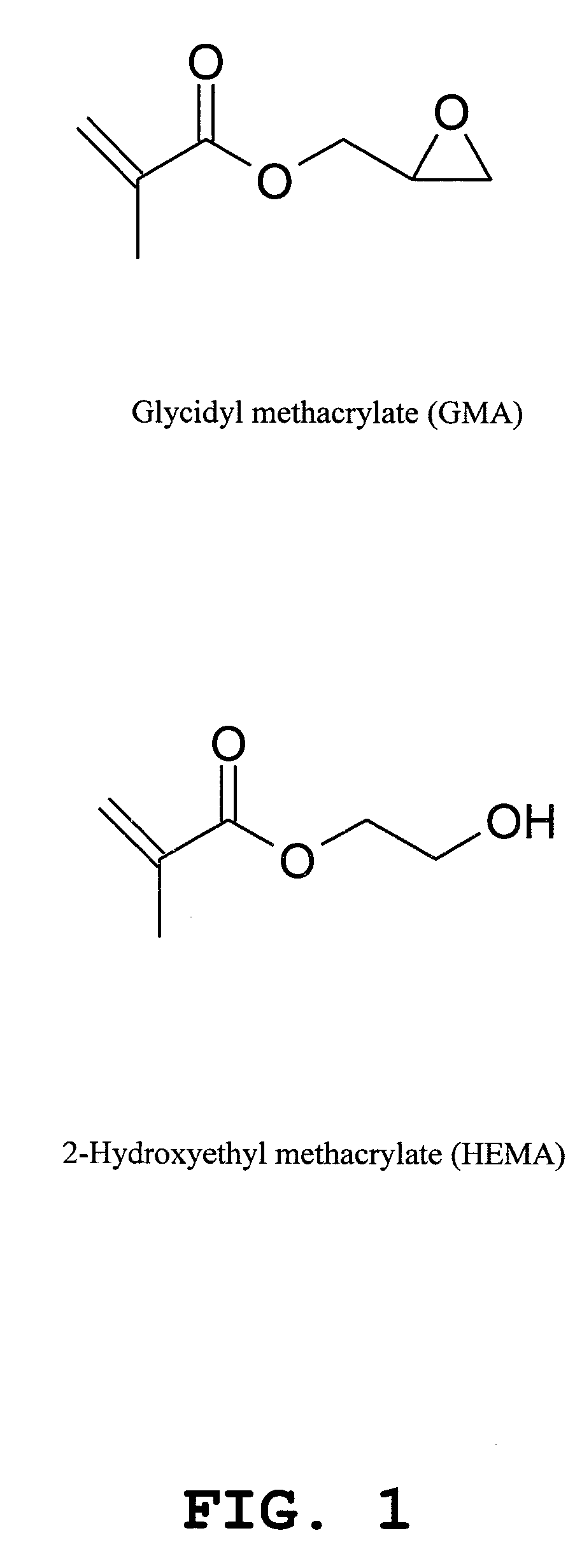
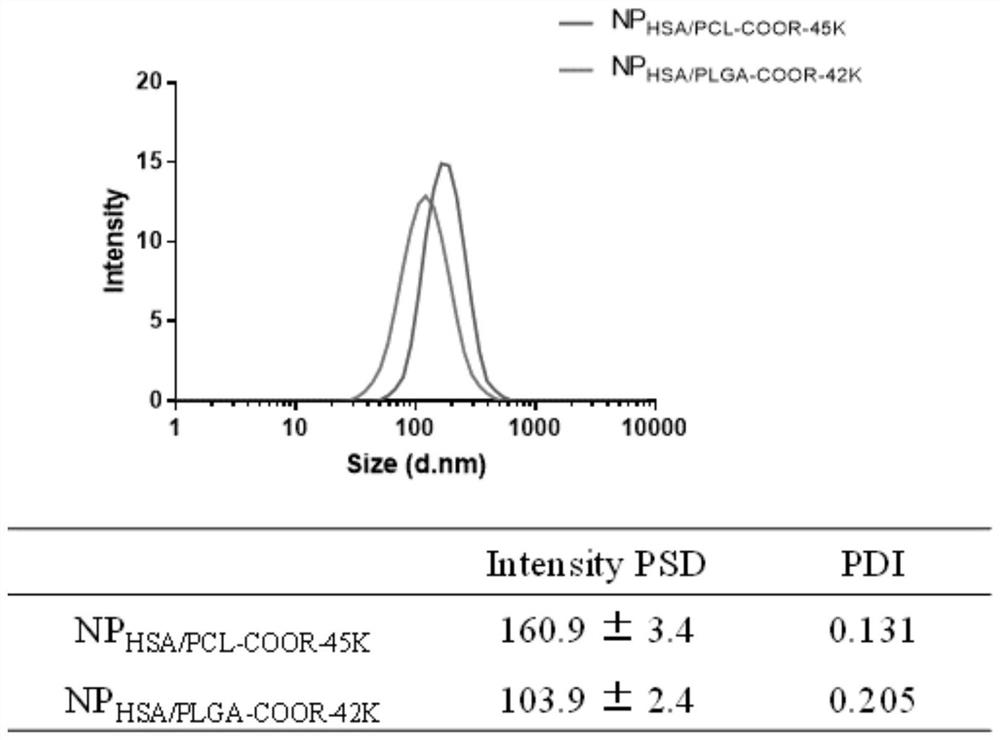
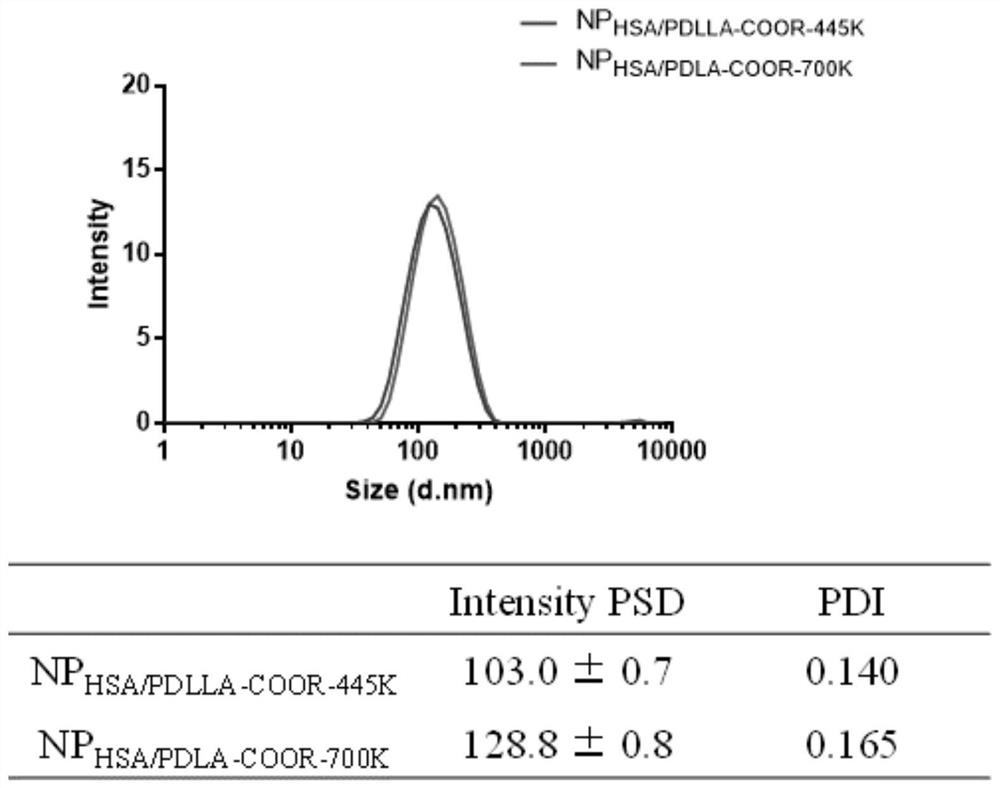
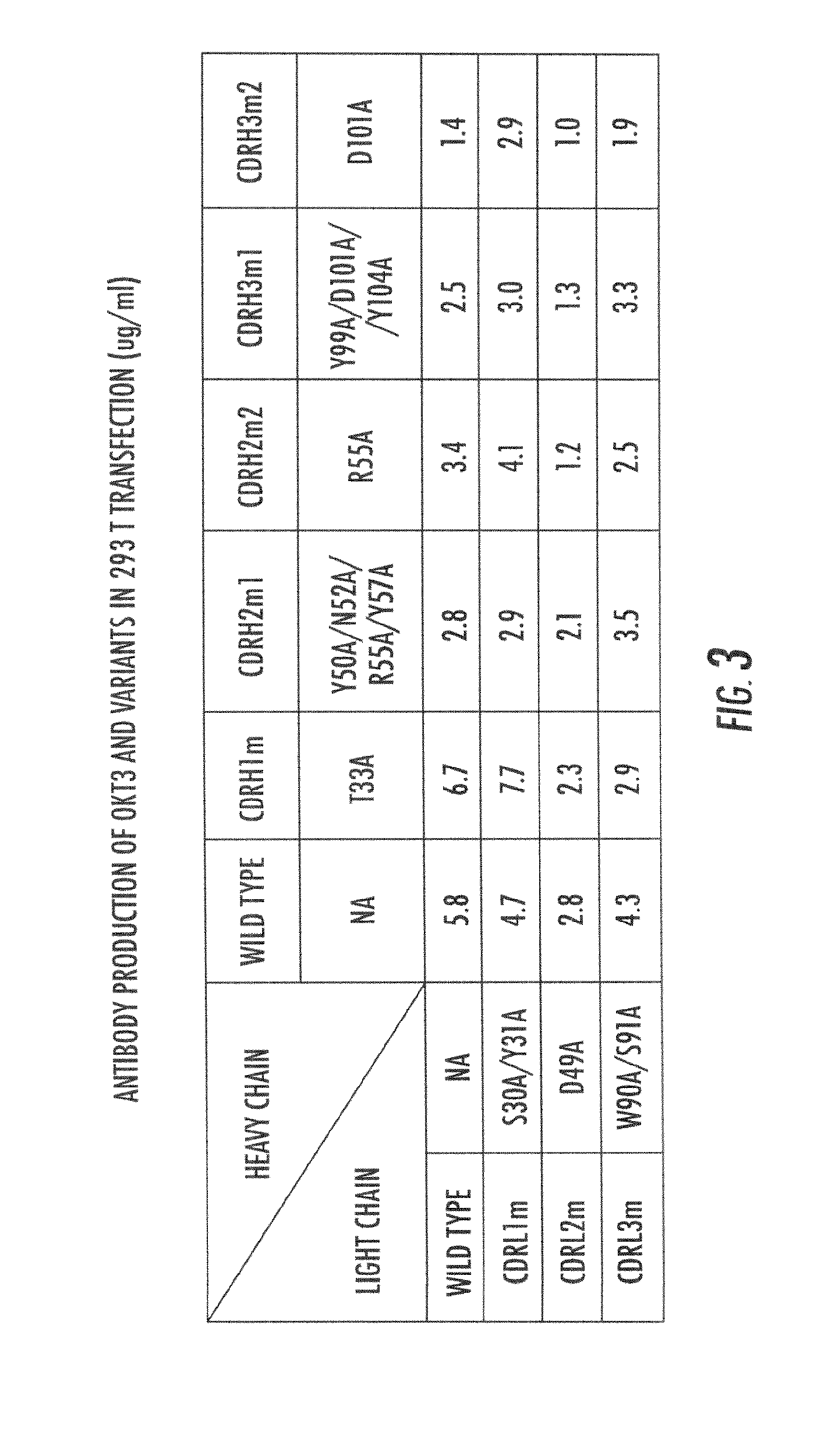
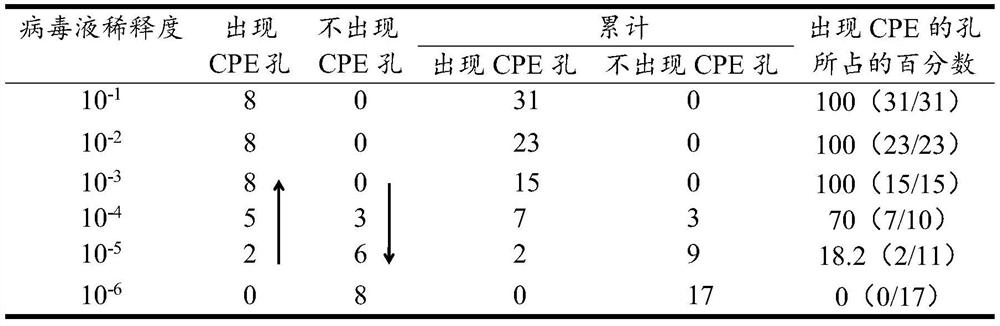
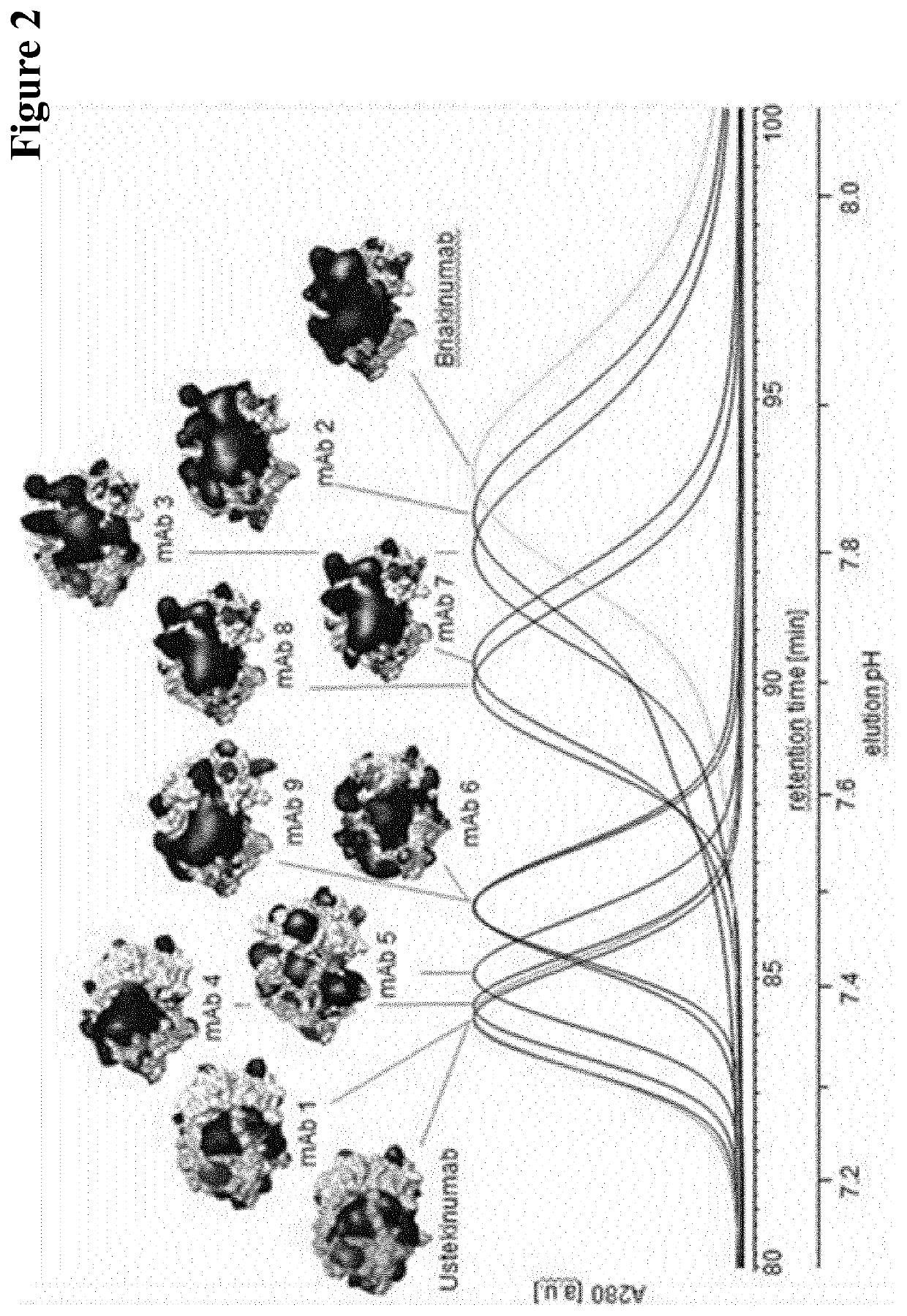
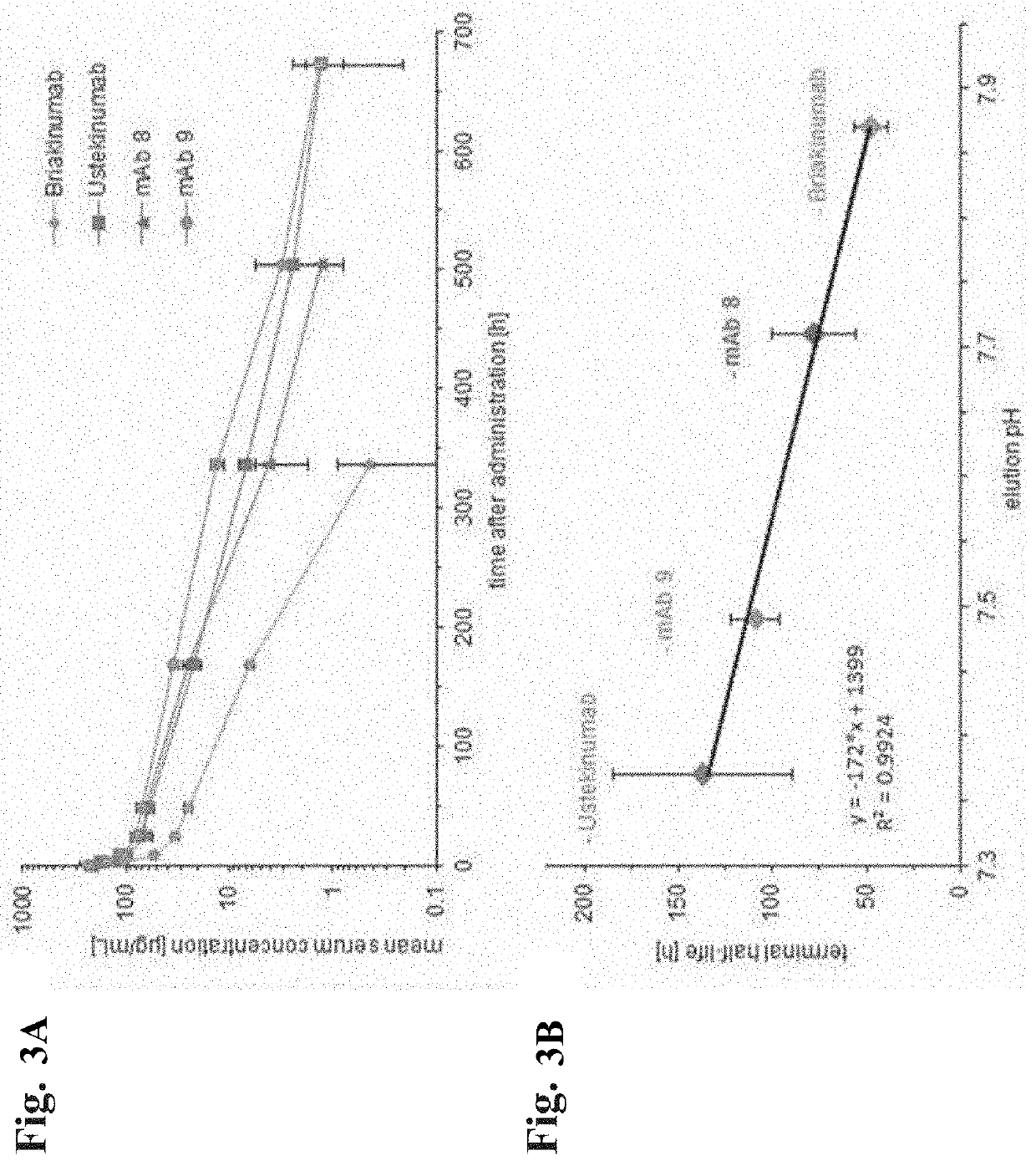
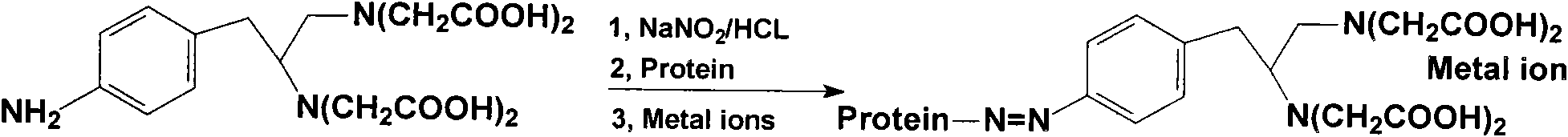Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Antibody Interactions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for fabrication of biochips with a macroporous polymer substrate
InactiveUS20050042363A1Large capacityImprove accessibilityNucleotide librariesPharmaceutical containersAnalytePolymer substrate
Macroporous polymer substrates have greater immobilization capacity for large biomolecules and better access for analytes than substrates used previously for microarrays. Microarrays are fabricated with macroporous polymer substrates, and nucleic acids, proteins and peptides are immobilized in the substrate. Microarrays with macroporous polymer substrates are useful in immunoassays, drug discovery studies and other biotechnological applications that involve large scale macromolecular interactions. Nucleic acid hybridizations, protein binding, and antigen-antibody interactions are analyzed using microarrays with macroporous polymer substrates.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY +2
Novel Lowered Affinity Antibodies And Methods of Making the Same
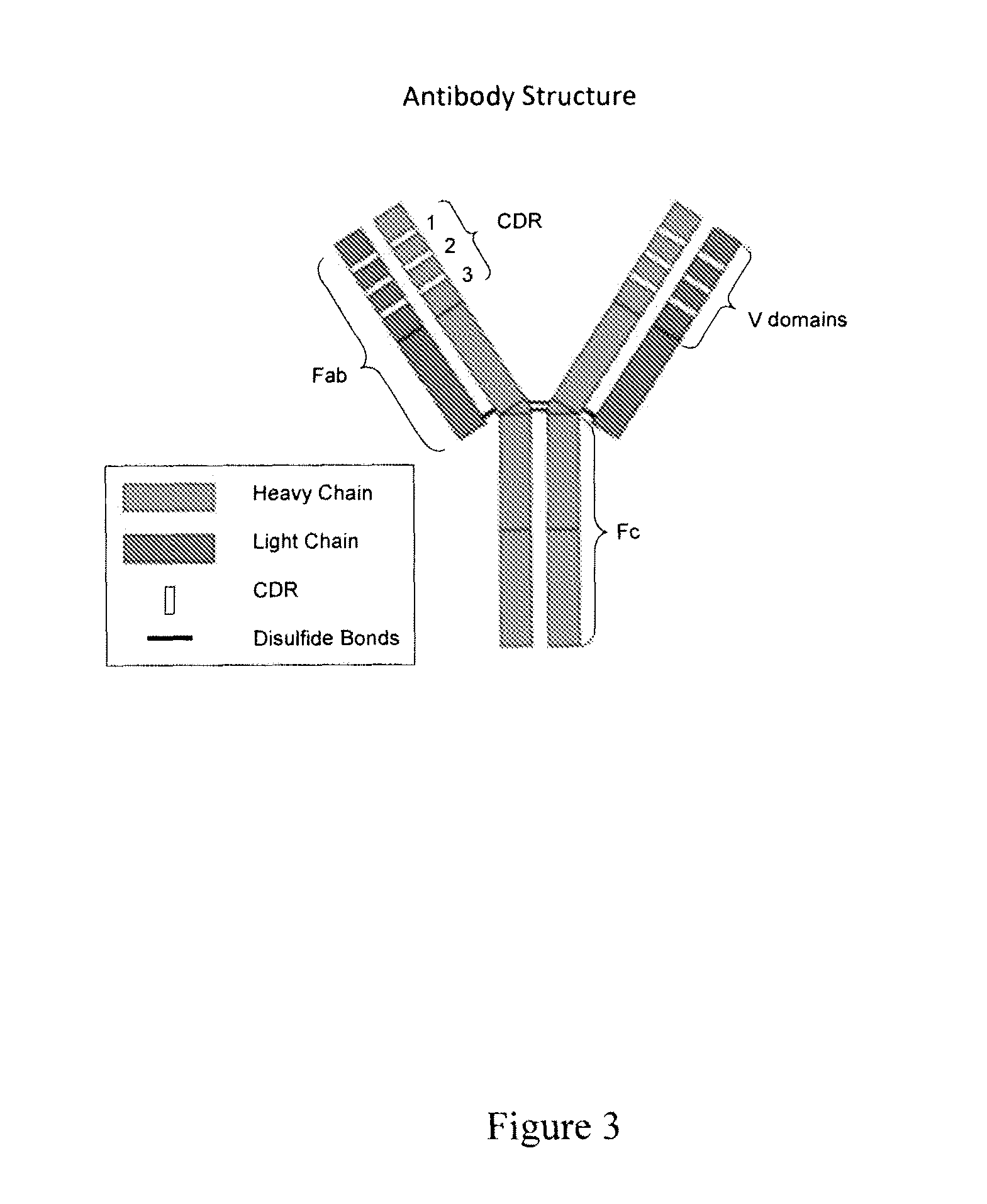
The present invention provides methods for making novel, rationally designed lowered affinity antibodies. The methods of the present invention make antibodies that have variable domains that have been designed to reduce or eliminate the antigen binding activity of the parental antibody without altering the overall (3) dimensional antibody structure. Using the antibodies made using methods of the present invention in various assays allows researchers to distinguish effects that result from specific antigen-antibody interactions from other, non-specific antibody effects.
Owner:AB BIOSCI
Methods, assays and kits for cancer diagnosis and screening utilizing glycan-binding and glycan epitopes
InactiveUS20100075344A1Highly reproducible resultImprove signal-to-noise ratioDisease diagnosisBiological testingCancer cellCancers diagnosis
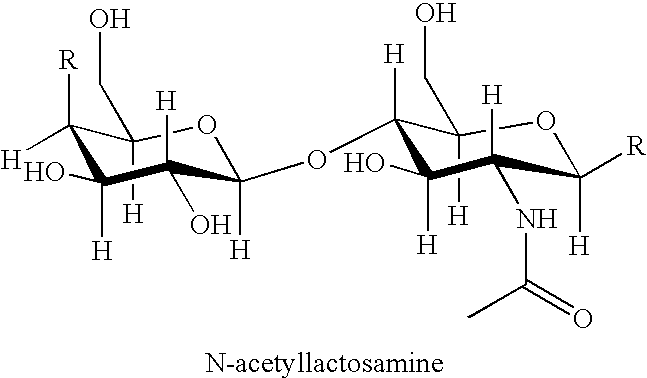
The invention relates to the diagnosis, monitoring, prognosis, and / or prediction of cancer utilizing the detection or measurement of glycan-protein interactions, particularly glycan-antibody interactions. The invention relates to carbohydrate-containing molecules that are utilized in bioanalytical systems, methods and kits for detecting neoplasia and methods related thereto and based thereon. In an exemplary embodiment glycans or glycopolymers are carried in an array, on beads or in a microfluidic system for diagnostic