Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49results about How to "Minimize jitter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
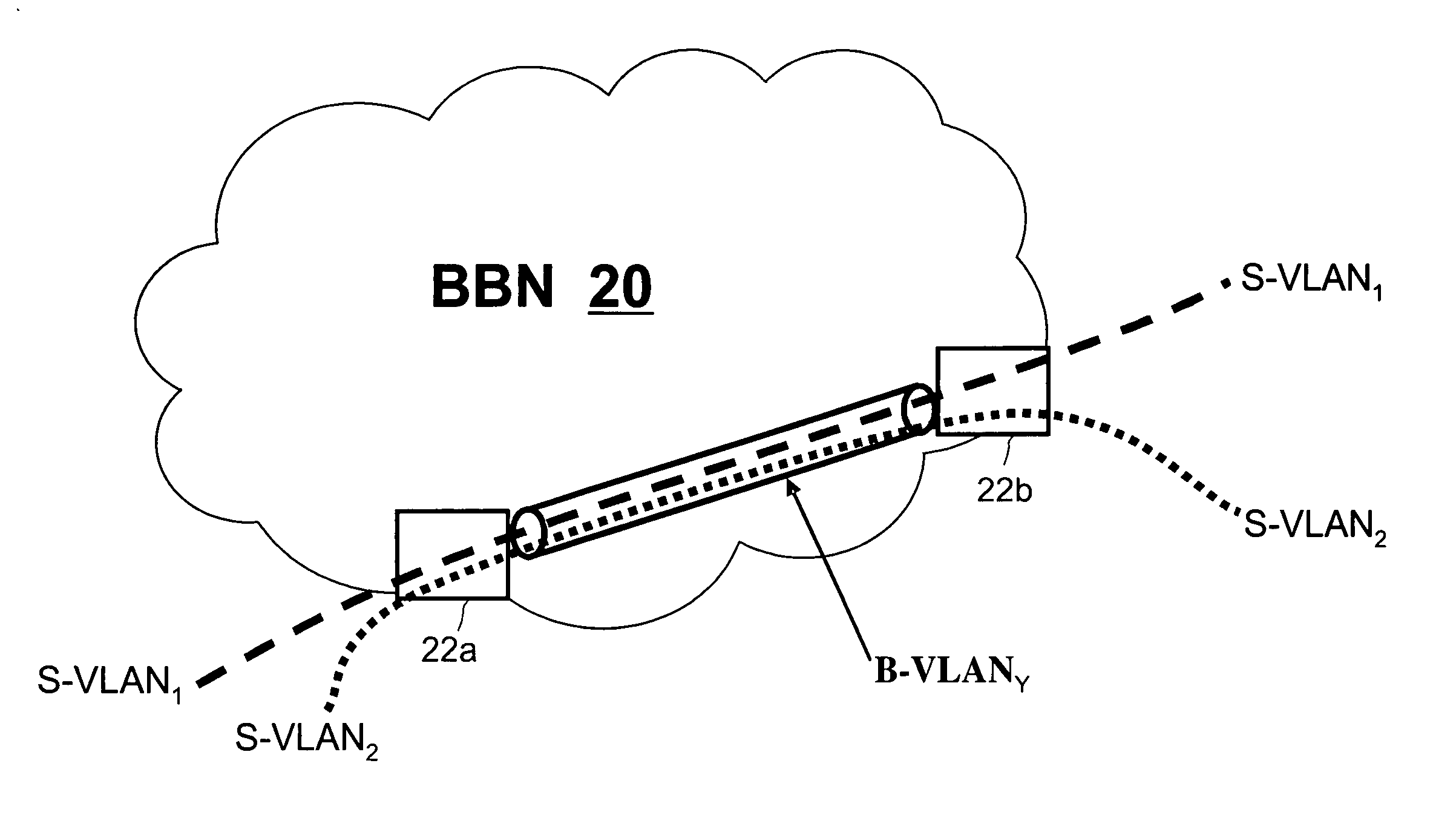
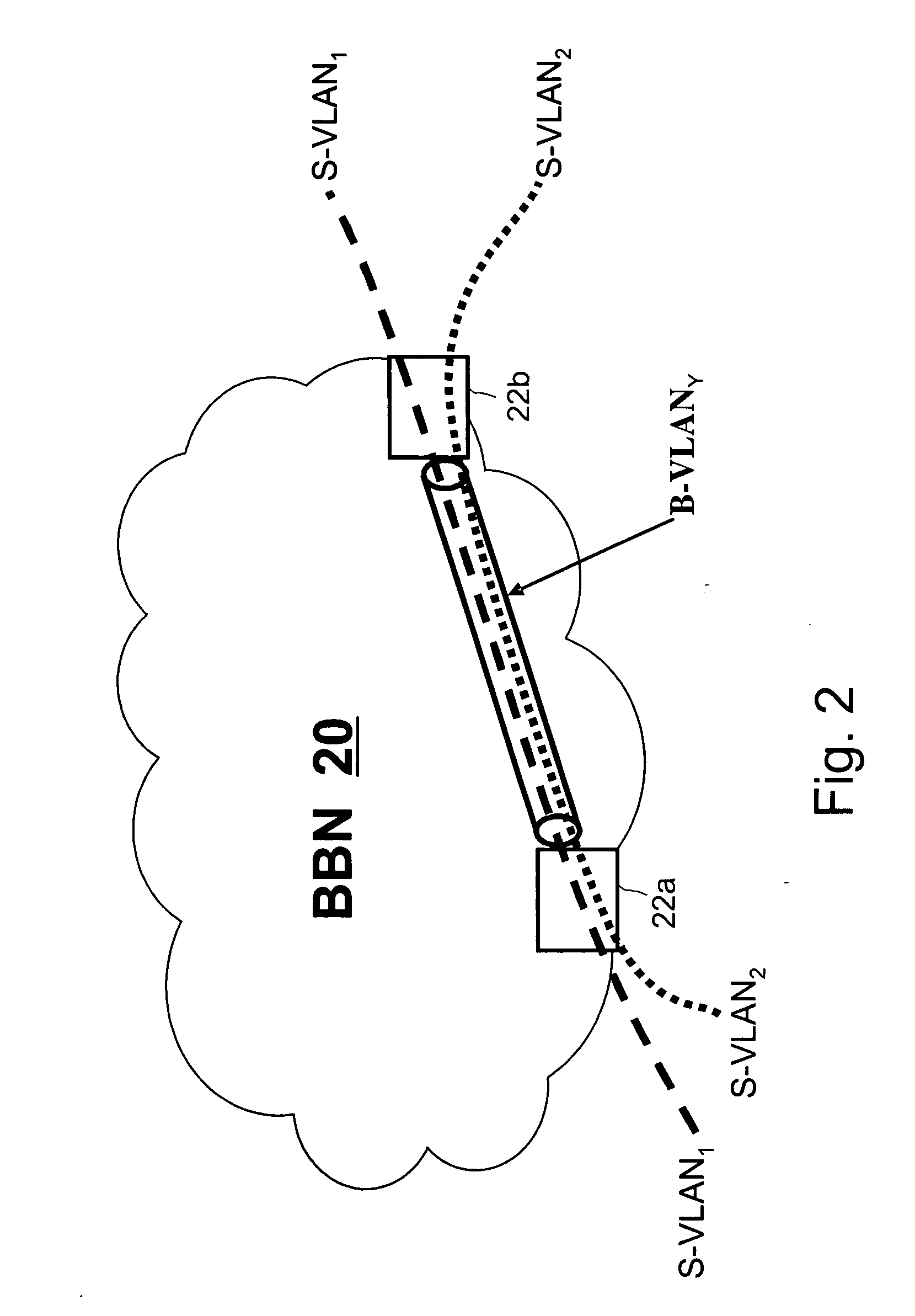
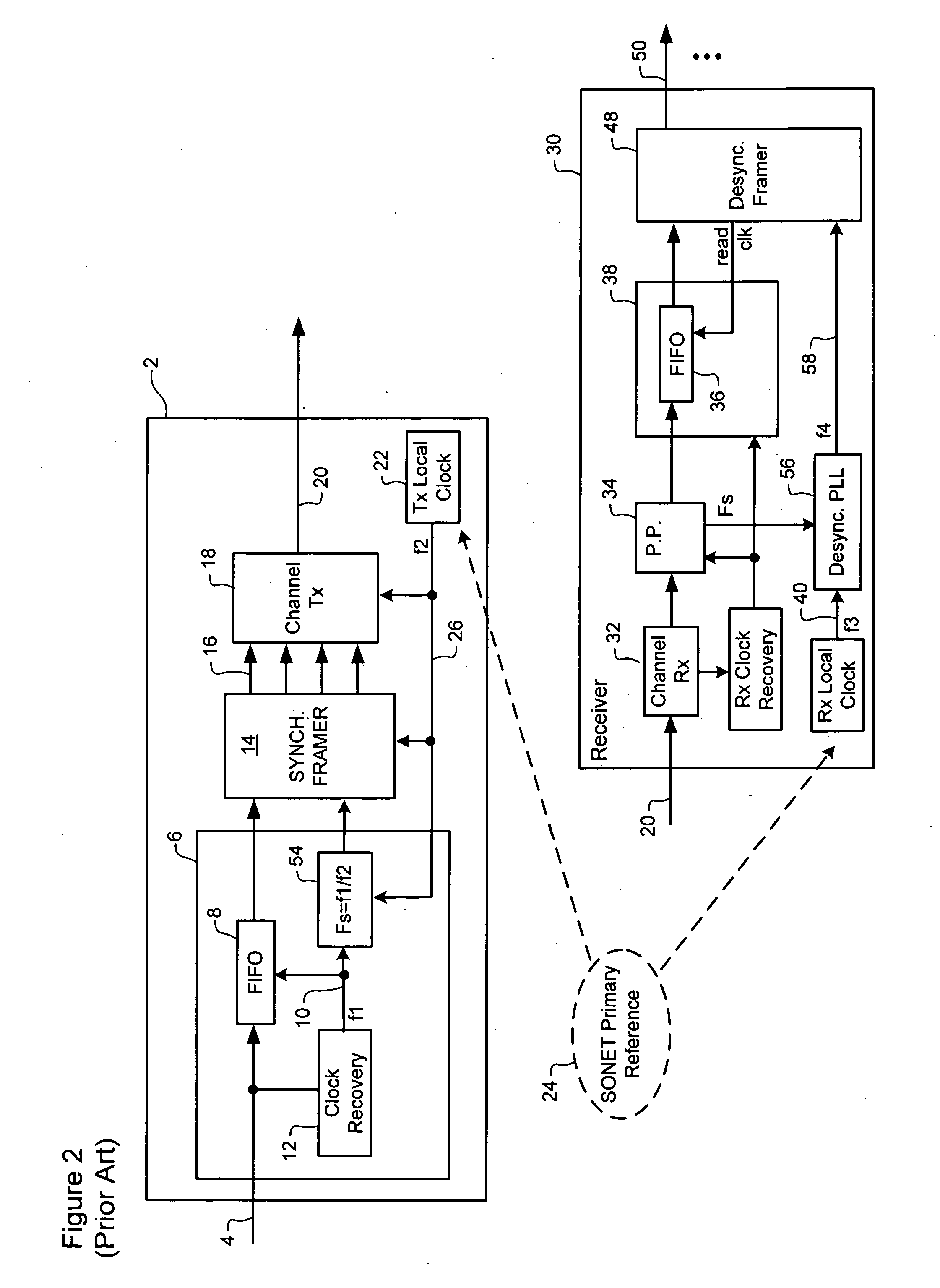
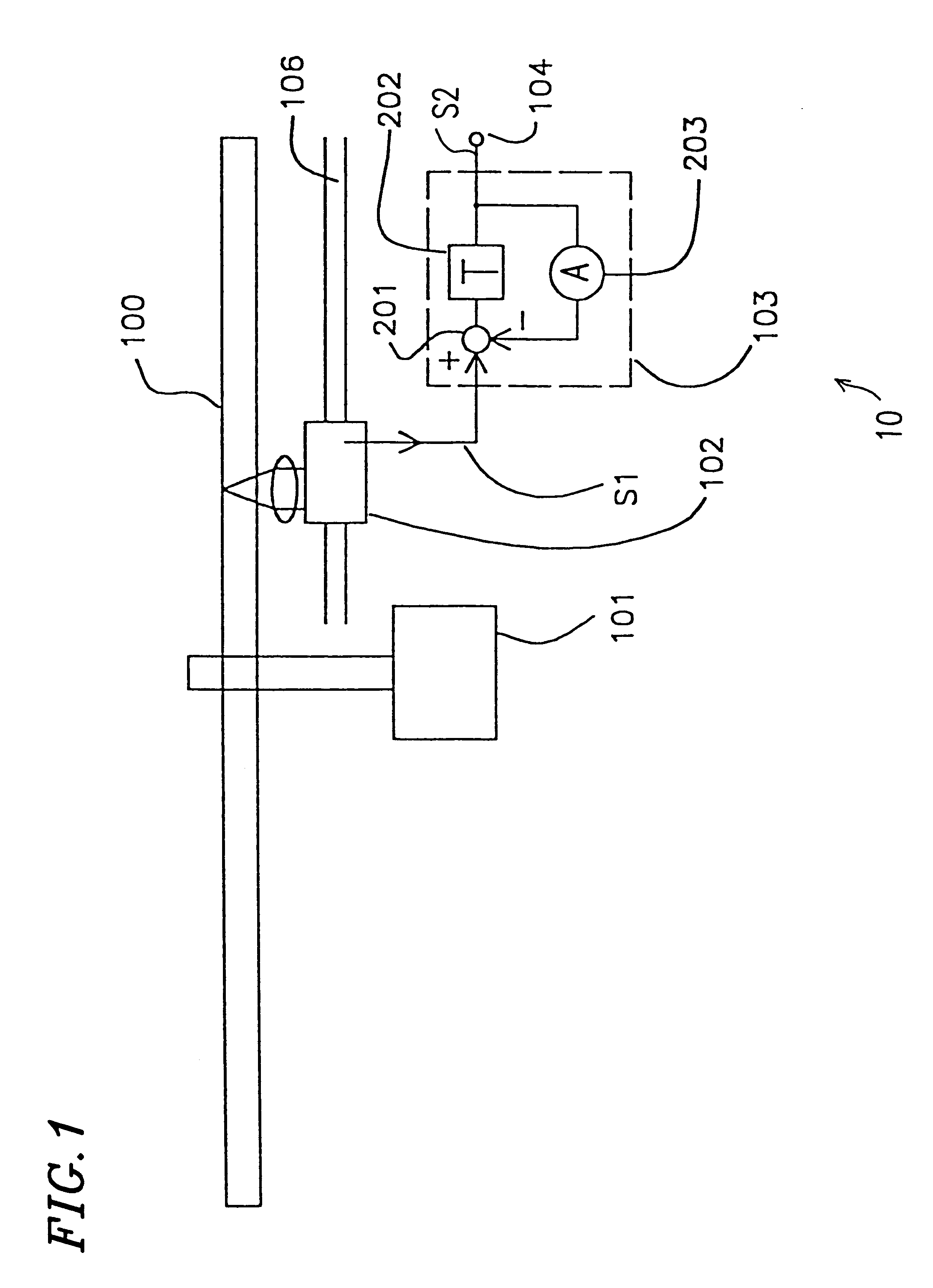
Multilink trunking for encapsulated traffic
InactiveUS20070098006A1Increase variabilityMinimize jitterEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexFrame basedEncapsulated data
A node of a frame-based network has a group of outgoing links which are to be treated as an aggregated group of links. A frame distributor performs a distribution function on data frames which are intended for transmission on the group of links. The frame distributor determines if the data frame is an encapsulated data frame which forms part of a tunnelled traffic path across the network. If the data frame does form part of a tunnelled traffic path across the network, the frame distributor allocates the data frame to one of the group of links using at least part of an identifier from the header of the data frame. The identifier represents a service with which the data frame is associated, a customer or user of the data frame, or the tunnelled traffic path, which have greater variability than the backbone destination and source addresses.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
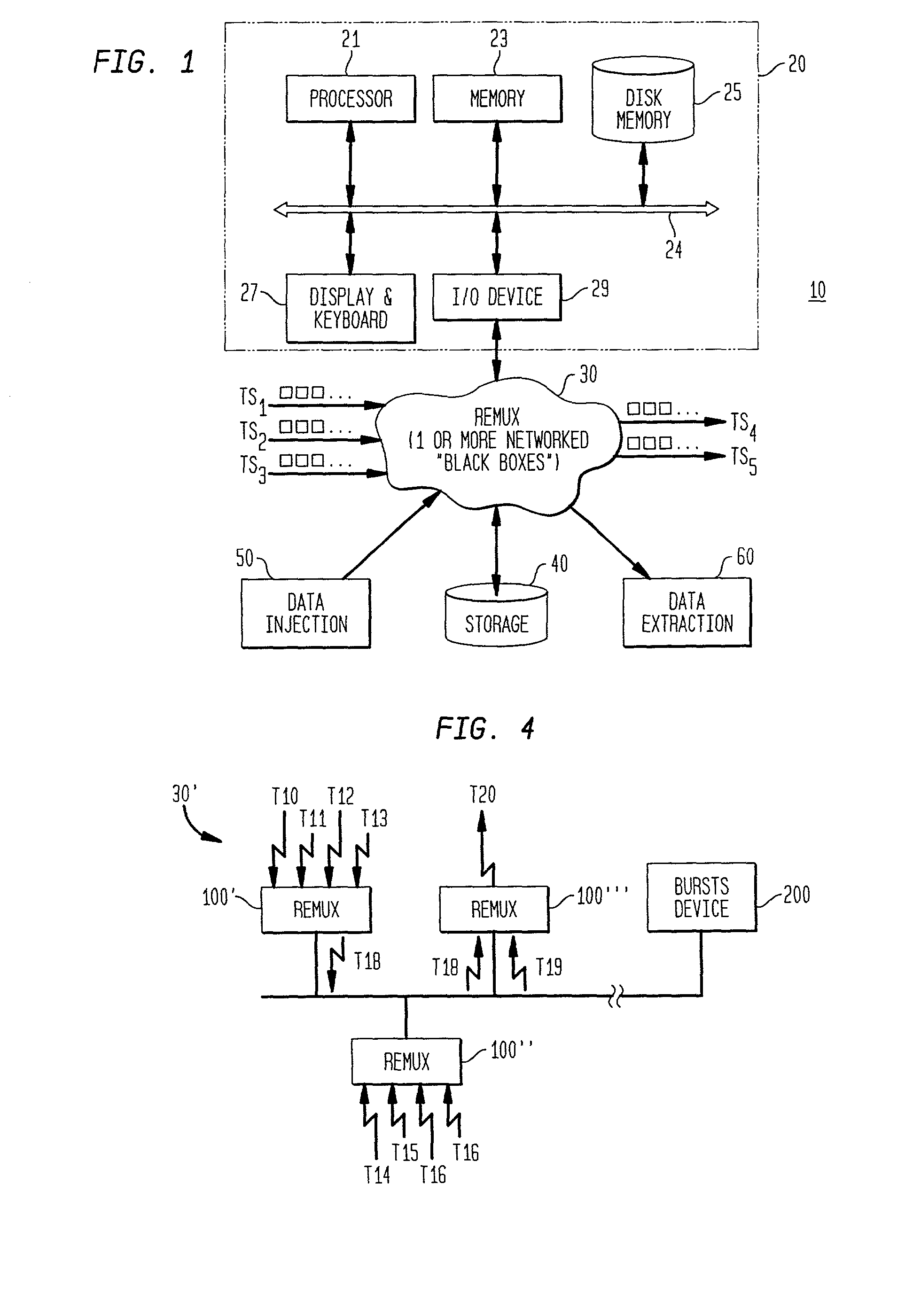
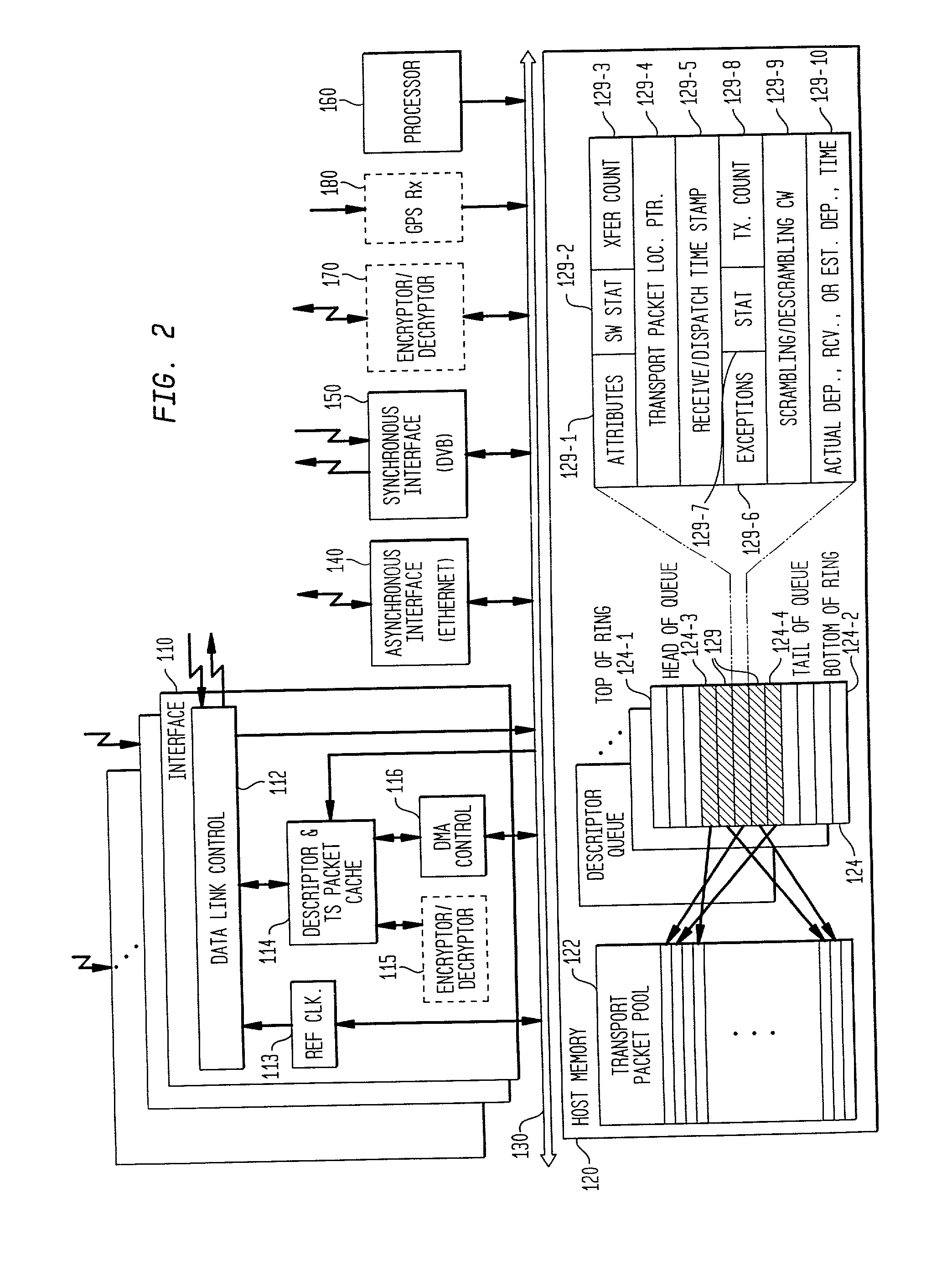
Network distributed remultiplexer for video program bearing transport streams
InactiveUS20020126711A1Flexible processIncrease flexibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexProgram clock referenceMultiplexing
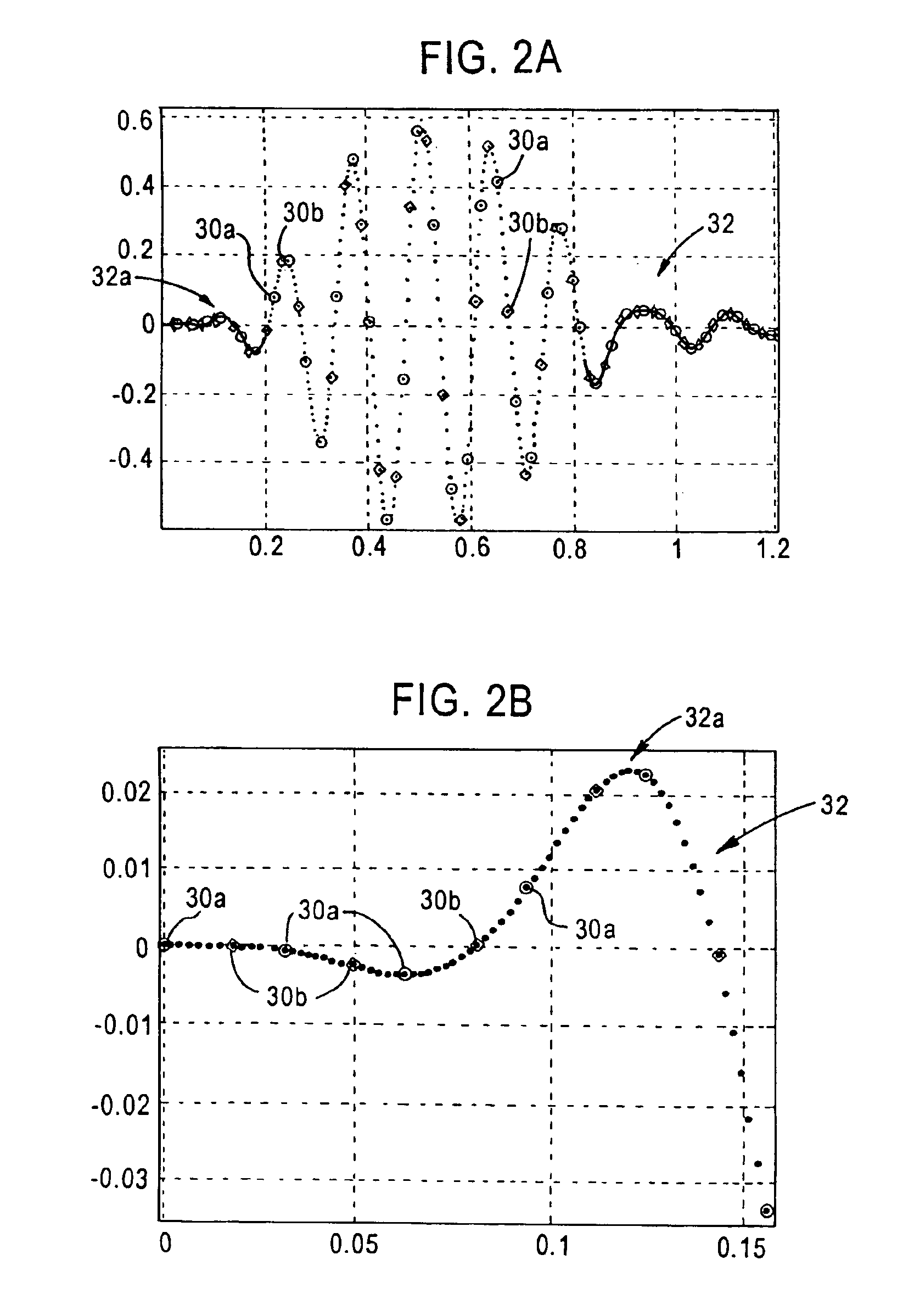
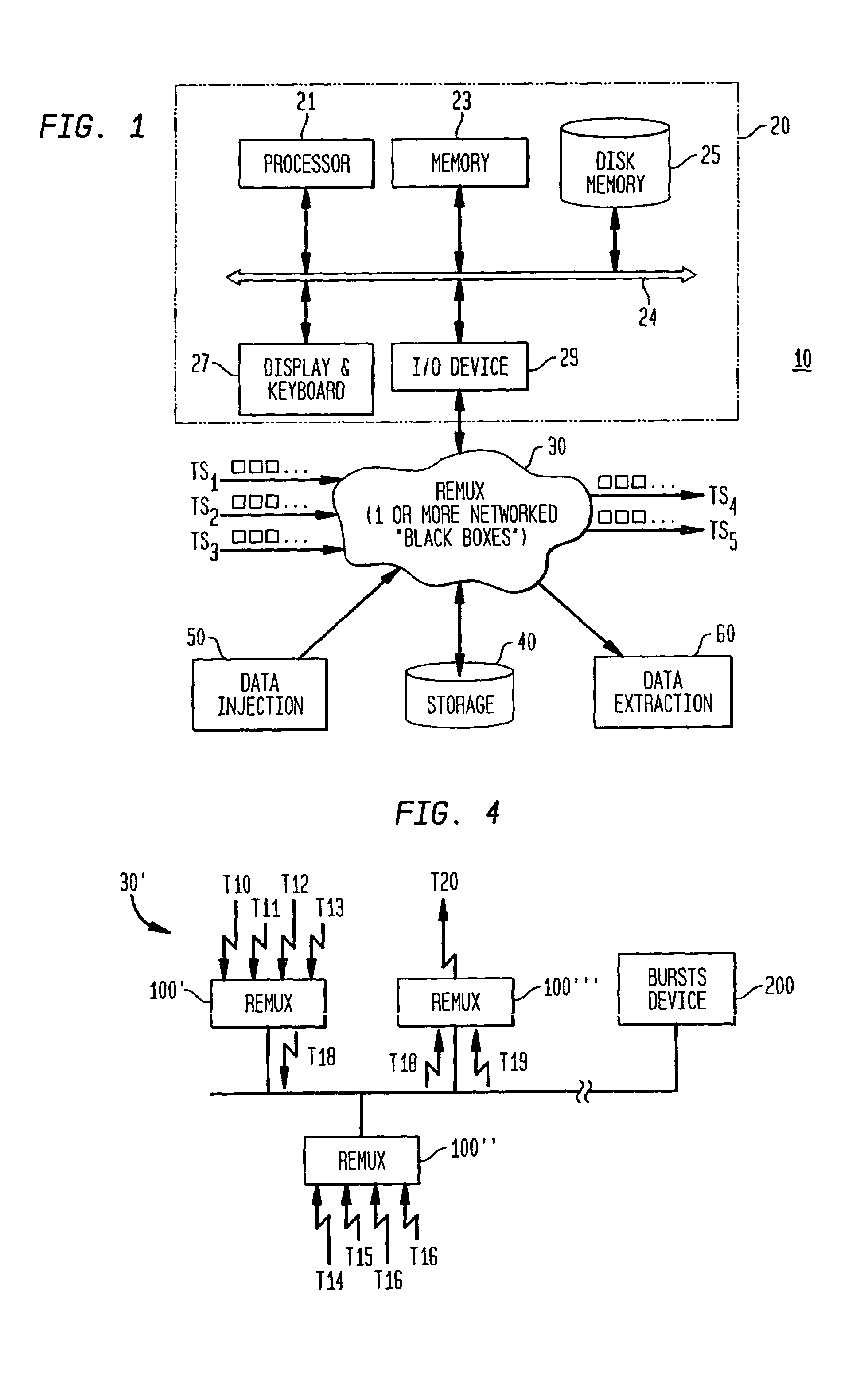
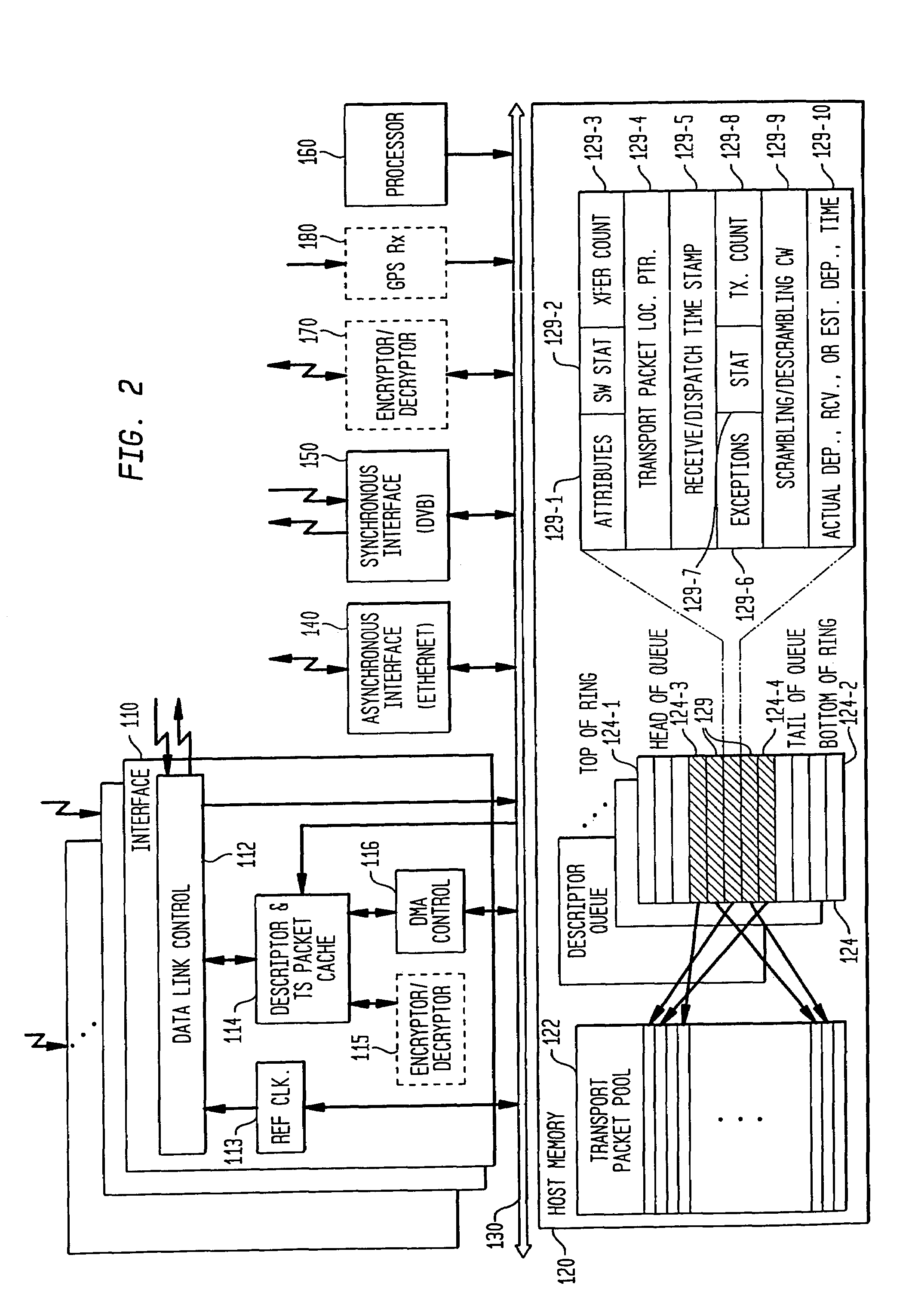
