Tumor patient gram-negative bacillus blood flow infection prognosis model and construction method
A technology for gram-negative bacilli and tumor patients, applied in the medical field, can solve problems such as poor adaptability and accuracy, inability to predict the risk of patient death in time, and inability to score in time, so as to achieve the effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
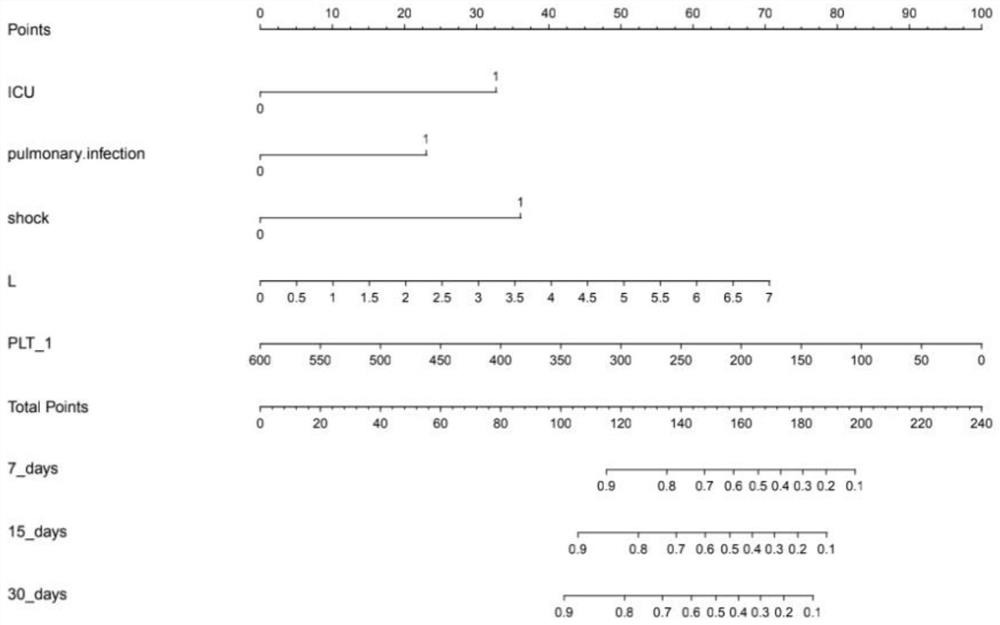
[0038] A prognostic model for Gram-negative bacillary bloodstream infection in tumor patients, including several optimal prognostic factors with prognostic ability selected from all risk factors, the corresponding evaluation scores of each optimal prognostic factor in different states, and The survival probability corresponding to the total score obtained after the addition of each evaluation score; wherein, the prognostic factors are mainly composed of platelet count, lymphocyte count, ICU, lung infection and shock; Prognostic factors include differential counts of platelets prior to death in tumor patients with Gram-negative bacilli bloodstream infection, differential counts of lymphocytes prior to death in tumor patients infected with Gram-negative bacilli, Gram-negative bacilli Whether the tumor patients with bloodstream infection entered the ICU before death, whether the tumor patients with Gram-negative bacillus bloodstream infection had the shock before death, and whethe...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 2 As shown, a method for constructing a prognostic model of Gram-negative bacillus bloodstream infection in tumor patients comprises the following steps:
[0054] a. Construct a database of tumor patients with Gram-negative bacillus bloodstream infection;
[0055] b. According to the survival status of patients with Gram-negative bacilli bloodstream infection within 30 days, patients in the Gram-negative bacilli patient database were divided into death group and non-death group;
[0056] c. Compare the laboratory and clinical data of the death group and the non-death group, and screen out the risk factors between the death group and the non-death group from the laboratory and clinical data;
[0057] d. Incorporate the risk factors screened out in the death group and non-death group into the Cox regression model, obtain the contribution, remove the risk factors with a p value greater than 0.05, and include the remaining risk factors with a p ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com