Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
77 results about "Amidase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
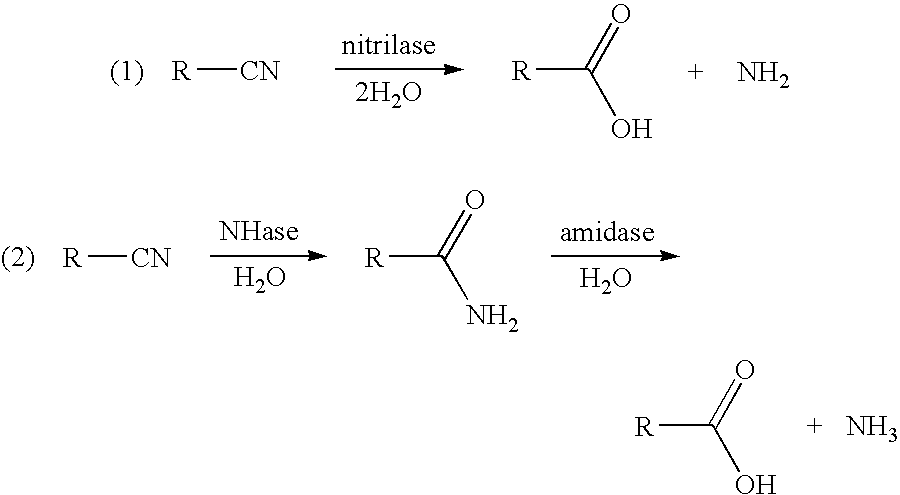
Catalysis of the reaction: a monocarboxylic acid amide + H2O = a monocarboxylate + NH3. [EC:3.5.1.4]
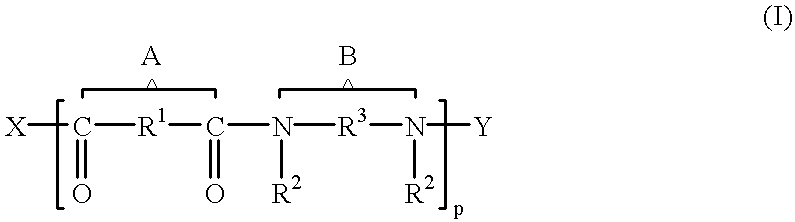
Enzymes and microorganisms having amidase activity for hydrolysing polyamides
The present invention relates to an enzyme with amidase activity, particularly towards substrates of the oligomer type derived from PA 6.6 (formula I) and / or PA 6 (formula II), said enzyme being characterized by a ratiowhich is greater than 2, preferably greater than or equal to 10 and particularly preferably greater than or equal to 50.More precisely, this enzyme consists of the peptide sequence corresponding to the attached sequence SEQ ID NO: 2.The invention further relates to the DNA which codes for this polypeptide SEQ ID NO: 2 and whose sequence corresponds to the attached sequence SEQ ID NO: 1.The invention further relates to the microorganisms capable of producing this enzyme and to the hydrolysis process in which this enzyme and / or these microorganisms are applied.
Owner:RHONE POULENC FIBERS & POLYMERES
Beta-lactamase detecting reagent composition, detection kit and detection method
InactiveUS20060014230A1Quick checkOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementΒ lactamasesNitrostyrol
The present invention provides a reagent composition for detecting β-lactamase including as a β-lactamase detection substrate 3-[2,4-dinitrostyryl]-7-(2-thienylacetamido]-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid, or 7-[2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy-imino)acetamido]-3-(2,4-dinitrostyryl)-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid, and at least one β-lactamase inhibitor selected from the group consisting of clavulanic acid, aztreonam, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and cloxacillin, which composition can detect β-lactamases rapidly and easily with high sensitivity. The present invention also provides a detection kit including the detecting reagent composition. Further, the present invention provides a β-lactamase detection method where a liquid specimen containing a target substance to be analyzed is brought into contact with the composition.
Owner:SHOWA YAKUHIN KAKO +1
Induction and stabilization of enzymatic activity in microorganisms
ActiveUS20070184528A1Improve stabilityCommercially useful levelSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismNitrile hydratase activity
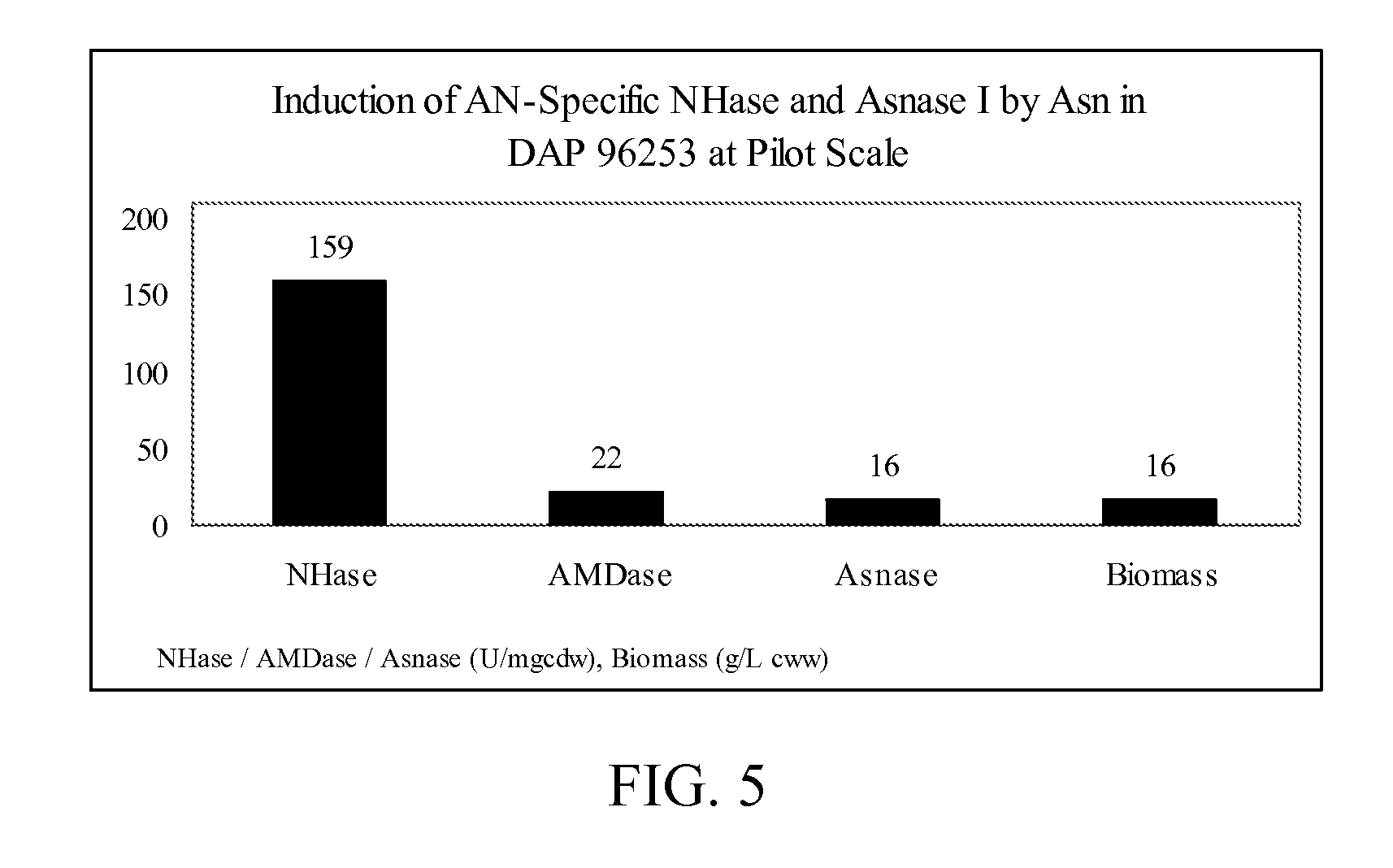
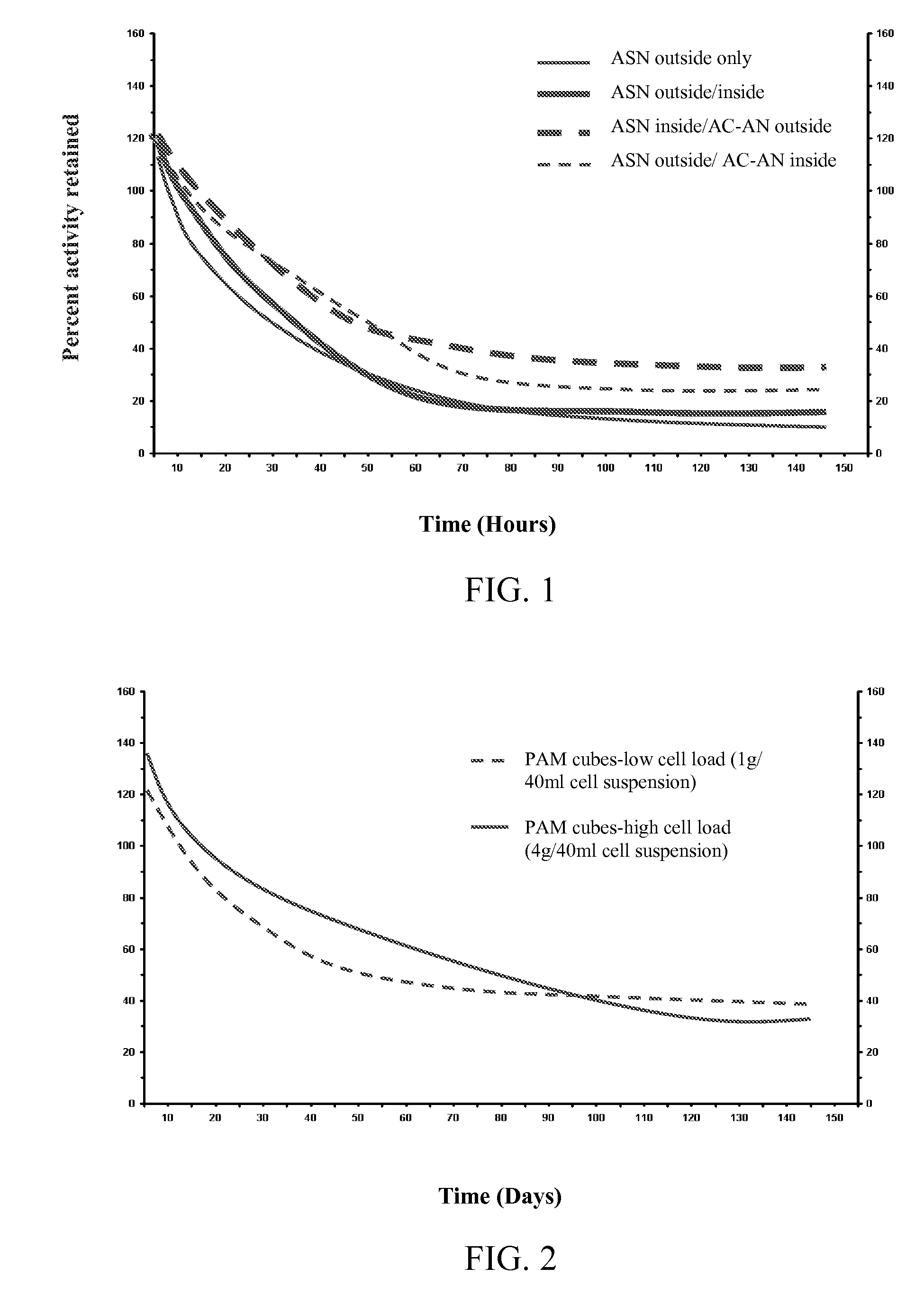
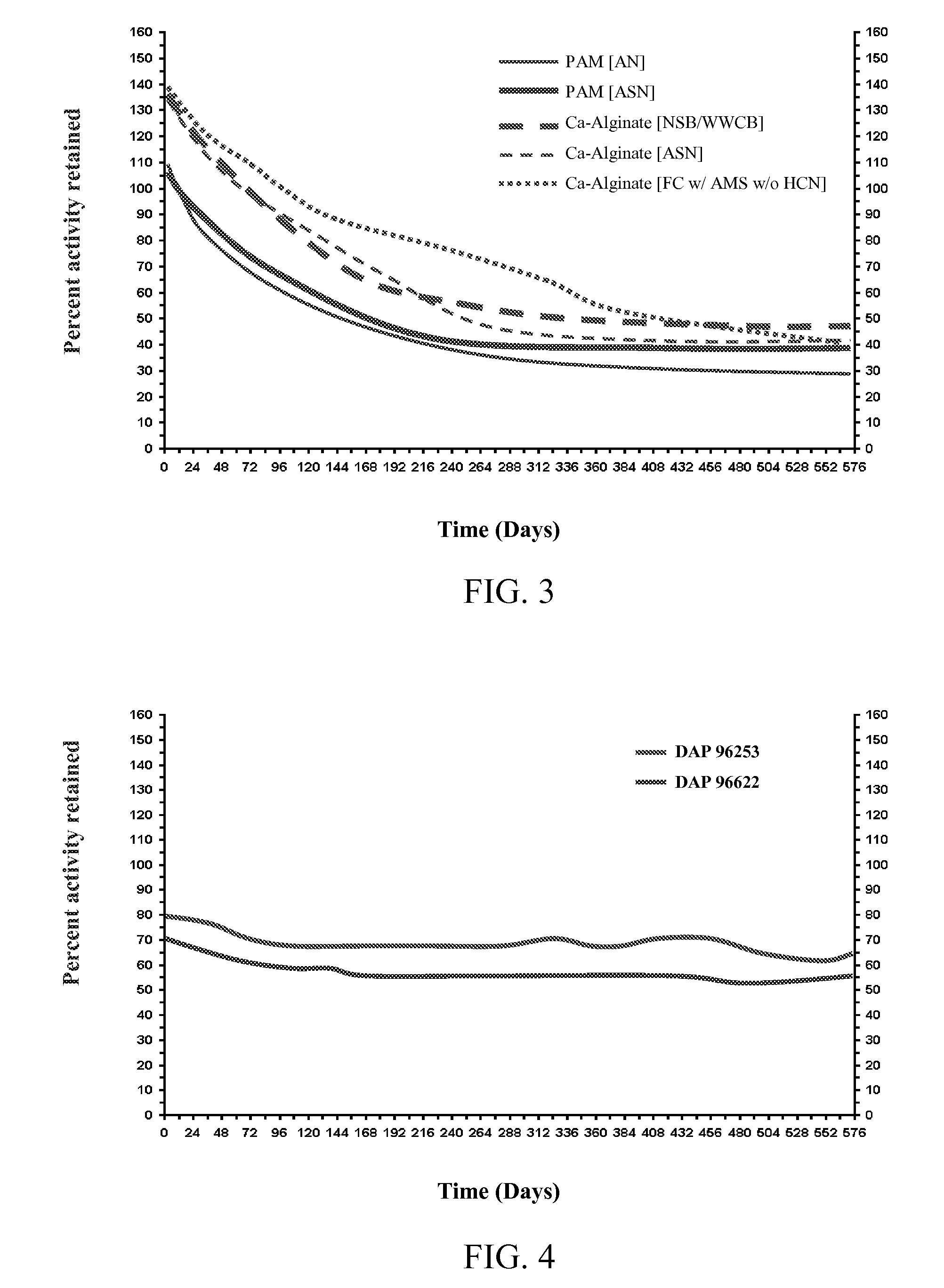
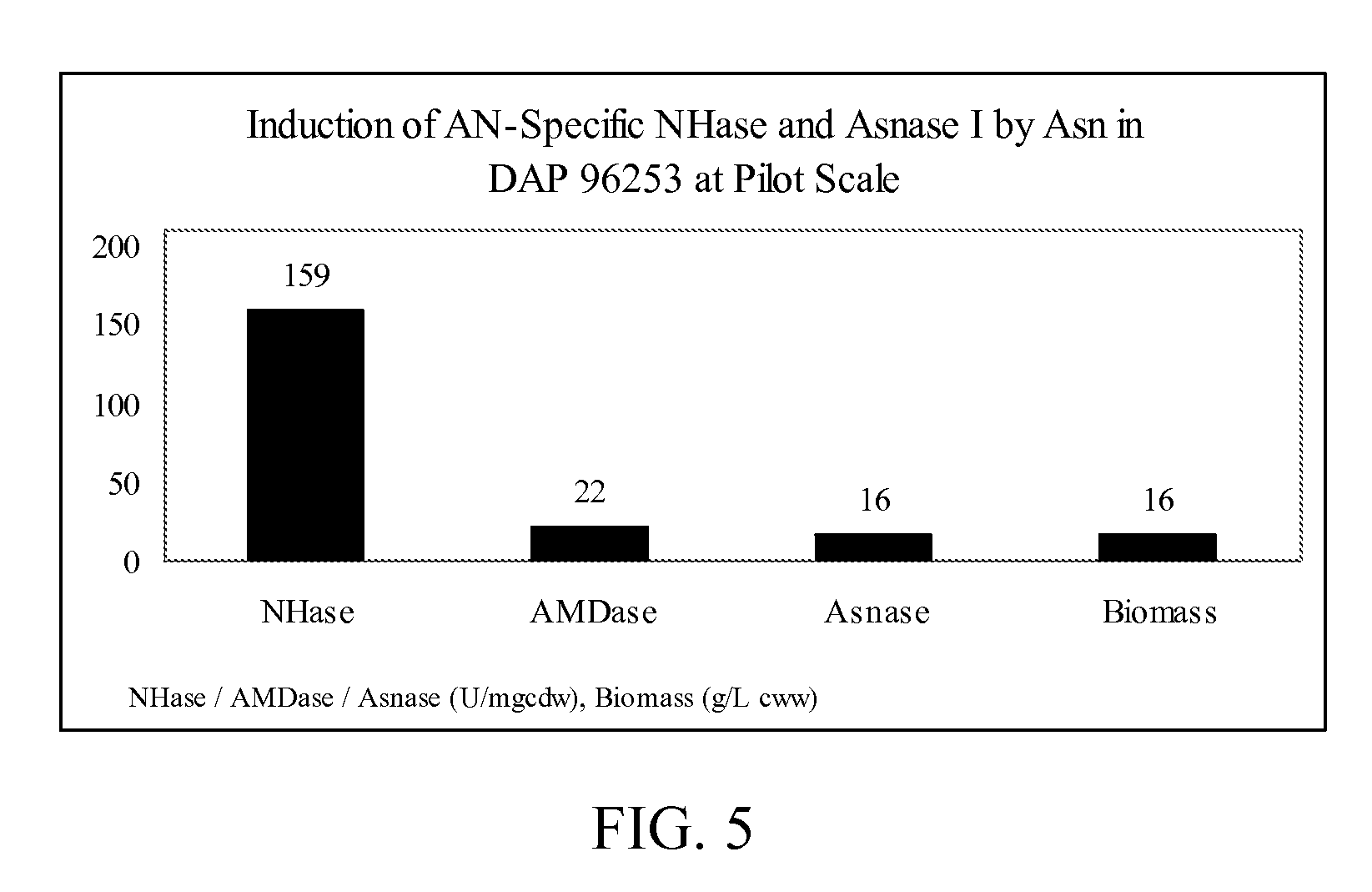
The present invention is directed to methods for inducing desired activity in enzymes or microorganisms capable of producing the enzymes. The invention is further directed to methods of stabilizing activity in microorganisms. In specific embodiments, the invention provides methods for inducing and stabilizing nitrile hydratase activity, amidase activity, and asparaginase I activity. The invention further provides compositions comprising enzymes or microorganisms having induced and / or stabilized activity.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
