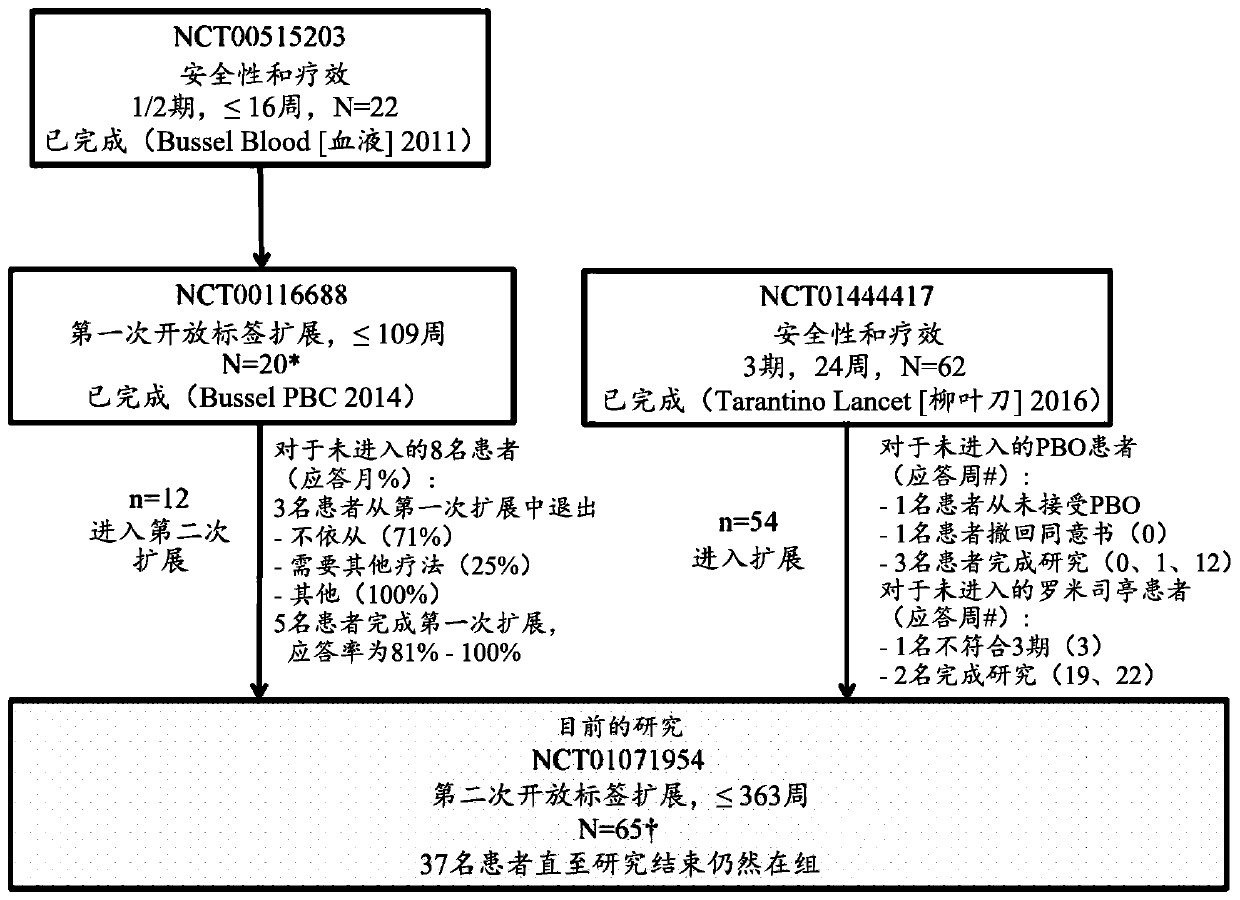
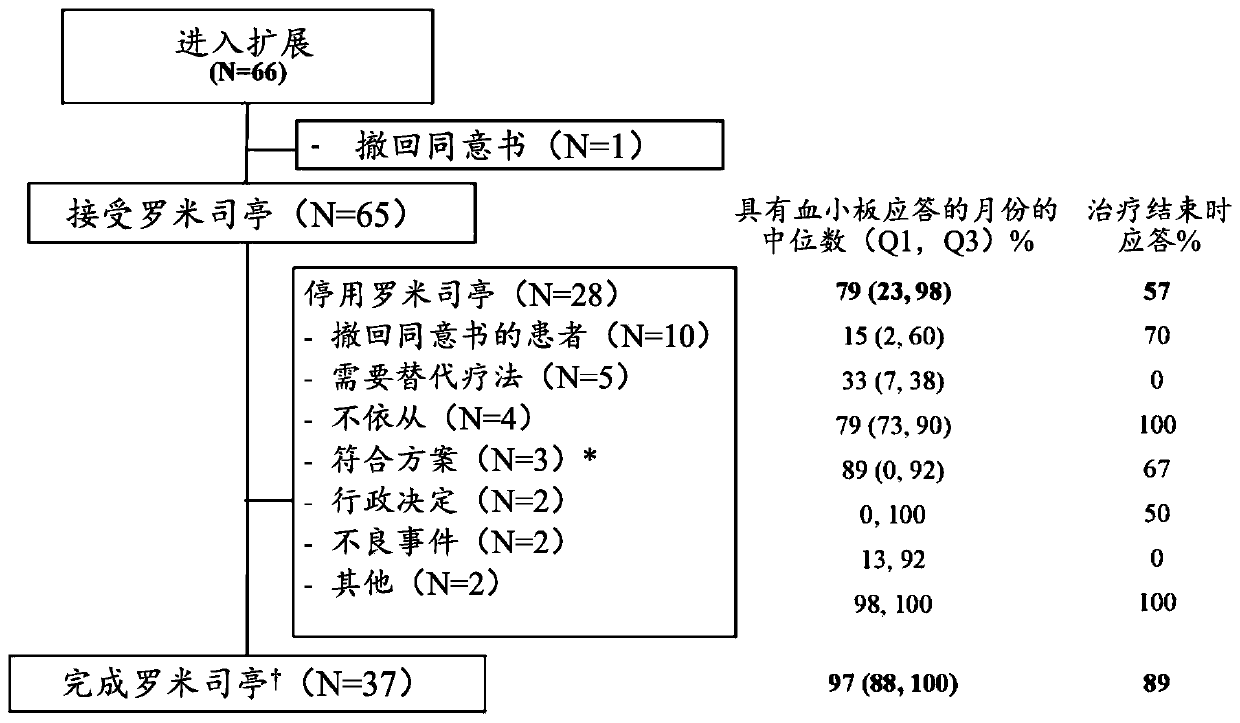
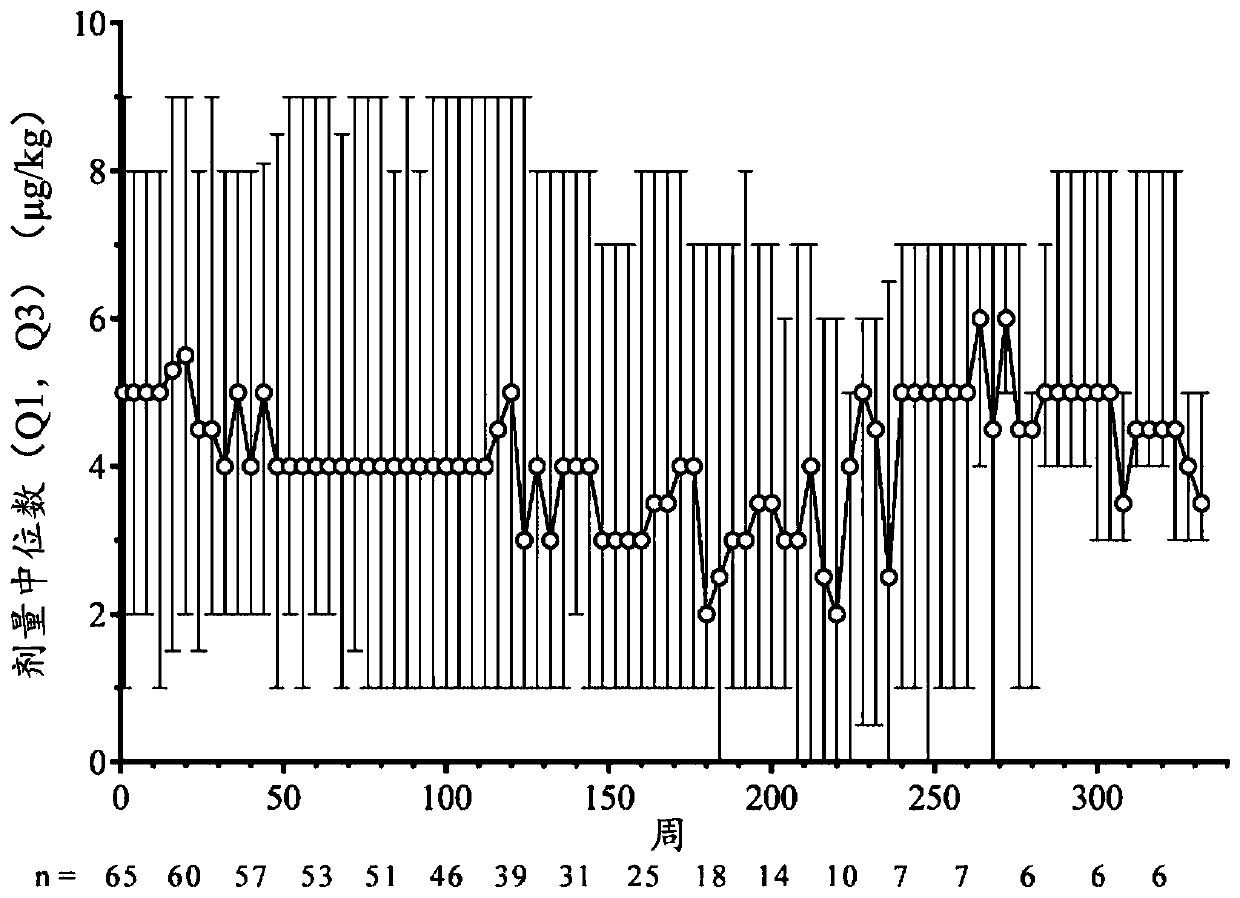
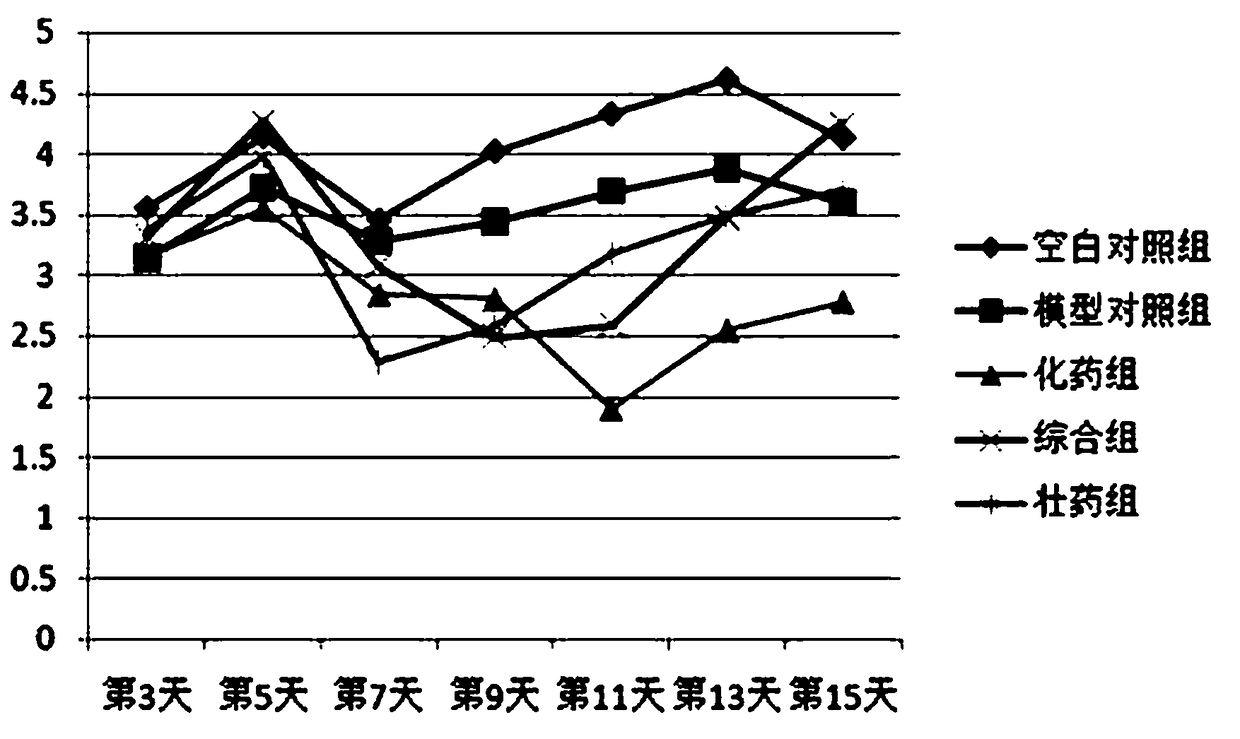
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Blood platelet counts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
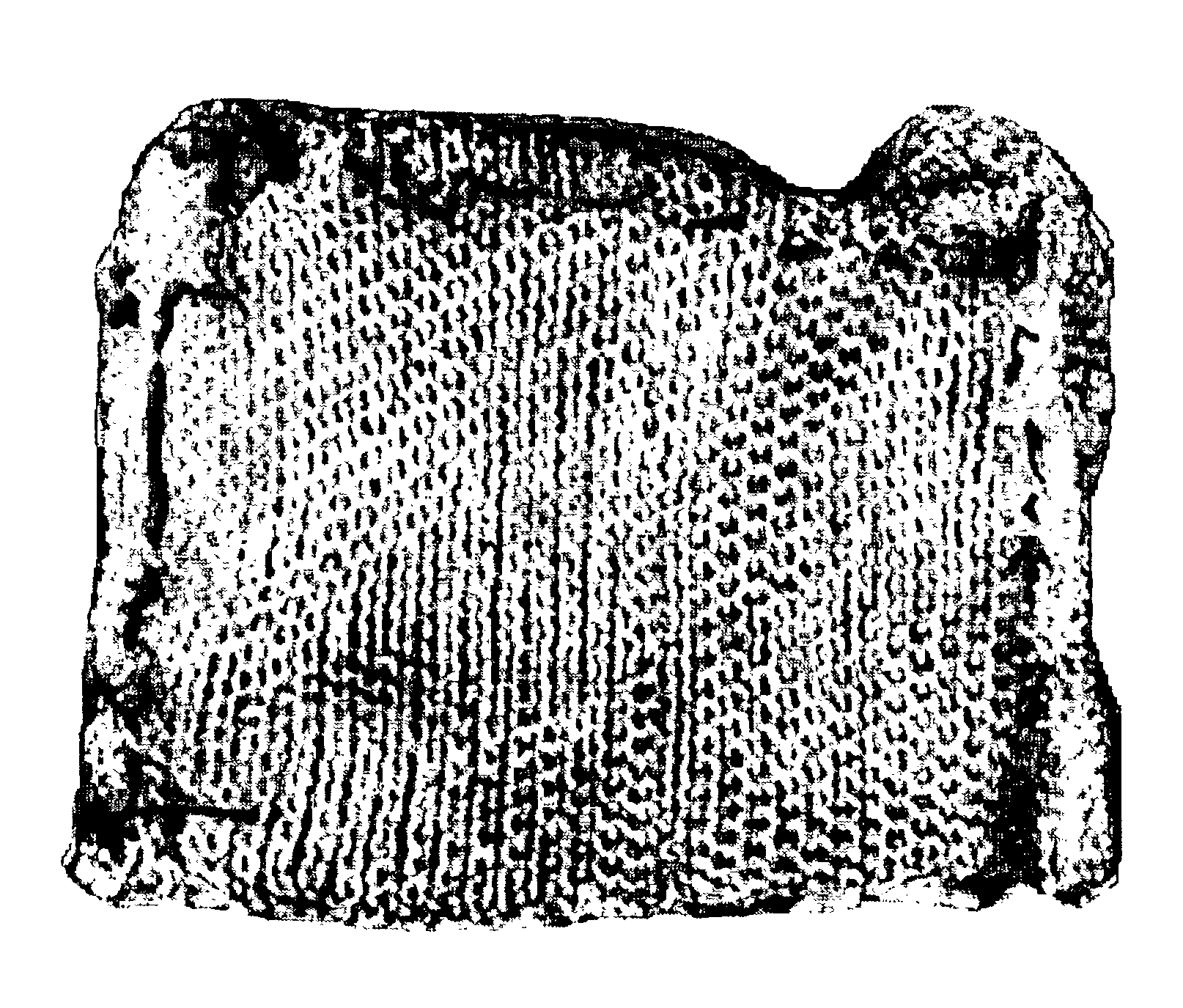
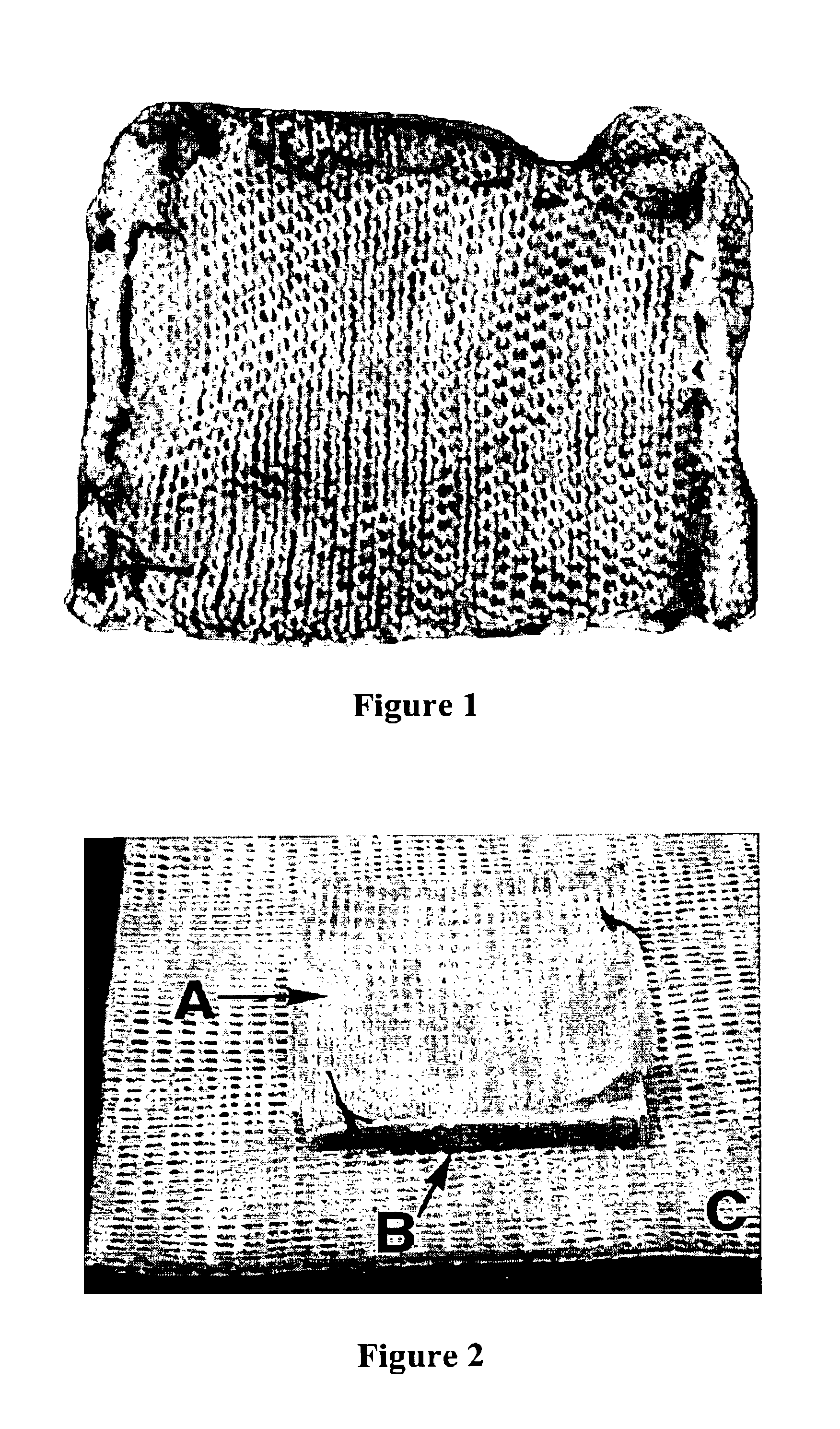
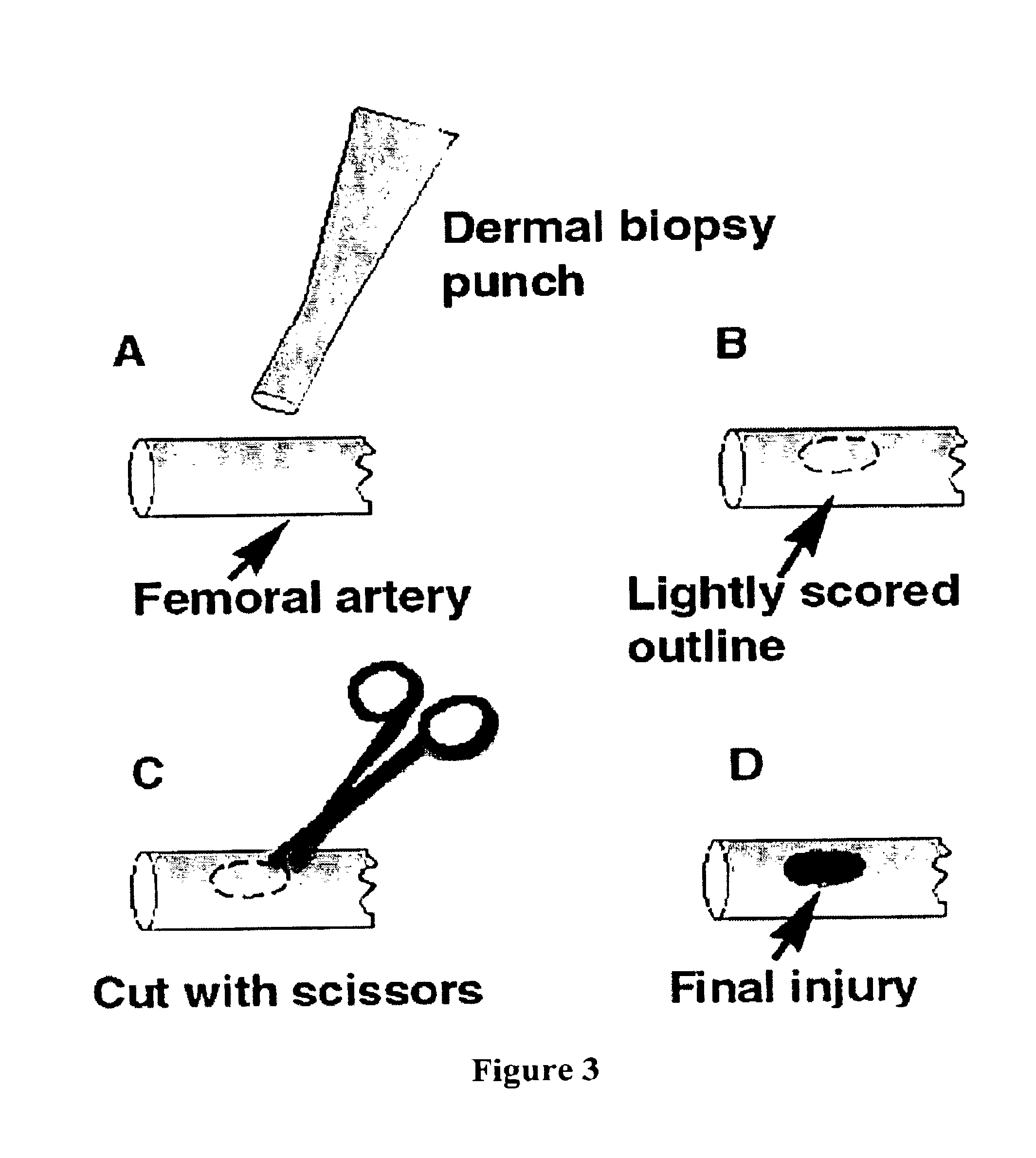
Fibrinogen bandages and arterial bleeding models and methods of making and using thereof
InactiveUS6891077B2Reduce the amount of solutionIncreasing of rate of clotSurgeryBaby linensBlood platelet countsClot formation
Disclosed herein are wound dressings comprising fibrinogen and at least one procoagulant such as propyl gallate in a therapeutic amount. Also disclosed are methods of treating wounds, increasing an amount of or rate of coagulation of blood from a wound, increasing an amount of or rate of clot formation over a wound, increasing blood platelet counts, activating a coagulation system, increasing the plasma concentration of fibrinogen, and decreasing the activated partial thromboplastin time. Also disclosed are an arterial bleeding model and methods of studying arterial bleeding.
