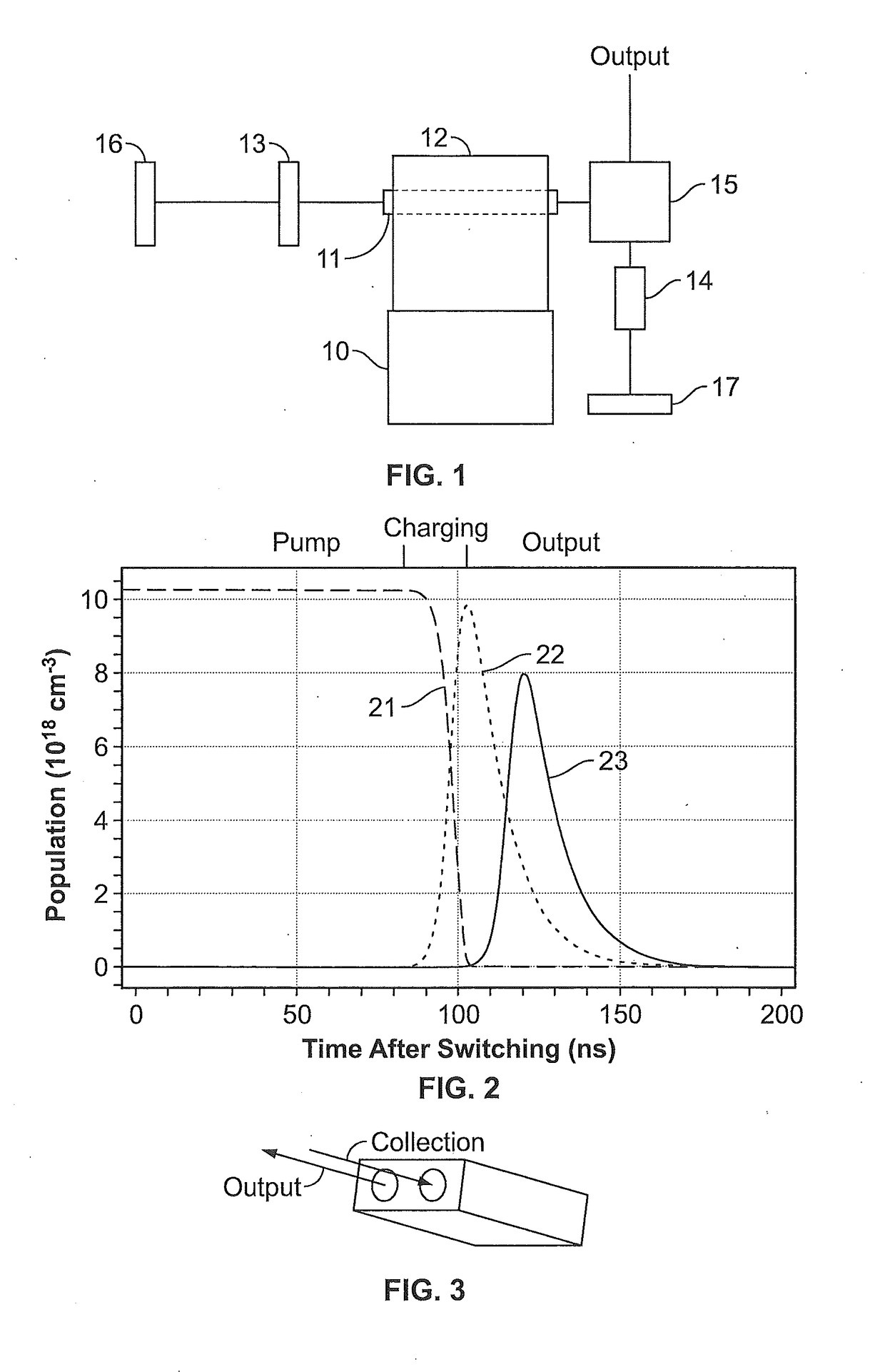
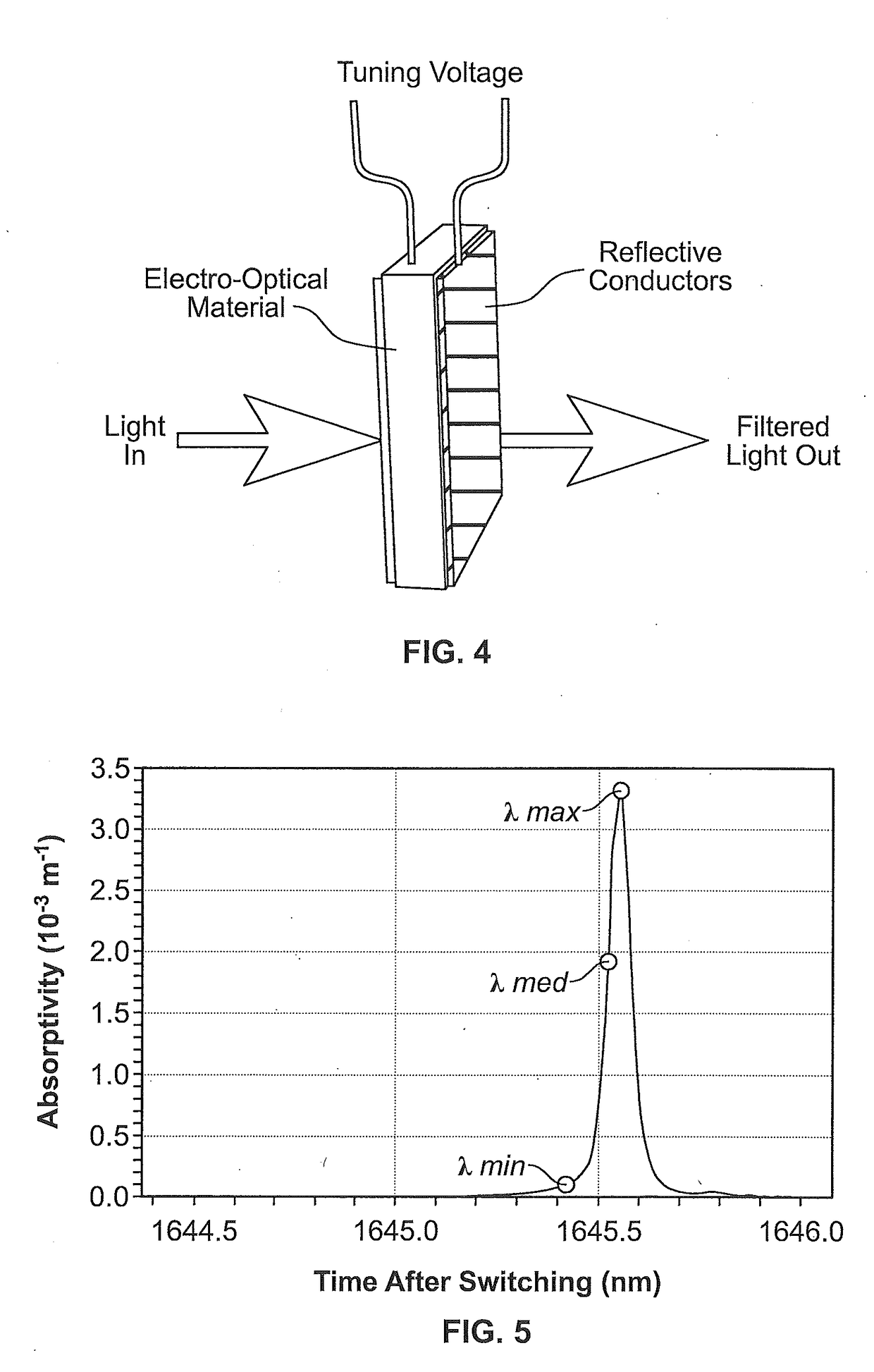
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Active laser medium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The active laser medium (also called gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from a higher energy state previously populated by a pump source.
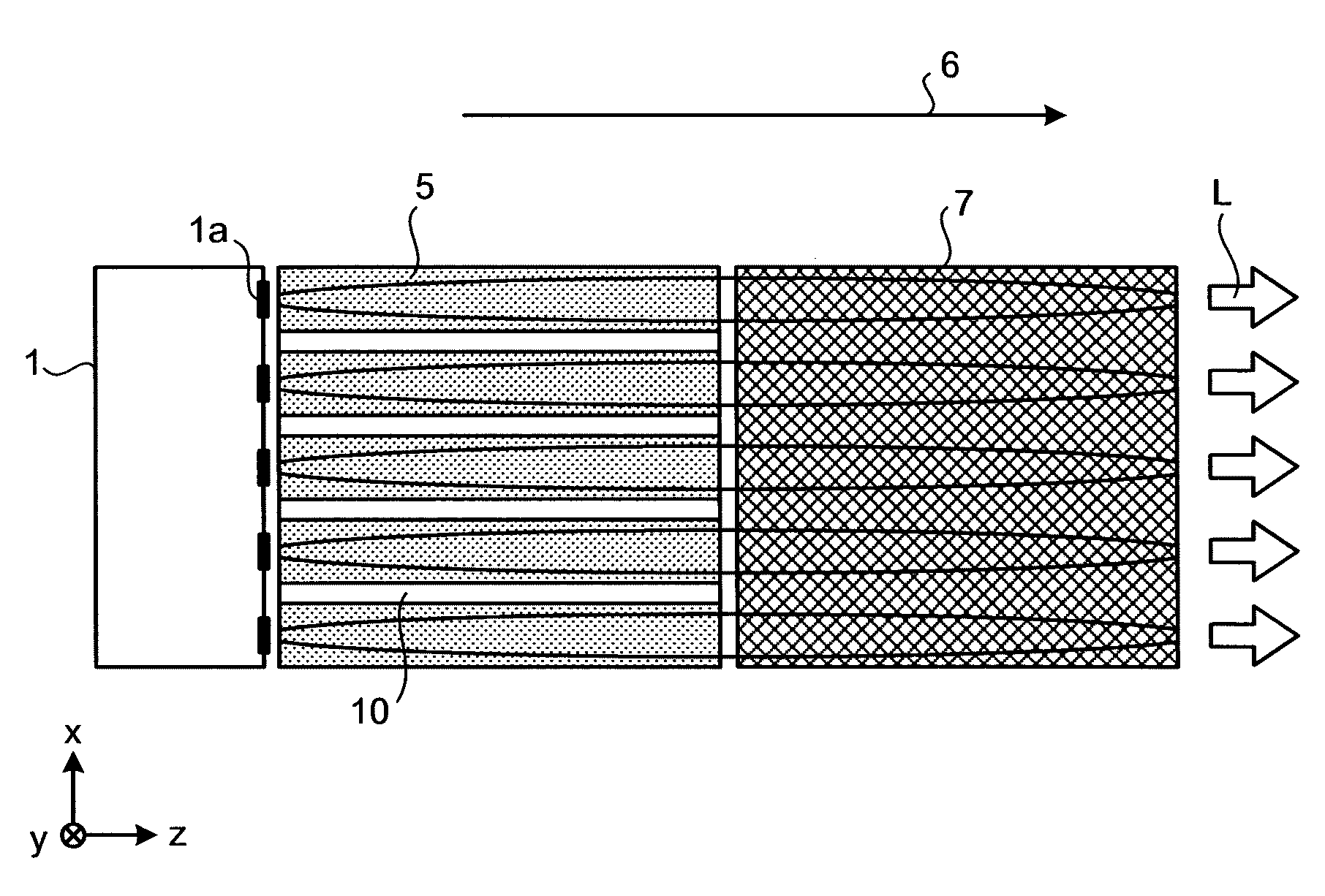
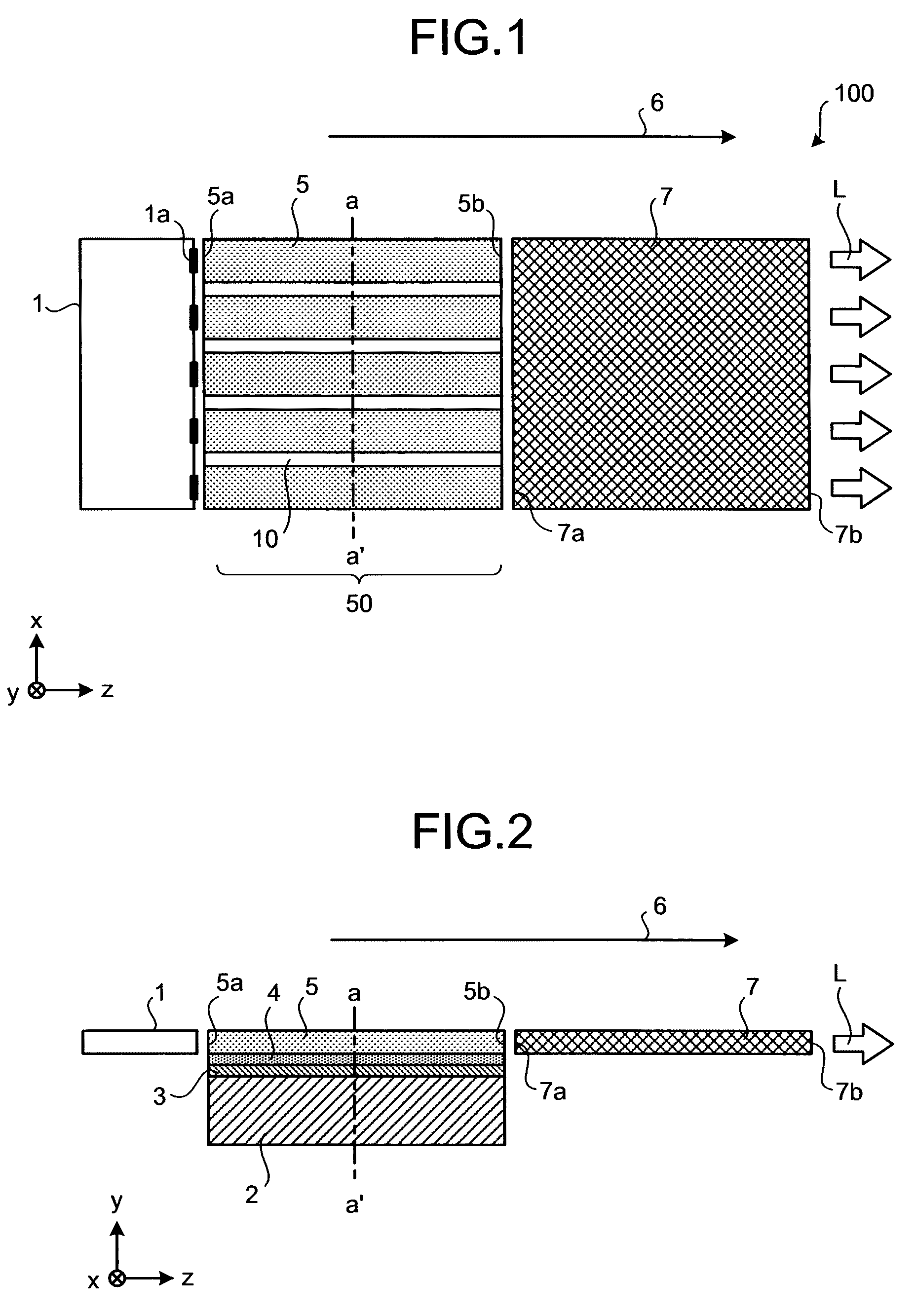
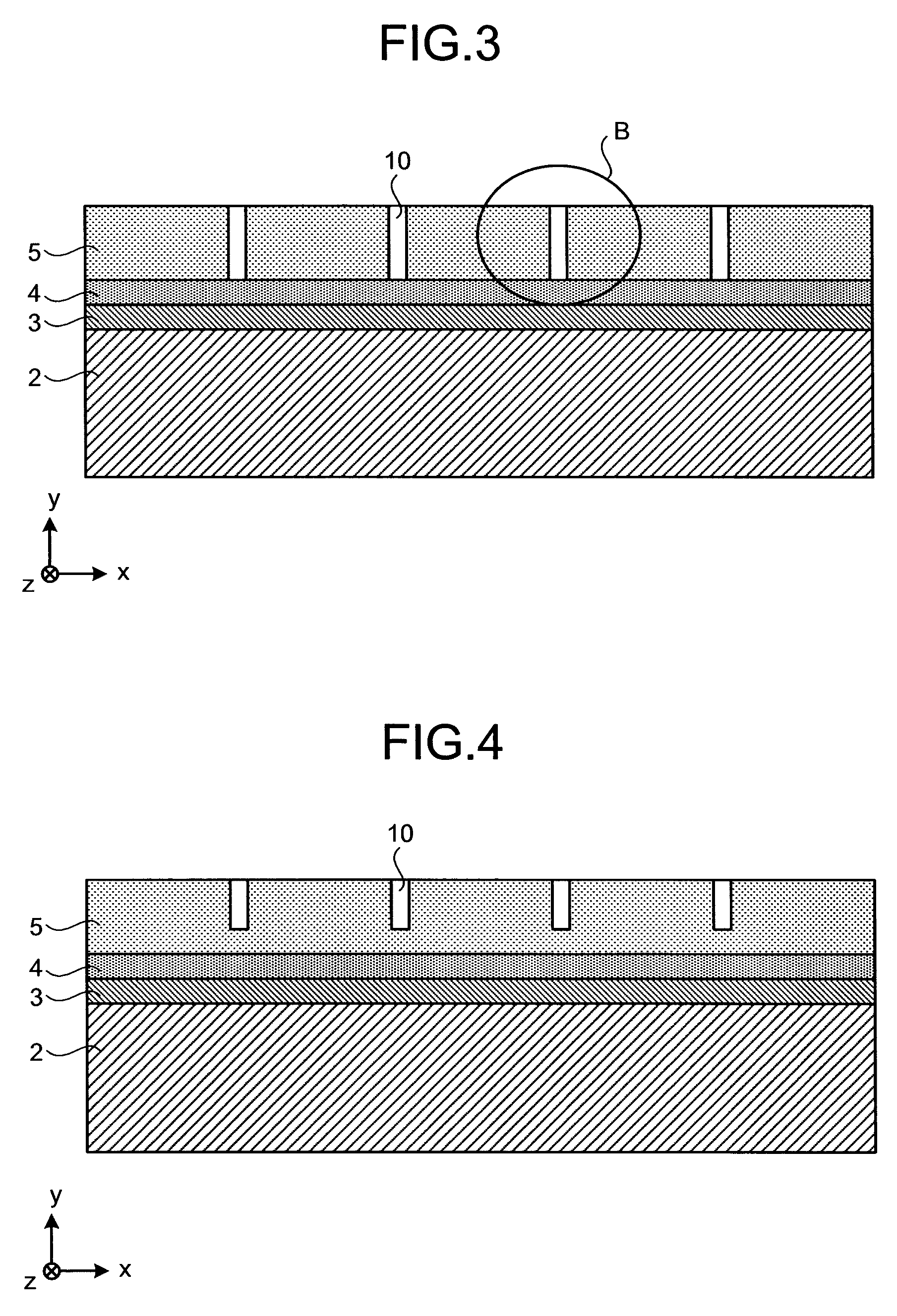
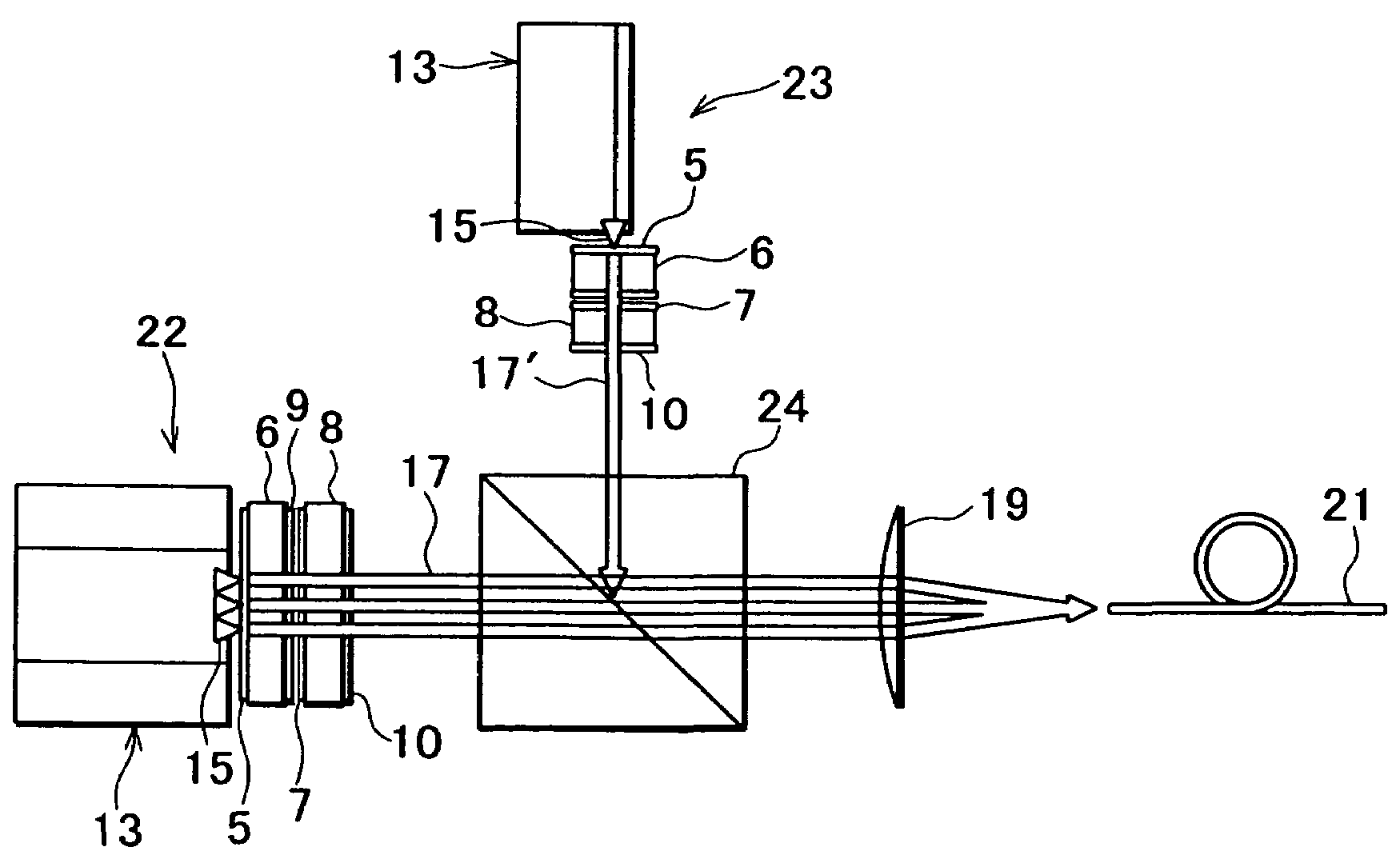
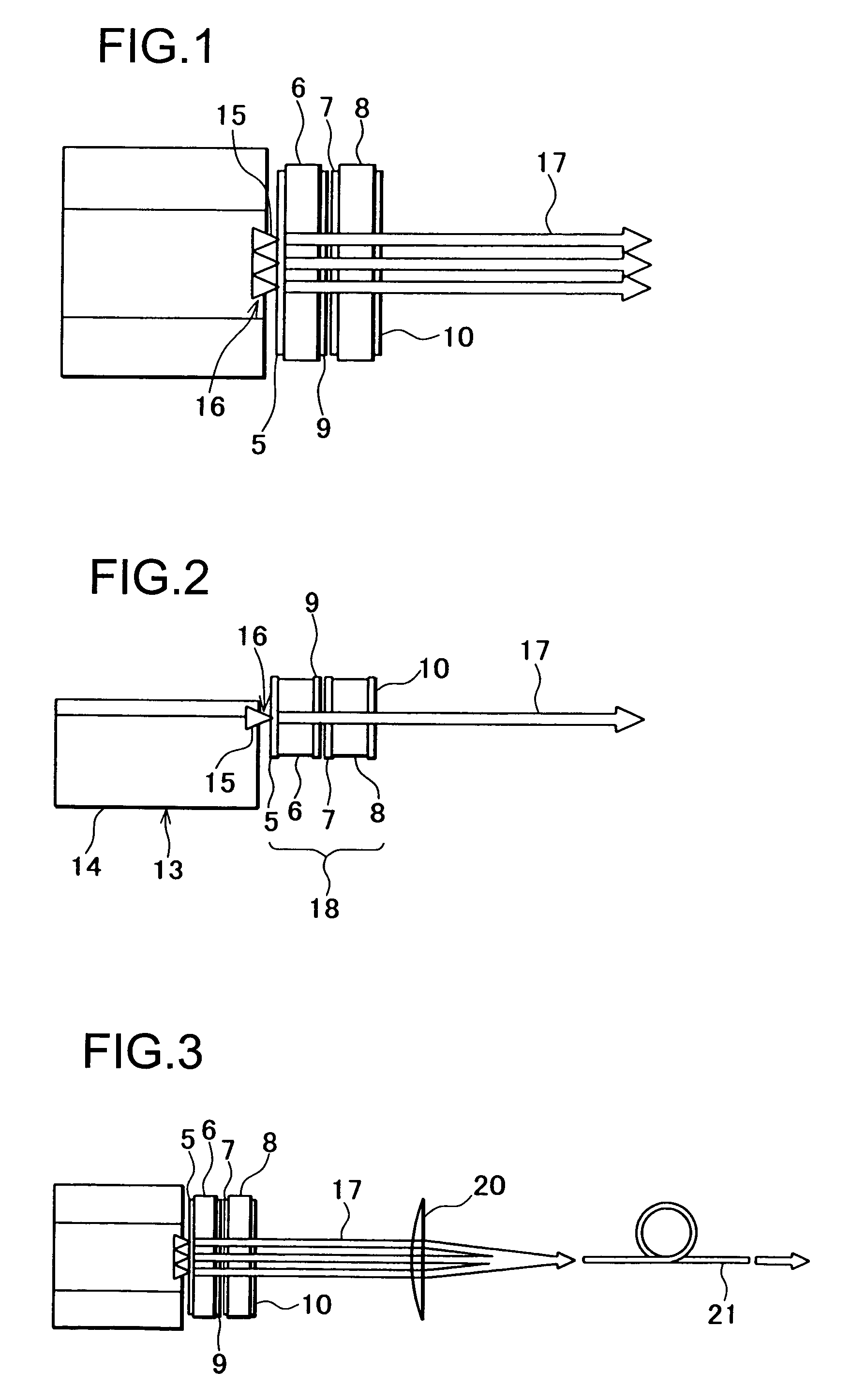
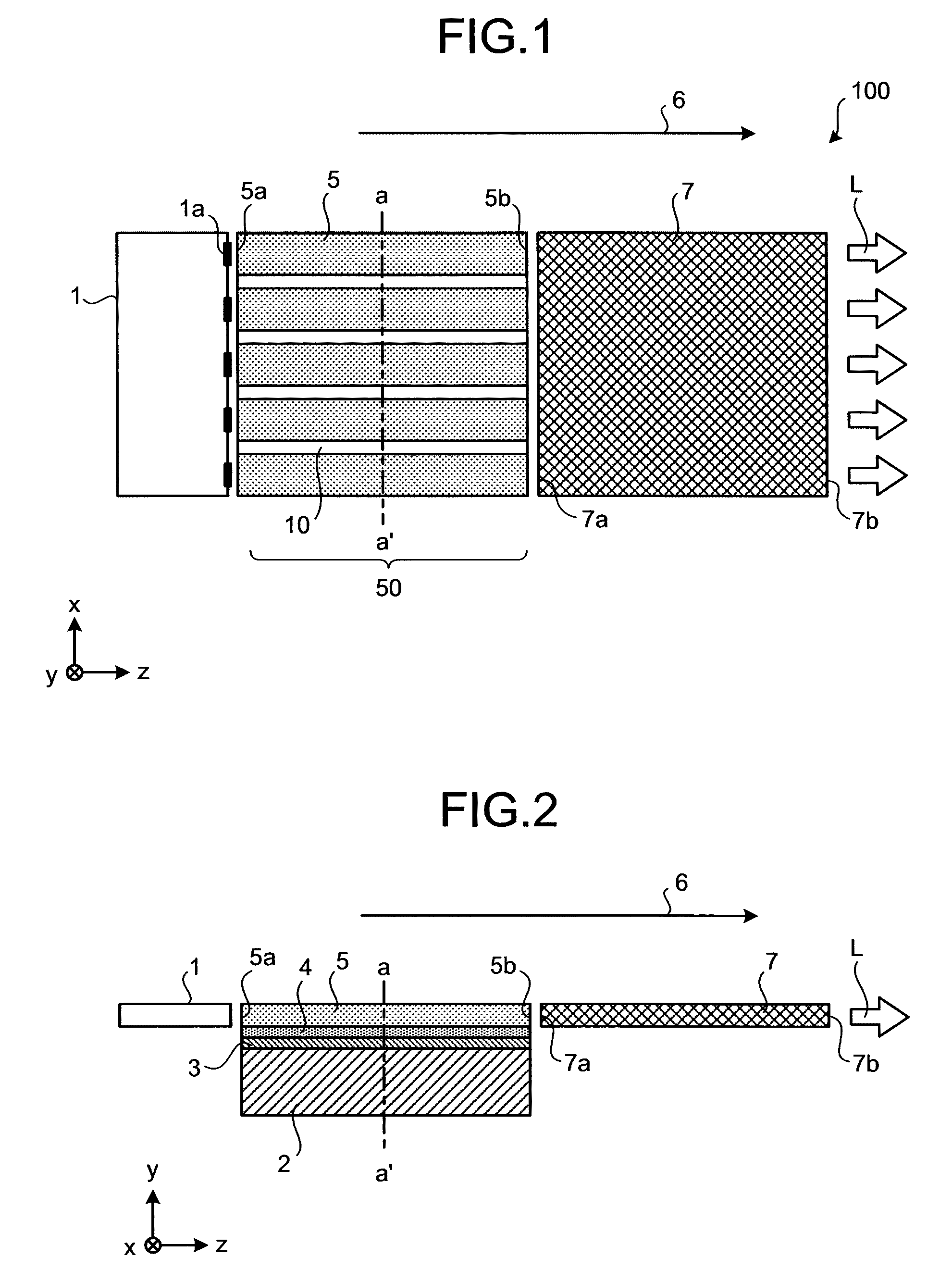
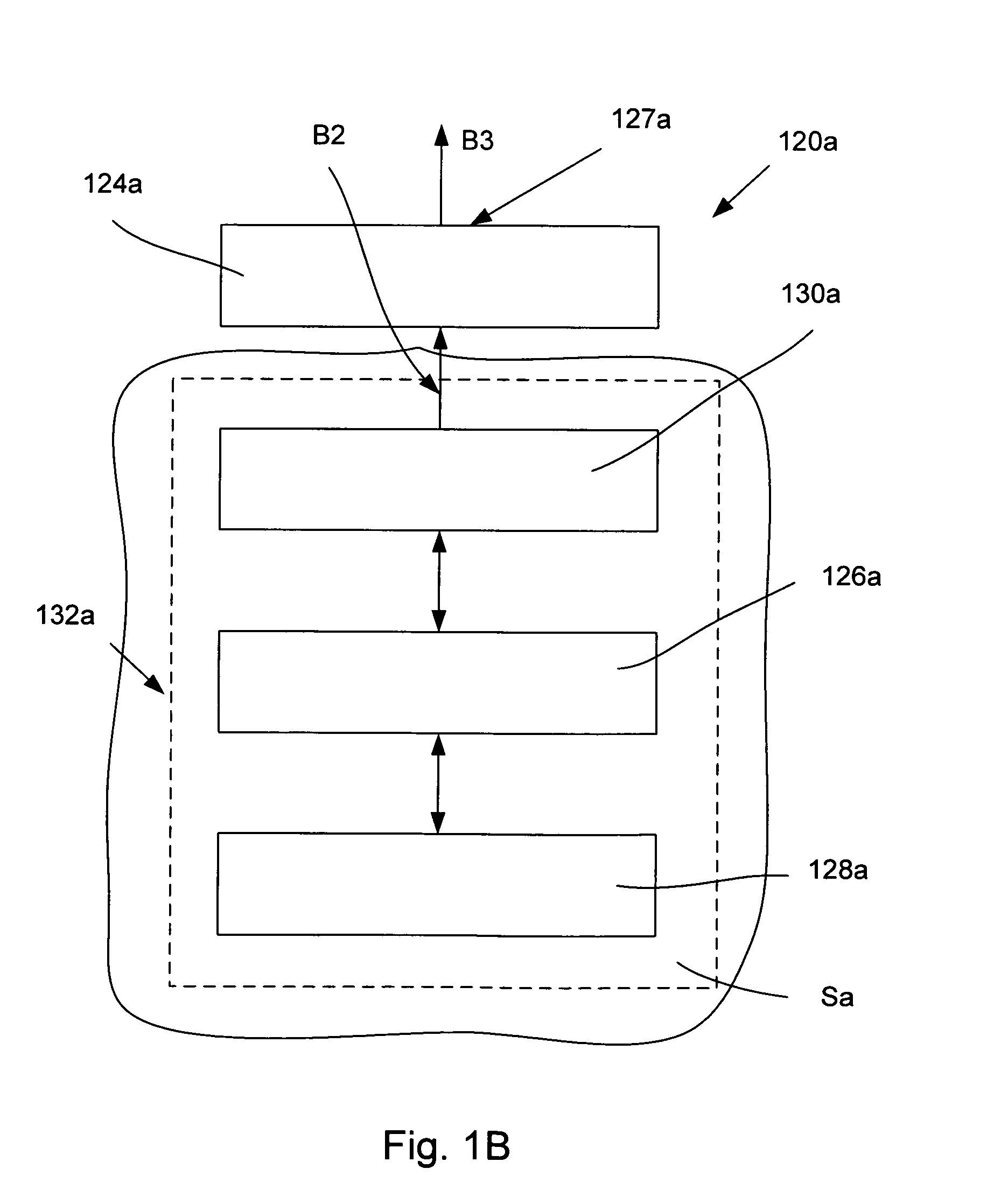
Slab type laser apparatus
ActiveUS20090316746A1Improve focus performanceInhibit swellingExcitation process/apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusAudio power amplifierGas laser
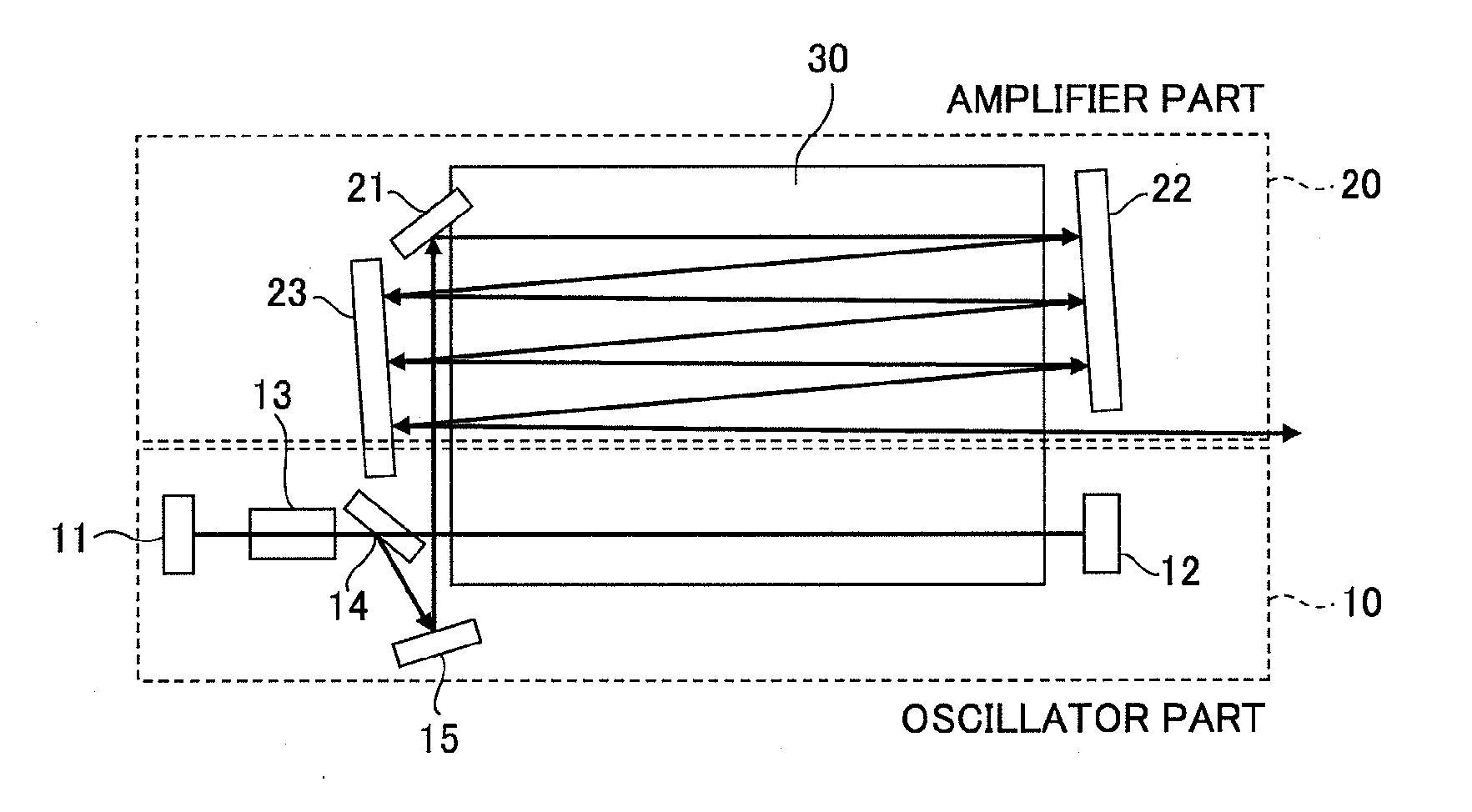
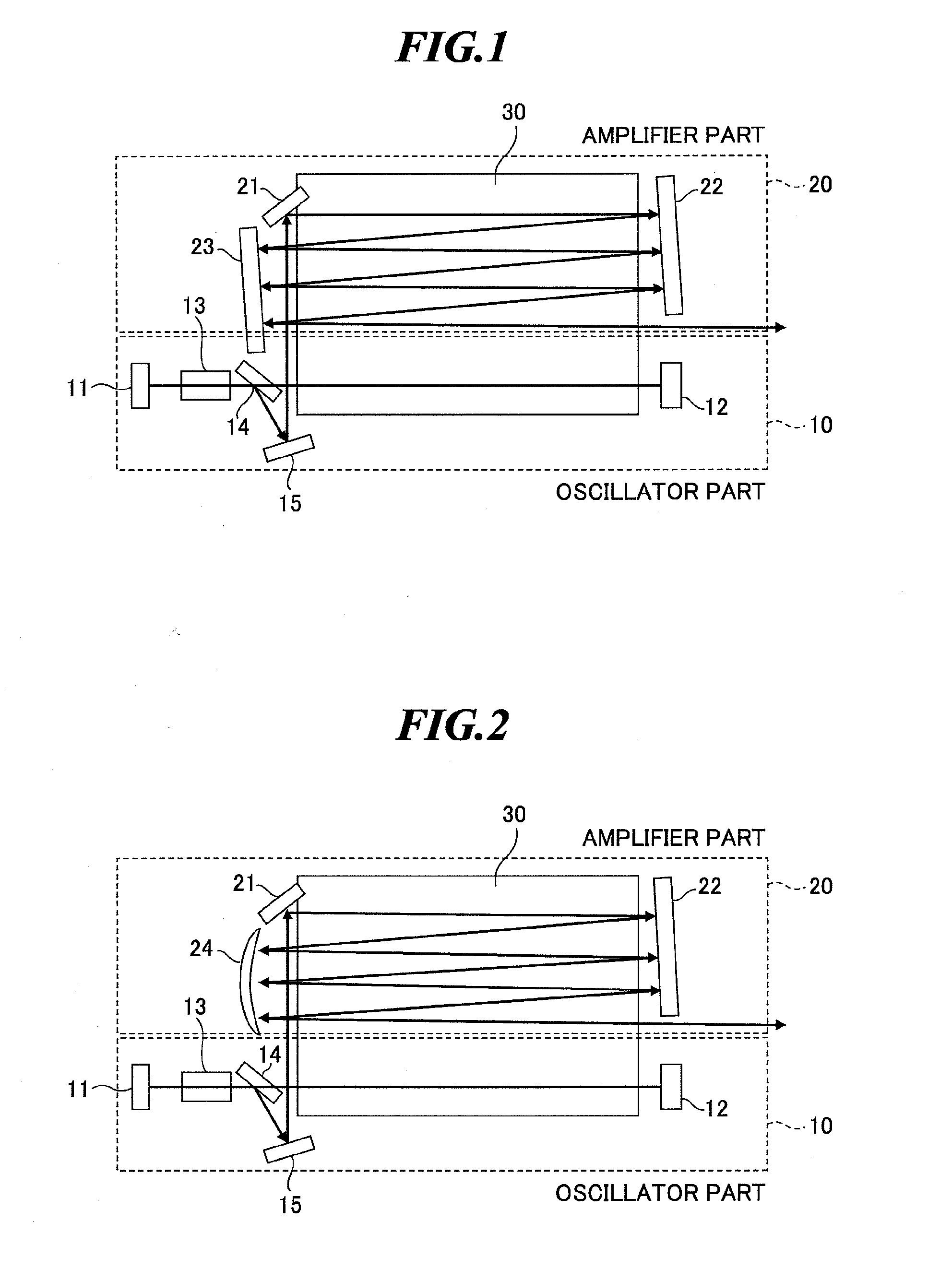
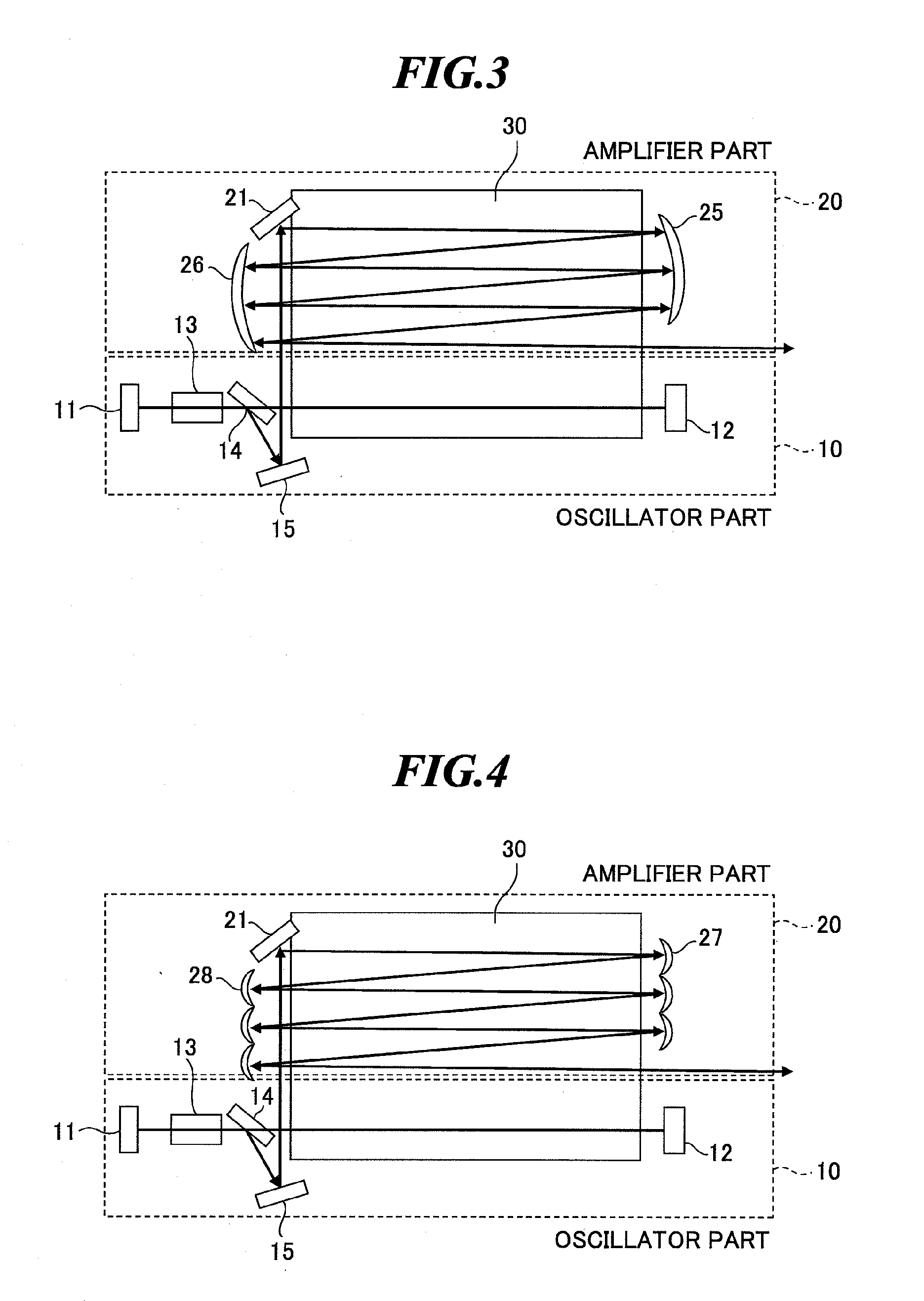
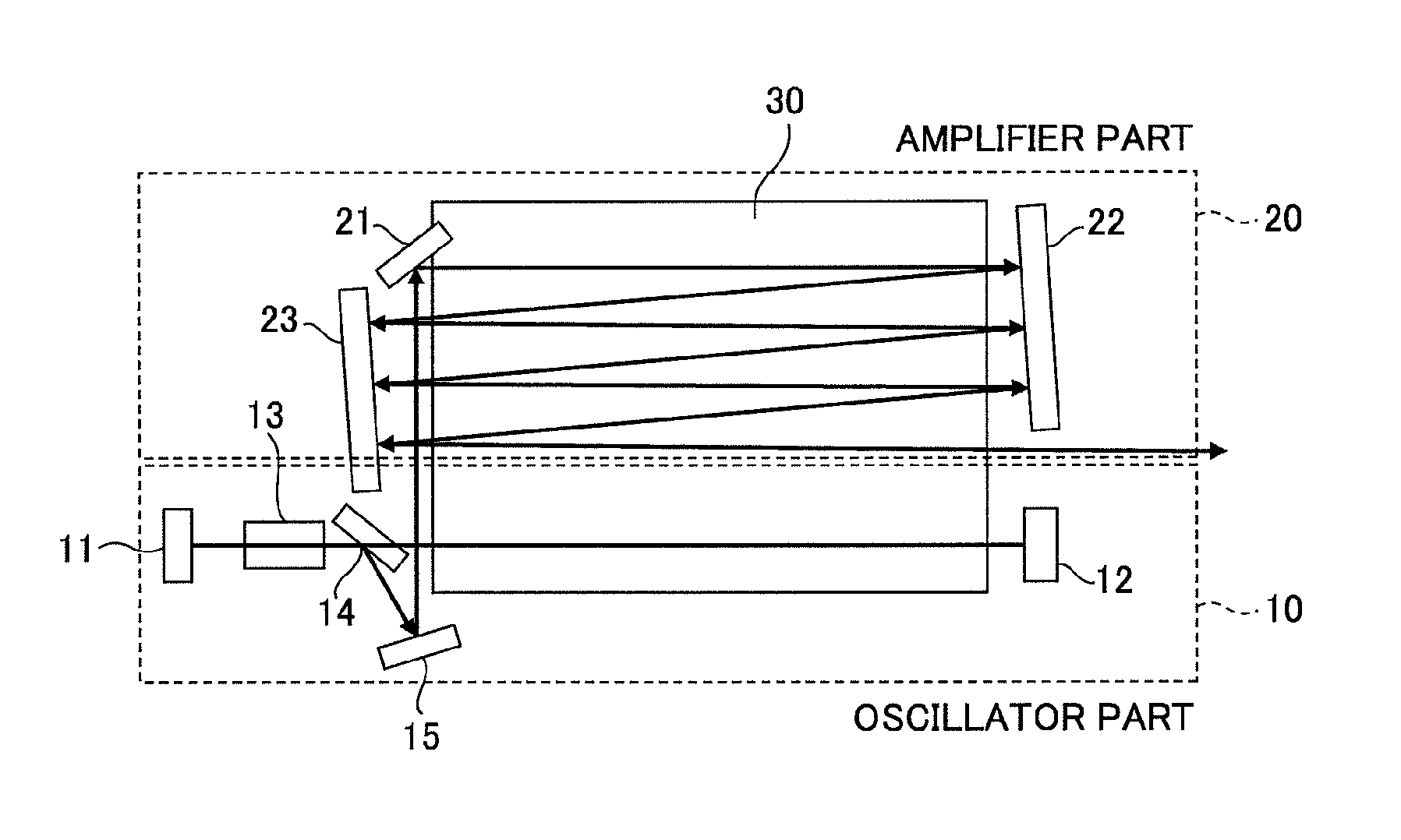
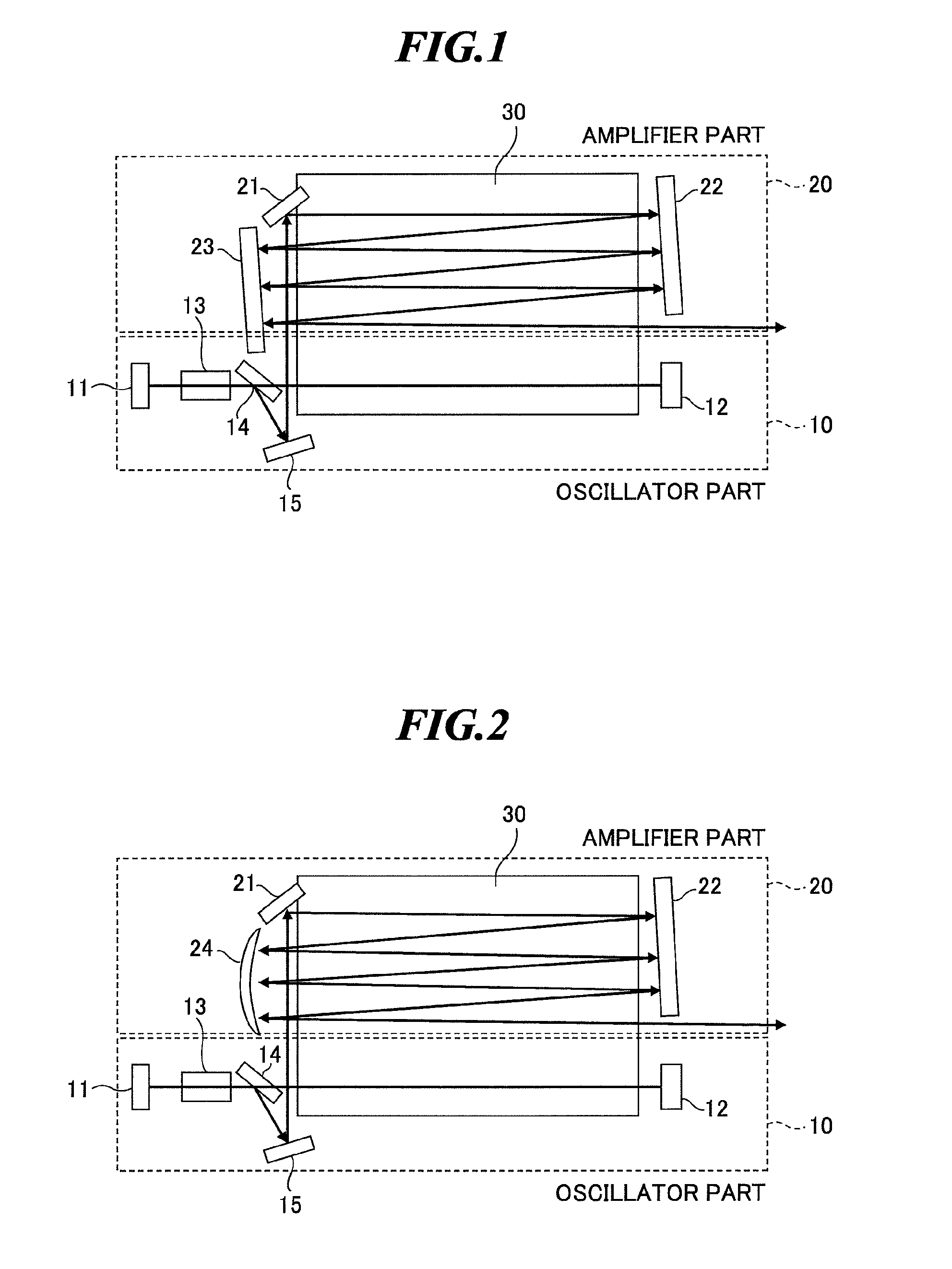
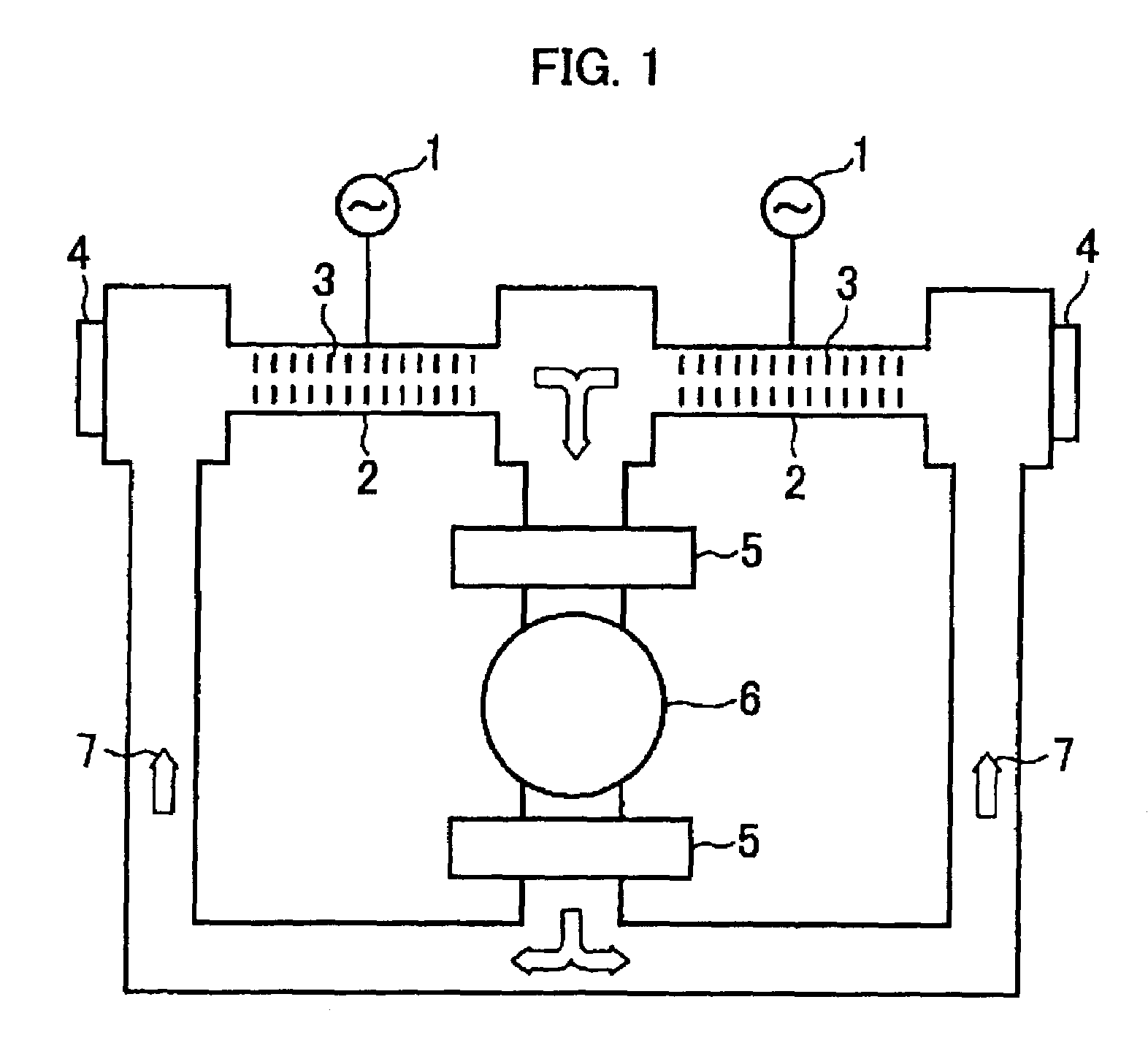
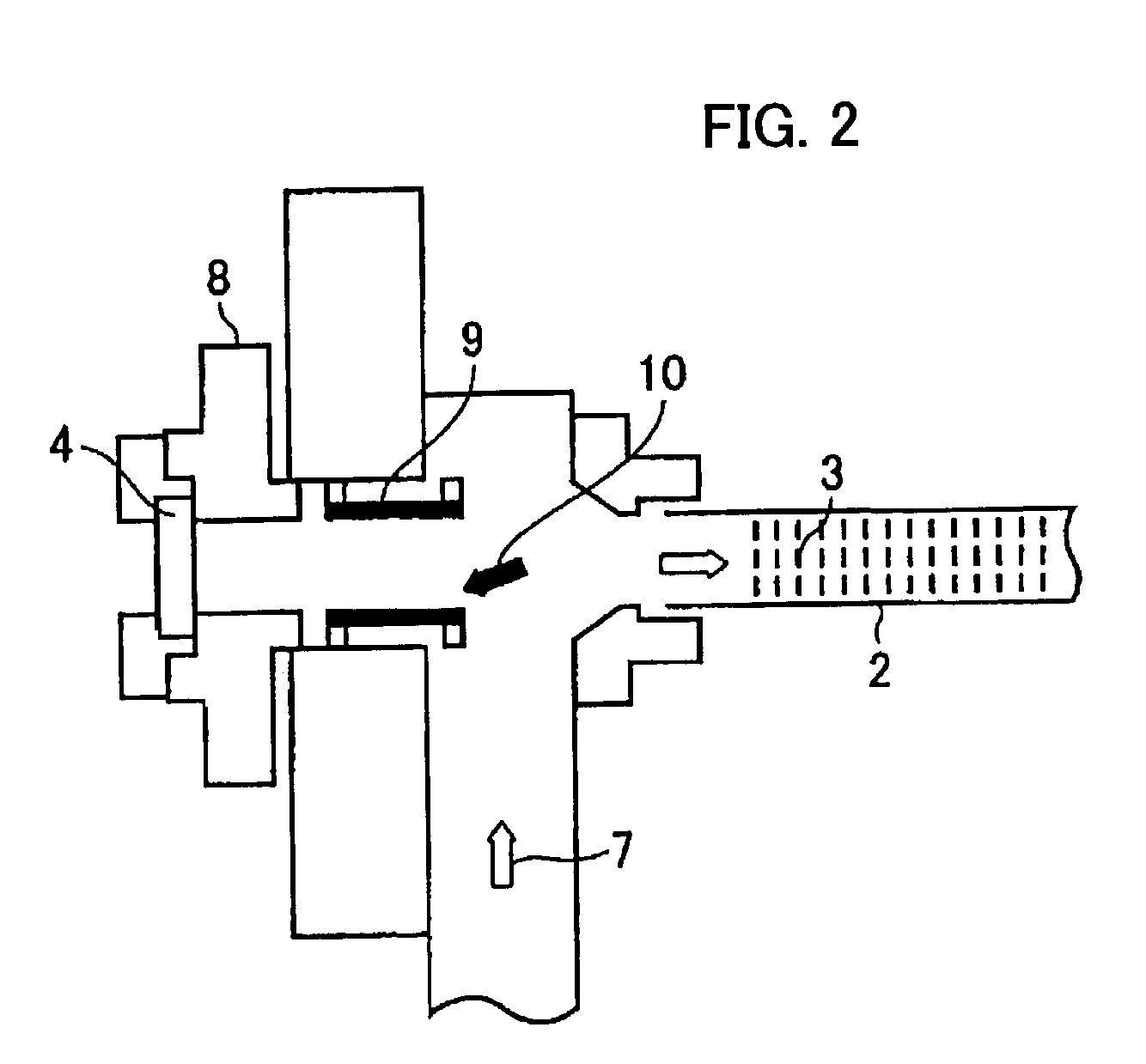
A slab type laser apparatus has a slab type gas laser medium part formed in a region defined by a pair of electrode flat plates oppositely disposed in parallel with each other in a space to be filled with a gas laser medium which is excited by high-frequency electric power. The apparatus includes an oscillator part including a pair of resonator mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between, and for amplifying a laser beam to have predetermined light intensity to emit the laser beam, and the amplifier part including a plurality of return mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between. The incident laser beam goes and returns plural times between the return mirrors, and the laser beam is amplified to have predetermined power.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
Fiber amplifier with integrated fiber laser pump
ActiveUS20080130102A1Efficient injectionSimple and compact and cheapLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierOptical coupling
An optical system adapted to amplify an input signal includes an optical pump supporting the input signal and an optical pump beam. The optical pump includes an input port, a first active medium coupled to the input port, and a pump output coupled to the first active medium. The optical amplifier includes an amplifier input optically coupled to the pump output and adapted to receive the input signal after passing through the optical pump, a second active medium coupled to the amplifier input, and an amplifier output adapted to output the amplified input signal.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
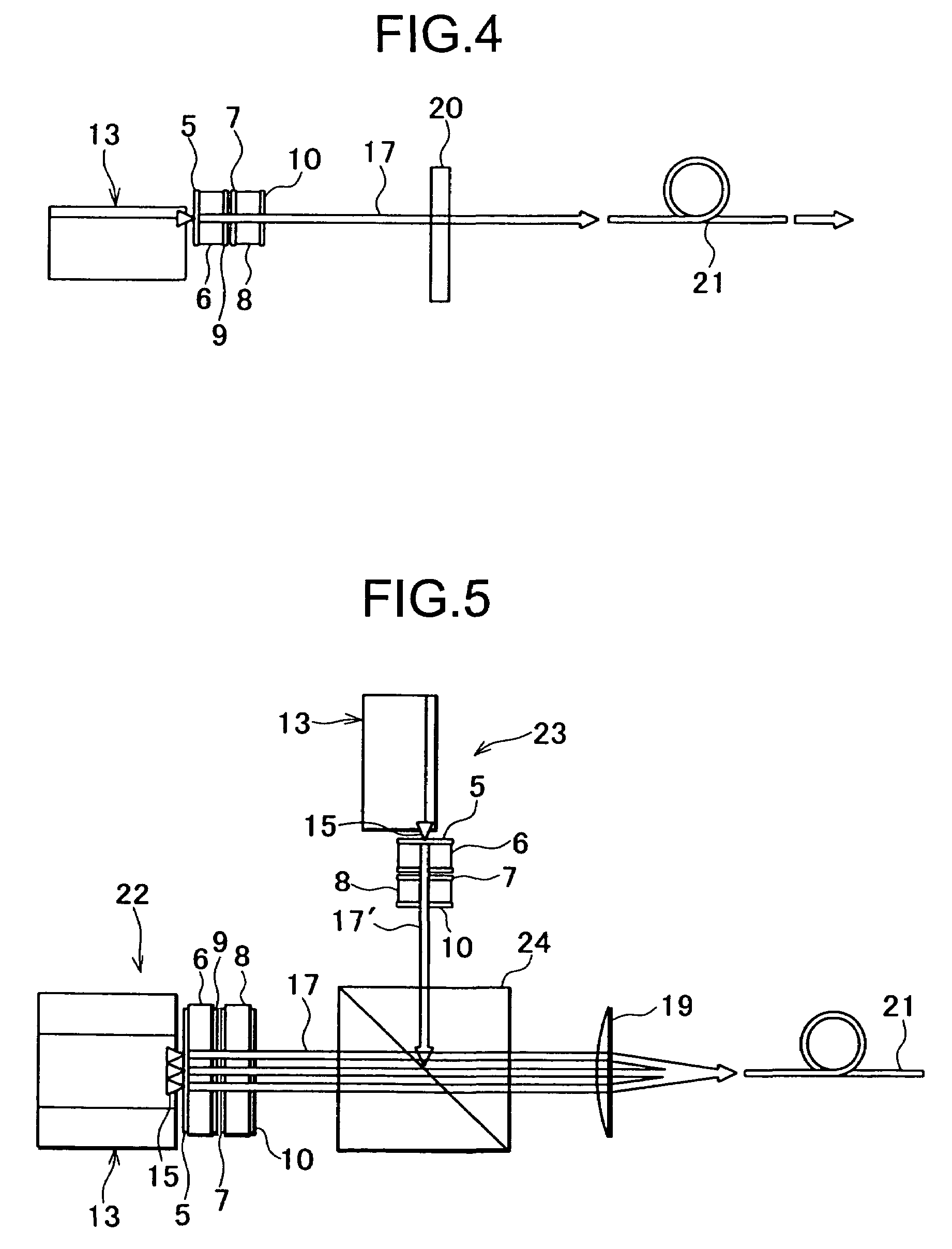
Slab type laser apparatus
ActiveUS7903715B2Improve focus performanceAmplify a laser beam efficientlyExcitation process/apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusAudio power amplifierGas laser
A slab type laser apparatus has a slab type gas laser medium part formed in a region defined by a pair of electrode flat plates oppositely disposed in parallel with each other in a space to be filled with a gas laser medium which is excited by high-frequency electric power. The apparatus includes an oscillator part including a pair of resonator mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between, and for amplifying a laser beam to have predetermined light intensity to emit the laser beam, and the amplifier part including a plurality of return mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between. The incident laser beam goes and returns plural times between the return mirrors, and the laser beam is amplified to have predetermined power.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
