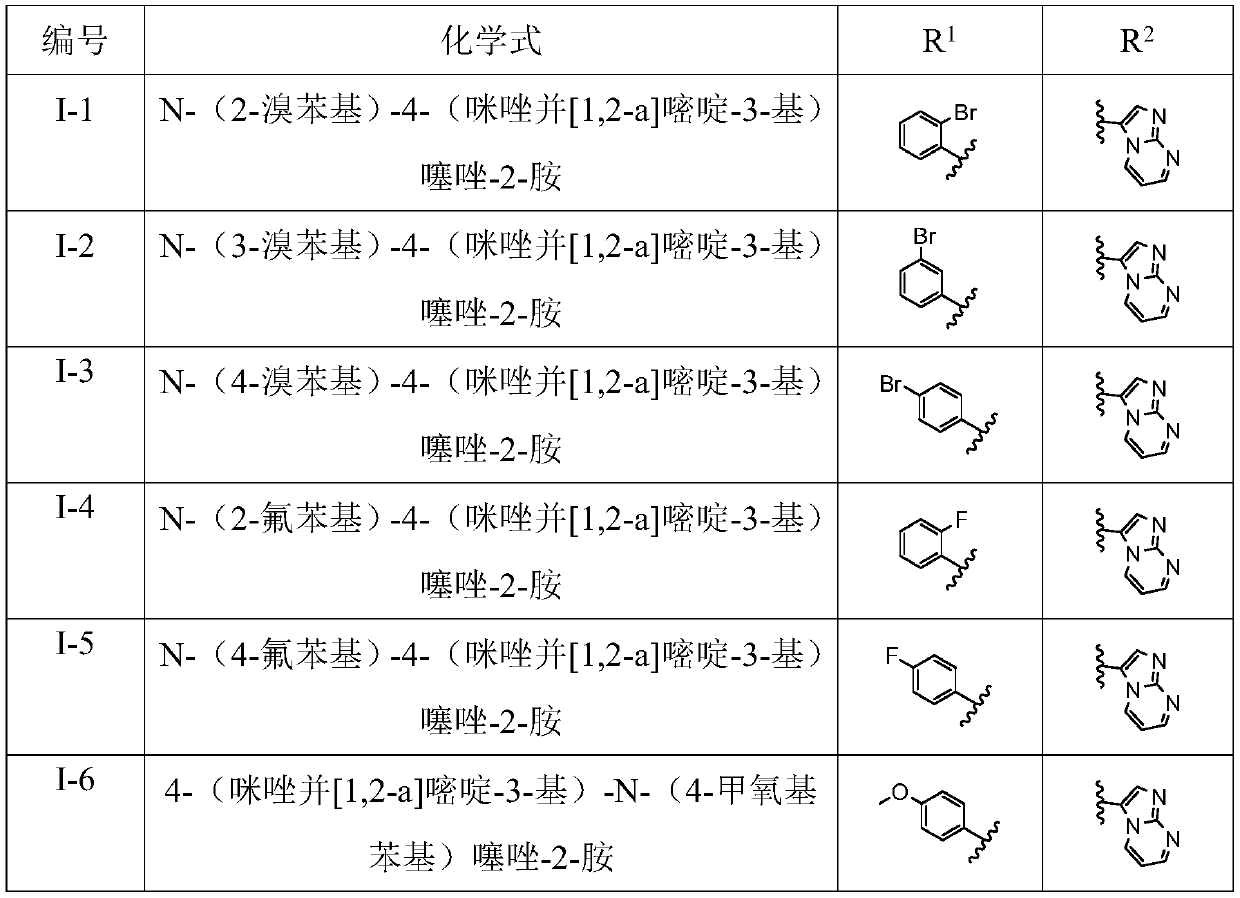
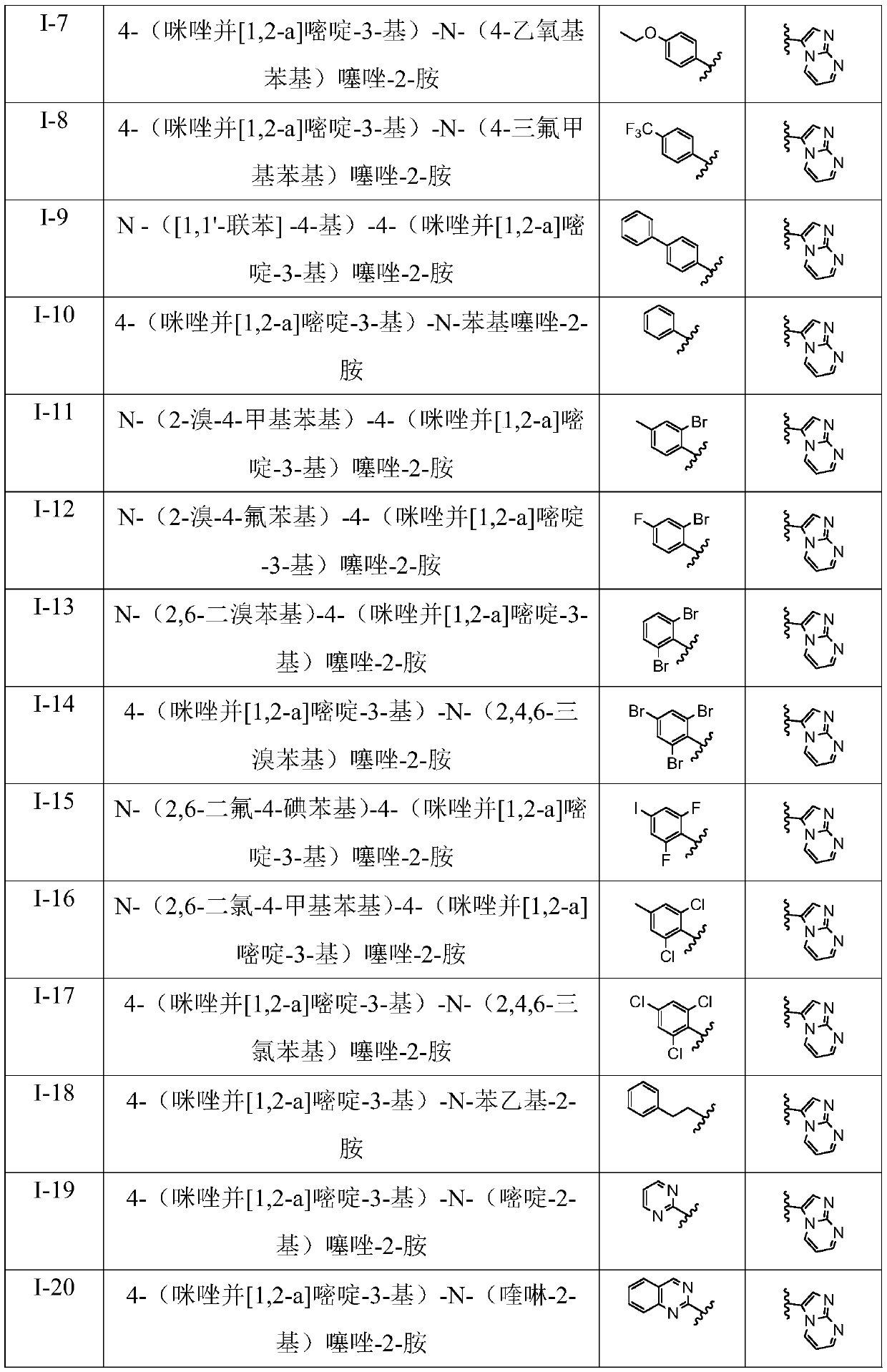
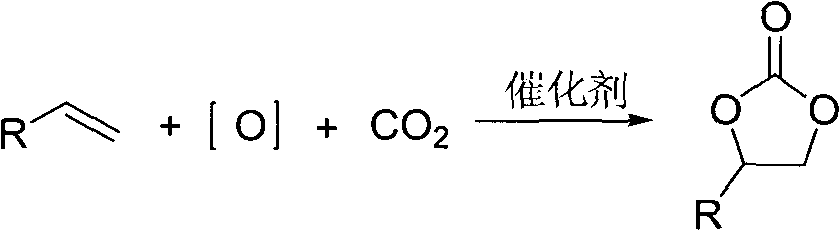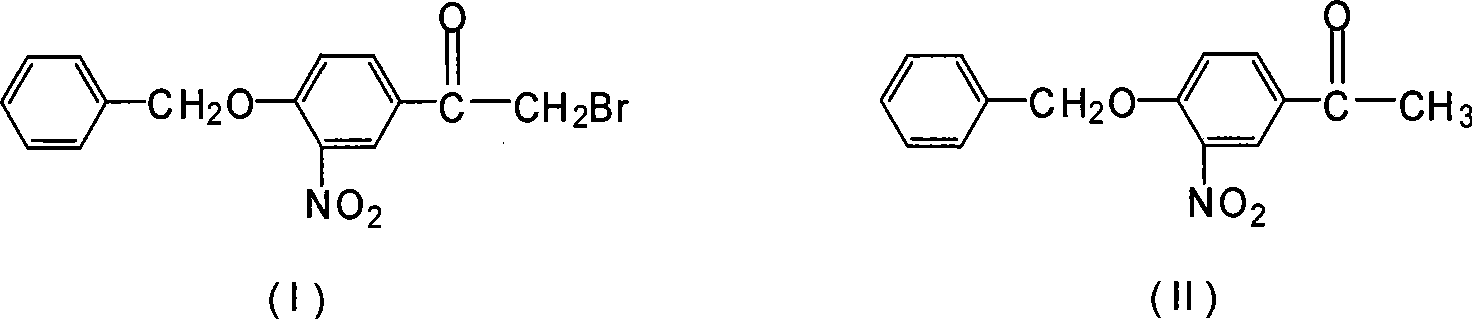Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Alpha-bromoacetophenone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
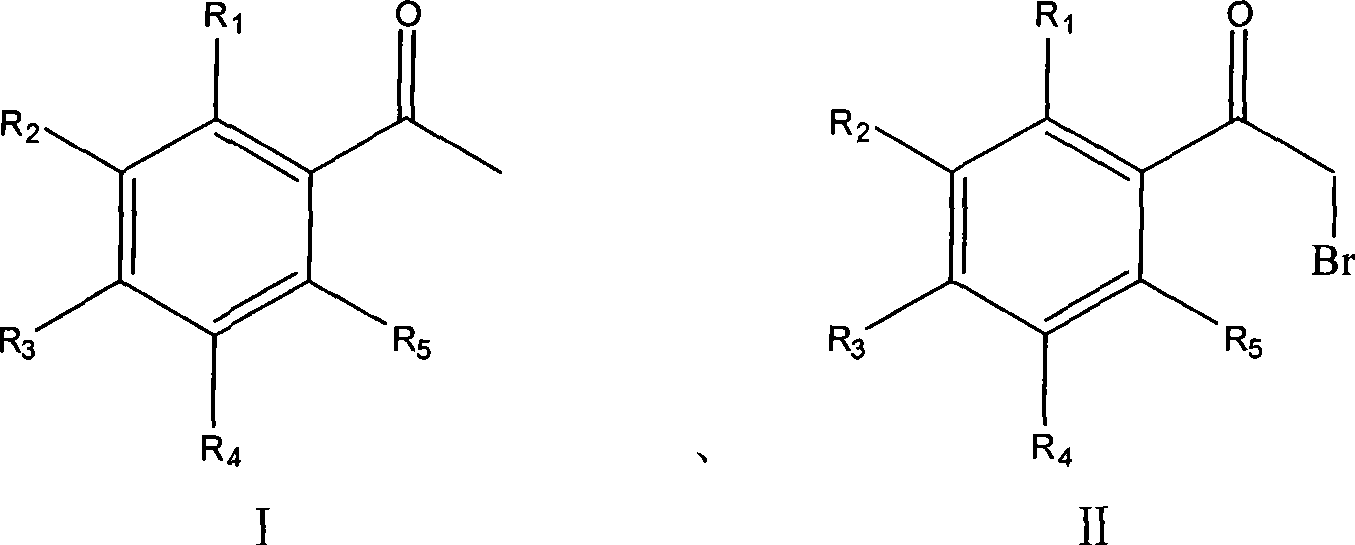
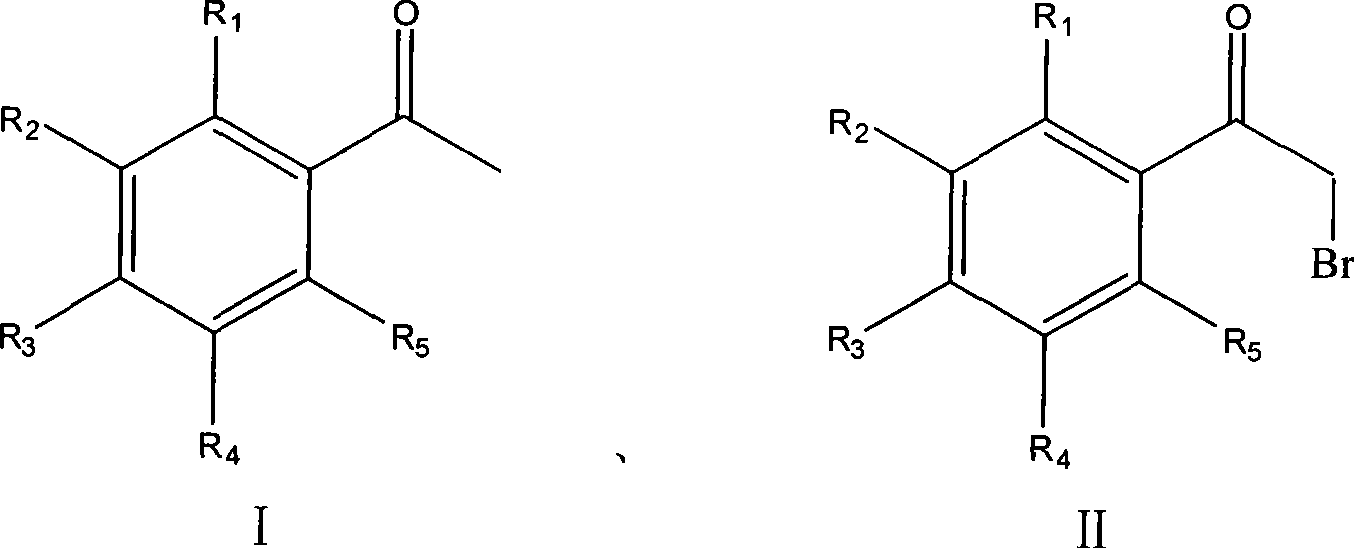
Process for synthesizing alpha-bromoacetophenone compound
InactiveCN101462935AHigh regional selectivityHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationOrganic solventAlpha-bromoacetophenone
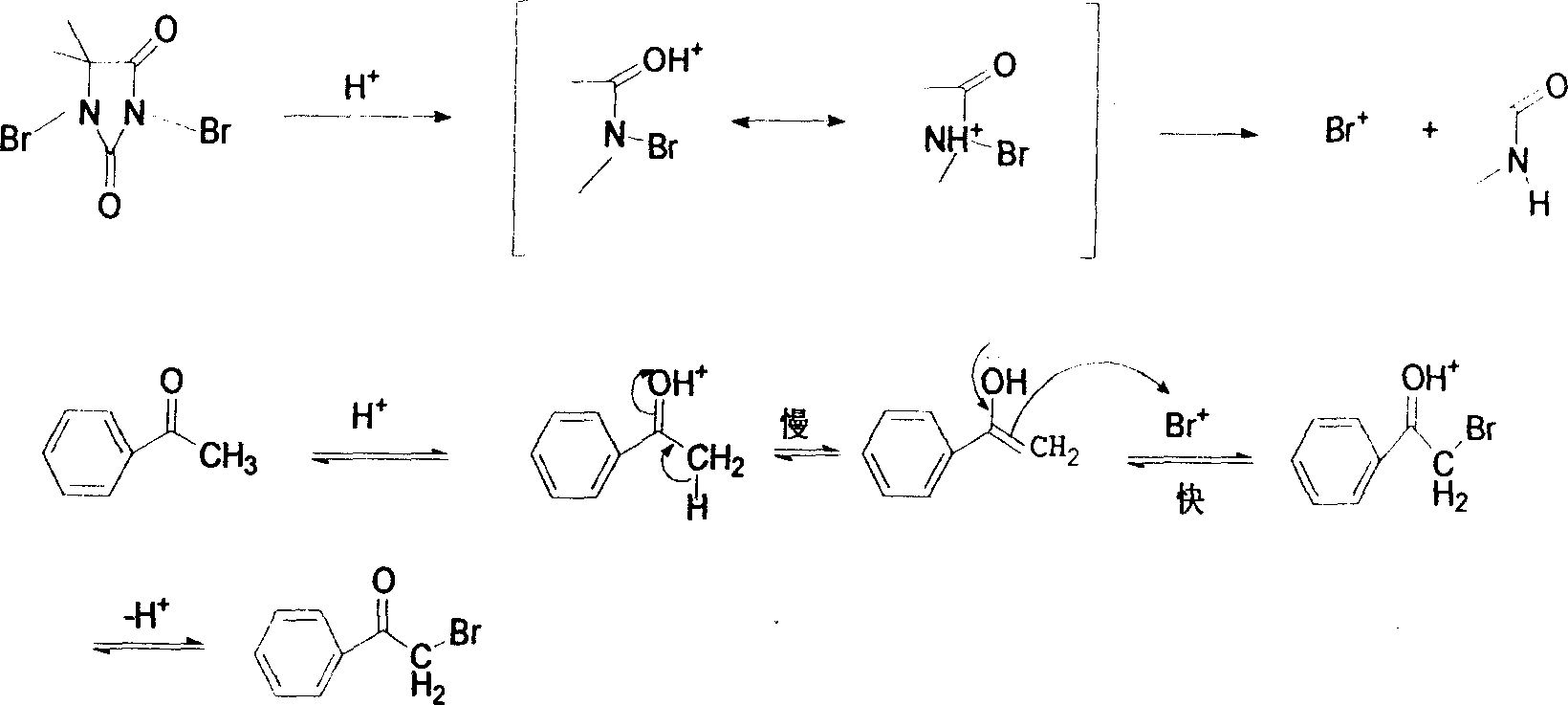
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing alpha-bromo acetophenone compound, which comprises the steps: hydrosulphite solution is added into the mixture of substituted phenylethanone and bromate at the temperature of 30-90 DEG C, and the mixture is stirred to react for 2-9h, and then is cooled, filtered, washed and dried, so that the alpha-bromo acetophenone compound is obtained. The method also has the advantages that the product has high product purity, the price of bromide reagent is low, aqueous phase is solvent instead of organic solvent, the pollution is little, the operation is simple, and the method is suitable for mass production.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
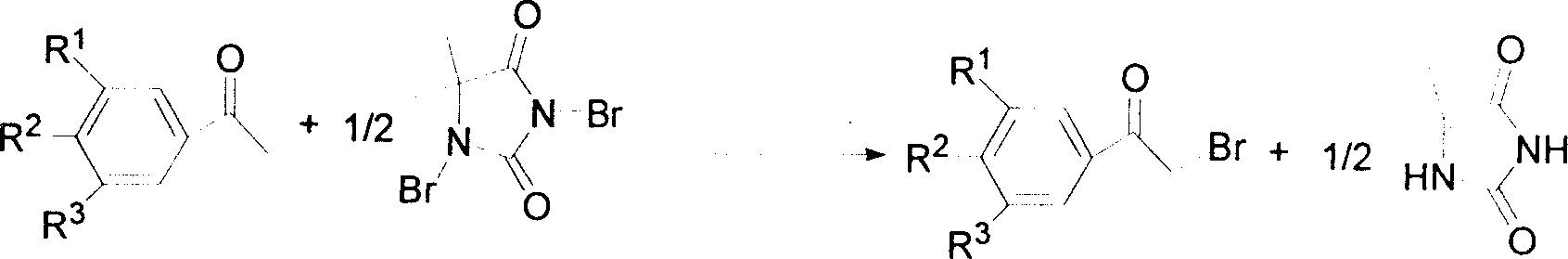
Method for synthesizing alpha-bromo-acetophenone
InactiveCN1733677AHigh selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationSlagDBDMH
The invention discloses a process for synthesizing bromoacetophenone, which comprises measuring acetophenone : acids : DBDMH by the molar weight of 1 : 0.1-1.0 : 0.5-1.0, charging acetophenone and acid as catalyst into containers, stirring and elevating temperature to 10-100 deg. C, dropping DBDMH solution, reacting 4-8 hours, stopping the reaction, decompressing for removing the filter liquor, charging the filter residue into iced water, washing the filtering slag to neutral, filtering to obtain dust cake, drying the dust cakes, obtaining alpha-bromoacetophenone, charging sodium carbonate into the filter liquor for neutralizing, removing water, washing residue with acetone, filtering, removing solvent, reclaiming by-product hydantoin.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Alpha-bromoacetophenone compound production method
InactiveCN1807382ARealize deep processing and utilizationAvoid recyclingOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationOrganic solventBromine
The preparation method for alpha-hypnone bromide comprises: stirring and heating to 90Deg, dripping the liquid bromine directly into hypnone compound aqueous solution to produce the product as an important drug intermediate and HBr gas. This invention is practical, belongs to a green chemical method without any toxic organic solvent, and has great economic value.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
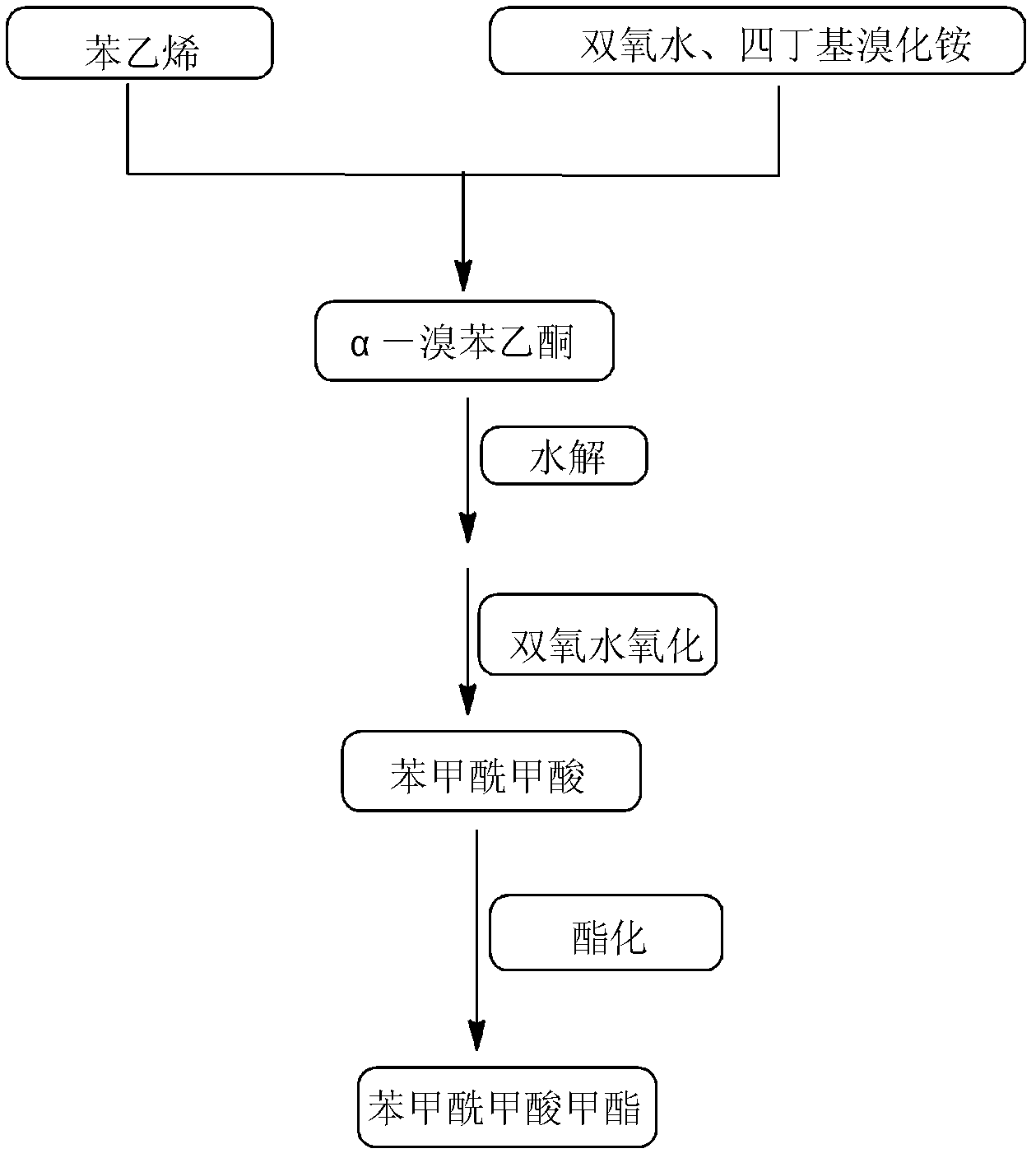
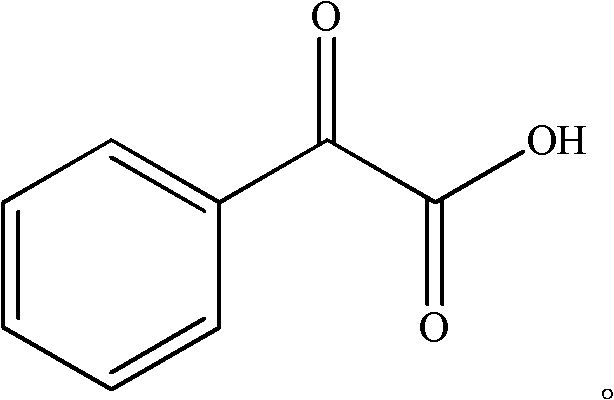