screening for risk of neoplasia, the existence of neoplasia in a patient, or for treatment monitoring. In such an embodiment, the bioanalytic system identifies binding interactions between molecules in a patient test sample (e.g., glycan compositions) and the glycans or glycopolymers. The glycan-binding compositions may be used to generate an immune response against cancer cell epitopes. Alternatively, antibody therapeutics can be developed that are useful for binding to glycan compositions on a cell surface.
Owner:VUSKOVIC MARKO +1
In vitro prediction of in vivo half-life
InactiveUS20170227547A1Reducing FcRn-dependent terminal half-lifeChanges the FcRn binding characteristicsSolid sorbent liquid separationImmunoglobulinsRetention timeHalf-life
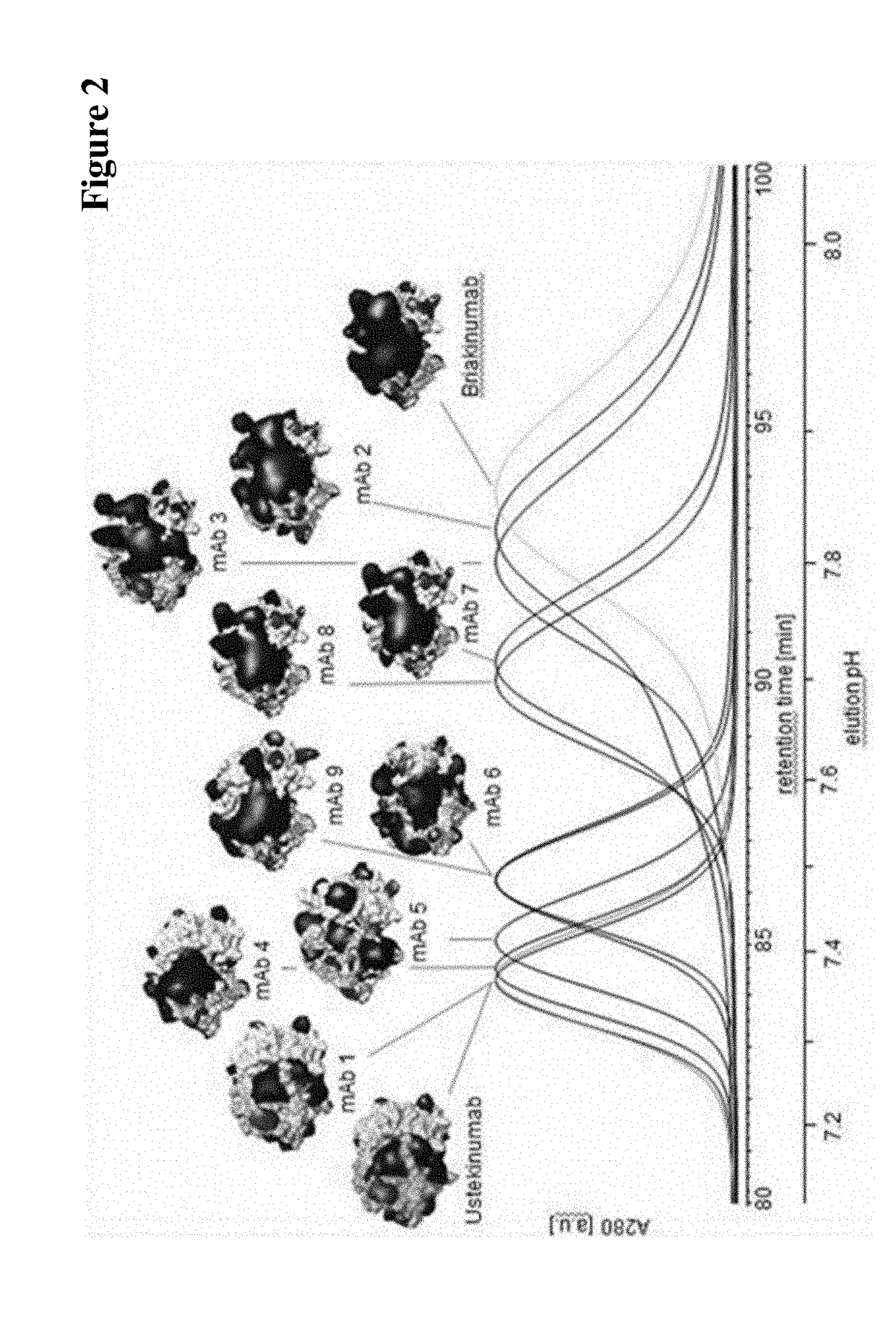
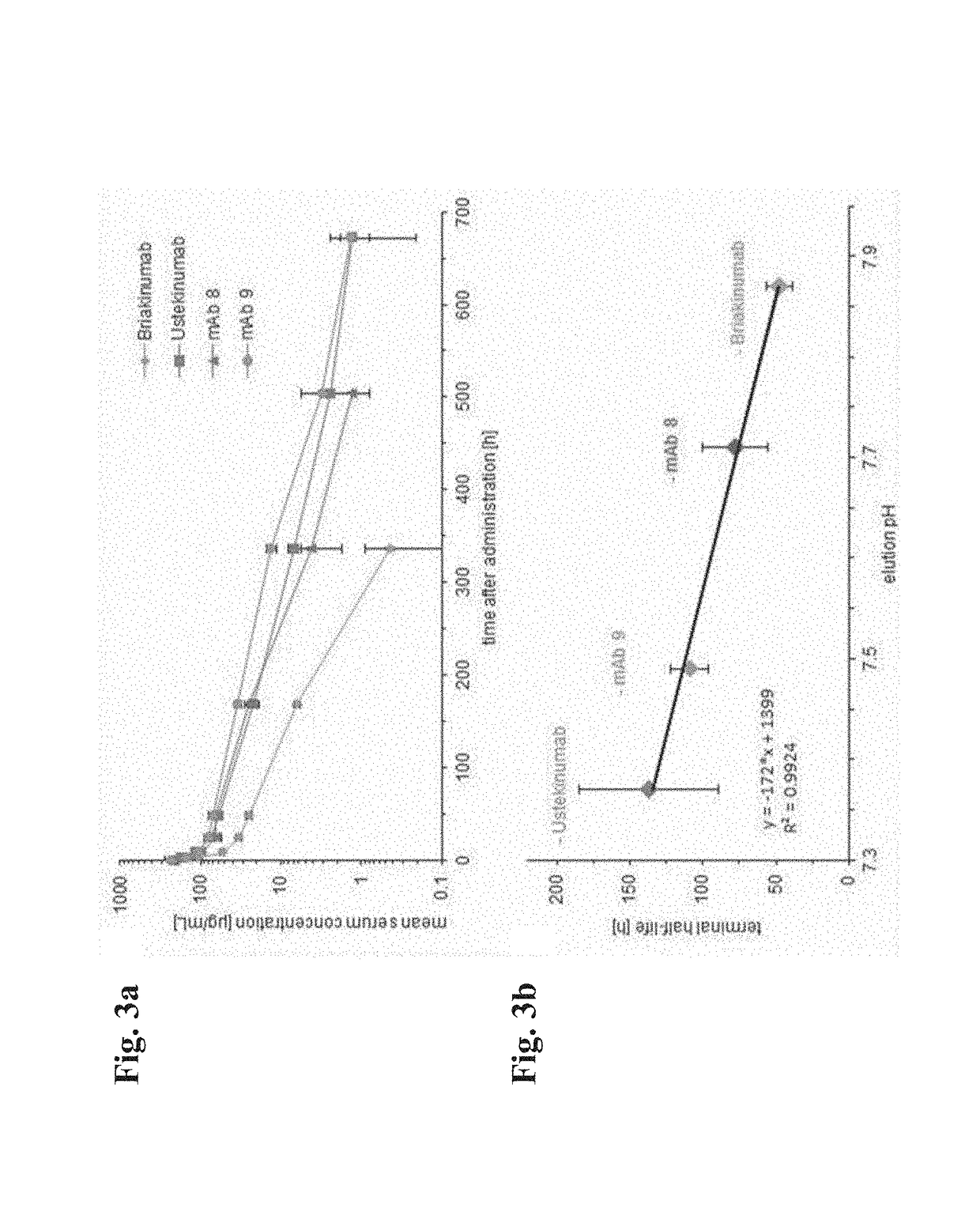
Herein is reported a method for determining the presence of antibody-Fab-FcRn interaction in an antibody-Fc-FcRn complex influencing the in vivo half-life comprising the steps of a) determining the retention time of the antibody on an FcRn affinity chromatography column with a positive linear pH gradient elution in the presence of a first sodium chloride concentration, and b) determining the retention time of the antibody on an FcRn affinity chromatography column with a positive linear pH gradient elution in the presence of a second sodium chloride concentration, whereby the presence of antibody-Fab-FcRn interaction in an antibody-Fc-FcRn complex influencing the in vivo half-life is determined if the retention time determined in step a) and the retention time determined in step b) are substantially different.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Method for detecting existence of heavy metal copper ion in sample and special kit thereof
InactiveCN101968481AHigh detection sensitivityEasy to prepareMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureSorbentPhysical chemistry
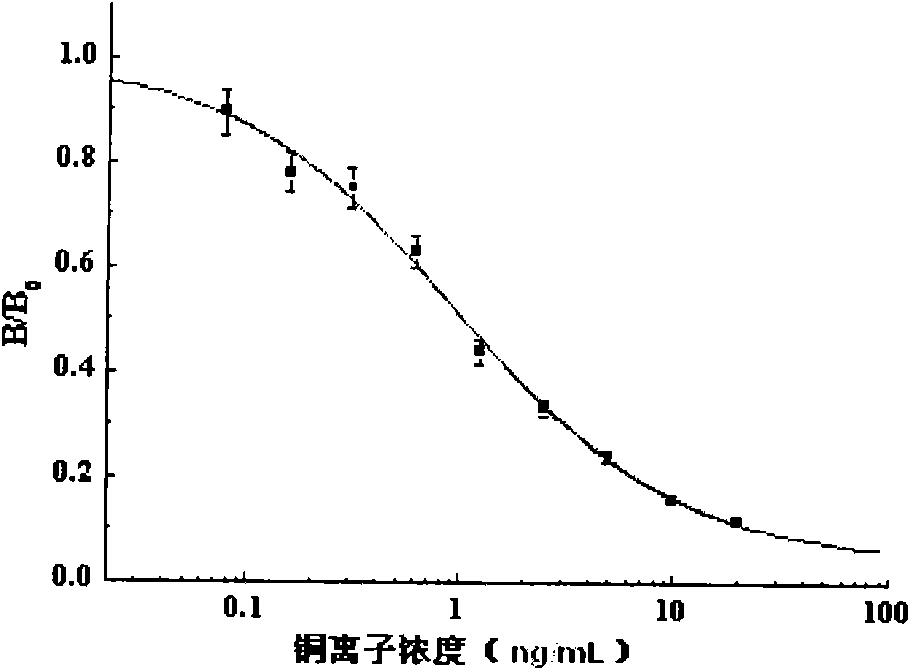
The invention discloses a method for detecting the existence of a heavy metal copper ion in a sample and a special kit thereof. The kit comprises a coating antigen and an antibody resistant to heavy metal to be detected, wherein the coating antigen and the antibody resistant to the heavy metal to be detected interact with each other; and the affinity between the coating antigen and the antibody resistant to the heavy metal to be detected is less than the affinity between the heavy metal to be detected and the antibody resistant to the heavy metal to be detected. Experiments prove that the preparation method of the coating antigen is simple and has clear synthesis steps, low synthesis cost and good effect in an unequal competition enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) detection method for preparing copper ions provided by the invention. The ELISA detection sensitivity of the coating antigen prepared by the method of the invention is enhanced remarkably. The method for preparing the coating antigen and a copper ion rapid immunological detection method established by the method have wide application prospects.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
