Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73results about How to "Small form" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
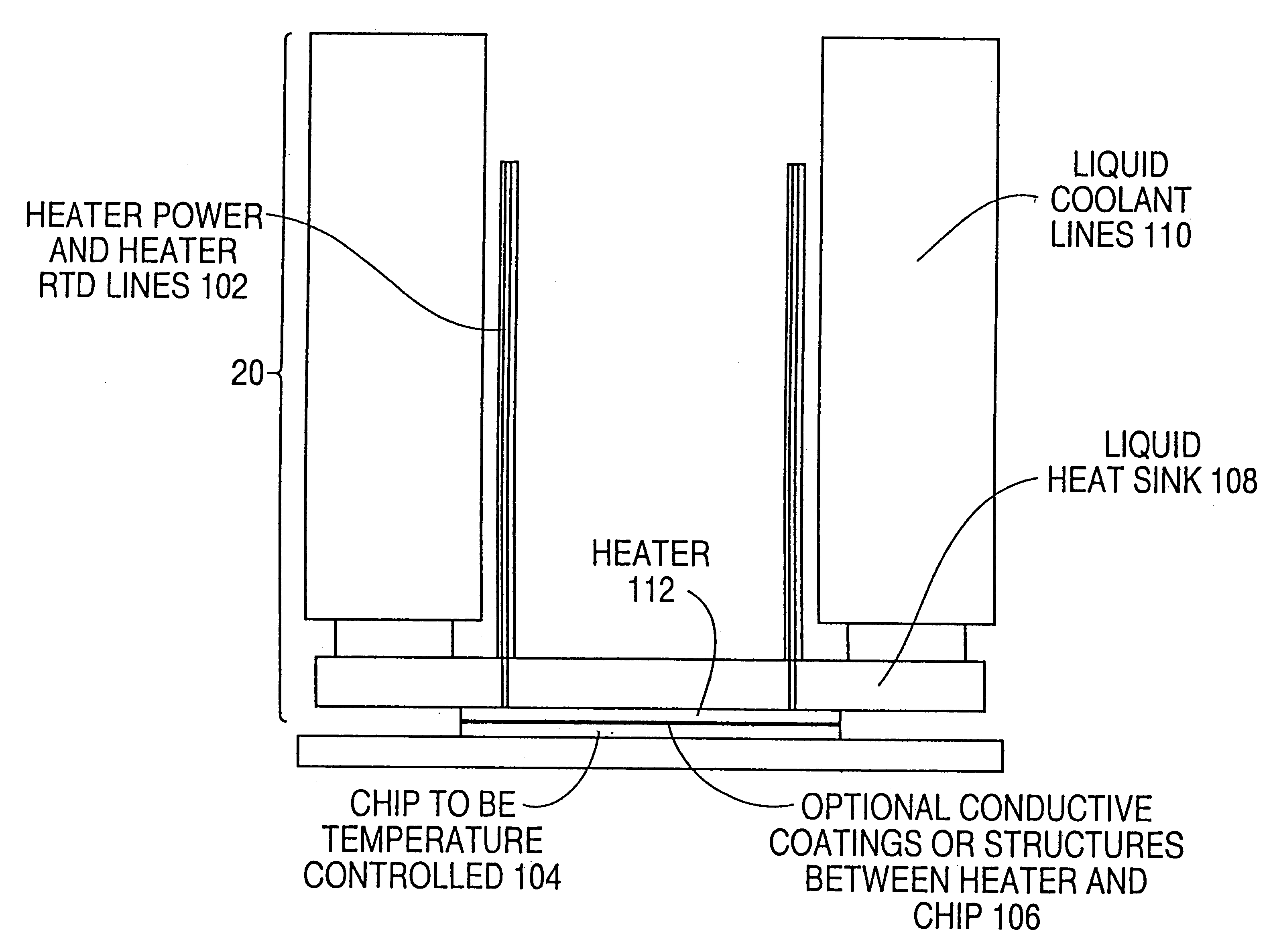
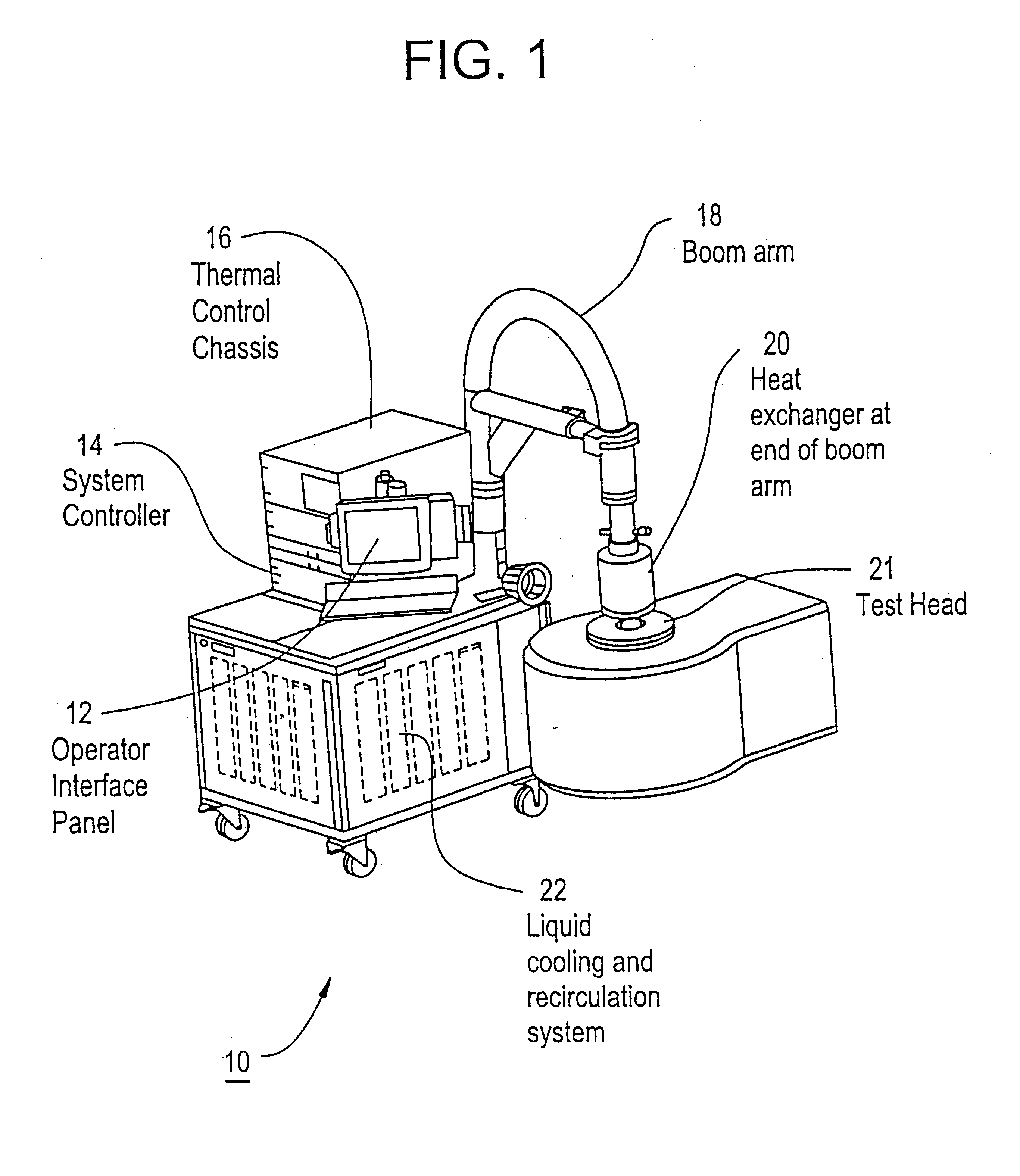
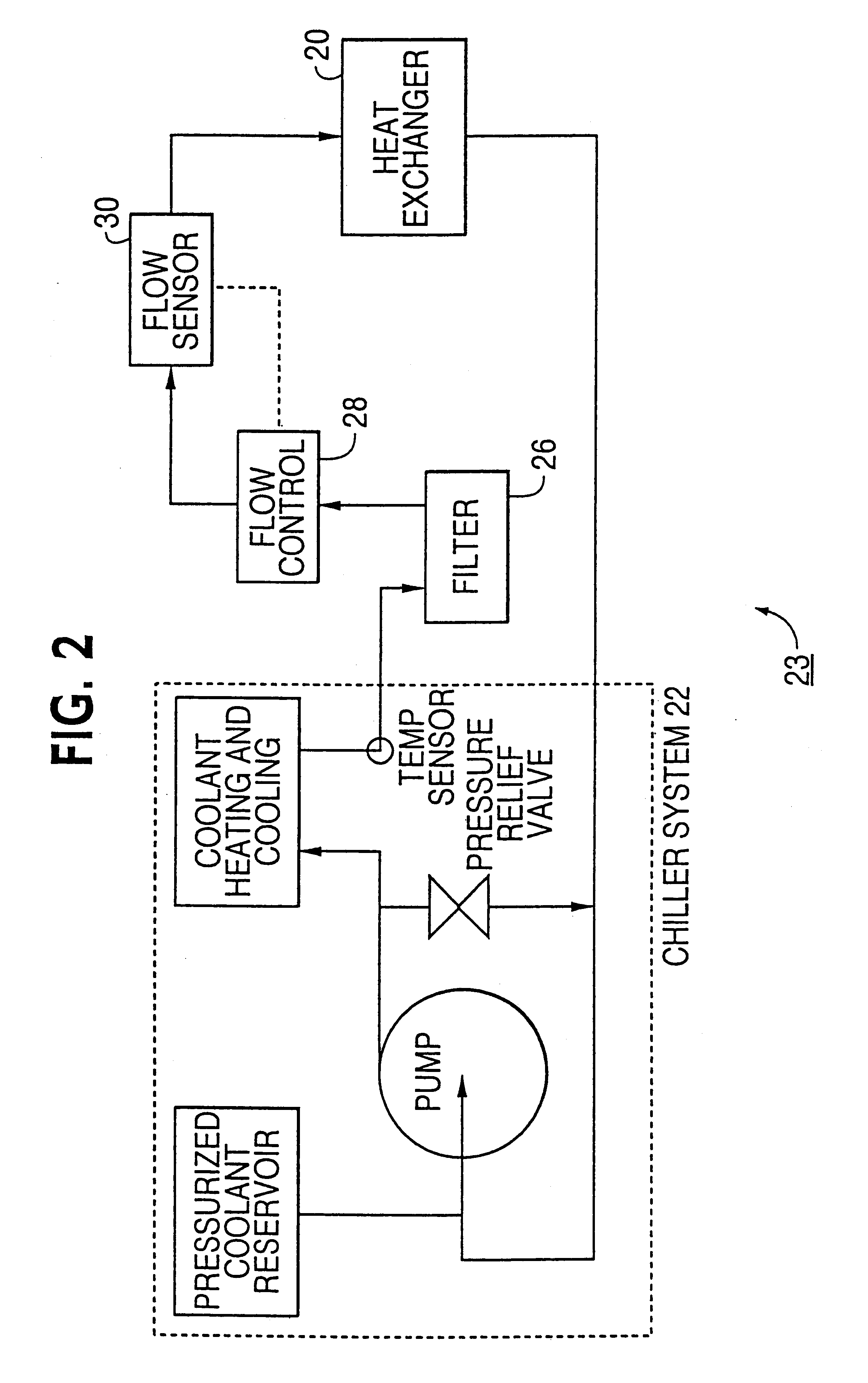
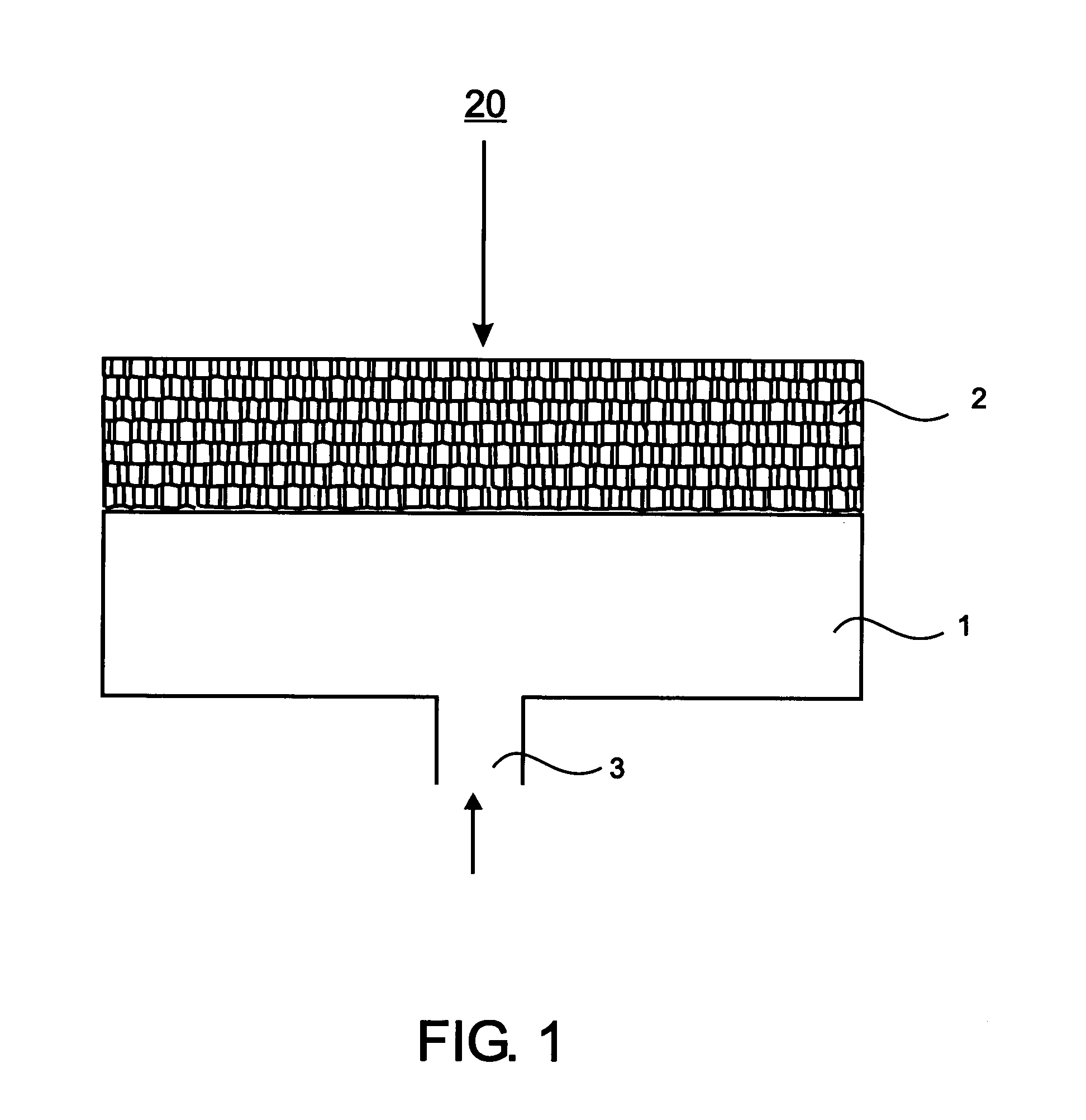
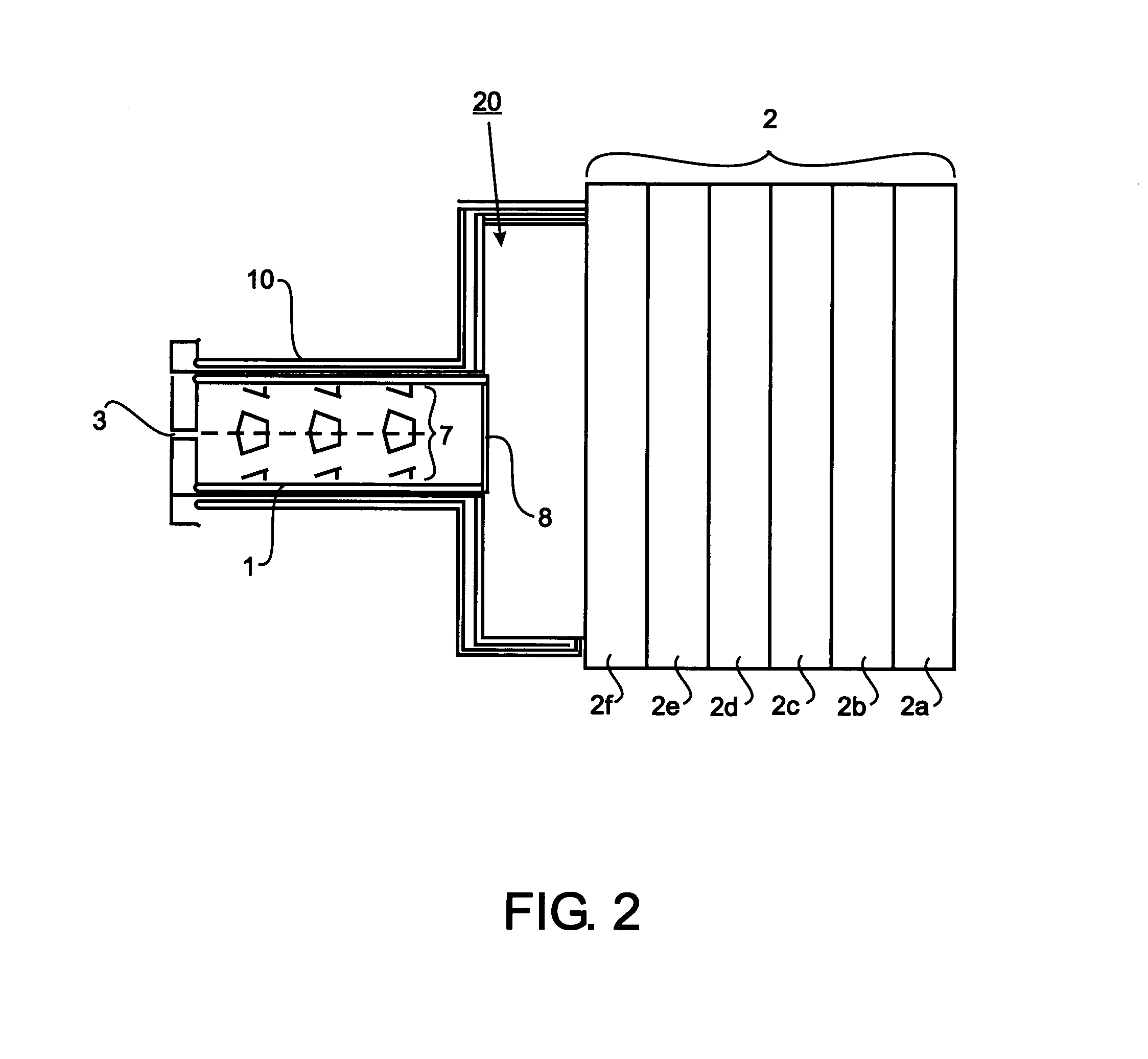
Apparatus, method and system of liquid-based, wide range, fast response temperature control of electric devices
InactiveUS6862405B2Rapid responseRapid temperature changeElectronic circuit testingTemperatue controlTemperature controlElectrical devices
An active temperature control system for a DUT utilizes a heat sink containing HFE7100 liquid and an electric heater. The liquid is cooled below the set point and the heater is used to bring the DUT up to the set point. Set points in the range of −10 degrees C. to +110 degrees C. can be achieved. The heat sink utilizes only a single coolant for all of the set points, allowing set points to be changed within a few minutes. At a given set point, the heater provides a quick response to offset the effect of self-heating and keep the set point deviation to within a few degrees C. Power following techniques can be utilized to achieve the quick response.
Owner:DELTA DESIGN
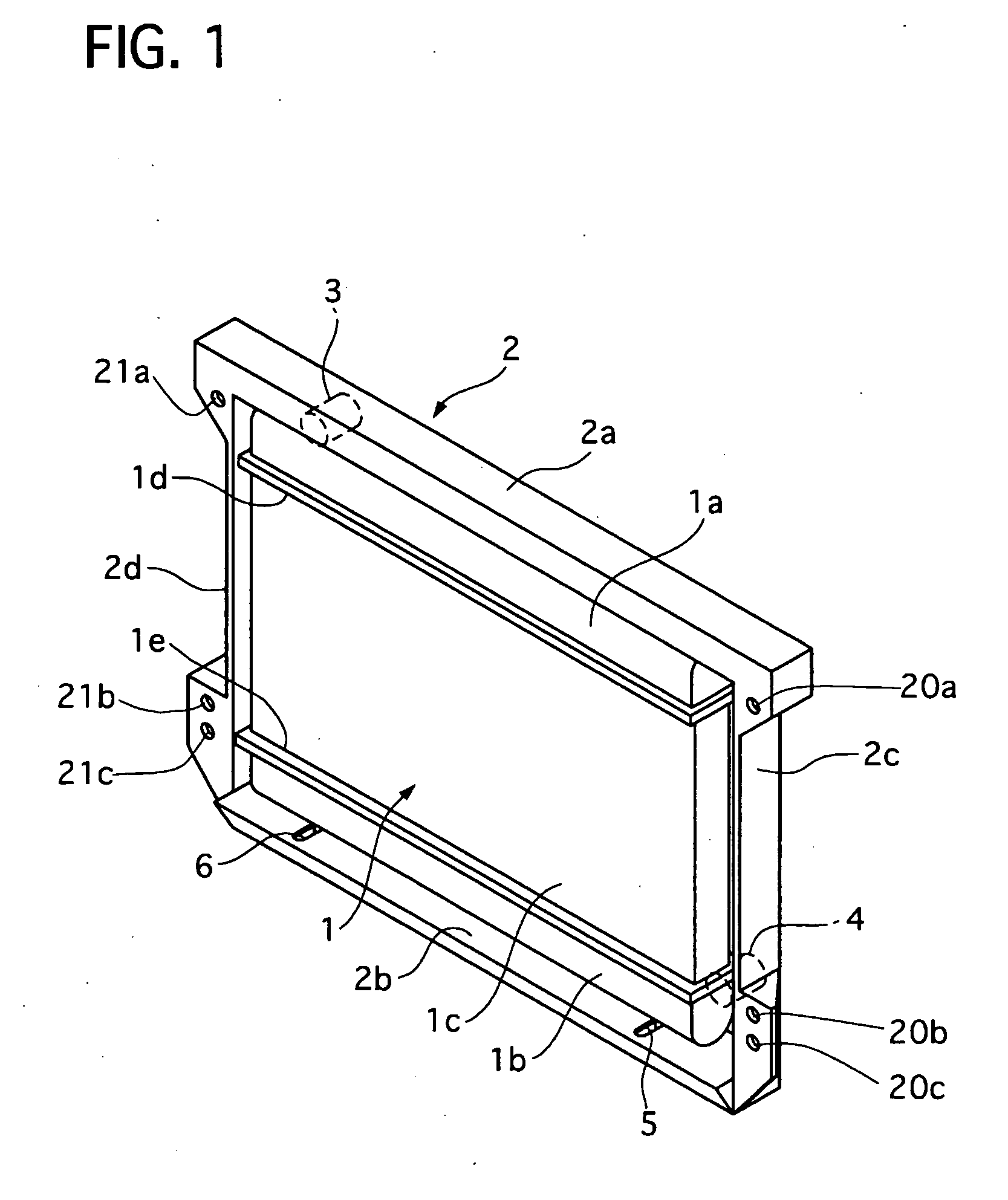
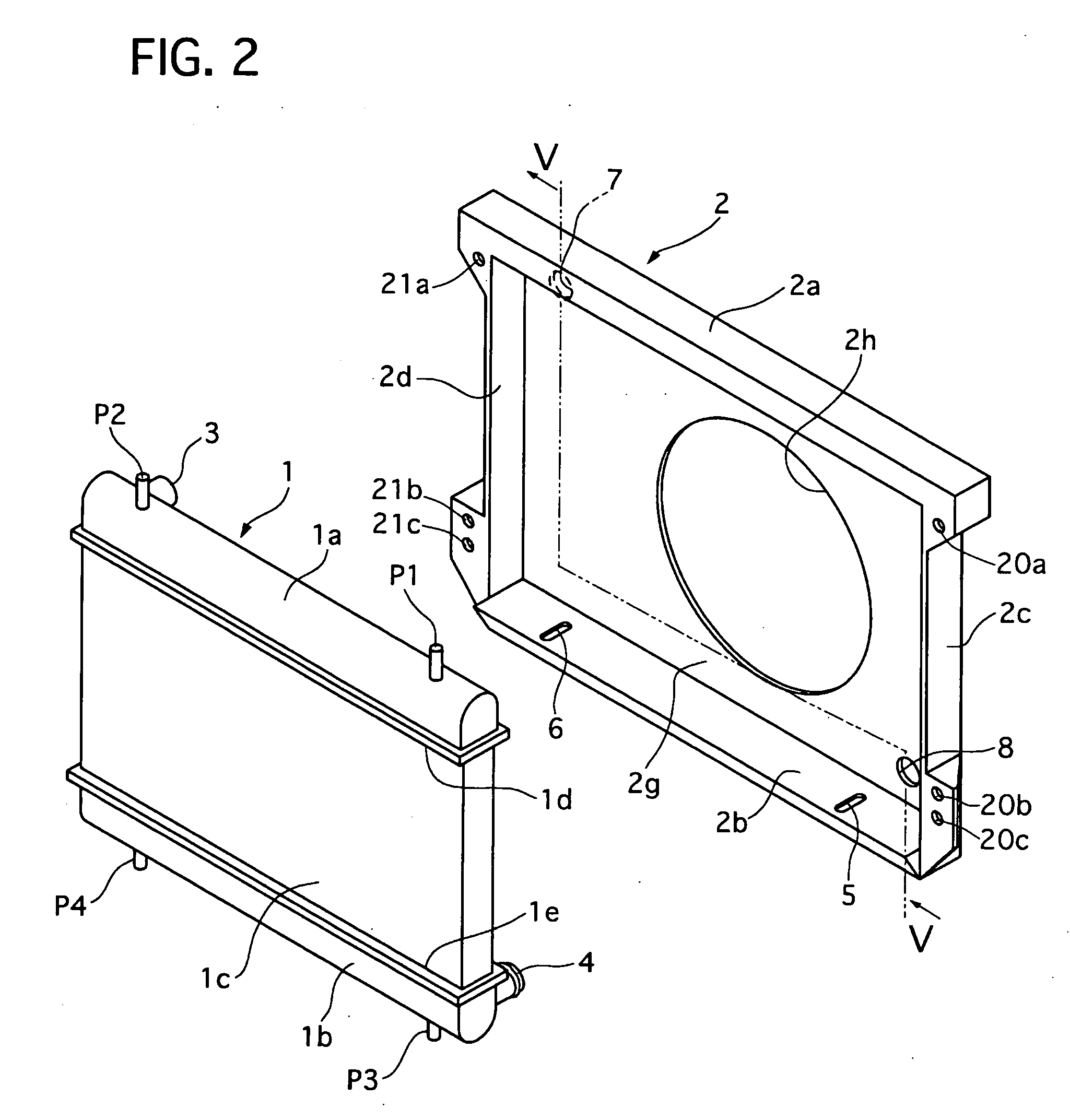
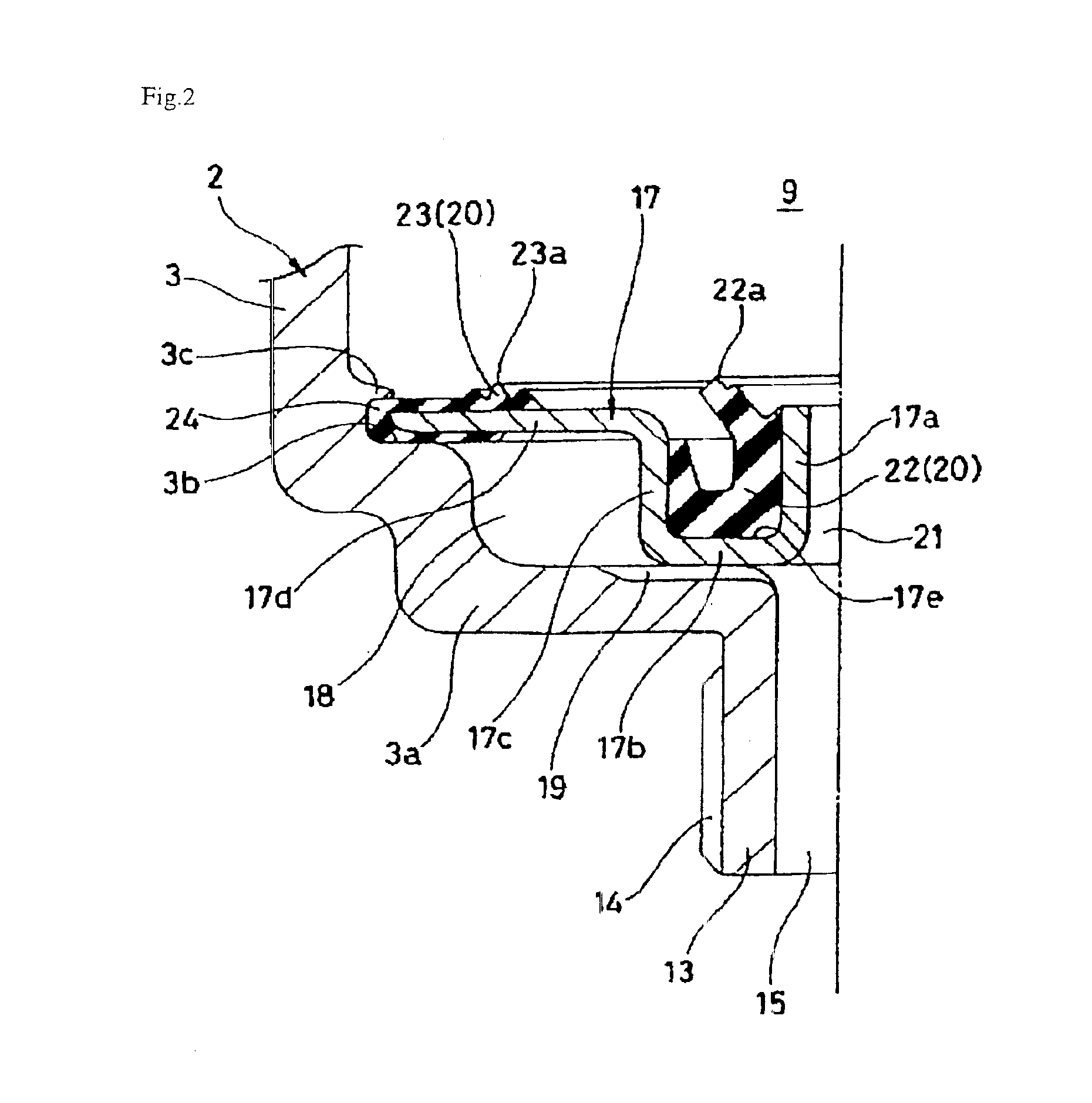
Radiator core support structure and its assembly method
InactiveUS20060213639A1Easy to slideReduce the impactIndirect heat exchangersHeat exchanger casingsMechanical engineeringHeat spreader
A radiator core support structure comprises a radiator core support and a heat exchanger. The former has a through-hole, and a fixing hole on its the lower portion. The latter has a pipe projecting rearward and introduceable in the through-hole and a lower mounting pin projecting downward from its bottom portion. The fixing hole is formed as an elongate hole extending toward the front side so that the pipe can be kept free from an interference between the pipe and the radiator core support when the lower mounting pin is inserted in a front side of the fixing hole and the heat exchanger is turned rearward around the front side of the fixing hole to stand erect. Then, the fixing hole allows the mounting pin to be slid rearward for introducing the pipe through the through-hole.