Owner:UNITED STATES ARMY U S ARMY MEDICAL RES & MATERIEL COMMAND
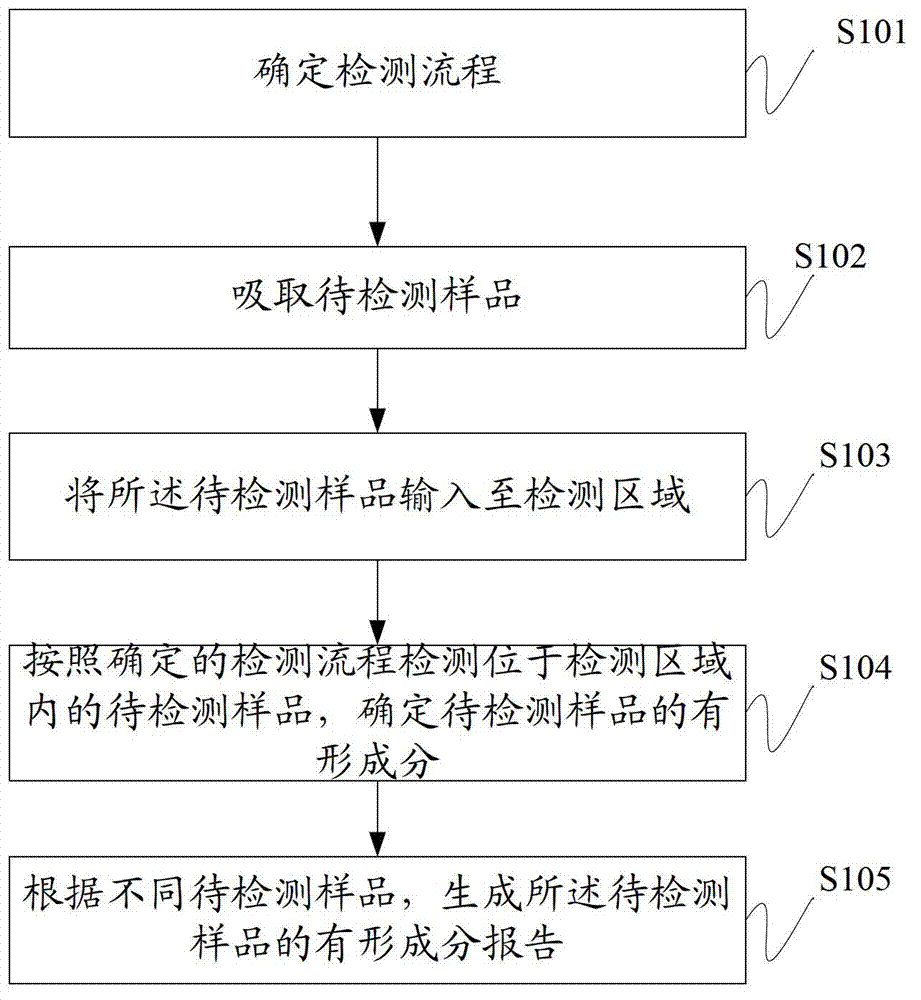
Sample analyzing method and comprehensive sample analyzer
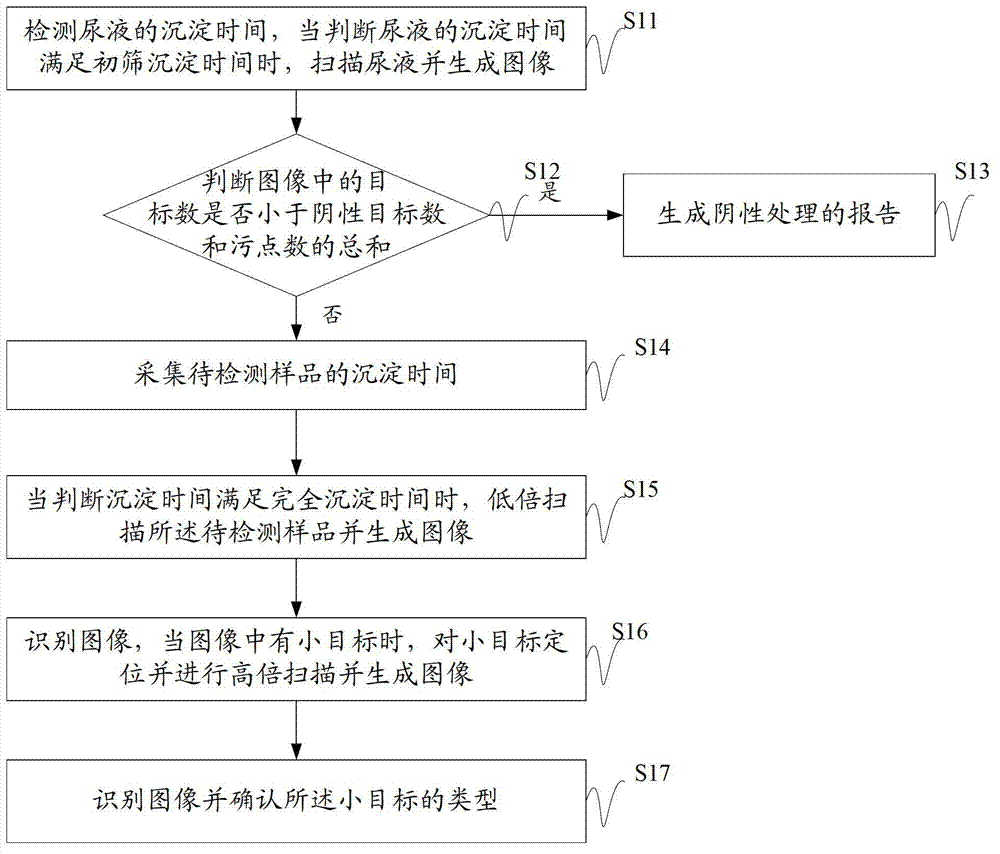
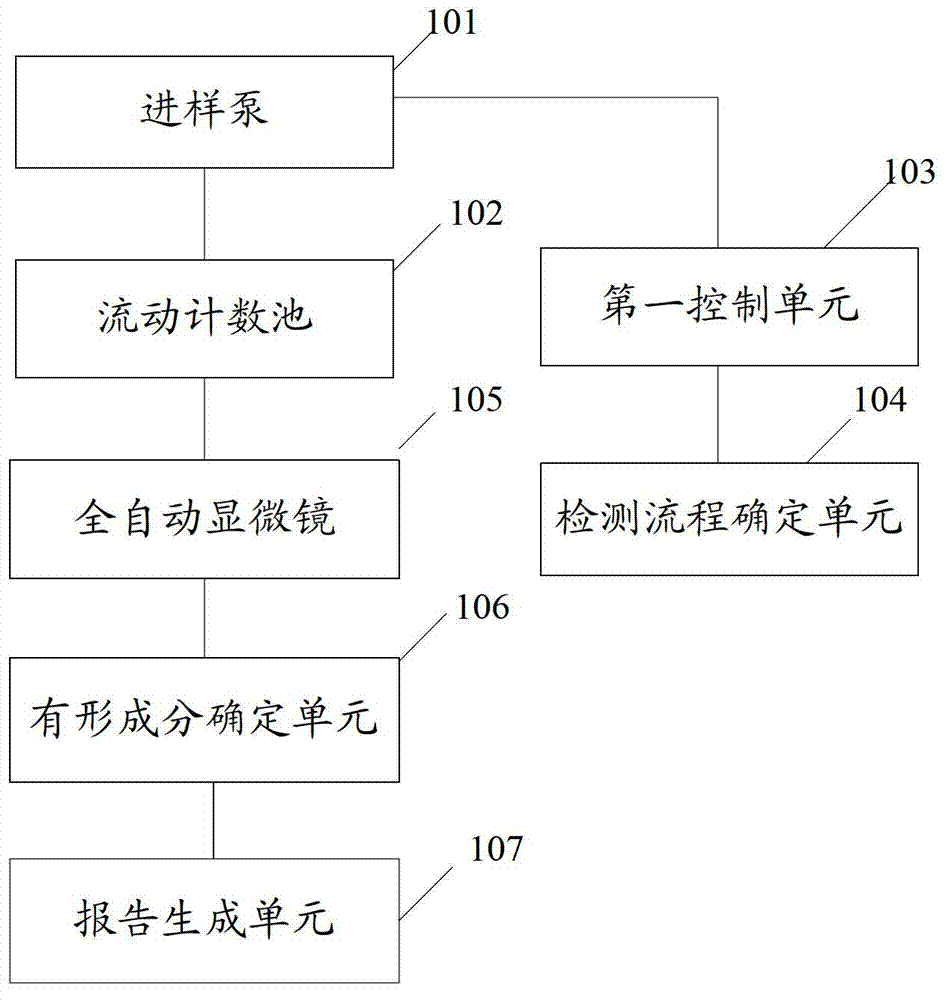
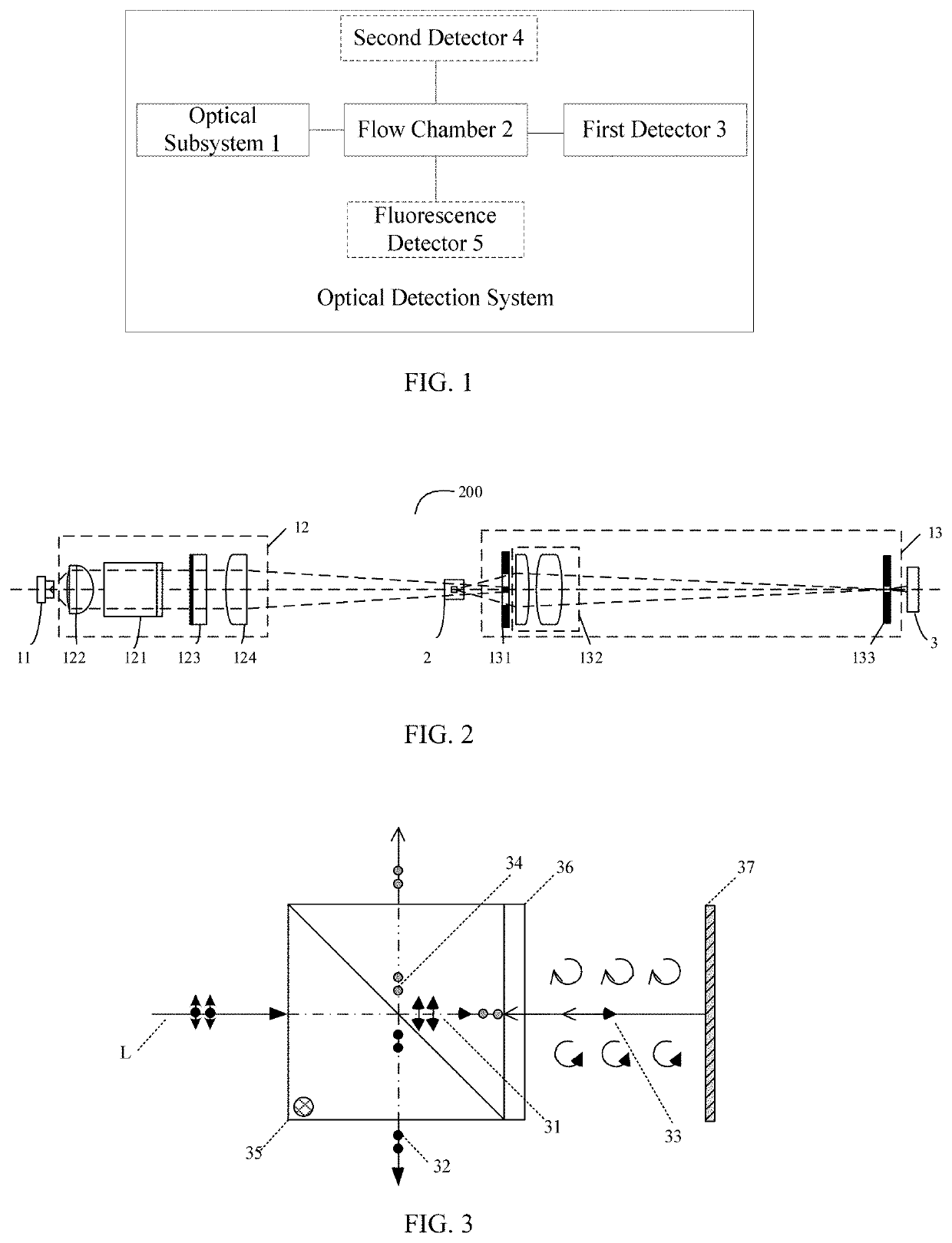
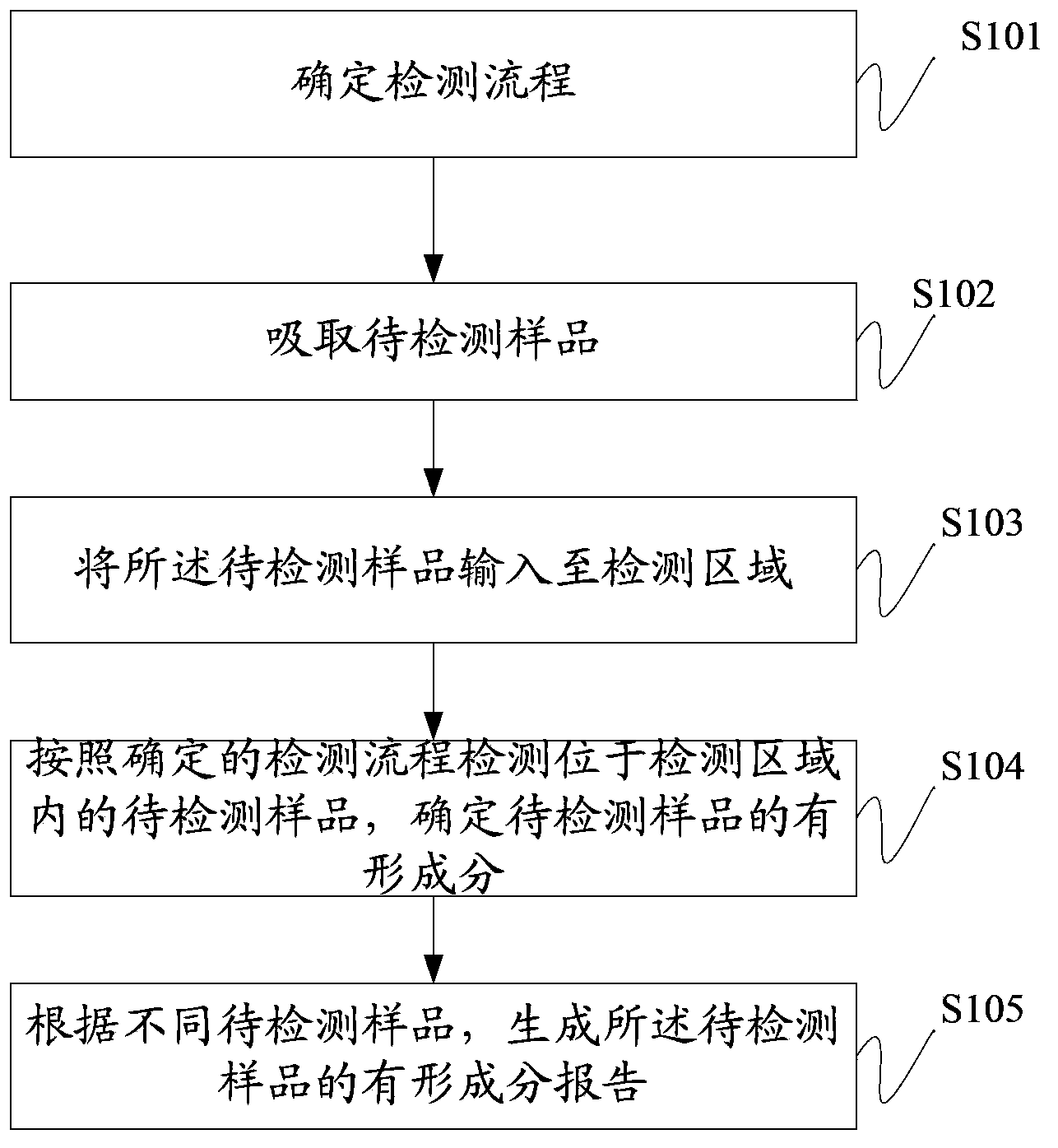
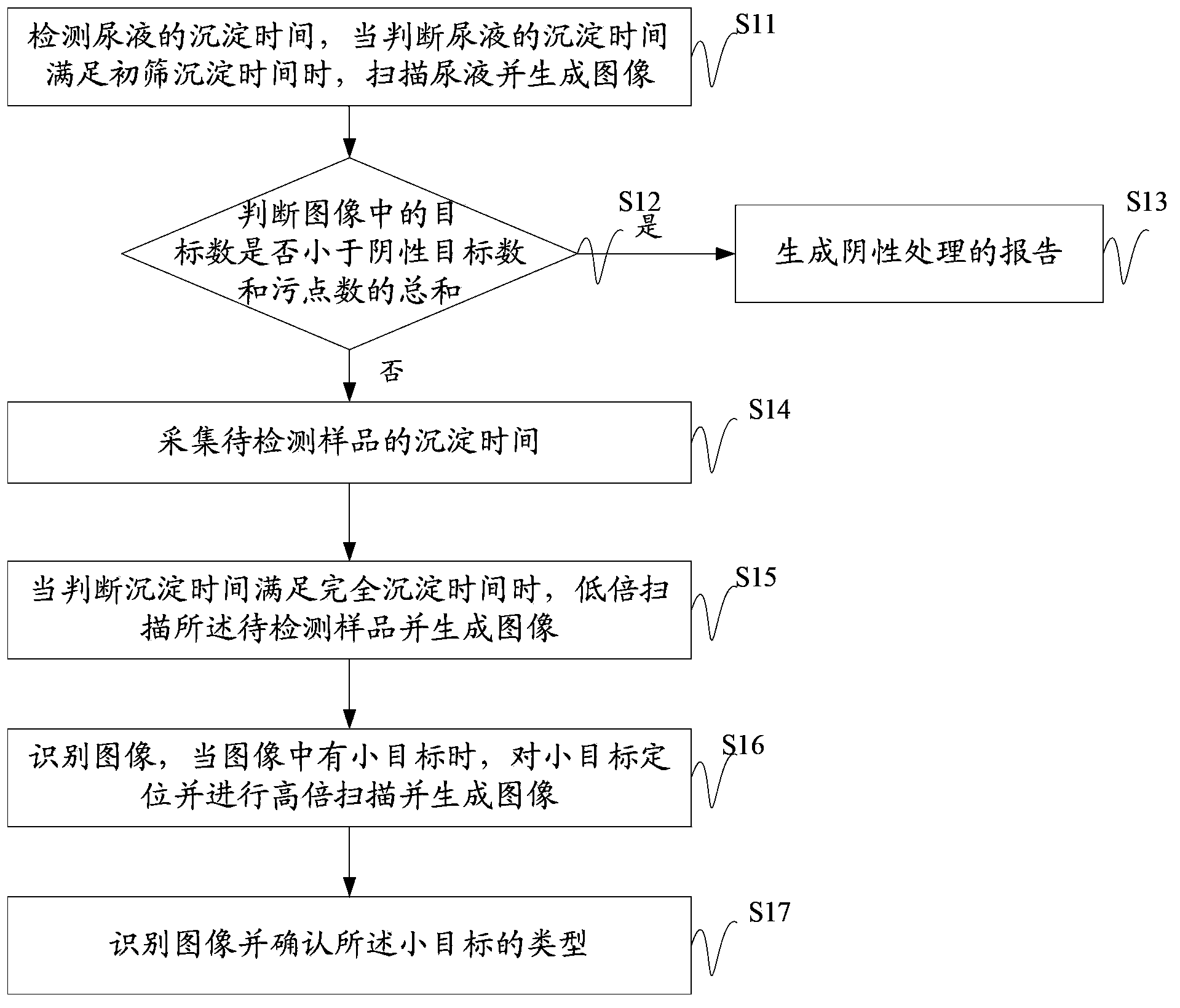
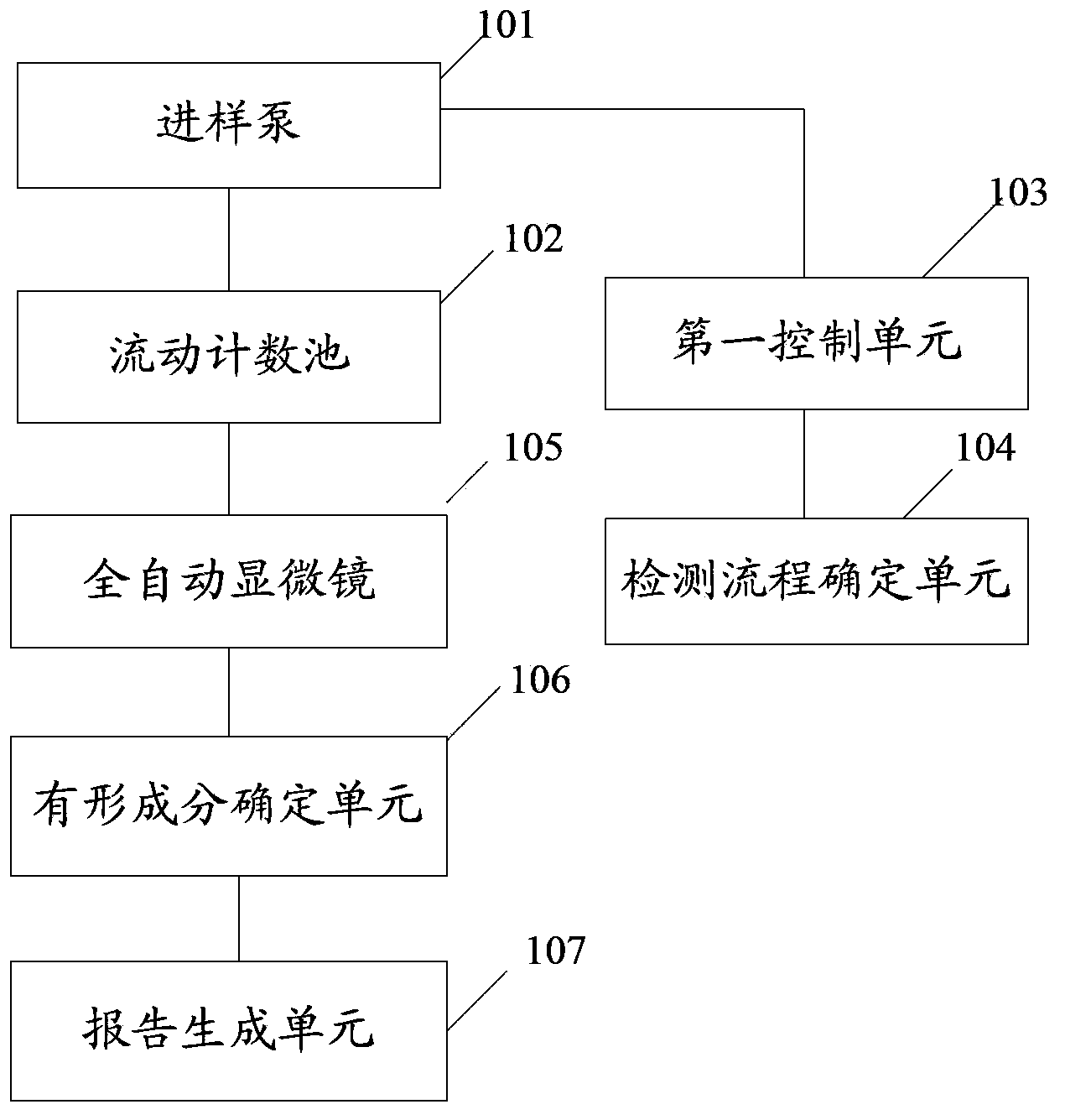
The invention discloses a sample analyzing method which can detect visible components of urine, blood and other body fluid on the same instrument to perform blood red blood cell counting and morphological analysis, blood differential blood counting and blood platelet counting analysis. The method includes: determining detection flow; absorbing samples to be tested; inputting the samples to be tested into a testing area; testing the samples to be tested, and determining the visible components in the samples to be tested; and producing a report of the visible component corresponding to the samples to be tested according to the different samples to be tested. In the sample analyzing method, when the detection flow corresponding to the detection types is determined, users can absorb the samples to be tested and input the samples to be tested into the testing area so as to detect the samples to be tested according to the determined detection flow and determine the visible components in the samples to be tested. Finally the report of the visible components of the samples to be tested is produced, and testing on various indexes of the samples to be tested is achieved.
Owner:AVE SCI & TECH CO LTD
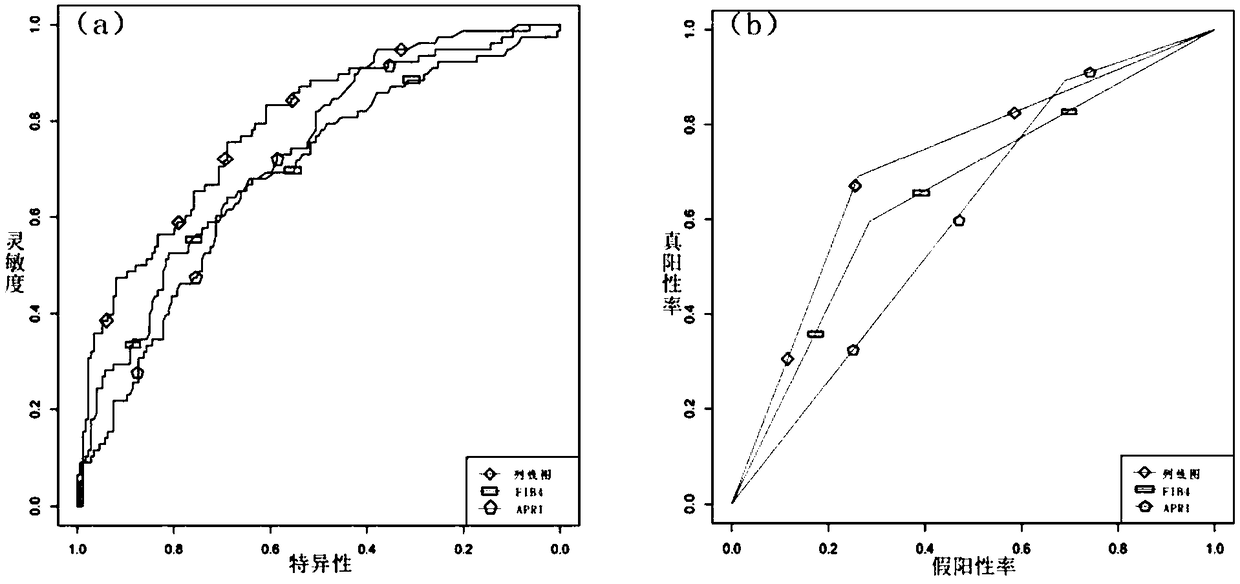
Non-invasive serological scoring model for hepatic fibrosis and design method thereof
InactiveCN109473175AReduce riskReduce the burden onHealth-index calculationBlood platelet countsLaminin
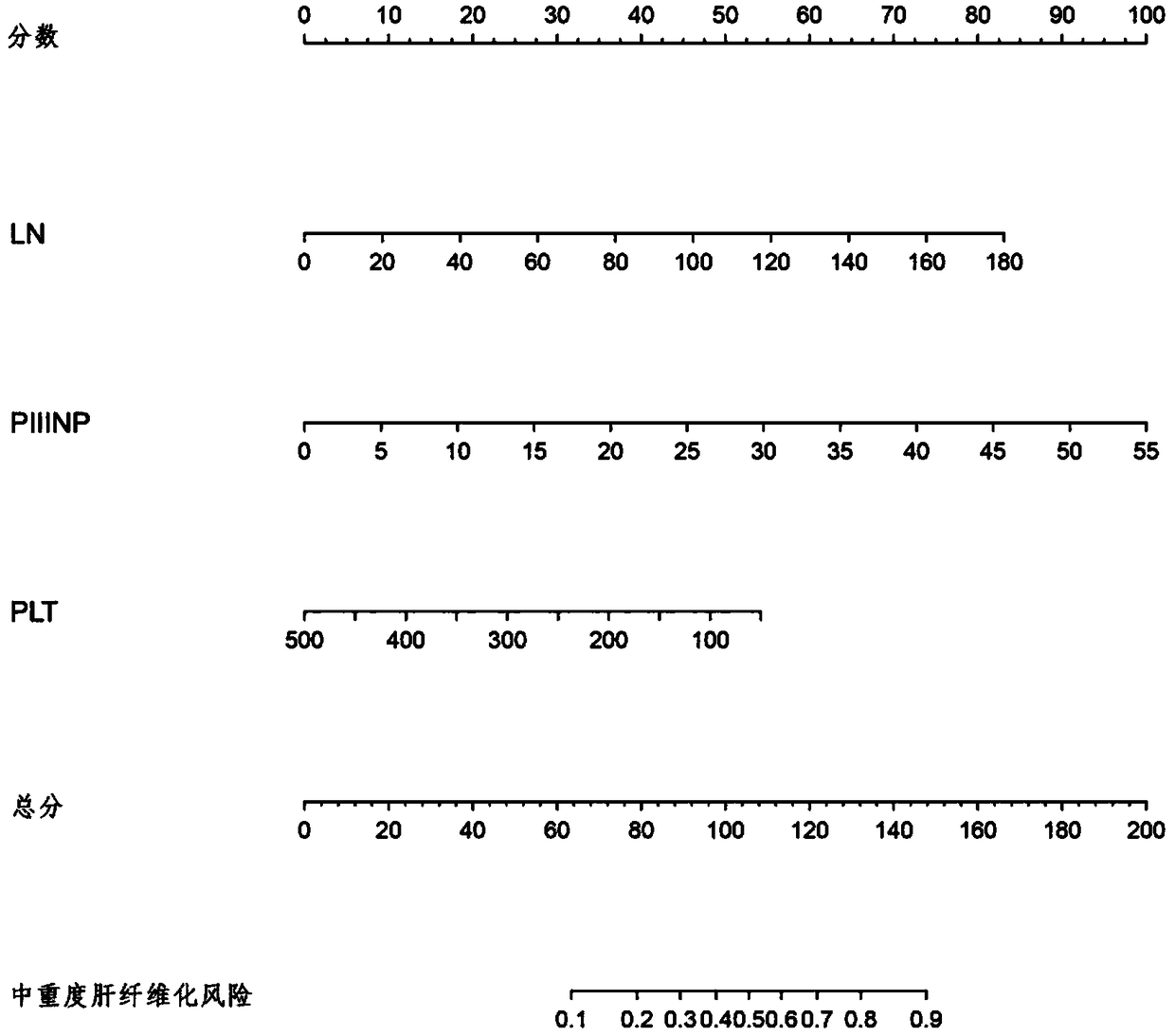
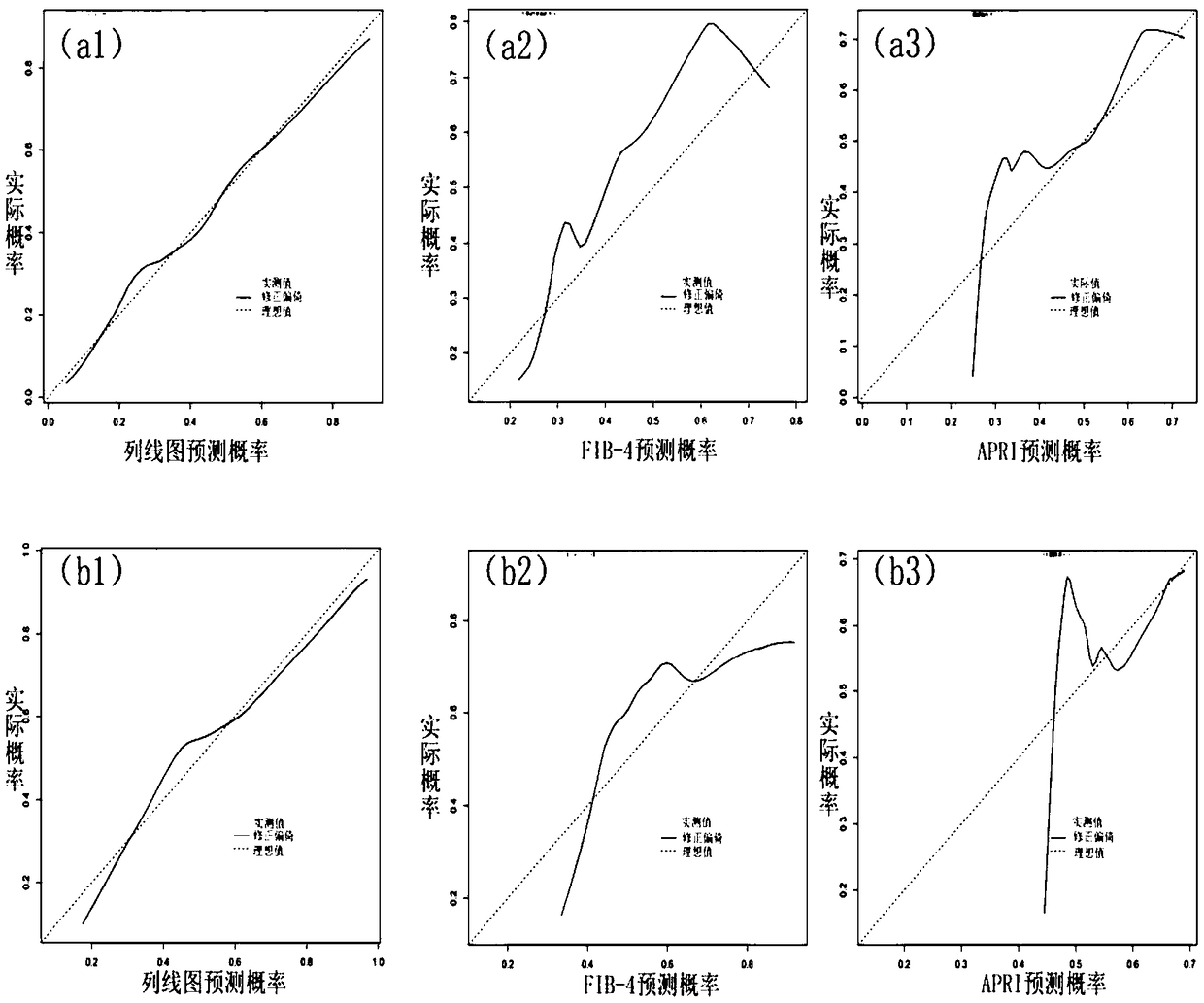
