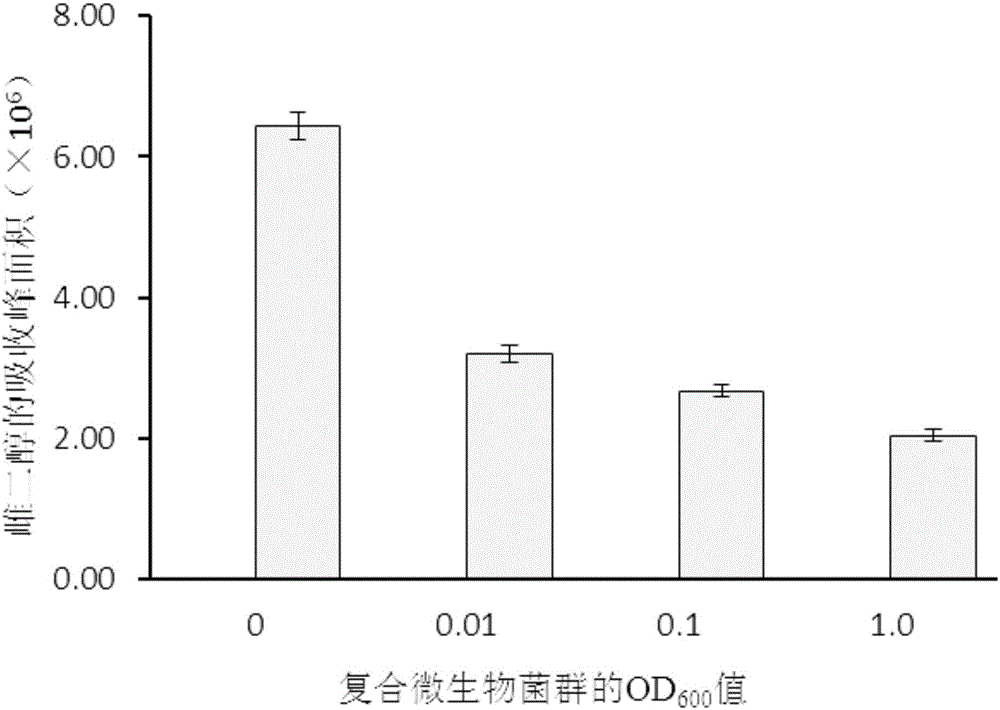
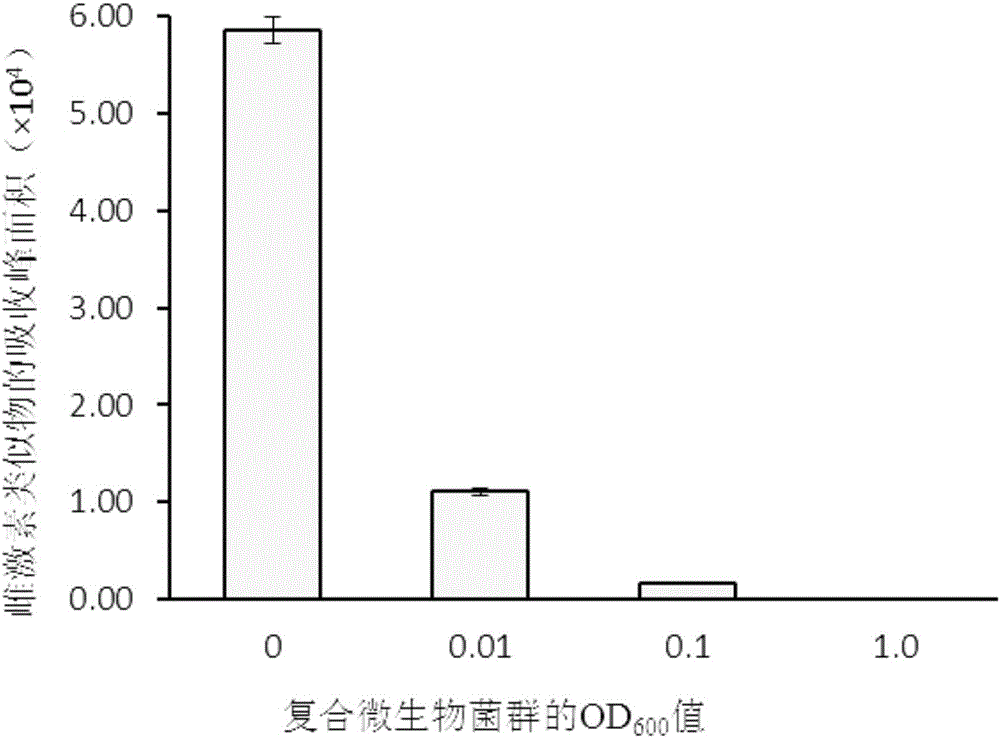
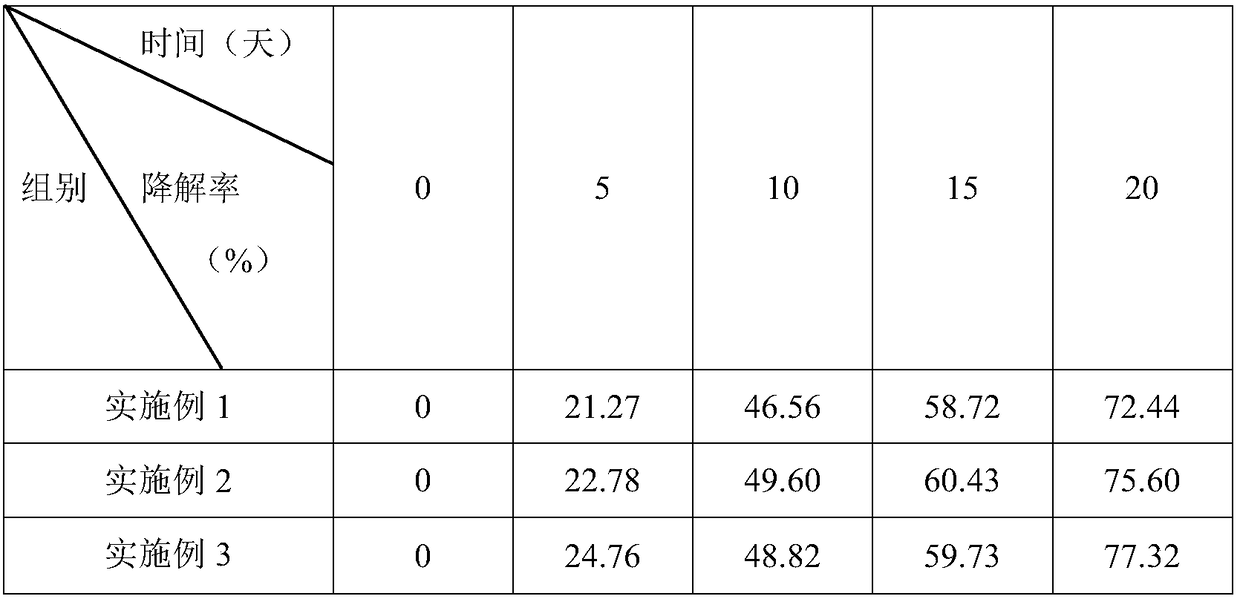
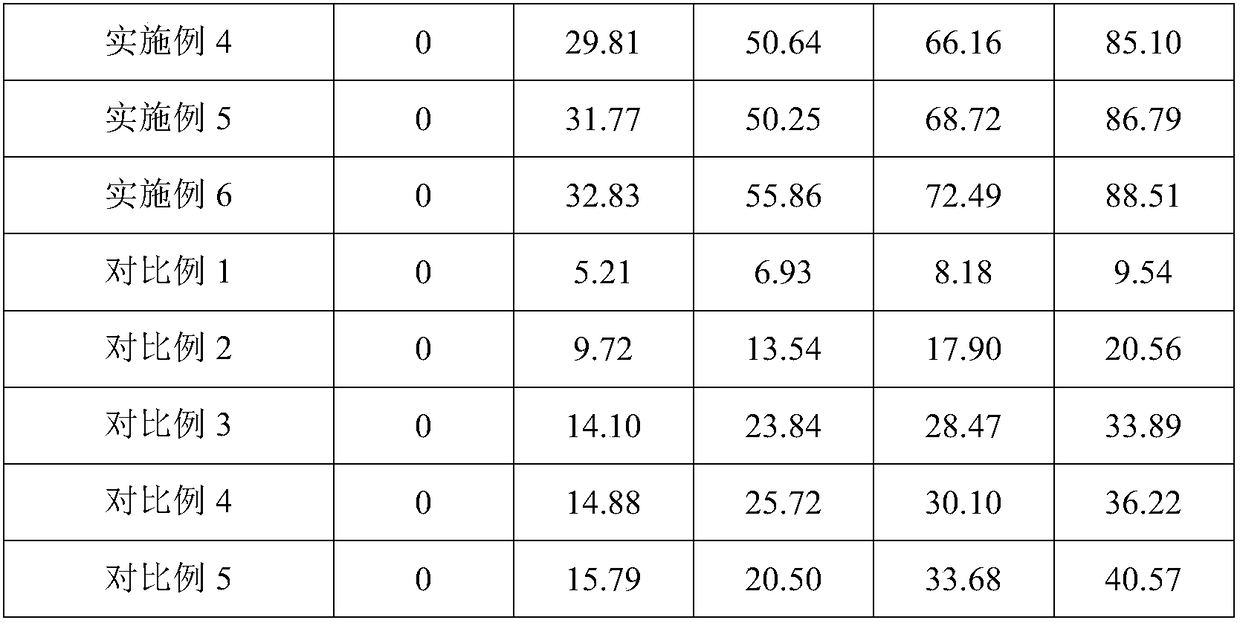
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Comamonas testosteroni" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Comamonas testosteroni is a Gram-negative soil bacterium. Strain I2gfp has been used in bioaugmentation trials, in attempts to treat the industrial byproduct 3-chloroaniline. C testosteroni is also a component in a microbial concoction Mammoth-P, developed by Mammoth microbe, that claims to increase bioavailable phosphorus to growing plants and increase yield and stem strength in plants.