High-selectivity synthesis method of benzoyl formic acid
InactiveCN102336656AReduce generationEmission reductionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSynthesis methodsAlpha-bromoacetophenone
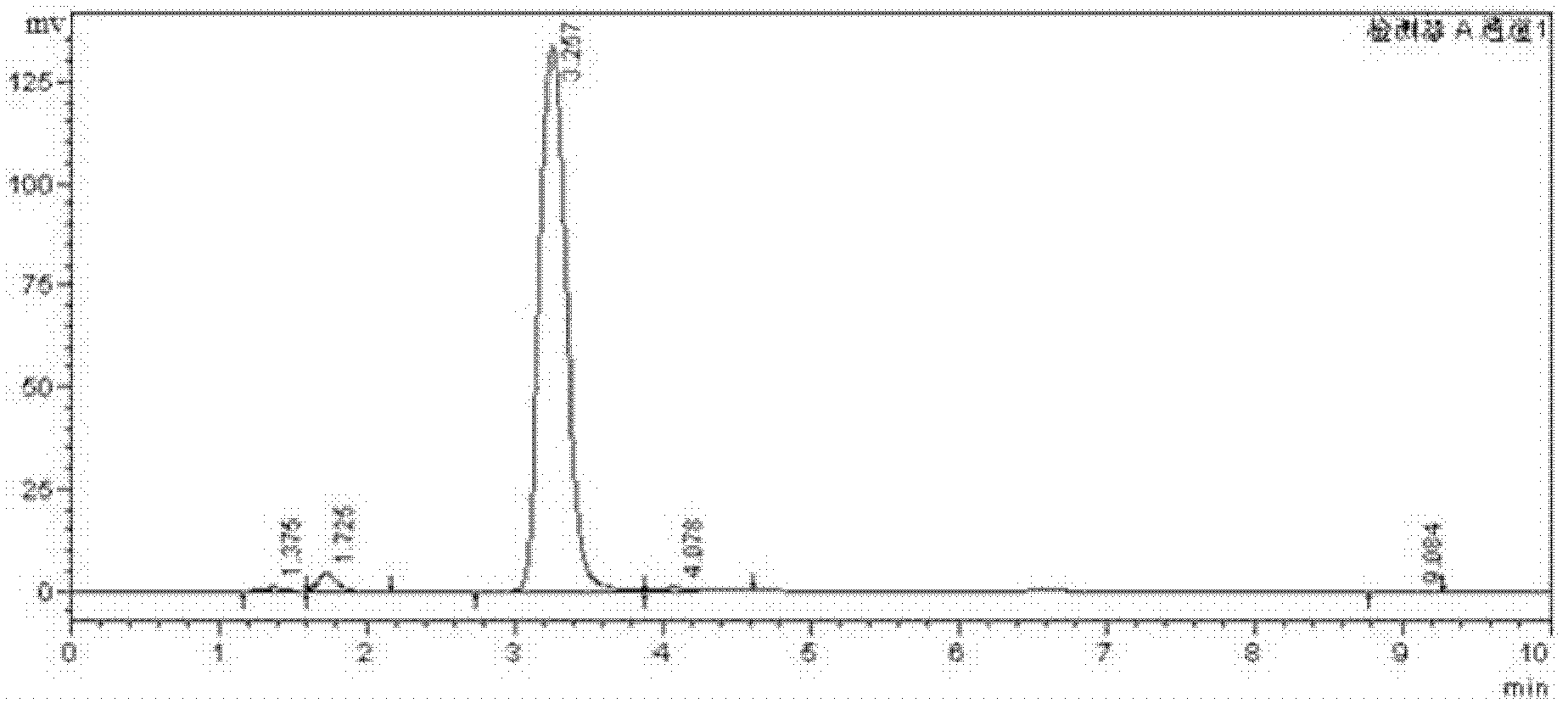
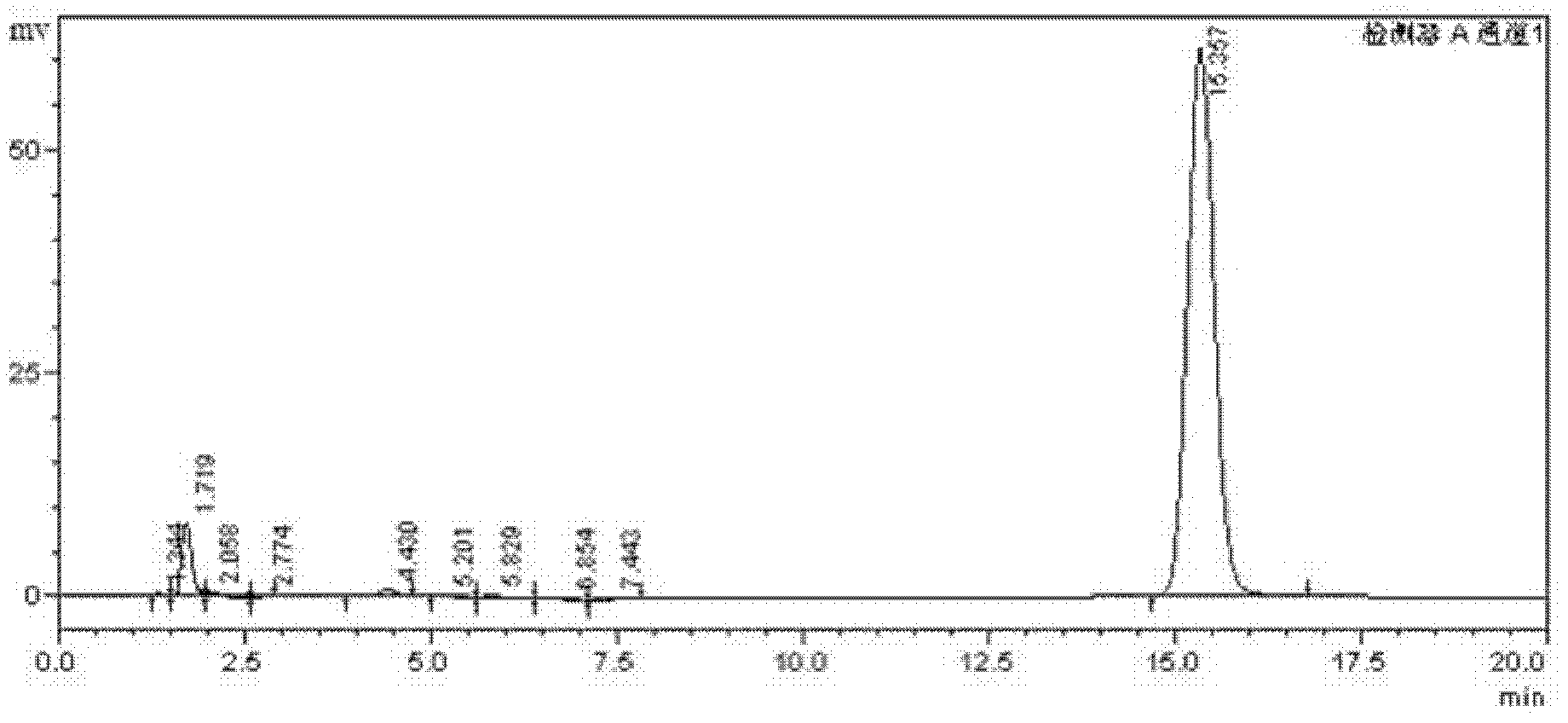
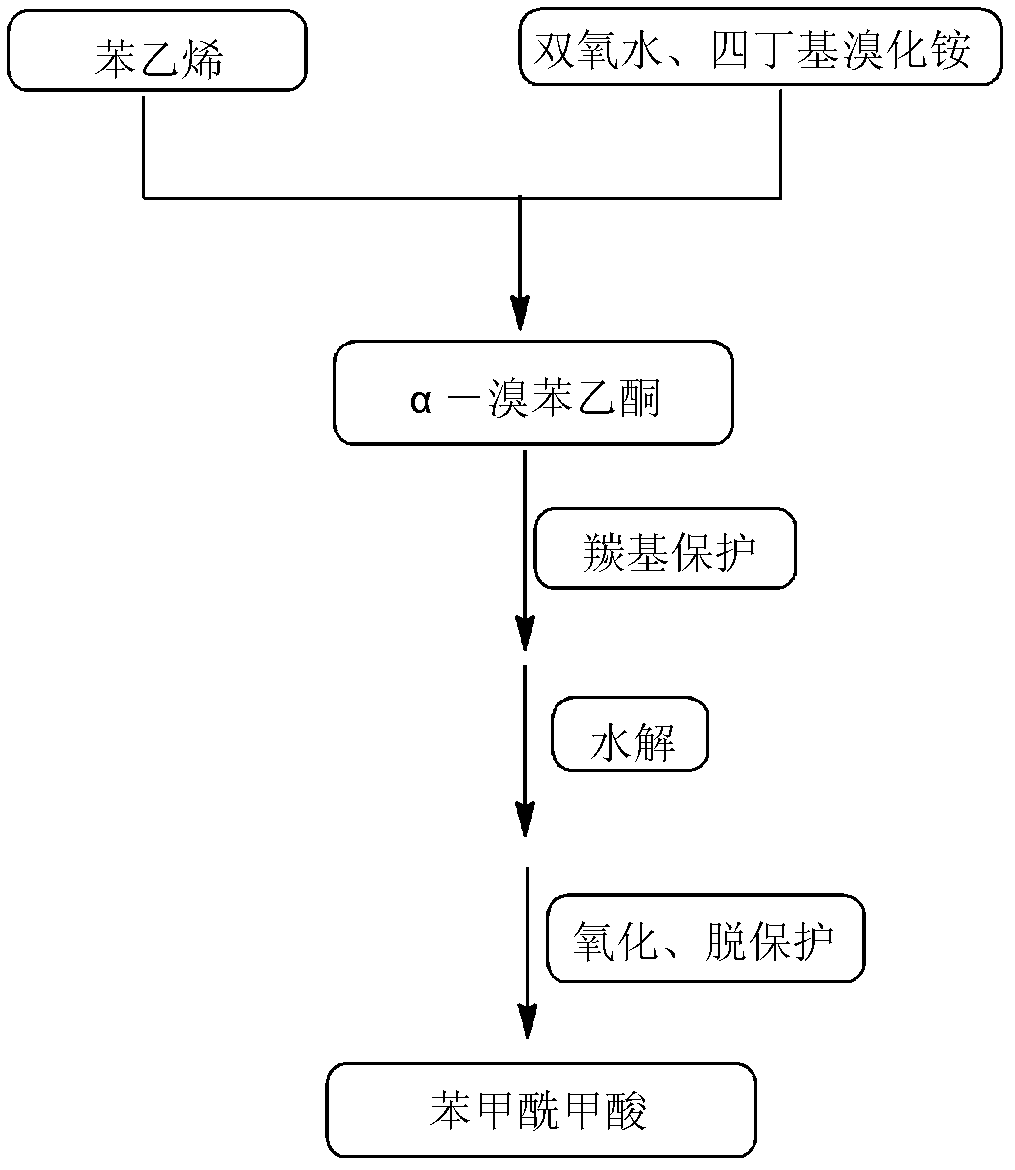
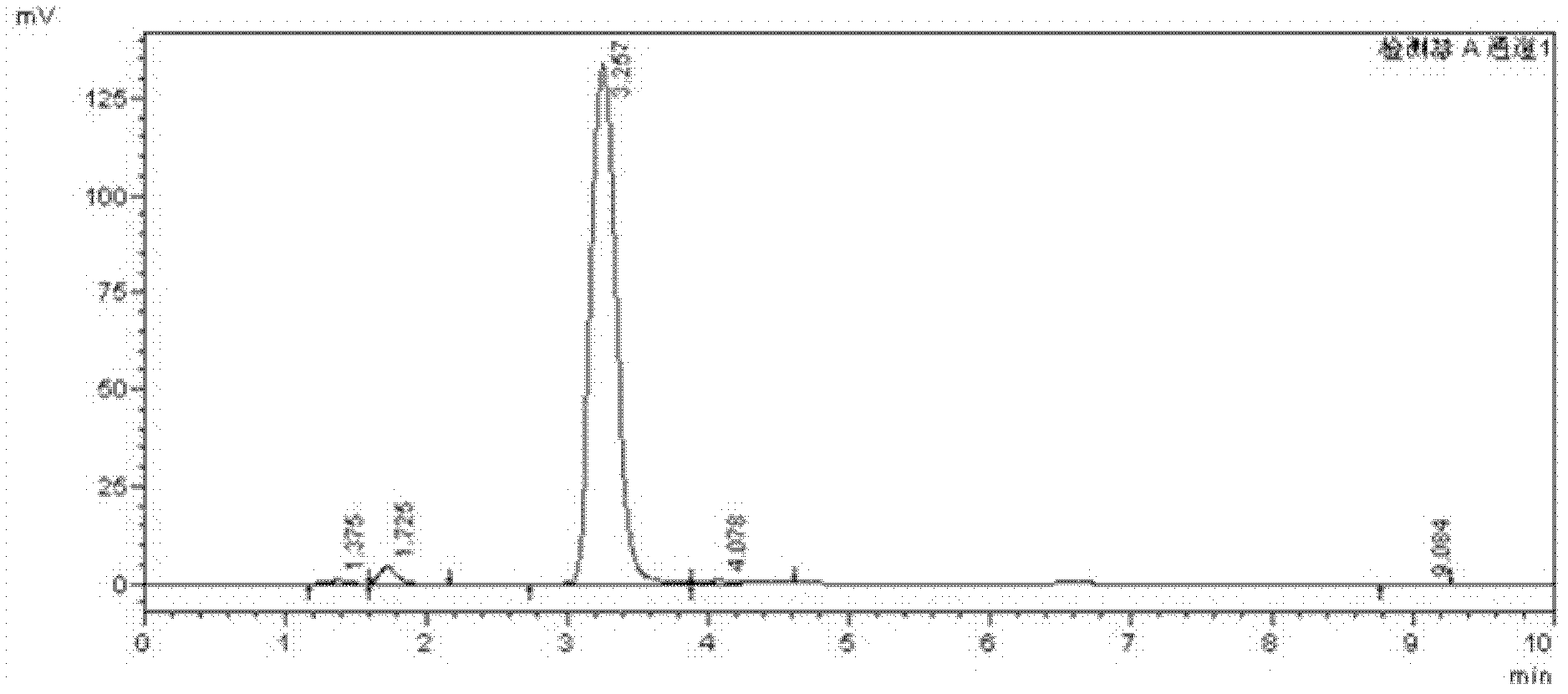
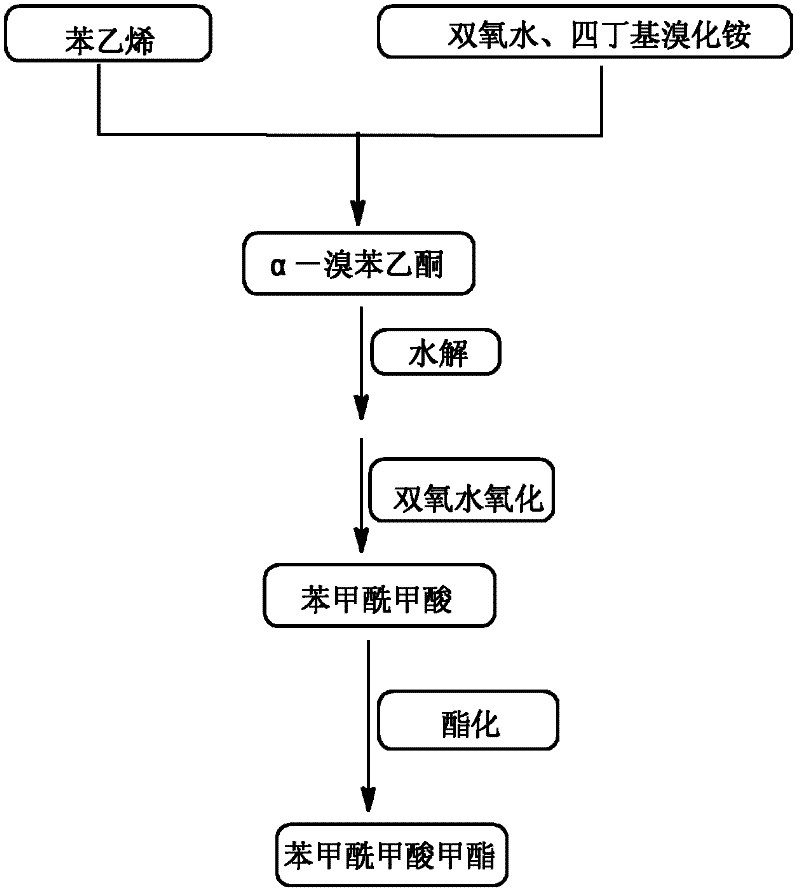
The invention discloses a high-selectivity synthesis method of benzoyl formic acid, which comprises the following steps: oxidizing styrene, which serves as the raw material, in a H2O2 / tetrabutylammonium bromide mixed system to generate alpha-bromophenethyl alcohol; oxidizing the generated alpha-bromophenethyl alcohol with H2O2 to generate alpha-bromoacetophenone; hydrolyzing the alpha-bromoacetophenone under alkaline conditions to generate alpha-hydroxyacetophenone; and oxidizing the alpha-hydroxyacetophenone with H2O2 to generate the target product benzoyl formic acid. In the invention, oxydol is used as an oxidant, and the byproduct is water, thereby reducing the generation of the organic byproducts and the discharge amount of inorganic salt (acid) waste water. Compared with other inorganic heavy metallic salt and inorganic mineral acid oxidization methods, the method disclosed by the invention enhances the cleanness of industrial preparation reaction, and reduces the environmental pollution. The invention enhances the product yield and purity: the yield is enhanced by nearly 13%, the total yield is up to 93.7%, and the product purity exceeds 95%; and other indexes are correspondingly enhanced.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
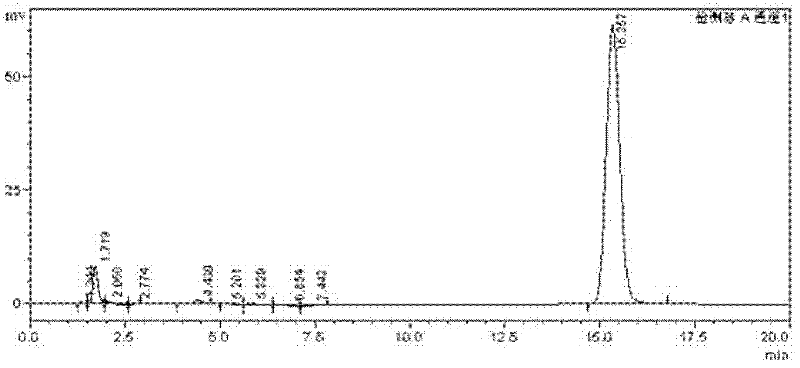
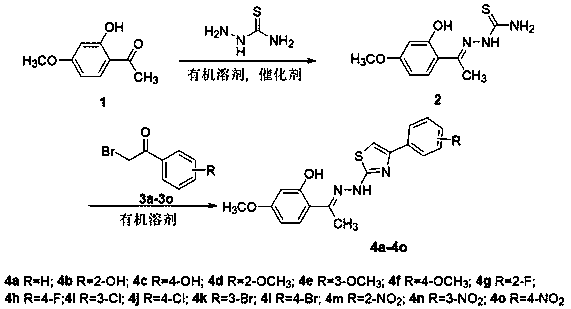
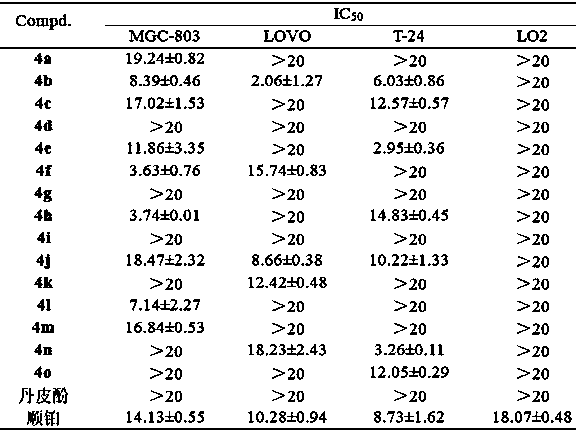
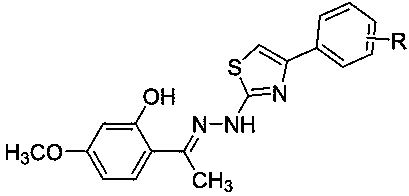
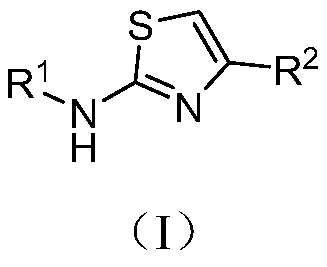
Paeonol thiazole derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109970679AShort preparation cycleEasy to operateOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsHydrogen atomHalogen
The invention discloses a paeonol thiazole derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The paeonol thiazole derivative has a structure shown in a formula (I), wherein R is a benzene ring substituent, and in particular one of hydrogen atom, halogen atom, hydroxyl group, methoxy group and nitro group. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: A, performing condensation reaction on paeonol and thiosemicarbazide to synthesize paeonol thiosemicarbazide; and B, reacting the prepared paeonol thiosemicarbazide with alpha-bromoacetophenone of different substituents to obtain the paeonol thiazole derivative. By the adoption of the paeonol thiazole derivative and the preparation method and application thereof, a new paeonol thiazole derivative is provided, which has the advantages of short preparation period, simple operation, low cost, high purity and stable quality of the obtained derivative; and experiments also show that antitumor activity of the derivative canbe improved by introducing an antitumor pharmacodynamic group thiazole on a paeonol skeleton, and the derivative can be used as the antitumor derivative.