Tunable liquid microsphere laser
ActiveCN104993371ALower the thresholdChange the refractive indexActive medium materialFiberLiquid medium
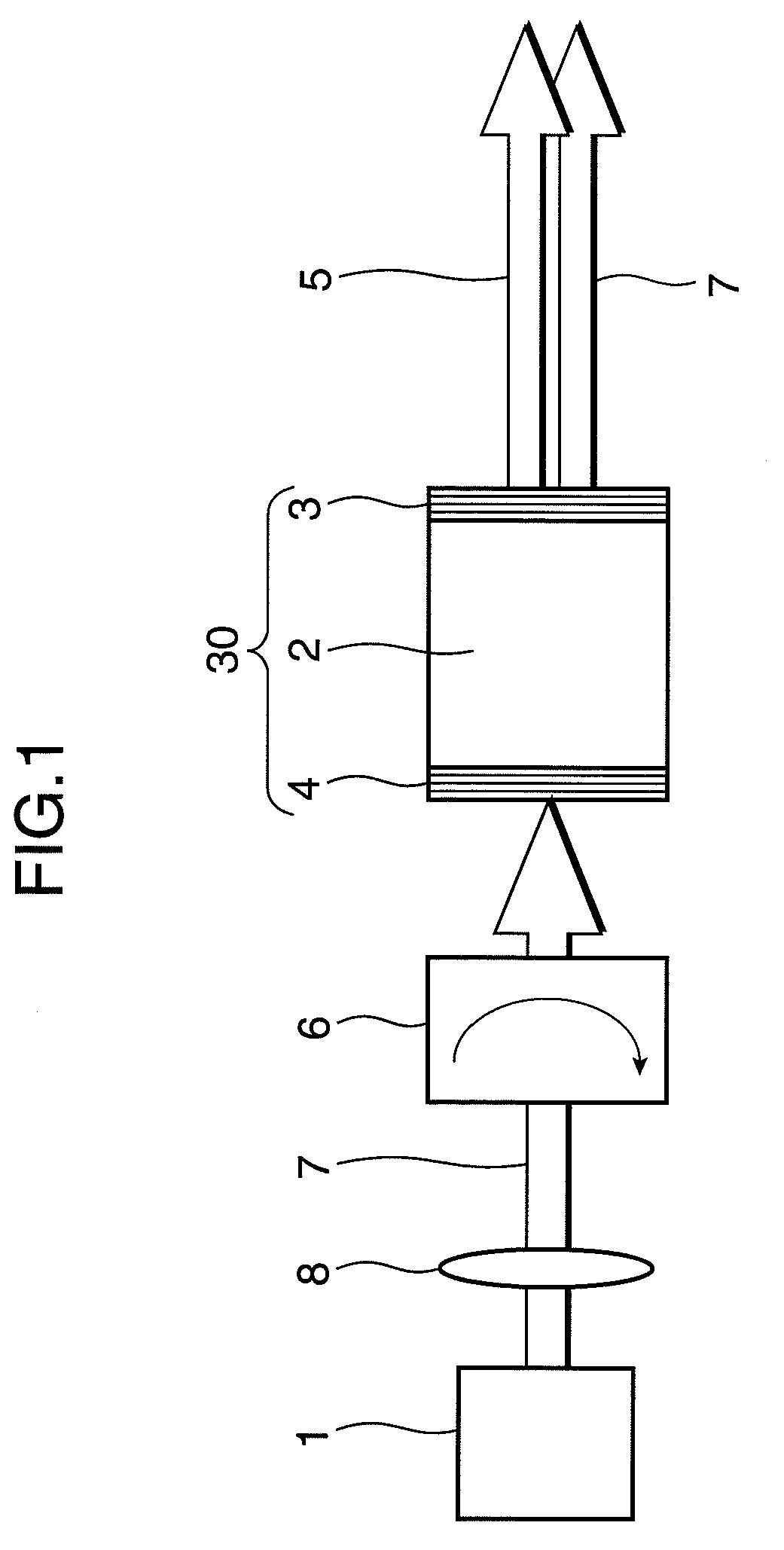
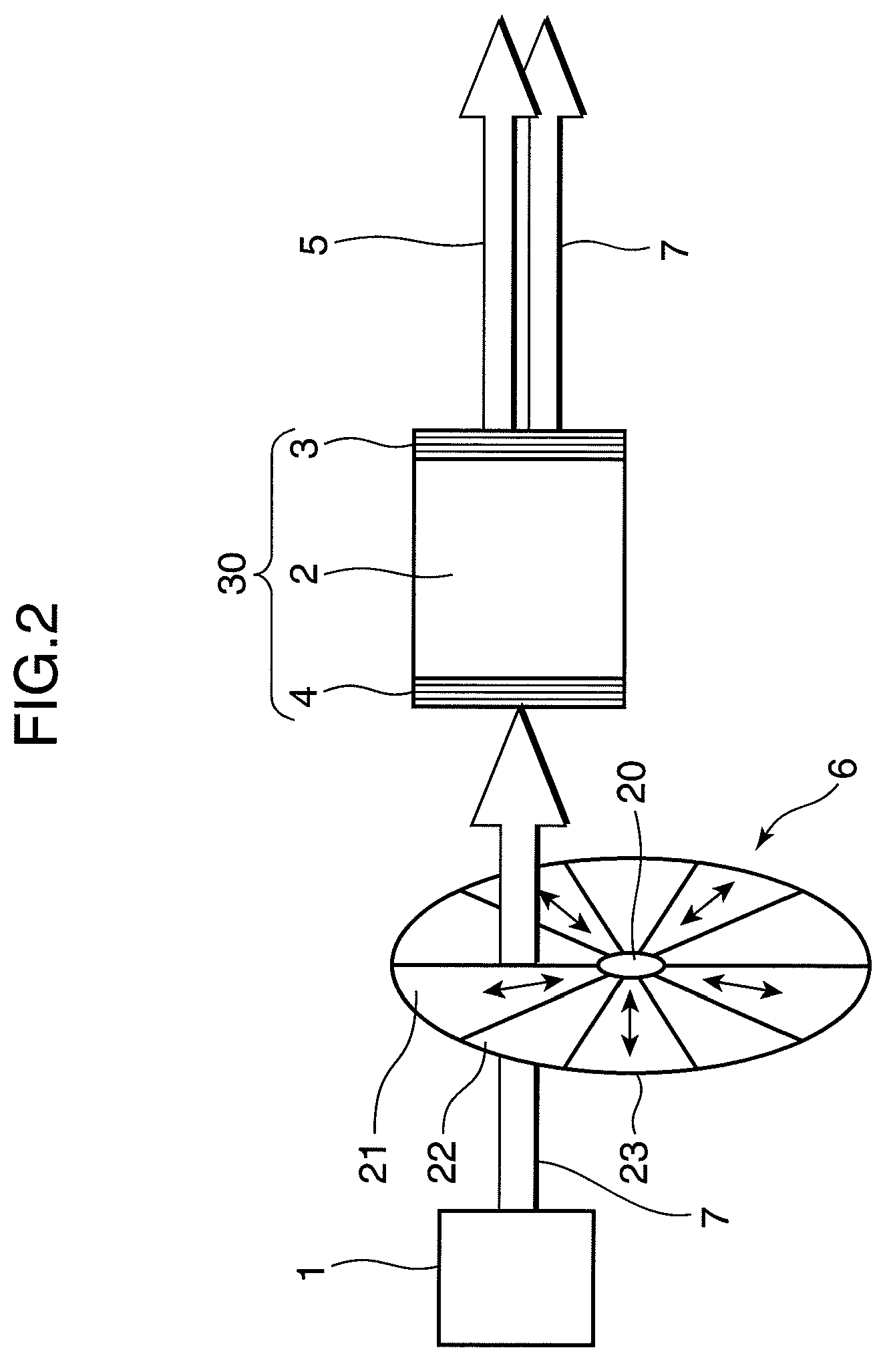
The invention provides a tunable liquid microsphere laser. A first capturing light source (1), a second capturing light source (2) and a pump light source (3) are connected to an excitation control part (7) through isolators. The excitation control part (7) is connected to a photodetector (9) through a 1*2 coupler (8). Another port of the 1*2 coupler (8) is a laser output port. The excitation control part (7) includes a first capturing fiber (7a), a second capturing fiber (7b), a pump light input fiber (7c), a laser output fiber (7d) and a liquid microsphere (7e). The liquid sphere is disposed between the pump light input fiber and the laser output fiber. The liquid microsphere includes active laser medium and is disposed in external transparent liquid medium (7f). According to the invention, by adopting fiber optical trap technology, the optical resonance principle and the laser principle, the tunable liquid microsphere laser is provided and has advantages of being high in stability, easy to operate, high in Q value, low in threshold value and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Intersubband quantum box stack lasers
ActiveUS20080043794A1Improve confinementEnergy efficiencyNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersPhotonic crystalWaveguide
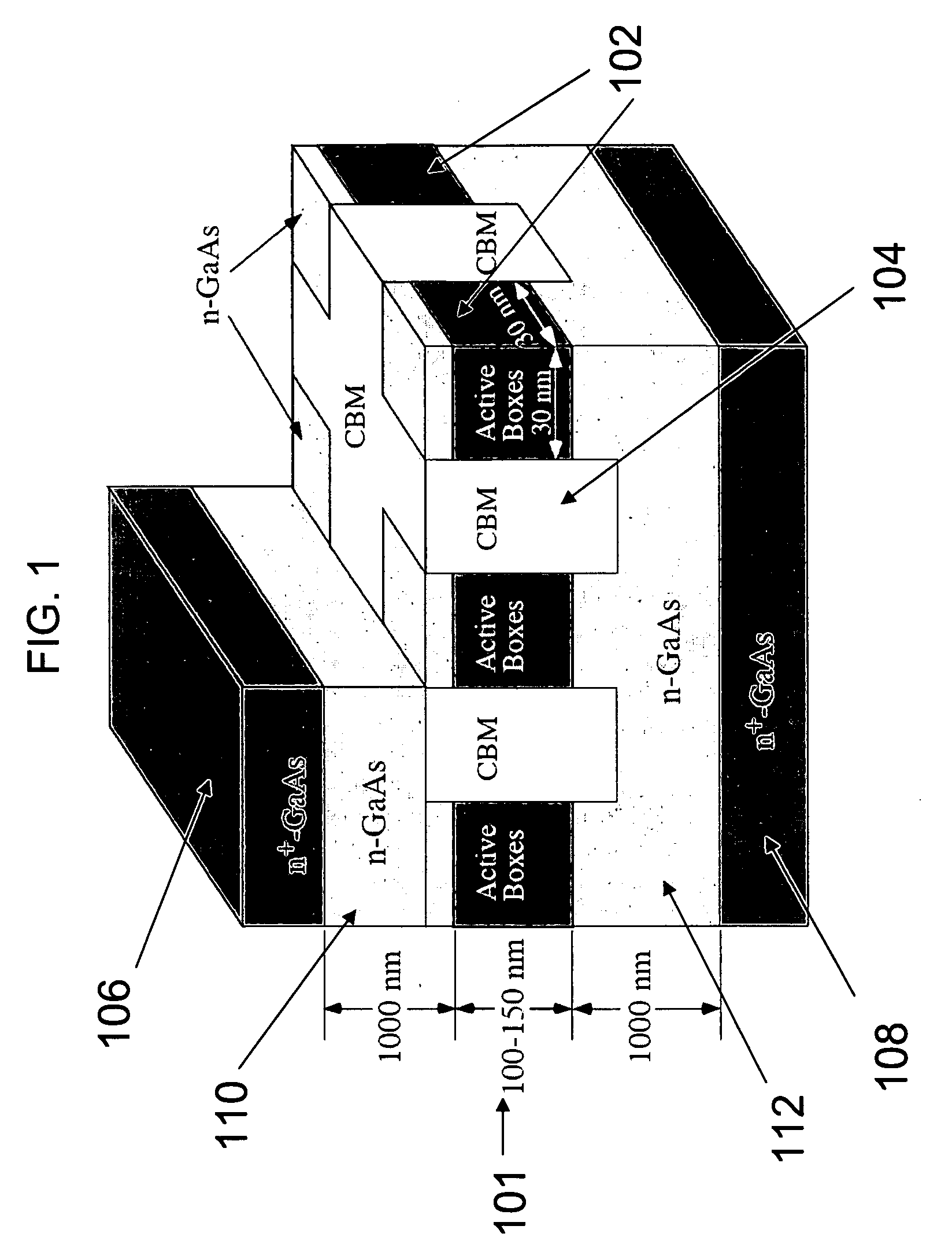
The present invention provides semiconductor lasers having an Active-Photonic-Crystal (APC) structure that allows scaling of the coherent power by using a waveguide having a periodic structure that selects operation in a single spatial mode from large-aperture devices. The lasers include an active medium that includes an array of quantum box ministacks, each ministack containing 2 to 5 vertically stacked, coupled quantum boxes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of manufacturing a laser diode with improved light-emitting characteristics
InactiveUS8451871B2Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexStimulated emission
The method of the invention is intended for manufacturing a laser diode with improved light-emitting characteristics. The method consists of providing certain components of a laser diode such as a wide-aperture lasing medium that has an active emitting layer with a first end and a second end, a DPH-mode reorganizer that contains a core and a plurality of nanogrooves made in the core and arranged in a pattern that accomplishes a given function and locally changes the refractive index of the core. The method further includes the steps of forming a semitransparent mirror on the second end of the active lasing medium and aligning the first end of the active emitting layer with the core of the DPH-mode reorganizer, thus forming a resonator of the laser diode. In the resonator, the light applied from the laser-active medium bounces back and forth between the DPH-mode reorganizer and the partially reflecting mirror, thereby enhancing stimulated emission.
Owner:OOO NANOOPTIC DEVICES
Spectrally pure short pulse laser
InactiveUS20170365974A1Reduce laser linewidthReduce usageActive medium materialColor/spectral properties measurementsWavelength filterLine width
