Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Simple optical system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
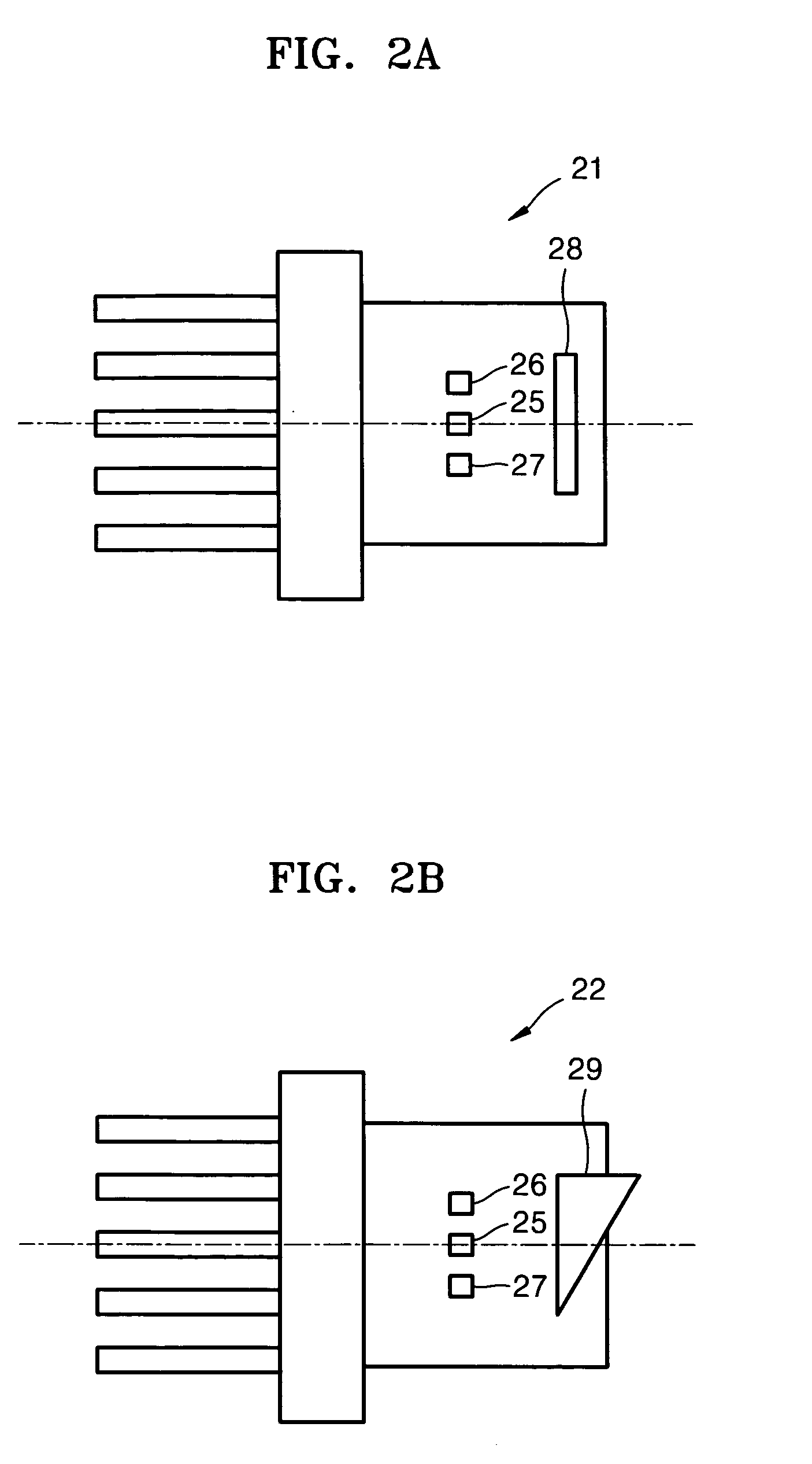
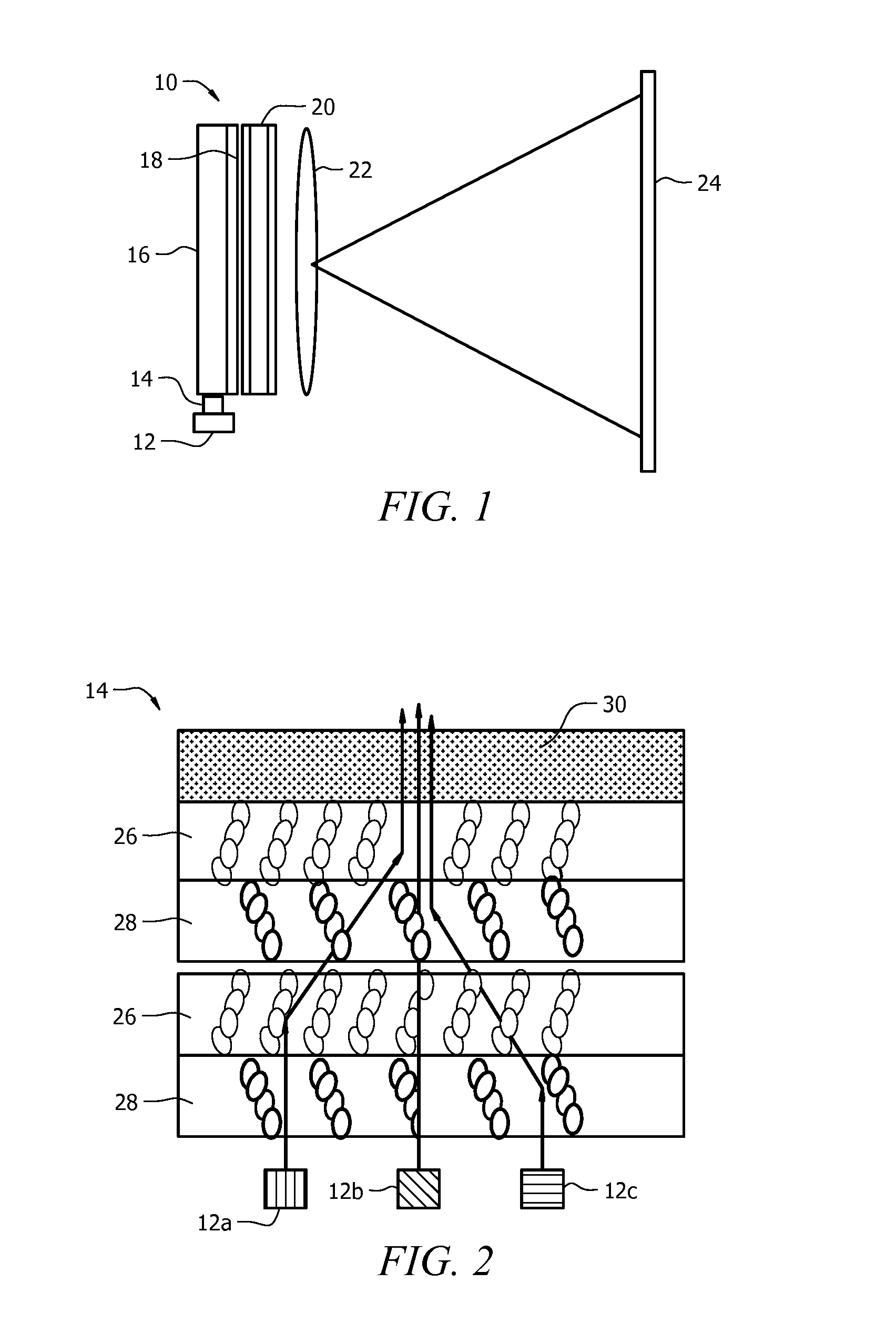
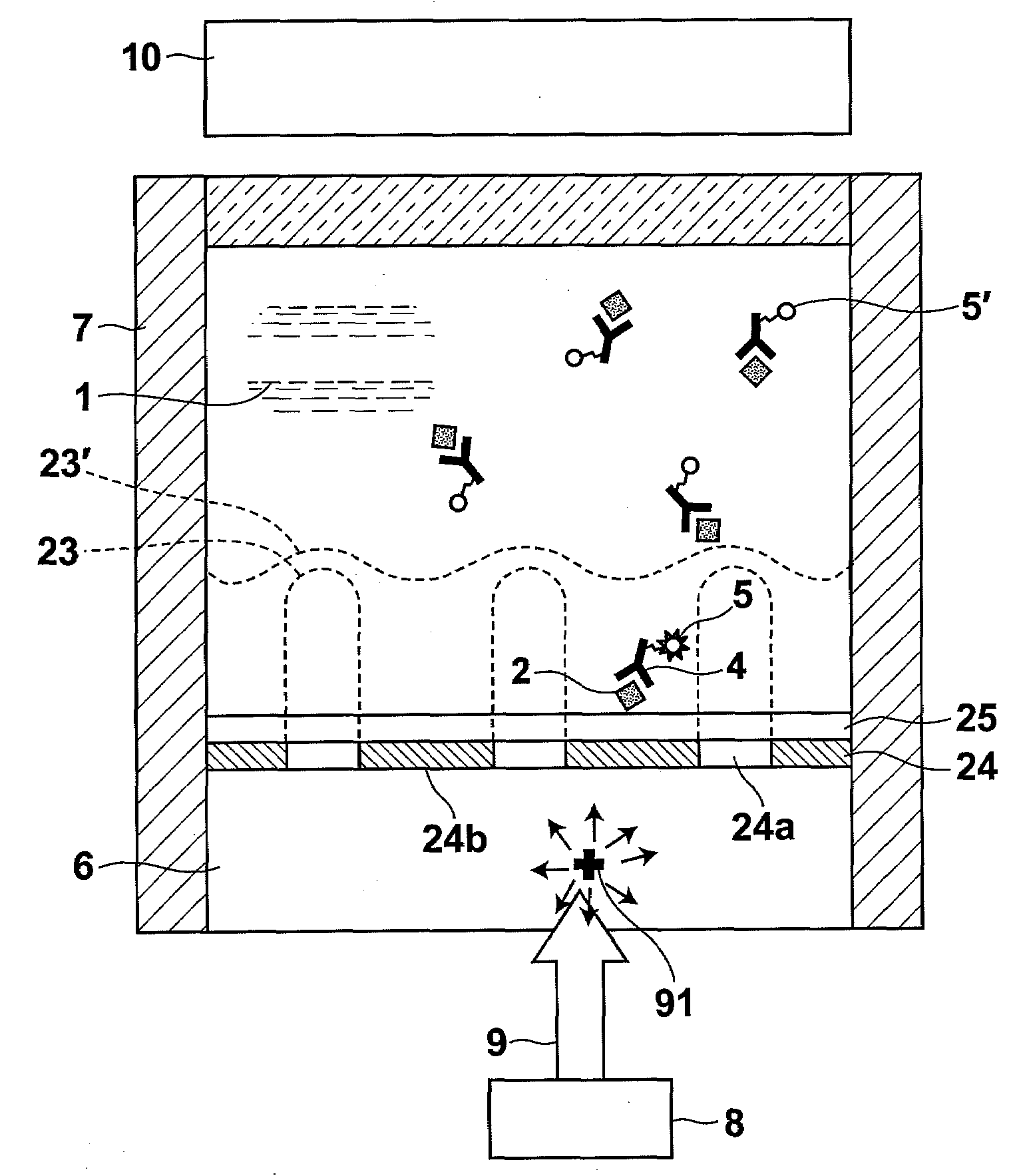
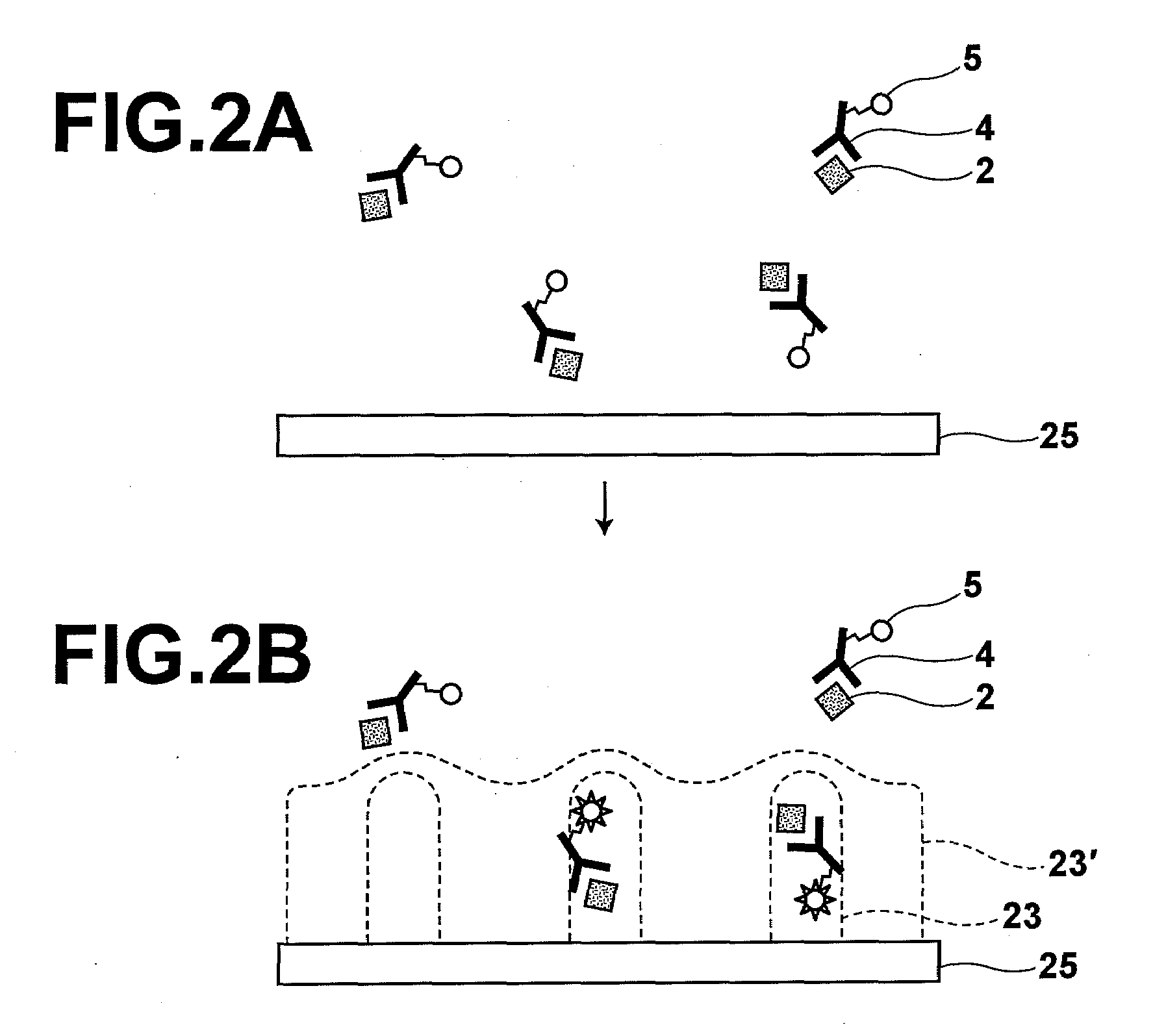
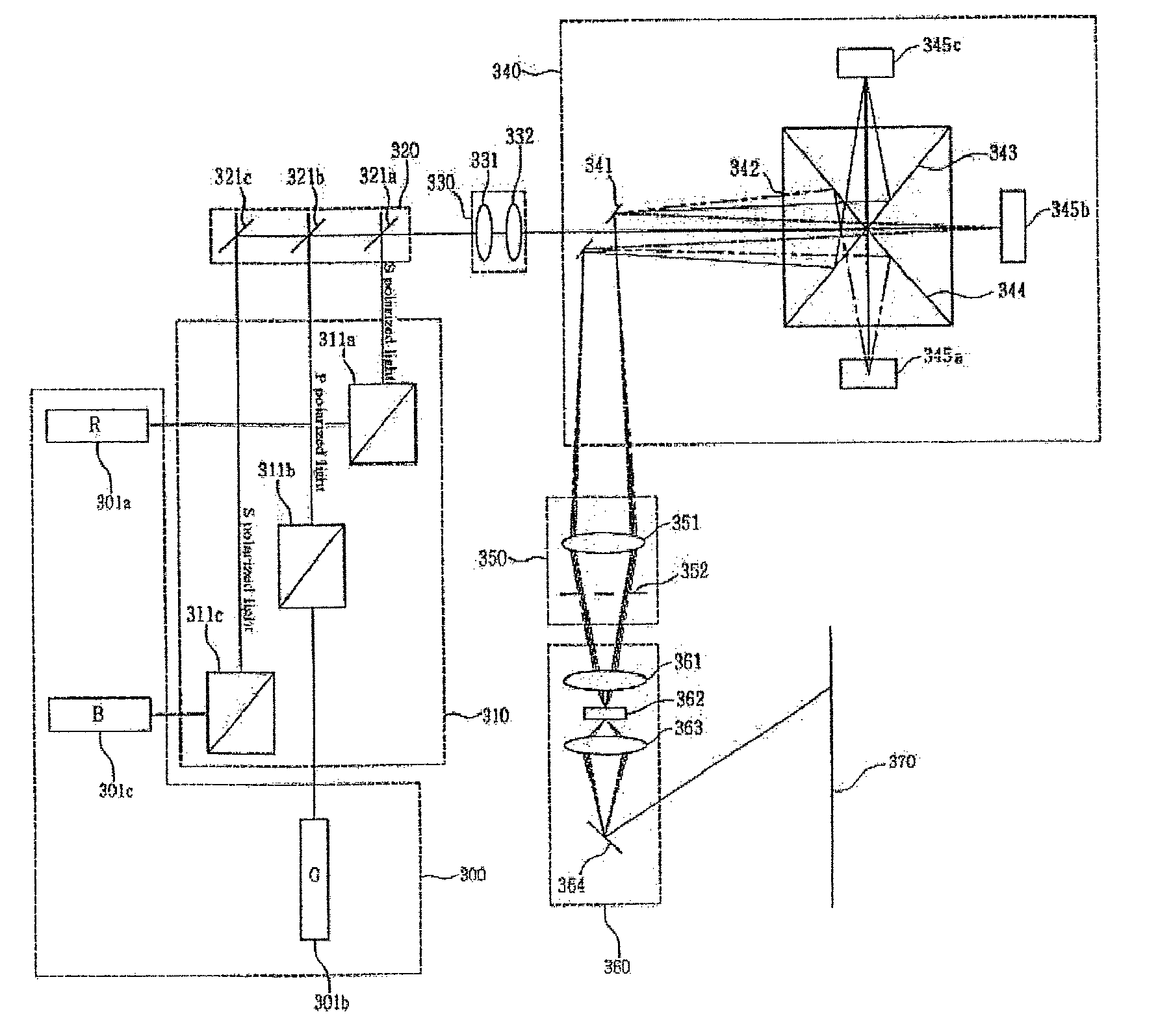
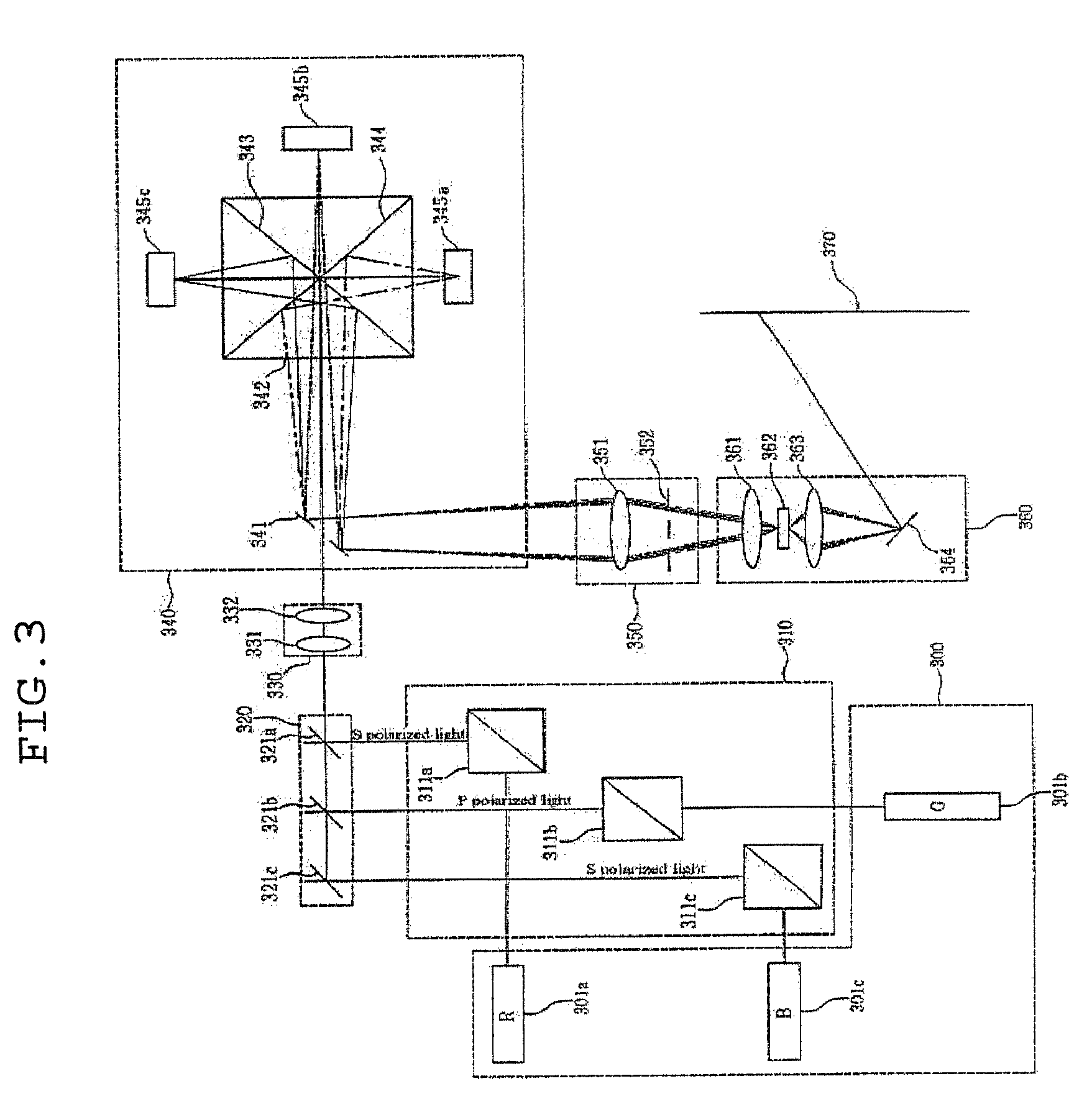
Display, instrument panel, optical system and optical instrument
InactiveUS20090290079A1Increase widthShorten the lengthPolarising elementsSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceOptical instrument
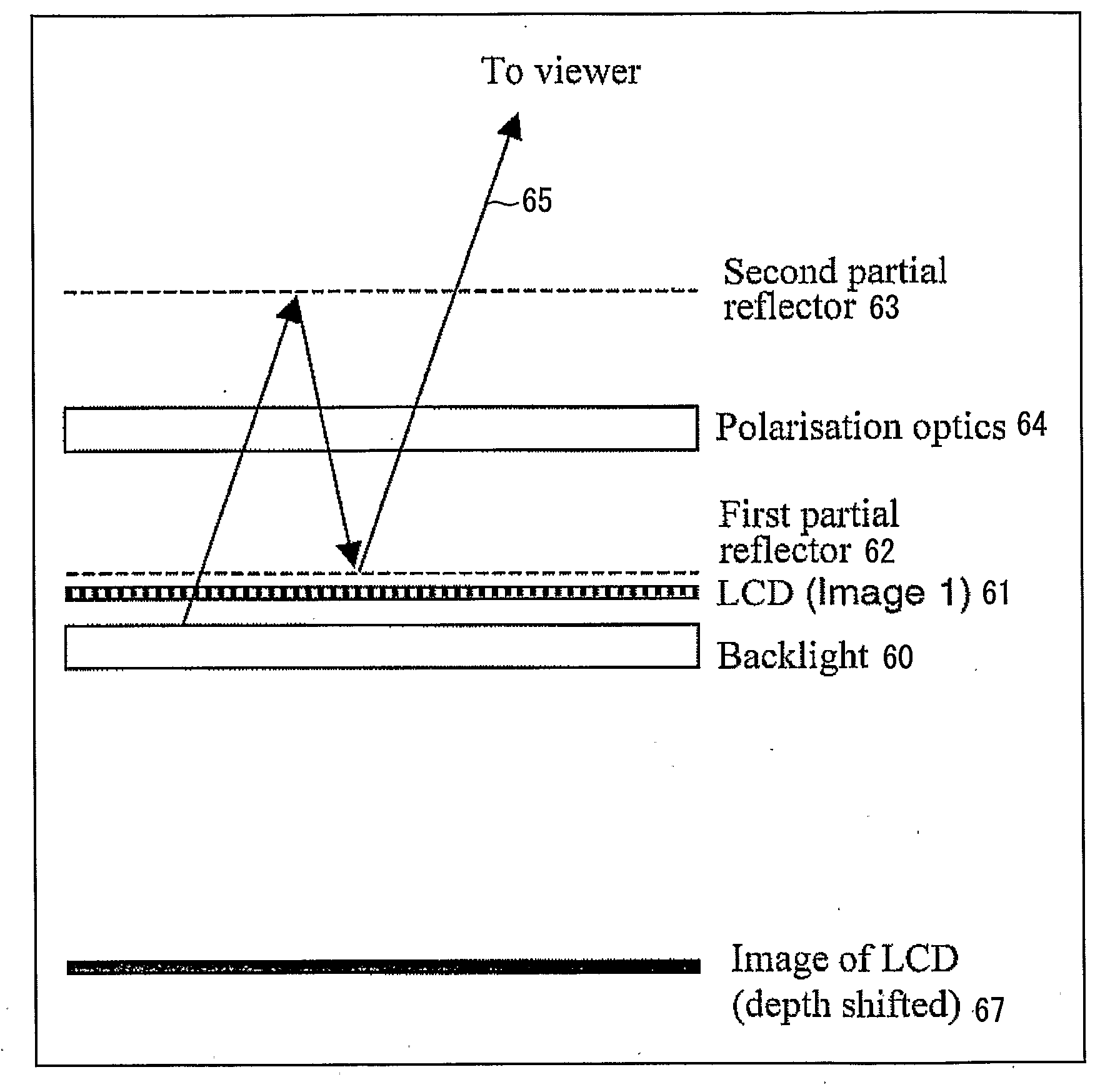
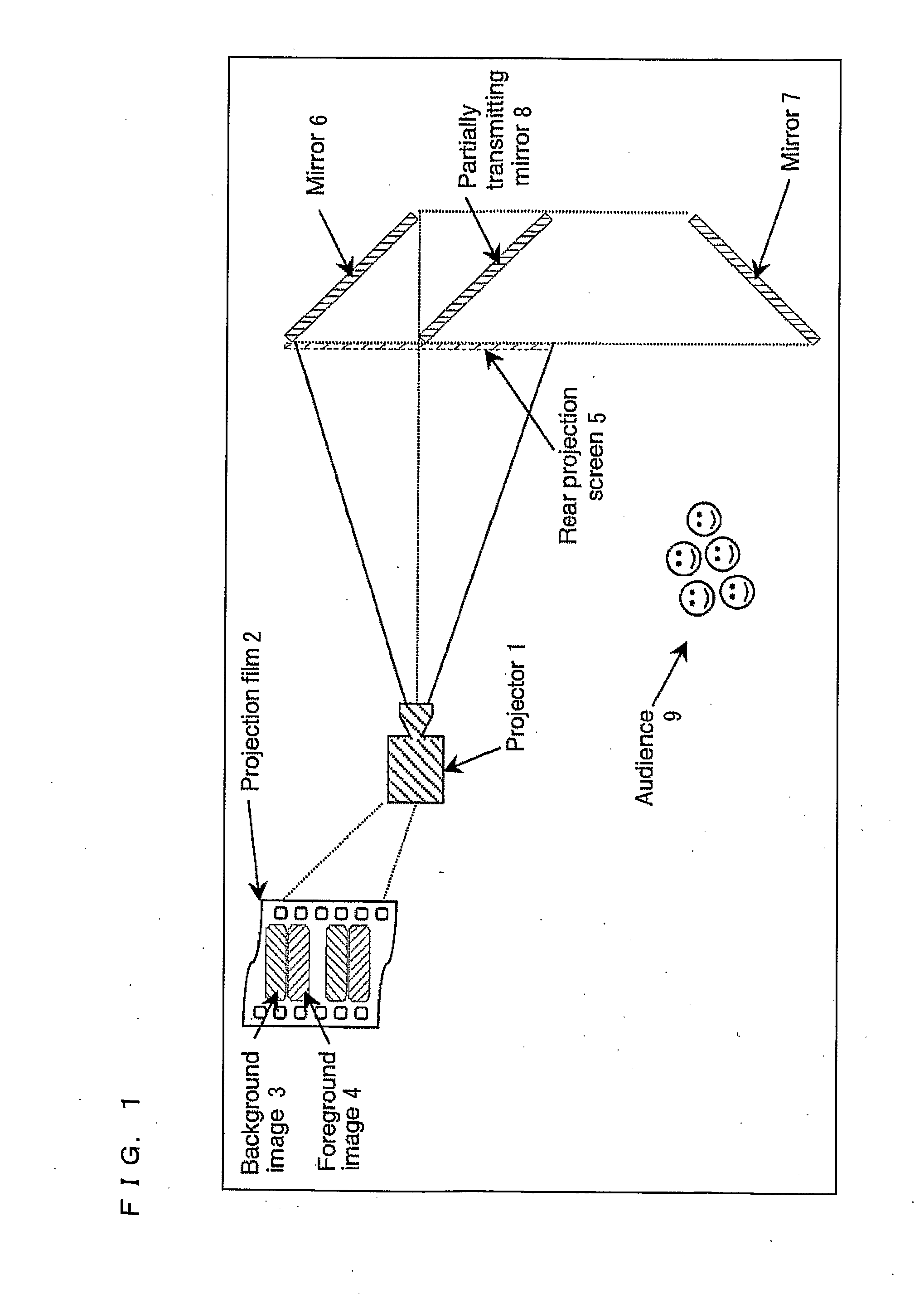
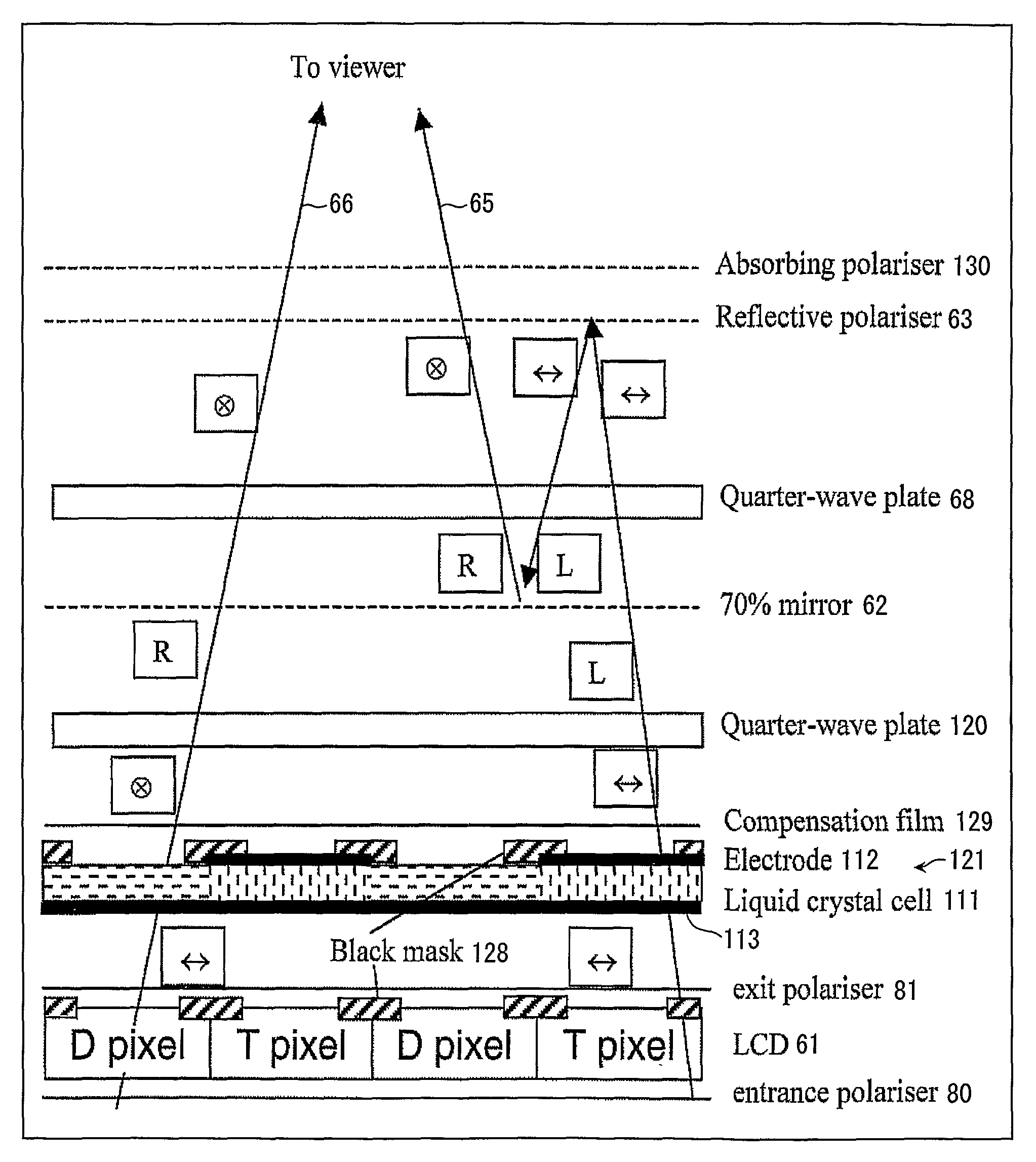
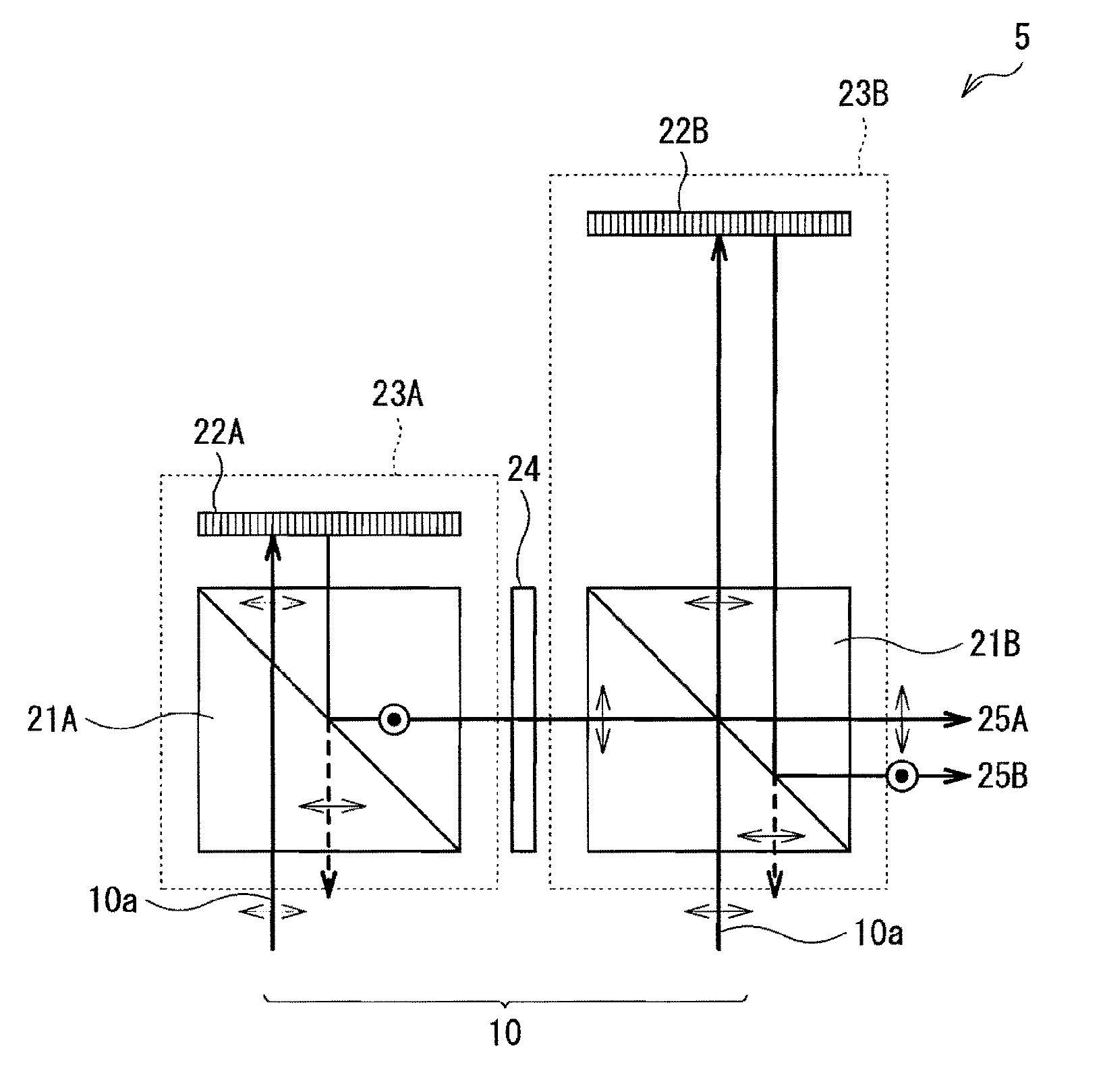
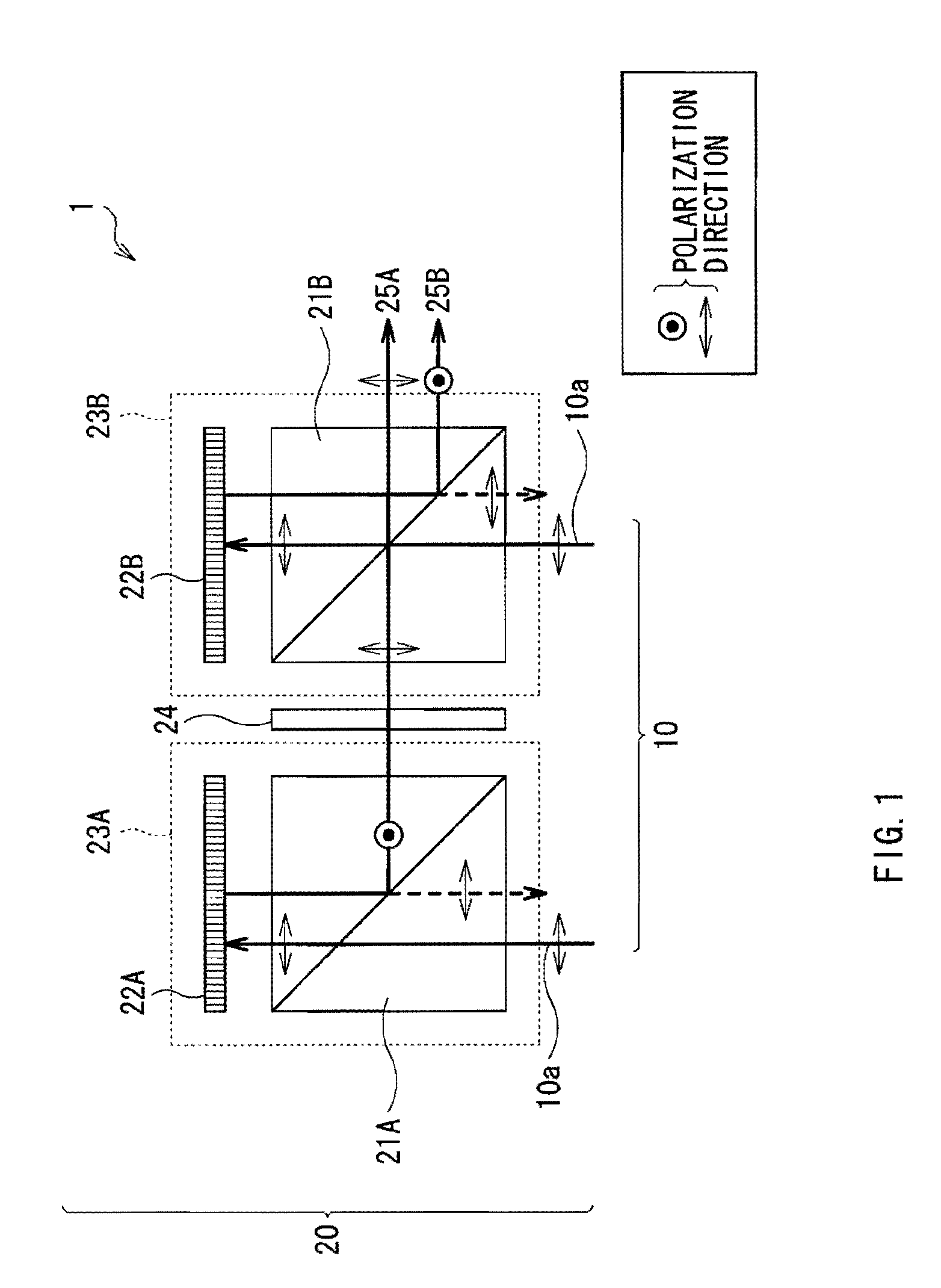
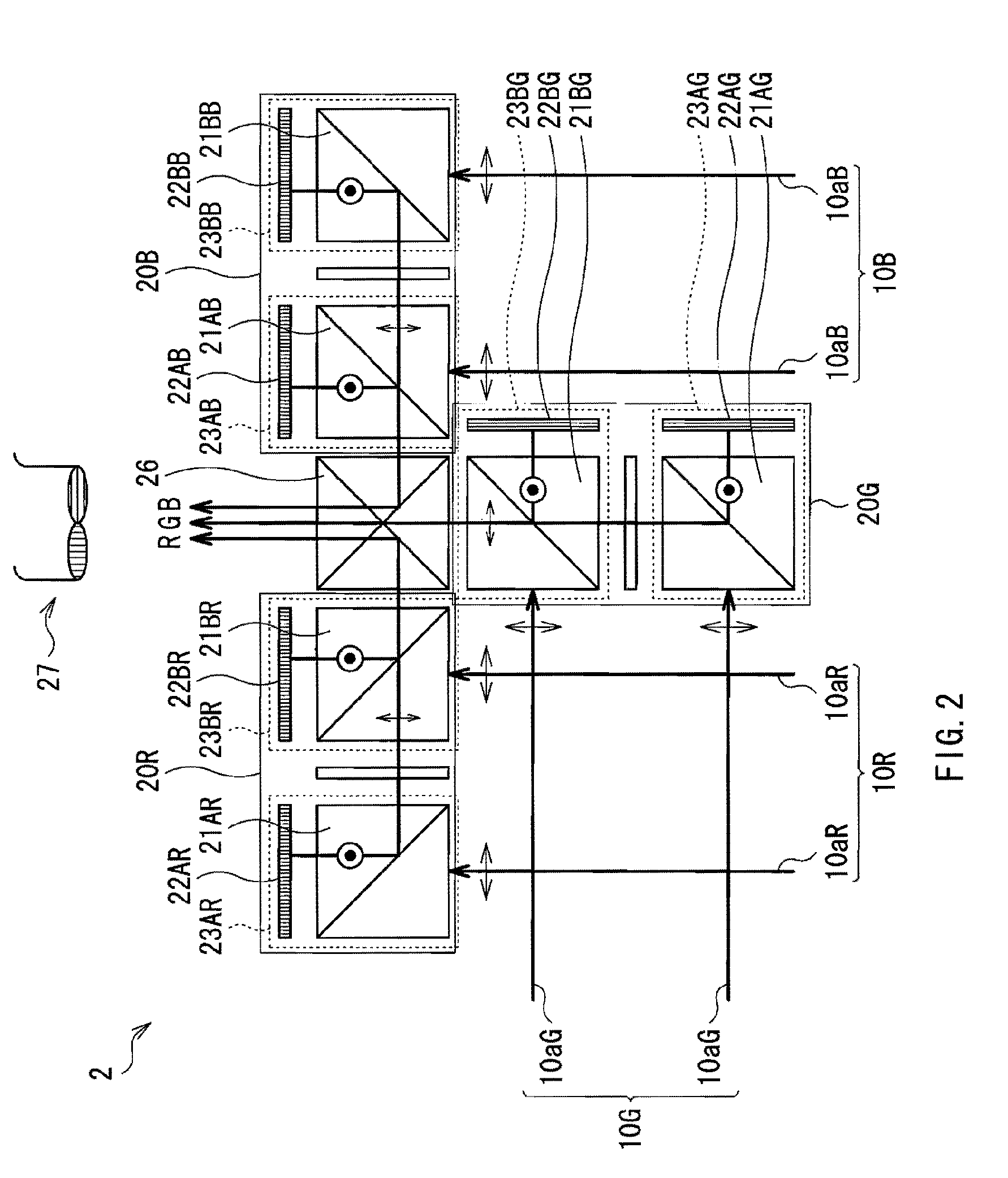
A multiple depth display provided for displaying images at different depths comprises a single display device (61), for displaying all of the images. An optical system (62, 63, 64) is disposed in front of the display device (61). The optical system comprises first and second spaced-apart partial reflectors (62, 63) and polarization optics (64) for providing first and second light paths for first and second images or sequences of images displayed by the device (61). The first light path (65) comprises partial transmission through the first reflector (62), partial reflection from the second reflector (63), partial reflection from the first reflector (62), and partial transmission through the second reflector (65) towards a viewing region.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display, instrument panel, optical system and optical instrument
ActiveUS20130057961A1Avoid emissionsReduce manufacturing costSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsDisplay deviceOptical instrument
