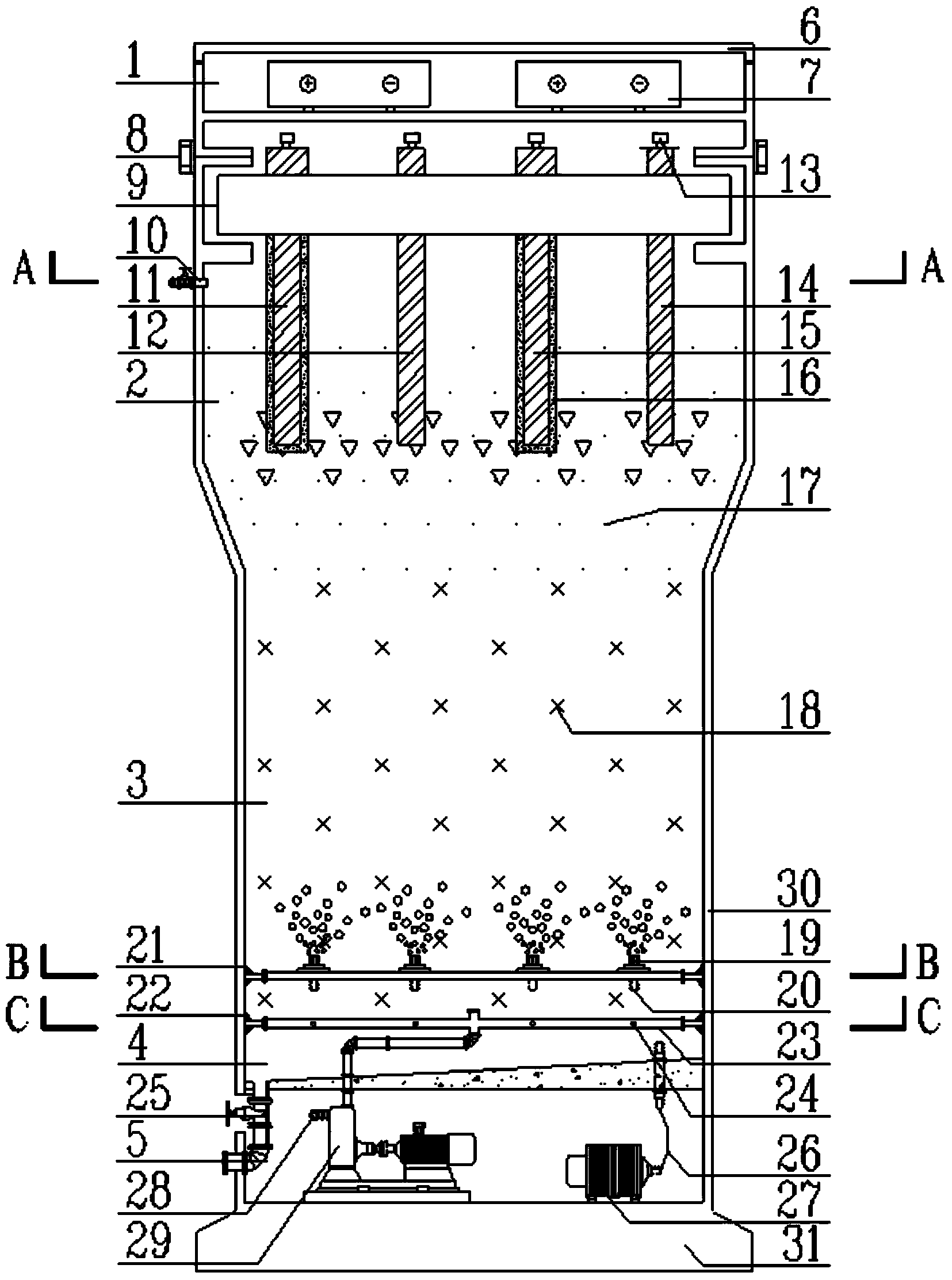
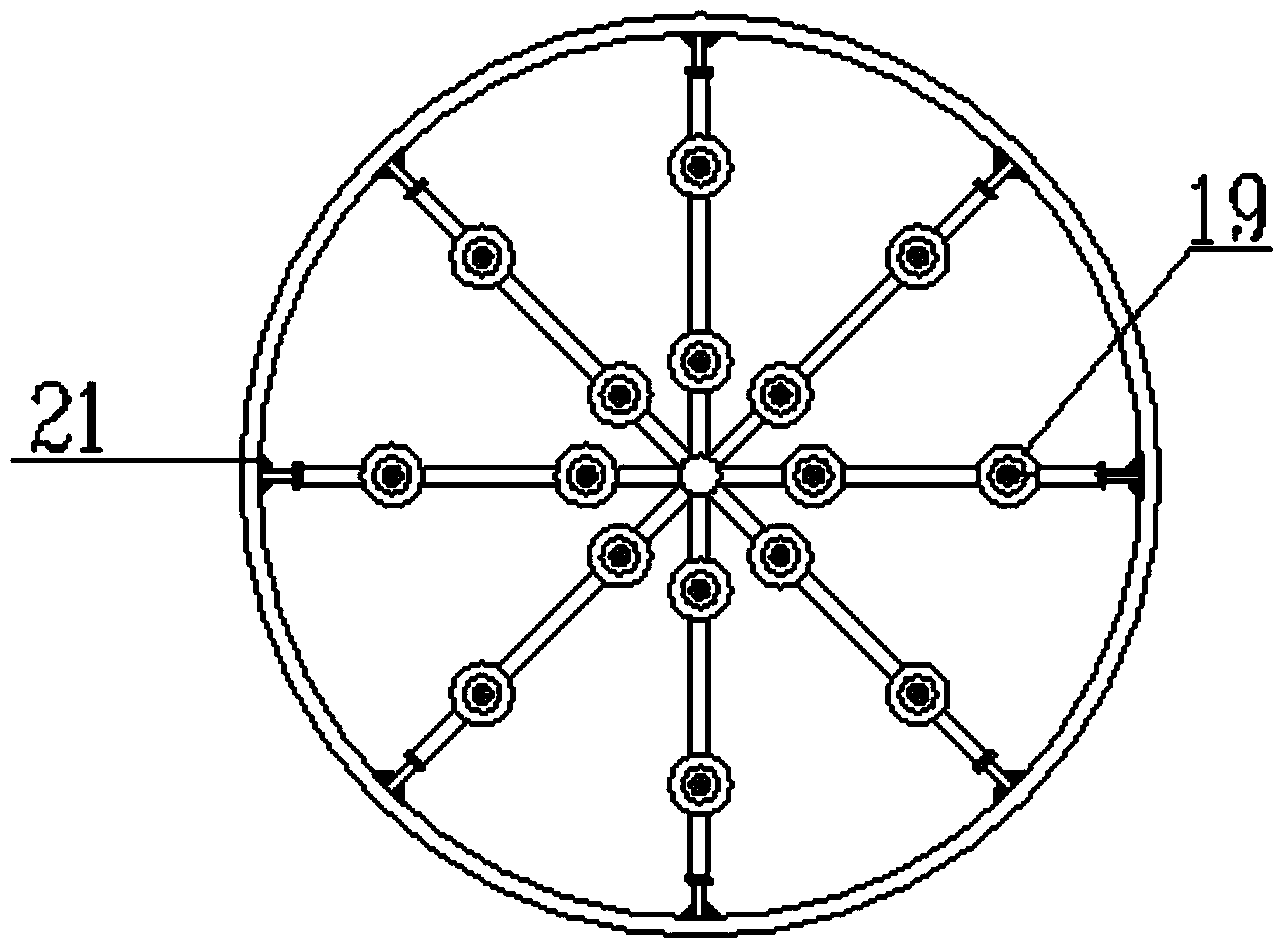
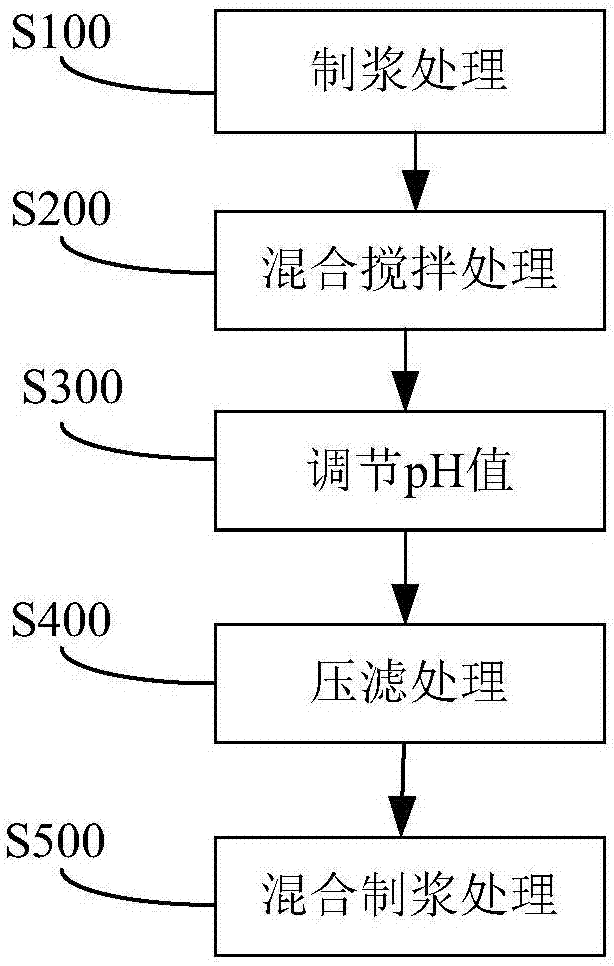
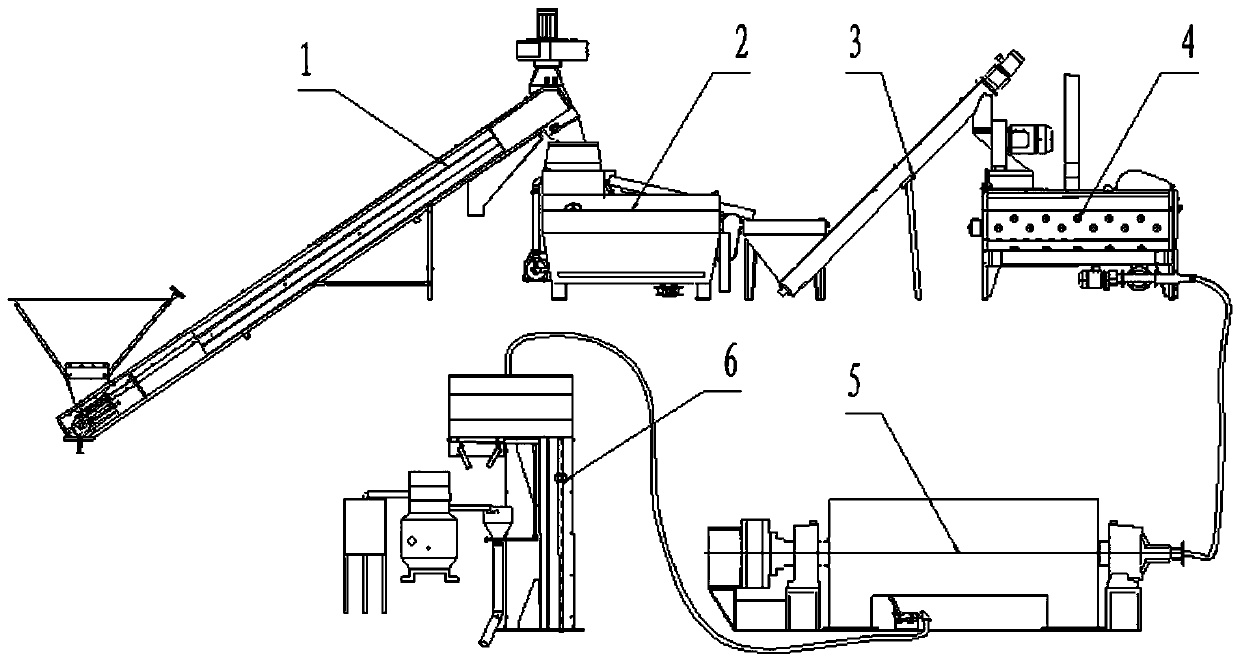
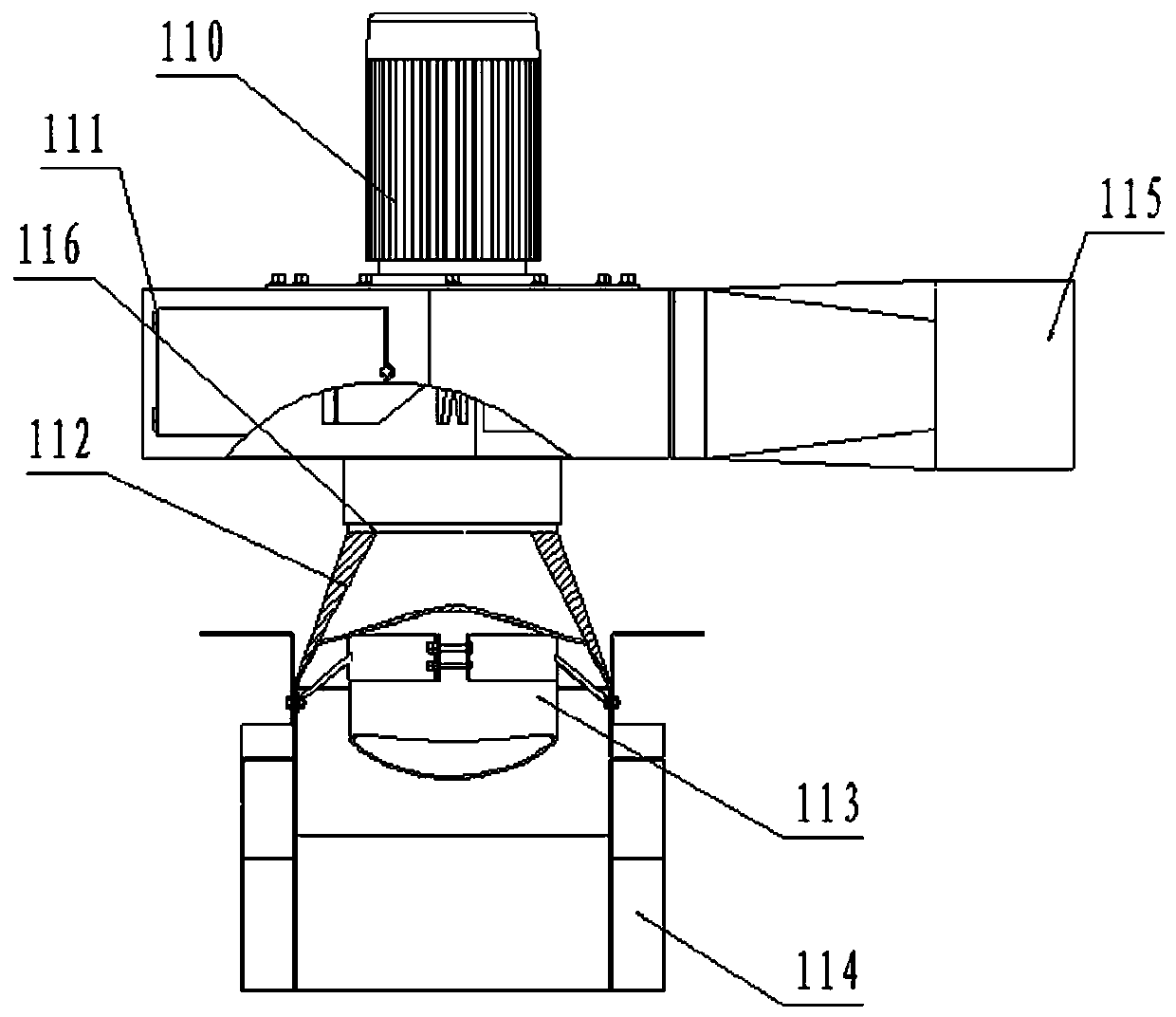
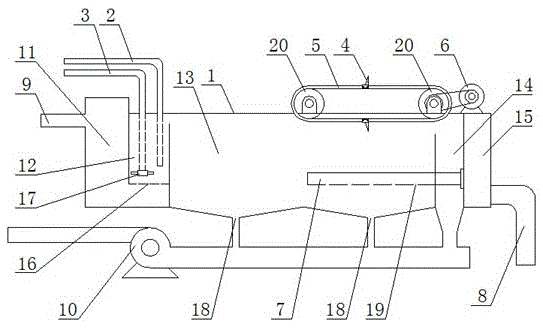
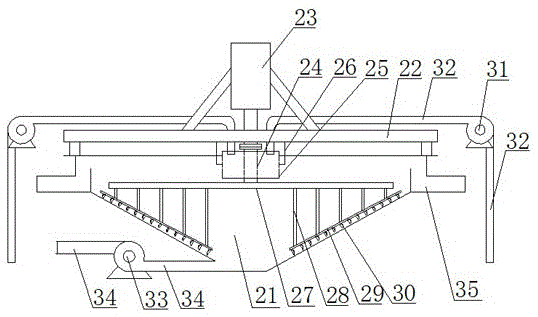
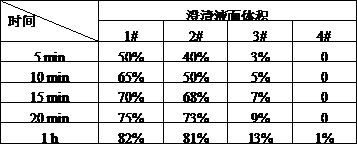
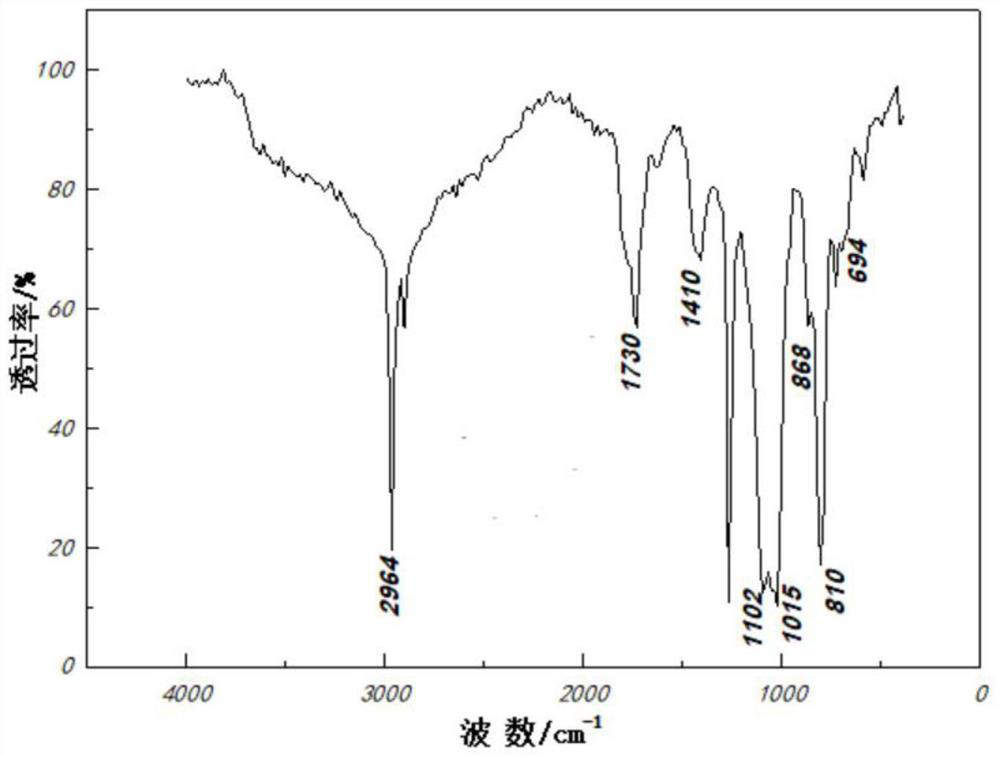
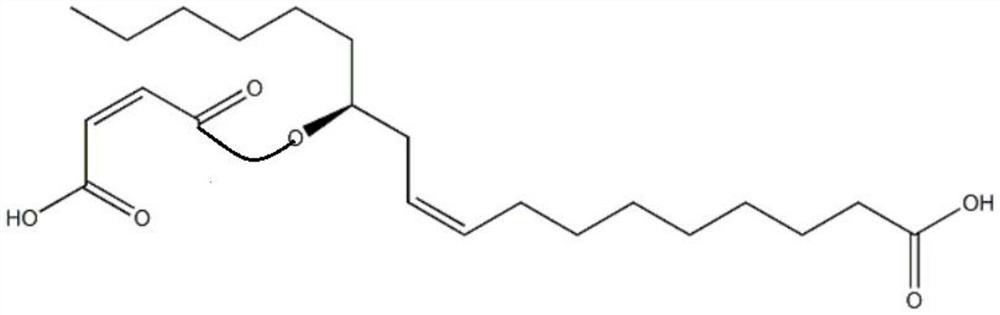
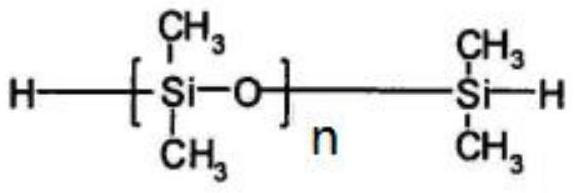
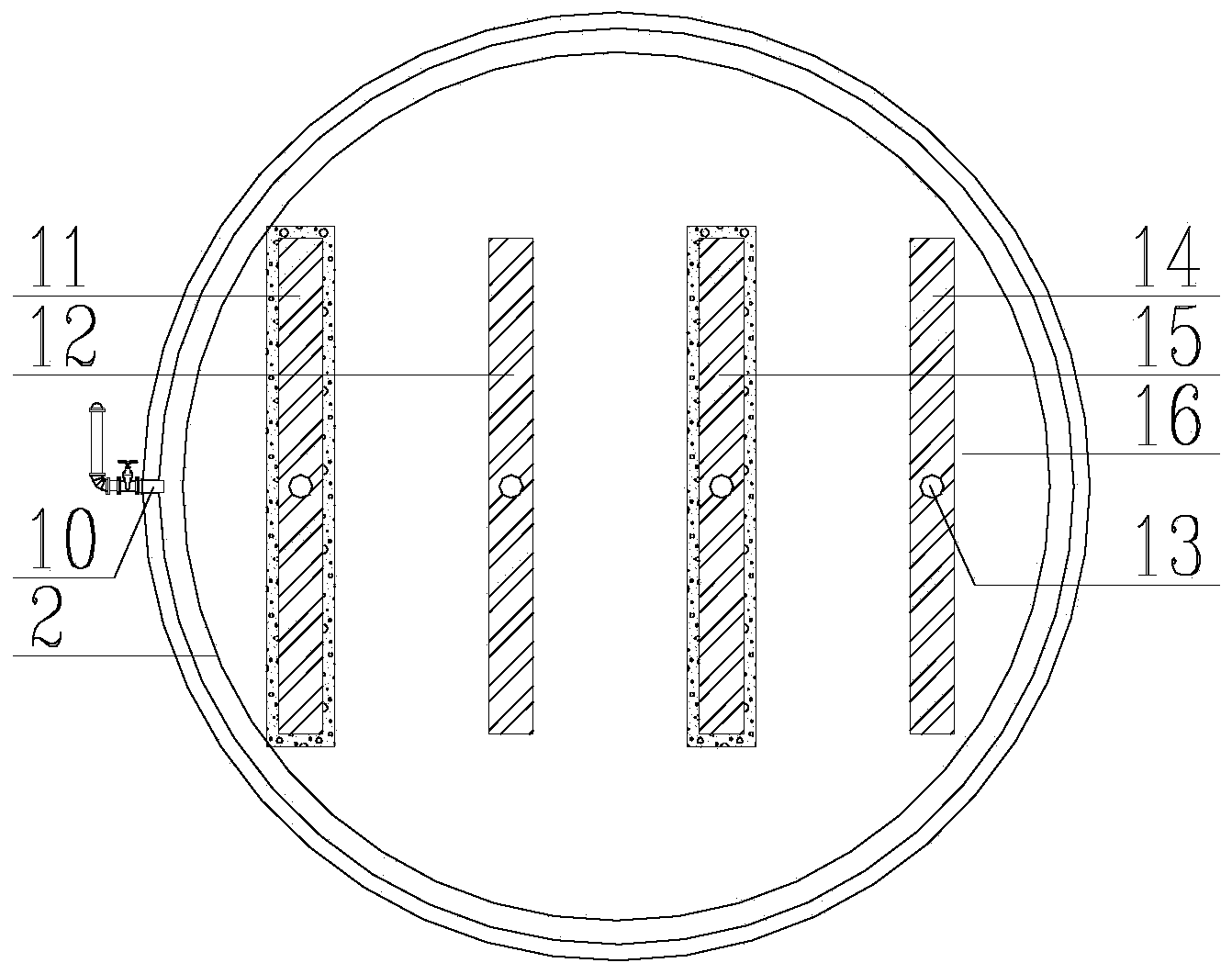Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53results about How to "Thorough solid-liquid separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
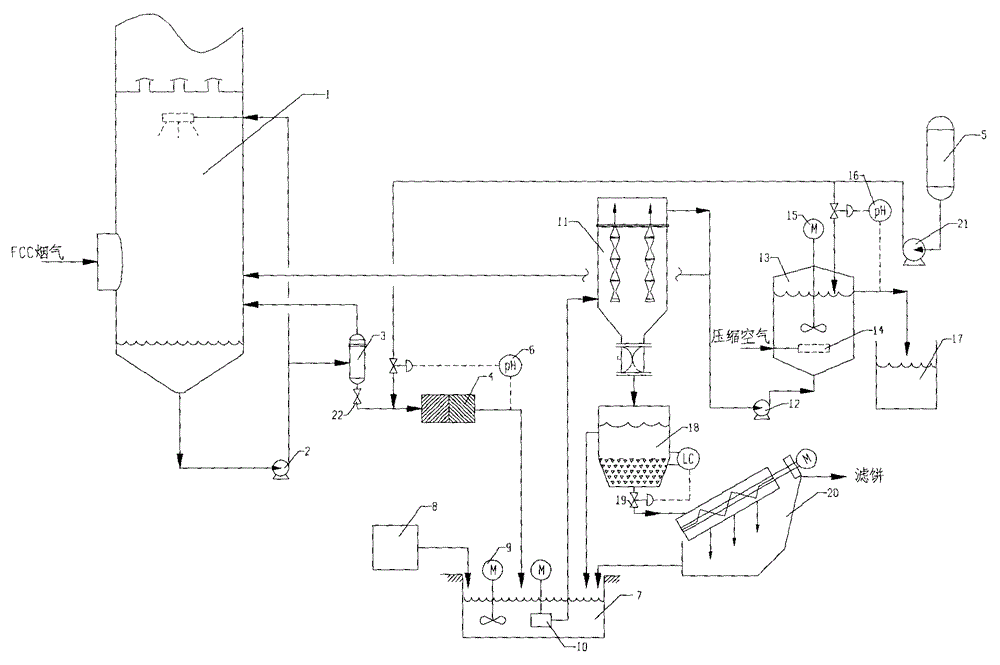
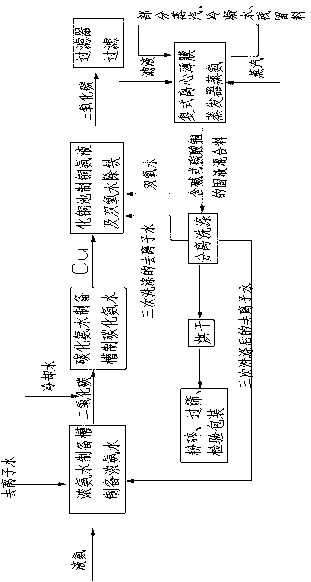
Process for treating waste liquid from catalytic cracking flue gas desulfurization
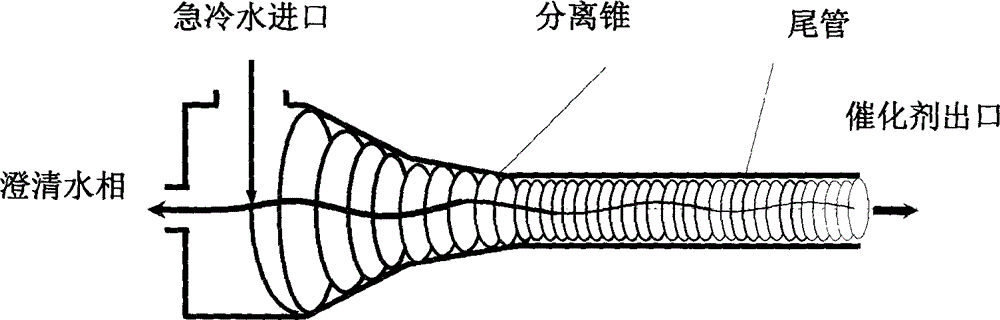
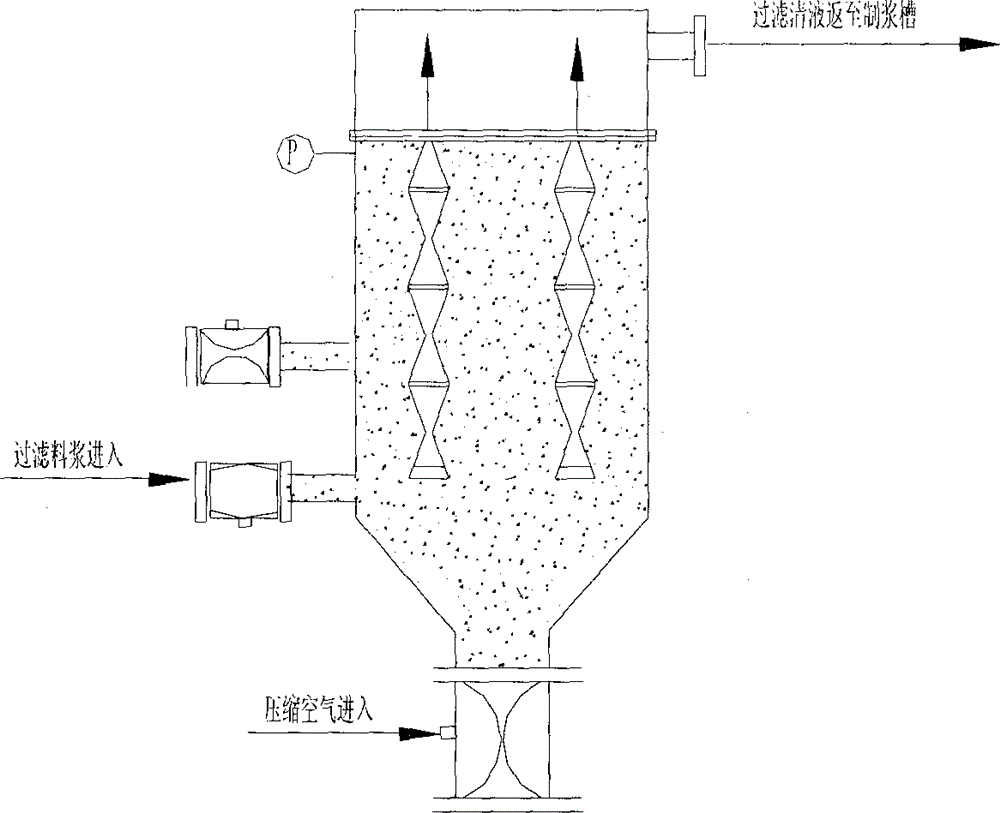
InactiveCN104418447AReduce dust concentrationReduce wearWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSludge treatmentLiquid wasteSlurry
The invention provides a process for treating waste liquids from catalytic cracking flue gas desulfurization. The process comprises the following steps: enabling a part of waste liquids from a quenching washing tower to enter a hydraulic cyclone separator so as to be subjected to solid-liquid separation, returning the thin liquids to the quenching washing tower so as to be recycled, enabling the thick liquids to enter a neutralization reactor so as to be subjected to neutralization reaction, enabling the neutralized waste liquids to enter a slurry pond so as to be mixed with a flocculating agent uniformly, and enabling the mixture to enter an expansion-drum type filter so as to be subjected to solid-liquid separation with a thick slurry and a supernatant being obtained; returning part of the supernatant to the quenching washing tower so as to be recycled, discharging the remaining supernatant into an oxidation tank, removing the pseudo-COD containing sulfite roots and bisulfite roots by oxidizing, and directly discharging the qualified sewage; enabling the thick slurry to enter a settling pond from the bottom of the expansion-drum type filter so as to be further settled, feeding the thick slurry subjected to settlement into a dewatering machine so as to be concentrated and dewatered, directly transporting the filter cakes obtained by dewatering the thick slurry, returning the filtrate from the dewatering of the thick slurry to the slurry pond, and mixing the filtrate with the waste liquids so as to be retreated. The process provided by the invention has the advantages of a stable and efficient treatment effect, strong shock resistance, low investment and small floor area occupation and convenience of operation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Household waste pretreatment device and pretreatment method adopting same