Owner:CALSONIC KANSEI CORP
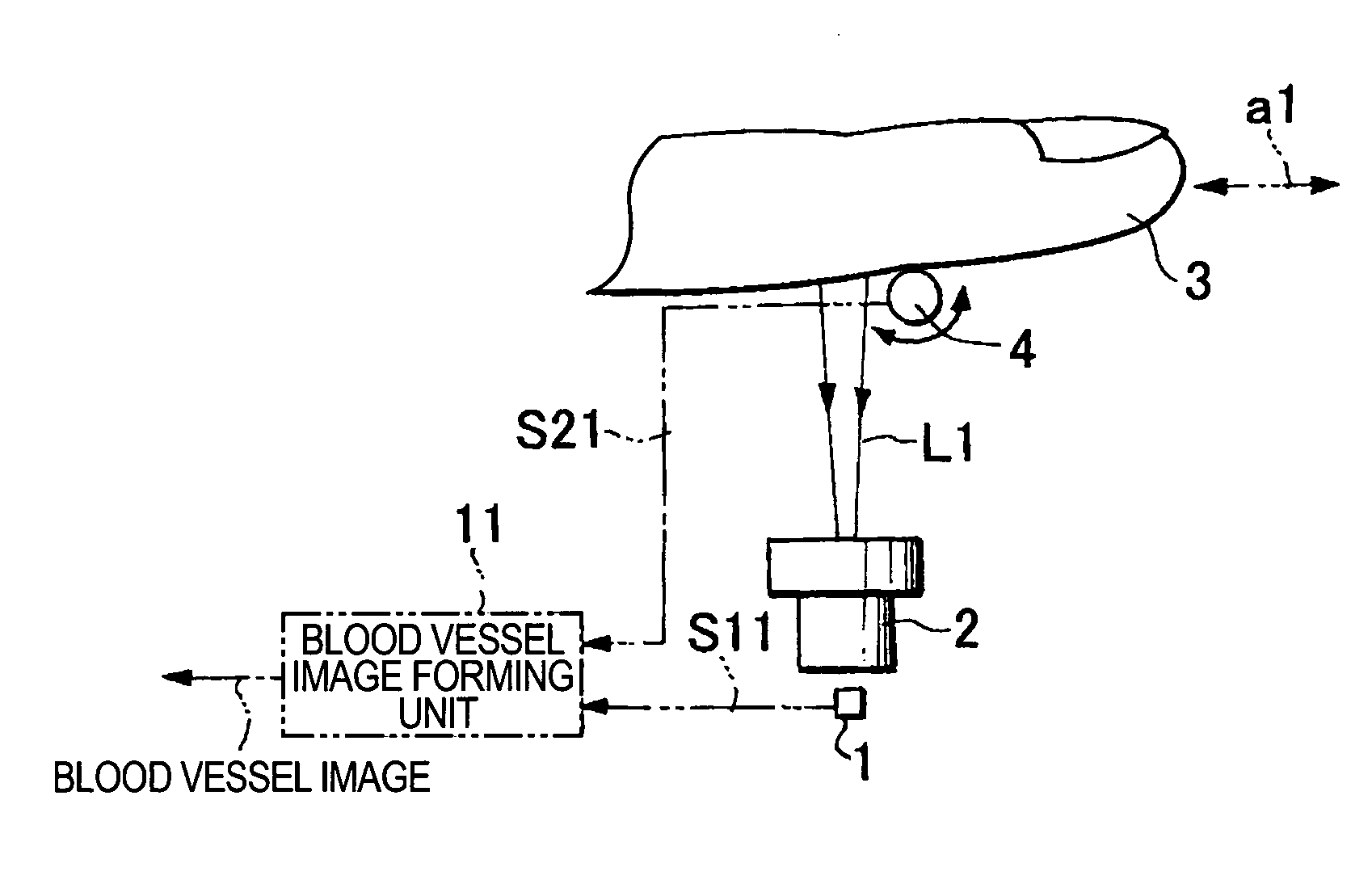
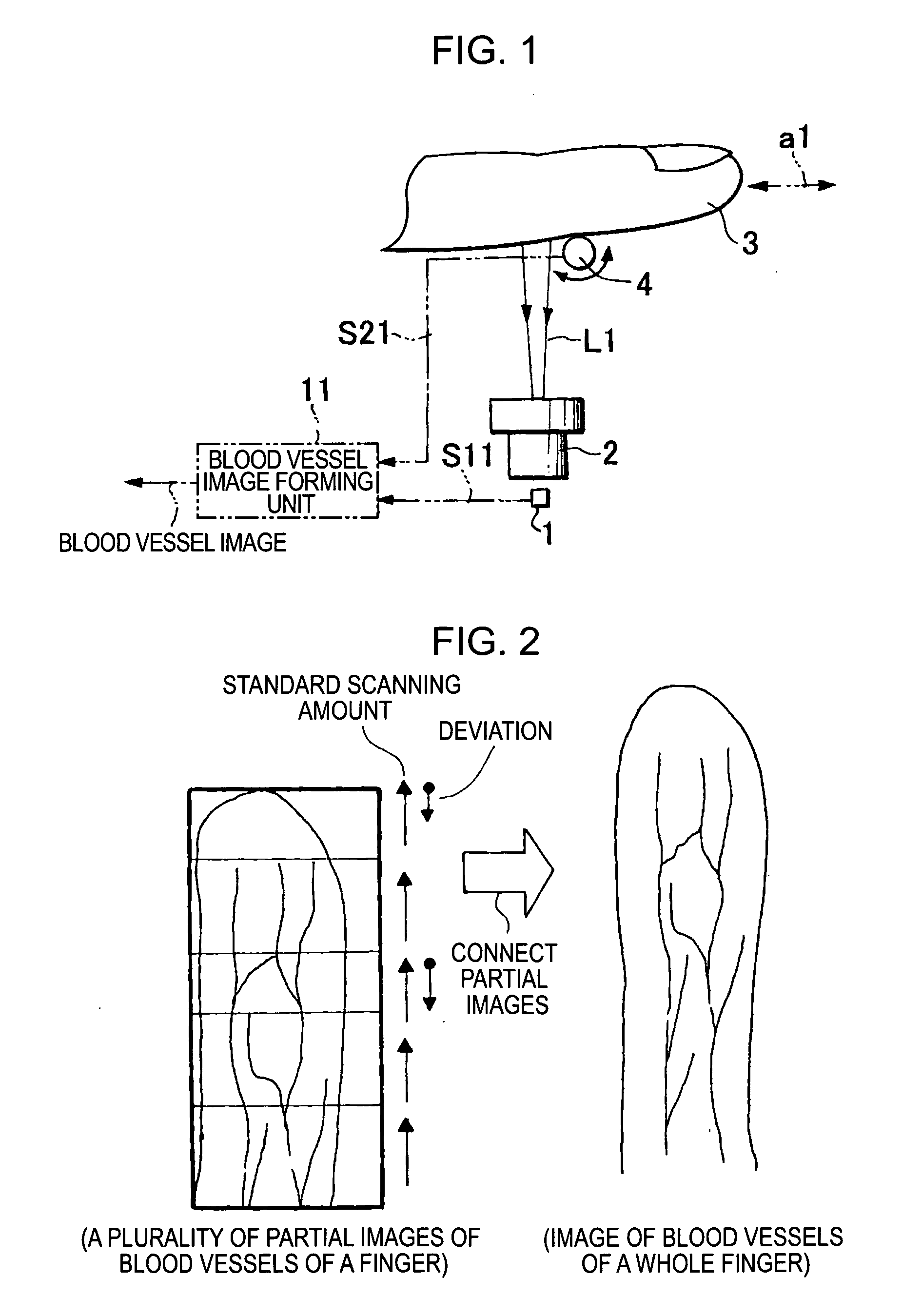
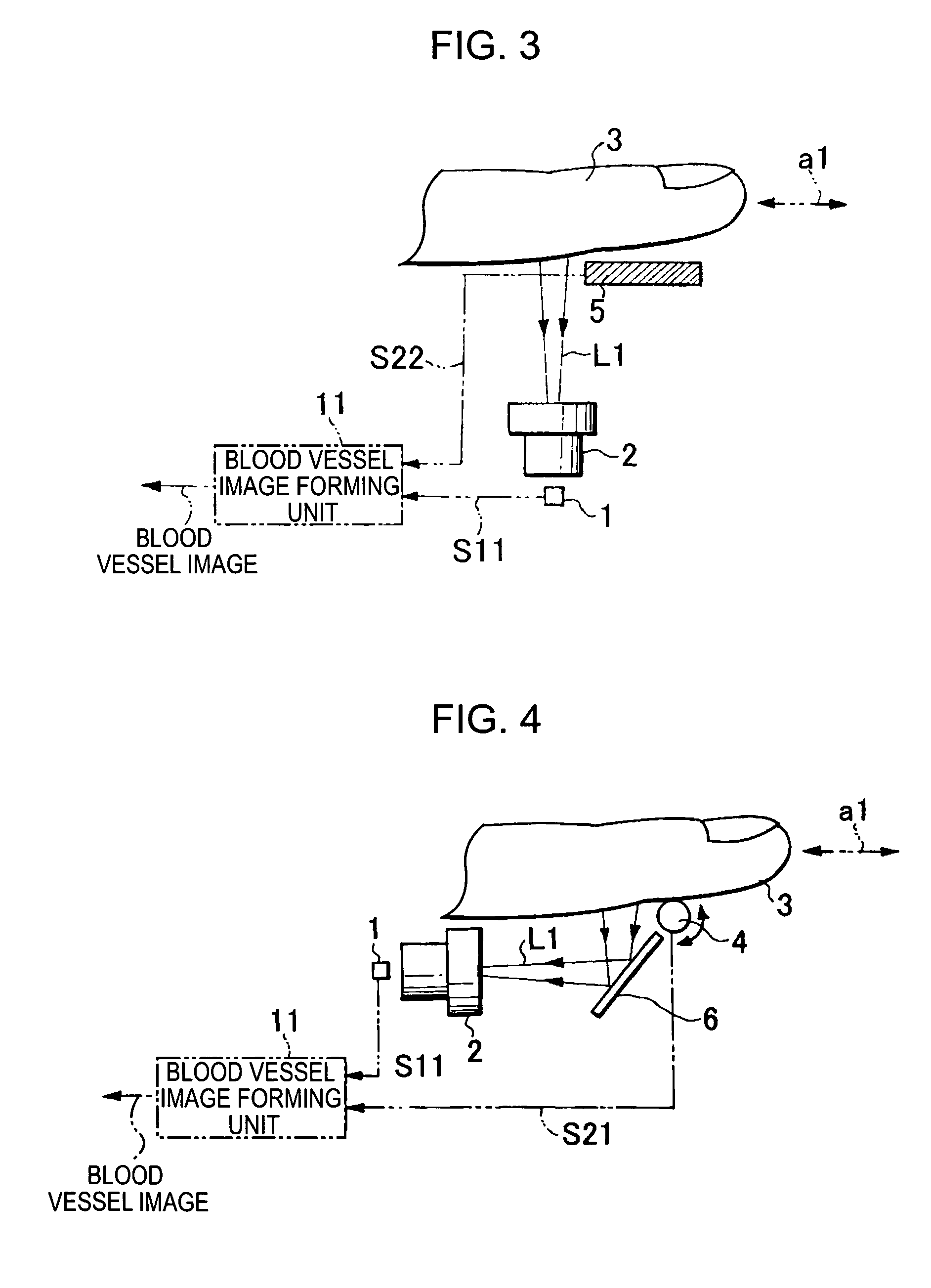
Image input apparatus and person authentication system using an image input apparatus
InactiveUS20060177107A1Improve accuracyHigh-precision acquisitionSubcutaneous biometric featuresBlood vessel patternsNetwork structureAuthentication system
A blood vessel image input apparatus is provided which is capable of acquiring a high-precision image of blood vessels of a body part, such as a finger, even if the finger is swept at a non-constant speed. The apparatus includes a solid-state line image sensor, a light source for illuminating the inside of the finger with light, an imaging optical system adapted to focus the light, emitted from the light source and passed through the inside of the finger, on the solid-state line image sensor such that a blood vessel image representing a network structure of veins in the finger is formed on the solid-state line image sensor, and a blood vessel image forming unit adapted to form a complete image of blood vessels by connecting a plurality of partial blood vessel images captured by the solid-state line image sensor while sweeping the finger.
Owner:CANON KK
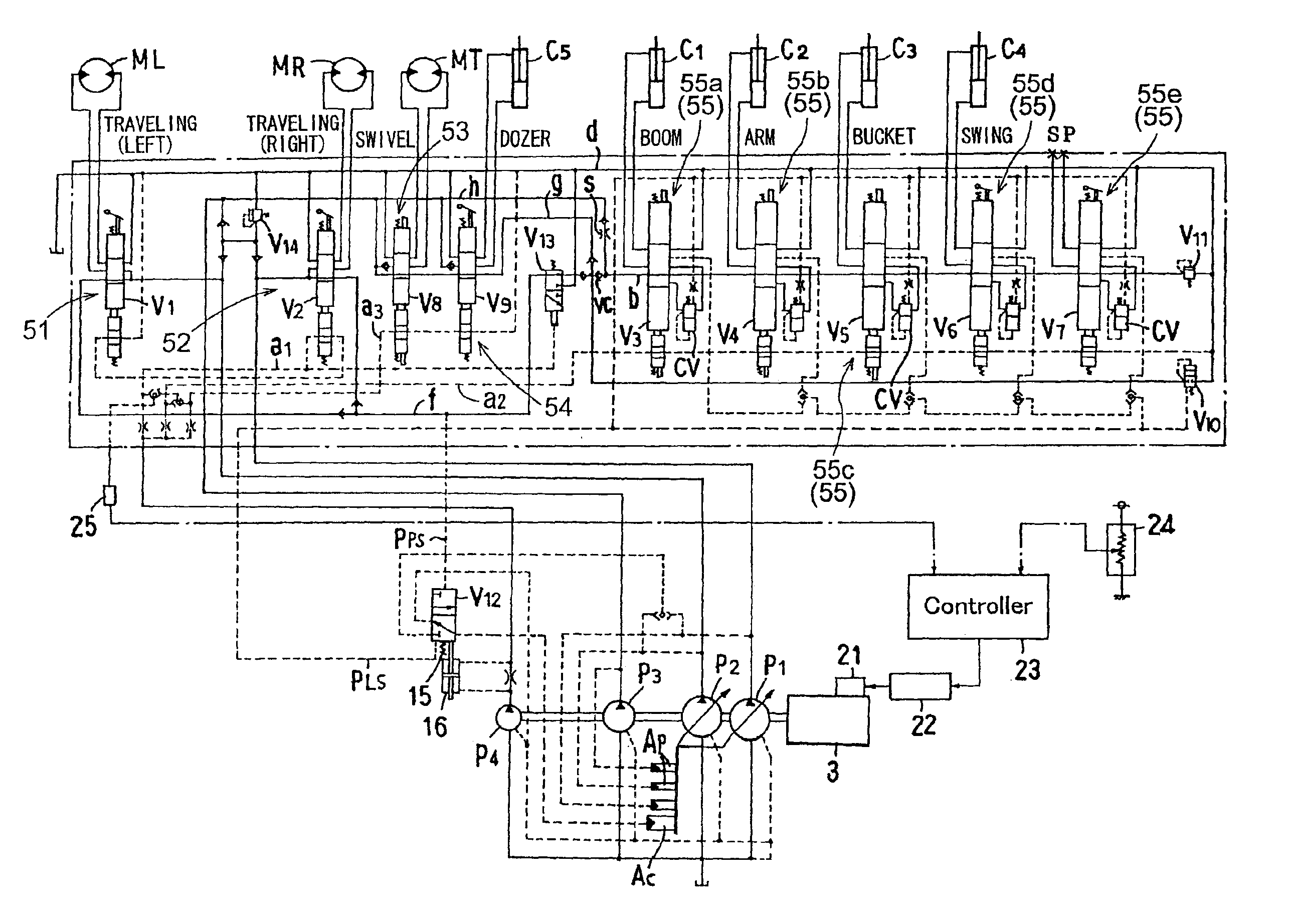
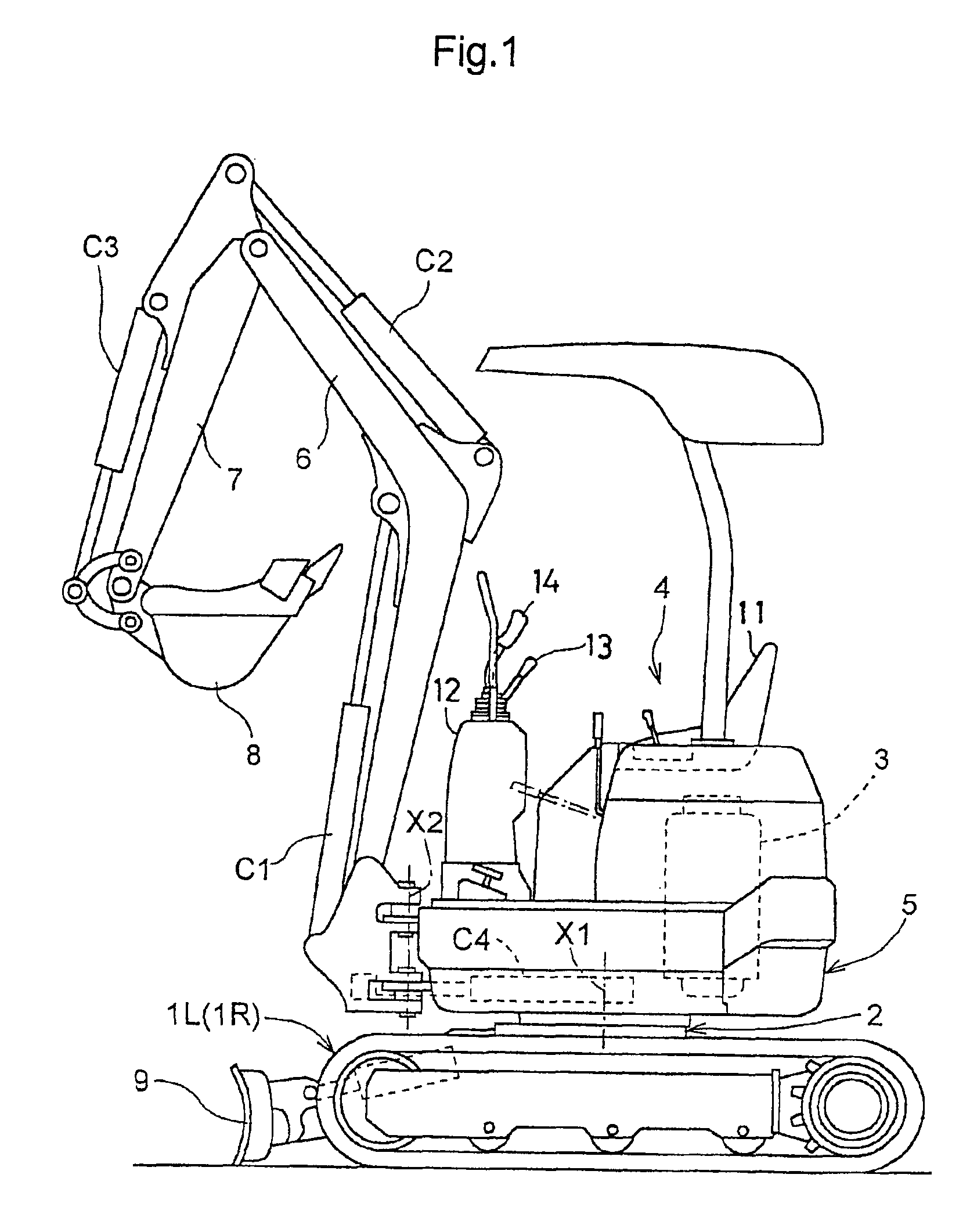
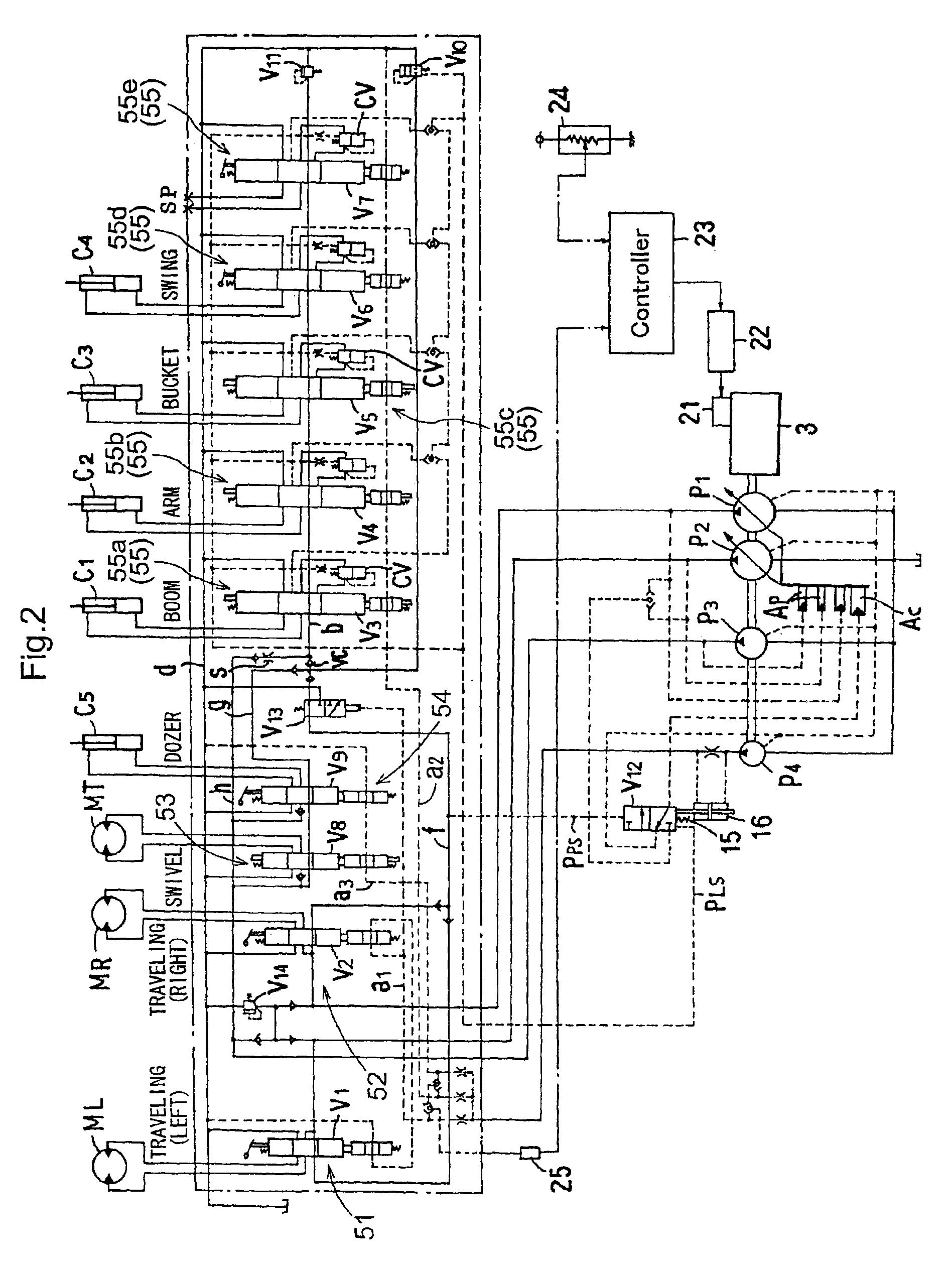
Hydraulic circuit for backhoe
InactiveUS7069674B2Reduce in sizeSimple processFluid couplingsServomotor componentsEngineeringSensing system
A hydraulic circuit for use with a backhoe includes first, second and third pumps; left and right traveling unit valve sections-receiving pressure oil from the first and second pumps independently of each other; a front implement valve section receiving combined pressure oil including oil from respective center oil passages of the left and right traveling unit valve sections; and a swiveling valve section receiving pressure oil from the third pump. A parallel oil passage having a restrictor extends parallel to a center oil passage of the swiveling valve section. The front implement valve section also receives pressure oil from the center oil passage of the swiveling valve section and the parallel oil passage. A load sensing system controls flow amounts of the first and second pumps according to a hydraulic load generated in a front implement operation.
