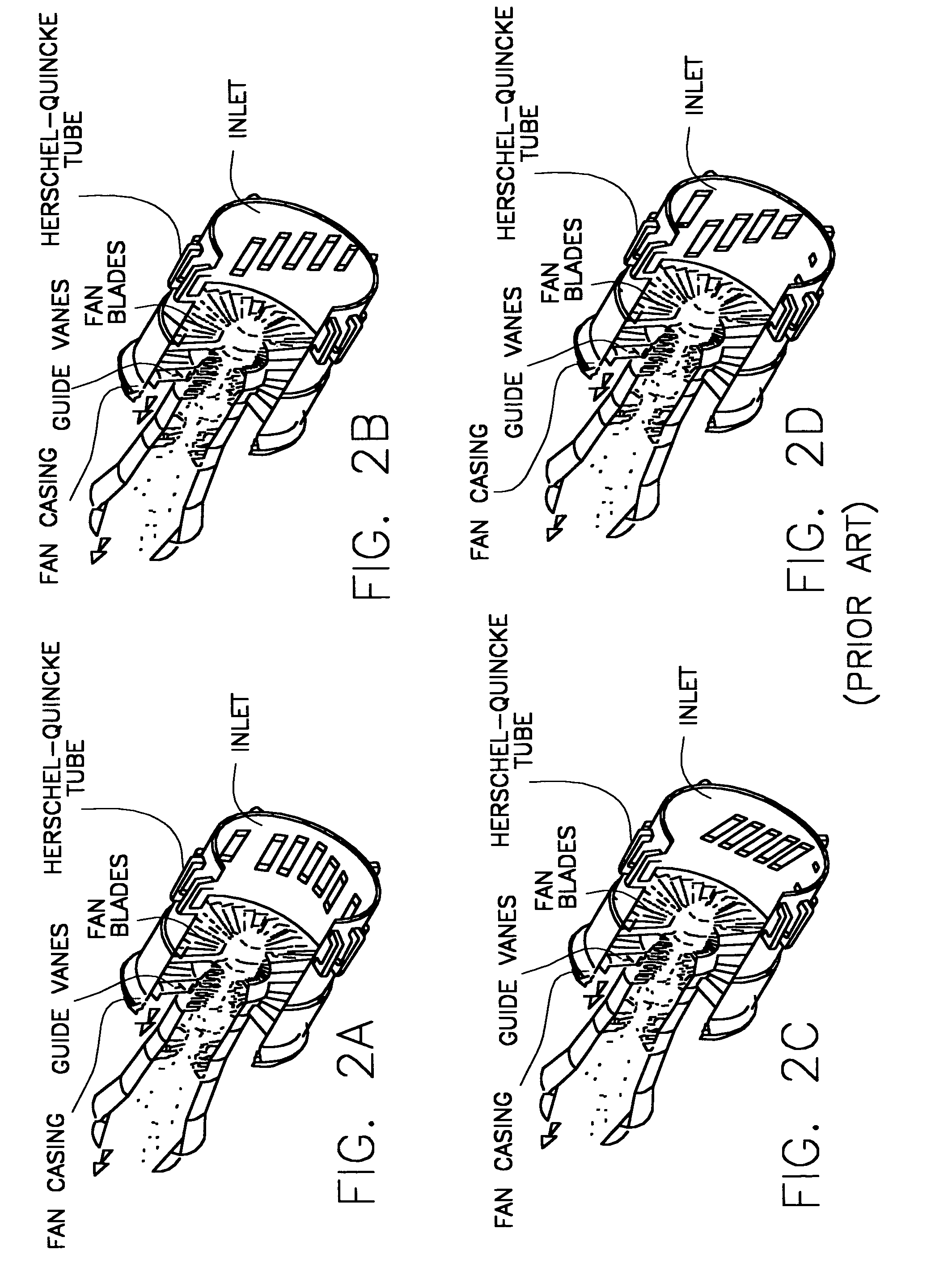
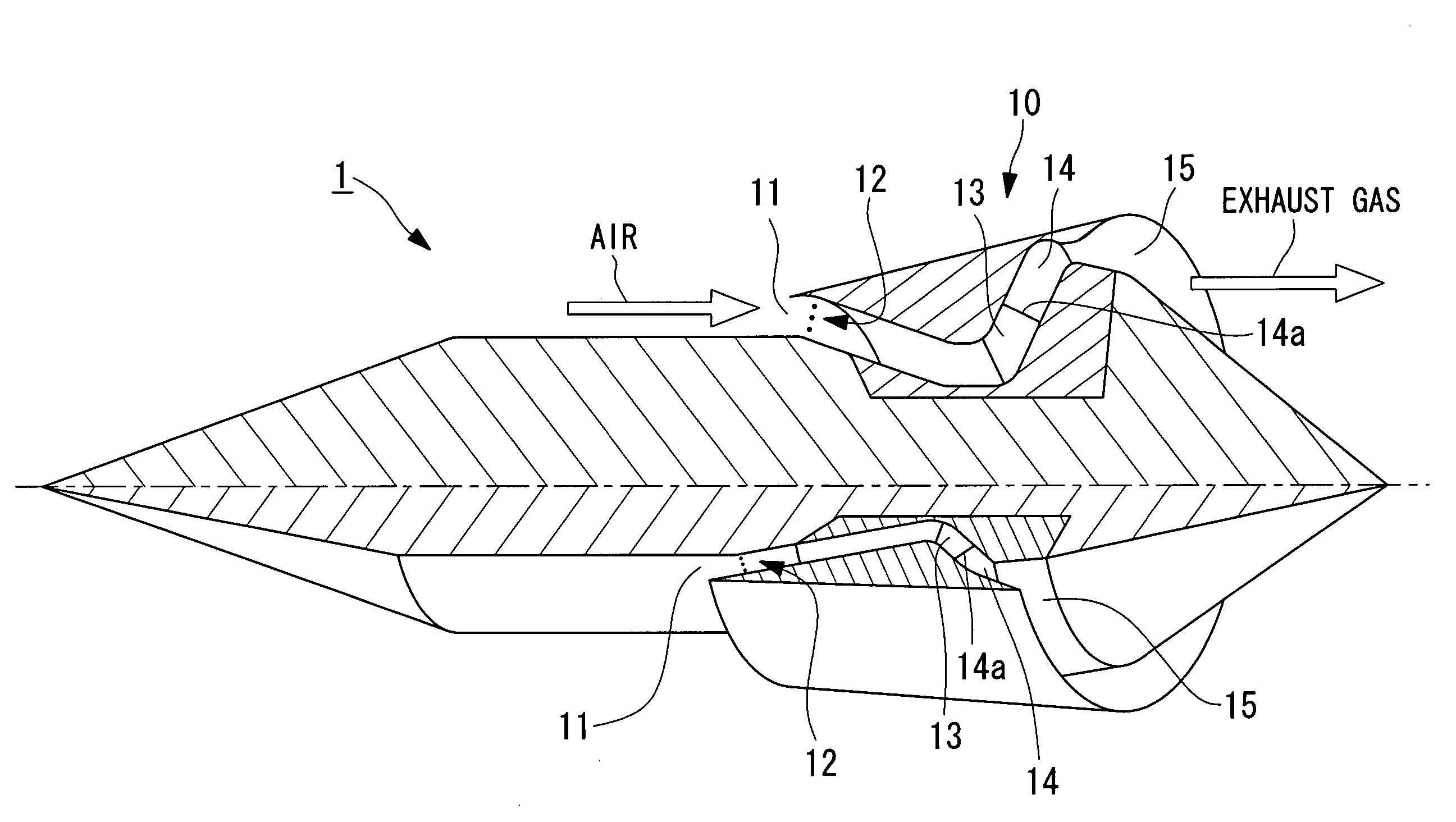
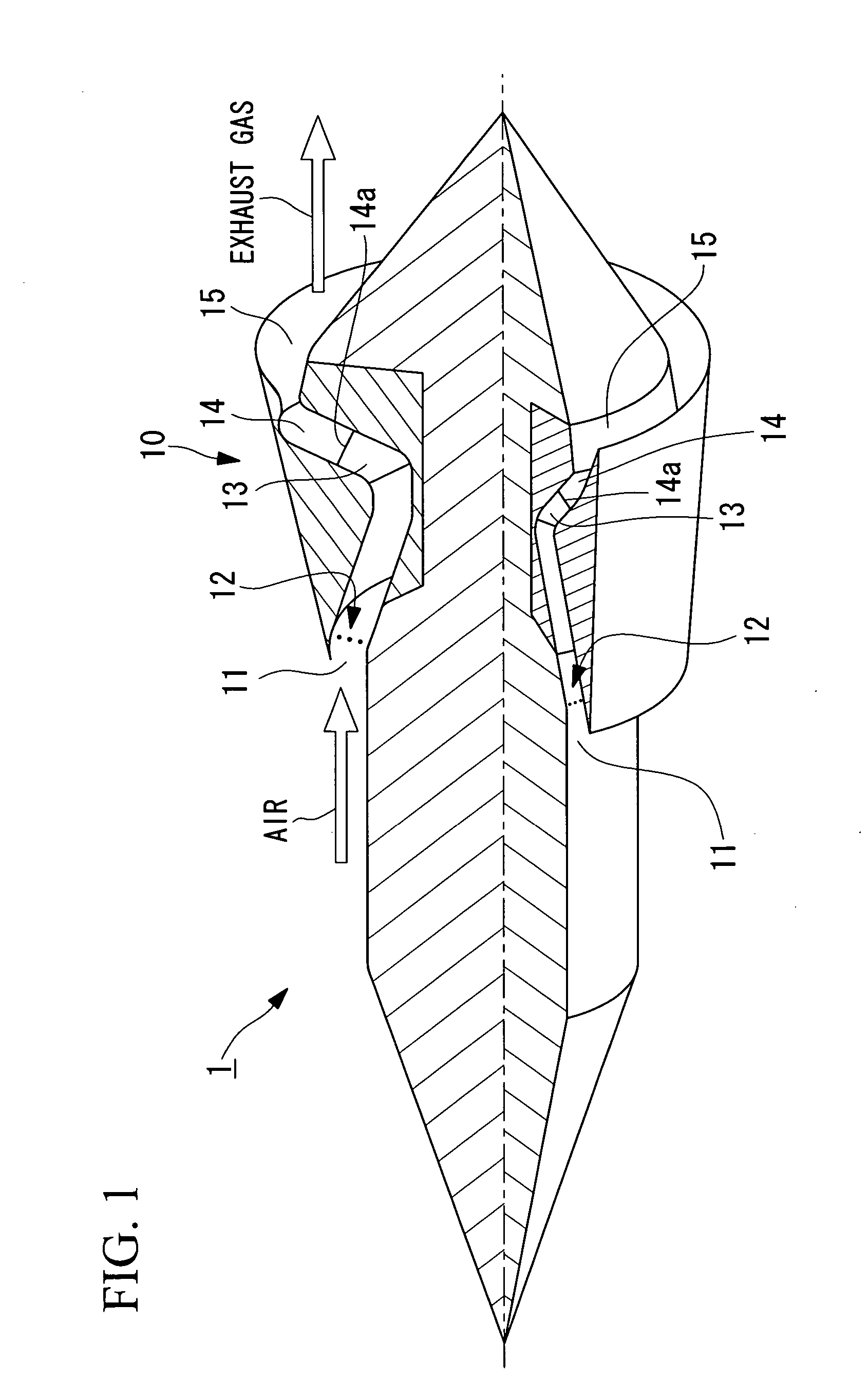
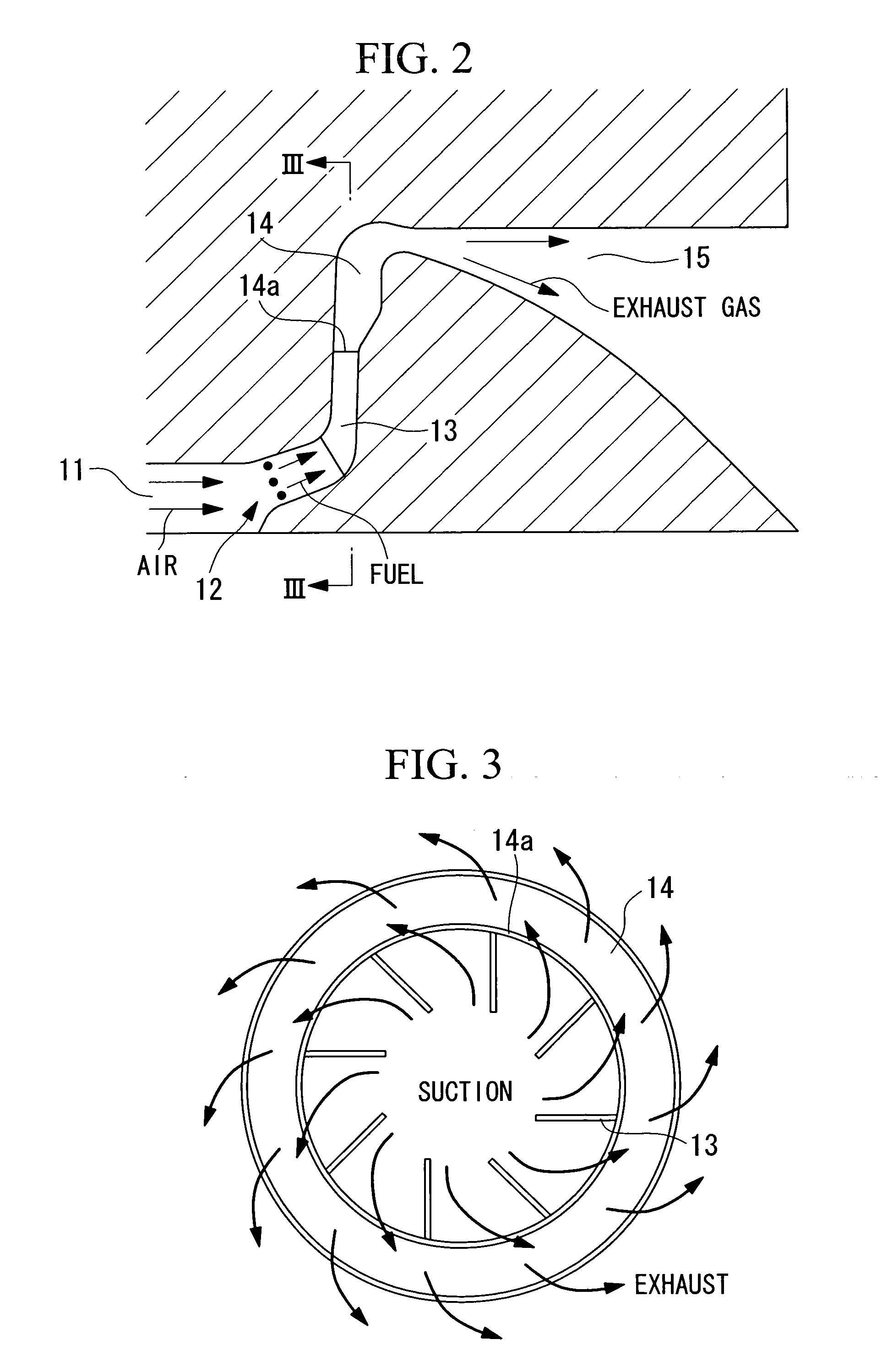
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72results about How to "Reduce engine noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
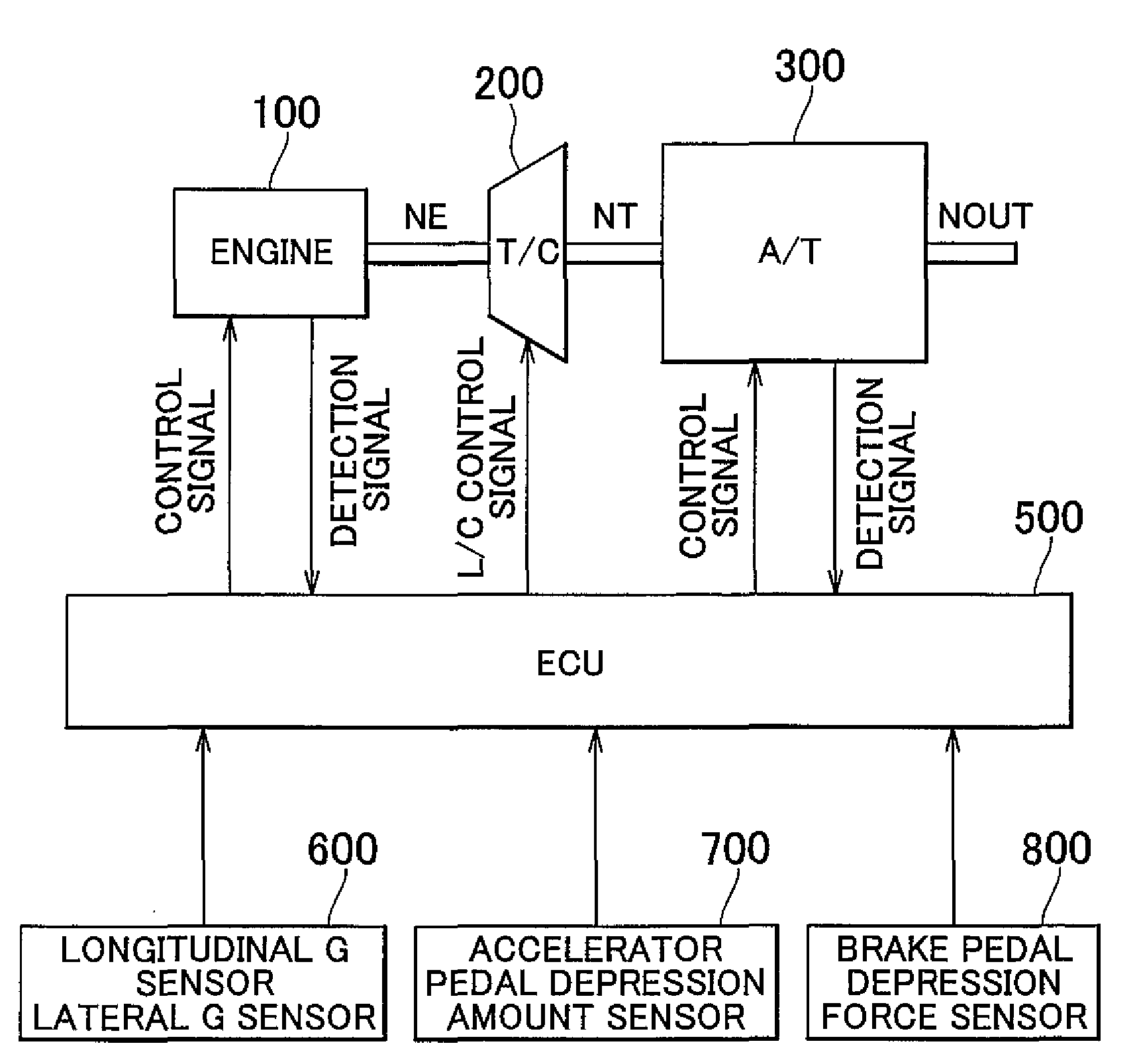
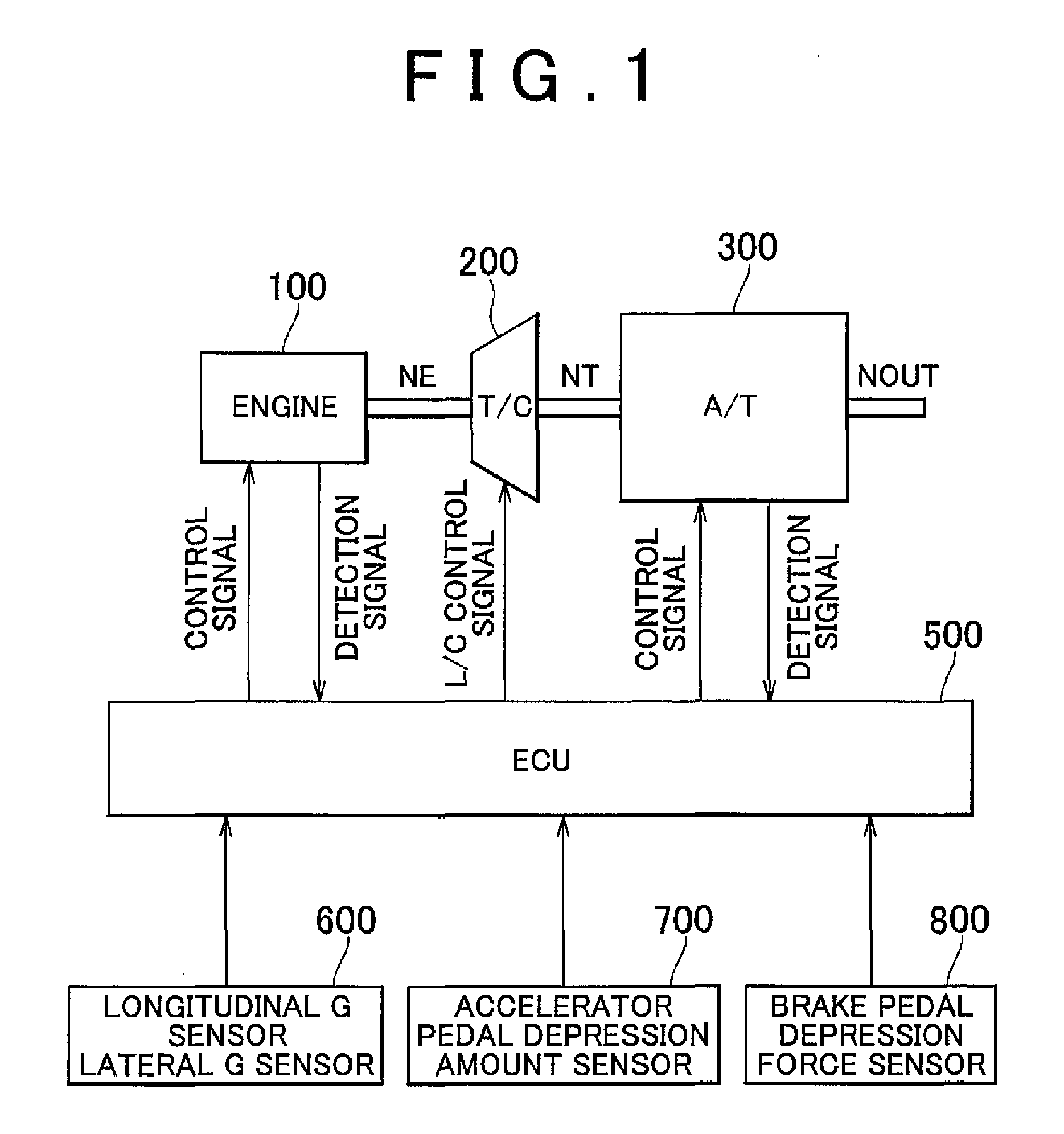
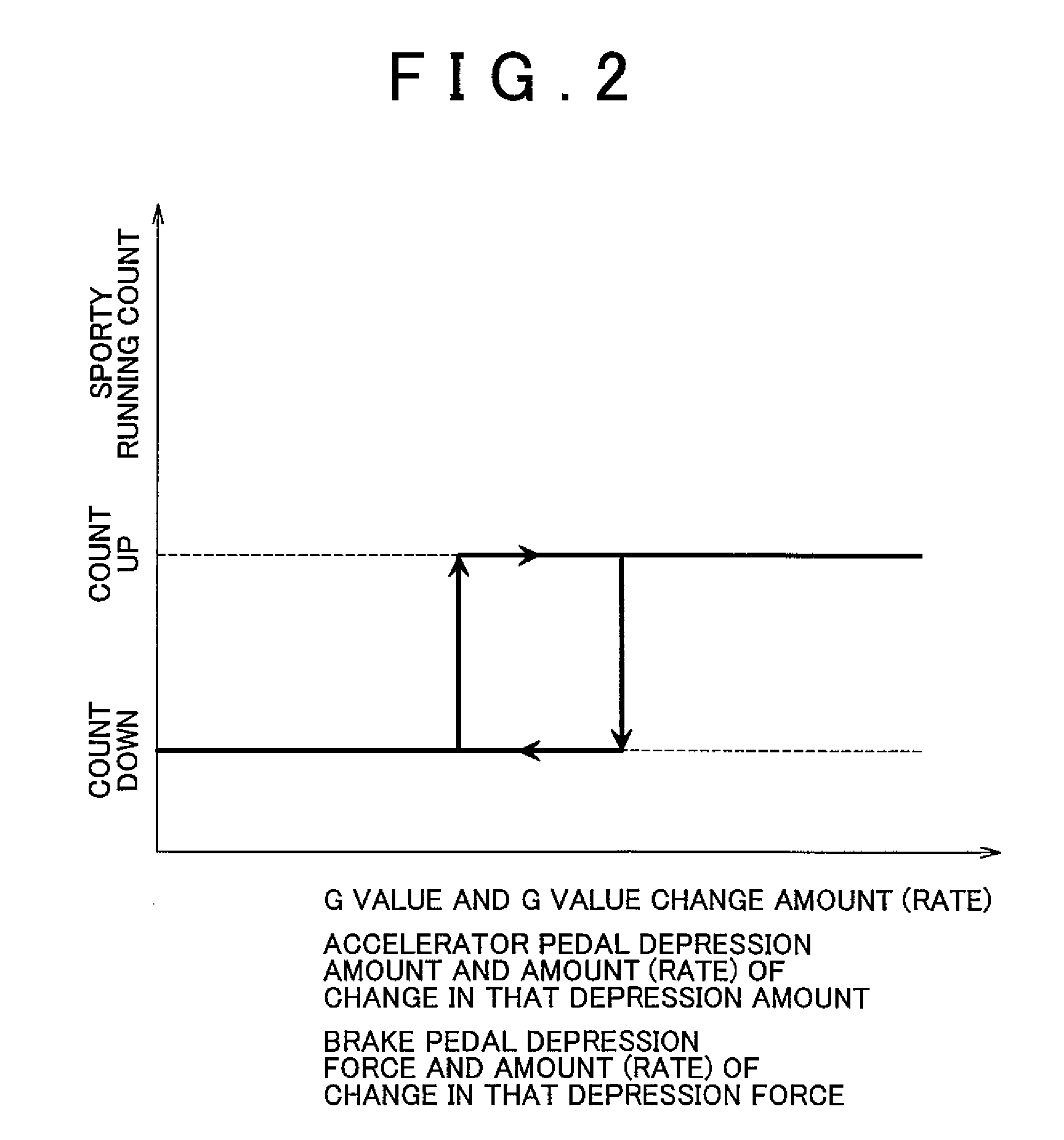
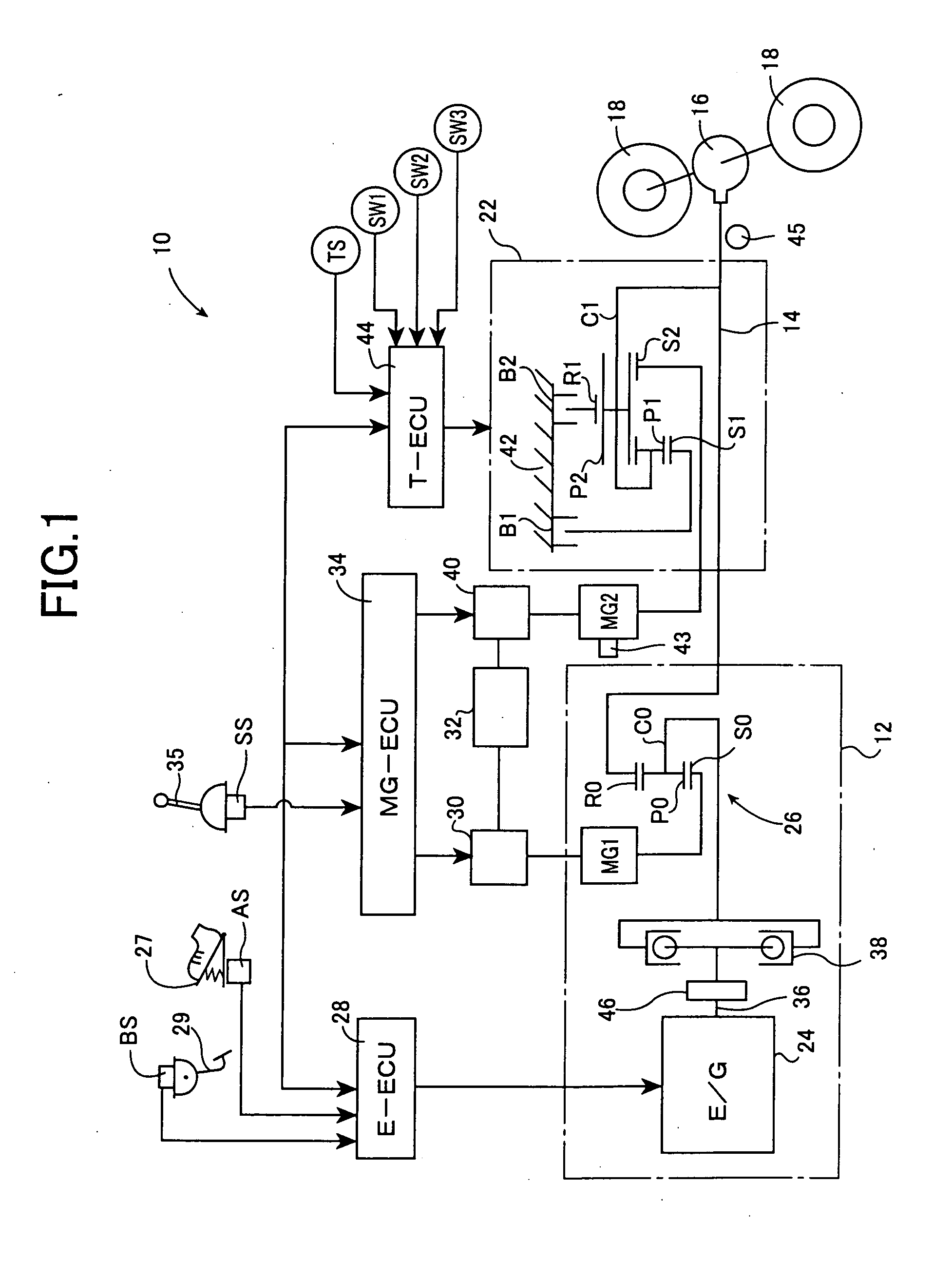
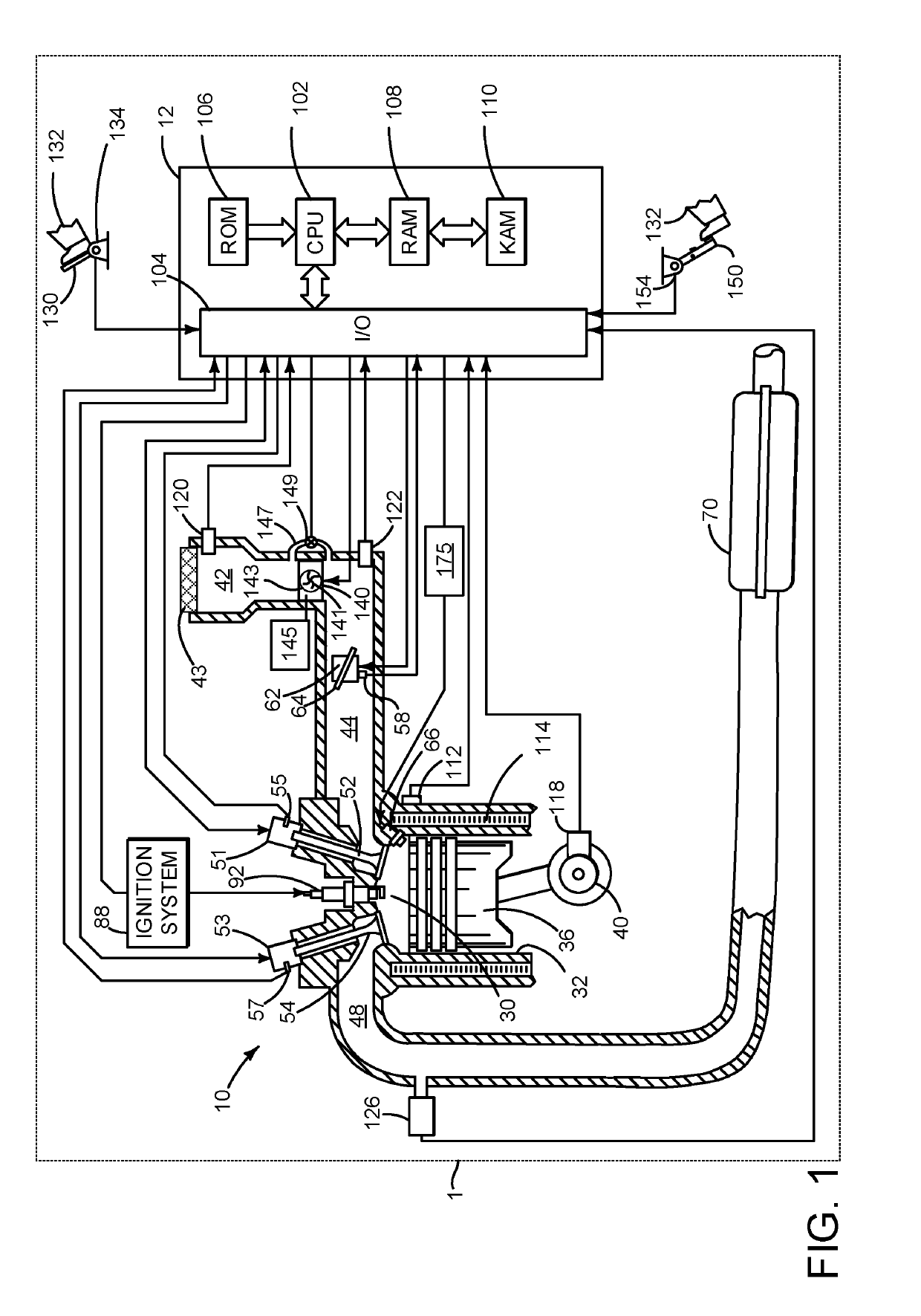
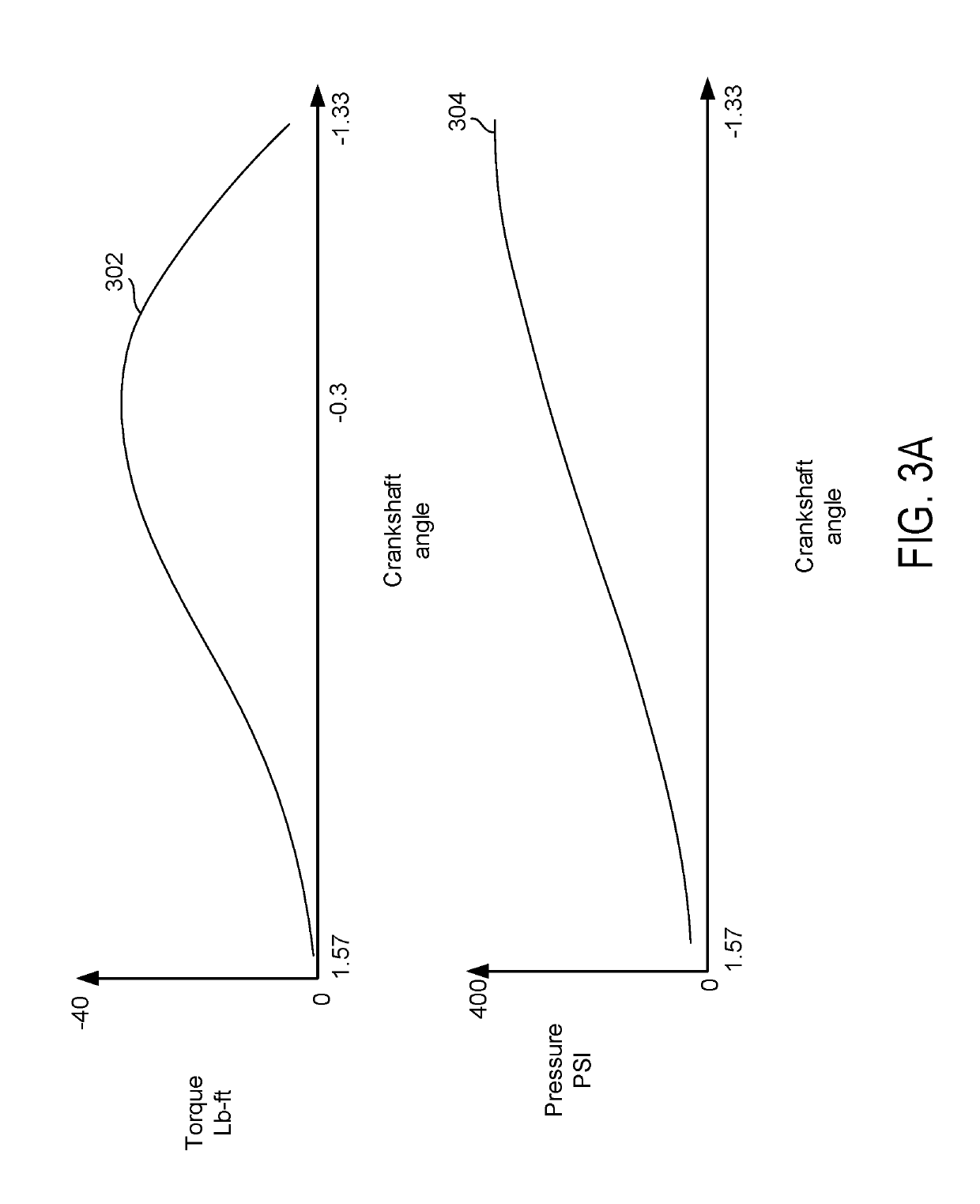
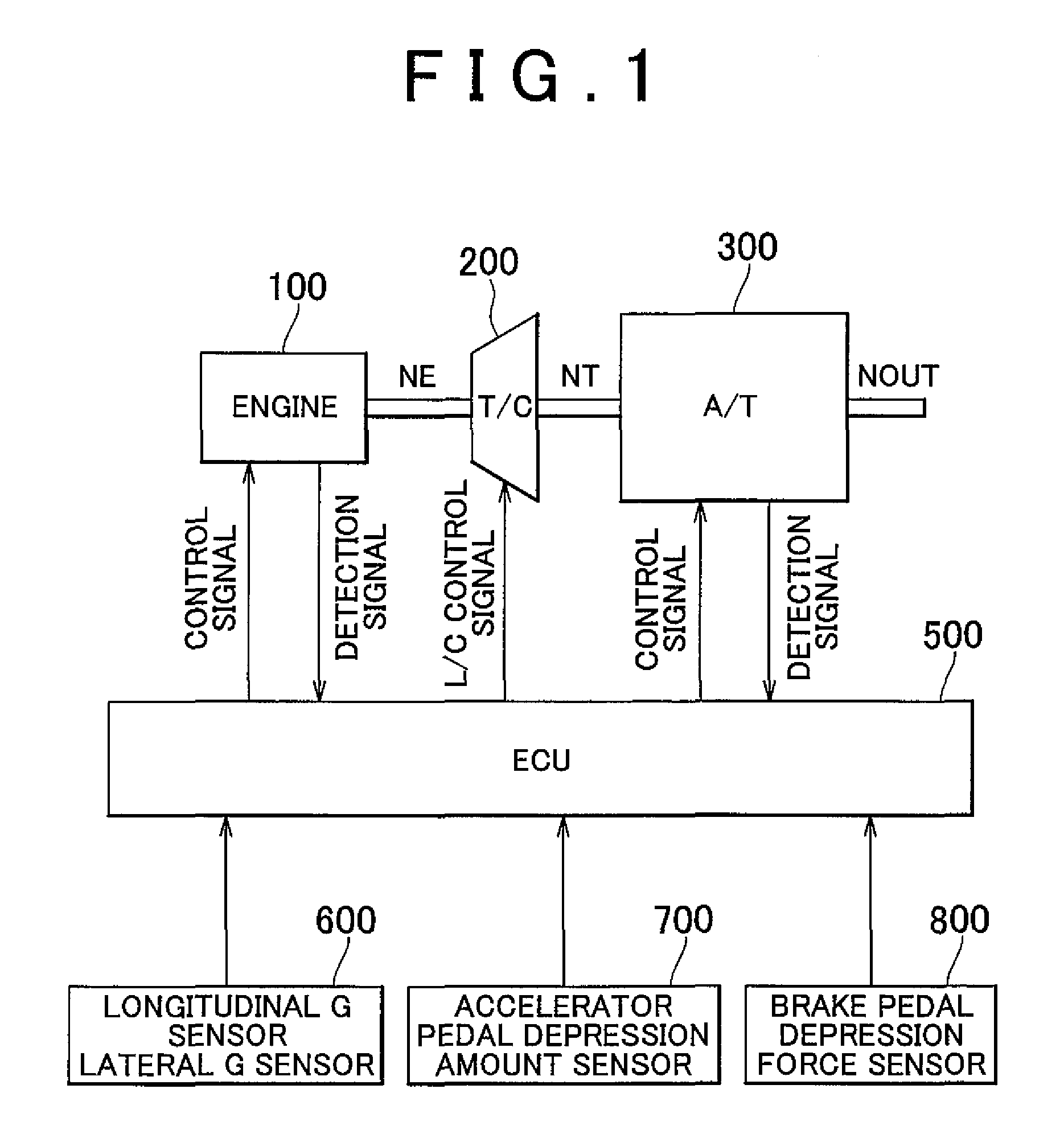
Control apparatus and control method of a vehicle, program for realizing that control method using a computer, and recording medium on which that program is recorded
