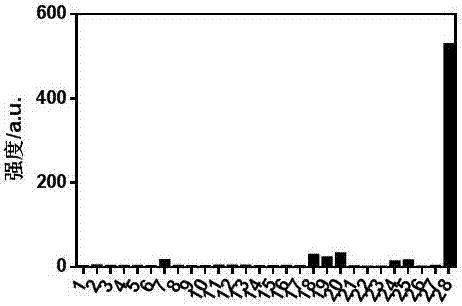
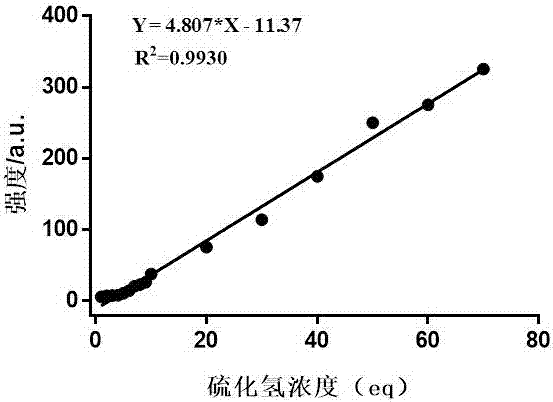
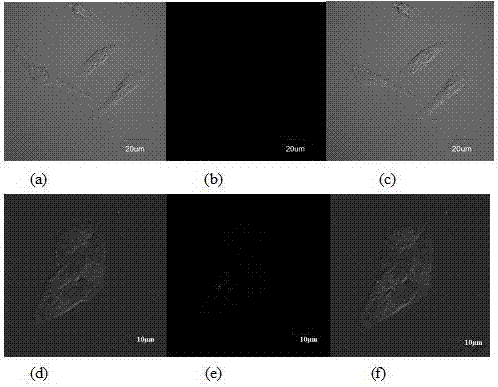
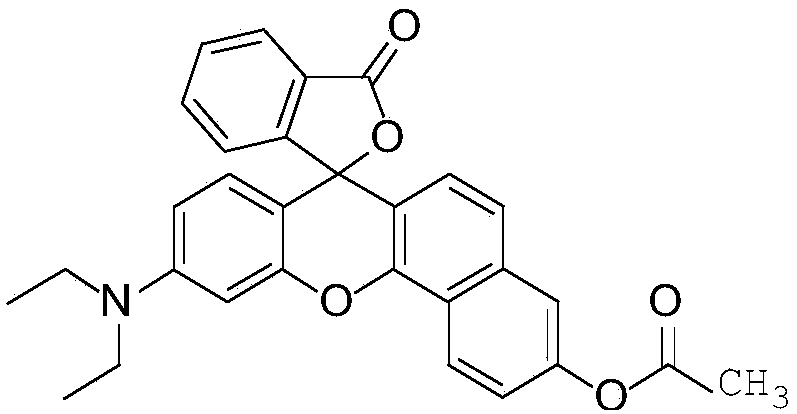
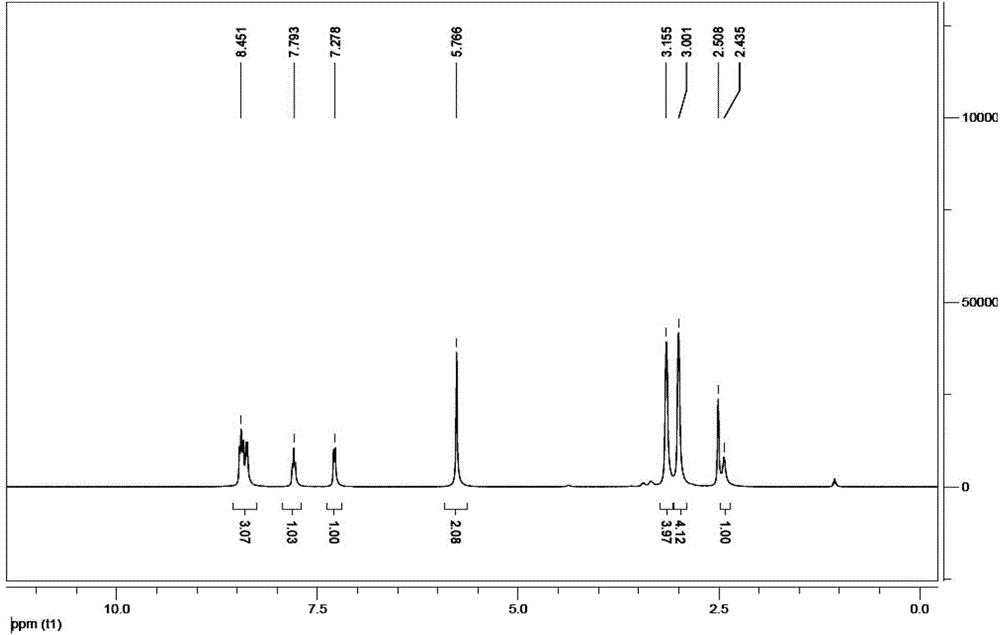
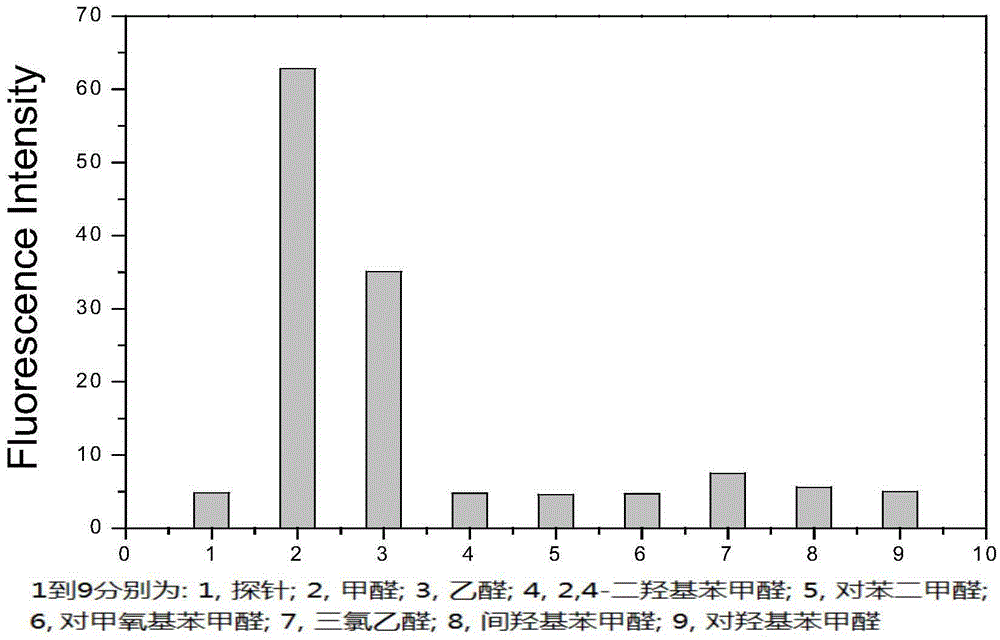
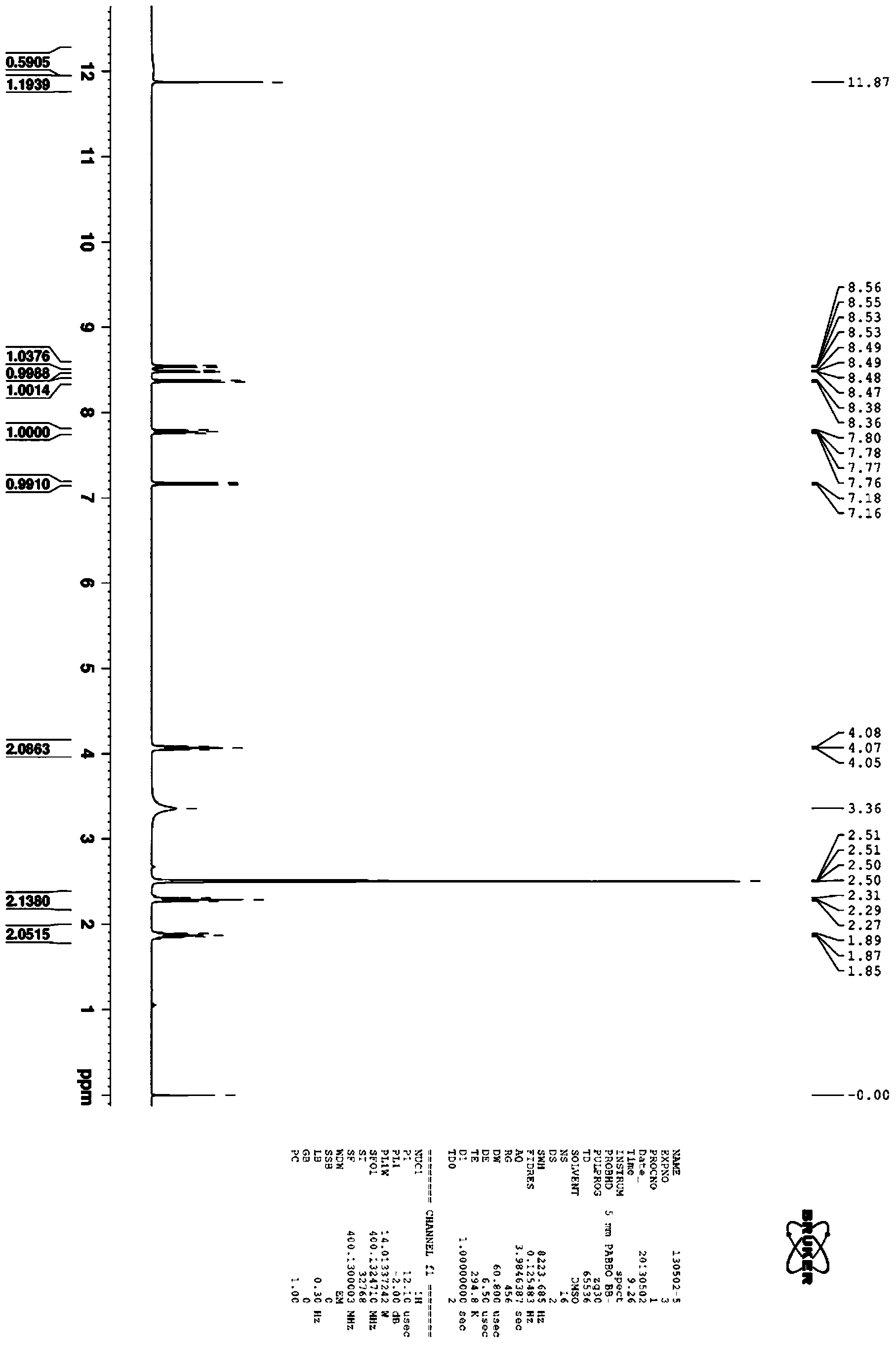
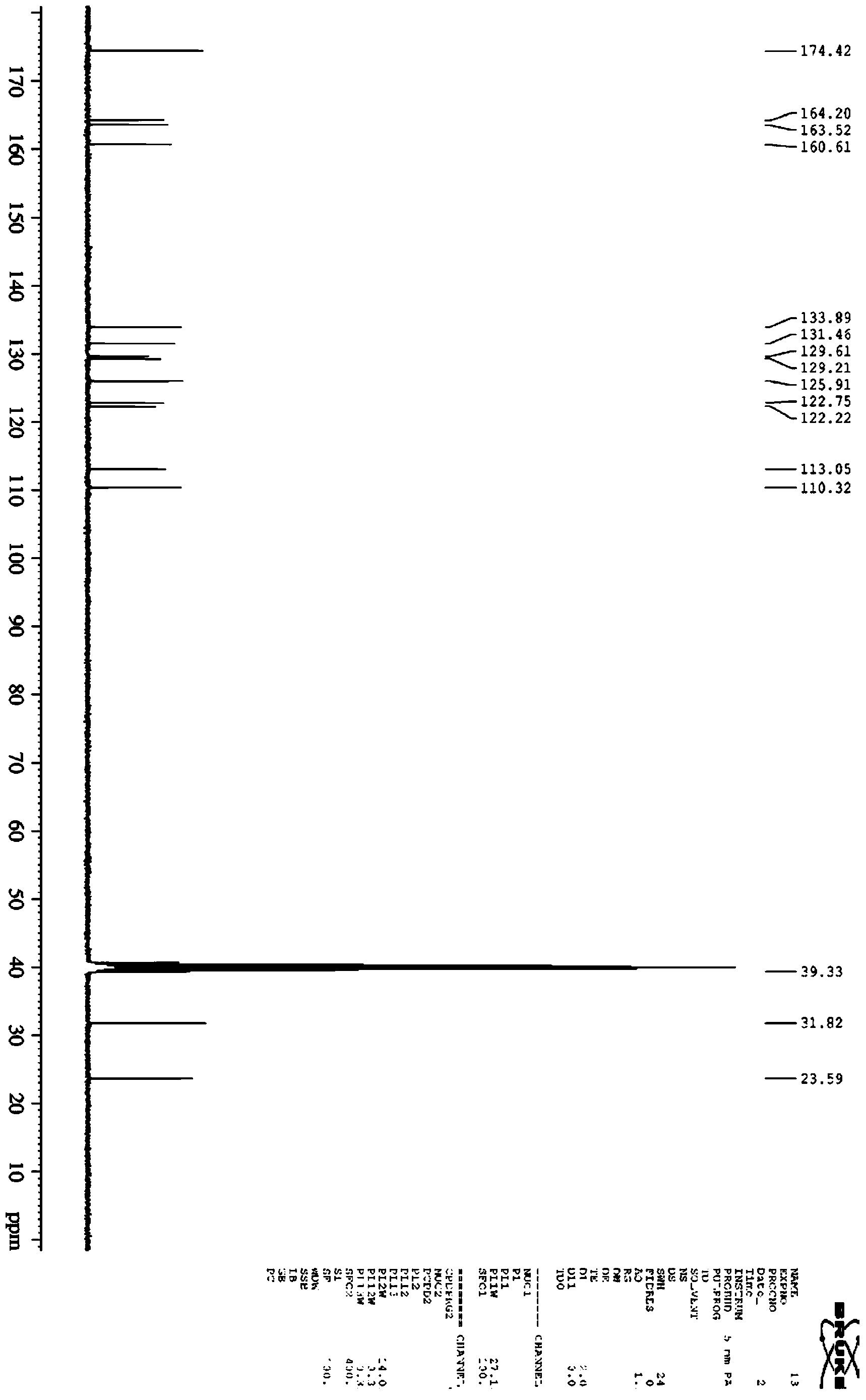
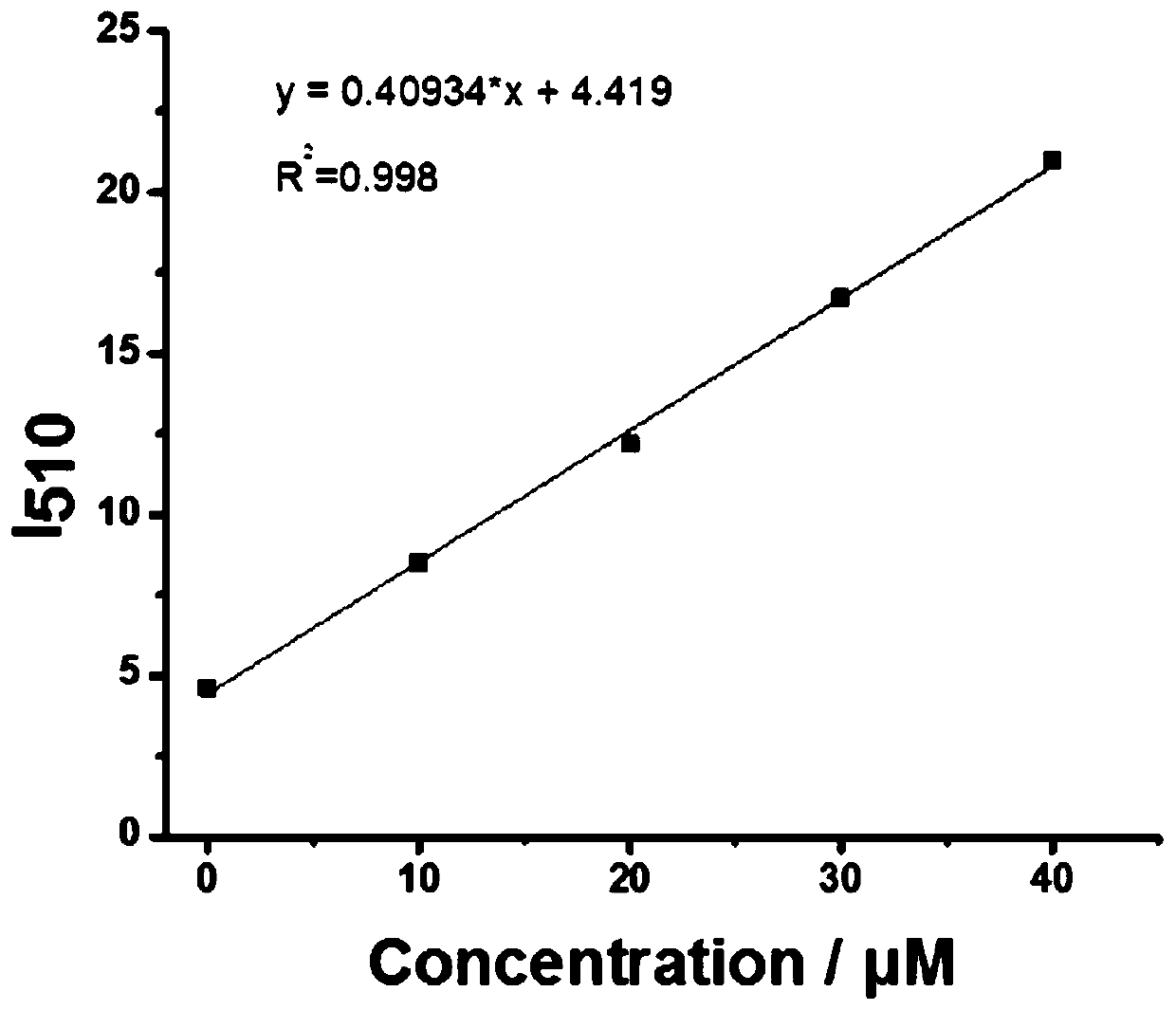
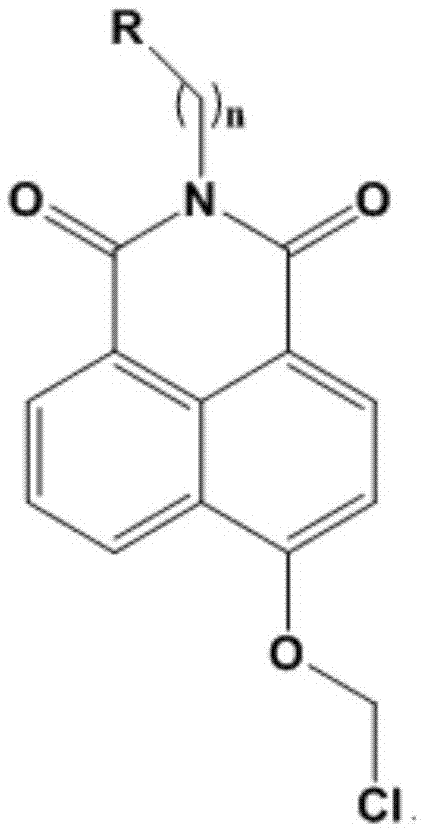
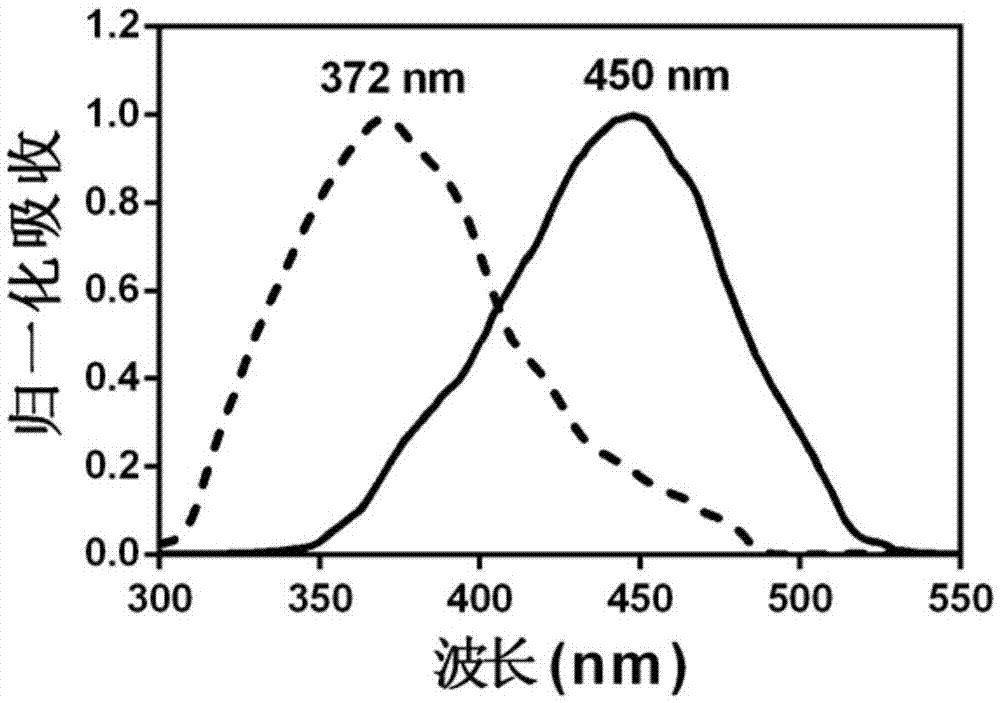
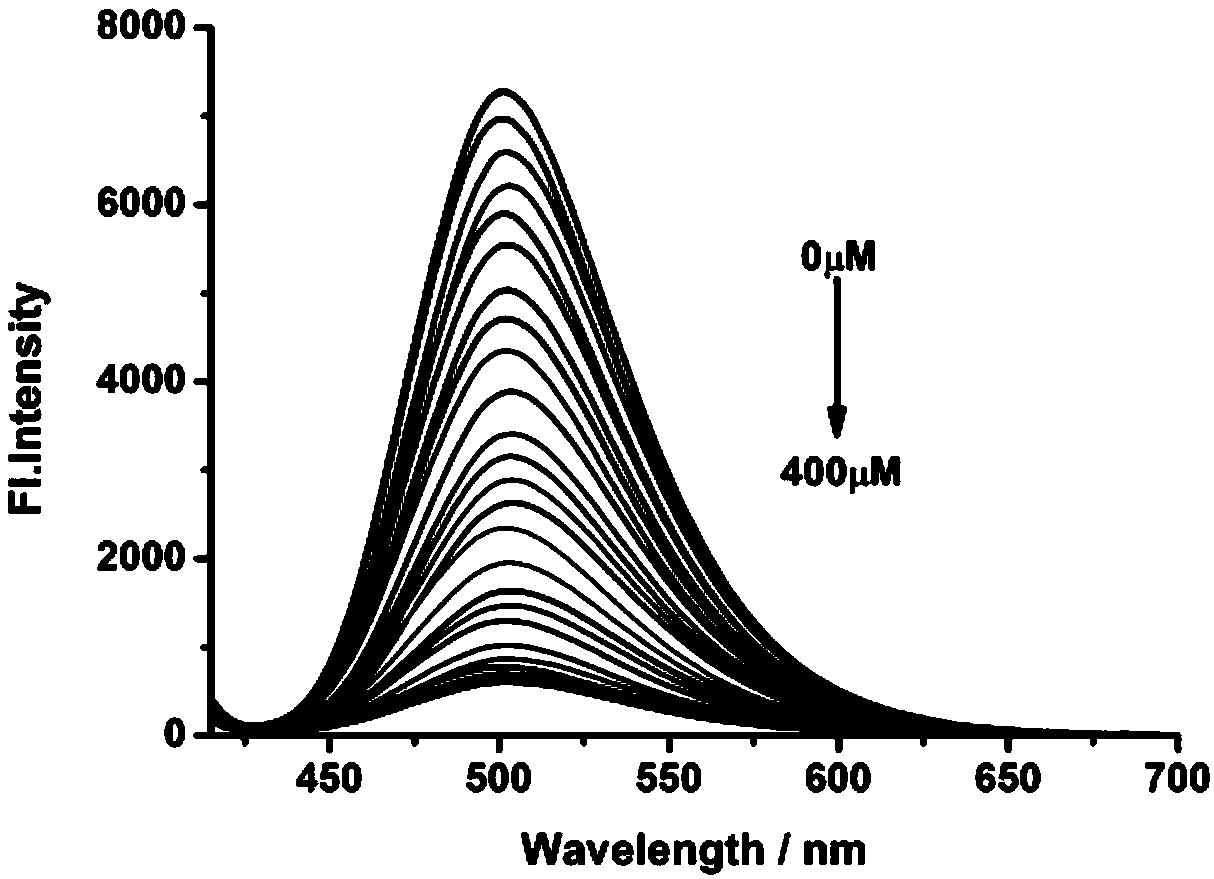
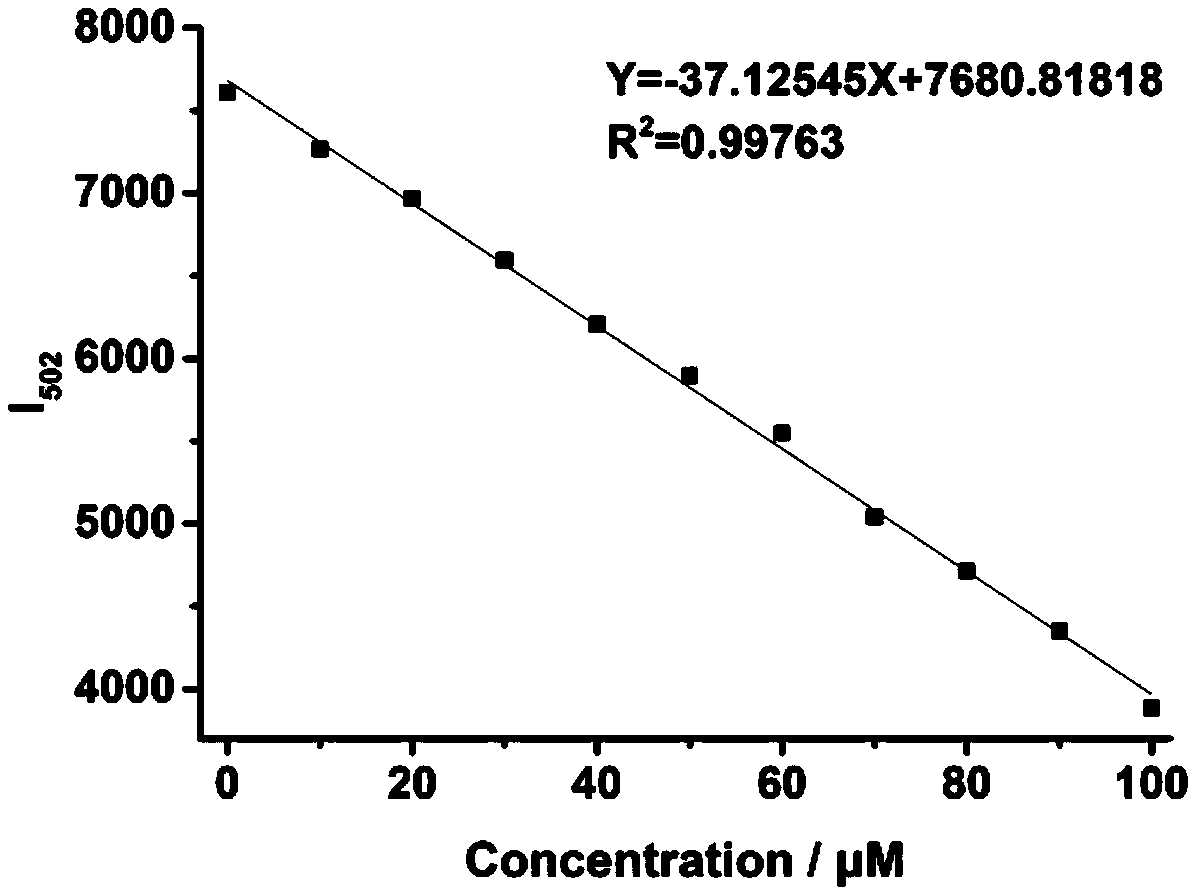
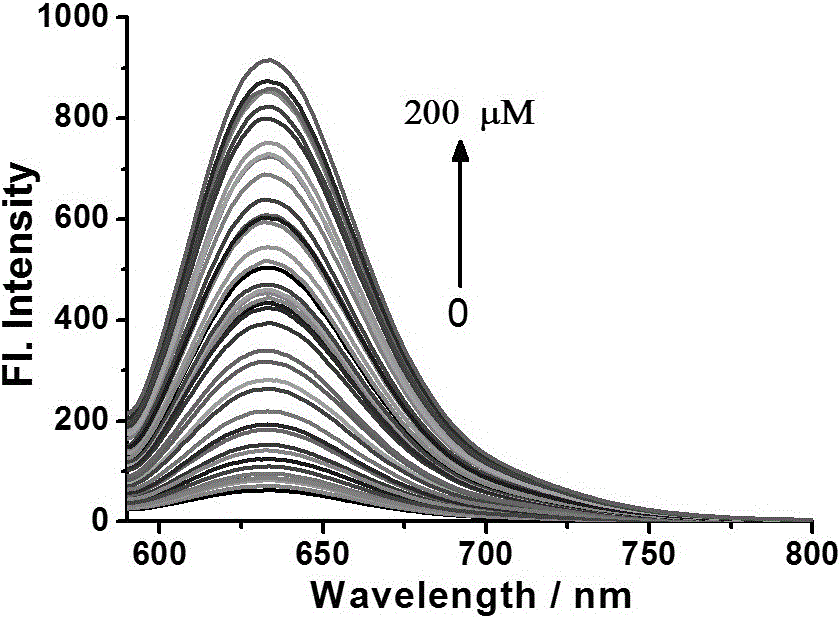
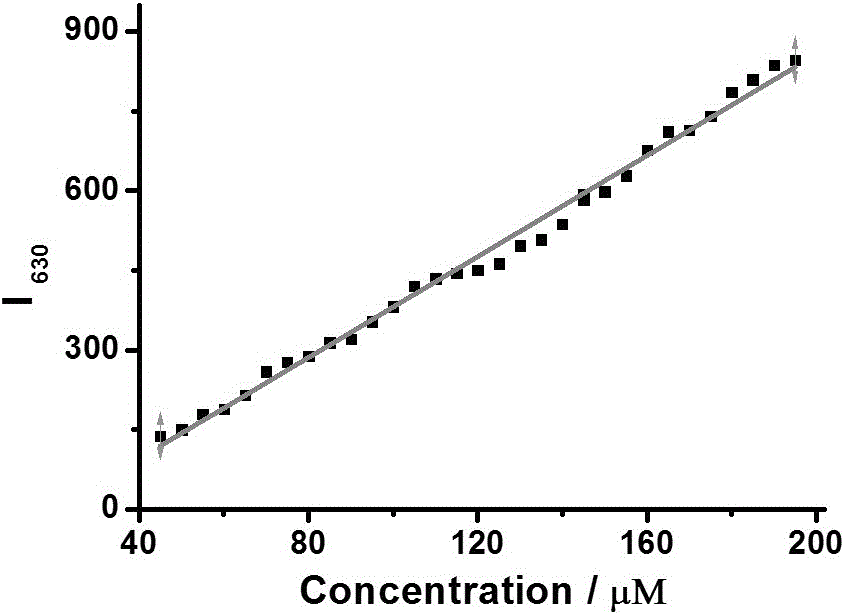
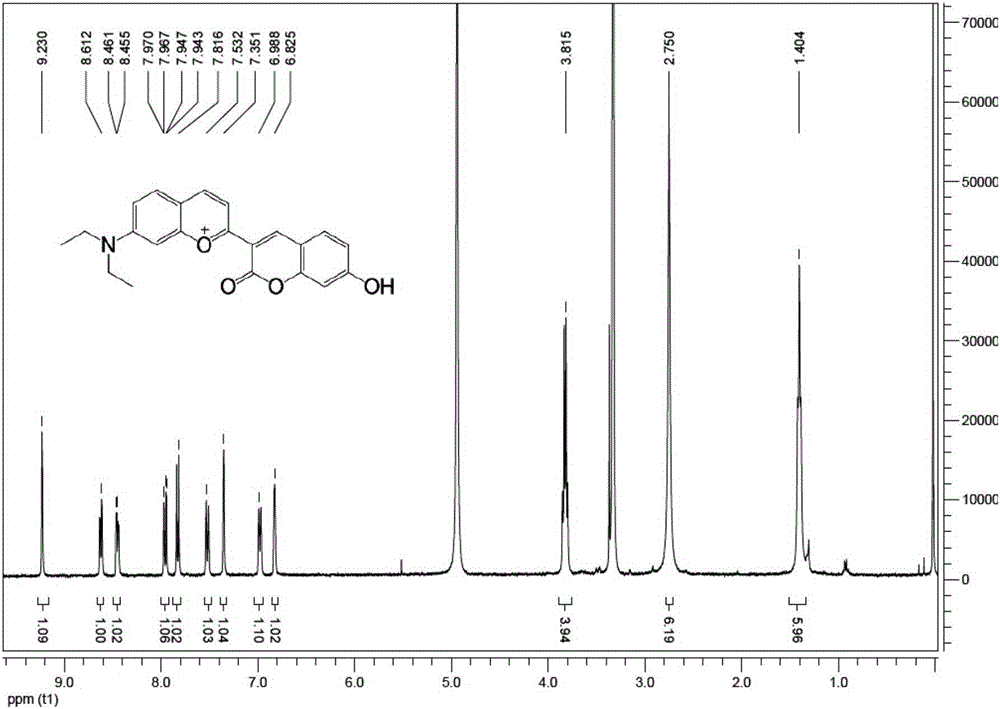
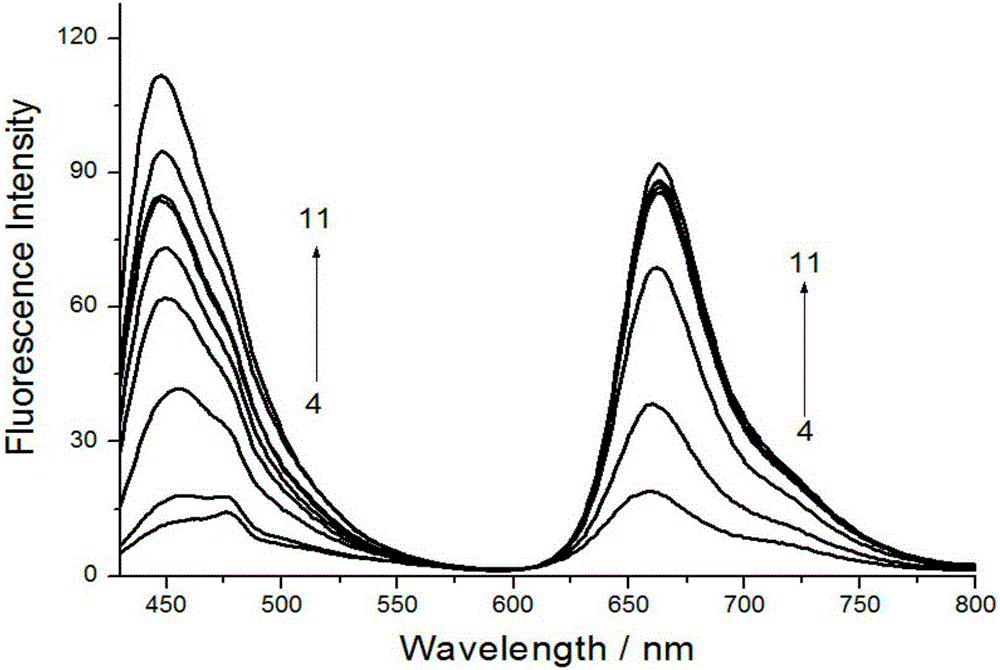
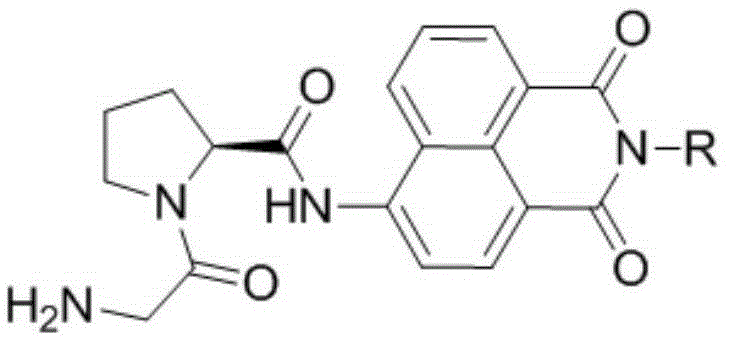
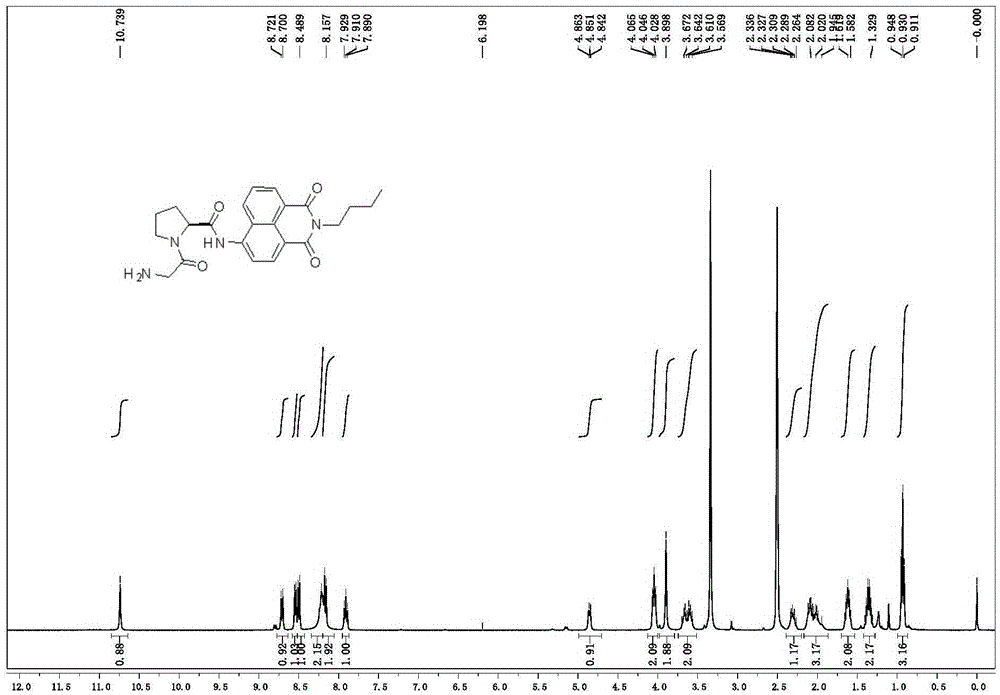
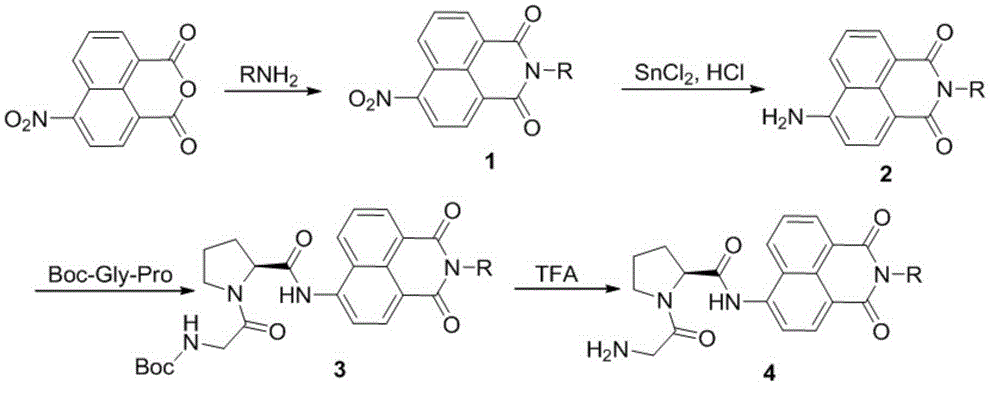
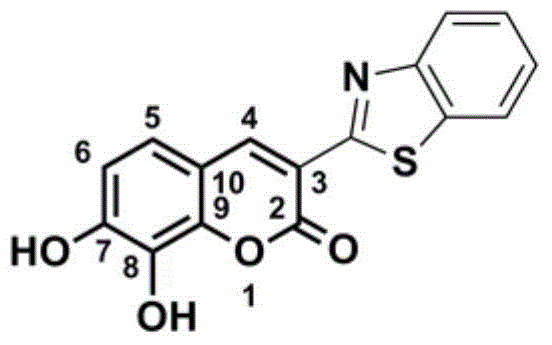
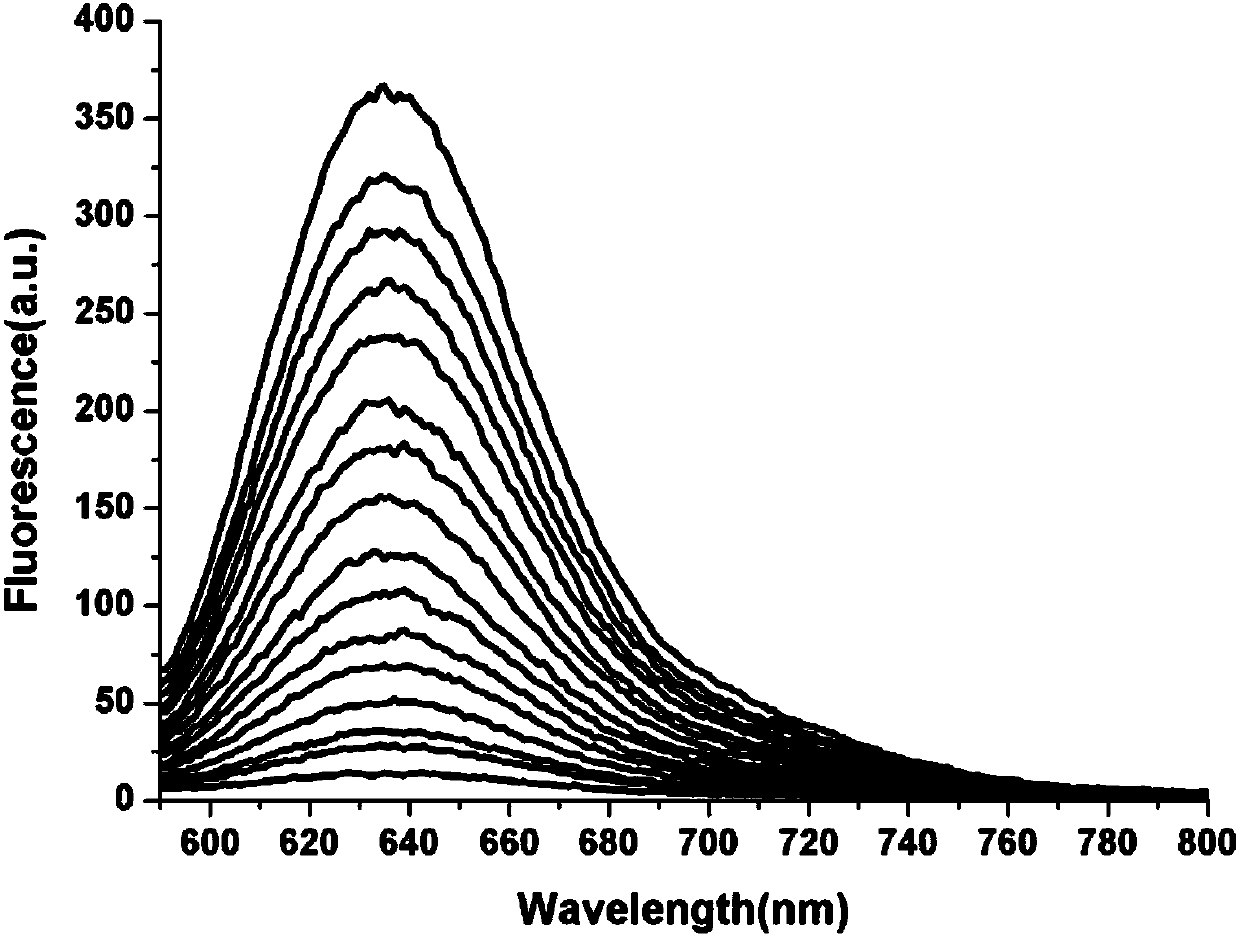
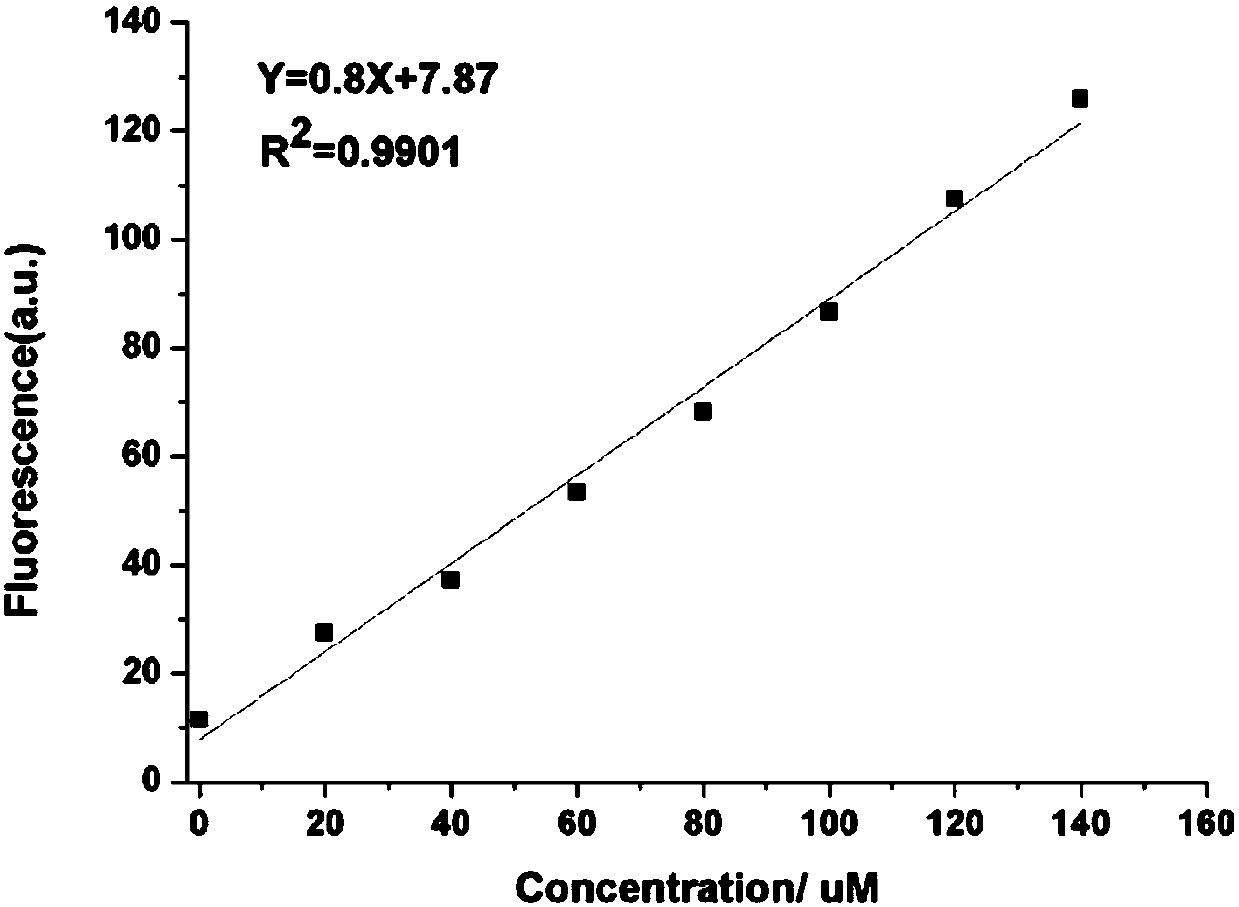
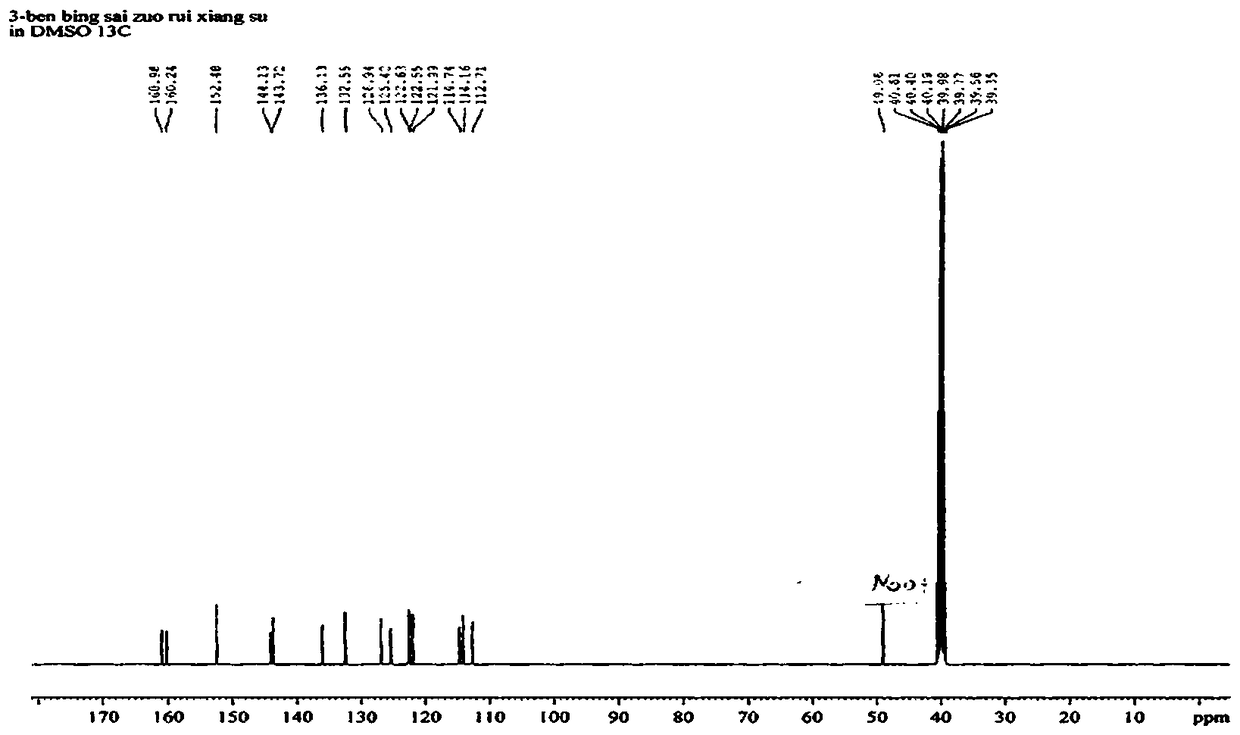
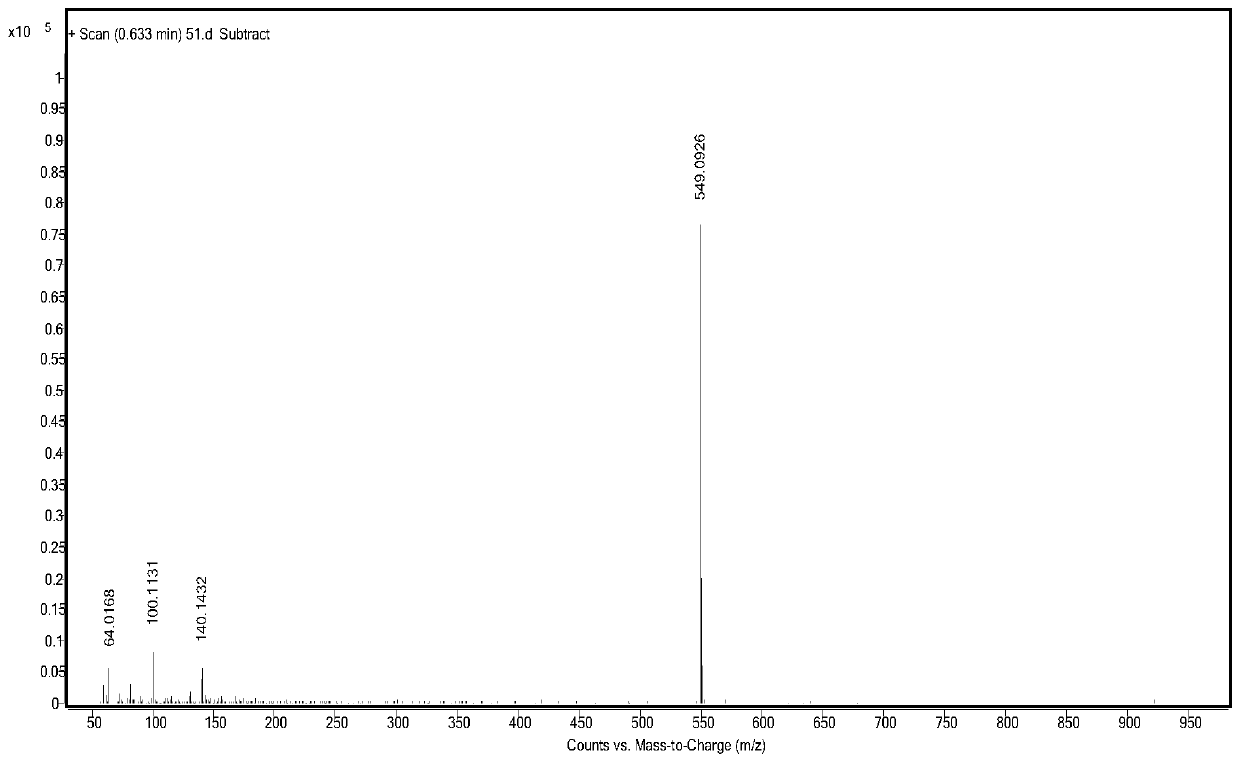
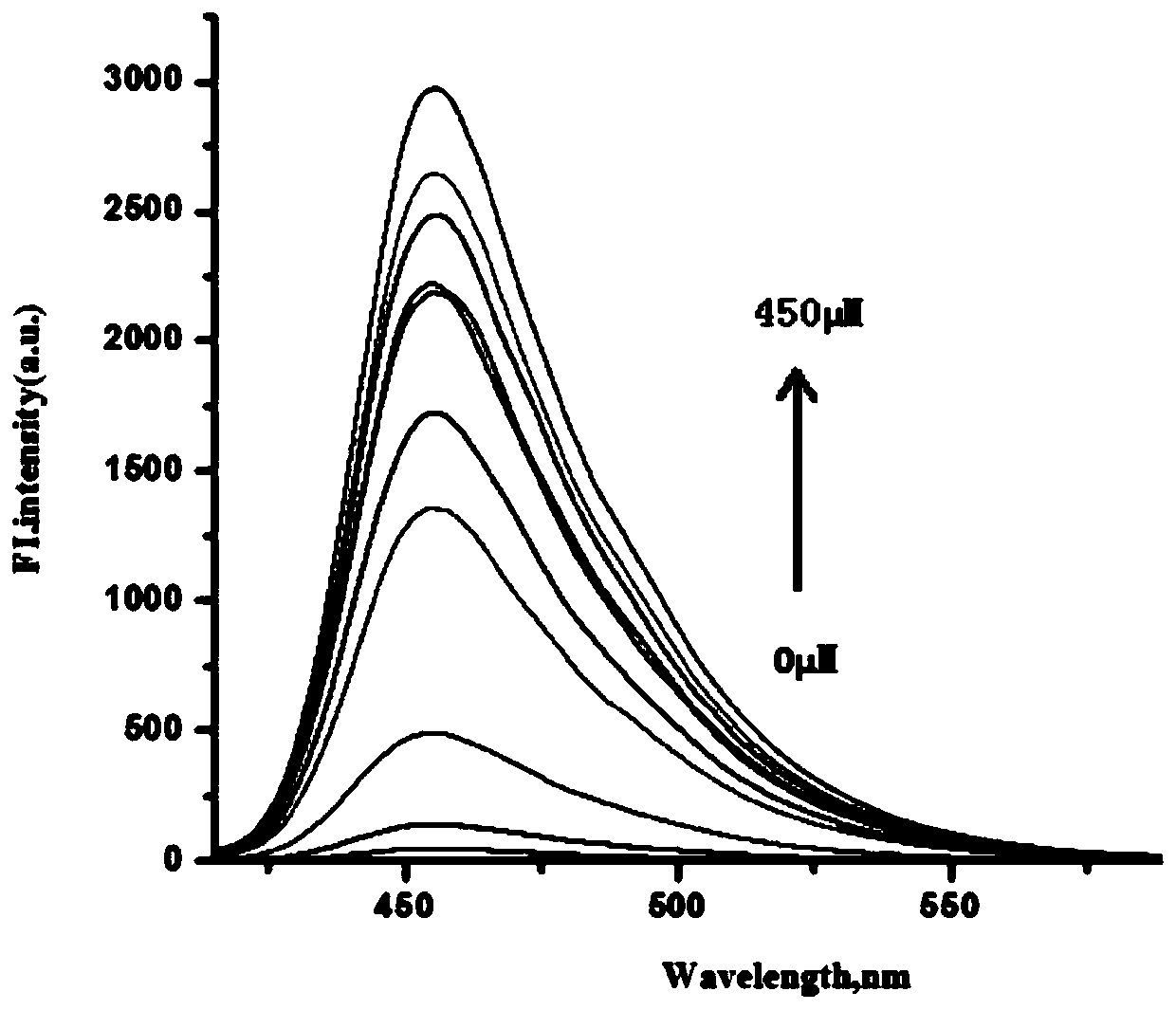
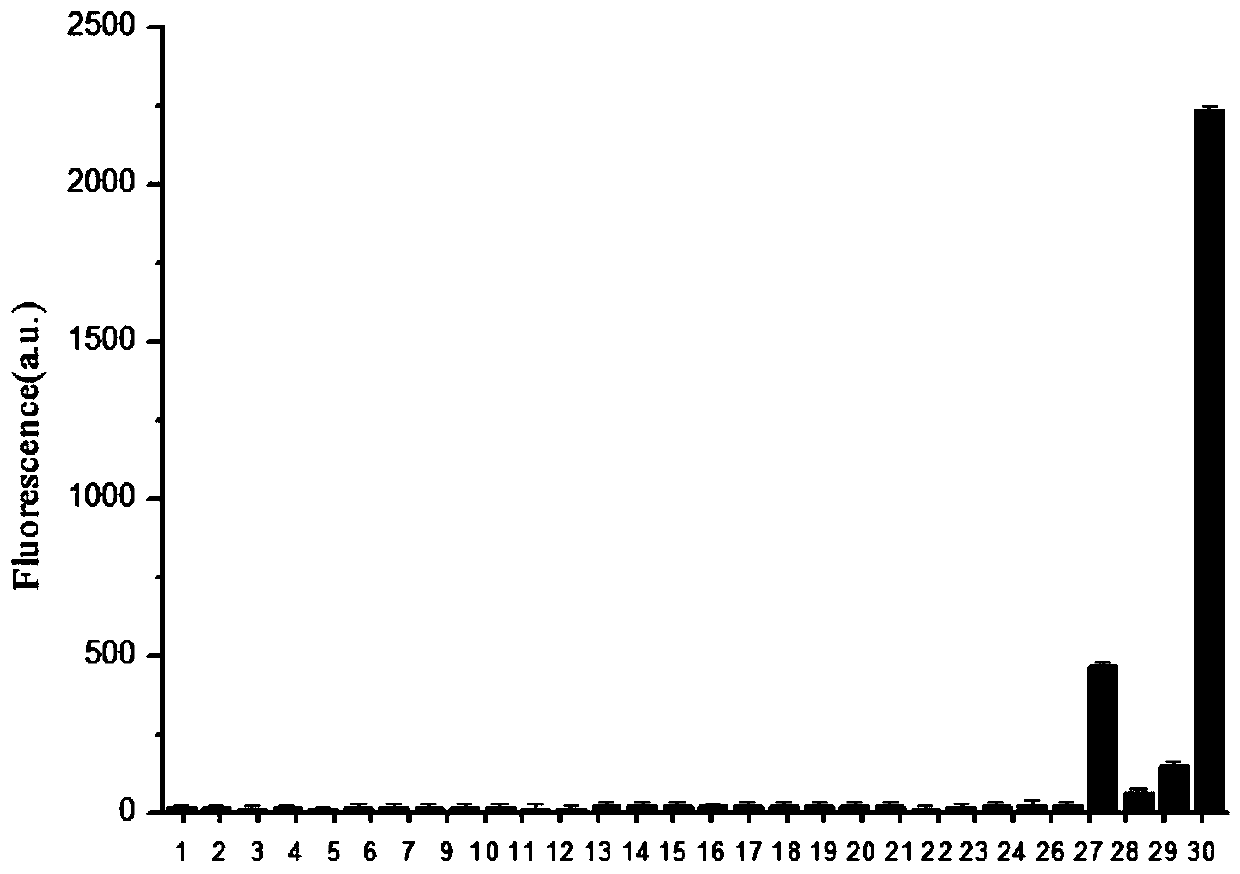
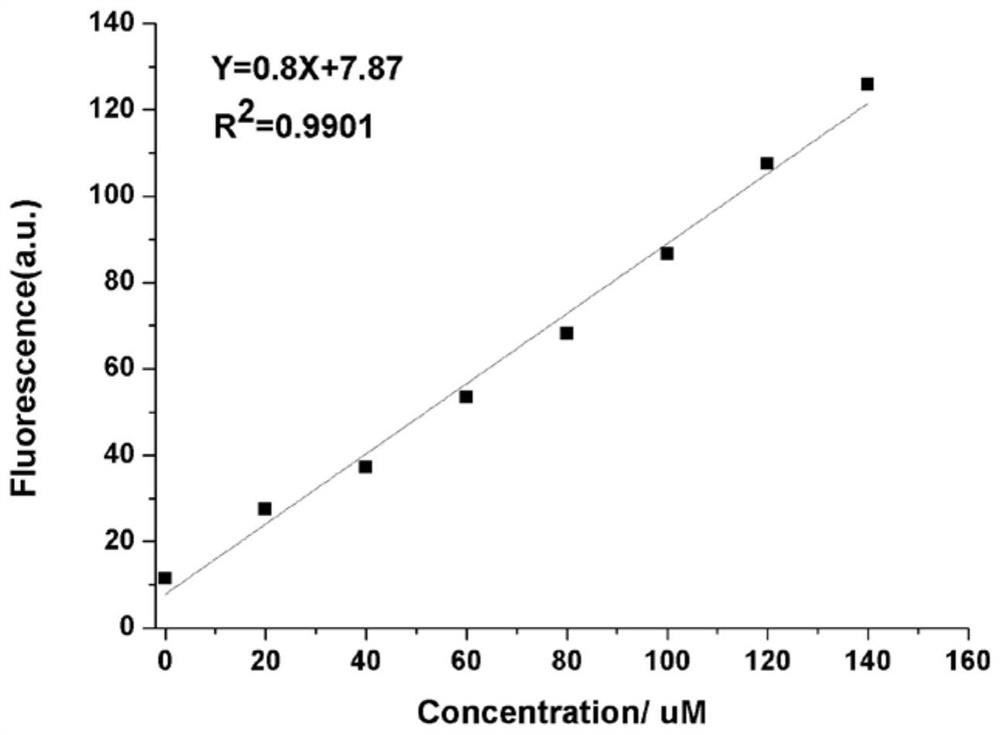
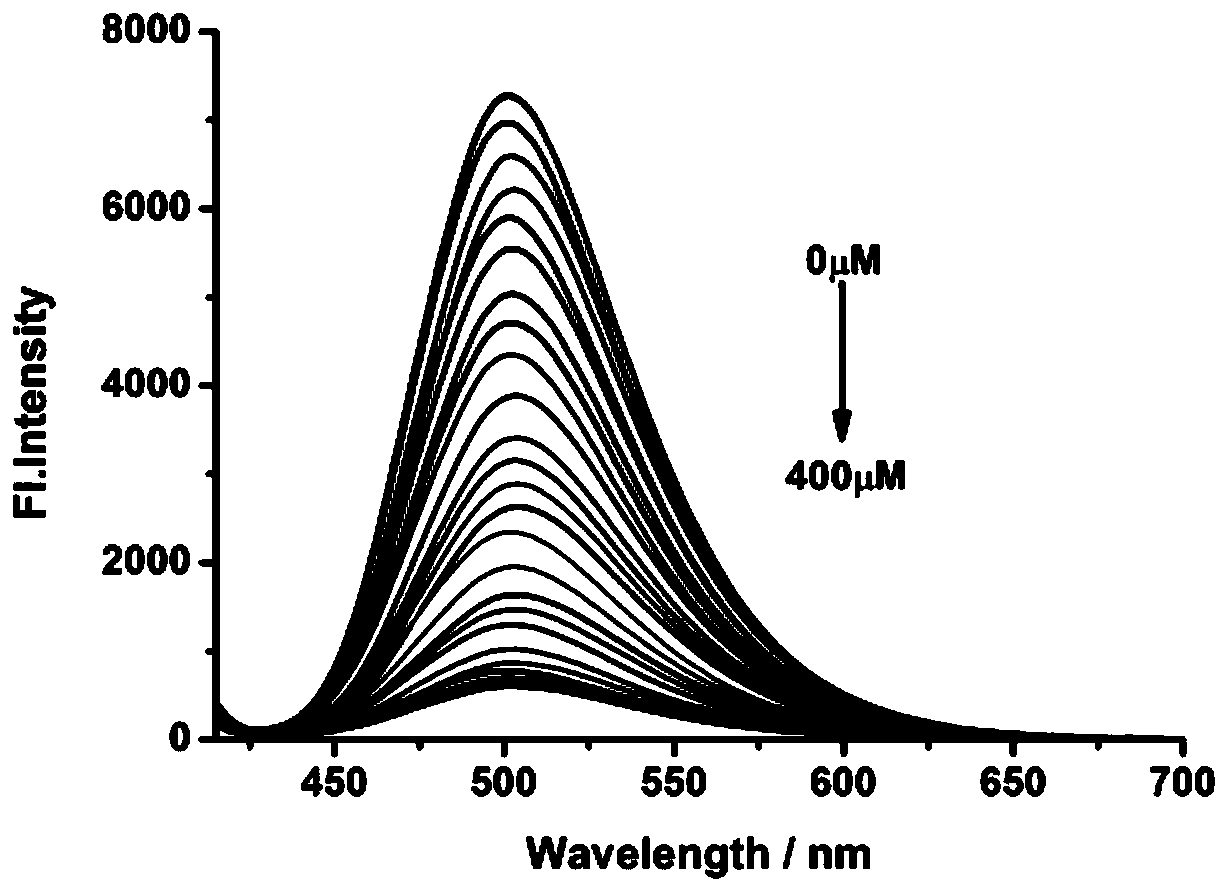
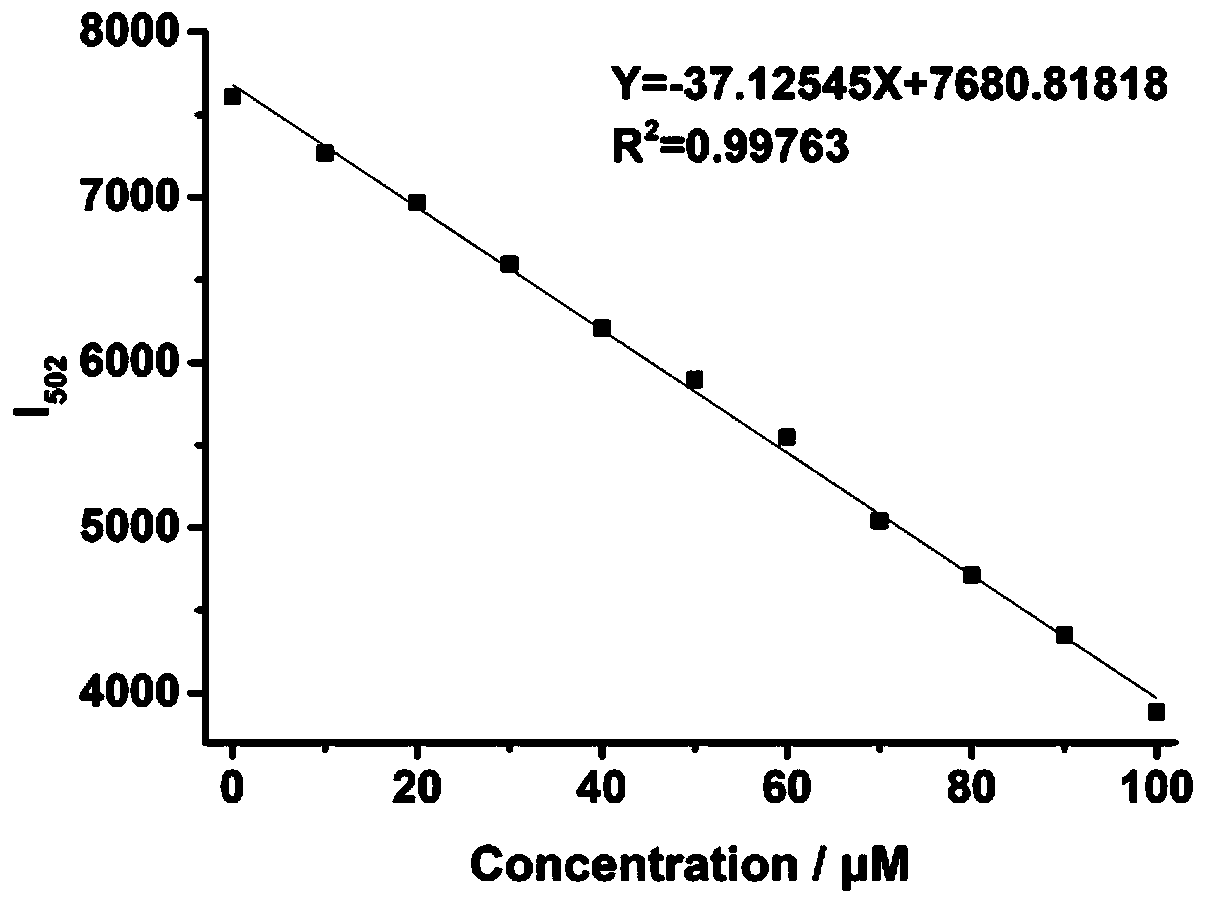
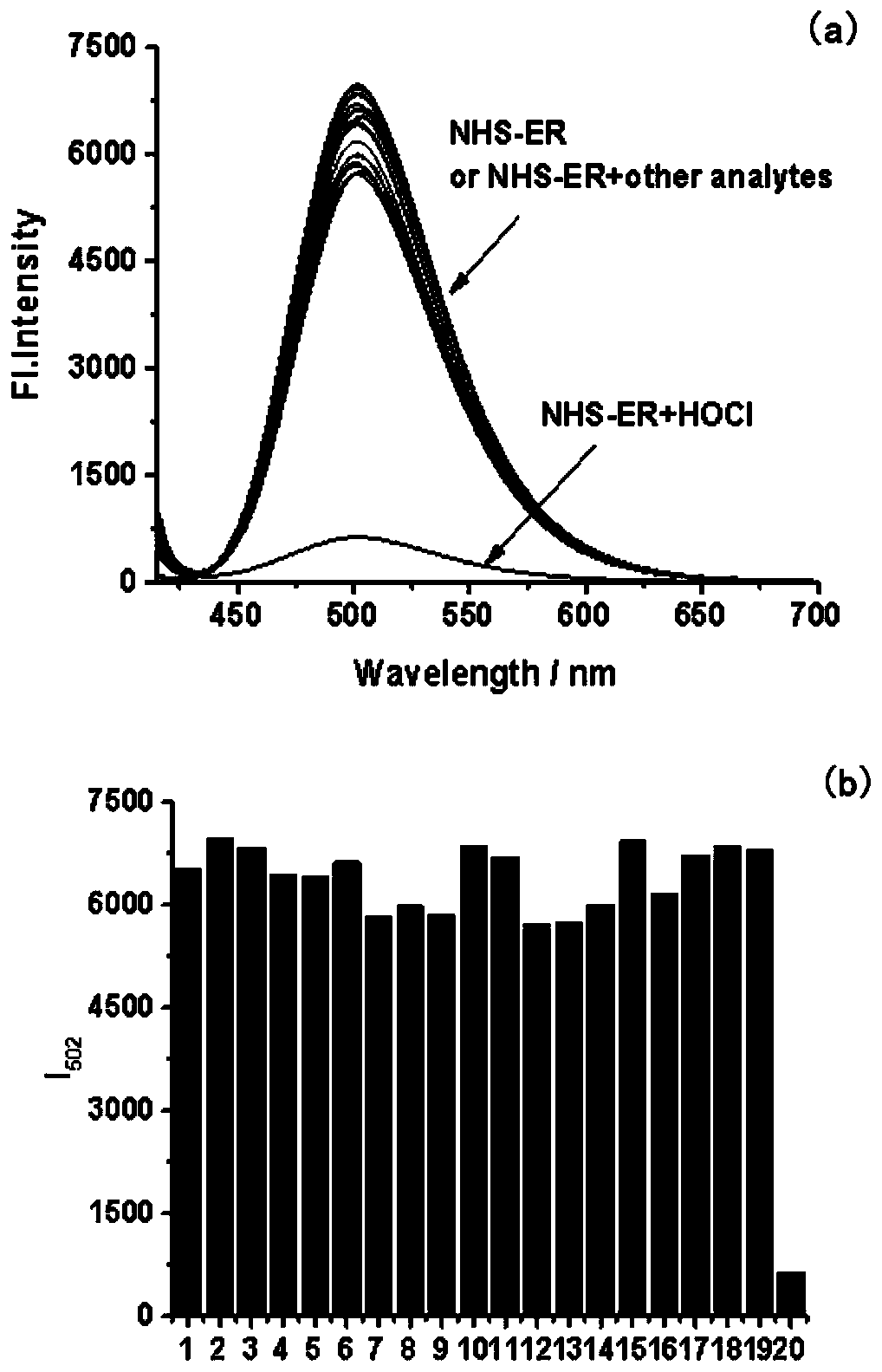
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59results about How to "Good fluorescence emission spectral characteristics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Application of high selectivity reaction type fluorescence probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide
InactiveCN107216270ASensitive detectionThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceFine chemical
The invention relates to an application of a highly selective reactive fluorescent probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide, which belongs to the field of fine chemical industry. The specific probe is 2‑{(6‑(dimethylamino)‑3‑(2,4‑dinitrophenoxy)naphthylacetamide‑2‑)methylene}malononitrile, which can be used to detect The presence of hydrogen sulfide in the in vitro environment and living cells is quantitatively determined within a certain range. The specific determination process of hydrogen sulfide is as follows: select 2‑{(6‑(dimethylamino)‑3‑(2,4‑dinitrophenoxy)naphthylacetamide‑2‑)methylene}malononitrile for thiolysis The buckle reaction is a probe reaction, and the hydrogen sulfide content in each system is determined by quantitatively detecting the amount of reaction products produced by selecting an appropriate probe concentration within the linear reaction range.