Owner:KUBOTA LTD
Analyte sensor receiver apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20180153450A1Enhances and enables performanceReduces wearer weightEndoradiosondesCatheterGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Receiver apparatus for use with an analyte sensor, and methods of operation and manufacturing. In one embodiment, the analyte sensor is an implanted / implantable blood glucose sensor, including oxygen-based detector elements. The receiver apparatus is a wireless-enabled small form-factor device with limited functionality that can be easily worn or kept with the user on a continual basis, thereby obviating the need for a more fully featured receiver or smartphone for extended periods of time (e.g., one week). The exemplary oxygen based analyte sensor, with high degree of stability over time, enables the user to divorce themselves from the more fully functioned receiver or smartphone, since no external calibration of the sensor is required during the extended period. In one variant, the device is a lightweight wristband. Other variants include e.g., pendants, finger-worn rings, arm or head bands, skin patches, and even dental, subcutaneous, or prosthetic implants.
Owner:GLYSENS
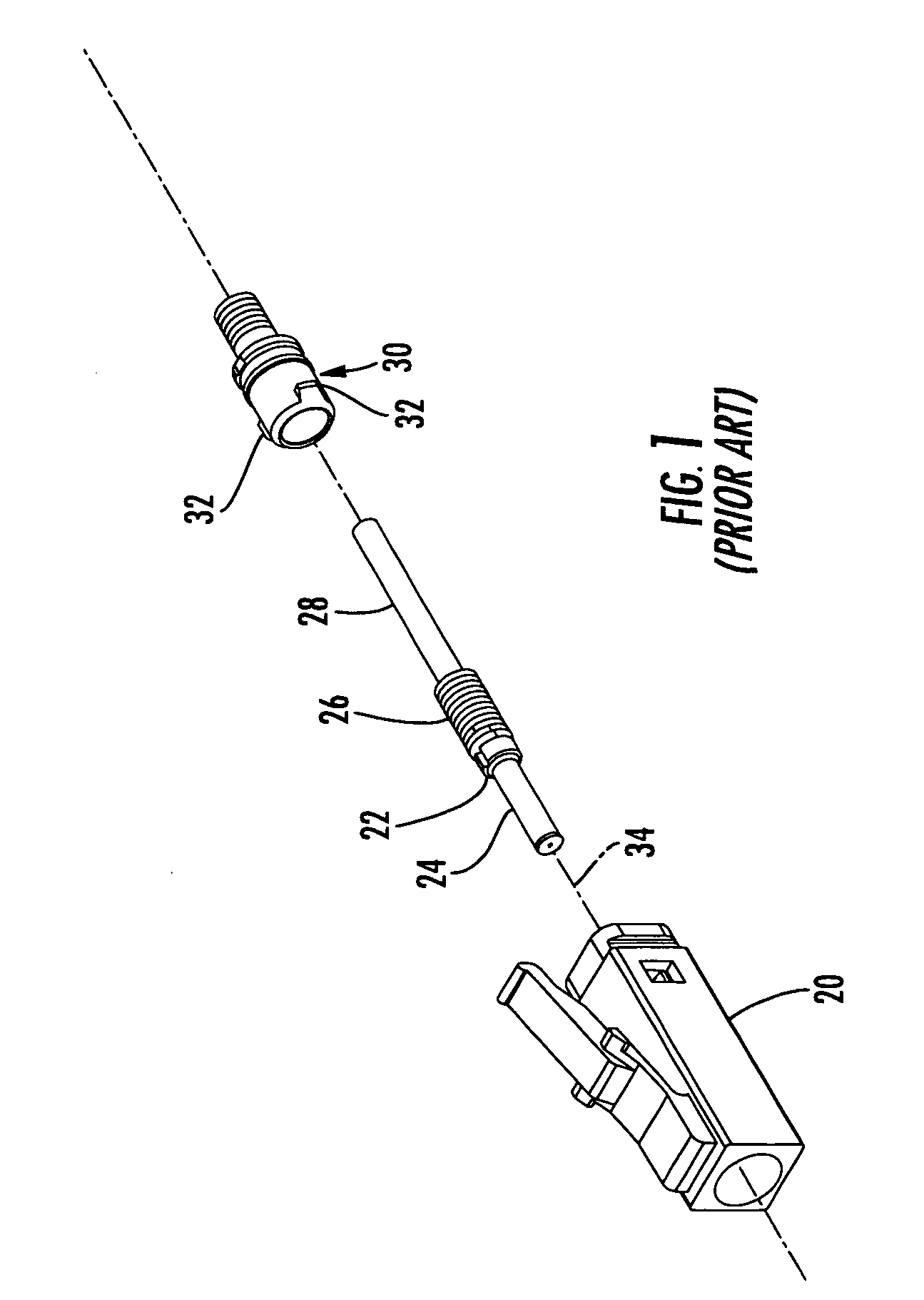
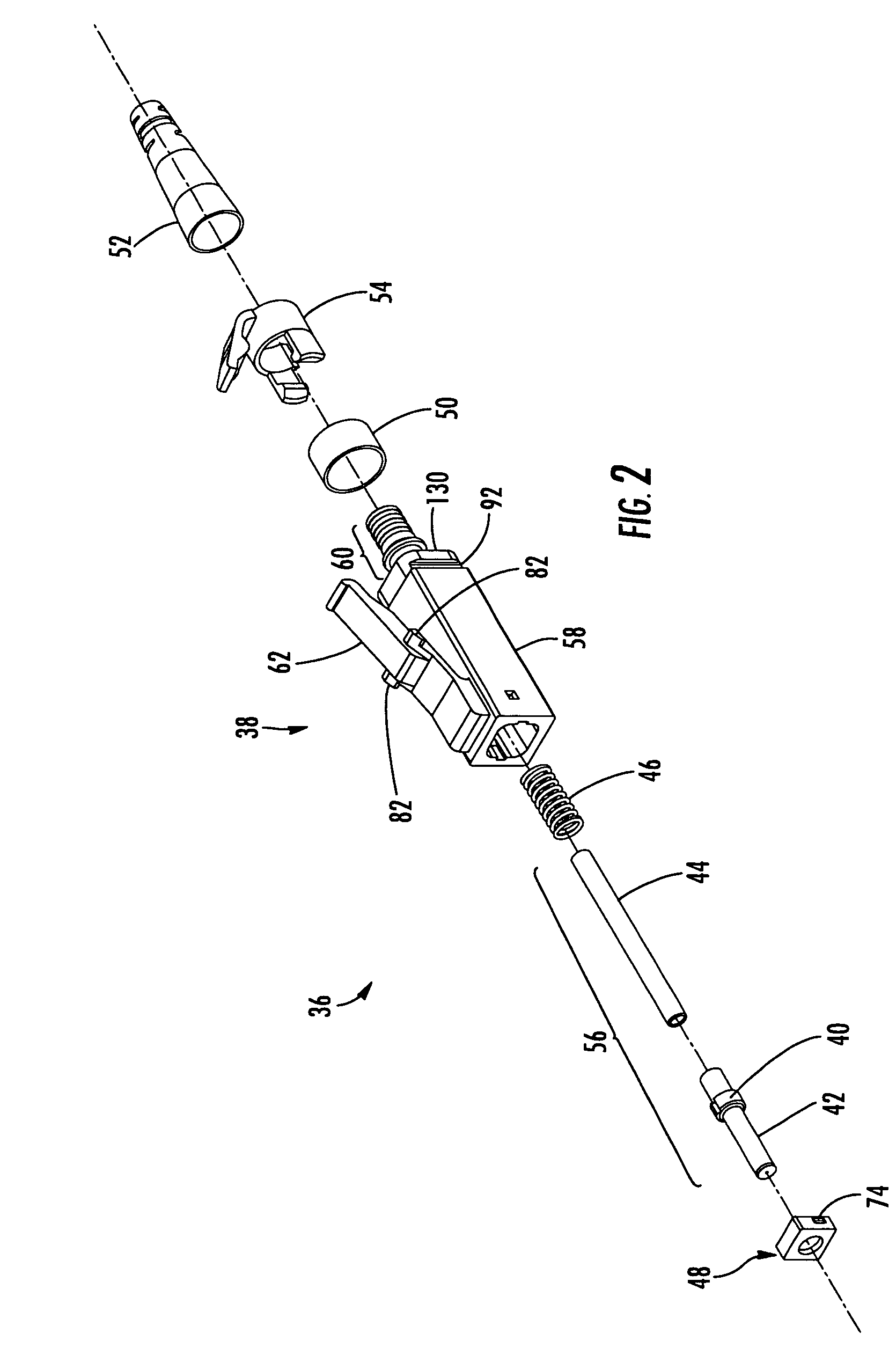
Optical fiber connector and method of assembly
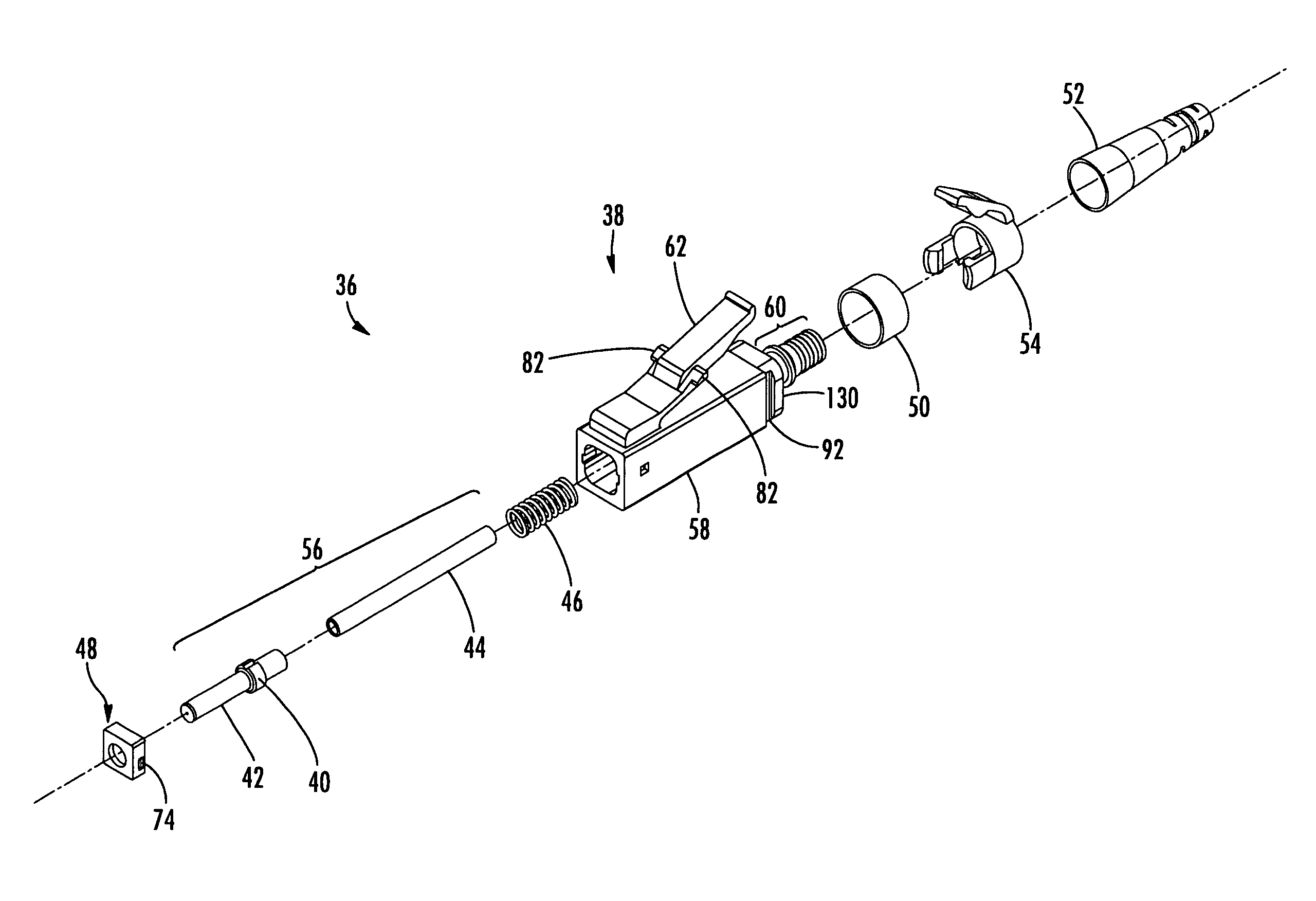
ActiveUS20070098331A1Small formMinimize snaggingCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical fiber connector
A method for assembling an optical fiber connector comprising providing a one piece housing comprising a tailpiece and a body defining a forward first end, a rearward second end and a passage extending longitudinally therebetween, inserting a spring element into the passage through the forward first end, inserting a subassembly comprising a ferrule, a ferrule holder and a lead-in tube into the passage through the forward first end, maintaining the spring within the passage between a shoulder defined by the one piece housing and a flange of the ferrule holder, and inserting a subassembly retainer into the passage through the forward first end.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
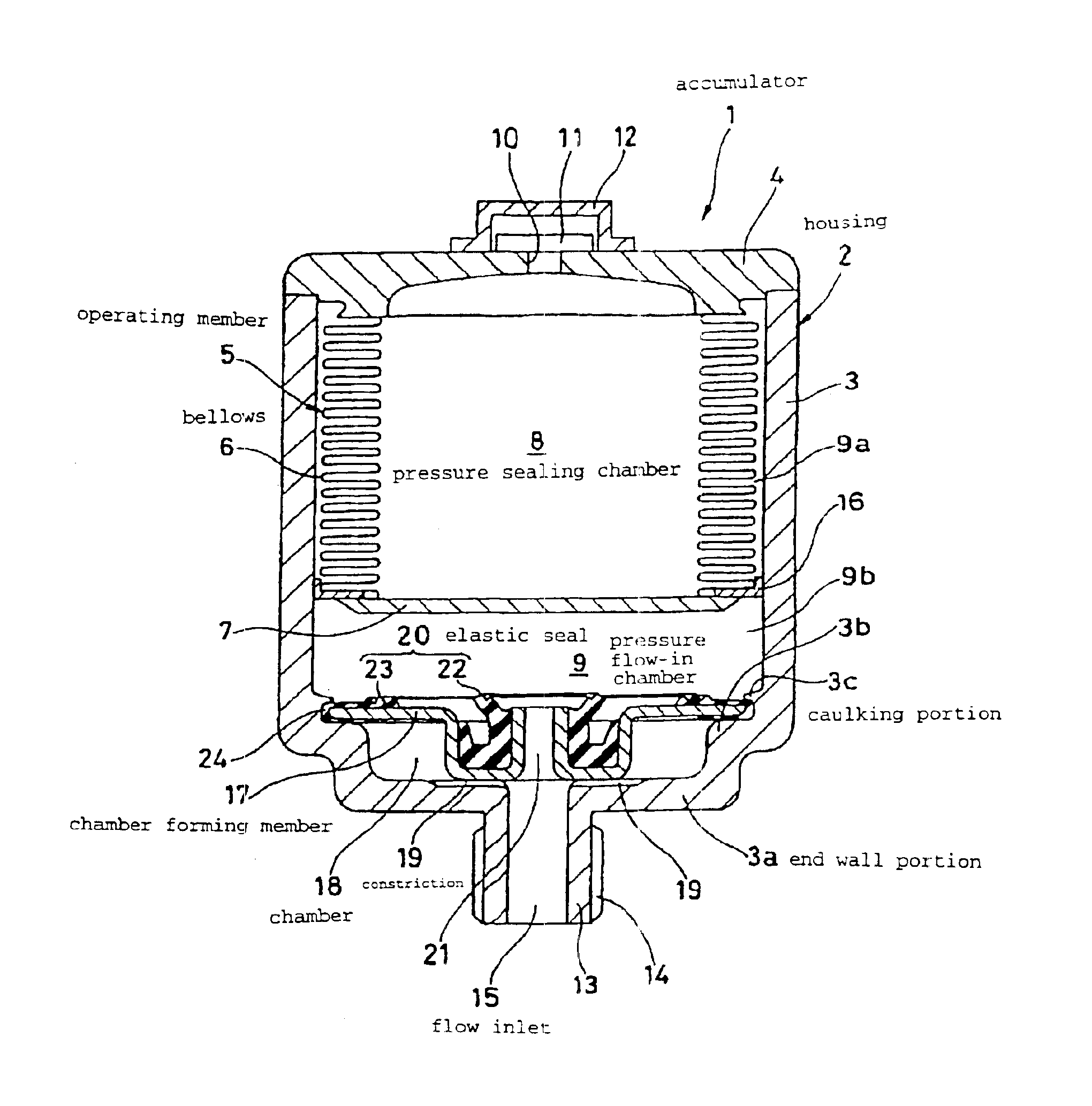
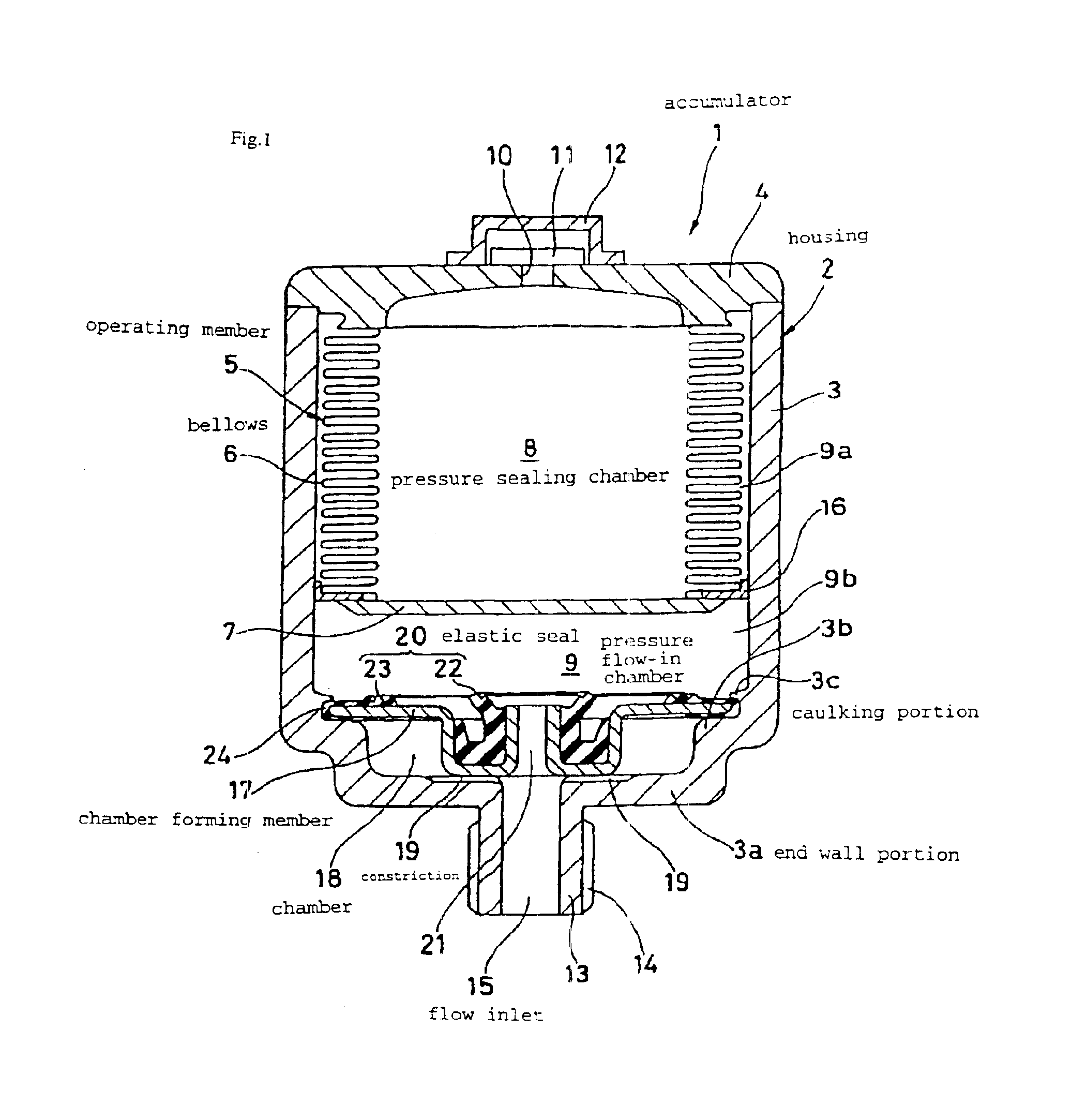
Accumulator
InactiveUS6848755B2Small formEasy to manufactureAccumulator installationsPipe elementsEngineeringHydraulic pressure
An accumulator (1) capable of suppressing a hydraulic pressure vibrating noise in the range of a sealed gas pressure or below and being reduced in size, wherein an operating member (5) having a bellows (6) is disposed in a housing (2) to partition the inside of the housing (2) into a pressure sealed chamber (8) and a pressure inflow chamber (9) and a fluid inlet (15) for leading pressure fluid from a system side to the pressure inflow chamber (9) is formed in the end wall part (3a) of the housing (2), a chamber forming member (17) is fixed to the inside of the housing (2), and a chamber (18) and a choke (19) are provided between the chamber forming member (17) and the end will part (3a) of the housing (2).