A method and system are provided for remultiplexing program bearing data. The remultiplexing method and system are applicable to MPEG-2 compliant transport streams carrying video programs. A descriptor based system is used for scheduling the timely output of transport packets wherein each descriptor records a dispatch time as well as a receipt time for each transport packet. The receipt time is used for estimating program clock reference adjustments, but final program clock reference adjustment is performed in hardware in relation to the precise output timing of each transport packets. A descriptor and transport packet caching technique is used for decoupling the synchronous receipt and transmission of transport packets from any asynchronous processing performed thereon. The descriptors can also be used for managing scrambling and descrambling control words (encryption and decryption keys). Remultiplexing functions may be distributed across a network. The remultiplexer can furthermore optimize the bandwidth of transport streams by replacing null transport packets with transport packet data to be inserted into the output transport stream. Program data transmitted via asynchronous communication links is re-timed and assistance is provided for outputting program data on such asynchronous communication links to reduce a variation in end-to-end delay incurred by the program data. Remultiplexing and program specific information can be searnlessly dynamically varied without stopping, or introducing a discontinuity in, the flow of outputted transport packets. A technique is also provided for locking multiple internal reference clock generators.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
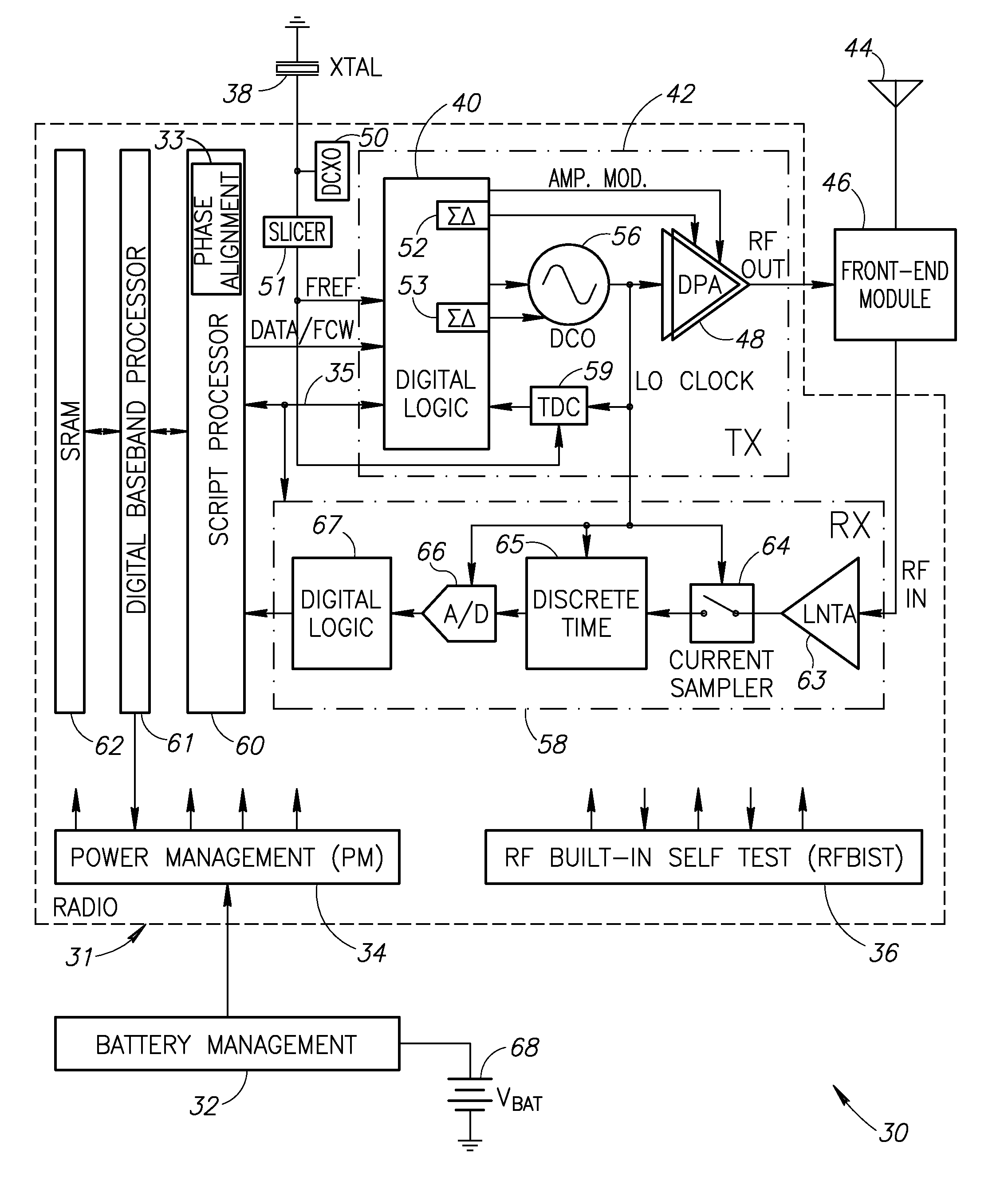
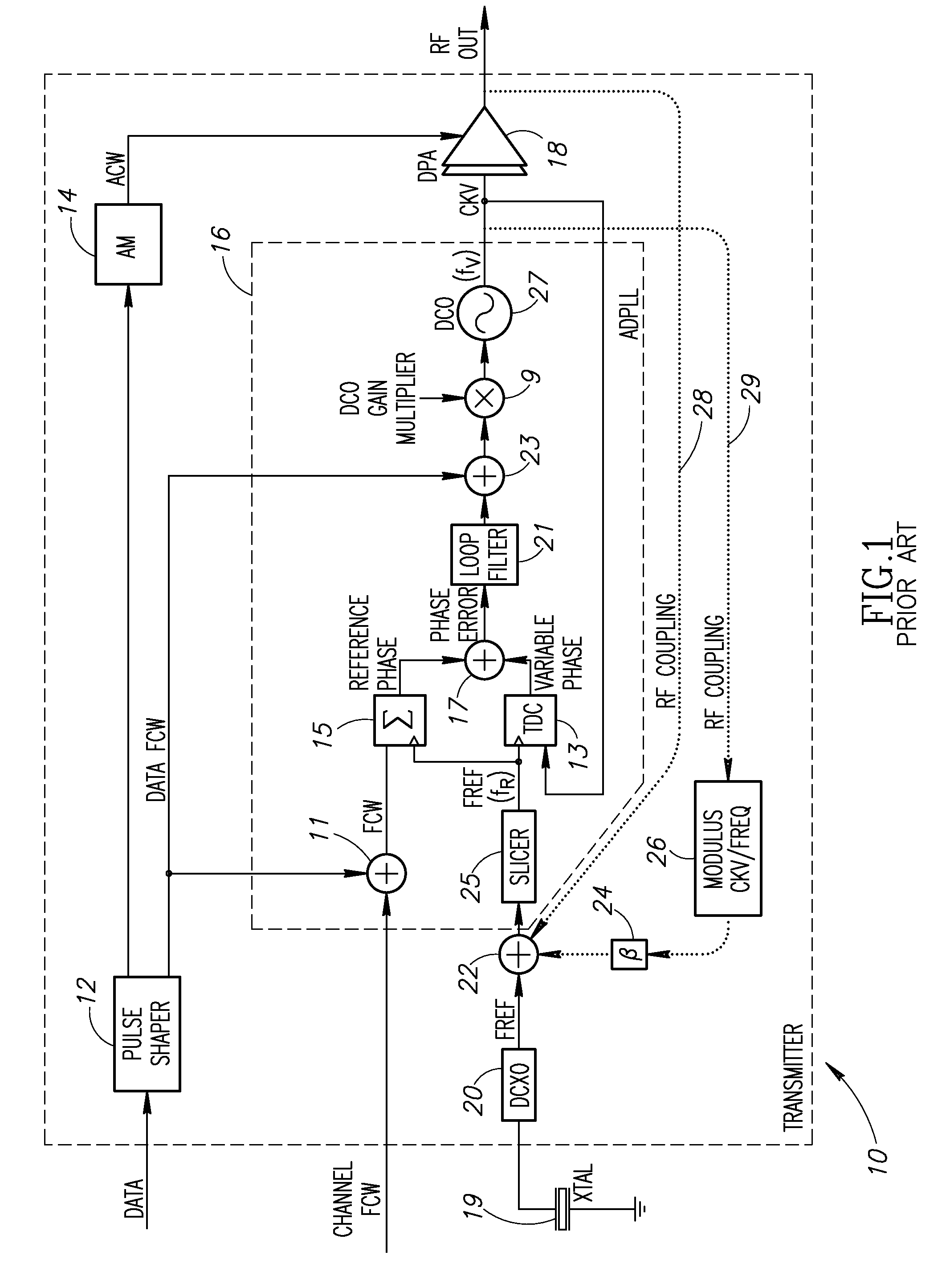
Phase alignment mechanism for minimizing the impact of integer-channel interference in a phase locked loop
InactiveUS20080192877A1Minimize impact of interferenceMinimize jitterPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionEngineeringPhase control