Owner:南京微瑞莱电子科技有限公司
Application of near infrared-emission fluorescent probe in quick pesticide residue detection
ActiveCN108318467AFast metabolismRapid responseFluorescence/phosphorescencePesticide residueEnzyme inhibition
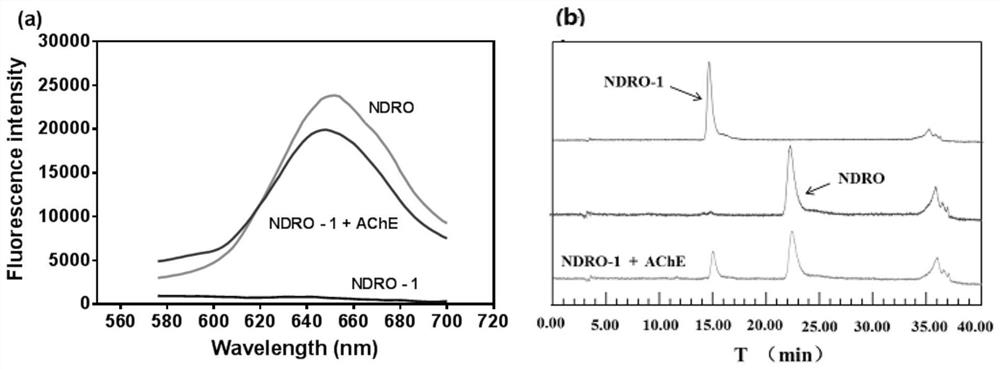
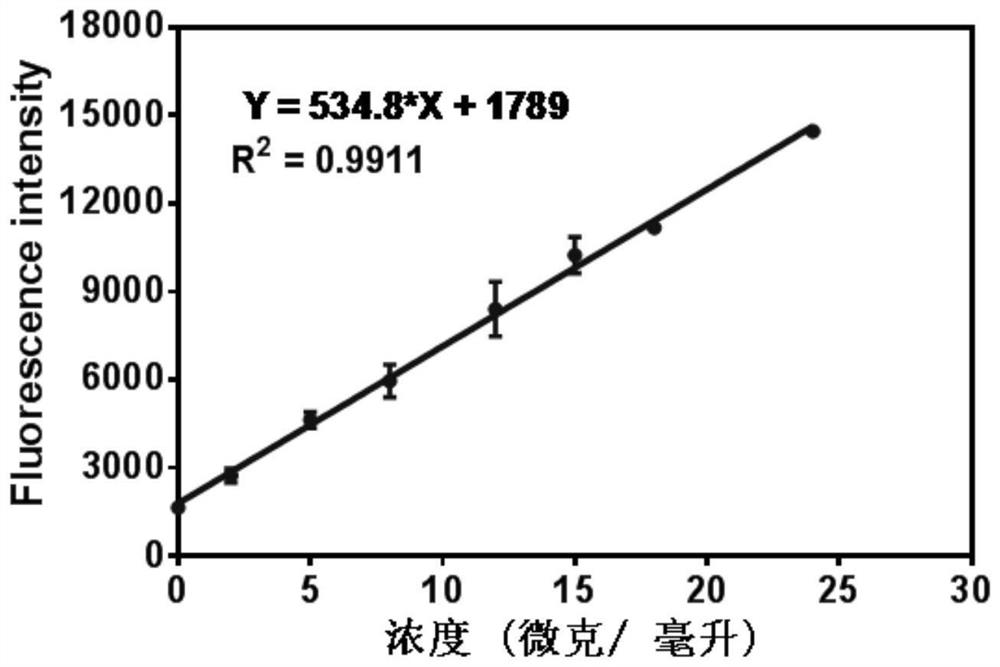
The invention discloses application of a near infrared-emission fluorescent probe in quick pesticide residue detection and belongs to the technical field of quick pesticide detection. The probe is based on rhoda-fluor fluorescence matrix and has specific activity on acetylcholine esterase AChE; by means of an enzyme inhibition detection principle, the probe can be applied to quick detection of organophosphorus pesticide and carbamate pesticide residues in food. The acetylcholine esterase AChE is extracted from duck blood; in an appropriate probe substrate range, enzyme activity and an inhibition rate can be represented by quantitatively detecting fluorescence intensity change of the probe. Four pesticide detection standard curves have small error, and R<2> is larger than 0.98; vegetable pesticide adding standard recovery most reaches 80 to 110%, so that the near infrared-emission fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention can be applied to quantitative, ppb-grade and quick detectionof organophosphorus and carbamate pesticide residues in the food.
Owner:王铮
Fluorescent test paper capable of rapidly detecting formaldehyde and application of fluorescent test paper
InactiveCN104792759AEasy to manufactureQuick checkFluorescence/phosphorescenceWhitening AgentsPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses fluorescent test paper capable of rapidly detecting formaldehyde. The fluorescent test paper is formed by fluorescent-whitening-agent-free test paper loaded with fluorescent probe naphthalimides derivative. The fluorescent test paper is deep green, the size of the test paper is (100-75)mm*(15-8)mm*(1-0.5)mm, the content of the naphthalimides derivative loaded on each fluorescent test paper is not less than 0.01mg, the test paper for a substrate is deep-green precision pH test paper, and the naphthalimides derivative loaded on the test paper for the substrate is N-amino-4-(1-piperazinyl)-1,8-naphthalimide, N-amino-4-(1-piperazinyl)-1,8-naphthalimid or N-amino-4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-1,8-naphthalimide. The fluorescent test paper is easy to prepare, convenient to use and capable of rapidly and accurately detecting and determining the formaldehyde in the environment.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Specific fluorescent probe for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT1A1 and application thereof