The invention relates to a non-invasive serological scoring model for hepatic fibrosis and a design method thereof. The model includes an input module, a processing module and an output module. The input module receives three independent predictors including blood platelet count, laminin and procollagen type 3. The processing module is connected with the input module and evaluates the situation ofhepatic fibrosis based on the independent predictors. The output module is connected with the processing module and outputs the score finally obtained by the module. The model can more accurately evaluate the situation of severe hepatic fibrosis for patients with chronic hepatitis. Compared with other models, the model only involves the three independent predictors including PLT, LN and PIIINP.The contained serological indicators are fewer, the accuracy and the practicability are higher, the model is more concise to use, popularization in clinical treatment and primary hospitals is facilitated, the probability of invasive examination is thus reduced, and the risk and burden of the patients are reduced.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for preparing PRP (platelet-rich plasma) of umbilical cord blood
A method for preparing PRP (platelet-rich plasma) of umbilical cord blood includes steps: subjecting fresh umbilical cord blood to low-speed centrifuging, removing a lower cell layer, and subjecting upper platelet containing plasma to ultrahigh-speed centrifuging until the liquid is separated into two layers including an upper plasma layer and a lower layer of precipitates which are platelets; removing the upper plasma layer, leaving a small quantity of plasma in an original centrifugal tube, well mixing, vibrating, counting the platelets, and well mixing according to a proportion that 1ml of plasma contains 1.2+ / -0.125 billion of platelets approximately. The platelet-rich plasma is effective in treatment of cartilage injuries, pain alleviation and function restoration and especially remarkable in treatment of senile osteoarthritis.