ActiveCN111659711AAchieve dehydrationAchieve liquefactionTransportation and packagingSolid waste disposalPretreatment methodHeat conducting
The invention discloses a household waste pretreatment device and a pretreatment method adopting same and belongs to the technical field of waste pretreatment. The household waste pretreatment devicecomprises a base, an outer cylinder arranged on the upper side of the base, a plurality of far-infrared heating pipes arranged on the inner wall of the outer cylinder in an annular array, an annular baffle plate arranged on the inner side of the outer cylinder and an inner cylinder arranged on the inner side of the annular baffle plate; the outer cylinder and the base are connected through a plurality of supporting legs for supporting; the upper part of the outer cylinder is open; the lower part of the outer cylinder is closed; a water outlet is formed in the lower part of the outer cylinder;a water discharging valve is mounted on the water outlet; the annular baffle plate is connected with the supporting legs through a plurality of groups of heat conducting connecting rods; the upper part and the lower part of the annular baffle plate are open; the upper part of the inner cylinder is open; the lower part of the inner cylinder is closed; a plurality of water draining holes are uniformly formed in the circumferential surface of the inner cylinder. The household waste pretreatment device skillfully integrates smashing, drying and solid-liquid separation and is skillful in concept.
Owner:JIANGSU HEHAI WATER SUPPLY & DRAINAGE EQUIP CO LTD
Combined electrolysis reactor and waste water treatment method thereof
ActiveCN103910414AReduce consumptionLow working voltageWater/sewage treatmentElectricityPower controller
The invention discloses a combined electrolysis reactor and a waste water treatment method thereof, belonging to the technical field of waste water treatment. The combined electrolysis reactor comprises a reactor and a reactor base, wherein a power supply chamber, a multidimensional electrode chamber, an iron-carbon micro-electrolysis chamber, a water distribution aeration chamber and an equipment chamber are sequentially inside the reactor from top to bottom; the power supply chamber is arranged in the top cover of the reactor and is provided with two power supply controllers; the multidimensional electrode chamber is arranged below the top cover of the reactor and consists of four electrode plates which are sequentially electrode plates a, b, d and c from left to right, wherein the electrode plates a and d are main anodes, the electrode plates b and c are main cathodes, and carbon packing fills in the