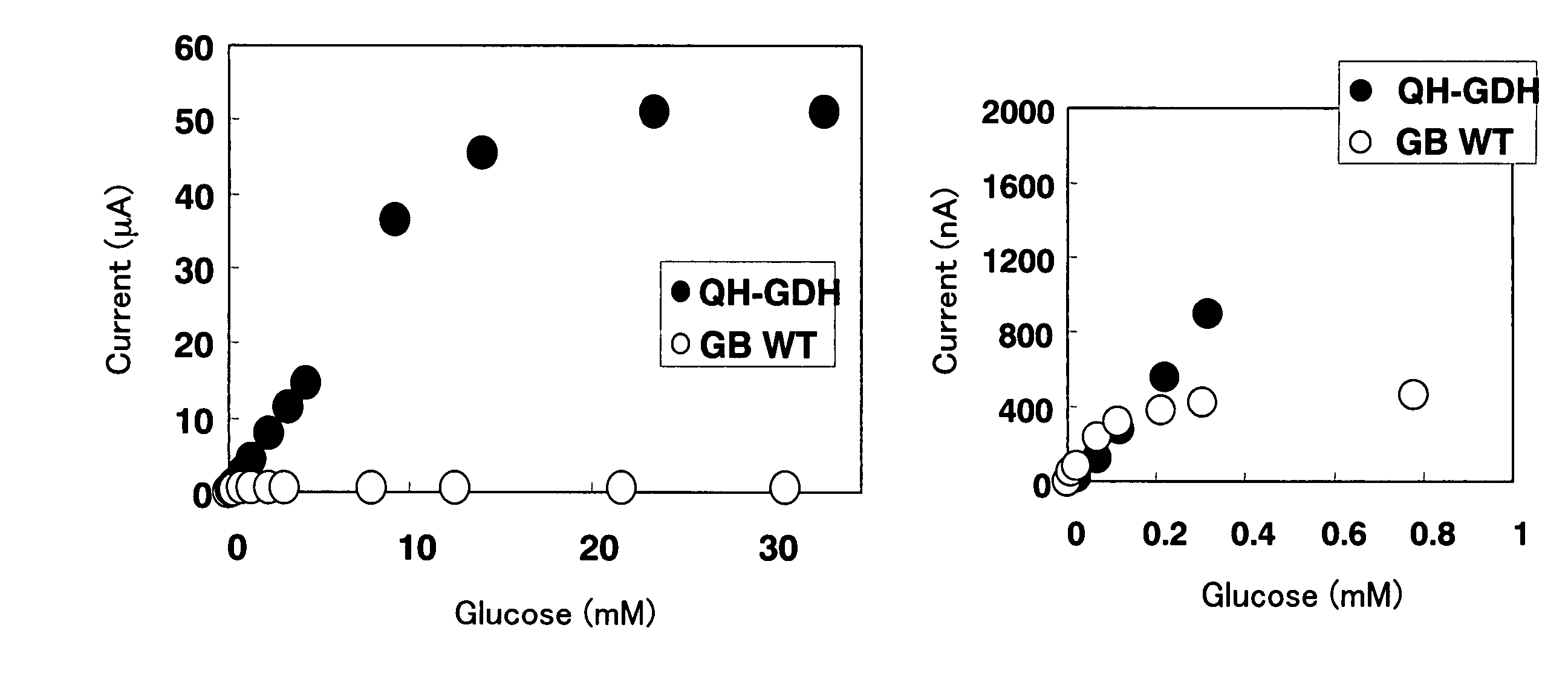
Glucose Dehydrogenase/Cytochrome Fusion Protein
A fusion protein of pyrroloquinoline quinone glucose dehydrogenase (PQQGDH) and a cytochrome is disclosed. PQQGDH is, for example, a water-soluble PQQGDH derived from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. The cytochrome is, for example, an electron transfer domain of quinohemoprotein ethanol dehydrogenase from Comamonas testosteroni. The fusion protein of the present invention shows intramolecular electron transfer from PQQ, a redox center, to the cytochrome, which allow construction of a direct electron transfer-type glucose sensor which requires no electron mediators.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Comamonas testosteroni strain for biological denitrificaion and application thereof
InactiveCN101560487AAnoxic denitrification is needed to solve biological denitrificationSolve processingBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismPhacus
The invention discloses a comamonas testosteroni strain for biological denitrificaion and application thereof. The comamonas testosteroni strain GAD4 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short) with preservation number CGMCC No. 2963 in March 19th, 2009. The strain is added to nitrogenous effluent with 2 to 6mg / L of dissolved oxygen to realize biological denitrificaion. The strain not only has the capability of heterotrophic nitrification, but also has the capability of aerobic denitrification. In the process of treating the nitrogenous effluent, only one aerobic stage is needed, the denitrification efficiency is high, and the operation is convenient and quick; and compared with the conventional biological denitrification process, the application has huge economic benefits.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Delftia with aerobic denitrifying capability and method of treating waste water by the same
InactiveCN101016525AStrong toleranceRealize simultaneous nitrification and denitrificationBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesNitriteSludge
The invention discloses a primotest clustered hair single cell bacterium (Comamonas testosteroni) WXZ-9 CGMCC No.1797 strain with aerobic denitrifying property and a method to denitrify the waste water; which is characterized by the following: possessing strong tolerance degree for dissolved oxygen; deacidizing nitrate and nitrite with distinctive speed under the condition of 10-98% saturated dissolved oxygen; seeding to active sludge; proceeding enriched culture; realizing the aerobic anti-nitration.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid fragments encoding nitrile hydratase and amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D and recombinant organisms expressing those enzymes useful for the production of amides and acids
The invention relates to the isolation, sequencing, and recombinant expression of genes encoding either a nitrile hydratase (NHase) or amidase (Am) from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D, where the NHase is useful for catalyzing the hydration of nitriles to the corresponding amides, and the amidase is useful for hydrolysis of amides to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Also provided are transformed host cells containing polynucleotides for expressing the nitrile hydratase or amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Para-chloro nitrobenzene degrading testosterone coma monad and its use
The present invention relates to one Comamonas testosteroni CNB1CGMCC No. 1028 strain, whose growing cell, cell suspension and immobile cell can degrade para-chloronitrobenzene. The strain can grow with para-chloronitrobenzene as unique carbon source, nitrogen source and energy source, so as to degrade and utilize para-chloronitrobenzene completely. During its growth, the strain first reduces nitro group into hydroxylamine, and produces 2-aminophenol 1, 6-bioxygenase to open the ring of 2-amino-5-chlorophenol into hydrocarbon through meta ring opening. The strain is suitable for the biological treatment of industrial effluent from para-chloronitrobenzene production and the biological repair of para-chloronitrobenzene polluted soil.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Testosterone coma monad with aerobic denitrifying capability and method of treating waste water by the same
The invention discloses a primotest clustered hair single cell bacterium (Comamonas testosteroni) WXZ-18 CGMCC No.1800 strain with aerobic denitrifying property and a method to denitrify the waste water; which is characterized by the following: possessing strong tolerance degree for dissolved oxygen; deacidizing nitrate and nitrite with distinctive speed under the condition of 10-98% saturated dissolved oxygen; seeding to active sludge; proceeding enriched culture; realizing the aerobic anti-nitration.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid fragments encoding nitrile hydratase and amidase enzymes from comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D and recombinant organisms expressing those enzymes useful for the production of amides and acids