Owner:孔五一
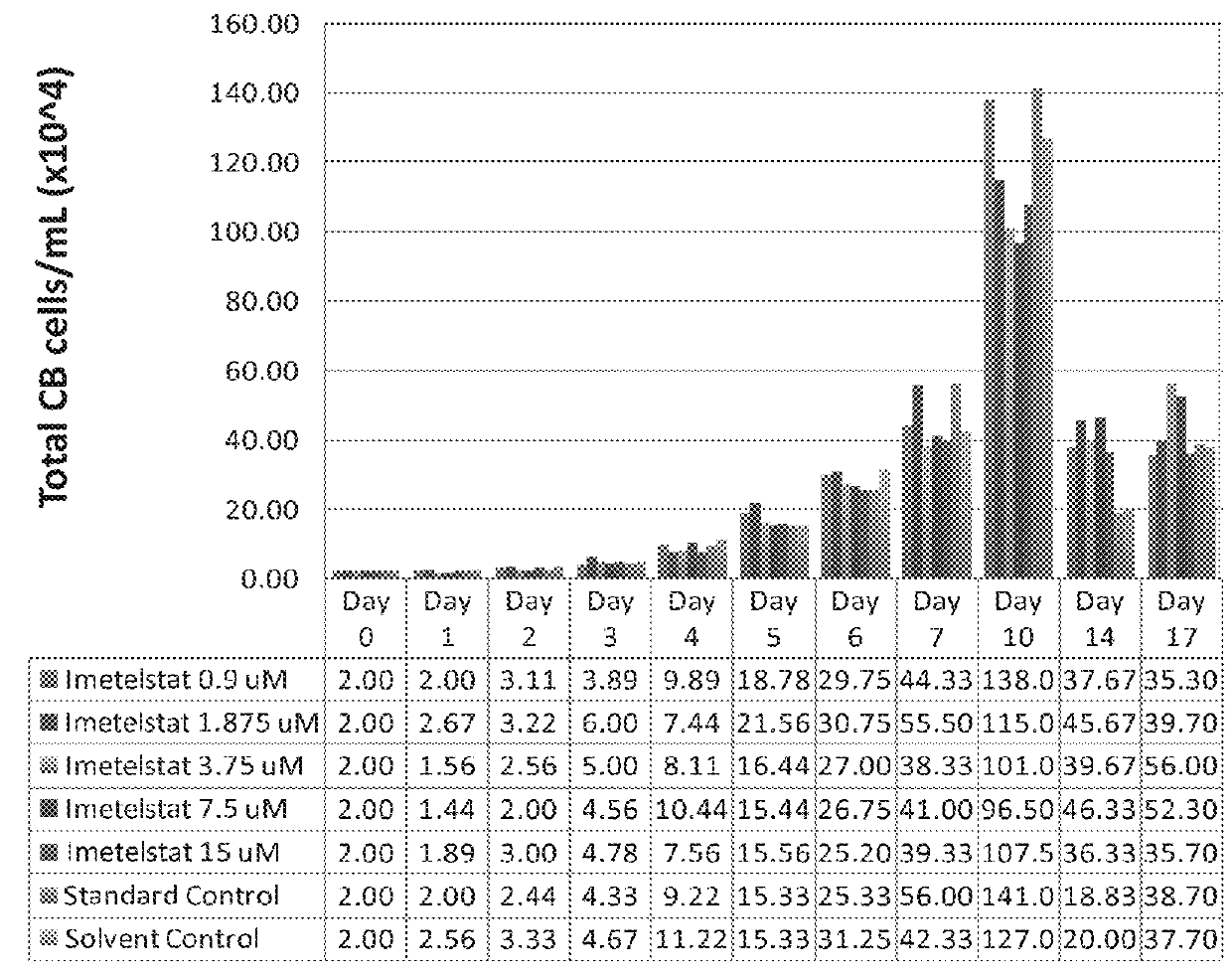
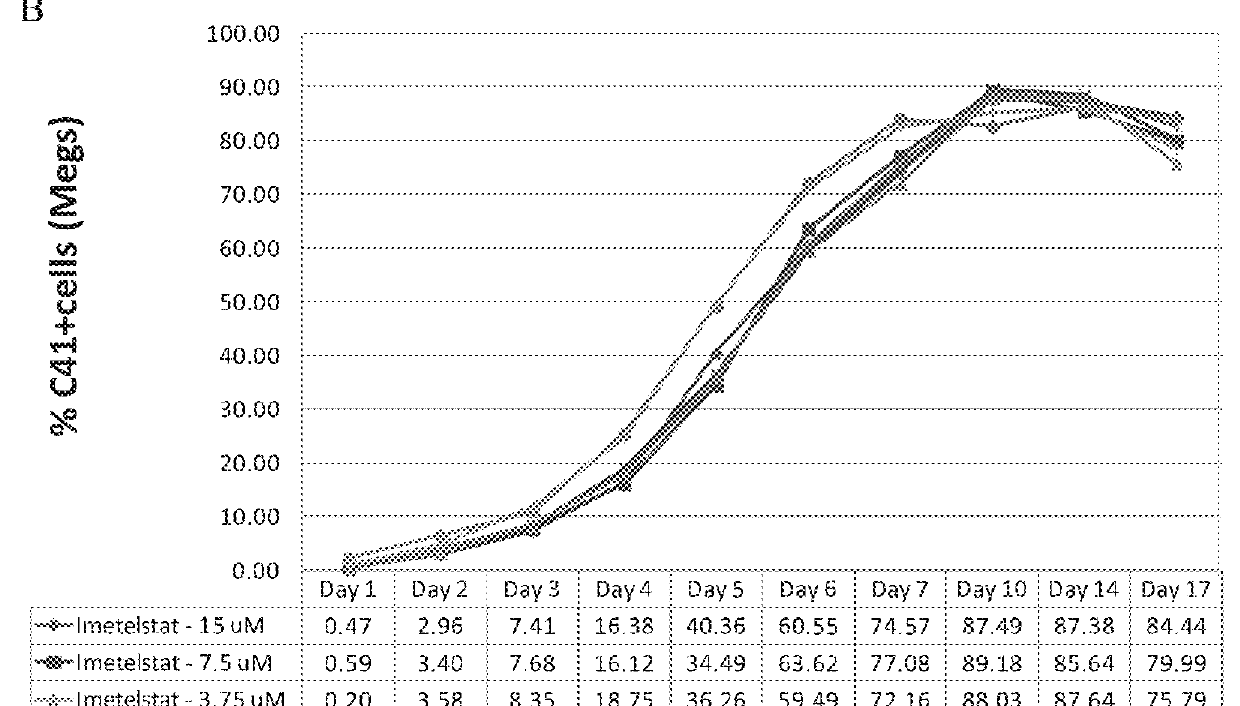
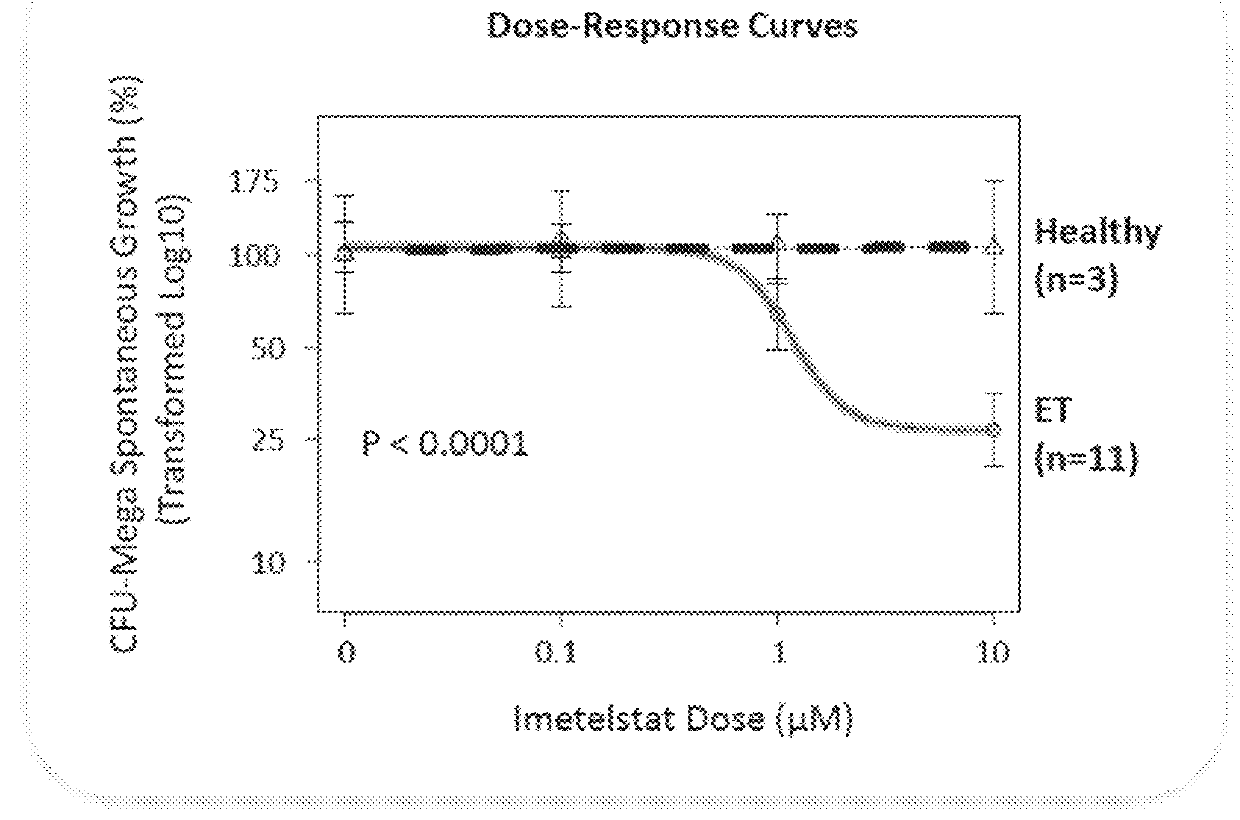
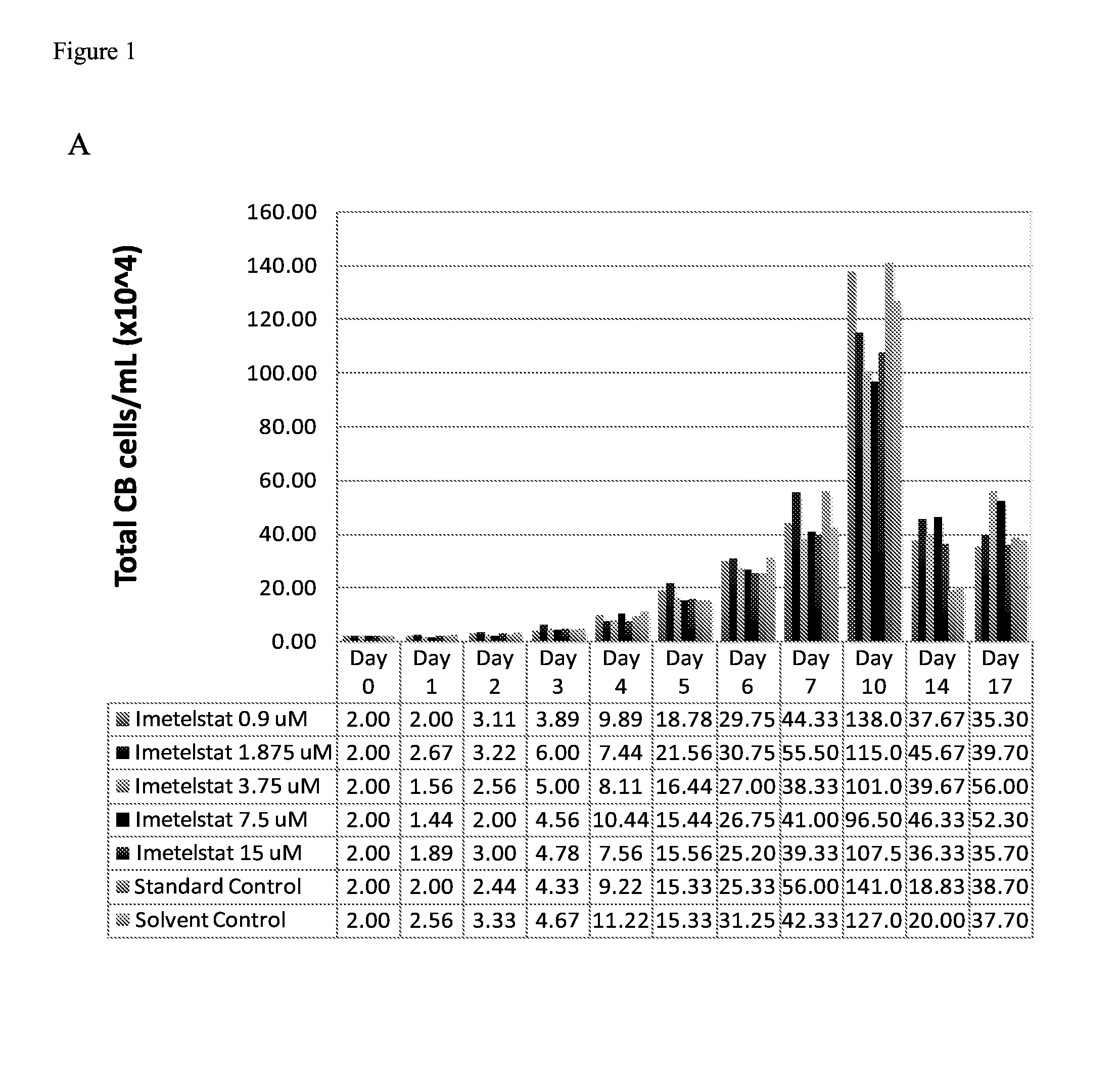
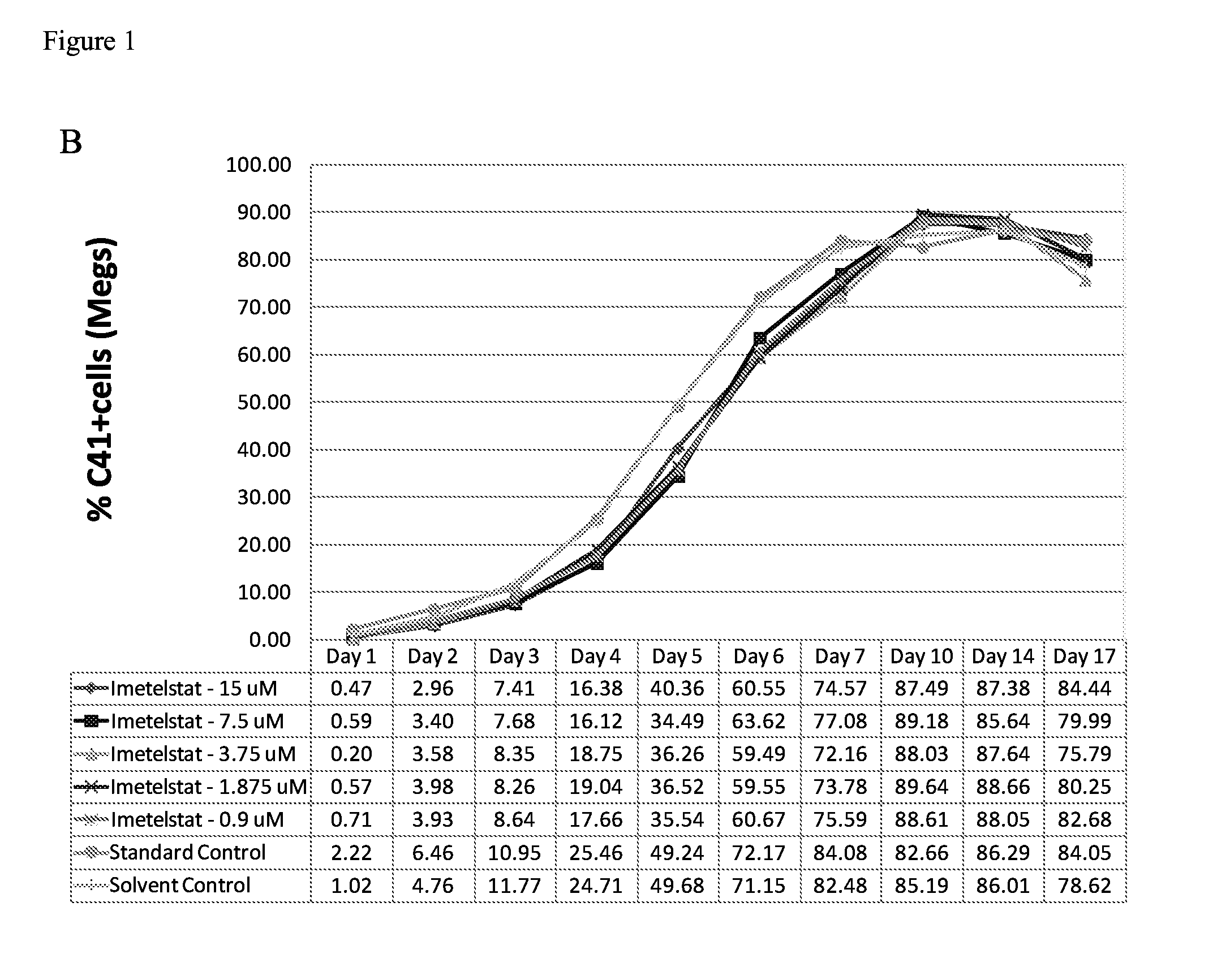
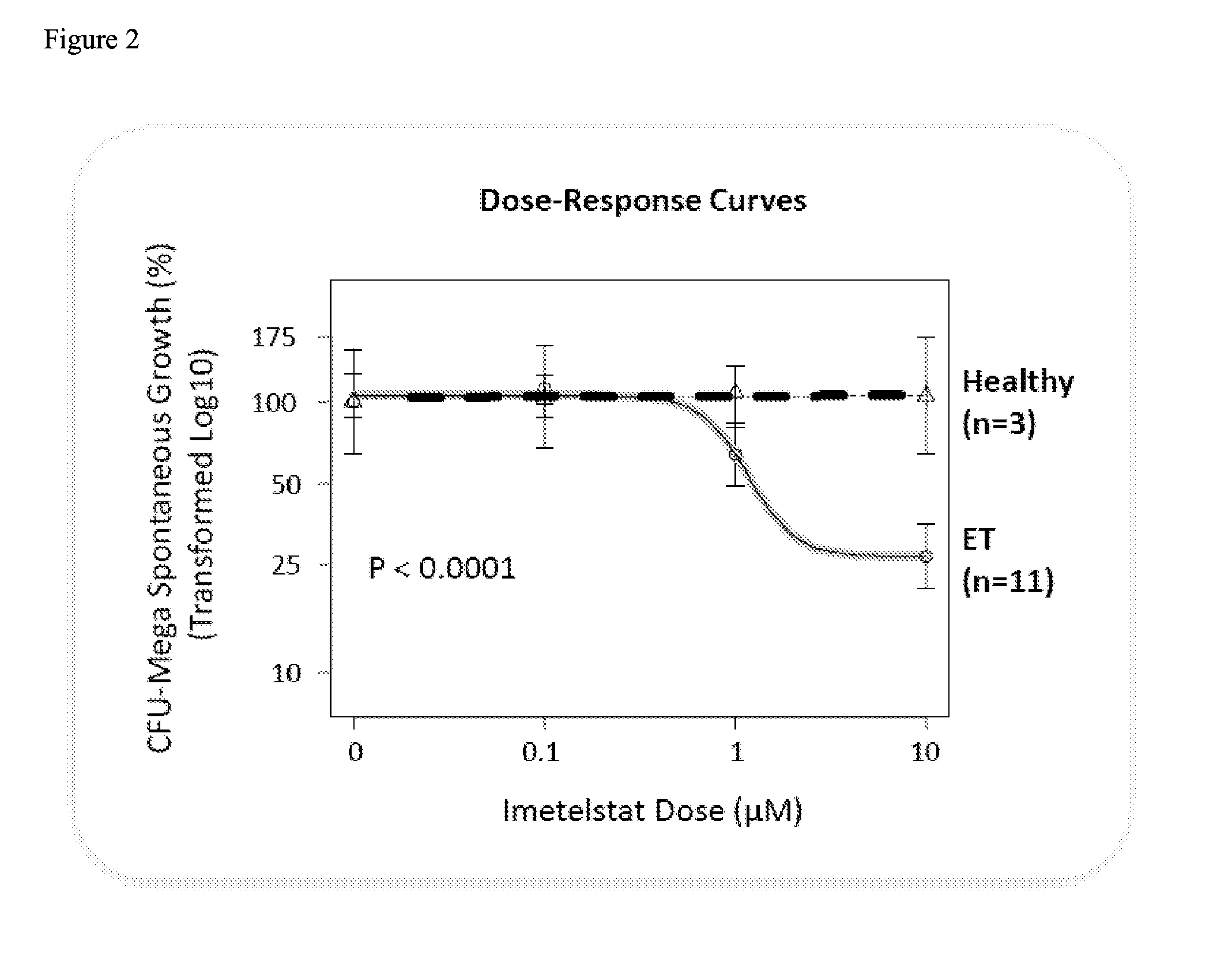
Use of telomerase inhibitors for the treatment of myeloproliferative disorders and myeloproliferative neoplasms
ActiveUS9375485B2Growth inhibitionRelieve symptomsPowder deliveryNanomedicineTelomeraseBlood platelet counts
Provided herein are methods for reducing neoplastic progenitor cell proliferation and alleviating symptoms associated in individuals diagnosed with or thought to have Essential Thrombocythemia (ET). Also provided herein are methods for using telomerase inhibitors for maintaining blood platelet counts at relatively normal ranges in the blood of individuals diagnosed with or suspected of having ET.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
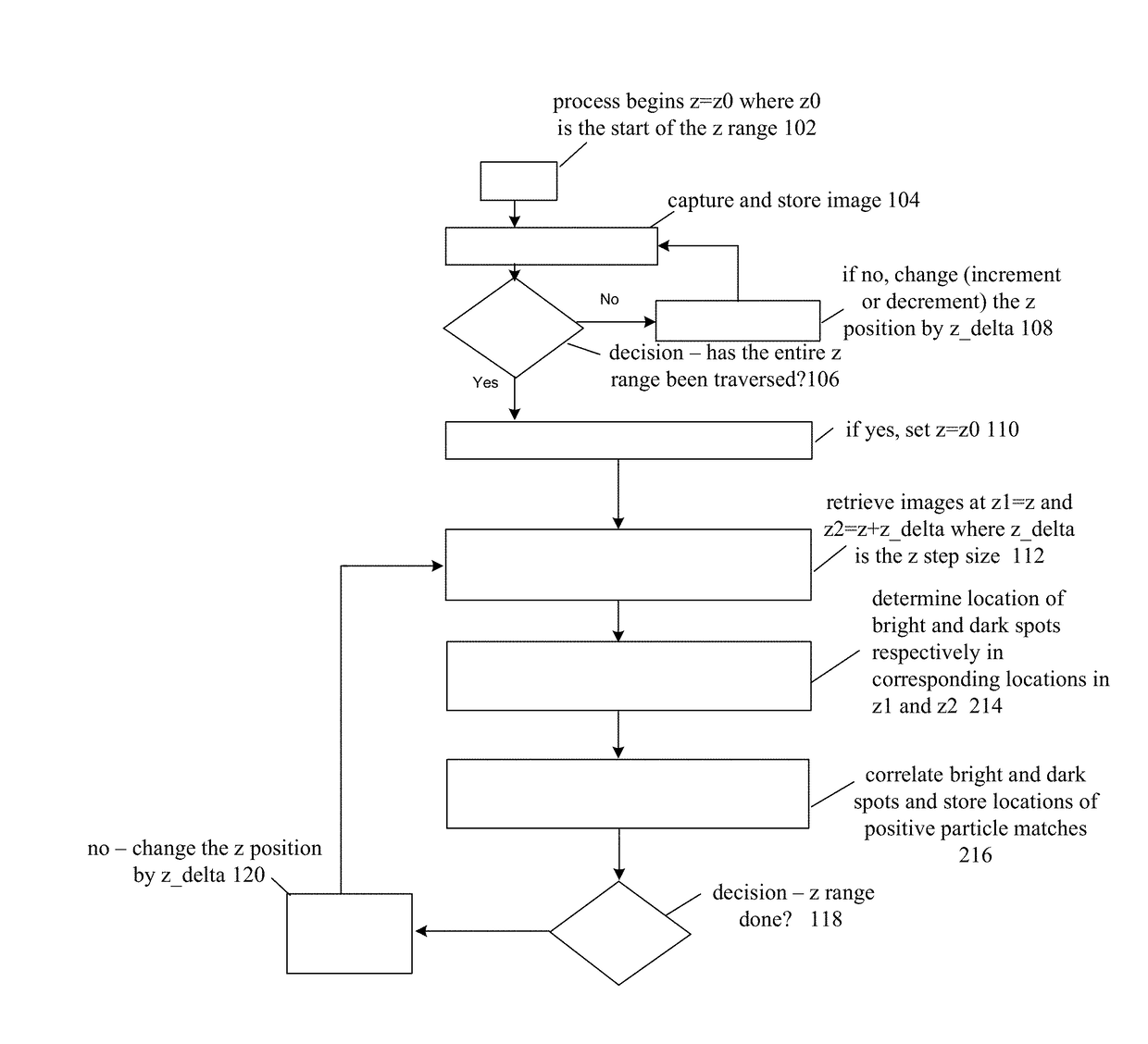
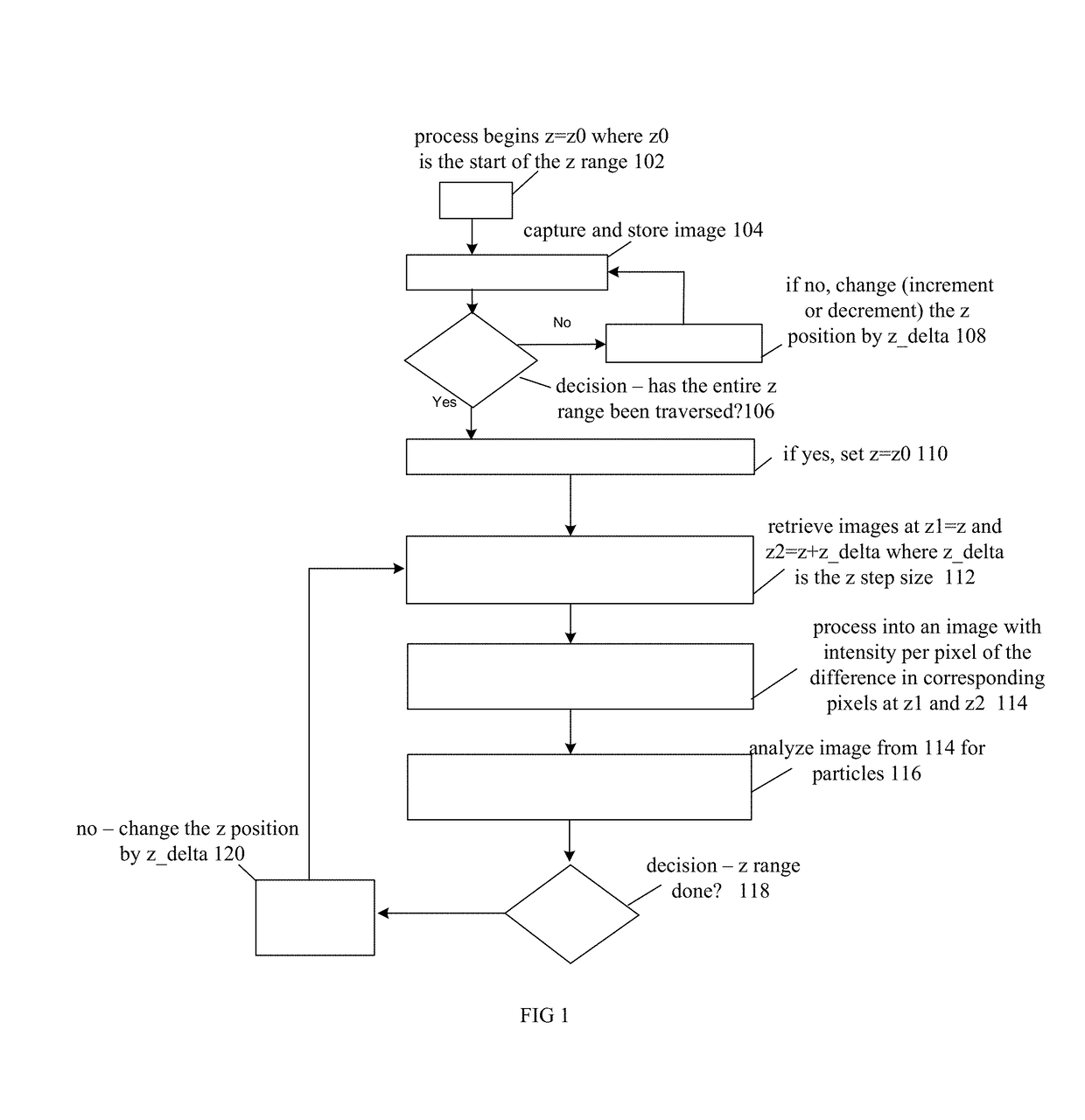
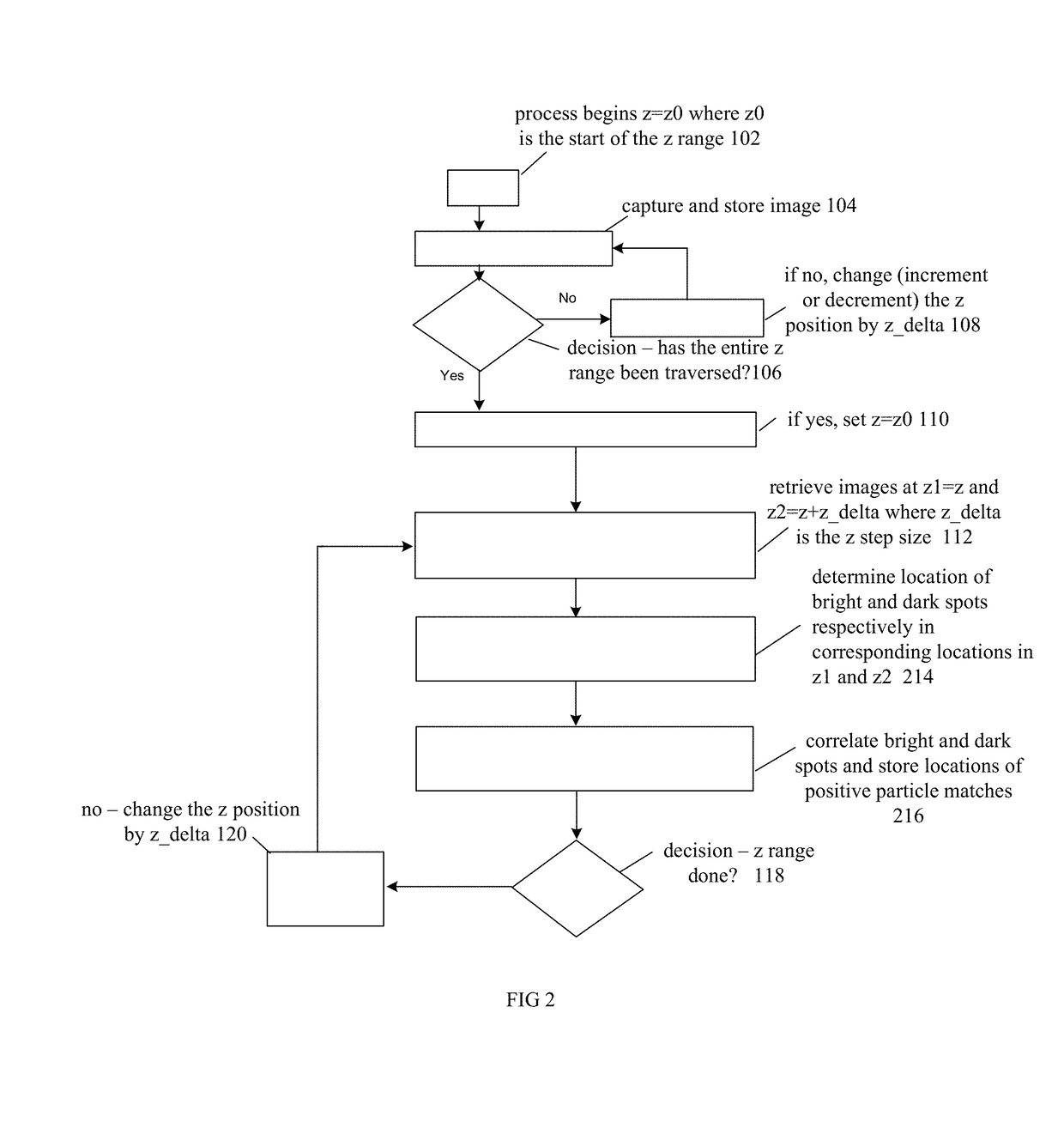