InactiveUS20080097674A1DegreeShorten speedDigital data processing detailsGearing controlDriver/operatorEmergency brake
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
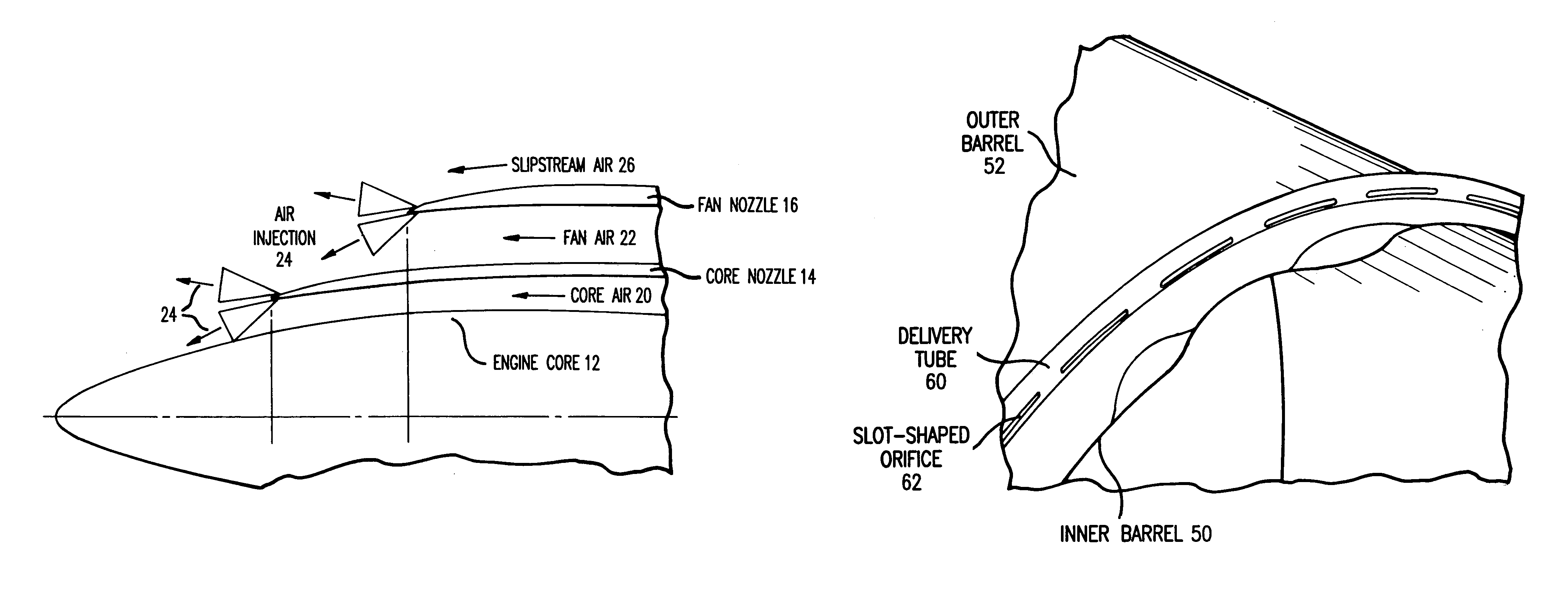
Apparatus, method and system for gas turbine engine noise reduction
InactiveUS7159383B2Reduce engine noiseMinimizing aircraft cruise performance lossesAircraft navigation controlPower plant exhaust arrangementsNoise generationAviation
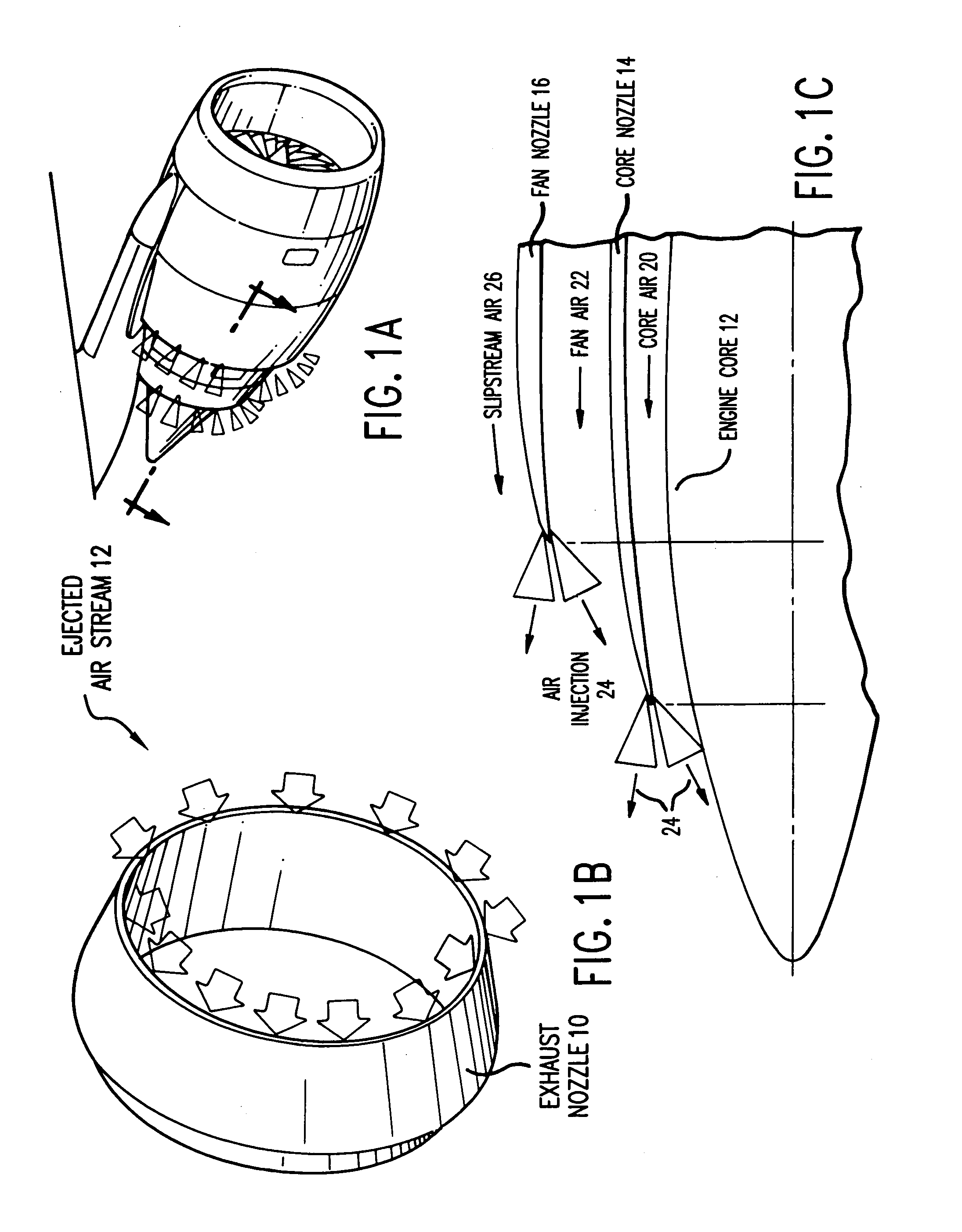
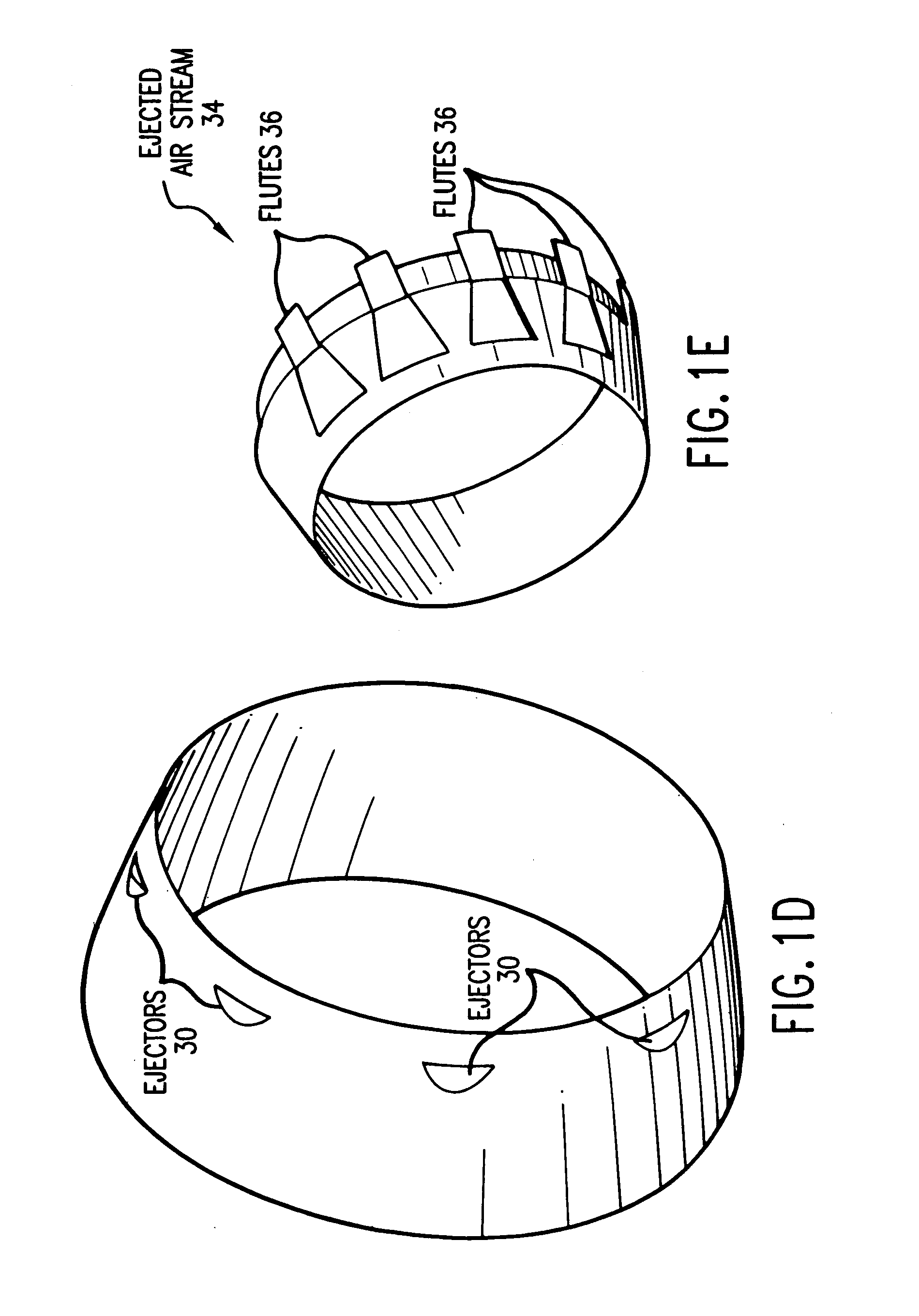
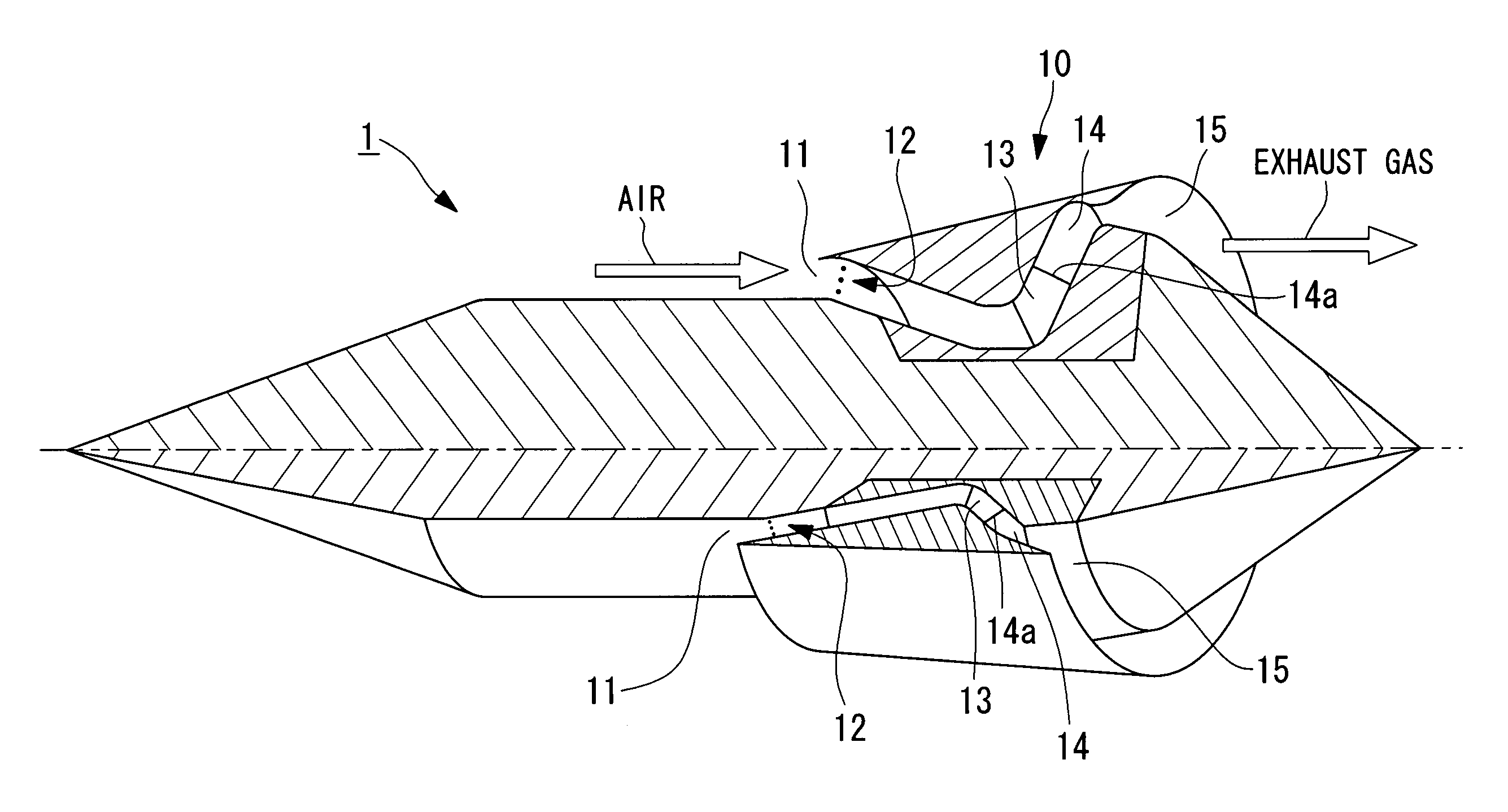
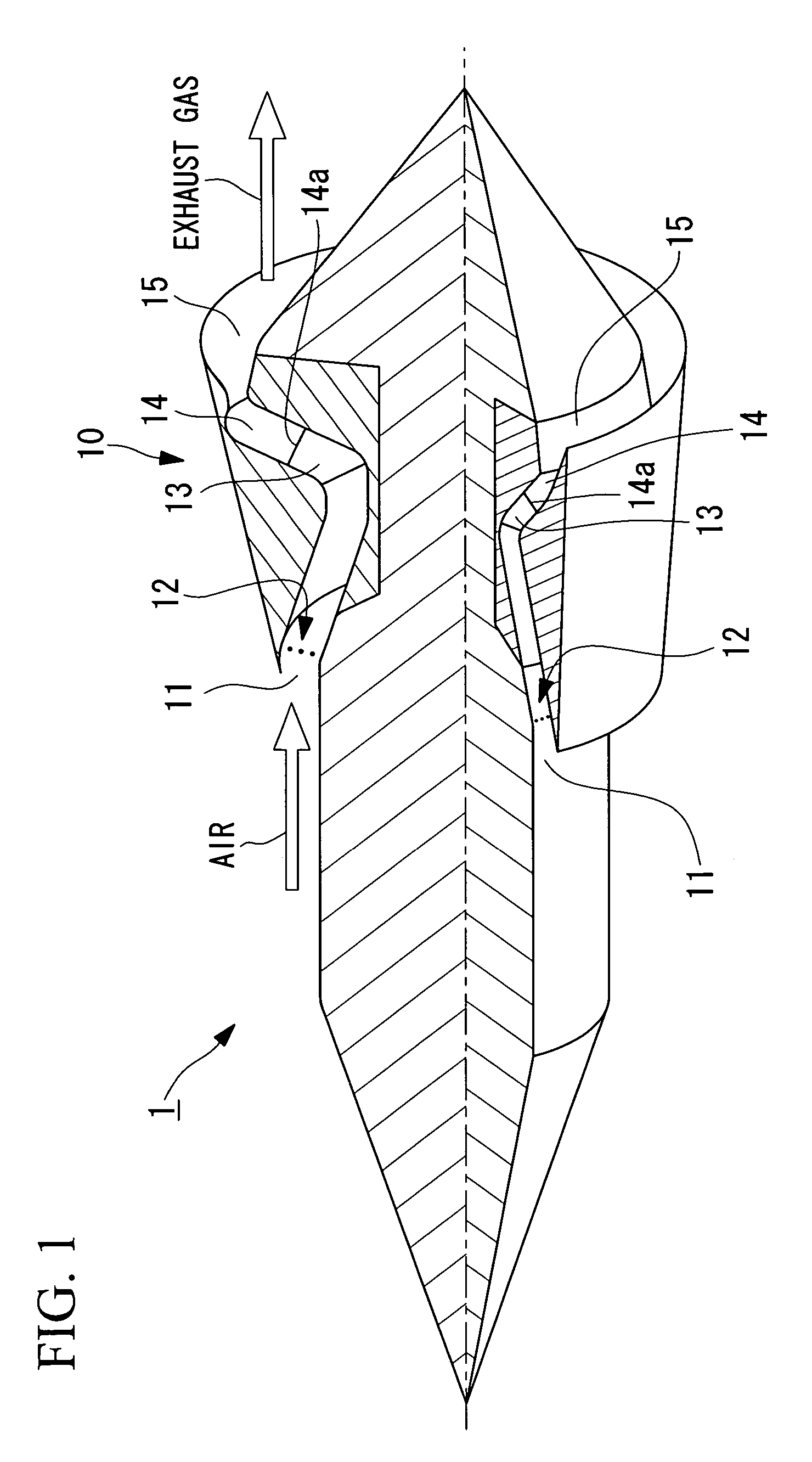