Owner:SHARP KK
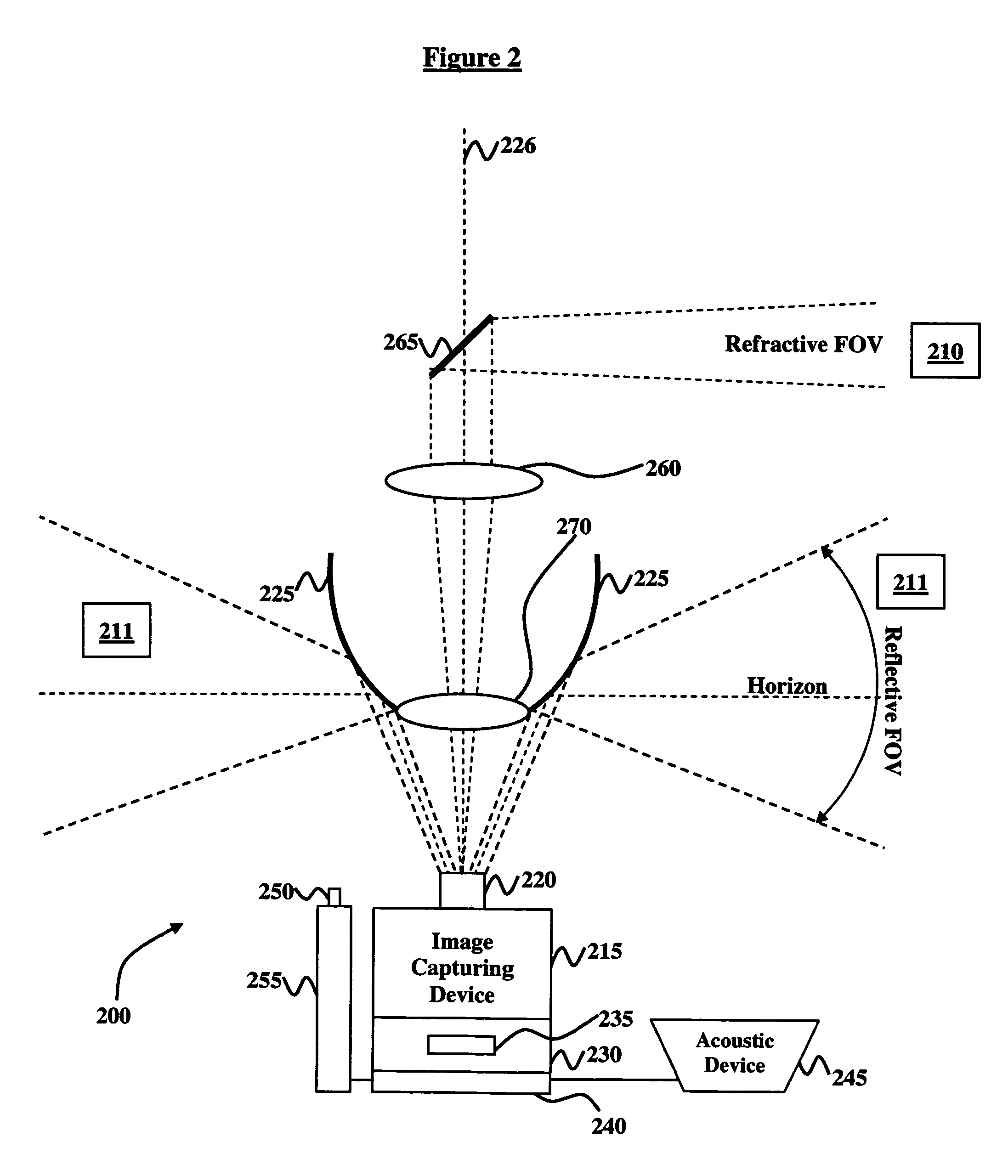
Optical detection and location of gunfire
InactiveUS7409899B1Improve imaging resolutionHigh resolutionSighting devicesPosition fixationSound sourcesComputer science
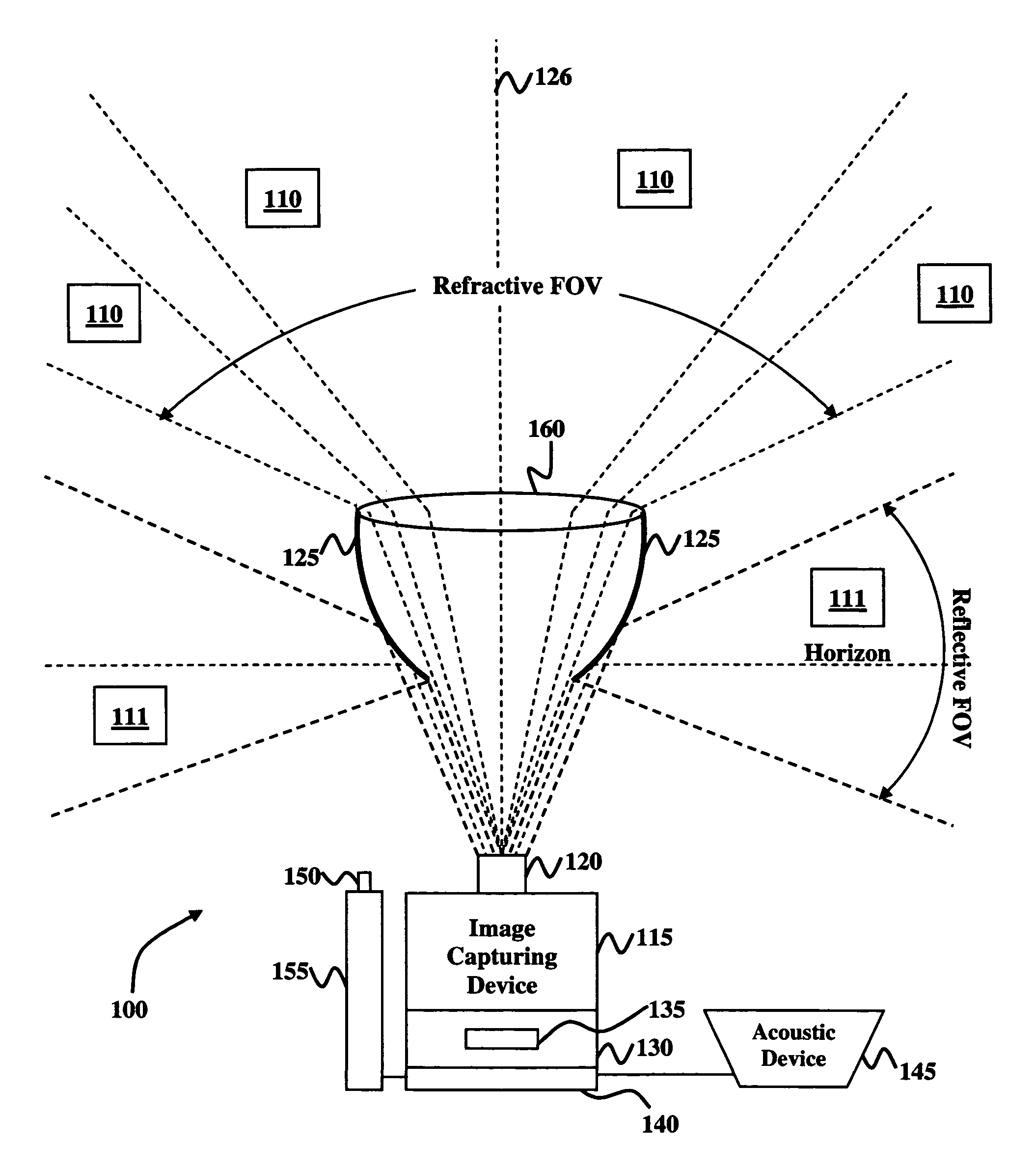
Disclosed is an optical gunfire detection system comprising an image-capturing device operable for detecting light; a narrowband Fraunhofer line filter connected to the image-capturing device, and operable for partially restricting transmission of the light; a convex parabolic reflector operable for transmitting images to the image-capturing device; a lens system; an image storage device connected to the image-capturing device, wherein the image storage device comprises a solid-state digital memory unit operable to store multiple seconds of video imagery; a real-time computer-implemented mechanism connected to the image storage device, the computer-implemented mechanism operable for detecting locations and classifications of gunfire associated with the images; an acoustic device in communication with the computer-implemented mechanism, and operable for verifying the classifications of the gunfire; a position laser operable for identifying the locations of the gunfire; and a defense mechanism comprising the laser pointer and operable to defend against a source of the gunfire.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
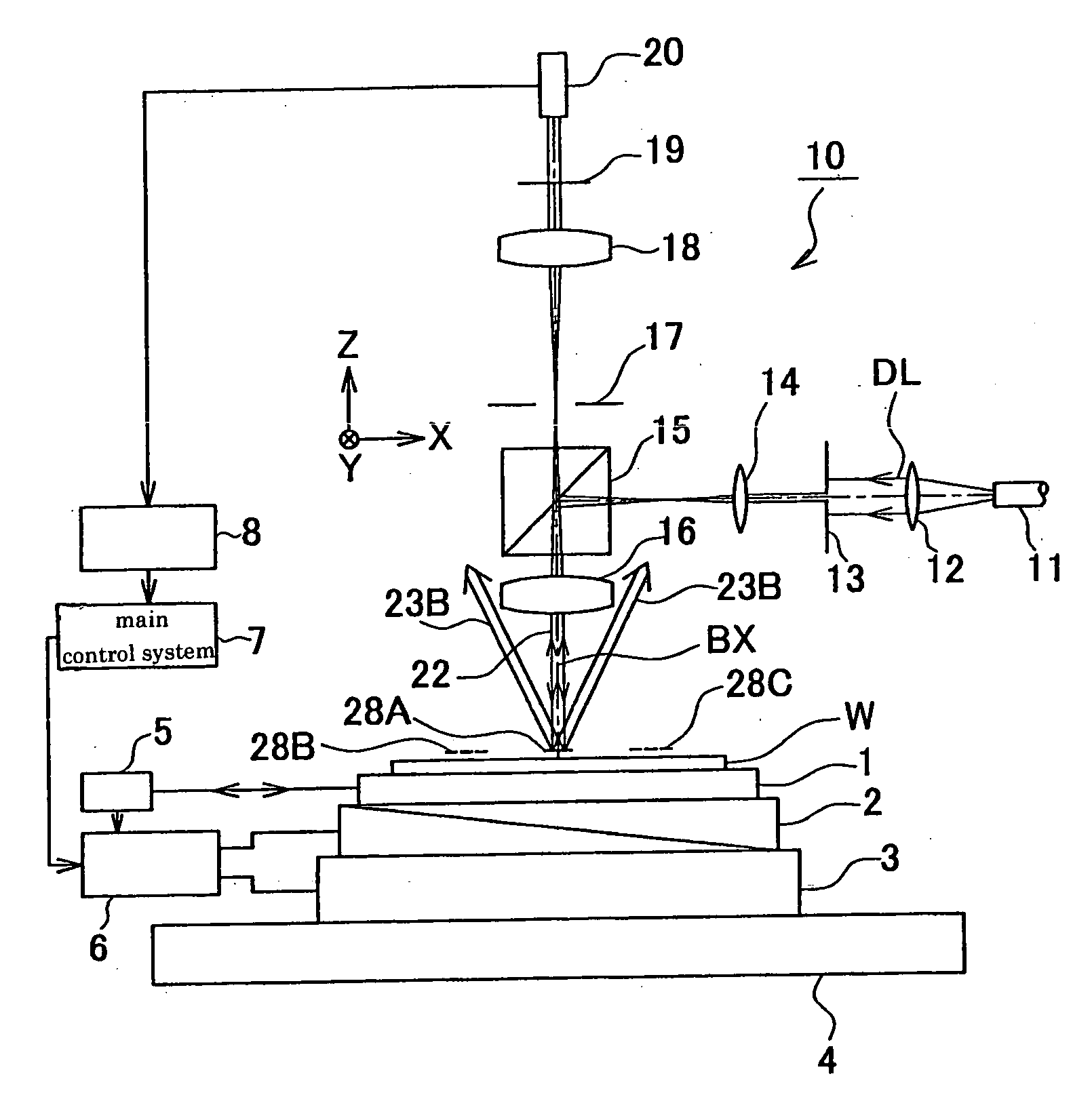
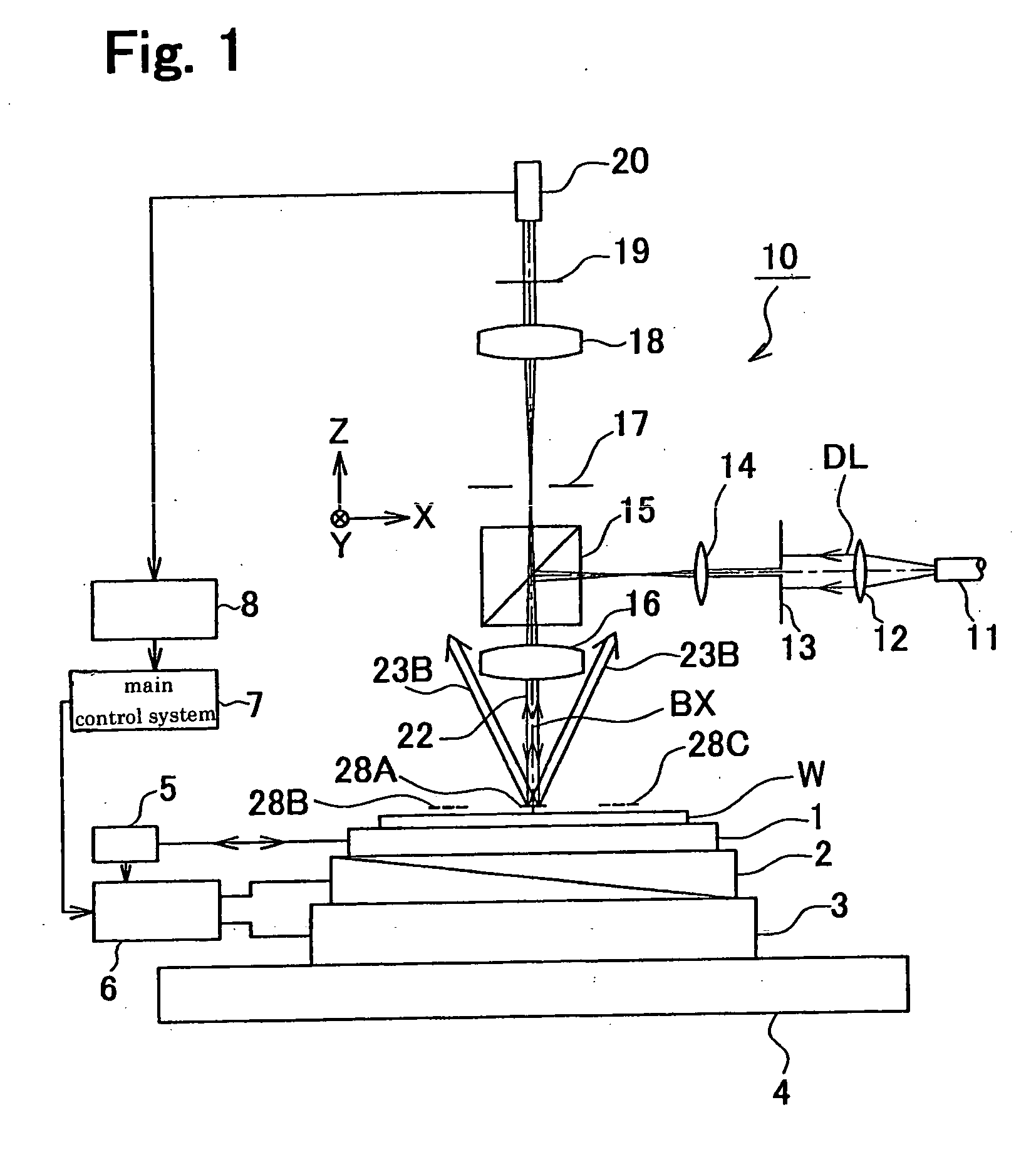
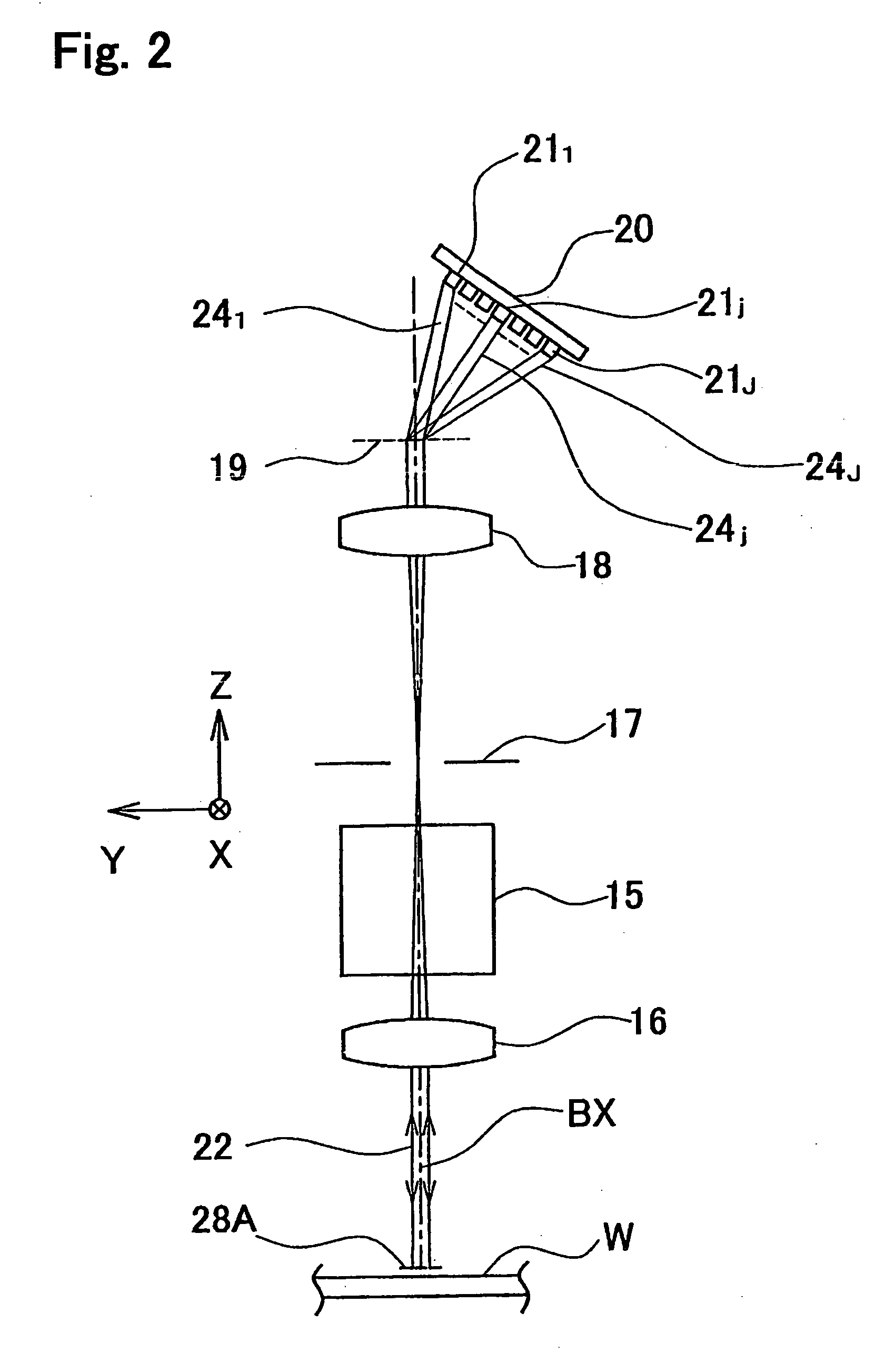
Positional information measuring method and device, and exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060250597A1Easy to detectImprove accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLength waveReflectometry