Optical platelet counter method
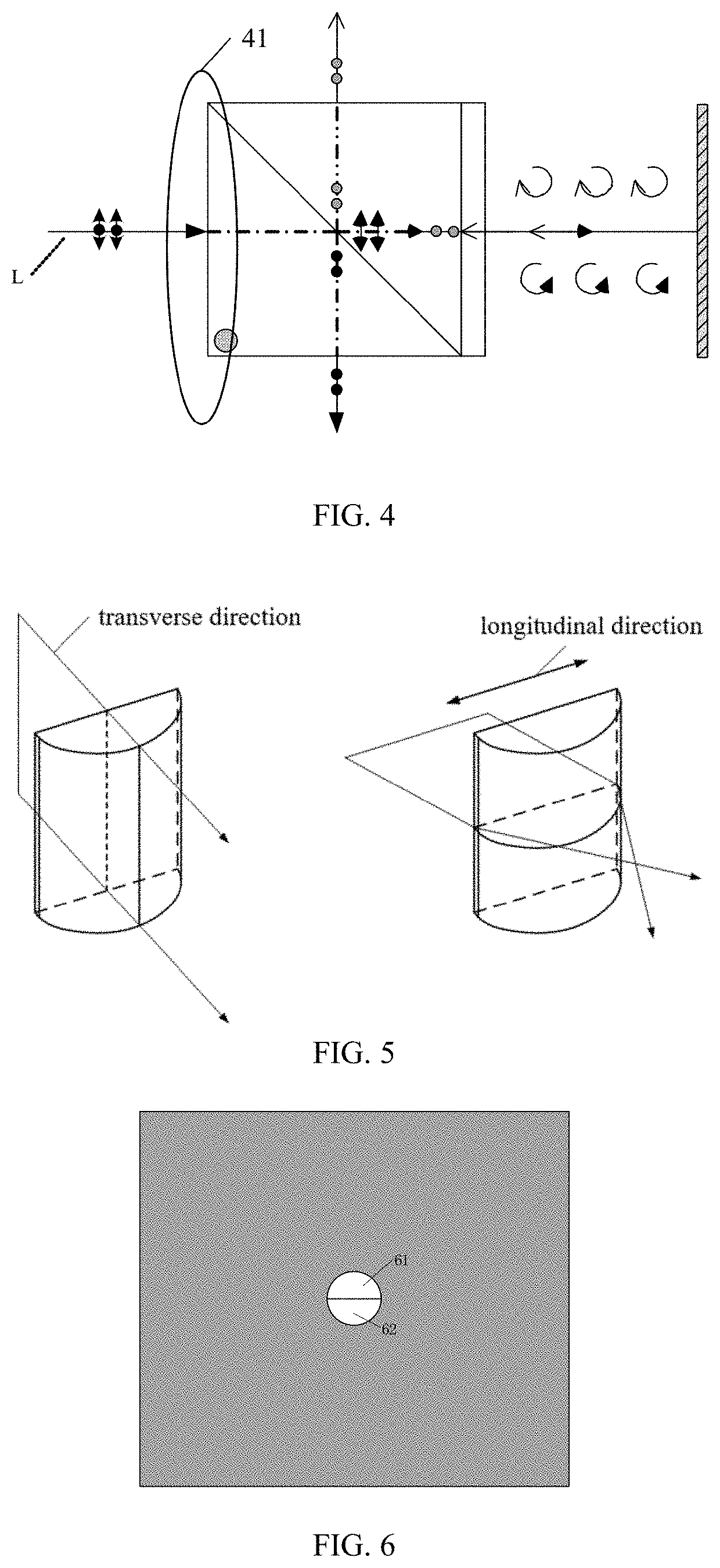
ActiveUS9690974B2Poor spherical aberrationBiological particle analysisMicroscopesOptical depthFluid bearing
Platelets or blood cells are detected in a fluid sample by adjusting a focal depth of a microscope through a range of values, the microscope having a mounted sample and an objective lens adapted with one or both of (a) a spherical aberration correction unmatched to a utilized cover plate for the sample, or (2) a numerical aperture unmatched to a utilized illumination source for the sample. Images are recorded at different specific focal depths and in multiple z planes of a fluid bearing the platelets, where the position of platelets may overlap on different of the multiple z planes that are recorded, the images recorded through the cover plate, thus causing the generation of a specific light-dark pattern indicative of platelets at particular positions and at multiple depths in the fluid media. The images are analyzed for the specific light-dark pattern.