A short-pulse, narrowband, line-selectable and tunable solid-state laser is described. The device requires a pump source, an active solid-state laser medium, an enclosing cavity, mirrors to contain the light, a method of removing the pulse from the cavity, a wavelength selection system, and a laser linewidth narrowing system. One implementation of this is an Er:YAG laser, side pumped by semiconductor lasers in the erbium absorption band near 1475 nm, with an intracavity etalon and a switchable spectral filter. To remove the pulse from the cavity, cavity dumping issues, which assures constant pulse energy and pulse length over a range of repetition rates, in this case from 100 Hz to 20 kHz. Line selection is obtained by use of wavelength filters and fine tuning with an etalon, which also acts as the linewidth narrowing system.
Owner:LUMINIT
Laser
A laser includes a total reflective mirror, an output mirror, a discharge lamp, and an active laser medium. The total reflective mirror, the output mirror, and the discharge lamp define a resonant cavity. The active laser medium is filled in the resonant cavity. The total reflective mirror includes a microstructure. The microstructure is concave ring-shaped structure. The concave ring-shaped structure has a depth and a width, and both the depth and the width are in a range from about 0.5λ to about 2λ, while λ is a working wavelength of the laser.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Velocity measurement device and laser range finder using a coherent detection
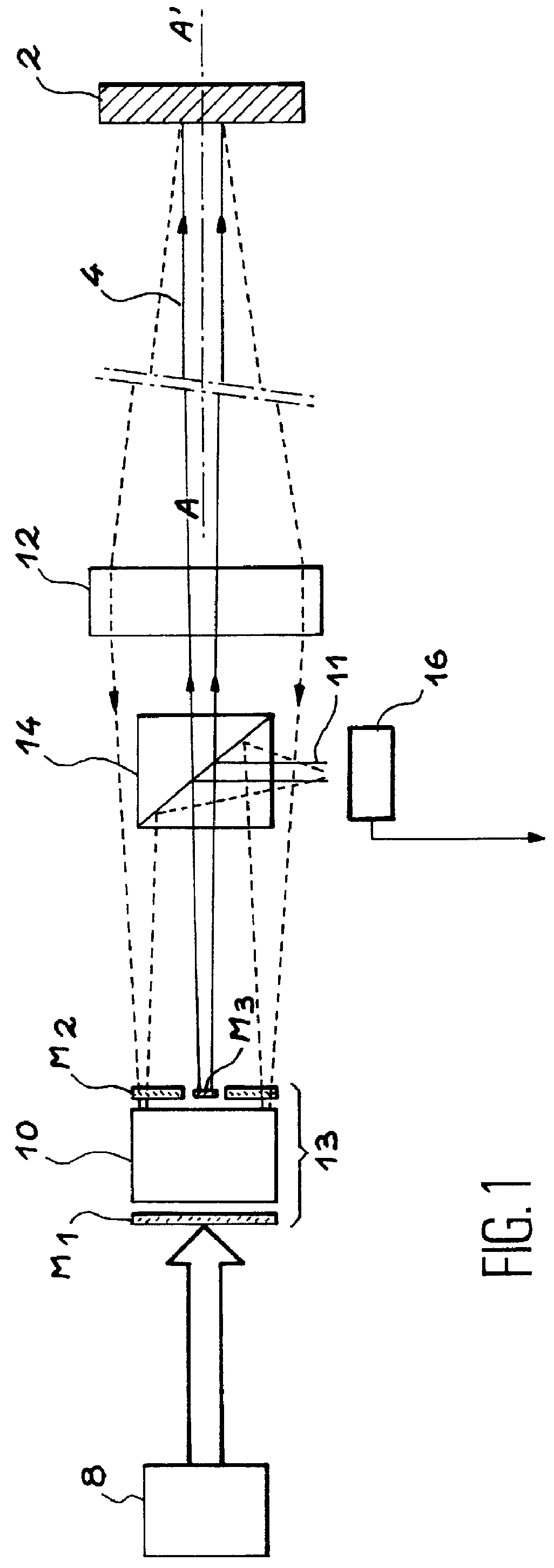
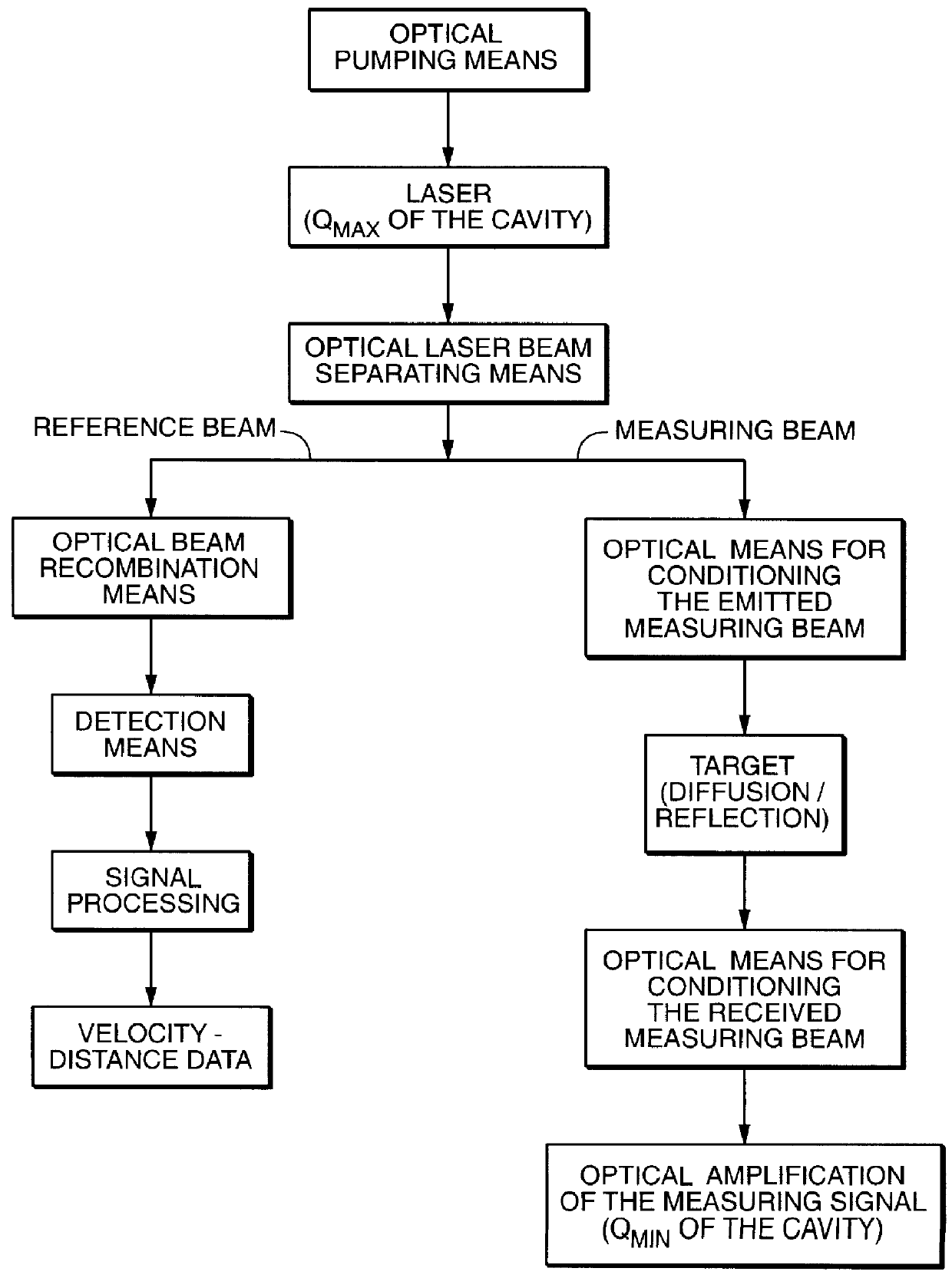
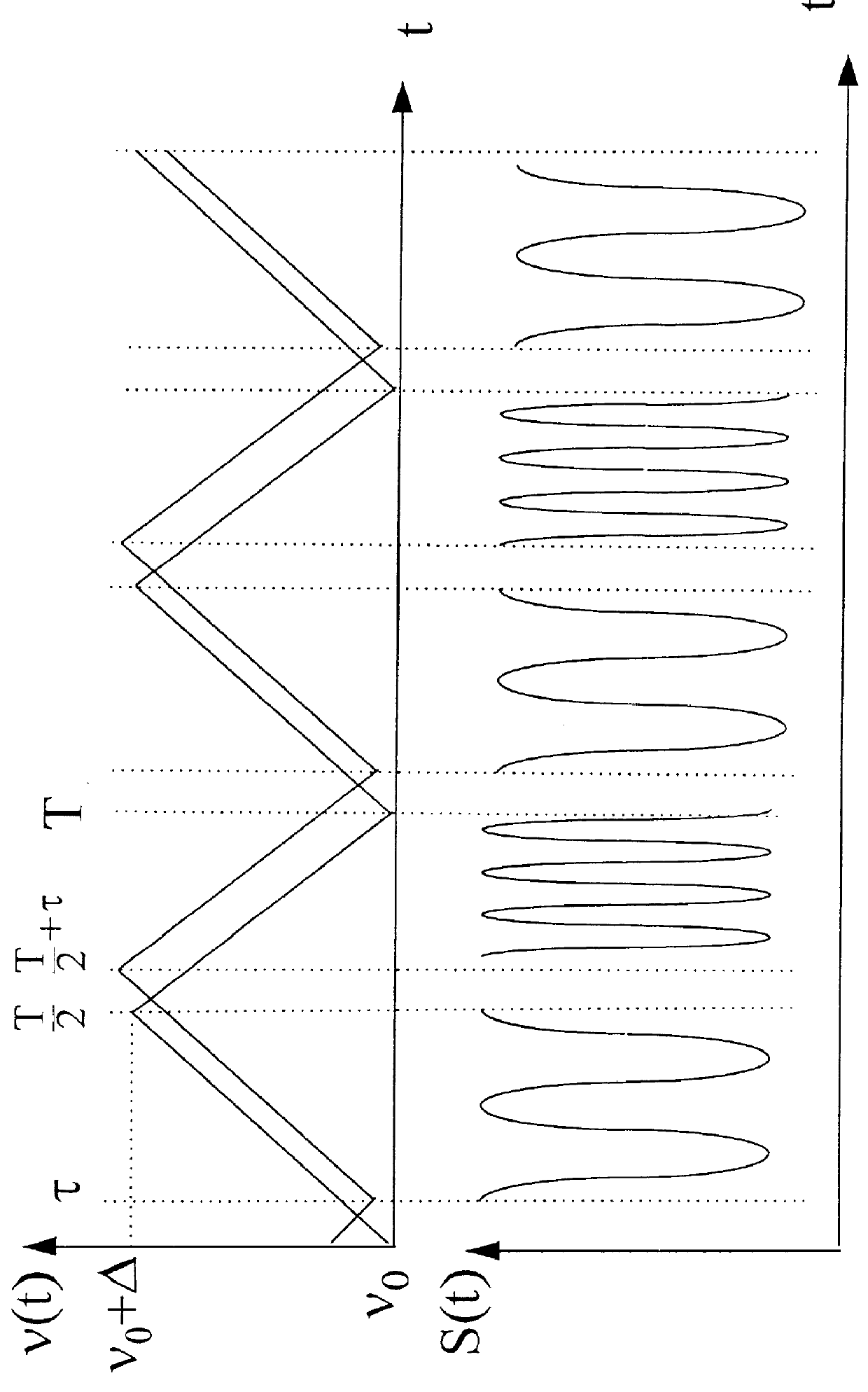
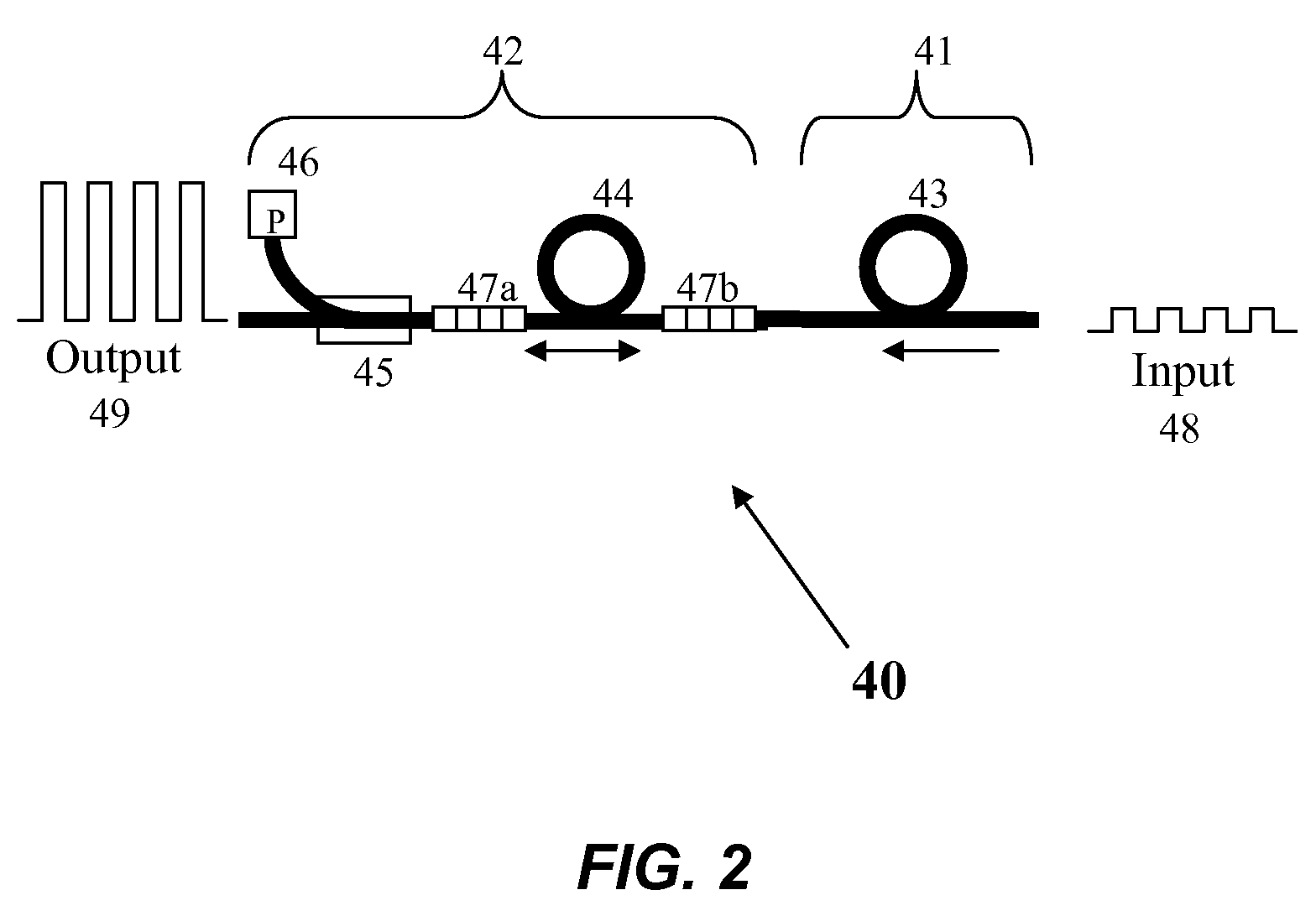
PCT No. PCT / FR97 / 01822 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 15, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 15, 1999 PCT Filed Oct. 13, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 16844 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 23, 1998The invention relates to a velocity measurement device of the coherent detection type comprising: an active laser medium (10), an input mirror (M1) and a first output mirror (M3) defining, with the laser medium, a first resonant cavity of quality factor Qmax making it possible to emit a laser beam (4), a second output mirror (M2) defining, with the active laser medium (10) and the input mirror (M1), a second resonant cavity of quality factor Qmin (<Qmax), making it possible to amplify a measuring signal from a target which has intercepted the laser beam (4) emitted with the aid of the first resonant cavity.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Fiber amplifier with integrated fiber laser pump
ActiveUS7738166B2Efficient injectionIncrease pump powerLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierOptical coupling
An optical system adapted to amplify an input signal includes an optical pump supporting the input signal and an optical pump beam. The optical pump includes an input port, a first active medium coupled to the input port, and a pump output coupled to the first active medium. The optical amplifier includes an amplifier input optically coupled to the pump output and adapted to receive the input signal after passing through the optical pump, a second active medium coupled to the amplifier input, and an amplifier output adapted to output the amplified input signal.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser
ActiveUS20140294033A1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialGas-discharge lampResonant cavity
A laser includes a total reflective mirror, an output mirror, a discharge lamp, and an active laser medium. The total reflective mirror, the output mirror, and the discharge lamp define a resonant cavity. The active laser medium is filled in the resonant cavity. The total reflective mirror includes a body, a metal film, and at least one microstructure. Each of the at least one microstructure is a step structure. The step structure includes a plurality of cylinders stacked with each other with respect to their diameters. Both the height and the diameter of the cylinders are in a range from about 0.5λ to about 2λ, while λ is a working wavelength of the laser.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