The invention relates to the isolation, sequencing, and recombinant expression of genes encoding either a nitrile hydratase (NHase) or amidase (Am) from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D, where the NHase is useful for catalyzing the hydration of nitriles to the corresponding amides, and the amidase is useful for hydrolysis of amides to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Also provided are transformed host cells containing polynucleotides for expressing the nitrile hydratase or amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Comamonas testosteroni LH-N5 and heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification microbial inoculum, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103146604AFacilitate large-scale production applicationSolve the problem of difficult removal of total nitrogenBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechococcusTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a Comamonas testosteroni LH-N5 CGMCC No.6975. The invention also discloses a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification microbial inoculum which comprises the Comamonas testosteroni LH-N5, or one or both of Achromobacter xylosoxidans subtype xylosoxidans LH-N25 and Paracoccus aminovorans LH-N40; and the strains are combined in any proportion. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the microbial inoculum. The microbial inoculum disclosed by the invention can solve the problem of difficulty in removing total nitrogen in the traditional reactor, can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in the water body in one reactor, has tolerance or degradation capability for phenols, amines, heterocycles, cyanides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other toxic substances in wastewater, is especially applicable to nitrogenous chemical wastewater, has the advantages of simple treatment process, stable effect and environmental toxicant impact resistance, and has very wide application prospects in various actual nitrogenous chemical wastewater treatment processes.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Biological modification method of dacron fabrics
InactiveCN101935952AIngenious designEasy to modifyBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentMegasonic cleaningDistilled water
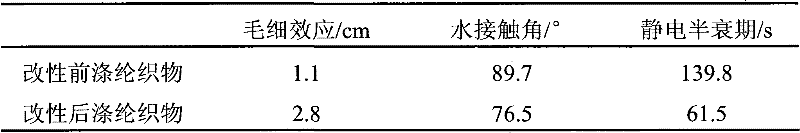
The invention discloses a biological modification method of dacron fabrics, mainly comprising the following steps: 1. culturing strains: culturing Comamonas testosteroni in a agarslant solid culture medium for 12-18h under the temperature of 30-37 DEG C, and storing in a refrigerator at the temperature of 4 DEG C; 2. preparing a dacron modified liquid: preparing 6 parts of dacron modified liquid with the terephthalic acid concentration of 1-3g / L (each part is 150ml), respectively filling in a conical flask, and packing and sterilizing for 25min under the temperature of 121 DEG C; 3. modifying the dacron fabrics: performing ultraviolet sterilization for 0.5h on 6 parts of dacron fabrics, implanting the Comamonas testosteroni in 3 parts of dacron modified solutions, adding 3 parts of dacron fabrics into the 3 parts of dacron modified liquid respectively, taking the other three parts of dacron fabrics as a reference, performing shake cultivation at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C and with the revolving speed of 200r / min, and performing catalytic modification on the dacron fabrics; and 4) flushing the fabrics by tap water trickles and distilled water in turn, cleaning the fabrics by ultrasonic and airing.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
High-efficient treatment method for biologically-enhanced coking waste water for biological membrane
ActiveCN102674618AWater quality fluctuates greatlyGuaranteed emission standardsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFluidized bedCoupling
The invention relates to a high-efficient treatment method for biologically-enhanced coking waste water for a biological membrane. The method comprises treating coking waste water by adopting an anaerobic organism filter and a three-phase aerobic biological circulating fluidized bed coupling process, wherein the method includes a membrane formation period and a normal running period; and in the membrane formation period, a membrane supporting carrier is firstly added into a reactor in the anaerobic organism filter and in the three-phase aerobic biological circulating fluidized bed coupling process, then Comamonas testosteroni CGMCC N0.4630 is fed for membrane formation, and an ecological island system is formed in the system after completion of film formation. Through the treatment of the process, the COD removal rate of the coking waste water can reach more than 94 percent, the NH3-N removal rate reaches more than 98 percent, the outlet water can achieve the first-level drainage standard and recycling standard of national sewage drainage standard (GB9878-1996), and 100 percent recycling of the waste water can be achieved.