Induction and stabilization of enzymatic activity in microorganisms
InactiveUS7531344B2Improve stabilityCommercially useful levelBacteriaHydrolasesMicroorganismNitrile hydratase activity
The present invention is directed to methods for inducing desired activity in enzymes or microorganisms capable of producing the enzymes. The invention is further directed to methods of stabilizing activity in microorganisms. In specific embodiments, the invention provides methods for inducing and stabilizing nitrile hydratase activity, amidase activity, and asparaginase I activity. The invention further provides compositions comprising enzymes or microorganisms having induced and / or stabilized activity.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
L-asparaginase mutant with improved enzyme activity and construction method thereof
InactiveCN105062997AIncreased potential for industrial applicationsReduce generationBacteriaHydrolasesGlycineSpecific enzyme
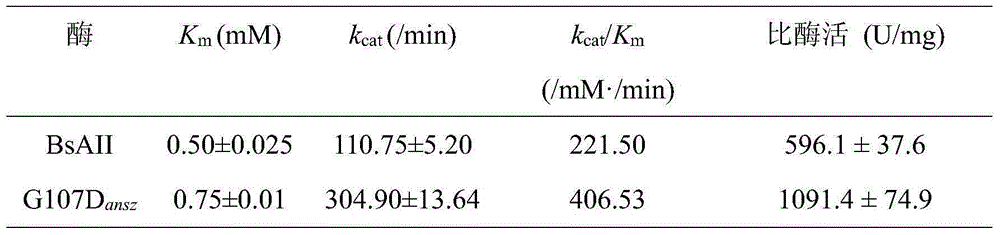
The invention discloses an L-asparaginase mutant with the improved enzyme activity and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. According to the L-asparaginase mutant, on the basis of amino acid shown in the SEQ ID NO.2, the 107th glycine is mutated into aspartic acid. The obtained mutant is expressed in bacillus subtilis, fermentation is performed in a shake flask for 24 h and then the enzyme activity is 961 U / mL; the enzyme activity of the mutant is improved by 80%, the appetency of a substrate is decreased by 50% compared with protoenzyme, the catalytic efficiency is improved by 84%, and meanwhile the specific enzyme activity is improved by 83%. According to the L-asparaginase mutant, it is shown that the 107th amino acid residue has a great influence on the enzyme catalytic action, a certain foundation is provided for research on the enzyme catalytic mechanism, and the enzyme industrial application potential is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Induction and stabilization of enzymatic activity in microorganisms
ActiveUS7531343B2Improve stabilityCommercially useful levelBacteriaHydrolasesMicroorganismNitrile hydratase activity
The present invention is directed to methods for inducing desired activity in enzymes or microorganisms capable of producing the enzymes. The invention is further directed to methods of stabilizing activity in microorganisms. In specific embodiments, the invention provides methods for inducing and stabilizing nitrile hydratase activity, amidase activity, and asparaginase I activity. The invention further provides compositions comprising enzymes or microorganisms having induced and / or stabilized activity.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
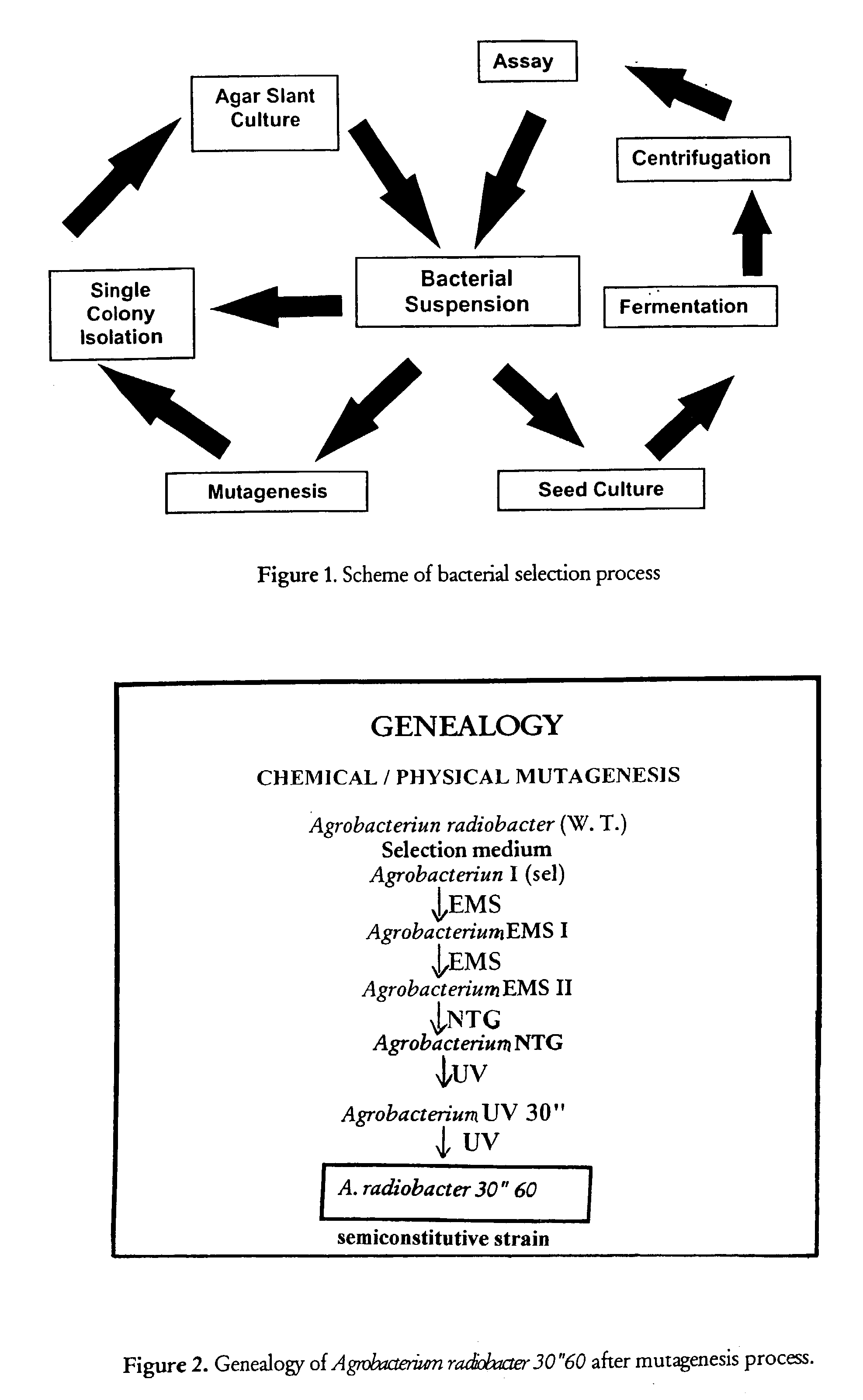
Micro-organism possessing enantioselective and regioselective nitrile hydratase/amidase activities
InactiveUS20030049807A1Improve enzymatic activityBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismRegioselectivity
The present invention is concerned with new micro organisms, preferably mutagenised, belonging to the genus Agrobacterium radiobacter able to convert nitriles and / or amides into their respective acids, in addition to conversion processes utilising said micro-organisms.