ActiveCN104342488AReduce testing costsThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug metabolismGlucuronosyltransferase
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Fluorescent probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide in cells, method for preparing fluorescent probe and application thereof
InactiveCN109735328APromote lysisHigh fluorescence intensityCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationChemical synthesisFluorescence
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide in cells, a method for preparing the fluorescent probe and application thereof. A chemical structural formula of the fluorescent probe is shown. Reaction can be carried out on 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene and reaction products of 4-ethynylbenzonitrile and 4-bromine-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde to obtain the fluorescent probe. The hydrogen sulfide in solution or the cells or organisms can be detected by the fluorescent probe by the aid of fluorescence. The fluorescent probe, the method and the application have the advantages that the fluorescent probe can be obtained by means of chemical synthesis, synthesis processes are simple and feasible, raw materials are inexpensive and are easily available, and accordingly the fluorescentprobe is low in preparation cost; the fluorescent probe is high in specificity, and interference due to other components can be prevented in detection procedures; the fluorescent probe is short in response time, high in sensitivity and excellent in fluorescence emission spectral characteristic, and the hydrogen sulfide in the cells can be quickly and accurately detected by the fluorescent probe;the fluorescent probe has a broad application prospect in research on the influence of the hydrogen sulfide in the biological cells on physiological and pathological procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Ratio type fluorescent probe substrate for cytochrome oxidase CYP1A and application thereof
ActiveCN105219374ANot easy to interfereAdvantages of in vitro activityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAlkaneDrug metabolism