gaps among the electrode plates; the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis chamber is positioned at the lower part of the multidimensional electrode chamber and is internally filled with iron-carbon packing; the water distribution aeration chamber is positioned at the lower part of the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis chamber and respectively carries out water distribution and aeration through a water distribution pump and an aeration pump in the equipment chamber. According to the combined electrolysis reactor, the treatment efficiency can be effectively improved, and the occurrence of passivation and hardening can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR IND HUAXING CONSTR +1
Method for preparing titanium dioxide slurry
InactiveCN106947295AReduce viscosityReduce or shield hydrogen bondsInorganic pigment treatmentHydrogenPulp treatment
The invention discloses a method for preparing a titanium dioxide slurry. The method comprises the following steps: pulping a titanium dioxide base material to obtain a titanium dioxide protoplasm; mixing and stirring the titanium dioxide protoplasm and an aluminum-containing compound to make the surfaces of titanium dioxide base material particles of the titanium dioxide protoplasm coated with an aluminum film in order to obtain aluminum coated titanium dioxide particles; adjusting the pH value of the slurry for coating the aluminum film to be less than 7 in order to obtain a pH value adjusted slurry; carrying out press filtration treatment on the pH value adjusted slurry to obtain a filter cake; and carrying out mixing and pulping treatment on the filter cake and a dispersant to obtain the titanium dioxide slurry. The method reduces or shields hydrogen bonds on the surfaces of the titanium dioxide base material particles through coating the surfaces of the titanium dioxide base material particles, so the titanium dioxide base material particles easily undergo solid-liquid separation to form the filter cake, sodium chloride is effectively removed, and the viscosity of the titanium dioxide slurry is reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN METALLURGICAL XINLI TITANIUM IND CO LTD
Method for continuously preparing high-purity low-chloride electroplating copper oxide
InactiveCN103011251AHigh purityQuick responseCopper oxides/halidesBASIC CUPRIC CARBONATEBasic copper carbonate
Owner:TAIXING SMELTING PLANT
Solid and liquid separator for materials
ActiveCN103657176AImprove stressThe moisture content of solids is reducedFiltration separationPush and pullLocking mechanism