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of minimizing the impact of interference on the phase error performance in a phase locked loop (PLL) at integer channels by adjustment of the phase of the interfering signal such that its impact on the reference signal is minimized. Phase control is achieved by use of the digital architecture of the ADPLL and its insensitivity to an arbitrary phase bias introduced between its digitally represented output and reference phase signals. The optimal phase relationship for each integer channel is determined through a calibration procedure in which the phase is swept and the optimal phase is recorded. Before the transmission of a payload on an integer channel, the phase relationship between the output RF signal and the input reference signal is adjusted to the value found to be optimal for that frequency, based on the values previously recorded during the calibration procedure.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
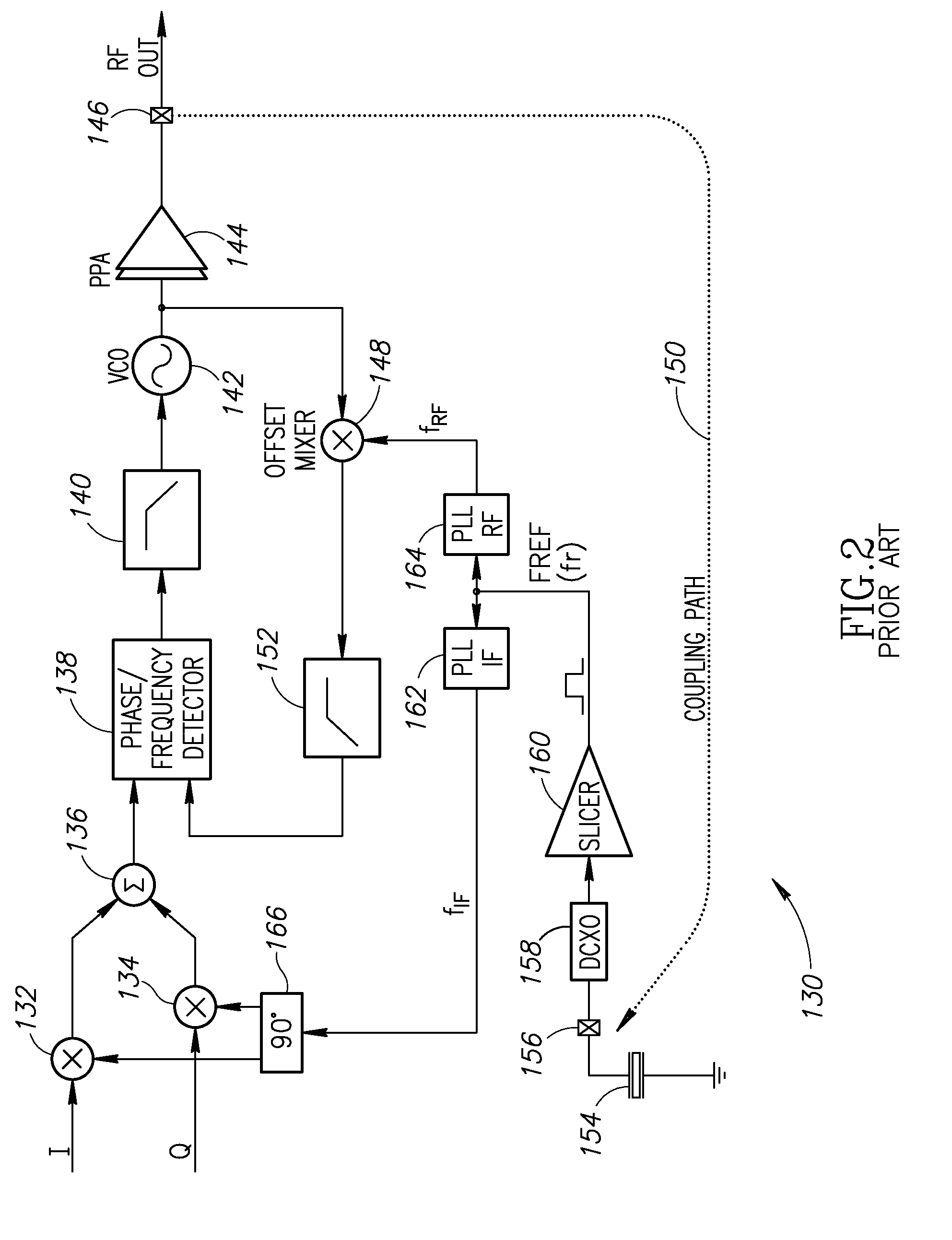
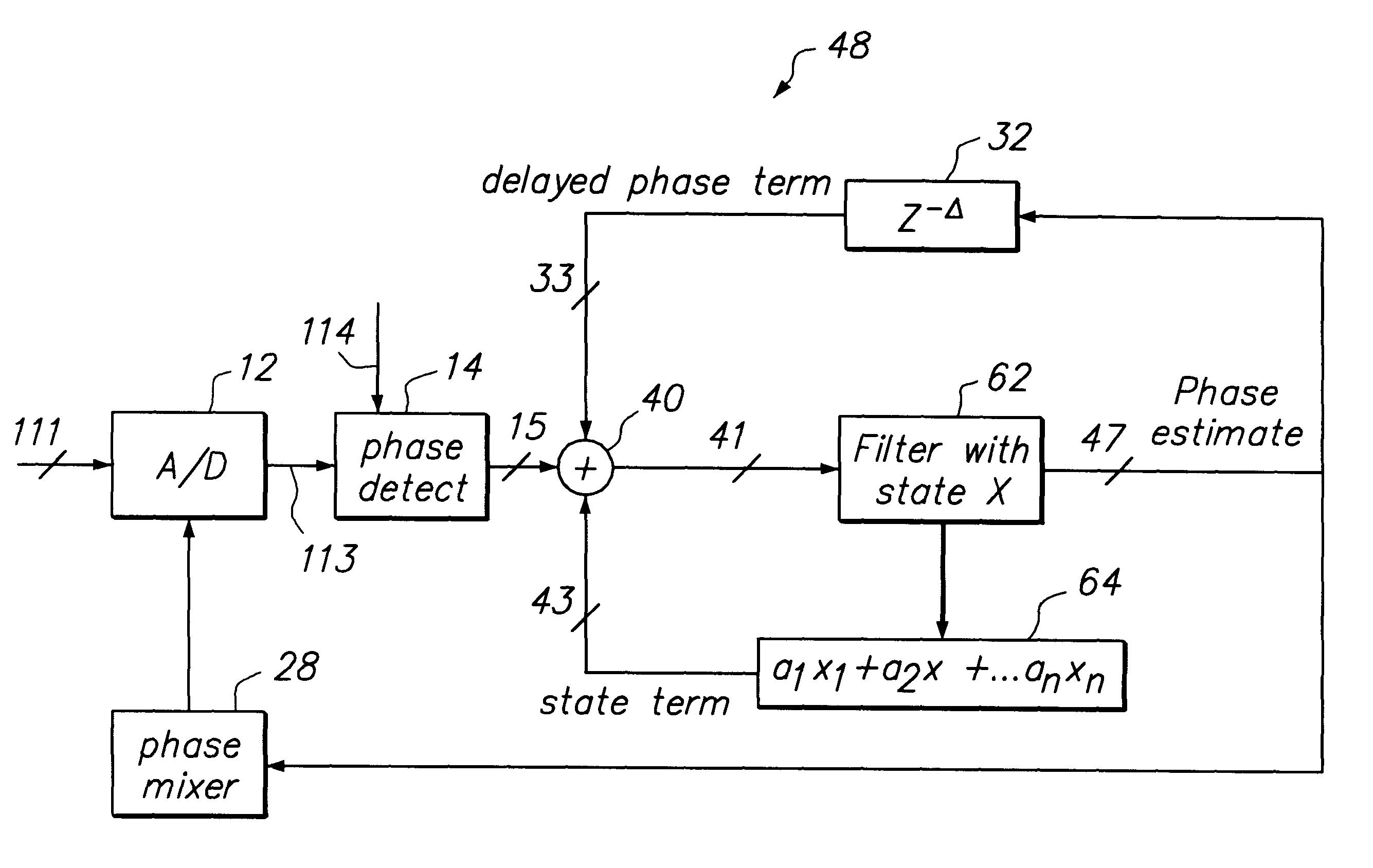
Loop latency compensated PLL filter
InactiveUS6236343B1Minimize jitterReduce sensitivityAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsPhase detectorSquare waveform
The loop latency compensated PLL filter comprising two additional feedback terms, a delayed phase compensation signal and a state compensation signal, that are provided as input of a PLL filter. Accordingly, the PLL filter input comprises two additional compensation input signals: the delayed phase compensation signal and the state compensation signal in addition to a phase estimated error output from a phase detector that is also coupled to the input of the PLL filter. Consequently, PLL filter thus is able to provide a latency compensated phase error control output that is fedback to control a phase mixer to generate a square waveform used to drive an A / D of the PLL in accordance with the principles of this invention. The loop latency compensated PLL of this invention thus minimizes the jitter of the PLL circuit, provides higher format efficiency, and also has reduced sensitivity to large bursty noises.