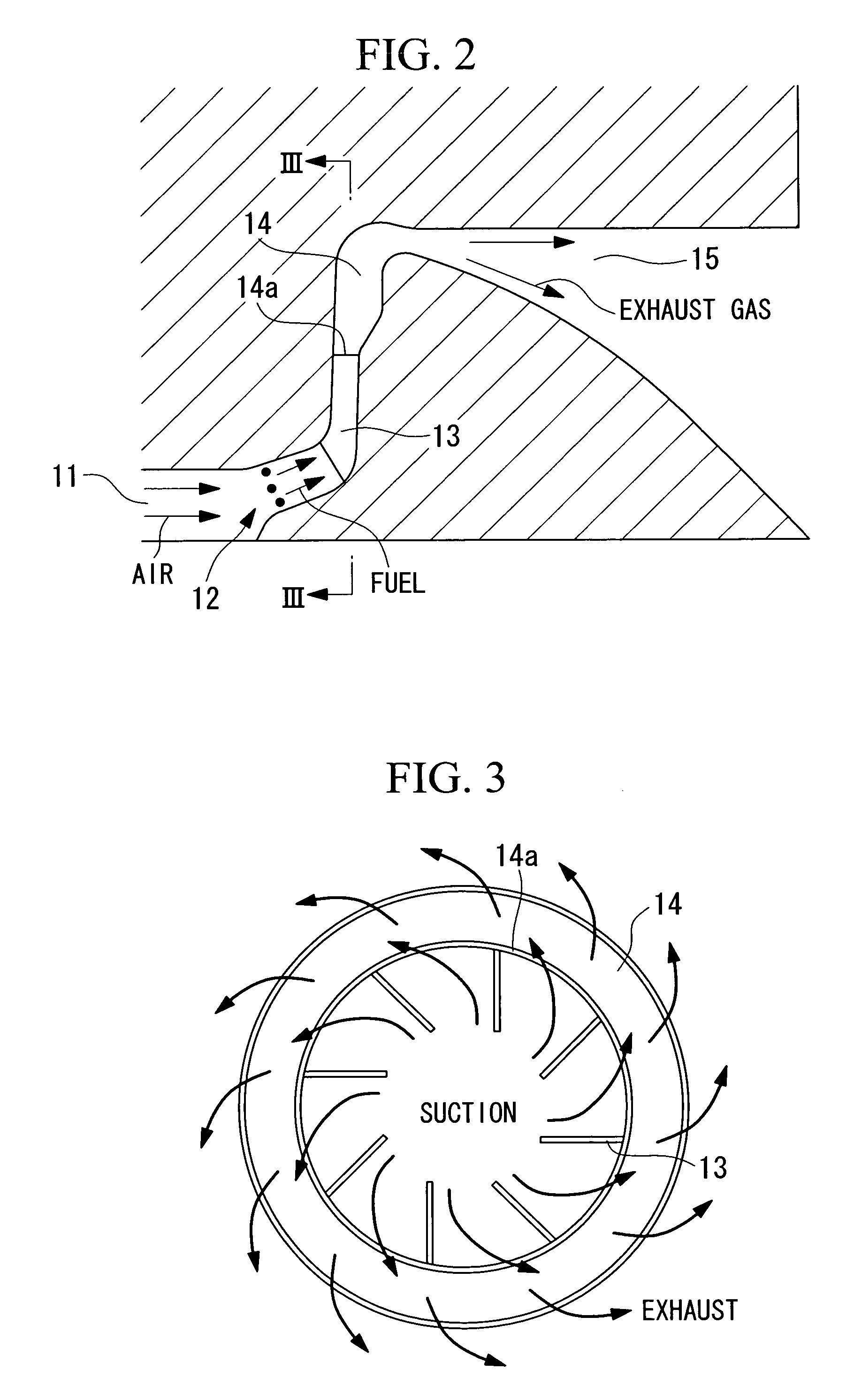
An apparatus for reducing gas turbine engine noise, such as noise generated by an aircraft gas turbine engine, comprises at least one and preferably a plurality of gas injectors for injecting gas such as high pressure engine bleed air, diverted core air, air obtained from a pressurized storage container or air obtained from a synthetic jet actuator into the area proximate to one or more engine nozzle portions, thereby disrupting the noise-generating gas streams generated by the engine exhaust and the travel of the airplane through the air. The apparatus is particularly useful for reducing engine noise during the takeoff period of aircraft flight.