The invention discloses a solid and liquid separator for materials. The solid and liquid separator comprises a frame, press plates, filter plates, a push-and-pull locking mechanism, a filter cloth mechanism, a filter cloth regeneration mechanism and a cleaning mechanism which are arranged on the frame, wherein the press plates and the filter plates are arranged on the frame in a sliding way alternately, and are matched to extrude a material, so that solid and liquid of the material can be separated; the push-and-pull locking mechanism is used for locking, pushing away all the press plates and filter plates, so that solid-liquid separation operation can be performed, or the material can be discharged; the filter cloth mechanism is used for separating solid and liquid of the material when the material is extruded; the filter cloth regeneration mechanism is used for washing to regenerate the filter cloth after the material is discharged; the cleaning mechanism is used for cleaning the material attached to the separator after solid and liquid of the material are separated. The solid and liquid separator has the characteristics of reasonable design, high structure strength, convenience in operation, complete solid and liquid separation, high separation efficiency, convenience in cleaning, long service life, log maintenance frequency, high reliability, strong practicality and the like, and is beneficial for greatly increasing production benefit of enterprises.
Owner:四川宝凯鑫诚环保科技有限公司
Garbage classification processing device
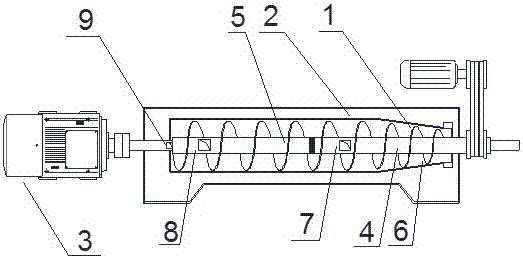
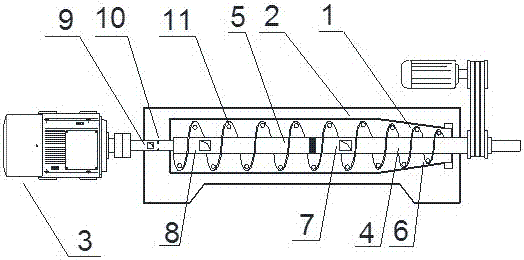
InactiveCN110682573AThorough solid-liquid separationEasy to follow upGrain treatmentsPressesHelical bladeElectric machinery
The invention discloses a garbage classification processing device. The garbage classification processing device includes a housing, a spring, a gear and a fixed dam. The interior of the housing is provided with a solid-liquid separation chamber. The bottom of the solid-liquid separation chamber is connected with a filtrate receiver. One side of the filtrate receiver communicates with an outlet pipe. A screw rod runs through the interior of the solid-liquid separation chamber. A first motor is fixed on one end of the screw rod. The first motor is located at the outside of the housing. The garbage classification processing device is provided with a crushing box. After water separation, the garbage is put into a crushing chamber by a material handling device and crushed by a crushing roller,and then enters the solid-liquid separation chamber. The screw rod drives the garbage to move to a discharge outlet through a screw blade in the solid-liquid separation chamber, meanwhile, squeezes the garbage to extrude the water in the garbage and separate the solid from the liquid. The solid and liquid separation is carried out on the crushed garbage so as to be more complete and provide convenience for the subsequent processing.