Owner:GUILIN PHARMA
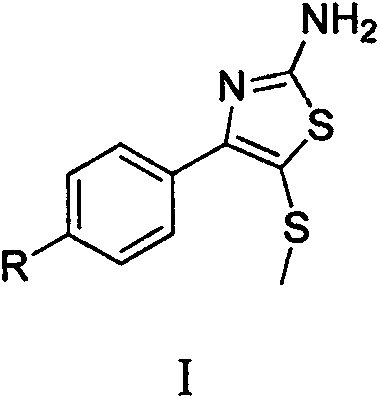
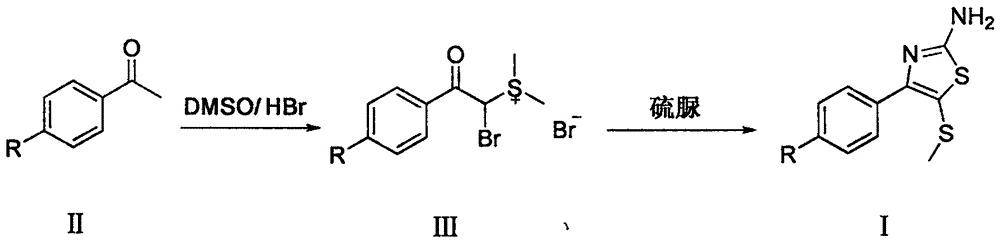
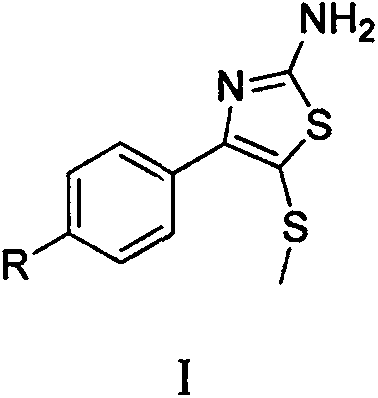
Synthetic method of 2-amino-4-aryl-5-methylthiothiazole compound
The invention belongs to the field of organic chemical synthesis technology and relates to an efficient and simple method for synthesis of a 2-amino-4-aryl-5-methylthiothiazole compound. The method of the invention comprises the following synthesis steps: (1) dissolving aryl ethylketone in a DMSO / HBr mixed system, heating and reacting to prepare alpha-bromoacetophenone dimethylsulfonium salt; and (2) dissolving the sulfonium salt prepared in the step (1) into water, adding thiourea, and stirring at room temperature; and adding ethanol, continuously heating and reacting to prepare 2-amino-4-aryl-5-methylthiothiazole.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
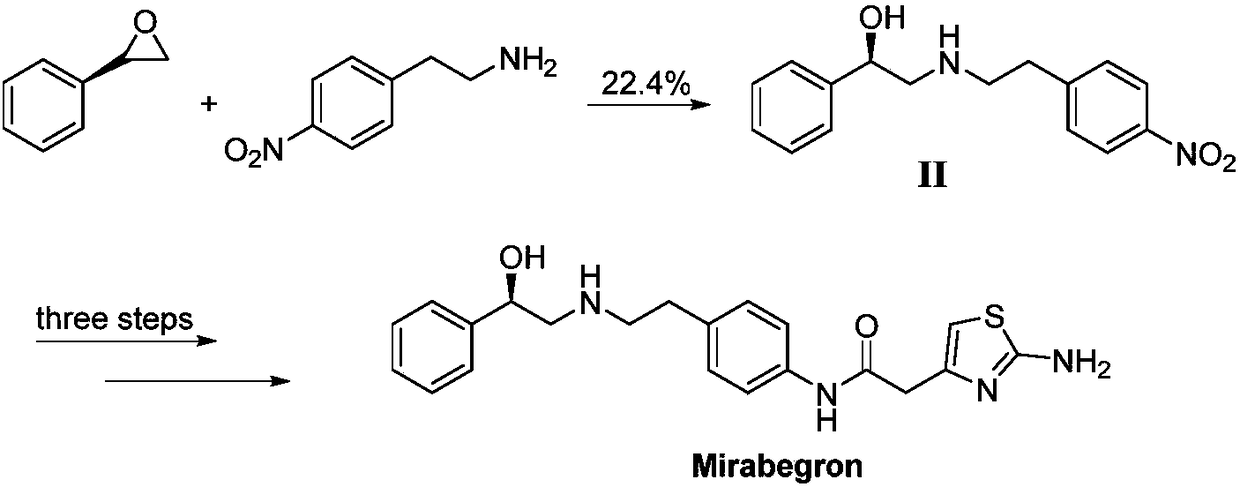
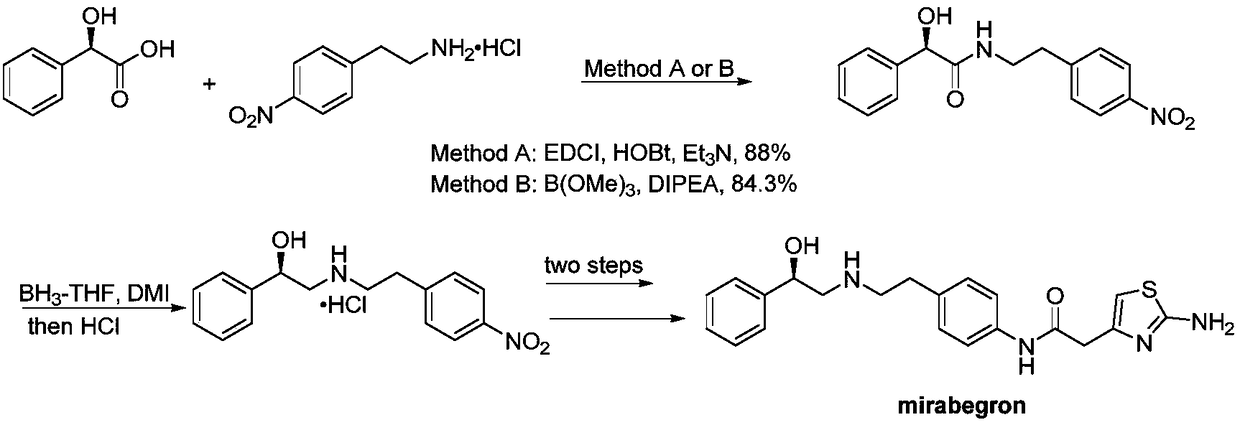
Synthesis of mirabegron intermediate (R)-2-(4-nitrophenethylamino)-1-phenylethanol hydrochloride
InactiveCN108658797AFeasibility of large industrial operationReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsStyrene oxideSynthesis methods
The invention discloses synthesis of a mirabegron intermediate (R)-2-(4-nitrophenethylamino)-1-phenylethanol hydrochloride. The synthesis comprises the following steps: firstly, enabling alpha-bromoacetophenone and 4-nitro-phenethylamine to react in a solvent in the presence of alkali to generate an intermediate I; then carrying out reduction reaction on the intermediate I under the action of a chiral inducing agent and a reducing agent to generate an intermediate II; enabling the intermediate II to react with concentrated hydrochloric acid in a solvent to generate a target product. Accordingto the synthesis method disclosed by the invention, EDCI (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide), HOBt (Hydroxybenzotriazole) and DMI (1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone) which have a relatively high price, and hypertoxic R-styrene oxide can be avoided; the synthesis method has the advantages of easiness for obtaining raw materials, low cost, simplicity in operation and few impurities and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI DEXINJIA BIOPHARM
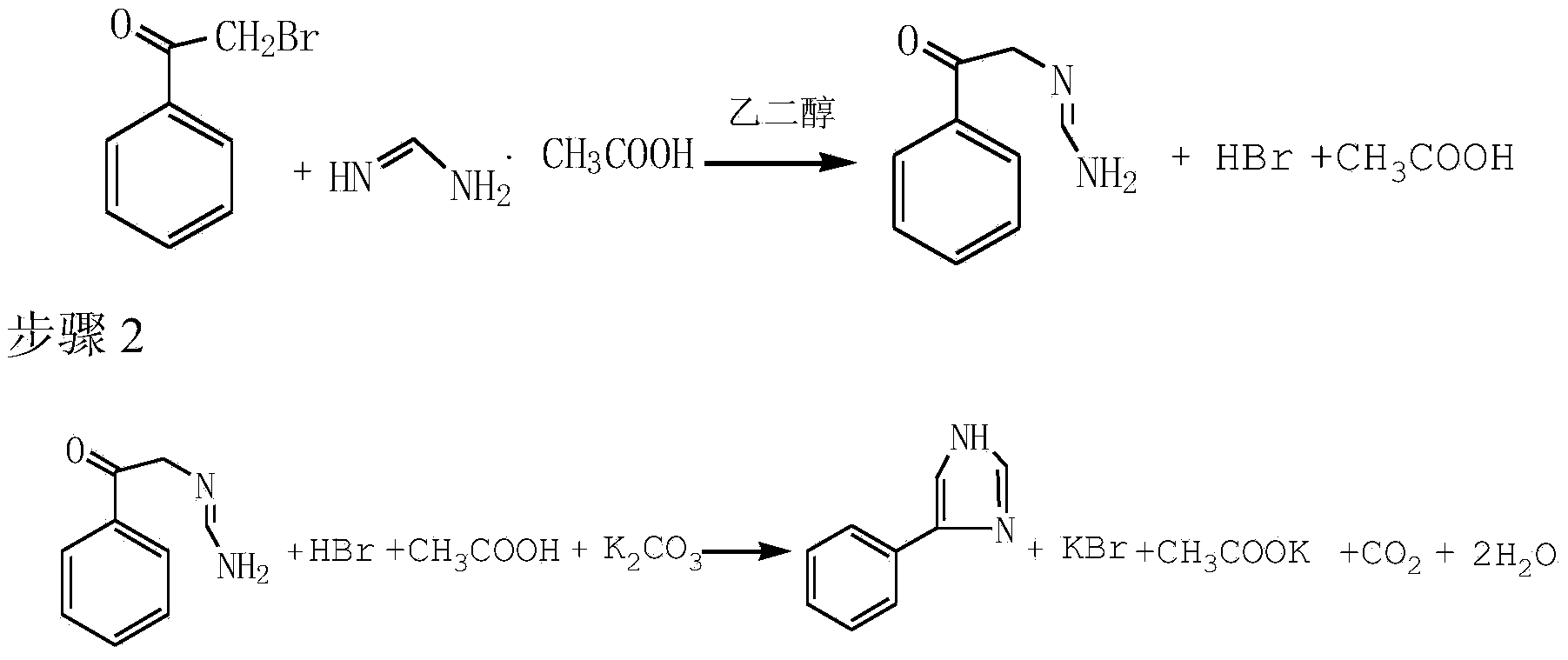
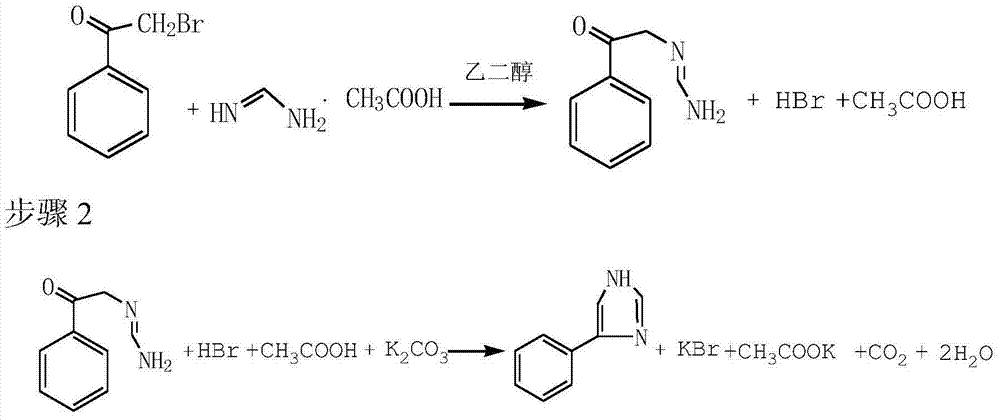
Preparation method of 4-phenylimidazole