Owner:ROHR INC
Assembly and method for aircraft engine noise reduction
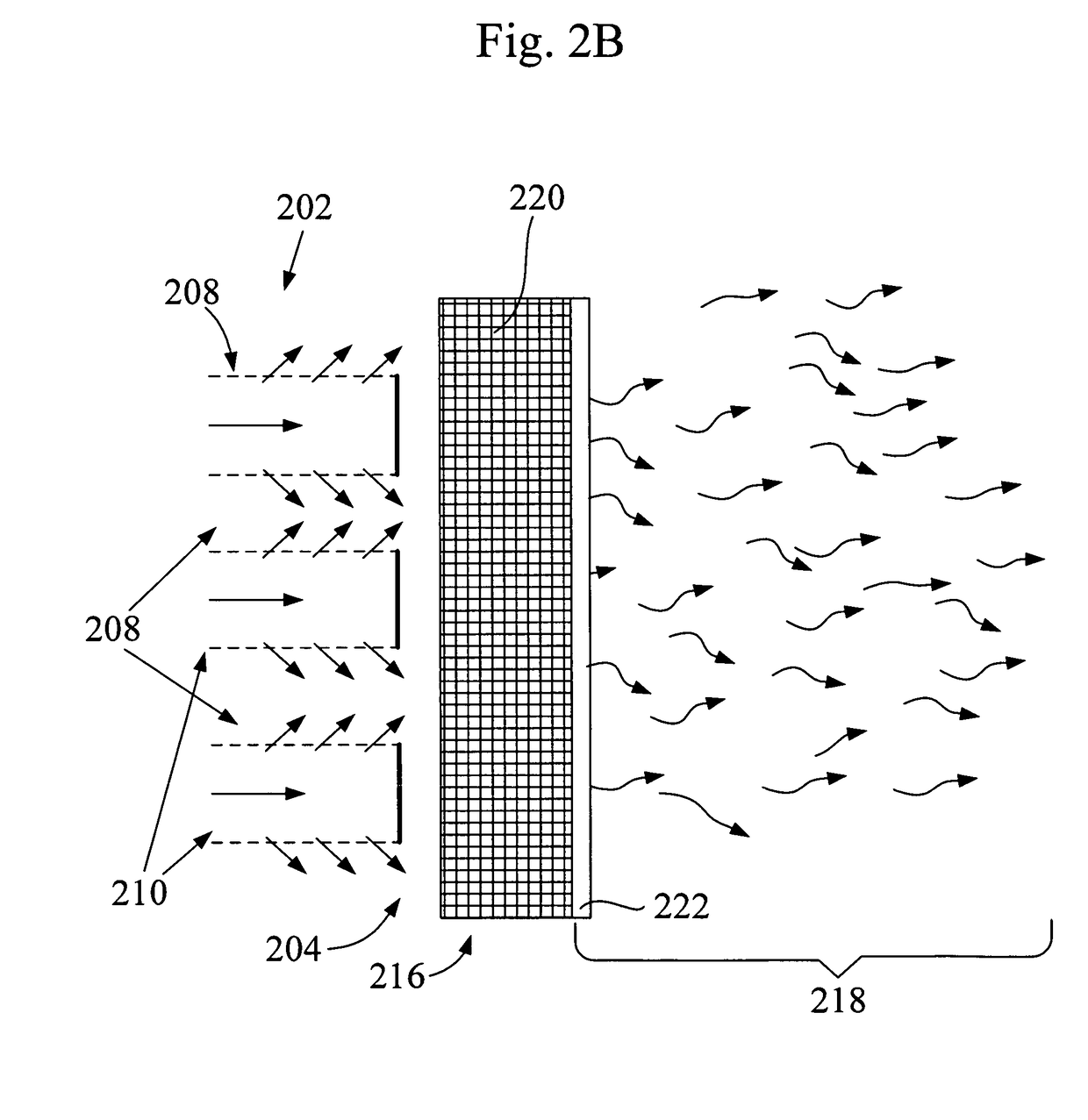
InactiveUS7047725B2Reduce engine noiseNoise reduction installationsCosmonautic vehiclesAirplaneHoneycomb
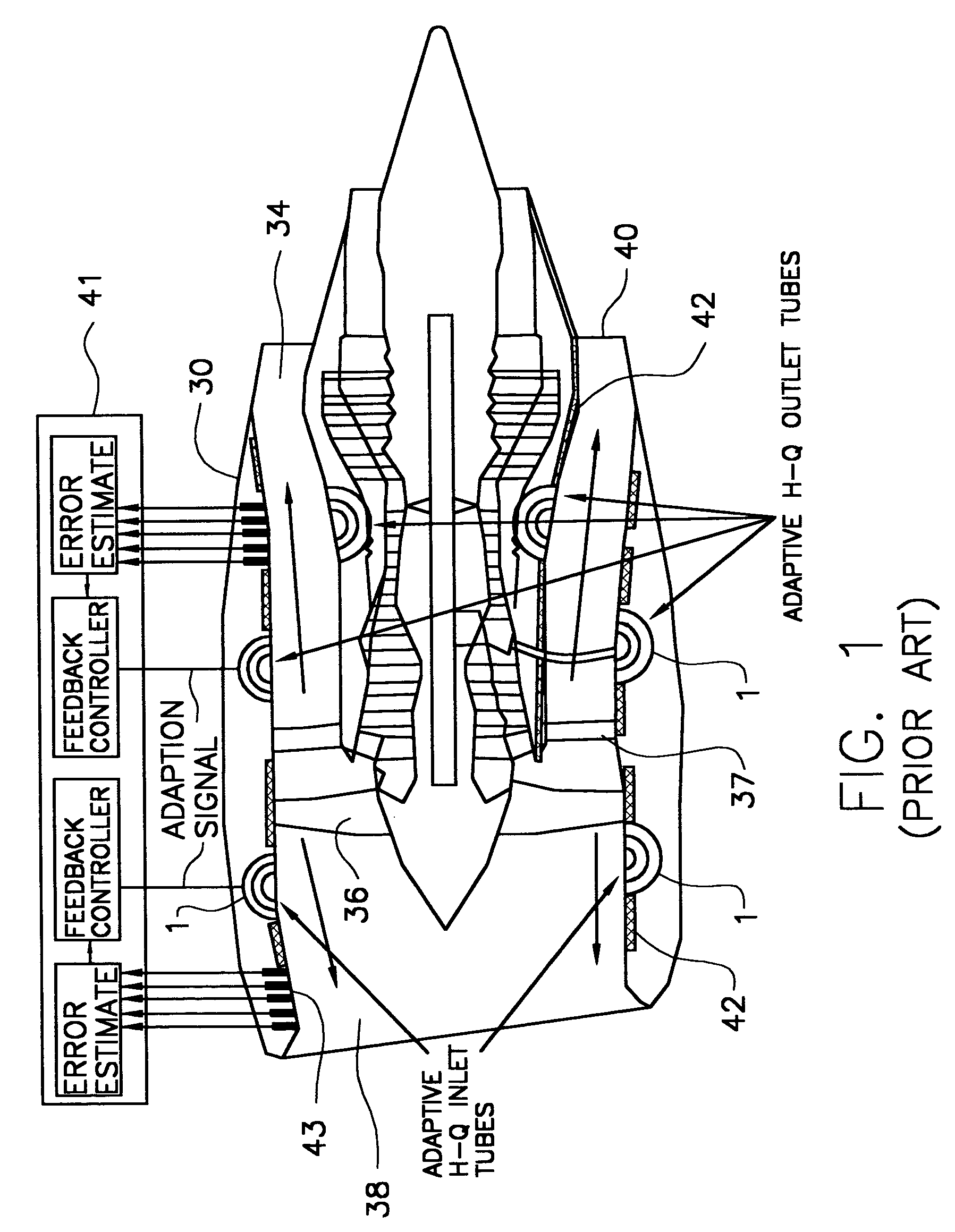
An assembly useful in reducing aircraft engine noise such as turbofan engine noise comprises: (a) a core portion comprising at least one entrance end and at least one exit end for the passage of acoustic energy therethrough; (b) a first member having an exterior face and an interior face, wherein the first member is adjacent to at least a part of the core portion, and the first member has a plurality of openings therein to permit the passage of acoustic energy therethrough; and (c) a second member having an exterior face and an interior face, wherein the interior face of the second member is adjacent to the core portion. The core portion may be a honeycomb acoustic structure, and the first member may be perforated to permit the passage of acoustic energy into and out of the conduit portion.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
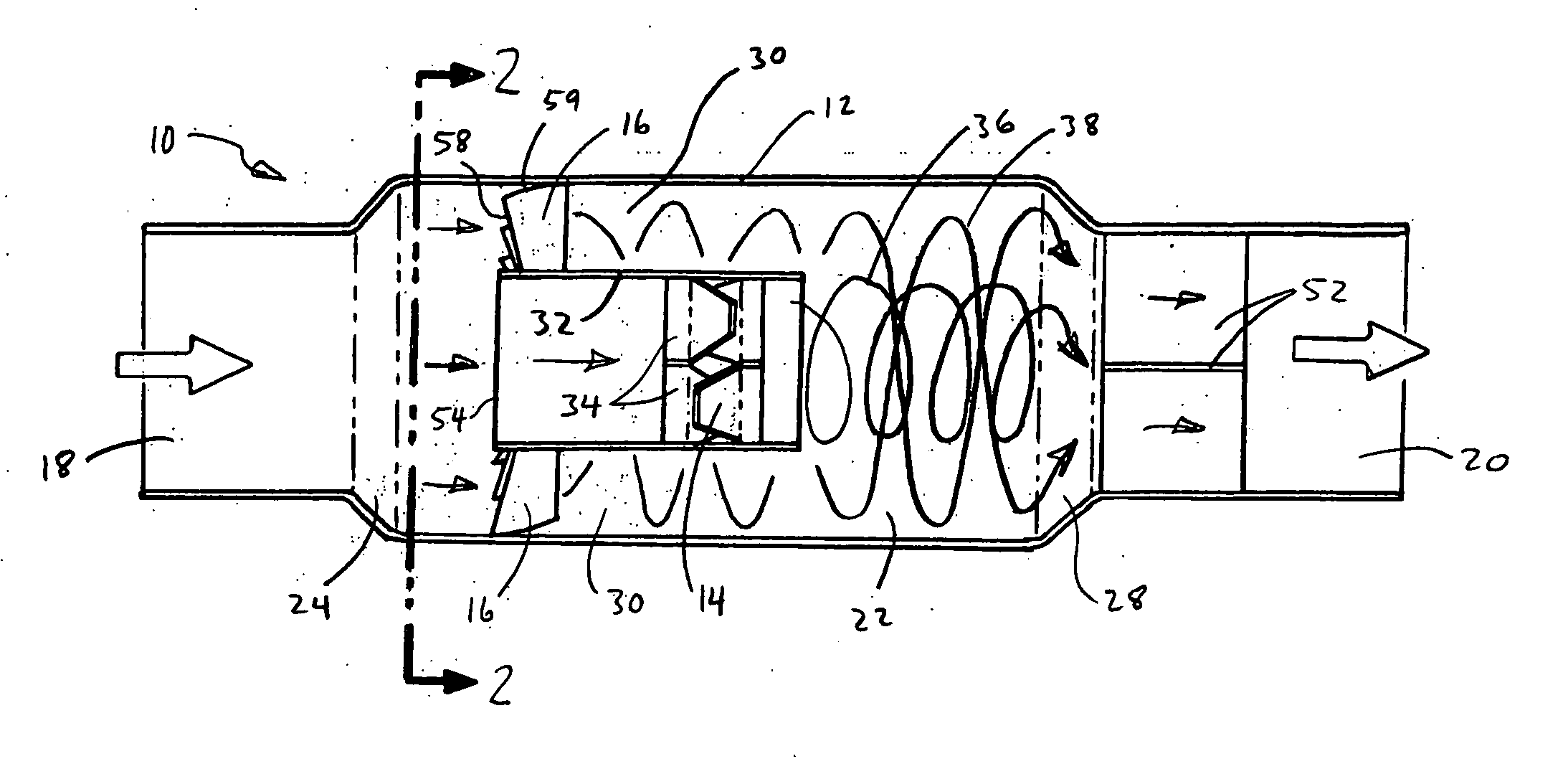
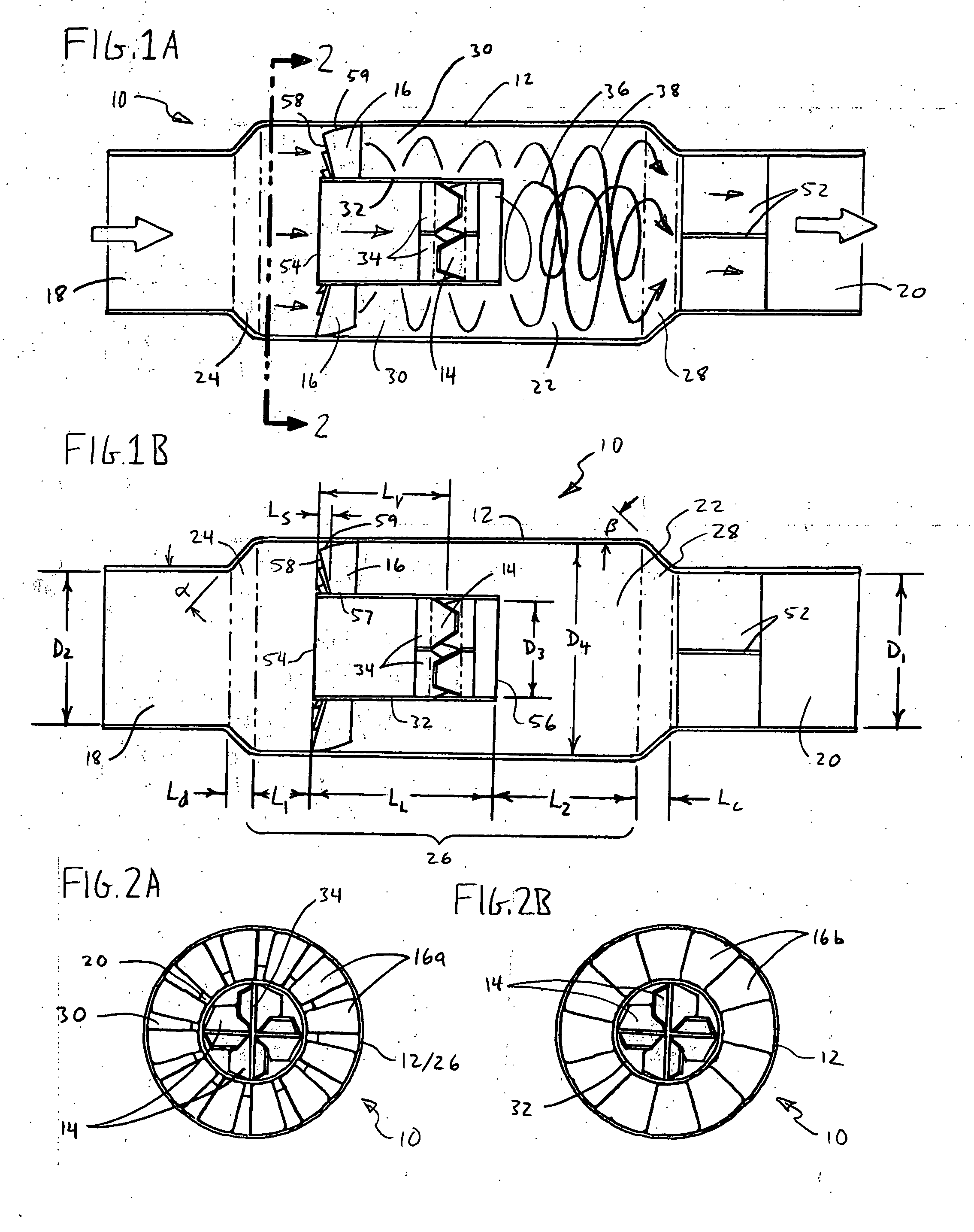
Channeling fluidic waveguide surfaces and tubes
InactiveUS20150337878A1Reduce fluid frictionReduce surfaceVehicle seatsVehicle body stabilisationJet engineEngineering
Waveguide or flow guide surfaces can improve the efficiency of fluid flow through tubes or over surfaces. When incorporated in a tube, the waveguides improve flow and function as sound absorbers making them useful in engine mufflers, firearm silencer / suppressors and jet engine exhaust attenuators. On surfaces, the waveguides can reduce fluid drag and find use on projectiles (e.g., bullets), airfoils for aircraft, and land borne vehicles. The waveguide array in either a tubular chamber or on a surface comprises a plurality of successive wave-like undulations inclined generally in the direction of flow and when employed in tubes extending inwardly to permit an unobstructed path for the fluid gas from entry to exit. The waves define annular wave cavities between their successive inwardly extending edges and the wall of the chamber with each cavity having a cavity mouth open to the unobstructed path. The waveguides are sized and spaced so that gas vortices are created within the cavities when gas flow occurs which vortices create a fluid boundary layer that assists the gas flow.