Owner:孙灯成
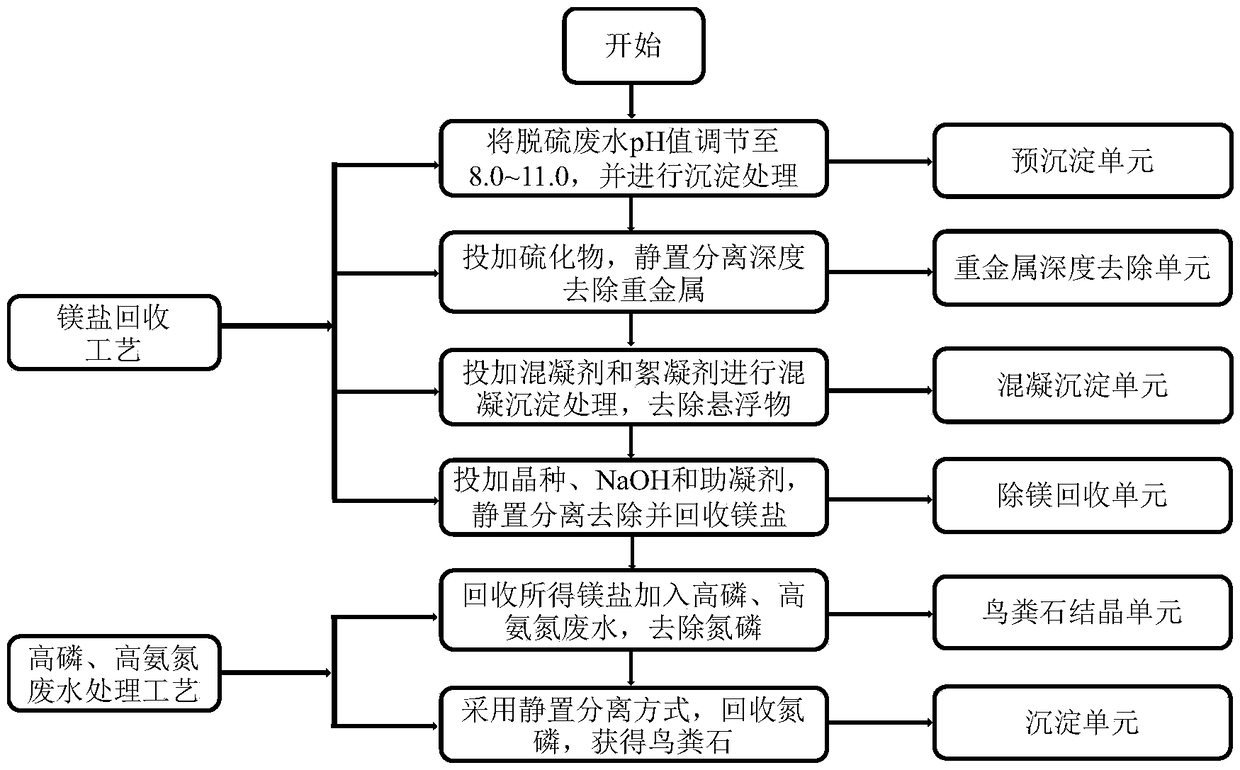
Method for removing nitrogen and phosphorus in wastewater by utilizing magnesium salt in desulfurization wastewater
InactiveCN109502720ASolve the problem of softening sludge disposalSolving Disposal ProblemsWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from gaseous effluentsSludgeMagnesium salt
The invention relates to a method for removing nitrogen and phosphorus in wastewater by utilizing a magnesium salt in desulfurization wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: (1) introducing desulfurization wastewater into a pre-precipitation unit, adding lime, and performing pre-precipitation treatment; (2) adding sulfide into a heavy metal advanced removal unit for advanced removalof heavy metals; (3) adding a coagulant and a coagulant aid into a coagulation precipitation unit for coagulation precipitation; (4) adding Mg(OH)2 seed crystal, NaOH and a coagulant aid are added into a magnesium removal recovery unit to remove Mg<2+> and recover a magnesium salt precipitate; and (5) adding the magnesium salt precipitate recovered in the step (4) into a struvite crystallization unit in which phosphorus / ammonia nitrogen wastewater is introduced, and carrying out reaction and precipitation to remove nitrogen and phosphorus from the wastewater. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention solves the difficult problem of treating desulfurization wastewater and softening sludge, realizes removal of phosphorus and nitrogen from wastewater while recovering nitrogen and phosphorus, and has practical significance of 'treating waste with waste' and recycling.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Economical rhizome type agricultural product cleaning machine
InactiveCN108856077ARealize automatic cleaningContinuous cleaning workCleaning using liquidsSludgeAgricultural engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural product cleaning equipment and discloses an economical rhizome type agricultural product cleaning machine. The economical rhizome type agricultural product cleaning machine comprises a tank rack; a U-shaped rack is fixedly mounted on the inner bottom of the tank rack; supporting shafts are fixedly mounted at the tops of one sides of thetank rack and the U-shaped rack; the top ends of the tank rack and the U-shaped rack are fixedly connected with the two ends of the bottom of the mounting rack correspondingly; and the exteriors of the supporting shafts are movably sleeved with a cleaning device. According to the economical rhizome type agricultural product cleaning machine, with the adoption of the cleaning device and a conveyingdevice, a double-shaft driving motor is adopted to drive a filter cylinder to rotate to allow rhizome type agricultural products in the filter cylinder to be in rolling state all the time, and the agricultural products in the filter cylinder are cleaned for removing sludge by cooperating with a high pressure water column or water spray sprayed out by a spray head, so that automatic cleaning is realized; the economical rhizome type agricultural product cleaning machine is labor-saving and quick; and the agricultural products in the filter cylinder are conveyed onto a conveying belt through threaded rods, and the cleaned agricultural products are conveyed outside equipment, so that continuous cleaning work is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN GATHER DUST TECH CO LTD
Medical operating room waste solid-liquid separation device
InactiveCN108786262AImprove work efficiencyPlay a shock absorbing roleFiltration circuitsOperating theatresEngineering
The invention discloses a medical operating room waste solid-liquid separation device, which includes a casing, wherein a first inclined plate is arranged inside the casing; the front side of the first inclined plate is fixedly connected with the front side of the inner wall of the casing; the back side of the first inclined plate is fixedly connected with the back side of the inner wall of the casing; the right side surface of the first inclined plate is fixedly connected with the right side surface of the inner wall of the casing; the left side surface of the first inclined plate is fixedlyconnected with the left side surface of the inner wall of the casing. According to the medical operating room waste solid-liquid separation device, through arranging a first filtering plate and a second filtering plate, waste is sequentially filtered by the second filtering plate and the first filtering plate before entering a net cage and performing centrifugal movement, bigger molecular particles in waste are filtered out by the second filtering plate and the first filtering plate, so that residual waste performs centrifugal movement inside the net cage to reduce deposit volume at the net meshes, thereby not only improving the solid-liquid separation effect, but also improving the working efficiency of staff as waste is avoided from being deposited at the net meshes.
Owner:李彦斌
Rapid sedimentation separation kettle for preparing lanolin cholesterol
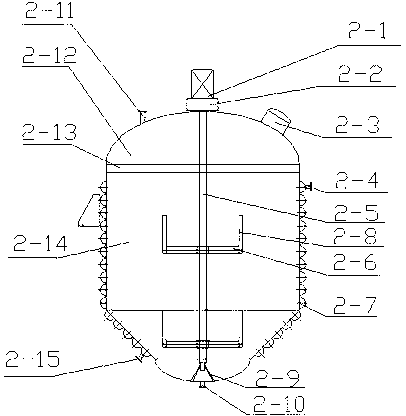
InactiveCN106731145ANot easy to loseFast fallSteroidsMoving filtering element filtersCholesterolLanolin
The invention relates to a sedimentation separation kettle, and particularly relates to a rapid sedimentation separation kettle for preparing lanolin cholesterol. A technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide the rapid sedimentation separation kettle for preparing lanolin cholesterol, wherein the rapid sedimentation separation kettle has the advantages of target object not easy to lose, thorough solid-liquid separation and rapid solid-liquid separation. In order to solve the above technical problem, the invention provides such a rapid sedimentation separation kettle for preparing lanolin cholesterol that the rapid sedimentation separation kettle comprises a first rotation shaft, a separation kettle, a feeding hopper, a cover plate, a second spring, a first slide rail, a first slide block, a first spring, a fixing plate, a second slide rail, a second slide block and the like; the middle of a top part of a base is connected with a collecting groove in a bolted connection manner. The rapid sedimentation separation kettle provided by the invention achieves the beneficial effects of target object not easy to lose, thorough solid-liquid separation and rapid solid-liquid separation, and can filter multiple times by arranging second filter cloth, a third pull rope, an electric wheel and a second hole.
Owner:上海翁大电气科技有限公司
Solid-liquid separation device for chemical materials
InactiveCN110882578AEasy to handleThorough solid-liquid separationFiltration circuitsMoving filtering element filtersForeign matterControl engineering
The invention discloses a solid-liquid separation device for chemical materials. A first filter conveyor belt and a second filter conveyor belt are connected, in a rolling manner, with a first filterscreen and a second filter screen, respectively. Water inlets are fixedly mounted at the top end of a main body of the separation device, and above the second filter conveyor belt and the second filter screen. An auxiliary filter device includes rollers, a square filter frame and a square filter screen, wherein the rollers are mounted on the periphery of the square filtering frame in a rolling manner, and the square filtering screen is inlaid in the square filter frame. By adoption of the first filter screen, the second filter screen and the auxiliary filter device which are three stages of filtering devices, solid-liquid separation is more thorough. The five groups of the water inlets are designed to facilitate the treatment of a large amount of industrial sewage so that the solid-liquidseparation device has strong adaptability. Two sets of brush rollers are used to clean foreign matters on the filter screens so that a solid-liquid separation mechanism can work effectively and continuously for long time.
Owner:湘潭市汇丰设备制造有限公司
Olive oil production line
ActiveCN107904001AEvenly brokenOvercome the side-to-side swing phenomenonFatty-oils/fats refiningFatty-oils/fats productionProduction lineElectrical control
The invention discloses an olive oil production line, comprising an electric control system, and a feeding and winnowing device, a cleaning and screening device, a spiral feeding device, a fusion device, a separating device and a purifying device which are successively arranged on the production line. Olive fruit is poured into the feeding and winnowing device to remove leaves and dust, and then enters the cleaning and screening device for cleaning and screening; the cleaned olive fruit falls into the spiral conveying device and is spirally lifted to fusion device of the production line by thespiral conveying device; the olive fruit undergoes crushing, stirring and fermentation, and sufficient fusion in the fusion device; pulp obtained after stirring fermentation is conveyed to the separating device of the production line to completely separate oil-water and pomace in the pulp; and the screened oil-water is completely conveyed to a storage unit in the purifying device and then entersa disc separator for high-speed separation to produce a pure high-quality oil product. With such a technical scheme, the olive oil production line has low cost, ensures the axis parallelism of rollers, is smooth in operation, good in dust removal effect, thorough in cleaning, crushing, stirring and fusion, and high in yield, and ensures oil quality.