Owner:承德市宏兴环保技术有限责任公司
Comamonas testosterone engineering bacteria and use thereof
The invention relates to a Comamonas testosteroni engineering bacterium. Directional regulation is adjusted and controlled to Comamonas testosterone through a DNA recombination technology, so as to produce Comamonas testosteroni AMCa 3 (CGMCC No.2364) having the capability of efficiently degrading steroid compounds. The engineering bacterium can effectively degrade testosterone, cholesterol and other steroid compounds, has good degradation effect to soils and livestock-poultry excreta seriously polluted by steroid compounds, and can be used for the treatment of livestock-poultry excreta, producing low-cholesterol food in food industry, and transforming steroid substances in the production of feed additives and dairy products for producing pollution-free food. The engineering bacterium has important significance in environmental remediation and agricultural application.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
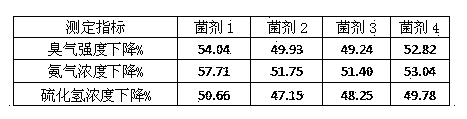
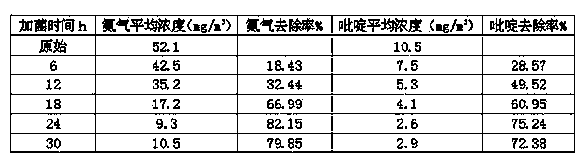
Application of microbial agent to malodorous gas pollution regulation
ActiveCN103432900AGood governanceEfficient removalDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementToxicantSulfur containing
The invention relates to application of a microbial agent to malodorous gas pollution regulation. Malodorous gas is nitrogen-containing or sulfur-containing inorganic / organic malodorous gas or volatile heterocyclic organic gas, and the microbial agent is formed by comamonas testosteroni LH-N5, achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans LH-N25CGMCC No.6972 and Paracoccus aminovorans LH-N40CGMCC No.6971 in any proportion. The microbial agent has a remarkable deodorization effect, can tolerate or degrade organic and toxic pollutants, is particularly suitable for deodorization and purification of nitrogen-containing or sulfur-containing inorganic / organic waste gas, is suitable for regulation of volatile heterocyclic toxic organic malodorous gas, has a simple treatment process and stable effects, is resistant to environmental toxicant impact, and has wide application prospect in malodorous gas pollution control.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
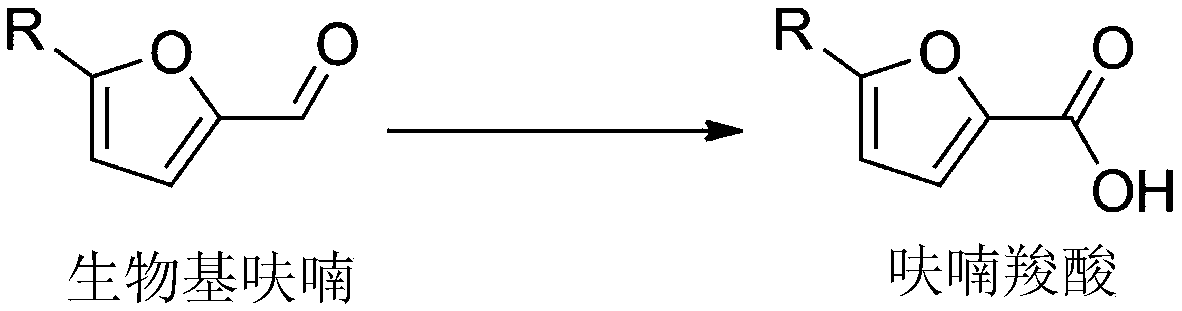
Comamonas testosteroni and application thereof in synthesizing of 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid
ActiveCN107365724AOvercome the disadvantages of being unfriendly to the environmentImprove toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationSubstrate concentration
The invention discloses Comamonas testosteroni and application thereof in the synthesizing of 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid. The Comamonas testosteroni SC1588 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on October 13th, 2016, and the preservation number of the Comamonas testosteroni SC1588 is CCTCC No. M2016562. The biological catalyst Comamonas testosteroni SC1588 has the advantages that the Comamonas testosteroni SC1588 has high tolerance to HMF, can catalyze a high-concentration substrate (160mM) to selectively oxidize to synthesize a target product, and yield reaches 98%; high substrate concentration, excellent reaction efficiency and good selectivity are achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Glucose dehydrogenase/cytochrome fusion protein
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Biological restoration method for p-chloronitrobenzene compound polluted environment
ActiveCN1803228AExtensive metabolic pathwayEfficient use ofBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationRestoration methodSewage
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Efficient mixed flora for treating sludge
InactiveCN105624063AEfficient decompositionBacteriaSpecific water treatment objectivesSludgeStenotrophomonas sp.
The invention discloses efficient mixed flora for treating sludge which comprises comamonas testosteroni, pseudomonas alcaligenes, stenotrophomonas rhizophila, pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes and azospirillum. The mixed flora can effectively decompose the sludge.