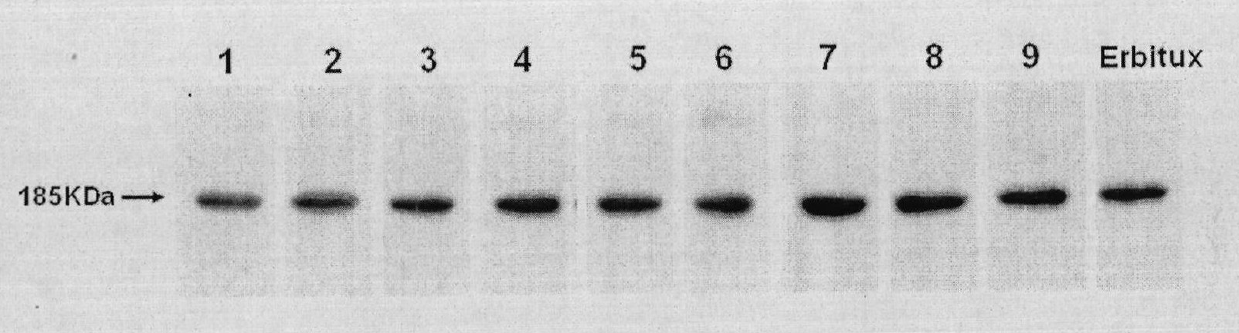
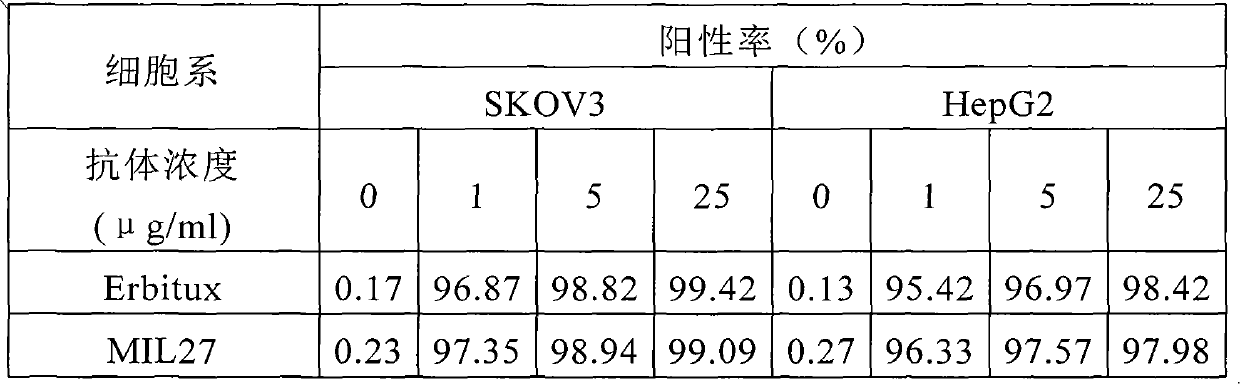
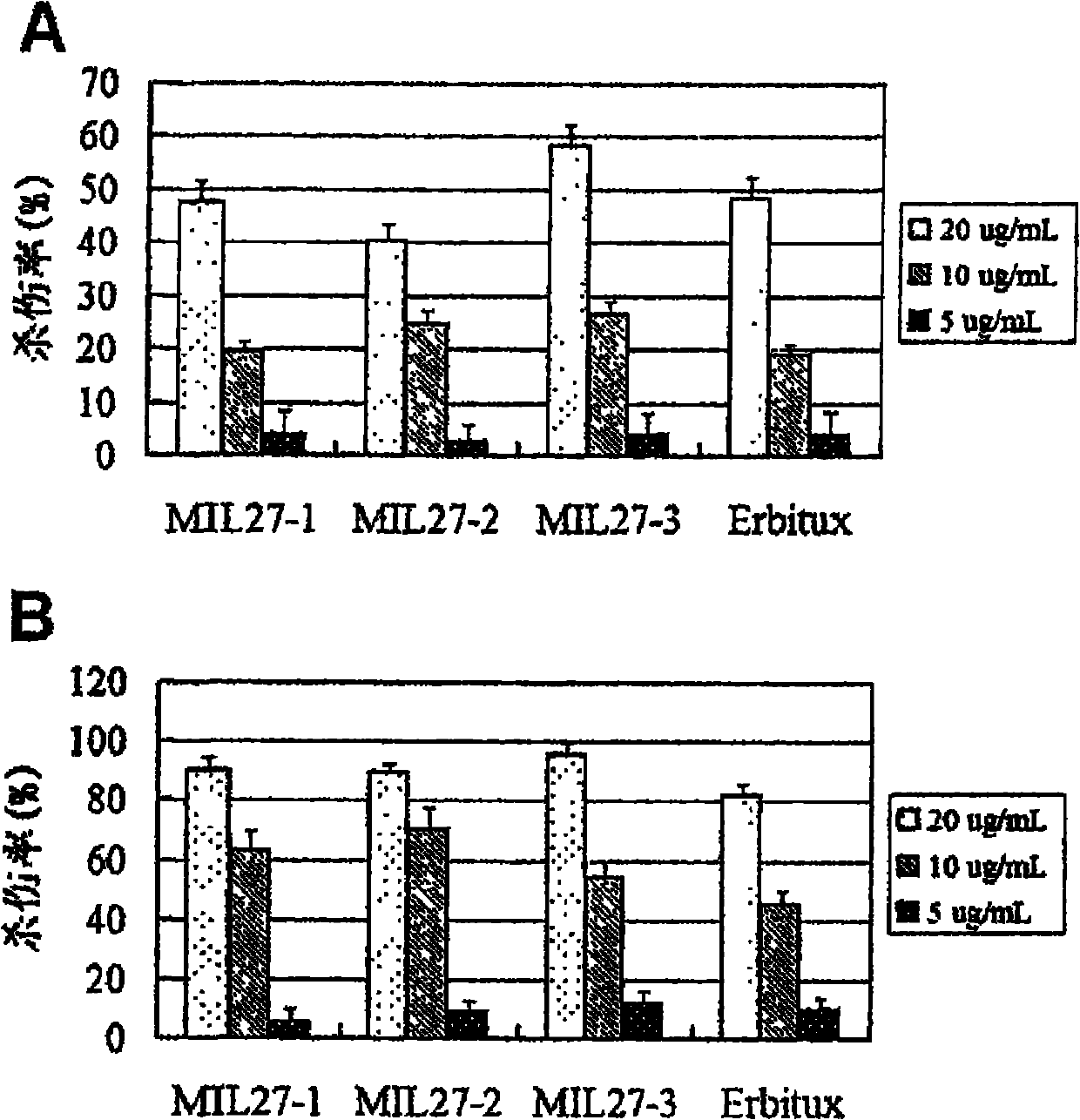
Preparation of novel anti-EGFR human source antibody MIL27 and application thereof
InactiveCN101948540AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCancer cellTumor cells
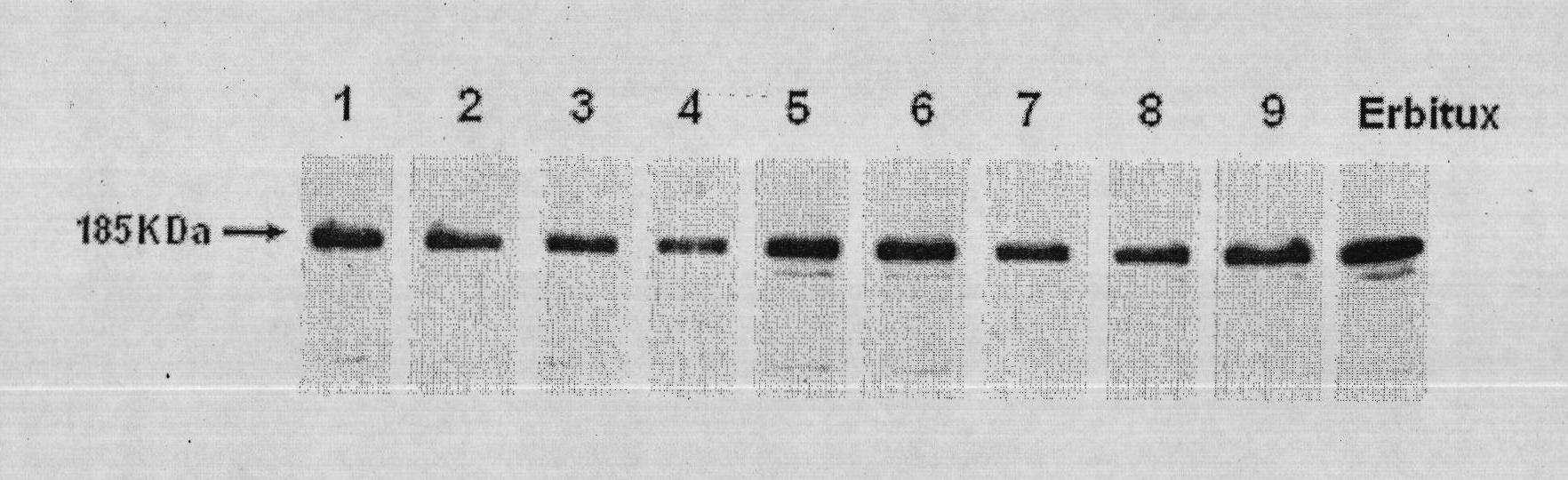
The invention discloses an anti-EGFR human source antibody MIL27 based on computer aided design and application thereof. The antibody can be used for obviously inhibiting and killing human cancer cell expressing EGFR. The invention is based on the interaction structure characteristic of EGFR protein extracellular region and functional antibody, computer virtual screening and design are adopted to obtain the anti-EGFR functional human source antibody MIL27, PCR method is applied to complete synthesis of antibody gene, eukaryotic expression vector is constructed, and MIL27 antibody capable of specifically identifying EGFR is expressed. The antibody MIL27 can effectively kill EGFR positive tumour cells, including blaster cancer cell and liver cancer cell. The antibody identifies EGFR new epitope, and competitive experiment verifies that the new epitope is different from EGFR epitope identified by Erbitux.
Owner:BEIJING MABWORKS BIOTECH +1
Methods, assays and kits for cancer diagnosis and screening utilizing glycan-binding and glycan epitopes
InactiveUS8298773B2Highly reproducible resultImprove signal-to-noise ratioDisease diagnosisBiological testingEpitopeCancer cell
The invention relates to the diagnosis, monitoring, prognosis, and / or prediction of cancer utilizing the detection or measurement of glycan-protein interactions, particularly glycan-antibody interactions. The invention relates to carbohydrate-containing molecules that are utilized in bioanalytical systems, methods and kits for detecting neoplasia and methods related thereto and based thereon. In an exemplary embodiment glycans or glycopolymers are carried in an array, on beads or in a microfluidic system for diagnostic screening for risk of neoplasia, the existence of neoplasia in a patient, or for treatment monitoring. In such an embodiment, the bioanalytic system identifies binding interactions between molecules in a patient test sample (e.g., glycan compositions) and the glycans or glycopolymers. The glycan-binding compositions may be used to generate an immune response against cancer cell epitopes. Alternatively, antibody therapeutics can be developed that are useful for binding to glycan compositions on a cell surface.