Owner:PARAFLUIDICS
Detonation engine and flying object provided therewith
InactiveUS20050284127A1Structure of engine can be simplifiedGuaranteed continuous outputMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesCombustionDetonation
A detonation engine which creates thrust by generating a detonation wave, wherein the overall engine structure is simplified, and continuous output can be obtained, comprises: a rotational flow generation device which generates rotational flow about an axis in a mixed gas of air and fuel or of oxygen and fuel; a detonation chamber arranged downstream from the rotational flow generation device, formed in a ring-shape radially extended and continuous in the circumferential direction, which continuously combusts in the circumferential direction the mixed gas in which the rotational flow is generated to generate detonation waves, and draws it in from the radial inside and exhausts it to the radial outside; and a nozzle which is connected to the detonation chamber, and jets the high temperature and pressure combustion gas generated by the detonation waves flowing from the detonation chamber, to the rear while expanding it, and converts it into thrust.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +2
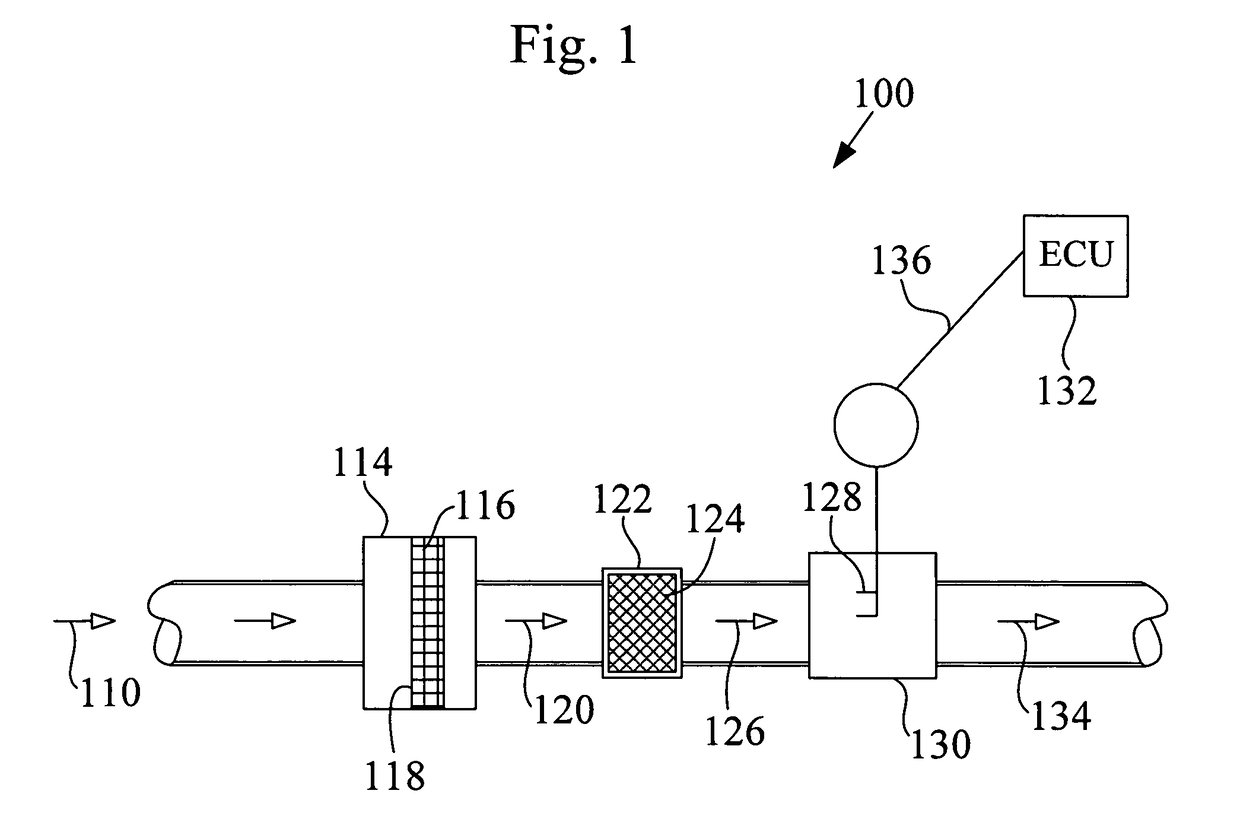
Flow vortex suppression apparatus for a mass air flow sensor
ActiveUS20100269583A1Reduce air turbulenceReduce turbulenceCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentFiberEngineering
In various aspects of the invention a flow vortex suppression apparatus for use in an air intake duct having a mass air flow sensor is disclosed. The flow vortex suppression apparatus includes an air flow permeable fibrous vortex dispersive media installed into the air duct in a position upstream of the mass flow sensor and configured to occlude the air duct such that air flow in the duct is constrained to pass through the vortex dispersive media. The vortex dispersive media is configured and adapted to diffuse vortices and reduce air turbulence of an air stream entering the mass flow sensor, thereby reducing variations and noise in a flow measurement signal from the mass air flow sensor.
Owner:MANN HUMMEL GMBH
System and method for improving cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS20170356375A1Improving engine fuel economyReduce engine noiseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMotor fuelAutomotive engineering
Systems and methods for operating an engine with deactivating and non-deactivating valves are presented. In one example, estimates of engine fuel consumption for operating the engine with a plurality of cylinder modes or patterns while a transmission is engaged in different gears are determined and are used as a basis for deactivating engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Detonation engine and flying object provided therewith
InactiveUS7784267B2Simple structureGuaranteed continuous outputMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesDetonationCombustion
A detonation engine which creates thrust by generating a detonation wave, wherein the overall engine structure is simplified, and continuous output can be obtained, comprises: a rotational flow generation device which generates rotational flow about an axis in a mixed gas of air and fuel or of oxygen and fuel; a detonation chamber arranged downstream from the rotational flow generation device, formed in a ring-shape radially extended and continuous in the circumferential direction, which continuously combusts in the circumferential direction the mixed gas in which the rotational flow is generated to generate detonation waves, and draws it in from the radial inside and exhausts it to the radial outside; and a nozzle which is connected to the detonation chamber, and jets the high temperature and pressure combustion gas generated by the detonation waves flowing from the detonation chamber, to the rear while expanding it, and converts it into thrust.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +2
Snowmobile Exhaust System
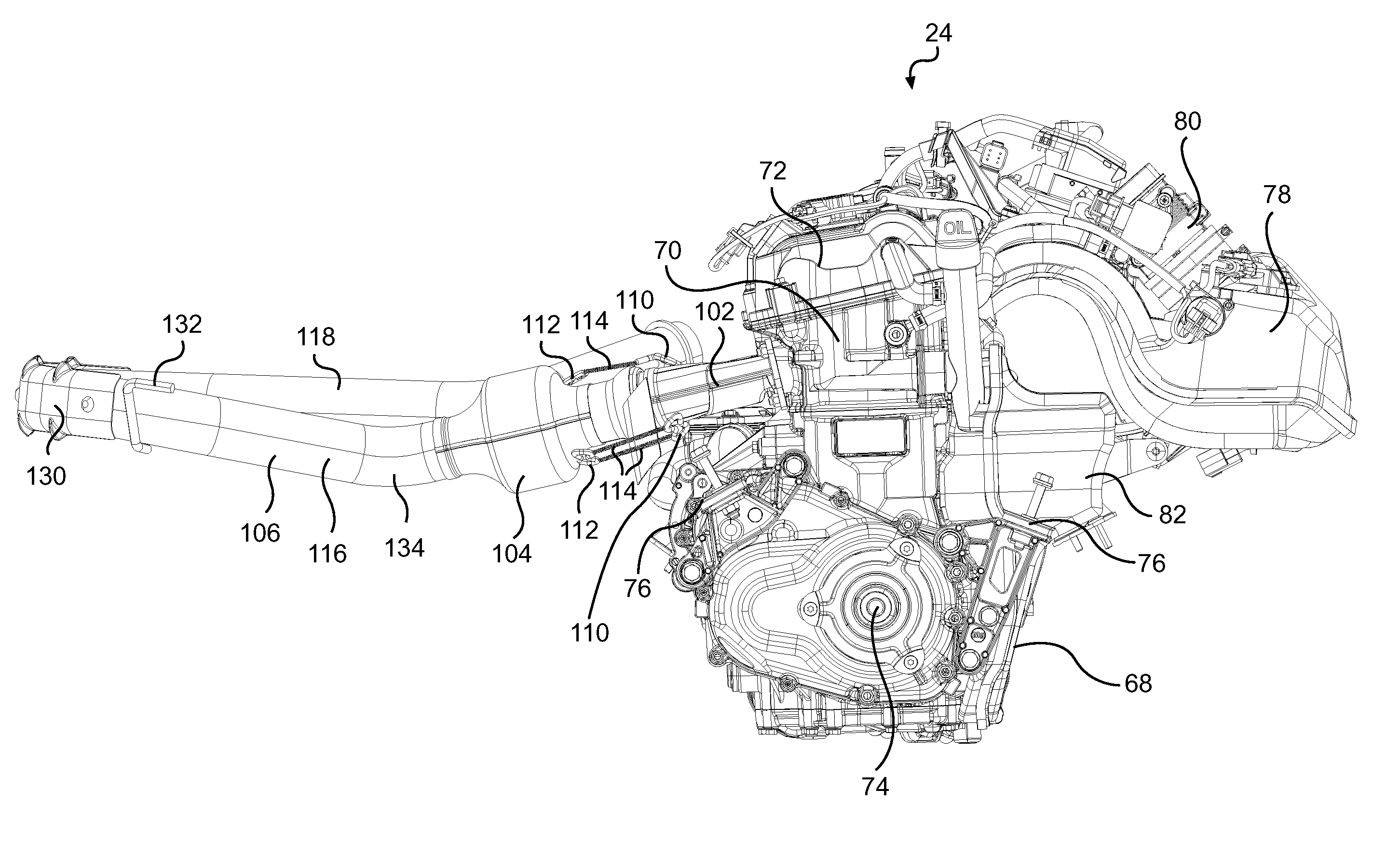
ActiveUS20100108427A1Reduce engine noiseReduce the amount requiredSnowmobilesSledgesFour-stroke engineEngine mount
A snowmobile has a four-stroke engine mounted in an engine cradle and an exhaust system connected to the engine. The exhaust system includes a generally U-shaped exhaust pipe extending forwardly from the engine to a first point disposed forwardly of the engine cradle, and of suspension assemblies of the skis, and extending rearwardly from the first point to a second point disposed rearwardly of a front of the engine cradle.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
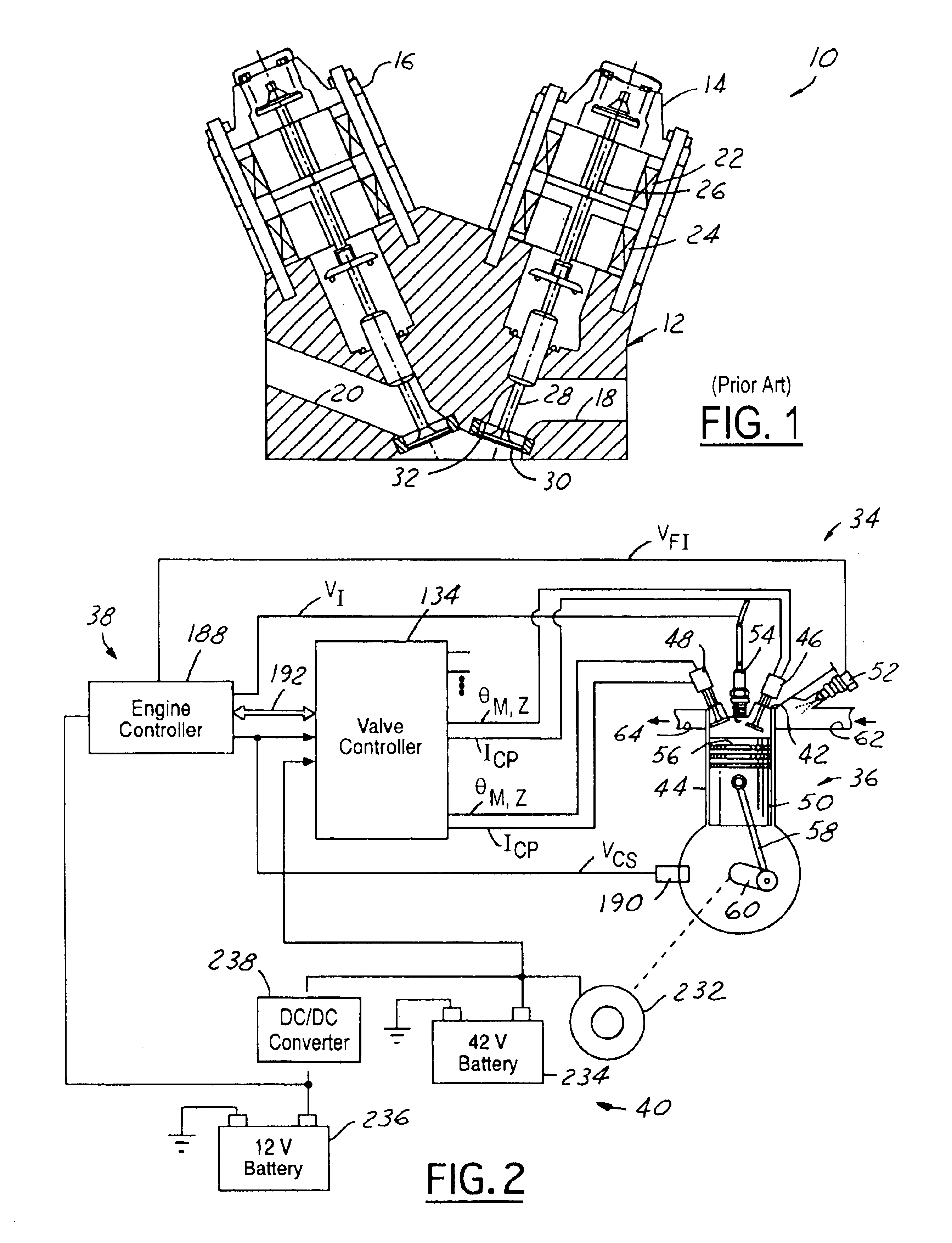
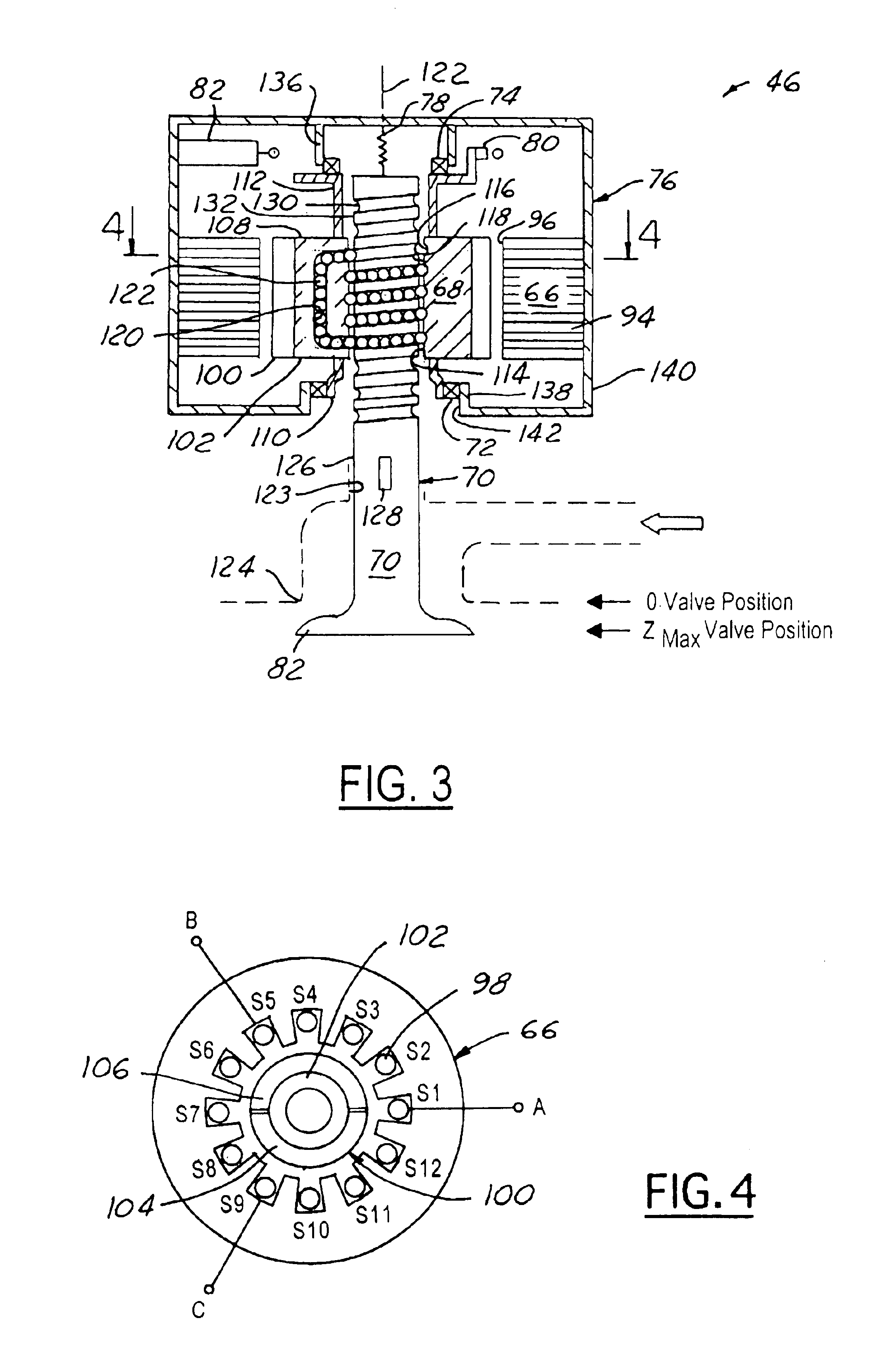
Electromechanical valve assembly for an internal combustion engine
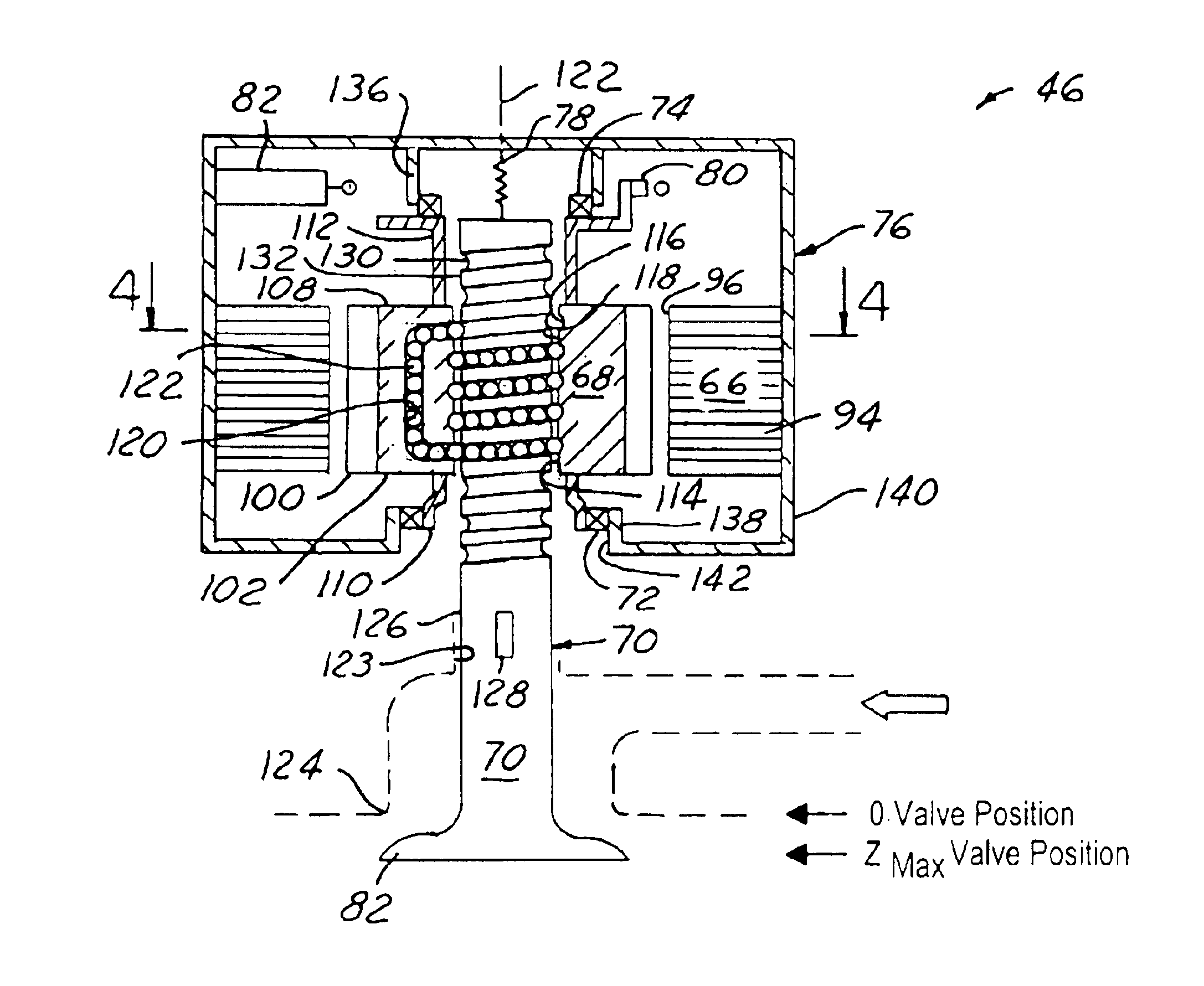
InactiveUS6840200B2Lower energy requirementsEasy to controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMachines/enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
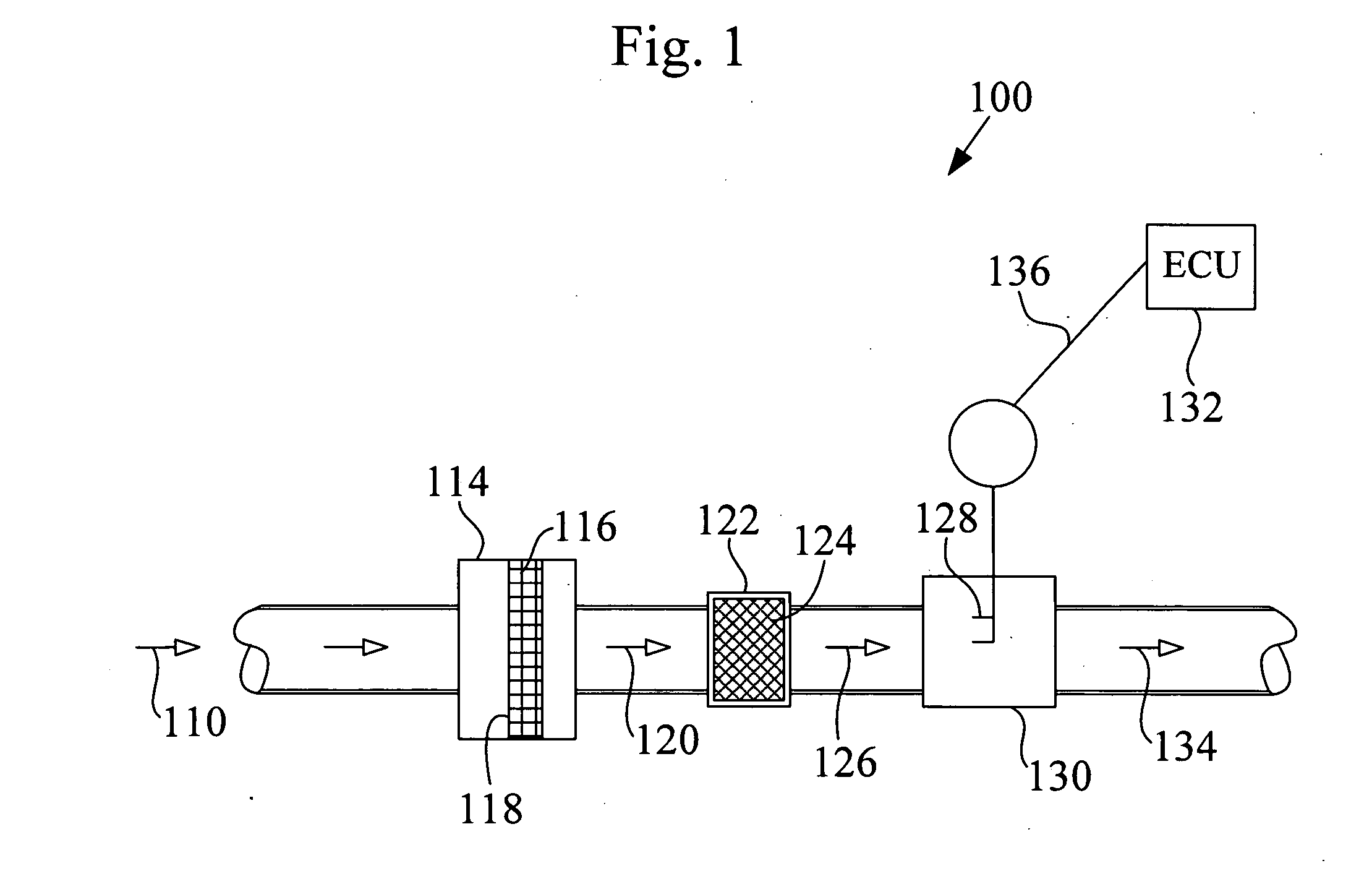
An electromechanical valve assembly 46 for an internal combustion engine 36 is provided. The valve assembly 46 includes a rotor 68 centered about a first axis 122 having a bore 114 extending generally axially therethrough. The valve assembly 46 further includes a stator 66 operatively disposed about the rotor 68 for producing a torque to cause rotation of the rotor 68 about the axis 122. Finally, the valve assembly 46 includes a valve 70 having a valve stem 126 and a valve head 84 The valve stem 126 extends generally axially through the bore 114 of the rotor 68. The valve stem 126 is also configured to move generally axially responsive to the rotation of the rotor 68 to selectively engage and disengage the valve head 84 with a valve seat 124 of the engine 36.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Gas flow enhancer for combustion engines