The invention discloses a preparation method of 4-phenylimidazole. The method comprises the following steps: 1) substitution, namely, dissolving alpha-bromoacetophenone into formamidine acetate, and reacting in ethylene glycol, so as to obtain a nucleophilic replace intermediate; 2) cyclizing, namely, adding potassium carbonate as an acid-binding agent, and controlling the temperature to carry out a cyclization reaction; and 3) post-treatment, namely obtaining the 4-phenylimidazole by post-treatment after the reaction is ended. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the 4-phenylimidazole is synthetized from conventional chemical raw materials; the preparation method is simple in process, less in reaction steps, and convenient to purify; an industrial operation is facilitated; the target product is white in color and luster; the content of the final product can be up to over 99%; the yield is greater than 45%.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG XINYI CHEM
Method for microwave synthesis of alpha-hydroxyacetophenone series compounds
InactiveCN101580445AStable pressureRapid responseOrganic compound preparationHydroxy group formation/introductionSynthesis methodsOrganic synthesis
The invention relates to a method for microwave synthesis of alpha-hydroxyacetophenone series compounds, which belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis. The method is a novel method and comprises the following steps: using alpha-bromoacetophenone series compounds and water as raw materials and placing the raw materials into a microwave reaction kettle, wherein the water also serves as a reaction medium; and under microwave radiation, synthesizing the alpha-hydroxyacetophenone series compounds through one step. The synthesis method is simple and quick, has high conversion rate, needs no organic media and catalysts, has no waste disposal and is environment-friendly. The method can greatly shorten the reaction time for synthesizing the alpha-hydroxyacetophenone series compounds and reduce the generation of byproducts, and is a high-efficiency and energy-saving environment-friendly synthesis method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
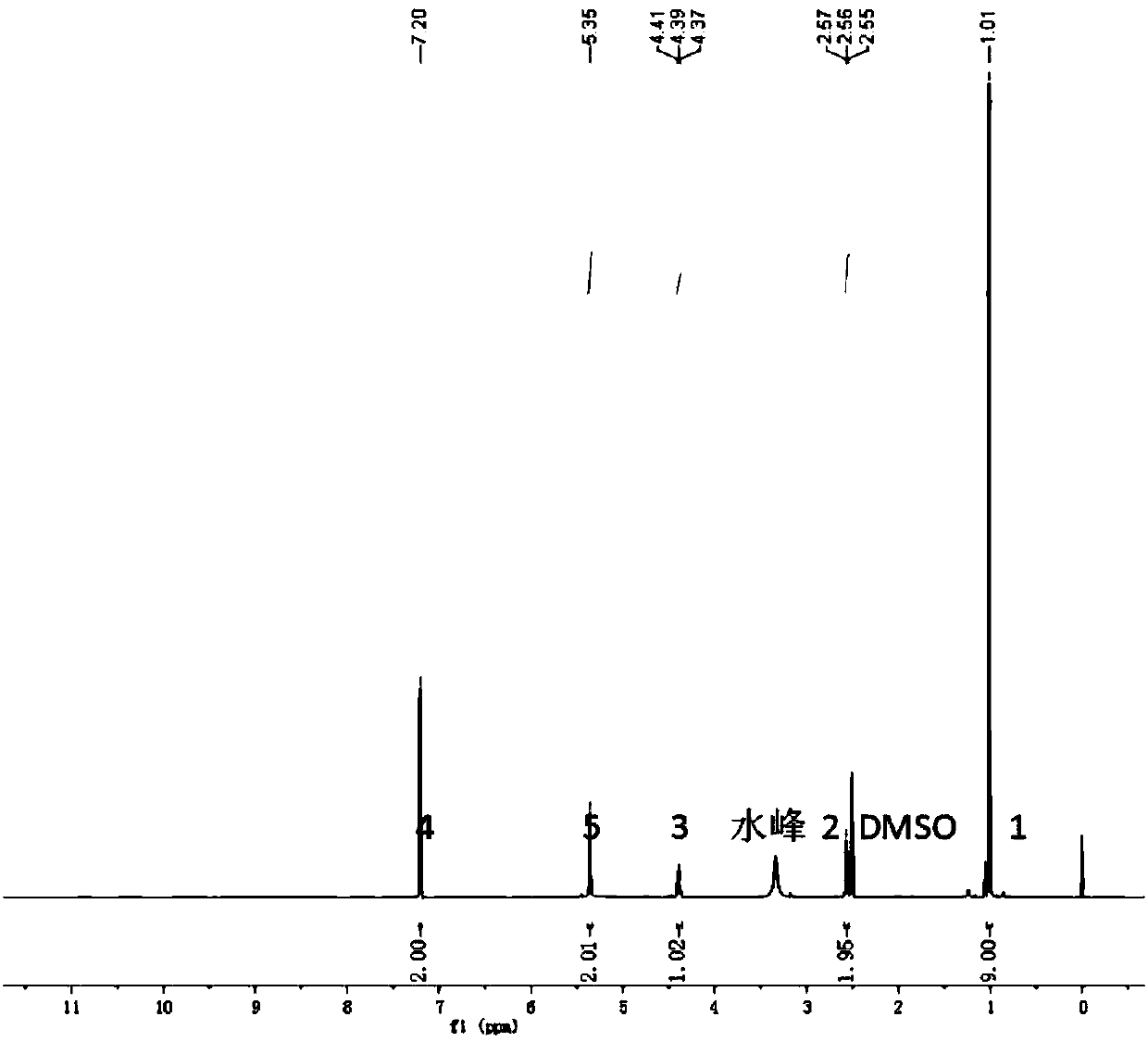
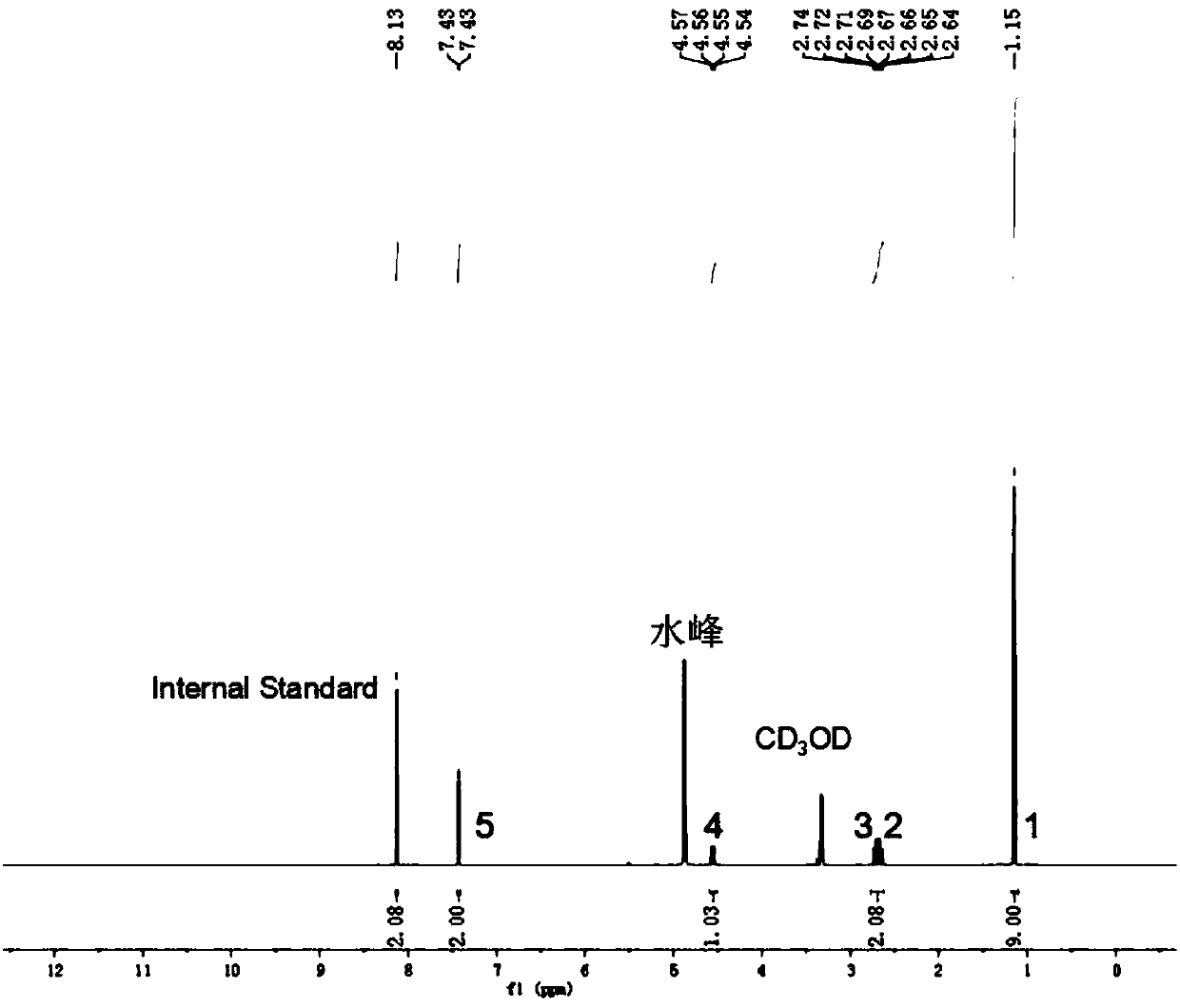
Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridine compound and its synthesis method
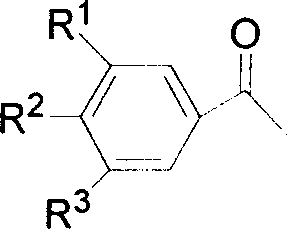
The invention relates to a benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and a synthetic method thereof. The benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound has a general formula shown in the specification, wherein R1 is phenyl, 3-bromo-phenyl, 4-bromo-phenyl, 4-chloro-phenyl, 4-methoxy-phenyl, 3-methyl-phenyl or 4-methyl-phenyl; R2 is hydrogen or 5-chlorine, 5-bromine, 5-tert-butyl, 3,5-ditert-butyl, 4-methoxy, 5-methoxy, 5-methyl, 3,5-dimethyl and 4,5-dimethyl; R3 is methyl or phenyl, 4-bromo-phenyl, 3-bromo-phenyl, 2-chloro-phenyl, 4-chloro-phenyl, 4-methoxy-phenyl and 4-methyl-phenyl. According to the synthetic method disclosed by the invention, alpha-bromoacetophenone or a derivative thereof as well as 4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-butylene-2-ketone or a derivative thereof are used as reactants, and a one-pot method is adopted to synthesize the benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound. The synthetic method is simple and convenient in step, mild in condition and high in yield.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Aminothiazole compound as well as preparation method and application thereof in resisting enterovirus 71