Owner:VUSKOVIC MARKO +1
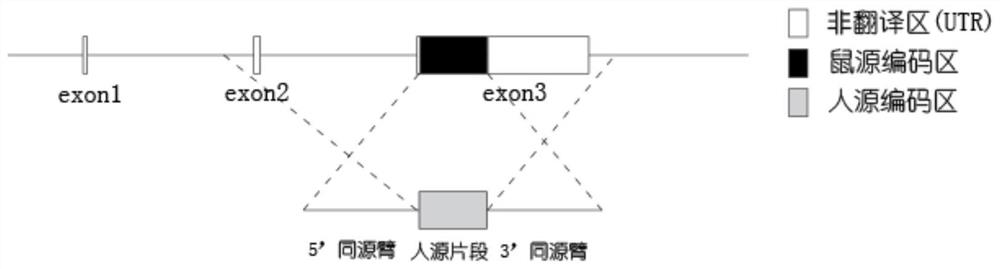
Construction method and application of humanized CCR2 gene modified animal model
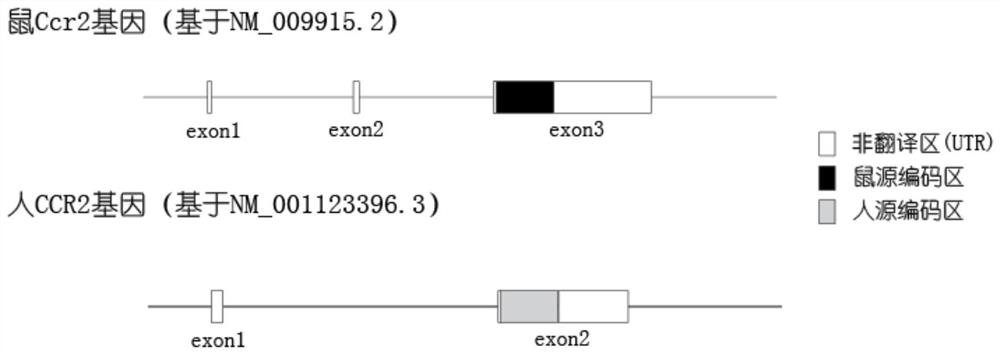
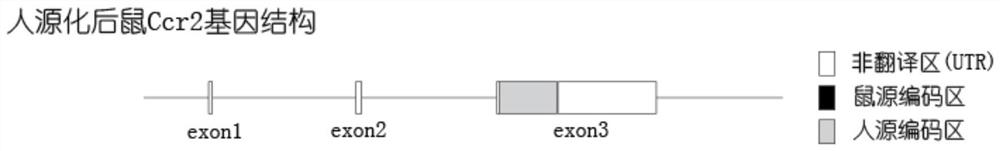
ActiveCN111690689APromote research progressRealize humanization transformationCompounds screening/testingDrug screeningAntiendomysial antibodiesProtide
The invention provides a construction method and application of a humanized CCR2 gene modified animal model, and relates to the technical field of biology. According to the humanized CCR2 gene modified animal model constructed by the invention, the research progress of the fields related to the human CCR2 gene or protein can be accelerated; for example, the humanized CCR2 gene modified animal model is used for replacing a human to test a drug; and an effective model and a powerful tool are provided for a preclinical experiment of a CCR2 target drug. Preferably, a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology is utilized in the invention; a mouse-derived Ccr2 gene is replaced with a human-derived CCR2 gene, so that a mouse model capable of interacting with an anti-human CCR2 antibody is constructed;compared with a common mouse, humanized transformation of key target molecules is achieved; and the mouse model can be used for screening and evaluating drugs for human CCR2 genes, and is a very idealpreclinical drug test model.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOMODEL ORGANISM SCI & TECH DEV
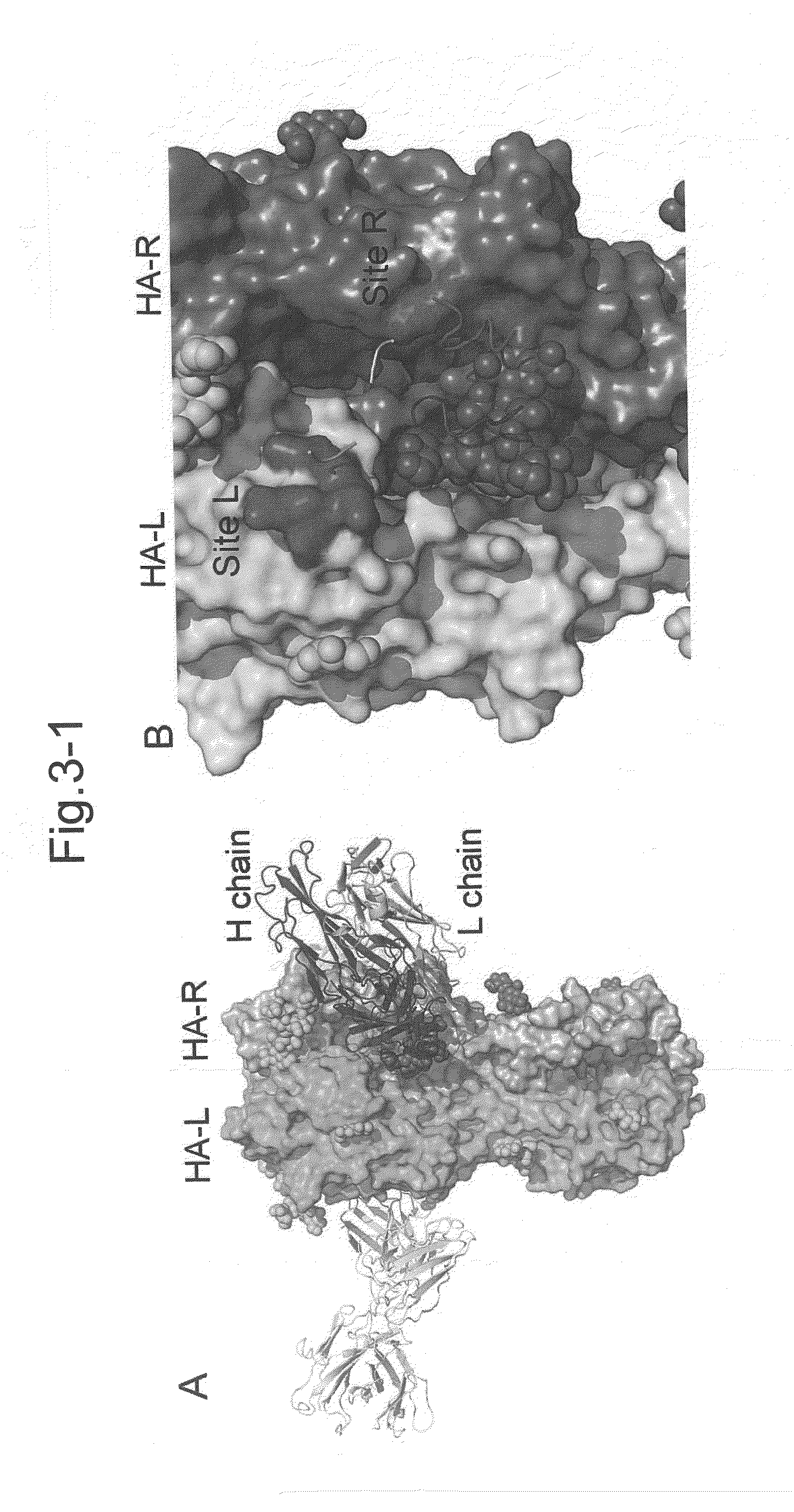
Novel epitope and mechanism of antigen-antibody interaction in an influenza virus
InactiveUS20140086927A1Molecular designMicrobiological testing/measurementHemagglutininNeutralizing antibody
Antibodies (Abs) play roles in protection against influenza. Neutralizing Abs either inhibit the binding of hemagglutinin (HA) to cellular receptors or prevent the conformational change of HA induced by low pH. The former Ab binds to the regions near the sialic acid-binding pocket on the globular head formed by HA1 and generally shows narrow strain specificity. The latter Ab binds to the stem region formed mainly by HA2 and shows broad strain specificity. We isolated a broadly neutralizing Ab against H3N2 viruses. X-ray analysis of the HA / Ab complex indicated that the Ab binds to the valley formed by two neighboring HA monomers at the side of the globular head. The Ab shows neutralizing activity by preventing the conformational change of HA induced at low pH.
Owner:FUJITA HEALTH UNIVERSITY
Methods, assays and kits for cancer diagnosis and screening utilizing glycan-binding and glycan epitopes
InactiveUS20140087957A1Highly reproducible resultImprove signal-to-noise ratioSaccharide librariesLibrary screeningCancer cellCancers diagnosis
The invention relates to the diagnosis, monitoring, prognosis, and / or prediction of cancer utilizing the detection or measurement of glycan-protein interactions, particularly glycan-antibody interactions. The invention relates to carbohydrate-containing molecules that are utilized in bioanalytical systems, methods and kits for detecting neoplasia and methods related thereto and based thereon. In an exemplary embodiment glycans or glycopolymers are carried in an array, on beads or in a microfluidic system for diagnostic screening for risk of neoplasia, the existence of neoplasia in a patient, or for treatment monitoring. In such an embodiment, the bioanalytic system identifies binding interactions between molecules in a patient test sample (e.g., glycan compositions) and the glycans or glycopolymers. The glycan-binding compositions may be used to generate an immune response against cancer cell epitopes. Alternatively, antibody therapeutics can be developed that are useful for binding to glycan compositions on a cell surface.
Owner:VUSKOVIC MARKO +1
Fluorescent biosensing method for inhibiting and analyzing and detecting interaction between micromolecules and binding protein based on restrictive incision enzyme FokI
InactiveCN101717824ASimple designSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceToxicantFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescent biosensing method for inhibiting and analyzing and detecting interaction between micromolecules and binding protein based on restrictive incision enzyme FokI, which comprises an interaction between an oligonucleotides DNA chain which is modified by organic micromolecules and a protein, formation conditions for the restrictive incision enzyme FokI dipolymer and selection of inhibition locus, and real-time fluorescence quantitative detecting technology based on a Taqman probe. By utilizing specificity combination of the micromolecules modifying among the oligonucleotides DNA chain and the binding protein thereof or antibodies, the interaction between the micromolecules and the protein and the micromolecules or the binding protein thereof can be detected through a real-time quantitative analysis on enzyme incision Taqman probe fluorescence based on the inhibition effect on the incision of the restrictive incision enzyme FokI by the interaction between the micromolecules and the proteins or the antibodies. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simple and convenient operation, and high specificity, and can be used for study on signal transduction and molecular regulation mechanism in biomedicine, safety detection of foods and agricultural products, detection on environmental toxicant, medicine screening and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Immunosensor