The invention discloses a ratio type fluorescent probe substrate for cytochrome oxidase CYP1A and an application thereof. The specific probe substrate has a hydroxynaphthalimide alkane acid structure and can be used for determining the CYP1A enzymatic activity in a biosystem. A flow for determining the CYP1A enzymatic activity comprises the following steps: selecting a hydroxynaphthalimide alkane acid demethylation reaction as a probe reaction, and determining the CYP1A enzymatic activity in various biological samples by quantitatively detecting the production amount of demethylation metabolites in a unit time. The ratio type fluorescent probe substrate disclosed by the invention can be used for quantitative evaluation for the CYP1A enzymatic activity in biological samples of different species and different individual sources and for quantitative determination for the CYP1A enzymatic activity in different-source animal tissue cell culture fluids and cell prepared products, so as to realize evaluation for the medicine disposition capacity of the important medicine metabolizing enzyme CYP1A. In addition, the probe reaction can also be used for rapidly screening a CYP1A inhibitor in vitro and evaluating the inhibition capacity of the inhibitor.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Detection reagent and quantitative detection method of human serum albumin
ActiveCN105572095ARealize quantitative detectionInhibition of charge transfer phenomenonFluorescence/phosphorescenceFine chemicalTransfer phenomenon
The invention provides a detection reagent and a quantitative detection method of human serum albumin and belongs to the technical field of fine chemical engineering. Based on a combining attribute of albumin and small molecules, the specific principle of the method is that HCAB can be specifically combined with the albumin, a charge transferring phenomenon in HCAB twisting molecules is inhibited and non-radiation transition is reduced, so that fluorescent light is recovered and quantitative detection of the albumin is realized. After the human serum albumin is excited under a physiological pH value condition (an excitation wavelength lambdaex is equal to 424nm), a stable fluorescent signal (an emission wavelength lambdaem is equal to 526nm) is generated. The fluorescent value intensity is in direct proportion to the concentration of the albumin; and according to a detected fluorescent value, the content of the albumin in a biological sample can be calculated. The method can be used for determining absolute content of the albumin in a plurality of types of biological samples including blood serum, urine and the like; and meanwhile, the method also has the advantages of high sensitivity, high accuracy, high environment interference resisting capability, easiness of carrying out high-flux detection and the like.