InactiveCN110590785AInhibitory activityLow toxicityOrganic chemistryAntiviralsThioureaAlpha-bromoacetophenone
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
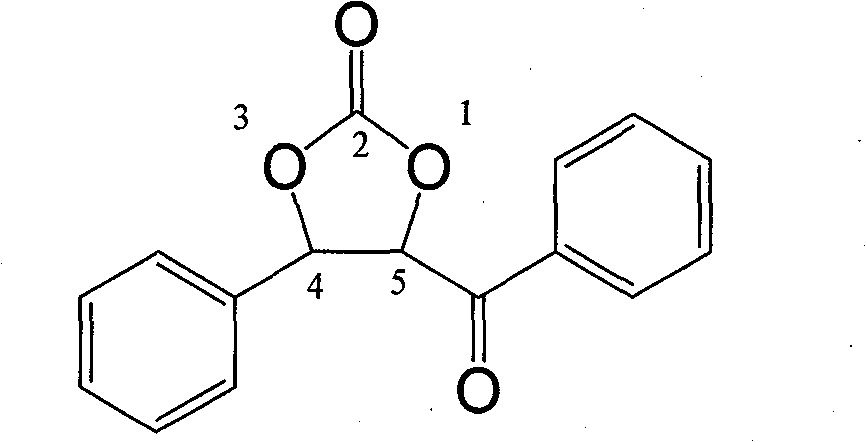
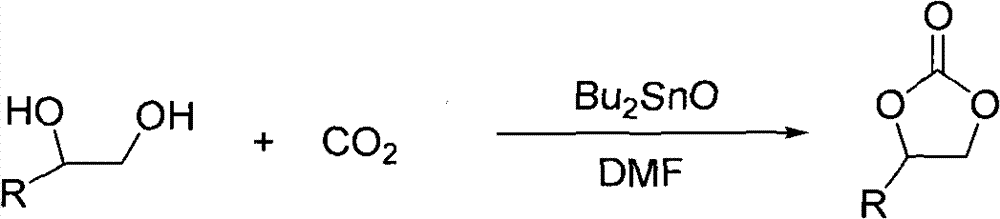
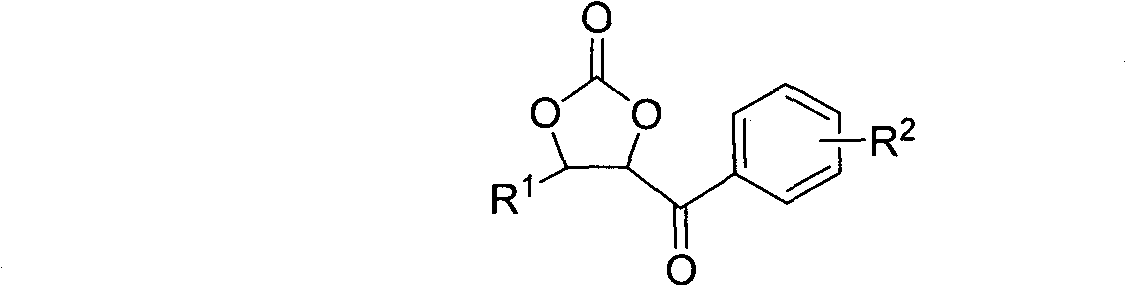
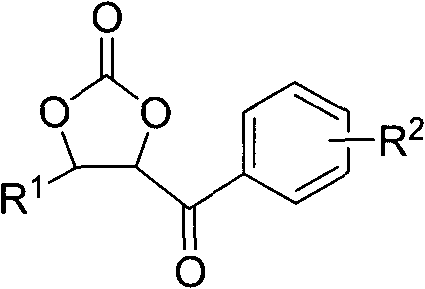
Cyclic carbonate compound and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN101805324AReaction raw materials are readily availableMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryBenzaldehydeSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a cyclic carbonate and a preparation method thereof. The formula of the cyclic carbonate related by the invention is disclosed in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving benzaldehyde or derivatives thereof and alpha-bromoacetophenone or derivatives thereof in an anhydrous dioxane solution; introducing carbon dioxide gas at the flow rate of 200-300 ml / min under atmospheric pressure at 10-55 DEG C while stirring; dropwisely adding diisopropyl lithium amide into the solution; leading the reaction system completely to react underthe conditions of stable carbon dioxide gas flow; and after the reaction finishes, quenching the reaction with saturated ammonium chloride solution, extracting with ethyl acetate, drying to remove the solvent, and carrying out silicagel column chromatography to obtain the target product.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
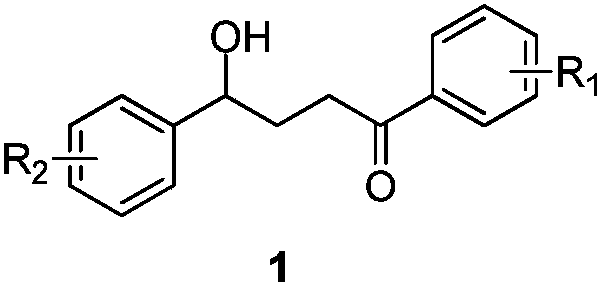
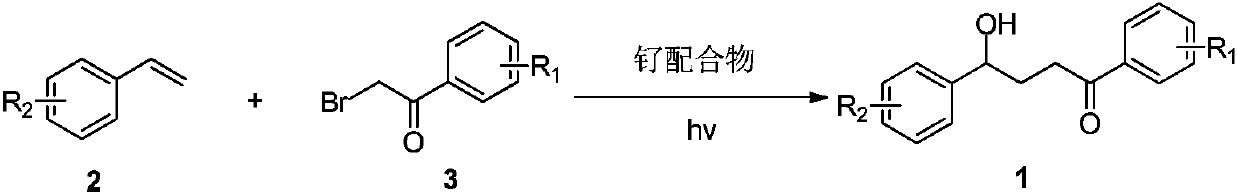
Gamma-hydroxy ketone derivatives and a synthesis method thereof
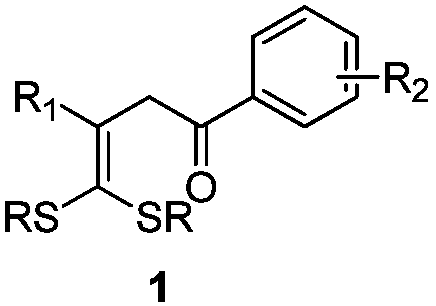
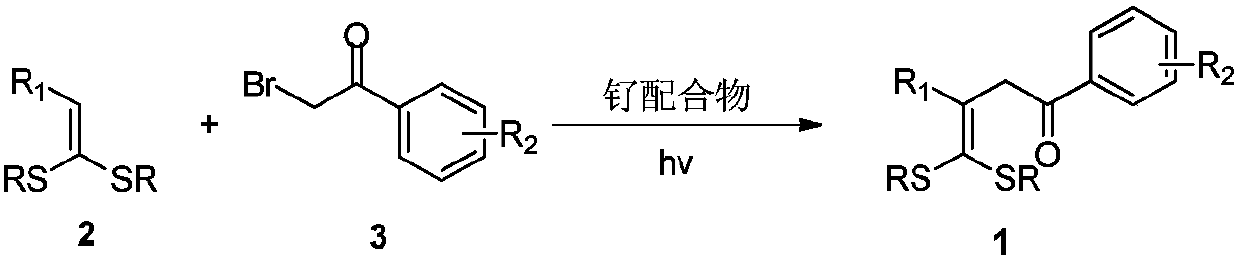
ActiveCN109867593AEasy to manufactureAchieving Hydroxyalkylation ReactionsOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationSynthesis methodsRuthenium
The invention discloses gamma-hydroxy ketone derivatives and a synthesis method thereof. Styrene adopted as a raw material and alpha-bromoacetophenone are subjected to a coupling reaction under the action of a ruthenium complex and illumination to synthesize a series of gamma-hydroxy ketone derivatives with different structures. The derivatives can be further converted into functional products. The method has the advantages of easily available raw materials, simple operation, mild reaction conditions, and diversified functional groups.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
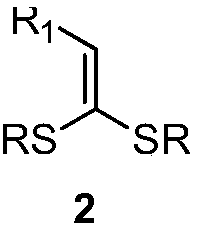
4,4-dialkylthio-1-phenyl-3-buten-1-one derivatives and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN109867614AEasy to manufactureRaw materials are easy to getEnergy efficient lightingSulfide preparationSynthesis methodsRuthenium