Owner:MAXTOR
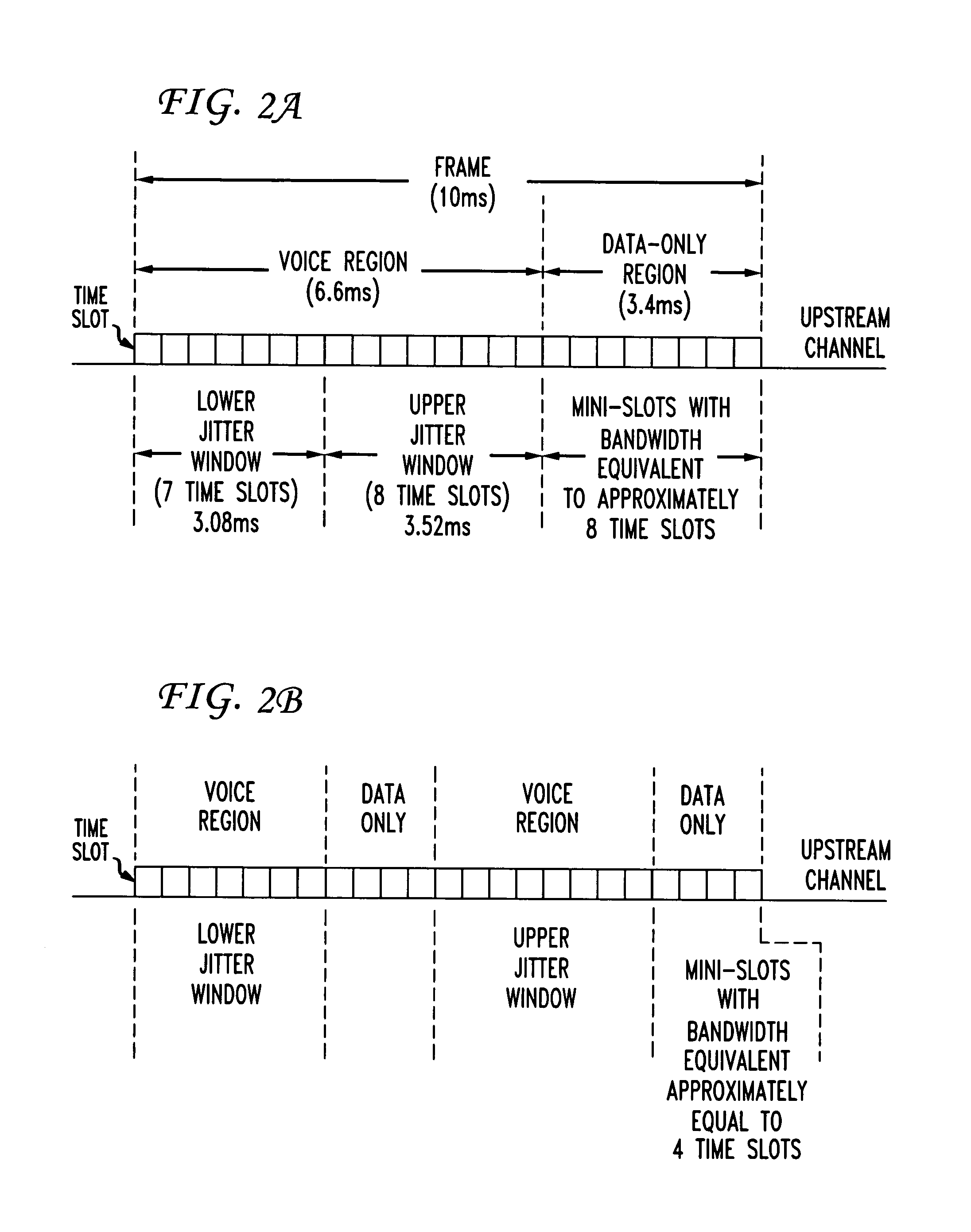
Upstream bandwidth allocation for packet telephony in a shared-media packet-switched access network
InactiveUS7269159B1Minimize jitterCable networksBroadband local area networksModem deviceTime duration
A method and apparatus is provided for allocating bandwidth and reducing jitter in an upstream transmission in a shared-media packet-switched access network with multiple upstream channels offering integrated Internet Protocol voice and high-speed data services. To allow multiple simultaneous CBR (constant-bit-rate) voice connections to be supported by a cable modem, when only a single channel can be accessed at a time, a method to select an upstream channel and assign to each connection a time slot in the upstream channel is provided. Jitter, i.e. packet delay variation, results when packets associated with a voice connection are not received at expected intervals. To maintain jitter within predetermined tolerances, the sequence of mini-slots in an upstream channel is divided into frames. Each frame will have a sequence of voice and data-only regions, and the voice region is divided into non-overlapping jitter windows of generally equal length. Even when an upstream channel change is required, each active voice connection is maintained in one of the jitter windows, thereby limiting jitter to the duration of a jitter window.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Digital delay locked loop and control method thereof
There is provided a digital delay locked loop (DLL) which is capable of minimizing a jitter by predicting and detecting a maximum jitter timing. The digital delay locked loop includes: a clock generator for generating a source clock and a reference clock; a delay line provided with a plurality of unit delays, for delaying the source clock by a predetermined time; a delay model for reflecting a delay time of an actual internal circuit to an output of the delay line; a phase comparator for comparing a phase of the reference clock with a phase of a feedback clock outputted from the delay model; a jitter detector for detecting a maximum jitter timing in response to a phase comparison signal outputted from the phase comparator and generating a multi-delay enable signal; and a delay controller for controlling a delay amount of the delay line by unit-delay unit or multi-delay unit in response to the phase comparison signal and the multi-delay enable signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Multilink trunking for encapsulated traffic
InactiveUS7697528B2Increase variabilityMinimize jitterEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityFrame based
A node of a frame-based network has a group of outgoing links which are to be treated as an aggregated group of links. A frame distributor performs a distribution function on data frames which are intended for transmission on the group of links. The frame distributor determines if the data frame is an encapsulated data frame which forms part of a tunnelled traffic path across the network. If the data frame does form part of a tunnelled traffic path across the network, the frame distributor allocates the data frame to one of the group of links using at least part of an identifier from the header of the data frame. The identifier represents a service with which the data frame is associated, a customer or user of the data frame, or the tunnelled traffic path, which have greater variability than the backbone destination and source addresses.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Bandwidth optimization of video program bearing transport streams
InactiveUS20050105486A1Flexible processIncrease flexibilityTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexProgram clock referenceComputer science
A method and system are provided for remultiplexing program bearing data. The remultiplexing method and system are applicable to MPEG-2 compliant transport streams carrying video programs. A descriptor based system is used for scheduling the timely output of transport packets wherein each descriptor records a dispatch time as well as a receipt time for each transport packet. The receipt time is used for estimating program clock reference adjustments, but final program clock reference adjustment is performed in hardware in relation to the precise output timing of each transport packets. A descriptor and transport packet caching technique is used for decoupling the synchronous receipt and transmission of transport packets from any asynchronous processing performed thereon. The descriptors can also be used for managing scrambling and descrambling control words (encryption and decryption keys). Remultiplexing functions may be distributed across a network. The remultiplexer can furthermore optimize the bandwidth of transport streams by replacing null transport packets with transport packet data to be inserted into the output transport stream. Program data transmitted via asynchronous communication links is re-timed and assistance is provided for outputting program data on such asynchronous communication links to reduce a variation in end-to-end delay incurred by the program data. Remultiplexing and program specific information can be seamlessly dynamically varied without stopping, or introducing a discontinuity in, the flow of outputted transport packets. A technique is also provided for locking multiple internal reference clock generators.
Owner:TANDBERG TELEVISION
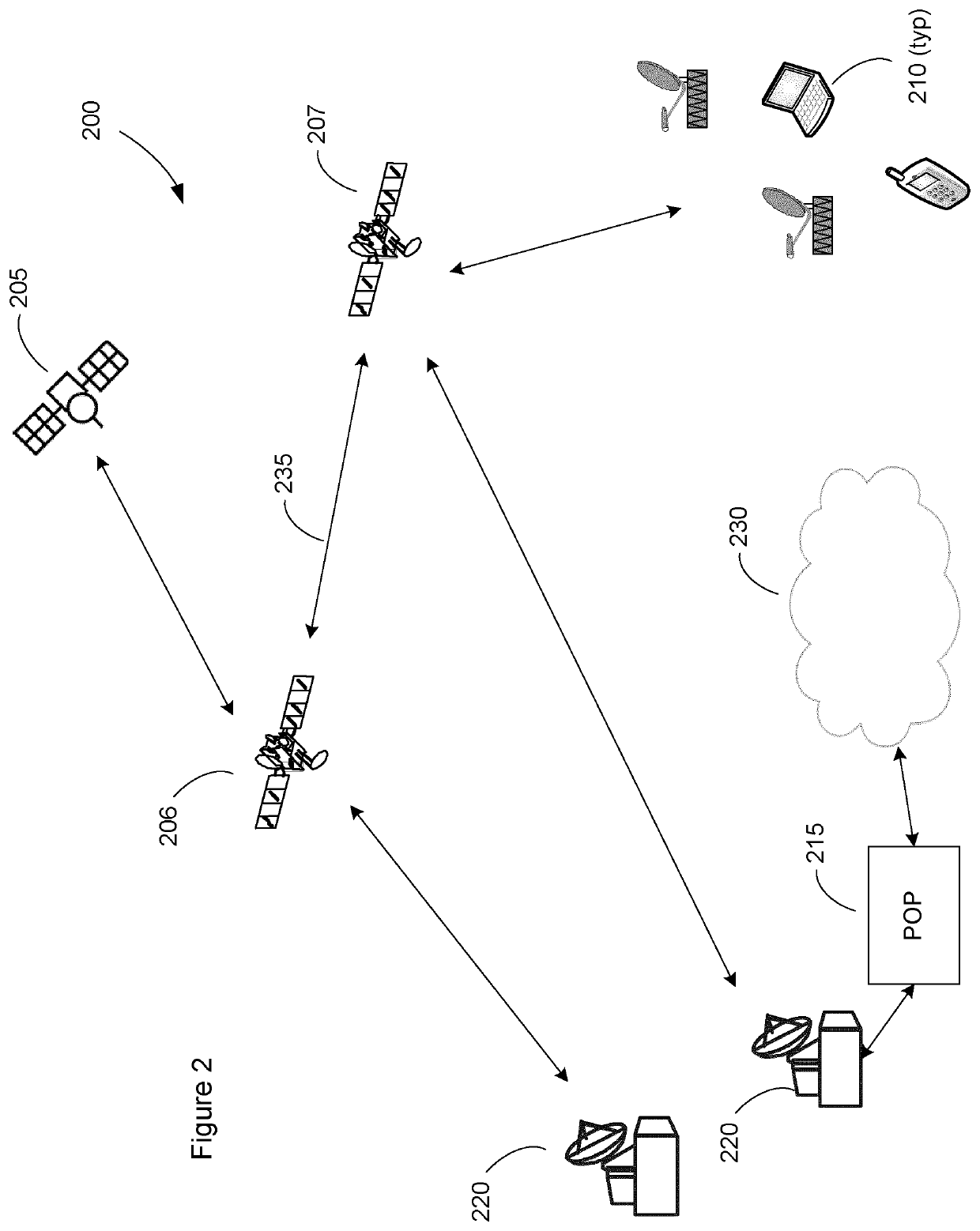
Resource deployment optimizer for non-geostationary and/or geostationary communications satellites
InactiveUS20220052756A1Late changeMinimize jitterNetwork traffic/resource managementActive radio relay systemsTelecommunicationsSatellite constellation
Systems, methods and techniques are presented for discovering optimal solutions to satisfy communication traffic demands to a NGSO and GSO satellite constellations used for telecommunication. When multiple ground demands (mobile and stationary) are present, a satellite constellation requires an assignment of satellite resources to optimally match the ground demands. The systems, methods and techniques presented can utilize an optimization structure to maximize the objective function, using linear programming in combination with simulation and predictive features. The techniques presented determine optimal or quasi-optimal allocation of scarce and highly constrained satellite resources in an efficient manner. These techniques take into account maximizing capacity while protecting other geostationary and non-geostationary networks.
Owner:TELESAT TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
High density, low jitter, synchronous USB expansion
InactiveUS20120059964A1Minimize jitterMinimize impactError detection/correctionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlComputer networkHigh density
A method of providing high density expansion of a USB network, the method comprising: attaching a plurality of USB hubs to adjacent slots in a PXI instrumentation chassis; configuring one of the USB hubs as a primary USB Hub; connecting an upstream port of the primary USB Hub to a USB network; configuring a first downstream port of the primary USB Hub to communicate across a first PXI Local Bus to a first adjacent USB Hub of the USB Hubs other than the primary USB Hub, the first adjacent USB Hub being adjacent to the primary USB Hub; configuring a plurality of other downstream ports of the primary USB Hub to provide expansion of the primary USB Hub; connecting an upstream port of the first adjacent USB Hub to the first PXI Local Bus, wherein the first PXI Local Bus is in the direction of the primary USB Hub; configuring a first downstream port of the first adjacent USB Hub to communicate across a second PXI Local Bus to a second adjacent USB Hub of the USB Hubs other than the primary USB Hub, the second adjacent USB Hub being adjacent to the first adjacent USB Hub; configuring a plurality of other downstream ports of the first adjacent USB Hub to provide expansion of the first adjacent USB Hub; and configuring any other of the USB hubs and the first adjacent USB Hub in like manner.