Owner:ANHUI SAIERTE CENTRIFUGE
Solid-liquid separating system in sewage treatment
ActiveCN106698713AEasy to handleShort processing cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFailure rateEngineering
The invention discloses a solid-liquid separating system in sewage treatment. A water inlet cavity, a mixing cavity, an air flotation cavity, a pollution discharge cavity and a water draining cavity are successively arranged in a pond through partitions respectively at intervals from left to right; a water inlet tube communicates with the water inlet cavity of the pond; the water inlet cavity communicates with the mixing cavity through a water hole formed in the bottom of the corresponding partition; one end of a gas feeding tube and one end of a chemical feeding tube are respectively positioned at the bottom of the mixing cavity; heights of the partitions on the left side and the right side of the air flotation cavity are lower than the height of an opening of the pond; a pollution discharge hole is formed in the bottom of the air flotation cavity; and a pollution discharge hole of the bottom of the pollution discharge cavity and a pollution discharge hole of the bottom of the air flotation cavity respectively communicate with a pollution discharge pump through pollution discharge tubes. The solid-liquid separating system in sewage treatment has the advantages that a chemical agent and sewage are mixed fully, solid-liquid separation is thorough, failure rate is reduced, the system is easy to maintain and repair, the sewage treatment effect is good, the treatment period is short, sludge can be discharged while precipitating, and the sewage treatment efficiency is improved effectively.
Owner:HUBEI JINHANJIANG REFINED COTTON
Method for preparing high soda ash type copper carbonate by adopting duplex centrifugal film evaporator
The invention discloses a method for preparing high soda ash type copper carbonate by adopting a duplex centrifugal film evaporator. The method comprises the following steps: using copper, liquid ammonia and high-purity carbon dioxide as the raw materials; firstly, preparing stronger ammonia water; secondly introducing the high-purity carbon dioxide into the stronger ammonia water so as to prepare carbonized ammonia water; reacting the carbonized ammonia water with pure copper under a certain air pressure so as to prepare a copper-ammino complexing solution; further evaporating by using the duplex centrifugal film evaporator, rotationally separating and scrapping so as to prepare the high soda ash type copper carbonate. By utilizing the method, the reaction speed is increased, the production period is shortened, the product is higher in purity, the production efficiency is greatly improved, the production cost is lower, the quality is significantly improved, and the product application is wider; and meanwhile by adopting the duplex centrifugal film evaporator, the method is high in yield, small in heat radiation and short in reaction time, the coal resource is saved, and the requirements on environmental-friendliness are met better and at the same time the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:TAIXING SMELTING PLANT
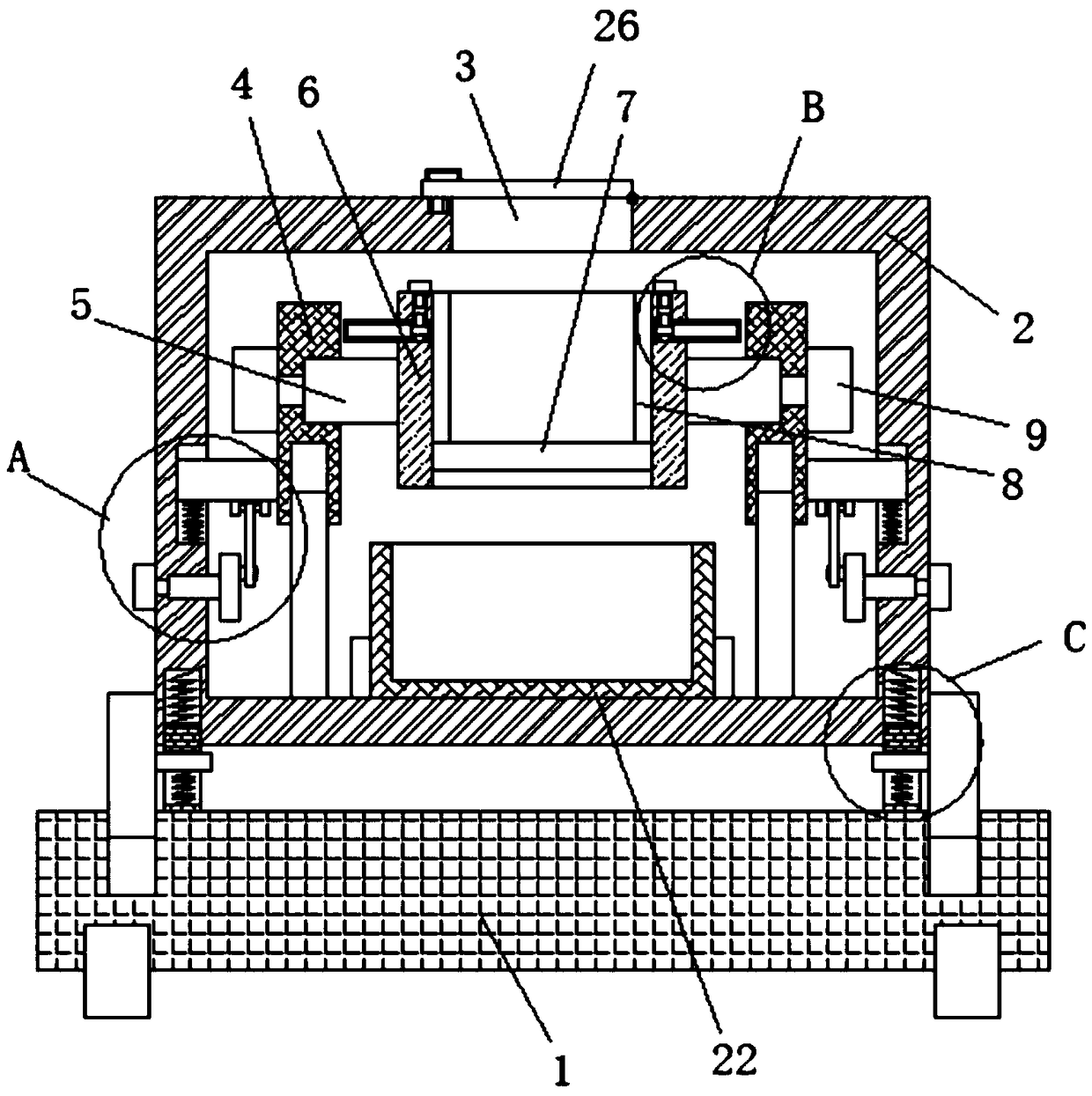
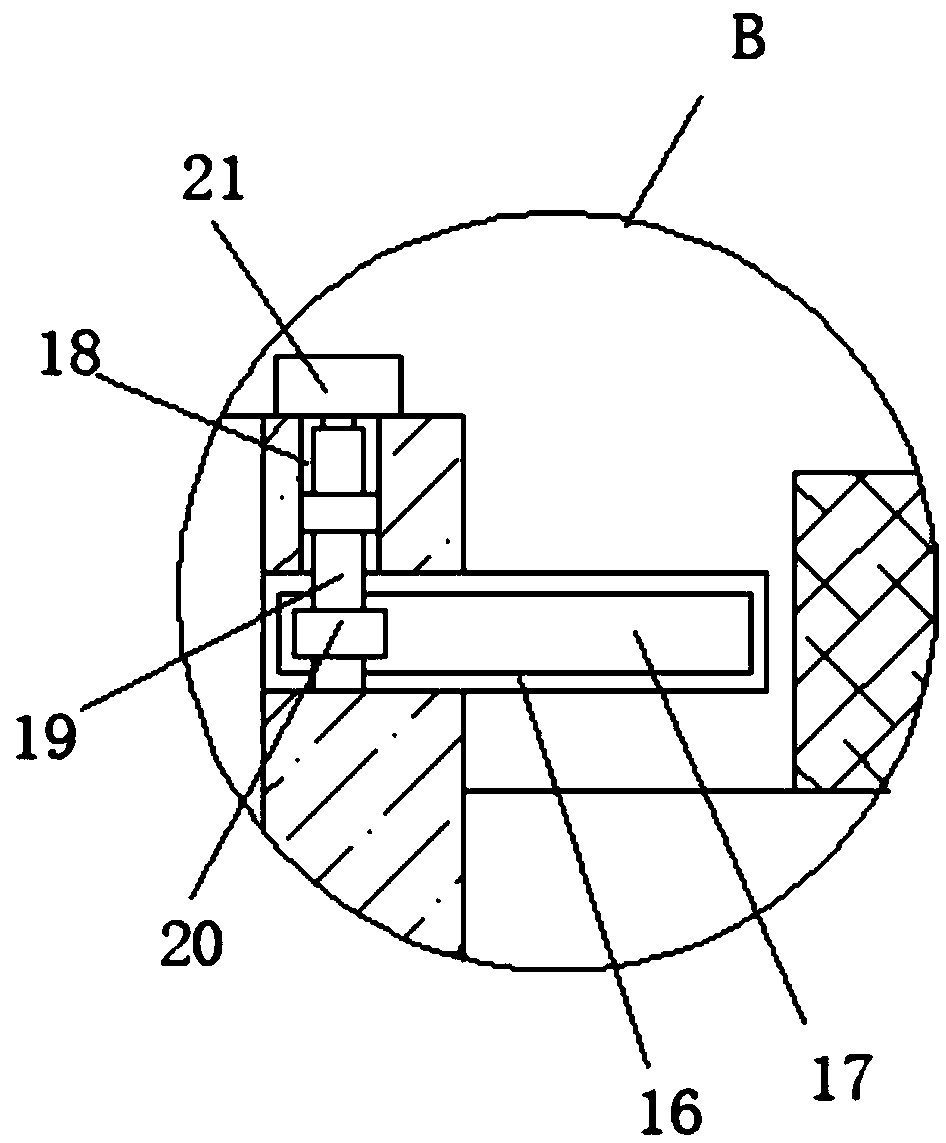
An organic waste pretreatment device
InactiveCN109201707AImprove vibrationFacilitate solid-liquid separationNon-rotating vibration suppressionSolid waste disposalSlide platePre treatment
An organic waste pretreatment device is disclosed. The device includes a pedestal above which a separation tank is arranged. A mounting tank the top and bottom of which are openings is mounted in theseparation tank. A filter plate is fixedly mounted in the mounting tank. Extruding plates are slidingly mounted on two sides of the inner wall of the mounting tank, and bottoms of the two extruding plates are in contact with the top of the filter plate. Two sides of the inner wall of the separation tank are provided with sliding slots in which sliding plates are slidingly mounted. Close sides of the two sliding plates are fixedly provided with mounting plates. The mounting tank is between the two mounting plates. The device can conveniently perform solid-liquid separation on organic waste so as to facilitate subsequent treatment. The filter plate can be vibrated conveniently to accelerate separation. The waste is extruded by the two extruding plates so that solid-liquid separation is morethorough. When the separation tank vibrates, a good vibration damping effect can be achieved.