Owner:IST BIOCHIM ITALANO GIOVANNI LORENZINI
Nucleic acid fragments encoding nitrile hydratase and amidase enzymes from comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D and recombinant organisms expressing those enzymes useful for the production of amides and acids
The invention relates to the isolation, sequencing, and recombinant expression of genes encoding either a nitrile hydratase (NHase) or amidase (Am) from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D, where the NHase is useful for catalyzing the hydration of nitriles to the corresponding amides, and the amidase is useful for hydrolysis of amides to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Also provided are transformed host cells containing polynucleotides for expressing the nitrile hydratase or amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Enzymes and micro organisms with amidase activity which hydrolyze polyamides
The present invention relates to a process for the enzymatic hydrolysis of polyamides 6.6 to give adipic acid monomers and hexamethylenediamine monomers. The present invention further relates to an enzyme with amidase activity particularly towards substrates of the oligomer type derived from PA 6.6 and / or PA 6, said enzyme being characterized in that it consists of a peptide sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1 in the attached sequence listing and / or at least one polypeptide homologous to this sequence. The invention further relates to the DNA coding for said enzyme and to the biological precursors thereof The invention further relates to the microorganisms capable of producing this enzyme and to the hydrolysis process in which this enzyme and / or these microorganisms are applied.
Owner:RHONE POULENC FIBERS & POLYMERES
Asparaginase mutant with enhanced enzyme activity
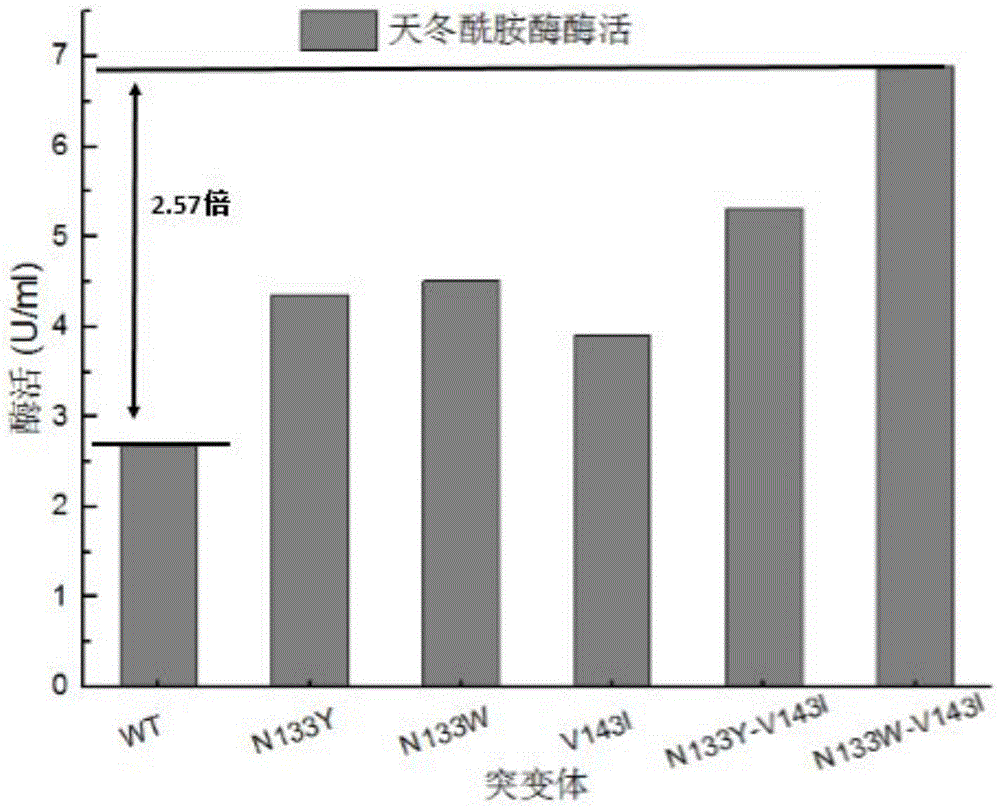
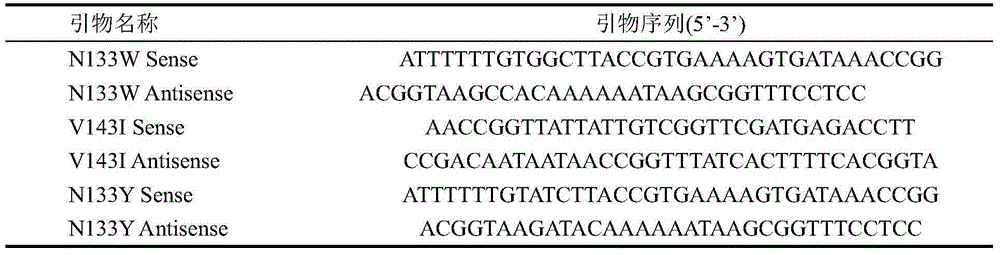
The invention discloses an asparaginase mutant with enhanced enzyme activity, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the asparaginase mutant, hydrophilic amino acid asparaginate and valine which are contained in an asparaginase molecule are mutated into tyrosine, tryptophan and isoleucine which have high hydrophobicity in a site-specific mutagenesis mode, so that the hydrophobicity inside the asparaginase molecule is changed, the enzyme activity, which is expressed by a strain, of asparaginase is remarkably improved, and the enzyme activity of the asparaginase is enhanced by 2.57 times. The improved strain is remarkably enhanced in enzyme producing capacity, more suitable for industrial application, reduced in production cost and improved in production efficiency.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving trypsin activity through artificially-designed self-activated leading peptide sequence
ActiveCN106893700AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease productionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiHeterologousPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a method for improving trypsin activity through an artificially-designed self-activated leading peptide sequence and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Trypsin of an artificial self-activated leading peptide sequence TPAPPSDDLGTFDDDDK is fused at an expression N end of a pichia pastoris engineered strain constructed by the method. Trypsin activity (trypsin amidase activity) of the yeast engineered strain GS115-Sedeif reaches 156U.mL-1, and esterase activity is 15015.8U.mL-1 (BAEE serving as a substrate), which are 1.82 times and 3.29 times of strain trypsin activity before modification. By the method, the key problem of low trypsin heterogeneous expression is solved. By applying the recombinant strain to produce trypsin, the method has the advantages of high yield, simplified fermentation process and convenience in industrial application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-efficient expression and application of amidohydrolase
The invention relates to the clone of amidohydrolase, and the construction, zymoprotein expression and industrial application of engineering bacteria, belongs to the field of bioengineering technology and mainly aims to solve the problems that amidohydrolase produced by natural bacteria is low in enzyme activity, low in bacterial concentration and difficult for production application. On the basis that the hydrolase is produced by fermenting Delftiatsuruhatensis in Delftia, an amidohydrolase gene is cloned to establish a full set of process of the fermentation, and inducible expression, and industrial production of the Escherichia coli gene engineering bacteria. Through the gene engineering modification, the amidase activity is over 3000 u / l, much higher than 300 u / l of the original strain; the actual application shows that the enzyme has a wide application scope, can be applied the production of side chains of statins, the production cost is greatly reduced and the realization of green chemistry is promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Amidase and coding gene, recombinant carrier, recombinant strain and application thereof
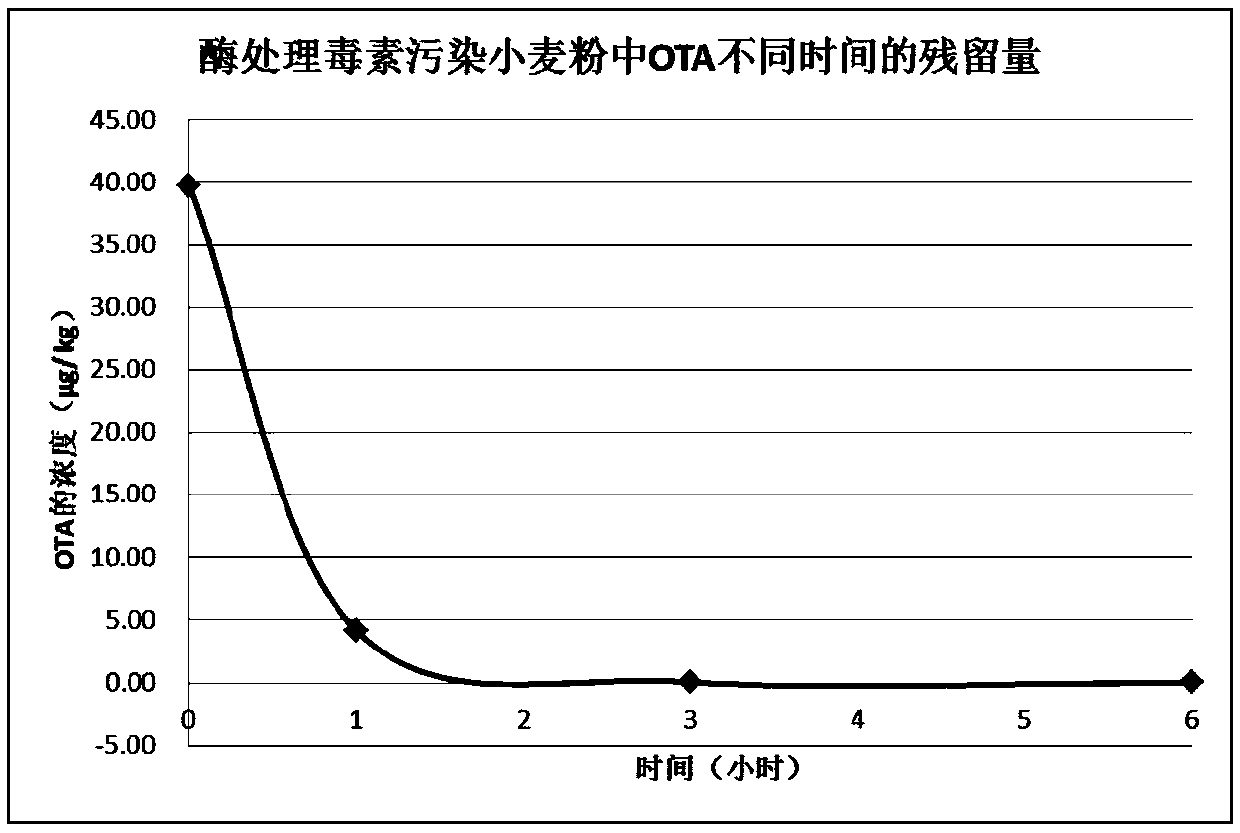
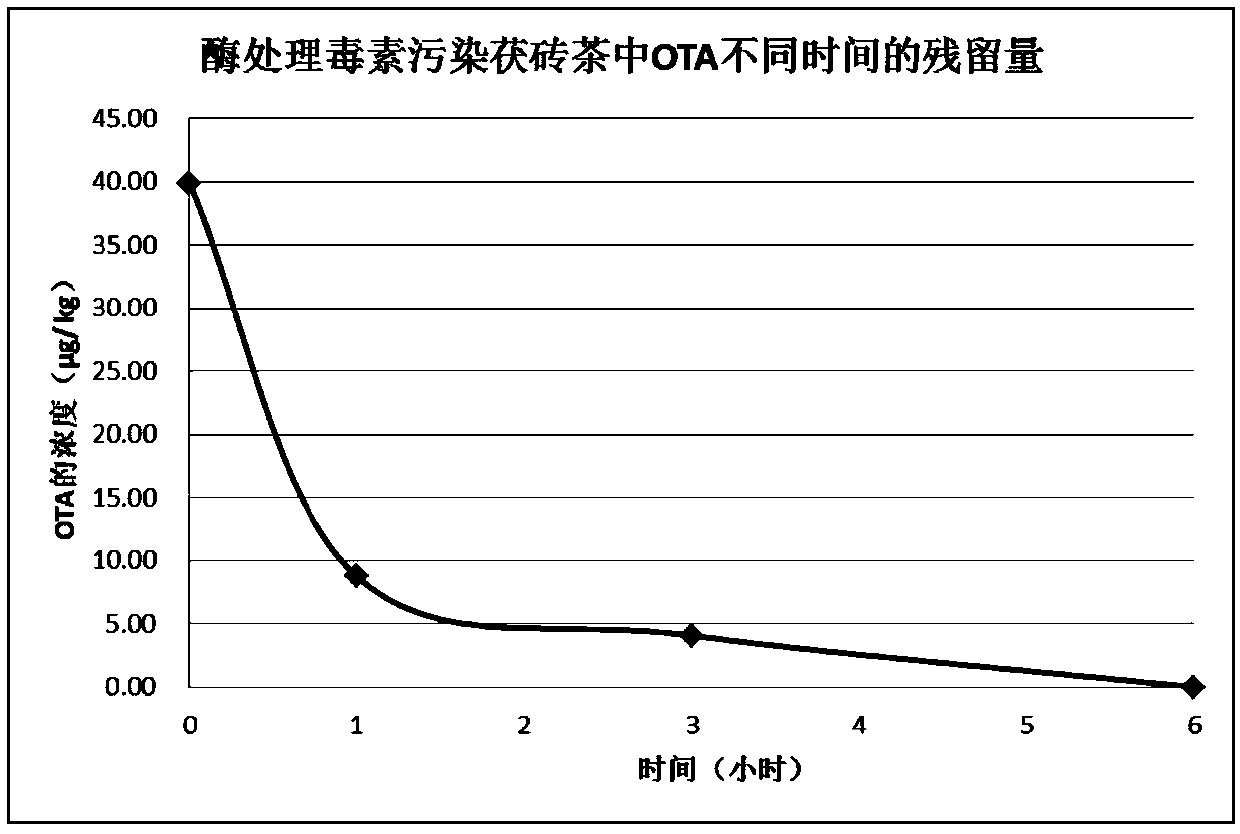
The invention provides amidase and a coding gene, recombinant carrier, recombinant strain and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The invention provides theamidase and the coding gene thereof, and also provides appropriate pH of the amidase and an application of the amidase to hydrolysis of ochratoxin and detoxifying of ochratoxin of foods. Under the room temperature condition, the amidase is used for treating ochratoxin A in a buffer system of which the pH is 7.3 for 2 minutes, the degradation rate of the ochratoxin A achieves 100%, and the degradation efficiency is unprecedented in the field.