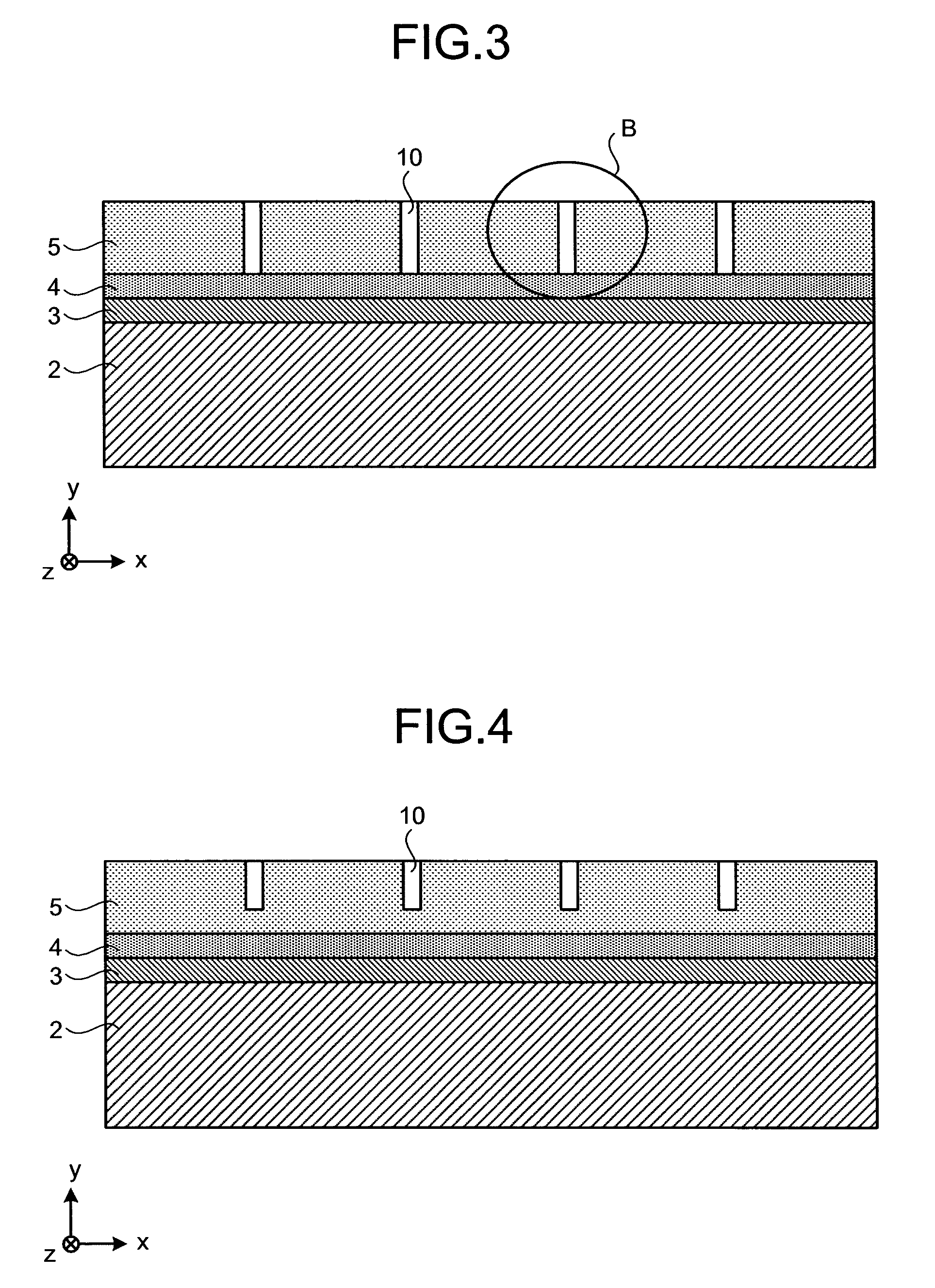
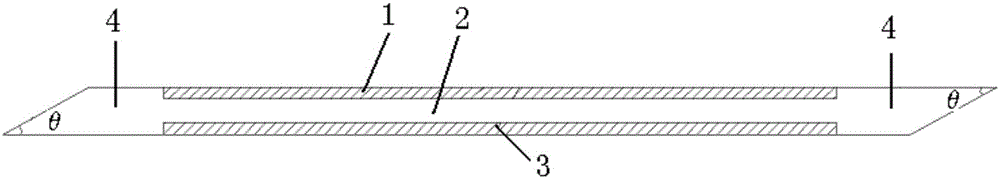
Solid-state laser element
ActiveUS8068525B2Shorten the propagation distanceLaser cooling arrangementsHigh power lasersOptical axis
To achieve a solid-state laser element capable of outputting a high-power laser, in a planar waveguide type solid-state laser element that causes a plurality of fundamental laser beams to oscillate in a direction of an optic axis within a flat plate-like laser medium, and forms a waveguide structure in a thickness direction of the laser medium, which is a direction perpendicular to a principal surface of the flat plate-like laser medium, the laser medium is separated in a principal-surface width direction of the laser medium, which is a direction perpendicular to the direction of the optic axis and the thickness direction of the laser medium, by a groove extending in the direction of the optic axis within the laser medium.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Planar waveguide laser device
ActiveUS20100189151A1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical axisWaveguide lasers
A planar waveguide laser device forms a waveguide by a plate-like laser medium having birefringence and clad attached to at least one of the surfaces of the laser medium perpendicular to its thickness direction, amplifies laser light by a gain produced by excitation light incident on the laser medium, and performs laser oscillation. The laser medium is formed of a material having an optic axis on a cross section perpendicular to the light axis, which is the laser travelling direction. The clad is formed of a material having a refractive index in a range between refractive indexes of two polarized lights that travel along the light axis in the laser medium and have oscillation surfaces that are orthogonal to each other. The planar waveguide laser device readily oscillates linearly polarized laser light.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS7082150B2Simple optical systemReduce the burden onSemiconductor laser arrangementsOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayLaser beams
A semiconductor laser device, comprising a semiconductor laser array for excitation having a plurality of semiconductor laser elements, and an optical resonator having a solid-state laser medium with a reflection mirror formed on one end surface and an output mirror provided in parallel to the reflection mirror, wherein laser beams emitted from the plurality of the semiconductor laser elements enter the optical resonator independently from each other, and the laser beams are respectively amplified and are projected by the optical resonator.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Light source device for pumping solid-state laser medium
InactiveUS6850549B2Easy maintenanceCompact structureSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSolid-state laser
A light source device for pumping a solid-state laser medium of a laser generator, which is compact and capable of economically using LD bars constituting the LD stack with easy maintenance. The light source device is constituted by a plurality of LD modules. Each LD module comprises a plurality of cooling devices on which LD bars are respectively mounted and connection plates on both sides thereof. The LD bars are stacked such that longitudinal directions thereof extend perpendicular to a stacking direction thereof. A desired number of LD modules are mechanically connected with each other using the connection plates to form the LD stack. A sealing member is intervened between confronting connection plates of adjacent LD modules, so that flow passages of coolant formed in the respective LD modules are continuously connected. The connection plates have functions of fixedly supporting the cooling devices of each LD module and electrically connecting the adjacent LD modules.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Cooling an active medium using raman scattering