Owner:NOK CORP
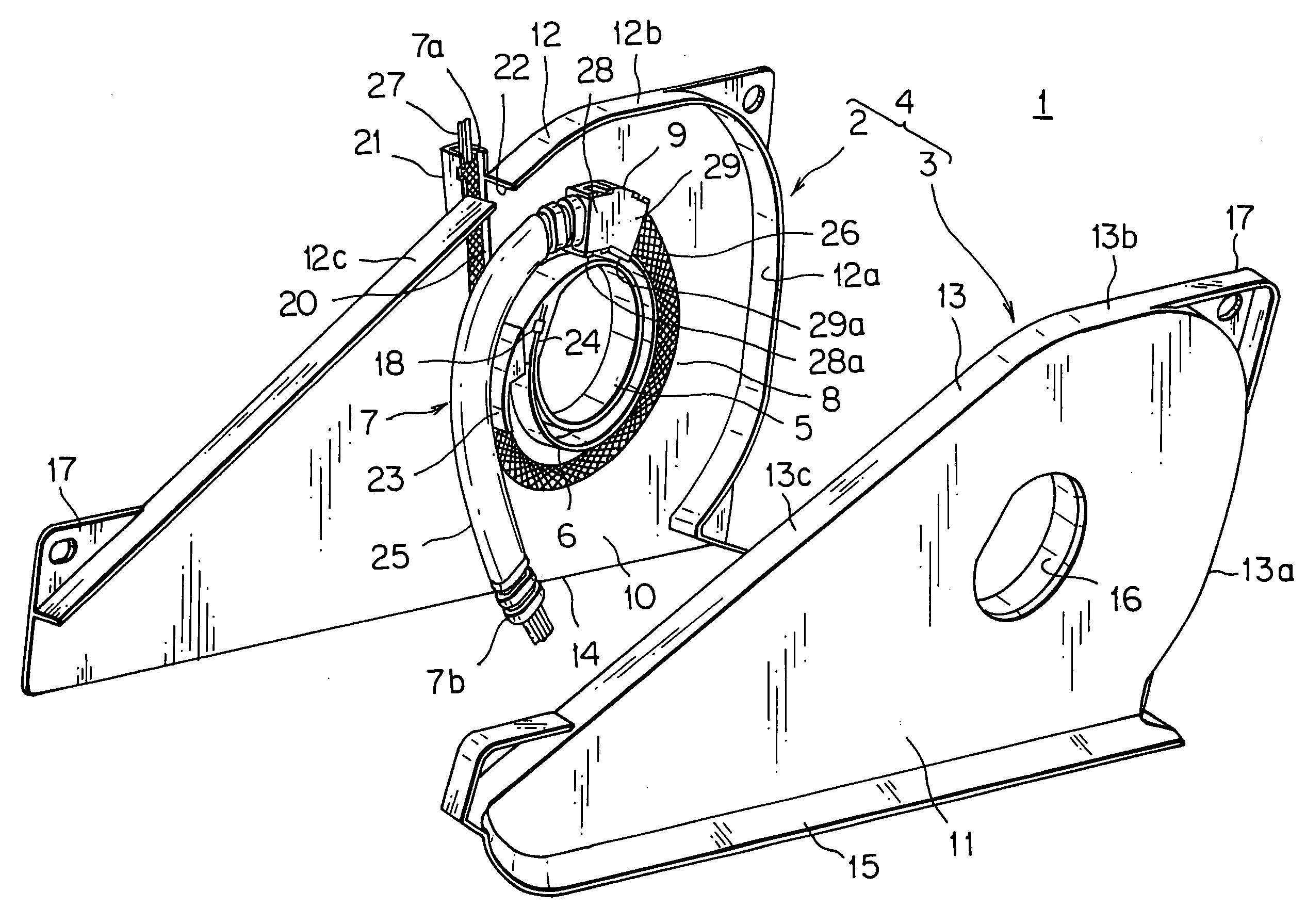
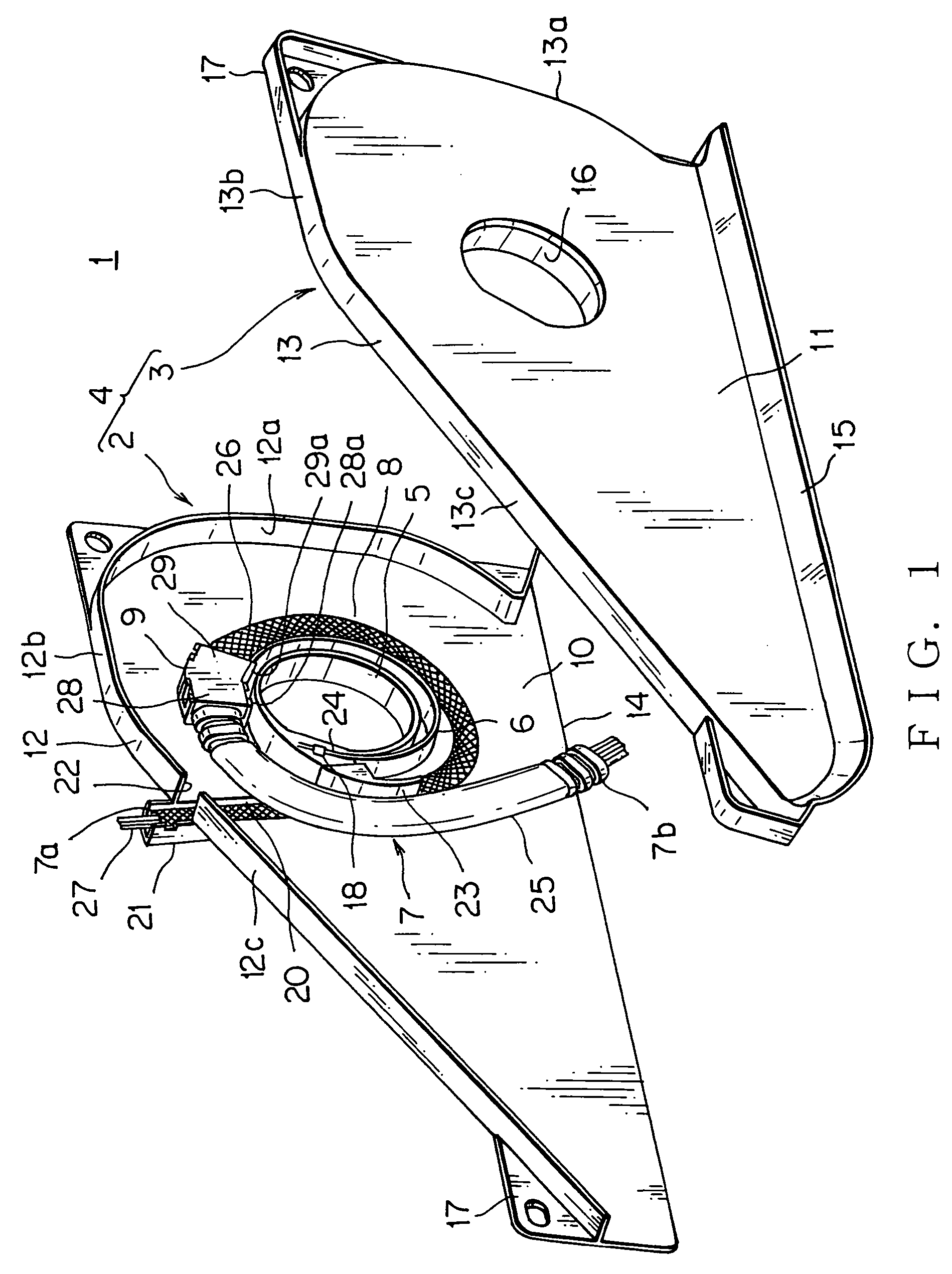
Electric supply apparatus
InactiveUS20060134970A1Small diameterIncrease flexibilityCable arrangements between relatively-moving partsInsulated cablesEngineeringCable harness
The present invention is to provide an electric supply apparatus having a wiring harness bent freely in a protector and prevented from outer interferences or rain water. An electric supply apparatus having a wiring harness includes a protector, a leaf spring disposed in the protector and a spring holder fixed to the leaf spring, wherein the spring holder holds one end portion of a flexible protective member of the wiring harness and one end portion of a rigid protective member of the wiring harness, and wherein the flexible protective member is disposed along the leaf spring and the rigid protective member is arranged from the spring holder to an opening for leading out the wiring harness. The flexible protective member has an insertion member at the one end portion, the insertion member is resin-molded with the flexible protective member and fixed to one side portion of the spring holder. The spring holder has protrusions penetrating into the flexible protective member and engaging with grooves of the rigid protective member.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
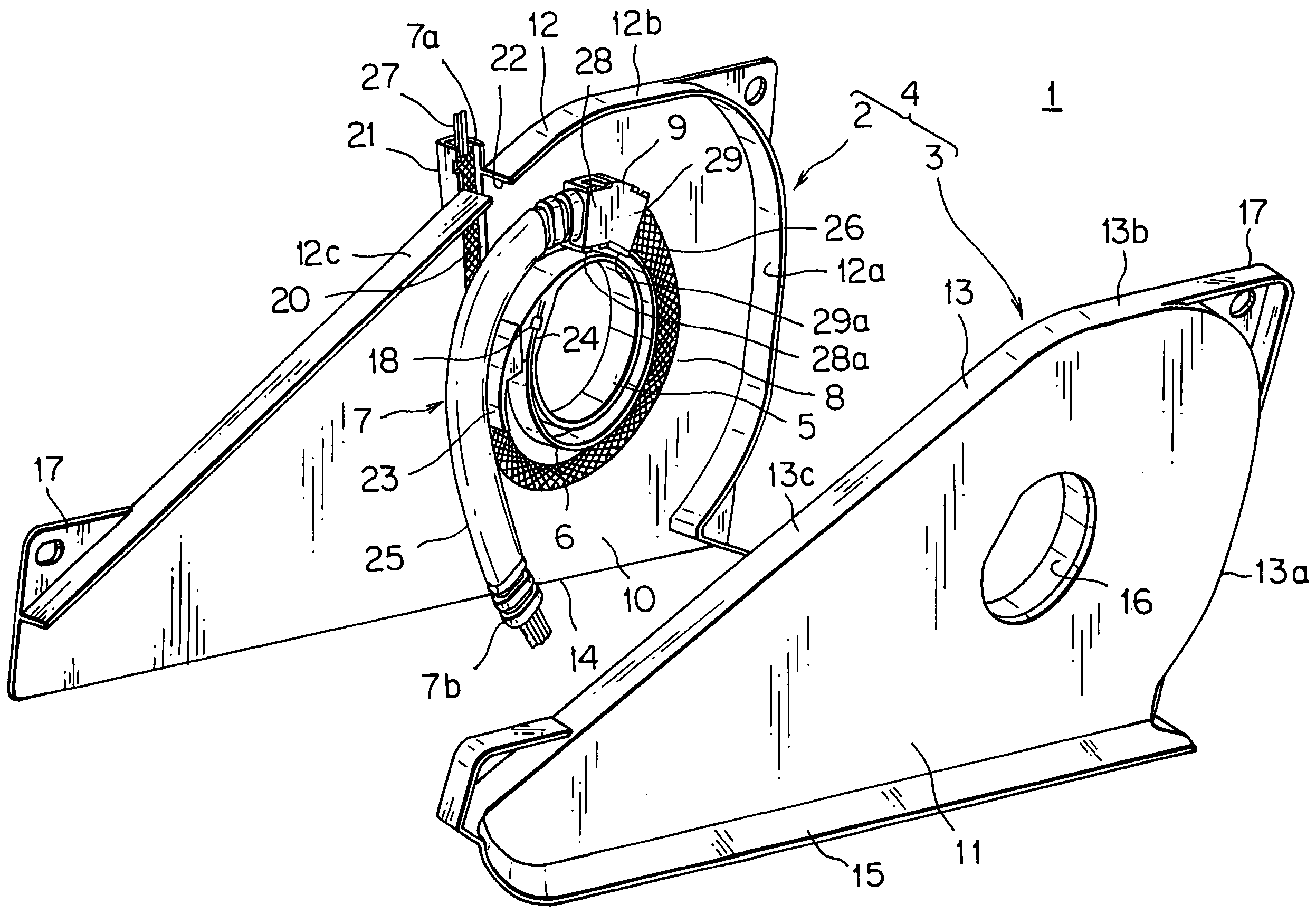
Electric supply apparatus
InactiveUS7297871B2Increase flexibilityLong lastingCable arrangements between relatively-moving partsInsulated cablesCable harnessLeaf spring
The present invention is to provide an electric supply apparatus having a wiring harness bent freely in a protector and prevented from outer interferences or rain water. An electric supply apparatus having a wiring harness includes a protector, a leaf spring disposed in the protector and a spring holder fixed to the leaf spring, wherein the spring holder holds one end portion of a flexible protective member of the wiring harness and one end portion of a rigid protective member of the wiring harness, and wherein the flexible protective member is disposed along the leaf spring and the rigid protective member is arranged from the spring holder to an opening for leading out the wiring harness. The flexible protective member has an insertion member at the one end portion, the insertion member is resin-molded with the flexible protective member and fixed to one side portion of the spring holder. The spring holder has protrusions penetrating into the flexible protective member and engaging with grooves of the rigid protective member.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Microwave sensor for measuring a dielectric property of a product
InactiveUS20050179443A1Prevent crashReduce the total massSafety devices for fibre treatmentResistance/reactance/impedenceVolumetric Mass DensityHigh field
The application relates to a microwave sensor for measuring a dielectric property, especially the density and / or moisture content of a product, having a microwave resonator, wherein a product introduced into the resonator interacts with a resonant microwave field generated in the resonator in order to determine suitable measured quantities, and is characterised in that at least two half-waves of the electric field are formed in the resonator in one direction, the product feed being effected in at least one region of high field intensity of one of the half-waves of the electric field.
Owner:TRUETZSCHLER GMBH & CO KG
Infrared sensor and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20100155601A1Small formSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReflective layerPhysics
An infrared sensor and a method of fabricating the same are provided. The sensor includes a substrate including a reflection layer and a plurality of pad electrodes, an interdigitated sensing electrode connected to the pad electrode and formed to be spaced apart from the reflection layer by a predetermined distance and a sensing layer formed on the sensing electrode and having an opening exposing a portion in which an interdigitated region of the sensing electrode connected to one pad region is separated from the sensing electrode connected to the other pad electrode. Therefore, the sensor has an electrode in a very simple constitution, and a sensing layer divided into rectangular blocks, so that current that non-uniformly flows into the electrode can be removed. Accordingly, the sensor in which current of the sensing layer can be uniformly flown, and noise is lowered can be implemented.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
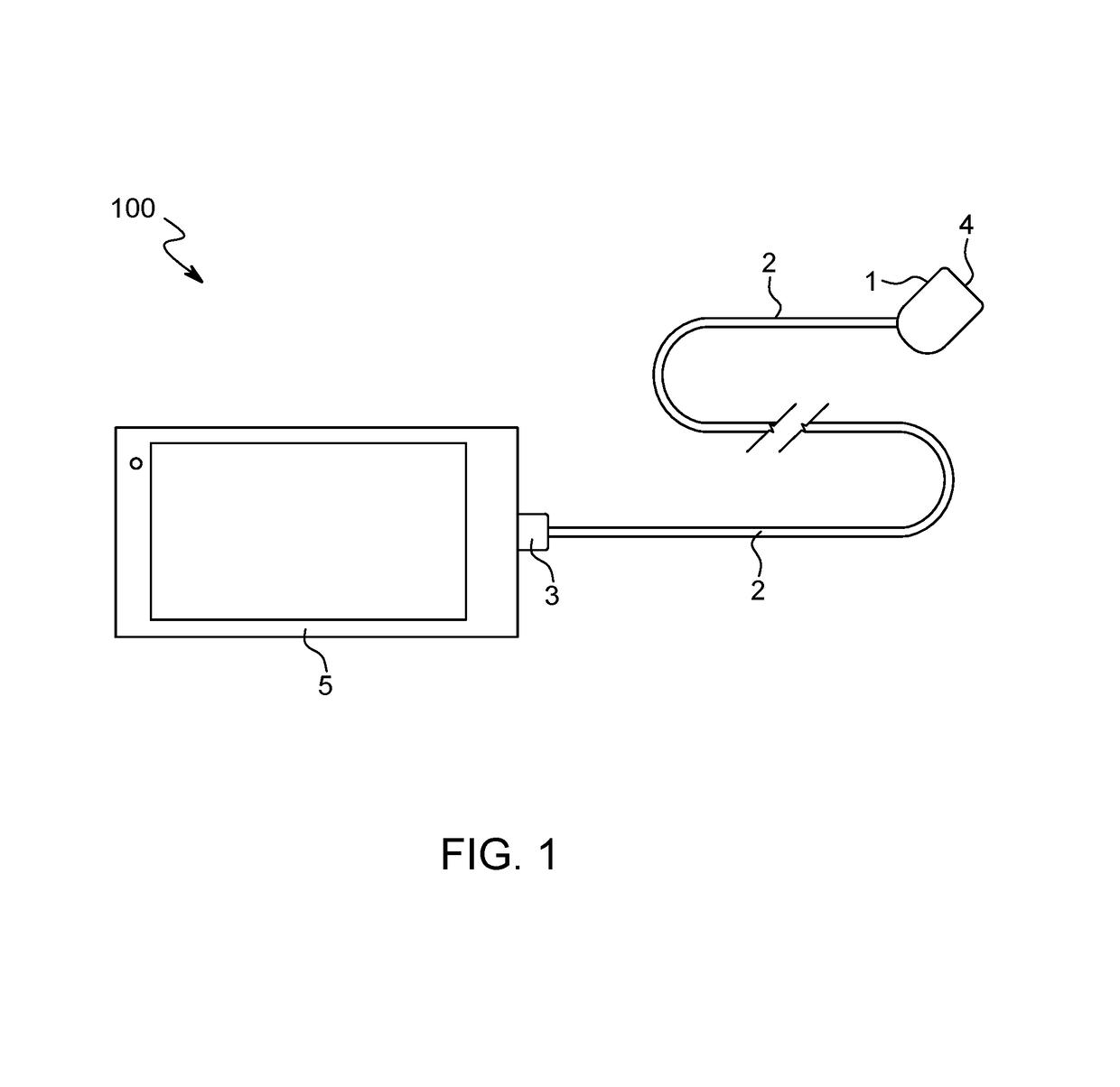
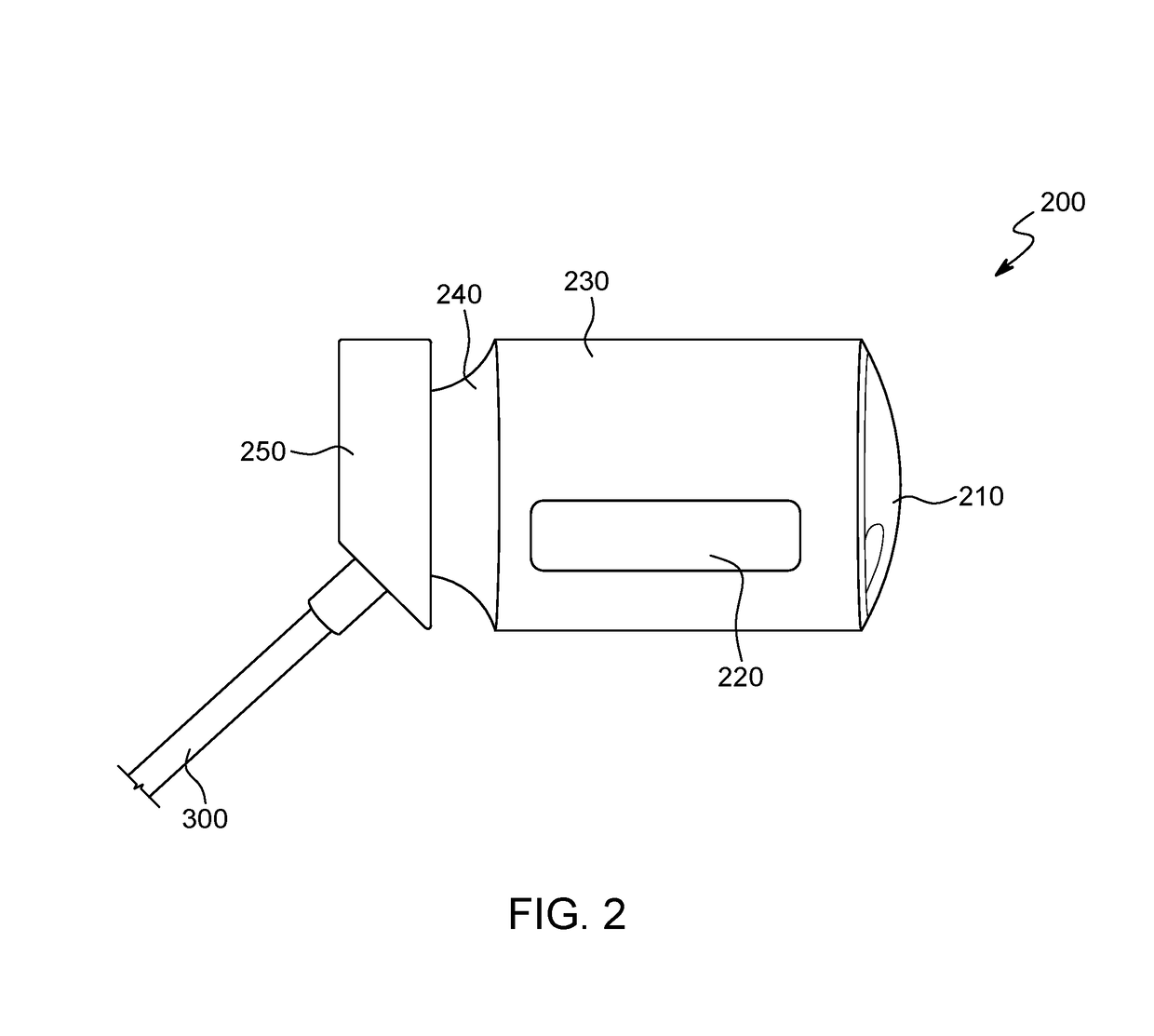
Portable Camera System
ActiveUS20170272640A1Selective couplingEasy to operateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensExternal camera
An operationally dependent external camera system for use with a portable computer device. The system includes a portable computer device, a camera, and an operation cord. The camera may include a lens, image sensor, circuit board, microphone, and control unit. The operation cord is coupled between the camera and the portable computer device to continuously transmit both data and electrical power between the portable computer device and the camera thereby making the camera operationally dependent on the portable computer device.