InactiveUS20060075745A1Increase back pressureReduce engine noiseInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCombustionEngineering
A gas flow enhancer for a combustion engine includes a housing, configured to receive an inlet flow of gas at an inlet pressure, and enclosing an expansion chamber. Disposed within the expansion chamber are a set of inner vanes and outer vanes, and a flow separator. The outer vanes are disposed outside the flow separator and produce an outer helical flow of the gas. The inner vanes are disposed within the flow separator and produce an inner helical flow of the gas, the inner helical flow having a higher velocity and lower pressure than the outer helical flow. The outer helical flow and inner helical flow are recombined at an outlet of the expansion chamber so as to produce an outlet laminar flow profile having a lower average pressure than the inlet pressure.
Owner:FREEDMAN LEN
Jet Engine Exhaust Nozzle Flow Effector
InactiveUS20080272232A1Reduce jet engine noiseReduce engine noiseAircraft stabilisationEfficient propulsion technologiesJet engineShape-memory alloy
A jet engine exhaust nozzle flow effector is a chevron formed with a radius of curvature with surfaces of the flow effector being defined and opposing one another. At least one shape memory alloy (SMA) member is embedded in the chevron closer to one of the chevron's opposing surfaces and substantially spanning from at least a portion of the chevron's root to the chevron's tip.
Owner:NASA
System and method of waste heat recovery and utilization
InactiveUS7891186B1Increase fuel consumptionImprove thermal efficiencyGas pressure propulsion mountingCombustion enginesAlternative fuelsHeat transfer fluid
A waste heat recovery system is provided for an internal combustion engine having a piston, a cylinder and an intake manifold, significantly improving gas mileage efficiency without reliance on alternative fuels. The system includes a heat loop having a heat transfer fluid, a compressor in fluid communication with the intake manifold to supply compressed air thereto, a Stirling engine operated and optimized via thermal communication with the heat loop, and operatively coupled to the compressor. The system includes a chiller in thermal communication with the heat loop, and with the intake manifold to cool the compressed air communicate to the cylinder. The system may include additional Stirling engines operating other devices, or being operated by a device, such as a propeller. A vehicle can incorporate the system and route fluid to and from a radiator. The system can be used in both portable and stationary applications.
Owner:PRIMLANI INDRU J
Fan blade
InactiveUS20090269189A1Reduce engine noiseAvoid rubbing contact damagePump componentsBlade accessoriesEngineeringFan blade
A fan blade for the fan of a gas turbine engine has a radially outer tip portion which, in use, is adjacent to a fan case of the engine. The tip portion includes a movable sealing element for sealing a gap between the tip portion and the fan case. The sealing element movably adapts to changes in the spacing of the gap to maintain a seal between the tip portion and the fan case.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
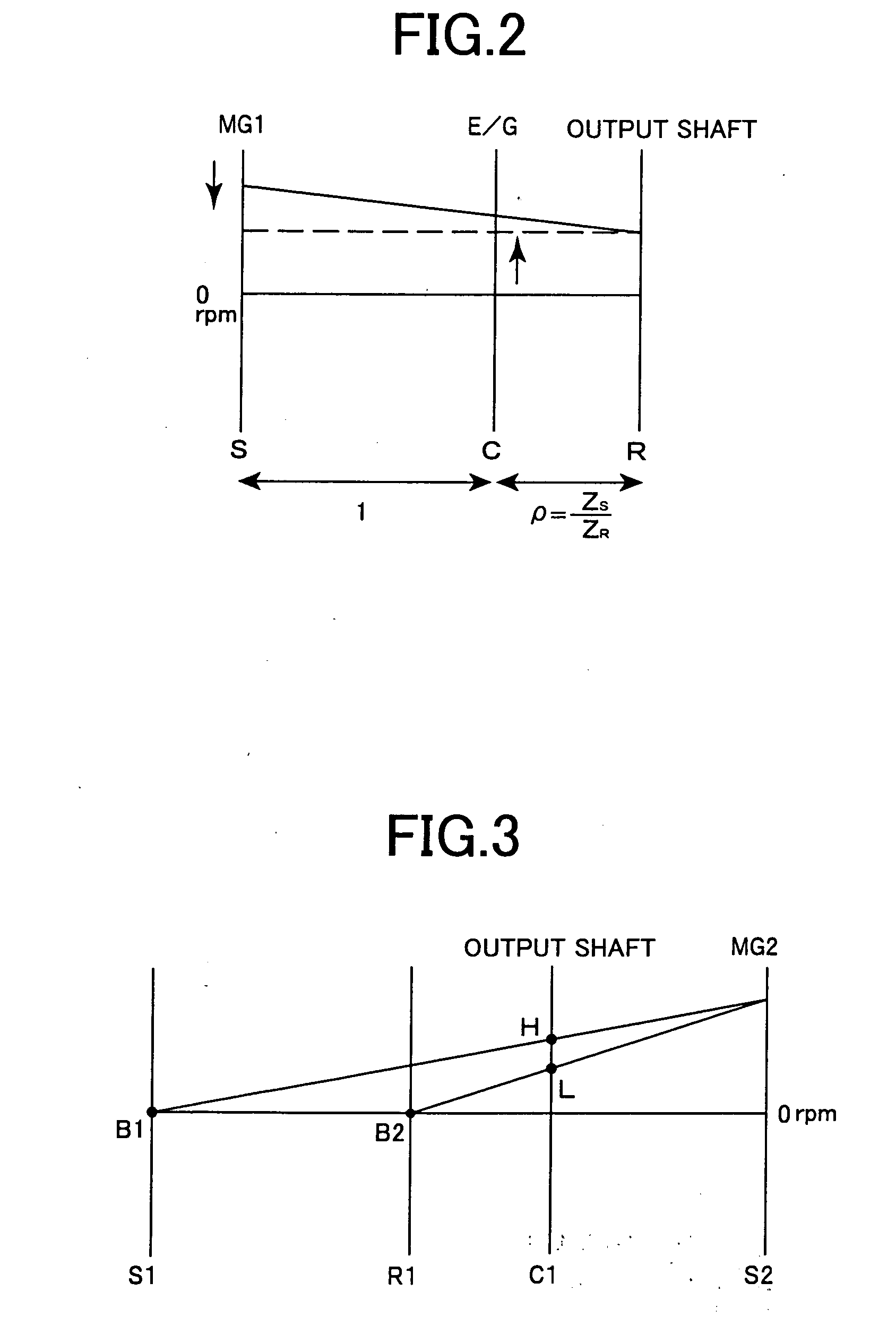
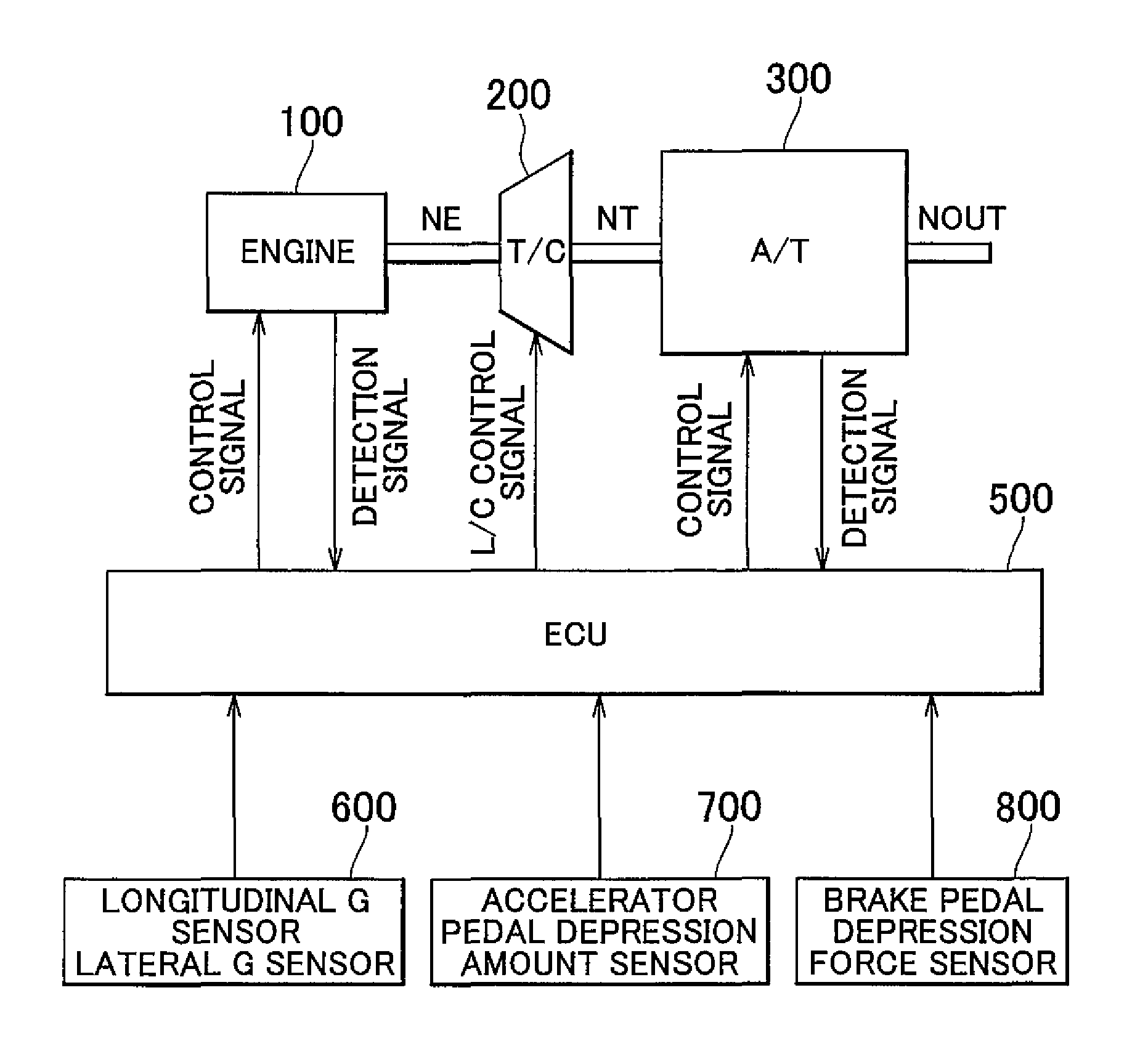
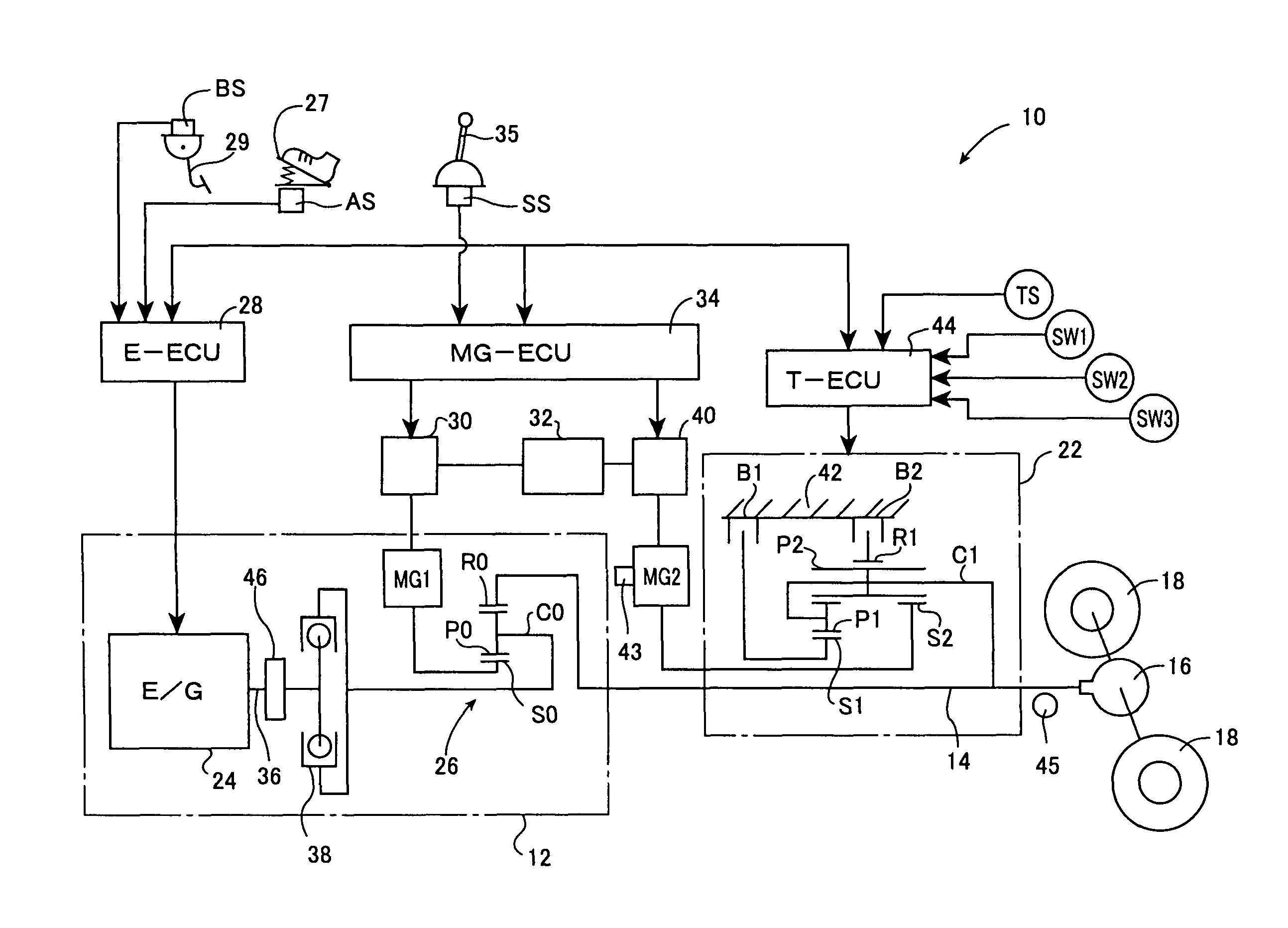
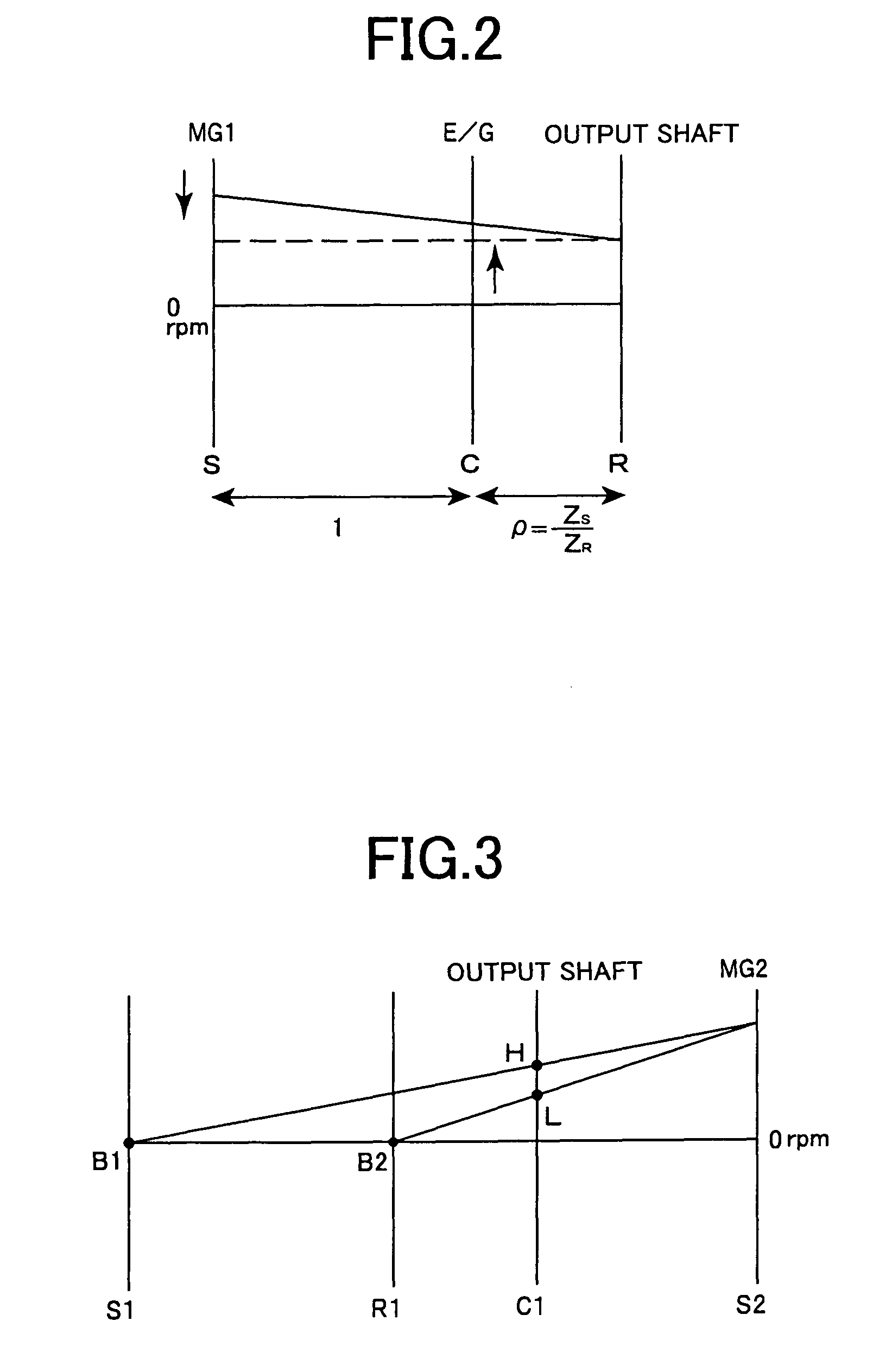
Drive Control Device For Hybrid Vehicle
Due to the reduction of a discharge amount of a mechanical oil pump by a lowering of the idling rotation speed, a slip in a hydraulic power transmission apparatus and a blow up of an electric motor for running due to a delay of the rising of the oil pressure upon the sudden start and the like are prevented. While avoiding the slip and the blow up, the idling rotation speed is lowered so as to make the engine noise small. When the return determination from the idling state is performed based on the shift operation from P to D, at step S5, a torque TMG2 of a second motor / generator MG2 is temporarily restricted. As a result, upon the sudden start from the idling state, even when the rising of the oil pressure delays, the second brake B2 engaged upon the starting is prevented from slipping, and the second motor / generator MG2 is prevented from blowing up. As a result, while avoiding the slip of the second brake B2 and the blow up of the second motor / generator MG2 due to the hydraulic response delay, an idling rotation speed N Eidl is lowered so that the engine noise can be reduced.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Flow vortex suppression apparatus for a mass air flow sensor
ActiveUS7905153B2Dampen noise levelReduce engine noiseCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentEngineeringMass flow sensor
Owner:MANN HUMMEL GMBH
Variable intake system of a vehicle
InactiveUS20060005798A1Reduce engine noiseLow costInternal combustion piston enginesAir intakes for fuelActuatorControl theory
A variable intake system of a vehicle includes an intake manifold having a runner, an opening / closing part for varying the runner length of the intake manifold, an actuator for driving the opening / closing part, and a vacuum part forming a vacuum chamber for driving the actuator. The vacuum part is disposed on an upper portion of the intake manifold such that noise from the engine may be decreased.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Throttle plate wedge