A position information measuring method capable of easily obtaining information on a relative position deviation between two marks by using scatterometry or reflectometry. Marks (25A) are formed on a wafer (W) at a pitch P1, and marks (28A) are formed on an intermediate layer (27) over them at a pitch P2 different from the pitch P1. A detection light (DL) is allowed to vertically enter the wafer (W) and a regular reflection light (22) from two marks (25A, 28A) only is spectrally separated on a wavelength basis for photoelectric converting. Wavelength-based reflectances are obtained from obtained detection signals, a reflectance at a specified wavelength is determined for each position in the measuring direction (X direction) of marks (25A, 28A), the shape of a Moire pattern formed by the overlapping of two marks (25A, 28A) is determined from the obtained reflectance distribution, and the position deviation amount of a mark (28A) is determined from the shape.
Owner:NIKON CORP
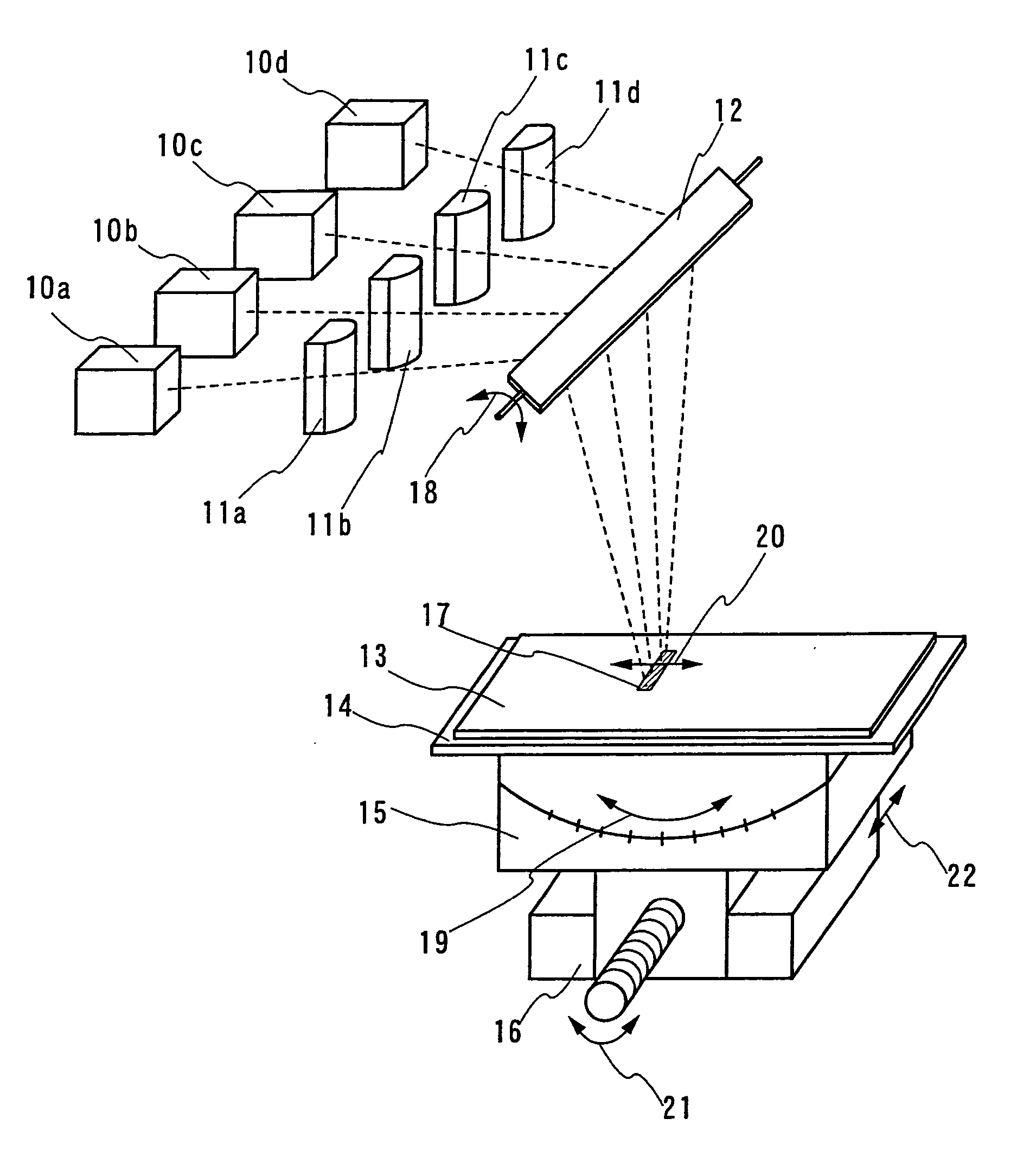
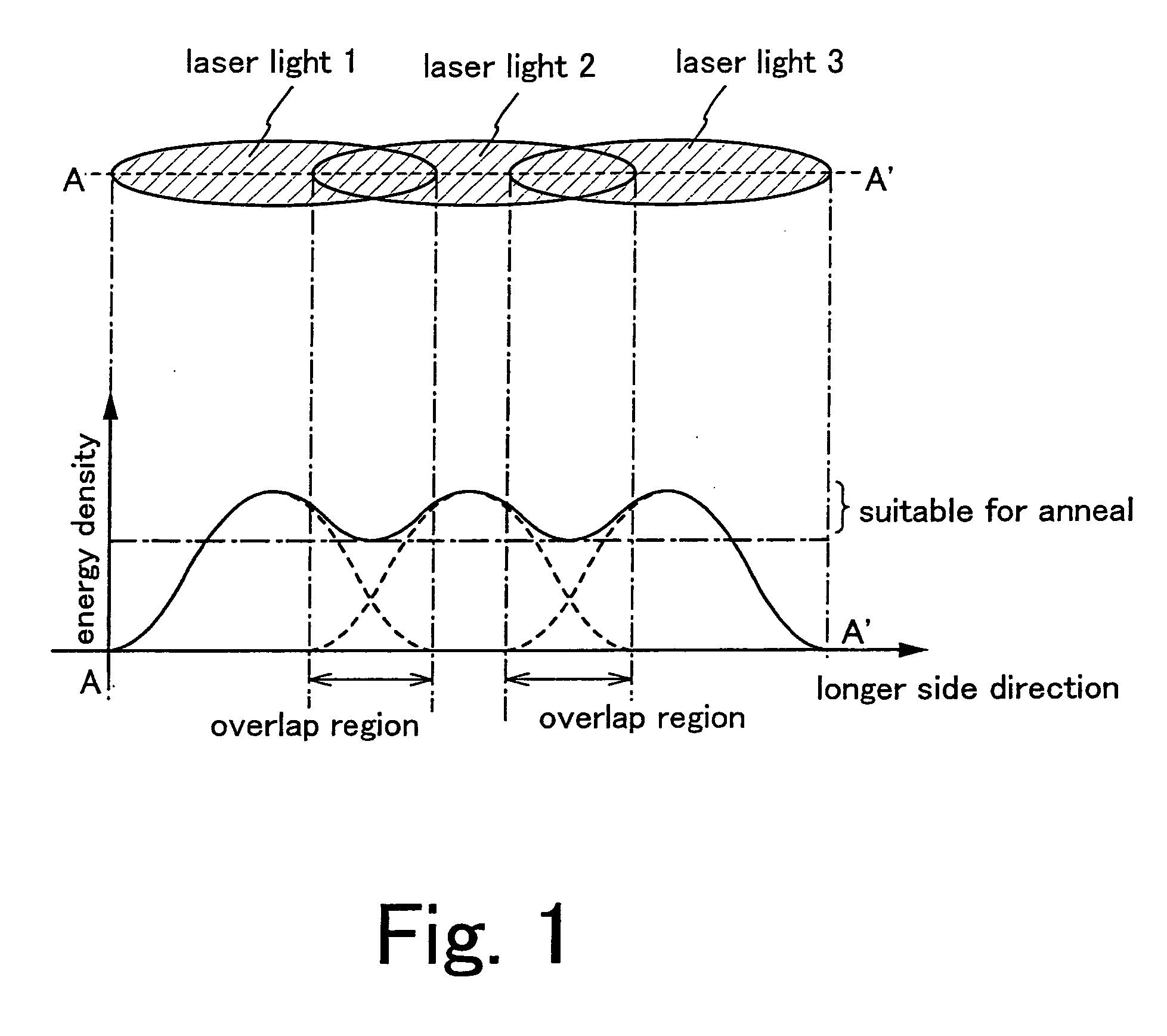
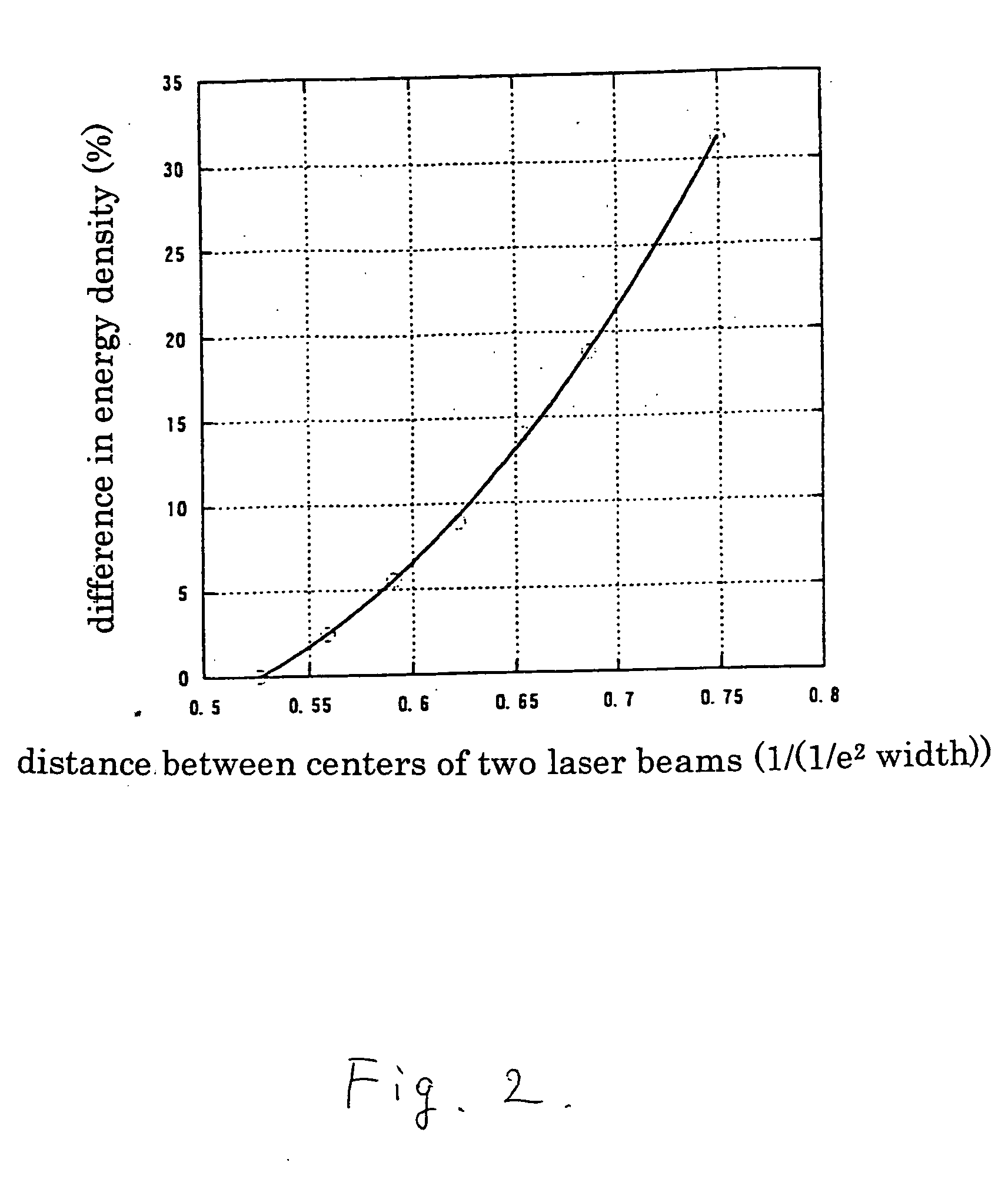
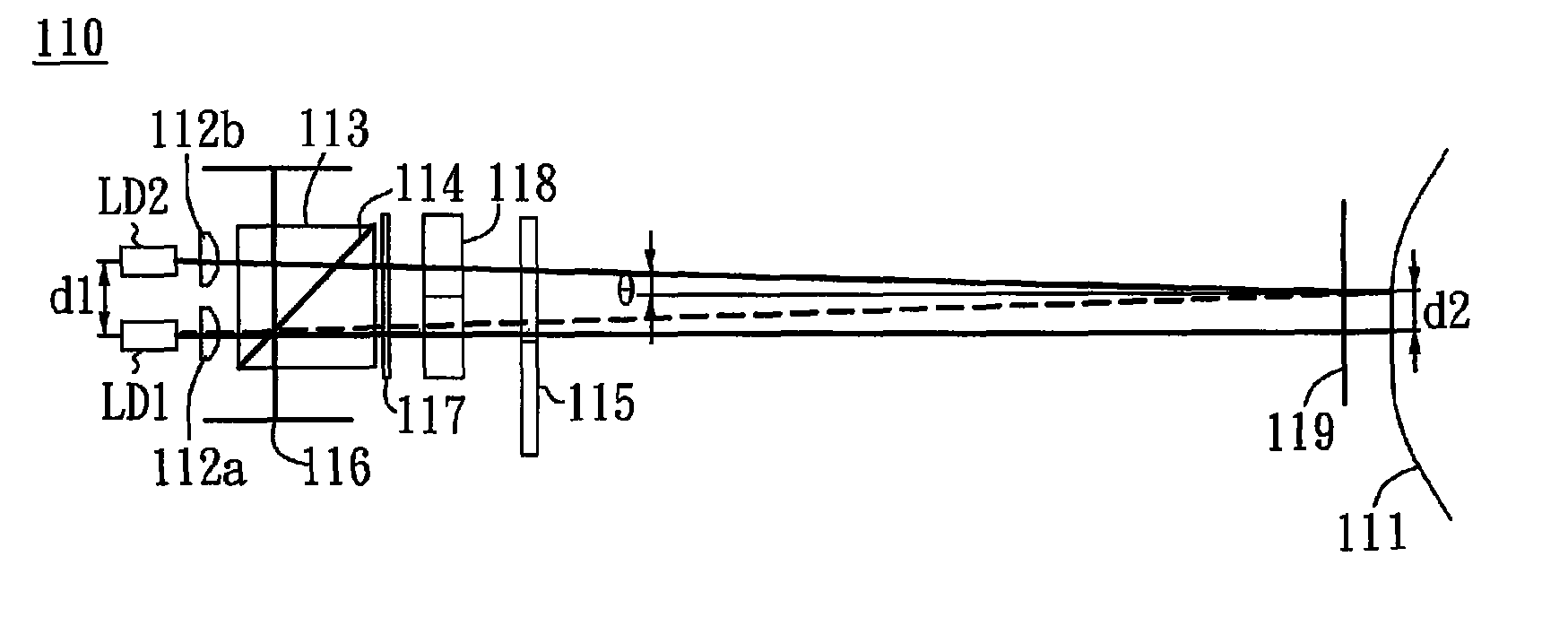
Laser beam irradiating apparatus, laser beam irradiating method, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6897889B2Reduce weightIncreased durabilityTransistorInking apparatusLight beamIrradiation laser
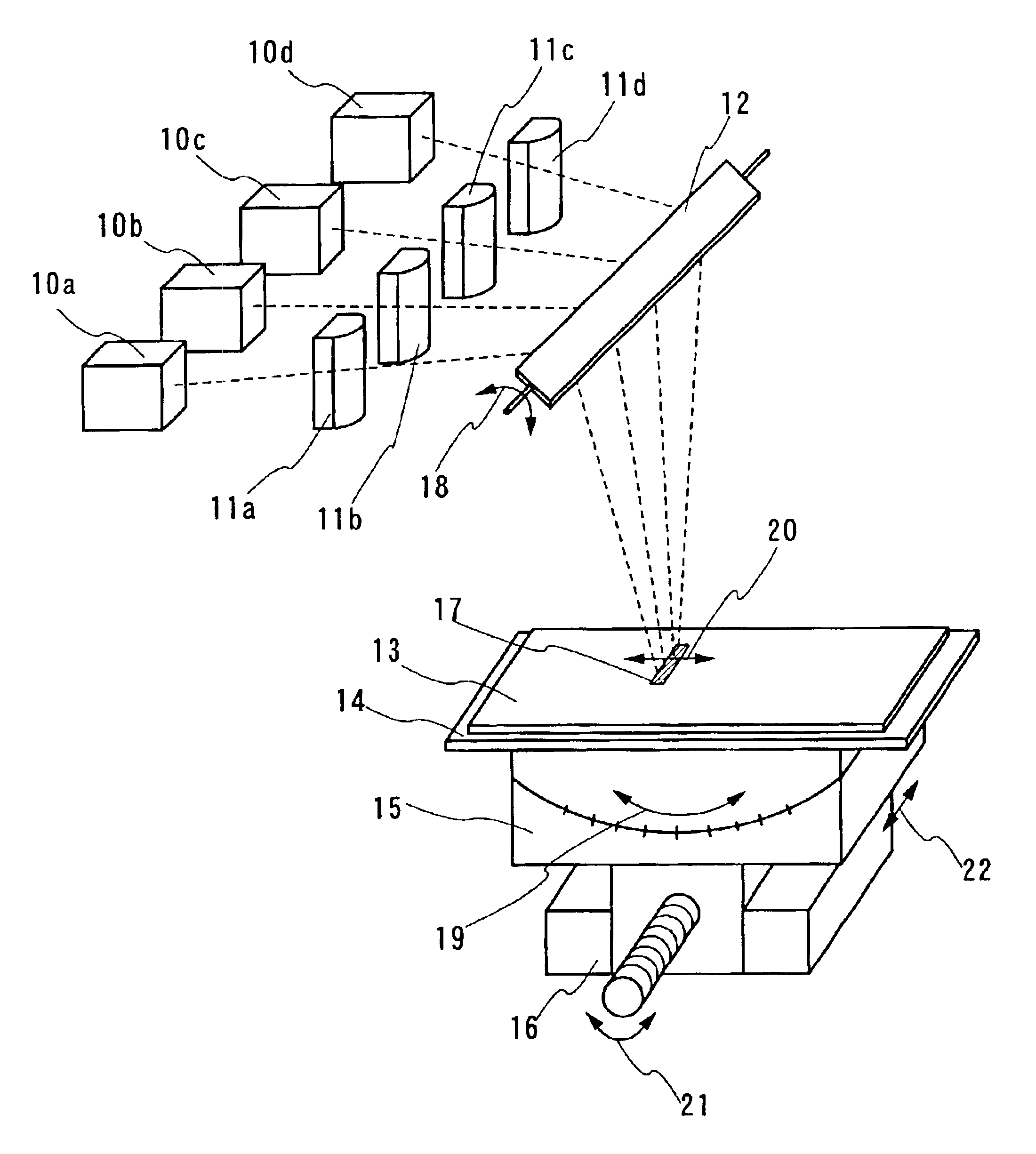
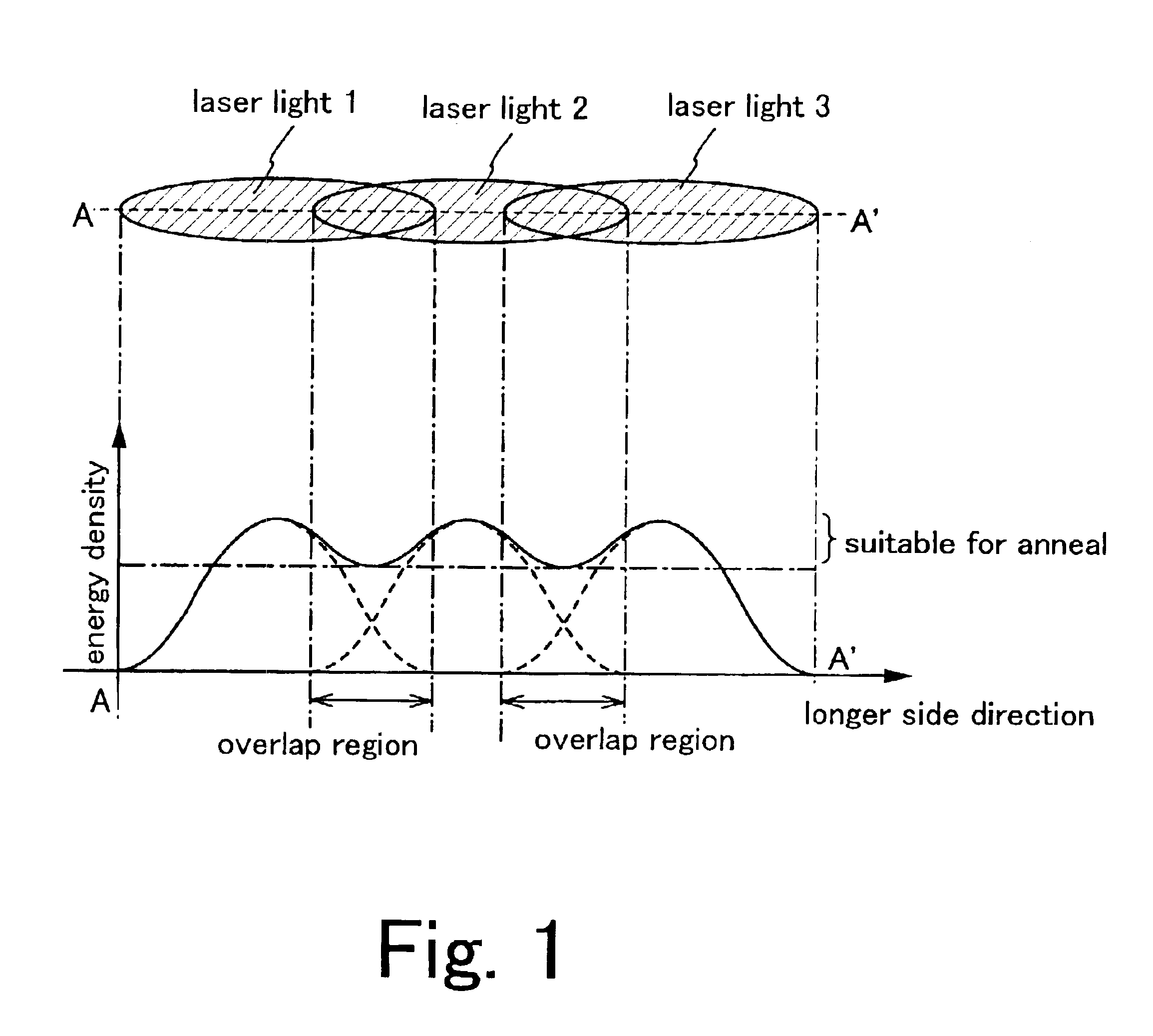
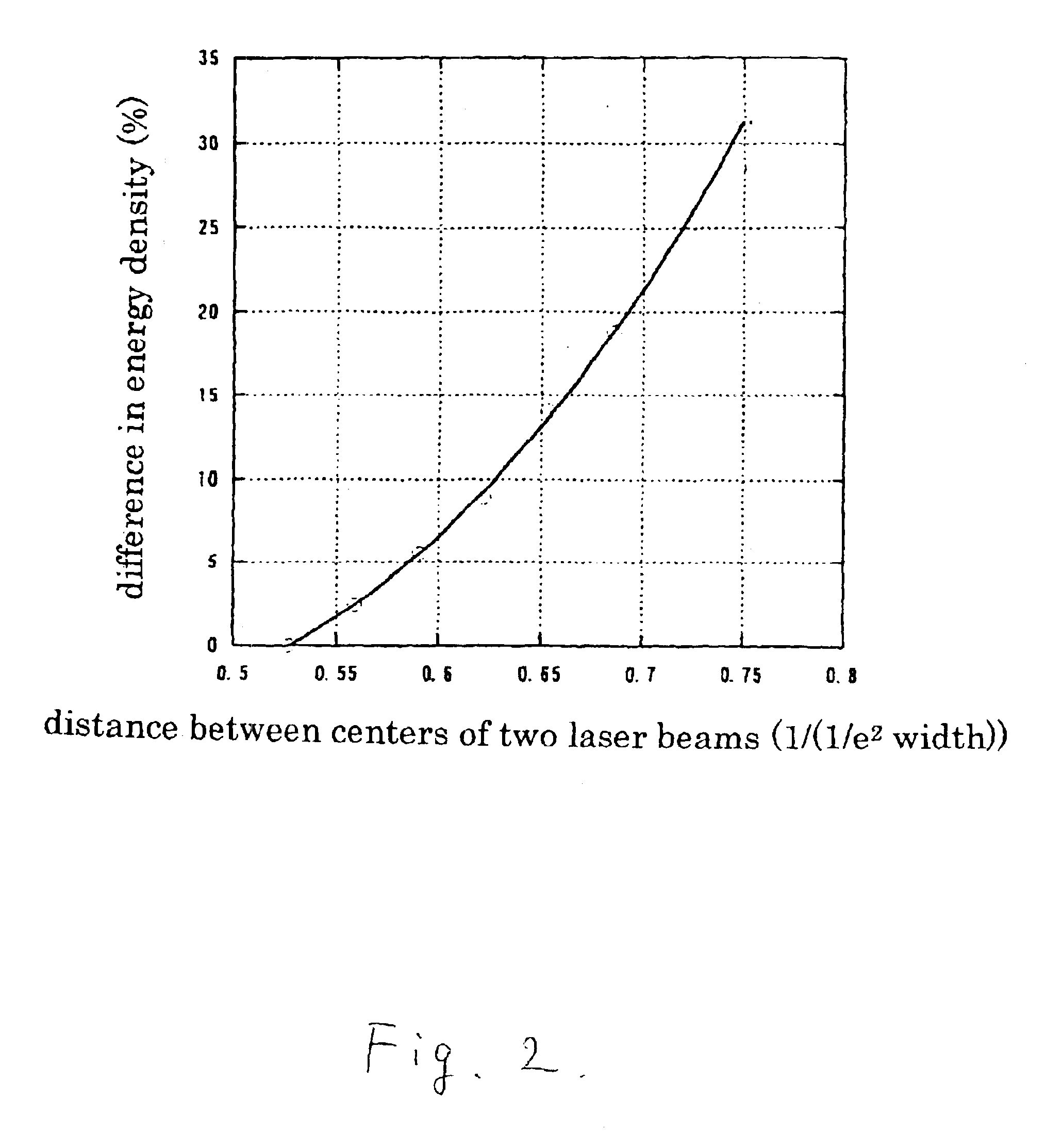
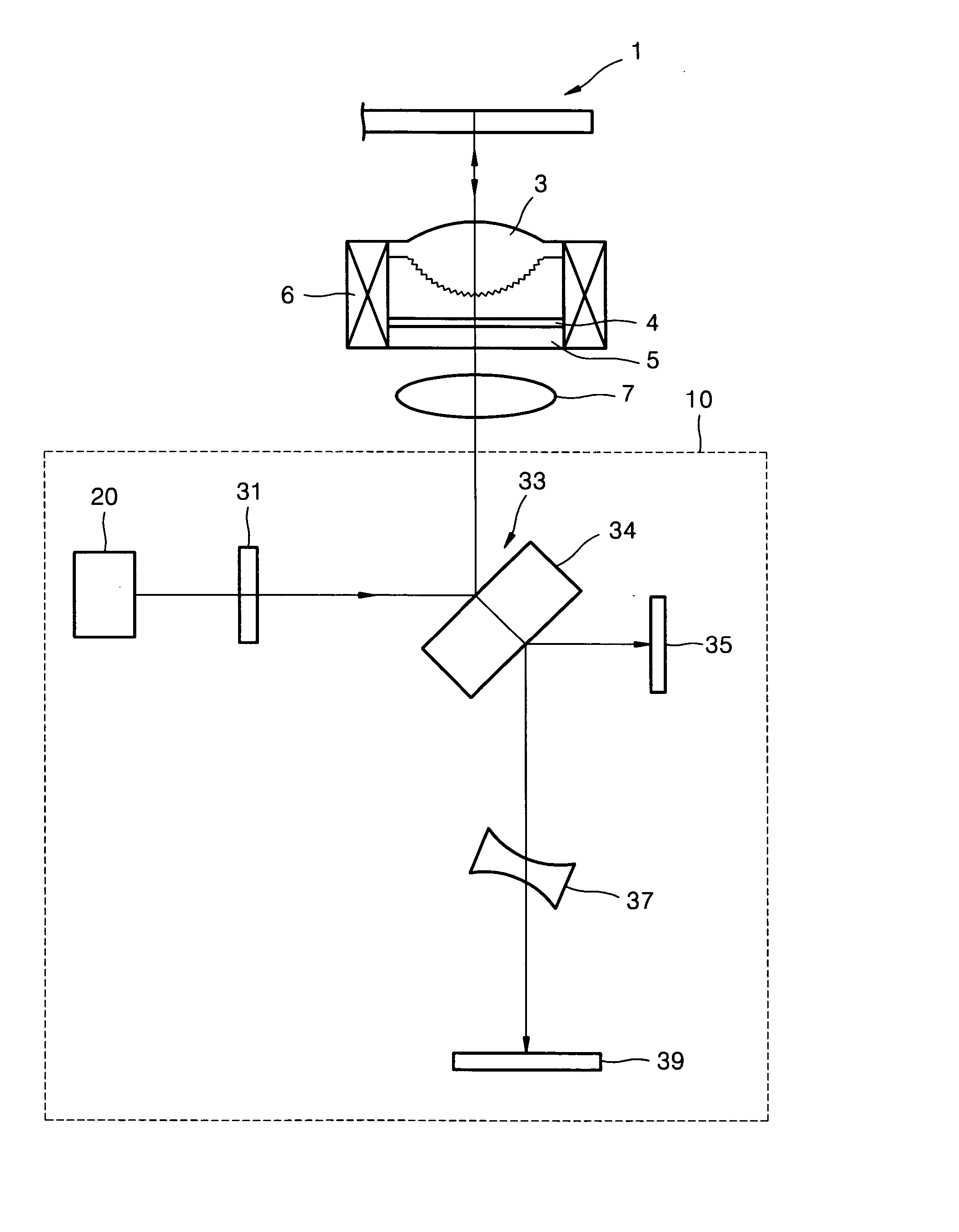
A laser beam irradiating apparatus capable of achieving uniform annealing efficiently by employing a simple optical system using laser beams having attenuated regions is disclosed. It is possible to provide a method of irradiating a laser beam using the laser beam irradiating apparatus, and to provide a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device including the laser beam irradiating method in the fabrication sequence thereof.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Compatible optical pickup