Owner:OPKIX INC
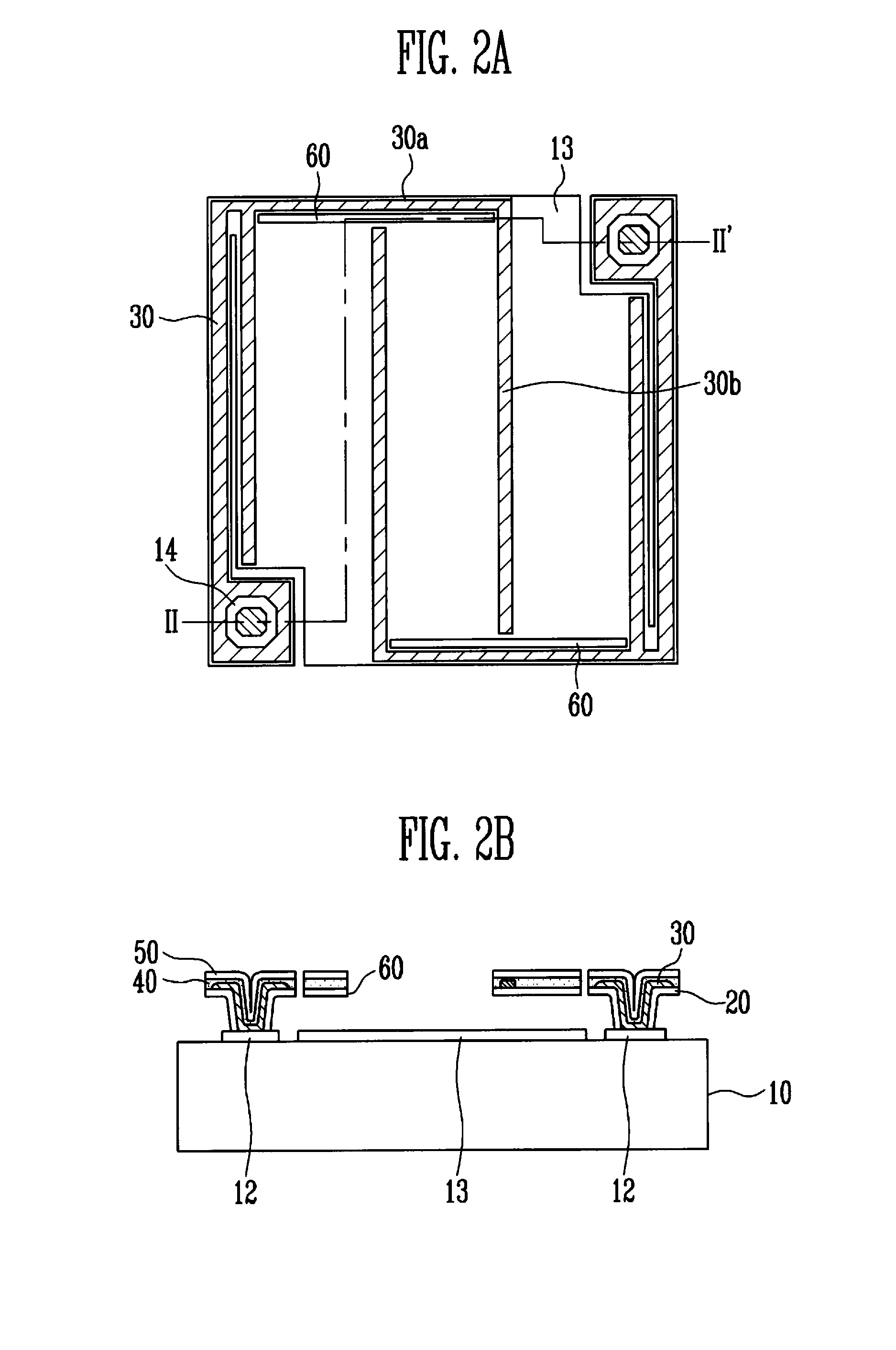
Circuit board and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050199420A1Small formSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorAmorphous phase
In a circuit board according to the present invention, on a substrate, in at least a portion of a phase change layer including a phase change material that is capable of changing alternately between an electrically insulating state and an electrically conductive state, a conductive path is formed that has been put into an electrically conductive state by a phase change in the phase change layer, wherein the phase change material includes a chalcogenide semiconductor, changes between the electrically insulating state and the electrically conductive state by irradiation of laser light, goes into the electrically conductive state in a crystalline phase, and goes into the electrically insulating state in an amorphous phase. In this way, a conductive path is formed by irradiating laser light onto a phase change layer using phase change in a phase change layer formed from a phase change material that is capable of changing alternately between an electrically insulating state and an electrically conductive state, and therefore very small-dimension minute vias and conductors can be formed. Furthermore, subsequent repair, rework, or trimming also is easy.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Motor and electric power steering system
InactiveUS20070272472A1Small sizeSmall air gapElectrical steeringSupports/enclosures/casingsElectric power steeringElectric power system
The invention provides a motor including: a cylindrical motor case having a bottom that supports an outer circumferential surface of a stator core by an inner circumferential surface thereof; and a bracket that supports an output shaft side bearing and closes an opening of the motor case; wherein the stator core is press-fitted into the motor case from the opening such that a part of the stator core is exposed from the motor case, and a part of the stator core that is not press-fitted to the motor case forms a sliding fitting wall capable of providing a sliding fitting connection with the bracket.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Magnet with electromagnetic coil/impedance/sensor element
InactiveUS7224161B2Small formSmall volumeMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleUltimate tensile strengthElectrical current
A magneto impedance sensor element with electromagnetic coil comprised of: a terminal board on which an extended groove which extends in one direction has been formed; an electromagnetic coil, made with one part of the coil formed in a spiral shape inside the extended groove in the terminal board, and joined to each tip of that coil the other part of the coil placed across the top of the groove; insulating material placed in the extended groove on the terminal board; and a magnetic sensitive body inserted within the insulating material, to which either high frequency or pulse electic current is applied. When either high frequency or pulse electrical current is applied to the magnetic sensitive body, voltage is output from the above electromagnetic coil in response to the intensity of the external magnetic field which is generated in the electromagnetic coil.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
Novel large-span assembly type hollow groined floor system
The invention discloses a novel large-span assembly type hollow groined floor system which is composed of a plurality of blocks of prefabricated floors capable of being spliced and concrete post-cast strips located between adjacent prefabricated floors. Each prefabricated floor comprises a top plate, a base plate, longitudinal ribbed beams and transverse ribbed beams, wherein the longitudinal ribbed beams and the transverse ribbed beams are arranged between the top plate and the base plate. The top plates and the base plates are parallel surface plates. The novel large-span assembly type hollow groined floor system effectively solves the problem of the traditional assembly type integrated floors of small span, poor rigidity and large concrete consumption. The concrete consumption at the connection positions of all the prefabricated floors is small, template consumption is small, and the prefabricated floors are few in shapes, convenient to construct, economical and practical. The integral floor system formed by assembling all the prefabricated floors is of a hollow groined structure and has the advantages of bidirectional force transfer, large rigidity, good shock resistance and small self weight and thickness. Light thermal insulation materials are filled in the hollow positions of the floor system so that the heat retaining property of the floor system is improved. Pipes can be arranged in the floor system in a penetrating mode without additional equipment layers, and therefore space is saved and storey clear height is increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
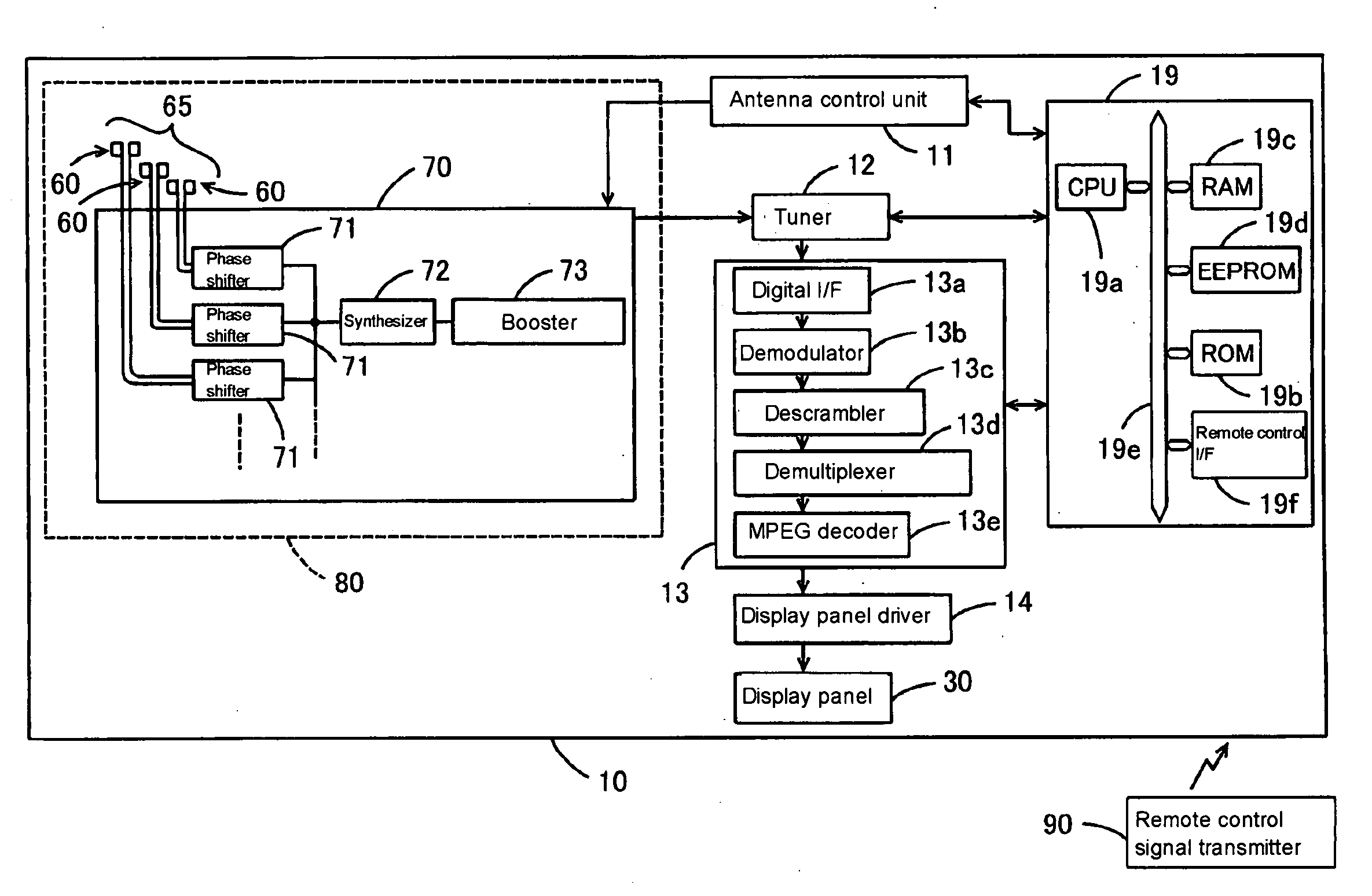
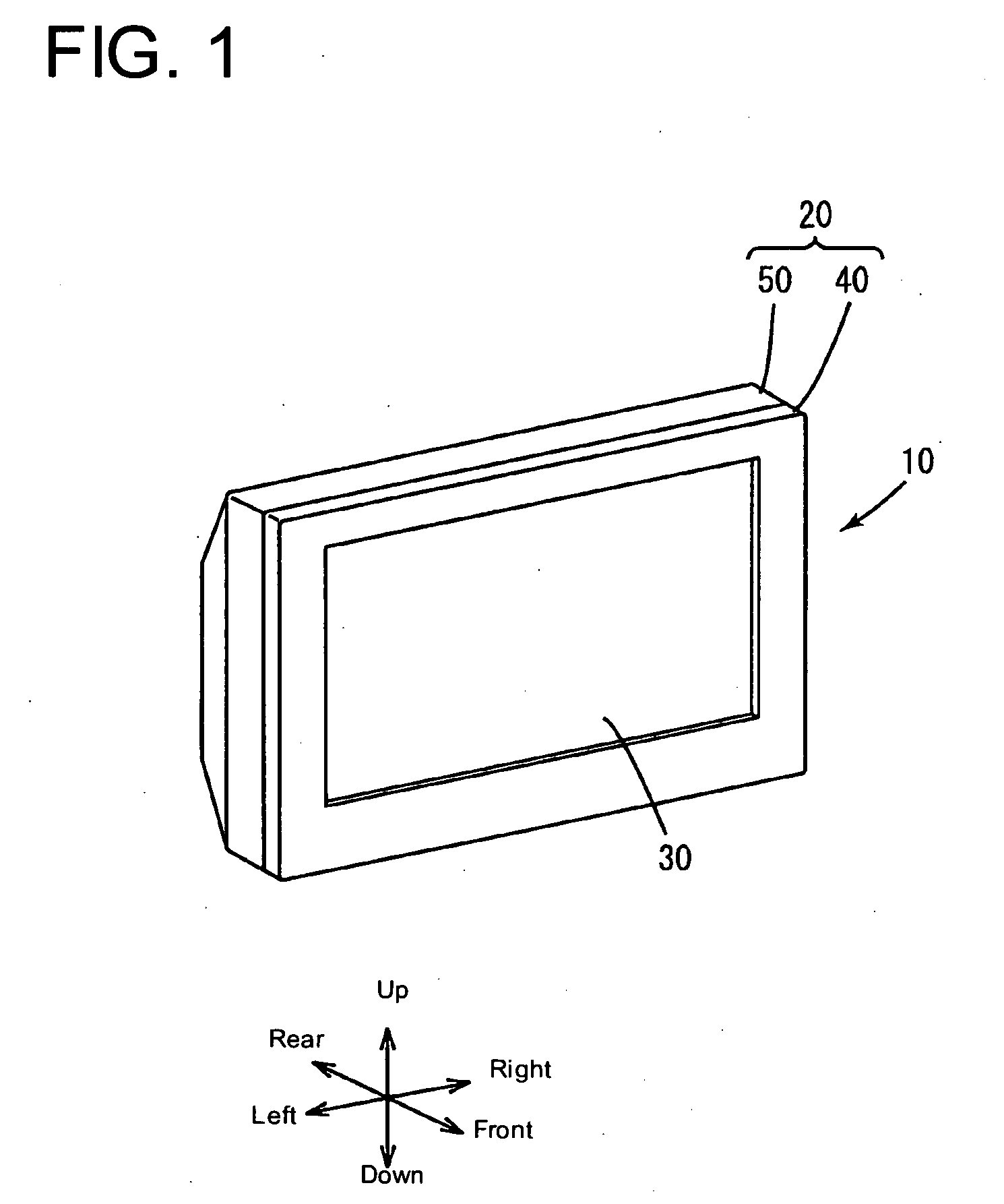
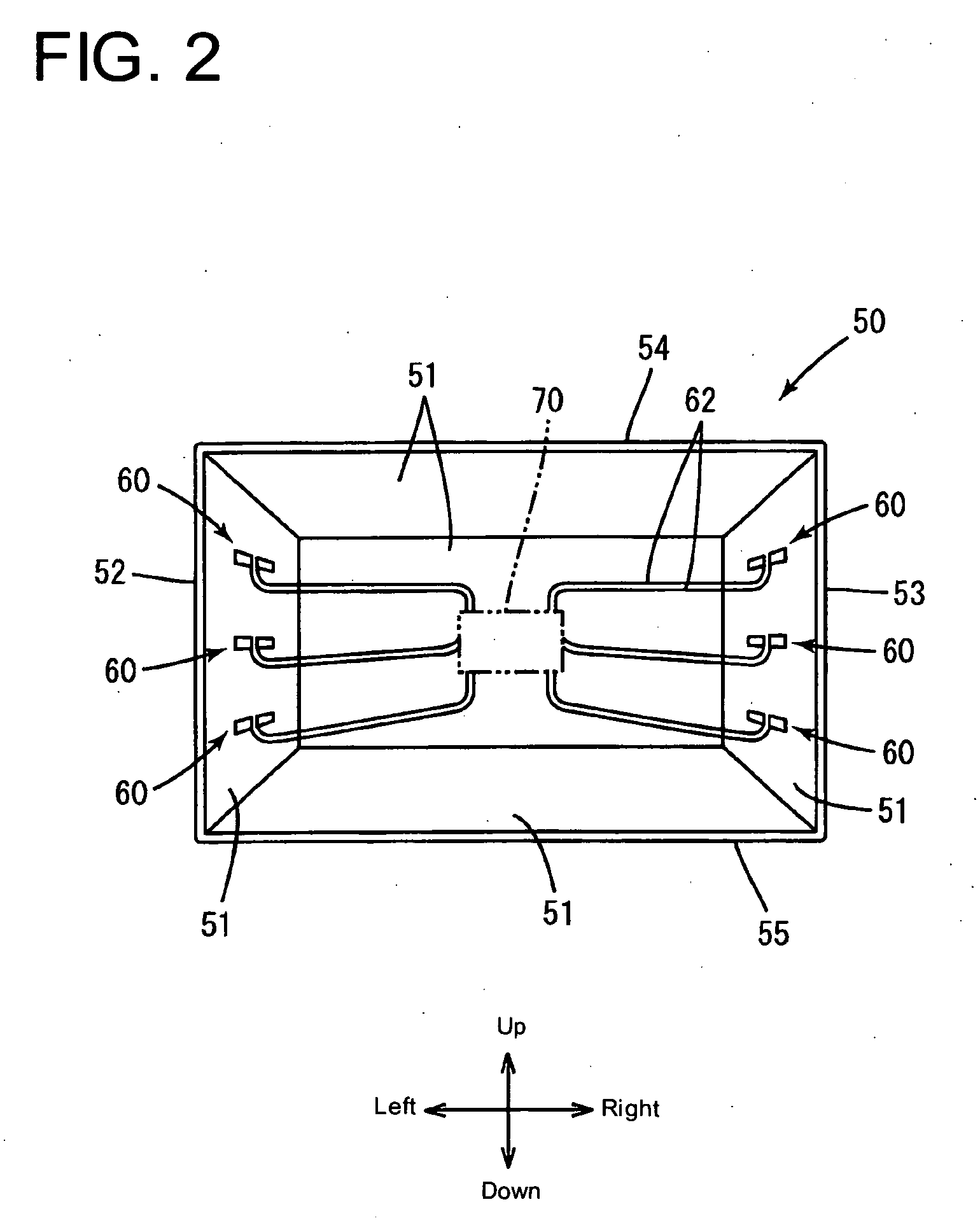
Television receiver and liquid crystal television receiver
InactiveUS20090096934A1Increase freedomSatisfactory sensitivityTelevision system detailsSpatial transmit diversityTelevision receiversEngineering
A television receiver having an antenna function for receiving broadcast signals includes an antenna group having plural variable directivities and including plural antennas formed in plural parts on inner and outer surfaces of walls of a cabinet or nonmetallic surfaces of component parts arranged in the cabinet so as to conform to the shapes of the corresponding surfaces, respectively, and a switching control unit capable of specifying a directivity for the antenna group to receive broadcast signals by the antenna group.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRO-COMMUNICATIONS +2
RFID tag antenna and RFID tag
InactiveUS20080122628A1Reduce variationShorten the lengthRadiating elements structural formsAntenna feed intermediatesTag antennaElectrical conductor
A first pattern is constituted by a pair of conductors each of which comprises only one turn of bent part. An edge part of one side of each of the pair of conductors is configured as a power feeding point. AC coupling section is formed between the power feeding points. And a second pattern is placed opposite to the first element by sandwiching a dielectric body.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Label printer
ActiveUS7900675B2Small formAdjustable positionLabelling non-rigid containersMechanical working/deformationEngineeringRelease liner
Owner:LINTEC CORP
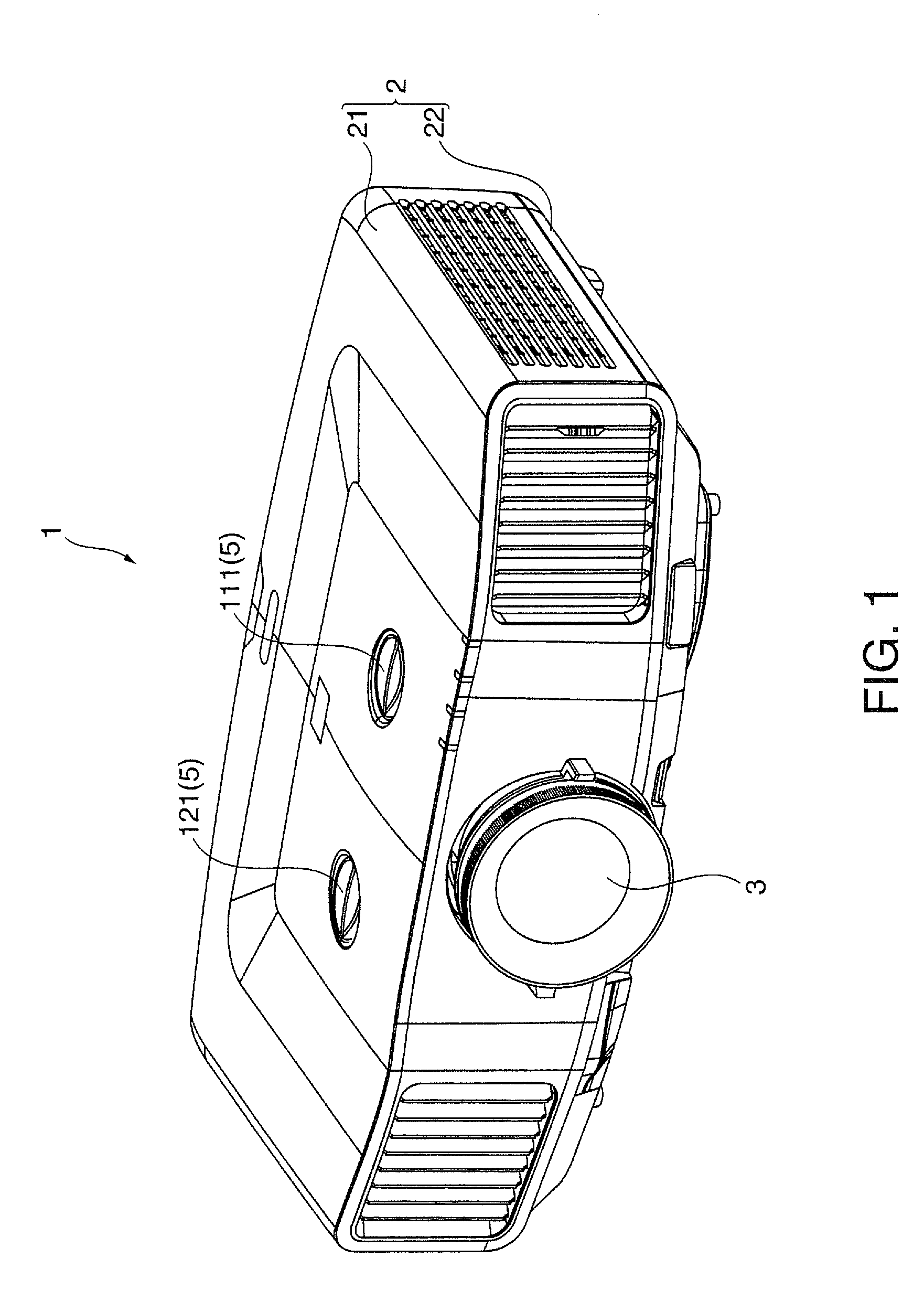
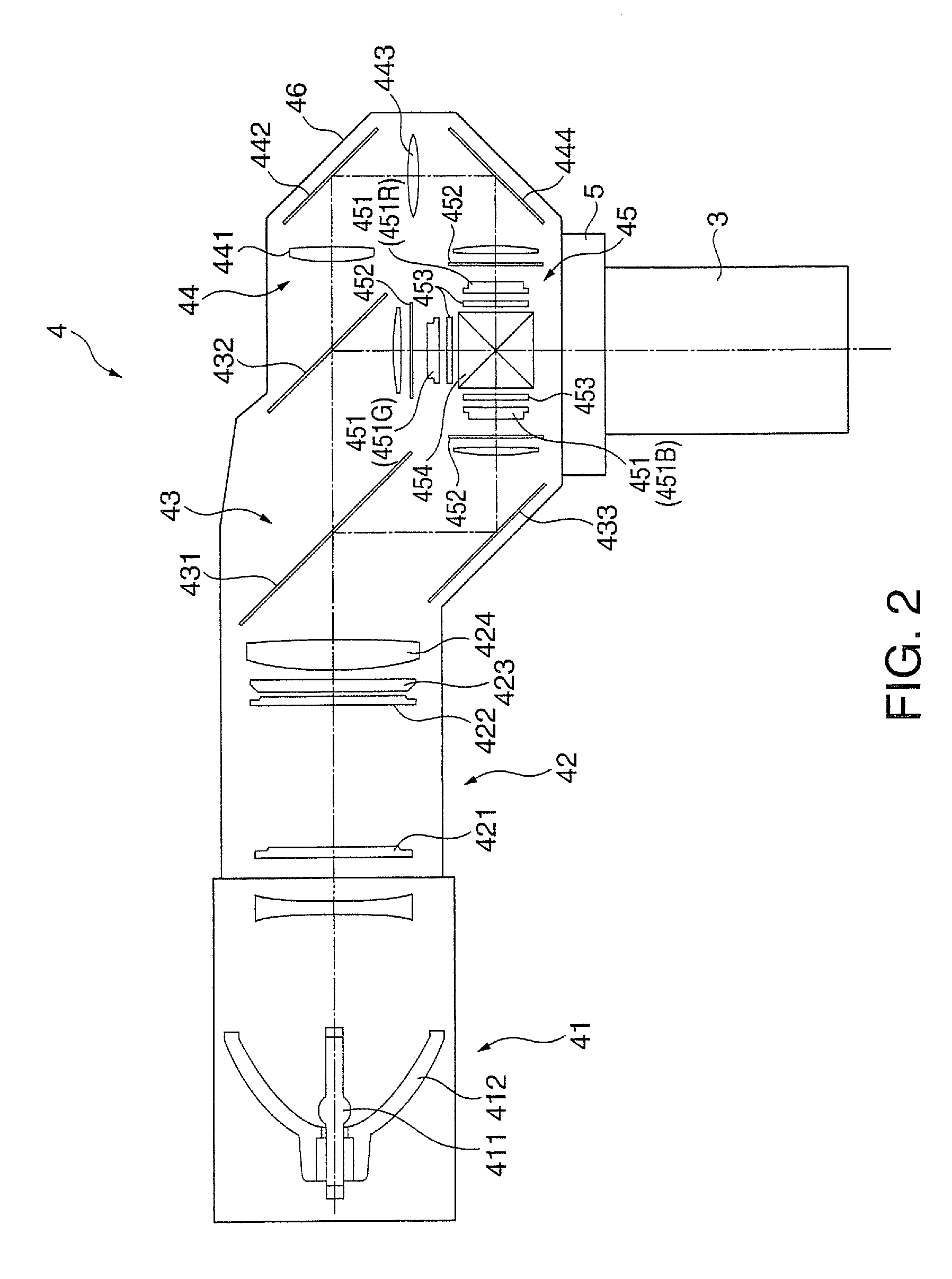
Projector
ActiveUS20090219505A1Easy to replaceImprove convenienceProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCouplingPhysics
A projector includes a projection optical device that magnifies and projects image light and a projection position adjusting device that moves the projection optical device in a plane orthogonal to a projecting direction and adjusts a projection position of the projection optical device. The projection position adjusting device includes a fixed member fixed in the projector, a first moving plate that supports the projection optical device and moves in a first axial direction and a second axial direction orthogonal to each other in the plane orthogonal to the projecting direction, a second moving plate that is interposed between the fixed member and the first moving plate, engages with the first moving plate, and moves in the second axial direction together with the first moving plate, adjusting and driving units that move the first moving plate and the second moving plate, and plural coupling members that movably couple the first moving plate to the fixed member. A coupling through hole of a stepped shape, which has a diameter dimension on a side close to the first moving plate smaller than that on a side separated from the first moving plate and has a step, is formed in the fixed member. Each of the coupling members includes a connecting member that is formed in a stepped shape, which has a sectional area on the other end side smaller than that on the one end side and has steps, and the other end of which is connected to the first moving plate in a state in which the connecting member is inserted in the coupling through hole and an interposed member that is arranged between the step of the connecting member and the step of the coupling through hole, urges the step of the connecting member and the step of the coupling through hole in directions away from each other, and brings the first moving plate into contact with the fixed member.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Magnet with electromagnetic coil/impedance/sensor element
InactiveUS20050116708A1Small formSmall volumeMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleUltimate tensile strengthElectrical current
A magneto impedance sensor element with electromagnetic coil comprised of: a terminal board (1) on which an extended groove (11) which extends in one direction has been formed; an electromagnetic coil(3), made with one part of the coil (31) formed in a spiral shape inside the extended groove (11) in the terminal board (1), and joined to each tip of that coil the other part of the coil (32) placed across the top of the groove; insulating material (4) placed in the extended groove (11) on the terminal board(1); and a magnetic sensitive body (2) inserted within the insulating material (4), to which either high frequency or pulse electic current is applied. When either high frequency or pulse electrical current is applied to the magnetic sensitive body, voltage is output from the above electromagnetic coil in response to the intensity of the external magnetic field which is generated in the electromagnetic coil.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
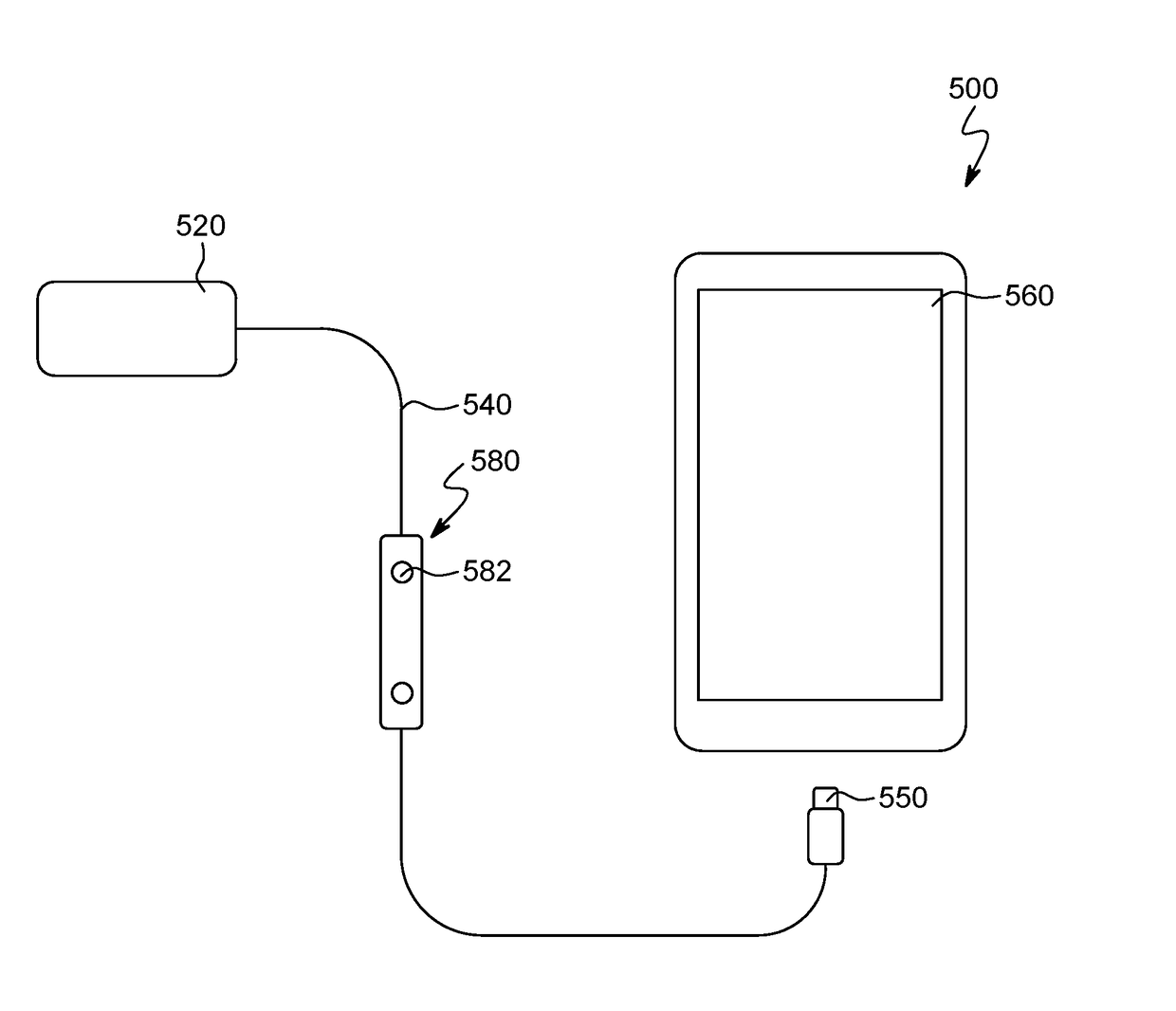
Powerline Control Interface for Frequency and Amplitude Modulation Transmitter
InactiveUS20120314781A1Minimum power consumptionReducing supply powerTransmission/receiving by modifying power source wavePower distribution line transmissionComputer hardwareControl signal
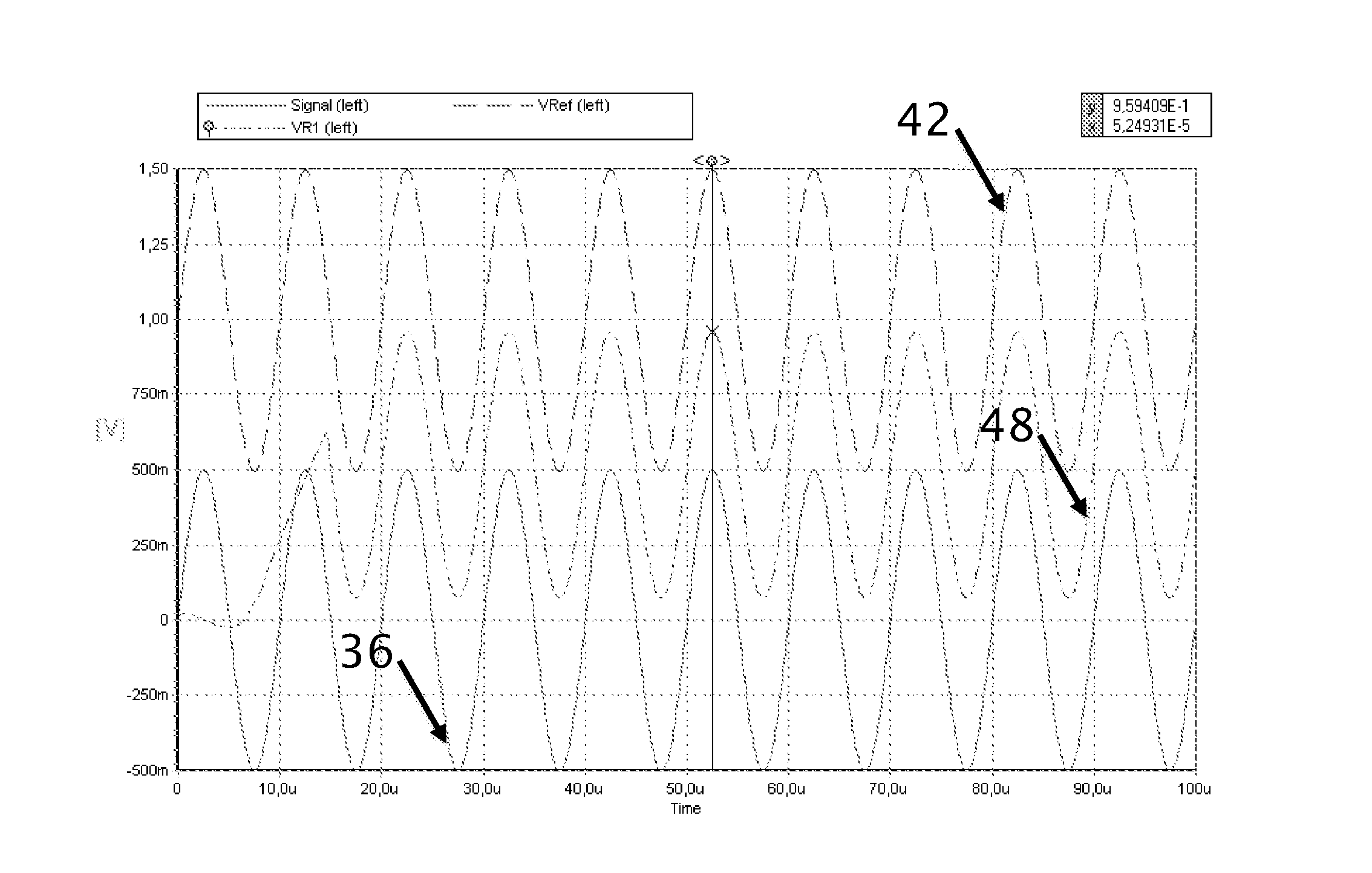
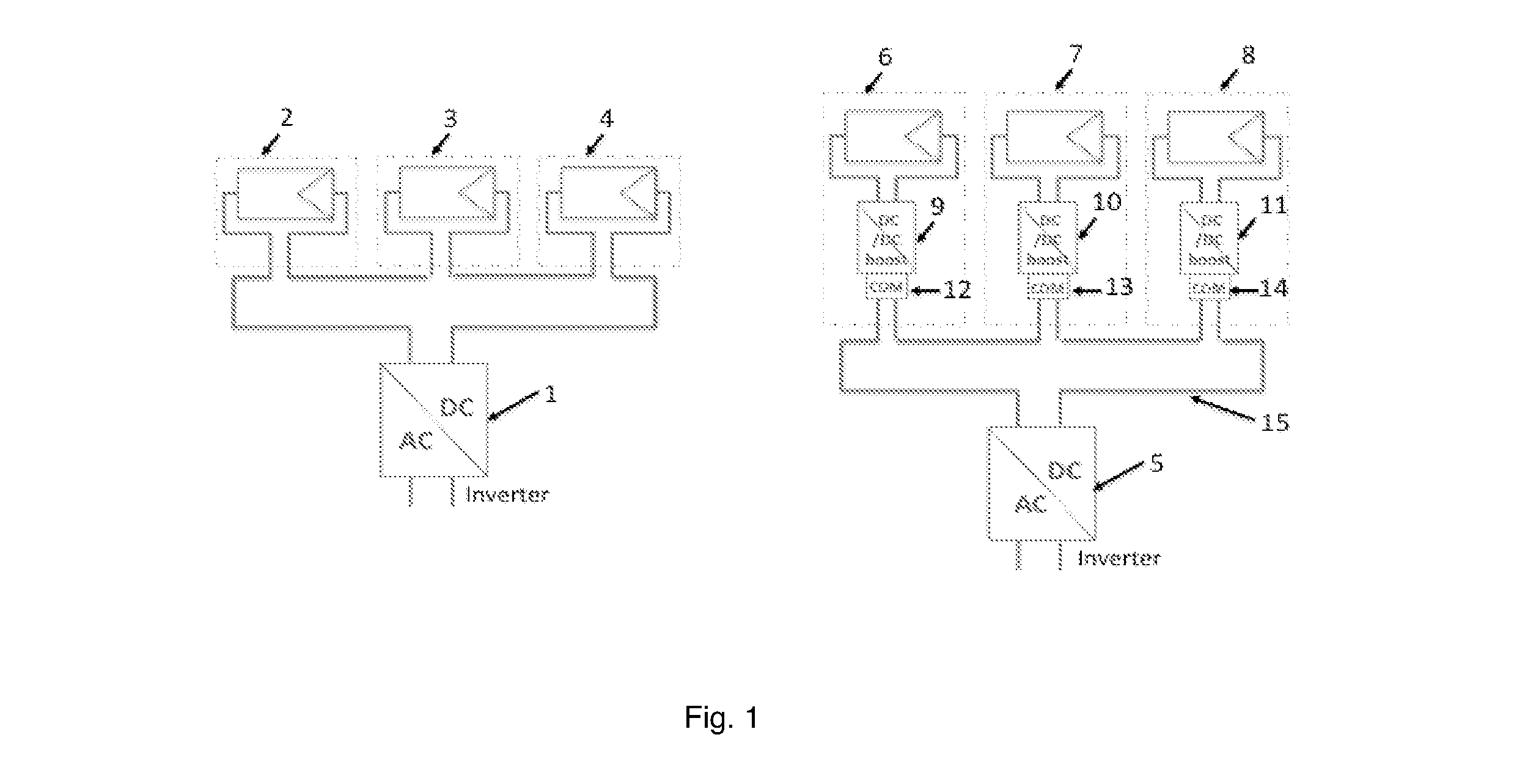
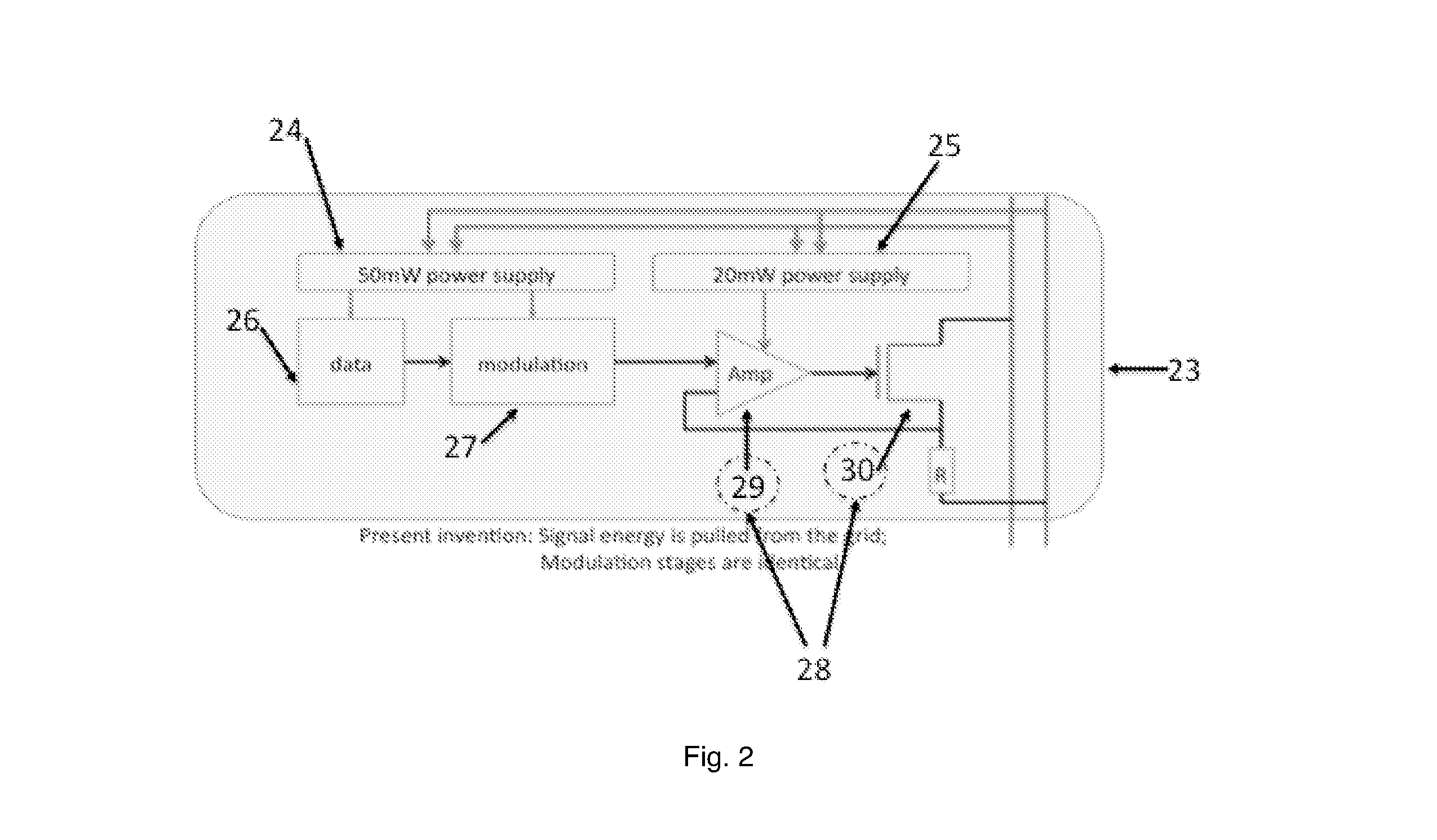
An apparatus is disclosed where a Powerline interface is used to transmitting data into the powerline grid network, where the powerline interface is pulling the required transmit energy from the power grid network, where the powerline interface is transmitting data using standard modulation such as ASK, FSK, S-FSK, QPSK, OFDM, etc. . . where the transmit data are passed on to the powerline interface by the use of an adapation stage, where a “control signal” is used to enable the transmitting of data by providing enough voltage to polarize the FET used in the control path.
Owner:BOIVIN DIDIER +1
Burners and combustion apparatus for carbon nanomaterial production
InactiveUS7279137B2Improve flame stabilityWider rangeMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesChemistryVapor pressure
The invention provides improved burners, combustion apparatus, and methods for carbon nanomaterial production. The burners of the invention provide sooting flames of fuel and oxidizing gases. The condensable products of combustion produced by the burners of this invention produce carbon nanomaterials including without limitation, soot, fullerenic soot, and fullerenes. The burners of the invention do not require premixing of the fuel and oxidizing gases and are suitable for use with low vapor pressure fuels such as those containing substantial amounts of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. The burners of the invention can operate with a hot (e.g., uncooled) burner surface and require little, if any, cooling or other forms of heat sinking. The burners of the invention comprise one or more refractory elements forming the outlet of the burner at which a flame can be established. The burners of the invention provide for improved flame stability, can be employed with a wider range of fuel / oxidizer (e.g., air) ratios and a wider range of gas velocities, and are generally more efficient than burners using water-cooled metal burner plates. The burners of the invention can also be operated to reduce the formation of undesirable soot deposits on the burner and on surfaces downstream of the burner.
Owner:FRONTIER CARBON CORP
Structure for mounting heat sink, and heat sink mounted using the structure
ActiveUS8995132B2Efficient use ofSmall formSnap fastenersDigital data processing detailsEngineeringHeat spreader
A new mounting structure is provided in which, when a heat sink is mounted (fixed) on a circuit board using a spring member, an anchor for fixing the spring member is formed in a very small size in plan view. In the present invention, at least one anchor for mounting a heat sink body on a circuit board is set in a projected state on the heat sink body side and both ends of a spring member are each directly or indirectly attached to an anchor, whereby the heat sink body is mounted on the circuit board. In the anchor, a main body section projecting on the circuit board is formed in a substantially circular shape or a polygonal shape. When the spring member is attached to the anchor, the spring member is attached to an attaching section in an externally fit state.
Owner:KATAOKA TETABUJI +1
Reinforced hose assembly
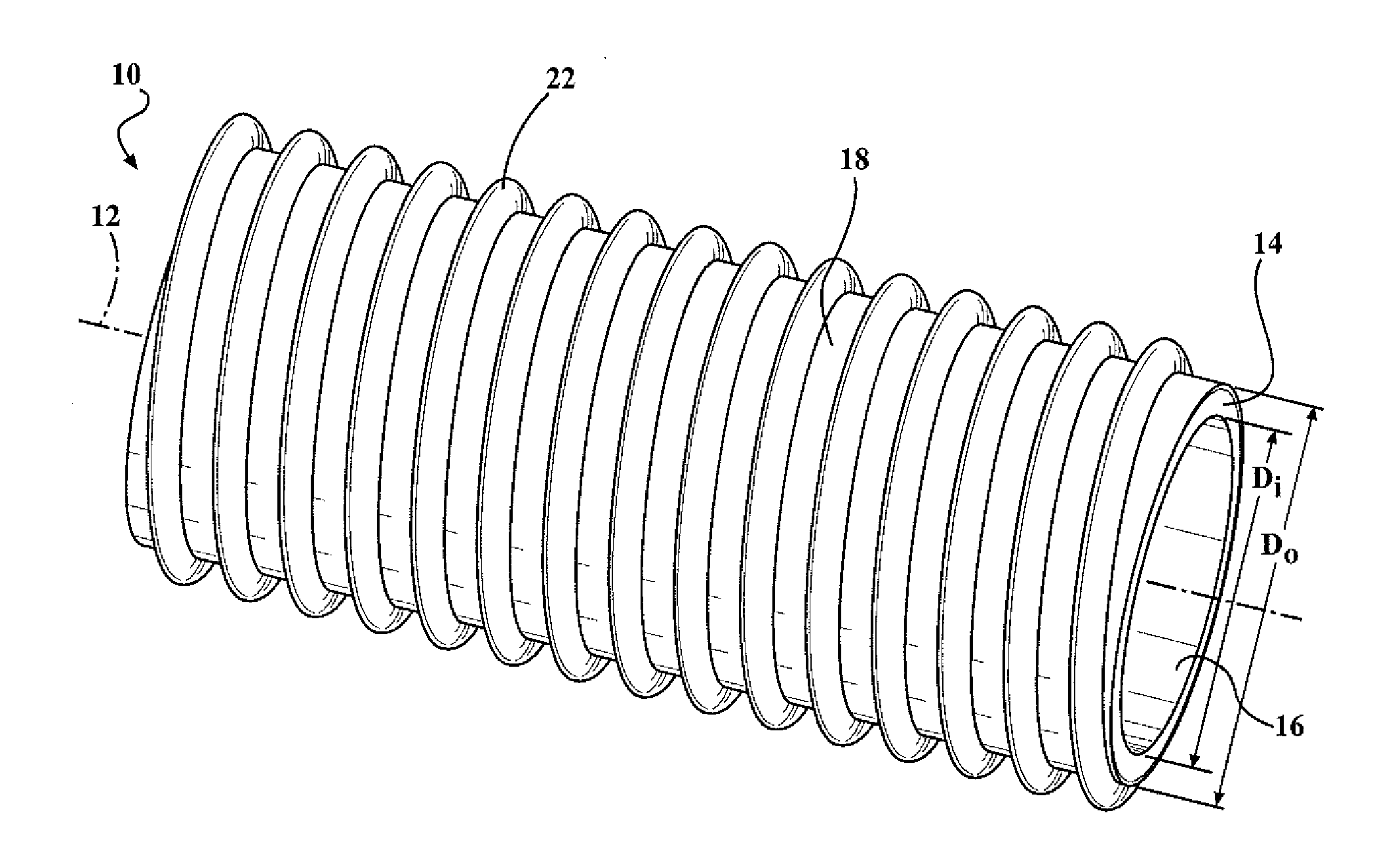
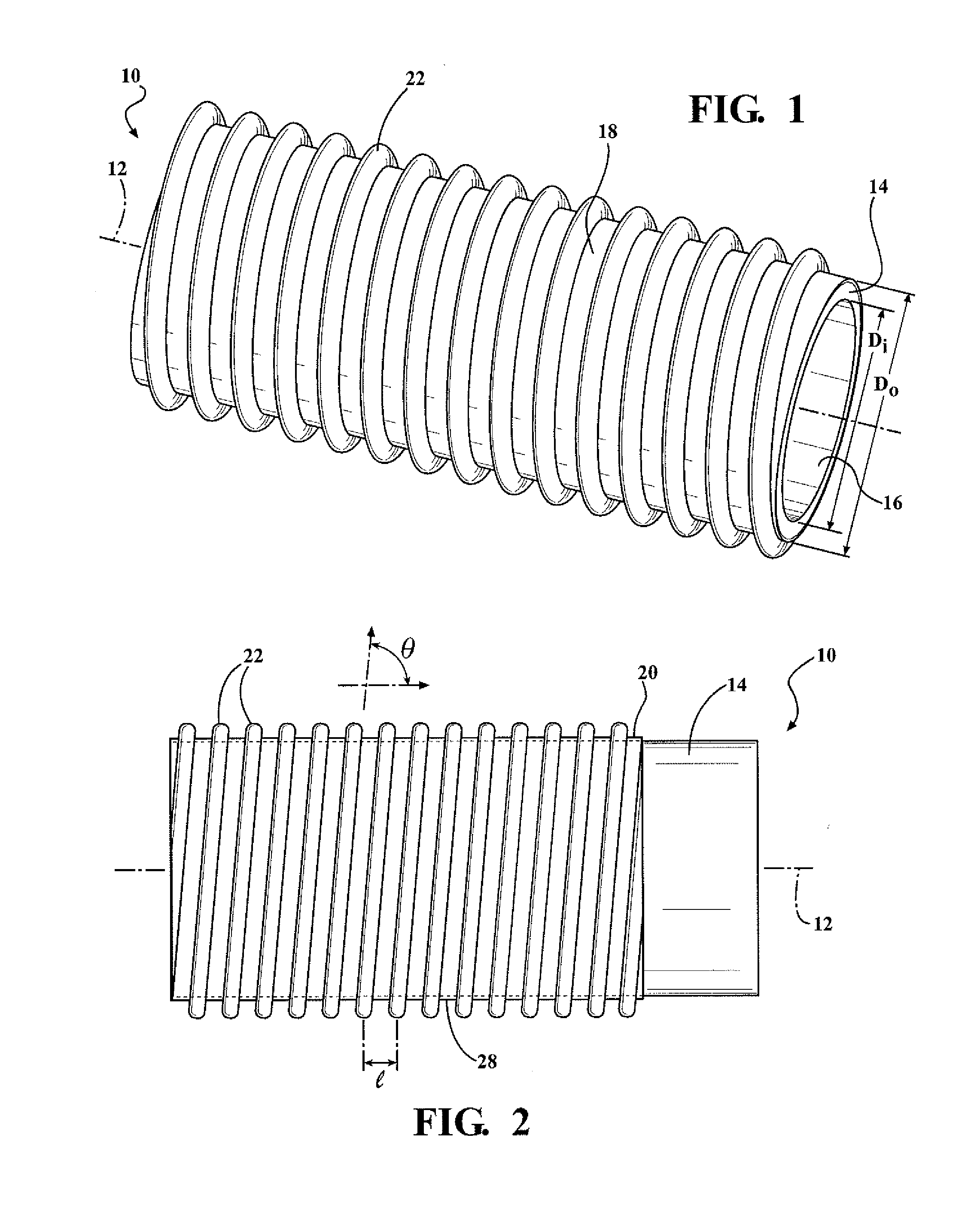
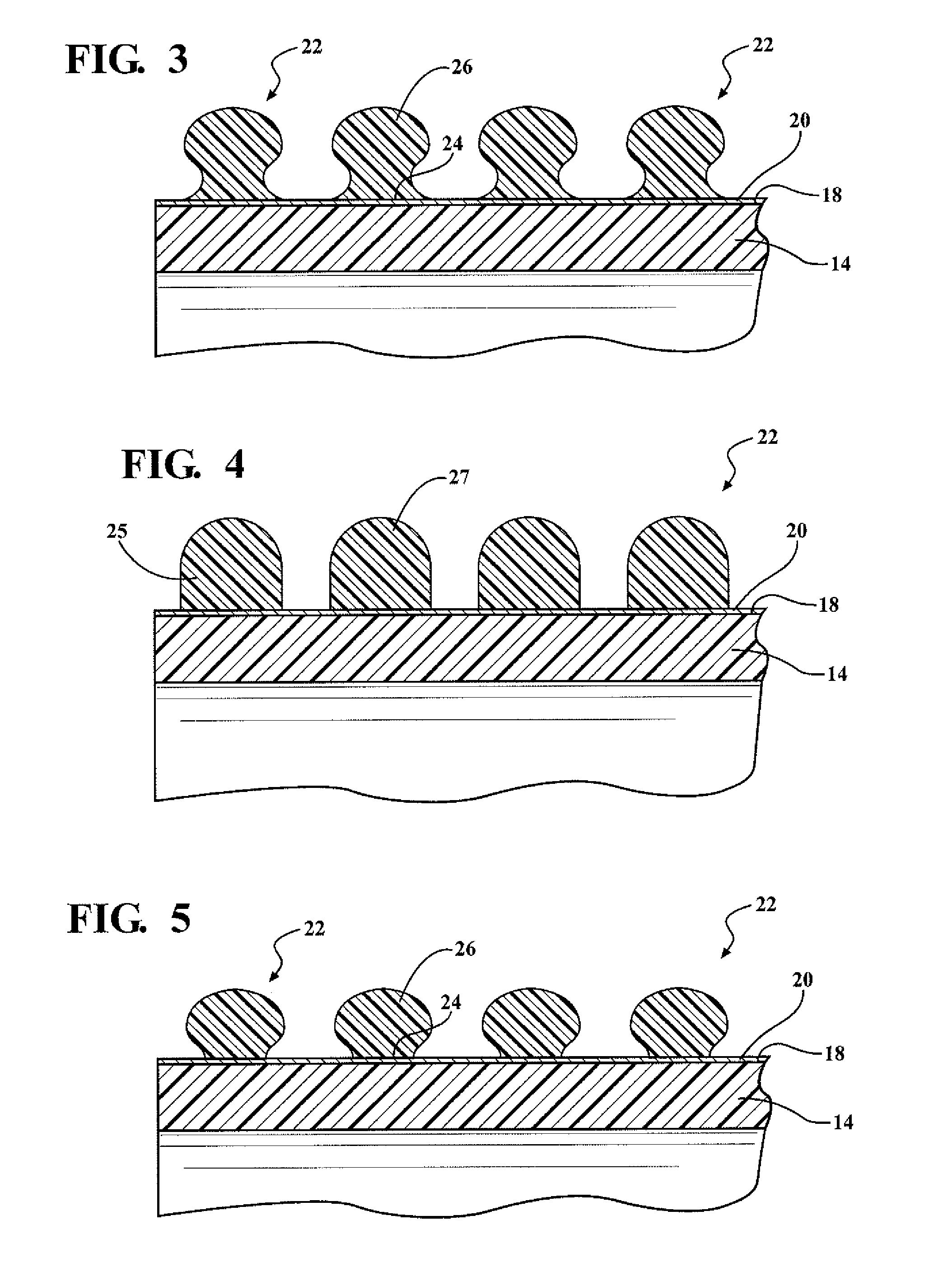
ActiveUS20110297268A1Adequate structural rigidityHigh strengthFlexible pipesTubular articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A reinforced hose assembly includes tubular inner layers with a uniform interior radial surface and an exterior radial surface. The tubular inner layer defines a longitudinal axis along a length thereof and comprises a first fluorocarbon polymer. The reinforced hose assembly also includes a bonding layer comprising a second fluorocarbon polymer. The bonding layer is disposed about the exterior radial surface of the tubular inner layer. The reinforced hose assembly also includes a reinforcing element comprising the second fluorocarbon polymer, attached to bonding layer and helically disposed about the tubular inner layer at a predetermined helical pitch measured relative to the longitudinal axis of the tubular inner layer.