Owner:江苏奥迈生物科技有限公司
Inhibitor of tricycro beta lactamase and preparation method
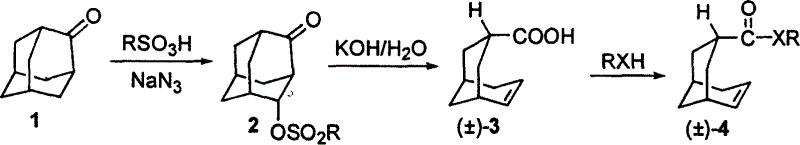
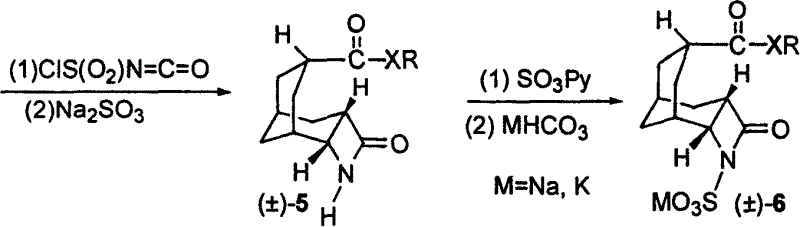
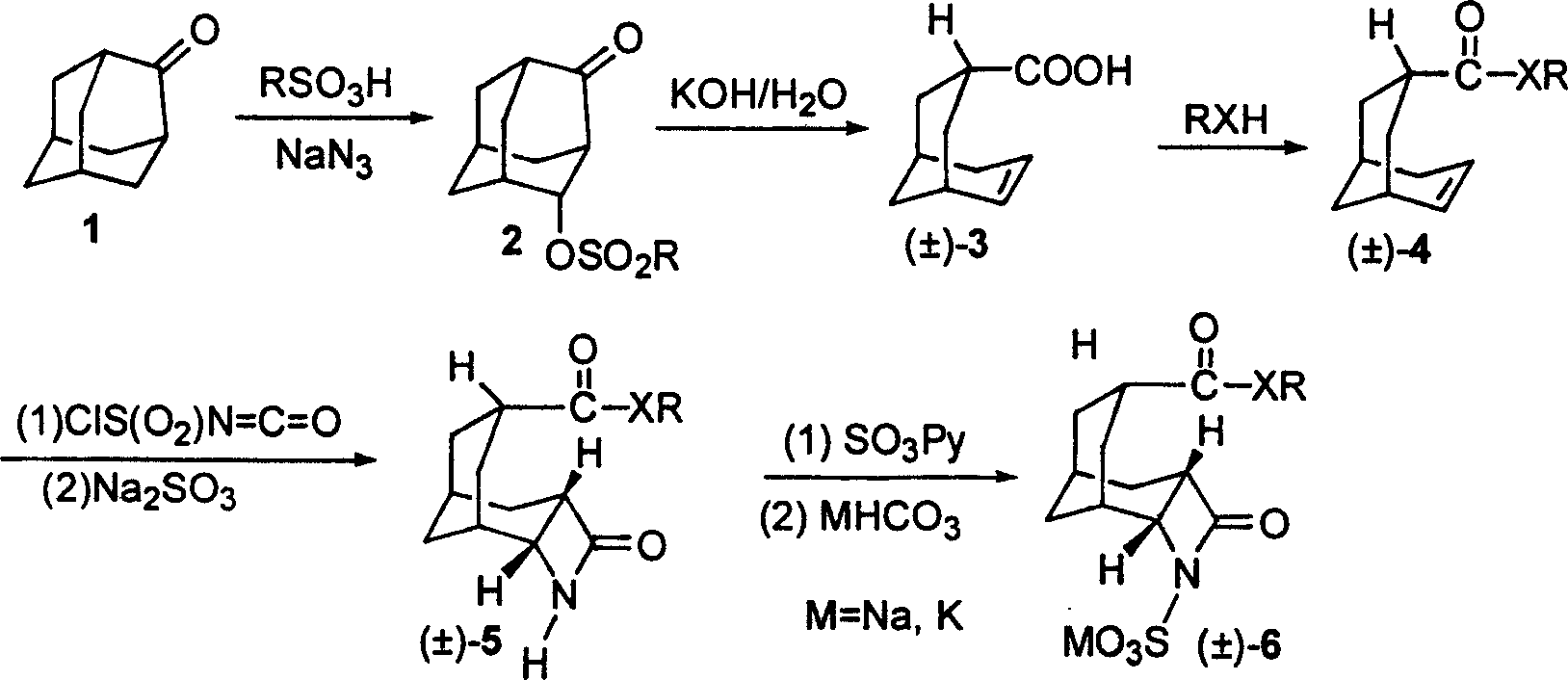
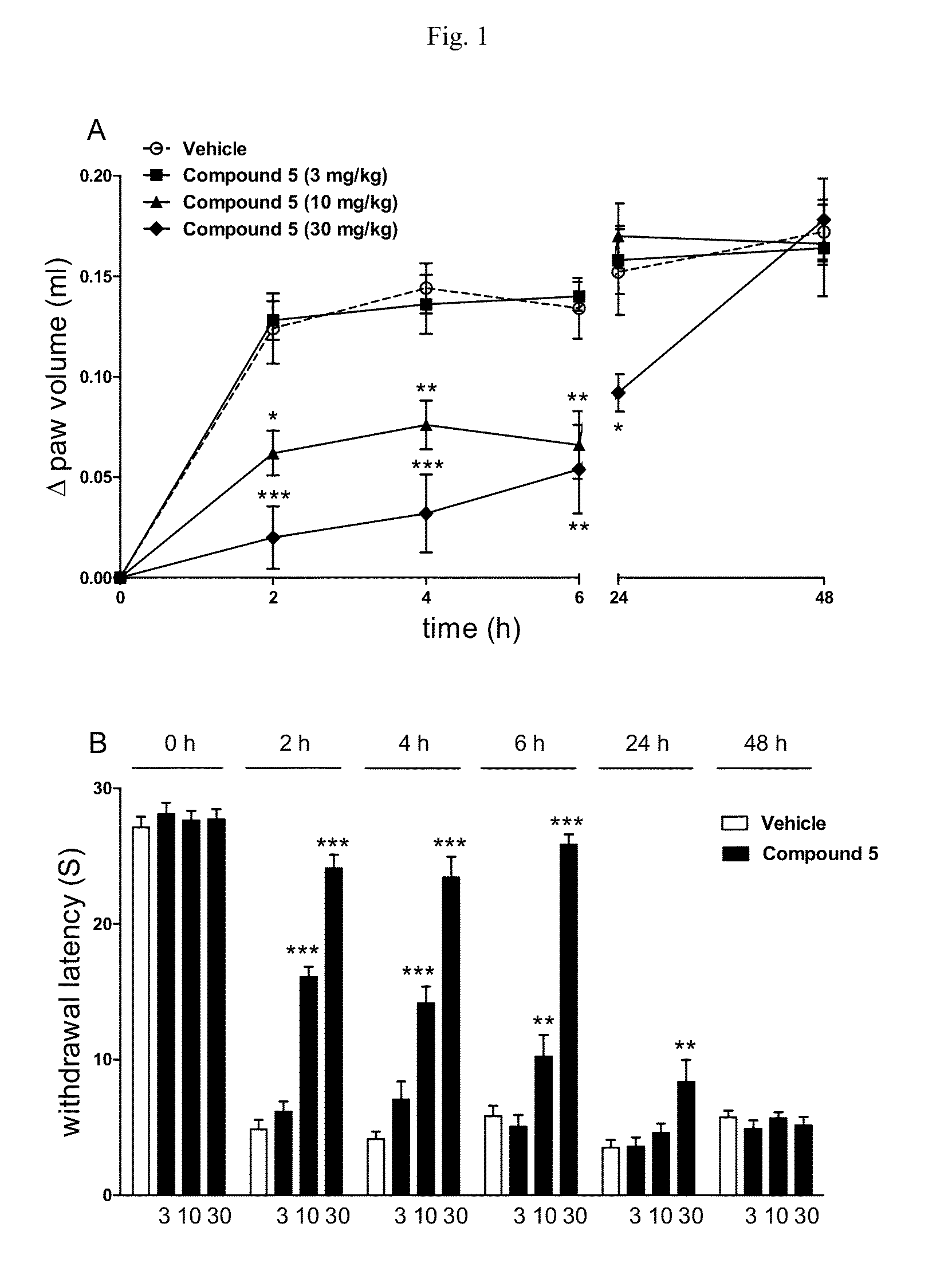
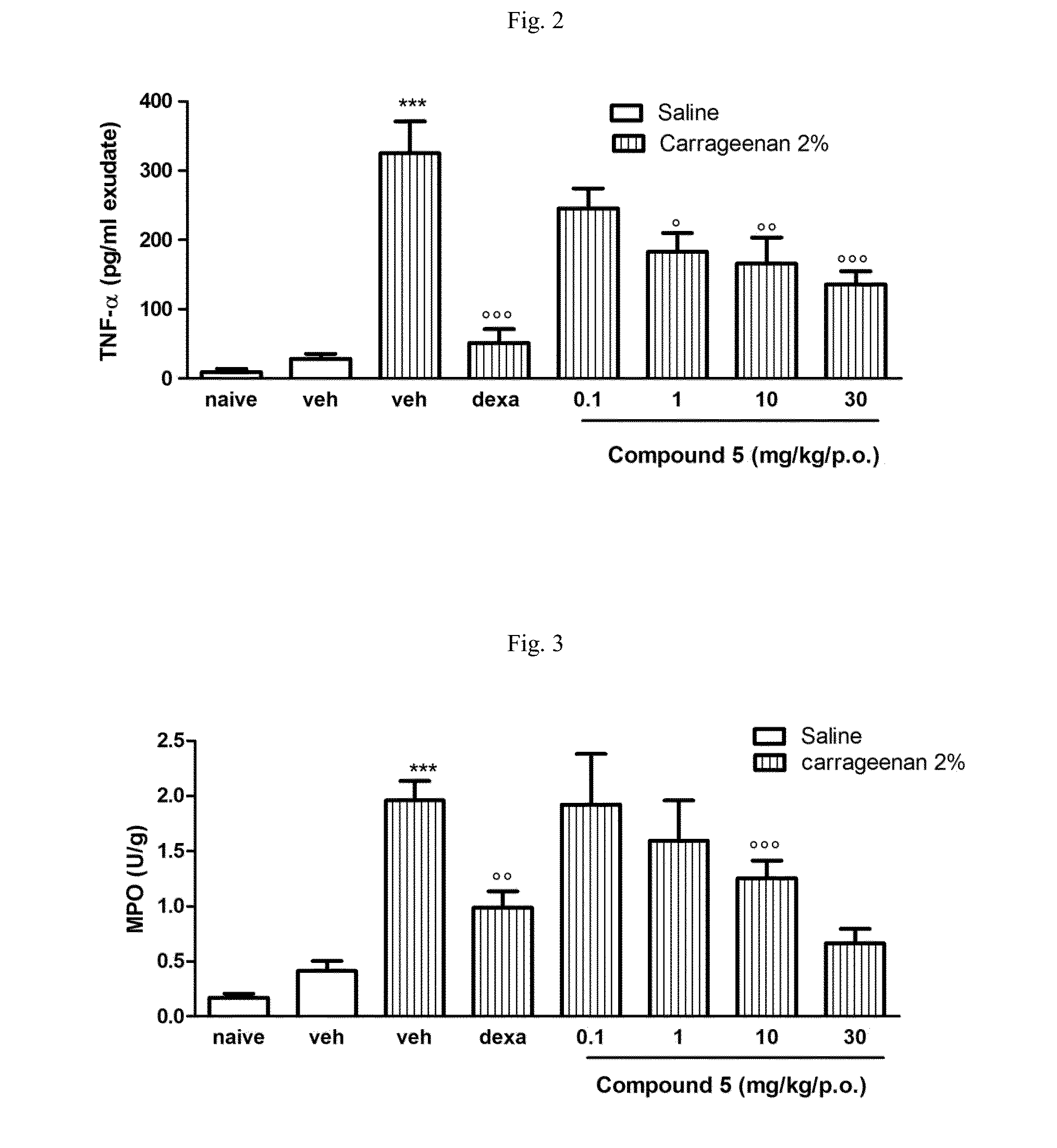
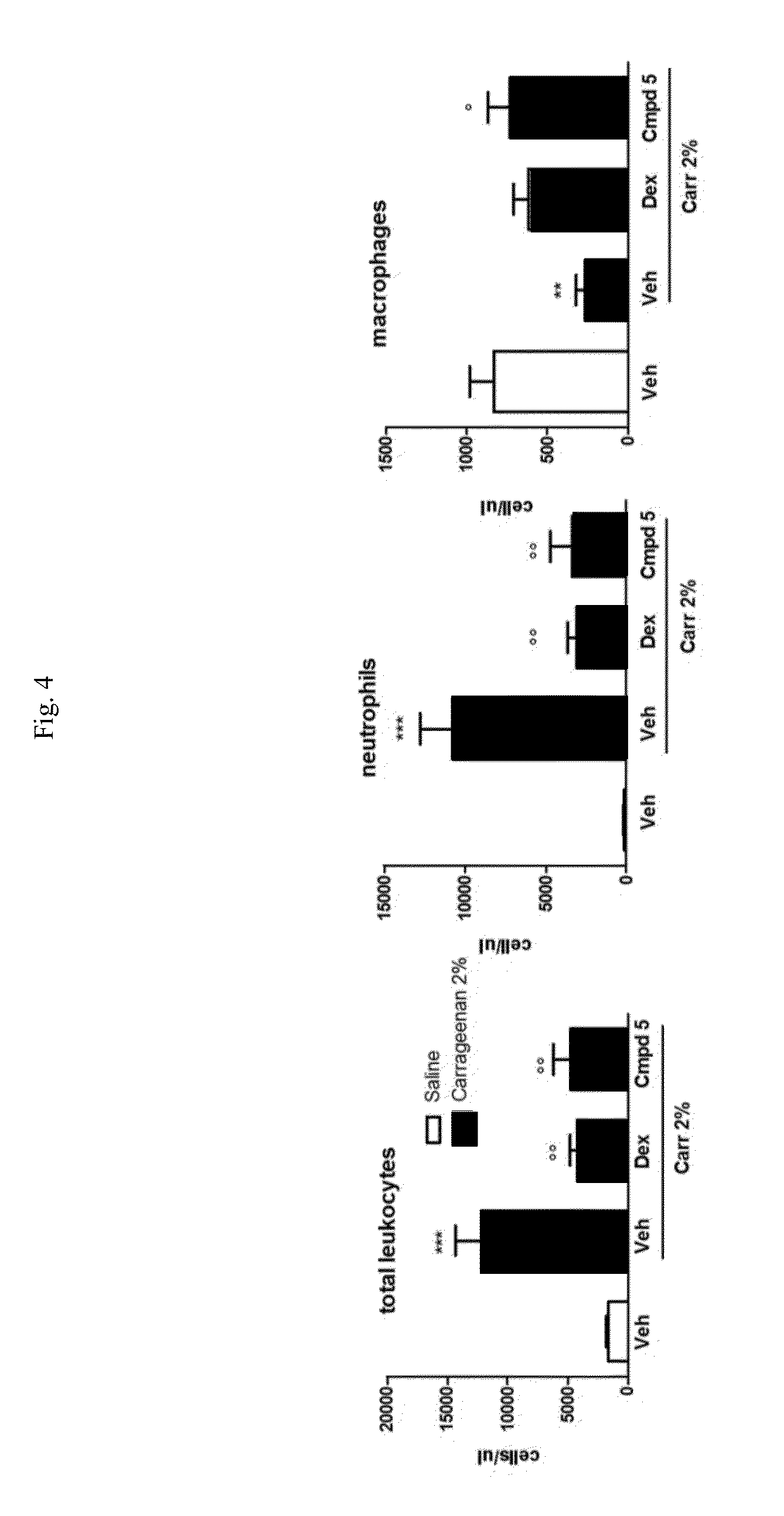
A tricyclo-beta-lactamase depressant is prepared through preparing 4-sulfonyloxy adamantane-2-one, preparing bicyclo [3,3,1]-nonyl-6-enyl-3-formic acid [(+ / -)-(3)], preparing bicyclo [3,3,1] nonyl-6-enyl-3-formate or amide (+ / -)-(4), preparing 4-oxy-3-azatricyclo [5,3,1,02.5] undecane-9-formate or amide (+ / -)-(5), and preparing 4-oxy-3-azatricyclo [5,3,1,02.5] undecane-9-formate or amide-N-sulfonate (+ / -)-(6) solid.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Carbamate derivatives of lactam based n-acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA) inhibitors
Described herein are compounds and pharmaceutical compositions which inhibit N-acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA). Described herein are methods for synthesizing the compounds set forth herein and methods for formulating these compounds as pharmaceutical compositions which include these compounds. Also described herein are methods of inhibiting NAAA in order to sustain the levels of palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) and other N-acylethanolamines (NAE) that are substrates for NAAA, in conditions characterized by reduced concentrations of NAE. Also, described here are methods of treating and ameliorating pain, inflammation, inflammatory diseases, and other disorders in which modulation of fatty acid ethanolamides is clinically or therapeutically relevant or in which decreased levels of NAE are associated with the disorder.
Owner:FOND INST ITAL DI TECH +1
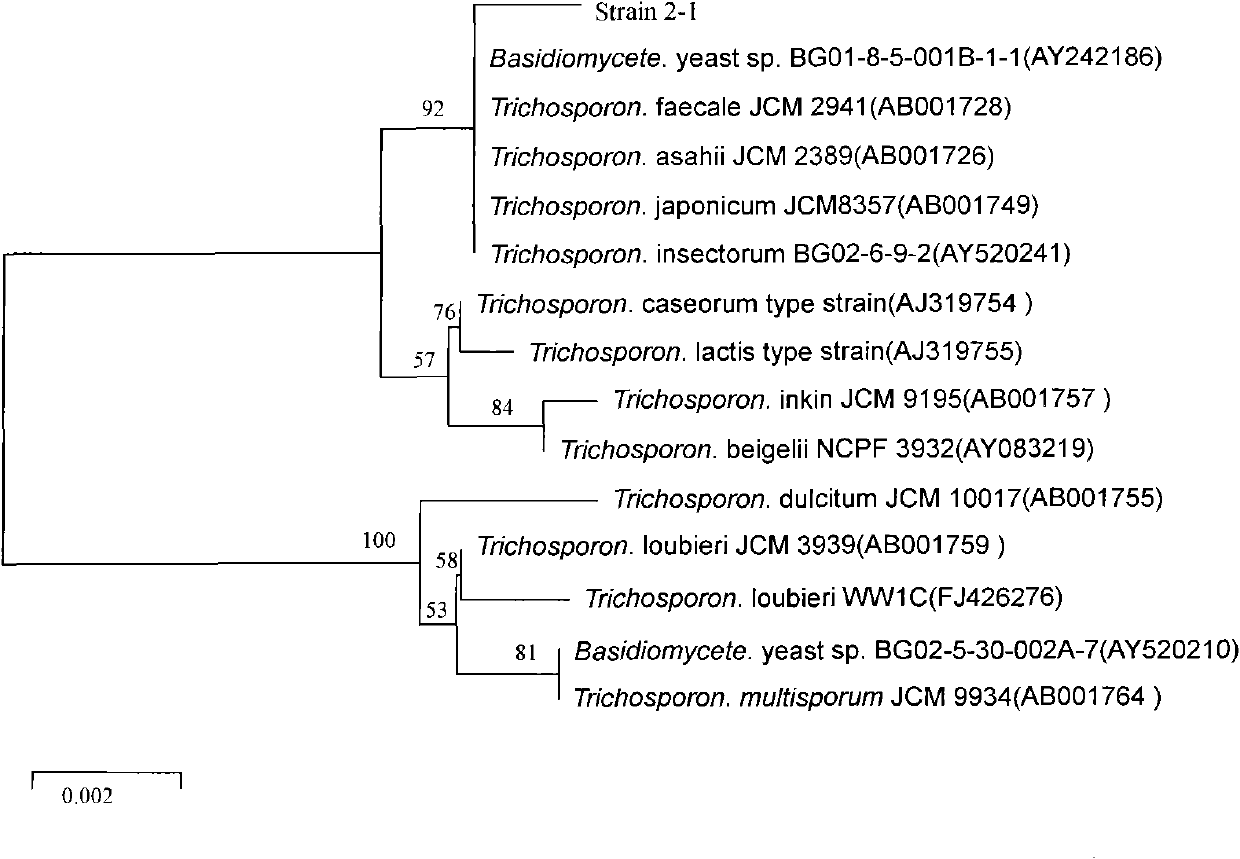
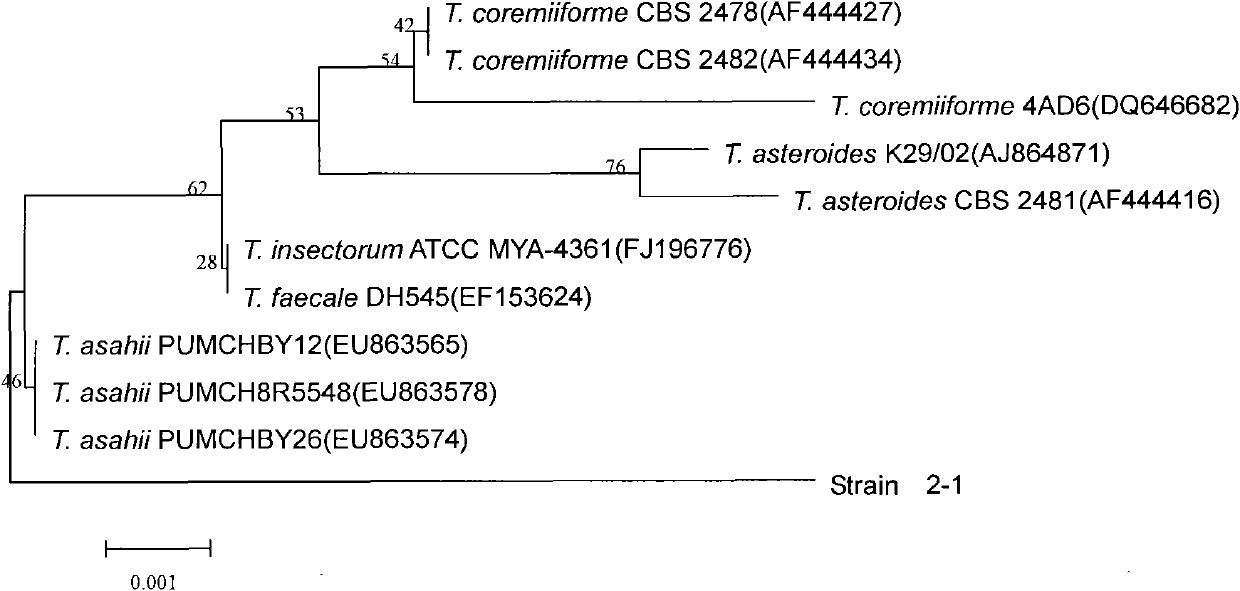
Trichosporon asahii 2-1 and application thereof in preparing acrylic acid
ActiveCN101768555AImprove conversion rateProcess greenFungiHydrolasesChemical synthesisVirulent characteristics
The invention provides an acrylic amidase strain-Trichosporon asahii 2-1 and application thereof in preparing an acrylic acid. The Trichosporon asahii 2-1 is collected in the China center for type culture collection of which the address is Mountain Luojia Wuhan University in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, 430072, with a collection date of January 19, 2010, and a collection number CCTCC No. is M2010017. The invention obtains a new strain producing amidase through screening and a mutagenesis strain with obviously enhanced amidase activity through mutagenesis improvement, prepares the acrylic acid by a biological method with the mutagenesis strain so as to replace a chemical synthesis method, and has the advantages of high conversion rate, environmental protection, green process, and the like. meanwhile, the acrylic amidase strain provides a most economic and effective method for treating aliphatic nitrile and amide compounds contained in industrial waste water because the strain can hydrolyze a highly virulent