The invention discloses 4,4-dialkylthio-1-phenyl-3-buten-1-one derivatives and a synthesis method thereof. Dithioketene acetal which is easy to prepare, which has structural diversity and multiple reaction centers, and which is adopted as a raw material and alpha-bromoacetophenone are subjected to a coupling reaction under the action of a ruthenium complex and illumination to synthesize a series of 4,4-dialkylthio-1-phenyl-3-buten-1-one derivatives with different structures. The derivatives can be further converted into functional products. The method has the advantages of easily available rawmaterials, simple operation, mild reaction conditions, and diversified functional groups.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and synthetic method thereof
The invention relates to a benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and a synthetic method thereof. The benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound has a general formula shown in the specification, wherein R1 is phenyl, 3-bromo-phenyl, 4-bromo-phenyl, 4-chloro-phenyl, 4-methoxy-phenyl, 3-methyl-phenyl or 4-methyl-phenyl; R2 is hydrogen or 5-chlorine, 5-bromine, 5-tert-butyl, 3,5-ditert-butyl, 4-methoxy, 5-methoxy, 5-methyl, 3,5-dimethyl and 4,5-dimethyl; R3 is methyl or phenyl, 4-bromo-phenyl, 3-bromo-phenyl, 2-chloro-phenyl, 4-chloro-phenyl, 4-methoxy-phenyl and 4-methyl-phenyl. According to the synthetic method disclosed by the invention, alpha-bromoacetophenone or a derivative thereof as well as 4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-butylene-2-ketone or a derivative thereof are used as reactants, and a one-pot method is adopted to synthesize the benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound. The synthetic method is simple and convenient in step, mild in condition and high in yield.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
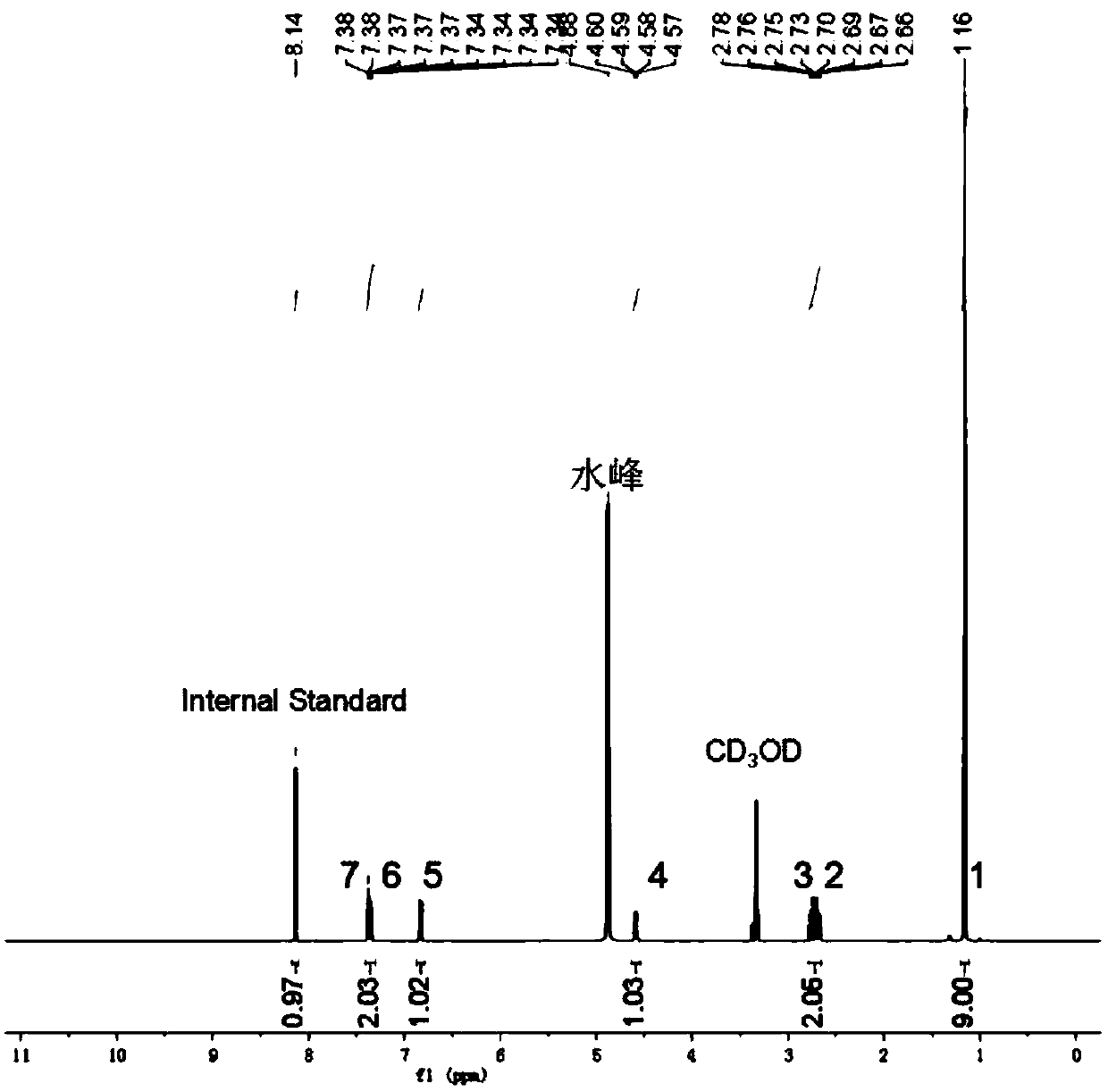
Synthesis method for 6-fluoroimidazo[1, 2-a]pyridine-3-phenyl ketone
InactiveCN104829615ARaw materials are easy to getReasonable priceOrganic chemistryN dimethylformamideSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a synthesis method for 6-fluoroimidazo[1, 2-a]pyridine-3-phenyl ketone. The method includes: reacting N-dimethylformamide dimethylacetal with 2-amino-5-fluoropyridine at 40-100DEG C to obtain an intermediate, without purification and under the action of alkali, subjecting the intermediate and alpha-bromoacetophenone to reaction in certain solvent at 60-160DEG C, at the end of reaction, performing cooling to room temperature, precipitating most high purity 6-fluoroimidazo[1, 2-a]pyridine3-phenyl ketone, adding water into mother liquor, and then carrying out extraction, washing, drying, and rotary evaporation concentration to obtain a 6-fluoroimidazo[1, 2-a]pyridine3-phenyl ketone crude product, and recrystallizing the crude product to obtain a pure product. The reaction raw materials are easily available, the prices are reasonable, the reaction conditions are mild, the method is easy to operate and control, the aftertreatment is simple, and the product has stable quality and high purity.