InactiveUS20090052482A1Easy to combineMore homogenous temperature distributionLaser using scattering effectsLaser cooling arrangementsControl systemThermal control system
A method is described for setting up a system comprising an active medium. The method comprises thermally controlling the system comprising an active medium by radiative cooling. The radiative cooling thereby is based on stimulated and / or coherent Raman scattering processes. In particular embodiments, the thermally controlling may be obtained by tailoring the efficiencies of the Raman scattering processes by optimising at least one of a number of system parameters. The invention furthermore relates to systems thus obtained, to methods for thermally controlling systems comprising an active medium that generate radiation and to computer program products for performing the methods for setting up systems comprising an active medium and thermally controlled by radiative cooling using stimulated and / or coherent Raman scattering processes.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Green welding laser
InactiveUS7088749B2Optical resonator shape and constructionNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalHarmonic
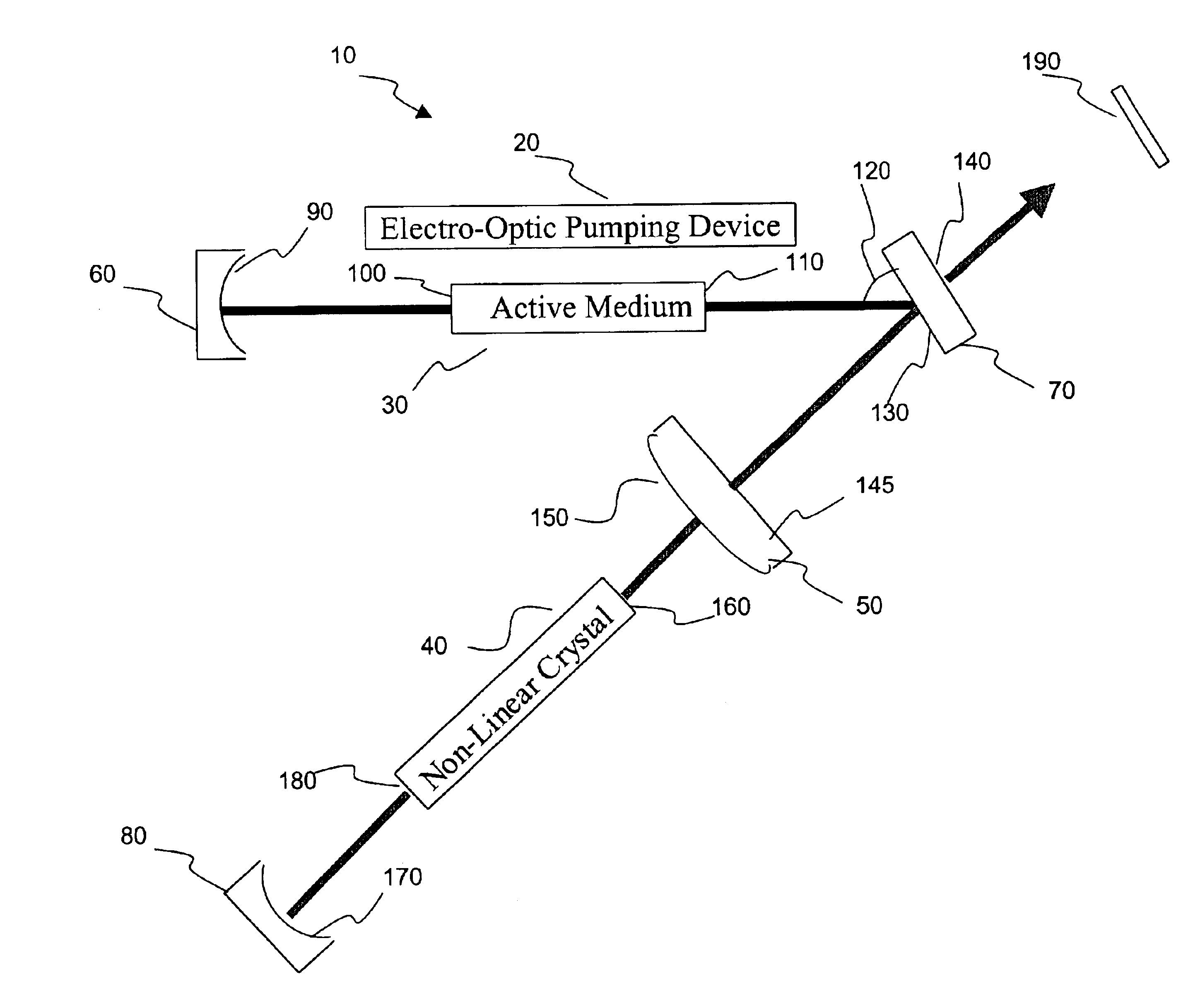
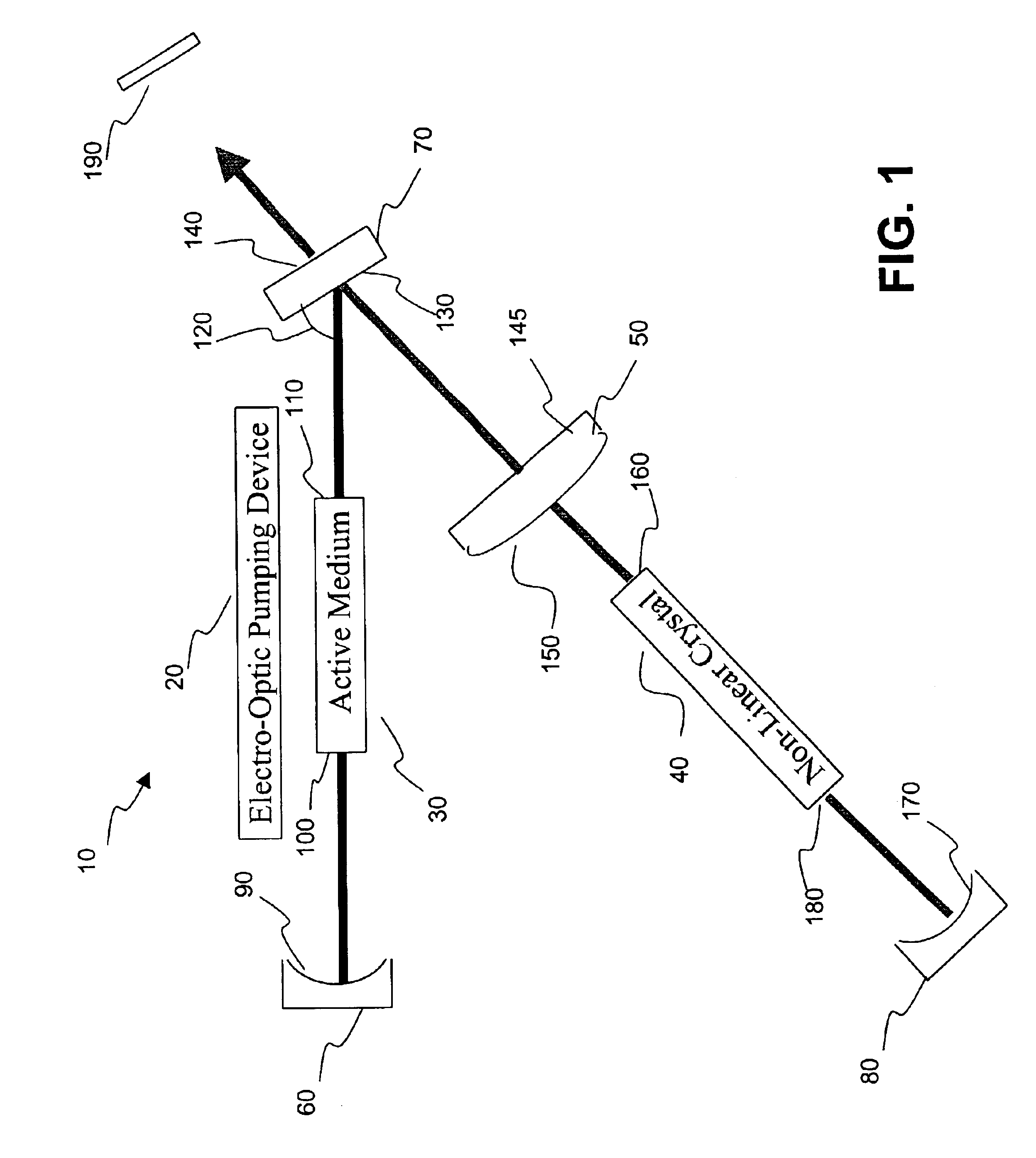
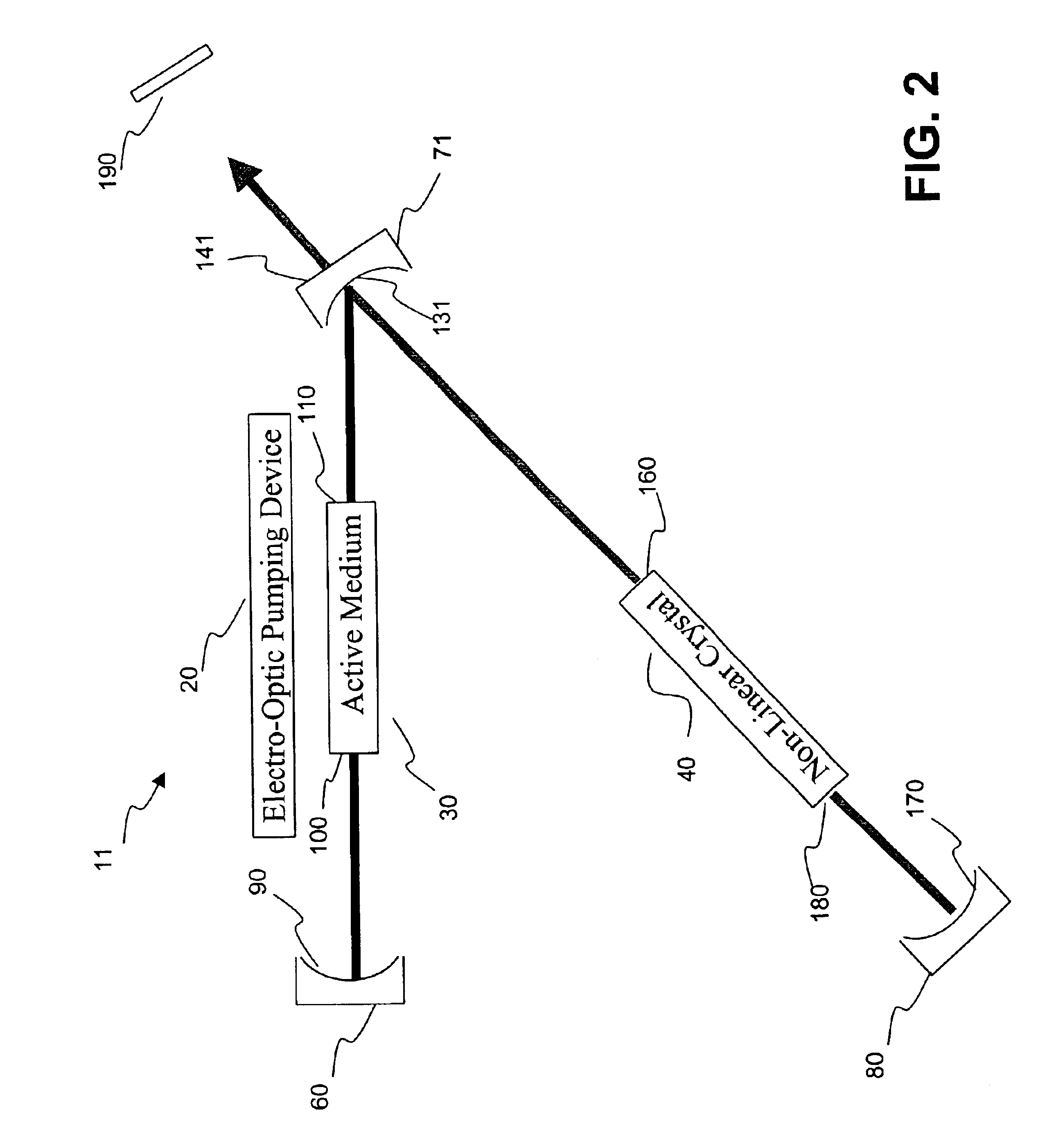
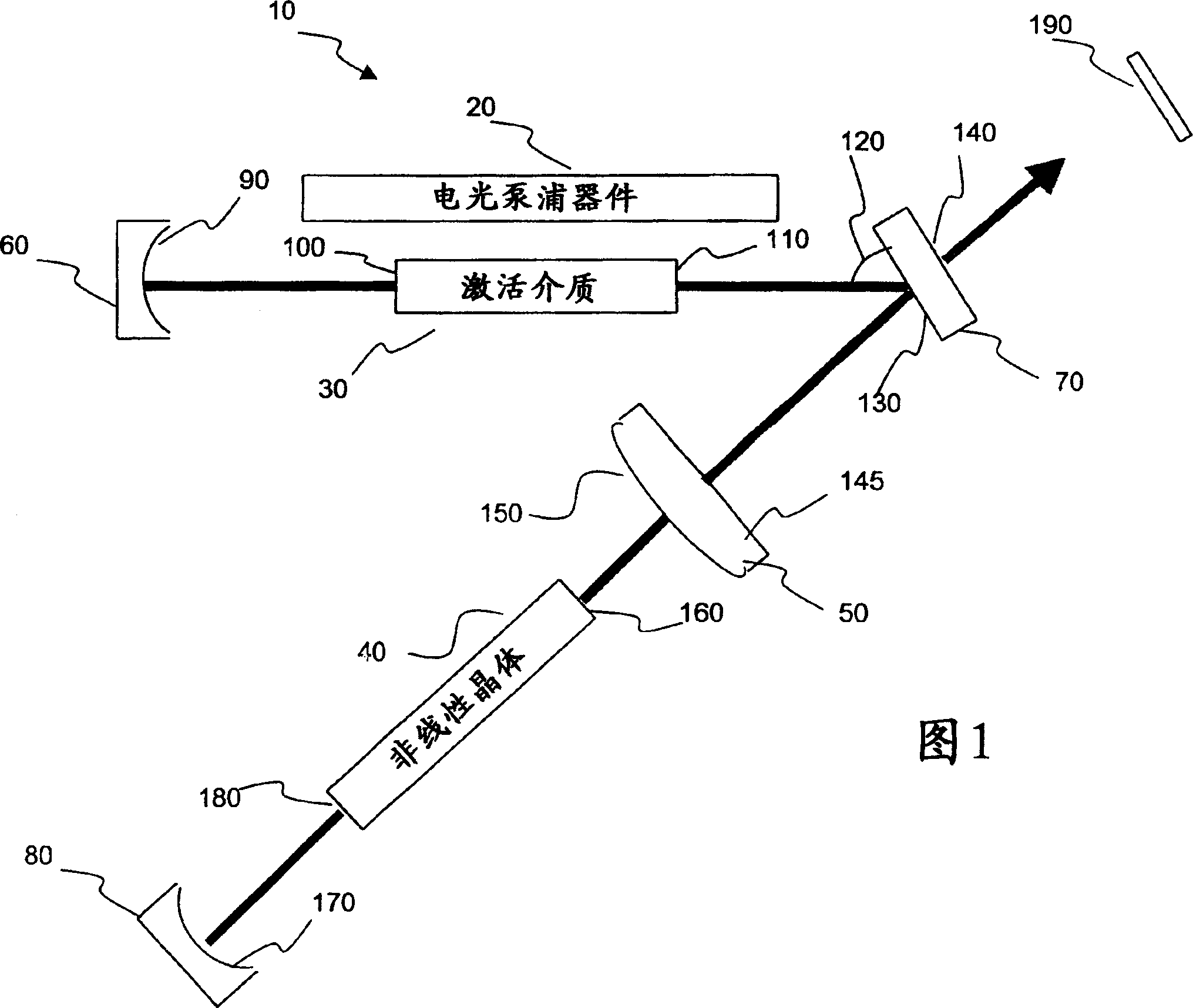
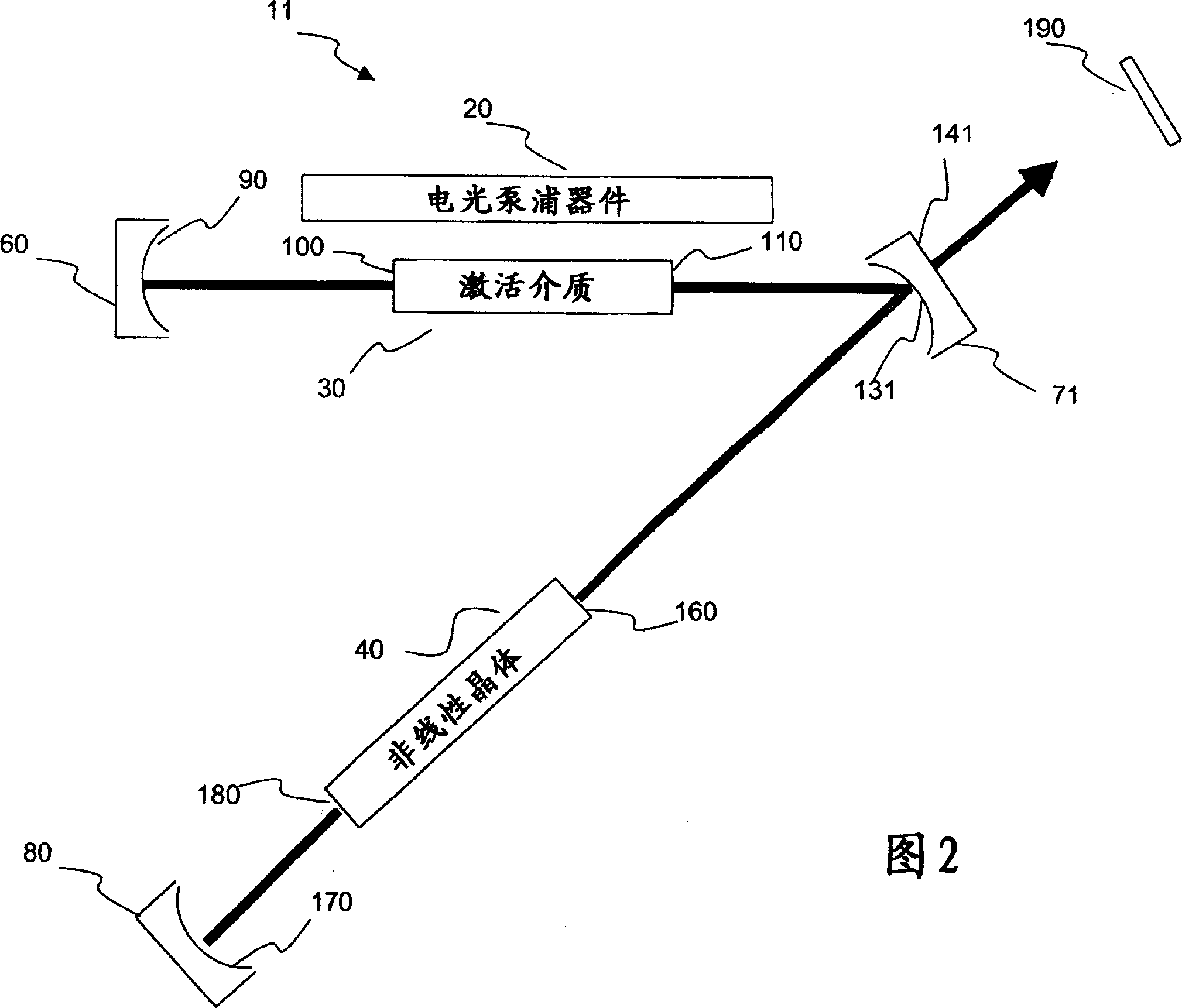
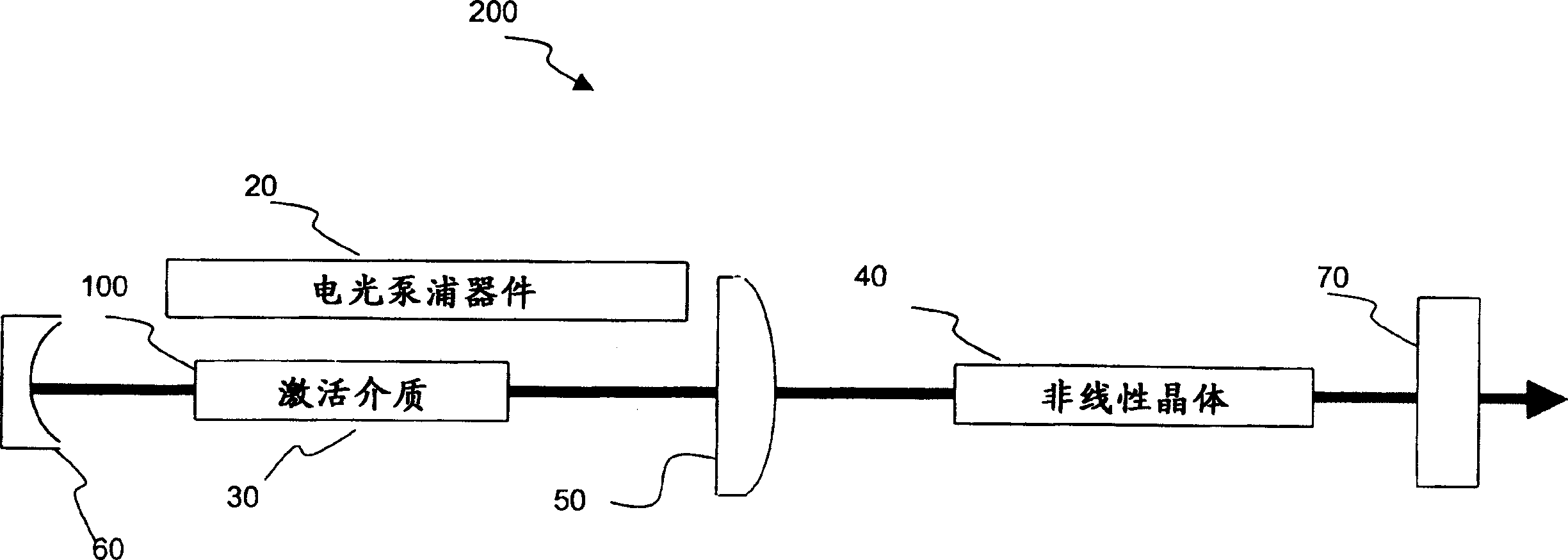
A harmonic system for use with metals and alloys such as titanium, steel, copper, gold, aluminum, etc. is disclosed. The harmonic laser system includes an oscillator cavity having a first end mirror and a harmonic separator mirror, an active medium positioned in the oscillator cavity, an electro-optic pump device for optically pumping the active medium to produce a first optical beam at a fundamental wavelength and a non-linear optical crystal positioned in the oscillator cavity to generate a second optical beam at a harmonic wavelength of the first optical beam, wherein the harmonic separator mirror outputs the second optical beam and reflects the first optical beam.
Owner:MIYACHI TECHNOS CORP 1 2 INTEREST
Solid-state laser element
ActiveUS20100303112A1Shorten the propagation distanceSemiconductor lasersLaser cooling arrangementsHigh power lasersOptical axis
To achieve a solid-state laser element capable of outputting a high-power laser, in a planar waveguide type solid-state laser element that causes a plurality of fundamental laser beams to oscillate in a direction of an optic axis within a flat plate-like laser medium, and forms a waveguide structure in a thickness direction of the laser medium, which is a direction perpendicular to a principal surface of the flat plate-like laser medium, the laser medium is separated in a principal-surface width direction of the laser medium, which is a direction perpendicular to the direction of the optic axis and the thickness direction of the laser medium, by a groove extending in the direction of the optic axis within the laser medium.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
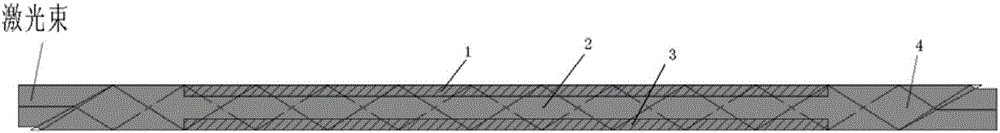
A surface gain lath medium with a high packing ratio and a manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106785877AImprove cooling effectEfficient separationActive medium materialLight beamNon doped