aliphatic nitrile compound and acrylic amide into acid substances with less virulence, thereby also having important practical significance in environmental improvement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Pantoea amidase, gene, vector, engineering bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a Pantoea amidase, a gene, a vector, an engineering bacterium and an application thereof in preparation of 1-cyancyclohexylacetic acid through biological catalysis of 1-cyancyclohexylacetamide. The amino acid sequence of the amidase is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. A synthesis technology of 1-cyancyclohexylacetic acid through biological catalysis by using the amidase is reported in the invention for the first time, and the technology has the substantial advantages of small catalyst dosage (2g / L), high substrate concentration (100g / L), short reaction time (20min), and high product conversion rate reaching 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Marine microorganism fermentation production method for low temperature gamma-lactamase
InactiveCN104630195AQuality is not affectedIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesMicroorganismGamma-lactamase
The invention relates to a marine microorganism fermentation production method for low temperature gamma-lactamase. The method comprises the following steps: firstly activating the strain used for producing the gamma-lactamase, performing cold acclimation step by step and growing the strain in low temperature environment, performing the enlarged cultivation step by step on the cold acclimated gamma-lactamase producing strain at 10-16 DEG C, inoculating the producing strain to the liquid fermentation medium according to the ratio of 3-9% of the volume of the fermentation liquor, cultivating for 72-144h at 10-16 DEG C to obtain the low temperature gamma-lactamase, further concentrating, separating and purifying the collected crude enzyme liquid according to the different requirements and different use objects for preparing the enzyme preparation different in activity, purity and dosage form. The low temperature gamma-lactamase prepared by the method has high enzyme activity and high catalytic efficiency under a low temperature, the enzyme preparation is simple, convenient and fast in application operation, and broad industrial development value and market application advantage can be achieved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
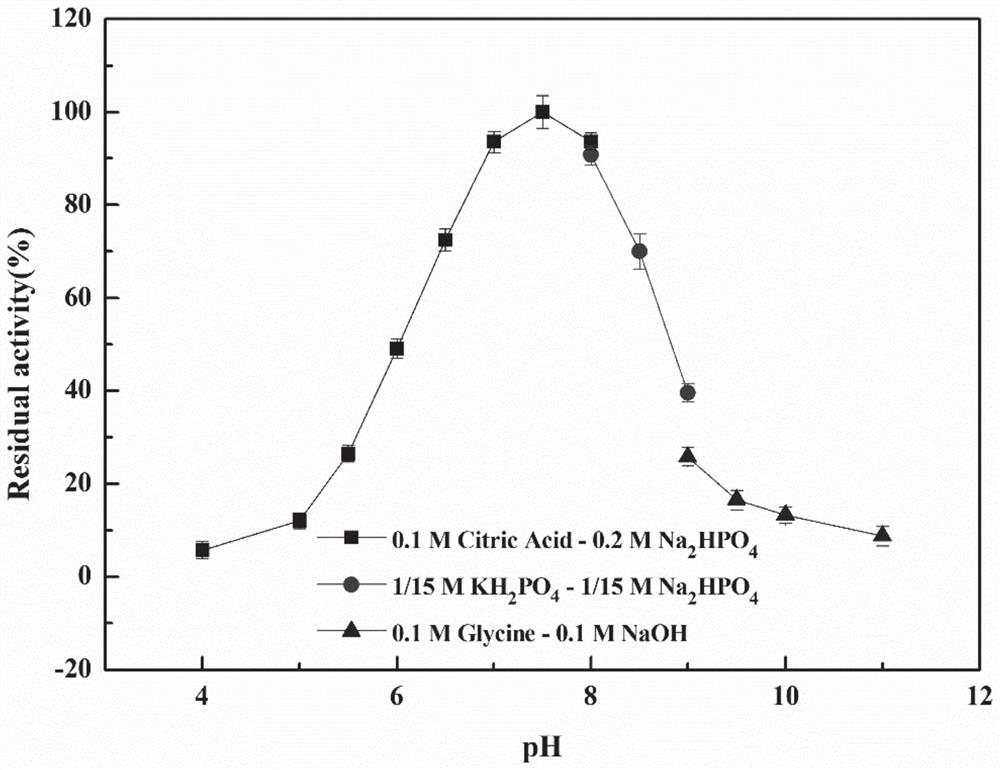
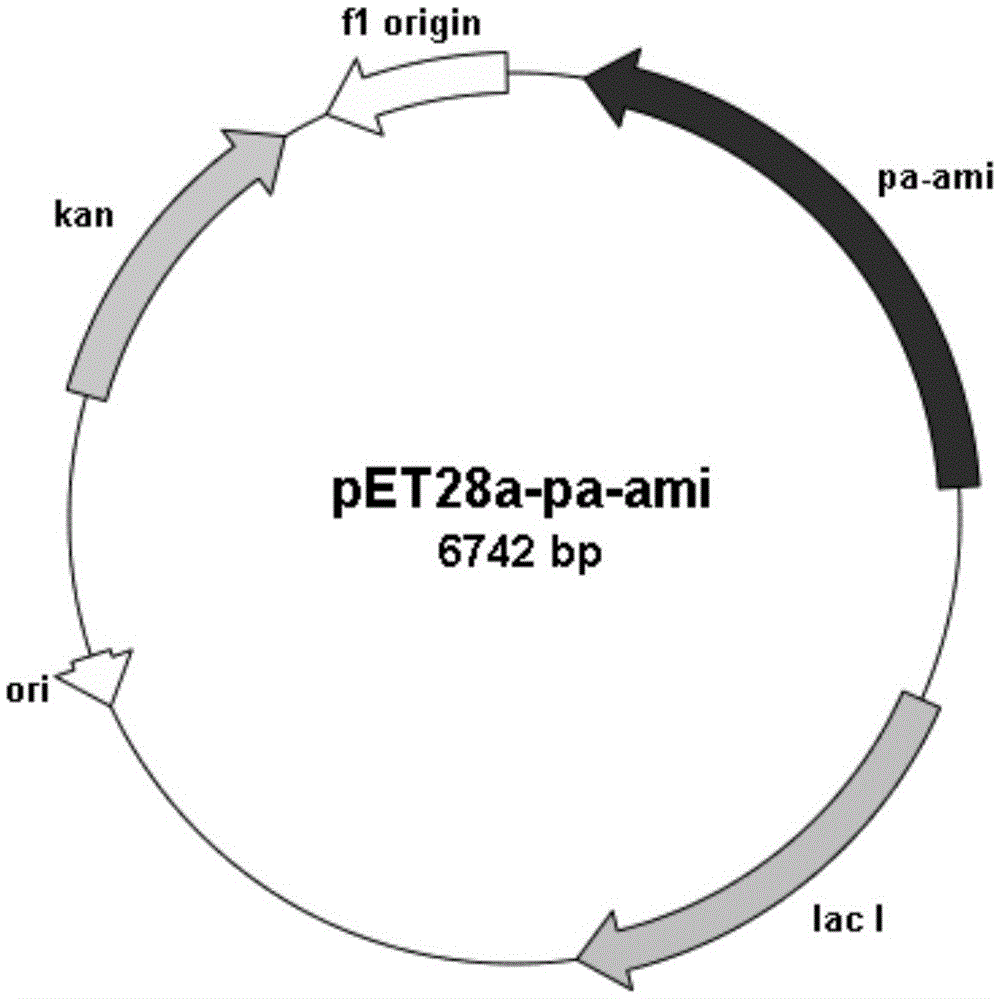
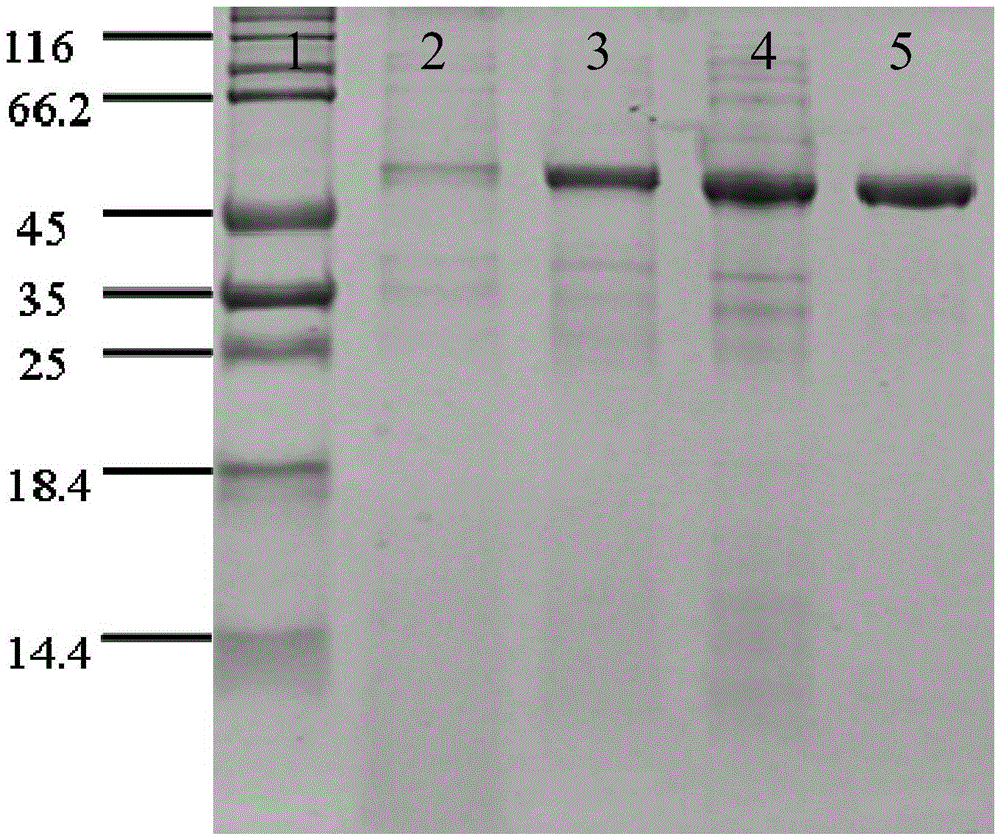
(-)-[gamma]-lactamase, gene, mutant, vector as well as preparation method and application of (-)-[gamma]-lactamase
ActiveCN105950595AHigh optical activityMild reaction conditionsHydrolasesFermentationMutantSubstrate concentration