Owner:CHRONOLOGIC PTY LTD
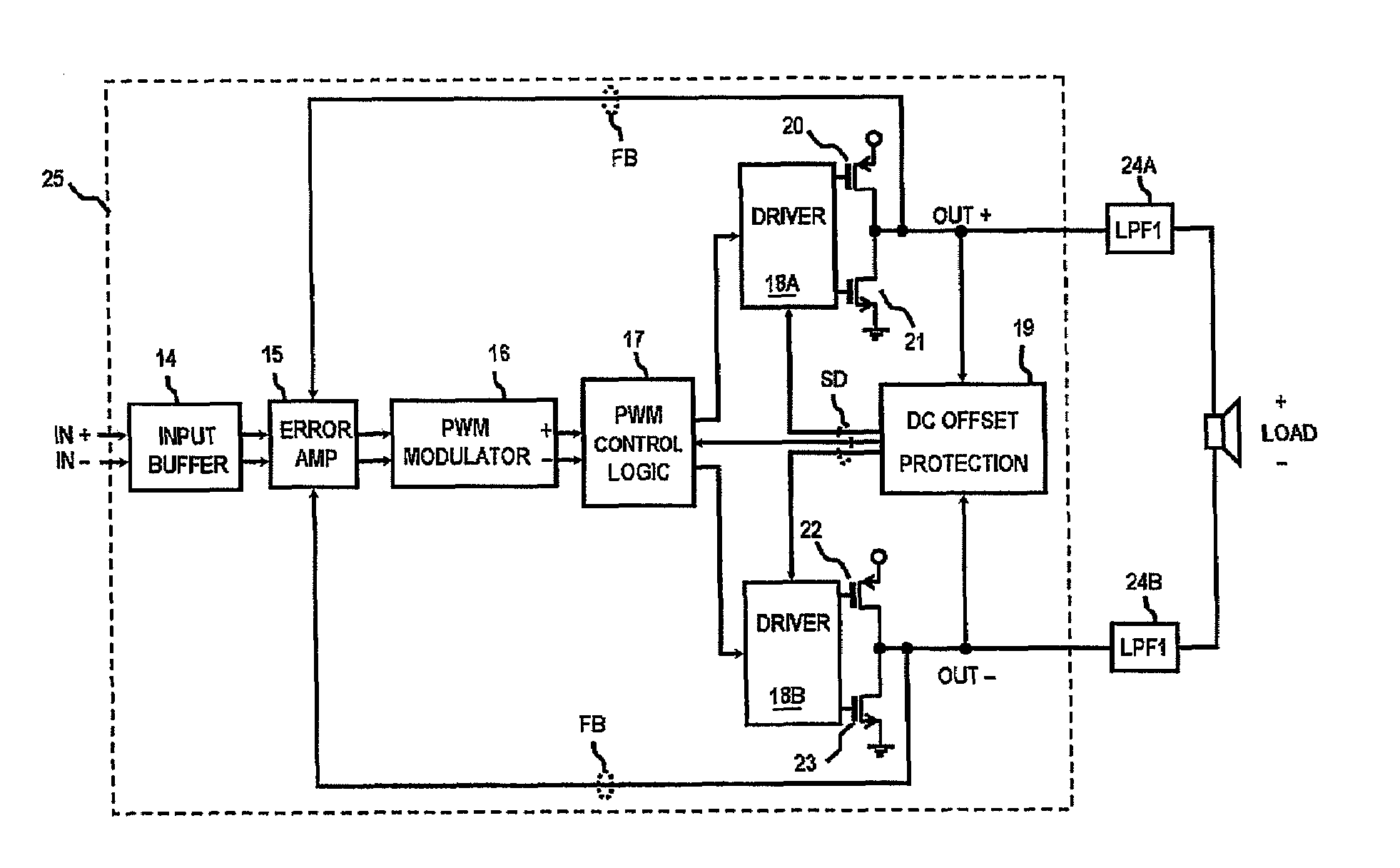
Output DC offset protection for class D amplifiers
InactiveUS7692488B2Minimize jitterNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierClass-D amplifier
A class D amplifier with output DC offset protection is disclosed. The DC offset protection receives a PWM input signals from the outputs and investigates the PWM output signals whether there is a large DC voltage difference is being reflected on the speaker load. If so, shutdown signal SD will be sent by the DC offset protection to the PWM control logic and gate driver, thus, shutting down the output of the class D system and preventing disastrous condition from being develop across the speaker.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
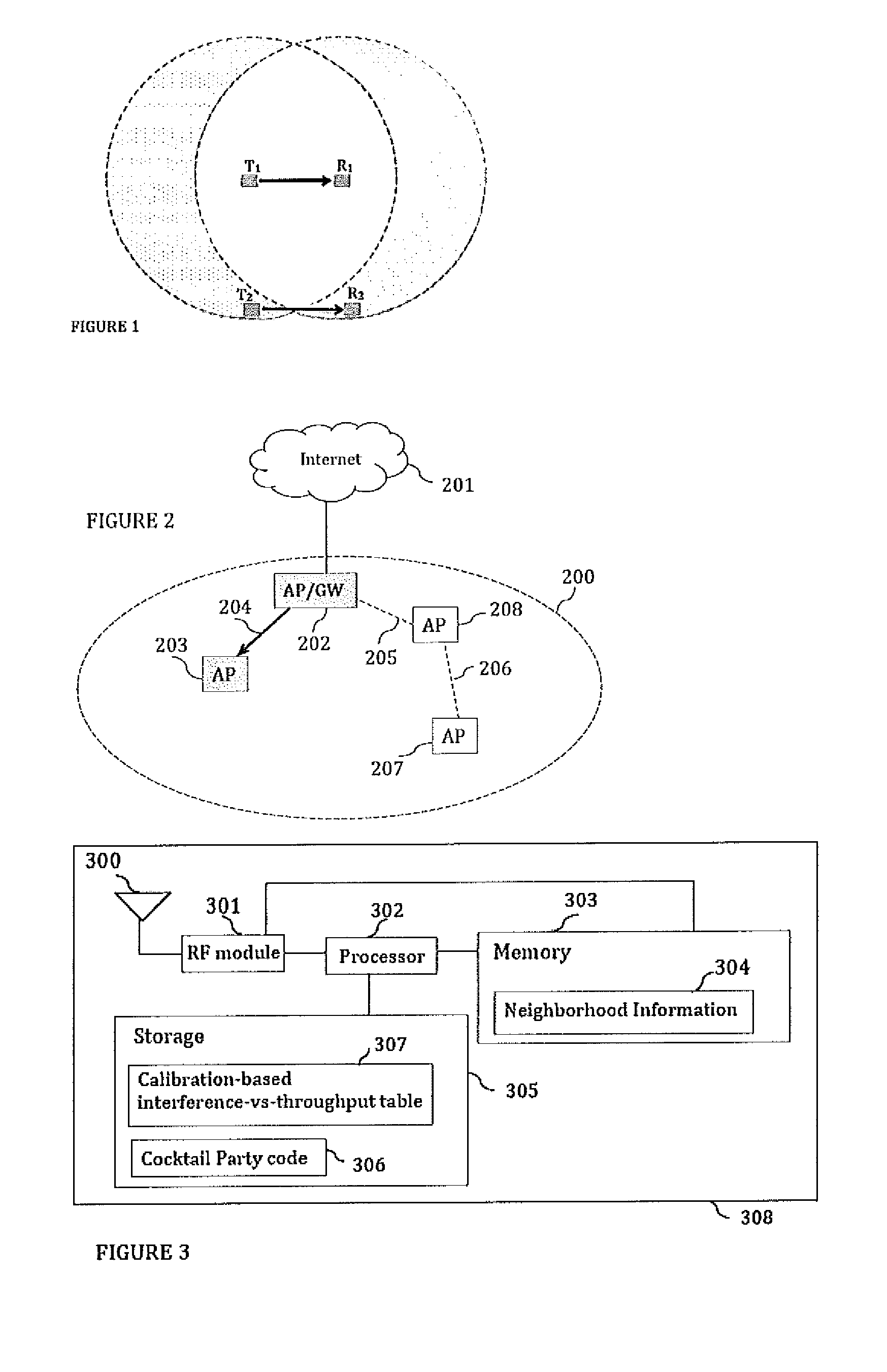
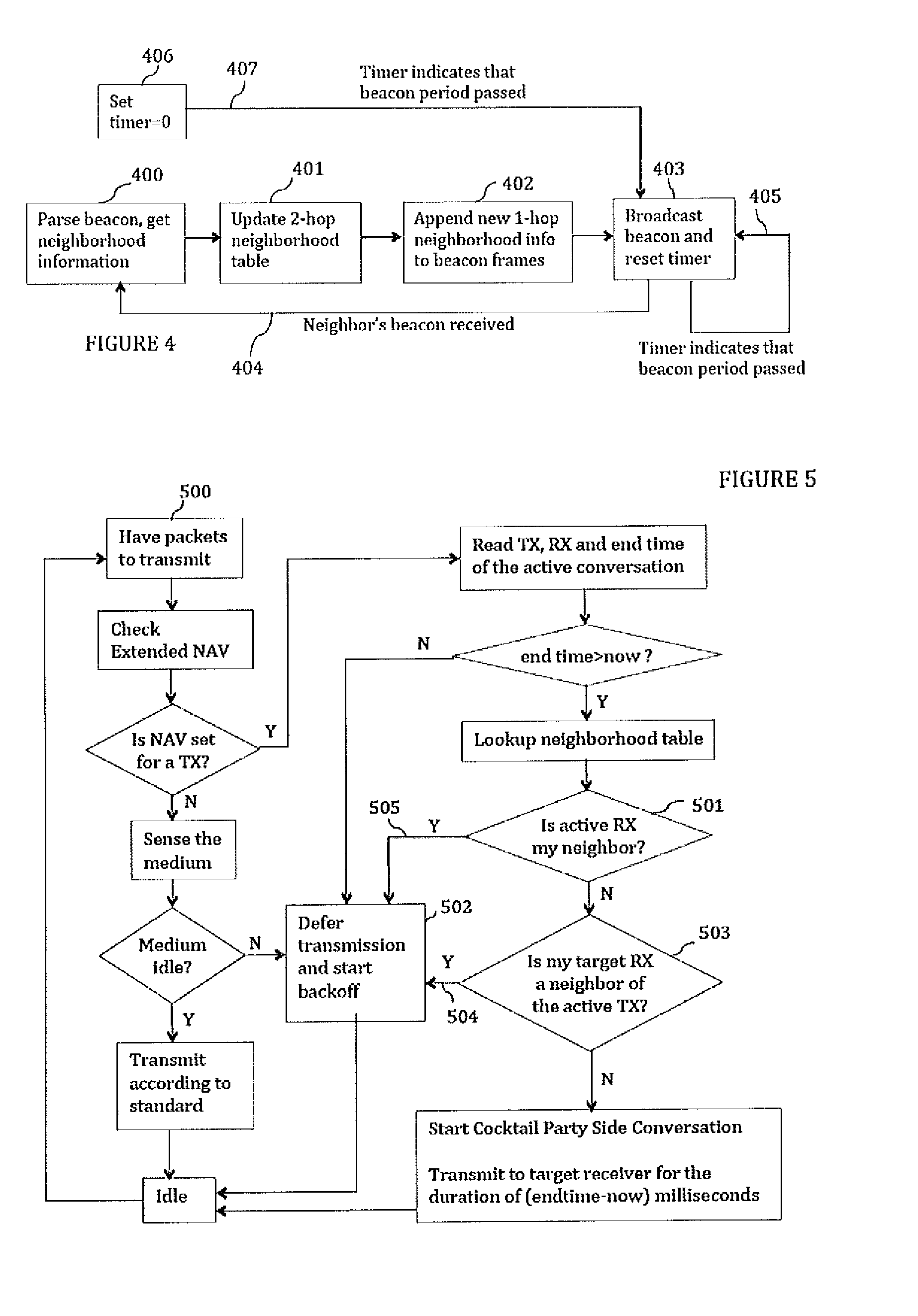
Cocktail party: side conversations and talking over in wireless mesh networks
ActiveUS20140254459A1Minimize jitterSpecial service provision for substationNetwork topologiesDistributed coordination functionProtocol design
The present disclosure proposes a method for minor modifications to the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) channel access mechanism in order to enable a greater number of concurrent communications in a unit area in compliance with the current protocol design. The method comprises equipping nodes with wider neighborhood information than what is obtained with IEEE 802.11, and with a device calibration that equips the device with the knowledge of its performance in the presence of interference. The present disclosure medium access mechanism increases the aggregate throughput with every additional concurrent communication that is enabled in the shared medium. Cocktail Party-capable devices can fairly coexist with 802.11 legacy DCF devices, and co-operate with these devices in the same network without changes to those devices or to the standard. The same or similar mechanisms can be applied to other systems and standards in order to enable concurrent communications in the same contention area.
Owner:AIRTIES SAS
PLL clock generator, optical disc drive and method for controlling PLL clock generator
InactiveUS7339861B2Simple configurationAccomplish phase locking quickly enoughPulse automatic controlFilamentary/web record carriersPhase differenceEngineering
A PLL clock generator generates an output signal with a frequency N times (where N≧1) as high as that of an input signal. The clock generator includes: a frequency divider for dividing the frequency of a clock signal by N so as to output a frequency-divided clock signal; a phase comparator for detecting a phase difference between the input signal and the output signal of the frequency divider so as to output a phase difference signal including information representing the phase difference; a LPF for smoothing the phase difference signal; a VCO for generating the clock signal, of which the frequency is determined by the output of the LPF, and outputting the clock signal to the frequency divider; and a phase shifter for shifting the phase of the output signal of the frequency divider in accordance with the phase difference signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Arrangement for reducing transmitted jitter
InactiveUS6907066B1Minimize jitterImprove performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationPhase correctionCommunications system
A pulse transmitter includes a phase correction module configured for detecting a phase error between a transmit clock and a prescribed clock specification at a transmit clock instance. The transmit clock instance represents an instance in time in which the pulse transmitter is to transmit data according to the prescribed clock specification. The pulse transmitter also includes pulse shape tables, each configured for outputting a corresponding waveform sample set of a prescribed waveform relative to a corresponding phase offset. Hence, the pulse transmitter is able to compensate for phase differences between the transmit clock utilized by the pulse transmitter and the prescribed clock specification, by outputting a selected waveform sample set that has a corresponding phase offset that compensates for the detected phase error, optimizing the performance of pulse position modulation communications systems that are adversely affected by transmit jitter.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Frequency dividing circuit
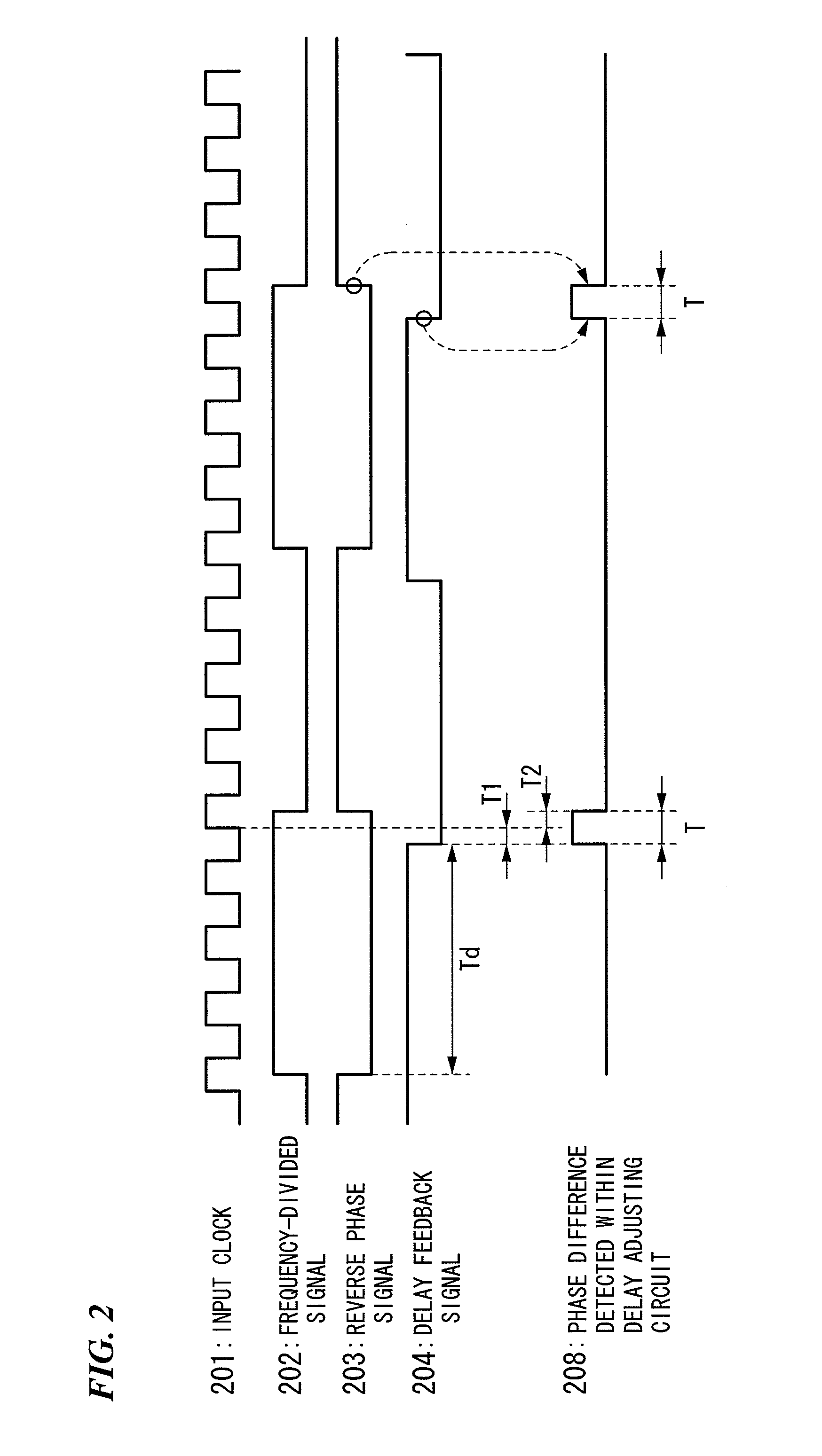
InactiveUS20080122498A1Minimize jitterCounting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageControl signalDividing circuits
A frequency dividing circuit includes: a D-type flip flop that outputs frequency-divided signal synchronized with input clock and reverse phase signal corresponding to the frequency-divided signal; a variable delay circuit that generates a delay feedback signal delayed by a specific delay time from the reverse phase signal input from the D-type flip flop and feeds back the delay feedback signal to the D-type flip flop; and a delay adjusting circuit that detects a phase difference between the reverse phase signal input from the D-type flip flop and the delay feedback signal input from the variable delay circuit, obtains detected results, and outputs to the variable delay circuit a control signal to perform control so that the delay time becomes time required to ensure setup / hold time of the D-type flip flop, based on the detected results.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Bandwidth optimization of video program bearing transport streams
InactiveUS7620073B2Minimize jitterTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexMPEG transport streamMultiplexing
An apparatus comprising an input capable of receiving a bandwidth optimized transport stream is provided. The bandwidth optimized transport stream can be produced by receiving a transport stream of variably compressed program data bearing transport packets and one or more null transport packets. One or more of the null transport packets is selectively replaced with another to-be-remultiplexed non-null data bearing transport packet. Independently of determining an amount of information carried by a program data bearing transport packets from time to time in the received transport stream, at least one selected program bearing transport packet is scheduled for output in an output remultiplexed bitstream.
Owner:TANDBERG TELEVISION
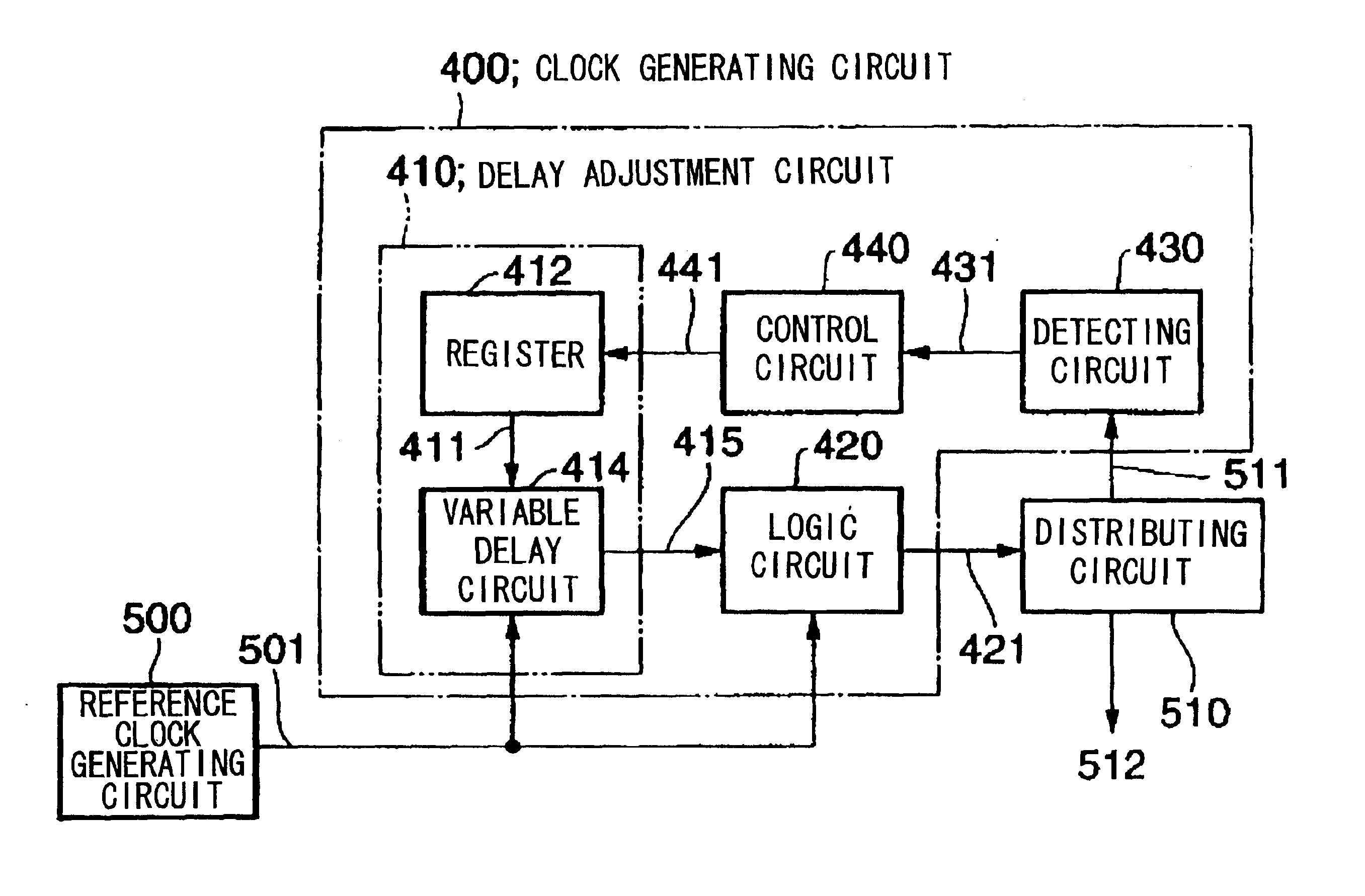
Delay adjustment circuit and a clock generating circuit using the same
InactiveUS6918050B2Minimize jitterDuty ratio can be compensatedPulse automatic controlError detection/correctionCapacitanceGate array
The present invention provides for adjusting the delay time interval of an input signal by controlling the internal register value and internal signal in a semiconductor integrated circuit device, or an external signal. The invention comprises a first gate array 10 for carrying out fine adjustment of the delay time interval of the input signal, capacitances 60 to 63 and 70 to 73 connected to the output side of a specified gate in the first gate array via first switching device 40 to 43, a second gate array 20 for carrying out rough adjustment of the delay time interval of the input signal; and a control device 30 that adjusts the delay time interval of the input signal by adjusting the capacitances connected to the output side of a specified gate in the first gate array and the number of gate stages in the second gate array 20.