InactiveUS8685714B2Generates noEasy to adaptBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid wasteAntigen-antibody interaction
This invention describes a quantitative, inexpensive, disposable immunosensor that requires no wash steps and thus generates no liquid waste. Moreover, in preferred embodiments of the sensor no timing steps are required of the user, and the sensor can be readily adapted to antigen-antibody interactions over a wide kinetic range.
Owner:UNIVERSAL BIOSENSORS
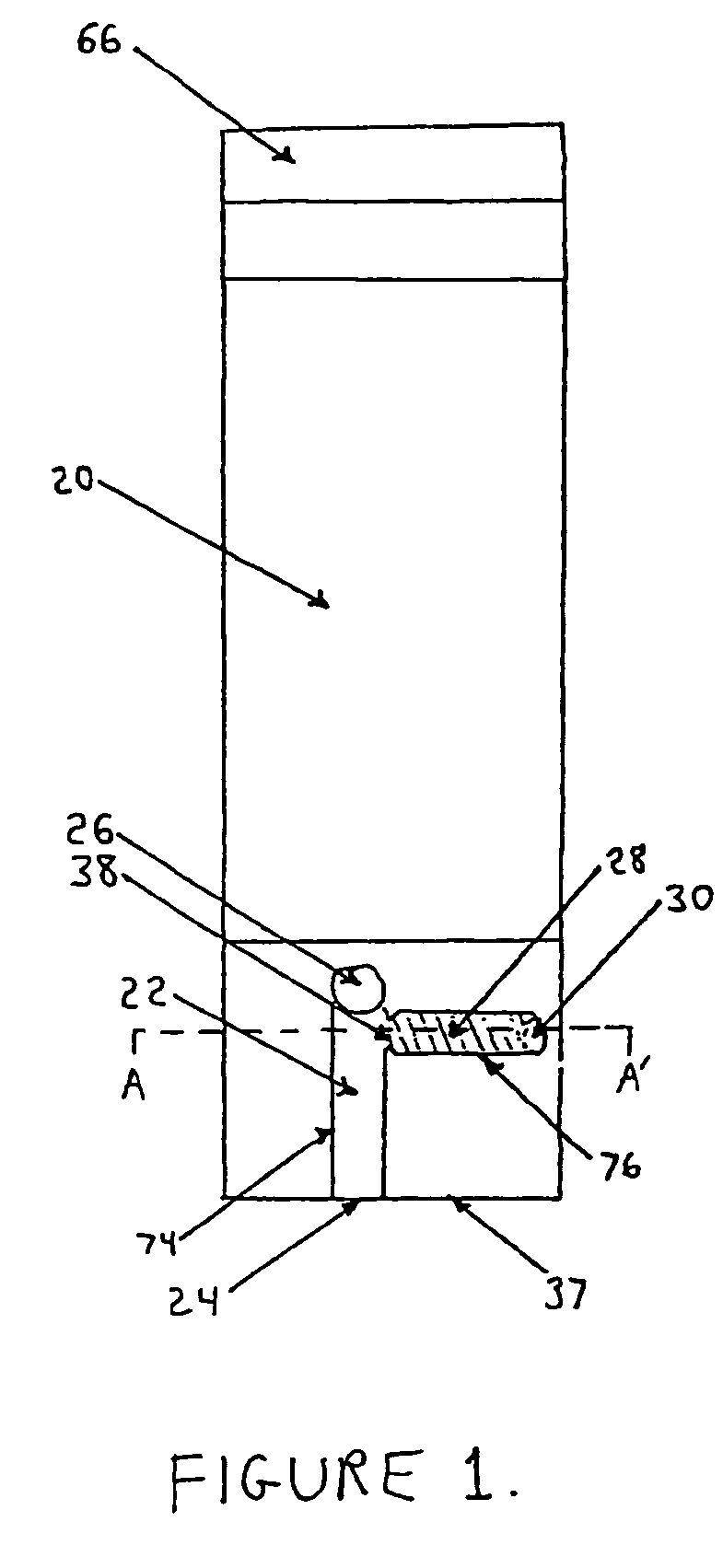
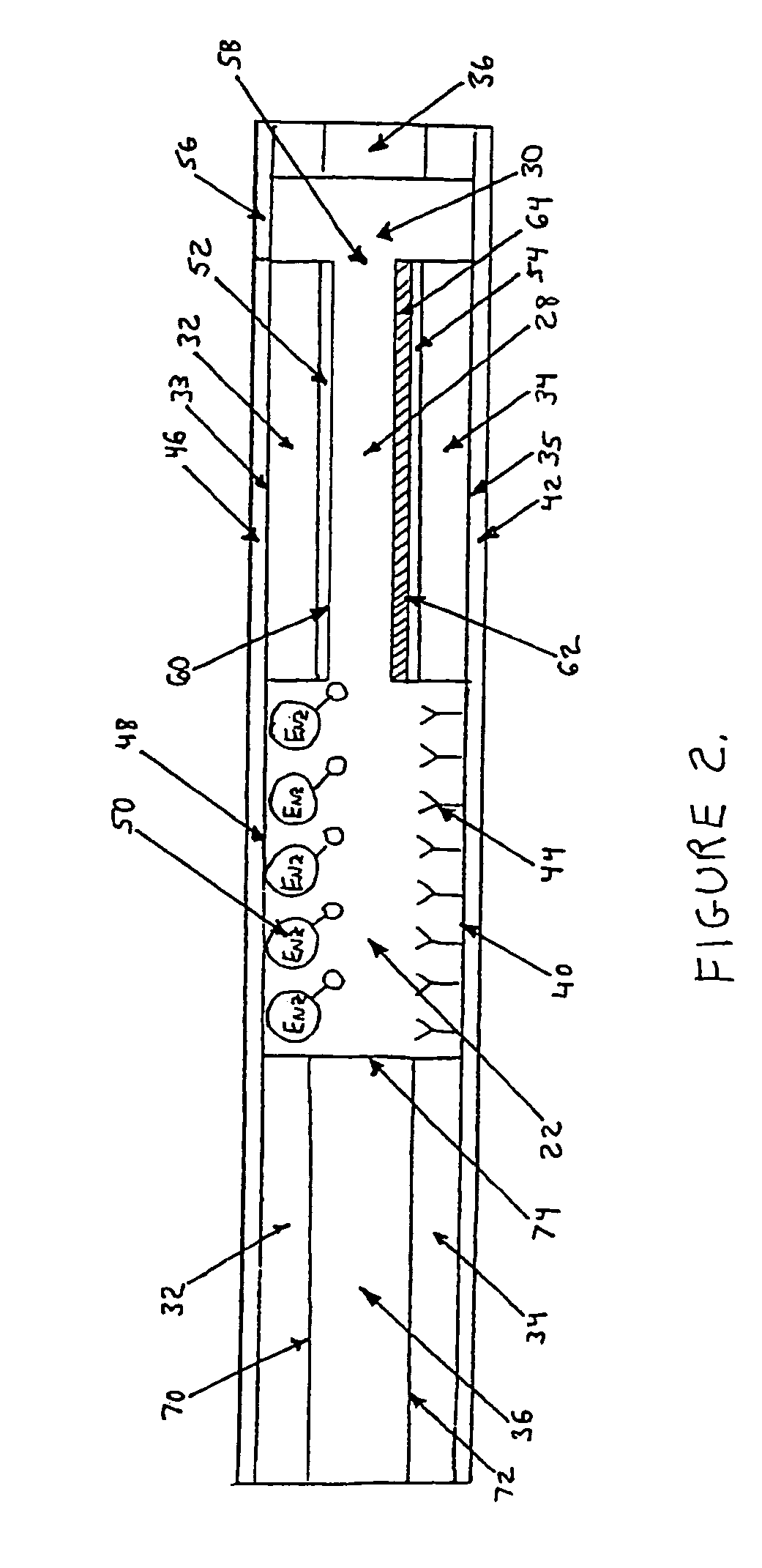
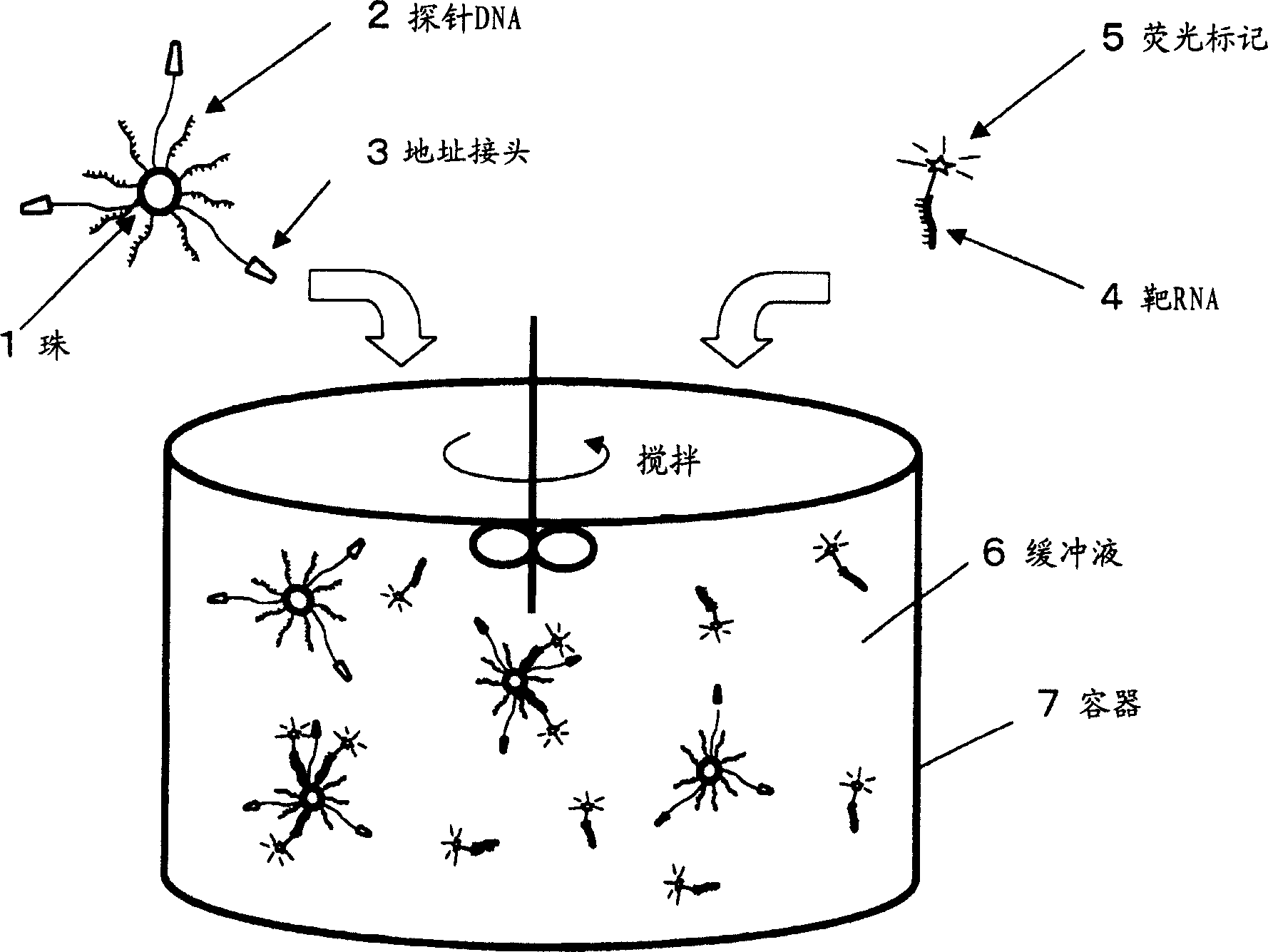
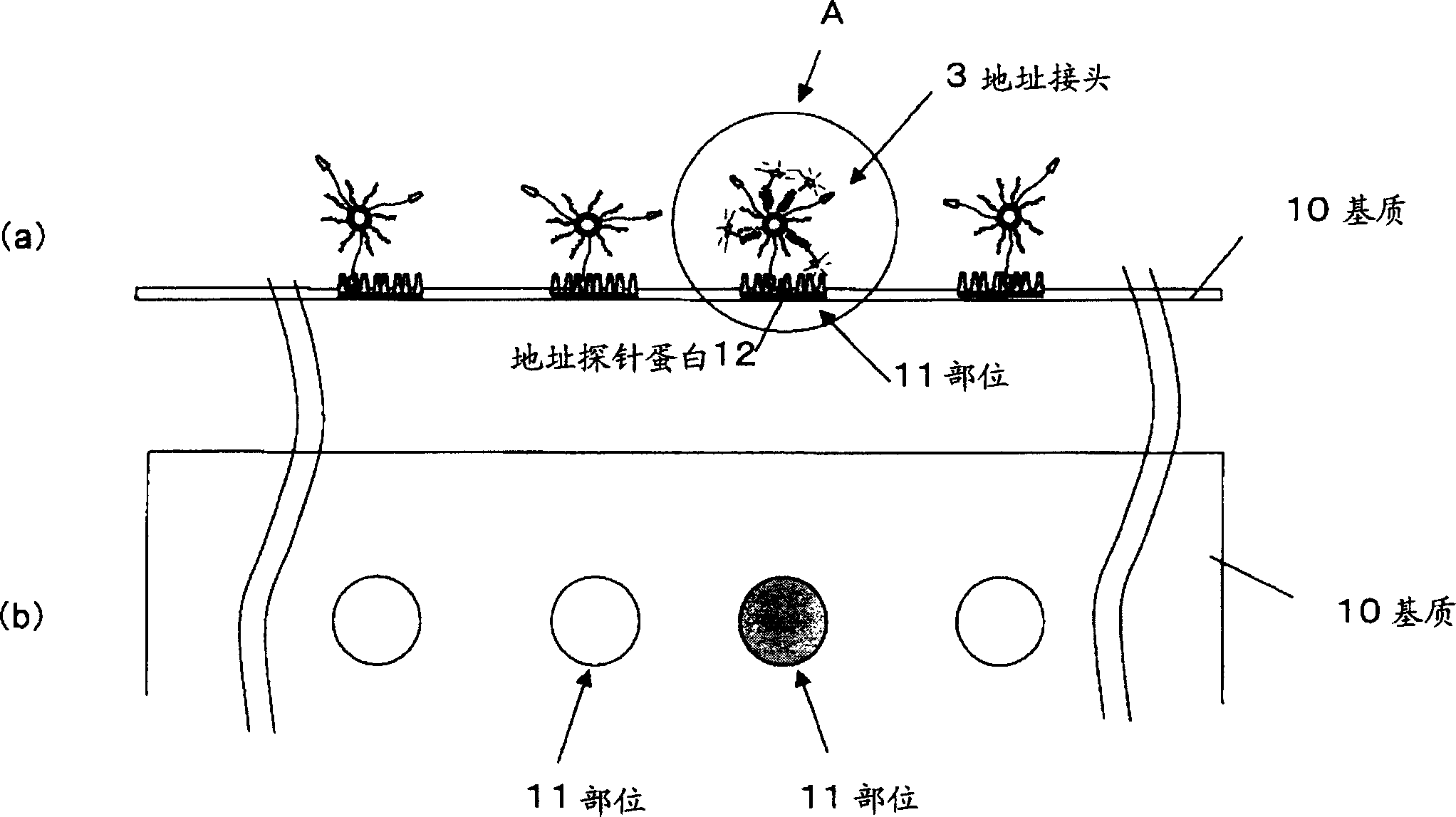
Method of detecting biopolymer, biochip, method of fixing antibody, and substrate for fixing antibody thereon
InactiveCN1629636AHigh detection sensitivityShorten detection timeBiological testingBiopolymerBiochip
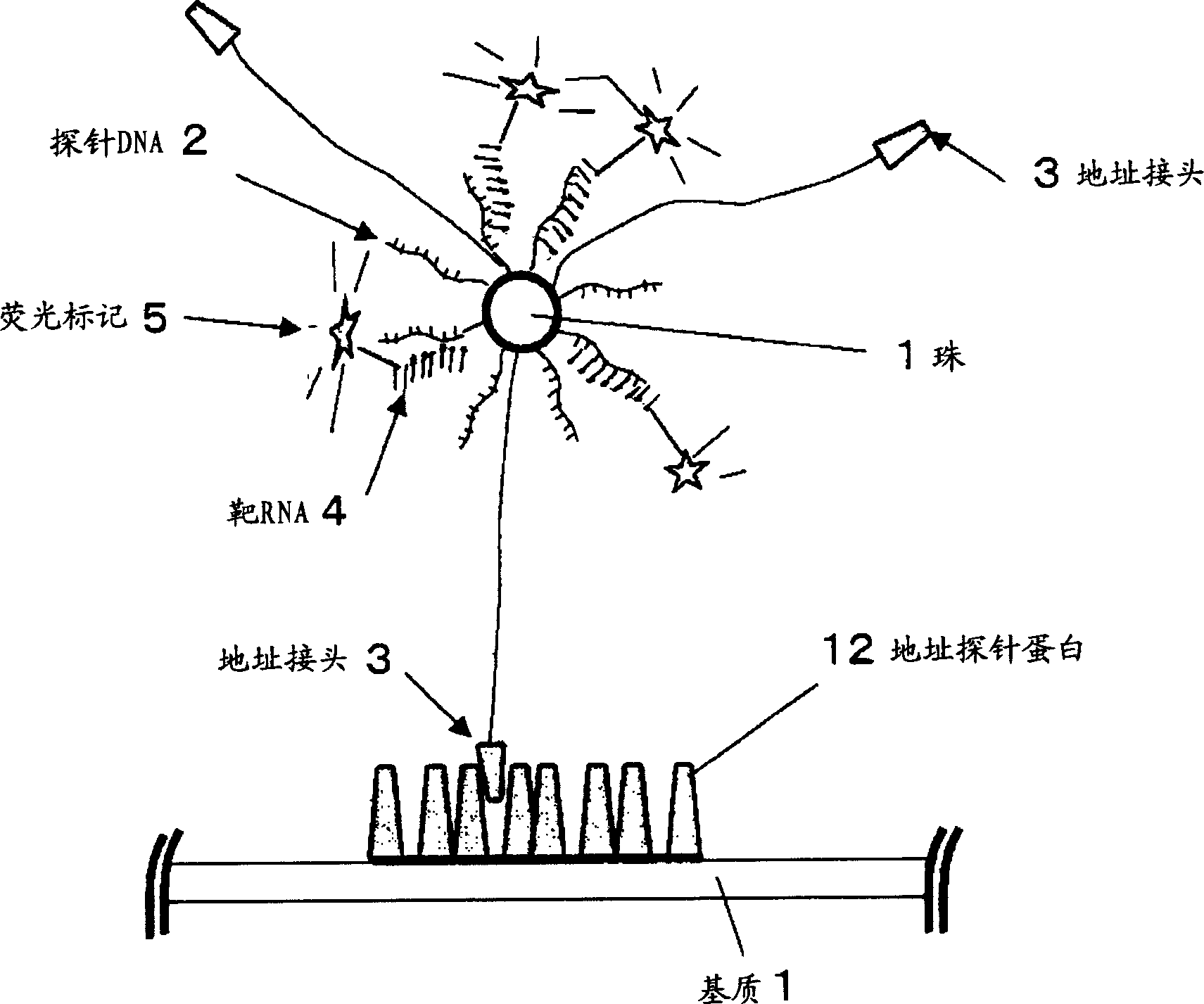
The present invention relates to a biopolymer detection method based on antigen-antibody interaction, wherein the method shows improved S / N ratio, improved detection sensitivity and reduced detection time. The present invention also relates to the application of these methods on biochips. The present invention also relates to an antibody immobilization method in which antibody molecules are immobilized on an amide group-containing gel, or an amide group-containing gel on an insoluble substance. Use of such gels prevents non-specific adsorption of antibody binding molecules. By embedding these antibody-binding molecules in such a gel, degradation of their antibody-binding activity is prevented. A method for detecting a biopolymer by capturing a target biopolymer to a substrate surface, comprising the following steps: (1) attaching a target biopolymer, together with a probe biopolymer and an antibody or address probe peptide or a peptide bound to them (2) hybridize the target biopolymer to the probe biopolymer; and (3) through the antigen-antibody interaction, through the address probe peptide Or biopolymer or polyclonal antibody molecules to recognize the address linker bound to the substrate. The method of immobilizing antibodies comprises the steps of: (1) applying a gel containing amide groups embedded with antibody binding molecules on a matrix of insoluble substances in two or three dimensions; and (2) attaching the bases of antibody molecules to the antibody binding molecule.
Owner:INTER UNIV RES INST RES ORG OF INFORMATION & SYST +1
Assay method and assay kit for hepatitis b virus s antigen
PendingCN111417854AReduce the impactVirus peptidesBiological material analysisAutoantibodyHepatitis B immunization
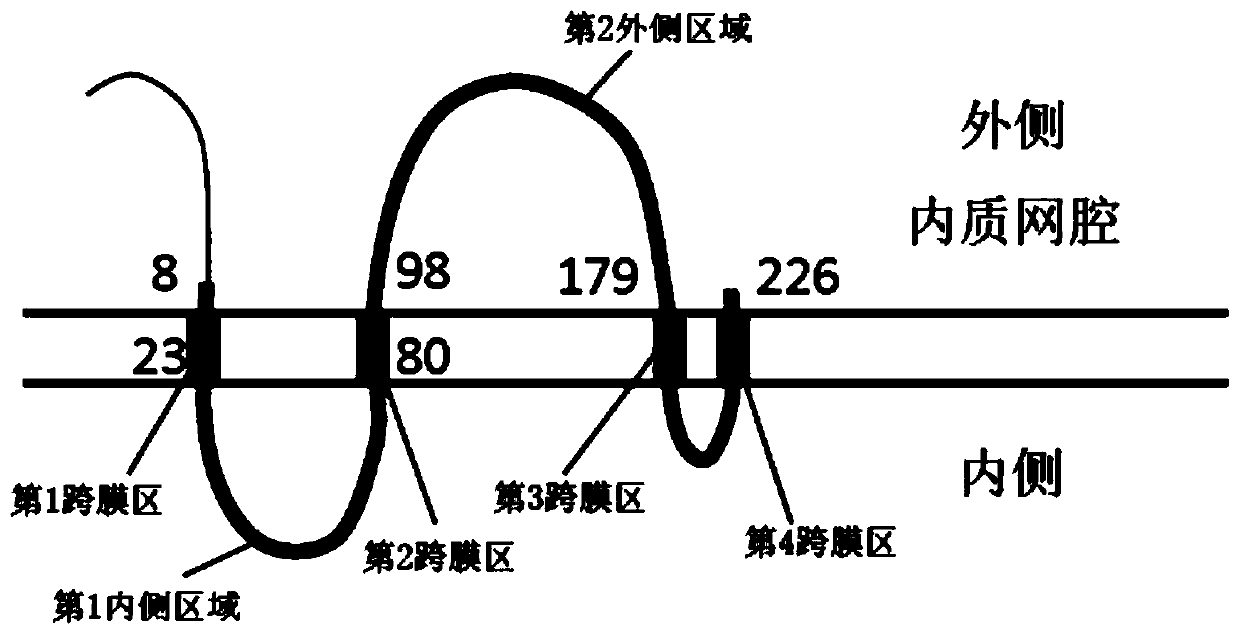
Disclosed are a high-sensitivity HBsAg assay method and assay kit that do not involve a strong acid or alkaline treatment during sample pretreatment and are not readily affected by autoantibodies. Anassay method for the hepatitis B virus s antigen in a sample that has been isolated from an organism, the method including: a pretreatment step for mixing the sample with a pretreatment reagent that includes a reducing agent to reduce the hepatitis B virus s antigen; and an immunoassay step for performing an immunoassay for hepatitis B virus s antigen on the pretreated sample using an antibody that can achieve an antigen-antibody interaction with a reduced peptide that comprises the 98th-179th amino acids of hepatitis B virus s antigen and / or an antigen-binding fragment of the antibody.
Owner:FUJIREBIO CO LTD
Protein type nanoparticle for delivery of multiple specific antibodies, and application and preparation method of protein type nanoparticle
ActiveCN112336873AImprove bindingTargeted combinationPowder deliveryAntibody ingredientsPolyesterAntibody fragments
The invention relates to a protein type nanoparticle for delivery of multiple specific antibodies, and application and a preparation method of the protein type nanoparticle. The protein type nanoparticle comprises polyester and protein with a hydrophobic structural domain; the hydrophobic structural domain of the protein is combined with the polyester through hydrophobic interaction; and the protein is at least one of albumin, globulin and cell wall protein. The protein type nanoparticle disclosed by the invention has excellent stability and biocompatibility, and can be used for preparing a multi-specific antibody delivery platform (alphaFc-NP) by bonding an anti-IgG-Fc antibody or an anti-IgG-Fc antibody fragment; the alphaFc-NP can be stably, rapidly, simply and conveniently combined with multiple specific antibodies through antigen-antibody interaction force; and furthermore, the treatment effect of the specific antibodies is enhanced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method, device and test kit for molecular-biological reactions
InactiveUS20130280695A1Avoid componentsGood protection against harmful environmental influenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSubstrate InteractionAntigen-antibody interaction
The invention relates to a device, method and test kit for carrying out molecular-biological reactions, wherein the different components for the molecular-biological reactions are located on a solid carrier in different, spatially separated compartments prior to the start of the reaction. The carrier is preferably a porous filter disk made of polyethylene. Fields of application are the amplification of nucleic acids, for example PCR or RealTime PCR, the reverse transcription of RNA in DNA enzyme-substrate interactions or antigen-antibody interactions, or protein synthesis.