Owner:YUNNAN SHENGQING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
2-amino phenol 1, 6-dioxygenase, its gene and use thereof
The present invention relates to one p-nitrobenzene chloride ring opening enzyme gene and its expression product. The gene is from Comamonas testosteroni CNB1 CGMCC No. 1028 strain, has size of 1770 bp, and contains two ORF opening read frames in the same direction of 942 bp and 813 bp separately, separated by 15 bp, coding two different protein products beta-subunit and alpha-subunit. Two beta-subunits and two alpha-subunits constitute one active enzyme molecule. The enzyme can catalyze the ring opening cracking in the 1 and the 6 place of 2-amino phenol and the direct ring opening cracking of p-nitrobenzene chloride. Therefore, the gene may be used in constituting gene engineering bacterian and produce active enzyme for treating sewage containing p-nitrobenzene chloride and similar compound and in biological conversion engineering.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microbial flora capable of rapidly degrading estrogen and analogs in chicken manure
PendingCN106434453AImprove degradation efficiencyReduce pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismHuman health
The invention discloses microbial flora capable of rapidly degrading estrogen and analogs in chicken manure and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. The microbial flora comprises equal amounts of Comamonas testosteroni ATCC11996, KF1-Fe (Comamonas testosteroni ATCC49202), Ca3, Cb7, M6, M2, A3, vibrio H5 and Brucella S19-1. The environment adaptability of strains and the degradation efficiency of the estrogen and analogs are improved under the coordinate symbiosis action of compound microbial flora, and the risk caused by environmental pollution to ecology and human health is effectively reduced.
Owner:JILIN BUSINESS & TECH COLLEGE
Comamonas testosteroni HHALA-001 and method for using comamonas testosteroni HHALA-001 to produce L-alanine
ActiveCN107267422AIncrease productivityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-AspartateChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and in particular relates to comamonas testosteroni HHALA-001 and a method for using the comamonas testosteroni HHALA-001 to produce L-alanine; the preservation number of the strain is CGMCCNo.14064; the comamonas testosteroni HHALA-001 is obtained by compound mutation and repeated screening, the strain has high enzyme activity, the enzyme activity can reach 11.80U-12.22U, the strain can be used for high expression of L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase, is used for production of the L-alanine by catalysis of L-aspartic acid, can greatly improve production efficiency and conversion rate of the L-alanine, helps to reduce production cost, and has good stability; after use of the strain, the conversion rate of the L-Aspartic acid can reach 99.9%; the comamonas testosteroni HHALA-001 fully meets industrial L-alanine strain mutagenesis and screening demands, can be used in industrial production, and has great economic value.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Compound microbial agent for treating soil pollution and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108251330AEfficient degradationSimple manufacturing methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentMicrobiology
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent comprises the following raw material components: a pseudomonas japonica culture, a comamonas testosteroni culture, a microbacillus culture and an acidovorax delafieldii culture; according to the invention, multiple bacterial cultures are subjected to mixed fermentation to prepare the compound microbial agent; and thecompound microbial agent has an effective degradation effect on organic residues such as nitrobenzene compounds formed by insecticides or pesticides in soil, and furthermore, special strains are subjected to mixed cultivation and multiple strains are subjected to mixed fermentation to provide a simple and easy preparation method.
Owner:江苏世邦生物工程科技有限公司
Construction and application of Comamonas testosteroni 3,17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3,17beta-HSD) gene reinforced strain
InactiveCN103074360AImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismEstriol
The invention relates to a construction of a Comamonas testosteroni 3,17beta-HSD gene reinforced strain, and belongs to the microbial field. The construction of the Comamonas testosteroni 3,17beta-HSD gene reinforced strain is characterized in that a recombinant plasmid is pK-Tacpromoter-3,17beta-HSD; and the construction comprises the following steps: carrying out PCR technological amplification, and target segment recovery and purification of a Comamonas testosteroni genome which is a template to connect with a pUCm-T carrier; 2, carrying out PCR technological amplification, and target segment recovery and purification of a plasmid pAH10 which is a template to connect with the pUCm-T carrier; 3, extracting a recombinant plasmid 3,17beta-HSD-T through adopting a column plasmid DNA small-amount extraction kit; and 4, respectively extracting the recombinant plasmid and pK-3,17beta-HSD through adopting the column plasmid DNA small-amount extraction kit. According to the invention, the Comamonas testosteroni 3,17beta-HSD gene reinforced strain is constructed for the first time and is applied, and the estriol degradation efficiency, the cholesterol degradation efficiency and the stosterone degradation efficiency of the Comamonas testosteroni 3,17beta-HSD gene reinforced strain are 30%, 15% and 150% higher than that of a wild Comamonas testosteroni strain respectively.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biological modification method of dacron fabrics
InactiveCN101935952BIngenious designEasy to modifyBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentMegasonic cleaningUltraviolet
The invention discloses a biological modification method of dacron fabrics, mainly comprising the following steps: 1. culturing strains: culturing Comamonas testosteroni in a agarslant solid culture medium for 12-18h under the temperature of 30-37 DEG C, and storing in a refrigerator at the temperature of 4 DEG C; 2. preparing a dacron modified liquid: preparing 6 parts of dacron modified liquid with the terephthalic acid concentration of 1-3g / L (each part is 150ml), respectively filling in a conical flask, and packing and sterilizing for 25min under the temperature of 121 DEG C; 3. modifyingthe dacron fabrics: performing ultraviolet sterilization for 0.5h on 6 parts of dacron fabrics, implanting the Comamonas testosteroni in 3 parts of dacron modified solutions, adding 3 parts of dacronfabrics into the 3 parts of dacron modified liquid respectively, taking the other three parts of dacron fabrics as a reference, performing shake cultivation at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C and withthe revolving speed of 200r / min, and performing catalytic modification on the dacron fabrics; and 4) flushing the fabrics by tap water trickles and distilled water in turn, cleaning the fabrics by ultrasonic and airing.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbiology, and particularly relates to a selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosteroni GX-A1 and an application of the same. The taxonomic name of the selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 is Comamonas testosterone; the selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on December 10, 2020, and the preservation number is GDMCC No.61357. The selenium-resistant strain Comamonas testosterone GX-A1 disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the removal rate of the selenium in the soil is up to 37.44% at most under the condition that the selenium concentration is 2000 mu g / mL. The result can provide strain resources for bioremediation of selenium-polluted areas and provide reference for development and utilization of selenium resources.