Owner:KONGSBERG ACTUATION SYST II
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7642662B2Solve the real problemLower packagingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsSolder ballSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes: solder balls provided on an upper package; and pads provided on a lower package and directly connected to the solder balls, wherein at least one of the pads serves as a fiducial mark. Further, a shape of at least one of the pads is different from that of other pads and an area of at least one of the pads is substantially equal to that of the other pads.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Projector with a projection position adjusting device
InactiveUS8038307B2Improve accuracySmall sizeProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A projector includes a projection optical device and a projection position adjusting device that includes a fixed member defining a hole having a step portion, a first plate that supports the projection optical device and a second plate disposed between the fixed member and the first plate. The projection position adjusting device further includes a connecting member having a step and being disposed in the hole of the fixed member and connected to the first plate, and an urging member disposed between the connecting member and the step portion of the hole of the fixed member. The urging member urges the step portion of the hole and the step of the connecting member away from each other, and urges the first plate into direct contact with the fixed member.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
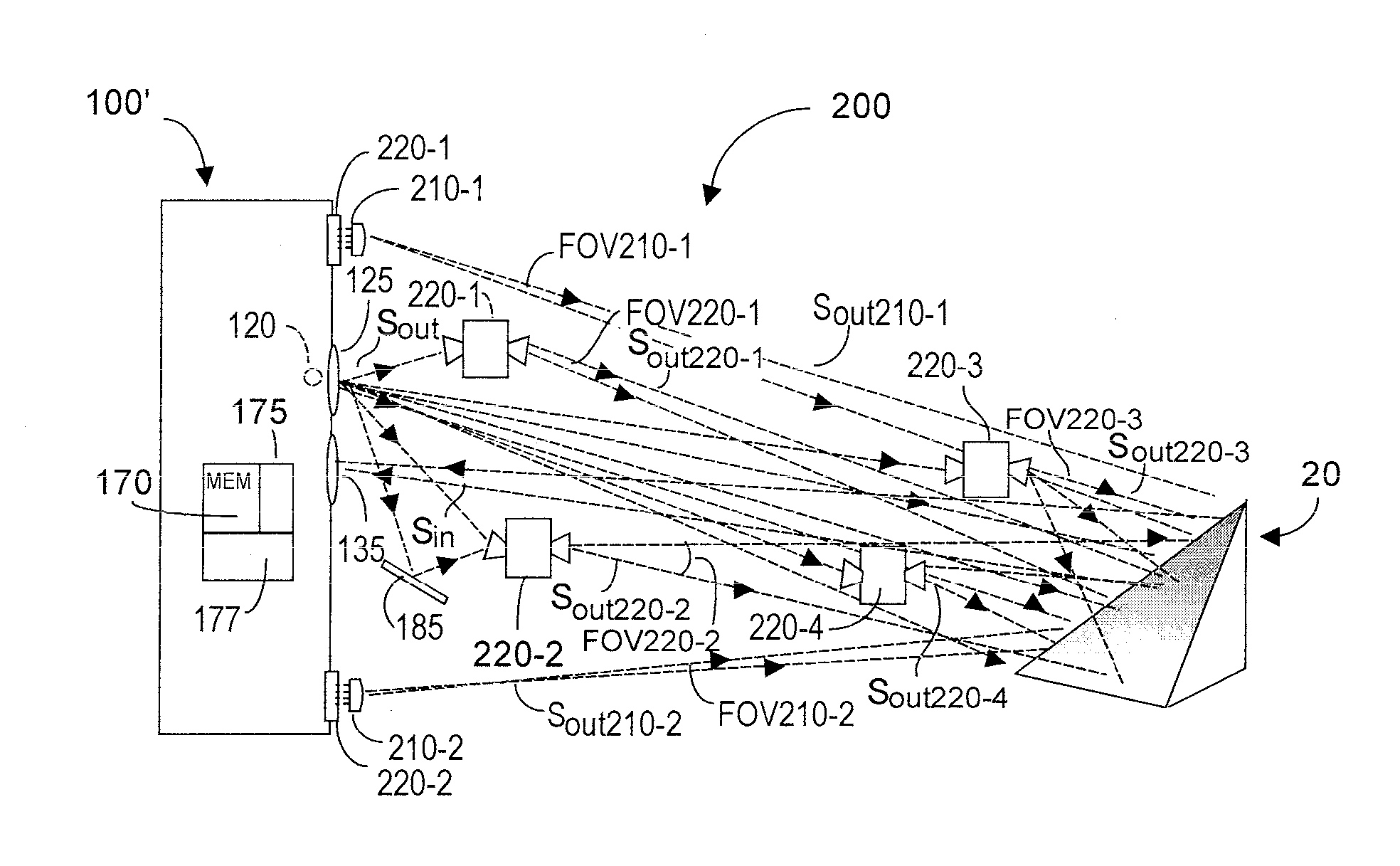
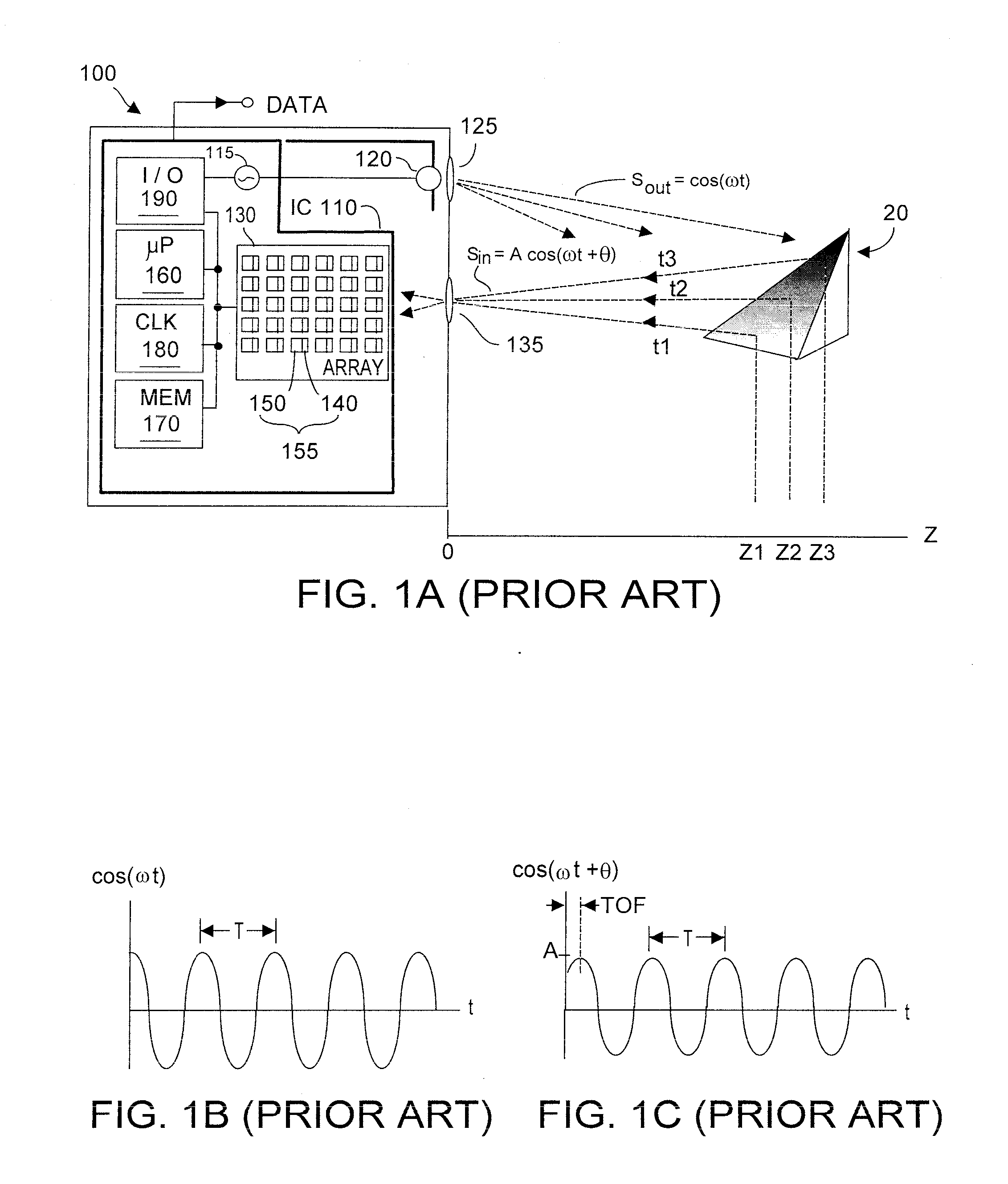
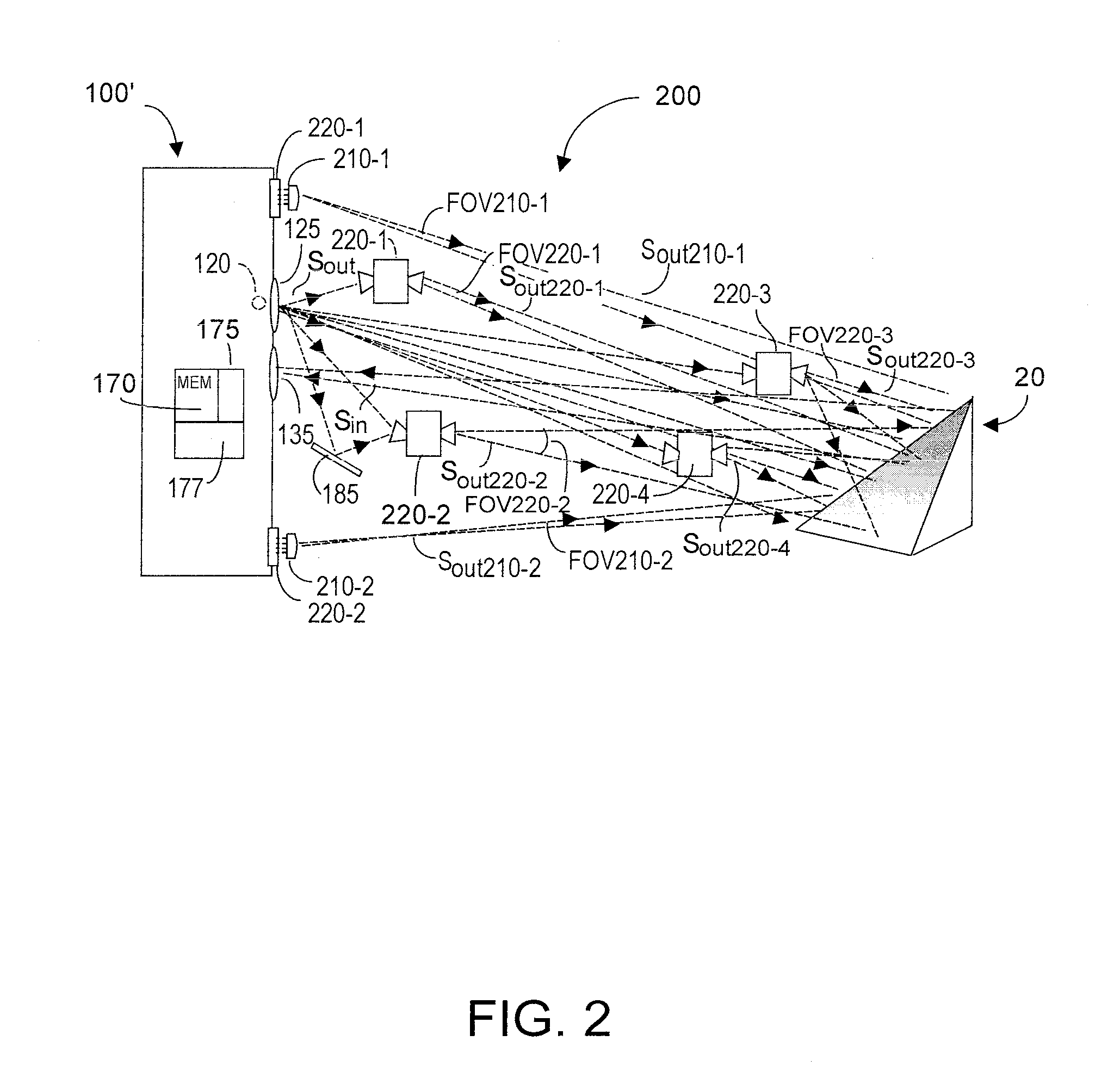
Multiple synchronized optical sources for time-of-flight range finding systems
ActiveUS20110188027A1Small cost and form factorMore optical energyOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical powerLight source
TOF system optical power is augmented using auxiliary optical emitter unit(s) that may be a wireless (WOE), or a plug-wired (PWOE). WOE units sense emitted TOF system optical energy Sout and emit optical energy Sout-n preferably dynamically synchronized in frequency and in phase to Sout as received by the WOE. Each WOE includes at least one optical sensor to detect Sout, and internal feedback ensuring that frequency and phase of the WOE emitted Sout-n optical energy are dynamically synchronized with frequency and phase of the TOF