Owner:AJ INNUSCREEN GMBH
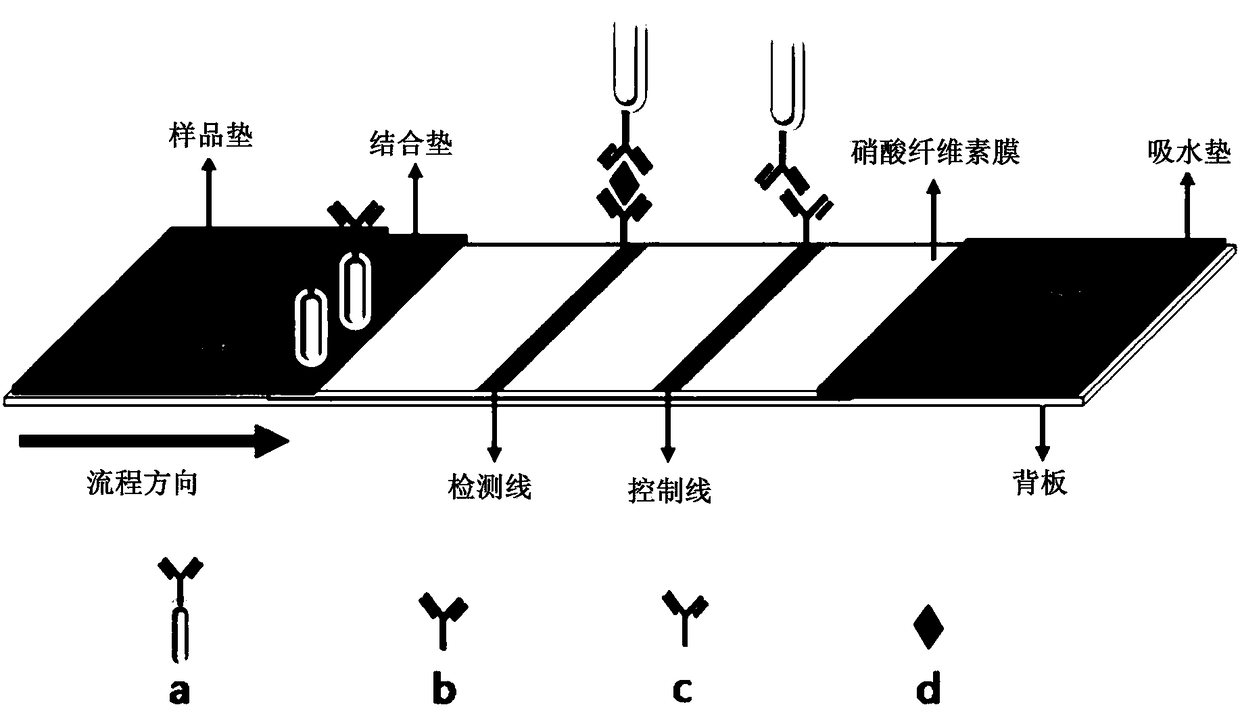
Test strip and method for detecting prostate tumor antigens
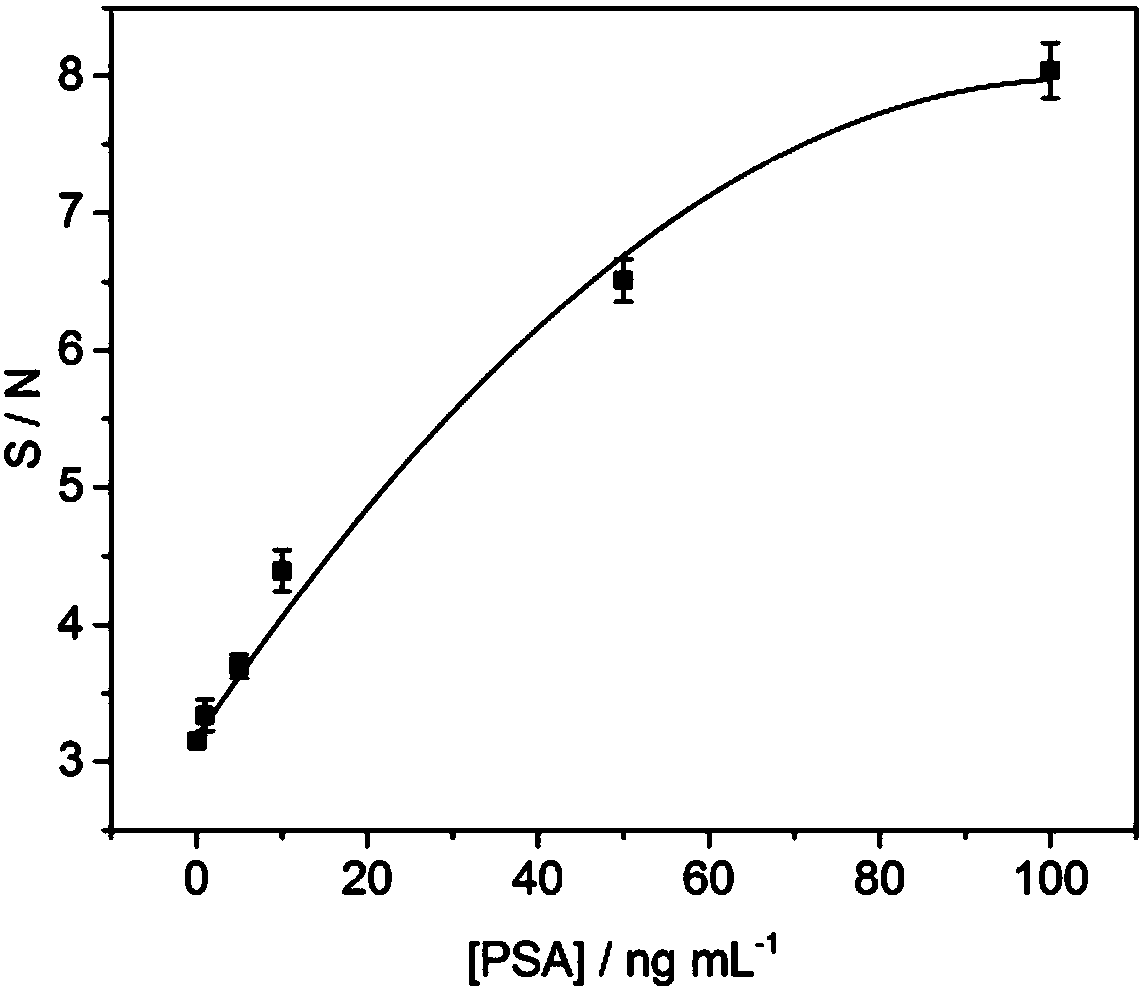
The invention provides a test strip and a method for detecting prostate tumor antigens. By the aid of the test strip and the method, the shortcomings of complicated operation and long time consuming of existing methods for detecting PSA (prostate specific antigens) and difficulty in meeting POC (point of care) quick diagnosis requirements can be overcome. PSA monoclonal antibodies II are labeled by gold nanorods by the aid of immunochromatography technologies, a nitrocellulose membrane is coated with goat anti-rat IgG and PSA monoclonal antibodies I, and the test strip for detecting the PSA isprepared by the aid of double-antibody sandwich processes. Liquid can flows through a binding pad and the nitrocellulose membrane step by step under capillary actions after PSA sample solution is added onto a sample pad of the test strip, and is bound with biological molecules, which are immobilized on the test strip, under antigen-antibody interaction, and a detection line visible to naked eyescan be generated. The test strip and the method are combined with microarray scanners, so that corresponding detection signal strength values can be obtained, and the PSA can be detected. The test strip and the method have the advantages that the method is simple and speedy, and is low in sample consumption and cost and short in detection time, the minimum concentration of the detectable PSA is 0.1 ng mL<-1>, the detection range is 0.1-100 ng mL<-1>, and clinical detection requirements can be met.
Owner:上海格荣生物科技有限公司
Method for detecting interaction of antibody and polypeptides by adopting capillary electrophoresis
InactiveCN102998357AEasy to operateHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
The invention relates to a method for detecting interaction of an antibody and polypeptides by adopting capillary electrophoresis, belonging to the field of bioanalysis. The method comprises the steps of firstly, mixing the antibody with polypeptides of different proportions, then carrying out capillary electrophoresis detection, simultaneously detecting an appearance time and a fluorescence intensity of an antibody polypeptide compound and a fluorescence polypeptide, integrating an electrophoresis peak of the antibody polypeptide compound, converting an integral area into a compound concentration, and calculating a dissociation constant (KD) of the antibody and the polypeptide according to a formula. The method can also be used for detecting a competition process of the interaction of two exogenous polypeptides and the antibody. Experiments prove that the method has the advantages of simpleness in operation, high detection sensitivity, and short required time. The method is a novel high-sensitivity technology for detecting the interaction of the polypeptides and the antibody through improvement of the traditional technology of detecting the interaction of the polypeptides and the antibody and combination with the advantages of high sensitivity and the like of fluorescence detection.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Novel molecular imprinting method for preparing simulation antibody and application of novel molecular imprinting method on bacterial detection
InactiveCN105973827AImprove mechanical propertiesStable deliveryColor/spectral properties measurementsMolecular imprintingComputational chemistry
The invention discloses a novel molecular imprinting method for preparing a simulation antibody and application of the novel molecular imprinting method on bacterial detection. According to the novel molecular imprinting method, a molecular imprinting film is prepared by blending two polymers with different properties and functional groups in proportion; uncross-linked blended polymers are particularly applied to the molecular imprinting technique of the simulation antibody, and the mutual action sites between the imprinting film and bacteria are increased by virtue of mutual action of simulation antigens-antibodies between the different functional groups of the polymers and the surfaces of the bacteria, so that the specific recognition capacity of the imprinting film is improved. According to the novel molecular imprinting method, the problems of poor specific recognition capacity and low sensitivity of a surface molecular imprinting technique can be solved, and a bacteria detection method having the characteristics of strong specific recognition capacity, high sensitivity, low cost, simplicity and feasibility can be provided.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
IFA neutralizing antibody detection method of PRRSV
PendingCN112362880ARealistic reaction interaction situationsBiological testingImmunoassaysNeutralising antibodyBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses an IFA neutralizing antibody detection method for PRRSV, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biological detection. The invention discloses an IFA neutralizing antibody detection method of PRRSV. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating an isopyknic PRRSV virus solution and clinical serum onto Marc145 cells, immobilizing, adding a primary antibody, adding a secondary antibody, and observing a result. According to the method, target cells are infected after interaction of whole viruses and antibodies, and the situation of interaction of the viruses and the neutralizing antibodies is truly reflected.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Fluorescent biosensing method for analyzing and detecting mutual action of organic micromolecules and combined protein based on T7 exonuclease inhibition
ActiveCN102643921ASimple designSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention provides a fluorescent biosensing method for analyzing and detecting mutual action of organic micromolecules and combined protein based on a T7 exonuclease inhibition. The method comprises mutual action of an oligonucleotide DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) single chain with the middle part modified by organic micromolecules and protein, selection of a T7 exonuclease inhibition site, and a real-time fluorescent quantitative detection technique based on a Taqman probe. The method provided by the invention can be used for detecting the mutual action of the organic micromolecules and the protein, and the organic micromolecules or conjugated protein thereof through the fluorescent real-time quantitative analysis of the Taqman probe subjected to enzyme digestion based on the inhibition effect of the mutual action of the organic micromolecules and the protein or an antibody to T7 exonuclease by utilizing the specific binding of the organic micromolecules modifying the middle part of the oligonucleotide DNA chain and the conjugated protein or antibody thereof. The method provided by the invention is high in sensitivity, simple and convenient in operation and strong in specificity, and can be used for signal transduction and molecule regulation and control mechanism research in biomedicine, food and farm product security detection, environmental poison detection,drug screening and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
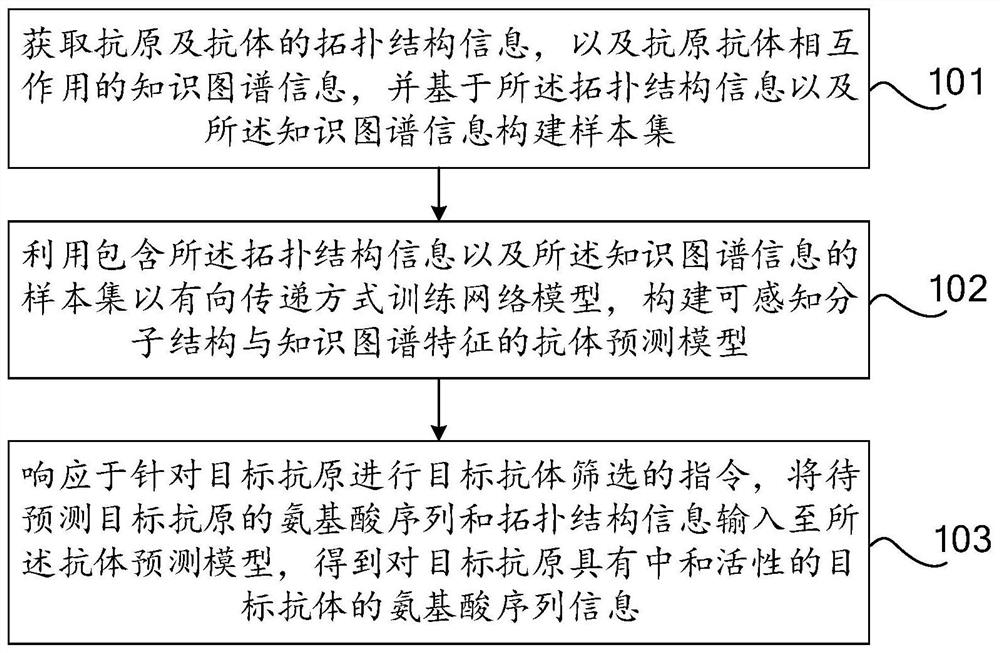
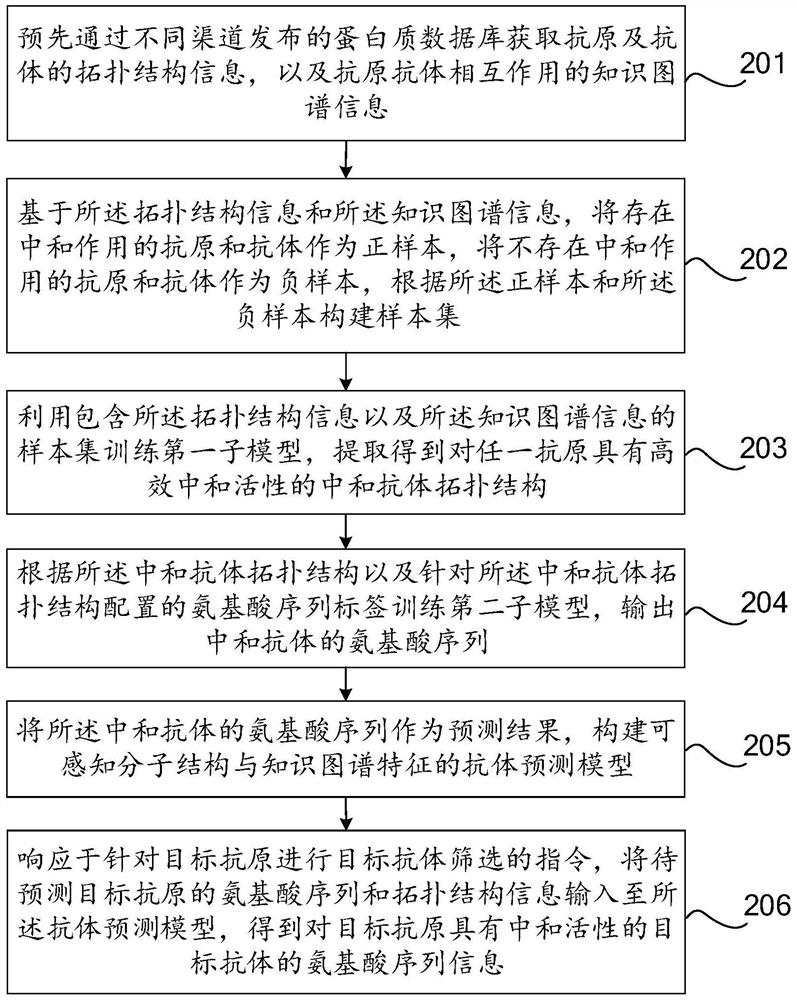
Machine learning-based antibody screening method and device
PendingCN113808664AImprove filtering effectPrecise positioningCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsNetwork modelAntibody screening
The invention relates to the technical field of artificial intelligence, and discloses a machine learning-based antibody screening method, which comprises the following steps: collecting topological structure information of an antigen and an antibody and knowledge graph information of the interaction of the antigen and the antibody, and constructing a sample set based on the topological structure information and the knowledge graph information; training a network model in a directed transmission mode by using a sample set containing topological structure information and knowledge graph information, and constructing an antibody prediction model capable of sensing the molecular structure and knowledge graph characteristics; and inputting the amino acid sequence and topological structure information of a to-be-predicted target antigen into the antibody prediction model in response to an instruction of screening the target antibody for the target antigen, so as to obtain amino acid sequence information of the target antibody with neutralizing activity on the target antigen. The method can learn and excavate the topological structure of the antigen and the antibody and the knowledge map characteristics of the interaction of the antigen and the antibody, and can be used as the prediction discovery of the neutralizing antibody, so that the screening effect of the antibody is improved.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method for PRRSV