Owner:FOCE TECH INT
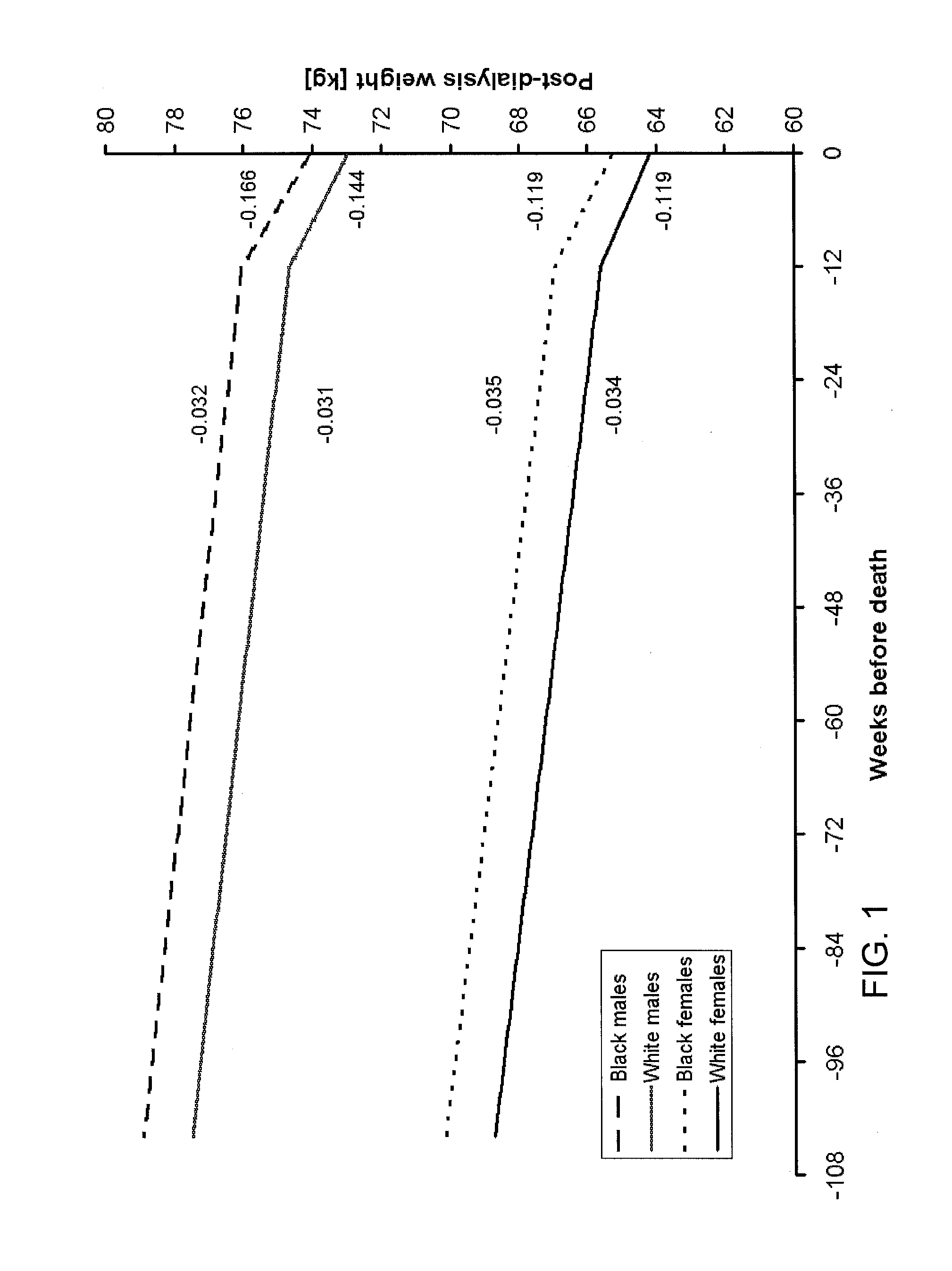
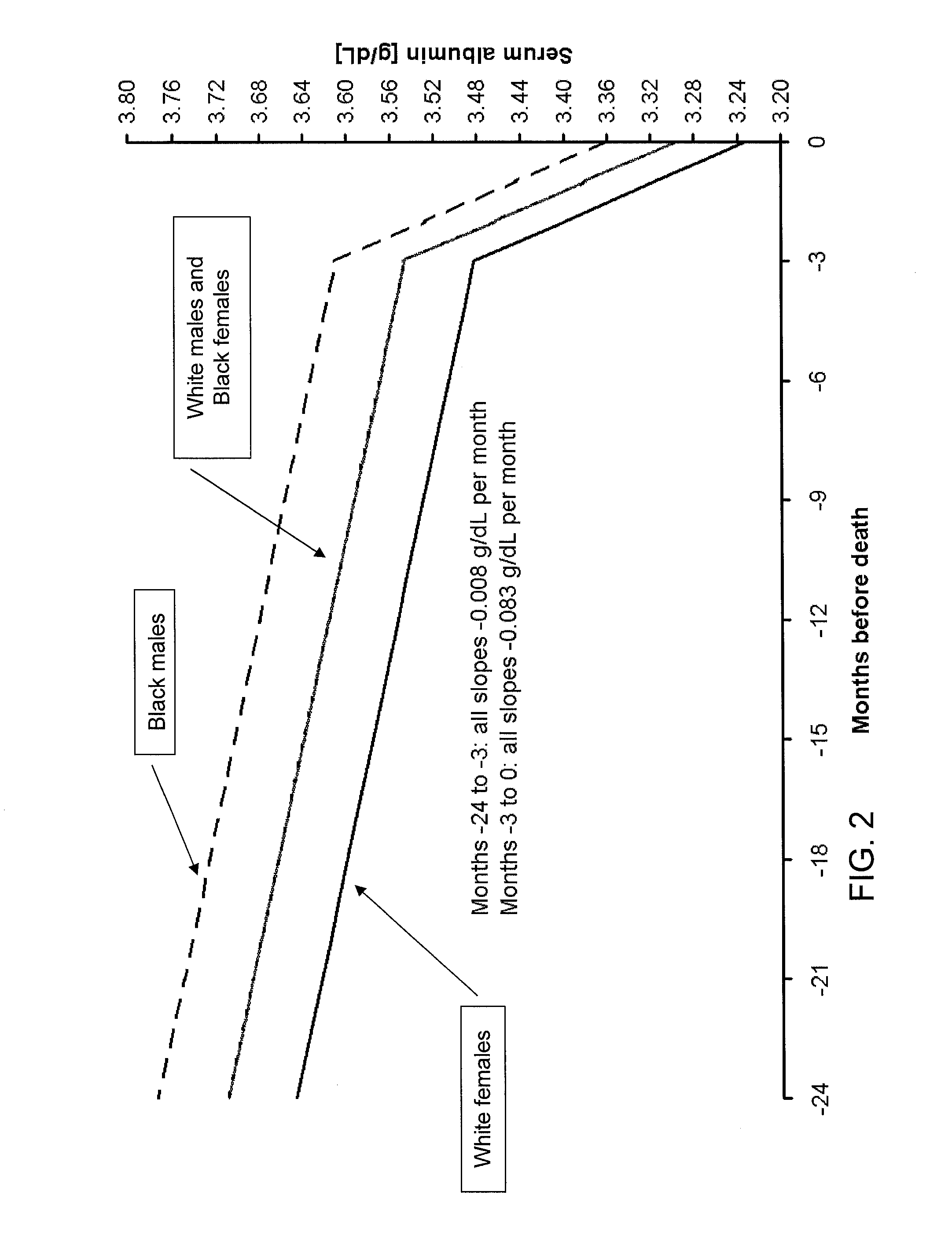
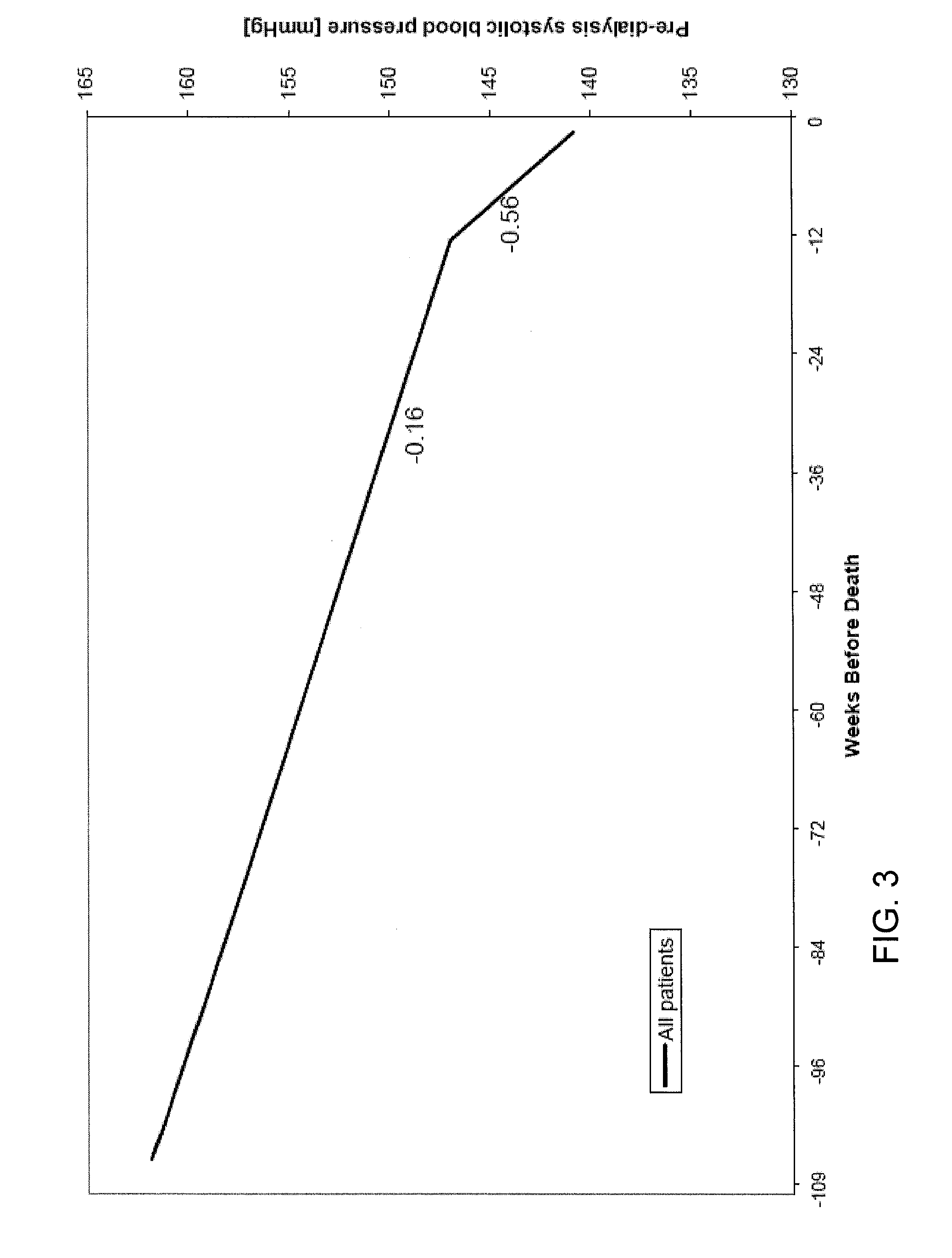
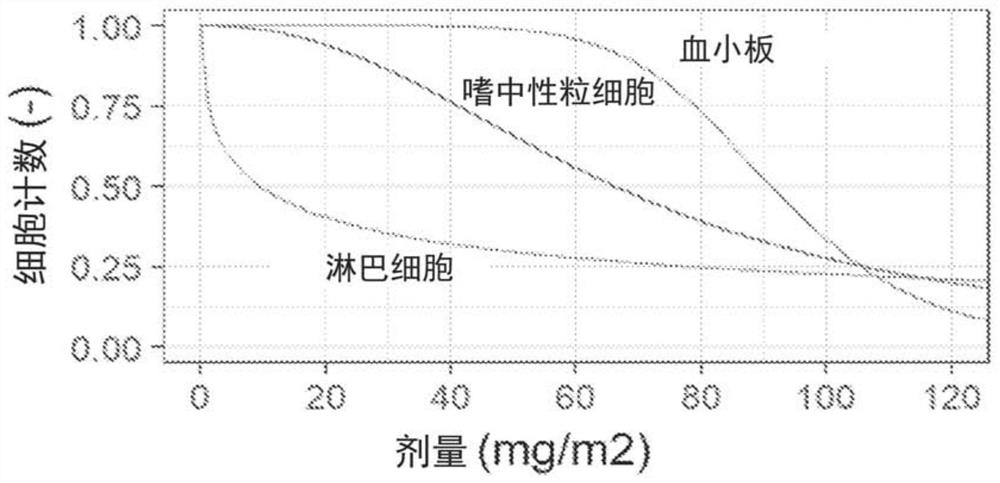
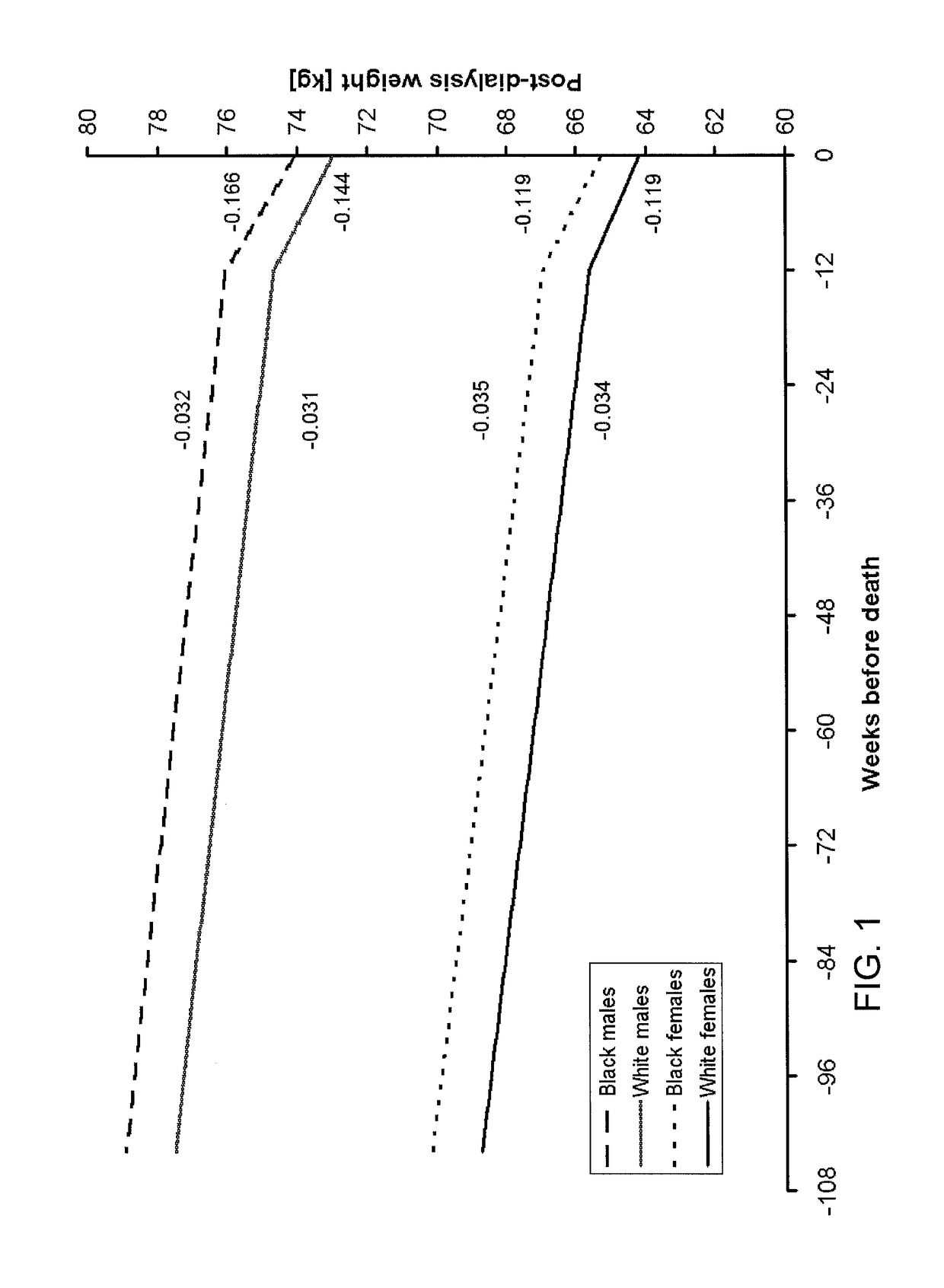
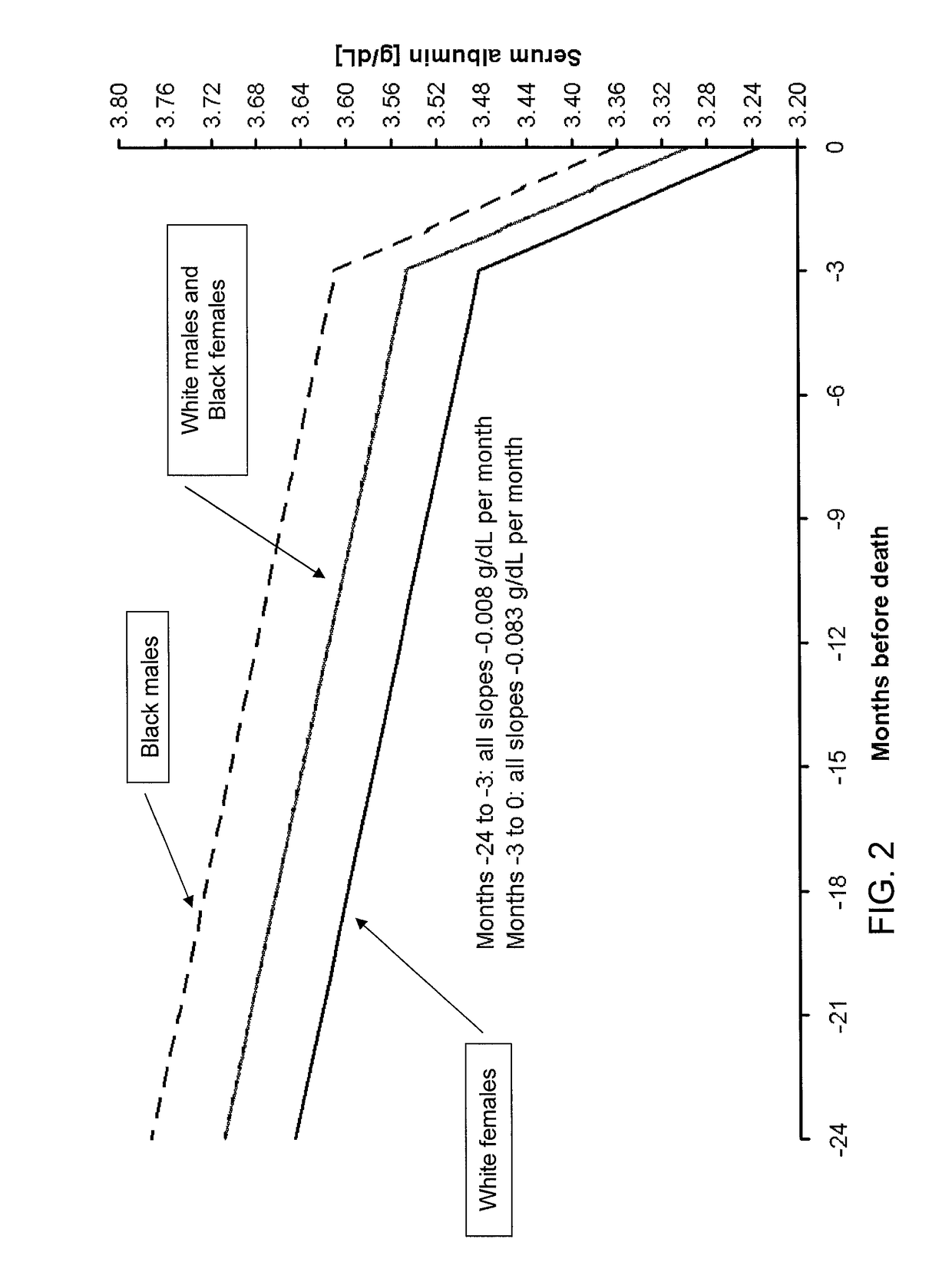
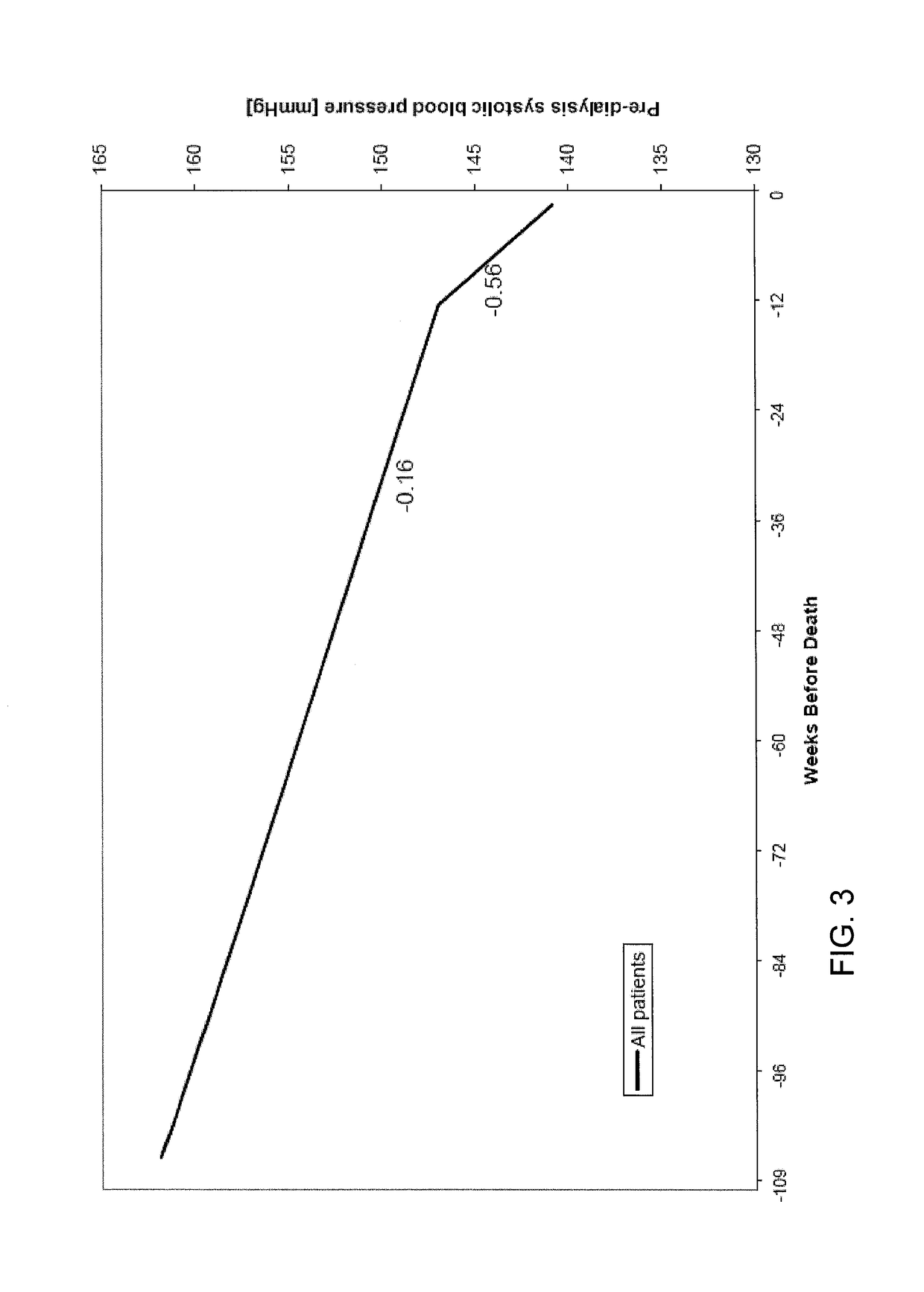
Method of identifying when a patient undergoing hemodialysis is at increased risk of death
ActiveUS20130244263A1Reduce mortalityIncreased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHaemodialysis machineIncreased risk
The invention is directed to a method of identifying a patient undergoing periodic hemodialysis treatments at increased risk for death that includes determining at least one of the patient's clinical or biochemical parameters, consisting of serum bicarbonate concentration level, serum potassium concentration level, serum calcium concentration level, hemoglobin concentration level, serum phosphorus concentration level, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, equilibrated normalized protein catabolic rate (enPCR), equilibrated fractional clearance of total body water by dialysis and residual kidney function (eKdrt / V), EPO resistance index, transferrin saturation index, serum ferritin concentration level, serum creatinine concentration level, platelet count, Aspartat-Aminotransferase level, and Alanin-Aminotransferase level at periodic hemodialysis treatments, and identifying a patient as having an increased risk for death if the patient has a significant change in the rate of change of at least one of the patient's clinical or biochemical parameters. The invention is also directed to a method of identifying an increased mortality risk factor for a patient undergoing periodic hemodialysis treatment. The method includes analyzing data of deceased patients that were previously undergoing periodic hemodialysis treatments by performing a longitudinal analysis backwards in time of changes in a clinical or biochemical parameter the patients, and identifying a significant change in the rate of decline or the rate of increase in a clinical or biochemical parameter before death of the patients.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Zhuang medicine composition assisted in resisting lung cancer
ActiveCN105126030AReduce appetite side effectsReduce inhibitionAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsMedicinal herbsBlood platelet counts
The invention discloses a Zhuang medicine composition assisted in resisting lung cancer. The Zhuang medicine composition is characterized by being prepared from the following Zhuang medicinal materials: Nyarinngoux (Chinese name: baihuasheshecao), Gaeubwnhgauh (Chinese name: baiying), Byaekloekhauj (Chinese name: longkui), Buenqcilienz (Chinese name: banzhilian), Ginghgun (Chinese name: guangxi eshu), Fouxndoengz (Chinese name: shishangbai), Swnjgyaeujhenj (Chinese name: huanghuadaoshuilian), Raggongox (Chinese name: lugen), GO gyauhgujlanz (Chinese name: jiaogulan) and Lozhangoj (Chinese name: luohanguo). The Zhuang medicine composition is combined with chemical drugs for curing lung cancer, can reduce the toxic and side effects of inappetence caused by the chemical drugs, reduce the damage of the chemical drugs to immune organs, increase white blood cell count, blood platelet count, red blood cell count and hemoglobin count to reduce the inhibiting effect on myelosuppression, reduce the content of glutamic-pyruvic transaminase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase to alleviate the damage to liver functions and increase the tumor suppression function of the chemical drugs. Namely, the Zhuang medicine composition is combined with the chemical drugs for curing the lung cancer and has the effects of toxicity reducing and efficacy enhancing.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Use of Telomerase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Myeloproliferative Disorders and Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
InactiveUS20150342982A1Reduced neoplastic progenitor cell proliferationReduce cell proliferationOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesTelomeraseBlood platelet counts
Provided herein are methods for reducing neoplastic progenitor cell proliferation and alleviating symptoms associated in individuals diagnosed with or thought to have myeloproliferative disorders, such as Essential Thrombocythemia (ET). Also provided herein are methods for using telomerase inhibitors for maintaining blood platelet counts at relatively normal ranges in the blood of individuals diagnosed with or suspected of having myeloproliferative disorders, such as ET.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Heparin-based blood sampler without platelet activation
PendingCN111356911AOrganic active ingredientsPreparing sample for investigationBlood platelet countsWhite blood count
The present invention relates to blood sampler and the preparation of blood samples that can be used for not only for blood gas, basic metabolic panel parameter analysis but also for a platelet countand / or white blood count, such as a 3-diff or 5-diff. The blood samples comprise at least one anticoagulant for the determination of blood gas and basic metabolic panel parameters and at least one anti-platelet agent.