Owner:SHANDONG YOUBANG BIOCHEM TECH
Phenylethanolamine-based beta receptor agonist synthesis method
ActiveCN109912434AThe synthesis method is simpleRaw materials are cheap and easy to getCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationM-aminoacetophenoneCupric bromide
The invention discloses a phenylethanolamine-based beta receptor agonist synthesis method, which comprises: S1: dissolving 4-aminoacetophenone in an organic solvent, carrying out a halogenation reaction with an electrophilic substitution reagent at a benzene ring to generate a halobenzene intermediate, and carrying out a nucleophilic substitution reaction on the halobenzene intermediate and a cyaniding agent in an organic solvent or water under the catalysis of a metal catalyst to generate an acetophenone intermediate; S2, carrying out a carbonyl alpha bromination reaction on the acetophenoneintermediate and cupric bromide in an organic solvent to generate an alpha-bromoacetophenone intermediate; S3, carrying out a reaction on the alpha-bromoacetophenone intermediate and tert-butylamine or isopropylamine in an organic solvent to generate an acetophenone amine intermediate; and S4, carrying out a reaction on the acetophenone amine intermediate and a reducing hydrogenation reagent in anorganic solvent to generate a phenylethanolamine-based beta receptor agonist. According to the present invention, the synthesis method has characteristics of simpleness, high efficiency, inexpensiveand easily-available raw materials and high atom utilization rate, the chemical purity of the synthesized product is more than 99%, and the food safety testing requirements are met.
Owner:上海安谱璀世标准技术服务有限公司
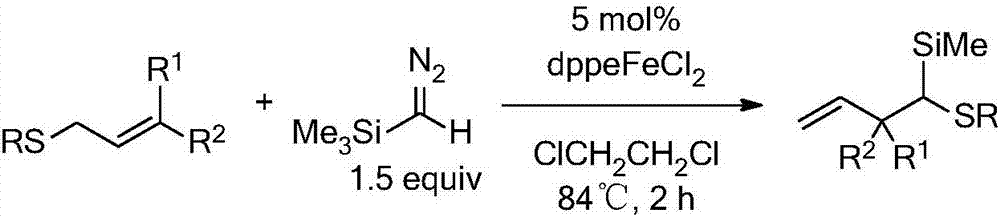
Synthesis method of alpha-acyl homoallyl thioether compound
The invention discloses a synthesis method of an alpha-acyl homoallyl thioether compound. A series of alpha-acyl homoallyl thioether compounds with application value are finally synthesized by adopting a three-component and one-pot method, taking an alpha-bromoacetophenone compound, a thiol compound and an allyl bromide compound as reactants, taking inorganic salt as an additive, taking an ultra-dry or anhydrous inorganic solvent as a solvent and reacting at the temperature of 60 DEG C to 130 DEG C. The synthesis method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that a series of the homoallyl thioether compounds with the potential application value are synthesized in high yield, and the utilization of a transition metal catalyst and a diazo compound can also be avoided; meanwhile, additives including strong acid, strong alkali and the like are not needed in a reaction process, and the protection of inert gas is not needed; the after treatment of reaction is simple.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
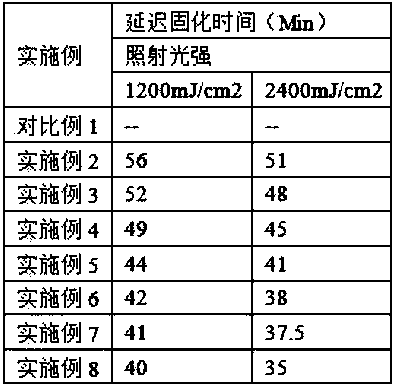
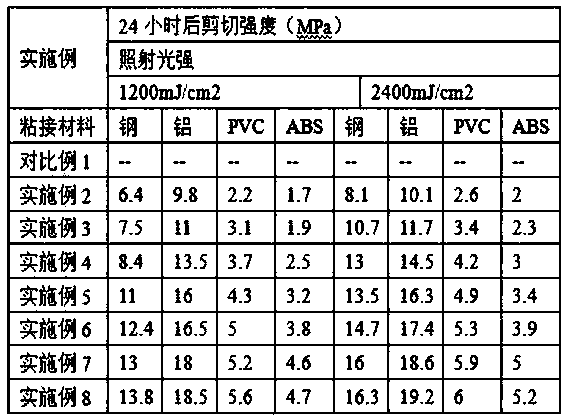
One-component epoxy adhesive capable of delayed curing induced by ultraviolet light and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104592923BSimple operation processCuring without heatNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesIon exchangeAlpha-bromoacetophenone
The invention relates to a UV-initiated delay-curable one-component epoxy adhesive. The adhesive is prepared from the following raw materials in percentages by weight: 30-60% of epoxy resin, 5-30% of a homemade quaternary photobase generator, 10-30% of a toughening agent and 5-20% of a filling agent, wherein the homemade quaternary photobase generator is synthesized from the following components of alpha-bromoacetophenone, terephthalic acid (TPA) and sodium tetraphenylborate by the following processes: reacting alpha-bromoacetophenone and an acetone liquid of terephthalic acid (TPA) at room temperature to prepare bromo-quaternary ammonium salt, filtering, drying and recrystallizing the product to obtain a crystal substance, dissolving the crystal substance in distilled water and carrying out anion exchange reaction on the distilled water with the crystal substance and sodium tetraphenylborate at room temperature to obtain a product, washing the product with distilled water and drying to obtain anion quaternary ammonium salt paired with tetraphenylborate. Compared with the prior art, the curing speed can be delayed to 30 minutes-60 minutes, the process is simple, neither heat curing nor mixing is needed, the adhesive is environmentally friendly and is convenient to use and is also simultaneously suitable for multiple opaque materials and can be widely used in the field of structural bonding.
Owner:YANTAI SEAYU NEW MATERIALS CORP LTD
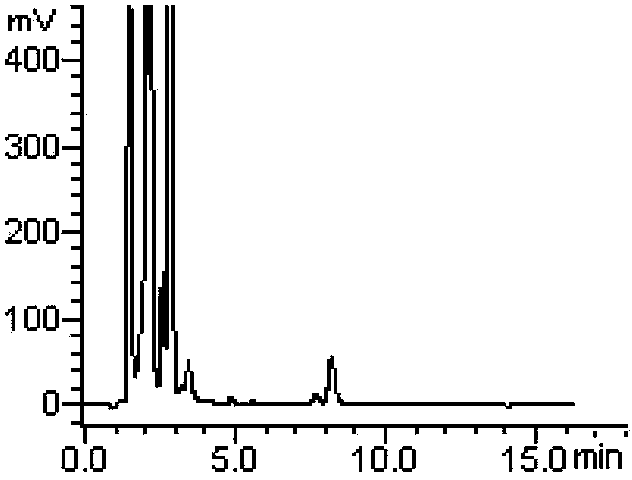
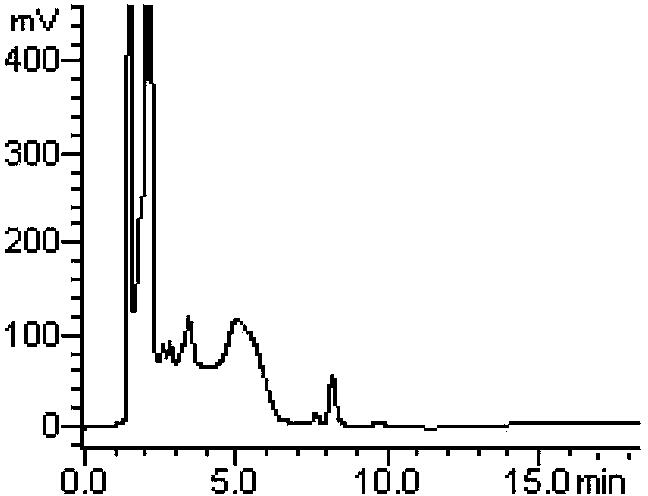
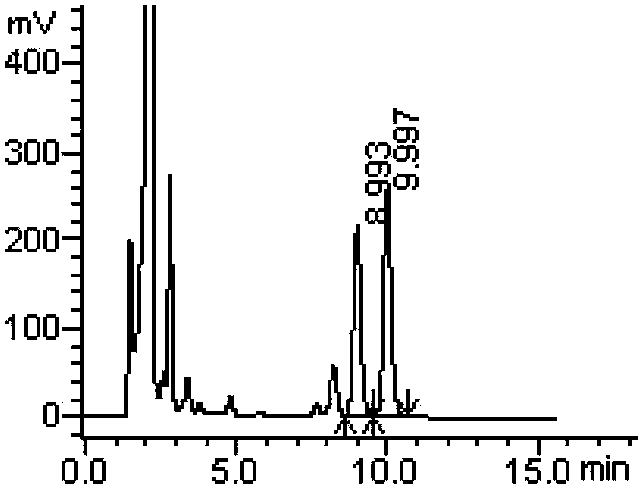
Method for measuring derivatization in valproic acid body fluid concentration process through high performance liquid chromatography
InactiveCN103197014BExtended service lifeHigh sensitivityComponent separationTetramethylammonium hydroxideValproic Acid
The invention relates to a method for measuring derivatization in a valproic acid body fluid concentration process through a high performance liquid chromatography. According to the method, triethylamine is replaced by quaternary ammonium hydroxide acetonitrile solution (tetramethylammonium hydroxide acetonitrile solution or tetrabutyl ammonium hydroxide acetonitrile solution or tetraethyl ammonium hydroxide acetonitrile solution) to catalyze valproic acid and is derived into phenyl ester which is ultraviolet detectable with a derivating agent (2,4'-dibromo acetophenone acetonitrile solution, alpha-bromoacetophenone acetonitrile solution, 2-bromo-p-nitroacetophenone acetonitrile solution or 4-bromo-7-herniarin acetonitrile solution), the derivating agent which is only 3-5 molar times that of amount of the reactants is required, and the derivatization yield above 95 percent can be achieved. The method has the advantages that the derivatization reaction is complete, the chromatogram base line is stable, endogenous impurity interference is avoided, the measurement result is accurate, the precision is high, the sensitivity is high, the using amount of the derivating agent is small, the pressure of the chromatographic column is hardly increased, and the service life of the chromatographic column is prolonged.