The invention relates to (-)-[gamma]-lactamase, a gene and a mutant of the (-)-[gamma]-lactamase, a recombinant expression plasmid and a recombinant expression transformant containing the gene and the mutant, a preparation method of the (-)-[gamma]-lactamase and an application of the (-)-[gamma]-lactamase in preparing (+)-[gamma]-lactam. Compared with the prior art, the (-)-[gamma]-lactamase disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being high in enzymatic activity and good in substrate concentration tolerance; the (+)-[gamma]-lactam, which is prepared through enzymatic catalysis, has the advantages of being mild in reaction condition, high in substrate concentration, low in catalyst dosage and the like; therefore, the (-)-[gamma]-lactamase has a good application prospect in industrial production of the (-)-[gamma]-lactamase which is an intermediate product of carbocyclic nucleoside drugs.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
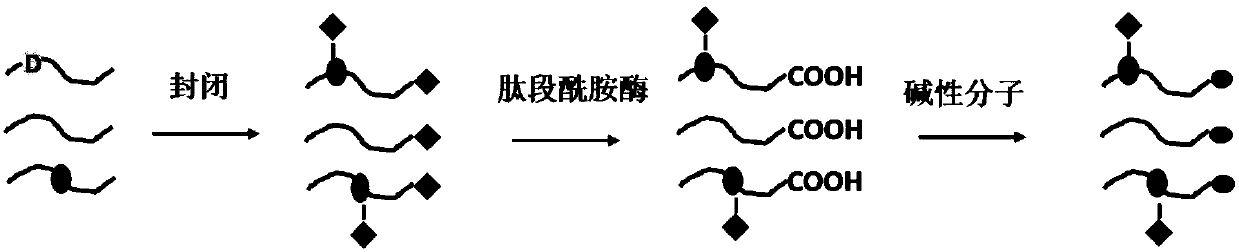
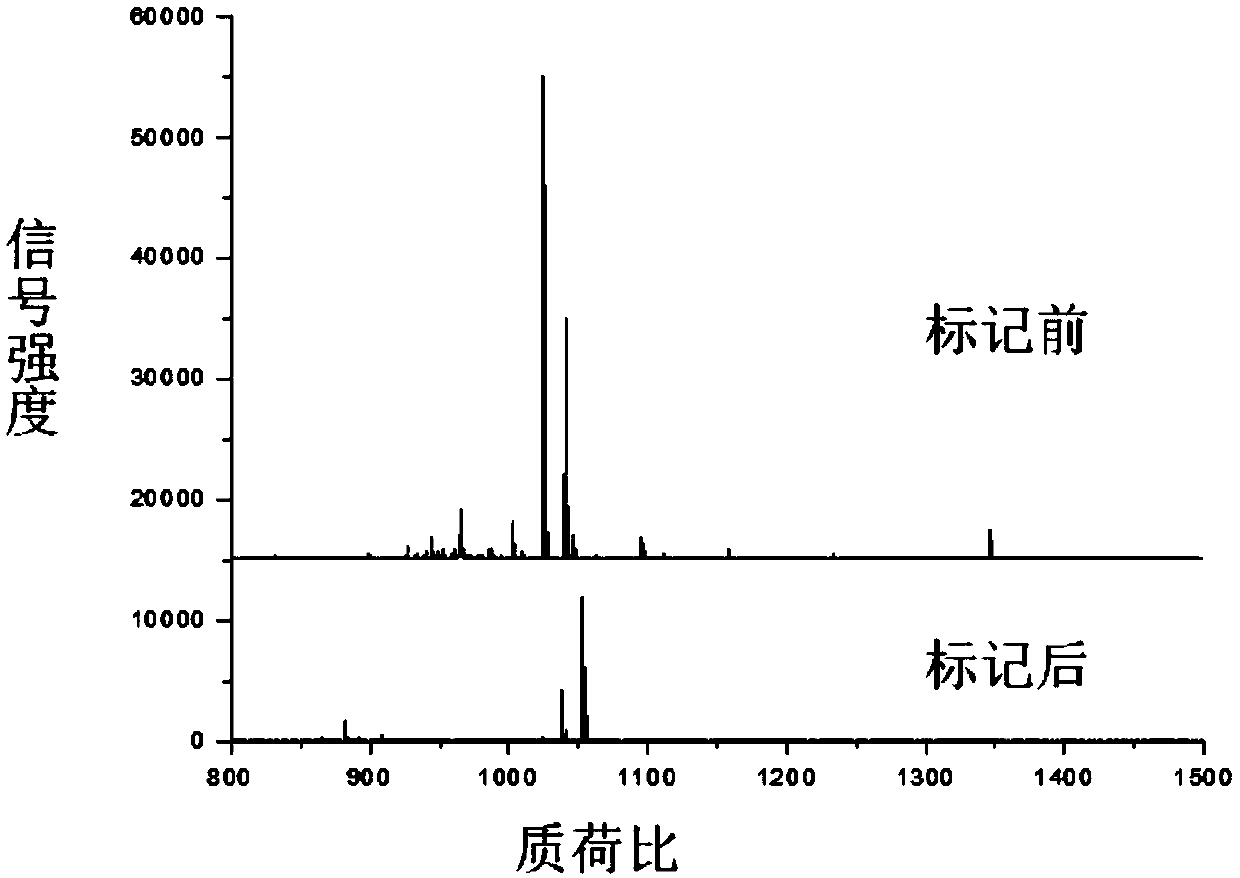
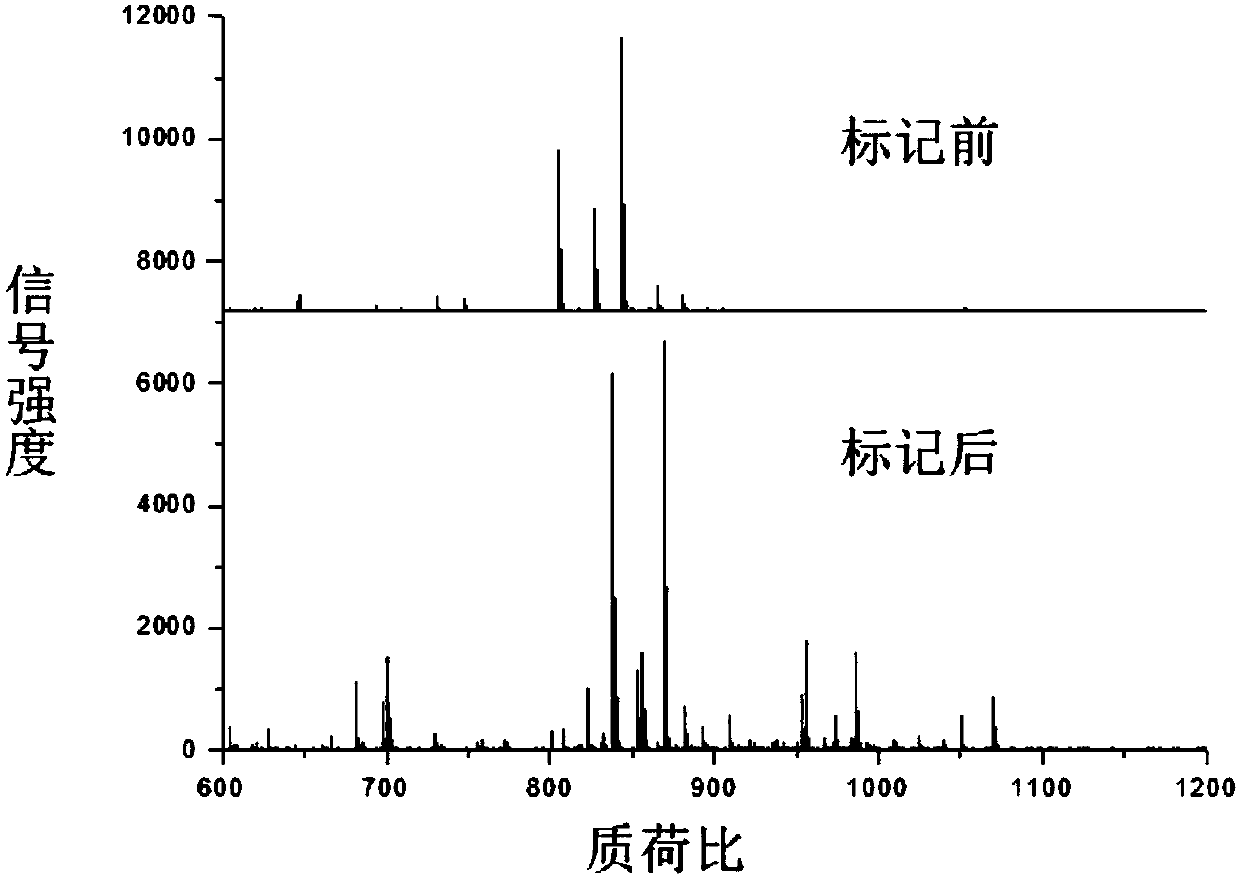
Method for improving mass spectrum fragmentation efficiency and response based on peptide fragment C-terminal chemical derivation
ActiveCN111208237AImprove reaction efficiencyNo hydrolysisComponent separationCarboxyl radicalSide chain
The invention relates to a method for improving mass spectrum fragmentation efficiency and response based on peptide fragment C-terminal chemical derivation. The method comprises three steps of reaction: firstly, sealing carboxyl at the tail end of a peptide fragment C or carboxyl at the tail end of the peptide fragment C and carboxyl of side-chain glutamic acid or aspartic acid; then, using peptide fragment amidase for specific hydrolysis and exposing carboxyl at the tail end of the peptide fragment C; and finally, carrying out chemical derivation of alkaline molecules on the exposed C-terminal carboxyl. Alkaline molecules marked at the tail end of the peptide fragment C can increase the number of y ions in the secondary mass spectrum and improve the fragmentation efficiency and responseof the peptide fragment in the mass spectrum so that the method is applied to improve the detection sensitivity of polypeptide drug peptides.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
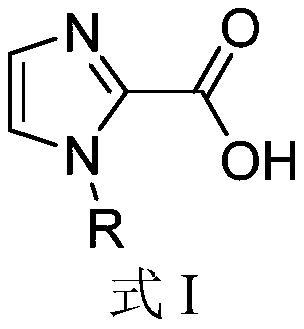
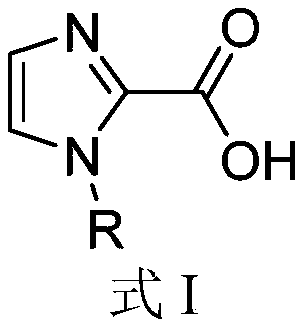
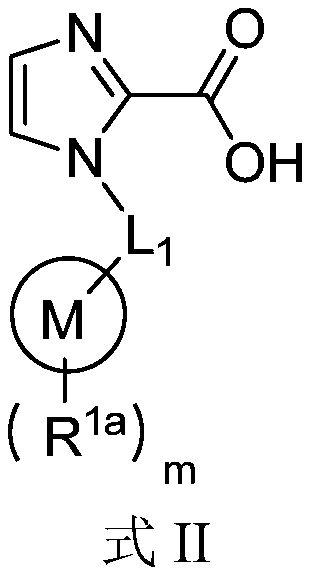
Application of 1-substituted-1H-imidazole-2-carboxylic acid compounds in preparation of metal beta-lactamase inhibitors
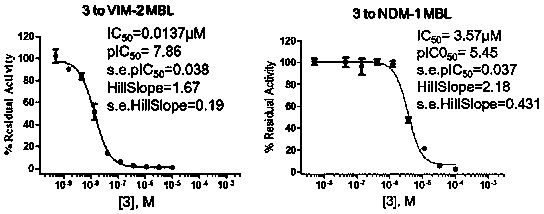
The invention relates to application of 1-substituted-1H-imidazole-2-carboxylic acid compounds in preparation of metal beta-lactamase inhibitors, and particularly discloses application of compounds shown in a formula I in preparation of metal beta-lactamase inhibitors or antibacterial combined medicines. Experiments prove that the compounds provided by the invention can be used for effectively inhibiting the activity of various MBL enzymes including VIM-2, NDM-1, IMP-1, VIM-1 and VIM-5; the compounds, especially the compounds 11, 13, 14, 29, 30, 34, 37 and 40, have an IC50 value of 2.13 [mu] Mor less on the VIM-2 type MBL enzymes, have a more significant inhibition effect than positive control drugs, and have very good potential in the preparation of MBL enzyme inhibitors. Meanwhile, thecompounds disclosed by the invention are combined with beta-lactam antibiotics, so that metal beta-lactamase generated by drug-resistant bacteria can be effectively inhibited, the antibacterial activity of the antibiotics is enhanced, and the compounds have a very good application prospect in preparation of antibacterial combined medicines.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation and use of 2-substituted-(S)-(3-mercapto-2-methylpropanoyl)-glycine derivatives