Owner:NEC CORP
Symbol timing recovery apparatus usable with VSB receiver and method thereof
InactiveUS20060176980A1Minimize jitterShorten the timeAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsGlovesSymbol timing offsetEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Recording medium, recording apparatus and recording method
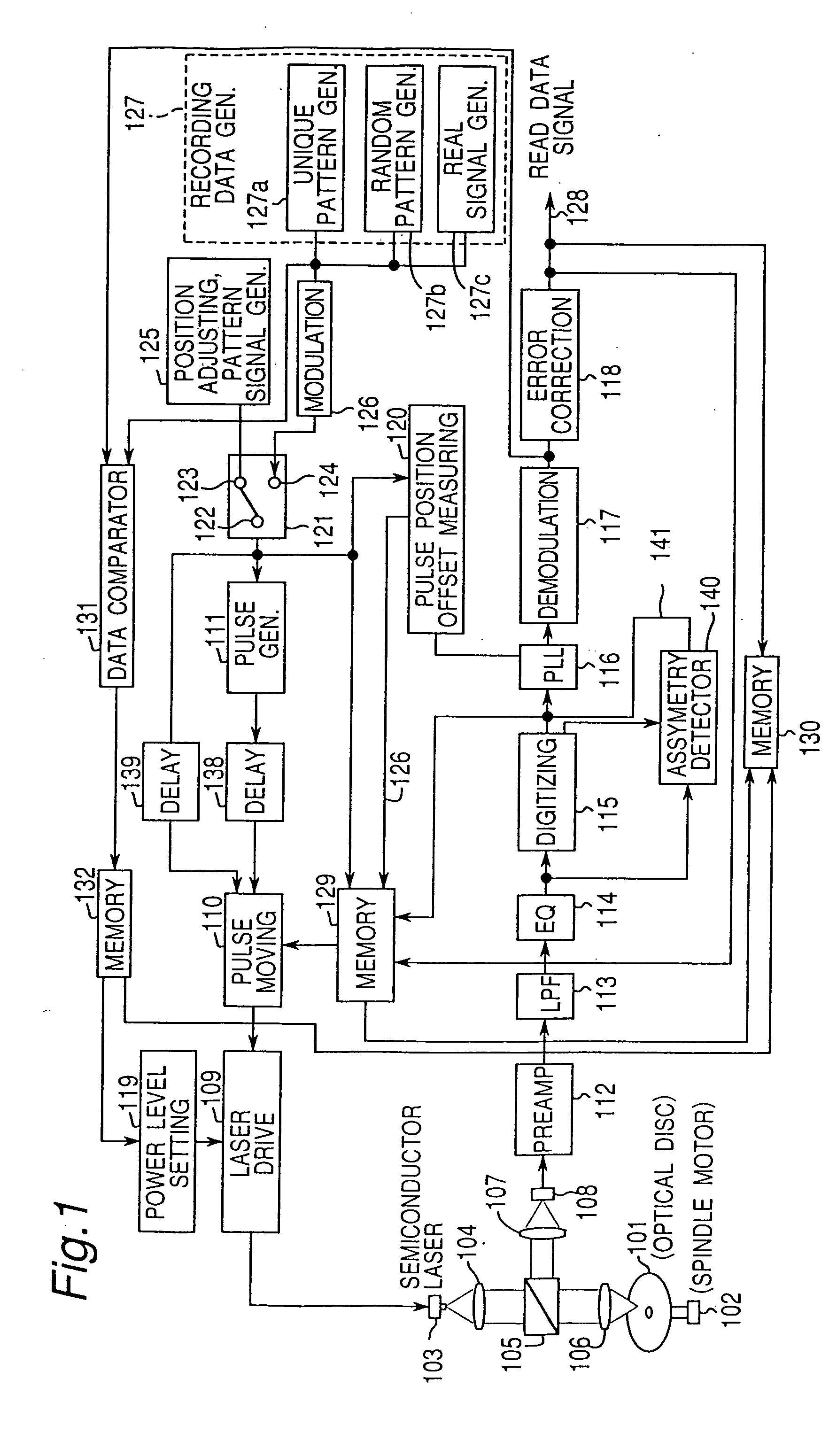
InactiveUS20050185558A1Minimize jitterTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesData recordingComputer science
Optimum movement of first and last signal pulses based on the data pattern is determined before data recording to record marks in the correct position. A specific pattern signal is read from a disc track and digitized with an appropriate slice level by the digitizing circuit (115). A pulse position offset measuring circuit (120) then measures specific edge intervals in the resulting digital signal. Movement of the first and last pulse by the pulse moving circuit (110) is then set so that the offset between the measured edge interval and a predetermined standard edge interval is ideally zero.
Owner:SHOJI MAMORU +3
Optical disk apparatus
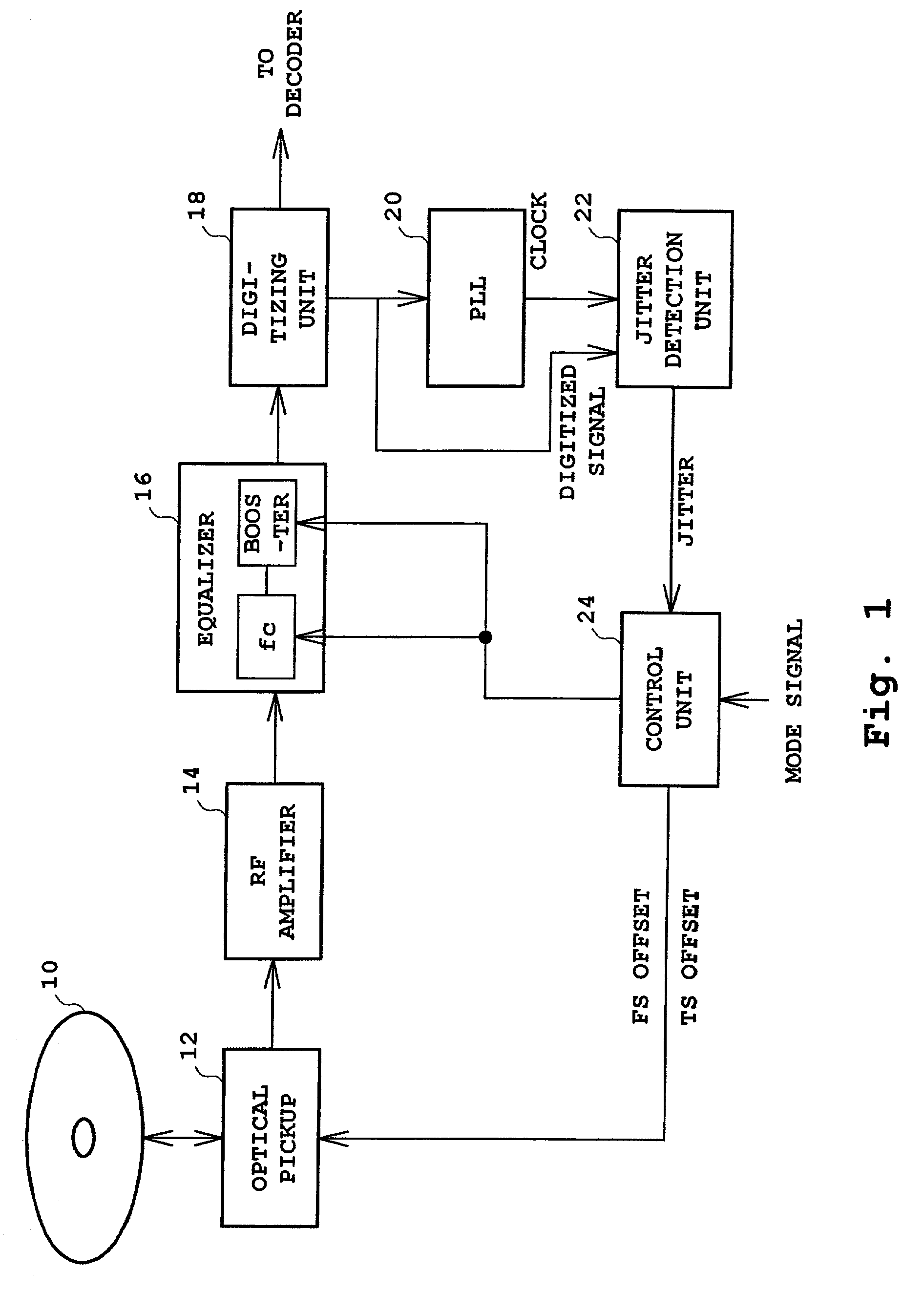
InactiveUS6999388B2Minimize jitterImprove characteristicCombination recordingTelevision system detailsOptical pickupEngineering
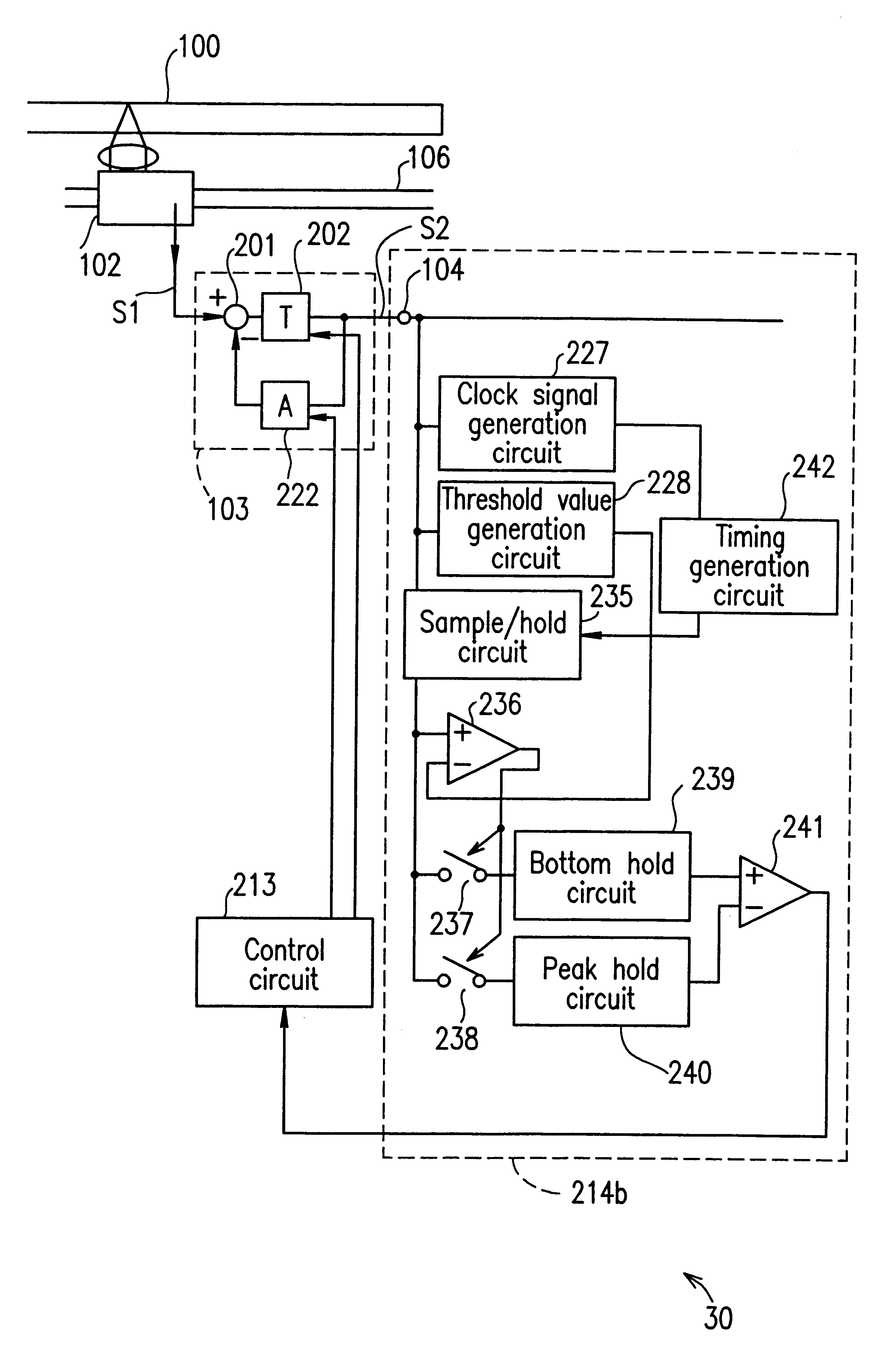
An optical disk apparatus capable of adjusting a focus servo and the like by precisely detecting a jitter amount. Light reflected from an optical disk is converted into an RF signal in an optical pickup and amplified by an RF amplifier before being supplied to an equalizer. The boost amount of the equalizer is set to zero during adjustment and set to a predetermined finite value (e.g., +20 dB) during normal recording and reproducing. By first setting the boost amount to zero, the delay characteristics of the RF signal from 3T to 11T are flattened such that an accurate jitter amount can be determined based on the integrated value of the phase differences of 3T to 11T, thereby allowing the optical pickup to be adjusted so as to minimize the jitter amount.
Owner:TEAC CORP
Recording medium, recording apparatus and recording method
InactiveUS20050180286A1Minimize jitterTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesDigitizationData recording
Optimum movement of first and last signal pulses based on the data pattern is determined before data recording to record marks in the correct position. A specific pattern signal is read from a disc track and digitized with an appropriate slice level by the digitizing circuit (115). A pulse position offset measuring circuit (120) then measures specific edge intervals in the resulting digital signal. Movement of the first and last pulse by the pulse moving circuit (110) is then set so that the offset between the measured edge interval and a predetermined standard edge interval is ideally zero.
Owner:SHOJI MAMORU +3
Video remultiplexer for dynamic remultiplexing, multi-mode operation and jitter reduced asynchronous communication
InactiveUS7693188B2Minimize jitterTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexMultiplexingAsynchronous communication
A method and system are provided for remultiplexing program bearing data. The remultiplexing method and system are applicable to MPEG-2 compliant transport streams carrying video programs. Remultiplexing functions may be distributed across a network. The remultiplexer can furthermore optimize the bandwidth of transport streams by replacing null transport packets with transport packet data to be inserted into the output transport stream. Remultiplexing and program specific information can be seamlessly dynamically varied without stopping, or introducing a discontinuity in, the flow-of outputted transport packets.