The invention discloses a surface gain lath medium with a high packing ratio and a manufacturing method thereof. The surface gain lath medium with the high packing ratio comprises a composite region and two non-doped regions respectively located at the left and right ends of the composite region. The composite region comprises three layers which are sequentially an upper doped layer, a non-doped layer and a lower doped layer sequentially from the top to the bottom. The non-doped regions and the non-doped layer are composed of matrix materials which are not doped with active ions. The upper and lower doped layers are composed of matrix materials doped with active ions. According to the invention, through reasonable design of the doped regions and the cutting angle of the lath laser medium, a gain region in a lath gets fully utilized to realize effective separating of pumping laser from oscillation laser and effectively avoid influences of a dichroic mirror on a laser system. Further, the surface gain lath medium with the high packing ratio of the invention has extremely strong heat radiation capability and facilitates realization of a highly-efficient, high-power and high-beam-quality laser output.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Green welding laser
ActiveCN1518178AOptical resonator shape and constructionNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalHarmonic
A harmonic system for use with metals and alloys such as titanium, steel, copper, gold, aluminum, etc. is disclosed. The harmonic laser system includes an oscillator cavity having a first end mirror and a harmonic separator mirror, an active medium positioned in the oscillator cavity, an electro-optic pump device for optically pumping the active medium to produce a first optical beam at a fundamental wavelength and a nonlinear optical crystal positioned in the oscillator cavity to generate a second optical beam at a harmonic wavelength of the first optical beam, wherein the harmonic separator mirror outputs the second optical beam and reflects the first optical beam.
Owner:UNITEK MIYACHI +1
Active optical device enabled by dielectric metamaterials
An array of dielectric resonators is formed on a substrate. Each resonator includes an active medium having an optical transition that is operative in a process of photodetection or photoemission. The active media each include a quantum well multilayer. The dielectric resonators in the array are each dimensioned to provide a resonance that lies substantially at the frequency of the optical transition.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
UV light generation by frequency conversion of radiation of a ruby laser pumped with a second harmonic of a solid-state laser
A system and method for generating ultraviolet laser radiation by pumping a ruby based active laser medium in a second complex laser cavity with an output from a first complex laser cavity. The laser system includes a first complex optical cavity a second complex optical cavity, an output from the first complex optical cavity at a second harmonic of the first fundamental frequency pumps a ruby based active medium of the second complex optical cavity. In some embodiments, the ruby based active medium can be Cr:Al2O3 type ruby.
Owner:KLASTECH KARPUSHKO LASER TECH
Device and process for mode-locking a laser
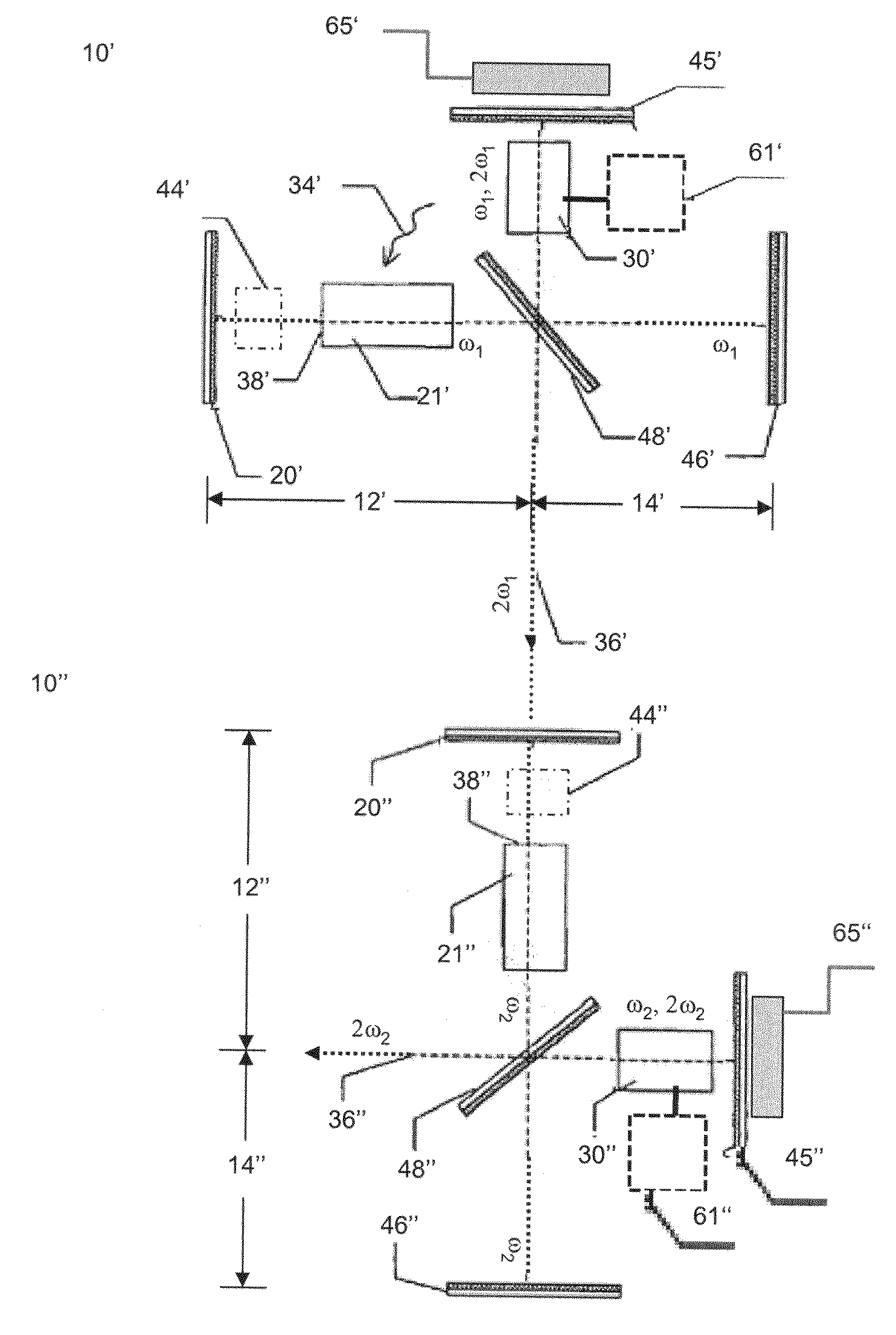
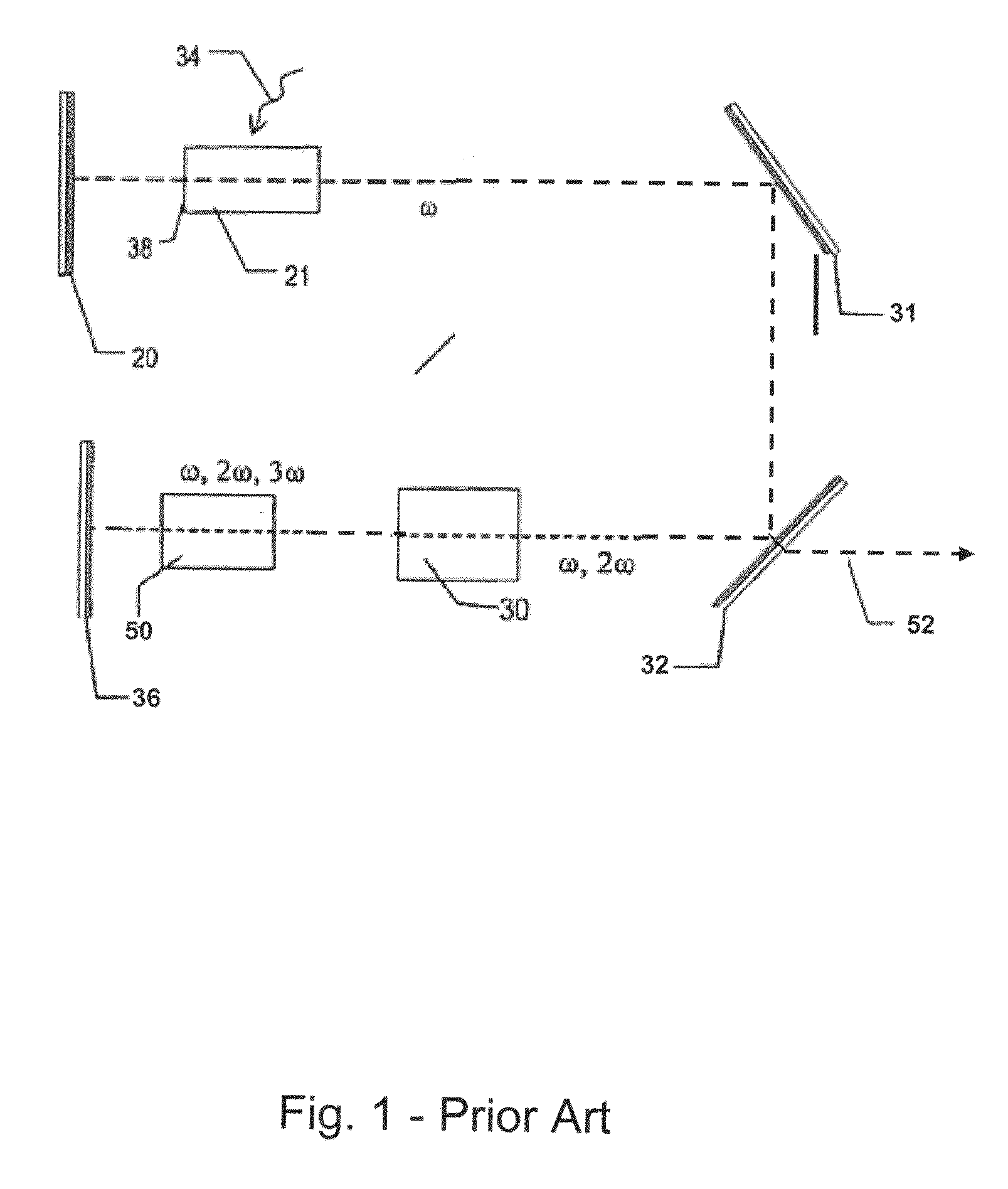
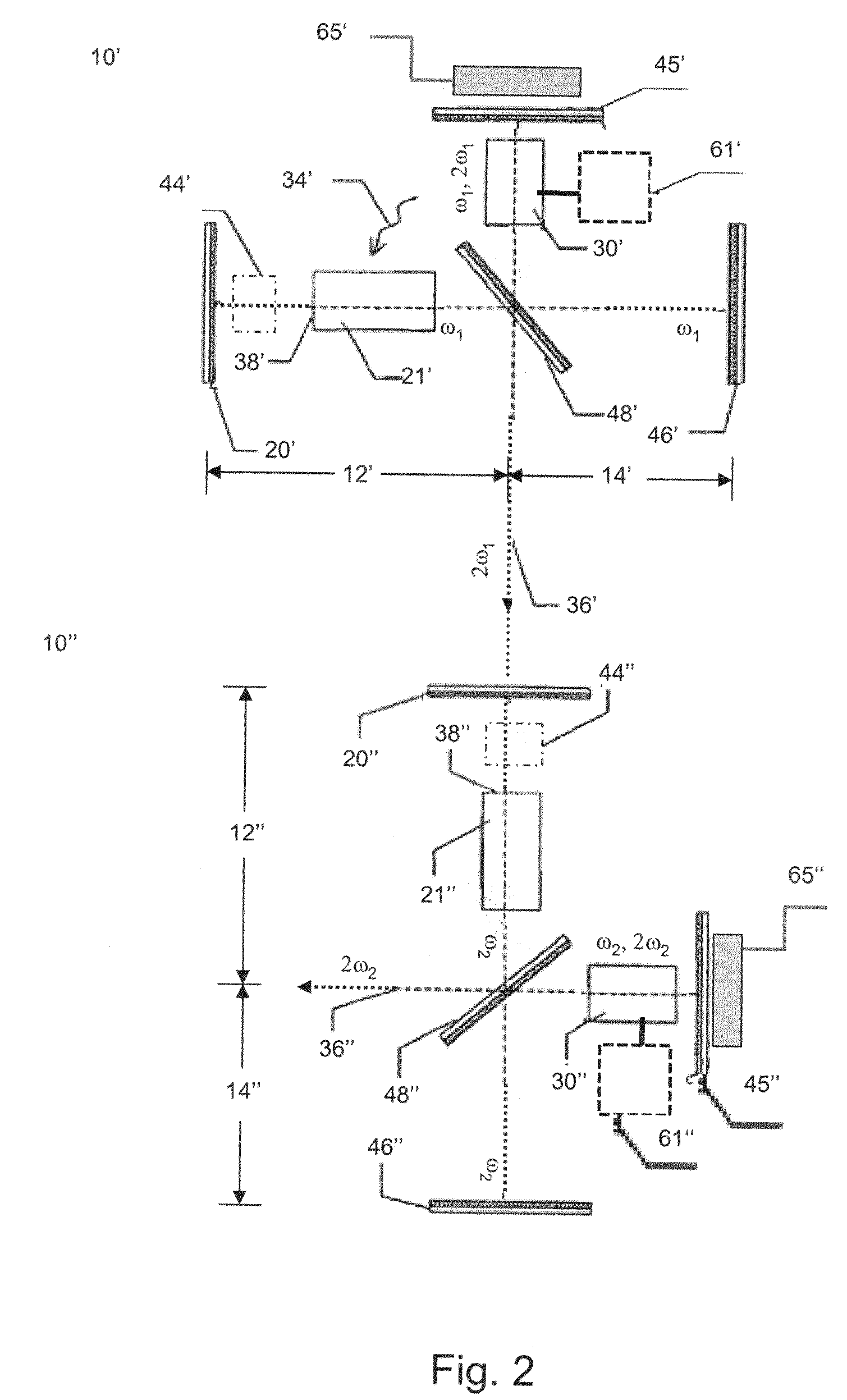
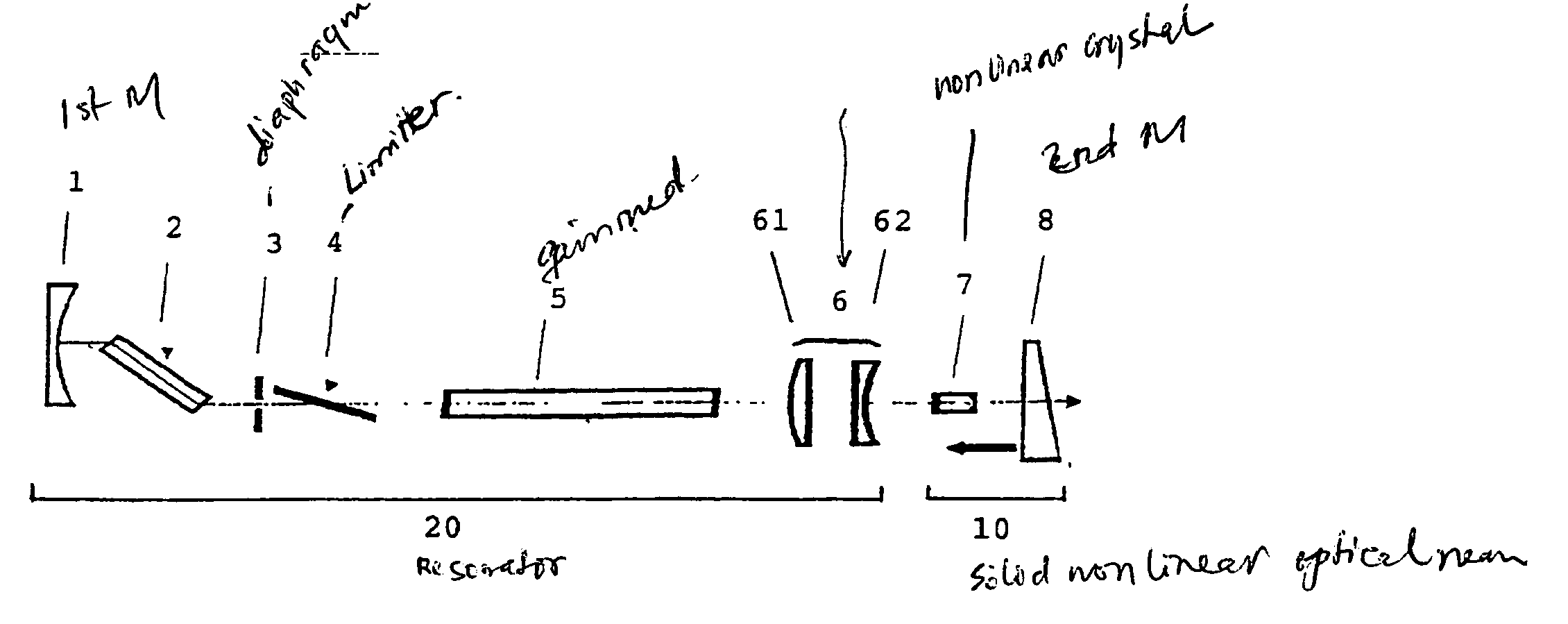