InactiveUS20050030878A1Simple processSimple optical systemRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupHigh density
An optical pickup which is compatible with at least one high density recording medium that uses a blue-violet beam and at least one lower density recording medium, the optical pickup including: an optical unit to selectively emit one of a plurality of beams with different wavelengths onto one of the at least one high density recording medium and the at least one lower density recording medium, and to receive the respective beam reflected from the respective recording medium; and a holographic objective lens to focus the respective beams emitted by the optical unit on a recording surface of the respective recording medium, the holographic objective lens including a first holographic lens region and a second holographic lens region located inside the first holographic lens region, wherein holographic patterns of the first and second holographic lens regions respectively produce a first effective numerical aperture (NA) for the at least one high density recording medium and at least one additional effective NA suitable for the at least one lower density recording medium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device for reducing speckle effect in a display system
InactiveUS20120206784A1Suppress speckle noiseSimple optical systemOptical elementsVibrating membraneLaser scanning
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for speckle noise reduction in laser scanning projection display. In particular, a MEMS device with a vibrating membrane through which light rays are refracted with temporally varying angles is provided for reducing the effect of speckling.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Embeddable 2-D projection nano engine for personal projector
ActiveUS8079718B1Speckle reductionImprove efficiencyProjectorsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorLight source
A projector has a transmissive spatial light modulator backlit by a collimated illuminator that includes a light source that outputs red, green, blue (RGB) light, and a combiner disposed in light-receiving relation to the light source for mixing or combining the RGB light. The combiner has cavity features associated therewith for outputting collimated light, where such light preferably has a divergent cone angle less than plus or minus fifteen degrees (+ / −15°).
Owner:JABIL CIRCUIT INC
Projection stereoscopic display
InactiveUS20100171890A1Reduce power consumptionHigh color purityProjectorsNon-linear opticsParallaxLiquid crystal
A projection stereoscopic display includes: a stereoscopic display optical system receiving linearly polarized light from the light source and displaying a first picture and a second picture both having binocular parallax by linearly polarized light with polarization directions orthogonal to each other, in which the stereoscopic display optical system includes: a reflective liquid crystal panel modulating and reflecting linearly polarized light from the light source in response to a picture signal, a first polarizing device splitting the first picture from reflected light from the reflective liquid crystal panel, a retardation device converting the polarization direction of the first picture into a direction orthogonal thereto, and a second polarizing device splitting the second picture from reflected light from the reflective liquid crystal panel, and superimposing the second picture on the first picture of which the polarization direction is converted by the retardation device.