Owner:王铮
High-specificity fluorescent probe of human carboxylesterase CES2 and application thereof
ActiveCN104650854AHas fluorescent propertiesSensitive detectionOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMetabolite3-Hydroxyflavone
A high-specificity fluorescent probe of human carboxylesterase CES2 and an application thereof. A substrate of the high-specificity fluorescent probe is an ester derivative of a 3-hydroxyl flavonoid compound, which can be used for detecting the existence of the CES2 in different bio-samples and quantitatively measuring the activity of the CES2. A particular measurement process of the enzyme activity includes following steps: selecting a hydrolysis reaction of the derivative of the 3-hydroxyl flavonoid compound as a probe reaction; selecting generation amount of a hydrolytic metabolite, 3-hydroxyl flavonoid, in unit time through quantitative detection with selection of a proper substrate concentration in a linear reaction section so that the actual activity of the CES2 enzyme in various bio-samples, cells, in-vivo organs and overall organs can be measured. The high-specificity fluorescent probe not only can be used for quantitative evaluation of the enzyme activity of the CES2 in the bio-samples from different sources, but also can be used for in-vitro quickly screening an inhibitor of the CES2 by means of the probe reaction.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Cytochrome oxidase CYP1A1 specific fluorescent probe, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN107022349AEasy to detect sensitivityHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCell preparationMetabolic enzymes
The invention relates to a cytochrome oxidase CYP1A1 specific fluorescent probe, a preparation method and applications thereof, wherein the specific probe substrate has a 4-hydroxynaphthalimide structure, and can be used for determining the CYP1A1 enzyme activity in a biological system. The CYP1A1 enzyme activity determination process comprises: selecting a 4-hydroxynaphthalimide dechloroethylation reaction as a probe reaction, and determining the activity of the CYP1A1 enzyme in various biological samples by quantitatively detecting the generation amount of the dechloroethylation metabolites per unit time. According to the present invention, the cytochrome oxidase CYP1A1 specific fluorescent probe can be used for the quantitative evaluation of the CYP1A1 enzyme activity in biological samples having different species and different individual sources, and the quantitative determination of the CYP1A1 enzyme activity in animal culture cell culture liquids and cell preparation products from different origins so as to evaluate the drug treatment capacity of the important drug metabolic enzyme CYP1A1; and the probe reaction can further be used for rapidly screening inhibitors and inducers of CYP1A1 in vitro and evaluating the inhibition ability.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-photon fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in cellular endoplasmic reticulum
InactiveCN109336815AReduce manufacturing costStrong specificityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisFluorescence
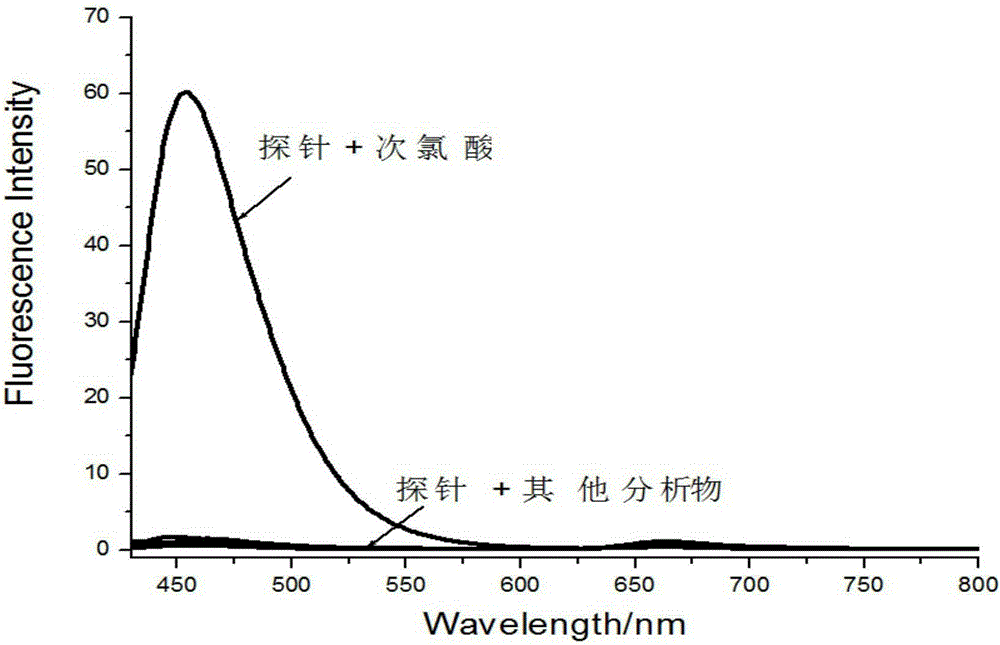
The invention provides a two-photon fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in a cellular endoplasmic reticulum. The two-photon fluorescent probe can be obtained through a three-step reaction by using 4-methylthio-1,8-naphthalic anhydride, trifluoroacetic acid and p-toluenesulfonyl chloride as raw materials. The two-photon fluorescent probe can be applied to detection of the hypochlorousacid in a solution or the cellular endoplasmic reticulum. The fluorescent probe can be obtained through chemical synthesis, a synthesis technology is simple and easy to implement, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the preparation cost is low, and the fluorescent probe is easy to popularize, has high specificity, is not interfered by other components, can be applied to real-time determination of the hypochlorous acid in the endoplasmic reticulum of a living cell and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
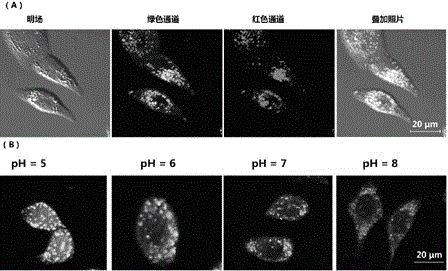
Fluorescence probe for detecting pH of lysosome in cancer cells
InactiveCN106117241AThe synthesis process is simpleRaw materials are cheap and easy to getOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCancer cellFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescence probe for detecting pH of lysosome in cancer cells. The fluorescence probe is a naphthalimide derivative containing biotin groups. The fluorescence probe is easy to prepare, low in cost and high in specificity, can rapidly detect the pH value of a solution environment, is not disturbed by other ingredients in the corresponding pH detection process, can be used for measuring the pH of the lysosome in the cancer cells, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescent probe for detecting cysteine in cell
InactiveCN106632212AThe synthesis process is simpleRaw materials are cheap and easy to getOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceStructural formulaPhotochemistry
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting cysteine in a cell. The fluorescent probe is a rhodamine dye derivative, and has a chemical structural formula shown in formula (I). The fluorescent probe is easy to prepare, low-cost and high in specificity, can be used for rapidly detecting the cysteine in the cell almost without interference of other components in a detection process, and has broad application prospect. (The chemical structural formula (I) is shown in the description.).
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescence probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in biological system and application of fluorescence probe
InactiveCN106544007AThe synthesis process is simpleRaw materials are cheap and easy to getOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureChemical reaction
The invention discloses a fluorescence probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in a biological system. The fluorescence probe is a benzopyran derivative containing different substituent groups, and the chemical construction general formula of the fluorescence probe is shown as the formula (I). The fluorescence probe is easy to manufacture and low in cost, has the high specificity, can make a chemical reaction with the hypochlorous acid to generate a corresponding oxidative product, cannot be disturbed by other components when the corresponding hypochlorous acid content detecting process is executed, can be used for quantitative and qualitative determination on the content of the hypochlorous acid in living cells and has the wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
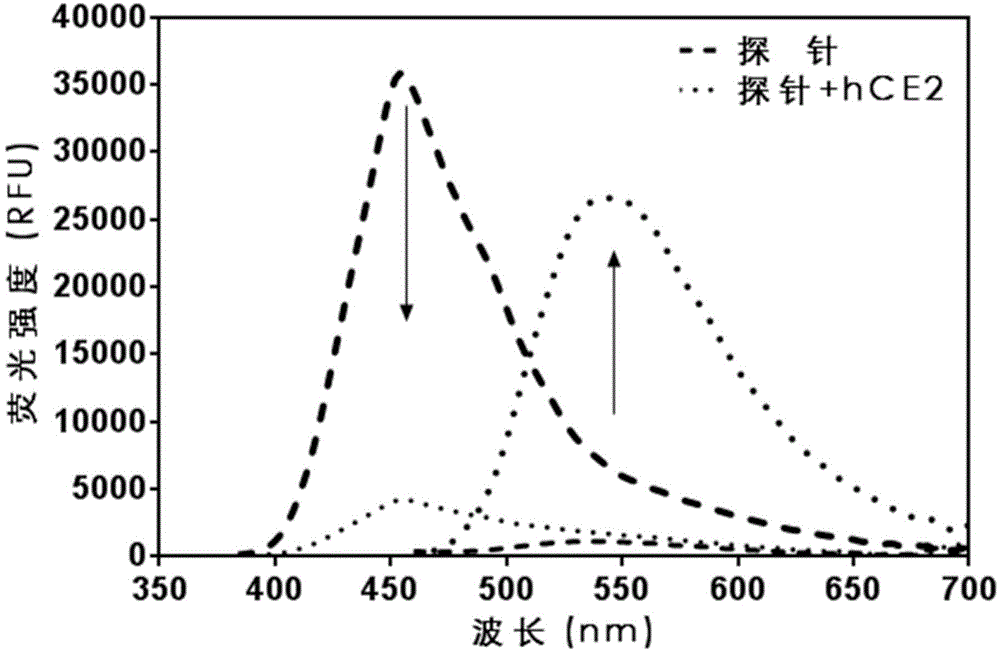
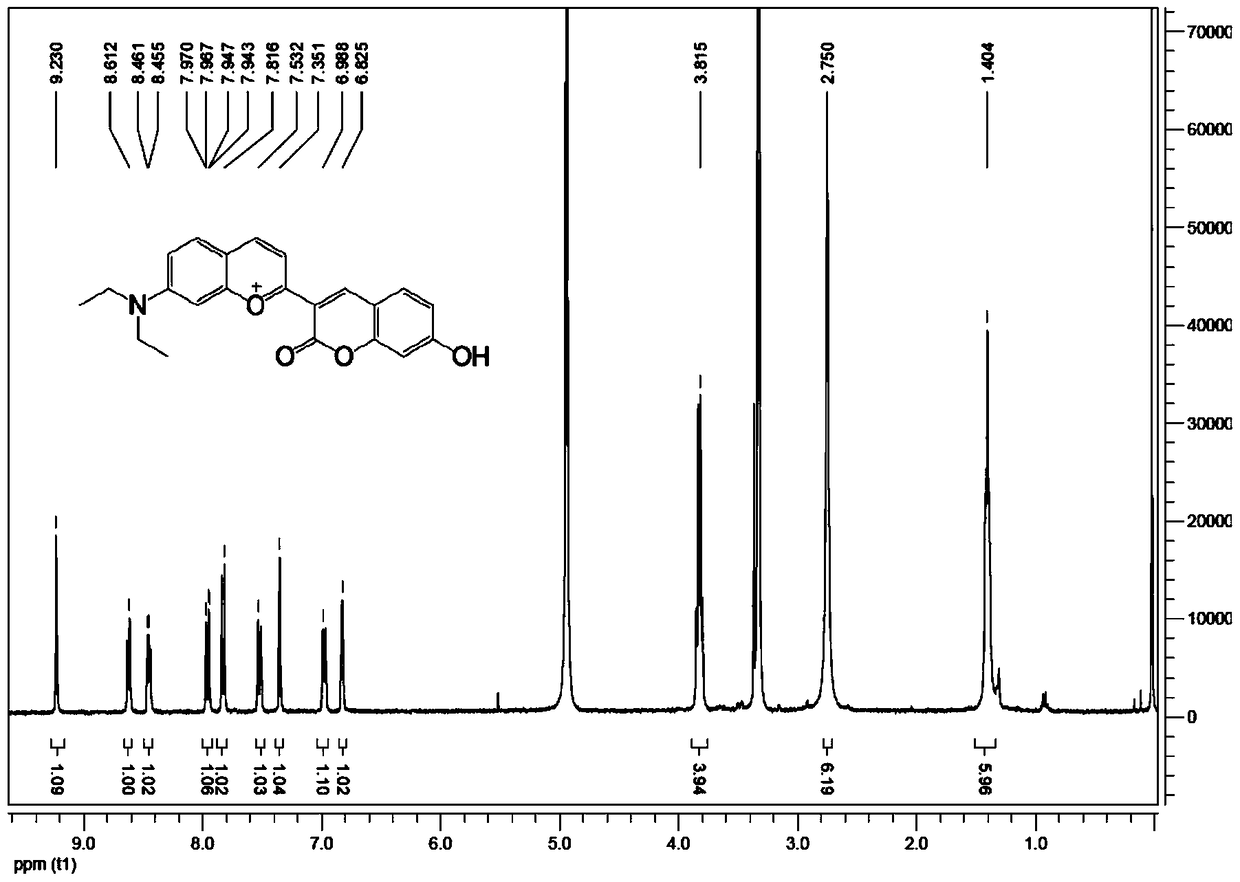
High-specificity fluorescent probe for human carboxylesterase hCE2 and application thereof
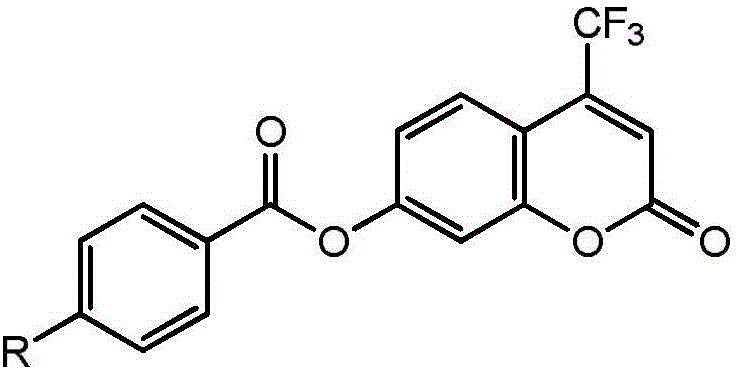
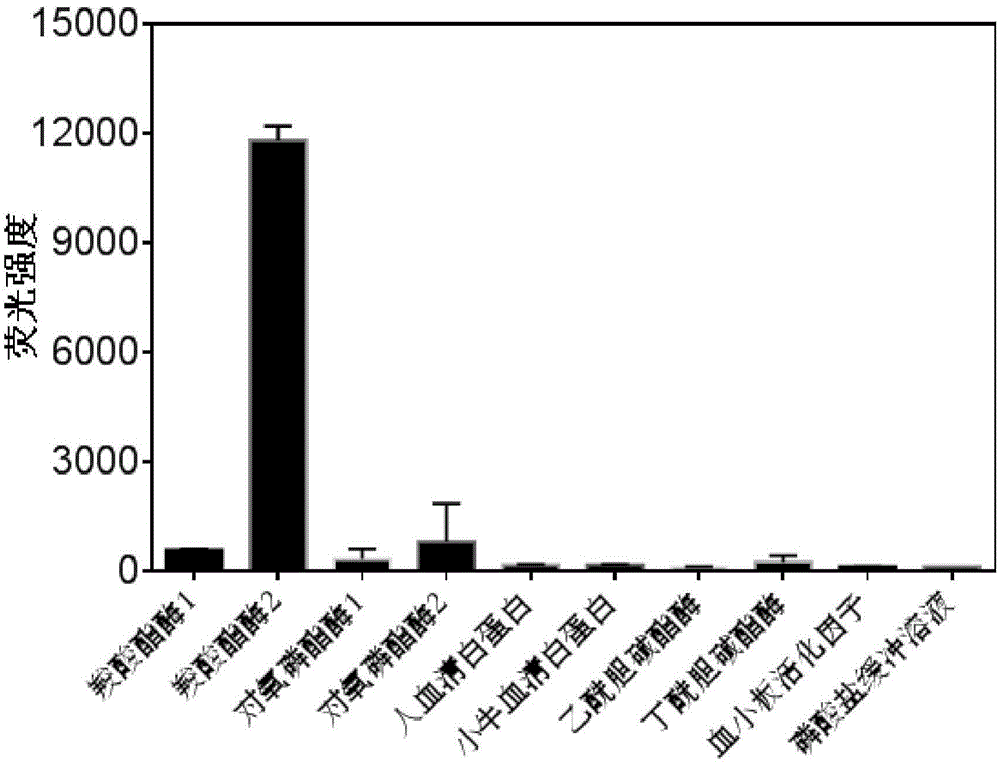
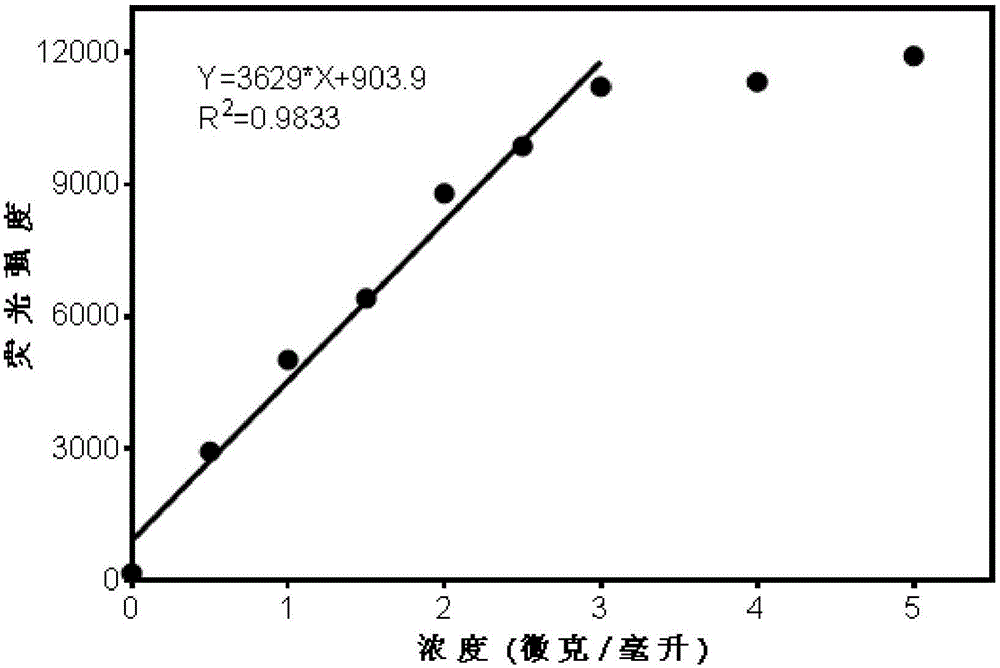
ActiveCN104592985AHas fluorescent propertiesSensitive detectionOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteFluorescence
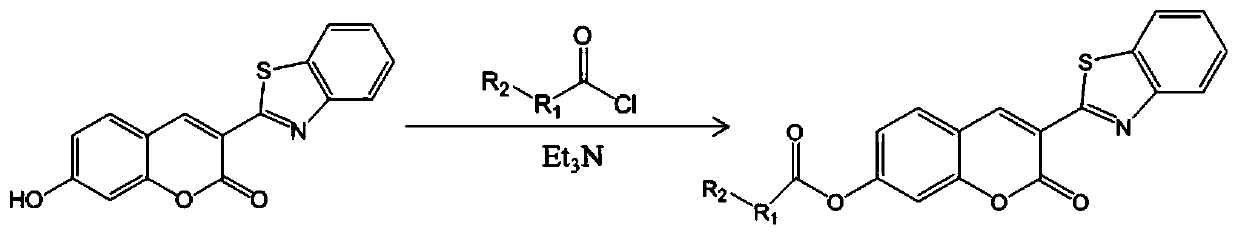
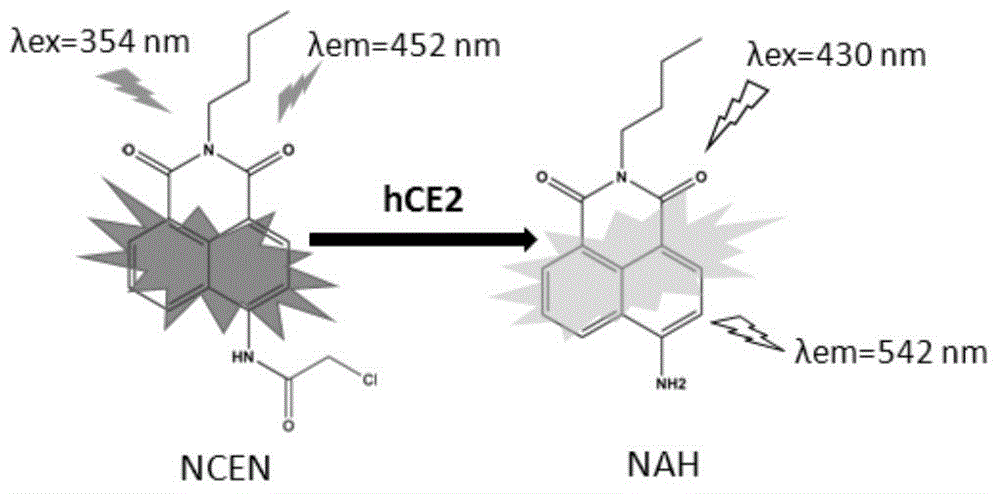
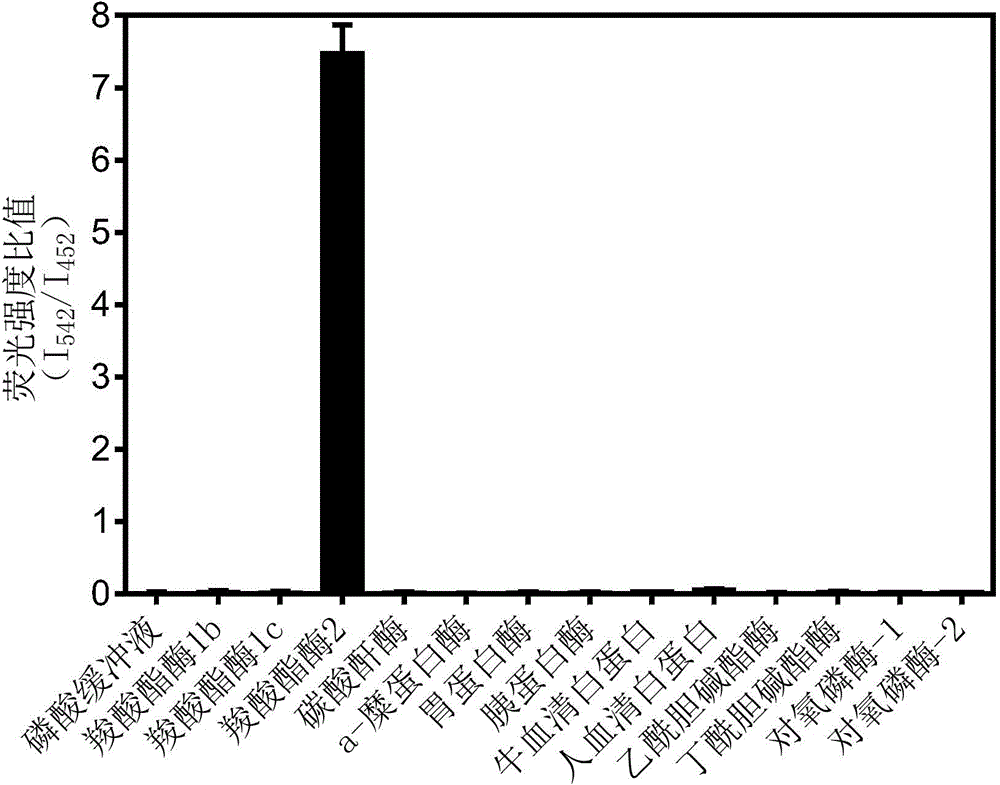
The invention discloses a high-specificity fluorescent probe for human carboxylesterase hCE2 and an application thereof. The substrate of the specific probe is an ester derivative of a 4-trifluoromethyl-7-umbelliferone compound and can be used for detection for the existence of hCE2 in different biological samples and quantitative determination for the vitality of hCE2. A specific flow for determining the enzymatic activity is as follows: selecting a hydrolysis reaction of the 4-trifluoromethyl-7-umbelliferone ester derivative as a probe reaction, selecting a proper substrate concentration, and determining the actual activity of the hCE2 enzyme in various biological samples, cells, carriers and overall organs by quantitatively detecting the generation amount of a hydrolysis metabolite 4-trifluoromethyl-7-umbelliferone in a unit time within a linear reaction interval. The high-specificity fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention can be used for quantitative evaluation for the activity of the hCE2 enzyme in biological samples from different sources; in addition, the probe reaction can also be used for rapidly screening an hCE2 inhibitor in vitro.