The invention relates to a device for a laser blocked-mode, especially for a pulsed laser, comprising a cavity resonator (20) which is defined by a first mirror (1) and a second mirror (8), and fitted with an amplifying active laser medium (5) for the amplification of a beam of laser radiation of a fundamental frequency (ω1) and a solid, non-linear optic means (10) comprising at least said second mirror (8) for reversible conversion of the radiation of the fundamental frequency (ω1) into radiation of a harmonic frequency (ω2) whereby said non-linear optic means (10) has a reflection factor which increases with the intensity of the radiation of a fundamental frequency. The invention is characterized in that said device also comprises a solid intensity limiter (4) in the cavity resonator (20), whereby the transmission factor of the laser radiation decreases with the intensity of said radiation. The invention also relates to a method for a laser blocked-mode, especially for a pulsed laser, using said device.
Owner:UNIV DE NAMUR
Short wavelength light source and optical device
InactiveUS8254415B2Easy to useSimple configurationLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor packageLaser light
A GaN-based semiconductor laser (1) emits first laser light of a single polarization and having a first wavelength. An optical resonator (30) includes a solid-state laser medium which is excited by incidence of the laser light and which oscillates second laser light having a second wavelength different from the first wavelength. A polarization switch (6) switches over at least one of polarization directions of the first laser light and the second laser light to thereby change the wavelength of laser light to be emitted from the optical resonator (30) or the intensity ratio between a plurality of laser light to be emitted from the optical resonator (30). With the above arrangement, a plurality of laser light can be used effectively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Laser system with protection device
ActiveUS20190323803A1Eliminate eye damageAvoid eye injuryLaser detailsSighting devicesLight beamVisible spectral range
A protection device for a laser system having at least one active laser and having at least one beam guide. Eye safety and / or protection for an exposed person is achieved using at least one additional laser as a warning laser which, operating in a visible spectral range, is used shortly before the active laser is used, and which, can cause at least one person to close his or her eyes and / or change his or her viewing direction away from the receptor point of the active laser beam on a target.
Owner:RHEINMETALL WAFFE MUNITION GMBH
Pump radiation arrangement and method for pumping a laser-active medium
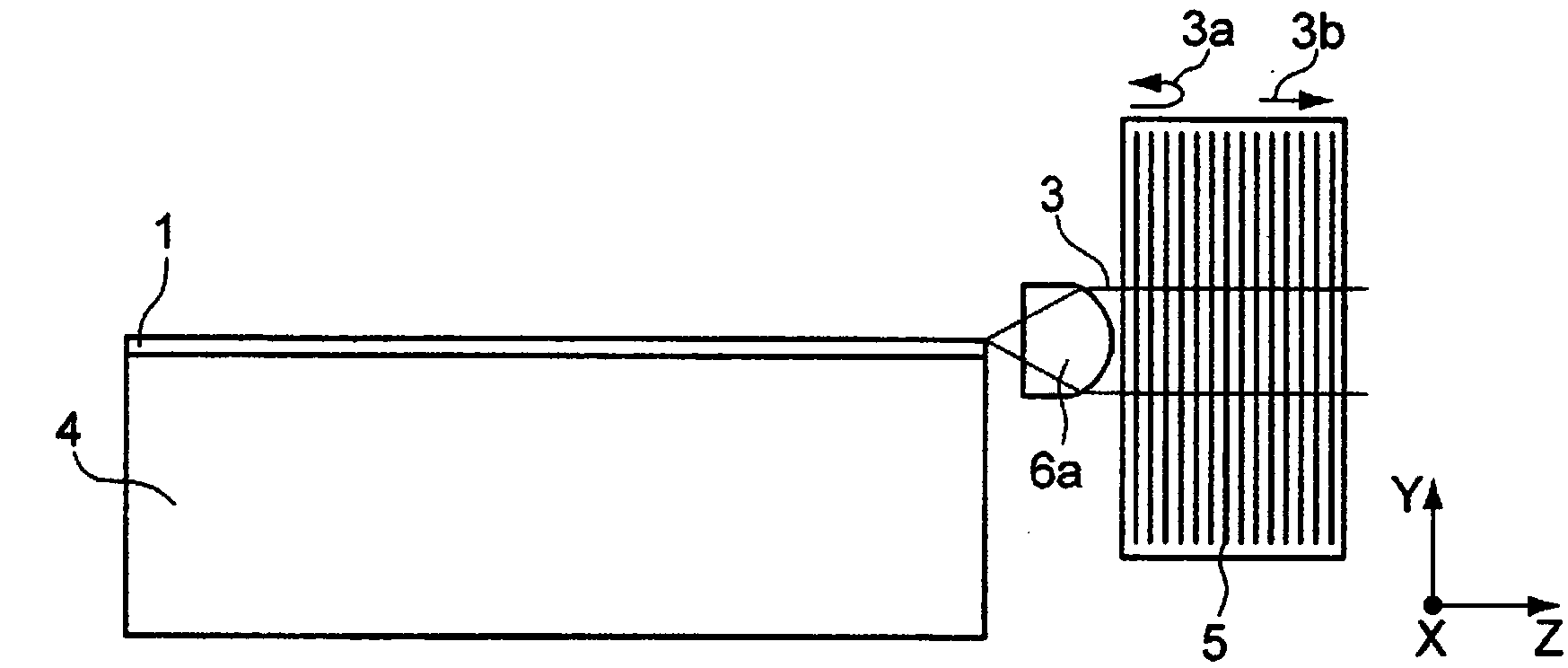
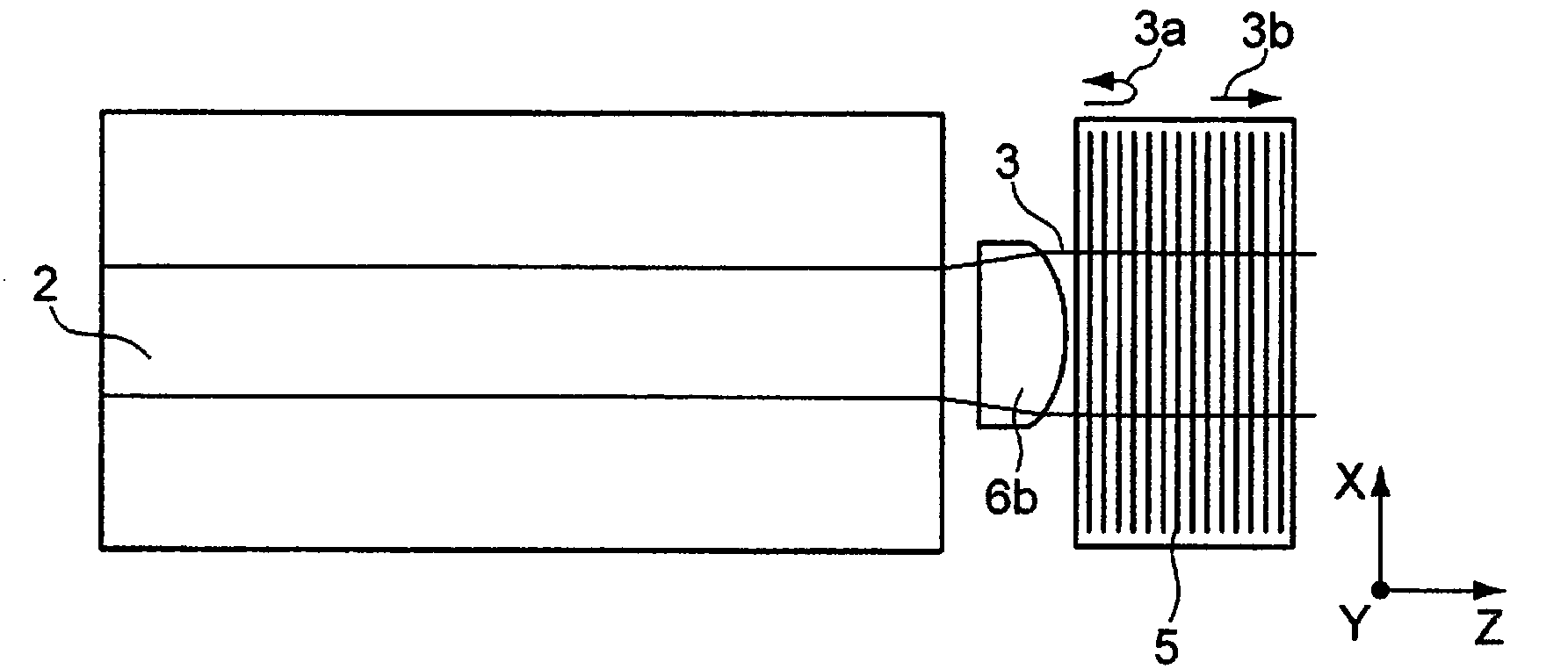
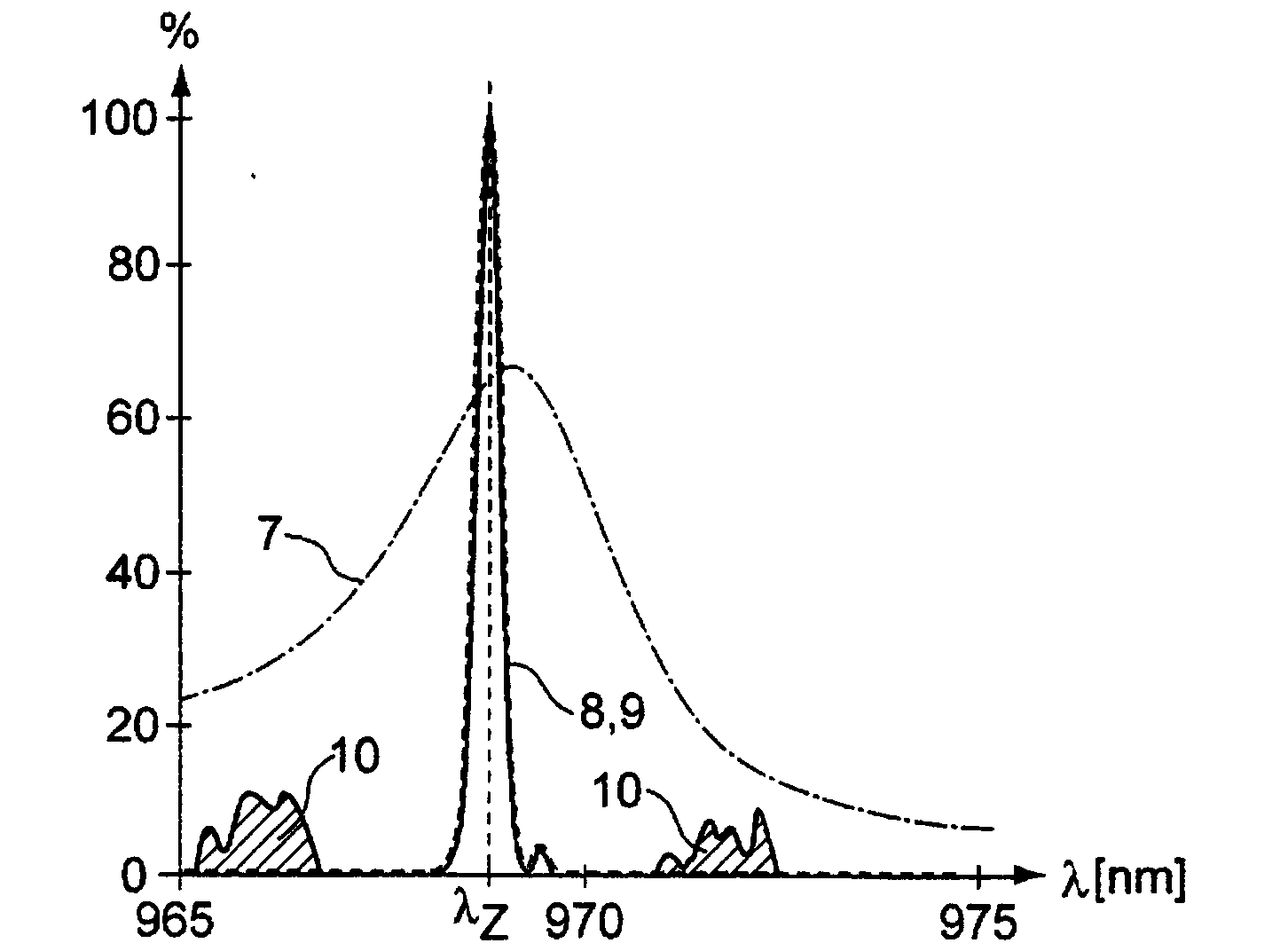
ActiveCN104321941ALaser optical resonator constructionActive medium materialFrequency spectrumLength wave
The invention relates to a pump radiation arrangement (11), comprising: a pump radiation source (1) for creating pump radiation (3), a medium (5) for stabilising the wavelengths of the pump radiation source (1), and a laser-active medium (12), through which the pump radiation (3) runs bidirectionally. The pump radiation arrangement (11) also has a retroreflector (14) for reflecting the pump radiation (3c) not absorbed by the laser-active medium (12) back to the pump radiation source (1), and a wavelength-selective element (15) for avoiding wavelength destabilisation of the pump radiation source (1) by filtering undesired spectral components (10) of the pump radiation (3c) not absorbed by the laser-active medium (12). For example, a laser diode with an external volume Bragg grating can be used for pumping, wherein a coupled resonator of the LD has a Yb:YAG as a laser-active medium, as well as a Fabry-Perot etalon for suppressing spectral components that are not suppressed by the narrow-band VBG.