PendingCN112379105AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityBiological testingImmunoassaysImmune effectsSerum neutralization test
The invention discloses an IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method for PRRSV, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biological detection. The IPMA neutralizing antibody detection methodfor PRRSV comprises the following steps: inoculating an isopyknic PRRSV virus solution and clinical serum onto Marc145 cells, fixing, adding a primary antibody, adding a secondary antibody and developing. The method provided by the invention provides certain technical support for prevention, vaccine evaluation and immune evaluation of PRRSV infected pigs; and the serum neutralization test can be used for detecting the PRRSV antibody level and evaluating the immune effect of the PRRS vaccine, and is expected to be applied to the production of actual vaccines. According to the method, target cells are infected after interaction of whole viruses and antibodies, and the situation of interaction of viruses and neutralizing antibodies is truly reflected; the method has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity and simple operation.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
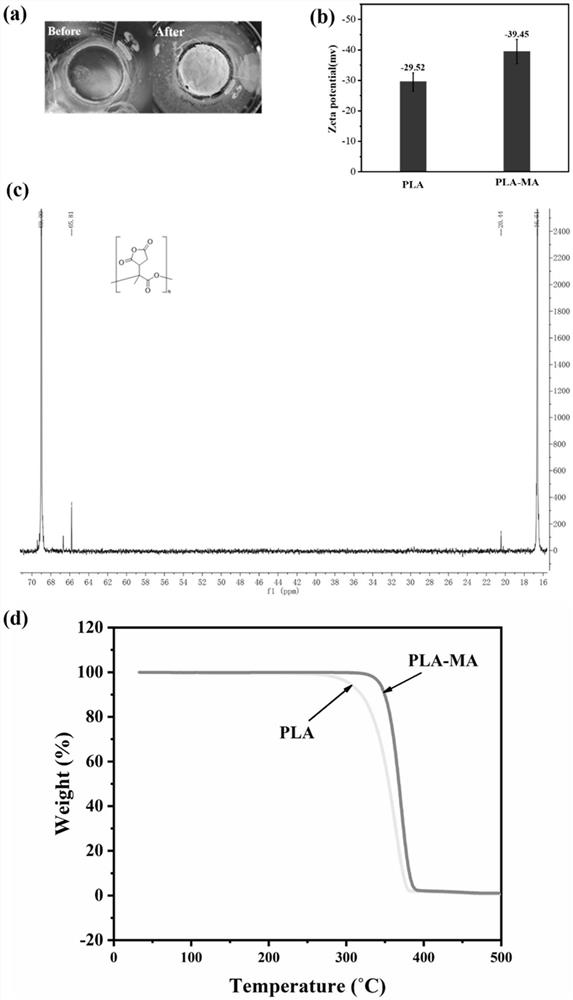
Quantum dot fluorescence coded polylactic acid microspheres as well as preparation method and application thereof
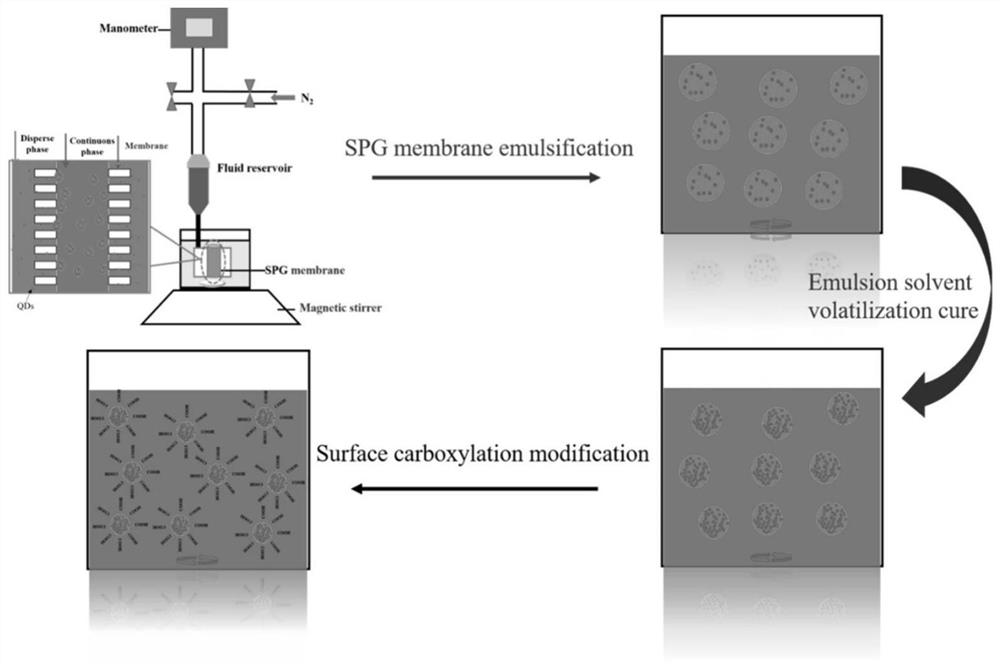
PendingCN114507524AUniform particle sizeActiveBiological material analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceImmune profilingImmuno detection
The invention discloses quantum dot fluorescence coded polylactic acid microspheres as well as a preparation method and application thereof, a liquid-phase suspension biochip system is constructed based on the quantum dot fluorescence coded polylactic acid microspheres, biological activity is rapidly judged through test strip immunoassay, and finally the quantum dot fluorescence coded polylactic acid microspheres are applied to immunodetection of tumor markers. According to the system, a novel polylactic acid fluorescent microsphere is used as a carrier, and water-phase CdTe QDs is used as a signal substance. The immunodetection system comprises a novel polylactic acid fluorescent microsphere-coated tumor marker capture antibody, a water-phase CdTe QDs-labeled tumor marker antibody, and a tumor marker antigen which is respectively connected with the novel polylactic acid fluorescent microsphere-coated tumor marker capture antibody and the water-phase CdTe QDs-labeled tumor marker antibody through antigen-antibody interaction. The method has the characteristics of quick reaction, good repeatability, simplicity and convenience in operation, high throughput, multi-index combined detection and high sensitivity in tumor marker detection.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Lowered affinity antibodies and uses therefor
The present invention provides novel, rationally designed lowered affinity antibodies for use in various in vivo and in vitro applications. The antibodies of the present invention have variable domains that have been designed to reduce or eliminate the antigen binding activity of the parental antibody without altering the overall 3 dimensional antibody structure. Using the antibodies of the present invention in various assays allows researchers to distinguish effects that result from specific antigen-antibody interactions from other, non-specific antibody effects.
Owner:AB BIOSCI
IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method of CSFV
PendingCN112611866AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityImmunoassaysImmune effectsSerum neutralization test
The invention discloses an IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method of CSFV and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention discloses an IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method for CSFV. The IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method comprises steps of virus inoculation, plate laying, fixation, primary antibody addition, secondary antibody addition and color development. The method provided by the invention provides certain technical support for prevention, vaccine evaluation and immune evaluation of pigs infected with CSFV; and the serum neutralization test can be used for detecting the level of the CSFV antibody and evaluating the immune effect of the CSF vaccine, and is expected to be applied to the production of actual vaccines. According to the method, target cells are infected after interaction of whole viruses and antibodies, and the situation of interaction of viruses and neutralizing antibodies is truly reflected; the kit has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity and simple operation.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Vitro prediction of in vivo half-life
PendingUS20210190795A1Reducing FcRn-dependent terminal half-lifeChanges the FcRn binding characteristicsSolid sorbent liquid separationImmunoglobulinsBiochemistryIn vivo
Herein is reported a method for determining the presence of antibody-Fab-FcRn interaction in an antibody-Fc-FcRn complex influencing the in vivo half-life comprising the steps of a) determining the retention time of the antibody on an FcRn affinity chromatography column with a positive linear pH gradient elution in the presence of a first sodium chloride concentration, and b) determining the retention time of the antibody on an FcRn affinity chromatography column with a positive linear pH gradient elution in the presence of a second sodium chloride concentration, whereby the presence of antibody-Fab-FcRn interaction in an antibody-Fc-FcRn complex influencing the in vivo half-life is determined if the retention time determined in step a) and the retention time determined in step b) are substantially different.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
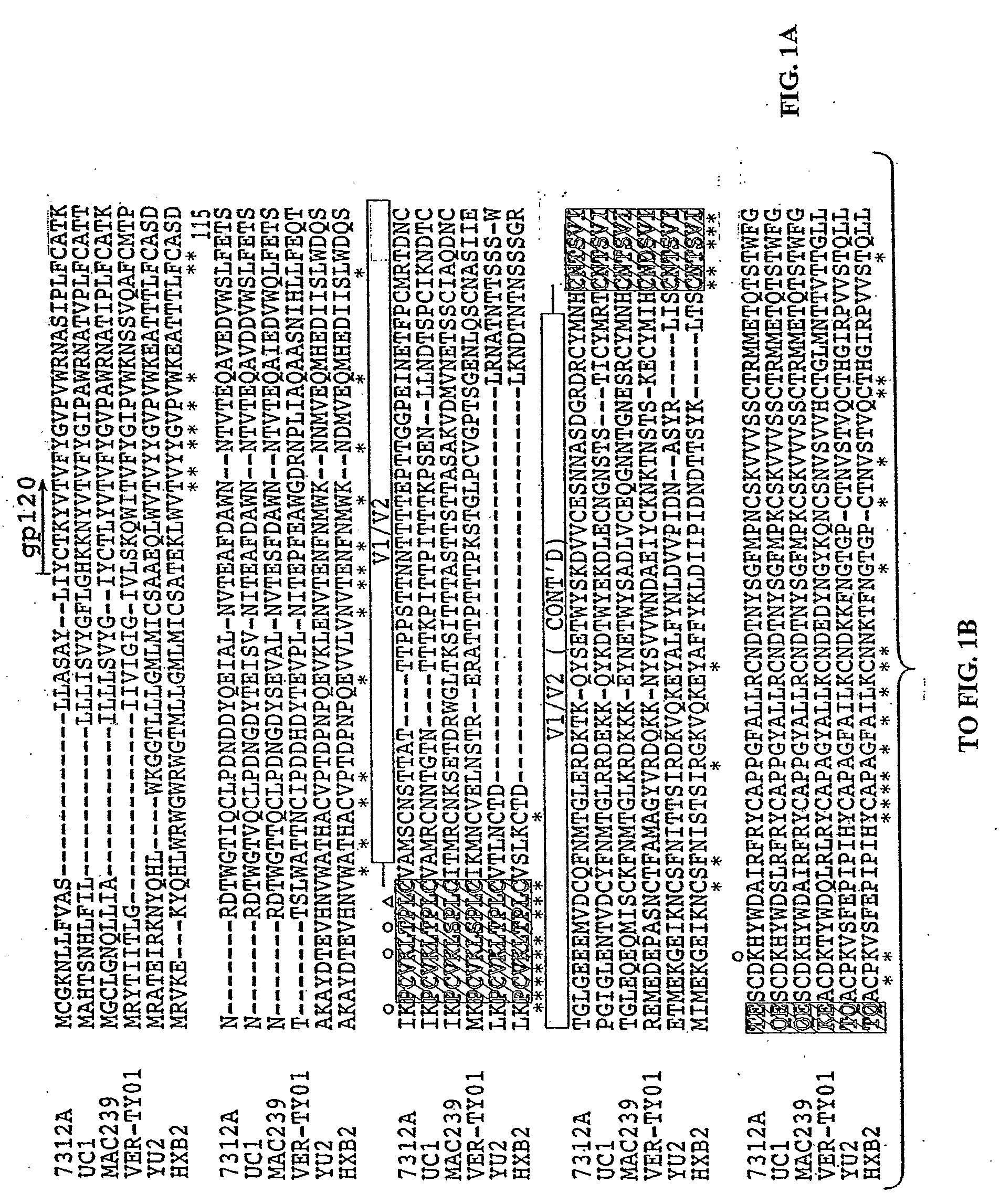
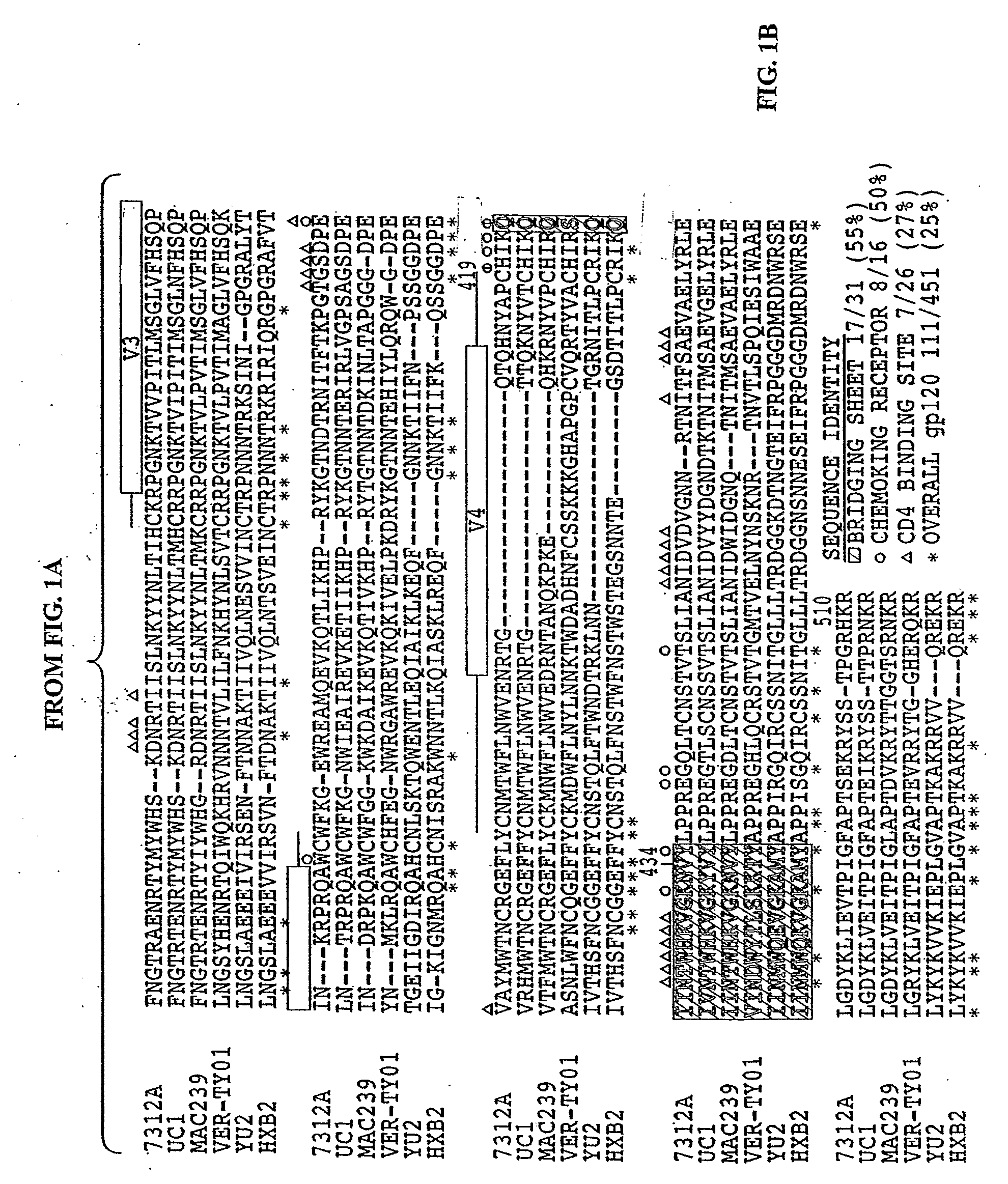
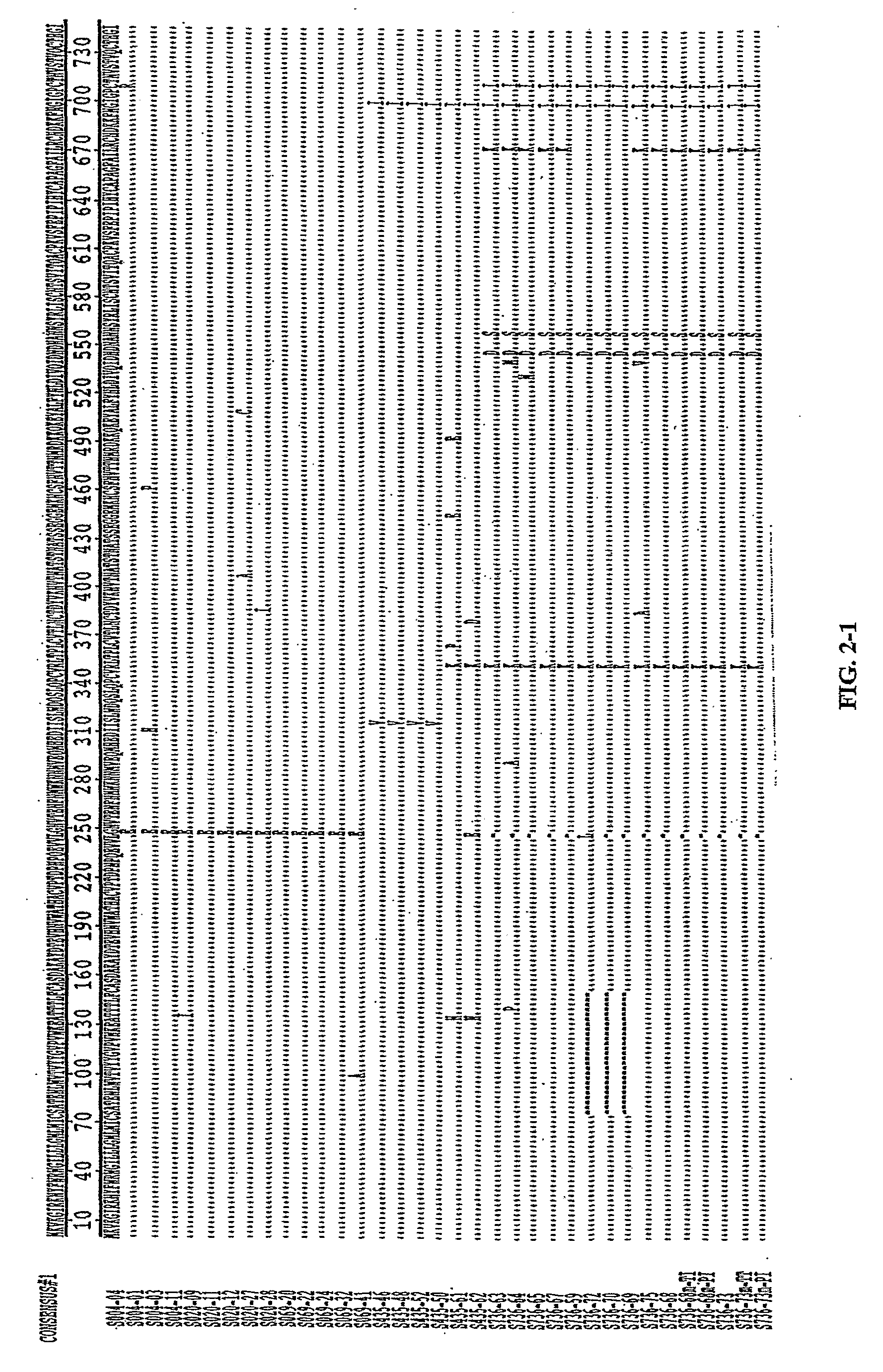
Molecular Scaffolds for HIV-1 Immunogens
InactiveUS20090162390A1Prevent and inhibit infectionOrganic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeHeterologous
Methods and compositions are provided which employ chimeric polypeptides having at least one heterologous epitope for a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) neutralizing antibody. These chimeric polypeptides behave as molecular scaffolds which are capable of presenting the various heterologous HIV-1 epitopes. The invention demonstrates that a heterologous epitope recognized by the HIV-1 neutralizing antibody can be more fully exposed to neutralizing antibodies when presented within the backbone of the chimeric polypeptide than when the epitope is presented within the context of an HIV-1 backbone. Polynucleotides encoding these chimeric polypeptides are also provided. Immunogenic compositions are provided which comprise a chimeric polypeptide having at least one heterologous epitope that interacts with an HIV-1 neutralizing antibody. Immuno genie compositions comprising chimeric polynucleotides encoding the chimeric polypeptides of the invention are also provided. Vaccines comprising such immunogenic compositions are also provided. Further provided are methods which employ the immunogenic compositions of the invention. Such methods include, for example, methods for eliciting an immune response in a subject, methods for generating antibodies specific for the chimeric polypeptide or the chimeric polypeptide, and methods for inhibiting or preventing infection by HIV-1 in a subject.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES HEREINAFTER THE GOVERNMENT +1
Design of novel anti-EGFR humanized antibody TGM10 and application thereof
The invention discloses a computer-assisted design of novel anti-EGFR humanized antibody TGM10 and application thereof. The antibody can be used for inhibiting the growth of human tumor cell for expressing EGFR. The invention obtains the novel anti-EGFR humanized antibody TGM10 by virtual screening and designing of a computer on the basis of the structural characteristic that an EGFR protein cell outer region interacts with the functional antibody. The PCR method is applied to carry out the total synthesis of antibody gene to build into a eukaryon expression carrier, and 9 types of TGM10 antibodies capable of specifically recognizing EGFR can be expressed. The antibody TGM10-1 can effectively kill the positive EGFR tumor cells comprising breast cancer cell lines SKOV3, liver cancer cell lines HepG2 and lung cancer cell lines A549.