InactiveCN108117502AEasy to prepareMild reaction conditionsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCaptoprilX-ray
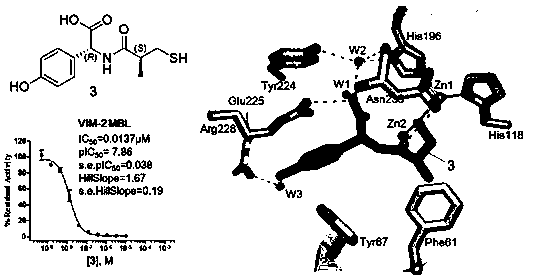
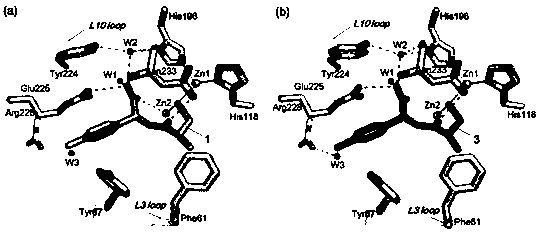
The invention provides a 2-substituted-(S)-(3-mercapto-2-methylpropanoyl)-glycine derivative with a structural formula represented by a formula I (shown in the description). The invention further provides a preparation process and use of the 2-substituted-(S)-(3-mercapto-2-methylpropanoyl)-glycine derivative. Pharmacodynamic tests prove that compounds has relatively good inhibitory activity to various metal beta lactamases (MBL), and particularly, a compound 3 has the optimal inhibitory activity and is remarkably superior to certain MBL small-molecule inhibitors such as captopril reported at present. X-ray crystal structure researches of compounds prove that the action mechanism between the compounds of the invention and MBL is characterized in that mercapto groups of the compounds are chelated with zinc ions at MBL active sites. Besides, antimicrobial activity tests prove that the compounds of the invention have very good bacteriostatic effect to multiple clinically separated superbacteria strains when being combined with beta-lactam antibiotic for use. The 2-substituted-(S)-(3-mercapto-2-methylpropanoyl)-glycine derivative has a clear and definite action mechanism and a remarkable pesticide effect, and new drug selection is likely to be provided for clinic.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
LPS Based Vaccines
The removal of the glycosidic phosphate from the reducing end of the derived LPS molecule creates an aldehydo functionality which causes the formation of an immunologically dominant neo-epitope. Conjugation to the reducing end of a carbohydrate molecule following removal of the glycosidic phosphate traps the reducing glucosamine residue in an open-chain form which surprisingly was found to dominate the immune response. We therefore modified our conjugation strategy to avoid this open-chain form, by utilising the amino functionality created by the isolated amidase activity from Dictyostelium discoideum, concomitant with a unique blocking and un-blocking strategy to protect the immunologically important phosphoethanolamine inner core residue. These antigenic structures are useful in producing vaccines and compounds helpful in combating Gram-negative bacteria. Also described are specific structures of the carbohydrate molecules derived from a variety of Gram-negative bacteria, which when presented appropriately as a glycoconjugate will facilitate a functional immune response to the target core oligosaccharide region.