Owner:LIUZHOU CITY HEALTHCARE HOSPITAL FOR WOMEN & CHILDREN
Cyclic carbonate compound and synthesis method thereof
The invention discloses a cyclic carbonate and a preparation method thereof. The formula of the cyclic carbonate related by the invention is disclosed in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving benzaldehyde or derivatives thereof and alpha-bromoacetophenone or derivatives thereof in an anhydrous dioxane solution; introducing carbon dioxide gas at the flow rate of 200-300 ml / min under atmospheric pressure at 10-55 DEG C while stirring; dropwisely adding diisopropyl lithium amide into the solution; leading the reaction system completely to react underthe conditions of stable carbon dioxide gas flow; and after the reaction finishes, quenching the reaction with saturated ammonium chloride solution, extracting with ethyl acetate, drying to remove the solvent, and carrying out silicagel column chromatography to obtain the target product.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
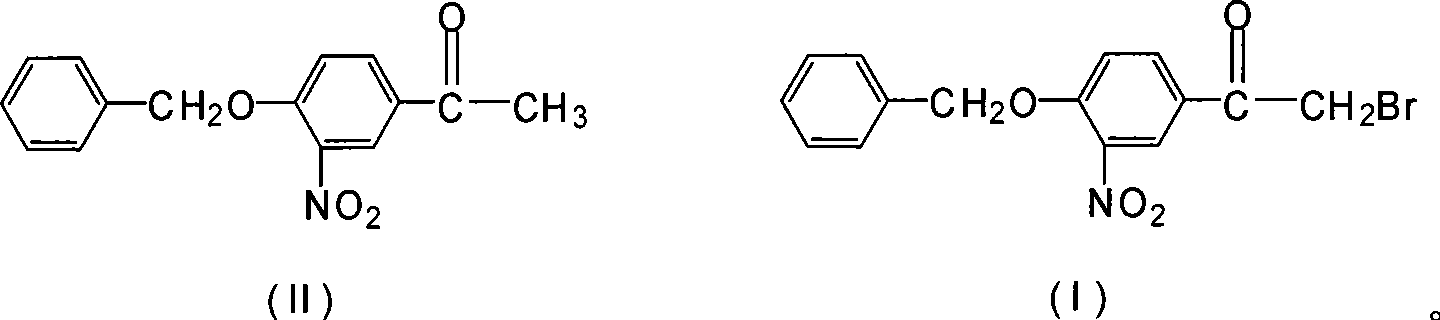
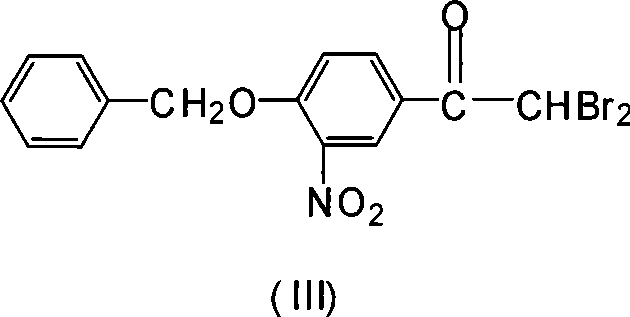
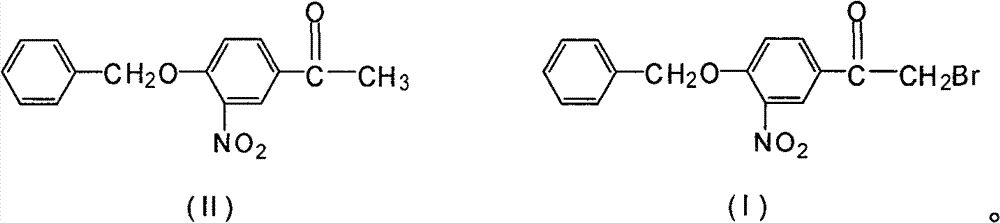
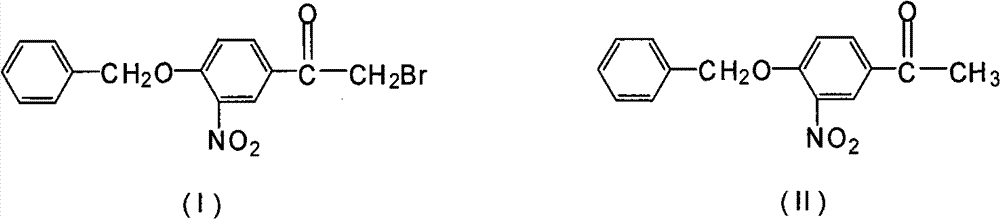
Novel synthesis method for 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxy-alpha-bromoacetophenone
InactiveCN101531597AReduced responseShort reaction timeOrganic chemistryPhysical/chemical process catalystsMethylene DichlorideSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a novel synthesis method for 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxy-alpha-bromoacetophenone having a structure represented by the formula (I), comprising the steps of: taking 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxyacetophenone having a structure represented by the formula (II) as raw material and taking phosphor or halide thereof as a catalyst; dissolving at first the 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxyacetophenone having the structure represented by the formula (II) and the catalyst in a reactive solvent; dropwise adding a mixed solution of bromine and the reactive solvent while maintaining the temperature in a range from negative 5 to 10 DEG C, after the addition, reacting for 1-5 hours while maintaining the temperature in a range from negative 5 to 10 DEG C, and filtering, washing and drying to obtain the 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxy-alpha-bromoacetophenone; the reactive solvent is selected from one of the group consisting of: ethyl acetate, methanol, ethanol, methylene dichloride, methenyl chloride, ethylidene dichloride and methylbenzene. The invention is mild in reaction conditions, friendly in reaction environment, short in reaction time, high in product yield and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Process for synthesizing alpha-bromoacetophenone compound
InactiveCN101462935BHigh purityHigh regional selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationOrganic solventAlpha-bromoacetophenone
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing alpha-bromo acetophenone compound, which comprises the steps: hydrosulphite solution is added into the mixture of substituted phenylethanone and bromate at the temperature of 30-90 DEG C, and the mixture is stirred to react for 2-9h, and then is cooled, filtered, washed and dried, so that the alpha-bromo acetophenone compound is obtained. The method also has the advantages that the product has high product purity, the price of bromide reagent is low, aqueous phase is solvent instead of organic solvent, the pollution is little, the operation issimple, and the method is suitable for mass production.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Novel synthesis method for 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxy-alpha-bromoacetophenone
InactiveCN101531597BReduced responseShort reaction timePhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic chemistryMethylene DichlorideSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a novel synthesis method for 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxy-alpha-bromoacetophenone having a structure represented by the formula (I), comprising the steps of: taking 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxyacetophenone having a structure represented by the formula (II) as raw material and taking phosphor or halide thereof as a catalyst; dissolving at first the 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxyacetophenone having the structure represented by the formula (II) and the catalyst in a reactive solvent; dropwise adding a mixed solution of bromine and the reactive solvent while maintaining the temperature in a range from negative 5 to 10 DEG C, after the addition, reacting for 1-5 hours while maintaining the temperature in a range from negative 5 to 10 DEG C, and filtering, washing and drying to obtain the 3-nitryl-4-benzyloxy-alpha-bromoacetophenone; the reactive solvent is selected from one of the group consisting of: ethyl acetate, methanol, ethanol, methylene dichloride, methenyl chloride, ethylidene dichloride and methylbenzene. The invention is mild in reaction conditions, friendly in reaction environment, short in reaction time, high in product yield and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of synthetic method of α-acyl homoallyl sulfide compound
Owner:WENZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of 4-phenylimidazole
InactiveCN103450089AWhite colorSimple processOrganic chemistryAlpha-bromoacetophenoneFormamidine acetate
The invention discloses a preparation method of 4-phenylimidazole. The method comprises the following steps: 1) substitution, namely, dissolving alpha-bromoacetophenone into formamidine acetate, and reacting in ethylene glycol, so as to obtain a nucleophilic replace intermediate; 2) cyclizing, namely, adding potassium carbonate as an acid-binding agent, and controlling the temperature to carry out a cyclization reaction; and 3) post-treatment, namely obtaining the 4-phenylimidazole by post-treatment after the reaction is ended. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the 4-phenylimidazole is synthetized from conventional chemical raw materials; the preparation method is simple in process, less in reaction steps, and convenient to purify; an industrial operation is facilitated; the target product is white in color and luster; the content of the final product can be up to over 99%; the yield is greater than 45%.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG XINYI CHEM
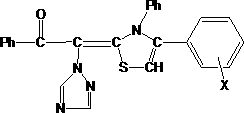
Method for synthesizing thiazole derivative containing acetophenone triazole group in ultrasonic solvent-free manner
ActiveCN107686481ANo pollution in the processNo separation and purificationOrganic chemistryUltrasound - actionPotassium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a thiazole derivative containing an acetophenone triazole group in an ultrasonic solvent-free manner. Three solids of alpha-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)acetophenone, phenyl isothiocyanate and potassium hydroxide are adopted as raw materials; foggy alpha-bromoacetophenone is enabled to react with the solids under ultrasonic action by adopting a liquid spraying manner; the reaction is promoted by adopting the solvent-free ultrasonic manner, and the method has the advantages of being simple in reaction equipment, higher in yield, quicker in speed, easy to operate, free from other side-products, free from a solvent, free from pollution and easy in separation and purification, and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-selectivity synthesis method of benzoyl formic acid
InactiveCN102336656BReduce generationEmission reductionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAlpha-bromoacetophenoneHigh selectivity
The invention discloses a high-selectivity synthesis method of benzoyl formic acid, which comprises the following steps: oxidizing styrene, which serves as the raw material, in a H2O2 / tetrabutylammonium bromide mixed system to generate alpha-bromophenethyl alcohol; oxidizing the generated alpha-bromophenethyl alcohol with H2O2 to generate alpha-bromoacetophenone; hydrolyzing the alpha-bromoacetophenone under alkaline conditions to generate alpha-hydroxyacetophenone; and oxidizing the alpha-hydroxyacetophenone with H2O2 to generate the target product benzoyl formic acid. In the invention, oxydol is used as an oxidant, and the byproduct is water, thereby reducing the generation of the organic byproducts and the discharge amount of inorganic salt (acid) waste water. Compared with other inorganic heavy metallic salt and inorganic mineral acid oxidization methods, the method disclosed by the invention enhances the cleanness of industrial preparation reaction, and reduces the environmental pollution. The invention enhances the product yield and purity: the yield is enhanced by nearly 13%, the total yield is up to 93.7%, and the product purity exceeds 95%; and other indexes are correspondingly enhanced.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
High selectivity synthesis method of benzoyl formic acid
InactiveCN102344361BReduce generationMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationSynthesis methodsAlpha-bromoacetophenone
The invention discloses a high selectivity synthesis method of benzoyl formic acid. With styrene as raw material, addition oxidation reaction is carried out in a mixed system of H2O2 and tetrabutyl ammonium bromide to obtain alpha-bromoacetophenone; then ethylene glycol and para-toluenesulfonic acid are added, reflow reaction is carried out to generate alpha-bromoacetophenone ethylene glycol; thegenerated alpha-bromoacetophenone ethylene glycol is hydrolyzed in potassium carbonate solution to generate alpha-hydroxyacetophenone ethylene glycol; the alpha-bromoacetophenone ethylene glycol reacts in the mixed system of H2O2 an tetrabutyl ammonium bromide to obtain 2-phenyl-1,3-dioxolame-2-carboxylic acid, and then deprotection reaction is carried out with oxalic acid to generate target product benzoyl formic acid. The synthesis method disclosed by the invention has high reaction yield, good reaction selectivity, low cost, simple technological process, mild reaction conditions and high product purity, and the defects of the traditional technological method that environment is severely polluted and cost is high are overcome, thus the synthesis method disclosed by the invention has industrial-scale production prospect.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Alpha-bromoacetophenone compound production method
InactiveCN100358854CRealize deep processing and utilizationAvoid recyclingOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationOrganic solventBromine
The preparation method for alpha-hypnone bromide comprises: stirring and heating to 90Deg, dripping the liquid bromine directly into hypnone compound aqueous solution to produce the product as an important drug intermediate and HBr gas. This invention is practical, belongs to a green chemical method without any toxic organic solvent, and has great economic value.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridine compound and its synthesis method Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridine compound and its synthesis method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6d8a91ff-360e-4783-80d3-9eff21627f8a/HDA0000446809740000011.PNG)
![Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridine compound and its synthesis method Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridine compound and its synthesis method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6d8a91ff-360e-4783-80d3-9eff21627f8a/HDA0000446809740000012.PNG)
![Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridine compound and its synthesis method Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridine compound and its synthesis method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6d8a91ff-360e-4783-80d3-9eff21627f8a/HDA0000446809740000021.PNG)
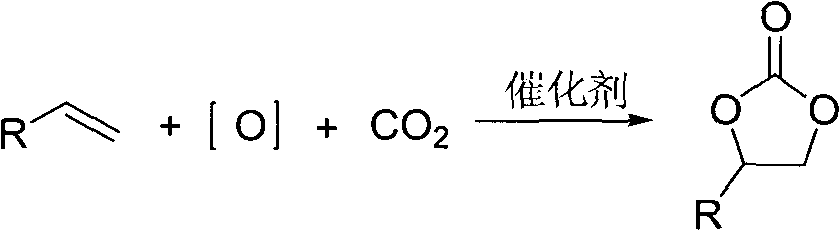
![Benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and synthetic method thereof Benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and synthetic method thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/29e971f4-2134-4ae5-9c33-2100a58d4dd1/HDA0000446809740000011.PNG)
![Benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and synthetic method thereof Benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and synthetic method thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/29e971f4-2134-4ae5-9c33-2100a58d4dd1/HDA0000446809740000012.PNG)
![Benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and synthetic method thereof Benzofuran [2, 3-c] pyridine compound and synthetic method thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/29e971f4-2134-4ae5-9c33-2100a58d4dd1/HDA0000446809740000021.PNG)
![Synthesis method for 6-fluoroimidazo[1, 2-a]pyridine-3-phenyl ketone Synthesis method for 6-fluoroimidazo[1, 2-a]pyridine-3-phenyl ketone](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/61c2b5ff-e766-473e-abae-262d69292051/450970DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.PNG)