Owner:SONY CORP
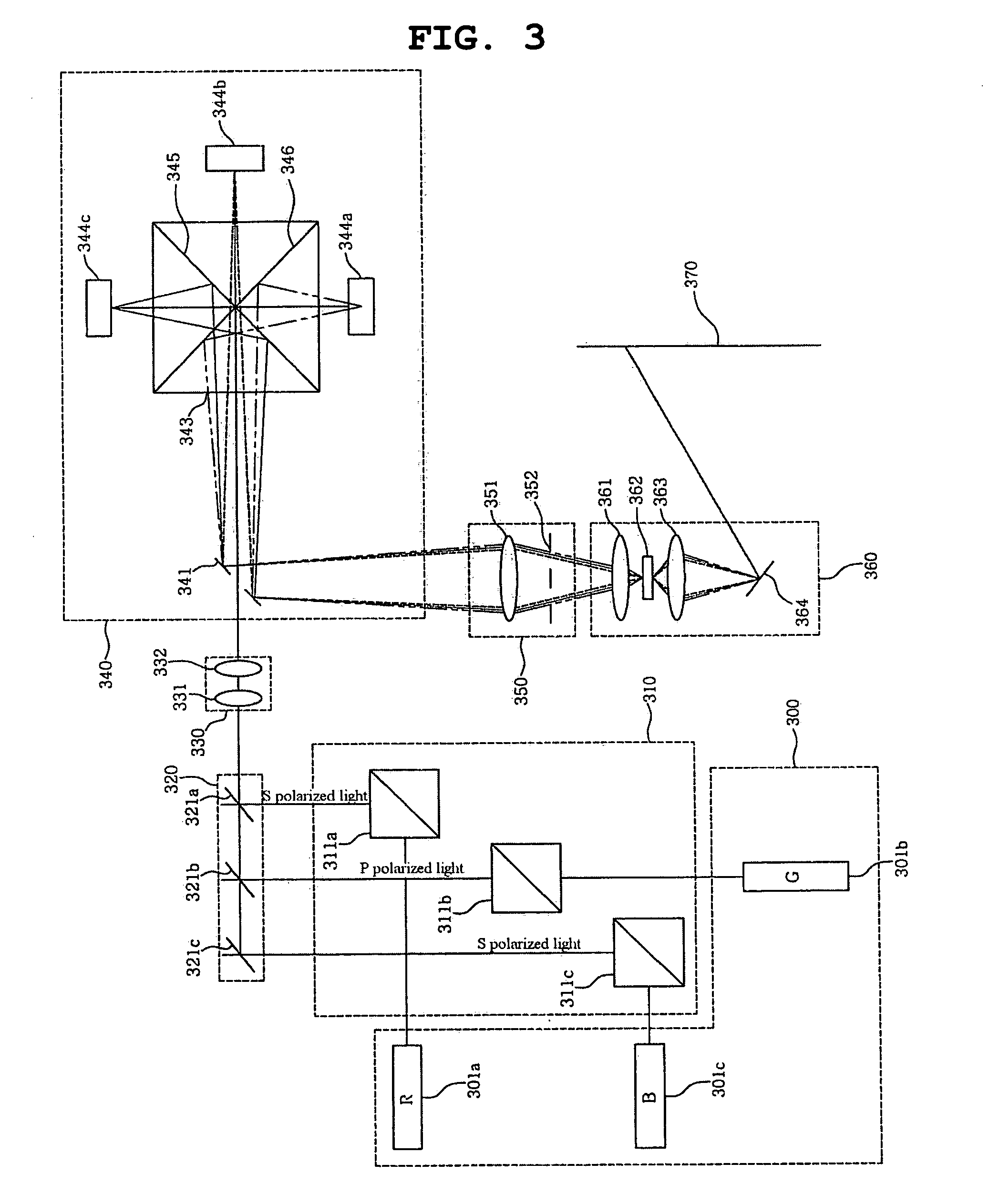
Color display device using separate diffracted light and illumination light
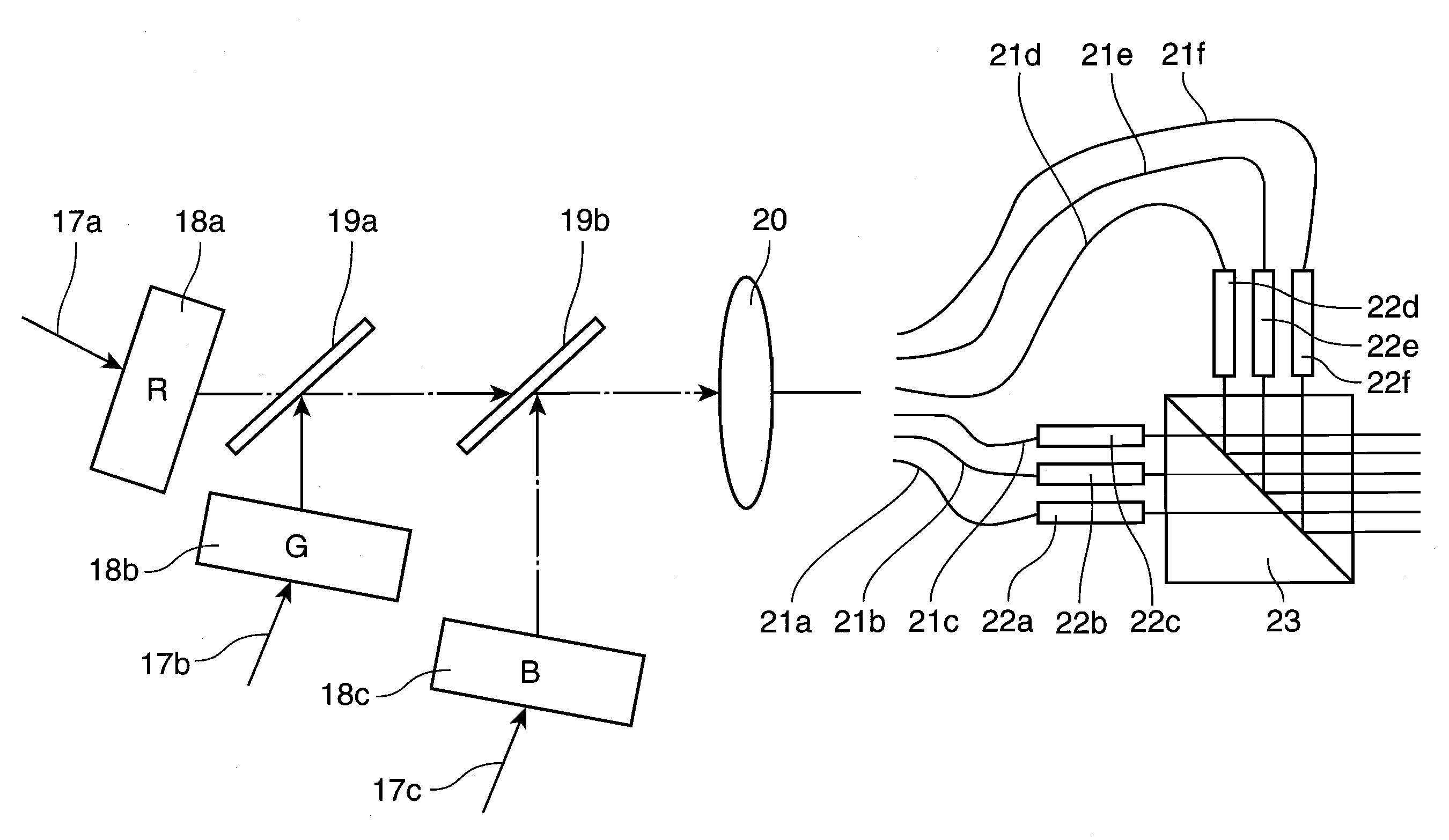
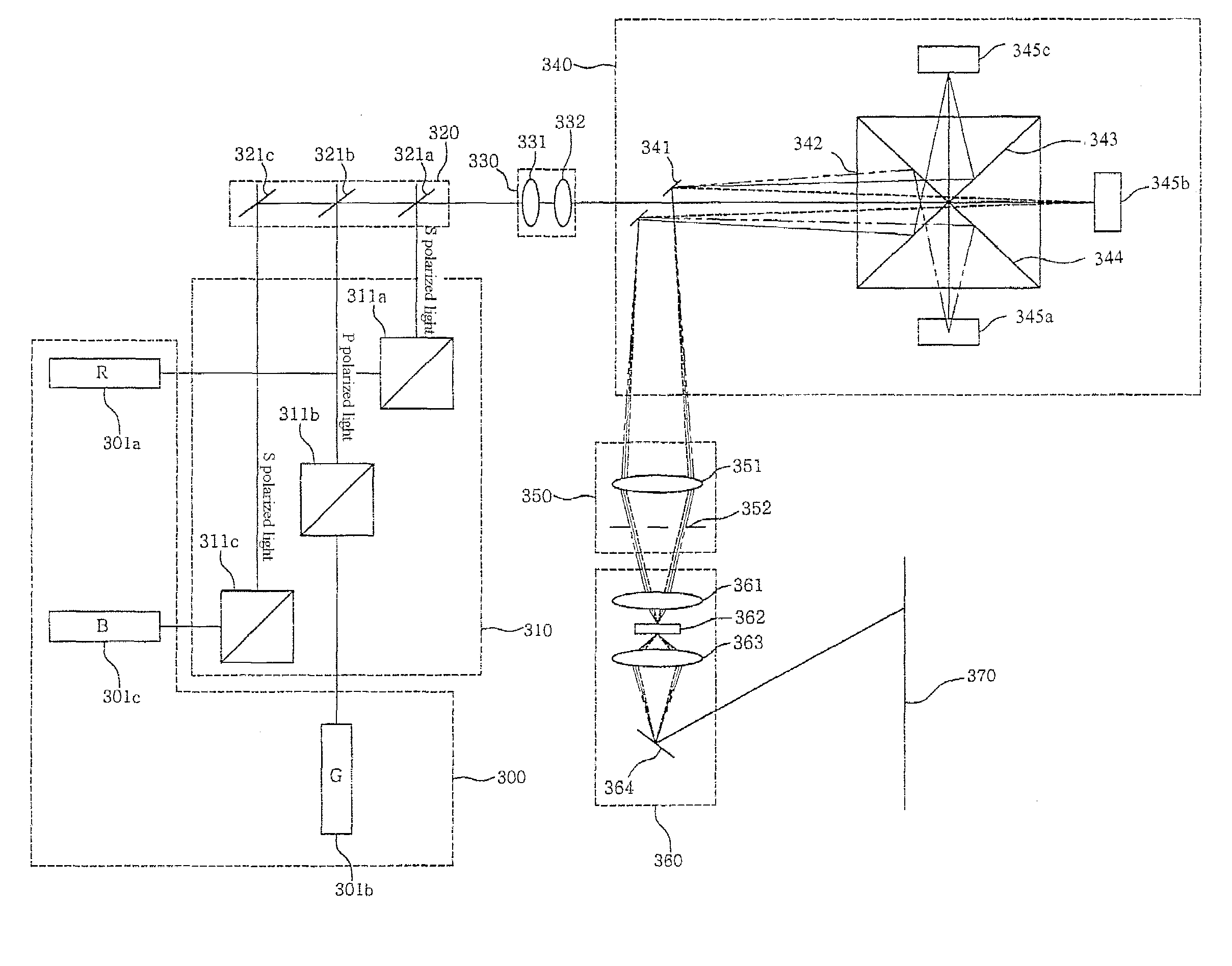
InactiveUS20060119941A1SimpleSimple optical systemTelevision system detailsProjectorsProjection systemLight beam
A display device is disclosed. The display device includes a condenser unit, an illumination lens system, a plurality of diffractive light modulators, a mirror for separating illumination light from diffracted light, a polarized beam separator, a filter unit and a projection unit. The condenser unit converges polarized light, and outputs the converged polarized light. The illumination lens system converts the polarized light into linear parallel light. The diffractive light modulators produce diffracted light beams having a plurality of diffraction orders. The mirror passes the polarized light therethrough using slits, and reflects the diffracted light beams toward a filter system. The polarized beam separator separates the polarized light on a wavelength basis and then allows the separated beams to be incident on corresponding diffractive light modulators, and converges the diffracted light beams and then outputs the converged light to the mirror. The filter system selects the diffracted light beams having desired diffraction orders from among diffracted light beams using a spatial filter. The projection system focuses the diffracted light beams, and projects the focused light beams onto a screen.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Laser beam irradiating apparatus, laser beam irradiating method, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050181550A1Increased durabilityReduce weightTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialLight beam
A laser beam irradiating apparatus comprising, a plurality of lasers, member for synthesizing a plurality of laser beams emitted respectively from the plurality of lasers into a single laser beam on a stage, and member for moving the synthesized laser beam on the stage while keeping a specific shape thereof. A semiconductor film can be crystallized or an impurity element doped therein can be activated by irradiating a laser beam to the semiconductor film from the laser beam irradiating apparatus arranged as above. Consequently, it is possible to provide a laser beam irradiating apparatus capable of achieving uniform annealing efficiently by employing an optical system simpler than a conventional one and using laser beams having attenuated regions. Also, it is possible to provide a method of irradiating a laser beam using the laser beam irradiating apparatus, and to provide a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device including the laser beam irradiating method in the fabrication sequence thereof.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
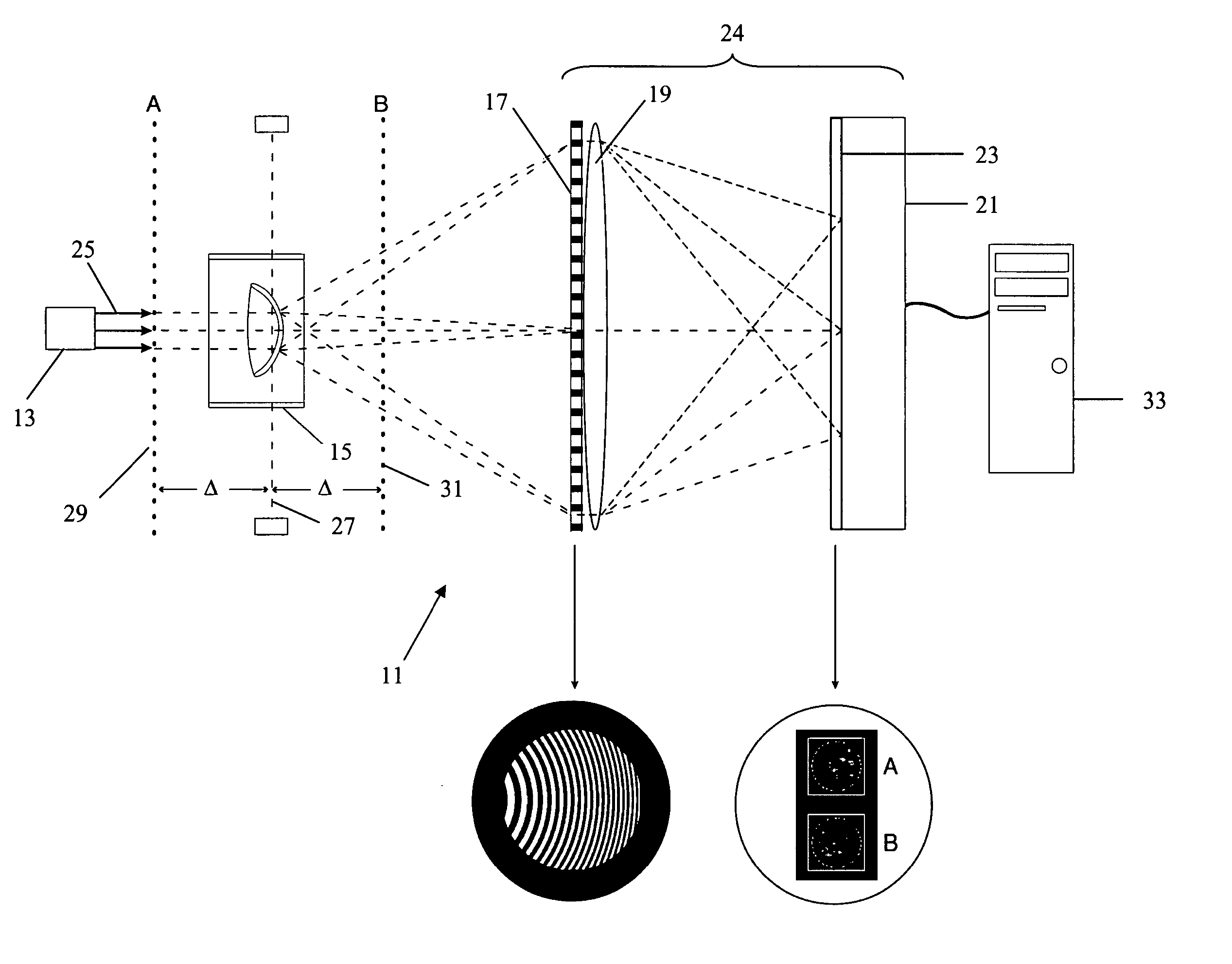
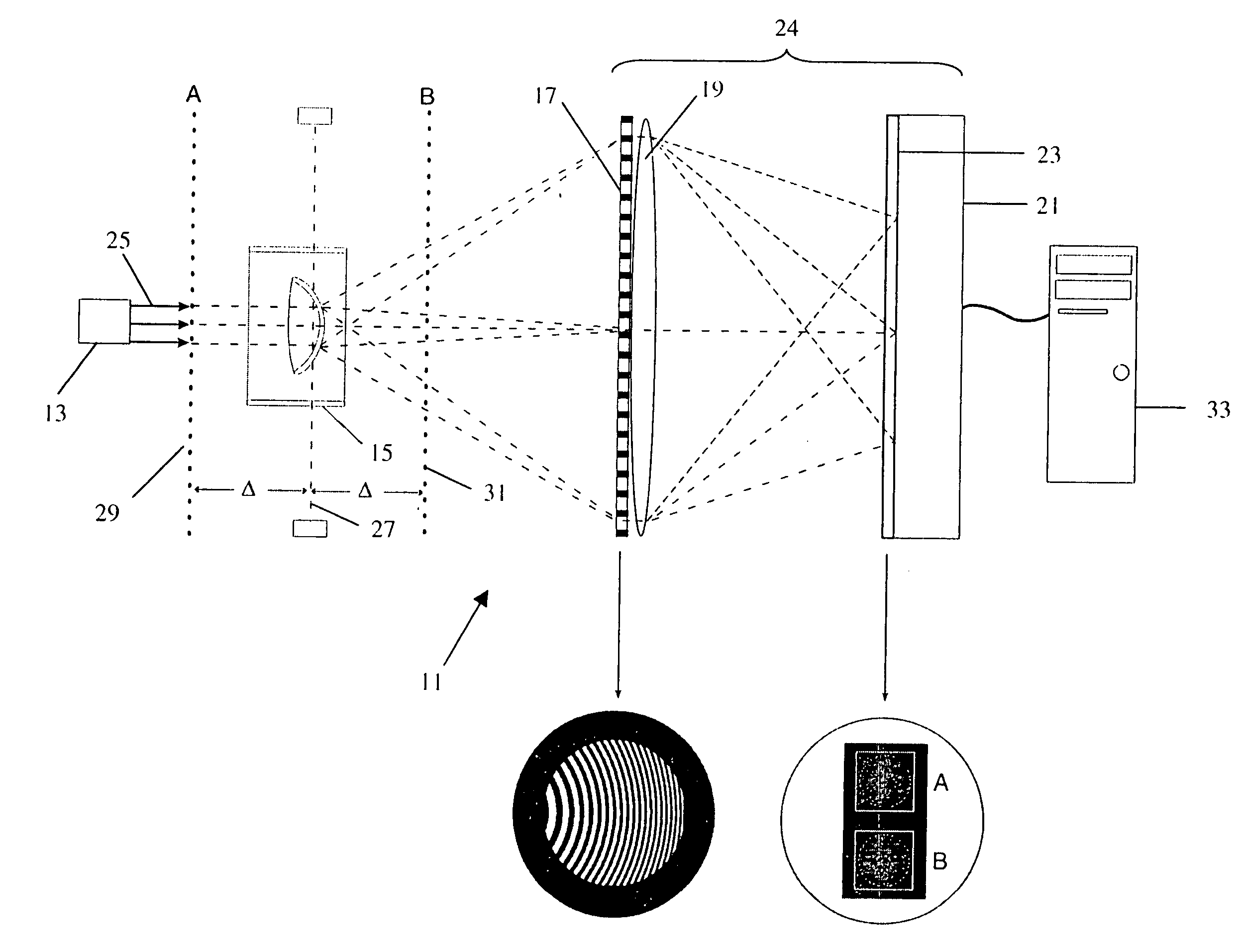
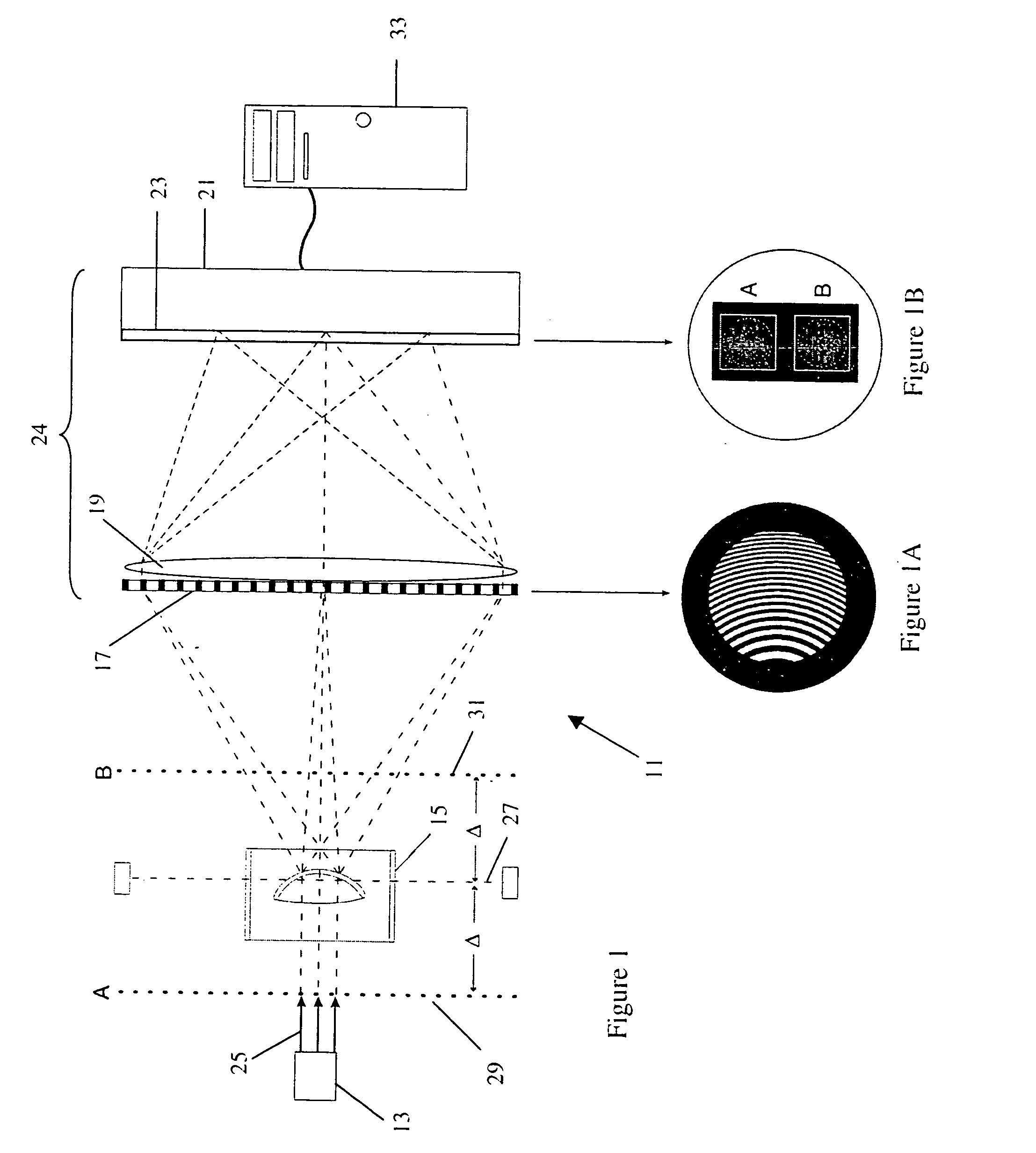
Wavefront characterization of corneas
Apparatus for determining if a cornea (whether in vitro or in vivo) has been modified (either surgically or otherwise). The method includes the steps of: passing a beam of collimated light a (either coherent or incoherent) through the cornea to produce a distorted wavefront; determining the characteristics of the distorted wavefront; and analyzing the distorted wavefront for characteristics that identify the presence of a modification. The analysis of the distorted wavefront can be for the presence of higher order aberrations, or Gausian characteristics which are indicative of modifications. More particularly, the method includes the steps of providing an optical system that has a pupil plane and an image plane at a detector; positioning the cornea in the pupil plane; passing a collimated beam of light through the cornea to produce at least two images in the image plane; determining the characteristics of the distorted wavefront; and analyzing the distorted wavefront for characteristics that identify the presence of a modification. The apparatus includes: a source of collimated light: an optical system including a distorted grating and an imaging lens (which have a pupil plane, first and second virtual planes, and an image plane); structure for positioning the cornea in the pupil plane; and a computer. The structure for positioning the cornea (which is immersed in a suitable storage fluid) includes first and second plano / plano lenses. The first and second plano lens, which are substantially and perpendicular to and centered with respect to the axis, have less than λ / 10 total distortions.