Owner:COX ANDREW D +3
Inhibitors of anandamide transport and their therapeutic uses
Nucleic acid and polypeptide sequences corresponding to FLAT, a partly cytosolic variant of the intracellular anandamide-degrading enzyme, fatty acid amide hydrolase-1 (FAAH-1), are provided. FLAT lacks amidase activity but binds the endocannibinoid anandamide and facilitates its transport into cells. A chemical scaffold for the inhibition of anandamide transport is identified. Compositions of the invention prevent anandamide internalization in vitro, interrupt anandamide deactivation in vivo, and cause profound CB1 cannabinoid receptor-mediated analgesia in a mouse model of inflammatory pain. Accordingly, the invention also provides methods, and pharmaceutical compositions for treating conditions in which the modulation of anandamide transport would be of benefit.
Owner:FOND INST ITAL DI TECH +1
3-hydroxycarboxylic acid production and use in branched polymers
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of a 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid from a 3-hydroxynitrile. More specifically, 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile is converted to 3-hydroxyvaleric acid in high yield at up to 100% conversion, using as an enzyme catalyst 1) nitrile hydratase activity and amidase activity or 2) nitrilase activity of a microbial cell. 3-Hydroxyvaleric acid is used as a substitute for ε-caprolactone in the preparation of highly branched copolyester.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Acrylamide-degrading self-cloning aspergillus oryzae
InactiveUS20150010676A1High activityEffectively and safely degradedHydrolasesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyAspergillus oryzae
Provided are self-cloning Aspergillus oryzae that expresses amidase without induction culture exhibiting high amidase degradation activity, and a method for reducing acrylamide in which this self-cloning Aspergillus oryzae is used. Self-cloning Aspergillus oryzae, which has a gene which codes a polypeptide with a specific amino acid sequence indicated in SEQ ID NO:1, or has a base sequence hybridizable to a complementary sequence of the gene encoding SEQ ID No:1 under stringent conditions, has a protein with amidase activity which the gene is expressed without induction culture, the process of reducing acrylamide by contact treatment with the above described self-cloning Aspergillus oryzae and acrylamide-containing matter, and a method of producing reduced acrylamide food or beverage.
Owner:UCC UESHIMA COFFEE CO LTD +1
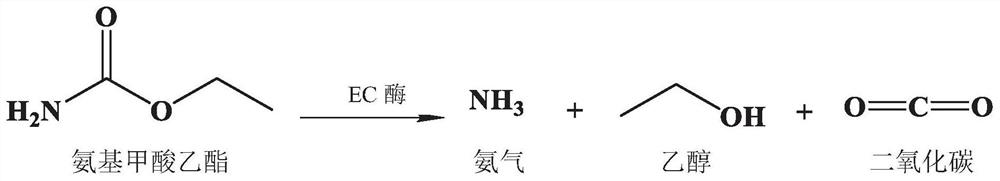
Ethyl carbamate hydrolase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN112342209AIncrease enzyme activityImprove toleranceHydrolasesBiofuelsAmidase activityEthyl ester
The invention discloses an ethyl carbamate hydrolase mutant and application thereof. The ethyl carbamate hydrolase mutant is obtained by mutation of an amidase gene of Agrobacterium tumefaciens d3, the amino acid sequence of wild amidase is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the ethyl carbamate hydrolase mutant is obtained by mutation of at least one site of R94P, I97L, S177C or G195A of the wild amidase.The amidase from the Agrobacterium tumefaciens d3 is obtained by screening, the residual enzyme activity is higher than 90% when the ethanol concentration is between 0% and 20%, the enzyme activity isquickly reduced when the ethanol concentration is higher than 25% , and the amidase shows excellent tolerance to low-concentration ethanol. Through semi-rational transformation, a mutant library with21 point mutations is constructed, four mutation sites (R94P, I97L, S177C and G195A) with improved enzyme activity are screened from the mutant library, and the enzyme activity of a combined mutant strain I97L / G195A is improved by 5.2 times and is improved to 2442U / L from original 395U / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Amidases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The present invention provides amidases, polynucleotides encoding the amidases, methods of making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention provides enzymes having secondary amidase activity, e.g., having activity in the hydrolysis of amides, including enzymes having peptidase, protease and / or hydantoinase activity. In alternative aspects, the enzymes of the invention can be used to used to increase flavor in food (e.g., enzyme ripened cheese), promote bacterial and fungal killing, modify and de-protect fine chemical intermediates, synthesize peptide bonds, carry out chiral resolutions, hydrolyze Cephalosporin C. The enzymes of the invention can be used to generate 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA) and semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotics, including caphalothin, cephaloridine and cefuroxime. The enzymes of the invention can be used as antimicrobial agents, e.g., as cell wall hydrolytic agents. The invention also provides a fluorescent amidase substrate comprising 7-(epsilon-D-2-aminoadipoyladipoylamido)-4-methylcoumarin.
Owner:DIVERSA
Novel amidase, gene for the same, vector, transformant, and method for production of optically active carboxylic acid amide and optically active carboxylic acid by using any one of those items
The present invention has its object to provide a novel polypeptide having amidase activity to selectively hydrolyze S-enantiomer in racemic nipecotamide, a DNA encoding the polypeptide, a vector containing the DNA, a transformant transformed with the vector, and a method for producing an optically active carboxylic acid amide and an optically active carboxylic acid in which a racemic carboxylic acid amide is hydrolyzed with the polypeptide or the transformant.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Yeast engineering bacteria for producing trypsin in high-yield manner and construction method of yeast engineering bacteria
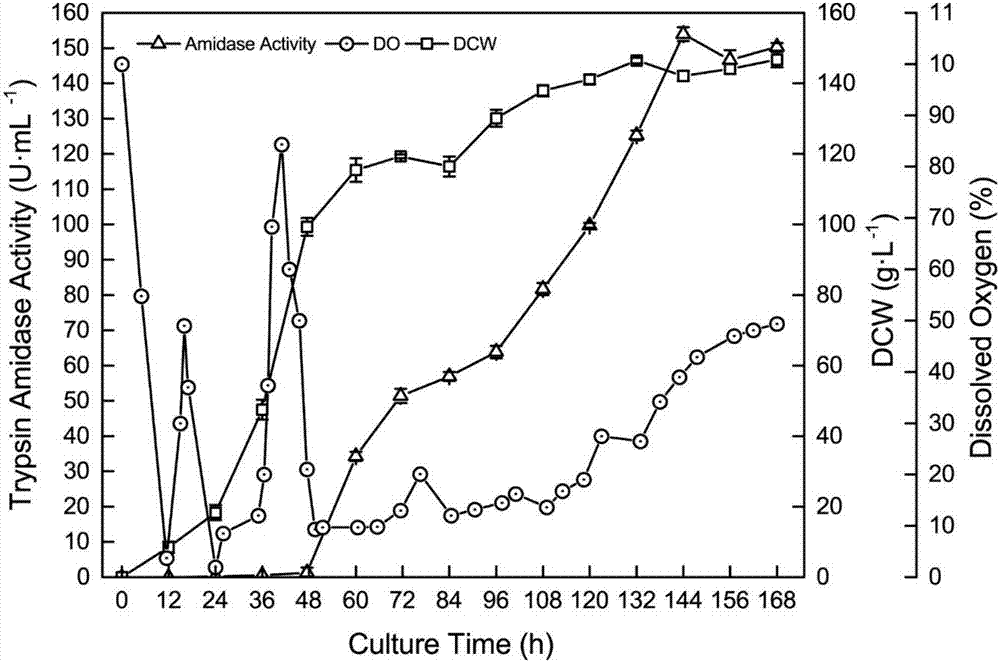
InactiveCN104328103AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesTrypsinogen activationAmidase activity
The invention discloses a yeast engineering bacteria for producing trypsin in a high-yield manner and a construction method of the yeast engineering bacteria, belonging to the genetic engineering field. According to the constructed yeast engineering bacteria, trypsin of thioredoxin is blended at the front expression end, and four aspartic acids and lysine (D4K) are inserted between the thioredoxin and the trypsin; the trypsin amidase activity (BAPNA (nitroaniline)) is 47.4U / mL and the esterase activity (BAEE (N-benzoyl-L-arginine-ethylester)) is 2667U / mL, the problems of trypsinogen activation and low yield are solved, and the trypsin production method by the yeast engineering bacteria has the advantages of high yield, simplified process and industrial application convenience.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
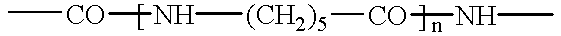








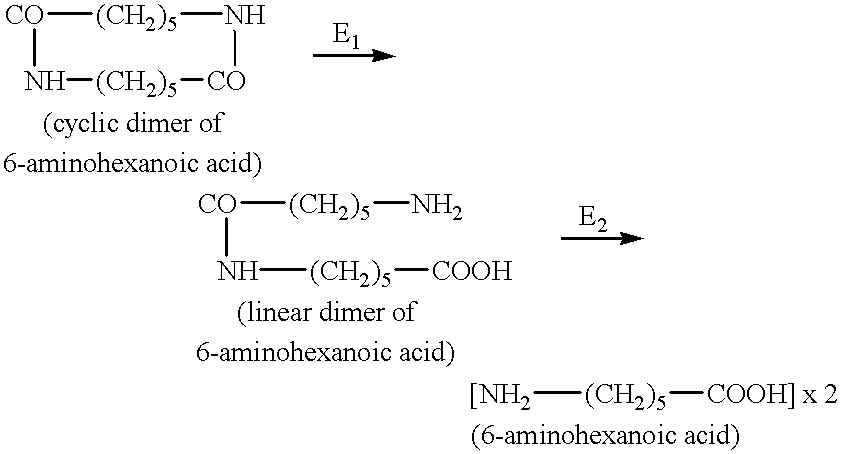






![(-)-[gamma]-lactamase, gene, mutant, vector as well as preparation method and application of (-)-[gamma]-lactamase (-)-[gamma]-lactamase, gene, mutant, vector as well as preparation method and application of (-)-[gamma]-lactamase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/dcdbcdad-834c-4ae5-82a7-74e96b4933f0/BDA0000993124060000061.PNG)
![(-)-[gamma]-lactamase, gene, mutant, vector as well as preparation method and application of (-)-[gamma]-lactamase (-)-[gamma]-lactamase, gene, mutant, vector as well as preparation method and application of (-)-[gamma]-lactamase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/dcdbcdad-834c-4ae5-82a7-74e96b4933f0/BDA0000993124060000071.PNG)
![(-)-[gamma]-lactamase, gene, mutant, vector as well as preparation method and application of (-)-[gamma]-lactamase (-)-[gamma]-lactamase, gene, mutant, vector as well as preparation method and application of (-)-[gamma]-lactamase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/dcdbcdad-834c-4ae5-82a7-74e96b4933f0/BDA0000993124060000072.PNG)