Owner:RADIOMETER AS
Thrombopoietin mimetics for the treatment of radiation or chemical induced bone marrow injury
Disclosed are transgenic non-human mammals, which useful for the screening of thrombopoietin mimetics, thrombopoietin receptor agonists, or thrombopoietin receptor antagonists active on the human thrombopoietin receptor. The transgenic non-human mammal has a genome that comprises a stably integrated transgene construct comprising a polynucleotide sequence encoding a humanized thrombopoietin receptor wherein said transgenic non-human mammal has a baseline blood platelet count corresponding to a physiological blood platelet count of a matched non-transgenic non-human mammal. The chimeric thrombopoietin receptor comprises either the transmembrane domain of a human thrombopoietin receptor or both the extracellular and transmembrane domains of a human thrombopoietin receptor operably coupled to a cytoplasmic domain of a non-human thrombopoietin receptor.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Calf spleen extractive and application thereof to idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura treatment
ActiveCN104352520AHigh yieldHigh activityUnknown materialsImmunological disordersBlood platelet countsSide effect
The invention provides a calf spleen extractive and application thereof to idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura treatment. The preparation technology of the calf spleen extractive comprises the steps of preparation and freeze thawing of a homogenate, and pH adjustment and film filtration under the synergistic effect of combinative enzymes, as well as sterile filtering and filling. The extraction rate of polypeptide and ribose in the calf spleen extractive is greatly increased, and the glycopeptide ratio is set to be 80-87. The activity, capable of treating ITP, of the calf spleen extractive is verified through blood platelet counting and CD4<+>CD25<+>T proportion in all the immune organs, and the result shows that the calf spleen extractive can remarkably improve the blood platelet level by 50% than the original process, the hematopoietic function is improved and no toxic or side effects is generated.
Owner:JILIN UNIV +1
System for predicting risk of death of patient
ActiveCN111627559AImprove accuracyImprove predictive performanceHealth-index calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringBlood platelet countsWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a system for predicting the risk of death of a patient. The system for predicting the risk of death of a patient comprises: a data acquisition module used for obtaining the medical history of a patient, physiological parameters of the patient and laboratory parameters of the patient, wherein the physiological parameters comprise the Glasgow Coma Scale of the patient, the heart rate of the patient, the systolic pressure of the patient and the oxygen saturation of the patient, and the laboratory parameters comprise the hemoglobin level, the leukocyte count, the creatinine concentration, the blood potassium concentration, the blood sodium concentration, the urea content, the platelet count, the total bilirubin concentration, the D-dimer level and the fibrinogen content of the patient; and a module for calculating the death risk of the patient used for calculating the information acquired in the data acquisition module so as to calculate the 7-day death rate (p) ofthe patient.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Platelet detection system based on error prediction model
ActiveCN113470770AImprove efficiencyLow costIndividual particle analysisLaboratory analysis dataBlood platelet countsMedicine
The present invention provides a platelet detection system based on an error prediction model. The system comprises a detection part, a control part and a re-detection part, wherein the detection part is used for detecting a portion of a sample based on impedance platelet count, the control part comprises a false positive judgment module, wherein the false positive judgment module can be used for judging by using an error prediction model based on data of the detection part, if the judgment is positive, the other part of the sample is added into the re-detection part for re-detection, and if the judgment is false positive, re-detection is not carried out any more; and the re-detection part is configured to detect the other portion of the sample by using a fluorescence platelet count (PLT-F).
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Application of ginsenoside in preparing antiphospholipid syndrome molecular targeting treatment medicine
The invention relates to application of ginsenoside in the pharmacy field, in particular to application of ginsenoside in preparing antiphospholipid syndrome molecular targeting treatment medicine. In a laboratory antiphospholipid syndrome mouse model, the compound can effectively lower the level of anticardiolipin antibodies, anti-beta2-GP1 antibodies and lupus anticoagulants in blood; meanwhile, in a pregnant mouse model, the compound effectively lower aCL activation, shortens partial thromboplastin time and reduces the blood platelet count and the abortion rate; safety study shows that the compound is high in safety, has no influence on the central nervous system, the cardiovascular system and the respiratory system and has no mutagenic action. It is indicated that the compound has high safety and a good inhibiting effect on the antiphospholipid syndrome at the test dose and can be used for treating the antiphospholipid syndrome.
Owner:延边安帝康华生物科技有限公司
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
InactiveCN104173563AControl bleeding symptomsLift countBlood disorderPlant ingredientsBlood platelet countsLigustrum vulgare
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from the following raw pharmaceutical materials in parts by weight: 20-28 parts of raw milkvetch root, 15-20 parts of prepared ligustrum lucidum, 10-15 parts of atractylodes macrocephala, 12-18 parts of raw rehmannia root, 15-20 parts of dodder seed, 12-18 parts of tree peony bark, 12-18 parts of Jiangnan herba selaginellae, 12-18 parts of herba agrimoniae, 12-18 parts of aizoon stonecrop and 4-8 parts of prepared liquorice root. The invention further provides application of the traditional Chinese medicine composition. The traditional Chinese medicine composition has the advantages that the compatibility of the traditional Chinese medicine composition disclosed by the invention accords with the principle of monarch-and-minister-and-assistant-and-guide of the traditional Chinese medicine, the traditional Chinese medicine composition can effectively control the bleeding symptom of a sufferer, improve the quality of life and increase the number of platelets and has a remarkable treatment effect on idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and no adverse reaction is caused, so that the traditional Chinese medicine composition has broad development and application prospects and is suitable for further popularization and application.
Owner:YUEYANG INTEGRATED TRADITIONAL CHINESE & WESTERN MEDICINE HOSPITAL SHANGHAI UNIV OF CHINESE TRADITIONAL MEDICINE
Blood detection method and blood analysis system
PendingUS20210102935A1Accurate detectionEasy to detectIndividual particle analysisBiological testingBlood platelet countsWhite blood cell
A blood detection method is provided, including: treating a blood sample with a first reagent to obtain a test sample, wherein the first reagent includes a hemolytic agent for lysing red blood cells in the blood sample into fragments having light scattering characteristics significantly different from those of platelets; passing particles in the test sample through a detection area of an optical detection system one by one, to obtain optical information of the test sample; and obtaining optical information of platelets according to at least two types of the optical information of the test sample. In the method, a platelet count is obtained by lysing red blood cells in a blood sample, and white blood cell subpopulations can be also differentiated.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Application of artemisinin compound in preparation of drugs for treating ITP
InactiveCN109939104ALow cost of treatmentReduce doseOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersBlood platelet countsGlucocorticoid
The invention discloses application of an artemisinin compound in preparation of drugs for treating ITP. It is unexpectedly discovered in clinical trials that blood platelet count holding time can beprolonged when drugs of artemisinin, especially artesunate or dihydroartemisinin treat patients with immune thrombocytopenia and patients with relapse of the immune thrombocytopenia, and it is indicated that the artemisinin drugs have a good therapeutic effect on the immune thrombocytopenia. Further studies show that the combination of the artemisinin drugs and other drugs, such as the combinationof the artemisinin drugs and glucocorticoids, can further reduce the dosage of glucocorticoid, gamma globulin and the like for treatment, thereby reducing the treatment cost of the patients and reducing the probability of significant complications. Reticulocytes as a toxicity sensitive index of the artemisinin drugs are strictly observed by the inventor, it is found that no significant differenceexists before and after the treatment, and it is further showed that the artemisinin drugs have good safety.
Owner:广州博奥技术有限公司
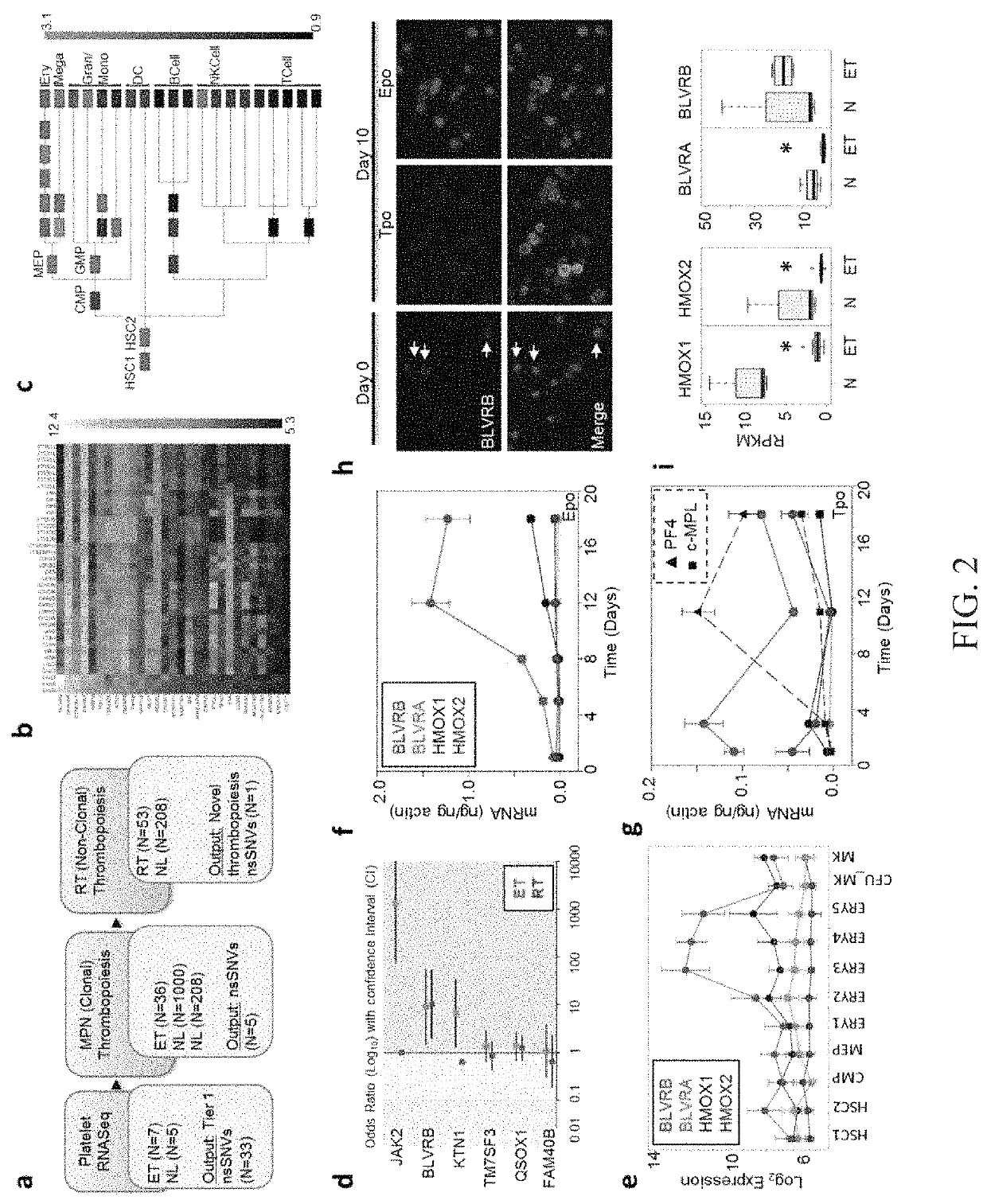
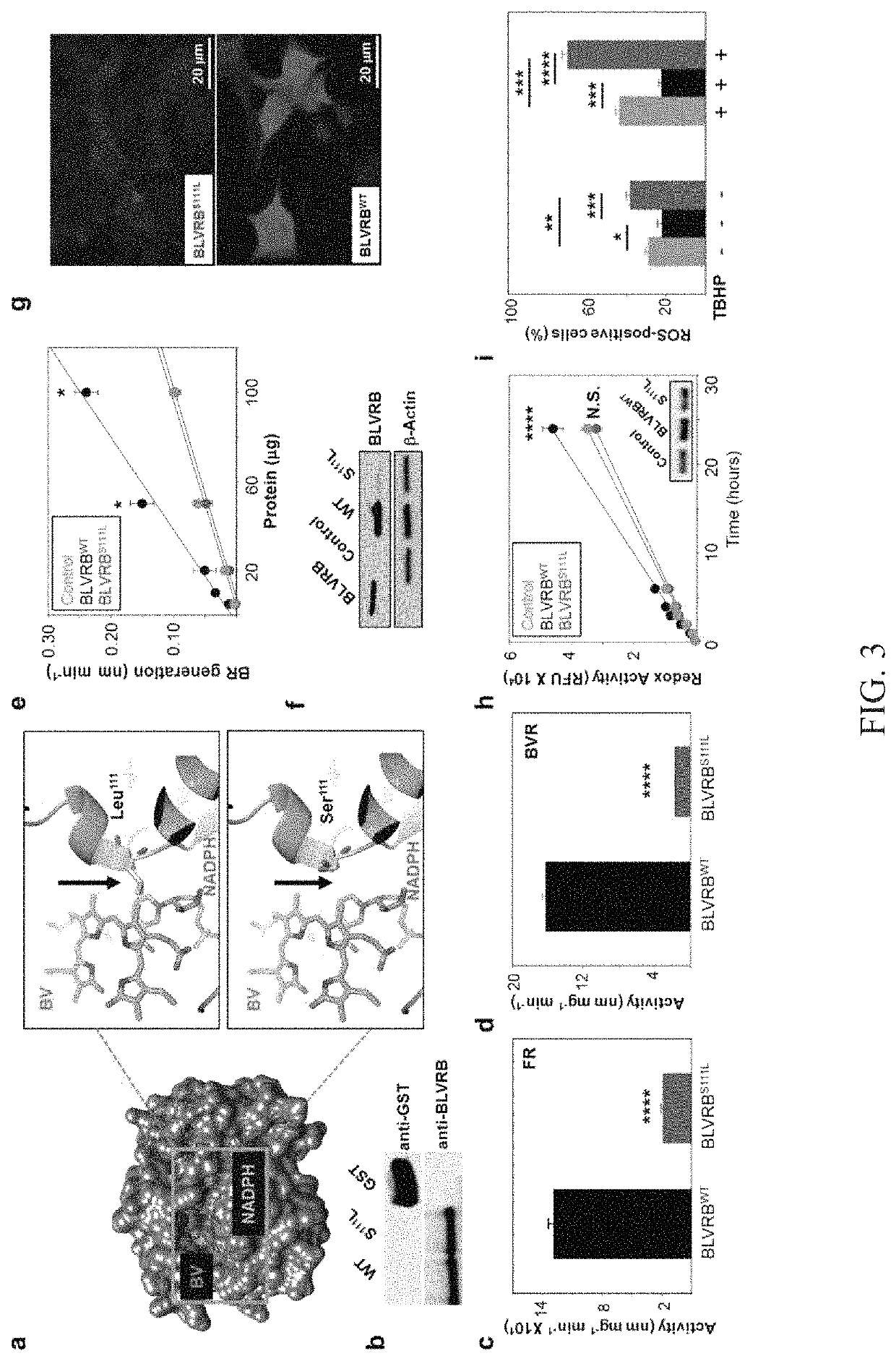
Methods for increasing platelet count by inhibiting biliverdin IXβ reductase
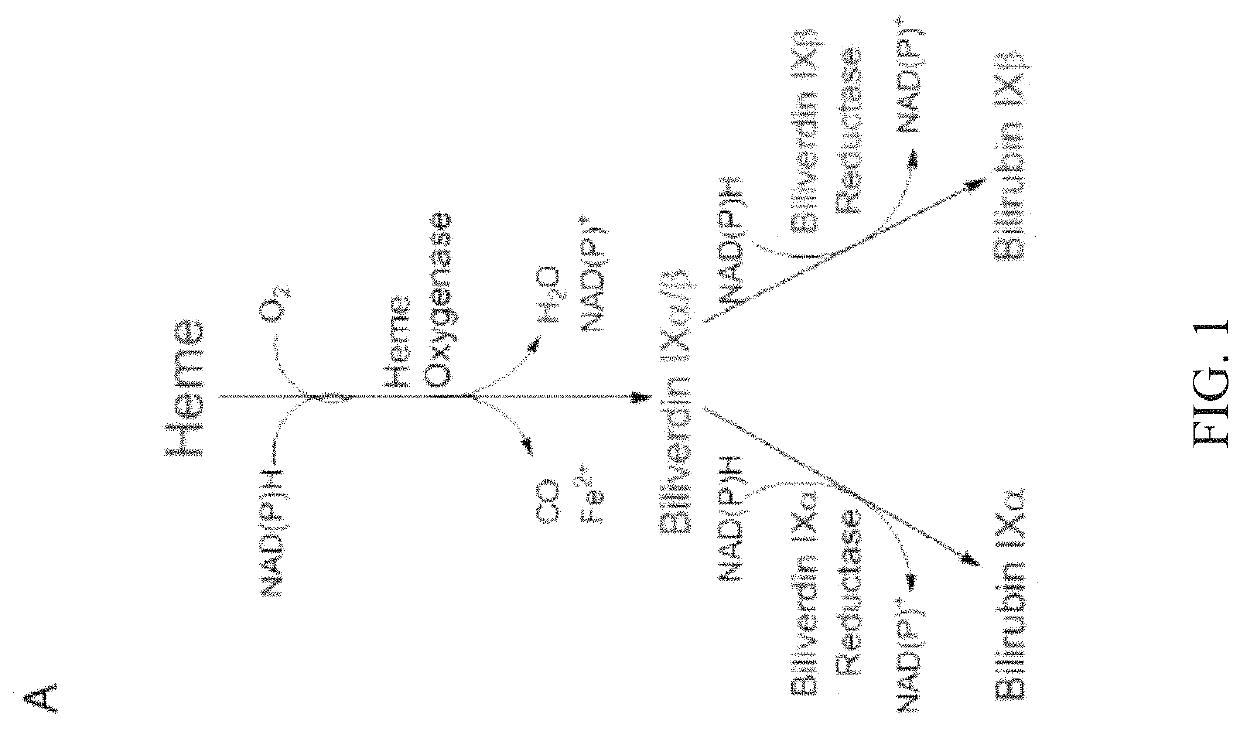
ActiveUS10543286B2Increased thrombopoiesisOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseBiliverdin
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Preparation for treating idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and preparation thereof
InactiveCN109106800ARaise countEnhance immune functionUnknown materialsPill deliverySide effectTreatment effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines, and particularly relates to a preparation for treating idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. The preparation is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5 to 20 parts of pig nail, 3 to 12 parts of rhizoma rehmanniae, 2 to 10 parts of radix paeoniae rubra, and 2 to 10 parts of cortex moutan radicis boiled by juice of radix rehmanniae recen. The preparation for treating the idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura has the advantages that the treatment effect is obvious; after the preparation is taken for three courses, the subcutaneous purpura and other symptoms are basically eliminated, and the blood platelet count is obviously increased; the function of obviously enhancing the immunity of the human body is realized, the preparation is especially suitable for female patients with menometrorrhagia symptoms, and is free of any toxic or side effect, and the application range is broad.