Owner:ERICSSON TELEVISION
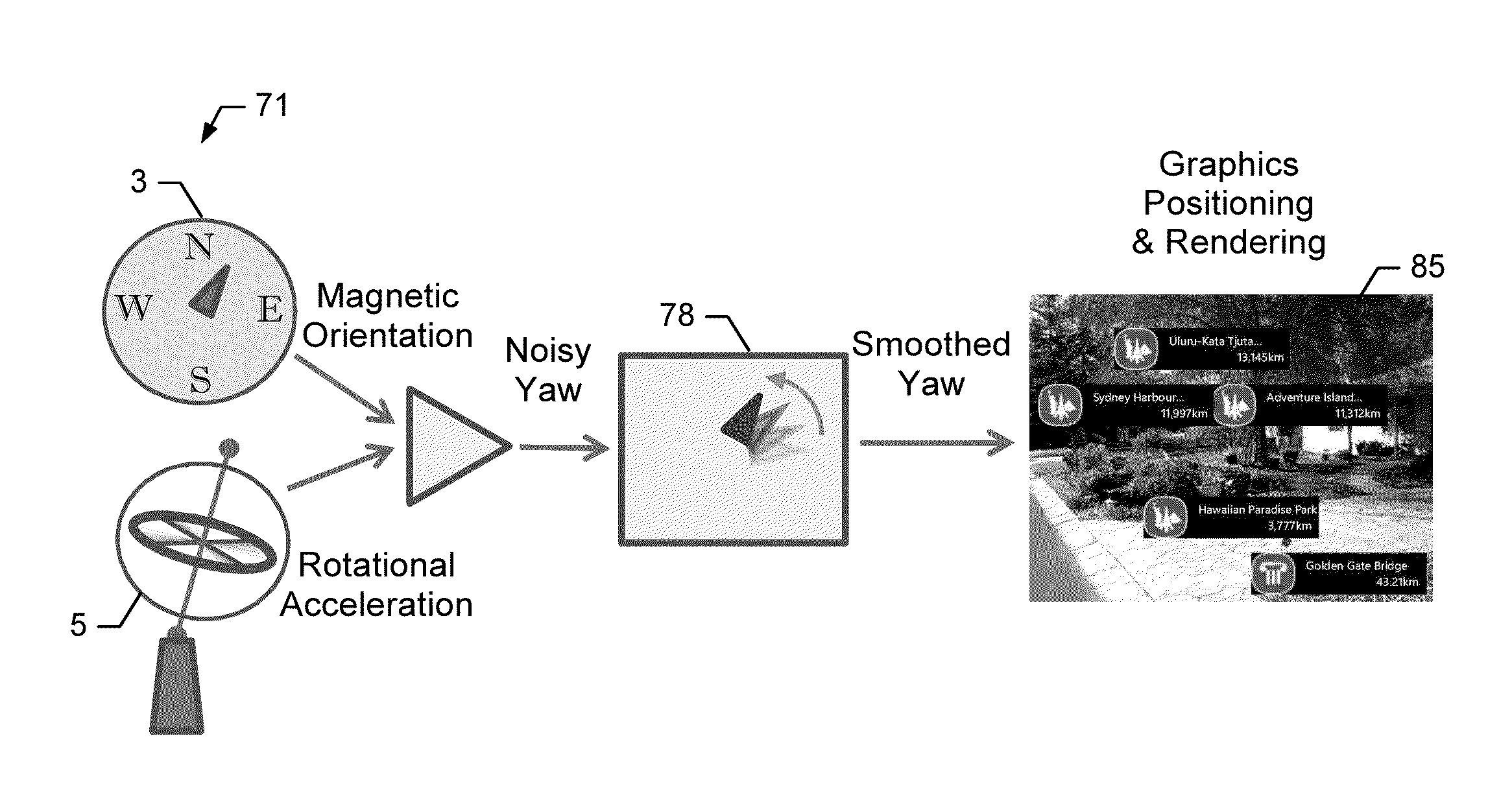
Methods, apparatuses and computer program products for smooth rendering of augmented reality using rotational kinematics modeling
InactiveUS20140015851A1Facilitate smoothingSmooth movementImage enhancementCathode-ray tube indicatorsAngular velocityComputer program
An apparatus for facilitating smooth rendering of augmented reality may include a processor and memory storing executable computer program code that cause the apparatus to at least perform operations including determining an orientation of a media capturing device capturing a real-world object(s) in a field of view. The kinematics model is predefined with data specifying a manner to determine orientations of the media capturing device. The computer program code may further cause the apparatus to periodically receive information from a sensor(s). The information may indicate an orientation is changed to a different orientation responsive to detection of a change in rotational angular velocity of the media capturing device. The computer program code may further cause the apparatus to adjust data of the kinematics model based on the information from the sensor(s) to estimate a current orientation of the media capturing device. Corresponding methods and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
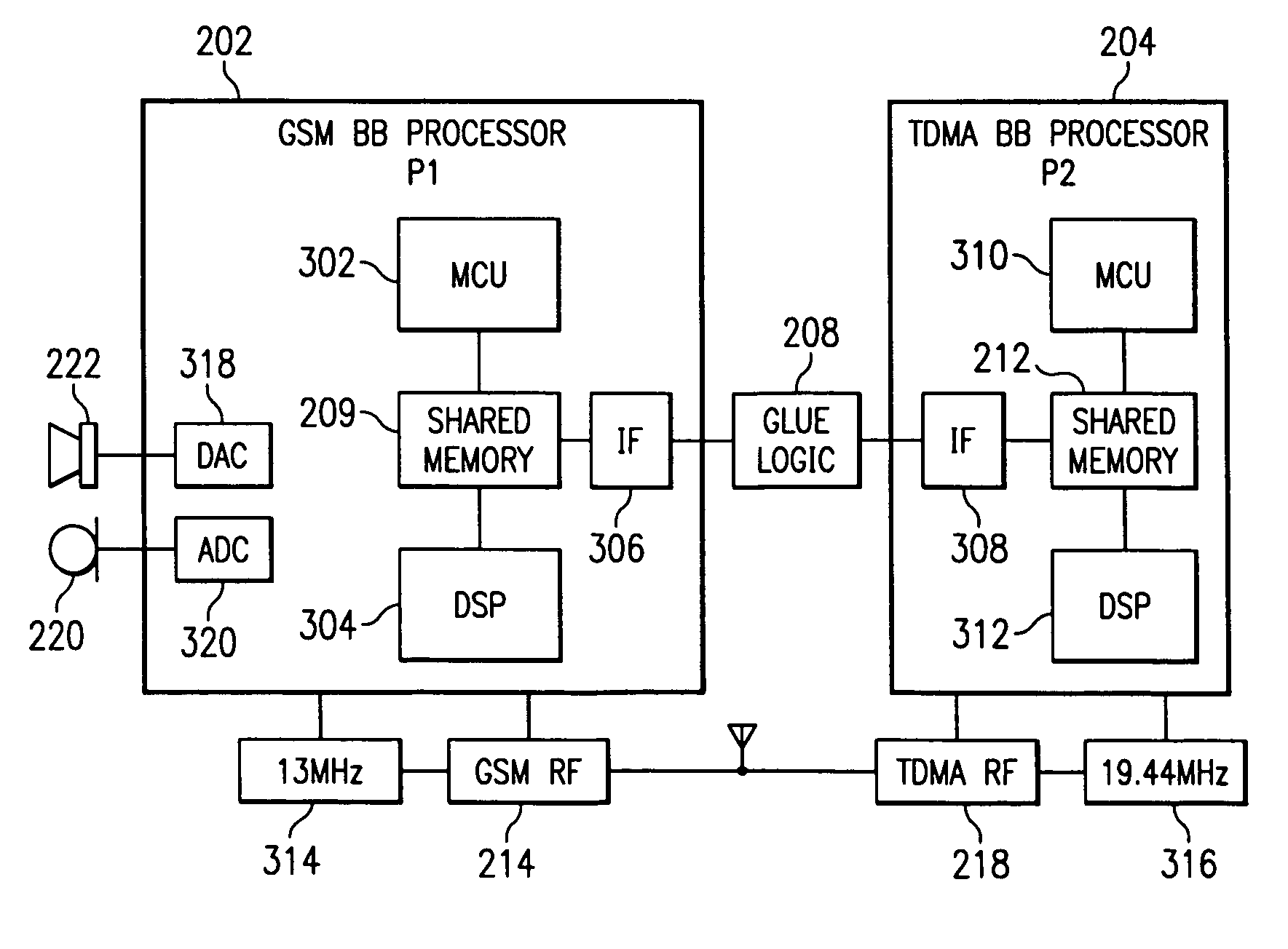
System and method for rate adaptation in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7103129B2Minimize jitterSubstation equipmentSynchronising arrangementConsecutive frameHeadphones
A wireless telephone includes first and second baseband processors. The first baseband processor functions as system master, and the second processor functions as system slave. The first baseband processor interfaces to system controls, such as power supply, man-machine interface (MMI), and the like. The master processor implements a first pair of buffers in the downlink direction and a second pair in an uplink direction. The buffers in the pairs are swapped periodically, based on an internal counter running on the master processor. The timing of the master processor is continuously adjusted to that of the slaved co-processor, by counting a number of samples received from the microphone respectively fed to the earpiece between the beginning of consecutive frames. The timing of the master processor is then adjusted accordingly. The output of the counter may be lowpass filtered to separate jitter from frequency deviation.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Current mode logic circuit with multiple frequency modes
ActiveUS20150333743A1Reduce power consumptionMinimize jitterElectric pulse generatorPulse shapingControl signalControl circuit
A device comprising a clock circuit, a control circuit, and a current mode logic (CML) circuit is disclosed. The clock circuit provides a first differential clock signal and the control circuit generates a control signal based at least in part on the frequency of the first differential clock signal. The CML circuit generates a second differential clock signal based at least in part on the first differential clock signal. The CML circuit operates in one of a plurality of different frequency modes based at least in part on the control signal and includes a number of variable resistors that are responsive to the control signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
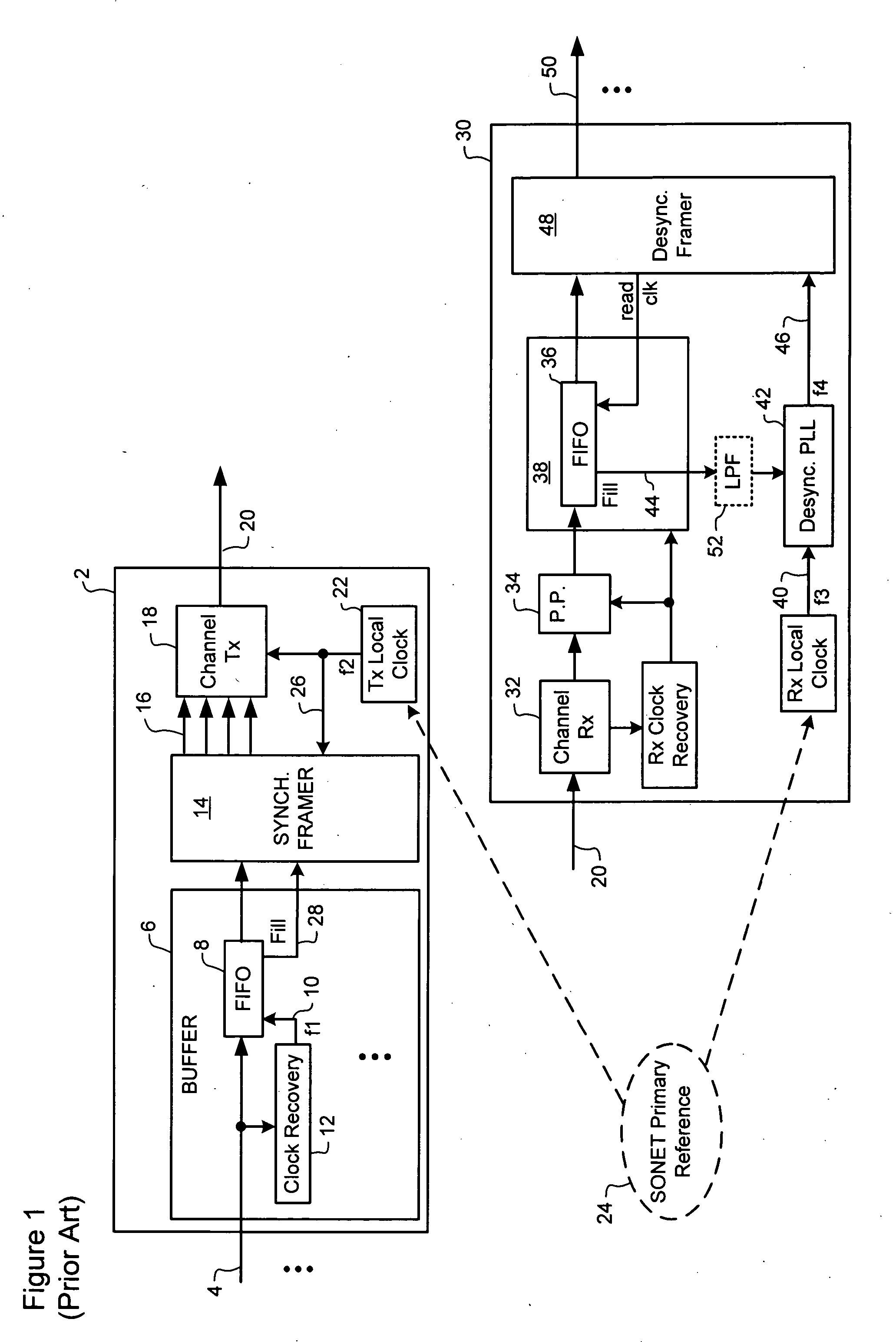
Methods and systems for reducing waiting-time jitter
ActiveUS20070053384A1Reducing waiting time jitterMinimize jitterError preventionTime-division multiplexData signalFrequency difference
A method of minimizing jitter in a system for rate adapting a data signal for transport through a synchronous network. A phase difference is measured between a data clock synchronous with the data signal and a local clock of the synchronous network. A timing reference (F) indicative of a frequency difference between the asynchronous data signal and the local clock is measured using the measured phase difference. Calculation of the timing reference includes compensating ambiguity in the measured phase difference.