Owner:南宁市博发科技有限公司
Method for treating bird waste water by novel mixed bacterium microbial fuel cell
InactiveCN109081425AImprove environmental adaptabilityPromote degradationTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsCulture fluidSludge
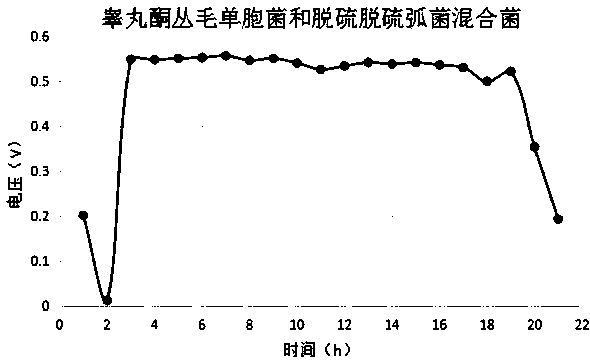
The invention relates to a method for treating bird waste water by a novel mixed bacterium microbial fuel cell. The method includes the steps: activating and then inoculating comamonas testosteroni and desulfovibrio into culture solution; culturing the closed comamonas testosteroni in a shaker, culturing the closed desulfovibrio in an incubator at constant temperature until a last phase of a logarithmic phase; uniformly mixing the cultured comamonas testosteroni and the cultured desulfovibrio, mixing mixture, nutrient solution, buffer solution and sludge according to the volume ratio of (1-3):(2-5):(1-3):(3-7), inoculating mixture into an anode chamber of the microbial fuel cell, enabling floras to be suspended in anode solution or adhered on an anode, and standing to degrade the bird waste water and generate power; updating anode solution once every 2-7 days, and retaining 10% of original mixture in the original anode chamber. The method has the advantages that mixed bacteria of the comamonas testosteroni and the desulfovibrio are applied to microbial fuel cells based on treatment of bird waste water, the degradation capability of the bird waste water can be effectively improved,and electric energy is generated.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Microbial agent capable of rapidly decolorizing aniline blue as well as preparation method and application of microbial agent
PendingCN114381389AImprove environmental adaptabilityImprove efficiencyBacteriaWater contaminantsMicrobial agentBioremediation
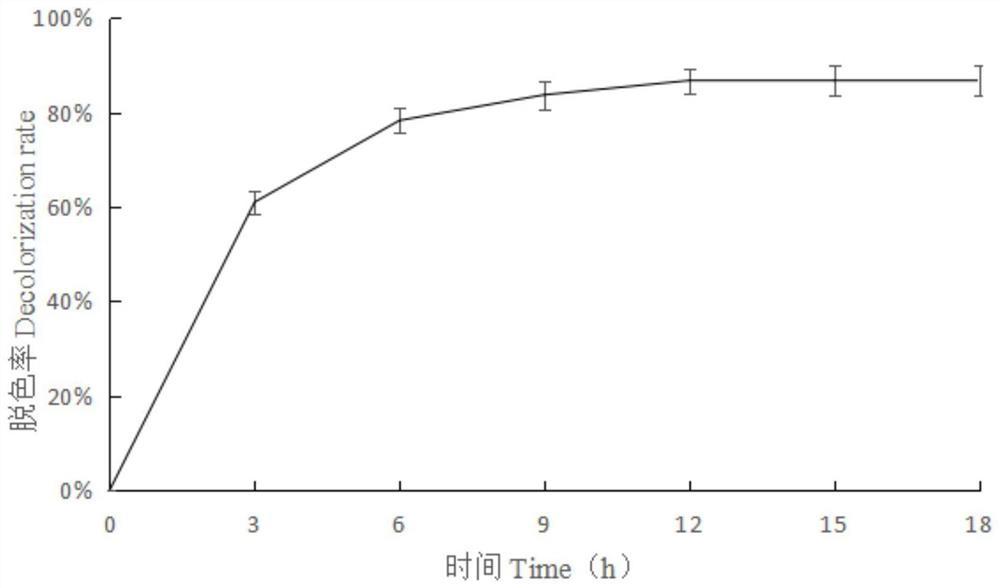
The invention relates to a microbial agent capable of rapidly decolorizing aniline blue as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. The comamonas testosteroni strain is prepared from comamonas testosteroni CT1, KF1, acinetobacter calcoaceticus LM1 and pseudomonas stutzeri JP1 which are equal in quantity. The method has the beneficial effects that the environmental adaptability and aniline blue decoloring efficiency of the strain are improved through the synergistic symbiotic effect of various microorganisms, the optimal degradation condition suitable for the strain is changed, the degradation capacity of the strain and the degradation efficiency of the triphenylmethane dye aniline blue are improved, and the ecological and human health risks caused by environmental pollution are effectively reduced; the method has the advantages that the method is simple, the decolorization rate reaches 86.0%, the decolorization effect is good, the cost is low, the operation is simple, the degradation efficiency is high, the environmental compatibility is good, the use of chemical reagents is reduced, the secondary pollution is avoided, and the method has a good application prospect in the aspect of bioremediation of the aniline blue polluted environment.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for producing L-alanine by bioconverting L-aspartic acid by free cell process
ActiveCN102690762BIncrease productivityReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesL-AspartateL-alanosine
The invention relates to a method for producing L-alanine by bioconverting L-aspartic acid by a free cell process, which comprises the following steps: bioconverting L-aspartic acid with Comamonas testosteroni HY-08D of self-screened high-yield L-aspartate-beta-decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.12, ASD or ADL) to produce L-alanine; and filtering, concentrating, crystallizing and drying to obtain the finished L-alanine product. The invention can enhance the production efficiency of L-alanine and lower the production cost.