emitted Sout optical energy. PWOE units need no internal feedback but are calibrated by the TOF system to cause a close match between frequency and phase of the PWOE-emitted optical energy with what would be emitted by the TOF system primary optical source. If PWOE(s) are used in isolation, delay difference between PWOE and the TOF primary optical energy source can be software-compensated.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
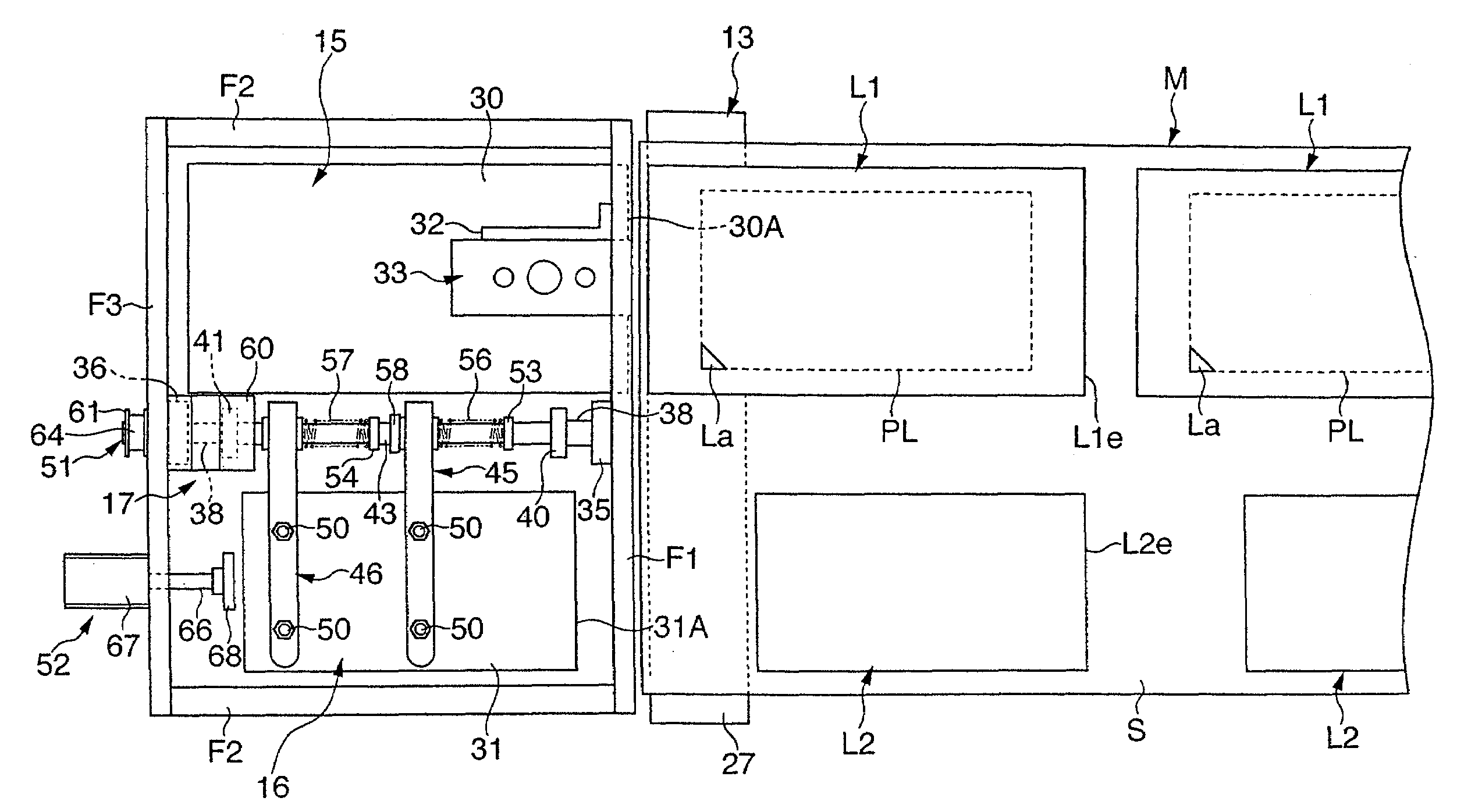
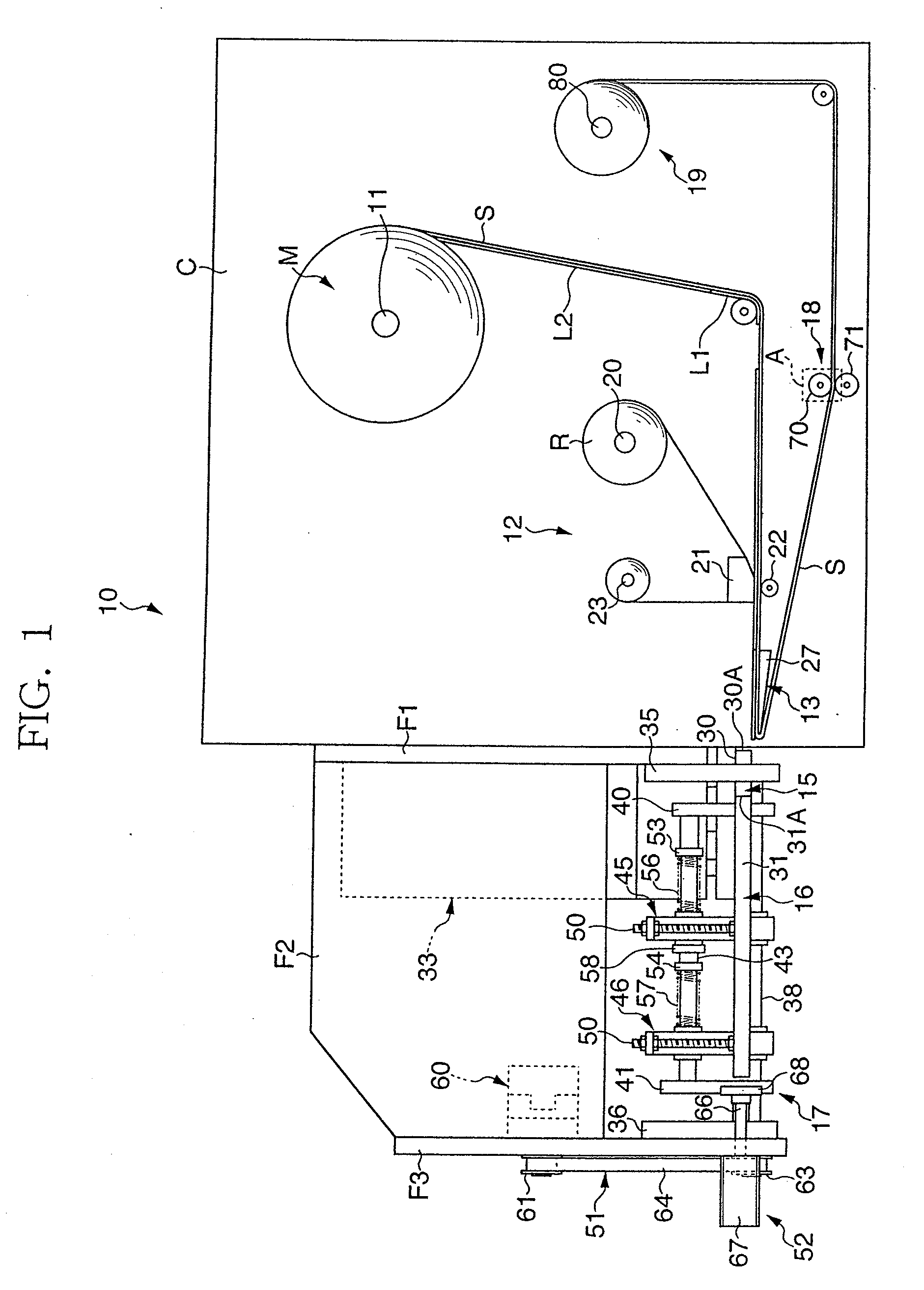
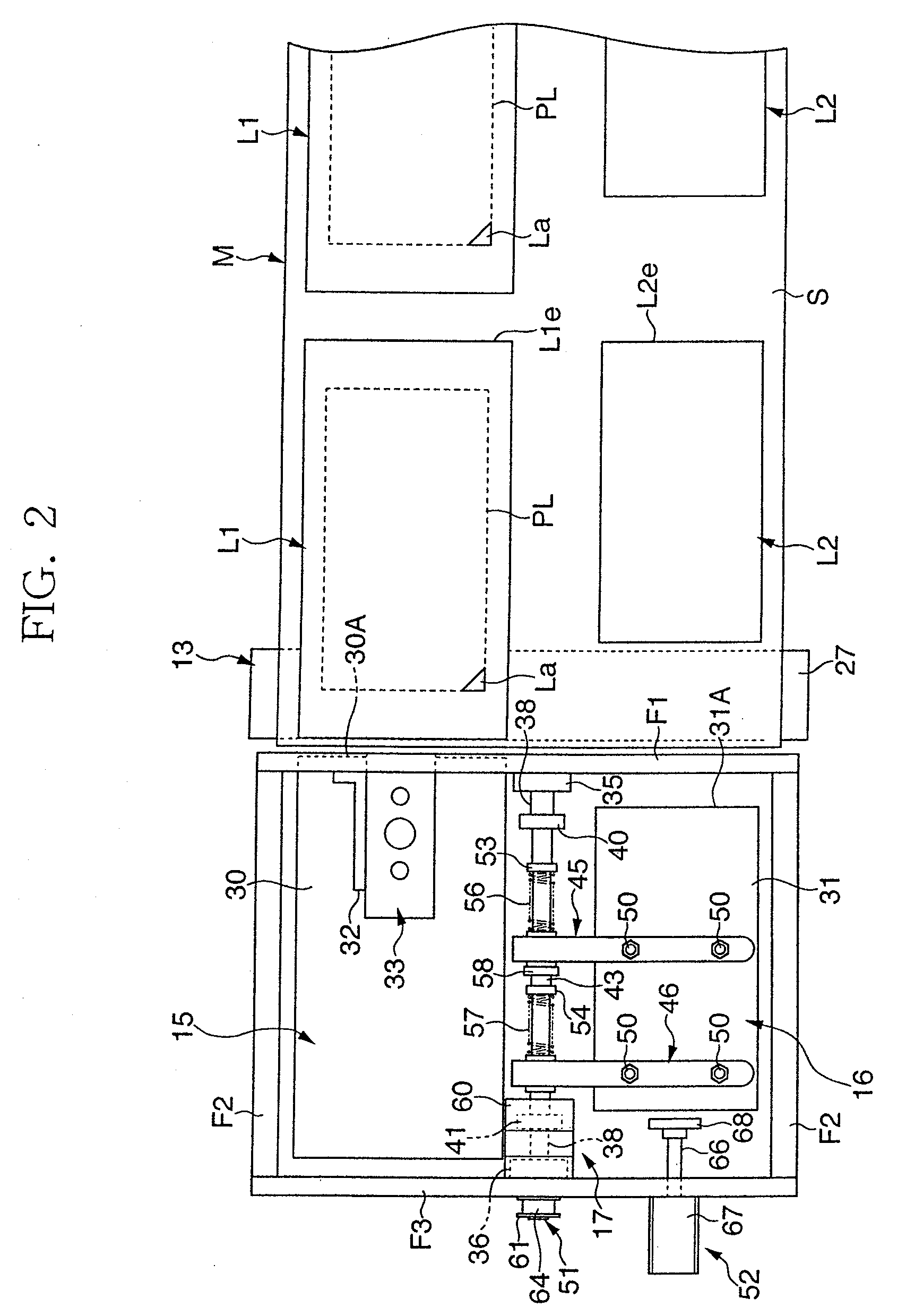
Label printer
ActiveUS20090272495A1Easy to tearAdjustable positionLabelling non-rigid containersMechanical working/deformationRelease linerElectrical and Electronics engineering
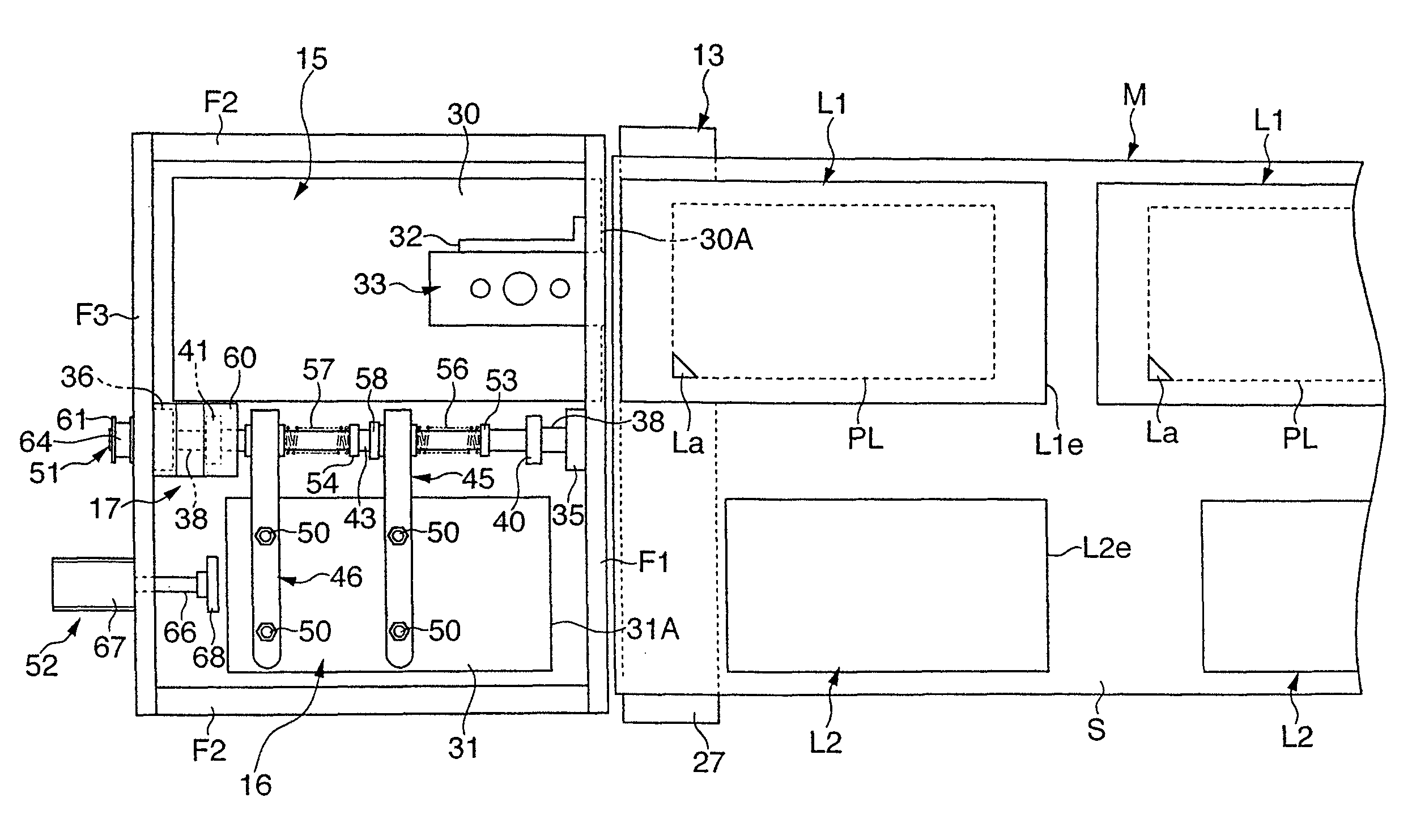
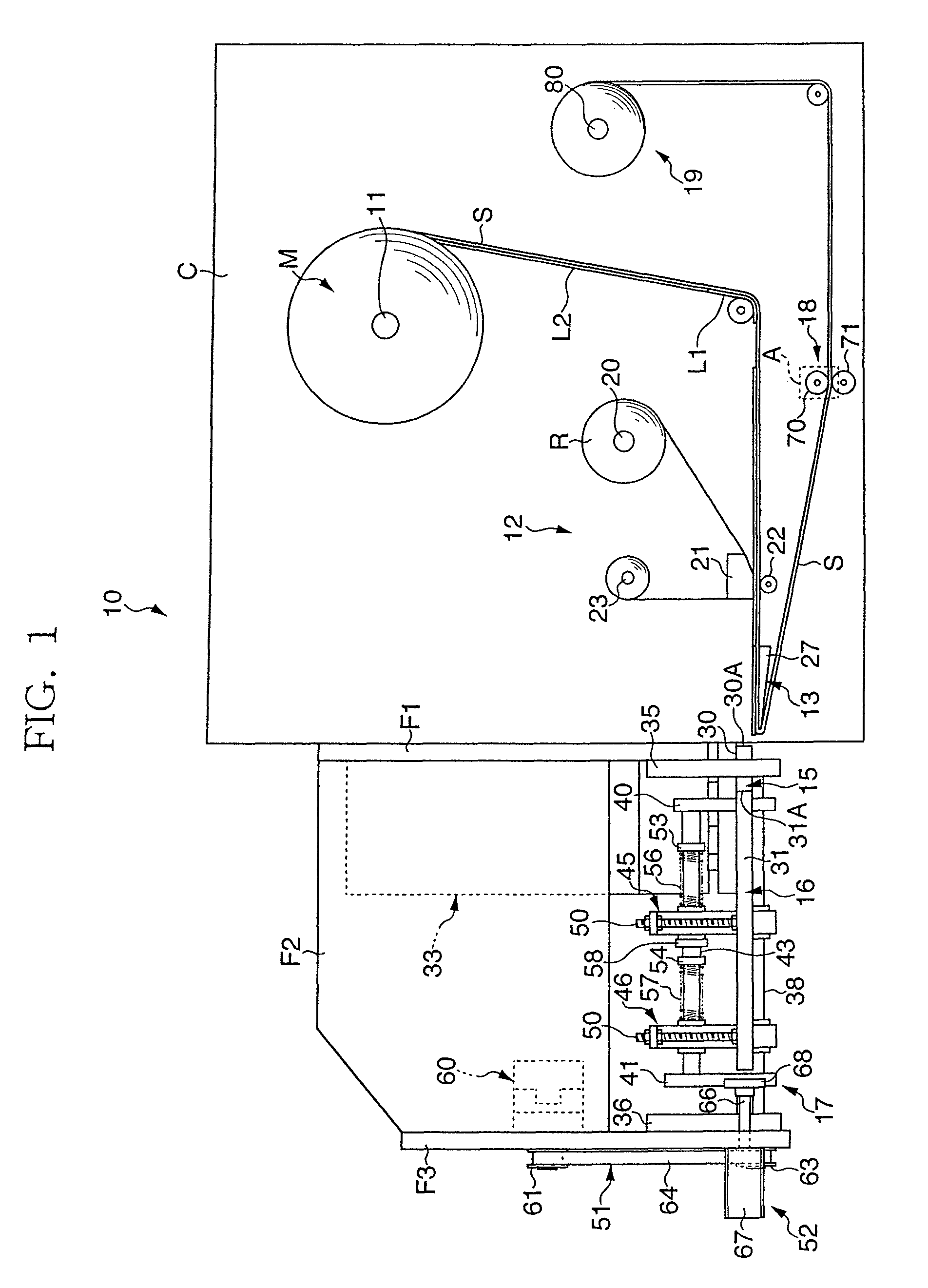
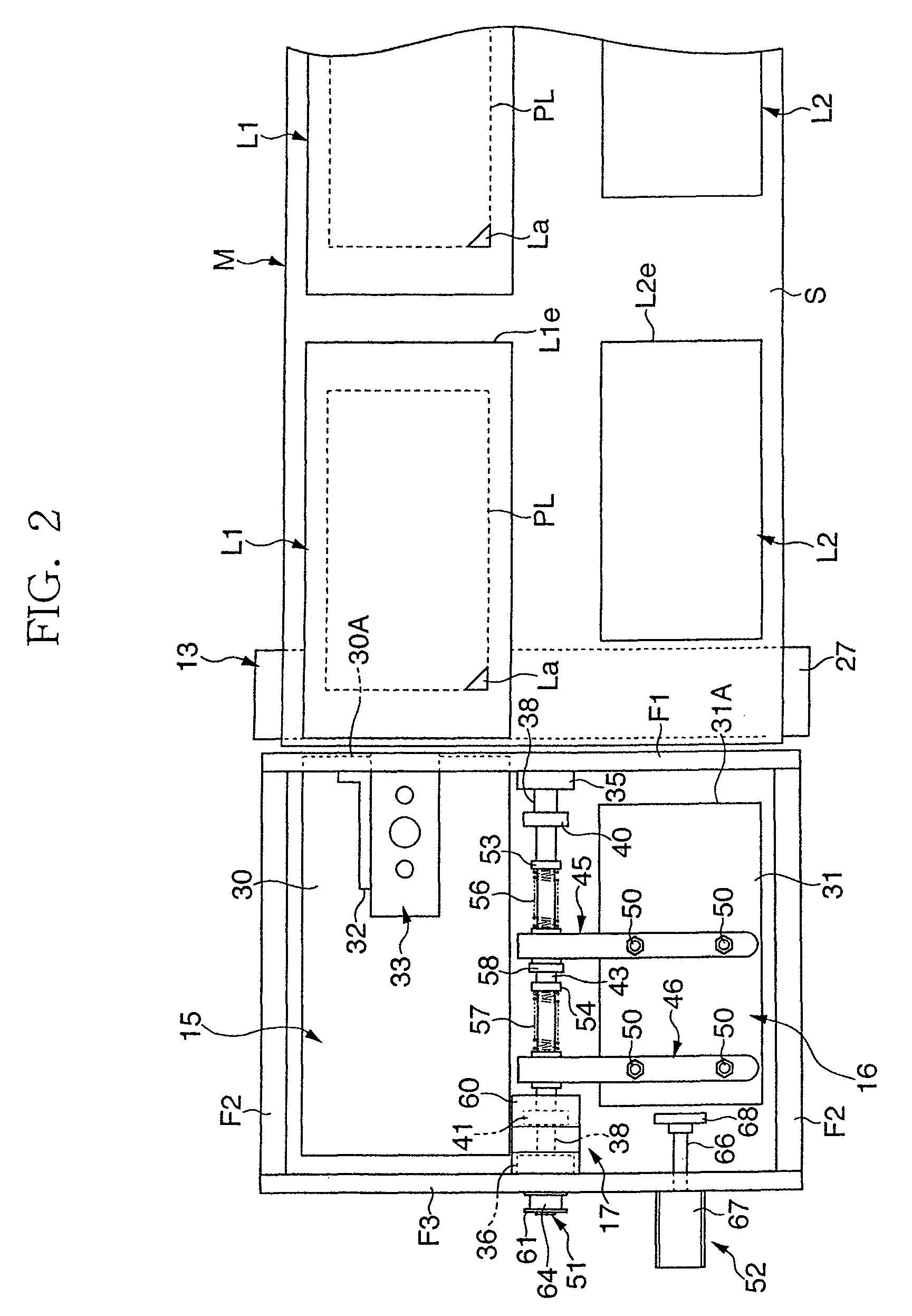
There is provided a printing device 12 that performs printing on each of first and second labels L1, L2 on the way of feeding out a raw strip sheet M, which is temporarily stuck with a first label L1 and a second label L2 having a smaller plane area than that of the first label on a release liner S, a peel plate 27 that peels off the first and second labels L1, L2 from the release liner S, first and second label suction plates 30, 31 that hold the respective peeled labels L1, L2, and a laminating device 17 that laminates the first and second labels L1, L2 with the adhesive layer of the second label L2 facing the adhesive layer of the first label L1. The adhesive layer of the first label L1 laminated with the second label L2 is exposed in a closed loop manner in an outer peripheral area all around the second label L2.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
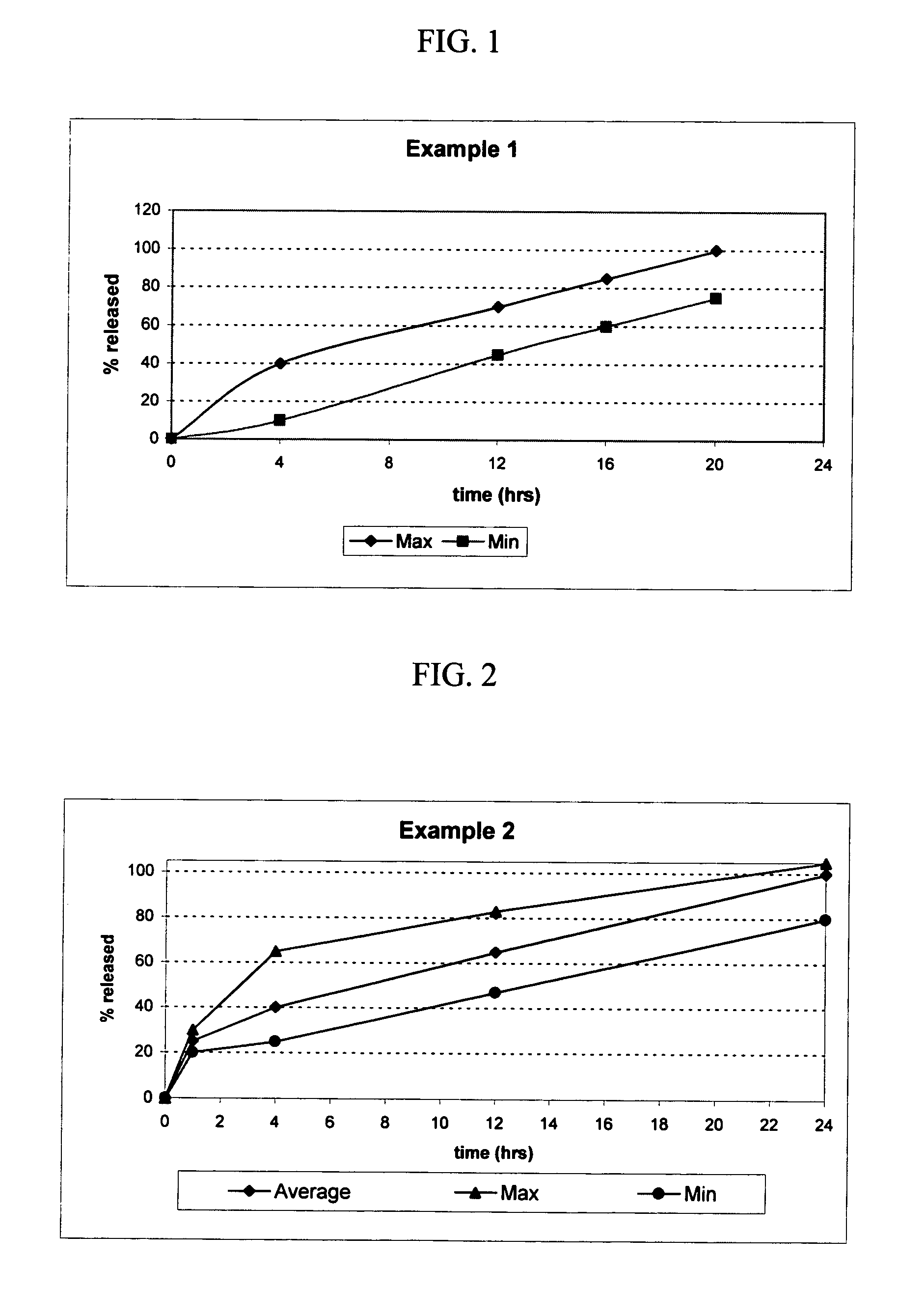
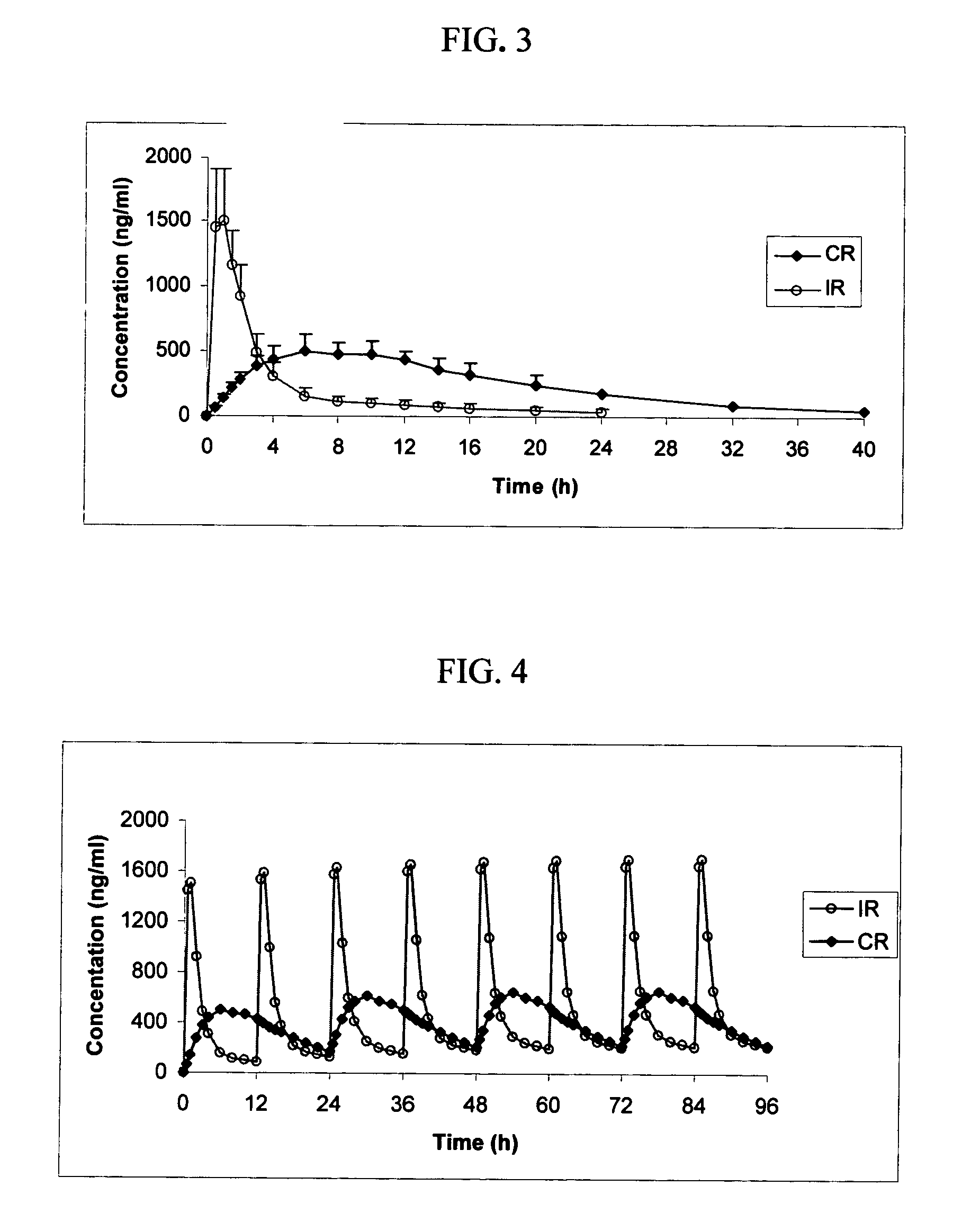
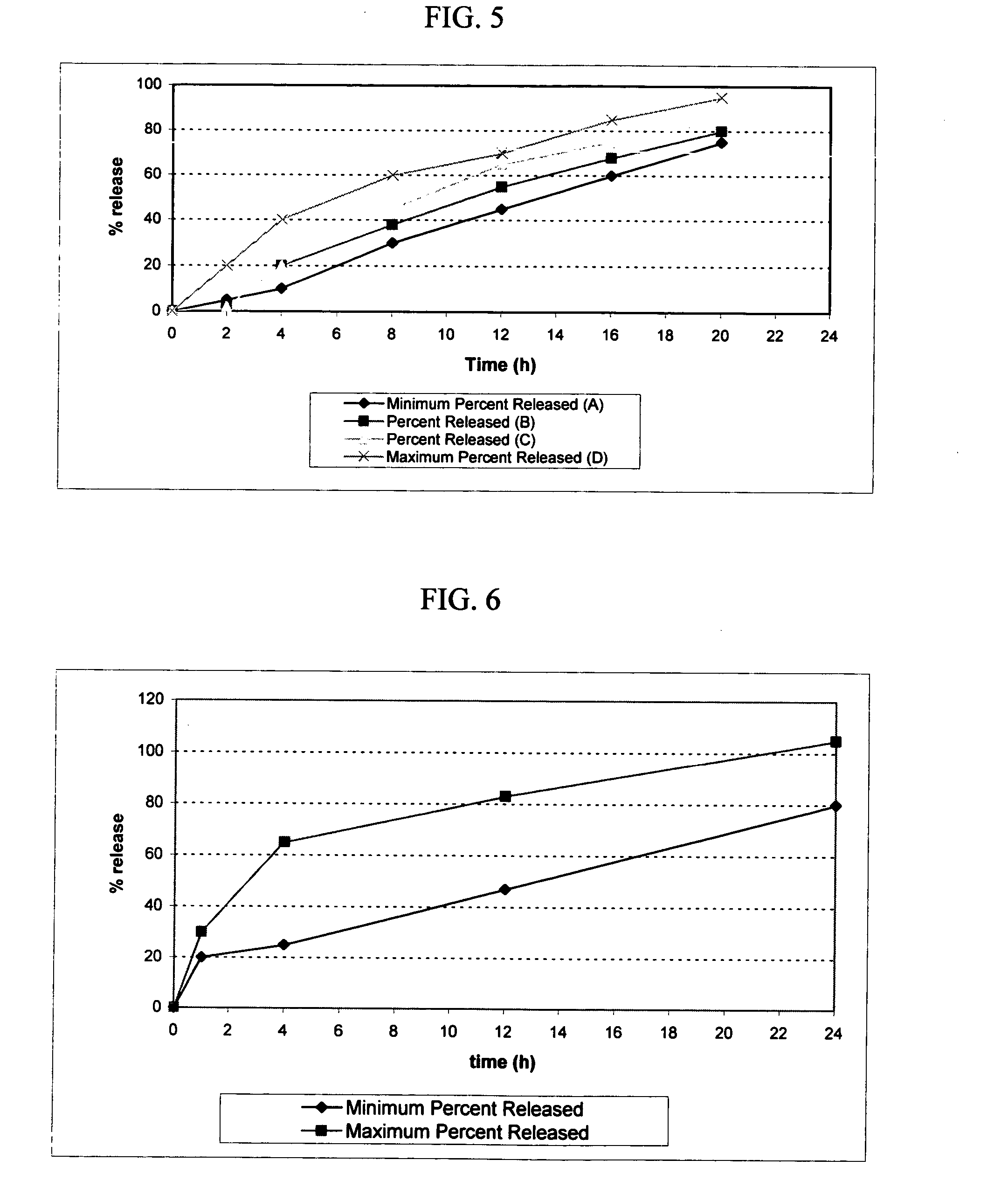
Osmotic device containing licofelone
The present invention provides an osmotic device containing controlled release licofelone and, optionally, a rapid release licofelone in an external coat. The osmotic devices provide a controlled release of licofelone to maintain therapeutically effective levels of licofelone in plasma when administered once per day. The device is useful for the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory related disorders. The present devices provide licofelone according to specific release profiles in combination with specific formulations.
Owner:OSMOTICA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com