Owner:BEIJING MABWORKS BIOTECH +1
A method for visually detecting antigen-antibody reaction and its application
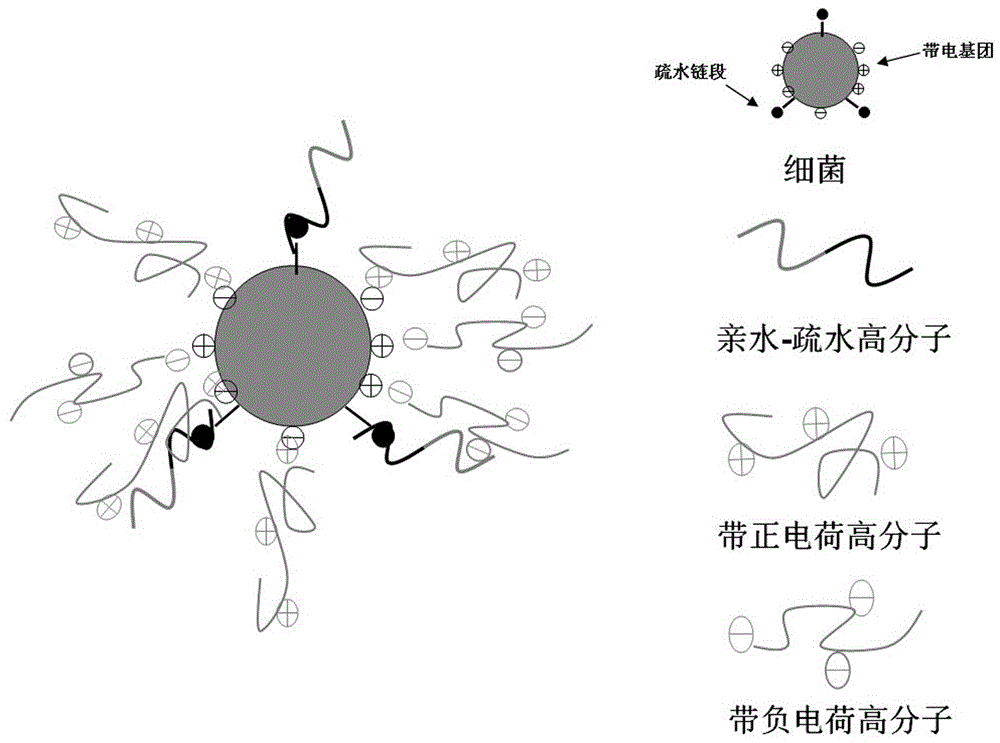
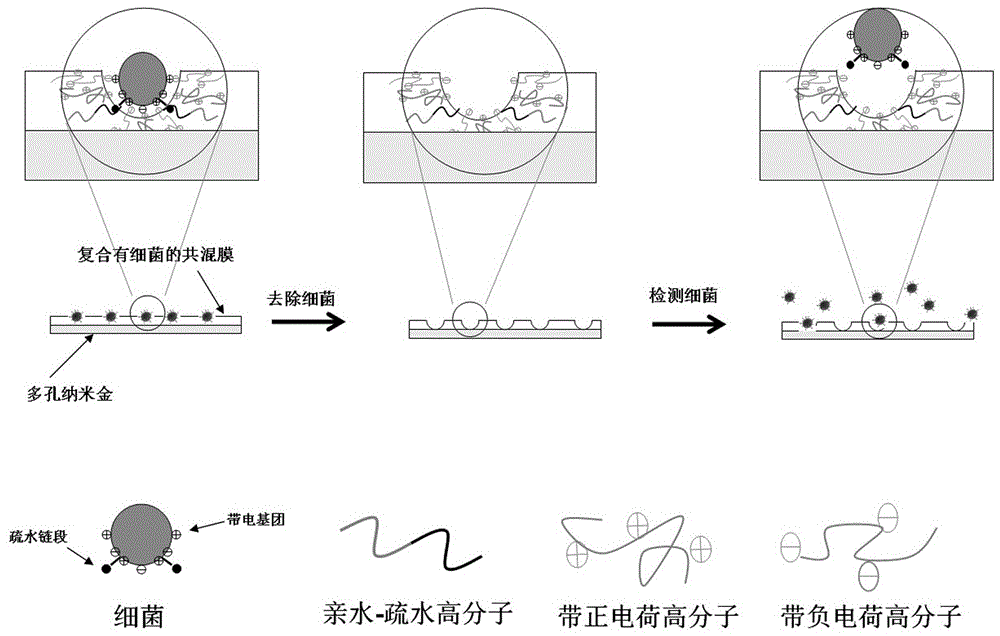
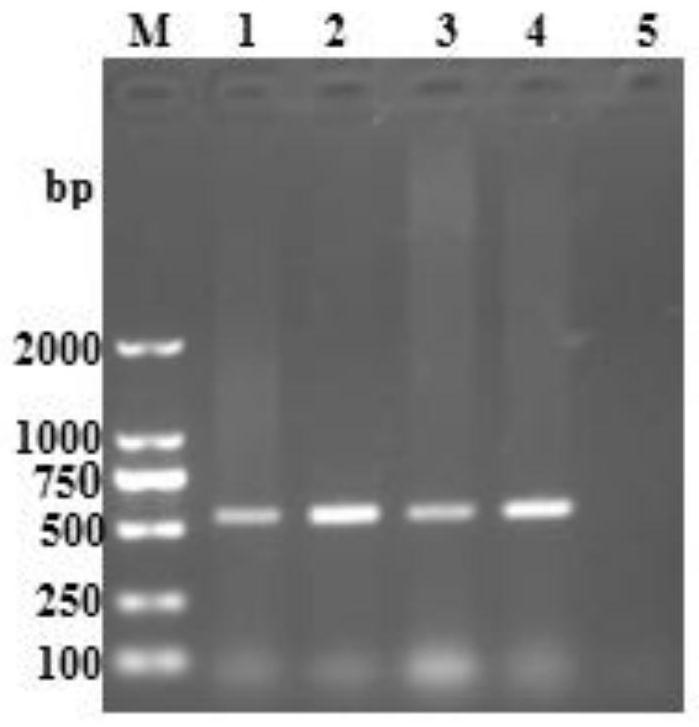
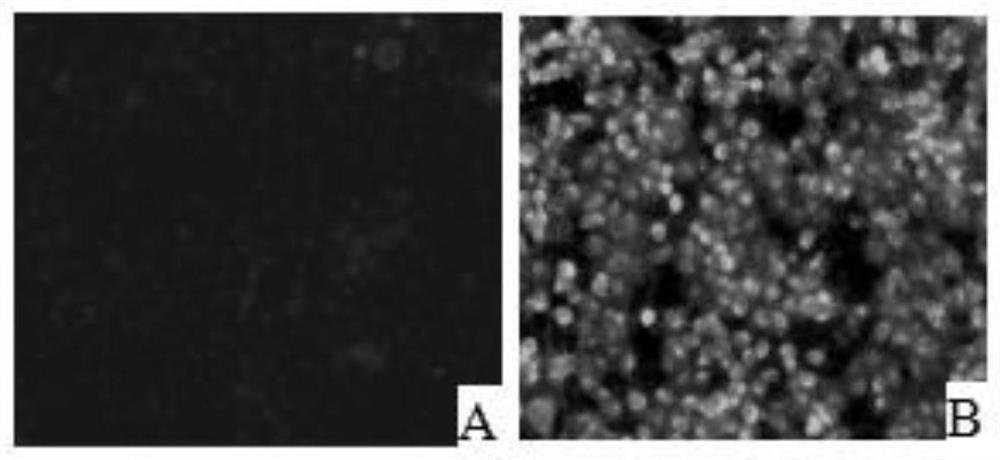
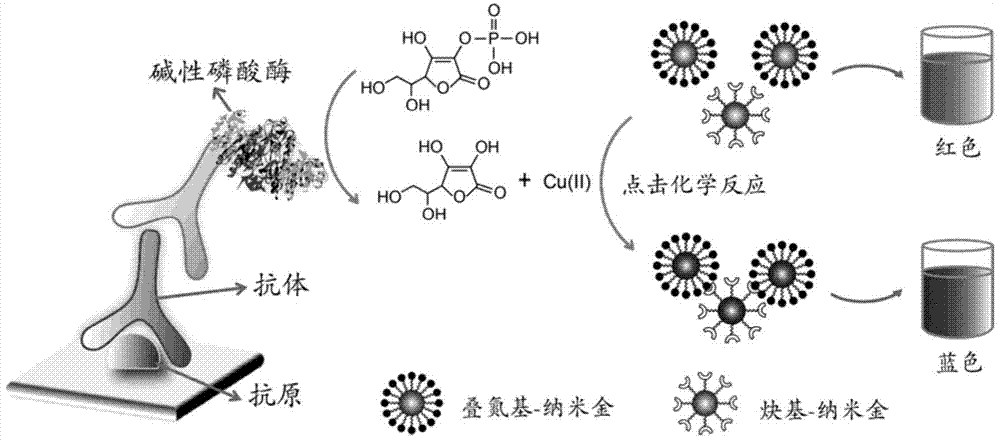
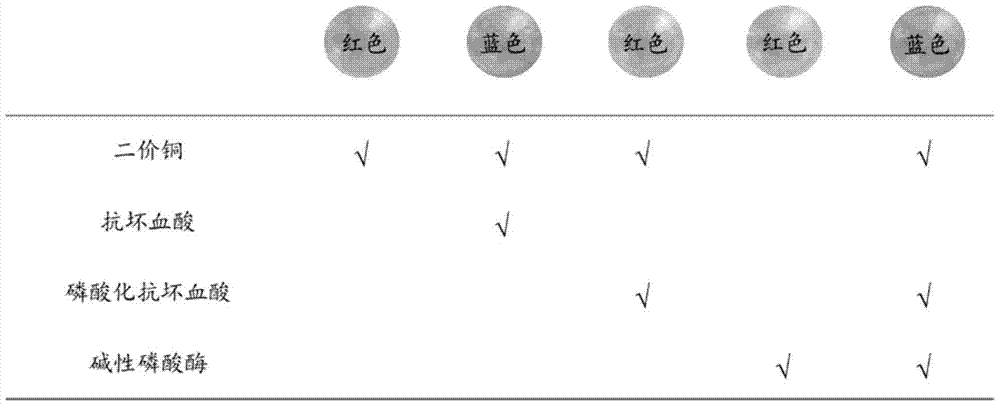
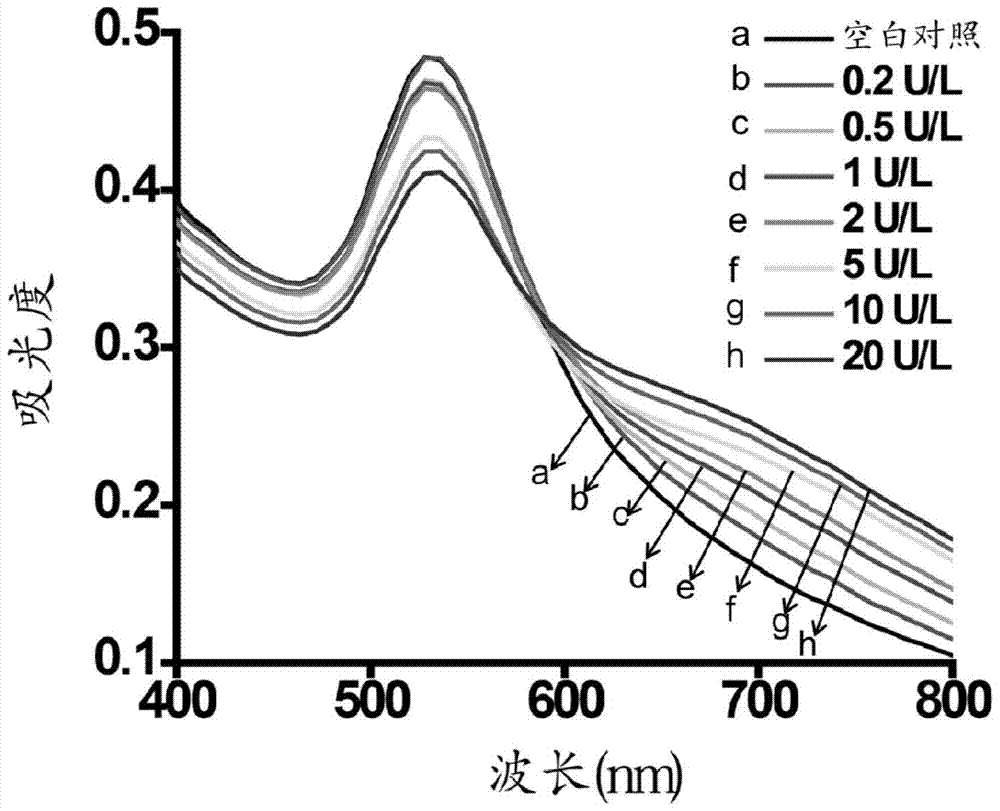
ActiveCN104089950BGet rid of dependenceEasy to readChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingChemical reactionNanoparticle
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com