Owner:郑州邦企信息科技有限公司
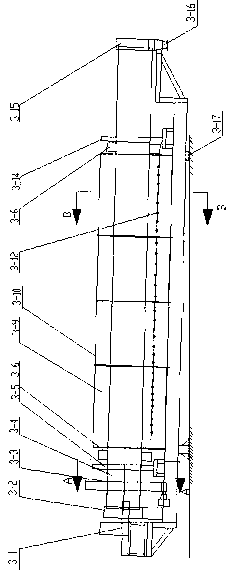
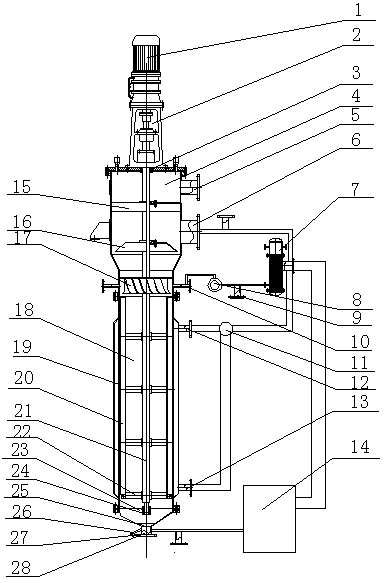
Horizontal spiral centrifuge
InactiveCN107497609AAccelerated settlementSolve the problem that cannot meet the requirements of high-purity montmorillonite centrifugal separation and purification processRotary centrifugesSpiral bladeMontmorillonite
The invention relates to a decanter centrifuge, comprising a screw pusher (1), a rotating drum (2) and a motor (3), and the motor (3) is used to drive the rotating drum (2) and the screw pushing device (1) Rotate on the same axis and in the same direction at the preset speed difference. There is a cavity in the drum (2). The central axes of the screw pusher (1) and the drum (2) are the same straight line. The screw pusher (1) Part is located inside the drum (2), and the screw propeller (1) includes an integral part formed by the discharge part (4) and the liquid discharge part (5), as well as the screw blade (6), the discharge part (4) and the liquid discharge part Both parts (5) are provided with cavities, the discharge part (4) and the liquid discharge part (5) are not connected, the discharge part (4) is provided with a discharge port (7), and the liquid discharge part (5) is provided with a liquid First outlet (8) and second outlet (9) for liquid. The decanter centrifuge provided by the invention has better solid-liquid separation effect and can be used for centrifugal separation and purification of montmorillonite in the production process of high-purity montmorillonite.
Owner:安吉高纯蒙脱石有限公司
Preparing method for bacillus natto powder
The invention provides a preparing method for bacillus natto powder. The method comprises the specific operation procedures that full and mildew-free soybeans and corn are selected, cleaned, dried, mixed and smashed; liquid fermenting is carried out, soybean powder and corn powder are placed into a fermenting tank, fermentation material water is added into the fermenting tank, then warming and standing fermenting are carried out, and fermenting time is 2-4 hours; then inoculation is carried out, bacillus natto is utilized as a strain source to carry out inoculation, the inoculation amount is 2-8%, after inoculating is carried out, standing fermenting is carried out, and fermenting time is 20-24 hours. According to the method, a separator is utilized for acting on the fermenting liquor, solid and liquid in the fermenting liquor can be separated more thoroughly, and smoothness of later-period operation of production is ensured, finally, the concentrated liquid is frozen in a vacuum mode, invasion of bacteria in the freezing process is avoided, purity of nattokinase powder is ensured, and quality of the nattokinase powder is ensured.
Owner:王军
Combined type extracting basket extracting tank
InactiveCN102755762AThorough solid-liquid separationEasy to realize automatic controlSolid solvent extractionSlagPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a combined type extracting basket extracting tank which comprises a tank body and an extracting basket, wherein a tank cover is arranged on the top of the tank body, and a pneumatic rotating bottom slag outlet door is arranged at the bottom. The combined type extracting basket extracting tank is characterized in that the extracting basket comprises a basket body and a basket bottom, wherein the basket body is fixed in the tank body; the basket bottom is arranged on the door body of the pneumatic rotating bottom slag outlet door through an adjusting cylinder; and the adjusting cylinder drives the basket bottom to in contact and separation with the bottom of the basket body for extracting and discharging slag. In work, after the pneumatic rotating bottom slag outlet door at the bottom of the extracting tank is closed, the adjusting cylinder on the pneumatic rotating bottom slag outlet door acts, and the pushing rod of the adjusting cylinder is adjusted to upwards extend to push the basket bottom to cling to the bottom of the basket body, thus forming the extracting basket. After the medicament is extracted in the extracting basket, and the extracting liquid is completely drained, the pushing rod of the adjusting cylinder is contracted, and therefore the basket bottom can be fallen to be separated from the bottom of the basket body, and the basket bottom is opened along with the pneumatic rotating bottom slag outlet door, so as to discharge the dreg completely.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIWIN PHARMA MACHINERY
Multifunctional waste bin
InactiveCN107685969AEasy to take outPrevent rotRefuse receptaclesRefuse cleaningWater storageWaste management
The invention provides a multifunctional waste bin. The multifunctional waste bin is characterized by comprising a lower barrel, a upper barrel, a barrel cover and a combined connection rod; the lowerbarrel comprises a supporting barrel body, a side drawing barrel body and a water storage box; the upper barrel comprises a compression annulus wall, a lower gear annulus wall, an upper gear annuluswall and an expansion annulus wall; the barrel cover is hinged to the expansion annulus wall, and an opening of the expansion annulus wall can be opened or closed; the combined connection rod comprises a positioning rod body, a main rod body, an auxiliary rod body, a drive gear, a driving assembly, top connection rod bodies, a middle connection rod body and telescoping connecting rod bodies. The multifunctional waste bin has the effects of compressing waste and separating water, meanwhile, the aim of expanding the volume of the waste bin is achieved through meshing of different gears, and besides, the stench in the waste bin can be effectively removed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DIHENG IND CO LTD
Solid and liquid separator for materials
ActiveCN103657176BImprove stressThe moisture content of solids is reducedFiltration separationPush and pullLocking mechanism
The invention discloses a solid and liquid separator for materials. The solid and liquid separator comprises a frame, press plates, filter plates, a push-and-pull locking mechanism, a filter cloth mechanism, a filter cloth regeneration mechanism and a cleaning mechanism which are arranged on the frame, wherein the press plates and the filter plates are arranged on the frame in a sliding way alternately, and are matched to extrude a material, so that solid and liquid of the material can be separated; the push-and-pull locking mechanism is used for locking, pushing away all the press plates and filter plates, so that solid-liquid separation operation can be performed, or the material can be discharged; the filter cloth mechanism is used for separating solid and liquid of the material when the material is extruded; the filter cloth regeneration mechanism is used for washing to regenerate the filter cloth after the material is discharged; the cleaning mechanism is used for cleaning the material attached to the separator after solid and liquid of the material are separated. The solid and liquid separator has the characteristics of reasonable design, high structure strength, convenience in operation, complete solid and liquid separation, high separation efficiency, convenience in cleaning, long service life, log maintenance frequency, high reliability, strong practicality and the like, and is beneficial for greatly increasing production benefit of enterprises.
Owner:四川宝凯鑫诚环保科技有限公司
Compound centrifugal film evaporator and method for preparing high-purity soda ash-type copper carbonate
InactiveCN103101956AQuick responseHigh purityEvaporationCopper compoundsMetallurgyBasic copper carbonate
The invention discloses a compound centrifugal film evaporator and a method for preparing high-purity soda ash-type copper carbonate. A steam deposal chamber of the compound centrifugal film evaporator is provided with a vapor-liquid filter and a vapor-liquid separator; a tail gas collecting opening and a secondary steam recovery opening are arranged at the outer wall of the steam deposal chamber; a distributing device is arranged at the top end of an evaporation chamber; a material inlet is arranged at the outer wall of the distributing device; the secondary steam recovery opening is communicated with the material inlet through a condenser and a feeding pump orderly; a sample collector is connected to one side of a discharge valve of a taper discharge chamber; a screw feeder is connected to the other side of the discharge valve; and the screw feeder is communicated with the material inlet through the condenser and the feeding pump orderly. According to the method for preparing the high-purity soda ash-type copper carbonate by the compound centrifugal film evaporator, pure copper, liquid ammonia, and high-purity carbon dioxide are taken as materials; a copper ammonia complexation solution is firstly prepared; and then the high-purity soda ash-type copper carbonate is prepared by the compound centrifugal film evaporator. Therefore, the production cycle is shortened; the product purity is higher; the yield is higher; and the production cost is lower.