Owner:TRUMPF LASER GMBH CO KG
Method for decreasing thermal capacitance laser medium thermal stress
InactiveCN1845399ASmall gradientReduce thermal stressLaser constructional detailsCapacitanceThermodynamics
The disclosed method to reduce the thermal stress of thermal-capacity laser medium comprises: during laser emitting, heating the un-pumping area of laser medium to decrease the temperature difference to pumping area and thereby reduce thermal stress.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser oscillator
InactiveUS7149237B2Avoid contaminationInhibit deteriorationExcitation process/apparatusActive medium materialElectric dischargeOrganic matter
A laser oscillator capable of preventing contamination of optical components by organic matter such as oil mist. Gas laser medium in an optical resonator constituted by optical components is pumped by an electric discharge generated in an electric discharge tube to produce a laser beam. The gas medium flows at high speed in the electric discharge tube incorporated in a circulating path including a blower. A part of lubrication oil of the blower is evaporated and mixed into the gas medium. Since the optical components are cooled by retaining mechanisms to prevent temperature rise of the components and a gas stagnation occurs between the optical component and the electric discharge tube, the evaporated oil mist tends to be congealed and adhered to a surface of the optical component. A photocatalyst arranged in the vicinity of the optical component effectively decomposes and removes the oil mist.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Light-enhancing device and method based on use of an optically active lasing medium in combination with digital planar holography
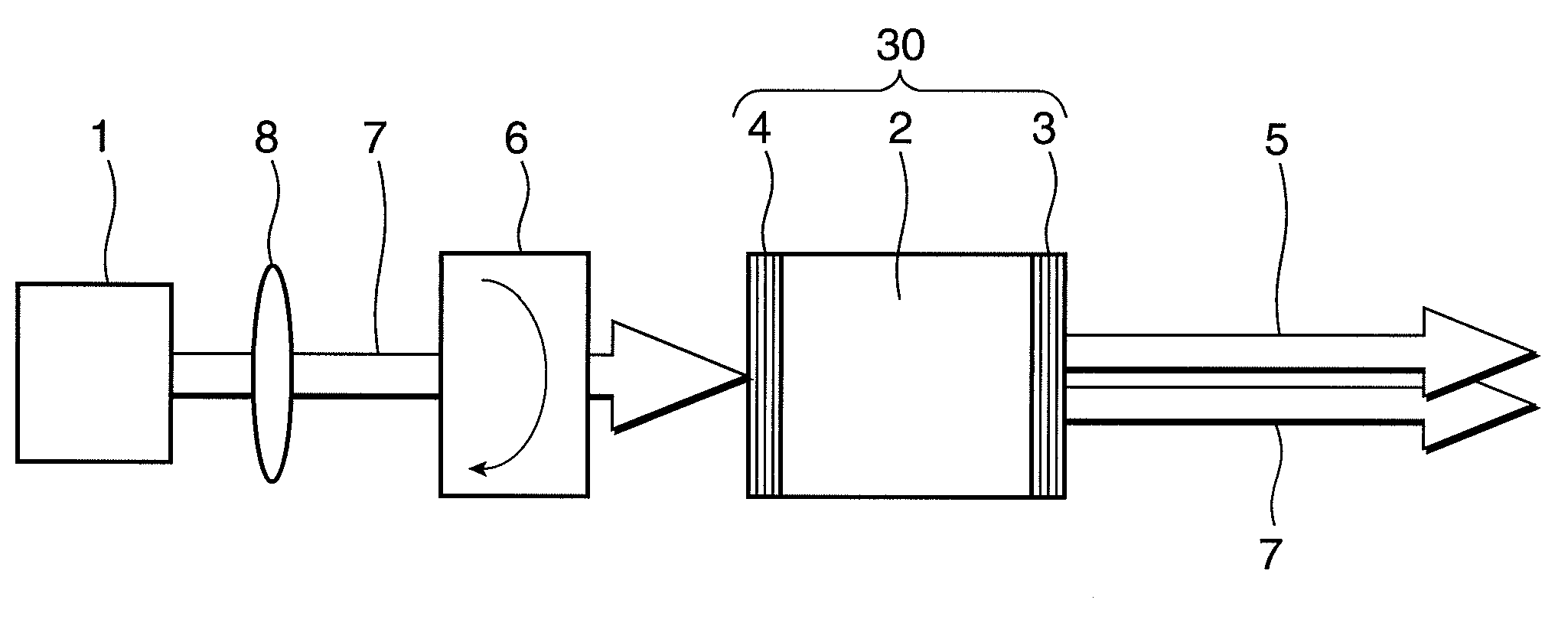
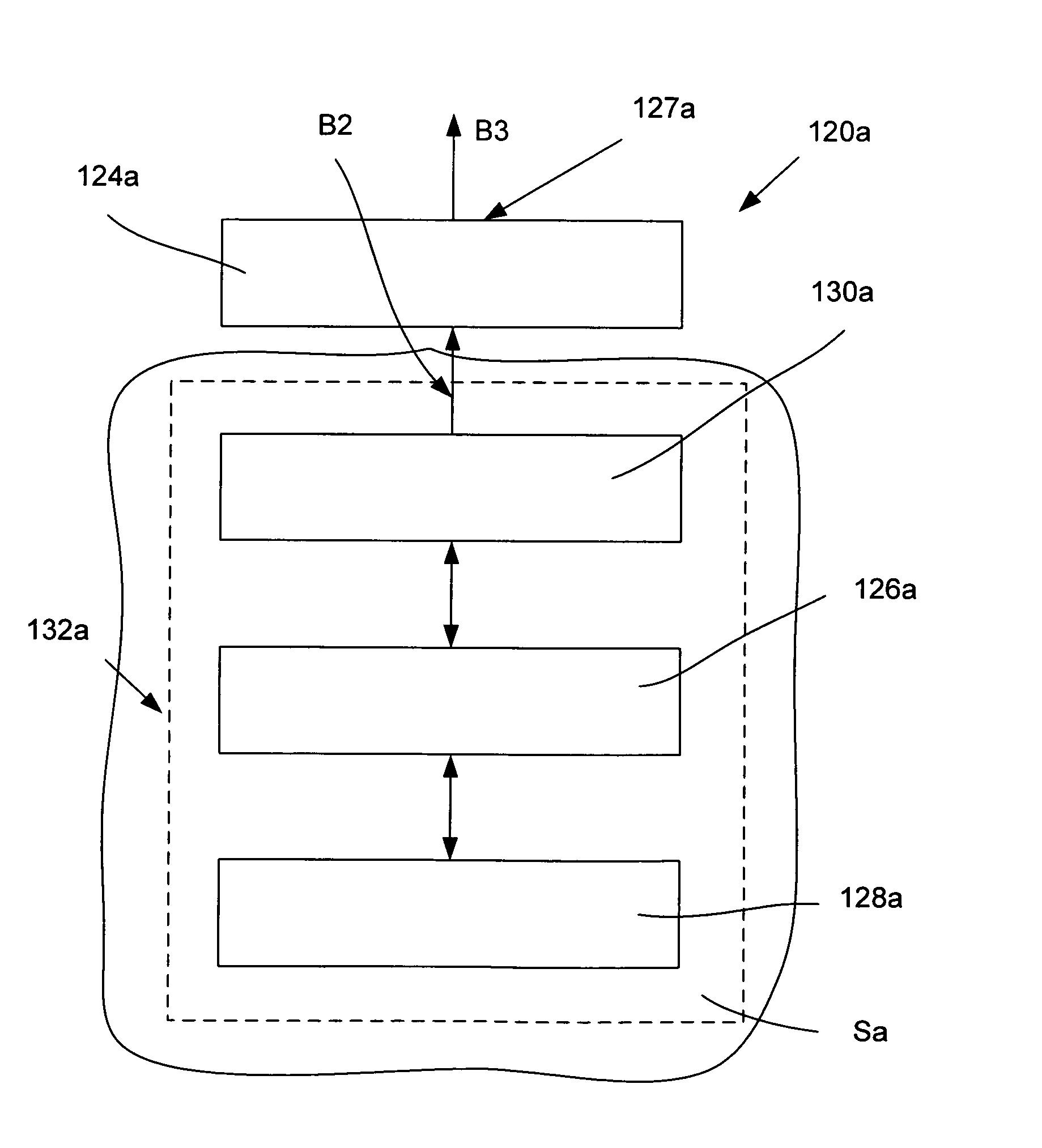
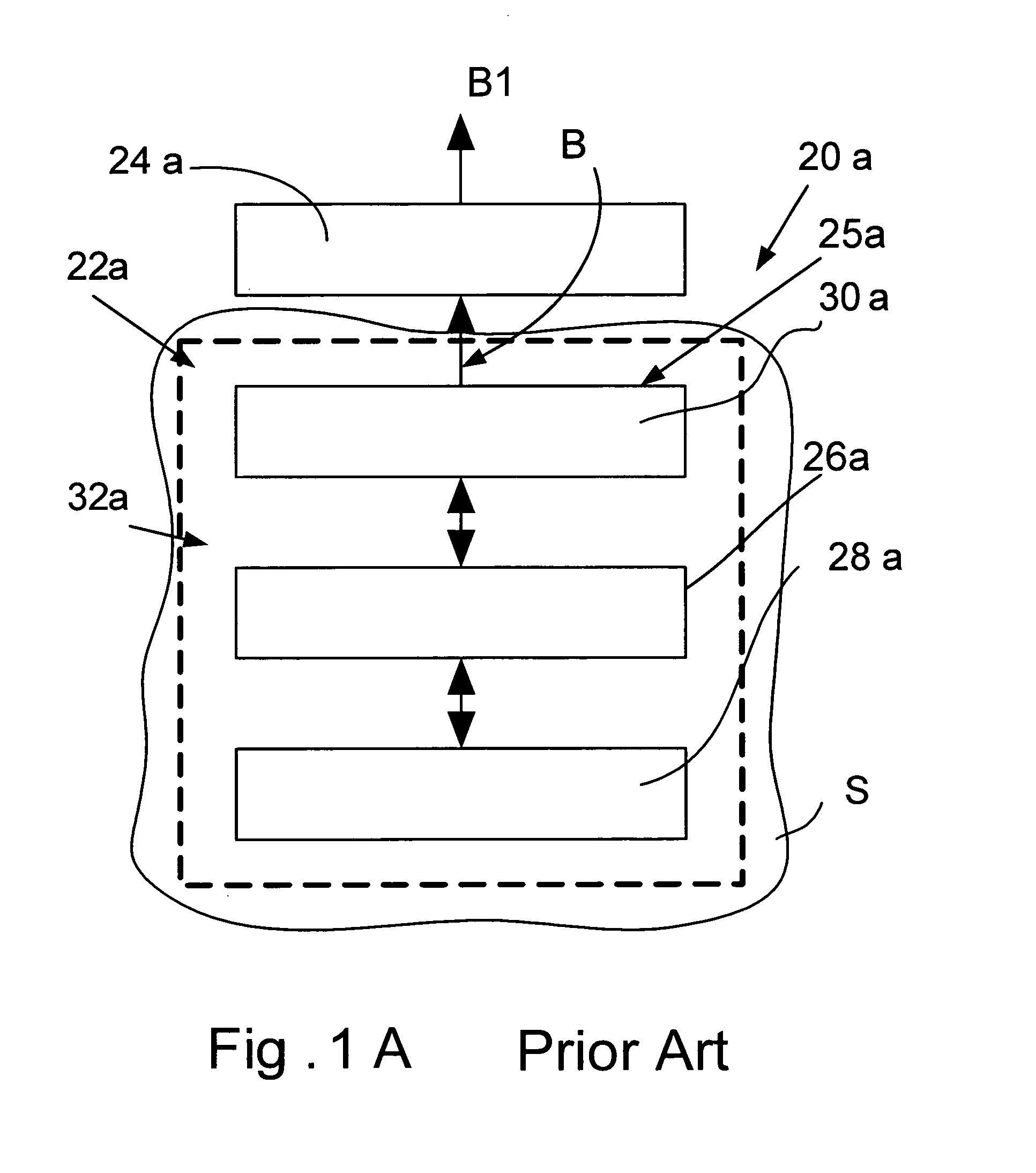
The light-enhancing system of the invention comprises a laser diode in which a fully reflecting mirror and / or a partially reflecting mirror of the laser diode is made in the form of digital planar holography (DPH) incorporating a mode-reorganization function that decreases divergence and improves brightness of the output beam of the system by suppressing high-order modes and gaining low-order modes, or mode. The holographic elements are made in the form of rectangular grooves that can be manufactured as binary features reproduced by methods of nanolithography or nanoimprinting.
Owner:OOO NANOOPTIC DEVICES
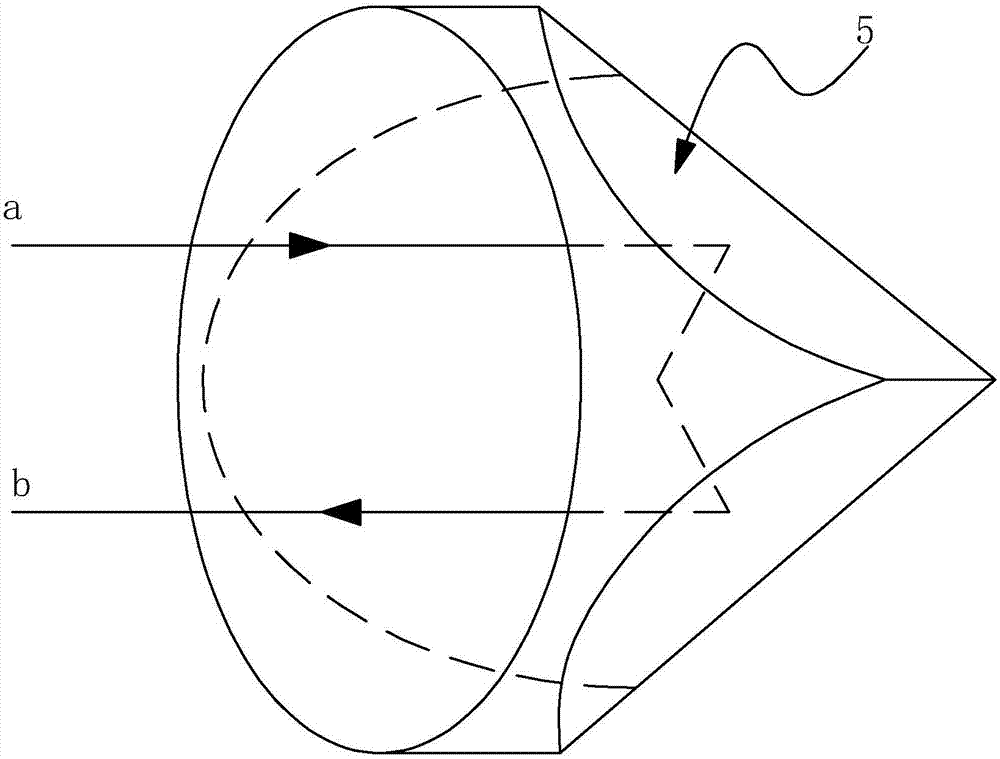
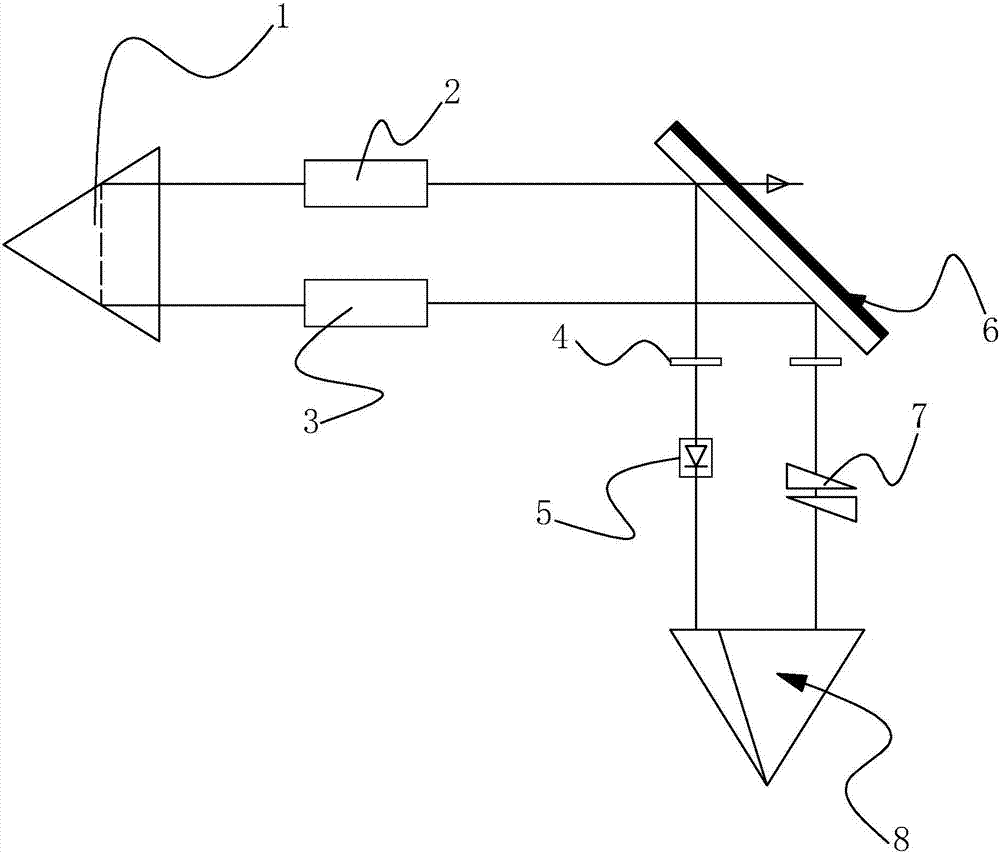
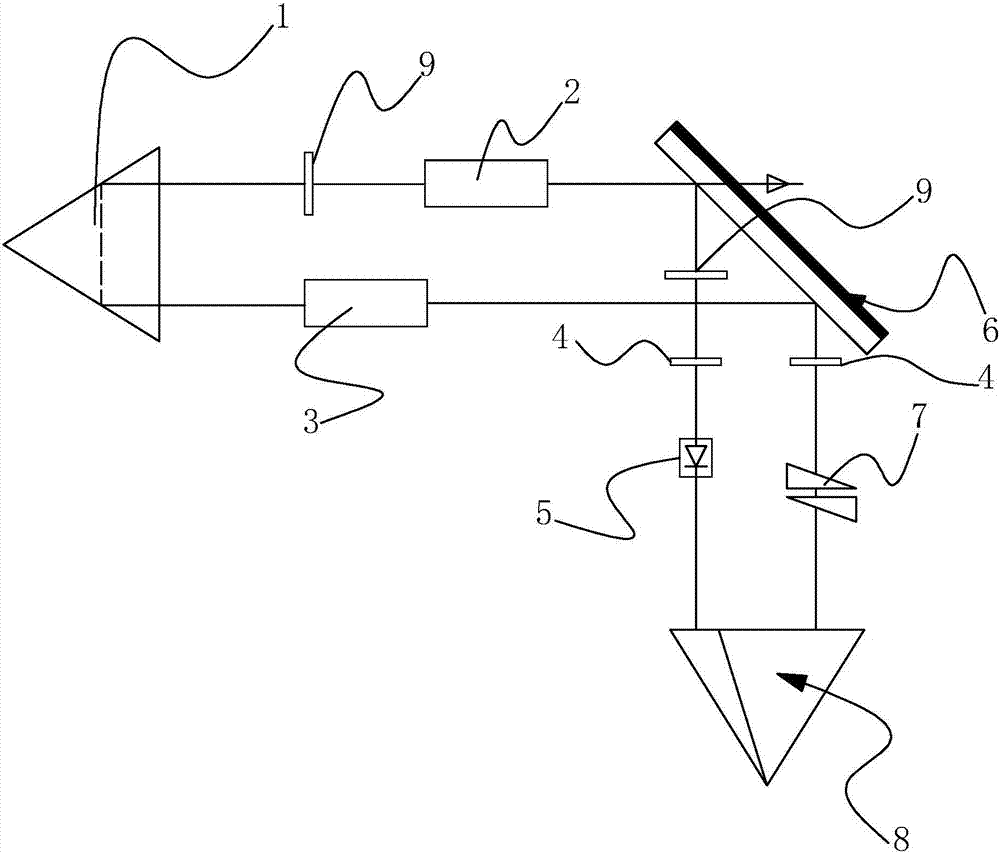
Pyramid annular resonant cavity
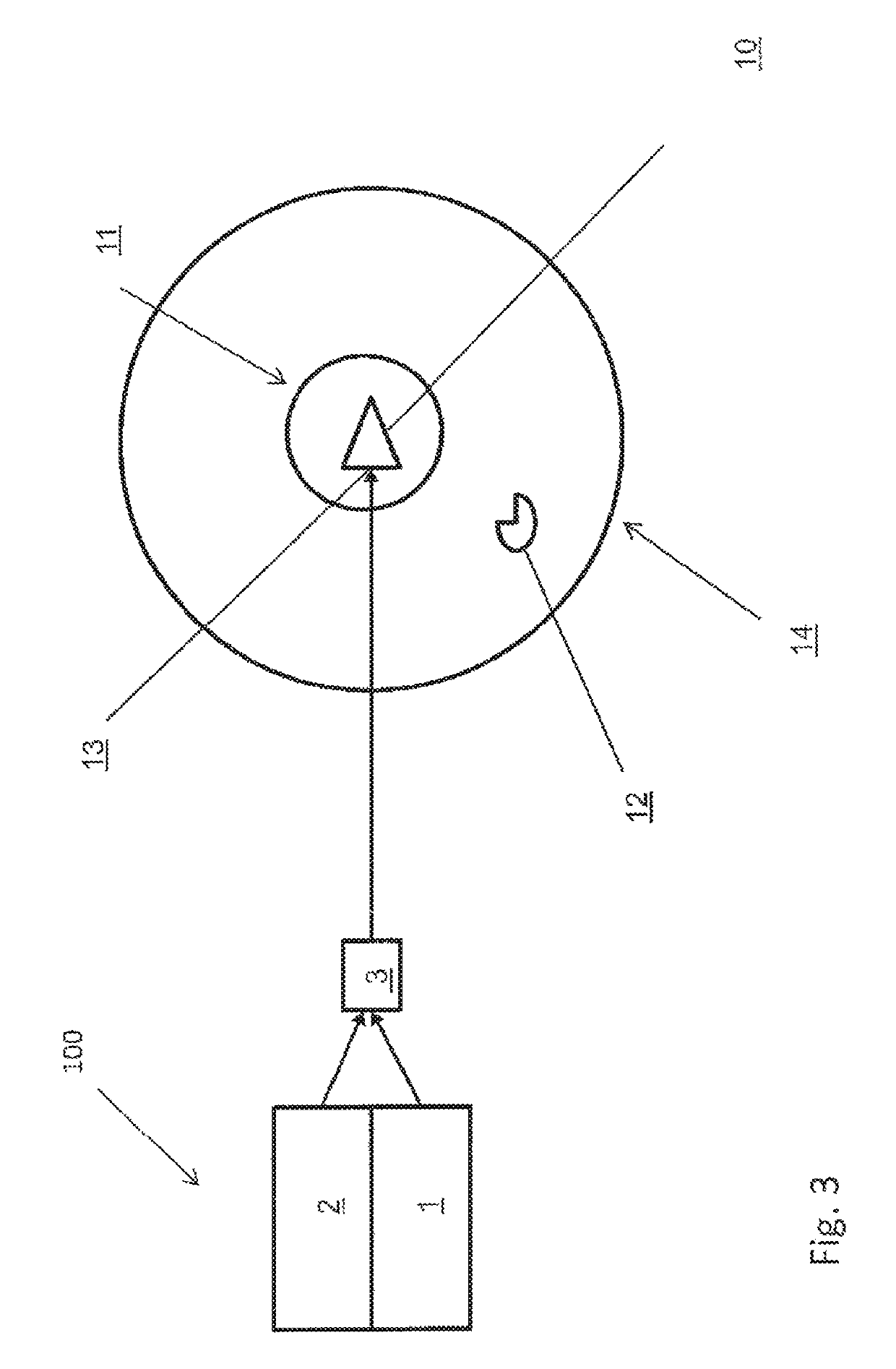
The invention discloses a pyramid annular resonant cavity, and solves technical problems in the prior art that a traveling wave cavity exerts precise requirements for the installation angle of a cavity mirror and cannot meet the application requirements in a severe environment. The main points of the technical scheme of the invention are that the resonant cavity comprises a cavity, an active laser material, a pyramid prism and a unidirectional operation control device, wherein the active laser material, the pyramid prism and the unidirectional operation control device are disposed in the cavity; the interior of the cavity also comprises a high-reflection mirror for reflecting fundamental frequency light, a cavity mirror for the output of modulated light and the reflection of fundamental frequency light, a nonlinear crystal, and a right-angle prism; light beams, emitted by the active laser material when the active laser material is activated by external pumping, vertically enter the right-angle prims and are reflected in a parallel manner; the light beams enter the nonlinear crystal and then enter the cavity mirror at an angle of 45 degrees, and are reflected to the unidirectional operation control device; emergent light is reflected by the pyramid prism to return to the active laser material. The resonant cavity reduces the requirements of the installation precision of all elements in a wall through the adjustment of the elements in the cavity, and meets the application requirements in a severe environment.
Owner:北京思通博远激光科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com