Owner:YANTAI HENGYUAN BIOENGINEERING CO LTD
2-amino phenol 1,6-dioxygenase, its gene and use thereof
The present invention relates to one p-nitrobenzene chloride ring opening enzyme gene and its expression product. The gene is from Comamonas testosteroni CNB1 CGMCC No. 1028 strain, has size of 1770 bp, and contains two ORF opening read frames in the same direction of 942 bp and 813 bp separately, separated by 15 bp, coding two different protein products beta-subunit and alpha-subunit. Two beta-subunits and two alpha-subunits constitute one active enzyme molecule. The enzyme can catalyze the ring opening cracking in the 1 and the 6 place of 2-amino phenol and the direct ring opening cracking of p-nitrobenzene chloride. Therefore, the gene may be used in constituting gene engineering bacterian and produce active enzyme for treating sewage containing p-nitrobenzene chloride and similar compound and in biological conversion engineering.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Co-expressing recombinant bacterium and application thereof in synthesizing furan carboxylic acid
PendingCN110591995AImprove toleranceHigh space-time yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFuran
The present invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering technology and biocatalysis, and discloses a co-expressing recombinant bacterium and an application thereof in synthesizing furan carboxylic acid. A double-enzyme co-expression technology is used to construct a co-expressing system of an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene derived from comamonas testosteroni SC1588 respectively with 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidoreductase and NADH oxidase genes in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain the co-expressing recombinant bacterium. The co-expressing recombinant bacterium can catalyze oxidationof substrates with high concentration (150-250 mM) to synthesize target products with a yield of 90% or more and a spatiotemporal yield as high as 5.6 g / L h. The prepared biocatalyst has advantages of high-concentration substrate tolerance, high catalytic activity, and high selectivity. Besides, the furan carboxylic acid synthesis technology is mild in conditions, green and highly efficient.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Aldehyde dehydrogenases, gene thereof, construction of recombinant strain and application of recombinant strain in synthesis of furancarboxylic acid
ActiveCN109536466AEfficient selective oxidation synthesisEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFuranGenetic engineering
The present invention relates to the fields of genetic engineering technology and biocatalysis, and discloses aldehyde dehydrogenases, a gene thereof, construction of a recombinant strain and an application of the recombinant strain in synthesis of furancarboxylic acid. A gene mining technology is used to screen five aldehyde dehydrogenases from comamonas testosteroni SC1588, and amino acid sequences of the aldehyde dehydrogenases are shown in SEQ ID. 1, SEQ ID. 2, SEQ ID. 3, SEQ ID. 4 or SEQ ID. 5. The five aldehyde dehydrogenases can all efficiently catalyze a bio-based furan selective oxidation to synthetize the corresponding furancarboxylic acid. The yield of a target product is up to about 90%, the highest yield can even reach 100%, and a space-time yield is up to 1.9 g.L<-1>.h<-1>. The production process is simple, production conditions are mild and production efficiency is high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Comonas testosteroni with denitrification and dephosphorization functions and application thereof
ActiveCN102531202ARealize synchronous removalSolve bottlenecksBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphateInorganic phosphorus
The invention relates to application of Comamonas Testosteroni with hetetrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification and dephosphorization functions to wastewater treatment. The strain can metabolize by taking organic carbon as a unique carbon source and ammonia nitrogen as a unique nitrogen source, and the ammonia nitrogen is directly converted into a gas product through a hetetrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification effect to fulfill the denitrification aim; the strain also can take nitrate nitrogen as a unique nitrogen source and converts the nitrate nitrogen into a gas product through an aerobic denitrification effect; and the strain also can intake inorganic phosphorus under the aerobic condition and convert the inorganic phosphorus into own components to fulfill the aim of removing the phosphorus from sewage. When the strain is applied to wastewater treatment, the nitrogen and the phosphorus can be synchronously removed under the single aerobic condition, a problem that wastewater is subjected to anaerobic phosphate release, anoxic denitrification and aerobic nitrification phosphorus-uptake by stages in the traditional wastewater treatment is well solved, and the invention has a wide application prospect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com