Owner:KESTREL CORP
Infrared Sensor and Method for Electrical Monitoring
ActiveUS20120170612A1Low costAvoid vortexThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansFresnel lensThermopile
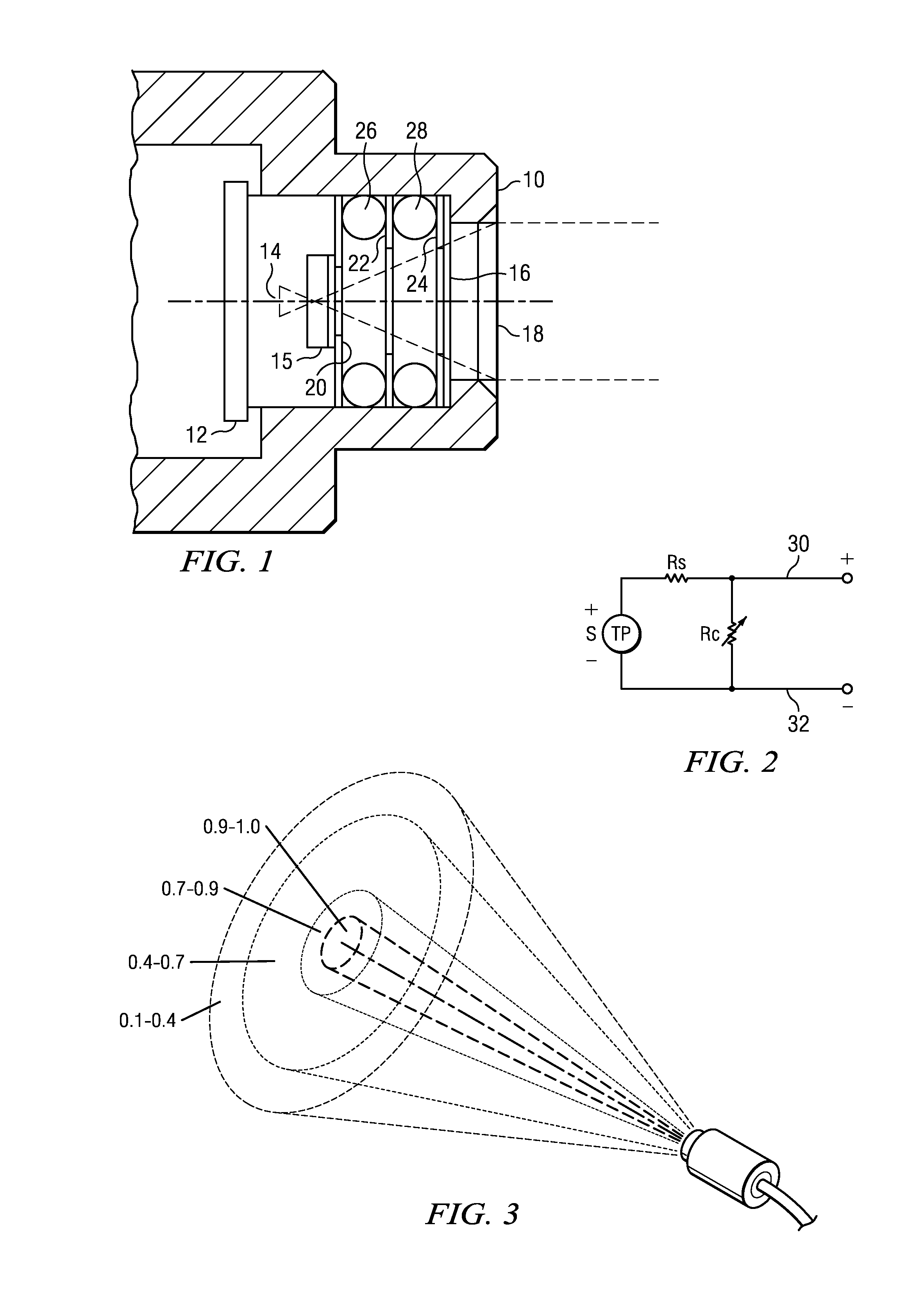
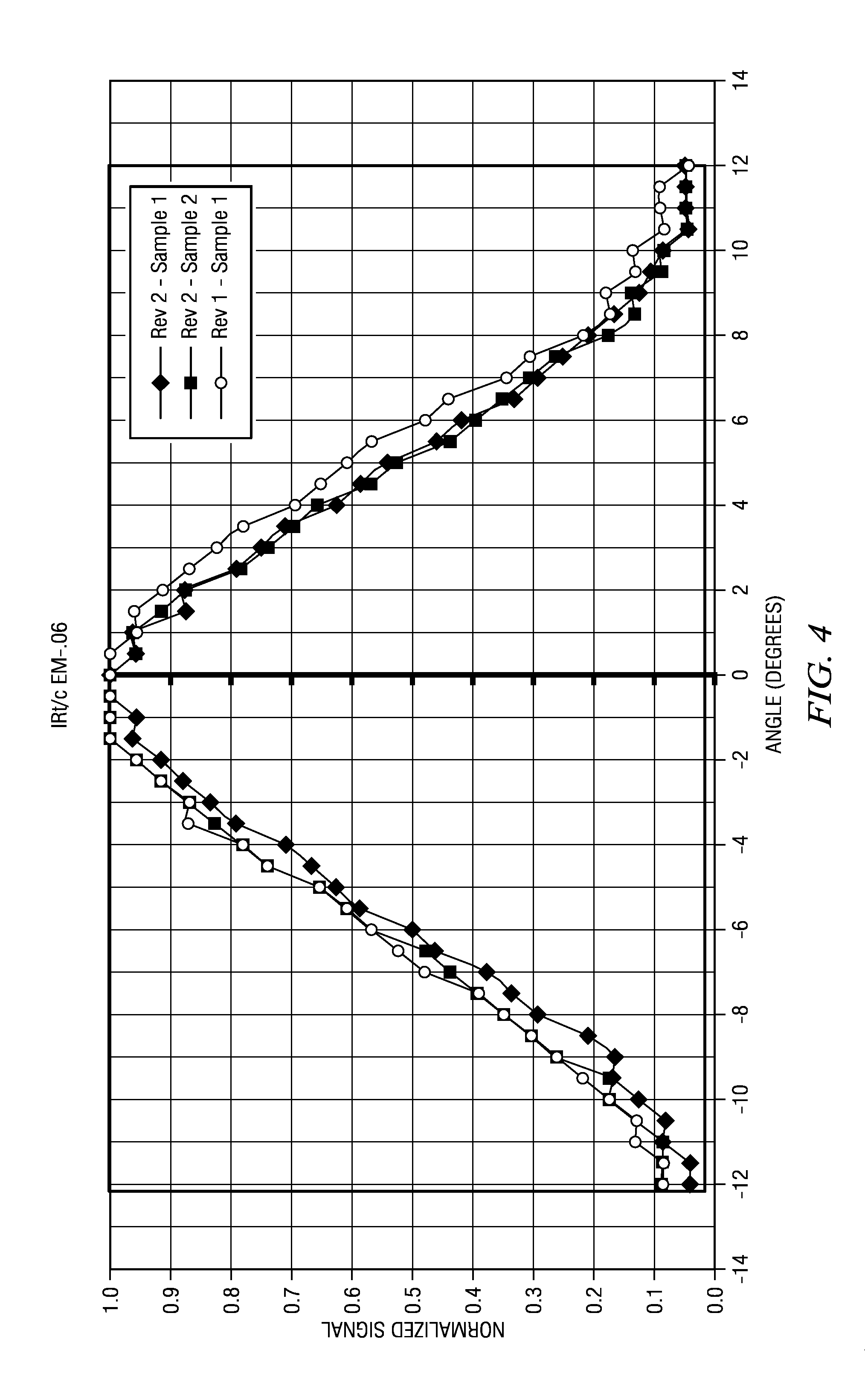
An inexpensive thermopile temperature detector is particularly adapted to monitoring of electrical equipment, such as a power bus bar, within an enclosed area such as a cabinet. The detector may have a plastic housing, a thermopile sensor and a plastic Fresnel lens. Each sensor also includes a calibrated element such that, but for calibration, the same sensor may be used for various applications for different target sizes and distance or, more generally, with respect to effective target percentage of field of view.
Owner:EXERGEN CORPORATION
Lighting apparatus, display apparatus, projection display apparatus, lighting method, image display method and image projection method
InactiveUS20090135376A1Light utilization efficiencySimple optical systemProjectorsColor photographyLight equipmentEffect light
Red light emitted from a red laser light source, green light emitted from a green laser light source and blue light emitted from a blue laser light source are incident on a first disc body of a color wheel, are transmitted or reflected in conformity with the colors of the lights in wavelength selecting regions of a second disc body every time the color wheel performs a predetermined rotation. AS being reflected by the first disc body, the lights are divided into different positions to be emitted from the color wheel and irradiated to irradiation regions successively switched by an upward or downward reciprocal movement of a mirror group.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wavefront characterization of corneas
Apparatus for determining if a cornea (whether in vitro or in vivo) has been modified (either surgically or otherwise). The method includes the steps of: passing a beam of collimated light a (either coherent or incoherent) through the cornea to produce a distorted wavefront; determining the characteristics of the distorted wavefront; and analyzing the distorted wavefront for characteristics that identify the presence of a modification. The analysis of the distorted wavefront can be for the presence of higher order aberrations, or Gausian characteristics which are indicative of modifications. More particularly, the method includes the steps of providing an optical system that has a pupil plane and an image plane at a detector; positioning the cornea in the pupil plane; passing a collimated beam of light through the cornea to produce at least two images in the image plane; determining the characteristics of the distorted wavefront; and analyzing the distorted wavefront for characteristics that identify the presence of a modification. The apparatus includes: a source of collimated light: an optical system including a distorted grating and an imaging lens (which have a pupil plane, first and second virtual planes, and an image plane); structure for positioning the cornea in the pupil plane; and a computer. The structure for positioning the cornea (which is immersed in a suitable storage fluid) includes first and second plano / plano lenses. The first and second plano lens, which are substantially and perpendicular to and centered with respect to the axis, have less than λ / 10 total distortions.
Owner:KESTREL CORP
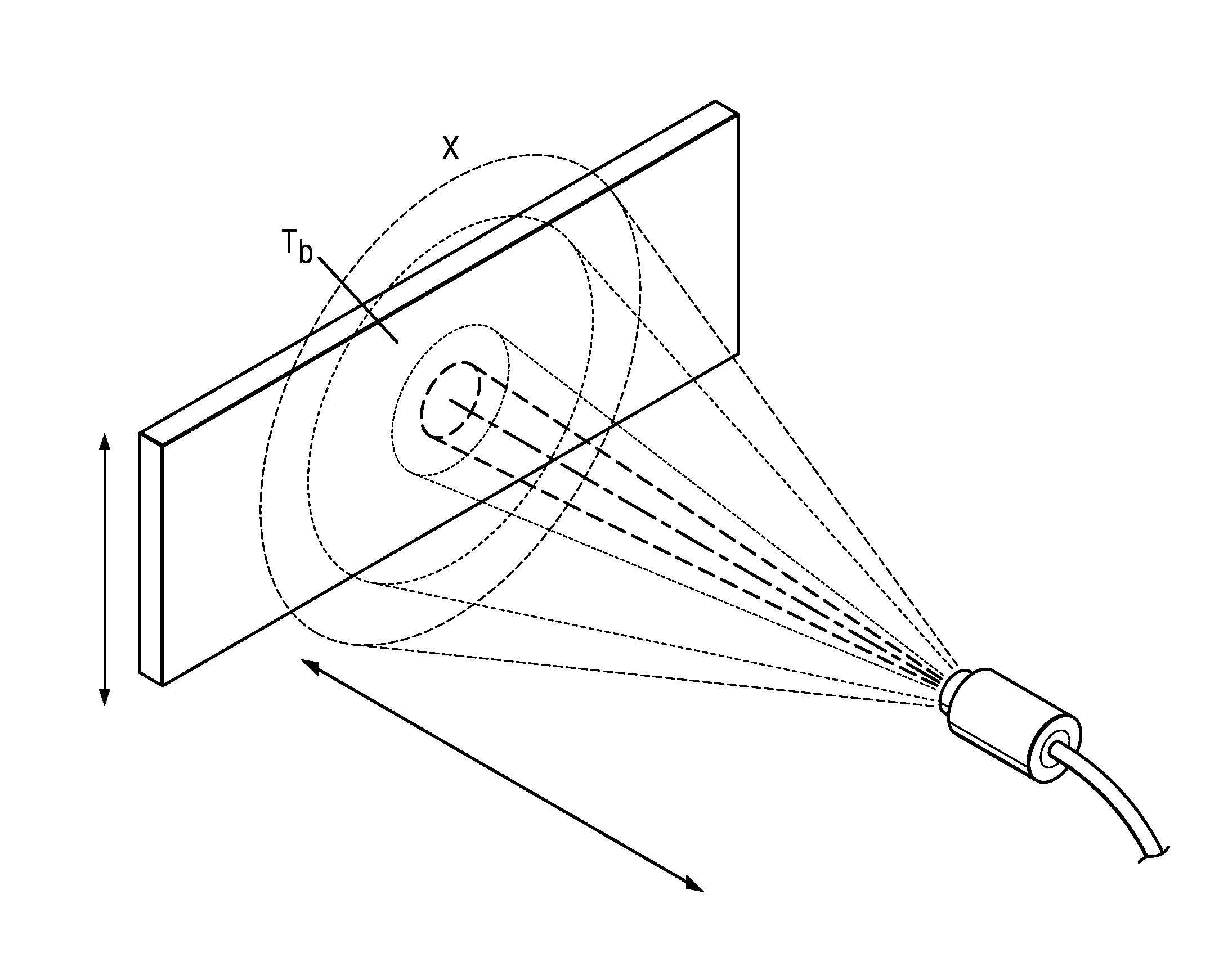
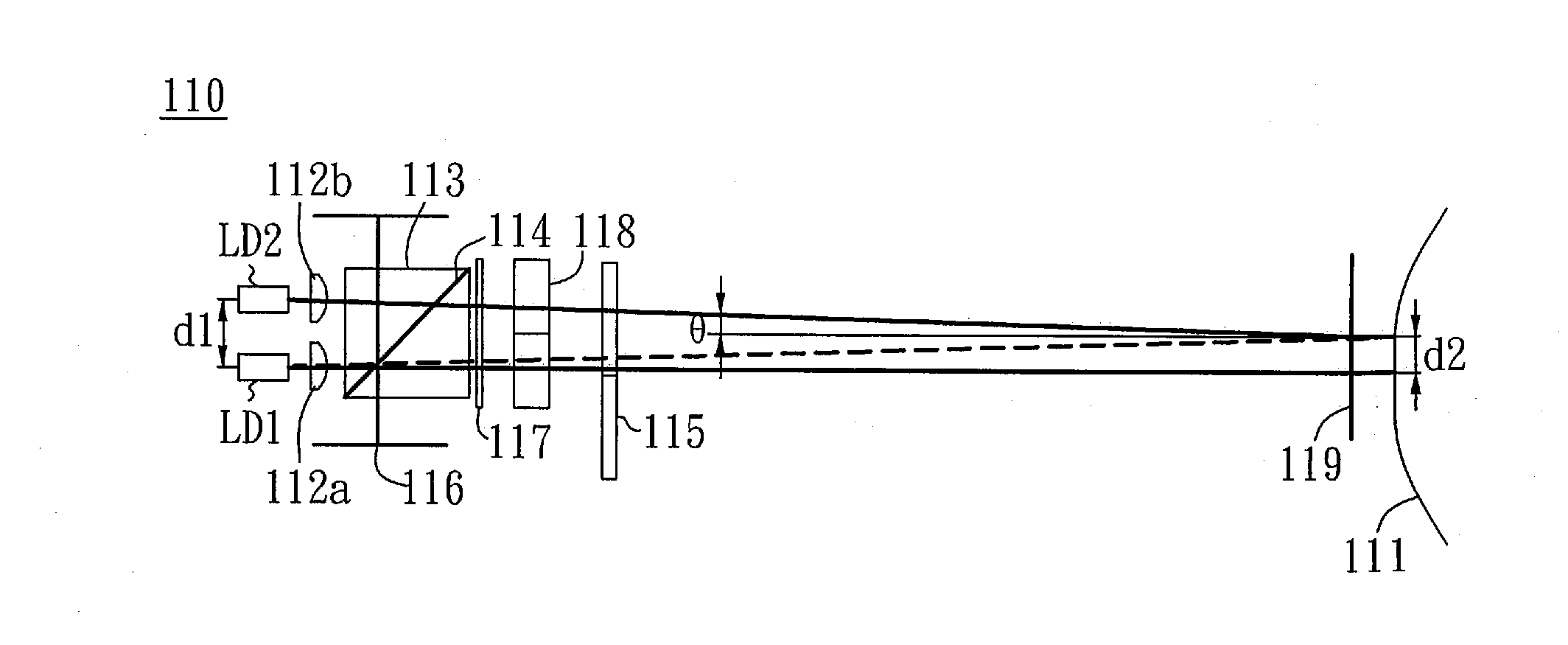
Apparatus and method for curvature and thin film stress measurement
ActiveUS20160102968A1Increase measurement rangeProduction cost be reduceUsing optical meansCondensersStress measurementLight source
Apparatus and method for curvature and thin film stress measurement are disclosed. The apparatus comprises two light sources and a detector. Two light beams from the two light sources with an angle are not parallel. The two light beams are collimated and projected onto a specimen with a pitch. The detector receives the light beams reflected from the specimen. The curvature of the specimen is calculated via a distance between spots of the light beams on the detector or a size variation of one of the spots.