InactiveUS6971632B2Improve drivabilityReduce engine noisePlug valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringControl theory
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Channeling fluidic waveguide surfaces and tubes
InactiveUS9739296B2Reduce noiseImprove accuracyEngine fuctionsSilencing apparatusJet engineSuppressor
Waveguide or flow guide surfaces can improve the efficiency of fluid flow through tubes or over surfaces. When incorporated in a tube, the waveguides improve flow and function as sound absorbers making them useful in engine mufflers, firearm silencer / suppressors and jet engine exhaust attenuators. On surfaces, the waveguides can reduce fluid drag and find use on projectiles (e.g., bullets), airfoils for aircraft, and land borne vehicles. The waveguide array in either a tubular chamber or on a surface comprises a plurality of successive wave-like undulations inclined generally in the direction of flow and when employed in tubes extending inwardly to permit an unobstructed path for the fluid gas from entry to exit. The waves define annular wave cavities between their successive inwardly extending edges and the wall of the chamber with each cavity having a cavity mouth open to the unobstructed path. The waveguides are sized and spaced so that gas vortices are created within the cavities when gas flow occurs which vortices create a fluid boundary layer that assists the gas flow.
Owner:PARAFLUIDICS
Ultra hush exhaust system (UHES)
ActiveUS20170191447A1Minimal lossReduce engine noiseEngine manufactureJet propulsion plantsActuatorStreamflow
An exhaust noise attenuation system mounted to a Jet Engine exit turbine frame for noise attenuation with an ULTRA THRUST REVERSER System mounted at the exhaust end, aft end of the exhaust noise attenuation system, to provide deceleration after landing of the aircraft. The exhaust noise attenuation system consists of double walled duct which can be either of constant circular, square or elliptic cross section or convergent section with variable cross-section area, made of sheet metal double walls with a perforated inner wall or skin except in the areas where there are solid non-perforated corrugations or hat sections which act as frames for structural integrity of the double walled duct, and a non-perforated outer wall or skin, with an appropriate noise attenuation material, assuming honeycomb for the sake of discussion since it is widely used, sandwiched between the inner perforated and outer solid skins of the duct. The sound attenuation material is placed in between the corrugations / hat sections over the perforations of the inner skin. The double walled duct is connected to a nozzle / ring bolted to the engine frame using two or more struts. In the shown figures the inventor used four (4) struts for depiction. Hinged inlet Doors are mounted at the forward end of the double skin duct, controlled by the pilot or the engine control system, to control the flow of ambient air sucked into the exhaust system by the eductor action, to optimize the engine performance, noise signature and reduce ram drag during flight. The doors can also be closed tight during flight to reduce ram drag and to create a smooth surface for the ambient air flowing over the surface of the exhaust system. However, the doors can be fitted with smaller doors or scoops to provide a limited amount of airflow to cool off the walls of the inner perforated duct. A movable exit cone can be used with the convergent duct configuration to optimize the exit area of the double walled duct to optimize the engine performance. An ULTRA THRUST REVERSER SYSTEM is mounted at the aft end of the double walled duct, consists of two improved design clamshell doors mounted on either side of the top and bottom of the double walled duct, fitted with two unique design actuators mounted one on each side of the external sides of the duct between the clamshell doors and the duct, possibly in a depression in the duct called blister, assuming them to be hydraulic actuators for discussion purposes. The actuators drive the clamshell doors using linkages pivoted to the exterior of the double walled duct, connecting the doors to the actuators, to deploy the doors aft of the double walled duct during deceleration after landing, diverting the exhaust gases forward to slow down the aircraft, but also drive the two movable fairings during thrust reverser operation to enclose the reversed exhaust flow forward to prevent its impingement on the skin of the aircraft.
Owner:OSMAN MEDHAT
Construction machine
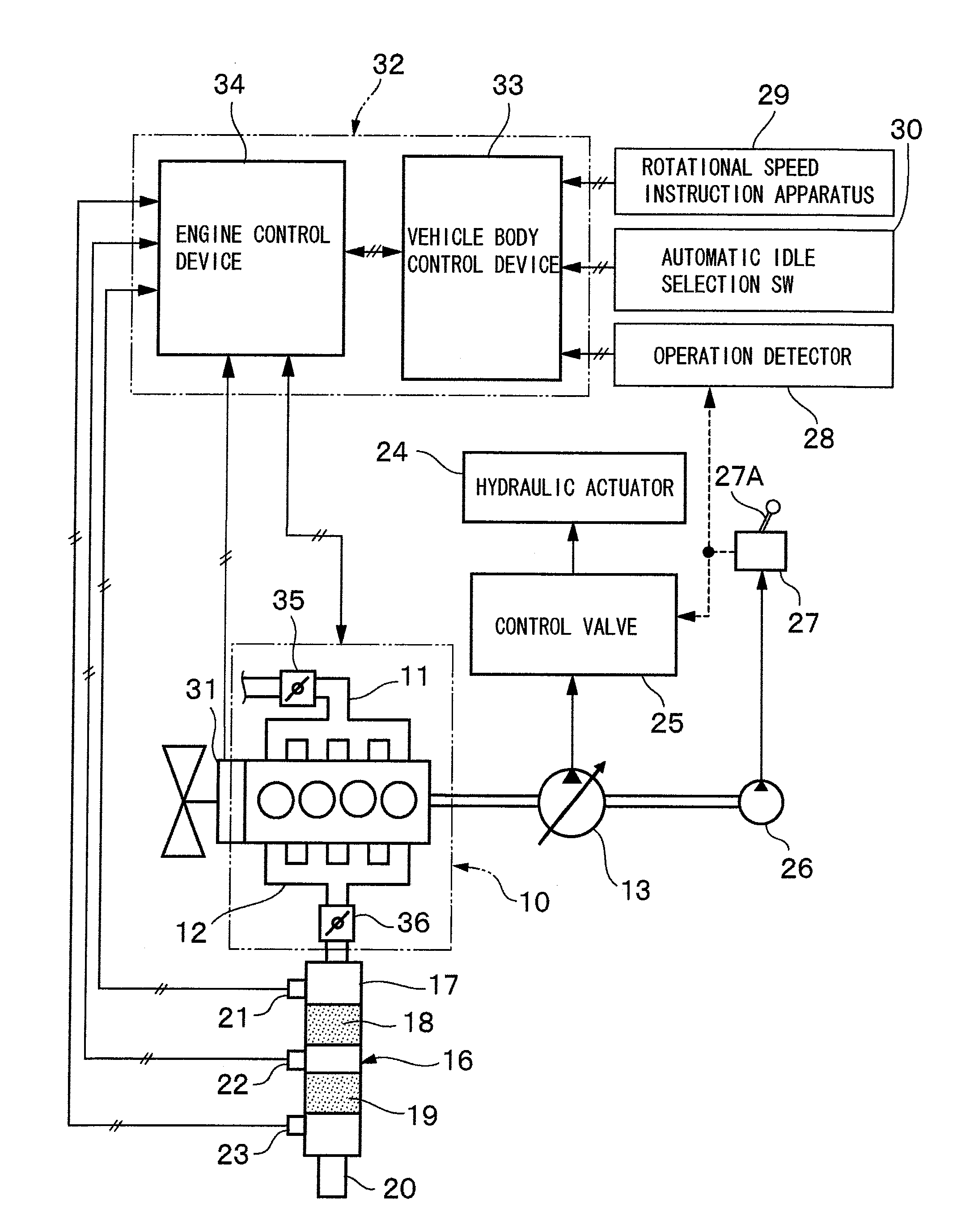
InactiveUS20140008140A1Saving and reduction of fuel consumptionReduce noiseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesControl valves
A regeneration apparatus for executing a regeneration process to an exhaust gas purifying apparatus and an engine control device that controls a rotational speed of an engine according to an instruction value by a rotational speed instruction apparatus are provided. When a directional control valve is in a neutral position, the engine control device controls the rotational speed of the engine to an automatic idle rotational speed (Nai) by an automatic idle selection unit regardless of the instruction value. However, when it is determined that the regeneration process of the exhaust gas purifying apparatus is executed in a state of controlling the rotational speed of the engine at the automatic idle rotational speed (Nai), the engine control device increases the rotational speed of the engine to a regeneration processing rotational speed (N1) higher than the automatic idle rotational speed (Nai).