Owner:CHANGSHU RES INST OF DALIAN UNIV OF TECH CO LTD
Fluorescent probe substrate for testing activity dipeptidyl peptidase IV and application of fluorescent probe substrate
ActiveCN106146611AStrong specificityThe synthesis process is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesMetaboliteFluorescence
The invention provides a fluorescent probe substrate for testing of activity dipeptidyl peptidase IV and application of the fluorescent probe substrate and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The fluorescent probe substrate is a C-4 amide derivative GPAN of naphthalimide and can be used for testing enzyme activity of DPP-IV in different biological systems. A process for testing enzyme activity of DPP-IV includes: selecting GPAN amide hydrolysis reaction as probe reaction; quantitatively detecting generation quantity of a GPAN dipeptidyl-removed metabolism product to test activity of DPP-IV in various biological samples. The fluorescent probe substrate can be used for quantitatively testing enzyme activity of DPP-IV in biological samples different in species and individual source and enzyme activity of DPP-IV in animal tissue cell culture liquid and cell preparation products different in source, and is expected to realize quantitative evaluation on activity of DPP-IV which is a metabolic enzyme important to human body. In addition, with the help of probe reaction, the fluorescent probe substrate can be used for quickly screening inhibitors or inducers of DPP-IV and evaluating inhibiting or inducing capability thereof.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Specific fluorescent probe for catechol-O-methyltransgerase (COMT) and application thereof
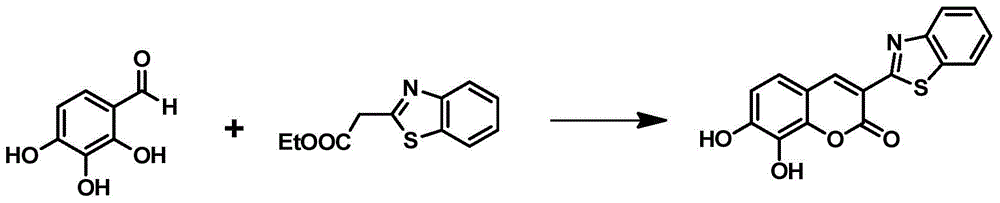
ActiveCN106467739ANot easy to interfereReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh fluxMutant
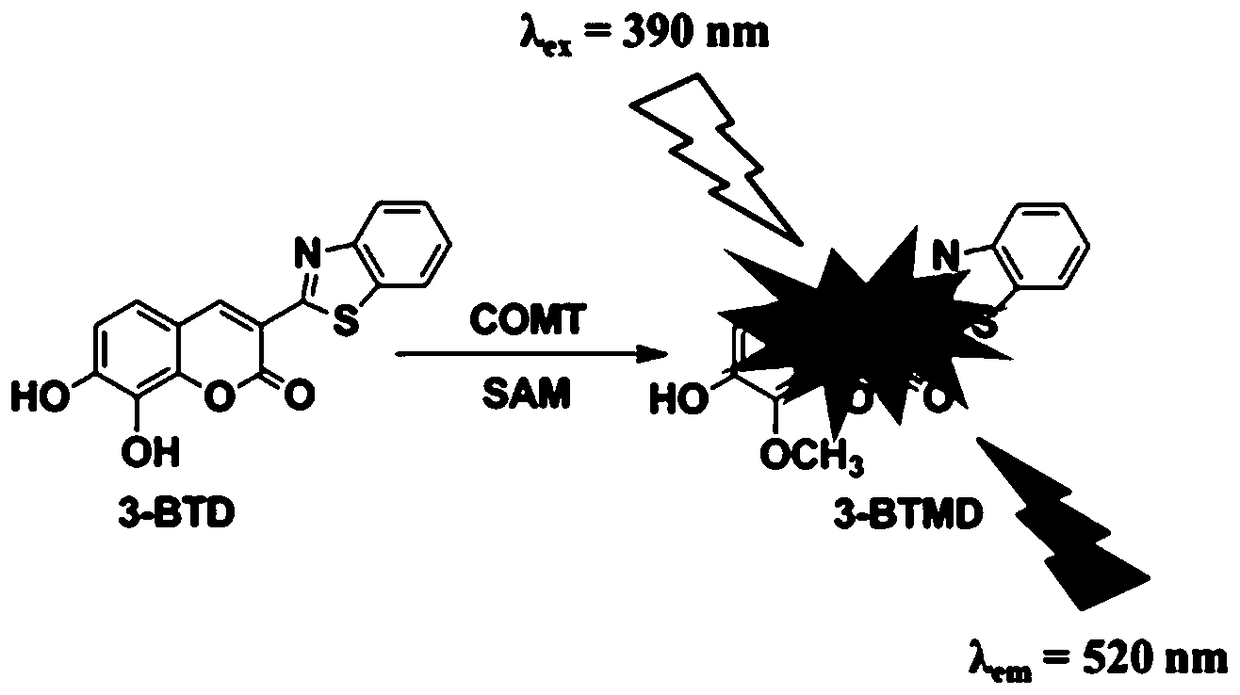
The invention provides a specific fluorescent probe for COMT and application thereof. A specific probe substrate provided by the invention is 3-benzothiazole-7,8-dihydroxycoumarin (3-BTD); the substrate can be specifically catalyzed by COMT to produce an 8-methoxy product and presents a fluorescence signal at a position of 520 nm; and the activity of COMT can be quantitatively determined by detecting changes of fluorescence intensity. The probe is applicable to quantitative assessment of the activity of COMT in biological samples from different sources, in-vitro rapid screening of inhibitors for COMT and evaluation of the inhibitory capability of the inhibitors. A method provided by the invention can be used for quantitative assessment of the actual activity of COMT in a variety of in-vitro biological samples and realizes rapid screening of inhibitors and quantitative assessment of the inhibitory capability of the inhibitors; the method is also applicable to evaluation of the catalytic activity of COMT of different species and COMT mutants with different amino acid sequences, so the method can assess the capability of COMT in metabolization of catechol drugs; and the method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high accuracy, good environment interference resisting capability, convenience in high-flux detection and inhibitor screening, etc.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
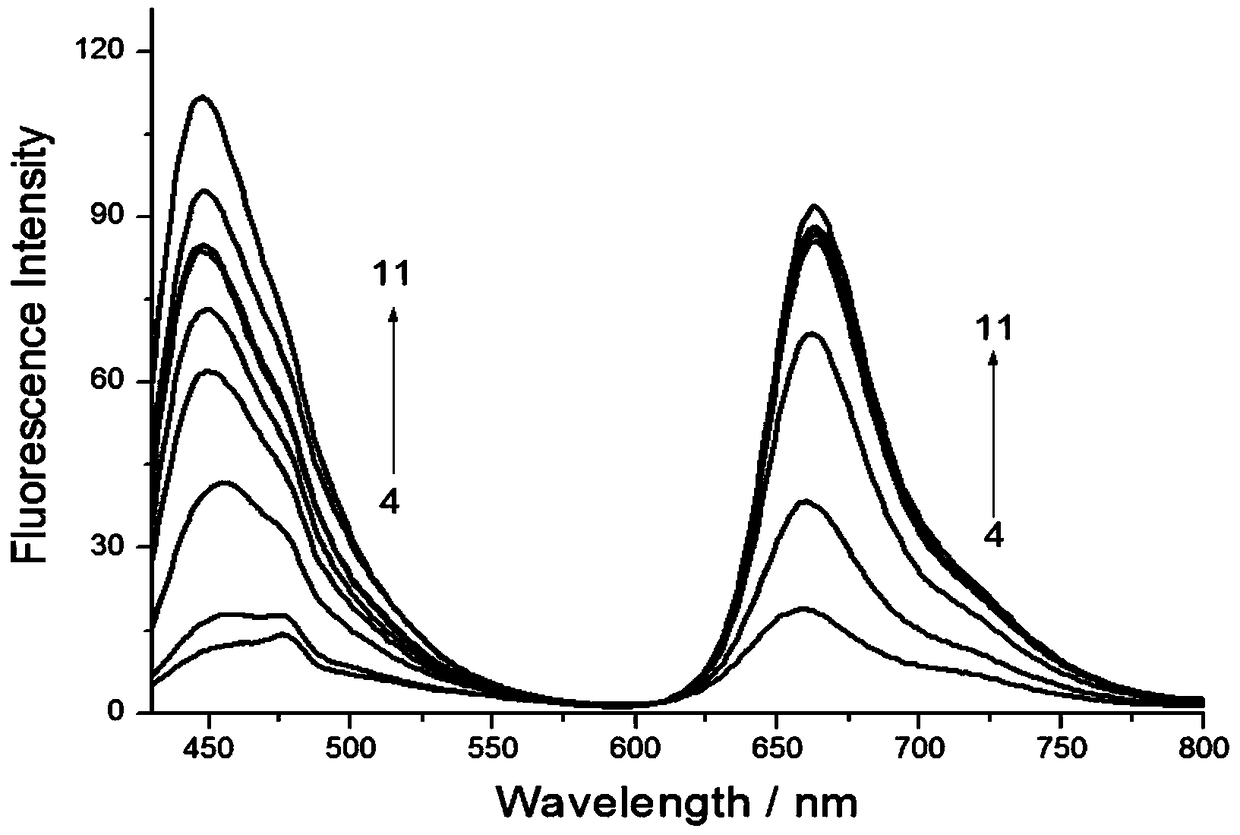
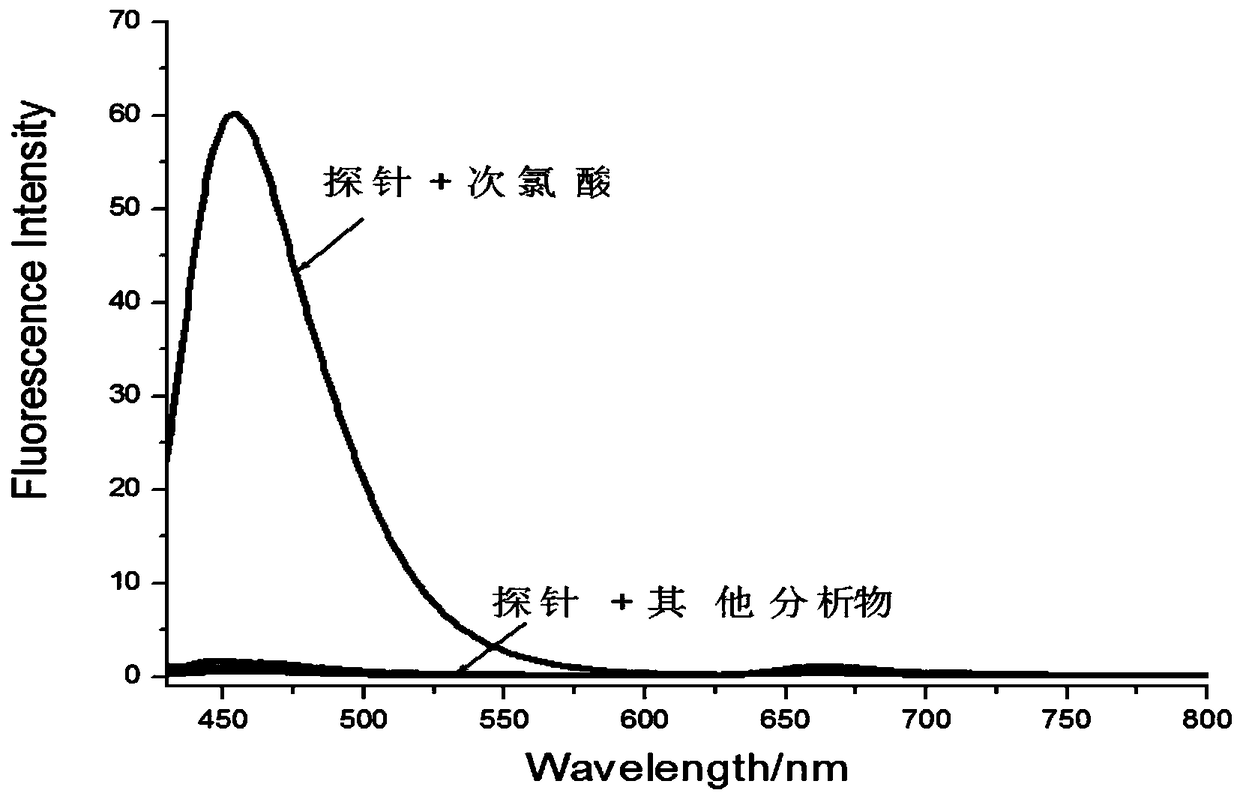
Ratio fluorescence probe for detecting hydroxylamine as well as synthesis method and application thereof
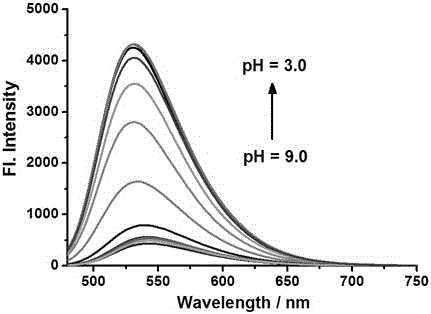
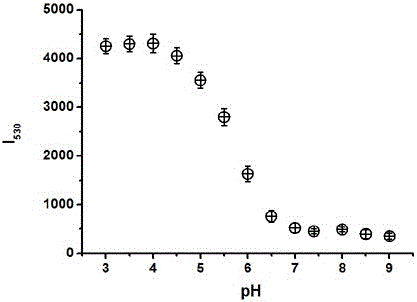
InactiveCN108218822AHigh sensitivityGood fluorescence emission spectral characteristicsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzoic acidHydroxylamine
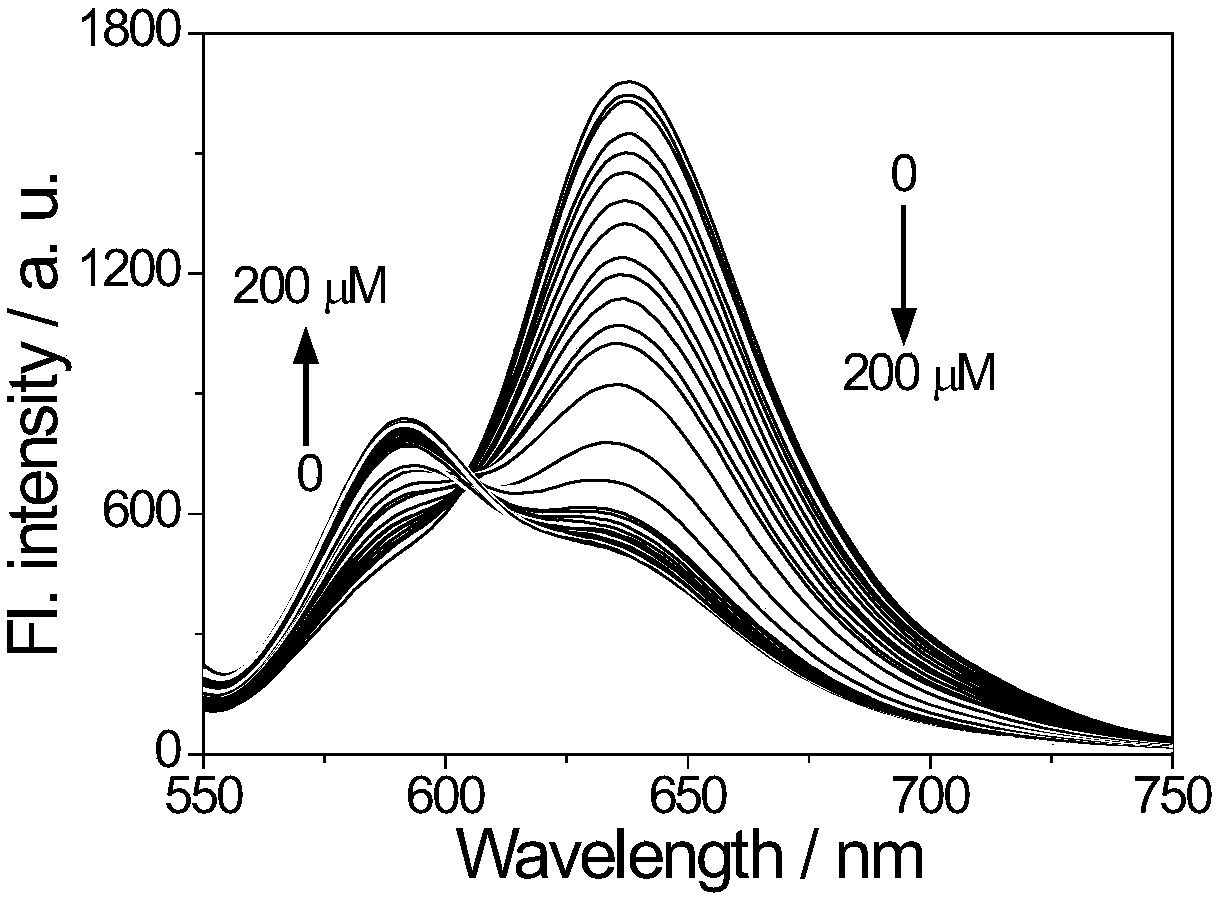
The invention provides a fluorescence probe for detecting hydroxylamine. The fluorescence probe is a rhodamine derivative containing biotin groups; benzoic acid groups are hydroxylamine response sites; a fluorescence peak value of the probe before the probe is reacted with hydroxylamine is about 637nm; the peak value of the probe after the probe is reacted with hydroxylamine is about 590nm; the hydroxylamine can be qualitatively detected through fluorescence intensity ratio change under two wavelengths; a linear relation is formed between the fluorescence intensity ratio under two wavelengthsand the concentration of hydroxylamine, so that the concentration of hydroxylamine can be quantitatively detected. The fluorescence probe is high in specificity, high in sensitivity and excellent in fluorescence emission spectrum characteristics (550-750nm).
