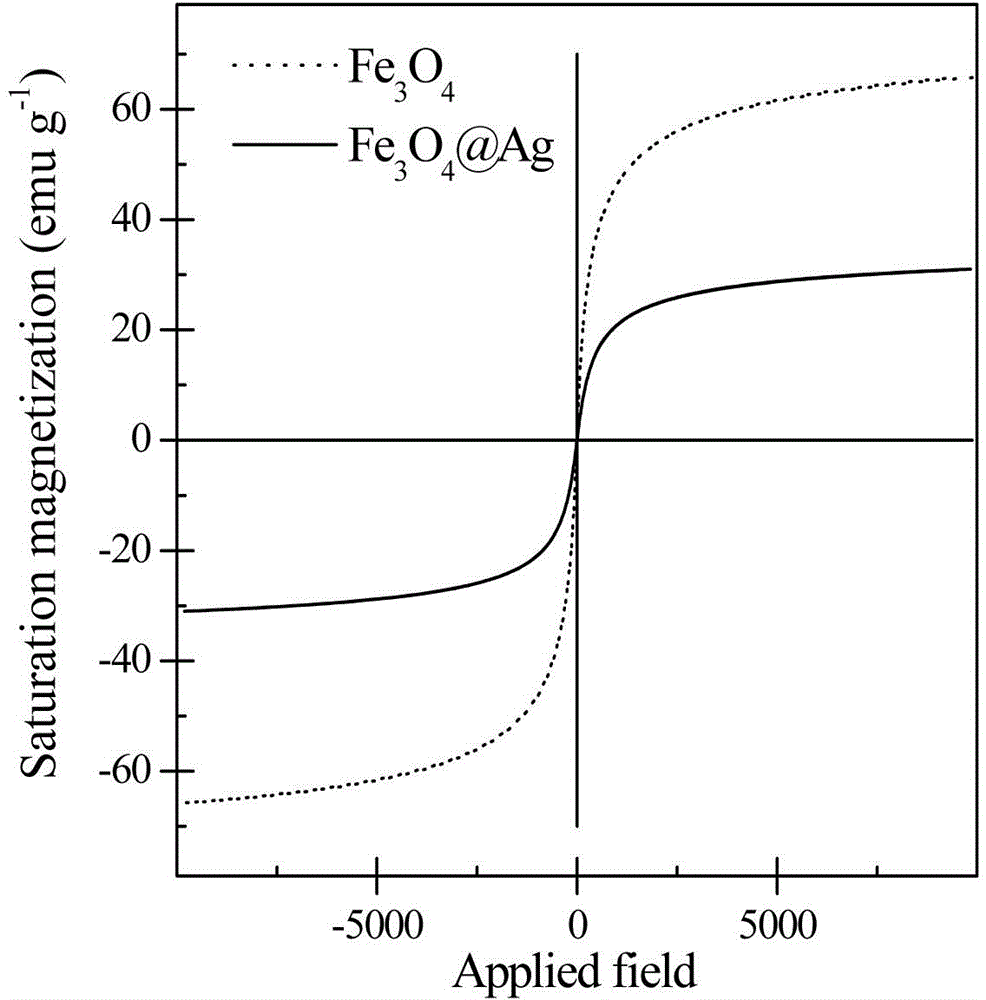
The invention relates to a method for detection of arsenic in underground water. The method adopts core-shell type Fe3O4 / Ag magnetic nanoparticles as the SERS substrate for enrichment and detection of arsenic in groundwater, and acquires an SERS spectrogram of trivalent arsenic and pentavalent arsenic through a portable Raman spectrometer. A series of experiments prove that the detection method adopted by the invention is simple and easy to operate, and can realize rapid detection of arsenic contaminated groundwater samples.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for restoring hydrochloric ether-contaminated groundwater by using in-situ electrochemical circulation wells
ActiveCN110357348AImprove repair effectLittle effect on propertiesWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentHydrogenRestoration method
The invention provides a method for restoring hydrochloric ether-contaminated groundwater by using in-situ electrochemical circulation wells. The method comprises the following steps: digging wells inan area with groundwater contamination and installing well casings in the wells, wherein every two wells form a group, one well in each group of wells is used as a water injection well while the other well is used as a pumping well, the top ends of the well casings are opened, the bottom ends of the well casings are closed, and a plurality of small holes are formed in the walls of the lower endsof the well casings; hanging anode plates and cathode plates in the water injection wells, wherein the anode plates and the cathode plates are respectively connected with the positive electrode and the negative electrode of a power source arranged out of the wells through wires; and turning on the power source to energize the anode plates and the cathode plates, continuously pumping groundwater inthe pumping wells into the water injection wells by using a water pump so strengthen groundwater flow circulation, wherein hydrogen and oxygen generated in the water injection well are diffused intoaquifers under the action of the groundwater flow circulation to promote the chemical / microbial degradation of hydrochloric ether in the groundwater. The restoration method provided by the invention is stable in effect and friendly to environment.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Magnetic field-based in-situ repair method for polluted groundwater
InactiveCN104291400ADoes not speed up the flowReduce disturbanceWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentMagnetic tension forceGroundwater recharge
The invention relates to a magnetic field-based in-situ repair method for polluted groundwater, belongs to the technical field of water treatment, and provides a groundwater in-situ repair method capable of solving the problems that nano-iron has low possibility of movement in groundwater and cannot be recycled after repair. The magnetic field-based in-situ repair method comprises the following steps: 1) digging one or more injection wells in the upstream of a polluted groundwater area; 2) digging a ditch-shaped trough in the downstream of the groundwater area; 3) arranging a magnet in the ditch-shaped trough, and reserving a certain area to serve as an iron-rich area; 4) injecting an nano-iron suspension into the polluted groundwater area, wherein nano-iron in the nano-iron suspension moves towards the magnet through the polluted area under the action of magnetic force; 5) starting an extraction pump to extract iron in the iron-rich area. The magnetic force of the magnet provides power for movement of the nano-iron in the groundwater, nano-iron can be enriched in the surface of the magnet after repair, and secondary pollution caused by repair can be avoided only by extracting out the nano-iron.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com