Owner:HERMES EPITEK
Color display device using separate diffracted light and illumination light
InactiveUS20060119942A1Simple processSimple optical systemTelevision system detailsProjectorsDiffraction orderDisplay device
A display device is disclosed. The display device includes a condenser unit, an illumination lens system, a plurality of diffractive light modulators, a mirror for separating illumination light from diffracted light, a polarized beam separator, a filter unit and a projection unit. The condenser unit converges polarized light, and outputs the converged polarized light. The illumination lens system converts the polarized light into linear parallel light. The diffractive light modulators produce diffracted light beams. The mirror passes the polarized light therethrough using slits, and reflects the diffracted light beams toward the filter system. The polarized beam separator separates the polarized light on a wavelength basis and then allows the separated beams to be incident on the diffractive light modulators, and converges the diffracted light beams and then outputs the converged light to the mirror. The filter system selects the diffracted light beams having desired diffraction orders from among diffracted light beams using a dichroic filter. The projection system focuses the diffracted light beams, and projects the focused light beams onto a screen.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Fluorescence sensor and method for producing thin metal film with apertures to be used by the fluorescence sensor
InactiveUS20090101836A1Low costHigh sensitivity detectionPhotometryLaminationThin metalExcitation beam
An excitation light beam is emitted from a light source. The excitation light beam propagates through a substrate and enters an interface between the substrate and a thin metal film having fine apertures with diameters less than or equal to the wavelength of the excitation light beam, provided on the surface of the substrate opposite that on which the excitation light beam is incident. Near field light is generated at the fine apertures. Fluorescent labels, included in a sample which is supplied to contact the thin metal film, are excited by the near field light and / or surface plasmon on the thin metal film induced by the near field light. The fluorescence emitted from the fluorescent labels is detected by a photodetector.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
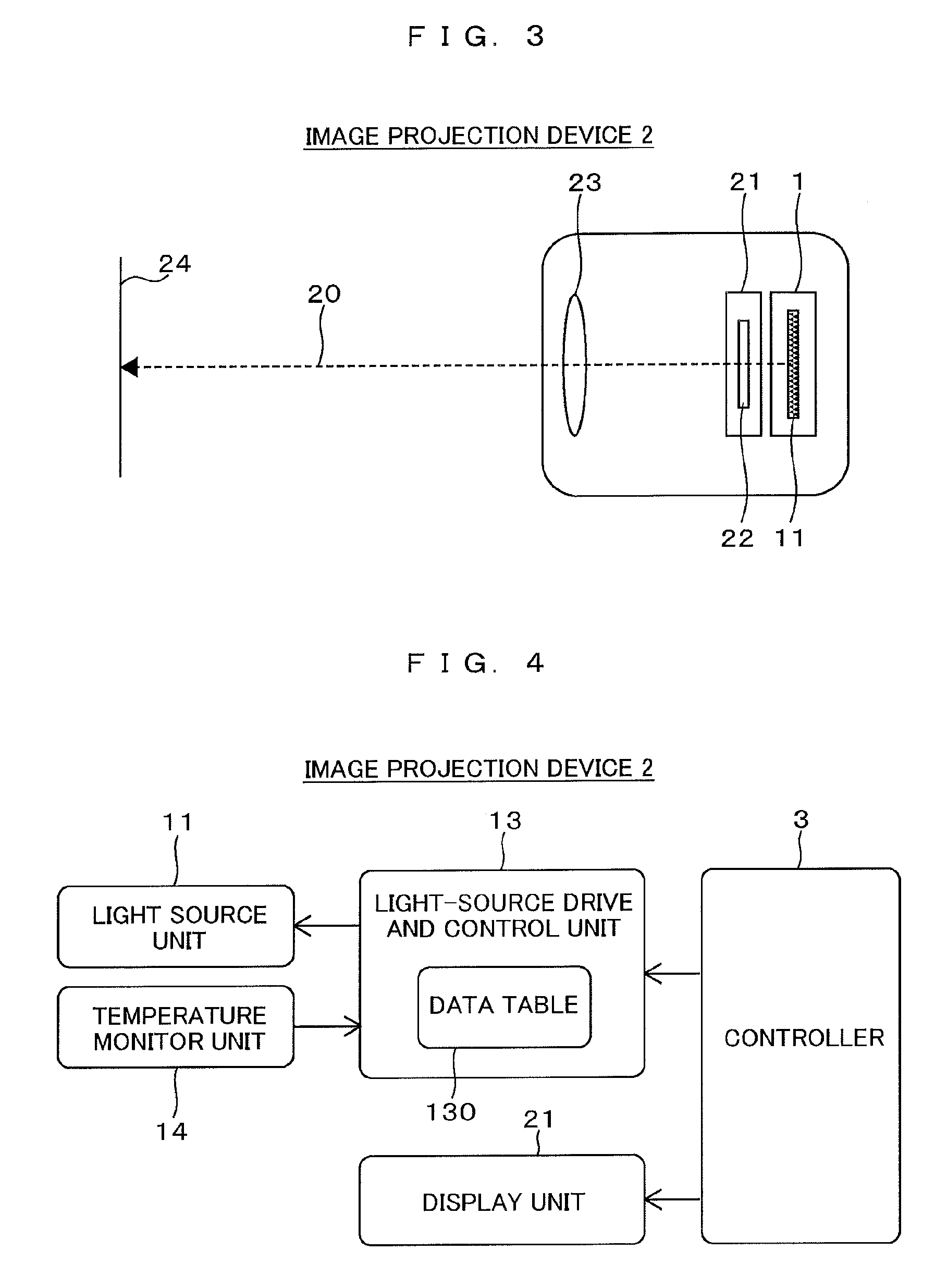
Light source module and image projection device
InactiveUS20150309400A1Small sizeReduce weightLighting support devicesProjectorsP–n junctionNanostructure
A light source module and an image projection device which can have high resolution and high optical efficiency are provided with a simple optical system. A light source module includes a light source unit formed by a plurality of stacked light emission surfaces which emit lights of at least red, blue, and green wavelength bands, and a light-source drive and control unit which supplies a driving current to the respective light emission surfaces of the light source unit. Each of the light emission surfaces of the light source unit has a nanostructure smaller than a wavelength of visible light near a p-n junction provided in a semiconductor having a larger band gap than the visible light, and emits a light of a corresponding one of the wavelength bands via a phonon level.
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE
See-Through Near-to-Eye Viewing Optical System
InactiveUS20170075120A1Reduce weightEffective filteringEarpiece/earphone mechanical/electrical switchesImage data processingEyepieceBeam splitter
A see-through near-to-eye viewing optical system, which can be used in a head-mounted augmented reality display system, is provided. The see-through near-to-eye viewing optical system of the present invention comprises an LED illumination system for generating a light and a pre-polarizer for concentrating said light onto a PBS. Then an LCOS panel receives and reflects said light towards a post-polarizer after generating an image. The light travels from the post-polarizer and passes through an eyepiece for magnifying the image, and continues towards a 50 / 50 beam splitter. Afterwards the beam splitter transmits said light and another light from the outside field of view to user's eyes simultaneously and thus, the user can see what is shown on the glass screen while still being able to see through it.
Owner:SYNDIANT
Optical pickup device and optical disc apparatus
InactiveUS20120213046A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce component countOptical detectorsRecord information storageOptical pickupGrating
In an optical pickup device for a simple optical system, a light beam emitted from a laser diode is split into first and second light beams by a polarized beam splitter, an optical disc is irradiated with the first light beam to obtain signal light, and the second beam is reflected by a reflection element to obtain reference light. Light beams of the signal light and the reference light are synthesized into one light beam, the synthesized light beam is separated into four light beams by a phase difference forming unit including a grating, a divided wave plate and a polarization grating, and different phase differences are afforded to the signal light and the reference light in each light beam. The four light beams are detected by one detector to generate the reproduction signal.
Owner:HITACHI MEDIA ELECTORONICS CO LTD
Compatible optical pickup
InactiveUS7586826B2Simple optical systemRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupHigh density
An optical pickup which is compatible with at least one high density recording medium that uses a blue-violet beam and at least one lower density recording medium, the optical pickup including: an optical unit to selectively emit one of a plurality of beams with different wavelengths onto one of the at least one high density recording medium and the at least one lower density recording medium, and to receive the respective beam reflected from the respective recording medium; and a holographic objective lens to focus the respective beams emitted by the optical unit on a recording surface of the respective recording medium, the holographic objective lens including a first holographic lens region and a second holographic lens region located inside the first holographic lens region, wherein holographic patterns of the first and second holographic lens regions respectively produce a first effective numerical aperture (NA) for the at least one high density recording medium and at least one additional effective NA suitable for the at least one lower density recording medium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pickup lens with phase compensator and optical pickup apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20060083122A1Prevent deviationLow wavefront aberrationRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupLength wave
A pickup lens with a phase compensator is composed of a condenser lens and a phase compensator. At least one surface of the condenser lens has a step-like annular zone structure to compensate wavefront aberration generated when recording and reproducing data on an information recording medium having a substrate thickness of t1 with a laser beam having a wavelength λ1 and wavefront aberration generated when recording and reproducing data on an information recording medium having a substrate thickness of t2 with a laser beam having a wavelength λ2. The phase compensator compensates wavefront aberration generated when recording and reproducing data on an information recording medium having a substrate thickness of t3 with a laser beam having a wavelength λ3.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Infrared sensor and method for electrical monitoring
ActiveUS9170158B2Avoid vortexImportant costPhotometry using reference valueThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsFresnel lensThermopile
An inexpensive thermopile temperature detector is particularly adapted to monitoring of electrical equipment, such as a power bus bar, within an enclosed area such as a cabinet. The detector may have a plastic housing, a thermopile sensor and a plastic Fresnel lens. Each sensor also includes a calibrated element such that, but for calibration, the same sensor may be used for various applications for different target sizes and distance or, more generally, with respect to effective target percentage of field of view.
Owner:EXERGEN CORPORATION
Wavefront characterization of corneas
Apparatus for determining if a cornea (whether in vitro or in vivo) has been modified (either surgically or otherwise). The method includes the steps of: passing a beam of collimated light a (either coherent or incoherent) through the cornea to produce a distorted wavefront; determining the characteristics of the distorted wavefront; and analyzing the distorted wavefront for characteristics that identify the presence of a modification. The analysis of the distorted wavefront can be for the presence of higher order aberrations, or Gausian characteristics which are indicative of modifications. More particularly, the method includes the steps of providing an optical system that has a pupil plane and an image plane at a detector; positioning the cornea in the pupil plane; passing a collimated beam of light through the cornea to produce at least two images in the image plane; determining the characteristics of the distorted wavefront; and analyzing the distorted wavefront for characteristics that identify the presence of a modification. The apparatus includes: a source of collimated light: an optical system including a distorted grating and an imaging lens (which have a pupil plane, first and second virtual planes, and an image plane); structure for positioning the cornea in the pupil plane; and a computer. The structure for positioning the cornea (which is immersed in a suitable storage fluid) includes first and second plano / plano lenses. The first and second plano lens, which are substantially and perpendicular to and centered with respect to the axis, have less than λ / 10 total distortions.
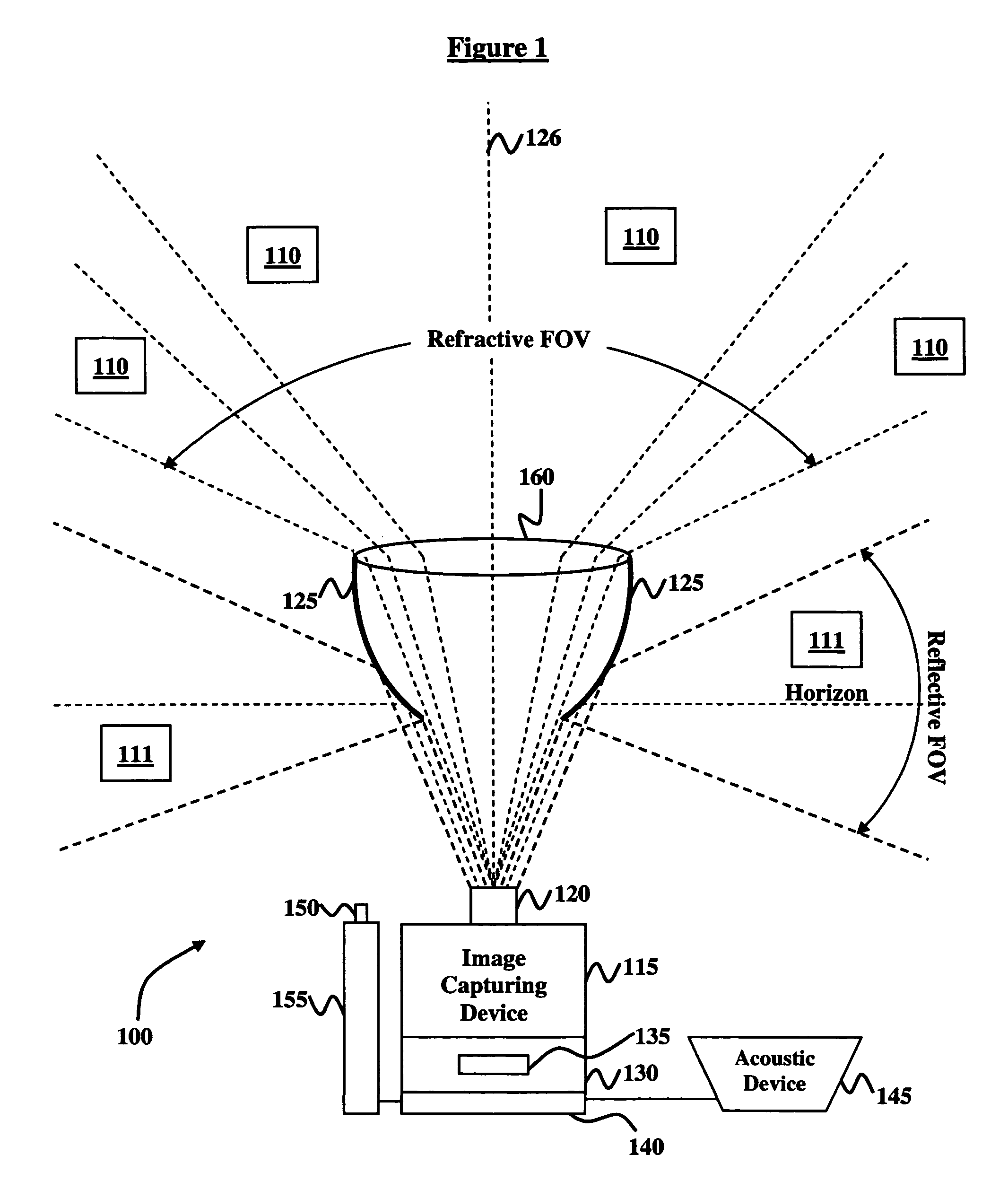
Owner:OTTEN LEONARD JOHN III +3
Display, instrument panel, optical system and optical instrument
InactiveUS9244286B2Avoid emissionsReduce manufacturing costSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsDisplay deviceOptical instrument
A multiple depth display provided for displaying images at different depths comprises a single display device (61), for displaying all of the images. An optical system (62, 63, 64) is disposed in front of the display device (61). The optical system comprises first and second spaced-apart partial reflectors (62, 63) and polarization optics (64) for providing first and second light paths for first and second images or sequences of images displayed by the device (61). The first light path (65) comprises partial transmission through the first reflector (62), partial reflection from the second reflector (63), partial reflection from the first reflector (62), and partial transmission through the second reflector (65) towards a viewing region.
Owner:SHARP KK
Color display device using separate diffracted light and illumination light
A display device includes a condenser unit, an illumination lens system, a plurality of diffractive light modulators, a mirror for separating illumination light from diffracted light, a polarized beam separator, a filter unit and a projection unit. The condenser unit converges polarized light, and outputs the converged polarized light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for curvature and thin film stress measurement
ActiveUS9551569B2Expand the measurement rangeCurvature of the chip can be measuredUsing optical meansCondensersLight beamLight source
Apparatus and method for curvature and thin film stress measurement are disclosed. The apparatus comprises two light sources and a detector. Two light beams from the two light sources with an angle are not parallel. The two light beams are collimated and projected onto a specimen with a pitch. The detector receives the light beams reflected from the specimen. The curvature of the specimen is calculated via a distance between spots of the light beams on the detector or a size variation of one of the spots.
Owner:HERMES EPITEK
Projection stereoscopic display
InactiveUS8451390B2Reduce power consumptionHigh color purityProjectorsNon-linear opticsParallaxOptical polarization
A projection stereoscopic display includes: a stereoscopic display optical system receiving linearly polarized light from the light source and displaying a first picture and a second picture both having binocular parallax by linearly polarized light with polarization directions orthogonal to each other, in which the stereoscopic display optical system includes: a reflective liquid crystal panel modulating and reflecting linearly polarized light from the light source in response to a picture signal, a first polarizing device splitting the first picture from reflected light from the reflective liquid crystal panel, a retardation device converting the polarization direction of the first picture into a direction orthogonal thereto, and a second polarizing device splitting the second picture from reflected light from the reflective liquid crystal panel, and superimposing the second picture on the first picture of which the polarization direction is converted by the retardation device.
Owner:SONY CORP
Color display device using separate diffracted light and illumination light
A display device is disclosed. The display device includes a condenser unit, an illumination lens system, a plurality of diffractive light modulators, a mirror for separating illumination light from diffracted light, a polarized beam separator, a filter unit and a projection unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com