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
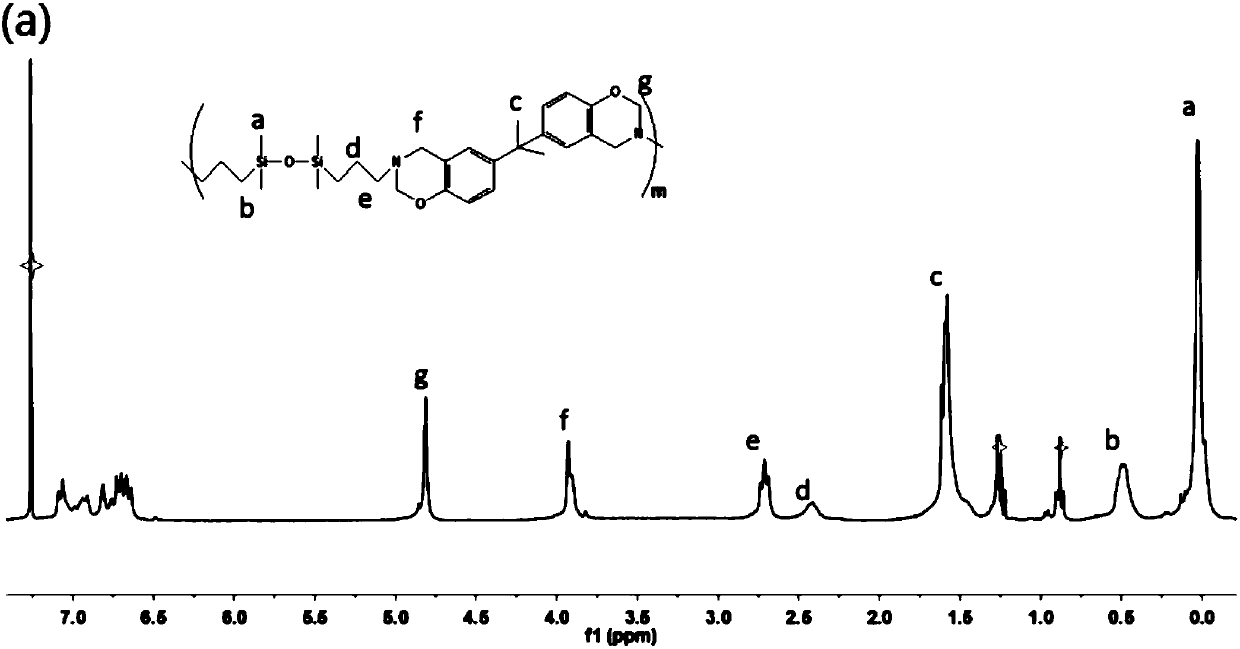
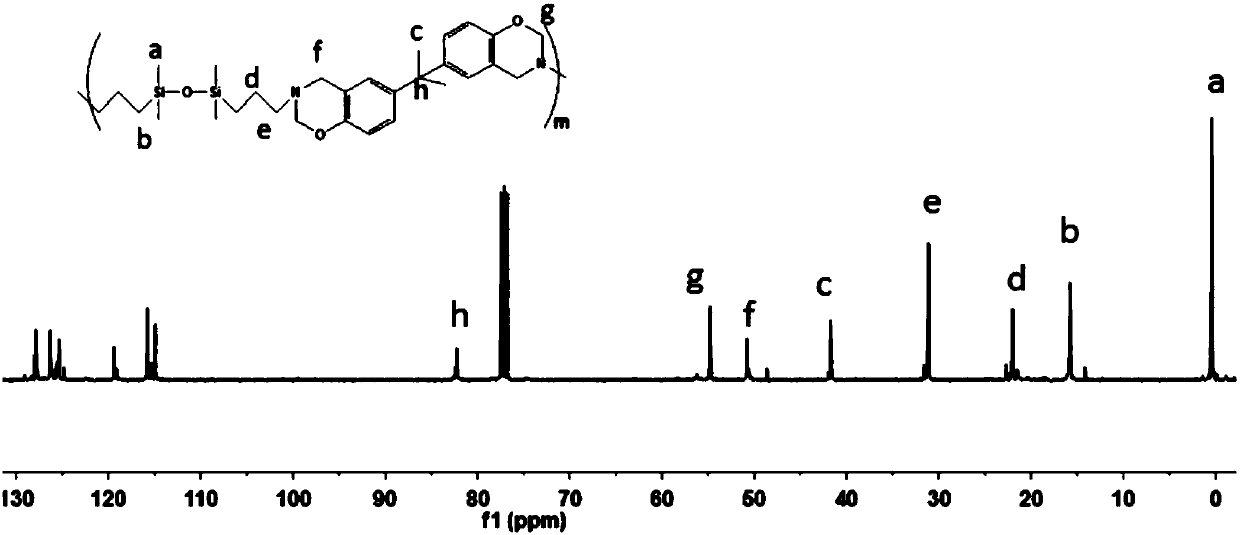
Novel polysiloxane-benzoxazine-based luminescent film and its application in UV-LED light
InactiveCN107629182AThe synthesis process is simpleRaw materials are cheap and easy to getLuminescent compositionsLength waveLED lamp
The invention discloses a novel polysiloxane-benzoxazine-based luminescent film and its application in a UV-LED light. A film matrix is a copolymer of siloxane and benzoxazine. The matrix polymer hasa general chemical formula shown in the description. Rhodamine B as a physical cross-linking site is introduced into the matrix and the film is prepared through a one-pot method. The luminescent filmis easy to prepare and realizes a low cost. The film can emit fluorescence in two wave bands under excitation of different wavelengths of fluorescence and regulation and control of the emission wave bands are realized through changing different excitation wavelengths. The film has a wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
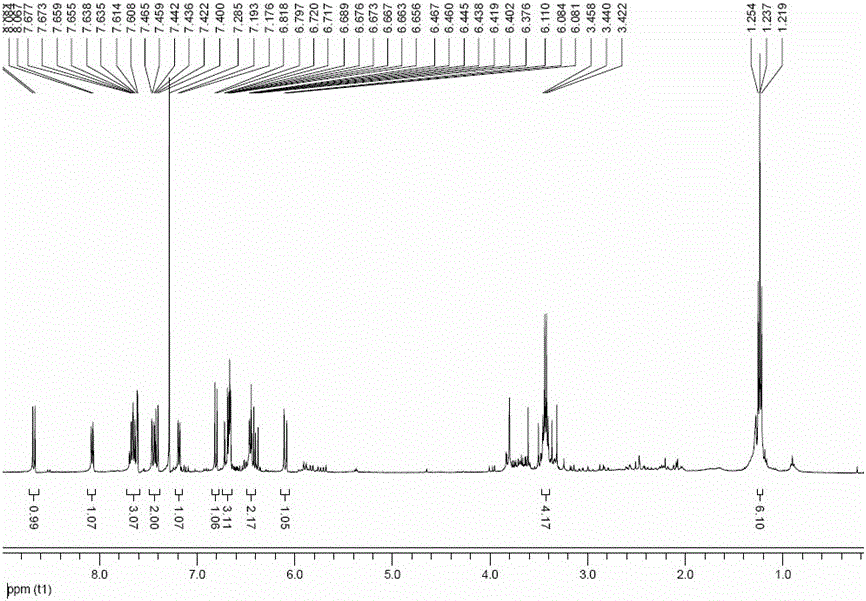
Dithiothreitol fluorescence probe
InactiveCN107915705AHigh sensitivityGood fluorescence emission spectral characteristicsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureParticle physics
The invention discloses a dithiothreitol fluorescence probe which has a chemical structural formula as shown in the specification. The dithiothreitol fluorescence probe can be used for detecting dithiothreitol in solutions and cells, and fluorescence detection conditions comprise a single photon excitation wavelength of 580nm, a two-photon excitation wavelength of 800nm, an emission wavelength of638nm and a detection band of 520-800nm.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Application of a near-infrared emitting fluorescent probe in the rapid detection of pesticide residues
ActiveCN108318467BThe synthesis process is simpleRapid responseFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesPesticide residue
Owner:王铮
Method for detecting activity of catechol-oxygen-methyltransferase in blood
InactiveCN108486220ANot easy to interfereAchieve interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisChemical synthesisFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for detecting the activity of catechol-oxygen-methyltransferase (COMT) in blood and belongs to the technical field of biological medicine. According to the invention,3-benzothiazole-7,8-dihydroxycoumarin (3-BTD) with high chemical stability is selected as the fluorescence substrate of COMT enzyme by virtue of the advantages of a high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection combined instrument on biological matrix interference resistance and detection sensitivity; meanwhile, a high-efficiency and high-sensitivity measuring method capable of quantitatively analyzing the activity of a trace amount of COMT in the blood is developed by combining a high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection technology. A fluorescence probe substrate adopted by the method can be obtained through chemical synthesis, the synthesis process is simple and practical, and the performance is stable. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high accuracy degree, high biological matrix interference resistance, high repeatability and the like, can be applied to detection on the activity of the COMT enzyme in the blood, and also canbe applied to quantitative measurement on the activity of the COMT enzyme in various mammal-derived cells or tissue preparation objects as well as screening and evaluation of a COMT inducer / activator.
Owner:沈阳北创医学检验所有限公司
Fluorescent probe for targeting detection of hydrogen sulfide in lysosome, and application thereof
InactiveCN110143931AHigh sensitivityGood fluorescence emission spectral characteristicsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisLysosomal targeting
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detection of hydrogen sulfide. The fluorescent probe can be used to detect hydrosulfide ions or sulfions in solutions or cells. The fluorescent probe ofthe invention can be obtained by chemical synthesis, and a synthesis technology of the fluorescent probe has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in implementation, cheap and easily available raw materials, low preparation cost, and easiness in promotion. The fluorescent probe of the invention has the advantages of good targeting property to the lysosome, high sensitivity to the lysosome, good fluorescence emission spectrum characteristics (415-600 nm), realization of the quantitative detection of H2S in the cell lysosome by drawing a standard curve, and achieving of the purpose of rapidly and accurately detecting H2S in the cell lysosome. The fluorescent probe of the invention has a high specificity, is not prone to be interfered by other components in the corresponding H2S detection process, can be used for real-time detection of H2S in the living cell lysosome, and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
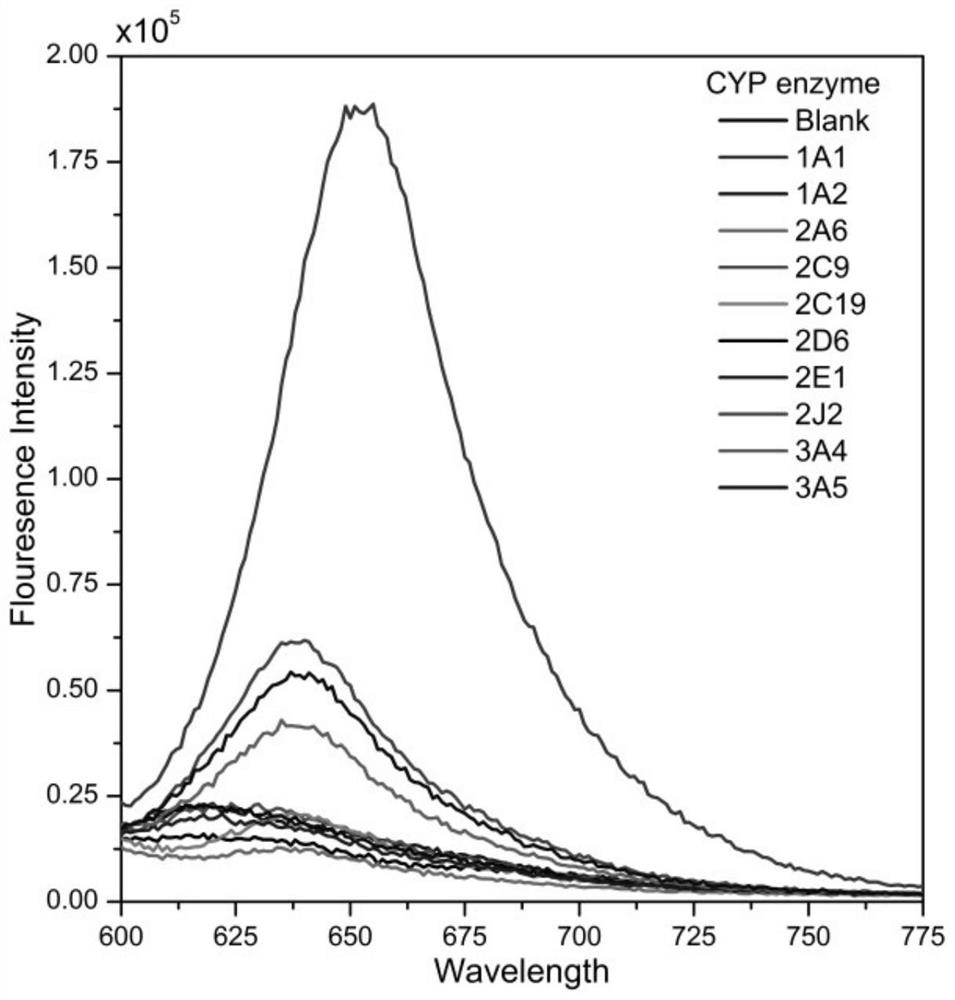
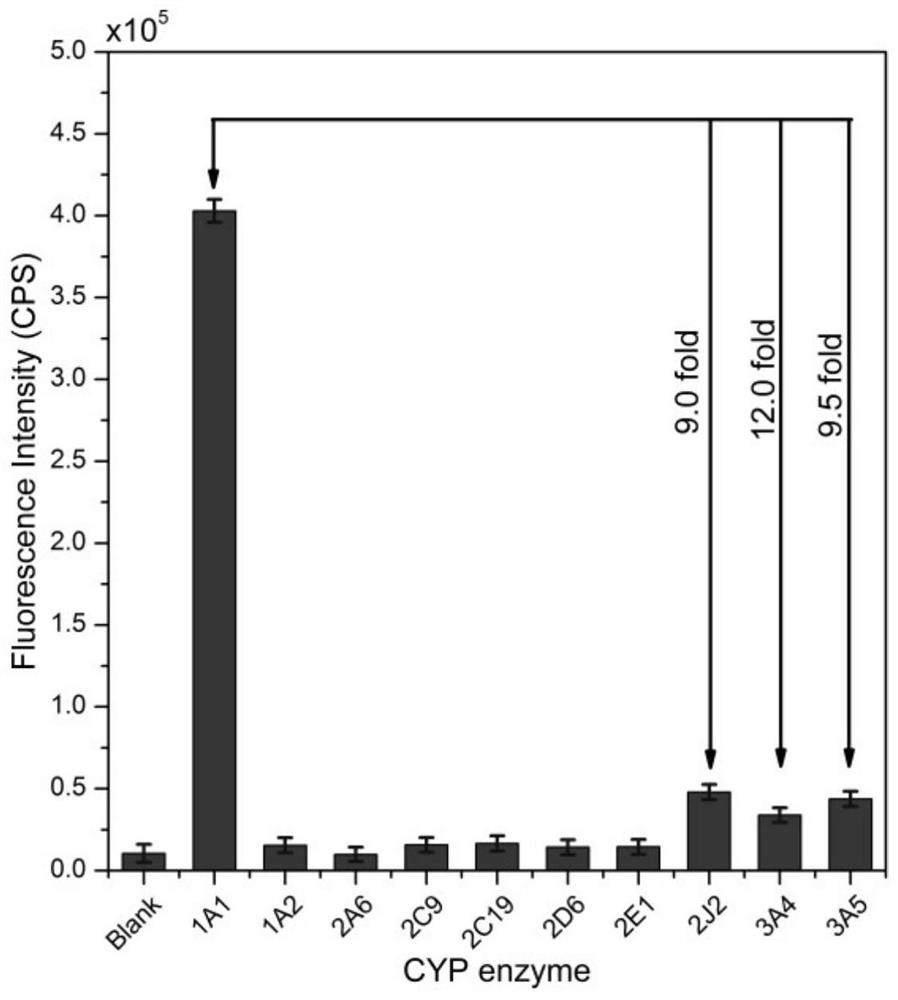
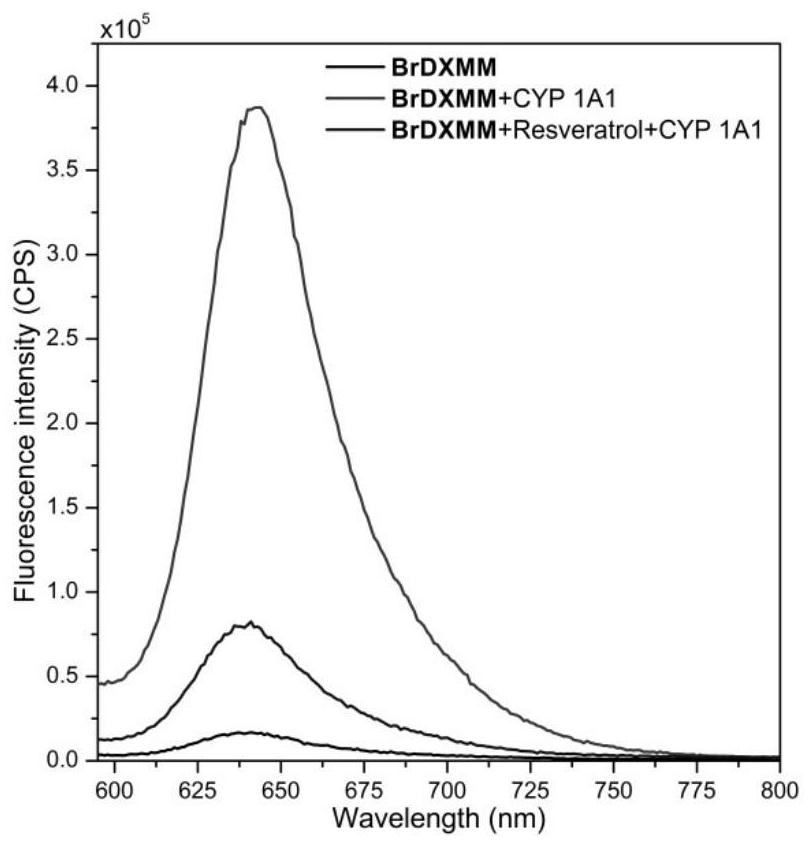
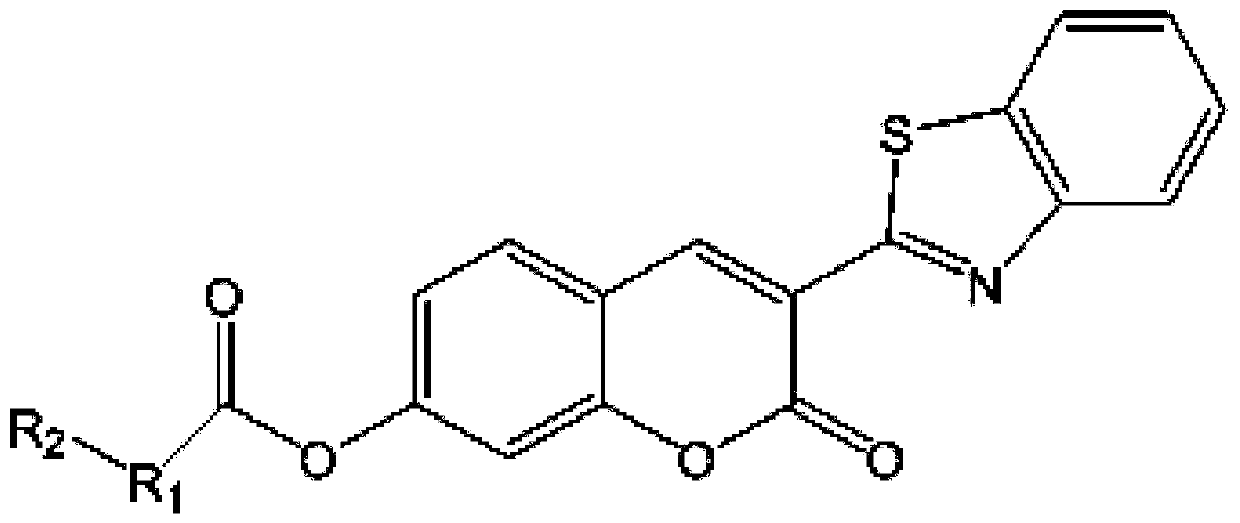
Near-infrared fluorescent probe for detecting CYP 1A1 enzyme
ActiveCN113582960AImprove signal-to-noise ratioGood biocompatibilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesFluorophore
The invention discloses a near-infrared fluorescent probe for detecting CYP 1A1 enzyme. According to the near-infrared fluorescent probe, a molecular structure is modified, so the molecular structure can realize specific detection on the CYP 1A1 enzyme, and the near-infrared fluorescent probe has high selectivity; meanwhile, the wavelength of fluorescence emitted by a fluorophore in the fluorescent probe is in a near-infrared region, so the interference of green light emitted by an organism can be avoided during fluorescence detection; BrDXMM is very weak in fluorescence performance, and HDXMM has good fluorescence emission spectrum characteristics (590-800 nm) under the same condition, so the BrDXMM and the HDXMM can be distinguished well, and the fluorescent probe has high signal-to-noise ratios in vivo and in vitro; the fluorescent probe also has good biocompatibility, and cell activity is still greater than 85% when cells are incubated for 24 hours by using a culture medium containing BrDXMM (100 [mu]M); and the fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention can be used for determining the activity of recombinant single enzyme in a solution and CYP 1A1 enzyme in living cells, in-vitro tissues, living zebra fish and tumor-bearing nude mouse, and is wide in an application range.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Fluorescent probe for detecting GSH with high specificity and application thereof
ActiveCN109705110AHigh detection sensitivityLow cytotoxicityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCoumarin 7On cells