Owner:CIENA
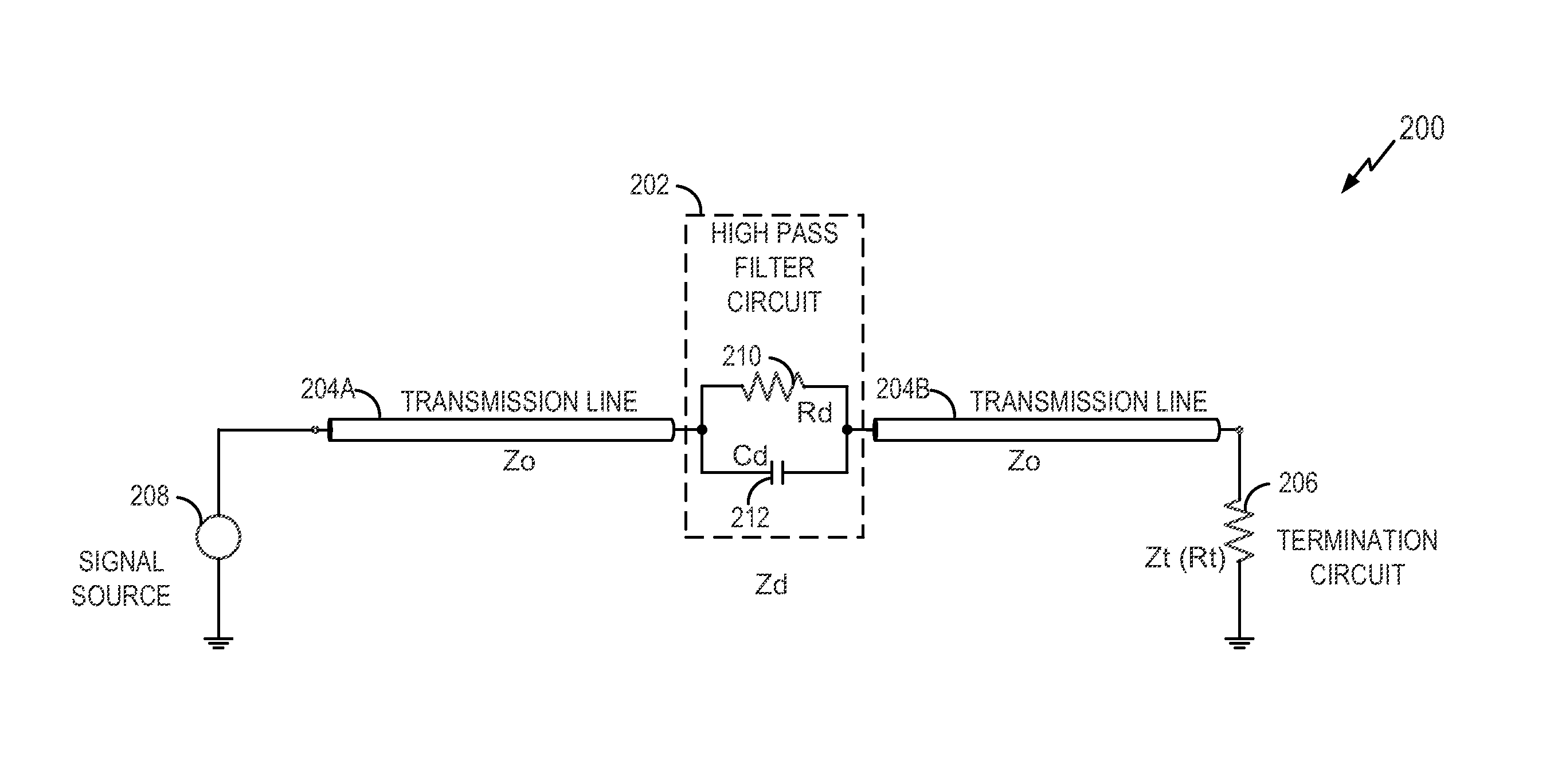
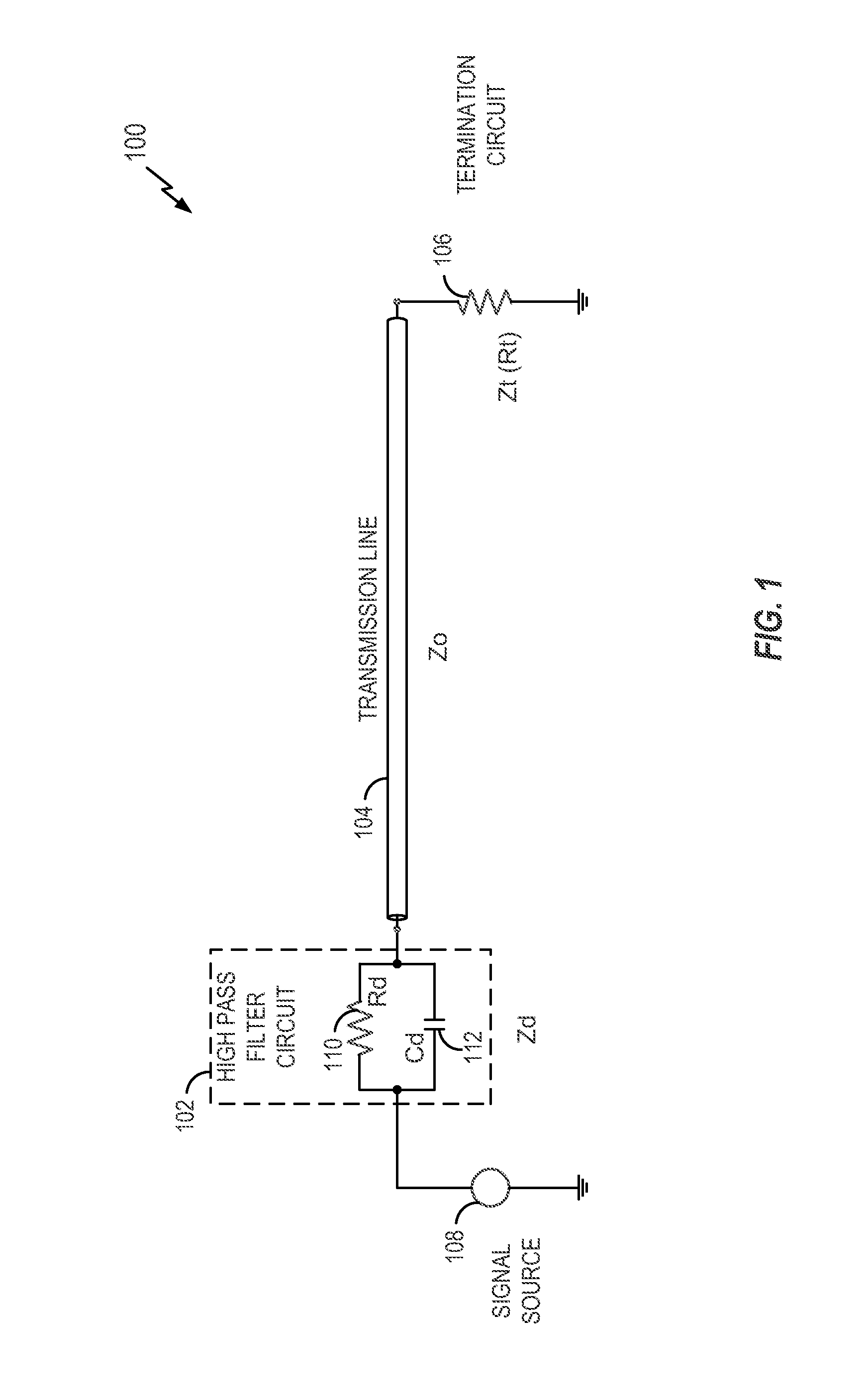
Signal interconnect with high pass filter
InactiveUS20160380607A1Maximize quality of eye diagramMinimize jitterInput/output impedence modificationMultiple-port networksHigh-pass filterTransmission line
A signal interconnect includes a transmission line, a termination circuit coupled to the transmission line, and a high pass filter circuit coupled in series along the transmission line. The high pass filter circuit includes a first resistive circuit and a first capacitive circuit coupled in parallel. The first resistive circuit has a resistance based on a difference between a resistance of the transmission line at a high frequency and a resistance of the transmission line at a low frequency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Optical disk device
InactiveUS7116617B2Increase jitterMinimize jitterFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesLaser lightOptoelectronics
Owner:TEAC CORP
Transparent sub-wavelength network
InactiveUS20090010280A1High clock fidelityAccurate signalTime-division multiplexLength waveClient-side
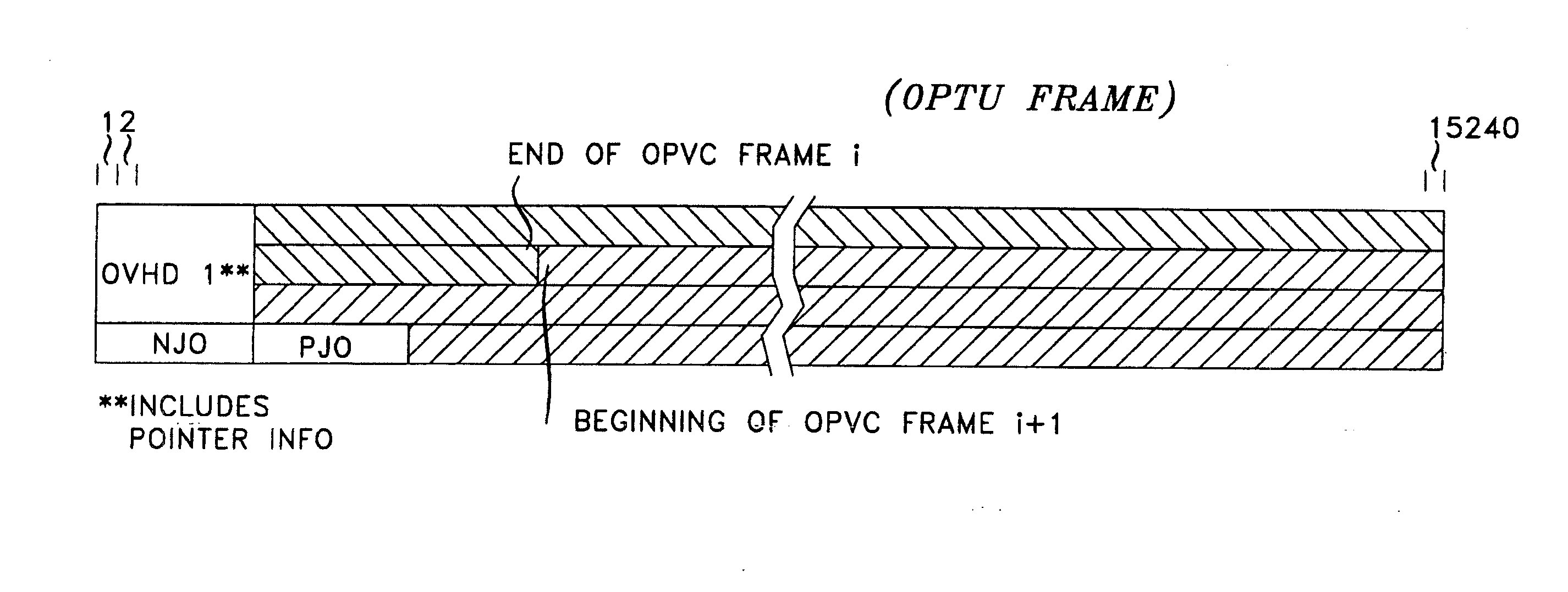
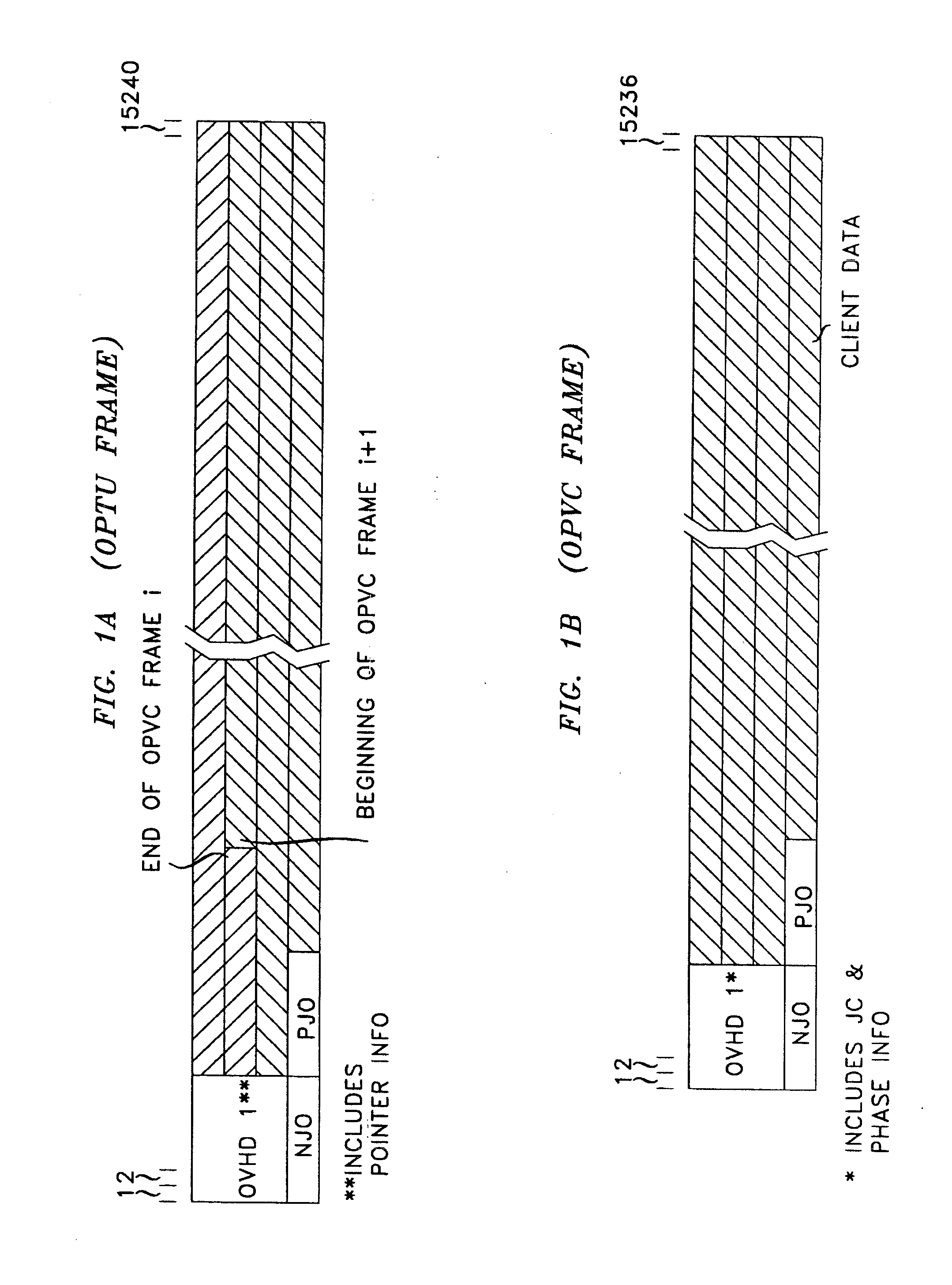
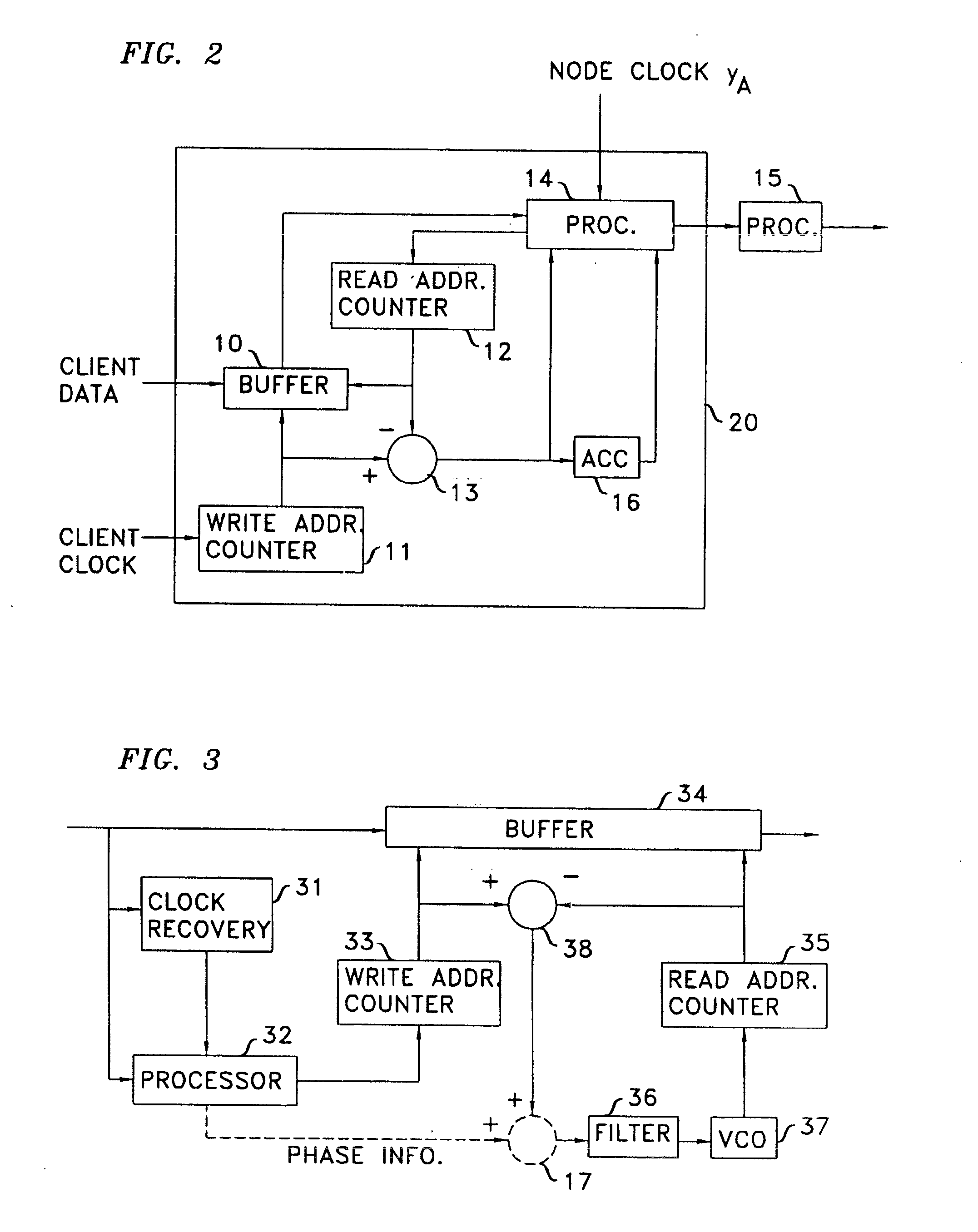
An arrangement that allows transmission of client signals with higher clock fidelity is achieved by developing a phase offset measure at an ingress node, communicating it to the egress node, and recovering the client's clock from the received data and from the received phase-offset information. The ability to recover the client's clock with high fidelity is enhanced by adaptive pointer processing in intermediate nodes and the egress node of the network that the client's signal traverses. The adaptive pointer processing filters incoming pointers from upstream nodes and injects new positive and negative pointer justifications in excess of what is minimally necessary to allow them to be filtered by successive nodes and insure proper transmission over a network that employs a protocol involving framing layer frames embedded in communication layer frames. Illustratively, the network protocol is an extended ITU Recommendation G.709 Digital Wrapper protocol, arranged to employ frames of 15240 columns by four rows.
Owner:CIENA
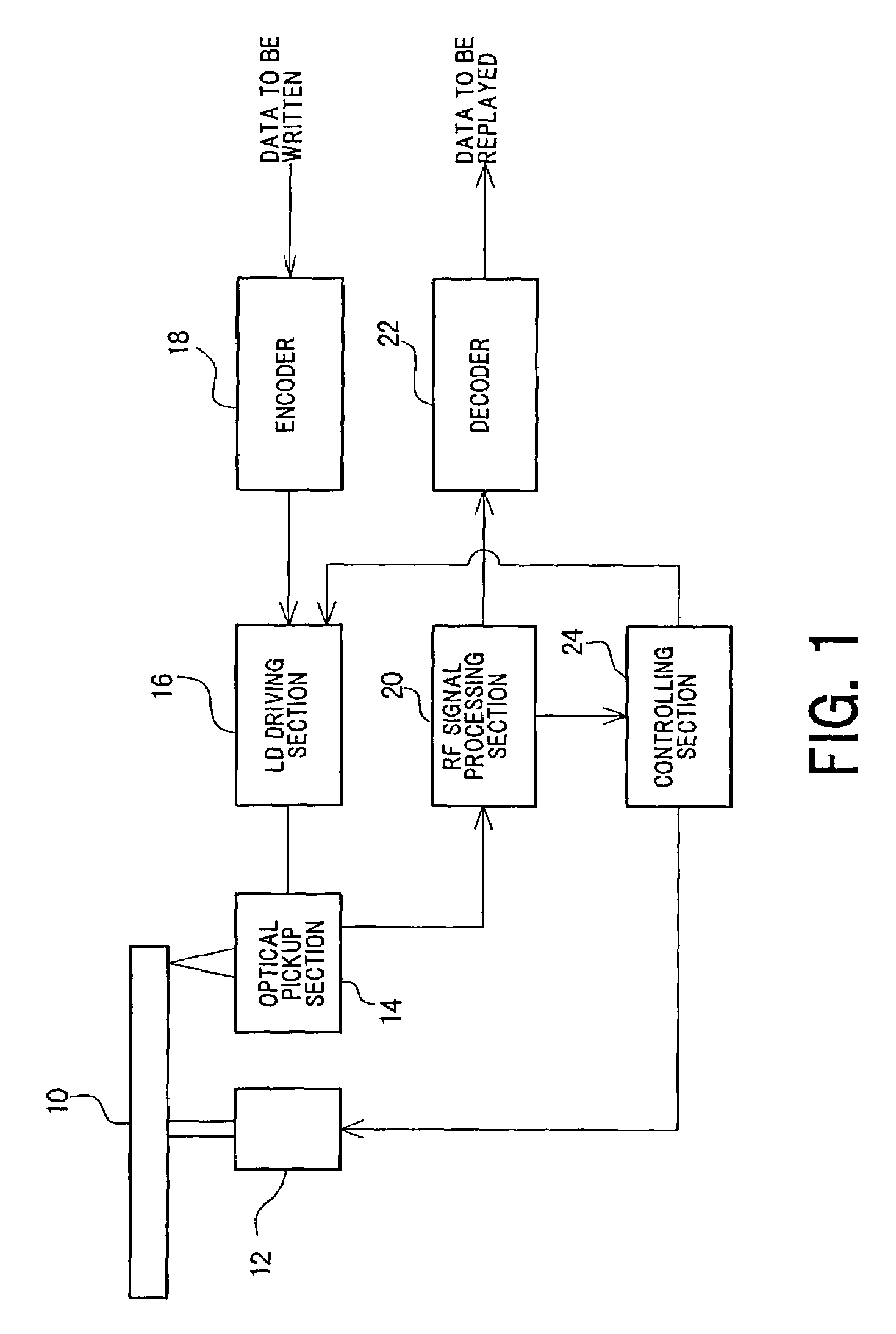
Optical information processing apparatus
InactiveUS6172959B1Minimize jitterReduce error rateRecord information storageCarrier monitoringOptical pickupInformation processing
An optical information processing apparatus includes: an optical head for radiating a light beam onto an information storage medium and generating a reproduction signal from the light beam reflected an / or diffracted from the information storage medium, the information storage medium carrying optically readable information recorded thereon; a transportation member for causing a relative movement of the optical head with respect to the information storage medium; and a signal processing circuit for receiving the reproduction signal generated by the optical head and processing the reproduction signal. The reproduction signal obtained from the information storage medium irradiated with the light beam includes first information from a mark near a boundary between a region which is heated by the light beam to no less than a predetermined temperature and a first region which is at a temperature below the predetermined temperature, and second information from a mark near a boundary between the region which is heated to no less than the predetermined temperature and a second region which is at a temperature below the predetermined temperature. The signal processing circuit separates the first information from the second information, or vice versa, thereby obtaining from the reproduction signal the information recorded on the information storage medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com