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Acoustic Side Cover for an Engine
InactiveUS20090056668A1Reduce engine noiseImprove fuel economyCasingsCeilingsEngineeringCylinder block
An apparatus for reducing engine noise includes a side cover configured to operatively connect to a side of an engine block. The side cover has a first layer configured to be adjacent to an outer surface of the side of the engine block. The first layer is made of a first acoustic-absorbing material. The side cover also has a second layer configured to be adjacent to the first layer opposite the engine block. The second layer is a second substantially rigid material establishing an acoustic barrier and is configured to operatively support at least one engine component such as an electrical or fluid line, such as by an integrally formed fastener or channel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
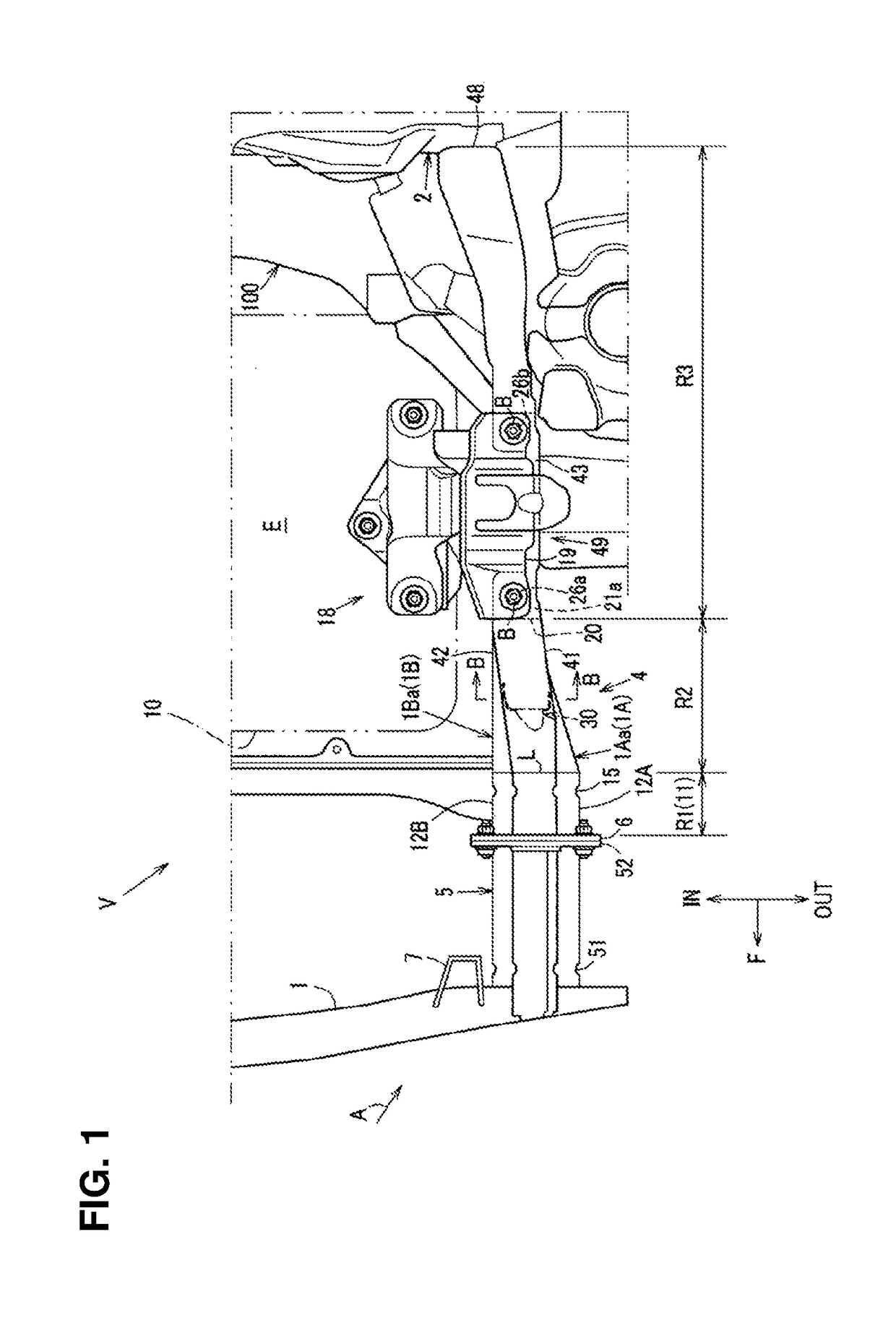
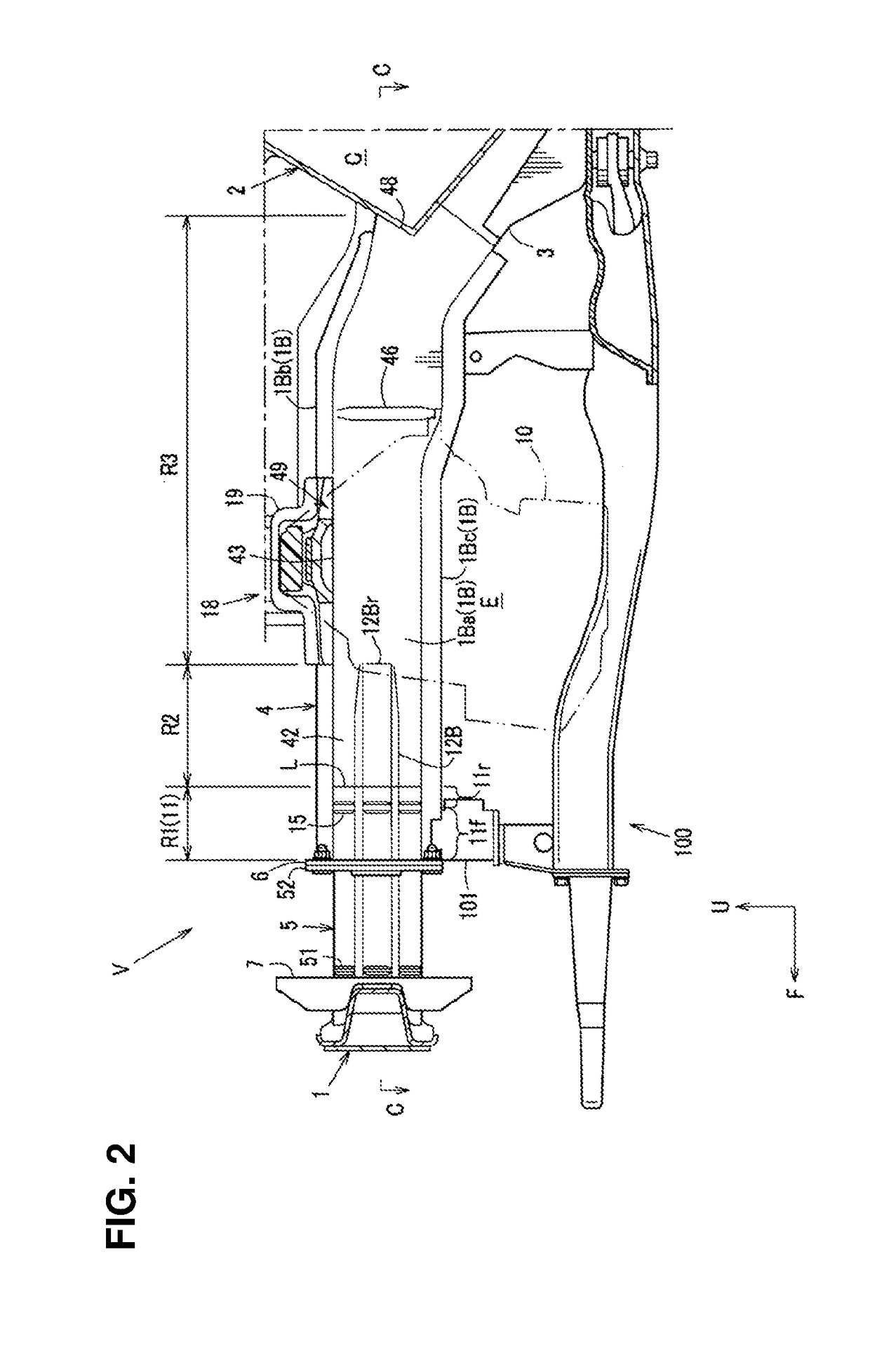
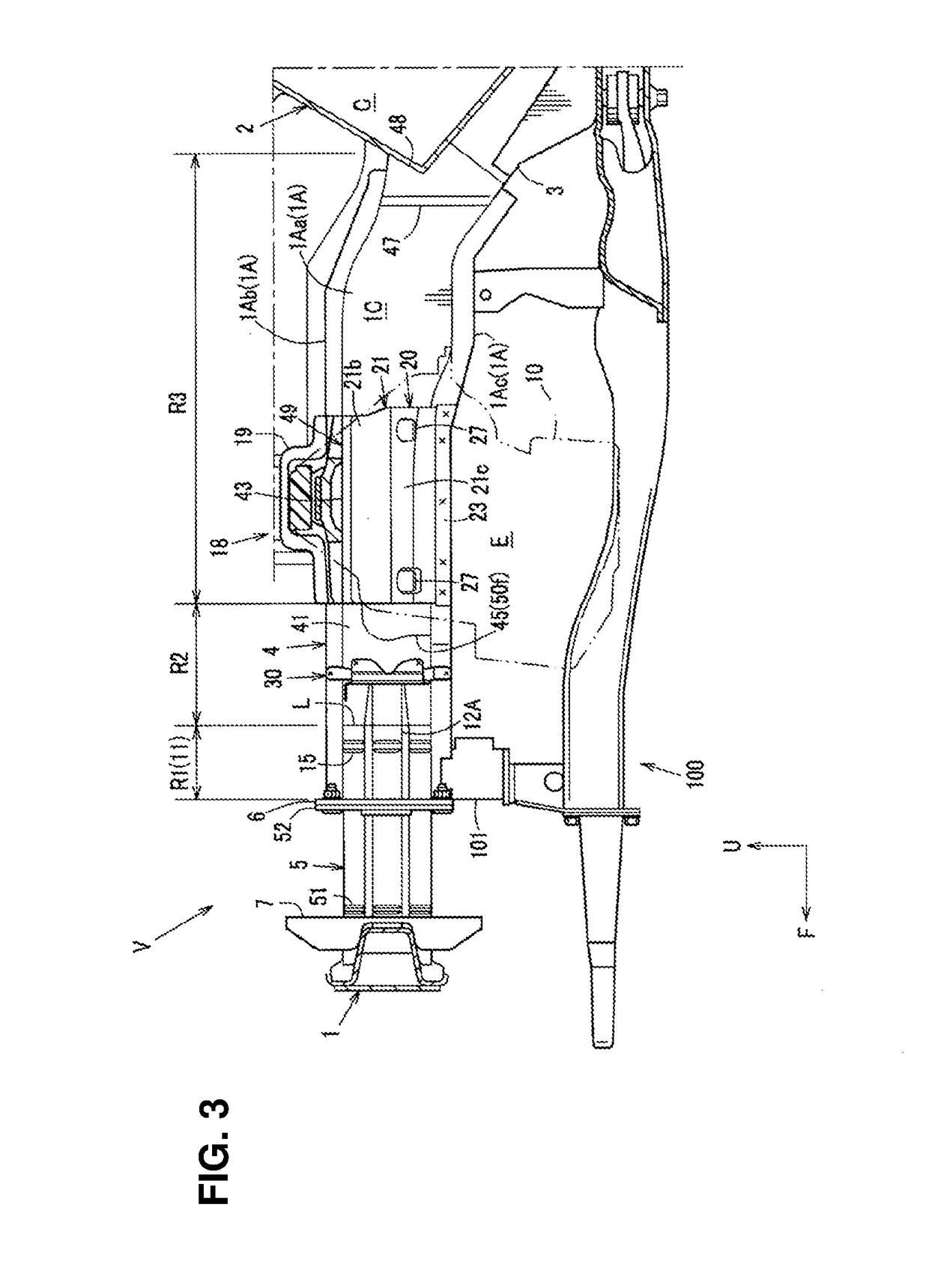
Front vehicle-body structure of vehicle
ActiveUS20190016389A1Promote absorptionImprove NVH performanceUnderstructuresSuperstructure subunitsShearing deformationEngineering
There are provided a front side frame having a closed cross section extending in a vehicle longitudinal direction and including a mount-bracket attachment part for attaching a PT mount bracket provided at a PT mount for supporting a powertrain and a crash can attached to a front end of the front side frame. The front side frame includes a compressive-deformation part which is configured to be compressively deformed in a vehicle frontal collision and extend rearward from the front end, having substantially the same sectional shape as the crash can. A gusset member for preventing shearing deformation of the closed cross section of the front side frame is provided at a portion of the front side frame between the mount-bracket attachment part and the compressive-deformation part.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Hydraulic Drive Device for Dump Truck
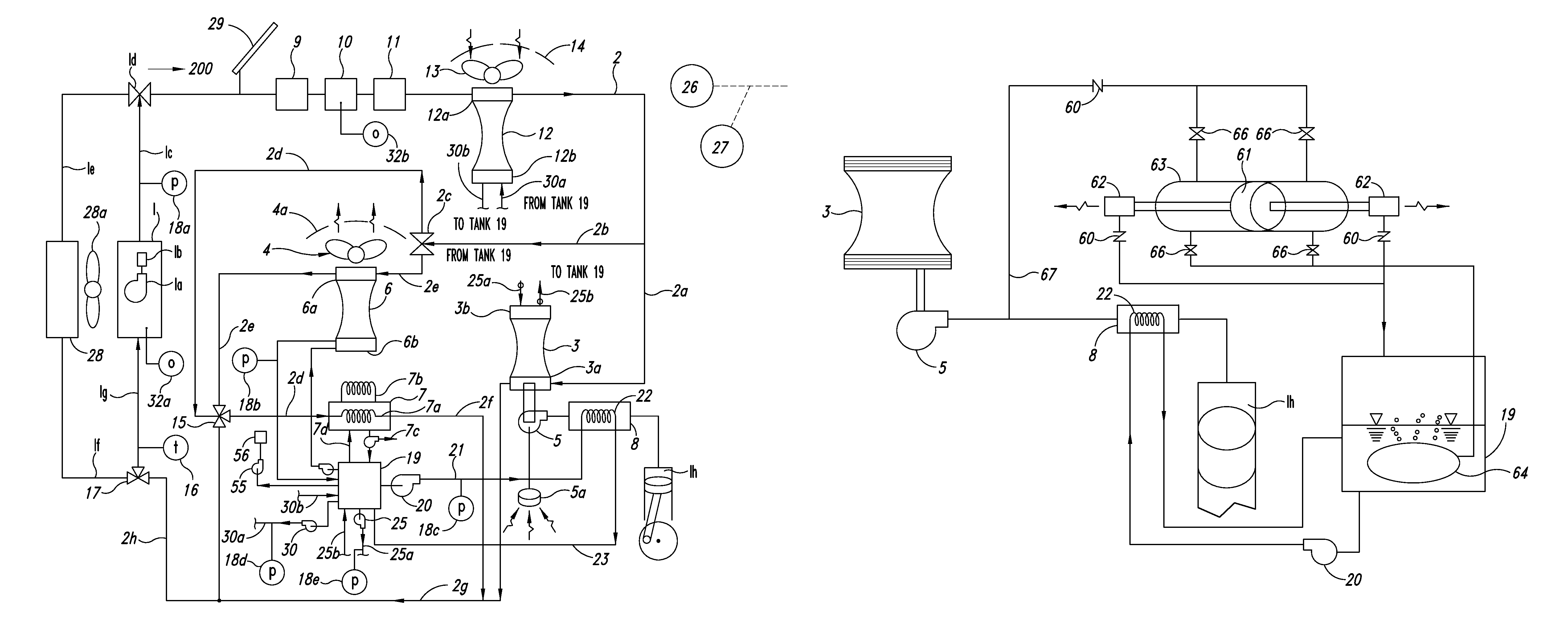
InactiveUS20090145121A1Prevent increase in engine rotation speedReduce engine noiseAuxillary drivesServomotorsElectricityElectric power system
[OBJECT] To provide a hydraulic drive system for a dump truck, which can prevent an excessive increase in engine rotation speed upon operation of a truck body.[MEANS FOR ACHIEVING THE OBJECT] A hydraulic drive system is provided with a generator 8 for outputting electricity corresponding to a rotation speed of an engine 7, an electric motor 11 drivable responsive to the electricity from the generator 8, hydraulic pumps 12a, 12b drivable by the electric motor 11, truck-body elevating cylinders 6 for pivoting a truck body 5 in an up-and-down direction, and a stroke detector 14 for detecting a stroke of the control apparatus of the truck-body elevating cylinders 6, and is also provided with a controller 19 for performing control of engine rotation speed. The controller 19 includes a motor electric-power computing means 19a for determining electric power for the electric motor 11, which corresponds to the stroke detected by the stroke detector 14, and a discrimination means 19b for discriminating whether or not the electricity from the generator 8 has become greater than the thus-determined electric power for the electric motor 1.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
System and method for providing engine braking
ActiveUS20190234317A1Increase brake ware brakeIncrease brake brake heatingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveEngine braking
Systems and methods for reducing noise and vibration that may be associated with engine braking are presented. In one example, intake and exhaust valve timings are adjusted to reduce engine noise and vibration at lower engine braking request levels. The engine intake and exhaust valve timings increase compression engine braking and decrease engine expansion braking for higher engine braking request levels.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control apparatus and control method of a vehicle, program for realizing that control method using a computer, and recording medium on which that program is recorded
InactiveUS7908065B2DegreeShorten speedDigital data processing detailsGearing controlEngineeringControl equipment
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Heat transfer enhancing agent
InactiveUS20130119302A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove cooling efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsHeat transfer efficiencyEngineering
An enhancing agent for increasing heat transfer efficiency is disclosed, which is an additive composed of a nano-scale powder and a micro-scale powder that is to be added into a heat-transfer fluid circulating in an heat exchange system or in a coolant circulating in a cooling system for enhancing the heat conductivity of the heat-transfer fluid or the coolant while helping the tank and the fluid passages used in those systems to maintain clean, and eventually enabling those systems to operate with improved heat dissipation effect. By adding the aforesaid enhancing agent into a cooling system of an internal-combustion engine, the heat shock inside the engine that is originated from the fuel burning in the engine can be reduced, resulting that not only the amount of green house gas emission is reduced, but also the chance of engine juddering that is generally originated from poor heat dissipation can be decreased.
Owner:HUANG YEN HAO +1
Drive control device for hybrid vehicle
Due to the reduction of a discharge amount of a mechanical oil pump by a lowering of the idling rotation speed, a slip in a hydraulic power transmission apparatus and a blow up of an electric motor for running due to a delay of the rising of the oil pressure upon the sudden start and the like are prevented. While avoiding the slip and the blow up, the idling rotation speed is lowered so as to make the engine noise small. When the return determination from the idling state is performed based on the shift operation from P to D, at step S5, a torque TMG2 of a second motor / generator MG2 is temporarily restricted. As a result, upon the sudden start from the idling state, even when the rising of the oil pressure delays, the second brake B2 engaged upon the starting is prevented from slipping, and the second motor / generator MG2 is prevented from blowing up. As a result, while avoiding the slip of the second brake B2 and the blow up of the second motor / generator MG2 due to the hydraulic response delay, an idling rotation speed N Eidl is lowered so that the engine noise can be reduced.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for adjusting a fuel pressure
InactiveUS20100229831A1High component stressRelieve pressureHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesBoundary valuesEngineering
A method is provided for adjusting a fuel pressure in a high pressure fuel accumulator of an accumulator injection system of an internal combustion engine as a first drive motor which, together with a second drive motor, is situated in a drive train, in which variable torque contributions of the internal combustion engine and of the second drive motor are superposed, an actual value of the fuel pressure, which sets in in response to a lower torque contribution of the internal combustion engine in the high pressure fuel accumulator, deviating from a setpoint value specified for higher torque contributions and at which the actual value, in response to an increase in the torque contribution from the lower value to the higher torque contribution of the internal combustion engine being adjusted to its higher setpoint value. The method stands out in that the adjustment is performed so that a rate of a change in the actual value does not exceed a specified boundary value during the adjustment. A control device equipped to perform the method is also provided.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
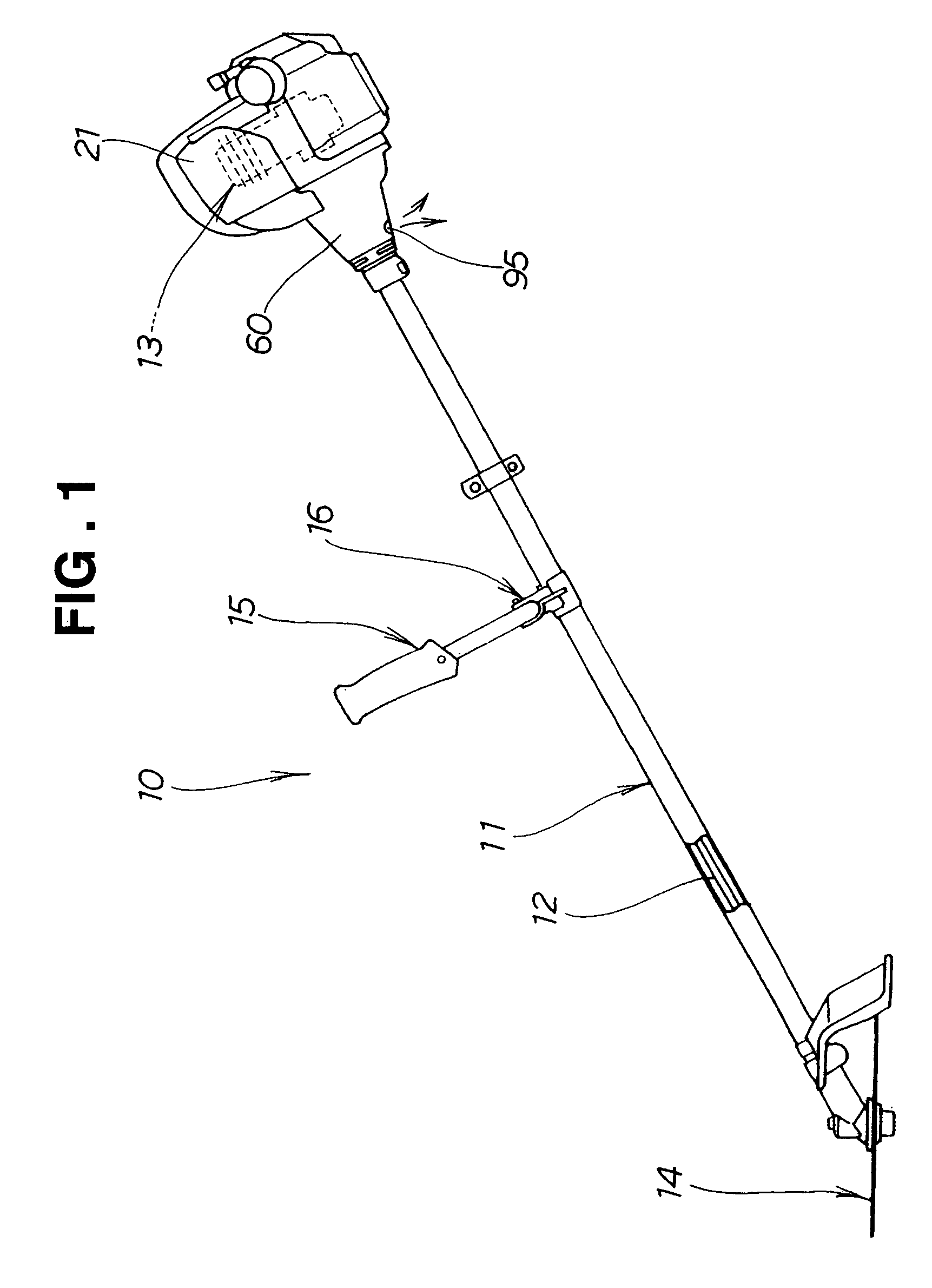
Bush cutting machine
InactiveUS7275325B2Reduce engine noiseSufficient workabilityRotary propellersExhaust apparatusPulp and paper industryMuffler
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com