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting GSH with high specificity and an application thereof. The fluorescent probe is 3-benzothiazolyl-coumarin-7-phenol ester derivatives. The fluorescent probe is used as specific probes for GSH, and ester bonds of the fluorescent probe can recognize sulfhydryl groups in GSH to form substitutes with fluorescent properties, which is off-On type fluorescence reaction. The invention connects coumarin and benzothiazole as a novel fluorescence probe, realizes detection through fluorescence generation and quenching, and has high detection sensitivity. The fluorescent probe provided by the invention has small cytotoxicity, the structure of the fluorescent probe takes coumarin as the mother nucleus, has small toxic effect on cells, has good biocompatibility, and can be widely applied in living cells and tissues. The detection process of the fluorescent probe in the invention is not easy to be interfered by the substrate of the biological system and the impurities, and can be used for quantitative determination of GSH in various biological systems.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
Human carboxylesterases 2 detection kit and application method and application thereof
InactiveCN106191210AThe synthesis process is simpleGood fluorescence emission spectral characteristicsMicrobiological testing/measurementSolventChemistry
The invention discloses a human carboxylesterases 2 detection kit and application method and application thereof. The kit comprises liquid A, liquid B, liquid C and a quality control standard substance, and the liquid A refers to a 100mM phosphate buffer solution with pH (potential of hydrogen) ranging from 5.5 to 10; the liquid B refers to a 0.1-10mM NCEN solution with an solvent of any optional one of methyl alcohol, acetonitrile or dimethyl sulfoxide; the liquid C refers to the acetonitrile or the methyl alcohol; the quality control standard substance refers to a 5mg / ml hCE2 solution. The kit is used for rapid quantitative detection of activity of the human carboxylesterases 2 and rapid screening and evaluation of enzyme inhibitors. The human carboxylesterases 2 detection kit and application method and application thereof have the advantages of simpleness in operation, low cost, flexibility and rapidness for per unit detection, and high-throughput detection can be achieved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in biological systems and its application
InactiveCN106544007BThe synthesis process is simpleRaw materials are cheap and easy to getOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureChemical reaction
The invention discloses a fluorescence probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in a biological system. The fluorescence probe is a benzopyran derivative containing different substituent groups, and the chemical construction general formula of the fluorescence probe is shown as the formula (I). The fluorescence probe is easy to manufacture and low in cost, has the high specificity, can make a chemical reaction with the hypochlorous acid to generate a corresponding oxidative product, cannot be disturbed by other components when the corresponding hypochlorous acid content detecting process is executed, can be used for quantitative and qualitative determination on the content of the hypochlorous acid in living cells and has the wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Application of a Class of Highly Specific Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Human Serum Albumin
ActiveCN106841128BThe synthesis process is simpleGood fluorescence emission spectral characteristicsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceMetaboliteAcridone
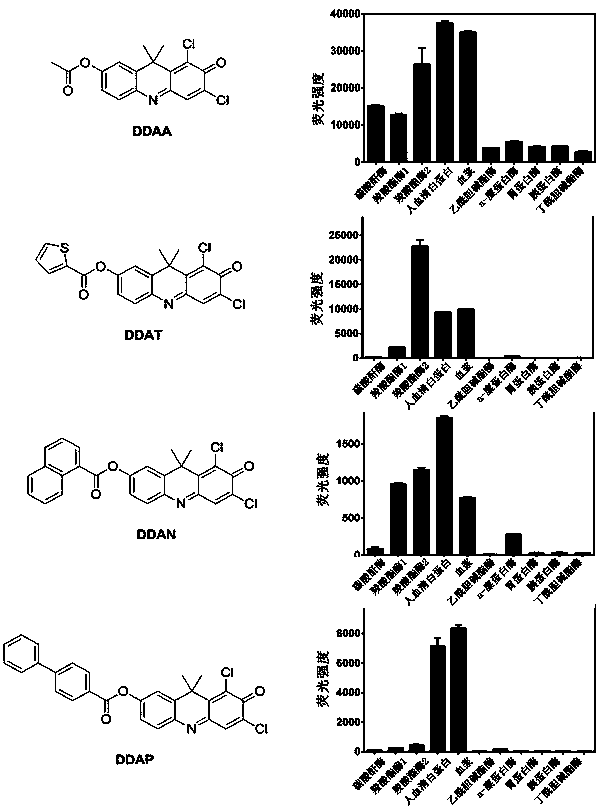
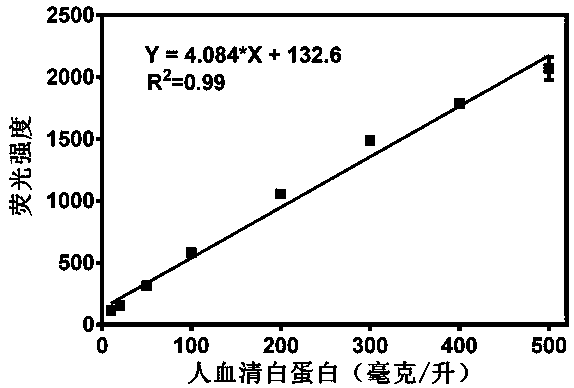
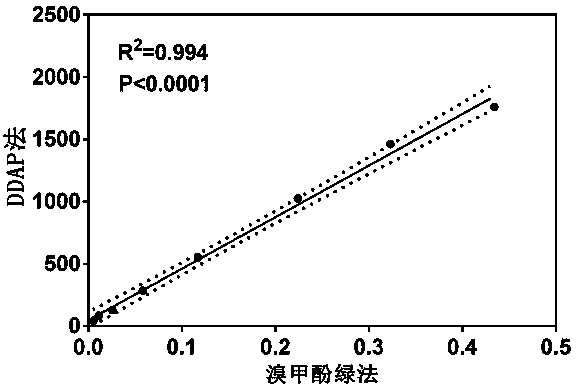
The invention relates to application of a high-specificity fluorescent probe for detecting human serum albumin, and belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering. The high-specificity fluorescent probe is a 1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxyl-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone compound ester derivative, and is used for detecting the existence of HAS (human serum albumin) in different biological samples and the quantitative measuring of activity. The enzyme activity measuring process specifically comprises the following steps of selecting hydrolysis reaction of the 1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxyl-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone compound ester derivative as probe reaction, and selecting proper primer concentration to detect the generation amount of a hydrolyzing metabolite (1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxyl-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone) in unit time within the online reaction zones, so as to measure the actual activity of the HAS in each biological sample. The high-specificity fluorescent probe can be used for quantitatively evaluating the activity of the HAS in different biological samples.
Owner:王铮
A specific two-photon fluorescent probe for monoamine oxidase a and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110343065BStrong specificityThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesMonoamine Oxidase A Gene
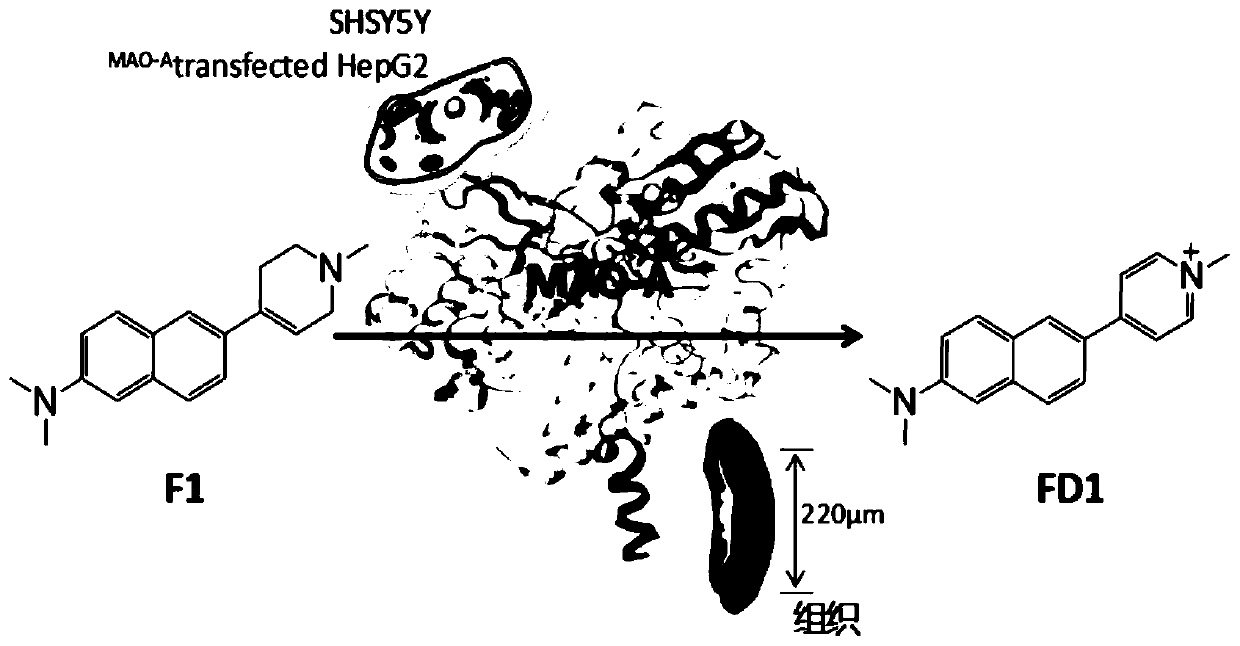
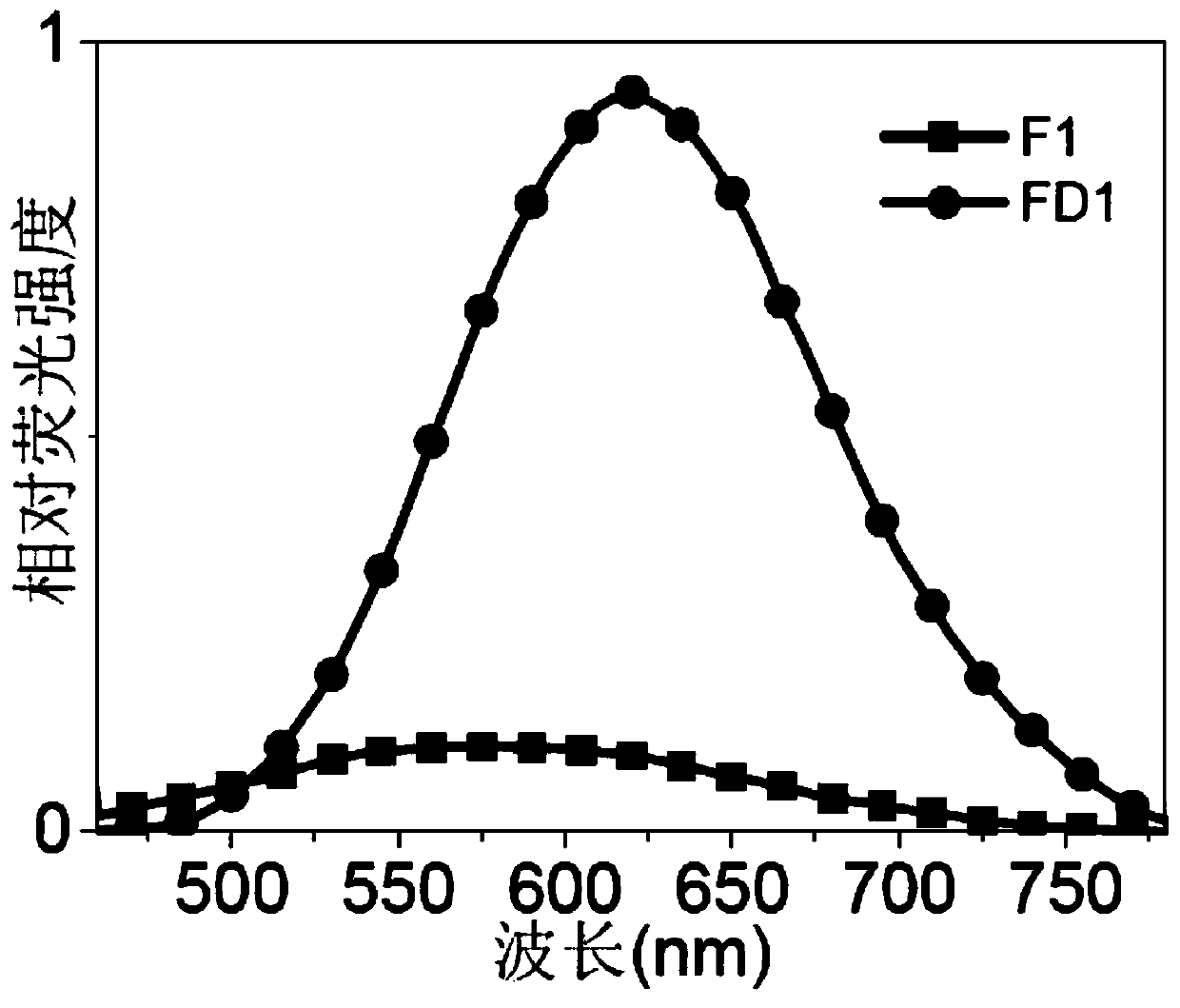
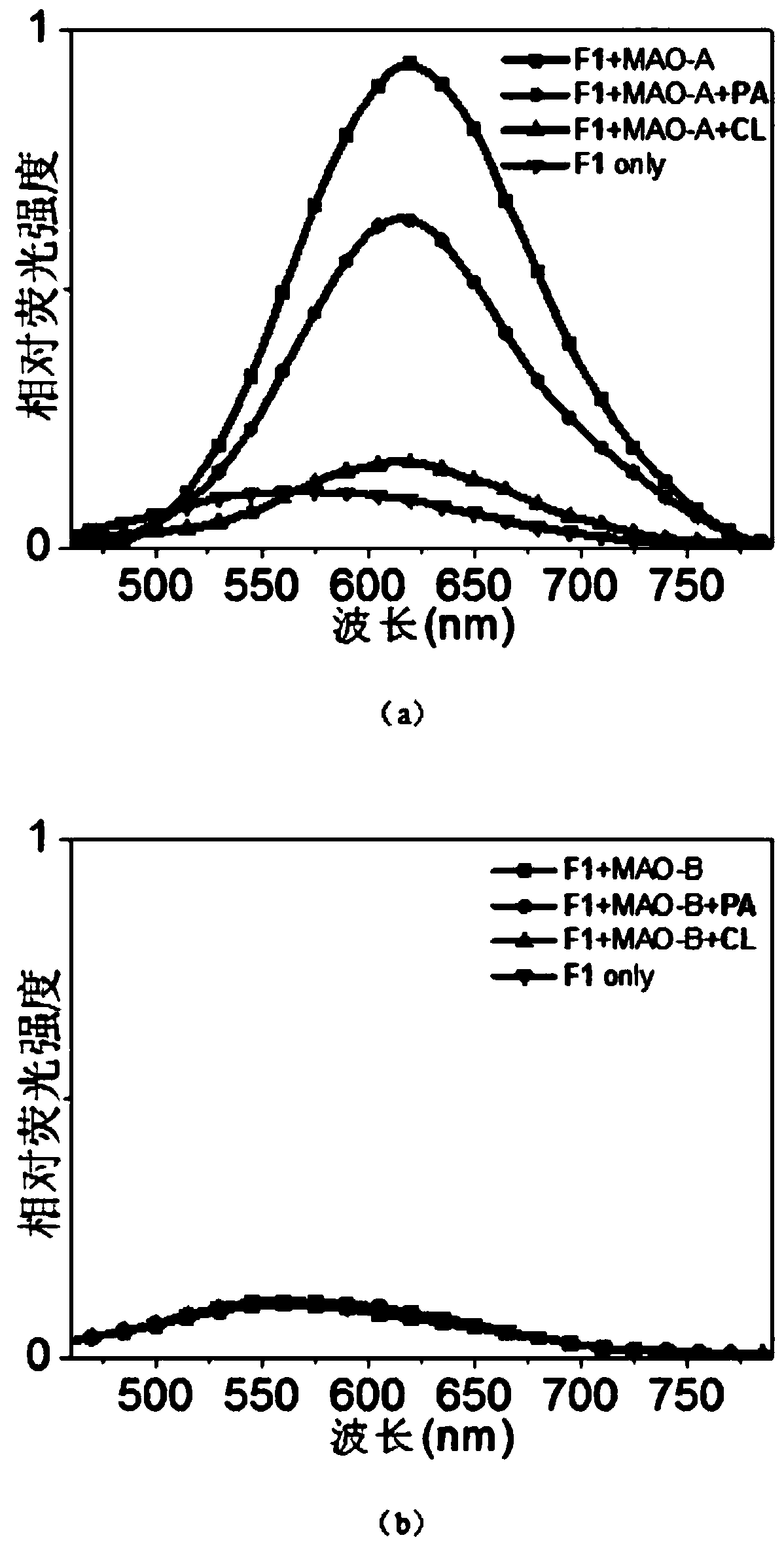
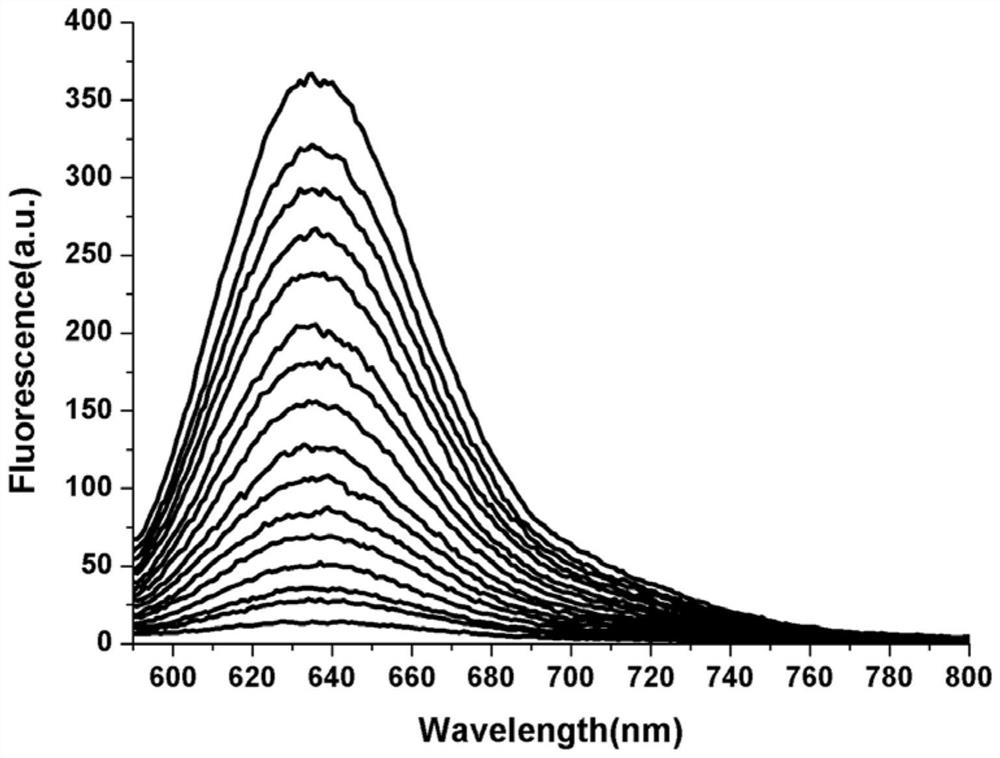
The invention relates to a specific two-photon fluorescent probe of monoamine oxidase A, and a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the field of organic fluorescent probes. Thespecific two-photon fluorescent probe comprises a compound F1 with a general formula (I) which is described in the specification; and the probe is designed by utilizing the spatial selectivity of enzyme and combining the idea of constructing a conjugated structure. The probe F1 successfully and specifically detects the activity of MAO-A in different biological samples (pure proteins, cell lysates,viable cells, mouse brain tissues and tumor tissues). The probe has high sensitivity and low cost, and is applicable to industrialization.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A Dithiothreitol Fluorescent Probe
InactiveCN107915705BAccurate detectionHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureMaterials science
A kind of dithiothreitol fluorescent probe, its chemical structure formula is:. The dithiothreitol fluorescent probe can be used to detect dithiothreitol in solution and cells, and the fluorescence detection conditions are as follows: a single-photon excitation wavelength is 580 nm, a two-photon excitation wavelength is 800 nm, and an emission wavelength is 638 nm. nm, the detection band is 520‑800 nm.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A two-photon fluorescent probe for the detection of hypochlorous acid in the endoplasmic reticulum
InactiveCN109336815BReduce manufacturing costStrong specificityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisFluoProbes
The invention provides a two-photon fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in a cellular endoplasmic reticulum. The two-photon fluorescent probe can be obtained through a three-step reaction by using 4-methylthio-1,8-naphthalic anhydride, trifluoroacetic acid and p-toluenesulfonyl chloride as raw materials. The two-photon fluorescent probe can be applied to detection of the hypochlorousacid in a solution or the cellular endoplasmic reticulum. The fluorescent probe can be obtained through chemical synthesis, a synthesis technology is simple and easy to implement, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the preparation cost is low, and the fluorescent probe is easy to popularize, has high specificity, is not interfered by other components, can be applied to real-time determination of the hypochlorous acid in the endoplasmic reticulum of a living cell and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com