Owner:TAIXING SMELTING PLANT
High-effective filter press with diaphragm filter plates
ActiveCN109011748AThorough solid-liquid separationEasy to peel filter clothFiltration separationEngineeringElectromagnetic valve
A high-effective filter press with diaphragm filter plates includes: a support, on which a top feeding pipe and a bottom feeding pipe are slidingly arranged. A row of electromagnetic valves are connected to the top feeding pipe, wherein a feeding port and a pressurized feeding port are respectively on each adjacent electromagnetic valve. A row of electromagnetic valves are connected to the bottomfeeding pipe, wherein feeding ports are connected to the electromagnetic valves on the bottom feeding pipe. The top feeding pipe and the bottom feeding pipe are respectively connected with driving apparatuses. Sliding bars are installed on the support, wherein pressurizing members and filtering members are alternately connected to the sliding bars in a sliding manner. A pressurizing member on oneend of the sliding bars is fixed to the sliding bars while an air cylinder is connected to a pressurizing member on the other end of the sliding bars. A first connector on each filtering member and asecond connector on each pressurizing member are connected to each other through a yoked connection rod. The filter press can completely separate solids and liquid, wherein a filter cake is easy to dry and strip off from a filter cloth. The filter press is large in one-time processing capacity and is free of removing the filter cake before every feeding operation. The filter press saves a large quantity of treatment time and can increase productivity of enterprises.
Owner:浙江胜达祥伟化工有限公司
Urban waste treatment equipment
ActiveCN108751659BRealize solid-liquid separationFacilitate solid-liquid separationSludge treatmentFiltration circuitsFecesEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses urban feces treatment equipment which comprises a box body, wherein the box body is internally provided with a drying mechanism, and the two sides of the side walls of the boxbody are respectively provided with support frames, a reclaiming mechanism matched with the drying mechanism is arranged on the support frames; the feces can be put into the drying mechanism by installing the drying mechanism, and water in the feces can be centrifugally separated by the drying mechanism to achieve the effect of solid-liquid separation; the liquid is separated from the drying mechanism and falls to the bottom of the box body for collection, and the solid can be collected by the reclaiming mechanism on the support framse at any time; after the feces is dried, the solid feces iscollected by the reclaiming mechanism for subsequent use; on the other side, the reclaiming mechanism can be lowered, and the drying mechanism can continue to carry out the drying process; the steps of drying and reclaiming can be carried out simultaneously to save time and allow the solid and liquid to be effectively separated, so that the efficiency of solid-liquid separation is greatly improved.
Owner:朱晓萍
Uneasy-to-block vertical type solid-liquid separator for kitchen and fruit and vegetable garbage
PendingCN109808216ALow investment costLow running costPressesAgricultural engineeringFruits and vegetables
The invention provides an uneasy-to-block vertical type solid-liquid separator for kitchen and fruit and vegetable garbage. The uneasy-to-block vertical type solid-liquid separator comprises a vertical type barrel body, wherein a discharging cabin is arranged at the top of the vertical type barrel body; a spiral shaft is arranged in the vertical type barrel body; the top end of the spiral shaft stretches out of the top of the discharging cabin; a squeezing block sleeves the spiral shaft; the squeezing block is in sliding connection with the spiral shaft; the squeezing block is of a semispherical structure; a solid-liquid separation screen mesh further covers the outer side of the spiral shaft located in the vertical type barrel body; the solid-liquid separation screen mesh is internally provided with a solid-liquid separation channel; a charging opening is formed in a side wall of the lower part of the vertical type barrel body; the feeding opening is communicated with the solid-liquidseparation channel; an arc-shaped surface of the squeezing block is arranged downward and covers the top of the solid-liquid separation channel; the spiral shaft is further provided with an isolationcover which is provided with a squeezing spring in a sleeving manner and covers the squeezing spring; an annular groove is formed in the top of the squeezing block; and the bottom end of the isolation cover is inserted into the annular groove and can move in the annular groove up and down. According to the uneasy-to-block vertical type solid-liquid separator, the squeezing block is of the semispherical structure and squeezed kitchen and fruit and vegetable garbage slides out of the discharging opening from the arc-shaped surface and a discharging dead angle is not easy to form.
Owner:WUXI TOGO ENVIRONMENT EQUIP
Solid-liquid separation type domestic sewage treatment device
InactiveCN108383279AThorough solid-liquid separationThorough treatmentWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSpecific water treatment objectivesOzone generatorSolid waste collection
The invention discloses a solid-liquid separation type domestic sewage treatment device. The solid-liquid separation type domestic sewage treatment device comprises a bottom plate, wherein a separation and disinfection cavity and a filtering cavity are formed in the bottom plate; a water inlet pipe is arranged at the upper end of the separation and disinfection cavity; an outlet of the water inletpipe is arranged in a rotary barrel; a rotary shaft is arranged at the middle part of the rotary barrel; a solid waste collection groove is formed in the right end of the rotary barrel; an ozone generator is arranged at the lower end of the left side of the separation and disinfection cavity; a blow-down opening is formed in the bottom of the left side of the separation and disinfection cavity; afirst water pipe is arranged at the right side of the separation and disinfection cavity; the first water pipe is communicated with the separation and disinfection cavity; a water pump is arranged atthe other end of the first water pipe; the water pump is arranged at the upper end of the filtering cavity; a second water pipe is arranged at an output end of the water pump; the outlet of the second water pipe is arranged in the filtering cavity; a filtering screen frame is arranged at the bottom of the outlet of the second water pipe. The solid-liquid separation type domestic sewage treatmentdevice disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, complete sewage treatment, solid-liquid separation and good sewage treatment effect.
Owner:赵锦山 +2
Urban feces treatment equipment
ActiveCN108751659ARealize solid-liquid separationFacilitate solid-liquid separationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningFiltration circuitsAnimal fecesEngineering
The invention discloses urban feces treatment equipment which comprises a box body, wherein the box body is internally provided with a drying mechanism, and the two sides of the side walls of the boxbody are respectively provided with support frames, a reclaiming mechanism matched with the drying mechanism is arranged on the support frames; the feces can be put into the drying mechanism by installing the drying mechanism, and water in the feces can be centrifugally separated by the drying mechanism to achieve the effect of solid-liquid separation; the liquid is separated from the drying mechanism and falls to the bottom of the box body for collection, and the solid can be collected by the reclaiming mechanism on the support framse at any time; after the feces is dried, the solid feces iscollected by the reclaiming mechanism for subsequent use; on the other side, the reclaiming mechanism can be lowered, and the drying mechanism can continue to carry out the drying process; the steps of drying and reclaiming can be carried out simultaneously to save time and allow the solid and liquid to be effectively separated, so that the efficiency of solid-liquid separation is greatly improved.
Owner:朱晓萍
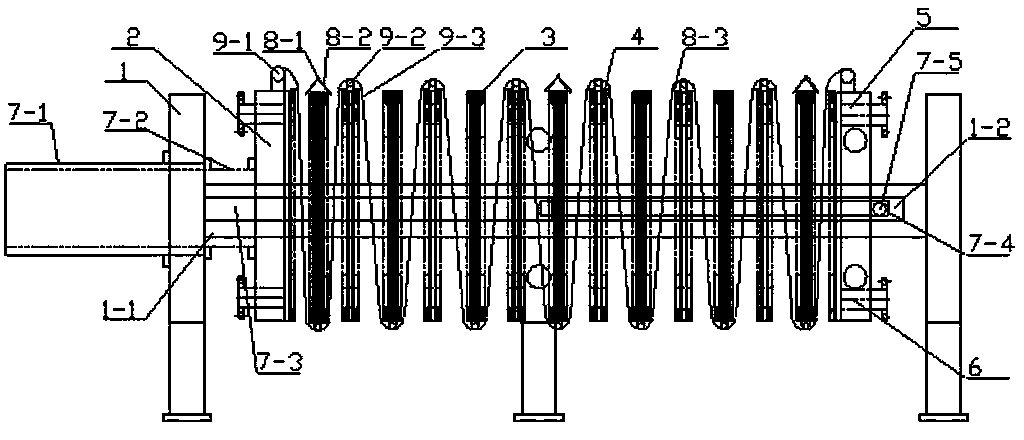
Spiral Filter Press Trash Grille Machine
ActiveCN105923665BSimple structureClever settingSludge treatmentTreatment involving filtrationGratingFiltration
The invention relates to the technical field of wastewater treatment equipment, in particular to a spiral pressure filtration type drain grating machine. The spiral pressure filtration type drain grating machine comprises a rotating shaft, a shell and a frame, wherein the shell is mounted on the frame, and the rotating shaft is mounted in the shell through bearing seats and is driven to rotate by a slowdown motor. A feeding bin is arranged above one end of the shell, a filter residue outlet is formed below the other end of the shell, a plurality of drain holes are formed below the shell, a first spiral blade, a second spiral blade, a third spiral blade and a fourth spiral blade are sequentially mounted on the rotating shaft from the feeding bin end, the pitch ratio of the first spiral blade to the second spiral blade to the third spiral blade to the fourth spiral blade is 3 to 2 to 1 to 1, and the length ratio of the first spiral blade to the second spiral blade to the third spiral blade to the fourth spiral blade is 16 to 15 to 4 to 1. The spiral pressure filtration type drain grating machine has the advantages of simple structure, little routine maintenance, thorough solid and liquid separation, low energy consumption and the like.
Owner:广西贵港市蓝月亮水处理环保科技有限公司
A comprehensive treatment method for salt mother liquor and salt mud
ActiveCN108502902BSignificant magnesium removal effectGuaranteed uptimeAlkali metal chloridesAlkali metal halide purificationFiltrationChloride
Owner:YULIN SALT IND CO LTD CNSG
Solid-liquid separation process for fluorescent whitening slurry wastewater
ActiveCN113620498AReduce CODReduce post-processing burdenWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater contaminantsFluorescenceSlurry
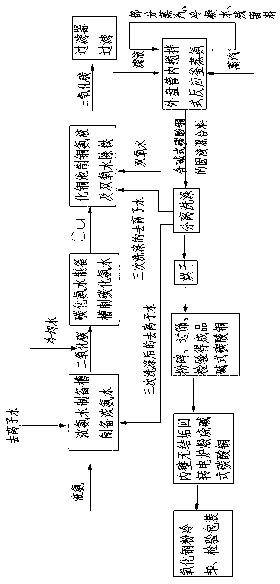
The invention relates to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and concretely relates to a solid-liquid separation process for fluorescent whitening slurry wastewater. According to the solid-liquid separation process for the fluorescent whitening slurry wastewater, the fluorescent whitening slurry wastewater can be economically and effectively subjected to solid-liquid separation, COD in liquid is greatly reduced, and the post-treatment burden of the liquid part is reduced; and post-treatment of the solid part is simplified. The process is simple, solid-liquid separation is thorough, and the operation cost is low.
Owner:奥仕集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com