Owner:珠海安生凤凰制药有限公司
Application of Ginsenosides in the Preparation of Molecular Targeted Therapy Drugs for Antiphospholipid Syndrome
The invention relates to application of ginsenoside in the pharmacy field, in particular to application of ginsenoside in preparing antiphospholipid syndrome molecular targeting treatment medicine. In a laboratory antiphospholipid syndrome mouse model, the compound can effectively lower the level of anticardiolipin antibodies, anti-beta2-GP1 antibodies and lupus anticoagulants in blood; meanwhile, in a pregnant mouse model, the compound effectively lower aCL activation, shortens partial thromboplastin time and reduces the blood platelet count and the abortion rate; safety study shows that the compound is high in safety, has no influence on the central nervous system, the cardiovascular system and the respiratory system and has no mutagenic action. It is indicated that the compound has high safety and a good inhibiting effect on the antiphospholipid syndrome at the test dose and can be used for treating the antiphospholipid syndrome.
Owner:延边安帝康华生物科技有限公司
Compositions and methods for managing female infertility
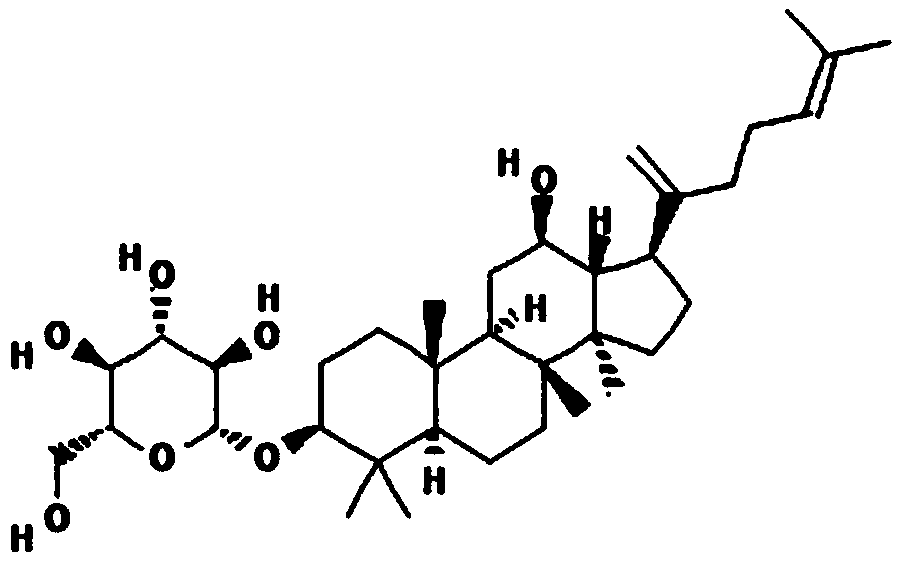
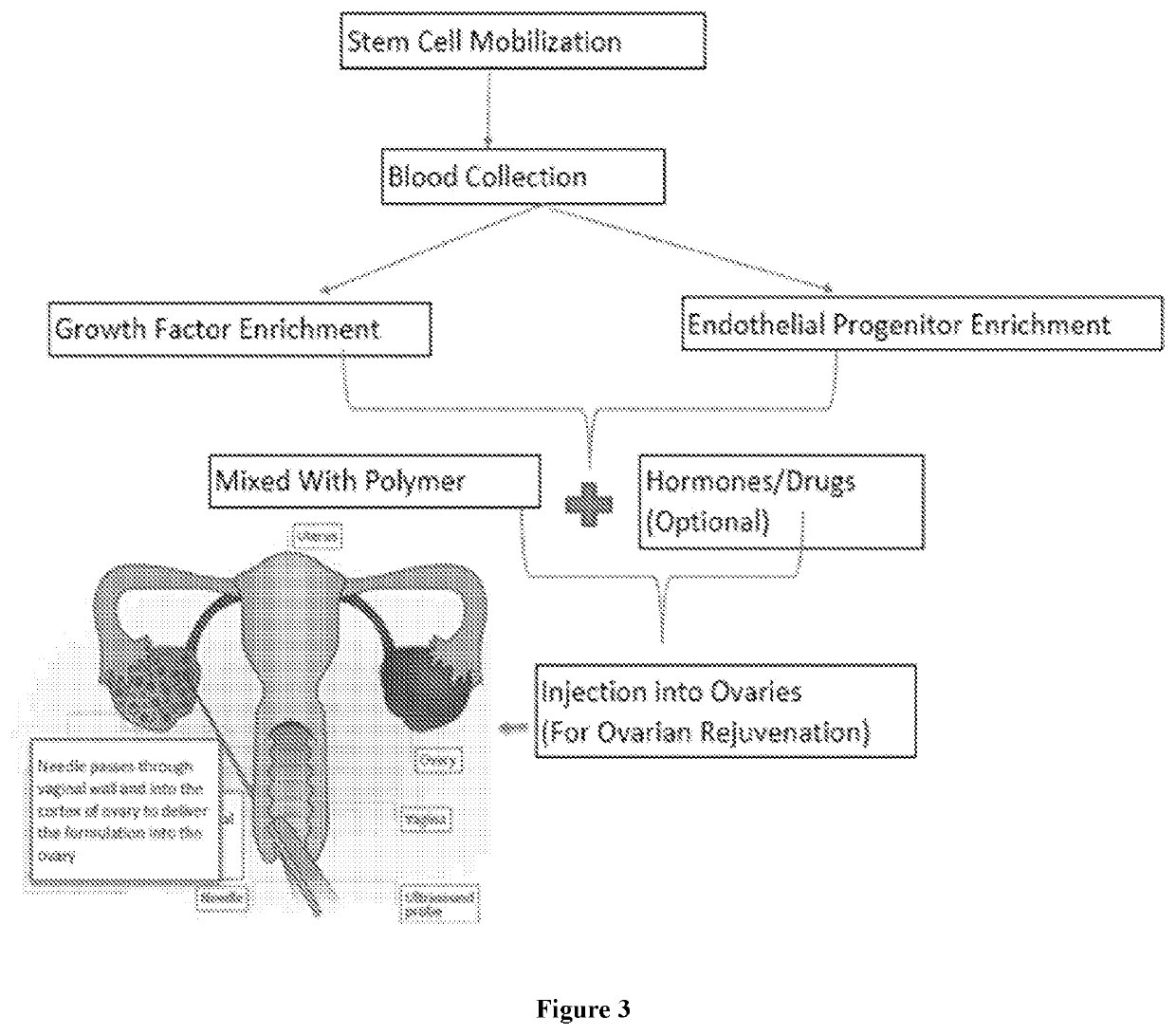
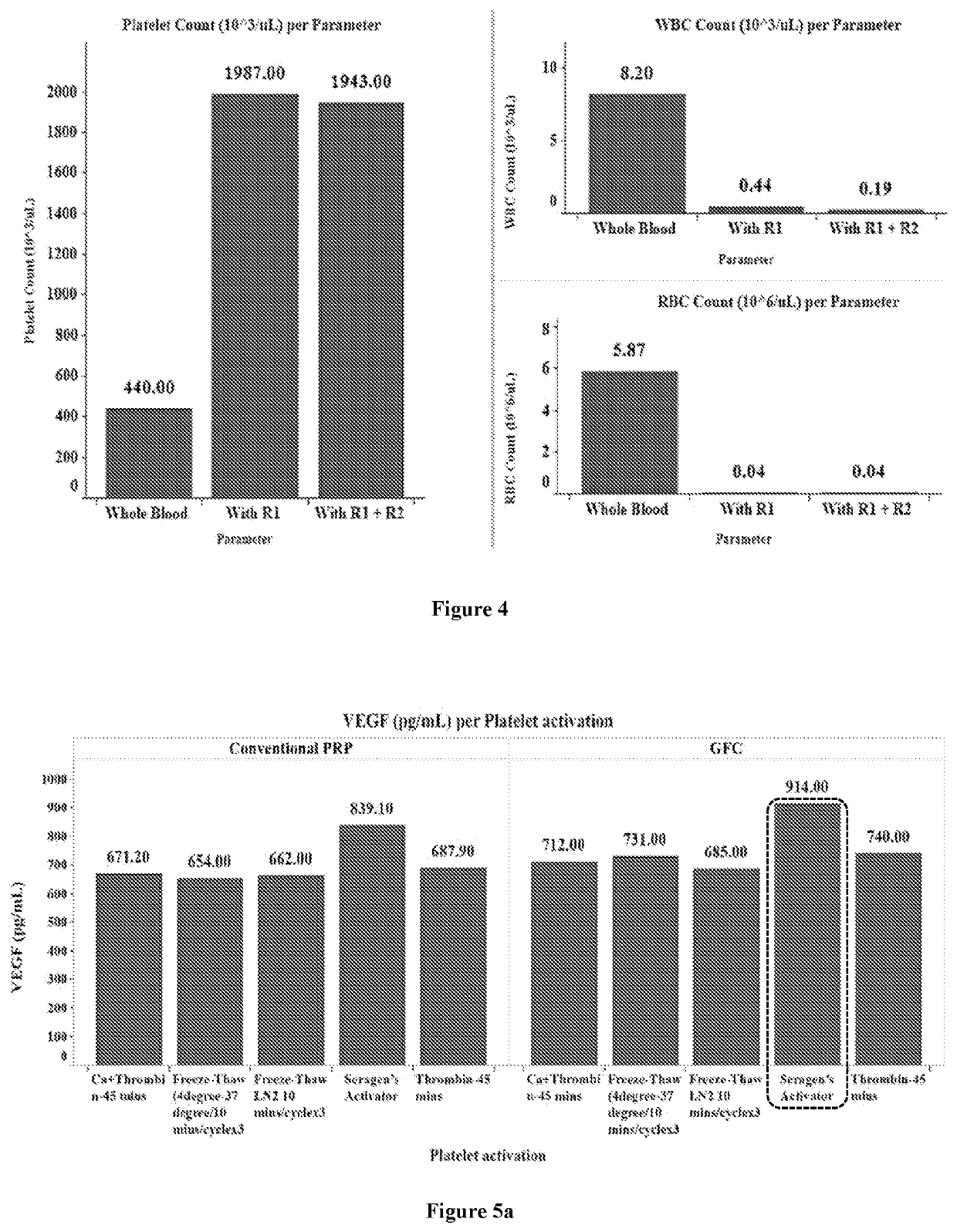
PendingUS20220249554A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsBlood platelet countsPhysiology
The present disclosure provides for compositions and methods for managing female infertility, caused by diminished ovarian reserve. More particularly, the present disclosure provides a platelet rich plasma (PRP) having one or more of significantly higher platelet count and significantly low RBC and WBC count as compared to the starting blood, and a method to arrive at the same. Consequently, a growth factor concentrate derived from the PRP and a method to arrive at the same are provided. Further provided, along with therapeutic applications for treatment of infertility caused by diminished ovarian reserve are also provided.
Owner:PALANIVEL VASANTHI +1
Method of treating idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP) with romiplostim
The present invention concerns a method of treating idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP) in a patient having ITP, which comprises: (a) administering romiplostim weekly to the patient; (b) increasing the weekly dose until a platelet count of at least about 50 to 200 * 109 / L is reached; (c) decreasing the weekly dose of romiplostim if the platelet count remains >= 200 * 109 / L for two consecutive weeks; (d) discontinuing romiplostim if the platelet count has remained >= 200 * 109 / L for two consecutive weeks when the weekly dose is 1 ug / kg or the platelet count is >= 400 * 109 / L; and (e) if aplatelet count >= 200 * 109 / L is reached within the first 4 to 12 weeks of treatment, maintaining a treatment-free period of at least about 24 weeks during which the patient receives no romiplostim.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Preparation method of platelet quality control product and application of prepared platelet quality control product
PendingCN111551414ASmall footprintReduce weightPreparing sample for investigationBlood platelet countsAnticoagulant Agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel platelet quality control product and application of the platelet quality control product prepared by the method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding an anticoagulant into animal whole blood, and performing centrifuging to obtain platelet-rich plasma; (2) centrifuging the platelet-rich plasma again to obtain upper-layer platelet-depleted plasma and bottom platelets, washing and centrifuging the bottom platelets for multiple times to obtain concentrated platelets, adding a loading solution, performing water bath at 37 DEG C, and performing centrifuging to obtain platelets loaded with a protective agent; and (3) adding a freeze-drying buffer solution into the platelets loaded with the protective agent, performing pre-freezing for 18-36 hours at the temperature of-60 DEG C to-80 DEG C, and then carrying out freeze-drying; and storing the freeze-dried powder at 2-8 DEG C. The platelet quality control product prepared by the method not only can be used for platelet counting, but also can be suitable for platelet in-vitro adhesion function and aggregation function detection.
Owner:上海原科实业发展有限公司
A kind of Zhuang medicine composition for auxiliary anti-lung cancer
ActiveCN105126030BReduce appetite side effectsReduce inhibitionAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsBlood platelet countsSide effect
The invention discloses a Zhuang medicine composition assisted in resisting lung cancer. The Zhuang medicine composition is characterized by being prepared from the following Zhuang medicinal materials: Nyarinngoux (Chinese name: baihuasheshecao), Gaeubwnhgauh (Chinese name: baiying), Byaekloekhauj (Chinese name: longkui), Buenqcilienz (Chinese name: banzhilian), Ginghgun (Chinese name: guangxi eshu), Fouxndoengz (Chinese name: shishangbai), Swnjgyaeujhenj (Chinese name: huanghuadaoshuilian), Raggongox (Chinese name: lugen), GO gyauhgujlanz (Chinese name: jiaogulan) and Lozhangoj (Chinese name: luohanguo). The Zhuang medicine composition is combined with chemical drugs for curing lung cancer, can reduce the toxic and side effects of inappetence caused by the chemical drugs, reduce the damage of the chemical drugs to immune organs, increase white blood cell count, blood platelet count, red blood cell count and hemoglobin count to reduce the inhibiting effect on myelosuppression, reduce the content of glutamic-pyruvic transaminase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase to alleviate the damage to liver functions and increase the tumor suppression function of the chemical drugs. Namely, the Zhuang medicine composition is combined with the chemical drugs for curing the lung cancer and has the effects of toxicity reducing and efficacy enhancing.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Compounds for treating multiple myeloma
The invention relates to tinostamustine for use in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Tinostamustine may cause side effects when administered to a patient, and it is desirable to minimise such effects. The present invention defines an improved treatment, wherein the dose of tinostamustine administered is varied based on the patient's platelet count.
Owner:MANDIFARMA INTERNESHNL KORPOREJSHN LIMITED
Method of identifying when a patient undergoing hemodialysis is at increased risk of death
ActiveUS10203321B2Reduce mortalityIncreased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHaemodialysis machineIncreased risk
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Tumor patient gram-negative bacillus blood flow infection prognosis model and construction method
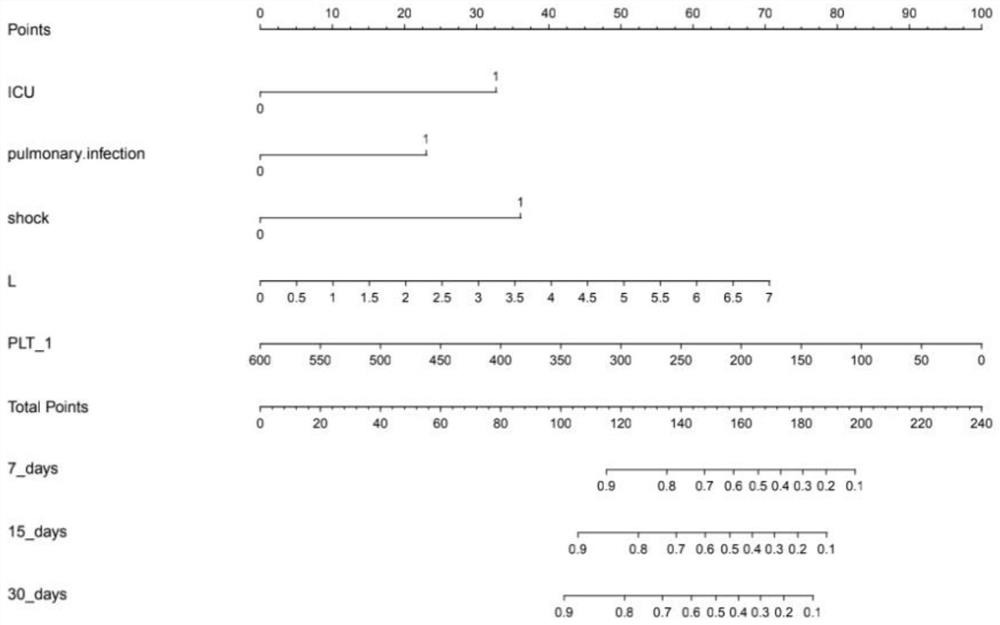
InactiveCN113744825AQuick forecastTimely forecastMedical simulationMedical data miningPulmonary infectionBlood platelet counts
The invention discloses a prognosis model for gram-negative bacillus blood flow infection of a tumor patient. The prognosis model comprises a plurality of optimal prognosis factors, evaluation scores corresponding to the optimal prognosis factors in different states and a survival probability corresponding to a total score obtained by adding the evaluation scores, wherein the prognosis factors mainly comprise platelet counting, lymphocyte counting, ICU (Intensive Care Unit), pulmonary infection and shock; wherein the optimal prognosis factors in different states include different counts of platelets before death of a gram-negative bacillus blood flow infected tumor patient, different counts of lymphocytes before death of the gram-negative bacillus blood flow infected tumor patient, different counts of the platelets before death of the gram-negative bacillus blood flow infected tumor patient, whether a gram-negative bacillus bloodstream infected tumor patient enters the ICU prior to death, whether a gram-negative bacillus bloodstream infected tumor patient has the shock prior to death, and whether a tumor patient has the pulmonary infection prior to being infected with gram-negative bacillus bloodstream infection. By means of the method, the death risk of the patient can be quickly, timely and accurately predicted.
Owner:SICHUAN CANCER HOSPITAL
A blood detection method and blood analysis system
ActiveCN111602052BAccurate detectionEasy to detectIndividual particle analysisBiological testingBlood platelet countsLysis
The invention discloses a blood detection method, comprising: processing a blood sample with a first reagent to obtain a test sample, the first reagent includes a hemolytic agent, and the hemolytic agent lyses red blood cells in the blood sample into its Fragments whose light scattering properties are significantly different from platelets; make the particles in the sample to be tested pass through the detection area of the optical detection system one by one, and obtain the optical information of the sample to be tested; and obtain according to at least two of the optical information Optical information of platelets. The method of the present invention obtains platelet count by lysing red blood cells in a blood sample, and can simultaneously distinguish white blood cell subgroups.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sample analyzing method and comprehensive sample analyzer
The invention discloses a sample analyzing method which can detect visible components of urine, blood and other body fluid on the same instrument to perform blood red blood cell counting and morphological analysis, blood differential blood counting and blood platelet counting analysis. The method includes: determining detection flow; absorbing samples to be tested; inputting the samples to be tested into a testing area; testing the samples to be tested, and determining the visible components in the samples to be tested; and producing a report of the visible component corresponding to the samples to be tested according to the different samples to be tested. In the sample analyzing method, when the detection flow corresponding to the detection types is determined, users can absorb the samples to be tested and input the samples to be tested into the testing area so as to detect the samples to be tested according to the determined detection flow and determine the visible components in the samples to be tested. Finally the report of the visible components of the samples to be tested is produced, and testing on various indexes of the samples to be tested is achieved.
Owner:AVE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com